Relationship between post-preparation pain and apical patency: A randomized clinical trial
|
|
|
- Donald Thomas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Relationship between post-preparation pain and apical patency: A randomized clinical trial Marwa E Sharaan 1*, Naguib M Aboul-Enein 2 1 College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, UAE 2 Department of Endodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Suez Canal University, Egypt *Presenting Author ABSTRACT Objective: This study was conducted to compare the post-preparation pain experience following root canal preparation with or without achieving and maintaining apical patency during root canal preparation. Materials and Methods: Root canal preparation was completed in the first visit for eighty patients. The patients were divided randomly into two groups where patency was either established and maintained during preparation or not. Pain was recorded before treatment, 6,12,18,24 and 48 hours after treatment. Patients assessed their severity of pain over the first two days following root canal preparation using a modified visual analog scale of (0-9). Results: Our results showed that no significant difference was found between the two groups. No significant difference was found between the two groups studied. No significance was found between all the previous preoperative clinical and radiographic findings and post-preparation pain, except preoperative pain. Conclusion: Apical patency did not increase the post preparation pain significantly Key words: post-preparation pain, apical patency. INTRODUCTION Postoperative pain after endodontic procedures is a frustrating occurrence for both patients and clinicians. Endodontic pain may occur before, during, or after endodontic treatment 1. During root canal instrumentation, dentinal and pulpal debris can block access to the apical third, increasing the possibility of transportation or perforation which may lead to postpreparation pain 2,3,4. Many researchers pointed out that apical blockage could be avoided by using patency file 5. Maintaining apical patency improved the delivery of irrigants into the apical third of large human root canals 6,7. Canal patency is performed by pushing small highly flexible files passively through apical constriction without widening it. Considering the rich collateral circulation and healing potential of the attachment apparatus, establishing and maintaining patency are non-harmful biological events 8. On the contrary, some clinicians suggested that repeated use of small patency files could push apical debris. They accused it by its responsibility for acute periapical inflammatory response and as a result, severe post operative pain 9,10. The concept of creating and maintaining canal patency is still controversial. The aim of this study was to evaluate whether establishing and maintaining apical patency would influence the incidence, degree or duration of postoperative pain. We did not find any published research assessing the incidence of postpreparation pain when apical patency was maintained during preparation. One recent research, Arias et al, studied the effect of apical patency on postoperative pain after obturation 3. MATERIALS AND METHODS A total of eighty patients consented to participate in this study at the clinic of endodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Suez Canal University. Patients of both sexes ranging from 14 to 60 years of age were selected. All teeth were permanent with mature apices. Patients received initial nonsurgical root canal therapy on a single tooth over two visits. Symptomatic and asymptomatic anterior and posterior 96 GMJ, 4 th Annual Scientific Meeting of Gulf Medical University Oral Proceedings 2012
2 teeth with pulpal and / or periapical pathosis were included in the study. The patients did not take any medications that could affect pain perception or inflammation. The patients were assigned randomly into two groups (40 per group). Apical patency was established and maintained during preparation in one group while it was not undertaken in the other. The working length of root canals were determined electronically by using the ipex apex locator (K Japan) and confirmed radiographically ( 0.5-1mm). In Group I, patency stainless steel k- file # 10 was moved 1 mm through the apical foramen during the root canal preparation after each file. In Group II apical patency was neither established nor maintained during preparation. The root canals were instrumented using a combination of passive step-back technique with hand instruments and crown down technique using hero shaper (Micromega France) nickel titanium rotary instruments. The root canals were prepared to an apical ISO that ranged from size #35 to # 55 (master apical file) depending on both root canal anatomy and initial diameter of root canal. Irrigation was continuously performed passively using 2ml of 2.25 % sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) solution between each file. Rc-prep paste (Premier USA) was used. All root canals were later dried with sterile paper points. After placing a dry sterile cotton pellet in the pulp chamber of each tooth, the access cavities were sealed with 4 mm Cavit )Espe Switzerland) as a temporary filling. Pain as experienced by the patients following the endodontic therapy was scored and recorded in a home report. Patients recorded pain score before treatment and 6, 12,18,24 and 48 hours after treatment. The patients assessed their severity of pain using a modified visual analogue scale (VAS). The degree of pain recorded at each period of observation was given a numerical value (0= no pain, 1-3= mild pain, 4-6= moderate pain, 7-9= severe pain). Two days after cleaning and shaping, the patients returned for obturation of their root canals bringing their completed questionnaires. All cases were obturated using lateral compaction technique. RESULTS Preoperative clinical and radiographic findings were recorded for two groups before treatment. These conditions were: preoperative pain, percussion/palpation Table 1. Correlation between clinical and radiographic findings and the post-preparation pain Clincal & Radiographic findings Min. -Max. Mean ± SD P valve Preoperative pain No ± 1.53 Yes ± 1.97 Percussion / palpation No ± 1.96 Yes ± 2.01 Swelling No ± 1.95 Yes ± 2.34 Radiographic radiolucency No lesion ± 1.85 Thickening of PDL ± 1.97 Lesion < mm ± 2.24 Lesion > mm Pulpal diagnosis Normal ± 1.73 Irreversible pulpitis ± 1.94 Necrotic pulp ± 2.03 Periradicular diagnosis Normal ± 1.89 Acute apical peridontitis ± 1.92 Chronic apical periodontitis ± 2.24 < 0.01 GMJ,4 th Annual Scientific Meeting of Gulf Medical University Oral Proceedings
3 senstivity, swelling, radiographic radiolucency, pulpal and periradicular status. No significant difference was found between the two groups studied. No significance was found between all the previous preoperative clinical and radiographic findings and postpreparation pain, except preoperative pain. When it existed, there was a higher tendency for post-preparation pain. There was a significant correlation between the presence of post-preparation pain and preoperative pain (p< 0.01) (Table 1). None of the patients developed symptoms of acute inflammation necessiating removal from the study. After 48 hrs. of root canal preparation of the patients, 44 % had no post-preparation pain, 41 % had mild pain, 14 % had moderate pain and 1 % had severe pain (Table 2). Table 2. Number of patients who experienced different degree of post-preparation pain in two groups after 48 hrs. of observation Pain degree No. % None Mild Moderate Severe 1 1 Total Post-preparation pain decreased with time in both groups tested. Although it was statistically insignificant, it was found that in group I, there was a tendency for an increase in post-preparation pain at 6 and 12 hrs. as compared to group II. On the other hand, there was a tendency of a decline in post-preparation pain at 24 and 48 hrs. in group I when compared to group II, with no significant difference (Table 3). DISCUSSION Post-preparation pain during root canal treatment was the focus of interest in this study. We aimed to assess the effect of apical patency on post-preparation pain. Endodontic pain was defined as pain of any degree that occurs after the initiation of root canal treatment 1. Clem defined postoperative pain as a pain existing in a patient who had previously experienced none as an increase in an already existing pain 12. Pain is an individual matter and dificullt to be measured accurately. Pain could be measured only according to the patient response 13. No pain research would be complete without addressing the subjectivity of the pain response. It is Table 3. Comparison between group I and group II at the different time intervals Variables Group I Group II P Pre-operative Min.-Max Mean ± SD 4.45 ± ± 2.54 Post 6hrs Min.-Max Mean ± SD 3.73 ± ± 2.67 Post 12hrs Min.-Max Mean ± SD 3.15 ± ± 2.54 Post 18hrs Min.-Max Mean ± SD 2.38 ± ± 2.26 Post 24hrs Min.-Max Mean ± SD 1.80 ± ± 1.95 Post 48hrs Min.-Max Mean ± SD 1.00 ± ± GMJ, 4 th Annual Scientific Meeting of Gulf Medical University Oral Proceedings 2012
4 a difficult concept to qualify or quantify the pain in any statistical analysis. Pain research was an area where subjective information is crucial and the questions to be answered are more complex or dependent on the patient s integration of the object (pain) and the response (action or impact) 14. In this study, preoperative clinical and radiographic findings as well as pulpal and periradicular diagnoses were collected from all patients. No significant difference in the distribution was found between two groups. These factors included perscussion / palpation senstivity, preoperative swelling, vitality of teeth, presence of periapical radiolucencies and apical periodontitis either chronic or acute. The contribution of these factors to the post-preparation pain revealed insignificant influence on the development of post-preparation pain. These findings were in agreement with those of other investigators However, some authors reported the significant effect of these factors on the development of interappointment pain. The factors included age, gender, tooth type, pulpal status, presence of preoperative pain, preoperative periapical diagnosis, size of periradicular lesions, allergies and presence of sinus tracts 15, In this investigation, the presence of preoperative pain was found to be the only significant factor influencing the incidence of post-preparation pain. This finding was in accordance with that in other studies 20,21,23,24, On the other hand, other investigations negated the association between the presence of preoperative pain and the incidence of postpreparation pain 19,25,26. In the current study, data revealed a decline in mean pain intensity over time for both groups after endodontic treatment. These findings were similar to those of other clinical studies that demonstrated a significant reduction in pain after root canal treatment 15,20,21,23. Negm explained the decrease in postoperative pain level could be a function of pain resolution with healing 1. Endodontic treatment by itself often provided pain relief 30. The decrease in pain might be due to a reduction in tissue levels of inflammatory mediators and interstitial tissue pressure that stimulate peripheral terminals of nociceptors 32. In the present study,it was found that pain persisted at different levels. The occurrence of post-preparation pain of mild intensity was not a rare event even when endodontic treatment had followed acceptable standards 16,18,21. The development of post-preparation pain of moderate to severe intensity has been demonstarted to be of unusal occurrence 34. In this study, the prevalence of 45% pain experience after 48 hrs. of root canal preparation was much higher than that reported in some studies 16,18,21 whereas it was lower compared to some others 13,24,27. This discrepancy could be attributed to differences in the preoperative status of the teeth and the treatment procedures. In the current study, the results showed that preparation of the apical foramen with patency had a decreased mean pain level at most of the time intervals. Preparation shorter of the apical foramen might leave a dentinal plug full of necrotic debris and bacteria which might cause inflammation and delayed healing. This plug could cause an increase in pain incidence especially when there was an apical inflammation with its subsequent pressure Using a patency file might remove the remaining debris, keeping the foramen free from any blocked infected debris, assuring a clean foramen 4,11,38. Furthermore, it could give the chance of venting in such cases of apical inflammation resulting in pain decline. The findings of the present study are in accordance with those others who emphasized the use of apical patency concept. Flanders stated that unless apical patency was established and maintained throughout the cleaning and shaping procedures, a portion of the root canal system was likley to be left untreated, inviting failure 38. The use of smaller files which maintained a limited apical opening reduces the extrusion of noxious material to the surrounding GMJ,4 th Annual Scientific Meeting of Gulf Medical University Oral Proceedings
5 tissue 4,11,39. It was also claimed that the amount of smear layer could be reduced by using patency files 9. Moreover, researchers reported the accessbility of instruments to apical constriction of root canals was closely related to treatment outcome. The success rate was lower in the group of cases with inaccessible apical constriction than where the canals had accessible constriction 40. Furthermore, in a recent study Sanchez at al. reported a well prepared apical foramen without any transportation using apical patency 41. On the contrary, others stated that apical patency encourged the extrusion of dentin chips, debris and irrigants and caused overenlargement of the apical foramen leading to periapical tissues damage 17,42,43. The periapical healing process of teeth in dogs with or without apical patency and after root filling was assessed in a study by Holland et al. 43 Signifcantly better healing was found in the group in which patency was not maintained. It should be noted that using large instruments at the patency length could result in severe periradicular injury, causing lack of apical stop and extrusion of a large amount of infected debris, which predisposed to the occurrence of postpreparation discomfort and /or jeopardized the outcome of endodontic therapy 10,44. A scanning electron microscope investigation showed cementum fractues and dentinal chips at the apex after penetration of a # 15 k-file through the foramen 10. In this study, small files (# 10 K-file) were used gently to guarantee that the canal was only negotiated without any futher apical enlargement. In general, we can say that apical patency did not display any significant influence on the incidence or intensity of postoperative pain. This finding was consistent with that of others who found that apical patency had no effect on the postoperative pain incidence 3,21,22. CONCLUSION Apical patency did not increase the post preparation pain significantly. RECOMMENDATION Comparing the advantages and the disadvanatges of apical patency, we recommend establishing and maintaining apical patency during root canal preparation. REFERENCES 1. Negm M. Intracanal use of a corticosteroid antibiotic compound for the management of post treatment endodontic pain. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2001;92: Al-Omari MA, Dummer PM. Canal blockage and debris extrusion with eight preparation techniques. Journal of Endod 1995; 21: Arias A etal.relationship between postendodontic pain, tooth diagnostic factors, and apical patency. Journal of Endod 2009; 35: Cailleteau JG, Mullaney TP.Prevalence of teaching apical patency and various instrumentation and obturation techniques in United States dental schools. Journal of Endod 1997;23: Cohen S and Burns RC. Pathways of the pulp, eighth ed., copyright, Mosby; 2002: Jorge Vera et al. Effect of Maintaining Apical Patency on Irrigant Penetration into the Apical Third of Root Canals When Using Passive Ultrasonic Irrigation: An In Vivo Study.Journal of Endod 2011 ;37: Jorge Vera et al. Effect of Maintaining Apical Patency on Irrigant Penetration into the Apical Two Millimeters of Large Root Canals: An In Vivo Study, An In Vivo Study, Journal of Endod 2012;38: Buchanan LS. Management of the curved root canal. J Calif Dent Assoc 1989;17: Goldberg F and Massone EJ. Patency file and apical transportation ; an in vitro study. J Endodon 2002;28: Gutiérrez JH, Brizuela C and Villota E. Human teeth with periapical pathosis after overinstrumentation and overfilling of the root canals: a scanning electron microscopic study. International Endodontic Journal 1999;2: Sathorn C, Parashos P and Messer H. The prevalence of postoperative pain and flare up in single and multiple endodontic treatment : a systemic review. Int Endo J 2008;41: Clem WH. Posttreatment endodontic pain. Journal of American Dental association 1970; Harrington J and Natkin E. Mid treatment flare ups. Dental clinics of North America 1992;36: Atchison K. understanding and utilizing qualitative research. Journal of Dental education 1996;60: GMJ, 4 th Annual Scientific Meeting of Gulf Medical University Oral Proceedings 2012
6 15. Georgopoulou M, Anastassiadis P and Sykaras S. Pain after chemomechanical preparation. Int Endo J 1986;19: Watkins CA, Logan HL and Kirchner L. Anticepated and experienced pain associated with endodontic therapy. J Am Dent Assoc 2002;133: Harrison J, Braumgartner C and Zielke D. Analysis of interappointment pain assocaited with the conmbined use of endodontic irrigants and medicament. J Endodon 1981;7: Martin H and Cunningham W. An evaluation of postoperative pain and incidence following endosonic and conventional root canal therapy. Oral Surg 1989;54: Torabinejad M, Cymerman J, Lemon R, et al. Effectiveness of various medications on postoperative pain following complete instrumentation. J Endodon 1994;20: Siqueira J, Rôças I, Favieri A, et al. Incidence of post operative pain after intra canal procedures based on antimicrobial strategy. J Endodon 2002;28: Torabinejad M, Kettering J, McGraw J, et al. Factors associated with endodotnic interappointment emergencies of teeth with necrotic pulps. J Endodon 1988;14: Genet JM, Weeslink PR and Thoden VSK. The incidence of preoperative and postoperative pain in endodontic therapy. Int Endo J 1986;19: Walton R and Fouad A. Endodontic interappointment flare ups: A prospective study of incidence and related factors. J Endodon 1992;18: Perez B and Moshonov J. Dental anxiety among patients undergoing endodontic treatment. J Endodon 1998;24: Albashaireh ZS and Alnegrish AS. Postobturation pain after single and multiple visit endodotnic therapy. A prospective study. Journal of Dentistry 1998;26: Glennon J, Ng Y, Setchell d, et al. Prevalence of and factors affecting post preparation pain in patients undergoing two visit root canal treatment. Int Endod J 2004;37: Ng Y, Glennon J, Setchell D, et al. Prevalence of and factors affecting post obturation pain in patients undergoing root canal treatment. Int Endod J 2004;37: Polycarpou N, Ng Y, Canavan D, et al. Prevalence of persistent pain after the treatment and factors affecting its occurance in cases with complete radiographic healing. Int Endod J 2005;38: Torabinejad M, Shabahang S and Bahjri K. Effect of MTAD on postopeative discomfort: A randomized clinical trial. J Endodon 2005;31: Chugal N, Clive J and Spangberg L. A prognostic model for assessment of the outcome of endodontic treatment: Effect of biologic and treatment variable. Oral Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2001;91: Keiser K and Hargreaves K. Building effective strategies for the management of endodontic pain.endo.topics 2002;3: Walton R and Torabinejad M. Principles and practice of endodontics, 3 rd ed. Phildephia: W.B. Saunders;2002: Siqueira J and Barnett F. Interappointment pain: Mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment. Endodontic Topics 2004;7: Stein T and Corcoran J. Anatomy of the root apex and its histologic changes with age. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol1990; 69: Morfis A, Sylaras S, Georgopoulou M, et al. Study of the apices of human permanent teeth with use of a scanning electron microscope. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1994;77: Gutiérrez JH and Aguayo P. Apical foraminal openings in human teeth. Number and location. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Endod 1995;79: Flanders D. Endodontic Patency: How to get it, How to keep it, Why it is so important. NYSDJ; 2002; Souza R. The importance of apical patency and cleaning of the apical foramen on root canal preparation. Braz Dent J 2006;17: Negishi J, Kwanami M and Ogami E. Risk analysis of failure of root canal treatment for teeth with inaccessible apical constriction. Journal of Dentistry 2005;33: Lambrianidis T, Tosounidou E and Tzoanopoulou M. The effect of manintaining apical patency on periapical extrusion. J Endodon 2001;27: Gonzalez SJA, Duran-Sindreu F, Albuquerque M, et al. Apical transportation created using three different patency instruments. International Endodontic Journal 2010;43: Ricucci D and Langeland K. Apical limit of root canal instrumentation and obturation, part 2. A histological study. Int Endo.J 1998;31: Holland R, Santanna A, Souza V, et al. Influence of apical patency and filling material on healing process of dogs teeth with vital pulp after root canal therapy. Braz Dent J 2005;16: Tinaz A, Alacam T, Uzun O, et al. The effect of disruption of apical constriction on periapical extrusion. J Endodon 2005;31: GMJ,4 th Annual Scientific Meeting of Gulf Medical University Oral Proceedings
Apical transportation created using three different patency instruments
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2010.01710.x Apical transportation created using three different patency instruments J. A. Gonzalez Sanchez, F. Duran-Sindreu, M. Albuquerque Matos, T. Garcia Carabaño, M. Mercade
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2010.01710.x Apical transportation created using three different patency instruments J. A. Gonzalez Sanchez, F. Duran-Sindreu, M. Albuquerque Matos, T. Garcia Carabaño, M. Mercade
ENDODONTIC PAIN CONTROL. Dr. Ameer H. AL-Ameedee Ph.D in Operative and Esthetic Dentistry
 ENDODONTIC PAIN CONTROL Dr. Ameer H. AL-Ameedee Ph.D in Operative and Esthetic Dentistry ENDODONTIC EMERGENCIES ARE CHALLENGE IN BOTH DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT -EVERY CASE IS A COMPLETE SEPARATE STORY Diagnostic
ENDODONTIC PAIN CONTROL Dr. Ameer H. AL-Ameedee Ph.D in Operative and Esthetic Dentistry ENDODONTIC EMERGENCIES ARE CHALLENGE IN BOTH DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT -EVERY CASE IS A COMPLETE SEPARATE STORY Diagnostic
The influence of the apical limit of root canal preparation on apical foramen transportation (laboratory study)
 The influence of the apical limit of root canal preparation on apical foramen transportation (laboratory study) Marwa El-Sayed Sharaan College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, UAE ABSTRACT
The influence of the apical limit of root canal preparation on apical foramen transportation (laboratory study) Marwa El-Sayed Sharaan College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, UAE ABSTRACT
In vitro Study of Apically Extruded Debris and Irrigant Following the Use of Conventional and Rotary Instrumentation Techniques
 Apr.-Jun. 2014, Volume 11, No. 2 (Serial No. 94) pp. 49-54 Journal of US-China Medical Science, ISSN 1548-6648, USA D DAV I D PUBLISHING In vitro Study of Apically Extruded Debris and Irrigant Following
Apr.-Jun. 2014, Volume 11, No. 2 (Serial No. 94) pp. 49-54 Journal of US-China Medical Science, ISSN 1548-6648, USA D DAV I D PUBLISHING In vitro Study of Apically Extruded Debris and Irrigant Following
Staining Potential of Calcium Hydroxide and Monochlorophenol Following Removal of AH26 Root Canal Sealer
 Staining Potential of Calcium Hydroxide and Monochlorophenol Following Removal of AH26 Root Canal Sealer Abstract Aim: The focus of this study was to examine the staining potential of calcium hydroxide
Staining Potential of Calcium Hydroxide and Monochlorophenol Following Removal of AH26 Root Canal Sealer Abstract Aim: The focus of this study was to examine the staining potential of calcium hydroxide
Principles of diagnosis in Endodontics. Pain History. Patient Assessment. Examination. Examination 11/07/2014
 Principles of diagnosis in Endodontics Diagnosis, pulpitis, perio-endo. Treatment planning & case selection Patients assessment Special tests which help us diagnose pulpal disease How reliable are they?
Principles of diagnosis in Endodontics Diagnosis, pulpitis, perio-endo. Treatment planning & case selection Patients assessment Special tests which help us diagnose pulpal disease How reliable are they?
Shah. Management of a maxillary second premolar with an S-shaped root canal - An endodontic. Management of a maxillary second premolar
 Case Report Management of a maxillary second premolar with an S-shaped root canal - An endodontic challenge Nabi Shahnaz 1, Amin Khalid 2, Hussain Aijaz 3, Baba Irfan Ashraf 4*, Aasim Farooq Shah 5 1 PG
Case Report Management of a maxillary second premolar with an S-shaped root canal - An endodontic challenge Nabi Shahnaz 1, Amin Khalid 2, Hussain Aijaz 3, Baba Irfan Ashraf 4*, Aasim Farooq Shah 5 1 PG
The evaluation of endodontic flare-ups and their relationship to various risk factors
 Onay et al. BMC Oral Health (2015) 15:142 DOI 10.1186/s12903-015-0135-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The evaluation of endodontic flare-ups and their relationship to various risk factors Emel Olga Onay
Onay et al. BMC Oral Health (2015) 15:142 DOI 10.1186/s12903-015-0135-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The evaluation of endodontic flare-ups and their relationship to various risk factors Emel Olga Onay
Large periapical lesion: Healing without knife and incision
 Large periapical lesion: Healing without knife and incision Ridhima Suneja College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, UAE ABSTRACT Three dimensional obturation of root space has always yielded
Large periapical lesion: Healing without knife and incision Ridhima Suneja College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, UAE ABSTRACT Three dimensional obturation of root space has always yielded
An In Vivo Evaluation of Two Types of Files used to Accurately Determine the Diameter of the Apical Constriction of a Root Canal: An In Vivo Study
 An In Vivo Evaluation of Two Types of Files used to Accurately Determine the Diameter of the Apical Constriction of a Root Canal: An In Vivo Study Sumeet Darda, BDS, MDS; Narendra Manwar, BDS, MDS; Manoj
An In Vivo Evaluation of Two Types of Files used to Accurately Determine the Diameter of the Apical Constriction of a Root Canal: An In Vivo Study Sumeet Darda, BDS, MDS; Narendra Manwar, BDS, MDS; Manoj
Corresponding Author:Dr.Sneha Vaidya 3
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. VII (Nov. 2017), PP 75-81 www.iosrjournals.org Efficacy of Endoactivator Irrigation
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 11 Ver. VII (Nov. 2017), PP 75-81 www.iosrjournals.org Efficacy of Endoactivator Irrigation
In vitro evaluation of root canal preparation with plastic endodontic rotary finishing file - A SEM study
 Original Research In vitro evaluation of root canal preparation with plastic endodontic rotary finishing file - A SEM study ASHUTOSH * ASEEM P. TIKKU ** ANIL CHANDRA ** PROMILA VERMA *** RAKESH K. YADAV
Original Research In vitro evaluation of root canal preparation with plastic endodontic rotary finishing file - A SEM study ASHUTOSH * ASEEM P. TIKKU ** ANIL CHANDRA ** PROMILA VERMA *** RAKESH K. YADAV
Comparison of the Different Techniques to Remove Fractured Endodontic Instruments from Root Canal Systems
 Comparison of the Different Techniques to Remove Fractured Endodontic Instruments from Root Canal Systems Nimet Gencoglu a Dilek Helvacioglu b Abstract Objectives: To evaluate the success of certain methods
Comparison of the Different Techniques to Remove Fractured Endodontic Instruments from Root Canal Systems Nimet Gencoglu a Dilek Helvacioglu b Abstract Objectives: To evaluate the success of certain methods
Influence of cervical preflaring on apical file size determination - An in vitro study
 Original Research Influence of cervical preflaring on apical file size determination - An in vitro study VASUNDHARA SHIVANNA * DEEPALI AGARWAL ** ABSTRACT Aim: To investigate the influence of cervical
Original Research Influence of cervical preflaring on apical file size determination - An in vitro study VASUNDHARA SHIVANNA * DEEPALI AGARWAL ** ABSTRACT Aim: To investigate the influence of cervical
Review of literature Single Visit versus Multiple Visit Root Canal Therapy
 Jaypee s International Journal Single of Clinical Visit versus Pediatric Multiple Dentistry, Visit Root Canal September-December Therapy 2008;1(1):17-24 Review of literature Single Visit versus Multiple
Jaypee s International Journal Single of Clinical Visit versus Pediatric Multiple Dentistry, Visit Root Canal September-December Therapy 2008;1(1):17-24 Review of literature Single Visit versus Multiple
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF APICALLY EXTRUDED DEBRIS AND IRRIGANT AFTER USING TWO ROTARY SYSTEMS (K3, RACE)
 ISSN: 1312-773X (Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2014201.459 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2014, vol. 20, issue 1 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF APICALLY EXTRUDED DEBRIS AND IRRIGANT
ISSN: 1312-773X (Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2014201.459 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2014, vol. 20, issue 1 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF APICALLY EXTRUDED DEBRIS AND IRRIGANT
NON-SURGICAL ENDODONTICS
 NON-SURGICAL ENDODONTICS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG009.03 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1
NON-SURGICAL ENDODONTICS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG009.03 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1
NON-SURGICAL ENDODONTICS
 NON-SURGICAL ENDODONTICS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG009.02 Effective Date: February 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1
NON-SURGICAL ENDODONTICS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG009.02 Effective Date: February 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1
Management of a Type III Dens Invaginatus using a Combination Surgical and Non-surgical Endodontic Therapy: A Case Report
 Management of a Type III Dens Invaginatus using a Combination Surgical and Non-surgical Endodontic Therapy: A Case Report Mithra N. Hegde, BDS, MDS, FPFA; Aditya Shetty, BDS, MDS; Rekha Sagar, BDS, MDS
Management of a Type III Dens Invaginatus using a Combination Surgical and Non-surgical Endodontic Therapy: A Case Report Mithra N. Hegde, BDS, MDS, FPFA; Aditya Shetty, BDS, MDS; Rekha Sagar, BDS, MDS
Post natal mesenchymal cells possibility to regenerate and repair dental structures.
 Post natal mesenchymal cells possibility to regenerate and repair dental structures. Received: February 2014 Accepted: April 2014 Martha Siragusa. msiragus@arnet.com.ar DDS, PhD. Endodontics Departments
Post natal mesenchymal cells possibility to regenerate and repair dental structures. Received: February 2014 Accepted: April 2014 Martha Siragusa. msiragus@arnet.com.ar DDS, PhD. Endodontics Departments
Case Note Retrieval of a separated file using Masserann technique: A case report
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2006), Vol. 4, No. 2, Issue 14, 238-242 Case Note Retrieval of a separated file using Masserann technique: A case report Pai ARV 1, Kamath MP 2, Basnet P 3 1 Associate
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2006), Vol. 4, No. 2, Issue 14, 238-242 Case Note Retrieval of a separated file using Masserann technique: A case report Pai ARV 1, Kamath MP 2, Basnet P 3 1 Associate
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION. By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur
 COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
Fundamentals of Endodontics Peter Briggs, Ahmed Farooq and Tracy Watford, Trish Moore and QED
 Fundamentals of Endodontics Peter Briggs, Ahmed Farooq and Tracy Watford, Trish Moore and QED Practical Hands-on course St George s Hospital, SW17 0QT St George s Dental Simulation Today Take the opportunity
Fundamentals of Endodontics Peter Briggs, Ahmed Farooq and Tracy Watford, Trish Moore and QED Practical Hands-on course St George s Hospital, SW17 0QT St George s Dental Simulation Today Take the opportunity
Comparison of Inter-Appointment Pain Between Ledermix and no Intracanal Medicament in Acute Apical Periodontitis
 Comparison of Inter-Appointment Pain Between Ledermix and no Intracanal Medicament in Acute Apical Periodontitis Abdul Qadir Dall, Rizwan Jouhar, Noor Ahmed Khoso Original Article ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To
Comparison of Inter-Appointment Pain Between Ledermix and no Intracanal Medicament in Acute Apical Periodontitis Abdul Qadir Dall, Rizwan Jouhar, Noor Ahmed Khoso Original Article ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To
ENDODONTIC MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLAR WITH SIX CANALS : A CASE REPORT
 ENDODONTIC MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLAR WITH SIX CANALS : A CASE REPORT Author Name: Sreenath Narayanan INTRODUCTION Accurate diagnosis and successful endodontic therapy is always a challenge
ENDODONTIC MANAGEMENT OF A MANDIBULAR FIRST MOLAR WITH SIX CANALS : A CASE REPORT Author Name: Sreenath Narayanan INTRODUCTION Accurate diagnosis and successful endodontic therapy is always a challenge
Examination of teeth and gingiva
 Examination of teeth and gingiva Siriporn Chattipakorn, DDS, PhD. SUBJECTIVE HISTORY Chief complaint In patient s own words My tooth hurts when I chew hard foods I can t drink cold drink I have bad breath
Examination of teeth and gingiva Siriporn Chattipakorn, DDS, PhD. SUBJECTIVE HISTORY Chief complaint In patient s own words My tooth hurts when I chew hard foods I can t drink cold drink I have bad breath
INCIDENCE OF ENDODONTIC FLARE-UPS USING EITHER CALCIUM HYDROXIDE OR CREOSOTE AS INTRACANAL MEDICAMENT IN SYMPTOMATIC TEETH
 Original Article INCIDENCE OF ENDODONTIC FLARE-UPS USING EITHER CALCIUM HYDROXIDE OR CREOSOTE AS INTRACANAL MEDICAMENT IN SYMPTOMATIC TEETH Dr. Shafqat Ali Shah BDS, FCPS (Pak), Senior Registrar, Department
Original Article INCIDENCE OF ENDODONTIC FLARE-UPS USING EITHER CALCIUM HYDROXIDE OR CREOSOTE AS INTRACANAL MEDICAMENT IN SYMPTOMATIC TEETH Dr. Shafqat Ali Shah BDS, FCPS (Pak), Senior Registrar, Department
Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth
 New Edition Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth A Decision Guide American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/treatmentoptions TREATMENT PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS The Treatment Options for the
New Edition Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth A Decision Guide American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/treatmentoptions TREATMENT PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS The Treatment Options for the
Jim Ruckman. 65 year-old Caucasian female presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #19.
 Case Report Jim Ruckman Non-Surgical Root Canal Therapy #19 65 year-old Caucasian female presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #19. Subjective Chief complaint: I was seen in the dental school
Case Report Jim Ruckman Non-Surgical Root Canal Therapy #19 65 year-old Caucasian female presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #19. Subjective Chief complaint: I was seen in the dental school
SIGNIFICANCE OF WORKING LENGTH IN RCT: A CASE REPORT
 SIGNIFICANCE OF WORKING LENGTH IN RCT: A CASE REPORT Dr Priyanka Bhushan MDS Public Health Dentistry, Asst Prof RIMS Dental College, Lamphelpat, Imphal, drpiyu24@yahoo.co.in Maj Kundan Kumar BDS Army Dental
SIGNIFICANCE OF WORKING LENGTH IN RCT: A CASE REPORT Dr Priyanka Bhushan MDS Public Health Dentistry, Asst Prof RIMS Dental College, Lamphelpat, Imphal, drpiyu24@yahoo.co.in Maj Kundan Kumar BDS Army Dental
Mid Mesial Canal in Mandibular Molars: Two Case Report and A Review of Literature
 ISSN 2455-4499; Vol.10, Issue 03 (March 2018) Pg. no. 27-32. Institute of Research Advances https://research-advances.org/index.php/irajas Mid Mesial Canal in Mandibular Molars: Two Case Report and A Review
ISSN 2455-4499; Vol.10, Issue 03 (March 2018) Pg. no. 27-32. Institute of Research Advances https://research-advances.org/index.php/irajas Mid Mesial Canal in Mandibular Molars: Two Case Report and A Review
Non-Surgical management of Apical third root fracture with MTA: A Case report
 International Journal Dental and Medical Sciences Research (IJDMSR) ISSN: 2393-073X Volume1, Issue 2 (Jul- 2017), PP 05-09 www.ijdmsr.com Non-Surgical management of Apical third root fracture with MTA:
International Journal Dental and Medical Sciences Research (IJDMSR) ISSN: 2393-073X Volume1, Issue 2 (Jul- 2017), PP 05-09 www.ijdmsr.com Non-Surgical management of Apical third root fracture with MTA:
Working length changes following straight-line access and different coronal flaring methods
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Working length changes following straight-line access and different coronal flaring methods Shiva Sadeghi 1 * DDS, MS and Zeinab Doago 2, DDS 1. Assistant Professor of Endodontics, Dental
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Working length changes following straight-line access and different coronal flaring methods Shiva Sadeghi 1 * DDS, MS and Zeinab Doago 2, DDS 1. Assistant Professor of Endodontics, Dental
The traumatic injury of an immature permanent tooth can lead to the loss of pulp
 Regenerative Treatment of an Immature, Traumatized Tooth With Apical Periodontitis: Report of a Case Elisabetta Cotti, DDS, MS, Manuela Mereu, DDS, and Daniela Lusso, DDS Abstract This case report describes
Regenerative Treatment of an Immature, Traumatized Tooth With Apical Periodontitis: Report of a Case Elisabetta Cotti, DDS, MS, Manuela Mereu, DDS, and Daniela Lusso, DDS Abstract This case report describes
Original Article Apical Periodontitis Pak Armed Forces Med J 2014; 64 (1): 39-45
 Original Article Apical Periodontitis Pak Armed Forces Med J 2014; 64 (1): 39-45 COMPARISON OF CALCIUM HYDROXIDE PASTE WITH KENACOMB (CORTICOSTEROID-ANTIBIOTIC PASTE) FOR POSTOPERATIVE ENDODONTIC PAIN
Original Article Apical Periodontitis Pak Armed Forces Med J 2014; 64 (1): 39-45 COMPARISON OF CALCIUM HYDROXIDE PASTE WITH KENACOMB (CORTICOSTEROID-ANTIBIOTIC PASTE) FOR POSTOPERATIVE ENDODONTIC PAIN
Bypassing Separated Instruments in the Root Canal Two Case Reports
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. XI (June. 2016), PP 08-13 www.iosrjournals.org Bypassing Separated Instruments in the
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. XI (June. 2016), PP 08-13 www.iosrjournals.org Bypassing Separated Instruments in the
Comparison of Spreader Penetration during Lateral Compaction of 0.04 and 0.02 Tapered Gutta-Percha Master Cones
 Original Article Comparison of Spreader Penetration during Lateral Compaction of 0.04 and 0.02 Tapered Gutta-Percha Master Cones M. Saatchi 1, L. Etesami 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Endodontics,
Original Article Comparison of Spreader Penetration during Lateral Compaction of 0.04 and 0.02 Tapered Gutta-Percha Master Cones M. Saatchi 1, L. Etesami 2 1 Assistant Professor, Department of Endodontics,
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter. Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July Volume 2
 Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
ENDODONTIC OVERFILLS:
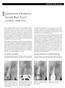 DENTISTRY TODAY May 1997 ENDODONTIC OVERFILLS: GOOD? BAD? UGLY? by Clifford J. Ruddle, D.D.S. Many dentists practice with the misconception overfills cause biological harm. 1 Many receive misinformation
DENTISTRY TODAY May 1997 ENDODONTIC OVERFILLS: GOOD? BAD? UGLY? by Clifford J. Ruddle, D.D.S. Many dentists practice with the misconception overfills cause biological harm. 1 Many receive misinformation
The accuracy of three different electronic root canal measuring devices: an in vitro evaluation
 91 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 44, No. 2, 91-95, 2002 Original The accuracy of three different electronic root canal measuring devices: an in vitro evaluation Ali Cemal Tinaz, Murat Maden, Cumhur Aydin
91 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 44, No. 2, 91-95, 2002 Original The accuracy of three different electronic root canal measuring devices: an in vitro evaluation Ali Cemal Tinaz, Murat Maden, Cumhur Aydin
Pediatric endodontics. Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR
 Pediatric endodontics Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR WHY TO PRESERVE PRIMARY TEETH? The preservation of the primary dentition until their normal anticipated exfoliation can be justified
Pediatric endodontics Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR WHY TO PRESERVE PRIMARY TEETH? The preservation of the primary dentition until their normal anticipated exfoliation can be justified
Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
Comparison Between Preoperative Use of Sublingual Piroxicam with that of Oral Ketorolac on..
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 10 Ver. 9 (October. 2018), PP 80-84 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison Between Preoperative Use
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 10 Ver. 9 (October. 2018), PP 80-84 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison Between Preoperative Use
Periapical healing outcome following single visit endodontic treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
 Journal section: Operative Dentistry and Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.52859 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.52859 Periapical healing outcome following single visit endodontic
Journal section: Operative Dentistry and Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.52859 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.52859 Periapical healing outcome following single visit endodontic
Technical quality of root canal treatment performed by undergraduate dental students
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Technical quality of root canal treatment performed by undergraduate dental students Bahareh Dadresanfar 1 * DDS, MS, Nahid Mohammadzadeh Akhlaghi 1 DDS, MS, Mehdi Vatanpour 1 DDS, MS,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Technical quality of root canal treatment performed by undergraduate dental students Bahareh Dadresanfar 1 * DDS, MS, Nahid Mohammadzadeh Akhlaghi 1 DDS, MS, Mehdi Vatanpour 1 DDS, MS,
Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice
 Calogero Bugea Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice 5 Feb 2016 Tooth Fractures are not rare, surface cracks, or craze lines, are relatively common in teeth. In most of cases they
Calogero Bugea Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice 5 Feb 2016 Tooth Fractures are not rare, surface cracks, or craze lines, are relatively common in teeth. In most of cases they
Comparison of removal of endodontic smear layer using NaOCl, EDTA, and different concentrations of maleic acid A SEM study
 Endodontology, Vol. 15, 2003 Comparison of removal of endodontic smear layer using NaOCl, EDTA, and different concentrations of maleic acid A SEM study *Prabhu SG **Rahim N ***Bhat KS ***Mathew J ABSTRACT
Endodontology, Vol. 15, 2003 Comparison of removal of endodontic smear layer using NaOCl, EDTA, and different concentrations of maleic acid A SEM study *Prabhu SG **Rahim N ***Bhat KS ***Mathew J ABSTRACT
The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Dentistry Myoungah Seo
 The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Dentistry Myoungah Seo A Masters Thesis Submitted to the Department of Dentistry and the Graduate School of Yonsei University in partial fulfillment
The Graduate School Yonsei University Department of Dentistry Myoungah Seo A Masters Thesis Submitted to the Department of Dentistry and the Graduate School of Yonsei University in partial fulfillment
Before we begin demonstrating the shock of paradigms on the instrumentation
 Shock of paradigms on the instrumentation of curved root canals Jesus Djalma Pécora DDS, MSc, PhD, Professor and chairman, Department of Restorative Dentistry, School of Dentistry of Ribeirão Preto, University
Shock of paradigms on the instrumentation of curved root canals Jesus Djalma Pécora DDS, MSc, PhD, Professor and chairman, Department of Restorative Dentistry, School of Dentistry of Ribeirão Preto, University
Smear layer removal evaluation of different protocol of Bio Race file and XPendo Finisher file in corporation with EDTA 17% and NaOCl
 Journal section: Operative Dentistry and Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.54179 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.54179 of different protocol of Bio Race file and XPendo Finisher file
Journal section: Operative Dentistry and Endodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.54179 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.54179 of different protocol of Bio Race file and XPendo Finisher file
WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2
 C L I N I C A L WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2 Peet van der Vyver 1 and Martin Vorster 2 1 Department of Odontology, School of Dentistry, University
C L I N I C A L WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2 Peet van der Vyver 1 and Martin Vorster 2 1 Department of Odontology, School of Dentistry, University
MTA PULPOTOMY ASSOCIATED APEXOGENESIS OF HUMAN PERMANENT MOLAR WITH IRREVERSIBLE PULPITIS: A CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 05 MTA PULPOTOMY ASSOCIATED APEXOGENESIS OF HUMAN PERMANENT MOLAR WITH IRREVERSIBLE PULPITIS: A CASE REPORT Nabi Shahnaz
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 05 MTA PULPOTOMY ASSOCIATED APEXOGENESIS OF HUMAN PERMANENT MOLAR WITH IRREVERSIBLE PULPITIS: A CASE REPORT Nabi Shahnaz
36 year-old Caucasian male presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #3.
 Case Report William Hu Non-Surgical Retreatment #3 36 year-old Caucasian male presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #3. Subjective Chief complaint: I was referred to see if you can do a new root
Case Report William Hu Non-Surgical Retreatment #3 36 year-old Caucasian male presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #3. Subjective Chief complaint: I was referred to see if you can do a new root
Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth: A Decision Guide
 Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth: A Decision Guide www.aae.org/treatmentoptions ROOT AMPUTATION, HEMISECTION, BICUSPIDIZATION Case One Hemisection of the distal root of tooth #19. 13 mo. Recall
Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth: A Decision Guide www.aae.org/treatmentoptions ROOT AMPUTATION, HEMISECTION, BICUSPIDIZATION Case One Hemisection of the distal root of tooth #19. 13 mo. Recall
5 Days Comprehensive Endodontic Course Topics
 5 Days Comprehensive Endodontic Course Topics 1. Pulp Dentin Complex/Retrogressive Changes: The significance of structural elements and its physiological, pathological and age related changes on the diagnosis
5 Days Comprehensive Endodontic Course Topics 1. Pulp Dentin Complex/Retrogressive Changes: The significance of structural elements and its physiological, pathological and age related changes on the diagnosis
Journal of Dental & Oro-facial Research Vol. 14 Issue 01 Jan. 2018
 Journal of Dental & Oro-facial Research Vol. 14 Issue 01 Jan. 2018 Management of Non-Vital Teeth with Open Apices using MTA: Two Case Reports *Karan Narang 1, Mohini Nayak 2, Abdul Wahed, 3 John V. George
Journal of Dental & Oro-facial Research Vol. 14 Issue 01 Jan. 2018 Management of Non-Vital Teeth with Open Apices using MTA: Two Case Reports *Karan Narang 1, Mohini Nayak 2, Abdul Wahed, 3 John V. George
Limitation of contemporary Endodontic treatment
 Limitation of contemporary Endodontic treatment Aetiology - MO Micro-organisms Biofilm Maria Lessani Objectives of Endodontic treatment? Changes in our understanding During RCT: CHEMO-mechanical preparation
Limitation of contemporary Endodontic treatment Aetiology - MO Micro-organisms Biofilm Maria Lessani Objectives of Endodontic treatment? Changes in our understanding During RCT: CHEMO-mechanical preparation
Management of Calcific Metamorphosis in Maxillary Central Incisor Using Newer Endodontic Aids: A Case Report
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Case Report Management of Calcific Metamorphosis in Maxillary Central Incisor Using Newer Endodontic Aids: A Case Report Shweta Verma*, Munish Goel, Prabhat Mandhotra,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Case Report Management of Calcific Metamorphosis in Maxillary Central Incisor Using Newer Endodontic Aids: A Case Report Shweta Verma*, Munish Goel, Prabhat Mandhotra,
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (2), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (2), Page 349-353 Endodontic Flare-Ups: A Study of Incidence and Related Factors Ayshah Abdullah Alshehri 1, Reem Abdullmuhsen Alshraim
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (2), Page 349-353 Endodontic Flare-Ups: A Study of Incidence and Related Factors Ayshah Abdullah Alshehri 1, Reem Abdullmuhsen Alshraim
CURRICULUM VETAE : ALAA EL DIN HUSSEIN DIAB : PHD. DEGREE IN ORAL & DENTAL SURGERY ENDODONTICS. KASR EL EINY,CAIRO UNIVERSITY
 CURRICULUM VETAE NAME : ALAA EL DIN HUSSEIN DIAB NATIONALITY : EGYPTIAN DATE OF BIRTH : 5 th of JULY 1965 PLACE OF BIRTH : GIZA. EGYPT MARITAL STATUS : MARRIED EDUCATION: 1992-1997 : PHD. DEGREE IN ORAL
CURRICULUM VETAE NAME : ALAA EL DIN HUSSEIN DIAB NATIONALITY : EGYPTIAN DATE OF BIRTH : 5 th of JULY 1965 PLACE OF BIRTH : GIZA. EGYPT MARITAL STATUS : MARRIED EDUCATION: 1992-1997 : PHD. DEGREE IN ORAL
VITAL PULP THERAPY USING PLATELET-RICH FIBRIN IN AN IMMATURE PERMANENT TOOTH : CASE REPORTS
 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 J Korean Acad Pediatr Dent 40(2) 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.2.120 VITAL PULP THERAPY USING PLATELET-RICH FIBRIN IN AN IMMATURE PERMANENT TOOTH : CASE REPORTS Ka-Young
ISSN (print) 1226-8496 J Korean Acad Pediatr Dent 40(2) 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.2.120 VITAL PULP THERAPY USING PLATELET-RICH FIBRIN IN AN IMMATURE PERMANENT TOOTH : CASE REPORTS Ka-Young
Maxillary Molar Endodontic Case Presentation. R.Bose. BDS (Manc 2010), General Dental Practitioner, Oxford/London.
 CASE REPO R T Maxillary Molar Endodontic Case Presentation R.Bose. BDS (Manc 2010), General Dental Practitioner, Oxford/London. Introduction Endodontology is concerned with the form, function and health
CASE REPO R T Maxillary Molar Endodontic Case Presentation R.Bose. BDS (Manc 2010), General Dental Practitioner, Oxford/London. Introduction Endodontology is concerned with the form, function and health
Journal of American Science, 2011; 7(9)
 Effect of apical patency apically extruded deris during canal enlargement using hand or rotary instruments Manar Mohamed Galal Hamouda, Hossam Mohamed Essam El-Din Tawfik, Ahmed Fawzy Aou Elezz, Dalia
Effect of apical patency apically extruded deris during canal enlargement using hand or rotary instruments Manar Mohamed Galal Hamouda, Hossam Mohamed Essam El-Din Tawfik, Ahmed Fawzy Aou Elezz, Dalia
Treatment Outcomes in Endodontics
 Invited review 10.5005/jp-journals-10047-0005 1 Raghu Srinivasan, 2 Ramya Raghu ABSTRACT The success of endodontic treatment has been of great interest to practitioners for many years now. Endodontic failures,
Invited review 10.5005/jp-journals-10047-0005 1 Raghu Srinivasan, 2 Ramya Raghu ABSTRACT The success of endodontic treatment has been of great interest to practitioners for many years now. Endodontic failures,
International Journal of Basic and Clinical Studies (IJBCS) 2014;3(1): Uysal I and Oztekin F
 Endodontic Treatment of Mandibular Incisors with Periapical Lesion by Using Single Instrument: Cone Beam Computed Tomography Imaging Ibrahim Uysal 1 Faruk Oztekin 2 1 PhD, Dicle University, Faculty of
Endodontic Treatment of Mandibular Incisors with Periapical Lesion by Using Single Instrument: Cone Beam Computed Tomography Imaging Ibrahim Uysal 1 Faruk Oztekin 2 1 PhD, Dicle University, Faculty of
The effects of file size, sodium hypochlorite and blood on the accuracy of Root ZX apex locator in enlarged root canals: an in vitro study
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2006;51:(2):153-157 The effects of file size, sodium hypochlorite and blood on the accuracy of Root ZX apex locator in enlarged root canals: an in vitro study
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2006;51:(2):153-157 The effects of file size, sodium hypochlorite and blood on the accuracy of Root ZX apex locator in enlarged root canals: an in vitro study
Clinical UM Guideline
 Clinical UM Guideline Subject: Endodontic Therapy Guideline #: 03-001 Current Effective Date: 03/24/2017 Status: New Last Review Date: 02/08/2017 Description This document addresses the procedure of endodontic
Clinical UM Guideline Subject: Endodontic Therapy Guideline #: 03-001 Current Effective Date: 03/24/2017 Status: New Last Review Date: 02/08/2017 Description This document addresses the procedure of endodontic
Surgical Retreatment of an Invaginated Maxillary Central Incisor Following Overfilled Endodontic Treatment: A Case Report
 Surgical Retreatment of an Invaginated Maxillary Central Incisor Following Overfilled Endodontic Treatment: A Case Report Hakan Ozbas a Rustem Kemal Subay b Melike Ordulu c ABSTRACT This case report presents
Surgical Retreatment of an Invaginated Maxillary Central Incisor Following Overfilled Endodontic Treatment: A Case Report Hakan Ozbas a Rustem Kemal Subay b Melike Ordulu c ABSTRACT This case report presents
Postoperative Pain After the Use of a Dexamethasone Rinse as an Irrigant Prior to Obturation
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Master's Theses (2009 -) Dissertations, Theses, and Professional Projects Postoperative Pain After the Use of a Dexamethasone Rinse as an Irrigant Prior to
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Master's Theses (2009 -) Dissertations, Theses, and Professional Projects Postoperative Pain After the Use of a Dexamethasone Rinse as an Irrigant Prior to
Journal of Advanced Medical and Dental Sciences of Scientific Research and Studies
 Journal of Advanced Medical and Dental Sciences Research @Society of Scientific Research and Studies Journal home page: www.jamdsr.com doi: 10.21276/jamdsr (e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599; (p) ISSN Print: 2348-6805
Journal of Advanced Medical and Dental Sciences Research @Society of Scientific Research and Studies Journal home page: www.jamdsr.com doi: 10.21276/jamdsr (e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599; (p) ISSN Print: 2348-6805
PROPAEDEUTICS OF CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY
 MEDICAL UNIVERSITY VARNA FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY AND ORAL PATHOLOGY QUESTIONNAIRE OF PROPAEDEUTICS OF CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY Academic year 2016/2017 Questions for
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY VARNA FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY AND ORAL PATHOLOGY QUESTIONNAIRE OF PROPAEDEUTICS OF CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY Academic year 2016/2017 Questions for
Cervical Root Resorption following Bleaching of Endodontically Treated Teeth
 0099-2399/90/1612-0570/$02.00/0 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Copyright 9 1990 by The American Association of Endodontists Printed in U.S.A. VOL. 16, NO. 12, DECEMBER 1990 Cervical Root Resorption following Bleaching
0099-2399/90/1612-0570/$02.00/0 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Copyright 9 1990 by The American Association of Endodontists Printed in U.S.A. VOL. 16, NO. 12, DECEMBER 1990 Cervical Root Resorption following Bleaching
Clinical Management of a Maxillary Lateral Incisor With Vital Pulp and Type 3 Dens Invaginatus: A Case Report
 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 30, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2004 CASE REPORT/CLINICAL TECHNIQUES Clinical Management of a Maxillary Lateral
JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 30, NO. 10, OCTOBER 2004 CASE REPORT/CLINICAL TECHNIQUES Clinical Management of a Maxillary Lateral
ENDO- DONTICS ENDODONTIC THERAPY
 ENDODONTIC THERAPY TRAINERS Dr. Christos Dandakis Dr. Konstantinos Kodonas Dr. Kalyva Maria From diagnosis to obturation Τhe aim of this course is the presentation and analysis of diagnostic and therapeutic
ENDODONTIC THERAPY TRAINERS Dr. Christos Dandakis Dr. Konstantinos Kodonas Dr. Kalyva Maria From diagnosis to obturation Τhe aim of this course is the presentation and analysis of diagnostic and therapeutic
Infection and microleakage the caused of endodontic failure
 Infection and microleakage the caused of endodontic failure Kurniasri Amas Achiar*, Gantini Subrata** *Department of Conservative Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry Universitas Padjadjaran **Department of
Infection and microleakage the caused of endodontic failure Kurniasri Amas Achiar*, Gantini Subrata** *Department of Conservative Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry Universitas Padjadjaran **Department of
Root canal therapy. Phase 1: Relief of pain
 Root canal therapy Root Canal therapy is required when the pulp becomes inflamed or infected. This can be caused by deep decay, recurring dental procedures on the tooth, or a crack or chip in the tooth.
Root canal therapy Root Canal therapy is required when the pulp becomes inflamed or infected. This can be caused by deep decay, recurring dental procedures on the tooth, or a crack or chip in the tooth.
KING SAUD UNIVERSITY College of Dentistry. Department of Restorative Dental Sciences DIVISION OF ENDODONTICS COURSE OUTLINE 323 RDS
 KING SAUD UNIVERSITY College of Dentistry Department of Restorative Dental Sciences DIVISION OF ENDODONTICS COURSE OUTLINE 323 RDS Pre-Clinical Endodontics Three (3) Credit Hours Third Year 2014-2015 Prepared
KING SAUD UNIVERSITY College of Dentistry Department of Restorative Dental Sciences DIVISION OF ENDODONTICS COURSE OUTLINE 323 RDS Pre-Clinical Endodontics Three (3) Credit Hours Third Year 2014-2015 Prepared
Nestor Cohenca Professor Department of Endodontics Department of Pediatric Dentistry Diplomate, ABE
 Clinical Application of High-Resolution CBCT in Endodontics Time to Change Strategy! Nestor Cohenca Professor Department of Endodontics Department of Pediatric Dentistry Diplomate, ABE cohenca@uw.edu Clinical
Clinical Application of High-Resolution CBCT in Endodontics Time to Change Strategy! Nestor Cohenca Professor Department of Endodontics Department of Pediatric Dentistry Diplomate, ABE cohenca@uw.edu Clinical
Case Report. July 2015; Vol. 12, No. 7. Vineet Agrawal 1, Sonali Kapoor 2, Mukesh Patel 3
 Case Report Ultrasonic Technique to Retrieve a Rotary Nickel-Titanium File Broken Beyond the Apex and a Stainless Steel File from the Root Canal of a Mandibular Molar: A Case Report Vineet Agrawal 1, Sonali
Case Report Ultrasonic Technique to Retrieve a Rotary Nickel-Titanium File Broken Beyond the Apex and a Stainless Steel File from the Root Canal of a Mandibular Molar: A Case Report Vineet Agrawal 1, Sonali
Effect of Apical Clearing and Apical Foramen Widening on Apical Ramifications and Bacterial Load in Root Canals: An Ex-vivo Stereomicroscopic Study
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2014) 55(2): 67 75 Original Article Effect of Apical Clearing and Apical Foramen Widening on Apical Ramifications and Bacterial Load in Root Canals: An Ex-vivo Stereomicroscopic Study
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2014) 55(2): 67 75 Original Article Effect of Apical Clearing and Apical Foramen Widening on Apical Ramifications and Bacterial Load in Root Canals: An Ex-vivo Stereomicroscopic Study
Root end preparation techniques Summary of papers
 Root end preparation techniques Summary of papers 34 Flath 1987 This paper presented 2 cases in which retrograde fillings were carried out using new sonic or ultrasonic instruments (endo files held in
Root end preparation techniques Summary of papers 34 Flath 1987 This paper presented 2 cases in which retrograde fillings were carried out using new sonic or ultrasonic instruments (endo files held in
Non-Surgical Endodontic Retreatment after Unsuccessful Apicectomy: A Case Report
 BALKAN JOURNAL OF STOMATOLOGY ISSN 1107-1141 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY Non-Surgical Endodontic Retreatment after Unsuccessful Apicectomy: A Case Report SUMMARY Introduction: Endodontic failure may arise mainly
BALKAN JOURNAL OF STOMATOLOGY ISSN 1107-1141 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY Non-Surgical Endodontic Retreatment after Unsuccessful Apicectomy: A Case Report SUMMARY Introduction: Endodontic failure may arise mainly
Effect of Apical Trephination on Postoperative Pain and Swelling in Symptomatic Necrotic Teeth
 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2001 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 27, NO. 6, JUNE 2001 Effect of Apical Trephination on Postoperative Pain and Swelling in Symptomatic
JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2001 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 27, NO. 6, JUNE 2001 Effect of Apical Trephination on Postoperative Pain and Swelling in Symptomatic
Complicated untreated apical periodontitis causing paraesthesia: A case report
 Aust Endod J 2017 CASE REPORT Complicated untreated apical periodontitis causing paraesthesia: A case report Domenico Ricucci, MD, DDS 1, * ; Simona Loghin, DDS 1 ; and Jose F. Siqueira Jr, DDS, MSc, PhD
Aust Endod J 2017 CASE REPORT Complicated untreated apical periodontitis causing paraesthesia: A case report Domenico Ricucci, MD, DDS 1, * ; Simona Loghin, DDS 1 ; and Jose F. Siqueira Jr, DDS, MSc, PhD
Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases
 Volume 2012, Article ID 590406, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/590406 Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases Surbhi Patel 1 and Pawan Patel
Volume 2012, Article ID 590406, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/590406 Case Report Endodontic Management of Maxillary Second Molar with Two Palatal Roots: A Report of Two Cases Surbhi Patel 1 and Pawan Patel
22 yo female presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #24
 Erick Sato Case Report Non-Surgical Root Canal Therapy #24 22 yo female presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #24 Subjective: Chief Complaint: My tooth is dark, and my dentist referred me for
Erick Sato Case Report Non-Surgical Root Canal Therapy #24 22 yo female presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #24 Subjective: Chief Complaint: My tooth is dark, and my dentist referred me for
JCDP ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION /jp-journals
 S Kiran et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1892 Comparative Evaluation of Smear Layer and Debris on the Canal Walls prepared with a Combination of Hand and Rotary ProTaper Technique using
S Kiran et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1892 Comparative Evaluation of Smear Layer and Debris on the Canal Walls prepared with a Combination of Hand and Rotary ProTaper Technique using
Influence of Instrument Size in Debriding Apical Third of the Root Canal System
 Influence of Instrument Size in Debriding Apical Third of the Root Canal System ABSTRACT Amara Latif Bajwa, Muhammad Qasim, Abdul Qadir Dall Original Article OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this study was to
Influence of Instrument Size in Debriding Apical Third of the Root Canal System ABSTRACT Amara Latif Bajwa, Muhammad Qasim, Abdul Qadir Dall Original Article OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this study was to
Chemomechanical debridement is an important part of endodontic treatment. Elimination
 Comparative Safety of Various Intracanal Irrigation Systems Pranav Desai, BDS, DDS, and Van Himel, DDS Abstract The objective of this project was to evaluate the safety of various intracanal irrigation
Comparative Safety of Various Intracanal Irrigation Systems Pranav Desai, BDS, DDS, and Van Himel, DDS Abstract The objective of this project was to evaluate the safety of various intracanal irrigation
Diagnosis and treatment of teeth with primary endodontic lesions mimicking periodontal disease: three cases with long-term follow ups
 Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) http://dx.doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.56 Diagnosis and treatment of teeth with primary endodontic lesions mimicking periodontal disease: three
Case report ISSN 2234-7658 (print) / ISSN 2234-7666 (online) http://dx.doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.56 Diagnosis and treatment of teeth with primary endodontic lesions mimicking periodontal disease: three
Creating a glide path for rotary NiTi instruments: part two
 Clinical Creating a glide path for rotary NiTi instruments: part two Peet van der Vyver 1 Introduction In part one of this series the author discussed the rationale for the preparation of a glide path
Clinical Creating a glide path for rotary NiTi instruments: part two Peet van der Vyver 1 Introduction In part one of this series the author discussed the rationale for the preparation of a glide path
Root Canal Treatment. with a mechanical treatment system. Clinical case
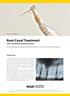 Endo motor with MANI Silk File Root Canal Treatment with a mechanical treatment system Case file by Markus Ludolph, Dortmund/Germany. Focus of activities: Endodontics. Clinical case In January of 2016,
Endo motor with MANI Silk File Root Canal Treatment with a mechanical treatment system Case file by Markus Ludolph, Dortmund/Germany. Focus of activities: Endodontics. Clinical case In January of 2016,
Management of Internal Resorption with Perforation
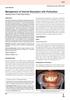 Mahendran Kavitha et al CSE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10047-0054 1 Mahendran Kavitha, 2 K Girija, 3 Shekar Shobana STRCT Internal root resorption is a pathologic intraradicular process in which there
Mahendran Kavitha et al CSE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10047-0054 1 Mahendran Kavitha, 2 K Girija, 3 Shekar Shobana STRCT Internal root resorption is a pathologic intraradicular process in which there
Endodontics. Lec.7 د. حسن الرماحي 5 th class. Obturation techniques
 Endodontics Lec.7 د. حسن الرماحي 5 th class Obturation techniques Broadly speaking, techniques of filling canals with gutta-percha can be divided into three main groups: 1- Use of cold gutta-percha. 2-
Endodontics Lec.7 د. حسن الرماحي 5 th class Obturation techniques Broadly speaking, techniques of filling canals with gutta-percha can be divided into three main groups: 1- Use of cold gutta-percha. 2-
Journal home page:
 Journal home page: http://www.journalijiar.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INNOVATIVE AND APPLIED RESEARCH RESEARCH ARTICLE Current trends in endodontic treatment: cleaning and shaping protocol followed by
Journal home page: http://www.journalijiar.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF INNOVATIVE AND APPLIED RESEARCH RESEARCH ARTICLE Current trends in endodontic treatment: cleaning and shaping protocol followed by
Influence of Fractured Instruments on the Success Rate of Endodontic Treatment
 Stephane Simon Pierre Machtou, Phillip Tomson, Nick Adams and Philip Lumley Influence of Fractured Instruments on the Success Rate of Endodontic Treatment Abstract: The fracture of an instrument is a recognized
Stephane Simon Pierre Machtou, Phillip Tomson, Nick Adams and Philip Lumley Influence of Fractured Instruments on the Success Rate of Endodontic Treatment Abstract: The fracture of an instrument is a recognized
Endodontal - Periodontal Interrelationship
 Endodontal - Periodontal Interrelationship THE CAUSATIVE FACTORS ARE COMMON: DENTAL BIOFILM BOTH CAN DESTROY ATTACHMENT APPARATUS BUT!!!! periodontitis is resulting in irreversible attachment loss only
Endodontal - Periodontal Interrelationship THE CAUSATIVE FACTORS ARE COMMON: DENTAL BIOFILM BOTH CAN DESTROY ATTACHMENT APPARATUS BUT!!!! periodontitis is resulting in irreversible attachment loss only
Periapical status, quality of root canal fillings and estimated endodontic treatment needs in an urban German population
 Endod Dent Traumatot 99; : 9 Printed in Denmark. Alt rigtits reserved Copyright Munksgaard 99 Endodontics & Dental Traumatology ISSN 0090 Periapical status, quality of root canal fillings and estimated
Endod Dent Traumatot 99; : 9 Printed in Denmark. Alt rigtits reserved Copyright Munksgaard 99 Endodontics & Dental Traumatology ISSN 0090 Periapical status, quality of root canal fillings and estimated
