Block iliac bone grafting enhances osseous healing of alveolar reconstruction in older cleft patients: A radiological and histological evaluation
|
|
|
- Wendy Greer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi: /medoral Block iliac bone grafting enhances osseous healing of alveolar reconstruction in older cleft patients: A radiological and histological evaluation Yifei Du 1,2, Weina Zhou 1,3, Yongchu Pan 4, Yanchi Tang 1,2, Linzhong Wan 1,2, Hongbing Jiang 1,2 1 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, Nanjing Medical University; Nanjing , People s Republic of China 2 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Affiliated Hospital of Stomatology, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China 3 Department of Polyclinic dentistry, Affiliated Hospital of Stomatology, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China 4 Department of Orthodontics, Affiliated Hospital of Stomatology, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China Correspondence: Number 136 Hanzhong Road Nanjing, China wanlinzhongren2006@163.com Received: 07/05/2017 Accepted: 06/12/2017 Du Y, Zhou W, Pan Y, Tang Y, Wan L, Jiang H. Block iliac bone grafting enhances osseous healing of alveolar reconstruction in older cleft patients: A radiological and histological evaluation. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal Mar 1;23 (2):e Article Number: Medicina Oral S. L. C.I.F. B pissn eissn: medicina@medicinaoral.com Indexed in: Science Citation Index Expanded Journal Citation Reports Index Medicus, MEDLINE, PubMed Scopus, Embase and Emcare Indice Médico Español Abstract Background: Older alveolar cleft patients (>12 years old) often have wide bone defect as well as teeth loss, resulting in poor osseous healing with conventional alveolar bone grafting (ABG). In this study, we investigated a surgical technique of block iliac bone grafting for the alveolar cleft reconstruction and evaluated the clinical and radiological outcomes of these cleft patients. Material and Methods: Fifteen patients were included in this study. All cases received preoperative cone bean computed tomography (CBCT) scans for the alveolar cleft evaluation. Osseous outcomes of block iliac bone grafting were assessed at 1 week, 3- and 6-month postoperatively. Volume changes and bone resorption rates were calculated using the measurement modules of Simplant software. Bone samples from one patient undergoing dental implantation were assessed by micro-ct and histological examination. The morbidities of donor-site were analyzed by clinical examination and questionnaire survey. Results: The average age of the case series was 18.53±2.50 years. The intraoral incision of thirteen cases healed well. However, two cases had oronasal fistula and graft exposure at 1-week postoperatively. The results of follow-up CBCT scans showed significant resistance to radiation on both sides of the bone graft, suggesting a good osseous healing and new bone formation. The mean residual bone volume was 1.68±0.26 cm 3, 1.29±0.23 cm 3 and 1.15±0.23 cm 3 at 1-week, 3- and 6-month postoperatively. Correspondingly, the mean bone resorption rates in 3- and 6-month postoperative were 21.78±6.88% and 30.66±8.97%, respectively. From micro-ct and HE examinations, the block bone samples exhibited a cancellous structure in which mature bone trabecula and functional blood vessels appeared. The average scores of donor-site morbidities were drastically decreased at 3- and 6-month postoperatively compared with those at 1-week postoperatively. e216
2 Conclusions: Our results demonstrated that block iliac bone grafting could achieve satisfying osseous outcomes in older alveolar cleft patients, and this technique provided favorable bony condition for further treatments, especially dental implantation. Key words: Alveolar bone grafting, Block bone grafting, Osseous healing, CBCT. Introduction Alveolar cleft patients need to undergo alveolar bone grafting (ABG) for repairing maxillary defect and providing bony support for tooth eruption. Conventional ABG using autogenous cancellous bone from anterior superior iliac crest is the gold standard, usually combined with orthodontic treatment (1). This surgicalorthodontic protocol is commonly recommended to the alveolar cleft patients of 7 to 11 years old, before the eruption of canine teeth in the period of mixed dentition. In this time period, the lateral incisor and the canine gradually develop into the cleft area (2-5). Therefore, ABG at this age window prevented the erupted teeth from exfoliating into the cleft site. In addition, the erupted teeth could play physiological stimulating effect, which prompted bone remodeling and reduced bone resorption (6,7). However, for older patients who have missed the age window, the results of conventional ABG were controversial and could be fraught with problems of wound dehiscence, graft infection and tooth eruption failure (8,9). Older patients of permanent dentition often had wider alveolar bone defect due to maxillary growth and tooth loss compared with young patients of deciduous or mixed dentition (9,10). The alveolar defect volume could reach to 5 cm3 in older cleft patients, while the residual bone defect was still 2 cm3 using conventional ABG at 6-month postoperatively (9). The failure of teeth eruption and lack of functional stimulation aggravated the bone resorption of conventional ABG (10). Moreover, the possibility of unhealthy oral habits like smoke may cause poor oral hygiene and increase the risk of bone graft infection in older patients (9,11). Thus, alveolar reconstruction in older cleft patients was a challenge to craniomaxillofacial surgeons. The effect of ABG on maxillofacial development was uncertain. Some researchers found no significant difference in maxillofacial growth between the cleft children having received ABG and the nongraft controls in general (12). Block bone grafting technique was recommended to patients over 15 years of age when early growth and development of premaxillary region have finished (1). Since this monolithic bone block technique was considered to lack the potential for growth consistent with maxillary development. However, block bone grafting technique has been widely used for bone augmentation in adults, with good long-term outcomes (13,14). The bone block could be trimmed to fit for the alveolar defect (15) or fixed with small titanium plates and screws (16). Recent studies reported on the use of block bone grafting in cleft patients of age window (17,18); however, for older alveolar cleft patients, this technique was rarely reported and the osseous outcomes of bone healing were not well investigated. In this study, we conducted a case series of older cleft patients of permanent dentition. Instead of conventional iliac cancellous bone grafting, the block iliac bone grafting with fixation was performed. The osseous outcomes and bone resorption rate were assessed by cone bean computer tomography (CBCT) scans. Bone samples from one patient undergoing dental implantation were analyzed by micro-ct and histological examinations. Donor-site morbidities were assessed by clinical examination and questionnaire survey. Material and Methods -Patients selection From February 2014 to May 2015, a series of 15 alveolar cleft patients with permanent dentition hospitalized at Centre of Cleft Lip and Palate, Stomatological Hospital affiliated to Nanjing Medical University was selected. All cases were clinically examined and received preoperative CBCT (NewTom VGi, Quantitative Radiology Corporation, Verona, Italy) scans for alveolar defect evaluation. The demographic and clinical data of the enrolled patients were given in Table 1. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the School of Stomatology, Nanjing Medical University, China, and written informed consent was obtained from all patients. -Operative technique Block iliac bone harvesting and trimming Block iliac bone harvesting was performed simultaneously with the alveolar preparation by two separate teams. The incision was made laterally to the anterior superior iliac crest. After dissecting iliac crest periosteum, the inner side of iliac crest was exposed carefully to avoid damage to the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve. With 3D reconstruction of the alveolar cleft defect, the prediction of the block bone was determined by preoperative CBCT scans. The osteotomy was performed with Piezosurgery on three sides of the anterior superior iliac crest to create a block bone. The final block iliac bone consisted of inner cortical bone and outer cancellous bone. The incision was sutured with layers and the block iliac bone was trimmed by Piezosurgery to fit for the cleft defect. e217
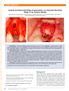
3 Table 1: Demographic and clinical data of the enrolled patients. Case Age/ Cleft Tooth Complications Further Revision Num. Gender site missing treatment 1 18/F R 11,12 - Ortho+Imp /M L 22 - Ortho /M L 22 - Ortho /M R 12 graft exposure Ortho /M L+R 12,22 - Ortho /M L 22 - Ortho /M L 22 oronasal fistula Ortho /F L 22 - Ortho /M L 22 - Ortho /M L 22 - Ortho+Imp /M L 22 - Ortho /M L+R 13,23 - Ortho /F L 22 - Ortho /M L 22 - Ortho /M R 12 - Ortho - M: Male, F: Female, R: Right, L: Left, L+R: left and right or bilateral, 12: right lateral incisor, 22: left lateral incisor, 13: right canine, 23: left canine, Ortho: orthodontic treatment, Imp: implantation. Block iliac bone grafting and fixation The alveolar cleft was carefully dissected to accept the bone block. The water-tight suturing of nasal mucosa was particularly important to prevent from the occurrence of oronasal fistula. The trimmed block iliac bone was then placed in the defect with its cortical surface to the buccal side. Micro-plate system (AO, USA) was used to fix block bone to bilateral sides of the defect (Fig. 1). The insufficiency of soft tissue to close the wound was very common and the solution was to separate and loosen the buccal and palatal gingival flaps around the alveolar cleft. The adequate vertical releasing incisions of bilateral gingival were needed, ensuring the closure with no tension. Outcome analysis Bone healing and volumetric measurement of block iliac bone graft All patients were visually monitored for postoperative e218
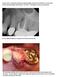
4 functional limitation were recorded. All patients were investigated by questionnaire to assess the level of postoperative pain, numbness and functional limitations. Standard visual analogue scale (VAS) was used for pain evaluation on a scale of 0 to 10. The numbness was catalogued as four levels (0 = no numbness; 1= mild numbness; 2 = moderate numbness; 3 = serious numbness). For functional limitations, a threepoint grading from 0 to 2 was used (0 = no restriction; 1= restriction with sporting; 2 = restriction with walking). These same surveys were used to measure the donor-site morbidity at follow-up time points postoperatively. Fig. 1: The bone block was fixated to the adjacent maxillae with a long titanium micro-plate. complications such as wound infection, oronasal fistula and bone graft exposure by intraoral examinations. Preoperative and follow-up (1-week, 3- and 6-month) CBCT scans were taken with the same radiation parameters. All data with DICOM format was imported into Simplant Pro software (Materialize, Leuven, Belgium) and the coronal, sagittal and horizontal planes of the block iliac bone graft were evaluated. To perform volume rendering, the block iliac bone graft was outlined on each slice using the drawing tools of Simplant software. Collection of all slices with the bone block was stacked to produce a 3D structure and the volume calculation was performed with the same protocol described in previous studies (6,10,14). The volume calculation for each case was repeated three times by the same observer (YC Tang) and the mean data at different follow-up time points was presented with V1 (1-week postoperative), V3 (3-month postoperative) and V6 (6-month postoperative). The resorption rate was calculated as a percentage using the formula (V1 V3 or V6)/ V1 100% (6). Block bone biopsy examination Bone samples were obtained from case 1 who received two dental implants, with a cylindrical shape of 3.5 mm in diameter and 5 mm in length. The bone samples were immediately sent for micro-ct scans. After that, the bone samples were fixed in 4% parofomaldehyde at 4ºC for 24 hours and decalcified in a solution of 10% ethylenediaminetetraacetic at 4ºC for 2 months. Then, these two samples were dehydrated in a graded series of alcohols and embedded in paraffin. Sections of 4 μm in thickness were prepared for hematoxylin and eosin staining. Morbidity The wound healing of iliac crest was examined and any complications such as wound infection, pain and Results -General evaluation The mean age of the patients was 18.53±2.50 years old. Thirteen unilateral alveolar cleft and 2 bilateral alveolar cleft patients were involved. Maxillary lateral incisor was lost in 13 patients, and maxillary canines of both sides were lost in 1 case of bilateral alveolar clefts. One case with right alveolar cleft lost right central and lateral incisors (Table 1). -Bone healing and resorption rate The intraoral wound of all patients was healed well at 1-week postoperatively. However, one case had bone graft exposure at the top of alveolar ridge at 1-month follow-up, which was settled following conservative treatment. Another case with oronasal fistula, resulted in uncontrolled chronic infection of the bone graft. This case was handled for a second surgery to remove the block bone. The unexpected results of these two cases may be due to dehiscence of incision and bone grafts exposure. All patients received orthodontic treatment at 3-month postoperatively, and were recruited to remove the micro-plate system at 6-month postoperatively. From CBCT scans at 1-week postoperatively, the distinct boundaries between block bone graft and bone defect of alveolar cleft were observed. While the scans at 3- and 6-month postoperatively showed that the boundaries were getting unclear, indicting new bone formation after bone graft procedures (Fig. 2). The mean volume of the block bone grafting at 1-week, 3- and 6-month postoperatively was 1.68±0.26 cm 3, 1.29±0.23 cm3 and 1.15±0.23 cm 3, respectively. Taking the volume at 1-week postoperatively as baseline reference, the mean resorption rate at 3- and 6-month postoperatively was 21.78±6.88% and 30.66±8.97% (Table 2). -Block bone samples examination The block bone samples exhibited a cancellous structure similar to ileum from general observation, which was further verified by micro-ct scans. The 3D reconstruction of micro-ct scans showed a porous form, containing multiple trabecula-like structures. Through hematoxylin and eosin staining, many functional blood vessels were concurrently found in the centre of the cal- e219
5 Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal Mar 1;23 (2):e A B Fig. 2: CBCT at 3- and 6-month postoperatively showed new bone formation in the bone graft site. A) The CBCT evaluation at 3-month postoperatively. B) The CBCT evaluation at 6-month postoperatively. cium deposition. Mature bone formation was observed in a well-proportioned distribution among the porous structures (Fig. 3). -Morbidity All patients had excellent healing of the iliac crest wound at 1-week postoperatively without any infection or bleeding. The mean pain scores were 6.47±1.67, 1.73±0.70 and 0 at 1-week, 3- and 6-month postoperatively, respectively. The follow-up results at 3-month postoperatively showed 6 patients suffered from mild numbness and 3 patients from functional restriction of sporting. However, no patient complained numbness or functional limitation at 6-month postoperatively (Table 3). Discussion The surgical-orthodontic procedure for alveolar cleft patient is usually performed between 7 and 11 years of age, consisting of ABG surgery and peri-operative orthodontic treatment. However, some patients miss this age window but need ABG treatment in a delayed fashion. For these older cleft patients, the conditions of the cleft site and oral hygiene are more complicated e220
6 Table 2: Volumetric calculation of bone graft at 1-week, 3- and 6-month postoperatively. Case Volume of bone graft(cm 3 ) Num. V1 V3(RR) V6(RR) (18.5%) 1.31 (24.2%) (7.2%) 1.33 (13.1%) (32.1%) 0.99 (36.5%) (22.6%) 0.93 (33.1%) (35.5%) 0.72 (47.8%) (22.9%) 1.02 (29.2%) (19.7%) 0.89 (32.5%) (22.8%) 1.19 (38.3%) (20.8%) 1.22 (29.5%) (19.5%) 1.06 (31.2%) (27.8%) 1.13 (39.6%) (19.3%) 1.29 (26.7%) (15.5%) 1.55 (19.7%) (20.7%) 1.43 (27.8%) Mean 1.68± ±0.23 (21.78±6.88%) 1.15±0.23 (30.66±8.97%) V1: volume of bone graft 1-week postoperatively, V2: volume of bone graft 3-month postoperatively, V3: volume of bone graft 6-month postoperatively, RR: resorption rate. than that of younger patients. In our case series, all patients were over 15 years old and had one or more teeth loss, predominantly in the location of lateral incisor. Meanwhile, the mean volume of block bone grafting at 1-week postoperatively was 1.68±0.26 cm 3 (Table 2), but the actual volume of alveolar defect could be more due to deficiencies of bone filling. The previous studies including ours, demonstrated that the volume of the cleft defect in younger patients was about 1.0 cm3 based on CBCT or CT scans (10,19-21). In older cleft patients, the volume of alveolar defect could reach to 5 cm 3 (9). In addition, the absence of permanent eruption could exacerbate the resorption of cancellous bone grafting, with bone resorption rate up to 36.6% at 6-month postoperatively. While the data was 10.4% if the permanent tooth erupted spontaneously into the bone graft field (6). These results indicated that the tooth loss and skeletal growth could expand the alveolar defect and may impair the osseous outcomes of conventional ABG treatment. The donor site of block bone could be iliac crest or mandible (16,17). Mandibular bone block could be less resorpted than that from iliac crest for it matched with the embryologic origin on craniofacial bone formation (22,23). However, we preferred bone block from iliac e221
7 A B Fig. 3: The bone samples of block iliac bone grafting. A) The general observation of the two bone samples from case 1. B) The hematoxylin and eosin-stained examination of bone samples (viewed at 200 magnification). crest rather than from genial or symphysis region, for it could provide adequate bone amount for our cases of wide cleft defect. After preparation of the cleft site, it was necessary to shape the bone block to fit for alveolar defect. Based on our experience, we considered preoperative three-dimensional evaluation of the cleft site and an appropriate bone shaping instrument as two important factors. For the former, CBCT could provide statistical information such as structure and size of the alveolar defect (24). For the latter, we recommend shaping the bones by Piezosurgery, which achieved a high degree of bone cutting efficiency with minimal damage (25). The block bone was fixed with micro-plate system to ensure a necessary stability of bone healing condition. In the follow-up examination of CBCT, the block bone graft and adjacent alveolar bone were fully integrated completely at 6-month postoperatively. The boundaries between the bone graft and alveolar cleft could not be identified, indicating the new bone formation in the cleft area. Micro-CT and histological findings of bone samples from case 1 also showed excellent mature bone structures. Interestingly, the block bone samples were rich in blood supply and had many functional vessels in the porous structure. This might provide some hints that a good revascularization of block iliac bone grafts contributed to nearly 70% of bone graft retention and new bone formation in 6 months after surgery. For angiogenesis of graft area was curial to bone healing and osseous integration (26). However, limited to the numbers of bone samples, firm conclusion was difficult to draw in the present study. More samples and further animal experiment were needed to elucidate the response of autogenesis ectopic block bone grafting. Base on current results, we only proved that the block iliac bone grafting could be an alternative for older alveolar cleft patients. Many studies judged the bone graft outcomes by restored marginal bone level percentages using the Bergland scale or Enemark grading system, usually by retroalveolar or panorex radiographs (27-29). However, this two-dimensional bone volume evaluation was considered to greatly overestimate the osseous results of bone grafting. Garib et al. found that the cancellous bone grafting became a thin bone plate on the teeth adjacent to cleft by CBCT scans, although the level of alveolar bone crest was shown to be normal in panorex films (30). These results highlighted the importance of selecting appropriate radiological methods and volumetric assessment programs. Previous studies had calculated the volume and bone resorption rate with same protocols (6,10). In this study, we analyzed the volume changes of block bone grafting by CBCT scanning. The mean bone resorption rates at 3- and 6-month postoperatively were 21.78±6.88% and 30.66±8.97%, respectively. These data were similar to the bone grafts in cleft patients of deciduous or mixed dentition (6,21). Although the success rate in cleft patients of advancing age decreased, the incidence of complications in the donor/receipt site of older cleft patients was not significantly different from that of young cleft patients (1,11,18). In our series, all patients experienced significant pain and walking dysfunction at 1-week postoperatively. While at 3-month postoperatively, the average scores of pain, numbness and functional limitation dramatically decreased. At 6-month postoperatively, all patients recovered with satisfactory results. These data suggested that the injury of block iliac bone harvesting was relative low in older cleft patients. Additionally, 2 of 15 cases had intraoral complications such as bone graft exposure and oronasal fistula. The incidence was higher than that in previous studies (31,32), reminding us of the importance of extensive separation of the gingival flaps around alveolar cleft. The shortcomings of this study were its relatively small patient cohort, short-term follow-up and lack of control group using conventional iliac cancellous bone grafting. Compared with pediatric cleft patients, the selec- e222
8 Table 3: Iliac morbidity investigation of postoperative pain, numbness and functional limitations at 1-week, 3- and 6-month postoperatively. Case Pain evaluation score Numbness Functional Limitations Num. Week 1 Month 3 Month 6 Week 1 Month 3 Month 6 Week 1 Month 3 Month Mean 6.47± ± ± ± ± ± tion bias of skeleton matured patients resulted in fewer patient samples. The 6- month follow-up was too short to analyze the final osseous outcomes of bone grafting, although the evaluation period for bone resorption rate was less than 1year in the previous studies (6,9). Conclusions The procedure of block iliac bone grafting with reliable fixation led to favorable osseous results in older cleft patients for alveolar reconstruction. It could provide sufficient bone amount for further dental implantation and orthodontic treatment. References 1. Boyne PJ, Sands NR. Combined orthodontic-surgical management of residual palato-alveolar cleft defects. Am J Orthod. 1976;70: Hall HD, Posnick JC. Early results of secondary bone grafts in 106 alveolar clefts. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1983;41: Amanat N, Langdon JD. Secondary alveolar bone grafting in clefts of the lip and palate. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 1991;19: Lee C, Crepeau RJ, Williams HB, Schwartz S. Alveolar cleft bone grafts: results and imprecisions of the dental radiograph. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1995;96: Newlands, L. C. Secondary alveolar bone grafting in cleft lip and palate patients. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;38: Zhang W, Shen G, Wang X, Yu H, Fan L. Evaluation of alveolar bone grafting using limited cone beam computed tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2012;113: Giudice G, Gozzo G, Sportelli P, Gargiuoli F, De Siate A. The role of functional orthodontic stress on implants in residual alveolar cleft. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;119: Kortebein MJ, Nelson CL, Sadove AM. Retrospective analysis of 135 secondary alveolar cleft grafts using iliac or calvarial bone. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1991;49: Dickinson BP, Ashley RK, Wasson KL, O Hara C, Gabbay J, e223
9 Heller JB, et al. Reduced morbidity and improved healing with bone morphogenic protein-2 in older patients with alveolar cleft defects. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;121: Zhou WN, Xu YB, Jiang HB, Wan L, Du YF. Accurate Evaluation of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography to Volumetrically Assess Bone Grafting in Alveolar Cleft Patients. J Craniofac Surg. 2015;26:e Dempf R, Teltzrow T, Kramer FJ, Hausamen JE. Alveolar bone grafting in patients with complete clefts: a comparative study between secondary and tertiary bone grafting. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2002;39: Chang HP, Chuang MC, Yang YH, Liu PH, Chang CH, Cheng CF, et al. Maxillofacial growth in children with unilateral cleft lip and palate following secondary alveolar bone grafting: an interim evaluation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;115: Sjöström M, Sennerby L, Lundgren S. Bone graft healing in reconstruction of maxillary atrophy. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2013;15: Fretwurst T, Nack C, Al-Ghrairi M, Raguse JD, Stricker A, Schmelzeisen R, et al. Long-term retrospective evaluation of the peri-implant bone level in onlay grafted patients with iliac bone from the anterior superior iliac crest. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2015;43: Cho-Lee GY, García-Díez EM, Nunes RA, Martí-Pagès C, Sieira-Gil R, Rivera-Baró A. Review of secondary alveolar cleft repair. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2013;3: Theologie-Lygidakis N, Chatzidimitriou K, Tzerbos F, Kolomvos N, Iatrou I. Development of surgical techniques of secondary osteoplasty in cleft patients following 12 years experience. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014;42: Mikoya T, Inoue N, Matsuzawa Y, Totsuka Y, Kajii TS, Hirosawa T. Monocortical mandibular bone grafting for reconstruction of alveolar cleft. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2010;47: Andersen, K., Norholt, S. E., Knudsen, J., Kuseler, A., Jensen, J. Donor site morbidity after reconstruction of alveolar bone defects with mandibular symphyseal bone grafts in cleft patients--111 consecutive patients. International journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery 2014;43: Andersen K, Nørholt SE, Knudsen J, Küseler A, Jensen J. Donor site morbidity after reconstruction of alveolar bone defects with mandibular symphyseal bone grafts in cleft patients--111 consecutive patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;43: Feichtinger M, Zemann W, Mossböck R, Kärcher H. Threedimensional evaluation of secondary alveolar bone grafting using a 3D- navigation system based on computed tomography: a two-year follow-up. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;46: Touzet-Roumazeille S, Vi-Fane B, Kadlub N, Genin M, Dissaux C, Raoul G, et al. Osseous and dental outcomes of primary gingivoperiosteoplasty with iliac bone graft: A radiological evaluation. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2015;43: Rahpeyma A, Khajehahmadi S. Chin bone graft for maxillary alveolar cleft:indications and limitations. J Craniofac Surg. 2014;25: Koole R. Ectomesenchymal mandibular symphysis bone graft: an improvement in alveolar cleft grafting? Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 1994;31: Amirlak B, Tang CJ, Becker D, Palomo JM, Gosain AK. Volumetric analysis of simulated alveolar cleft defects and bone grafts using cone beam computed tomography. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;131: Nordera P, Spanio di Spilimbergo S, Stenico A, Fornezza U, Volpin L, Padula E. The cutting-edge technique for safe osteotomies in craniofacial surgery: the piezosurgery bone scalpel. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;120: Chim SM, Tickner J, Chow ST, Kuek V, Guo B, Zhang G, et al. Angiogenic factors in bone local environment. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013;24: Bergland O, Semb G, Abyholm FE. Elimination of the residual alveolar cleft by secondary bone grafting and subsequent orthodontic treatment. Cleft Palate J. 1986;23: Enemark H, Jensen J, Bosch C. Mandibular bone graft material for reconstruction of alveolar cleft defects: long-term results. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2001;38: Francis CS, Mobin SS, Lypka MA, Rommer E, Yen S, Urata MM, Hammoudeh JA. rhbmp-2 with a demineralized bone matrix scaffold versus autologous iliac crest bone graft for alveolar cleft reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;131: Garib DG, Yatabe MS, Ozawa TO, Filho OG. Alveolar bone morphology in patients with bilateral complete cleft lip and palate in the mixed dentition: cone beam computed tomography evaluation. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2012;49: Sivak WN, Macisaac ZM, Rottgers SA, Losee JE, Kumar AR. Management of failed alveolar bone grafts: improved outcomes and decreased morbidity with allograft alone. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014;133: Macisaac ZM, Rottgers SA, Davit AJ 3rd, Ford M, Losee JE, Kumar AR. Alveolar reconstruction in cleft patients: decreased morbidity and improved outcomes with supplemental demineralized bone matrix and cancellous allograft. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;130: Acknowledgments This study was supported in part by The Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD, ) and The Project Funded by Jiangsu Provincial Commission of Health and Family Planning (Z201511). Conflict of Interests The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper. *Dr. Linzhong Wan and Dr Hong bing Jiang are both the corresponding authors to this paper for they contributed equally. e224
Comparative outcome assessment between secondary and tertiary alveolar cleft grafting
 Page 1 of 7 Cleft & Craniofacial Comparative outcome assessment between secondary and tertiary alveolar cleft grafting AGhanem 1 *, AF Sadakah 2, S Abdel Fattah 1, M El Kassaby 1 Abstract Introduction
Page 1 of 7 Cleft & Craniofacial Comparative outcome assessment between secondary and tertiary alveolar cleft grafting AGhanem 1 *, AF Sadakah 2, S Abdel Fattah 1, M El Kassaby 1 Abstract Introduction
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Localised vertical relapse following orthodontic correction in young growing patients with cleft lip/ palate:
 266 > http://dx.doi.org/10.17159/2519-0105/2017/v72no6a4 Localised vertical relapse following orthodontic correction in young growing patients with cleft lip/ palate: Case studies potentially leading to
266 > http://dx.doi.org/10.17159/2519-0105/2017/v72no6a4 Localised vertical relapse following orthodontic correction in young growing patients with cleft lip/ palate: Case studies potentially leading to
The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting
 44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
ALVEOLAR BONE GRAFTING OF ALVEOLAR CLEFT WITH CANCELLOUS ILIAC BONE GRAFT : A CASE REPORT. Case Report. University Journal of Dental Sciences
 ALVEOLAR BONE GRAFTING OF ALVEOLAR CLEFT WITH CANCELLOUS ILIAC BONE GRAFT : A CASE REPORT 1 2 3 4 Vikas Kunwar Singh, Ruchika Tiwari, Sunil Sharma, Mridula Trehan 1,2 3 Reader, Professor & Head, Dept.
ALVEOLAR BONE GRAFTING OF ALVEOLAR CLEFT WITH CANCELLOUS ILIAC BONE GRAFT : A CASE REPORT 1 2 3 4 Vikas Kunwar Singh, Ruchika Tiwari, Sunil Sharma, Mridula Trehan 1,2 3 Reader, Professor & Head, Dept.
Influence of the Alveolar Cleft Type on Preoperative Estimation Using 3D CT Assessment for Alveolar Cleft
 Influence of the Alveolar Cleft Type on Preoperative Estimation Using 3D CT Assessment for Alveolar Cleft Hang Suk Choi, Hyun Gon Choi, Soon Heum Kim, Hyung Jun Park, Dong Hyeok Shin, Dong In Jo, Cheol
Influence of the Alveolar Cleft Type on Preoperative Estimation Using 3D CT Assessment for Alveolar Cleft Hang Suk Choi, Hyun Gon Choi, Soon Heum Kim, Hyung Jun Park, Dong Hyeok Shin, Dong In Jo, Cheol
Late Results of the Secondary Alveolar Bone Grafting in Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Patients
 Late Results of the Secondary Alveolar Bone Grafting in Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Patients Stomatologija, 5:17-21, 2003 SUMMARY The reconstruction of the continuity of the cleft alveolar
Late Results of the Secondary Alveolar Bone Grafting in Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Patients Stomatologija, 5:17-21, 2003 SUMMARY The reconstruction of the continuity of the cleft alveolar
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla
 CASE REPORT Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla Alberto Monje,* Florencio Monje, Fernando Suarez,* Raúl González-García, Laura Villanueva-Alcojol,
CASE REPORT Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla Alberto Monje,* Florencio Monje, Fernando Suarez,* Raúl González-García, Laura Villanueva-Alcojol,
INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE
 INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE Joint Degree Master Program: Implantology and Dental Surgery (M.Sc.) Specialized Modules: List of individual modules Specialized Module 1 Basic principles of implantology
INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE Joint Degree Master Program: Implantology and Dental Surgery (M.Sc.) Specialized Modules: List of individual modules Specialized Module 1 Basic principles of implantology
Original Research. Contributors: 1
 Received: 10 th October 2014 Accepted: 20 th January 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research Prospective Analysis of Secondary Alveolar Bone Grafting in Cleft Lip and
Received: 10 th October 2014 Accepted: 20 th January 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research Prospective Analysis of Secondary Alveolar Bone Grafting in Cleft Lip and
International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
Evaluation of enamel pearls by cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT)
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17475 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17475 Evaluation of enamel pearls by cone-beam computed tomography
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.17475 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17475 Evaluation of enamel pearls by cone-beam computed tomography
Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
Treatment of Alveolar Cleft Performing a Pyramidal Pocket and an Autologous Bone Grafting
 TECHNICAL EXPERIENCE Treatment of Alveolar Cleft Performing a Pyramidal Pocket and an Autologous Bone Grafting Paolo Giovanni Morselli, MD,*Þ Renzo Giuliani, MD,þ Valentina Pinto, MD,*Þ Carlo Maria Oranges,
TECHNICAL EXPERIENCE Treatment of Alveolar Cleft Performing a Pyramidal Pocket and an Autologous Bone Grafting Paolo Giovanni Morselli, MD,*Þ Renzo Giuliani, MD,þ Valentina Pinto, MD,*Þ Carlo Maria Oranges,
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Tooth Transplantation to Bone Graft in Cleft Alveolus
 Tooth Transplantation to Bone Graft in Cleft Alveolus Soren HiLLeRurp, D.D.S., Lic.opont. ERIK DAHL, D.D.S., DR.ODONT. OLE ScHwarTz, D.D.S., Lic.opont. ERIK Huorting-Hansen, D.D.S., DR.ODoONT. Autotransplantation
Tooth Transplantation to Bone Graft in Cleft Alveolus Soren HiLLeRurp, D.D.S., Lic.opont. ERIK DAHL, D.D.S., DR.ODONT. OLE ScHwarTz, D.D.S., Lic.opont. ERIK Huorting-Hansen, D.D.S., DR.ODoONT. Autotransplantation
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
Complications after Use of Iliac Bone Graft for Post Cleft Alveolar Bone Defect
 American Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Page Surgery 1 of 7 http://ivyunion.org/index.php/maxillofacial Research Article Complications after Use of Iliac Bone Graft for Post Cleft Alveolar Bone Defect
American Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Page Surgery 1 of 7 http://ivyunion.org/index.php/maxillofacial Research Article Complications after Use of Iliac Bone Graft for Post Cleft Alveolar Bone Defect
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION
 original articles FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION Stefan Peev 1, Borislav Ivanov 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Tihomir Georgiev
original articles FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION Stefan Peev 1, Borislav Ivanov 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Tihomir Georgiev
Oral Health and Dentistry
 Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Early secondary closure of alveolar clefts with mandibular symphyseal bone grafts and b-tri calcium phosphate (b-tcp)
 Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010; 39: 424 429 doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2010.02.004, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com Clinical Paper Cleft Lip and Palate and Palate Early secondary closure
Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010; 39: 424 429 doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2010.02.004, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com Clinical Paper Cleft Lip and Palate and Palate Early secondary closure
Long-term success for osteointegrated
 CASE REPORT Symphyseal Bone Cylinders Tapping With the Dental Implant Into Insufficiency Bone Situated Esthetic Area at One-Stage Surgery: A Case Report and the Description of the New Technique Umut Tekin,
CASE REPORT Symphyseal Bone Cylinders Tapping With the Dental Implant Into Insufficiency Bone Situated Esthetic Area at One-Stage Surgery: A Case Report and the Description of the New Technique Umut Tekin,
Reconstruction of large oroantral defects using a pedicled buccal fat pad
 Yang et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:7 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40902-018-0144-6 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery CASE REPORT Open Access Reconstruction
Yang et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:7 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40902-018-0144-6 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery CASE REPORT Open Access Reconstruction
Intramembranous autogenous bone graft is the gold
 CASE LETTER CBCT Morphologic Analysis of Edentulous Posterior Mandible for Mandibular Body Bone Graft Jae-Min Song, DDS, MSD, PhD 1 Jae-Yeol Lee, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Yong-Deok Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD 2,3 * INTRODUCTION
CASE LETTER CBCT Morphologic Analysis of Edentulous Posterior Mandible for Mandibular Body Bone Graft Jae-Min Song, DDS, MSD, PhD 1 Jae-Yeol Lee, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Yong-Deok Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD 2,3 * INTRODUCTION
BUILDING A. Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation. 70 OCTOBER 2016 // dentaltown.com
 BUILDING A MANDI Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation by Dr. Fayette C. Williams Fayette C. Williams, DDS, MD, FACS, is clinical faculty at John Peter Smith Hospital in Fort Worth, Texas,
BUILDING A MANDI Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation by Dr. Fayette C. Williams Fayette C. Williams, DDS, MD, FACS, is clinical faculty at John Peter Smith Hospital in Fort Worth, Texas,
LATERAL CEPHALOMETRIC EVALUATION IN CLEFT PALATE PATIENTS
 POLSKI PRZEGLĄD CHIRURGICZNY 2009, 81, 1, 23 27 10.2478/v10035-009-0004-2 LATERAL CEPHALOMETRIC EVALUATION IN CLEFT PALATE PATIENTS PRADEEP JAIN, ANAND AGARWAL, ARVIND SRIVASTAVA Department of Plastic
POLSKI PRZEGLĄD CHIRURGICZNY 2009, 81, 1, 23 27 10.2478/v10035-009-0004-2 LATERAL CEPHALOMETRIC EVALUATION IN CLEFT PALATE PATIENTS PRADEEP JAIN, ANAND AGARWAL, ARVIND SRIVASTAVA Department of Plastic
Evaluation of the validity of the Bolton Index using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT)
 Journal section: Clinical and Experimental Dentistry Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.18069 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.18069 Evaluation of the validity of the Bolton Index using
Journal section: Clinical and Experimental Dentistry Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.18069 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.18069 Evaluation of the validity of the Bolton Index using
IMPACTED CANINES. Unfortunately, this important tooth is the second most common tooth to be impacted after third molars
 IMPACTED CANINES After we talked about impacted third molars, today we ll discuss about maxillary impacted canines in upper dental arch, how to manage these cases as a dental surgeon. You will study about
IMPACTED CANINES After we talked about impacted third molars, today we ll discuss about maxillary impacted canines in upper dental arch, how to manage these cases as a dental surgeon. You will study about
Years of research and advancement in
 Immediate Implants with Guided Bone Regeneration Using Titanium Mesh and Alloplast in an Infected Site: A Case Report Mahesh et al Dr. Lanka Mahesh 1 Dr. Ajay Bibra 2 Dr. Vishal Gupta 3 Abstract Years
Immediate Implants with Guided Bone Regeneration Using Titanium Mesh and Alloplast in an Infected Site: A Case Report Mahesh et al Dr. Lanka Mahesh 1 Dr. Ajay Bibra 2 Dr. Vishal Gupta 3 Abstract Years
Diagnosis and Treatment of a Large Central Ossifying Fibroma of the Mandible. Clinical Case
 Clinical Case Diagnosis and Treatment of a Large Central Ossifying Fibroma of the Mandible A 36 year old African American Female presented to the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinic at
Clinical Case Diagnosis and Treatment of a Large Central Ossifying Fibroma of the Mandible A 36 year old African American Female presented to the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinic at
Case Report Decompression of the inferior alveolar nerve to treat the pain of the mandible caused by fibrous dysplasia-case report
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):19535-19539 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0014642 Case Report Decompression of the inferior alveolar nerve to treat the pain of the mandible caused by fibrous dysplasia-case
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):19535-19539 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0014642 Case Report Decompression of the inferior alveolar nerve to treat the pain of the mandible caused by fibrous dysplasia-case
Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation
 Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation Abstract Objective The aim of this article was to investigate postoperative swelling of the maxillary
Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation Abstract Objective The aim of this article was to investigate postoperative swelling of the maxillary
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/31632 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mensink, Gertjan Title: Bilateral sagittal split osteotomy by the splitter-separator
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/31632 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mensink, Gertjan Title: Bilateral sagittal split osteotomy by the splitter-separator
Radiographic assessment of lower third molar prior to surgery: A report of four cases
 Radiographic assessment of lower third molar prior to surgery: A report of four cases V Sreenivas Prasad Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman,
Radiographic assessment of lower third molar prior to surgery: A report of four cases V Sreenivas Prasad Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman,
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Reconstruction of a Mandibular Osteoradionecrotic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap.
 Case Report Reconstruction of a Mandibular Osteoradionecrotic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap. Using Synthes ProPlan CMF, Patient Specific Plate Contouring (PSPC) and the MatrixMANDIBLE Plating
Case Report Reconstruction of a Mandibular Osteoradionecrotic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap. Using Synthes ProPlan CMF, Patient Specific Plate Contouring (PSPC) and the MatrixMANDIBLE Plating
The Sandwich Bone Augmentation Technique. Jia-Hui Fu* and Hom-Lay Wang*
 CASE REPORT The Sandwich Bone Augmentation Technique Jia-Hui Fu* and Hom-Lay Wang* Introduction: Horizontal ridge width reduction after tooth extraction is a common clinical scenario. As such, when implant-supported
CASE REPORT The Sandwich Bone Augmentation Technique Jia-Hui Fu* and Hom-Lay Wang* Introduction: Horizontal ridge width reduction after tooth extraction is a common clinical scenario. As such, when implant-supported
Correlations between initial cleft size and dental anomalies in unilateral cleft lip and palate patients after alveolar bone grafting
 UPSALA JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, 2016 VOL. 121, NO. 1, 33 37 http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/03009734.2015.1134733 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlations between initial cleft size and dental anomalies in unilateral
UPSALA JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, 2016 VOL. 121, NO. 1, 33 37 http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/03009734.2015.1134733 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlations between initial cleft size and dental anomalies in unilateral
Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material- A case Report
 A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
 Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
UCL Repair: Emphasis on Muscle Dissection and Reconstruction
 UCL Repair: Emphasis on Muscle Dissection and Reconstruction Unilateral cleft lip repair is performed using rotation-advancement technique. Markings are made on columella base, redlines, Cupid s bow on
UCL Repair: Emphasis on Muscle Dissection and Reconstruction Unilateral cleft lip repair is performed using rotation-advancement technique. Markings are made on columella base, redlines, Cupid s bow on
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
Application of augmented reality for inferior alveolar nerve block anesthesia: A technical note
 Technical Note pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2017;17(2):129-134 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.2.129 Application of augmented reality for inferior alveolar nerve block
Technical Note pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2017;17(2):129-134 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.2.129 Application of augmented reality for inferior alveolar nerve block
Benefits of CBCT in Implant Planning
 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants. by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD
 Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
MODIFIED SINGLE ROLL FLAP APPROACH FOR SIMULTANEOUS IMPLANT PLACEMENT AND GINGIVAL AUGMENTATION
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature:
 CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature: CF Hoogendijk Maxillo- facial and Oral surgery: Trauma: 1. Facial trauma for the confirmation or exclusion of fractures
CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature: CF Hoogendijk Maxillo- facial and Oral surgery: Trauma: 1. Facial trauma for the confirmation or exclusion of fractures
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Three-dimensional assessment of the alveolar bone defect in unilateral cleft lip and palate patients
 Three-dimensional assessment of the alveolar bone defect in unilateral cleft lip and palate patients Poster No.: C-2009 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Haba, Y. Deçolli, A. Nemtoi,
Three-dimensional assessment of the alveolar bone defect in unilateral cleft lip and palate patients Poster No.: C-2009 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Haba, Y. Deçolli, A. Nemtoi,
Vertical Augmentation
 Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Professor, Department of Craniofacial Orthodontics, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital,
 Dr. Ellen Wen-Ching Ko, DDS, MS Professor, Department of Craniofacial Orthodontics, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan Professor, Graduate Institute of Craniofacial and Dental Science, Chang
Dr. Ellen Wen-Ching Ko, DDS, MS Professor, Department of Craniofacial Orthodontics, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan Professor, Graduate Institute of Craniofacial and Dental Science, Chang
Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines
 Original Research Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines Seyed Hossein Hoseini Zarch 1, Farzin Heravi 2, Adineh Javadian Langaroodi 3,
Original Research Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines Seyed Hossein Hoseini Zarch 1, Farzin Heravi 2, Adineh Javadian Langaroodi 3,
botiss dental bone & tissue regeneration biomaterials mucoderm 3D-Regenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic
 dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials 3DRegenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic mucoderm Soft Tissue Graft Indications mucoderm is a collagen tissue matrix derived of animal dermis
dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials 3DRegenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic mucoderm Soft Tissue Graft Indications mucoderm is a collagen tissue matrix derived of animal dermis
REFERENCES for PLATELET RICH PLASMA (PRP)
 REFERENCES for PLATELET RICH PLASMA (PRP) Daif ET. Autologous blood injection as a new treatment modality for chronic recurrent temporomandibular joint dislocation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
REFERENCES for PLATELET RICH PLASMA (PRP) Daif ET. Autologous blood injection as a new treatment modality for chronic recurrent temporomandibular joint dislocation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
Ridge Split Procedure
 Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Platform switching for marginal bone preservation around dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
 Platform switching for marginal bone preservation around dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Atieh MA, Ibrahim HM, Atieh AH. J Periodontol. 2010 Oct;81(10):1350-66. BACKGROUND: Platform
Platform switching for marginal bone preservation around dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Atieh MA, Ibrahim HM, Atieh AH. J Periodontol. 2010 Oct;81(10):1350-66. BACKGROUND: Platform
Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig
 Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family
 ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs
 Current Applied Physics 5 (2005) 507 511 www.elsevier.com/locate/cap Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs Ui-Won Jung a, Hee-Il
Current Applied Physics 5 (2005) 507 511 www.elsevier.com/locate/cap Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs Ui-Won Jung a, Hee-Il
Comparing osteogenic effects between concentrated growth factors and the acellular dermal matrix
 Original Research Craniofacial Biology Comparing osteogenic effects between concentrated growth factors and the acellular dermal matrix Luo HUANG (a) Rui ZOU (a) Jinquan HE (a) Kexiong OUYANG (a) Zhengguo
Original Research Craniofacial Biology Comparing osteogenic effects between concentrated growth factors and the acellular dermal matrix Luo HUANG (a) Rui ZOU (a) Jinquan HE (a) Kexiong OUYANG (a) Zhengguo
New innovations in craniomaxillofacial fixation: the 2.0 lock system
 LECTURE New innovations in craniomaxillofacial fixation: the 2.0 lock system Brian Alpert, Rolf Gutwald1 and Rainer Schmelzeisen1 Departments of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery and Surgical & Hospital Dentistry,
LECTURE New innovations in craniomaxillofacial fixation: the 2.0 lock system Brian Alpert, Rolf Gutwald1 and Rainer Schmelzeisen1 Departments of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery and Surgical & Hospital Dentistry,
Educational Training Document
 Educational Training Document Table of Contents Part 1: Resource Document Disclaimer Page: 2 Part 2: Line Item Grade Sheets Page: 3 Release: 11/2016 Page 1 of 6 Part 1: Resource Document Disclaimer The
Educational Training Document Table of Contents Part 1: Resource Document Disclaimer Page: 2 Part 2: Line Item Grade Sheets Page: 3 Release: 11/2016 Page 1 of 6 Part 1: Resource Document Disclaimer The
Case Report. Eduardo Yugo Suzuki a ; Masayo Watanabe b ; Boonsiva Buranastidporn c ; Yoshiyuki Baba d ; Kimie Ohyama e ; Masatoshi Ishii f
 Case Report Simultaneous Maxillary Distraction Osteogenesis Using a Twin-Track Distraction Device Combined with Alveolar Bone Grafting in Cleft Patients: Preliminary Report of a Technique Eduardo Yugo
Case Report Simultaneous Maxillary Distraction Osteogenesis Using a Twin-Track Distraction Device Combined with Alveolar Bone Grafting in Cleft Patients: Preliminary Report of a Technique Eduardo Yugo
3 Dimensional Diagnosis Unravelling Prognosis of Multiple Impacted Teeth A Case Report
 3 Dimensional Diagnosis Unravelling Prognosis of Multiple Impacted Teeth A Case Report Adusumilli Gopinath 1, Naveen Admala Reddy 2, Mayur G Rohra 3 1 Professor, Department of Orthodontics, AME S Dental
3 Dimensional Diagnosis Unravelling Prognosis of Multiple Impacted Teeth A Case Report Adusumilli Gopinath 1, Naveen Admala Reddy 2, Mayur G Rohra 3 1 Professor, Department of Orthodontics, AME S Dental
The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up
 643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
ORTHOGNATHIC SURGERY
 ORTHOGNATHIC SURGERY MEDICAL POLICY Effective Date: February 1, 2017 Review Dates: 1/93, 7/95, 10/97, 4/99, 10/00, 8/01, 12/01, 4/02, 2/03, 1/04, 1/05, 12/05, 12/06, 12/07, 12/08, 12/09, 12/10, 12/11,
ORTHOGNATHIC SURGERY MEDICAL POLICY Effective Date: February 1, 2017 Review Dates: 1/93, 7/95, 10/97, 4/99, 10/00, 8/01, 12/01, 4/02, 2/03, 1/04, 1/05, 12/05, 12/06, 12/07, 12/08, 12/09, 12/10, 12/11,
Periapical radiography and cone beam computed tomography for assessment of the periapical bone defect 1 week and 12 months after root-end resection
 (2009) 38, 531 536 2009 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org RESEARCH Periapical radiography and cone beam computed tomography for assessment of the periapical bone defect 1 week
(2009) 38, 531 536 2009 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org RESEARCH Periapical radiography and cone beam computed tomography for assessment of the periapical bone defect 1 week
Case Report. Orthognathic Correction of Class II Open Bite. Using the Piezoelectric System and MatrixORTHOGNATHIC Plating System.
 Case Report Orthognathic Correction of Class II Open Bite. Using the Piezoelectric System and MatrixORTHOGNATHIC Plating System. Orthognathic Correction of Class II Open Bite. Using the Piezoelectric System
Case Report Orthognathic Correction of Class II Open Bite. Using the Piezoelectric System and MatrixORTHOGNATHIC Plating System. Orthognathic Correction of Class II Open Bite. Using the Piezoelectric System
More than bone regeneration. A total solution.
 More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
Pattern of bone resorption after extraction
 Teeth loss Pattern of bone resorption after extraction 50% in 1st year 2/ 3 in first 3 months Reich KM, Huber CD, Lippnig WR, Um C, Watzek G, Tangl S. (2011, 17). Atrophy of Residual Alveolar Ridge following
Teeth loss Pattern of bone resorption after extraction 50% in 1st year 2/ 3 in first 3 months Reich KM, Huber CD, Lippnig WR, Um C, Watzek G, Tangl S. (2011, 17). Atrophy of Residual Alveolar Ridge following
Working together as a team, the periodontist
 The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
Augmentation in Two Stages of Atrophic Alveolar Bone Prior to Dental Rehabilitation: A Case Report
 Augmentation in Two Stages of Atrophic Alveolar Bone Prior to Dental Rehabilitation: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The aim of this report is to describe a significantly deficient case of alveolar bone that
Augmentation in Two Stages of Atrophic Alveolar Bone Prior to Dental Rehabilitation: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The aim of this report is to describe a significantly deficient case of alveolar bone that
The Use of Concentrated Growth Factors and Autogenous Bone for Periodontal Soft Tissue Augmentation and Bone Regeneration: A Case Report
 The Use of Concentrated Growth Factors and Autogenous Bone for Periodontal Soft Tissue Augmentation and Bone Regeneration: A Case Report Xuan Ying, Yue Chen*, Ning Luo, Lei Shi, Yuxin Tong, Jiayu Zhang
The Use of Concentrated Growth Factors and Autogenous Bone for Periodontal Soft Tissue Augmentation and Bone Regeneration: A Case Report Xuan Ying, Yue Chen*, Ning Luo, Lei Shi, Yuxin Tong, Jiayu Zhang
Envelope approach for onlay bone grafting: Preliminary surgical and prosthetic results
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.16.e45 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.16.e45 : Preliminary surgical and prosthetic results Federico Hernández-Alfaro
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.16.e45 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.16.e45 : Preliminary surgical and prosthetic results Federico Hernández-Alfaro
BONE GRAFTING IN TREATMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE 337
 PRIMARY BONE GRAFTING IN THE TREATMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO ALVEOLAR COLLAPSE By FRANK ROBINSON, F.R.C.S., and BARRIE WOOD, L.D.S. Burns and Plastic Surgery Unit, Booth Hall
PRIMARY BONE GRAFTING IN THE TREATMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO ALVEOLAR COLLAPSE By FRANK ROBINSON, F.R.C.S., and BARRIE WOOD, L.D.S. Burns and Plastic Surgery Unit, Booth Hall
2018 Dental Code Set For dates of service from 1/1/ /31/2018
 D0120 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION - ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0140 LIMITED ORAL EVALUATION - PROBLEM FOCUSED D0150 COMPREHENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION - NEW OR ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0160 DETAILED AND EXTENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION
D0120 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION - ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0140 LIMITED ORAL EVALUATION - PROBLEM FOCUSED D0150 COMPREHENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION - NEW OR ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0160 DETAILED AND EXTENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION
2018 Dental Code Set
 D0120 D0140 D0150 D0160 D0180 D0210 D0220 D0230 D0240 D0250 D0251 D0270 D0272 D0273 D0274 D0277 D0290 D0310 D0330 D0340 D0350 D0393 D0470 D0502 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION ESTABLISHED PATIENT LIMITED ORAL
D0120 D0140 D0150 D0160 D0180 D0210 D0220 D0230 D0240 D0250 D0251 D0270 D0272 D0273 D0274 D0277 D0290 D0310 D0330 D0340 D0350 D0393 D0470 D0502 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION ESTABLISHED PATIENT LIMITED ORAL
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report
 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
Treatment of severe unilateral open bite and crossbite in cleft lip and palate patients
 European Journal of Orthodontics 6 (1984) 294-3(12 1984 European Orthodontic Society Treatment of severe unilateral open bite and crossbite in cleft lip and palate patients Hans Enemark Aarhus, Denmark
European Journal of Orthodontics 6 (1984) 294-3(12 1984 European Orthodontic Society Treatment of severe unilateral open bite and crossbite in cleft lip and palate patients Hans Enemark Aarhus, Denmark
THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S.
 THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S. Skeletal anchorage, the concept of using the facial skeleton to control tooth
THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S. Skeletal anchorage, the concept of using the facial skeleton to control tooth
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Pre op Failed endodontic treatment with sinus involvement.
 Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH
 PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH Headline Contents Headline Appendix 4 5 7 8 13 14 Clinical Benefits Self-Forming Porous Scaffold
PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH Headline Contents Headline Appendix 4 5 7 8 13 14 Clinical Benefits Self-Forming Porous Scaffold
Is PRP useful in alveolar cleft reconstruction? Platelet-rich plasma in secondary alveoloplasty
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.15.e619 Is PRP useful in alveolar cleft reconstruction? Ramon Luaces-Rey 1, Jorge Arenaz-Búa 1, José-Luis López-Cedrún-Cembranos
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.15.e619 Is PRP useful in alveolar cleft reconstruction? Ramon Luaces-Rey 1, Jorge Arenaz-Búa 1, José-Luis López-Cedrún-Cembranos
Closure of an Oronasal Fistula in an Irradiated Palate by Tissue and Bone Distraction Osteogenesis CASE REPORT
 Closure of an Oronasal Fistula in an Irradiated Palate by Tissue and Bone Distraction Osteogenesis Peter J. Taub, MD* James P. Bradley, MD* Henry K. Kawamoto, MD, DDS* Los Angeles, California Pittsburgh,
Closure of an Oronasal Fistula in an Irradiated Palate by Tissue and Bone Distraction Osteogenesis Peter J. Taub, MD* James P. Bradley, MD* Henry K. Kawamoto, MD, DDS* Los Angeles, California Pittsburgh,
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Ectopic upper canine associated to ectopic lower second bicuspid. Case report
 Original Article Published on 15-06-2001 In Italiano, per favore En Español, por favor Ectopic upper canine associated to ectopic lower second bicuspid. Case report A.R. Mazzocchi* * MD DDS. Corresponding
Original Article Published on 15-06-2001 In Italiano, per favore En Español, por favor Ectopic upper canine associated to ectopic lower second bicuspid. Case report A.R. Mazzocchi* * MD DDS. Corresponding
Newport News Public Schools Summary Schedule of Services Delta Dental PPO EPO Plan
 Newport News Public Schools Summary of Services Delta Dental PPO EPO Plan Services In-Network Out-of-Network PPO Premier All Other Diagnostic & Preventive Oral Exams & Teeth Cleanings Fluoride Applications
Newport News Public Schools Summary of Services Delta Dental PPO EPO Plan Services In-Network Out-of-Network PPO Premier All Other Diagnostic & Preventive Oral Exams & Teeth Cleanings Fluoride Applications
A SOFTWARE TOOL USED IN 3D EVALUATION OF THE ALVEOLAR BONE DEFECT IN BILATERAL CLEFT LIP AND PALATE PATIENTS
 Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2014 vol. 118, no. 3 DENTAL MEDICINE ORIGINAL PAPERS A SOFTWARE TOOL USED IN 3D EVALUATION OF THE ALVEOLAR BONE DEFECT IN BILATERAL CLEFT LIP AND PALATE PATIENTS Yllka
Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2014 vol. 118, no. 3 DENTAL MEDICINE ORIGINAL PAPERS A SOFTWARE TOOL USED IN 3D EVALUATION OF THE ALVEOLAR BONE DEFECT IN BILATERAL CLEFT LIP AND PALATE PATIENTS Yllka
TOPICS. T O P I C S Day 1. Implant Locations. Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla. Anatomy and risk factors Option 1: Short implants
 T O P I C S Day 1 Factors influencing the long-term stability of dental implants Surgical procedures in posterior sites: Standard implant placement with or without flap elevation Surgical procedures in
T O P I C S Day 1 Factors influencing the long-term stability of dental implants Surgical procedures in posterior sites: Standard implant placement with or without flap elevation Surgical procedures in
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry
 Group 1 and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry Michael M. Bornstein, PD Dr Med Dent 1 /Bilal Al-Nawas, Prof Dr Med, Dr Med
Group 1 and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry Michael M. Bornstein, PD Dr Med Dent 1 /Bilal Al-Nawas, Prof Dr Med, Dr Med
Sinus Augmentation Studies Methods and Definition
 FDA approved indications for Infuse Bone Graft in the Maxillofacial Skeleton Alveolar Ridge Augmentation (Buccal Wall Defects) in the Maxilla Maxillary Sinus Floor augmentation Sinus Augmentation Studies
FDA approved indications for Infuse Bone Graft in the Maxillofacial Skeleton Alveolar Ridge Augmentation (Buccal Wall Defects) in the Maxilla Maxillary Sinus Floor augmentation Sinus Augmentation Studies
