Clinical Management of Kennedy Class II Cases Using Osseointegrated Dental Implants
|
|
|
- Reginald McKinney
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Clinical Management of Kennedy Class II Cases Using Osseointegrated Dental Implants Thesis Submitted in the Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Doctor Degree in Removable Prosthodontics By Ahmed Emad Eldin Hussein Fayyad B.D.S M.D.Sc.2008 (Cairo University) Faculty of Oral and Dental Medicine Cairo University 2012
2 Supervisors Prof. Dr. Samira Ibrahim Professor of Removable Prosthodontics Faculty of Oral and Dental Medicine Cairo University Dr.Ashraf Emil Eskandar Associate Professor of Removable Prosthodontics Faculty of Oral and Dental Medicine Cairo University Dr. Iman Abd-Elwahab Radi Associate Professor of Removable Prosthodontics Faculty of Oral and Dental Medicine Cairo University Faculty of Oral and Dental Medicine Cairo University 2012
3 Acknowledgment First and foremost, I am greatly thankful and grateful to Allah for granting me the chance to accomplish this work. I would like to express my most sincere gratitude and grateful appreciation to Prof. Dr. Samira Ibrahim, Professor of Prosthodontics Faculty of Oral and Dental Medicine, Cairo University. I was fortunate to conduct this work under her valuable supervision. I am deeply grateful to Dr. Ashraf Emil, Associate professor of Prosthodontics, Faculty of Oral and Dental Medicine, Cairo University for his precious help, encouragement, guidance, valuable effort and great cooperation. I am really thankful to Dr. Iman Abd-Elwahab Radi, Associate Professor of Prosthodontics, Faculty of Oral and Dental Medicine, Cairo University, who guided me in a very generous manner throughout the whole practical work. Special thanks to Prof. Dr. Khaled Zekry Professor of Prosthodontics, Faculty of Oral and Dental Medicine, Cairo University who spent every effort to spread his experience and knowledge to everyone in the department. He is been not only a professor but a father to me. I would like to thank my colleagues and all the staff members of the departement especially Dr. Amr Hosny Lecturer of Prosthodontics, Faculty of Oral and Dental Medicine, Cairo University, who continuously helped me throughout this study. Last but not least, I would like to thank my dear parents and my wife for their support throughout my studying period. i
4 List of Contents Page Acknowledgment Table of contents List of figures i ii v Introduction 1 Review of Literature: 3 I. Problems and Management of Kennedy Class II Cases: A. Problems of Kennedy class II cases: B. Proposed solutions for Kennedy class II cases II. Clinical and Radiographic Evaluation. A. Conventional imaging modalities 1. Intra-oral radiographs 2. Extra-oral radiographs B. Digital imaging modalities Extra-oral digital radiography 40 ii
5 2. Intra-oral digital radiography 42 Aim of the Study. 44 Materials and Methods. 45 Results. 83 Discussion: Discussion of methodology. Discussion of results Summary and Conclusions. 103 Bibliography 105 Arabic Summary iii
6 List of Figures Figure Page Fig. (1) Osteometer. 47 Fig. (2) Maxillary and mandibular primary impressions. 49 Fig. (3) Diagnostic set-up. 51 Fig. (4) Preoperative panoramic radiograph. 51 Fig. (5) The surgical stent with the prepared slot. 53 Fig. (6) Marking the proposed implant site. 54 Fig. (7) The crestal incision. 55 Fig. (8) The reflected flap. 55 Fig. (9) A round surgical bur used to mark the drilling site. 56 Fig. (10) Drilling of the osteotomy. 57 Fig. (11) Paralleling tool in the implant bed. 58 Fig. (12) The implant in its sterile package. 59 Fig. (13) Implant installation using a ratchet. 59 Fig. (14) Implant completely seated in place and flushed with bone. 60 Fig. (15) The healing collar screwed in place. 60 Fig. (16) Suturing of the flap. 61 Fig. (17) Milling wax. 63 Fig. (18) The milling machine. 64 Fig. (19) Milling the wax pattern of the primary coping. 65 iv
7 Fig. (20) Finishing of the metal primary coping on the milling machine. 65 Fig. (21) Checking the primary coping in the patient s mouth. 66 Fig. (22) The wax pattern of the unilateral prosthesis. 68 Fig. (23) The metal framework of the unilateral partial overdenture 69 Fig. (24) The finished unilateral partial over-denture. 69 Fig. (25) The wax pattern of the bilateral partial over-denture. 71 Fig. (26) The casted bilateral design. 72 Fig. (27) The finished bilateral partial over-denture. 72 Fig. (28) The finished bilateral partial over-denture in the patient s mouth. 73 Fig. (29) The Digora machine. 75 Fig. (30) The periapical film holder 75 Fig. (31) The radiographic template. 77 Fig. (32) A direct digital radiograph for bone level analysis. 80 Fig. (33) A direct digital radiograph for bone density analysis. 81 Fig.( 34) A line chart representing changes by time in mean bone height around the natural abutments and the implants in group I. 86 Fig.( 35) A line chart representing changes by time in mean bone height around the natural abutments and the implants in group II. 87 v
8 Fig.( 36) A bar chart representing the mean amount of bone loss around the natural abutments and the implants in the two groups. 89 Fig.( 37) A line chart representing changes by time in mean bone density around the natural abutments and the implants in group I. 90 Fig.(38) Fig.(39) A line chart representing changes by time in mean bone density around the natural abutments and the implants in group II. A bar chart representing the mean % increase in bone density around the natural abutments and the implants of the two groups vi
9 List of Tables Table. (1) Patient satisfaction. 83 Page Table. (2) Table. (3) Table. (4) Mean marginal bone level measurements for the natural teeth and the implants in both groups. The mean values, standard deviation (SD) values and results of paired t-test by time for mean bone level changes around the implants and natural teeth of group I The mean values, standard deviation(sd) values and results of paired t-test by time in mean bone level around implants and the natural abutments of group II Table. (5) The mean bone loss, standard deviation (SD) values and results of Mann-Whitney U test for comparison between the two groups. 88 Table. (6) The mean difference, standard deviation (SD) values and results of paired t-test for the change by time in mean bone density around the natural abutments and the implants of group I. 90 Table. (7) The mean difference, standard deviation(sd) values and results of paired t-test for the change by time in mean bone density around the natural abutments and the implants of group II. 91 Table. (8) The mean %, standard deviation (SD) values and results of Mann-Whitney U test for comparison between the two groups. 93 vii
10 Introduction Different treatment modalities have been proposed for the management of distal extension cases. However, controversy exists about the most suitable line of treatment that can satisfy the patient's needs. The challenge in unilateral distal extension cases is even more than the bilateral ones. This is because in most of the cases restored with a conventional partial denture, the patient is not satisfied because of comparing it with the intact side. Generally speaking, problems of distal extension base partial dentures are mainly due to the absence of posterior abutments and the difference in support between the periodontal ligament of the abutment tooth and the mucoperiosteum covering the edentulous ridge. This causes the denture base to rotate under loading, thereby exerting excessive torque on the abutment teeth leading to their early loss (Holmes, 2001). Various design concepts were suggested to solve the problem of unilateral distal extension cases, among which is the use of osseointegrated dental implants, thus converting the distal extension base removable partial denture from a tooth-tissue supported prosthesis with its problems into a tooth-implant-supported one ( Jang et al., 1998). Even a single implant placed in a strategic position provides indefinite range of options for removable prosthesis with high success rates (Krennmair et al., 2007). Telescopic crown retained removable partial denture is one of the options which provides satisfactory support and retention together with preservation of the surrounding supporting structures. Applying the concept of simplifying the design dictates a unilateral partial denture for class II cases. This design could be more easily accepted by the patients. However, 1
11 Introduction extension of the prosthesis to the other side for the purpose of cross arch stabilization has been recommended by many authors (Krennmair et al., 2007). Now a question arises, which is better, to construct a unilateral design which is usually accepted by the patients or a bilateral design keeping in mind to preserve the health of the supporting structures? 2
12 Review of Literature I. Problems and Management of Kennedy Class II Cases: A. Problems of Kennedy class II cases: Brudvic (1999) stated that the problems associated with the Kennedy class II (unilateral free end saddle) partial dentures are support, poor stability, and minimal retention. These problems are attributed to the lack of distal tooth support, in addition to the difference in resiliency between the mucoperiosteum and the periodontal ligament. The lever action resulting from this difference are potentially destructive to the abutments and the surrounding tissues (Cunha et al., 2008). 1. Support: Support is defined as the quality inherent in the dental prosthesis acting to resist the displacement towards the basal tissues or underlying structures (The Academy of Proshodontics, 2005). It is the major problem in the distal extension base removable partial dentures. Due to the absence of the posterior abutment, the partial denture shares its support between the teeth and the edentulous ridge, which differs markedly in the viscoelastic response to loading. The mucosa covering the edentulous ridge is much more easily displaced than the periodontal ligament of the abutment teeth and has a slower rate of recovery that may extend to several hours. The difference in displacement between the mucosa and the periodontal ligament was 3
13 Review of Literature estimated to be up to13 times (Holmes, 2001 and Kuzmanovic et al. 2004). Consequently, when functional pressure is applied to the distal extension base removable partial dentures, it moves towards the mucosal tissues and rotates around the fulcrum line connecting the two main occlusal rests, with the greatest movement taking place at the most posterior extent of the denture base. The resultant rotational forces are extremely damaging to the abutment teeth and must be controlled if clinical treatment is to be successful (Carr and Brown, 2011). 2. Retention: Retention is defined as the quality inherent in the dental prosthesis acting to resist the forces of dislodgment along the path of placement (The Academy of Proshodontics, 2005). It was reported that retention which can be obtained mechanically by placing retaining elements on the abutment teeth is termed primary retention. On the other hand, secondary retention depends on physical means and frictional resistance which is provided by the intimate contact of minor connectors with the guiding plane, denture base and major connectors with the underlying tissues. The secondary retention is proportionate to the accuracy of the impression technique, accuracy of denture base fit and the total area of contact involved (Carr and Brown, 2011). 4
14 Review of Literature Retaining elements could be either attachments or clasps. Various designs of intracoronal and extracoronal attachments were suggested for retaining the distal extension base removable partial denture. It was found that attachments were more advantageous than clasp-retained removable partial dentures since they provide superior esthetics, better retention and distribution of occlusal forces to the supporting structures (Saito et al., 2003). Among the suggested attachments are conical crown telescopic retainer which was found to provide a stable occlusion during function offering adequate retention without subjecting the abutment teeth to excessive tourqing. However, almost 80% of the load is borne by the abutment teeth, which could jeopardize the health of their periodontium (Saito et al., 2003). Davenport et al. (2005) mentioned that, muscular control of the tongue and the cheek is of importance for retention and success of lower free end saddle dentures. 3. Stability and Bracing: Stability is defined as the quality of the removable dental prosthesis to be firm and steady to resist displacement by functional horizontal or rotational stresses, while bracing is defined as the quality of a removable dental prosthesis that resists horizontal component of masticatory forces (The Academy of Proshodontics, 2005). As mentioned earlier, the distal extension base removable partial denture rotates when forces are applied to the denture base. Since it can be assumed that 5
15 Review of Literature this rotation may create horizontal and lateral forces, the presence of stabilizing components in proper relation to the horizontal axis of the abutment teeth becomes important. Several components play a role in stabilizing the removable partial denture, among which are the minor connectors and guiding planes, all play a role in counteracting the lateral forces falling on the partial denture and in preventing its horizontal shift. Furthermore, in distal extension base removable partial dentures, it is advisable to provide cross-arch stabilization by placing a rigid clasp on the intact side of the arch (Phoenix et al., 2003). The maximum coverage by the denture base minimizes the lateral forces on the remaining structures, providing additional resistance to horizontal movement. Moreover, stabilizing elements must distribute stresses equally on all supporting teeth without overstressing any tooth (Mitrani et al., 2003). B. Proposed solutions for the Kennedy class II cases: Arslan et al. (2006) and D'Sauza and Dua (2011) stated that rehabilitation of a partially edentulous patient can be established using a wide range of prosthetic treatment options. Depending upon the clinical needs and demands, restoration of the lost structures can be achieved by using simple conventional clasp retained removable partial denture, attachment retained removable partial denture, partial overdenture, fixed partial denture or dental implants. An orthodontic solution for unilateral free end saddle cases was also proposed. Recently tissue engineering was proposed as an alternative solution for the problem. 6
16 Review of Literature The different treatment modalities of restoring partially edentulous cases aimed to improve the masticatory function and esthetics, to restore the posterior occlusal support and vertical dimension of occlusion, and to avoid compromising the patient s oral health (Grossmann et al., 2009). 1. Conventional clasp retained removable partial denture: In the past, the clasp retained removable partial denture was the conventional and most commonly used method in restoring a unilateral free end saddle case (Carr and Brown 2011). Carr and Brown (2011) claimed that construction of a clasp retained removable partial denture is easier, less time consuming, less expensive and requires less technical skills than other restorations. A well designed clasp-retained removable partial denture can restore function effectively and can aid in preservation of the remaining natural teeth and tissues. However, it has some disadvantages. Clasps are often unaesthetic, caries may develop beneath clasp components, and if improperly designed it will produce adverse effect on the abutments and the other supporting structures. In a conventional removable partial denture, problems of Kennedy class II could be reduced or eliminated by taking the following into consideration: a. Occlusal load reduction: It has been suggested that reduction of the load transmitted, whether vertical or lateral, to the supporting structures could be achieved through maximum denture base extension, using canines and premolars instead of 7
17 Review of Literature molars, leaving a tooth off the base, decreasing the size of the occlusal table width, development of balanced harmonious occlusion, placing the artificial teeth over the center of the ridge crest and reduction of the cusp angles (Book et al., 1992 and Carr and Brown, 2011). This also was proved by Rodrigues et al., 2002 who stated that the use of resilient layer situated between the artificial teeth and the denture base can act as an effective shock absorber that reduces the magnitude of the forces exerted upon the supporting structures during function which in turns reduces the rate of residual ridge resorption. b. Load Distribution between the Teeth and the Ridge Frechette (2001) stated that the distribution of functional stresses between the edentulous ridge and the abutment teeth represents a great challenge to any prosthodontist when treating a patient having a free end saddle. To enhance support in such a case, supporting elements must be distributed, as widely as possible, between the teeth and the residual ridge aiming to decrease the stresses on the abutment teeth. (1). Stress-Breaking The Academy of Prosthodontics (2005) defines the stress-breaker (stressdirector) as, a device or system that relieves specific dental structures of part or all of the occlusal forces and redirects those forces to other bearing structures or regions. 8
18 Review of Literature Stress breaking action may be obtained either through rigid or non rigid connection between the denture base and the direct retainer. One way of accomplishing this is by combining a rigid connection with a flexible clasp. The flexible clasp, such as the wrought wire clasp or the gingivally approaching clasp, was found to resemble a stress-breaking device since its flexibility reduces the horizontal forces on the abutment teeth. There are also some precision attachments, such as the Dalbo and the Crismani attachments that offer non rigid connection between the base and the direct retainer, which permits nearly total relief of stresses on the abutment teeth. The use of a movable joint between the denture base and the retainer was also advocated. These devices vary in their range of movement depending on the complexity of their design. Another method is incorporating a split major connector between the denture base and the direct retainer. This design allows movement of the base independent of the rigid tooth support, thereby reducing stresses on the abutment teeth (Johnson and Stratton, 1980, Preiskel, 1984, Reitz and Caputo, 1985 and Car and Brown 2011). It was revealed that the absence of stress breaking action in using non resilient attachment could result in failure, but with the use of resilient attachments, both function and esthetics can be achieved with better stress distribution on the abutment teeth (Owel, 1995 and Ku et al., 2000). (2). Impression Technique Several studies evaluated distal extension base removable partial dentures made with different impression techniques. It was demonstrated that denture base movement is directly related to the impression technique. Therefore, it is 9
19 Review of Literature advisable to record the functional rather than the resting form of the distal extension area in order to distribute the load between the teeth and the edentulous ridge. It was found that the altered-cast impression technique was the best regarding load distribution between the supporting structures. Other techniques, such as the sectional impression technique and the single selective pressure technique were also described (Holmes, 2001 and Carr and Brown, 2011). (3). Mesial Placement of the Occlusal Rest Ogata et al. (1993) clarified that rotation of the distal extension base around the fulcrum line induces heavy stresses on the anterior abutment teeth leading to its looseness. The idea that the occlusal rest of the distal extension base removable partial denture should be located on the mesial side of the abutment tooth rather than on the distal side is strongly supported. The rationale behind this idea is that the force delivered to the mesial aspect of the abutment tooth will tend to tip that tooth forward, maintaining a tight contact with the tooth immediately anterior to it and gaining stabilization and support from the remaining anterior teeth. In addition, as the rest is moved more anteriorly, the arc of rotation at any given point on the base becomes flatter and its direction becomes more perpendicular to the ridge, thereby increasing the area of the ridge that provides support to the denture (Frechette, 2001 and Mizuutchi et al., 2002). 10
20 Review of Literature c. Wide Distribution of Load over the Edentulous Ridge: A denture base should cover as much of the residual ridge as possible and be extended to the maximum within the physiologic tolerance of the limiting border structures or tissues. The broader the coverage of the edentulous area is, the greater the distribution of load and the less the load per unit area (Carr and Brown, 2011). d. Load Distribution between the Teeth: Splinting of the abutment teeth: Splinting is defined as the joining of two or more teeth into a rigid unit by means of fixed or removable restorations to provide support or bracing (The Academy of Prosthodontics, 2005). Splinting with a fixed restoration is recommended in removable partial dentures retained by precision attachments, especially in distal extension base cases. It was found that splinting of at least two abutment teeth was mandatory, as it results in a significant reduction in the stresses transmitted to them and a marked decrease in their mobility (El Charkawi and El Wakkad, 1996). Increasing the number of splinted abutment teeth to more than two does not result in reduction of the stresses transmitted to their periodontium. However, in cases with abutment teeth having weak periodontal support, it may be necessary to include more teeth within the splint (El Charkawi and EL Wakkad, 1996, Wang et al., 1998 and Itioh et al., 1998). 11
Principles of. By: Dr. Ahmad Rabah
 Principles of By: Dr. Ahmad Rabah 1. Utilize what's present: Whenever possible, select a design that fits the teeth and soft tissues, rather than choosing one that requires tissue alteration. When minimal
Principles of By: Dr. Ahmad Rabah 1. Utilize what's present: Whenever possible, select a design that fits the teeth and soft tissues, rather than choosing one that requires tissue alteration. When minimal
It has been proposed that partially edentulous maxillectomy
 CLASSICAL ARTICLE Basic principles of obturator design for partially edentulous patients. Part II: Design principles Mohamed A. Aramany, DMD, MS* Eye and Ear Hospital of Pittsburgh and University of Pittsburgh,
CLASSICAL ARTICLE Basic principles of obturator design for partially edentulous patients. Part II: Design principles Mohamed A. Aramany, DMD, MS* Eye and Ear Hospital of Pittsburgh and University of Pittsburgh,
Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama
 Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Principles of Removable Partial Denture Design Difference in Prosthesis Support and Influence on Design: For a tooth-supported prosthesis, the movement potential is less
Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Principles of Removable Partial Denture Design Difference in Prosthesis Support and Influence on Design: For a tooth-supported prosthesis, the movement potential is less
Surveying. 3rd year / College of Dentistry/University of Baghdad ( ) Page 1
 د. فائزة Lec.3 Prosthodontics Surveying The ideal requirements for successful removable partial denture are: 1. Be easily inserted and removed by the patient. 2. Resist dislodging forces. 3. It should
د. فائزة Lec.3 Prosthodontics Surveying The ideal requirements for successful removable partial denture are: 1. Be easily inserted and removed by the patient. 2. Resist dislodging forces. 3. It should
SURVEYING OF REMOVABLE PARITAL DENTURES FEB, 11, 2015
 SURVEYING OF REMOVABLE PARITAL DENTURES FEB, 11, 2015 Dental Surveyor: It is a mechanical device used to determine the relative parallelism of the teeth surfaces and the undercuts areas in relation to
SURVEYING OF REMOVABLE PARITAL DENTURES FEB, 11, 2015 Dental Surveyor: It is a mechanical device used to determine the relative parallelism of the teeth surfaces and the undercuts areas in relation to
DENT Advanced Topics in Removable Prosthodontics, Winter 2008
 University of Michigan Deep Blue deepblue.lib.umich.edu 2008-01 DENT 718 - Advanced Topics in Removable Prosthodontics, Winter 2008 Shotwell, Jeffrey Shotwell, J. (2008, April 23) Advanced Topics in Removable
University of Michigan Deep Blue deepblue.lib.umich.edu 2008-01 DENT 718 - Advanced Topics in Removable Prosthodontics, Winter 2008 Shotwell, Jeffrey Shotwell, J. (2008, April 23) Advanced Topics in Removable
Indirect retainers. 1 i
 8 1 i Indirect retainers Factors Influencing Effectiveness Indirect Retainers Auxiliary Functions Indirect Retainers Forms Indirect Retainers Auxiliary occlusal rest Canine extensions fiom occlusal rests
8 1 i Indirect retainers Factors Influencing Effectiveness Indirect Retainers Auxiliary Functions Indirect Retainers Forms Indirect Retainers Auxiliary occlusal rest Canine extensions fiom occlusal rests
Component parts of Chrome Cobalt Removable Partial Denture
 Lec. 5 د.بسام الطريحي Component parts of Chrome Cobalt Removable Partial Denture Major connectors: Are either bars or plates, the difference between them is in the amount of tissue covers. Plates are broad
Lec. 5 د.بسام الطريحي Component parts of Chrome Cobalt Removable Partial Denture Major connectors: Are either bars or plates, the difference between them is in the amount of tissue covers. Plates are broad
INDIAN DENTAL JOURNAL
 ATTACHMENT RETAINED CAST PARTIAL DENTURE USING RHEIN 83 OT-CAP Dr. Charu Gupta 1 Dr. Harshul Sharma 2 Dr. Merrily Nongsiej 3 Dr. AbhinavShekhar 4 1 Senior Resident, Department of Prosthodontics, King George
ATTACHMENT RETAINED CAST PARTIAL DENTURE USING RHEIN 83 OT-CAP Dr. Charu Gupta 1 Dr. Harshul Sharma 2 Dr. Merrily Nongsiej 3 Dr. AbhinavShekhar 4 1 Senior Resident, Department of Prosthodontics, King George
DL 313 Removable Partial Dentures II
 DL 313 Removable Partial Dentures II Survey & Design Survey The procedure of studying the relative parallelism or lack of parallelism of the teeth and associated structures so as to select a path of placement
DL 313 Removable Partial Dentures II Survey & Design Survey The procedure of studying the relative parallelism or lack of parallelism of the teeth and associated structures so as to select a path of placement
SCD Case Study. Attachments in Prosthodontics
 SCD Case Study Attachments in Prosthodontics Precision attachments are retention units milled out of alloy. They have male and female parts that fit together with tolerances of 10 microns. It is important
SCD Case Study Attachments in Prosthodontics Precision attachments are retention units milled out of alloy. They have male and female parts that fit together with tolerances of 10 microns. It is important
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 1:10 January, Ahmad Fahmy 1, Ehab M. Abuelroos 2 and Mohammad M. Nada 3
 Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 1:10 January, 2008 Effect of Using Attachment on Implant Supported Distal Extension Lower Partial Over-dentures Ahmad Fahmy 1, Ehab M. Abuelroos 2 and Mohammad M.
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (I), 1:10 January, 2008 Effect of Using Attachment on Implant Supported Distal Extension Lower Partial Over-dentures Ahmad Fahmy 1, Ehab M. Abuelroos 2 and Mohammad M.
Osseointegrated implant-supported
 CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
Telescopic Retainers: An Old or New Solution? A Second Chance to Have Normal Dental Function
 Telescopic Retainers: An Old or New Solution? A Second Chance to Have Normal Dental Function Joseph B. Breitman, DMD, FACP, 1,2 Scott Nakamura, DMD, 3 Arnold L. Freedman, DDS, 4 & Irving L. Yalisove, DDS
Telescopic Retainers: An Old or New Solution? A Second Chance to Have Normal Dental Function Joseph B. Breitman, DMD, FACP, 1,2 Scott Nakamura, DMD, 3 Arnold L. Freedman, DDS, 4 & Irving L. Yalisove, DDS
DENT Advanced Topics in Removable Prosthodontics, Winter 2008
 University of Michigan Deep Blue deepblue.lib.umich.edu 2008-01 DENT 718 - Advanced Topics in Removable Prosthodontics, Winter 2008 Shotwell, Jeffrey Shotwell, J. (2008, April 23) Advanced Topics in Removable
University of Michigan Deep Blue deepblue.lib.umich.edu 2008-01 DENT 718 - Advanced Topics in Removable Prosthodontics, Winter 2008 Shotwell, Jeffrey Shotwell, J. (2008, April 23) Advanced Topics in Removable
Construction of Removable Partial Denture
 Construction of Removable Partial Denture Peter Hermann Department of Prosthodontics Semmelweis University Treatment options for edentulous spaces Fixed prosthodontics (crowns/bridges) Removable prosthodontics
Construction of Removable Partial Denture Peter Hermann Department of Prosthodontics Semmelweis University Treatment options for edentulous spaces Fixed prosthodontics (crowns/bridges) Removable prosthodontics
Prosthetic V. Removable dentures I.
 Prosthetic V. Removable dentures I. Removable dentures Partial Complete (full) lenka.roubalikova@tiscali.cz 2 Prosthetic dentistry replacement of Damaged teeth reconstruction of the crown (inlays, crowns)
Prosthetic V. Removable dentures I. Removable dentures Partial Complete (full) lenka.roubalikova@tiscali.cz 2 Prosthetic dentistry replacement of Damaged teeth reconstruction of the crown (inlays, crowns)
Removable Partial Dentures
 Removable Partial Dentures Replacement of missing teeth Fixed partial denture Removable partial denture Complete removable Transitional denture Partial removable Implant retained prosthodontics No prosthetic
Removable Partial Dentures Replacement of missing teeth Fixed partial denture Removable partial denture Complete removable Transitional denture Partial removable Implant retained prosthodontics No prosthetic
Arrangement of the artificial teeth:
 Lecture Prosthodontic Dr. Osama Arrangement of the artificial teeth: It s the placement of the teeth on a denture with definite objective in mind or it s the setting of teeth on temporary bases. Rules
Lecture Prosthodontic Dr. Osama Arrangement of the artificial teeth: It s the placement of the teeth on a denture with definite objective in mind or it s the setting of teeth on temporary bases. Rules
Removable partial dentures
 Removable partial dentures Feb, 4, 2015 McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics, Twelfth Edition Carr, Alan B 1 Prosthesis that replaces the missing teeth and associated supporting structures in a
Removable partial dentures Feb, 4, 2015 McCracken's Removable Partial Prosthodontics, Twelfth Edition Carr, Alan B 1 Prosthesis that replaces the missing teeth and associated supporting structures in a
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note
 Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois Phone: Fax:
 Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D. 2325 N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois 60614 Phone: 312-608-6881 Fax: 773-296-0601 Samanthawchou@gmail.com What is our role as the dentist? "We live in a culture in which people
Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D. 2325 N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois 60614 Phone: 312-608-6881 Fax: 773-296-0601 Samanthawchou@gmail.com What is our role as the dentist? "We live in a culture in which people
م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION
 Lec.1 م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION االسنان طب Prosthodontics is the branch of dentistry pertaining to the restoration and maintenance of oral function, comfort, appearance,
Lec.1 م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION االسنان طب Prosthodontics is the branch of dentistry pertaining to the restoration and maintenance of oral function, comfort, appearance,
CLASSIFICATION OF RPDs AND PARTIALLY EDENTULOUS ARCHES
 د.حكمت جميل Lec: 2 Prosthodontic CLASSIFICATION OF RPDs AND PARTIALLY EDENTULOUS ARCHES The classification of RPDs and partially edentulous arches simplifies communication and discussions. Requirements
د.حكمت جميل Lec: 2 Prosthodontic CLASSIFICATION OF RPDs AND PARTIALLY EDENTULOUS ARCHES The classification of RPDs and partially edentulous arches simplifies communication and discussions. Requirements
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This
 1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment
 Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment Complete dentures have largely become the domain of the denturist due to the dissatisfaction general dentists feel with this treatment. Multiple visits,
Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment Complete dentures have largely become the domain of the denturist due to the dissatisfaction general dentists feel with this treatment. Multiple visits,
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF VARNA FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PROSTHETIC DENTAL MEDICINE GOVERNMENT EXAMINATION SYLLABUS
 MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF VARNA FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PROSTHETIC DENTAL MEDICINE GOVERNMENT EXAMINATION SYLLABUS OF PROSTHETIC DENTAL MEDICINE ACADEMIC YEAR 2016/2017 1 1. Biomechanics of
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF VARNA FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PROSTHETIC DENTAL MEDICINE GOVERNMENT EXAMINATION SYLLABUS OF PROSTHETIC DENTAL MEDICINE ACADEMIC YEAR 2016/2017 1 1. Biomechanics of
Frequency of the Various Classes of Removable Partial Dentures and Selection of Major Connectors and Direct/Indirect Retainers
 Turk J Med Sci 31 (2001) 445-449 TÜB TAK Filiz KEYF Frequency of the Various Classes of Removable Partial Dentures and Selection of Major Connectors and Direct/Indirect Retainers Received: November 30,
Turk J Med Sci 31 (2001) 445-449 TÜB TAK Filiz KEYF Frequency of the Various Classes of Removable Partial Dentures and Selection of Major Connectors and Direct/Indirect Retainers Received: November 30,
SCD Case Study. Implant-supported overdentures
 SCD Case Study Implant-supported overdentures An implant-retained overdenture may be indicated in patients with changed anatomy, neuromuscular disorders, significant gag reflex or considerable ridge resorption
SCD Case Study Implant-supported overdentures An implant-retained overdenture may be indicated in patients with changed anatomy, neuromuscular disorders, significant gag reflex or considerable ridge resorption
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior
 Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Uppers are from Mars, Lowers from Venus Clarifying Overdentures
 Uppers are from Mars, Lowers from Venus Clarifying Overdentures M. Nader Sharifi, D.D.S., M.S. Thomas P. Hinman Dental Meeting Atlanta, GA March 23, 2017 About Your Speaker: M. Nader Sharifi, D.D.S., M.S.
Uppers are from Mars, Lowers from Venus Clarifying Overdentures M. Nader Sharifi, D.D.S., M.S. Thomas P. Hinman Dental Meeting Atlanta, GA March 23, 2017 About Your Speaker: M. Nader Sharifi, D.D.S., M.S.
Mesial Step Class I or Class III Dependent upon extent of step seen clinically and patient s growth pattern Refer for early evaluation (by 8 years)
 Orthodontics and Dentofacial Development Overview Development of Dentition Treatment Retention and Relapse Growth of Naso-Maxillary Complex Develops postnatally entirely by intramenbranous ossification
Orthodontics and Dentofacial Development Overview Development of Dentition Treatment Retention and Relapse Growth of Naso-Maxillary Complex Develops postnatally entirely by intramenbranous ossification
Fixed Partial Dentures /FPDs/, Implant Supported. in implant prosthodontics
 Fixed Partial Dentures /FPDs/, Implant Supported Prosthesis/ISP/ in implant prosthodontics Prof.dr.Tamas Divinyi Semmelweis University, Faculty of Dentistry Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
Fixed Partial Dentures /FPDs/, Implant Supported Prosthesis/ISP/ in implant prosthodontics Prof.dr.Tamas Divinyi Semmelweis University, Faculty of Dentistry Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
Journal of American Science 2010;6(9) Emiel A. M. Hanna *1 and Salah A. F. Hegazy 2
 Modified Rotation Joint Connection Unite Versus Double Aker Clasp used for Bracing of Maxillary unilateral Free End Removable Partial Dentures (In Vitro Analysis of Stresses on Principle Abutments and
Modified Rotation Joint Connection Unite Versus Double Aker Clasp used for Bracing of Maxillary unilateral Free End Removable Partial Dentures (In Vitro Analysis of Stresses on Principle Abutments and
Rehabilitation of Resorbed Mandibular Ridge with Implant Supported Overdenture- A Clinical Report
 Rehabilitation of Resorbed Mandibular Ridge with Implant Supported Overdenture- A Clinical Report 1 2 1 1 Mittal R, Saxena D, Rao S, Kumar M Abstract: Statement of Problem: Complete denture rehabilitation
Rehabilitation of Resorbed Mandibular Ridge with Implant Supported Overdenture- A Clinical Report 1 2 1 1 Mittal R, Saxena D, Rao S, Kumar M Abstract: Statement of Problem: Complete denture rehabilitation
Overdenture: A Way of Preventive Prosthodontics
 CASE REPORT Overdenture: A Way of Preventive Prosthodontics Gorakhnath B Shinde 1 and Wadkar AP 2 Quick Response Code ABSTRACT: doi:... 1 Post Graduate Student 2 Professor and PG Guide Department of Prosthodontics
CASE REPORT Overdenture: A Way of Preventive Prosthodontics Gorakhnath B Shinde 1 and Wadkar AP 2 Quick Response Code ABSTRACT: doi:... 1 Post Graduate Student 2 Professor and PG Guide Department of Prosthodontics
Life Science Journal 2013;10(4) Retention Force Measurement of Telescopic Crowns with Different Clearance Fit
 Retention Force Measurement of Telescopic Crowns with Different Clearance Fit Hala Hassan 1, Fatma El Zahraa A. Sayed 2, Enas Mesallum 3 1 Private Practice, Cairo, Egypt 2 Prof., Faculty of Dentistry,
Retention Force Measurement of Telescopic Crowns with Different Clearance Fit Hala Hassan 1, Fatma El Zahraa A. Sayed 2, Enas Mesallum 3 1 Private Practice, Cairo, Egypt 2 Prof., Faculty of Dentistry,
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Diagnosis. overt Examination. Definitive Examination. History. atient interview. Personal History. Clinical Examination.
 Diagnosis overt Examination History Definitive Examination atient interview Personal History Mental Attitude Medical History Dental History Clinical Examination Extra Oral Oral Radiographic Evaluation
Diagnosis overt Examination History Definitive Examination atient interview Personal History Mental Attitude Medical History Dental History Clinical Examination Extra Oral Oral Radiographic Evaluation
أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل CROWN AND BRIDGE جامعة تكريت كلية. Lec. (2) طب االسنان
 Lec. (2) CROWN AND BRIDGE أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل Patient selection and examination A thorough diagnosis must first be made of the patient's dental condition, considering both hard and soft tissues. this
Lec. (2) CROWN AND BRIDGE أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل Patient selection and examination A thorough diagnosis must first be made of the patient's dental condition, considering both hard and soft tissues. this
DIAGNOSTIC/PREVENTIVE SERVICES
 DIAGNOSTIC/PREVENTIVE SERVICES Diagnostic Services D0120 Periodic oral evaluation 100% 100% D0140 Limited oral evaluation problem focused 100% 100% D0150 Comprehensive oral evaluation 100% 100% D0160 Detailed
DIAGNOSTIC/PREVENTIVE SERVICES Diagnostic Services D0120 Periodic oral evaluation 100% 100% D0140 Limited oral evaluation problem focused 100% 100% D0150 Comprehensive oral evaluation 100% 100% D0160 Detailed
Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System)
 Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System) Mucosa-supported complete prostheses with poor fit greatly reduce people's quality of life. This is why the importance of implant-supported
Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System) Mucosa-supported complete prostheses with poor fit greatly reduce people's quality of life. This is why the importance of implant-supported
Distal extension base removable partial dentures exhibit composite type of support
 Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (3), 379:393 September, 2008 stress analysis study of two treatment modalities rehabilitating distal extension cases with few remaining natural teeth Magdy Eid Mohammed
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (3), 379:393 September, 2008 stress analysis study of two treatment modalities rehabilitating distal extension cases with few remaining natural teeth Magdy Eid Mohammed
Corresponding author: *Heba Wageh Abo-Zaed Elsaed. DOI: / Page
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. II (July. 2017), PP 114-119 www.iosrjournals.org Double-Arm Clasp with Anterior Placed
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. II (July. 2017), PP 114-119 www.iosrjournals.org Double-Arm Clasp with Anterior Placed
CAUSE OF TECHNICAL FAILURES OF CONICAL CROWN-RETAINED DENTURE (CCRD): A CLINICAL REPORT
 J Korean Acad Prosthodont : Volume 41, Number 6, 2003 CAUSE OF TECHNICAL FAILURES OF CONICAL CROWN-RETAINED DENTURE (CCRD): A CLINICAL REPORT Yang-Jin Yi, D.D.S.,M.S.D.,Ph.D., Lee-Ra Cho, D.D.S.,M.S.D.,Ph.D.,
J Korean Acad Prosthodont : Volume 41, Number 6, 2003 CAUSE OF TECHNICAL FAILURES OF CONICAL CROWN-RETAINED DENTURE (CCRD): A CLINICAL REPORT Yang-Jin Yi, D.D.S.,M.S.D.,Ph.D., Lee-Ra Cho, D.D.S.,M.S.D.,Ph.D.,
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
Prosthodontic Rehabilitation with Overdenture Using Modified Impression Technique: A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 10 Ver.VII (Oct. 2015), PP 102-107 www.iosrjournals.org Prosthodontic Rehabilitation with Overdenture
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 10 Ver.VII (Oct. 2015), PP 102-107 www.iosrjournals.org Prosthodontic Rehabilitation with Overdenture
4/15/2015. Secondary Impressions: Anatomic and Physiologic Impressions. April, 8, Impressions for tooth-supported RPDs
 Secondary Impressions: Anatomic and Physiologic Impressions Impressions for tooth-supported RPDs April, 8, 2015 Impressions for tooth and tissue supported RPDs In tooth-supported removable partial denture
Secondary Impressions: Anatomic and Physiologic Impressions Impressions for tooth-supported RPDs April, 8, 2015 Impressions for tooth and tissue supported RPDs In tooth-supported removable partial denture
ACRYLIC REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE(RPD)
 ACRYLIC REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE(RPD) is a dental prosthesis which artificially supplies teeth and associated structure in a partially edentulous arch, made from acrylic resin and can be inserted and
ACRYLIC REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE(RPD) is a dental prosthesis which artificially supplies teeth and associated structure in a partially edentulous arch, made from acrylic resin and can be inserted and
FIXED PROSTHODONTICS
 FIXED PROSTHODONTICS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG017.02 Effective Date: May 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE... 1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS... 1 COVERAGE
FIXED PROSTHODONTICS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG017.02 Effective Date: May 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE... 1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS... 1 COVERAGE
Immediate Complete Denture: A Case Report
 Human Journals Case Report July 2018 Vol.:10, Issue:1 All rights are reserved by Ruby et al. Immediate Complete Denture: A Case Report Keywords: immediate denture, dental prosthesis ABSTRACT Ruby*, Manish
Human Journals Case Report July 2018 Vol.:10, Issue:1 All rights are reserved by Ruby et al. Immediate Complete Denture: A Case Report Keywords: immediate denture, dental prosthesis ABSTRACT Ruby*, Manish
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants. by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD
 Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide
 Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide Drago, Carl DDS, MS ISBN-13: 9780813828831 Table of Contents Contributors. Foreword. Acknowledgments. Chapter 1. Introduction To Implant Dentistry. 1. Introduction.
Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide Drago, Carl DDS, MS ISBN-13: 9780813828831 Table of Contents Contributors. Foreword. Acknowledgments. Chapter 1. Introduction To Implant Dentistry. 1. Introduction.
Recommended Professional Fee
 Fee Guide Development & Negotiation Committee 2018 Recommended Professional Fee and Laboratory Fee Guide Abbreviations T: Time Units / 1 Unit = 15 Minutes G: Gold L: Lab Disbursement E: Extra Expense B.R.:
Fee Guide Development & Negotiation Committee 2018 Recommended Professional Fee and Laboratory Fee Guide Abbreviations T: Time Units / 1 Unit = 15 Minutes G: Gold L: Lab Disbursement E: Extra Expense B.R.:
Curriculum Vitae. A) Personal Data: B) Educational Background:
 Curriculum Vitae A) Personal Data: Name: Hussein Gamil El Charkawi Date of birth: 30/5/1956 Tel Home: 202 2519 7282 Tel Office: 202 3346 0353-202 2517 1697 Mobile: 012 2150 439 Fax: 202 3346 0352 Home
Curriculum Vitae A) Personal Data: Name: Hussein Gamil El Charkawi Date of birth: 30/5/1956 Tel Home: 202 2519 7282 Tel Office: 202 3346 0353-202 2517 1697 Mobile: 012 2150 439 Fax: 202 3346 0352 Home
International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences
 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences www.ijmrhs.com Volume 3 Issue 2 (April - Jun) Coden: IJMRHS Copyright @2014 ISSN: 2319-5886 Received: 1 st Jan 2014 Revised: 5 th Feb 2014 Accepted:
International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences www.ijmrhs.com Volume 3 Issue 2 (April - Jun) Coden: IJMRHS Copyright @2014 ISSN: 2319-5886 Received: 1 st Jan 2014 Revised: 5 th Feb 2014 Accepted:
Long-term success of osseointegrated implants
 Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Implant and Tooth Supported Full-Mouth Rehabilitation with Hobo Twin-Stage Technique
 10.5005/JP-Journals-10012-1099 Koshika Tandon et al CASE REPORT Implant and Tooth Supported Full-Mouth Rehabilitation with Hobo Twin-Stage Technique Koshika Tandon, Ajay Singh, Himanshu Gupta, Rajdeep
10.5005/JP-Journals-10012-1099 Koshika Tandon et al CASE REPORT Implant and Tooth Supported Full-Mouth Rehabilitation with Hobo Twin-Stage Technique Koshika Tandon, Ajay Singh, Himanshu Gupta, Rajdeep
TOOTH SUPPORTED MANDIBULAR OVERDENTURE: A FORGOTTEN CONCEPT
 TJPRC: International Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry & Research (TJPRC:IJPDR) Vol. 1, Issue 1, Jun 2017, 5-10 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. TOOTH SUPPORTED MANDIBULAR OVERDENTURE: A FORGOTTEN CONCEPT ANSUIA GUPTA 1,
TJPRC: International Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry & Research (TJPRC:IJPDR) Vol. 1, Issue 1, Jun 2017, 5-10 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. TOOTH SUPPORTED MANDIBULAR OVERDENTURE: A FORGOTTEN CONCEPT ANSUIA GUPTA 1,
Very small abutment head easy and secure handling. Ankylos. The SmartFix concept. Prosthetic solution on angled implants
 Very small abutment head easy and secure handling Ankylos The SmartFix concept Prosthetic solution on angled implants Stable prosthetic fit The area supporting the prosthesis is extended distally by the
Very small abutment head easy and secure handling Ankylos The SmartFix concept Prosthetic solution on angled implants Stable prosthetic fit The area supporting the prosthesis is extended distally by the
M.D.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION. (Revised Regulations) Branch VI PROSTHODONTICS. (For Candidates admitted from onwards)
 September 2008 [KT 389] Sub. Code: 2422. (Revised Regulations) Branch VI PROSTHODONTICS (For Candidates admitted from 2004-2005 onwards) Paper II REMOVABLE PROSTHODONTICS AND Time : Three hours Q.P. Code
September 2008 [KT 389] Sub. Code: 2422. (Revised Regulations) Branch VI PROSTHODONTICS (For Candidates admitted from 2004-2005 onwards) Paper II REMOVABLE PROSTHODONTICS AND Time : Three hours Q.P. Code
Jaw relation registration in RPD
 Jaw relation registration in RPD Why to Record the Jaw Relations? To establish and maintain a harmonious relationship with all oral structures and to provide a masticatory apparatus that is efficient and
Jaw relation registration in RPD Why to Record the Jaw Relations? To establish and maintain a harmonious relationship with all oral structures and to provide a masticatory apparatus that is efficient and
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1.
 Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Complete denture impressions
 Lec.5 Complete denture impressions د. غسان الطائي Dental Impression: a negative imprint of an oral structure used to produce a positive replica of the structure to be used as a permanent record or in the
Lec.5 Complete denture impressions د. غسان الطائي Dental Impression: a negative imprint of an oral structure used to produce a positive replica of the structure to be used as a permanent record or in the
DIGITAL DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING FOR PLACEMENT AND RESTORATION OF SINGLE IMPLANTS IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA By Timothy Kosinski, DDS
 DIGITAL DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING FOR PLACEMENT AND RESTORATION OF SINGLE IMPLANTS IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA By Timothy Kosinski, DDS Dental implants have undergone many positive advances in recent
DIGITAL DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING FOR PLACEMENT AND RESTORATION OF SINGLE IMPLANTS IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA By Timothy Kosinski, DDS Dental implants have undergone many positive advances in recent
synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions
 synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions INTRODUCTION synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations 1 The synocta Meso abutments, available
synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions INTRODUCTION synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations 1 The synocta Meso abutments, available
Arrangement of posterior artificial teeth Standardized parameters Curve of Wilson Curve of Spee
 . Arrangement of posterior artificial teeth Posterior teeth are set up in tight centric occlusion. The mandibular teeth are set in the wax occlusion rim over the residual ridge in their ideal buccolingual
. Arrangement of posterior artificial teeth Posterior teeth are set up in tight centric occlusion. The mandibular teeth are set in the wax occlusion rim over the residual ridge in their ideal buccolingual
BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
 Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5734 BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5734 BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
Prosthodontic Rehabilitation of Different Clinical Situation
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 1, January 2014 1 Prosthodontic Rehabilitation of Different Clinical Situation 1 Dr. K. Raghavendra Reddy, 2 Dr. Prafulla
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 1, January 2014 1 Prosthodontic Rehabilitation of Different Clinical Situation 1 Dr. K. Raghavendra Reddy, 2 Dr. Prafulla
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Dr.Adel F.Ibraheem Partial Veneer Crown(Three quarter crown) Three quarter (¾ )crown: Uses: Indications ---- For posterior teeth ;
 Lecture.9 Dr.Adel F.Ibraheem Partial Veneer Crown(Three quarter crown) *It is a cast metal crown restoration that cover only a part of the clinical crown, most commonly used type of partial veneer crown
Lecture.9 Dr.Adel F.Ibraheem Partial Veneer Crown(Three quarter crown) *It is a cast metal crown restoration that cover only a part of the clinical crown, most commonly used type of partial veneer crown
Selection and arrangement of teeth in rpd
 Selection and arrangement of teeth in rpd upon completion of the articulator mounting and a thorough assessment of the occlusal requirements, the practitioner should be able to perform the proper arrangement
Selection and arrangement of teeth in rpd upon completion of the articulator mounting and a thorough assessment of the occlusal requirements, the practitioner should be able to perform the proper arrangement
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/24/14 REVISED DATE: 04/23/15, 04/28/16, 06/22/17, 06/28/18 POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Dental
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Advanced restorative techniques and the full mouth reconstruction: the use of gold copings in bridgework
 Clinical Advanced restorative techniques and the full mouth reconstruction: the use of gold copings in bridgework Paul Tipton 1 Introduction From the studies produced by Lindhe and Nyman, described earlier
Clinical Advanced restorative techniques and the full mouth reconstruction: the use of gold copings in bridgework Paul Tipton 1 Introduction From the studies produced by Lindhe and Nyman, described earlier
Concepts of occlusion Balanced occlusion. Monoplane occlusion. Lingualized occlusion. Figure (10-1)
 Any contact between teeth of opposing dental arches; usually, referring to contact between the occlusal surface. The static relationship between the incising or masticatory surfaces of the maxillary or
Any contact between teeth of opposing dental arches; usually, referring to contact between the occlusal surface. The static relationship between the incising or masticatory surfaces of the maxillary or
Clasp design. Many RPD design principles are based. prosthetics PRACTICE
 8 J. Clasp design C. Davenport, 1 R. M. Basker, 2 J. R. Heath, 3 J. P. Ralph, 4 P-O. Glantz, 5 and P. Hammond, 6 PRACTICE In this article statements related to the design of clasps are listed and discussed.
8 J. Clasp design C. Davenport, 1 R. M. Basker, 2 J. R. Heath, 3 J. P. Ralph, 4 P-O. Glantz, 5 and P. Hammond, 6 PRACTICE In this article statements related to the design of clasps are listed and discussed.
Active Clinical Treatment Case 48
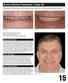 Active Clinical Treatment Case 48 Treating Clinicians: Drs. Jung Nam, Scott G. Cohen and Soojin Kim Initial smile Final smile Initial Presentation: January 2004 Age at Initial Presentation: 59 Active Treatment
Active Clinical Treatment Case 48 Treating Clinicians: Drs. Jung Nam, Scott G. Cohen and Soojin Kim Initial smile Final smile Initial Presentation: January 2004 Age at Initial Presentation: 59 Active Treatment
Occlusion in complete denture
 Occlusion in complete denture Occlusion is a concept that is pertinent to all dental patients wheather they have their own teeth or not.it is a term used to describe the contact relationship between the
Occlusion in complete denture Occlusion is a concept that is pertinent to all dental patients wheather they have their own teeth or not.it is a term used to describe the contact relationship between the
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations
 Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
Should Implants Be Connected to Natural Teeth
 Should Implants Be Connected to Natural Teeth by Gordon J. Christensen, DDS, MSD, PhD Gordon J. Christensen, DDS, MSD, PhD, is a practicing prosthodontist in Provo, Utah, and an adjunct professor at the
Should Implants Be Connected to Natural Teeth by Gordon J. Christensen, DDS, MSD, PhD Gordon J. Christensen, DDS, MSD, PhD, is a practicing prosthodontist in Provo, Utah, and an adjunct professor at the
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry
 Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Our ultimate goal is to provide you and your patients with the highest standards in implant case planning
Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Our ultimate goal is to provide you and your patients with the highest standards in implant case planning
REMOVABLE PROSTHODONTICS
 REMOVABLE PROSTHODONTICS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG020.03 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1
REMOVABLE PROSTHODONTICS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG020.03 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1
Types of prostetic appliances Dr. Barbara Kispélyi
 Semmelweis University Faculty of Dentistry Department of Prosthodontics Types of prostetic appliances Dr. Barbara Kispélyi Types of prostetic appliances Types of the fixed prostetic appliances According
Semmelweis University Faculty of Dentistry Department of Prosthodontics Types of prostetic appliances Dr. Barbara Kispélyi Types of prostetic appliances Types of the fixed prostetic appliances According
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Table of Contents. Flexi-Overdenture Characteristics
 A s with Flexi-Post Flexi-Overdenture has the unique threaded split shank that creates maximum retention with minimum stress to the root. It is manufactured in stainless steel for the direct/non-coping
A s with Flexi-Post Flexi-Overdenture has the unique threaded split shank that creates maximum retention with minimum stress to the root. It is manufactured in stainless steel for the direct/non-coping
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry
 Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Scheduled Dental Benefit Plan Schedule of Dental Allowances
 Diagnostic Scheduled Dental Benefit Plan Schedule of Dental Allowances 0120 Periodic Oral Evaluation (once in 5 months after comprehensive) 20.00 0140 Limited Oral Evaluation 20.00 0150 Comprehensive Oral
Diagnostic Scheduled Dental Benefit Plan Schedule of Dental Allowances 0120 Periodic Oral Evaluation (once in 5 months after comprehensive) 20.00 0140 Limited Oral Evaluation 20.00 0150 Comprehensive Oral
Prosthodontic Management of Combination Syndrome Case with Metal Reinforced Maxillary Complete Denture and Mandibular Teeth supported Overdenture
 Case Report imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Periodontics and Prosthodontics DOI: 10.21767/2471-3082.100041 Prosthodontic Management of Combination Syndrome Case with Metal Reinforced Maxillary Complete
Case Report imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Periodontics and Prosthodontics DOI: 10.21767/2471-3082.100041 Prosthodontic Management of Combination Syndrome Case with Metal Reinforced Maxillary Complete
Comparison of Different Methods of Abutment Splinting and Attachments on Teeth Kinetics (Part I)
 wjd Ahmed N Elsherbini, Wilhelm Niedermeier Original Article 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1464 Comparison of Different Methods of Abutment Splinting and Attachments on Teeth Kinetics (Part I) 1 Ahmed N Elsherbini,
wjd Ahmed N Elsherbini, Wilhelm Niedermeier Original Article 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1464 Comparison of Different Methods of Abutment Splinting and Attachments on Teeth Kinetics (Part I) 1 Ahmed N Elsherbini,
2015 Member Speaker Forum. Chair: L. Scott Brooksby, DDS, BS. Friday, October 23, :30 AM 3:45 PM. Coral Ballroom. 3.
 2015 Member Speaker Forum Chair: L. Scott Brooksby, DDS, BS Friday, October 23, 2015 11:30 AM 3:45 PM Coral Ballroom 3.25 CE Credits 11:30 a.m. 3:45 p.m. Member Speaker Forum 11:30 11:40 a.m. Introduction
2015 Member Speaker Forum Chair: L. Scott Brooksby, DDS, BS Friday, October 23, 2015 11:30 AM 3:45 PM Coral Ballroom 3.25 CE Credits 11:30 a.m. 3:45 p.m. Member Speaker Forum 11:30 11:40 a.m. Introduction
Interdisciplinary Treatment Planning in Transitioning Periodontally Hopeless Dentition
 Interdisciplinary Treatment Planning in Transitioning Periodontally Hopeless Dentition A clinical case review I NTRODUCTION Decreasing risk in an advanced periodontally diseased dentition presents a great
Interdisciplinary Treatment Planning in Transitioning Periodontally Hopeless Dentition A clinical case review I NTRODUCTION Decreasing risk in an advanced periodontally diseased dentition presents a great
Paper submission. Denture repair with the application of a magnetic attachment to the inner crown of a telescopic crown: A 3-year follow-up case
 Paper submission Denture repair with the application of a magnetic attachment to the inner crown of a telescopic crown: A 3-year follow-up case A. Izumida Department of Comprehensive Dentistry, Tohoku
Paper submission Denture repair with the application of a magnetic attachment to the inner crown of a telescopic crown: A 3-year follow-up case A. Izumida Department of Comprehensive Dentistry, Tohoku
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
Nagri D et al. Linear occlusion and Neutral Zone recording for severely resorbed ridges
 Doi:10.21276/ledent.2018.02.01.02 Case Report LINEAR OCCLUSION AND NEUTRAL ZONE RECORDING USING TISSUE CONDITIONER REPORT OF A SEVERELY RESORBED RIDGE Divya Nagri, 1Ashish Kakkar, 2Neeraj Mittal, 3Lovely
Doi:10.21276/ledent.2018.02.01.02 Case Report LINEAR OCCLUSION AND NEUTRAL ZONE RECORDING USING TISSUE CONDITIONER REPORT OF A SEVERELY RESORBED RIDGE Divya Nagri, 1Ashish Kakkar, 2Neeraj Mittal, 3Lovely
Massachusetts Family High Dental Plan with Enhanced Child Orthodontia
 SCHEDULE OF BENEFITS Massachusetts Family High Dental Plan with Enhanced Child Orthodontia This Schedule of Benefits lists the services available under the MetLife plan, as well as the co-insurance payments
SCHEDULE OF BENEFITS Massachusetts Family High Dental Plan with Enhanced Child Orthodontia This Schedule of Benefits lists the services available under the MetLife plan, as well as the co-insurance payments
