Sound Waves. Sound and Sensa3on. Chapter 9. Sound waves are composed of compression and rarefac3on of air molecules. Domain
|
|
|
- Arnold Matthews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 9 Majority of illustra3ons in this presenta3on are from Biological Psychology 4 th edi3on ( Sinuer Publica3ons) Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of compression and rarefac3on of air molecules. Vibra3ng membrane (water here) like that of a drum causing air molecules to compress and rarefy 2 Sound and Sensa3on Physical Domain Psychological Frequency Intensity Quality Pitch Loudness Timbre 3 1
2 Frequency and Pitch Frequency is defined as vibra3on in number of cycles per second measured in hertz (Hz). Pitch is our percep3on of frequency. 4 Intensity and Loudness Intensity is the amount of energy (measured in decibels, db) in a wave, represented or determined by its amplitude. This relates to perceived loudness. 5 Example of Loudness Loud Thunder (120 db) outdoor- lightszone.com Normal Conversa3on (60 db) 6 2
3 Quality and Timbre Quality of sound is based on fundamental frequencies. We recognize the differences in the sound of a zither from a guitar due to 3mbre. Zither Guitar 7 Fundamental Frequencies A one fundamental frequency (F1) like a pure tone produced by a tuning fork is a simple sound. However most sounds are complex and have many fundamental frequencies (F1, F3, F5 etc) e.g., piano. 8 Fourier Transforma3on 1. A mathema3cal way of decomposing complex wave pa`erns into simple waves is called Fourier Transforma3on. 2. The pa`ern decomposes into fundamentals or harmonics (overtones), making it possible for us to dis3nguish among musical instruments or other sounds
4 The External Ear The ear has three divisions or parts: external, middle, and inner ear. External ear or pinna collects sounds and filters sound frequencies. 10 The Middle Ear Consists of a chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three 3ny bones (malleus, incus, stapes) that transfer vibra3ons of the eardrum on to the cochlea s oval window. 11 The Inner Ear Inner ear contains the cochlea. A snail shaped organ with two large fluid- filled canals (ves3bular and tympanic) and a small canal (middle). The ves3bulocochlear nerve (VIII) leaves cochlea. 12 4
5 The Unwound Cochlea Unwound cochlea is broad at the base and tapers at the apex. The basilar membrane is narrow at the base, but broadens at the apex. 33 mm 0.1 mm Base Apex 0.5 mm Cochlea Basilar Membrane 13 The Basilar Membrane Basilar membrane separates tympanic and middle canals. The organ of Cor3 sits on top of this membrane and contains two sets of hair cells that carry auditory messages to the brain. hyperphysics.phy- astr.gsu.edu 14 Hair Cells and Transduc3on Inner and outer hair cells have afferent and efferent pathways. Mechanical pressure on these hair cells results in acous3cal transduc3on, conver3ng mechanical energy into neural energy. 15 5
6 Hair Cells Inner Hair Cells There are 3500 inner hair cells (IHC) in the cochlea IHC connect to auditory nerve fibers About 90-95% of these fibers carry auditory messages to the brain Outer Hair Cells There are 12,000 outer hair cells (OHC) in the cochlea OHC can change their length to s3ffen the basilar membrane. OHC are involved with cochlear amplifica3on Electron micrograph of hair cells 16 Tip Links Stereocilia open channels through 3p links in IHC that let K + enter the cell. This depolarizes the cell, Ca 2+ enters the cell to release neurotransmi`er glutamate. 17 Auditory Pathway Primary Auditory Cortex MGN MGN Primary Auditory Cortex Inferior Colliculus Inferior Colliculus Superior Olivary Nucleus Superior Olivary Nucleus Cochlear Nucleus Cochlear Nucleus Cochlea Cochlea 18 6
7 19 Place Theory Chiefly Helmholtz and later von Békésy suggested that sound frequencies s3mulate basilar membrane at specific places resul3ng in perceived pitch. Summarized some3mes as pitch is which. Helmholtz ( ) Von Békésy ( ) 20 Place Theory Békésy showed that different frequencies from high to low registered on the basilar membrane extending from the base (cochlear window) to the apex of the cochlea. 21 7
8 Temporal Theory 1. Place theory works well to explain frequencies up to 1600Hz, but humans can hear frequencies close to 20,000Hz. 2. To explain that Weaver proposed the temporal theory. He suggested that the rate of nerve impulses matched the frequency of a sound. Glen Weaver ( ) 22 Temporal Theory 3. Weaver used the volley principle of firing rounds of bullets to explain how neurons fire volleys of impulses to sense high frequency sounds. Sound Frequency Nerve impulse 1000 Hz 2000 Hz 23 Localiza3on of Sound 1. When sound reaches one ear faster (latency differences) than the other makes us localize the sound in space. 2. Sounds that reach one ear louder than the other (intensity differences) also result in its localiza3on. 24 8
9 Throwing Sound: Illusion Ventriloquists use the illusion of throwing sound from the mouth piece of a prop which moves. Clyde, Kevin Johnson & Ma3lda 25 Hearing Prosthe3cs Prosthe3cs to replace cochlea in the inner ear. 26 9
Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception
 Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception Overview of Questions What is it that makes sounds high pitched or low pitched? How do sound vibrations inside the ear lead to the perception
Chapter 11: Sound, The Auditory System, and Pitch Perception Overview of Questions What is it that makes sounds high pitched or low pitched? How do sound vibrations inside the ear lead to the perception
Intro to Audition & Hearing
 Intro to Audition & Hearing Lecture 16 Chapter 9, part II Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 Sine wave: one of the simplest kinds of sounds: sound for which pressure
Intro to Audition & Hearing Lecture 16 Chapter 9, part II Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Fall 2017 1 Sine wave: one of the simplest kinds of sounds: sound for which pressure
Sound Waves. Sensation and Perception. Sound Waves. Sound Waves. Sound Waves
 Sensation and Perception Part 3 - Hearing Sound comes from pressure waves in a medium (e.g., solid, liquid, gas). Although we usually hear sounds in air, as long as the medium is there to transmit the
Sensation and Perception Part 3 - Hearing Sound comes from pressure waves in a medium (e.g., solid, liquid, gas). Although we usually hear sounds in air, as long as the medium is there to transmit the
Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function.
 Hearing Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function. 19/11/2014 Sound A type of longitudinal mass wave that
Hearing Sound and its characteristics. The decibel scale. Structure and function of the ear. Békésy s theory. Molecular basis of hair cell function. 19/11/2014 Sound A type of longitudinal mass wave that
Auditory System. Barb Rohrer (SEI )
 Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
Auditory System Barb Rohrer (SEI614 2-5086) Sounds arise from mechanical vibration (creating zones of compression and rarefaction; which ripple outwards) Transmitted through gaseous, aqueous or solid medium
MECHANISM OF HEARING
 MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
MECHANISM OF HEARING Sound: Sound is a vibration that propagates as an audible wave of pressure, through a transmission medium such as gas, liquid or solid. Sound is produced from alternate compression
Hearing. PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers. Module 14. Hearing. Hearing
 PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
PSYCHOLOGY (8th Edition, in Modules) David Myers PowerPoint Slides Aneeq Ahmad Henderson State University Worth Publishers, 2007 1 Hearing Module 14 2 Hearing Hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves The
Hearing: Physiology and Psychoacoustics
 9 Hearing: Physiology and Psychoacoustics Click Chapter to edit 9 Hearing: Master title Physiology style and Psychoacoustics The Function of Hearing What Is Sound? Basic Structure of the Mammalian Auditory
9 Hearing: Physiology and Psychoacoustics Click Chapter to edit 9 Hearing: Master title Physiology style and Psychoacoustics The Function of Hearing What Is Sound? Basic Structure of the Mammalian Auditory
Receptors / physiology
 Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
Hearing: physiology Receptors / physiology Energy transduction First goal of a sensory/perceptual system? Transduce environmental energy into neural energy (or energy that can be interpreted by perceptual
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages
 PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
PSY 215 Lecture 10 Topic: Hearing Chapter 7, pages 189-197 Corrections: NTC 09-1, page 3, the Superior Colliculus is in the midbrain (Mesencephalon). Announcements: Movie next Monday: Case of the frozen
Auditory System Feedback
 Feedback Auditory System Feedback Using all or a portion of the information from the output of a system to regulate or control the processes or inputs in order to modify the output. Central control of
Feedback Auditory System Feedback Using all or a portion of the information from the output of a system to regulate or control the processes or inputs in order to modify the output. Central control of
Deafness and hearing impairment
 Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
Auditory Physiology Deafness and hearing impairment About one in every 10 Americans has some degree of hearing loss. The great majority develop hearing loss as they age. Hearing impairment in very early
Hearing I: Sound & The Ear
 Hearing I: Sound & The Ear Overview of Topics Chapter 5 in Chaudhuri Philosophical Aside: If a tree falls in the forest and no one is there to hear it... Qualities of sound energy and sound perception
Hearing I: Sound & The Ear Overview of Topics Chapter 5 in Chaudhuri Philosophical Aside: If a tree falls in the forest and no one is there to hear it... Qualities of sound energy and sound perception
Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing
 Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing - We can hear a limited range of frequency between 20 Hz 20,000 Hz (human hearing acuity is between 1000 Hz 4000 Hz). - The ear is divided into 3 parts. Those are:
Unit VIII Problem 9 Physiology: Hearing - We can hear a limited range of frequency between 20 Hz 20,000 Hz (human hearing acuity is between 1000 Hz 4000 Hz). - The ear is divided into 3 parts. Those are:
Sound. Audition. Physics of Sound. Properties of sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Sound Audition Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition. Sound. Physics of Sound. Perception of sound works the same way as light.
 Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Audition Sound Perception of sound works the same way as light. Have receptors to convert a physical stimulus to action potentials Action potentials are organized in brain structures You apply some meaning
Hearing. istockphoto/thinkstock
 Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
Hearing istockphoto/thinkstock Audition The sense or act of hearing The Stimulus Input: Sound Waves Sound waves are composed of changes in air pressure unfolding over time. Acoustical transduction: Conversion
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear
 ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
ENT 318 Artificial Organs Physiology of Ear Lecturer: Ahmad Nasrul Norali The Ear The Ear Components of hearing mechanism - Outer Ear - Middle Ear - Inner Ear - Central Auditory Nervous System Major Divisions
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 29. Hearing
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 29 A dangerous device. Hearing The sound stimulus is changes in pressure The simplest sounds vary in: Frequency: Hertz, cycles per second. How fast the
Required Slide. Session Objectives
 Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Auditory Physiology Required Slide Session Objectives Auditory System: At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Characterize the range of normal human hearing. 2. Understand the components
Hearing I: Sound & The Ear
 Hearing I: Sound & The Ear Overview of Topics Chapter 5 in Chaudhuri Philosophical Aside: If a tree falls in the forest and no one is there to hear it... Qualities of sound energy and sound perception
Hearing I: Sound & The Ear Overview of Topics Chapter 5 in Chaudhuri Philosophical Aside: If a tree falls in the forest and no one is there to hear it... Qualities of sound energy and sound perception
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.01 Recitation (R02)
Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, Auditory system. http:
 Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, 2018 Auditory system http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html The physics of sound Measuring sound intensity We are sensitive to an enormous range of intensities,
Systems Neuroscience Oct. 16, 2018 Auditory system http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html The physics of sound Measuring sound intensity We are sensitive to an enormous range of intensities,
Hearing Sound. The Human Auditory System. The Outer Ear. Music 170: The Ear
 Hearing Sound Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Hearing Sound Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Music 170: The Ear. Tamara Smyth, Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016
 Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 1 Hearing Sound Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
Music 170: The Ear Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego (UCSD) November 17, 2016 1 Hearing Sound Sound interpretation in the auditory system is done by
HEARING. Structure and Function
 HEARING Structure and Function Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Analyse Function of auditory system Discriminate
HEARING Structure and Function Rory Attwood MBChB,FRCS Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Analyse Function of auditory system Discriminate
Learning Targets. Module 20. Hearing Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages.
 Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
Learning Targets Module 20 Hearing 20-1 Describe the characteristics of air pressure waves that we hear as sound. 20-2 Explain how the ear transforms sound energy into neural messages. 20-3 Discuss how
Ganglion Cells Blind Spot Cornea Pupil Visual Area of the Bipolar Cells Thalamus Rods and Cones Lens Visual cortex of the occipital lobe
 How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
The speed at which it travels is a function of the density of the conducting medium.
 Sound is a compression wave which (unlike light) must have a medium to conduct it. If the medium is uniform in density, the sound will spread at as a uniform ring of circles (actually spheres). The speed
Sound is a compression wave which (unlike light) must have a medium to conduct it. If the medium is uniform in density, the sound will spread at as a uniform ring of circles (actually spheres). The speed
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
Auditory Physiology Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1. Describe the morphology and function of the following structures:
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003
 ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003 As always, the Honor Code is in effect and you ll need to write the code and sign it at the end of the exam. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Although
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2003 As always, the Honor Code is in effect and you ll need to write the code and sign it at the end of the exam. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Although
COM3502/4502/6502 SPEECH PROCESSING
 COM3502/4502/6502 SPEECH PROCESSING Lecture 4 Hearing COM3502/4502/6502 Speech Processing: Lecture 4, slide 1 The Speech Chain SPEAKER Ear LISTENER Feedback Link Vocal Muscles Ear Sound Waves Taken from:
COM3502/4502/6502 SPEECH PROCESSING Lecture 4 Hearing COM3502/4502/6502 Speech Processing: Lecture 4, slide 1 The Speech Chain SPEAKER Ear LISTENER Feedback Link Vocal Muscles Ear Sound Waves Taken from:
Sound and Hearing. Decibels. Frequency Coding & Localization 1. Everything is vibration. The universe is made of waves.
 Frequency Coding & Localization 1 Sound and Hearing Everything is vibration The universe is made of waves db = 2log(P1/Po) P1 = amplitude of the sound wave Po = reference pressure =.2 dynes/cm 2 Decibels
Frequency Coding & Localization 1 Sound and Hearing Everything is vibration The universe is made of waves db = 2log(P1/Po) P1 = amplitude of the sound wave Po = reference pressure =.2 dynes/cm 2 Decibels
Before we talk about the auditory system we will talk about the sound and waves
 The Auditory System PHYSIO: #3 DR.LOAI ZAGOUL 24/3/2014 Refer to the slides for some photos. Before we talk about the auditory system we will talk about the sound and waves All waves have basic characteristics:
The Auditory System PHYSIO: #3 DR.LOAI ZAGOUL 24/3/2014 Refer to the slides for some photos. Before we talk about the auditory system we will talk about the sound and waves All waves have basic characteristics:
THE EAR AND HEARING Be sure you have read and understand Chapter 16 before beginning this lab. INTRODUCTION: hair cells outer ear tympanic membrane
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** THE EAR AND HEARING ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** THE EAR AND HEARING ******************************************************************************************************
Auditory System & Hearing
 Auditory System & Hearing Chapters 9 part II Lecture 16 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Spring 2019 1 Phase locking: Firing locked to period of a sound wave example of a temporal
Auditory System & Hearing Chapters 9 part II Lecture 16 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Spring 2019 1 Phase locking: Firing locked to period of a sound wave example of a temporal
PSY 214 Lecture 16 (11/09/2011) (Sound, auditory system & pitch perception) Dr. Achtman PSY 214
 PSY 214 Lecture 16 Topic: Sound, auditory system, & pitch perception Chapter 11, pages 268-288 Corrections: None needed Announcements: At the beginning of class, we went over some demos from the virtual
PSY 214 Lecture 16 Topic: Sound, auditory system, & pitch perception Chapter 11, pages 268-288 Corrections: None needed Announcements: At the beginning of class, we went over some demos from the virtual
Vision and Audition. This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems.
 Vision and Audition Vision and Audition This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems. The description of the organization of each begins with
Vision and Audition Vision and Audition This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems. The description of the organization of each begins with
BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221
 BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221 Time: MW 10:25 11:40 AM Recitation: F 10:25 11:25 AM Room: Hutchinson 473 Lecturer: Dr. Kevin Davis Office: 303E Meliora Hall Office hours: M 1 3 PM kevin_davis@urmc.rochester.edu
BCS 221: Auditory Perception BCS 521 & PSY 221 Time: MW 10:25 11:40 AM Recitation: F 10:25 11:25 AM Room: Hutchinson 473 Lecturer: Dr. Kevin Davis Office: 303E Meliora Hall Office hours: M 1 3 PM kevin_davis@urmc.rochester.edu
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing
 Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing The Human Ear Temporal Bone Found on each side of the skull and contains the organs for hearing and balance Divided into four major portions: - squamous - mastoid - tympanic
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing The Human Ear Temporal Bone Found on each side of the skull and contains the organs for hearing and balance Divided into four major portions: - squamous - mastoid - tympanic
Auditory System & Hearing
 Auditory System & Hearing Chapters 9 and 10 Lecture 17 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Spring 2015 1 Cochlea: physical device tuned to frequency! place code: tuning of different
Auditory System & Hearing Chapters 9 and 10 Lecture 17 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Spring 2015 1 Cochlea: physical device tuned to frequency! place code: tuning of different
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 30. Organ of Corti
 Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 30 Waves, waves, waves. Organ of Corti Tectorial membrane Sits on top Inner hair cells Outer hair cells The microphone for the brain 1 Hearing Perceptually,
Auditory Physiology PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 30 Waves, waves, waves. Organ of Corti Tectorial membrane Sits on top Inner hair cells Outer hair cells The microphone for the brain 1 Hearing Perceptually,
SPECIAL SENSES: THE AUDITORY SYSTEM
 SPECIAL SENSES: THE AUDITORY SYSTEM REVISION OF PHYSICS: WAVES A wave is an oscillation of power, sound waves have two main characteristics: amplitude, which is the maximum displacement or the power of
SPECIAL SENSES: THE AUDITORY SYSTEM REVISION OF PHYSICS: WAVES A wave is an oscillation of power, sound waves have two main characteristics: amplitude, which is the maximum displacement or the power of
Hearing. By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa
 Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
Chapter 7. Audition, the Body Senses, and the Chemical Senses. Copyright Allyn & Bacon 2004
 Chapter 7 Audition, the Body Senses, and the Chemical Senses This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Chapter 7 Audition, the Body Senses, and the Chemical Senses This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Otoconia: Calcium carbonate crystals Gelatinous mass. Cilia. Hair cells. Vestibular nerve. Vestibular ganglion
 VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Balance/Equilibrium) The vestibular stimulus is provided by Earth s, and. Located in the of the inner ear, in two components: 1. Vestibular sacs - gravity & head direction 2. Semicircular
VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Balance/Equilibrium) The vestibular stimulus is provided by Earth s, and. Located in the of the inner ear, in two components: 1. Vestibular sacs - gravity & head direction 2. Semicircular
Hearing: the function of the outer, the middle and inner ear. Hearing tests. The auditory pathways
 Hearing: the function of the outer, the middle and inner ear. Hearing tests. The auditory pathways Dr. Gabriella Kékesi 74. Hearing: the function of the outer, the middle and inner ear. Hearing tests.
Hearing: the function of the outer, the middle and inner ear. Hearing tests. The auditory pathways Dr. Gabriella Kékesi 74. Hearing: the function of the outer, the middle and inner ear. Hearing tests.
Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις
 Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics University of Cyprus Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις Διάλεξη 11 Ακουστικό και Αιθουσιαίο Σύστημα (Auditory and Vestibular Systems) Introduction Sensory Systems Sense of
Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics University of Cyprus Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις Διάλεξη 11 Ακουστικό και Αιθουσιαίο Σύστημα (Auditory and Vestibular Systems) Introduction Sensory Systems Sense of
Hearing. By Jack & Tori
 Hearing By Jack & Tori 3 Main Components of the Human Ear. Outer Ear. Middle Ear. Inner Ear Outer Ear Pinna: >Visible part of ear and ear canal -Acts as a funnel to direct sound Eardrum: >Airtight membrane
Hearing By Jack & Tori 3 Main Components of the Human Ear. Outer Ear. Middle Ear. Inner Ear Outer Ear Pinna: >Visible part of ear and ear canal -Acts as a funnel to direct sound Eardrum: >Airtight membrane
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2009
 ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2009 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect. At the end of the exam, I ll have you write and sign something to attest to that fact. The exam should contain no surprises,
ID# Exam 2 PS 325, Fall 2009 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect. At the end of the exam, I ll have you write and sign something to attest to that fact. The exam should contain no surprises,
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HEARING.HEALTH.MIL. HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1
 HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1 TEMPORAL MUSCLE TEMPORAL BONE EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL MALLEUS INCUS STAPES SEMICUIRCULAR CANALS COCHLEA VESTIBULAR
HEARING GUIDE PREPARED FOR CLINICAL PROFESSIONALS HCE_ClinicalProvider-Flip_FINAL01.indb 1 TEMPORAL MUSCLE TEMPORAL BONE EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL MALLEUS INCUS STAPES SEMICUIRCULAR CANALS COCHLEA VESTIBULAR
to vibrate the fluid. The ossicles amplify the pressure. The surface area of the oval window is
 Page 1 of 6 Question 1: How is the conduction of sound to the cochlea facilitated by the ossicles of the middle ear? Answer: Sound waves traveling through air move the tympanic membrane, which, in turn,
Page 1 of 6 Question 1: How is the conduction of sound to the cochlea facilitated by the ossicles of the middle ear? Answer: Sound waves traveling through air move the tympanic membrane, which, in turn,
Consciousness and Blindsight
 Consciousness and Blindsight Blindsight: The ability to respond appropriately to visual inputs while lacking the feeling of having seen them These patients are unable to see, but are able to reach for
Consciousness and Blindsight Blindsight: The ability to respond appropriately to visual inputs while lacking the feeling of having seen them These patients are unable to see, but are able to reach for
Outline. The ear and perception of sound (Psychoacoustics) A.1 Outer Ear Amplifies Sound. Introduction
 The ear and perception of sound (Psychoacoustics) 1 Outline A. Structure of the Ear B. Perception of Pitch C. Perception of Loudness D. Timbre (quality of sound) E. References Updated 01Aug0 Introduction
The ear and perception of sound (Psychoacoustics) 1 Outline A. Structure of the Ear B. Perception of Pitch C. Perception of Loudness D. Timbre (quality of sound) E. References Updated 01Aug0 Introduction
Representation of sound in the auditory nerve
 Representation of sound in the auditory nerve Eric D. Young Department of Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University Young, ED. Neural representation of spectral and temporal information in speech.
Representation of sound in the auditory nerve Eric D. Young Department of Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University Young, ED. Neural representation of spectral and temporal information in speech.
Chapter 3. Sounds, Signals, and Studio Acoustics
 Chapter 3 Sounds, Signals, and Studio Acoustics Sound Waves Compression/Rarefaction: speaker cone Sound travels 1130 feet per second Sound waves hit receiver Sound waves tend to spread out as they travel
Chapter 3 Sounds, Signals, and Studio Acoustics Sound Waves Compression/Rarefaction: speaker cone Sound travels 1130 feet per second Sound waves hit receiver Sound waves tend to spread out as they travel
Perception of Sound. To hear sound, your ear has to do three basic things:
 Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
Perception of Sound Your ears are extraordinary organs. They pick up all the sounds around you and then translate this information into a form your brain can understand. One of the most remarkable things
ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997
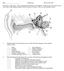 ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997 Good luck on this exam. Answer each question carefully and completely. Keep your eyes foveated on your own exam, as the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect (as always). Have
ID# Final Exam PS325, Fall 1997 Good luck on this exam. Answer each question carefully and completely. Keep your eyes foveated on your own exam, as the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect (as always). Have
Music and Hearing in the Older Population: an Audiologist's Perspective
 Music and Hearing in the Older Population: an Audiologist's Perspective Dwight Ough, M.A., CCC-A Audiologist Charlotte County Hearing Health Care Centre Inc. St. Stephen, New Brunswick Anatomy and Physiology
Music and Hearing in the Older Population: an Audiologist's Perspective Dwight Ough, M.A., CCC-A Audiologist Charlotte County Hearing Health Care Centre Inc. St. Stephen, New Brunswick Anatomy and Physiology
College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH
 College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH 13 2017-2018 ***************************************************************** o Introduction : The ear is the organ that detects
College of Medicine Dept. of Medical physics Physics of ear and hearing /CH 13 2017-2018 ***************************************************************** o Introduction : The ear is the organ that detects
PSY 214 Lecture # (11/9/2011) (Sound, Auditory & Speech Perception) Dr. Achtman PSY 214
 PSY 214 Lecture 16 Topic: Sound, Auditory System & Speech Perception Chapter 11, pages 270-289 Corrections: None Announcements: CD is available outside Dr Achtman s office if you would like to see demonstrations
PSY 214 Lecture 16 Topic: Sound, Auditory System & Speech Perception Chapter 11, pages 270-289 Corrections: None Announcements: CD is available outside Dr Achtman s office if you would like to see demonstrations
Acoustics Research Institute
 Austrian Academy of Sciences Acoustics Research Institute Modeling Modelingof ofauditory AuditoryPerception Perception Bernhard BernhardLaback Labackand andpiotr PiotrMajdak Majdak http://www.kfs.oeaw.ac.at
Austrian Academy of Sciences Acoustics Research Institute Modeling Modelingof ofauditory AuditoryPerception Perception Bernhard BernhardLaback Labackand andpiotr PiotrMajdak Majdak http://www.kfs.oeaw.ac.at
Lecture 6 Hearing 1. Raghav Rajan Bio 354 Neurobiology 2 January 28th All lecture material from the following links unless otherwise mentioned:
 Lecture 6 Hearing 1 All lecture material from the following links unless otherwise mentioned: 1. http://wws.weizmann.ac.il/neurobiology/labs/ulanovsky/sites/neurobiology.labs.ulanovsky/files/uploads/purves_ch12_ch13_hearing
Lecture 6 Hearing 1 All lecture material from the following links unless otherwise mentioned: 1. http://wws.weizmann.ac.il/neurobiology/labs/ulanovsky/sites/neurobiology.labs.ulanovsky/files/uploads/purves_ch12_ch13_hearing
Chapter 13 Physics of the Ear and Hearing
 Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
Hearing 100 times greater dynamic range than vision Wide frequency range (20 ~ 20,000 Hz) Sense of hearing Mechanical system that stimulates the hair cells in the cochlea Sensors that produce action potentials
THE COCHLEA AND AUDITORY PATHWAY
 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD February 23, 2012 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea
Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD February 23, 2012 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea
SPHSC 462 HEARING DEVELOPMENT. Overview Review of Hearing Science Introduction
 SPHSC 462 HEARING DEVELOPMENT Overview Review of Hearing Science Introduction 1 Overview of course and requirements Lecture/discussion; lecture notes on website http://faculty.washington.edu/lawerner/sphsc462/
SPHSC 462 HEARING DEVELOPMENT Overview Review of Hearing Science Introduction 1 Overview of course and requirements Lecture/discussion; lecture notes on website http://faculty.washington.edu/lawerner/sphsc462/
Lecture 3: Perception
 ELEN E4896 MUSIC SIGNAL PROCESSING Lecture 3: Perception 1. Ear Physiology 2. Auditory Psychophysics 3. Pitch Perception 4. Music Perception Dan Ellis Dept. Electrical Engineering, Columbia University
ELEN E4896 MUSIC SIGNAL PROCESSING Lecture 3: Perception 1. Ear Physiology 2. Auditory Psychophysics 3. Pitch Perception 4. Music Perception Dan Ellis Dept. Electrical Engineering, Columbia University
Topic 4. Pitch & Frequency
 Topic 4 Pitch & Frequency A musical interlude KOMBU This solo by Kaigal-ool of Huun-Huur-Tu (accompanying himself on doshpuluur) demonstrates perfectly the characteristic sound of the Xorekteer voice An
Topic 4 Pitch & Frequency A musical interlude KOMBU This solo by Kaigal-ool of Huun-Huur-Tu (accompanying himself on doshpuluur) demonstrates perfectly the characteristic sound of the Xorekteer voice An
PHYS 1240 Sound and Music Professor John Price. Cell Phones off Laptops closed Clickers on Transporter energized
 PHYS 1240 Sound and Music Professor John Price Cell Phones off Laptops closed Clickers on Transporter energized The Ear and Hearing Thanks to Jed Whittaker for many of these slides Ear anatomy substructures
PHYS 1240 Sound and Music Professor John Price Cell Phones off Laptops closed Clickers on Transporter energized The Ear and Hearing Thanks to Jed Whittaker for many of these slides Ear anatomy substructures
HEARING AND PSYCHOACOUSTICS
 CHAPTER 2 HEARING AND PSYCHOACOUSTICS WITH LIDIA LEE I would like to lead off the specific audio discussions with a description of the audio receptor the ear. I believe it is always a good idea to understand
CHAPTER 2 HEARING AND PSYCHOACOUSTICS WITH LIDIA LEE I would like to lead off the specific audio discussions with a description of the audio receptor the ear. I believe it is always a good idea to understand
How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz
 The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
The Marvelous Ear How Do Our Ears Work? Quiz 1. How do humans hear sounds? 2. How does human hearing work? Sketch and label the system. 3. Do you know any sensors that detect sound and how they might do
Structure, Energy Transmission and Function. Gross Anatomy. Structure, Function & Process. External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer Ear
 Gross Anatomy Structure, Energy Transmission and Function IE N O ME 1 Structure, Function & Process 4 External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer third is cartilaginous Inner 2/3 is osseous Junction
Gross Anatomy Structure, Energy Transmission and Function IE N O ME 1 Structure, Function & Process 4 External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer third is cartilaginous Inner 2/3 is osseous Junction
Innervation of the Cochlea. Reading: Yost Ch. 8
 Innervation of the Cochlea Reading: Yost Ch. 8 Fine Structure of the Organ of Corti Auditory Nerve Auditory nerve (AN) is a branch of the VIII th cranial nerve (other branch is vestibular). AN is composed
Innervation of the Cochlea Reading: Yost Ch. 8 Fine Structure of the Organ of Corti Auditory Nerve Auditory nerve (AN) is a branch of the VIII th cranial nerve (other branch is vestibular). AN is composed
Hearing Lectures. Acoustics of Speech and Hearing. Auditory Lighthouse. Facts about Timbre. Analysis of Complex Sounds
 Hearing Lectures Acoustics of Speech and Hearing Week 2-10 Hearing 3: Auditory Filtering 1. Loudness of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more) 2. Pitch of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more)
Hearing Lectures Acoustics of Speech and Hearing Week 2-10 Hearing 3: Auditory Filtering 1. Loudness of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more) 2. Pitch of sinusoids mainly (see Web tutorial for more)
THE COCHLEA AND AUDITORY PATHWAY
 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD April 14, 2010 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea HyperBrain
Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD April 14, 2010 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea HyperBrain
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1
 SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
SENSORY SYSTEM VII THE EAR PART 1 Waves Sound is a compression wave The Ear Ear Outer Ear Pinna Outer ear: - Made up of the pinna and the auditory canal Auditory Canal Outer Ear Pinna (also called the
Presentation On SENSATION. Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur
 Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
The Ear. The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear.
 The Ear The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The Ear There are three components of the outer ear: Pinna: the fleshy outer part of the ear which
The Ear The ear can be divided into three major parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The Ear There are three components of the outer ear: Pinna: the fleshy outer part of the ear which
Mechanical Properties of the Cochlea. Reading: Yost Ch. 7
 Mechanical Properties of the Cochlea CF Reading: Yost Ch. 7 The Cochlea Inner ear contains auditory and vestibular sensory organs. Cochlea is a coiled tri-partite tube about 35 mm long. Basilar membrane,
Mechanical Properties of the Cochlea CF Reading: Yost Ch. 7 The Cochlea Inner ear contains auditory and vestibular sensory organs. Cochlea is a coiled tri-partite tube about 35 mm long. Basilar membrane,
SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing
 SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: 12-13 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing The Physics Of Hearing On completion of this section, you should be able to:
SUBJECT: Physics TEACHER: Mr. S. Campbell DATE: 15/1/2017 GRADE: 12-13 DURATION: 1 wk GENERAL TOPIC: The Physics Of Hearing The Physics Of Hearing On completion of this section, you should be able to:
Converting Sound Waves into Neural Signals, Part 1. What happens to initiate neural signals for sound?
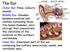 The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
The Ear Outer Ear: Pinna. Collects sounds. Middle Ear: Chamber between eardrum and cochlea containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea
Auditory and vestibular system
 Auditory and vestibular system Sensory organs on the inner ear inner ear: audition (exteroceptor) and vestibular apparatus (proprioceptor) bony and membranous labyrinths within the temporal bone (os temporale)
Auditory and vestibular system Sensory organs on the inner ear inner ear: audition (exteroceptor) and vestibular apparatus (proprioceptor) bony and membranous labyrinths within the temporal bone (os temporale)
Signals, systems, acoustics and the ear. Week 5. The peripheral auditory system: The ear as a signal processor
 Signals, systems, acoustics and the ear Week 5 The peripheral auditory system: The ear as a signal processor Think of this set of organs 2 as a collection of systems, transforming sounds to be sent to
Signals, systems, acoustics and the ear Week 5 The peripheral auditory system: The ear as a signal processor Think of this set of organs 2 as a collection of systems, transforming sounds to be sent to
Topic 4. Pitch & Frequency. (Some slides are adapted from Zhiyao Duan s course slides on Computer Audition and Its Applications in Music)
 Topic 4 Pitch & Frequency (Some slides are adapted from Zhiyao Duan s course slides on Computer Audition and Its Applications in Music) A musical interlude KOMBU This solo by Kaigal-ool of Huun-Huur-Tu
Topic 4 Pitch & Frequency (Some slides are adapted from Zhiyao Duan s course slides on Computer Audition and Its Applications in Music) A musical interlude KOMBU This solo by Kaigal-ool of Huun-Huur-Tu
Digital Speech and Audio Processing Spring
 Digital Speech and Audio Processing Spring 2008-1 Ear Anatomy 1. Outer ear: Funnels sounds / amplifies 2. Middle ear: acoustic impedance matching mechanical transformer 3. Inner ear: acoustic transformer
Digital Speech and Audio Processing Spring 2008-1 Ear Anatomy 1. Outer ear: Funnels sounds / amplifies 2. Middle ear: acoustic impedance matching mechanical transformer 3. Inner ear: acoustic transformer
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 7: Audition, the Body Senses, and the Chemical Senses
 Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 7: Audition, the Body Senses, and the Chemical Senses This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 7: Audition, the Body Senses, and the Chemical Senses This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours)
 HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
HEAR YE! HEAR YE! (1.5 Hours) Addresses NGSS Level of Difficulty: 4 Grade Range: 3-5 OVERVIEW In this activity, students will construct a model ear to learn how different materials transmit sound. Topic:
Exam 3 study guide As always, please feel free to me questions any time.
 Exam 3 study guide As always, please feel free to email me questions any time. (gboynton@u.washington.edu). Many of the experiments below are associated with a researcher (e.g. Britten et al.). You don
Exam 3 study guide As always, please feel free to email me questions any time. (gboynton@u.washington.edu). Many of the experiments below are associated with a researcher (e.g. Britten et al.). You don
Human Acoustic Processing
 Human Acoustic Processing Sound and Light The Ear Cochlea Auditory Pathway Speech Spectrogram Vocal Cords Formant Frequencies Time Warping Hidden Markov Models Signal, Time and Brain Process of temporal
Human Acoustic Processing Sound and Light The Ear Cochlea Auditory Pathway Speech Spectrogram Vocal Cords Formant Frequencies Time Warping Hidden Markov Models Signal, Time and Brain Process of temporal
Chapter 3: Anatomy and physiology of the sensory auditory mechanism
 Chapter 3: Anatomy and physiology of the sensory auditory mechanism Objectives (1) Anatomy of the inner ear Functions of the cochlear and vestibular systems Three compartments within the cochlea and membranes
Chapter 3: Anatomy and physiology of the sensory auditory mechanism Objectives (1) Anatomy of the inner ear Functions of the cochlear and vestibular systems Three compartments within the cochlea and membranes
The cochlea: auditory sense. The cochlea: auditory sense
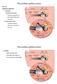 Inner ear apparatus 1- Vestibule macula and sacculus sensing acceleration of the head and direction of gravity 2- Semicircular canals mainly for sensing direction of rotation of the head 1 3- cochlea in
Inner ear apparatus 1- Vestibule macula and sacculus sensing acceleration of the head and direction of gravity 2- Semicircular canals mainly for sensing direction of rotation of the head 1 3- cochlea in
Chapter 15 Hearing & Equilibrium
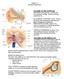 Chapter 15 Hearing & Equilibrium ANATOMY OF THE OUTER EAR EAR PINNA is the outer ear it is thin skin covering elastic cartilage. It directs incoming sound waves to the EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL, which is
Chapter 15 Hearing & Equilibrium ANATOMY OF THE OUTER EAR EAR PINNA is the outer ear it is thin skin covering elastic cartilage. It directs incoming sound waves to the EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL, which is
Assistive Technology Project. Presented By: Rose Aldan
 Assistive Technology Project Presented By: Rose Aldan Hearing Aid How Your Ear Works An auditory wonder Your ears appear to be relatively simple structures. But they are, in fact, only part of the complex
Assistive Technology Project Presented By: Rose Aldan Hearing Aid How Your Ear Works An auditory wonder Your ears appear to be relatively simple structures. But they are, in fact, only part of the complex
au/images/conductive-loss-new.jpg
 Biology of the ear http://www.nal.gov. au/images/conductive-loss-new.jpg Agenda Pre-test Lecture Group Gesture Types of hearing losses Audiograms Views Post-test Pretest!! See how much you know Answer
Biology of the ear http://www.nal.gov. au/images/conductive-loss-new.jpg Agenda Pre-test Lecture Group Gesture Types of hearing losses Audiograms Views Post-test Pretest!! See how much you know Answer
Sensory Processes Sensory Systems
 9 th Lecture (9b) Wed 04 Feb 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh Sensory Processing Chapter 13 1 Sensory Processes Sensory Systems
9 th Lecture (9b) Wed 04 Feb 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh Sensory Processing Chapter 13 1 Sensory Processes Sensory Systems
Sensory Processes Sensory Systems
 9 th Lecture (9b) Wed 04 Feb 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh Sensory Processes Sensory Systems Ch13 in your text Sensory Processing
9 th Lecture (9b) Wed 04 Feb 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh Sensory Processes Sensory Systems Ch13 in your text Sensory Processing
Hearing. Juan P Bello
 Hearing Juan P Bello The human ear The human ear Outer Ear The human ear Middle Ear The human ear Inner Ear The cochlea (1) It separates sound into its various components If uncoiled it becomes a tapering
Hearing Juan P Bello The human ear The human ear Outer Ear The human ear Middle Ear The human ear Inner Ear The cochlea (1) It separates sound into its various components If uncoiled it becomes a tapering
Transfer of Sound Energy through Vibrations
 secondary science 2013 16 Transfer of Sound Energy through Vibrations Content 16.1 Sound production by vibrating sources 16.2 Sound travel in medium 16.3 Loudness, pitch and frequency 16.4 Worked examples
secondary science 2013 16 Transfer of Sound Energy through Vibrations Content 16.1 Sound production by vibrating sources 16.2 Sound travel in medium 16.3 Loudness, pitch and frequency 16.4 Worked examples
