Cephalometric Comparison of Treatment with Twin Block Appliance in Skeletal Class II Div 1 Patients with Normal and Vertical Growth Pattern
|
|
|
- Ferdinand Newton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Sciences 2018, Volume 6, Issue 2, Page No: Copyright CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Available Online at: eissn No : pissn No Cephalometric Comparison of Treatment with Twin Block Appliance in Skeletal Class II Div 1 Patients with Normal and Vertical Growth Pattern Vahid Mollabashi 1, Maryam Behtari Nezhad 2, Maryam Shahdoost 3, Faezeh Yousefi 4, Kimia Saadat 5 * 1Assistant Professor of Orthodontic Department, Dental Research Center, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran 2General Dentist, Orthodontic Department, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran 3Department of Biostatistics and Epidemiologyy, School of Public Health, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran 4Assistant Professor of Dento-Maxillofacial Radiology Department, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran 5Under-graduated student, School of Dentistry, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran DOI: /jrmds ABSTRACT Regarding the effects of increase in vertical dimension on the outcomes of treatment with functional appliances, this study was designed to evaluate the differences between the outcome of treatment with twin block appliance in patients with normal and vertical growth pattern. This prospective cohort study was done by counting all (census) method so any patient with class II malocclusion due to mandibular deficiency was entered to the study with an informed consent. Each subject had immediate pre-post treatment lateral cephalograms. There were 11 patients in normal (FMA 28) & 16 patients in vertical (FMA>28) group. Pre-post treatment lateral cephalograms were digitized and analyzed by Dolphin Imaging software. The data were then subjected to Paired t test & ANKOVA analysis. There was a statistically significant (p<0.05) reduction in overjet, U1-NA, U1-SN, ANB in both groups. Patients with normal growth pattern show a statistically significant (p<0.05) increase in L1-NB, AFH & IMPA. In patients with vertical growth pattern a statistically significant (p<0.05) increase in SNB, L1-NB, Co-Go, Co-Gn, AFH, PFH, PFH/AFH, LAFH & ANS-PNS can be mentioned. In comparison between two groups, there was statistically no significant difference in any variable after treatment. Twin block appliance is effective in correcting skeletal class II malocclusion and there is statistically no significant difference in any variable after treatment between two groups. Key words: Growth, Orthodontic Appliance, Functional, Cephalometry HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Vahid Mollabashi, Maryam Behtari Nezhad, Maryam Shahdoost, Faezeh Yousefi, Kimia Saadat, Cephalometric Comparison of Treatment with Twin Block Appliance in Skeletal Class II Div 1 Patients with Normal and Vertical Growth Pattern, J Res Med Dent Sci, 2018, 6 (2): , DOI: /jrmds Corresponding author: Kimia Saadat Received: 17/01/2018 Accepted: 20/02/2018 INTRODUCTION Skeletal class II malocclusion is the most prevalent disorder in orthodontics, which is diagnosed by deficiency and under development of mandible or overgrowth of maxillary arch; Even though most of the class II patients suffer from deficiency in ant-posterior position of mandible [1]. Some studies mentioned that the abnormal position of the jaws or atypical growth pattern of dental and craniofacial structures can effect on pharyngeal dimensions, Physical attractiveness and etc. [2,3]. Whenever a child faces a skeletal problem, the ideal solution is correction by growth modification, in such a way the problem is corrected by overgrowth of one arch relative to the other. There are different methods to correct skeletal class II but the main focus is on the growth modification treatment [4]. Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science Vol. 6 Issue 2 March
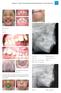
2 In 1980s, functional appliances achieved impressive results in class II correction with mandibular growth stimulation [4]. Growth modification in maxilla, improvement of mandibular growth and position, and changes in dental and muscular relations are the effects, expected from functional appliances [1]. Functional appliances also affect anterior and posterior teeth eruption to correct class II relationship. However, it should be noticed that in patients with mandibular deficiency, posterior teeth eruption helps class II correction only when there is a noticeable growth in vertical dimension. In fact, if mandibular posterior teeth eruption exceeds ramus vertical advancement, the mandibular growth will be more visible in vertical aspect than in forward and help class II correction [4]. Although any effort for growth modification would better be achieved at the peak of pubertal growth; in order to achieve maximum skeletal effects and minimal dentoalveolar changes [3]. Twin block is the most effective appliance in class II malocclusion correction between different types of fix and removable appliances [5]. According to a classification of Charles H. Tweed in 1946, patients were classified into multiple groups regarding their response to the treatment and treatment prognosis. If the Frankfort-mandibular plan angle is between 16 and 28, the growth vector has been downward and forward to a degree which is normal. These patients usually benefit from a normal occlusion and a skeletal growth pattern with a negligible deviation from normal. A permanent treatment with a perfect esthetic could be expected in these patients. If the Frankfort-mandibular plan angle is between 28 and 35, the growth vector is not so favorable. The prognosis is moderate, and it will be worse with FMA increase. Rarely an orthodontic treatment can be useful and beneficial to whom the Frankfort mandibular plan angle is more than 35[6]. Regarding that, treatment effects of twin block appliance can be camouflaged by an increase in lower anterior face height (due to treatment effects or normal growth), it seems that patients with different growth patterns respond differently to this kind of treatment. So, this study is designed to compare the treatment responses to twin block appliance in patients with normal and vertical growth pattern. MATERIALS AND METHODS Participants and Inclusion criteria Every patient with skeletal class II div I malocclusion who need functional treatment were entered to the study with an informed consent. Inclusion criteria Skeletal class II div I malocclusion due to mandibular deficiency ANB angle>4 Overjet> 6mm Between 9-13 years of age Exclusion criteria Patients with any systemic disease Patients who use any systemic drug, effective on growth and skeletal metabolism Patients who need any choice of tooth movement except palatal expansion Both groups treated by one orthodontist and received the same modification of Clark twin block appliance with Adams on first premolars and a labial bow in mandible, and Adams on first molars, labial bow and expansion screw in maxilla. During the treatment 20 patients received palatal expansion of necessity. All patients received pretreatment lateral cephalogram with the same machine (CranexD, Soredex, Tusuula, Finland). The sample then was divided into two groups according to the means of FMA angle, calculated from three separate measurements by one investigator with an interval of one week. Patients with 16<FMA 28 were selected as the normal group and patients with 28<FMA 35 as the vertical growth pattern group. At the end of functional therapy second radiograph were taken from any patients remaining in the study with the same terms as the beginning of treatment. Requirements to finish the functional therapy and taking the second radiograph were as follows: At least 6 months after the start of functional therapy Patient in permanent dentition Overjet 3mm Class l molar and canine relationship At the end of the study pre and post lateral cephalograms were digitized and analyzed with Dolphin imaging software, version Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science Vol. 6 Issue 2 March
3 premium. Finally, all of the measurements were subjected to SPSS software tests. Sample size calculation and statistical analysis All the patients referred to dental school and met the inclusion criteria were chosen and entered to the research with an informed consent. At the end of recruiting phase, a sample of 36 patients with Class II div I malocclusion due to mandibular deficiency were collected. In order to reduce the error of the method pre and post lateral cephalograms were digitized and analyzed 3 times with an interval of one week by one investigator. These measurements then were used to calculate the means for each variable and finally the means of all measurements were recorded in a check list and subjected to SPSS software tests. In order to evaluate the changes resulting from treatment, paired sample t test was done for each variable, separately for each group. To compare the effect of treatment groups (normal and vertical growth pattern) on studied cephalometric variables, ANKOVA analysis was used. RESULTS At the end of recruitment phase, a sample of 36 patients, matching all of the inclusion criteria, were chosen and entered to the research with an informed consent. At the end of the study, 4 patients were excluded from the study due to poor cooperation, 1patient due to an open occlusion in second radiograph, 1 because of using headgear and 3 patients because of using a different version of x-ray machine to take second radiograph. So, the sample size reduced to 27 cases, including 11patients in normal and 16 in vertical growth pattern group. At the end of the study, the sample consisted of 27 patients, including 11 cases in normal and 16 cases in vertical group. There were 13 boys and 14 girls. Distribution of sex frequency in two groups displayed in (Table 1), showed statistically no significant difference between the frequency of sex distribution in two groups (p=0.6). Age distribution comparative test also showed no significant difference between the means of age in two groups (p=0.06). The mean age was 11.1±0.3 in normal & 10.53±0.3 in vertical growth pattern group. Also the average of treatment time was calculated 12.8±3.9 months in normal & 13.7±3.9 months in vertical group, which revealed statistically no significant difference between two groups (p=0.5). Table 1: The frequency of variable sex in each normal and vertical growth pattern group Sex Male female Total Group Horizontal Vertical Total Count % within group Count % within group Count % within group Numbers analyzed for each outcome To evaluate the changes from treatment protocol, paired sample t test was done for all variables separately in two groups. Results are displayed in (Tables 2, 3). According to these tables there was a statistically significant reduction in means of Overjet (P<0.001), U1-NA (P=0.006) and ANB (P<0.001) and increase in means of L1-NB (P=0.002), AFH (P=0.049) and the angle IMPA (P=0.007) in patients with normal growth pattern. In this group, no significant change happened in measurements related to mandible. Even though there was an increase in a few variables like Co- Go, Go-Me and LAFH. As a result of treatment in patients with vertical growth pattern, a statistically significant reduction in overjet (P<0.001), ANB (P<0.001), U1-NA (P=0.013), U1-SN (P=0.005)& a statistically significant increase in SNB (P<0.001), L1-NB (P<0.001), Co-Go (P<0.001), Co-Gn (P<0.001), AFH (P=0.001), PFH (P<0.001), PFH/AFH (P=0.043), LAFH (P<0.001), & ANS-PNS (P=0.005) can be mentioned. The size of variables before treatment were assessed by independent sample t test and significant differences were seen in size of some variables including IMPA, Co-G, Co-Gn, Go-Me, Ar- Go-Me, PFH and ANS-PNS between two groups. To evaluate the relationship between different growth patterns and the size of variables after treatment ANKOVA analysis was done. The results of ANKOVA analysis are shown in (Table 4, 5) Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science Vol. 6 Issue 2 March
4 The evaluation of results showed that in significance level of 0.05, after modulation of "variable size before treatment" the effect of group was not significant in none of the variables. Table 2: The mean of linear variables before and after of applying treatment for normal and vertical growth pattern groups Variable Before±( SD) After±(SD) Difference±(SD) P-value Overjet normal 8/76±(1/98) 2/49±(1/58) 6/27±(2/5) vertical 8/86±(1/88) 2/64±(1/10) 6/22±(2/3) L1-NB normal 5/18±(1/8) 6/71±0(1/7) 1/53±(1/0) *0/002 vertical 5/20±(1/9) 7/11±(1/8) 1/90±(1/2) U1-NA normal 4/75±(2/3) 2/68±(1/5) -2/07±(1/8) *0/006 vertical 5/04±(1/8) 3/82±(2/5) -1/22±(1/6) *0/013 Co-Go normal 49/73±(3/64) 52/06±(4/4) 2/33±(3/2) 0/52 vertical 43/97±(2/4) 46/76±(4/2) 2/76±(2/4) Co-Gn normal 106/04±(8/8) 109/22±(7/8) 3/18±(7/3) 0/205 vertical 97/38±(4/4) 103/11±(4/7) 5/73±(3/3) Go-Me normal 69/25±(7/2) 70/73±(5/7) 1/48±(4/1) 0/291 vertical 59/77±(5/4) 62/38±(5/7) 2/60±(6/2) 0/12 AFH normal 108/51±(7/5) 112/09±(7/4) 3/58±(4/9) *0/049 vertical 103/03±(5/3) 107/48±(5/7) 4/44±(2/4) PFH normal 72/93±(5/8) 74/06±(5/3) 1/13±3/95 0/782 vertical 62/46±(4/1) 66/88±(5/2) 4/42±(2/5) PFH/AFH(%) normal 0/67±(0/11) 0/64±(0/03) -0/03±(0/1) 0/386 vertical 0/60±(0/03) 0/62±(0/03) 0/02±(0/02) *0/043 LAFH normal 61/83±(5/4) 63/81±(5/1) 1/98±(4/0) 0/154 vertical 59/30±(3/8) 62/01±(3/7) 2/71±(2/3) LAFH/AFH (%) normal vertical 0/57±(0/01) 0/57±(0/01) 0/57±(0/01) 0/57±(0/01) -<0/001 0/001 0/942 0/384 ANS-PNS normal 48/55±(2/7) 49/07±(2/9) 0/52±(2/3) 0/50 vertical 44/26±(2/5) 45/79±(3/0) 1/52±(1/4) *: significance level of 0.05; **: standard deviation Table 3: The mean of angular variables before and after of applying treatment for normal and vertical growth pattern Variable Before±( SD) After±(SD) Difference±(SD) P-value FMA normal 25/49±(2/7) 26/11±(2/7) 0/62±(0/8) 0/53 vertical 33/50±(2/5) 34/27±(3/0) 0/77±(1/5) 0/07 SNA normal 80/78±(3/4) 79/93±(4/1) -0/85±(2/1) 0/243 vertical 80/11±(4/2) 80/52±(4/8) 0/41±(1/8) 0/415 SNB normal 74/07±(3/.) 74/92±(3/1) 0/84±(2/3) 0/279 vertical 73/04±(3/7) 75/37±(4/0) 2/32±(2/0) ANB normal 6/72±(1/1) 5/01±(1/6) -1/71±.(./9) *<./001 vertical 7/07±(1/8) 5/13±(2/7) -1/93±(1/3) *<./001 IMPA normal 103/34±(5/9) 107/13±(5/3) 3/78±(3/4) *0/007 vertical 96/12±(5/4) 98/69±(4/4) 2/56±(4/8) 0/59 U1-SN normal 108/39±(6/1) 102/55±(5/0) -5/83±(6/0) *0/014 vertical 111/08±(6/2) 107/23±(6/9) -3/84±(4/4) *0/005 Interincisal angle normal vertical 114/12±(8/8) 111/62±(8/3) 116/05±(5/5) 113/72±(7/5) 1/92±(7/7) 2/09±(7/0) 0/452 0/266 Ar-Go-Me normal 126/02±(5/1) 126/92±(5/3) 0/89±(2/2) 0/23 vertical 134/76±(5/0) 135/89±(4/2) 1/13±(1/9) *0/04 Y-Axis normal 69/16±(2/5) 69/10±(2/7) -0/06±(1/2) 0/87 vertical 71/11±(2/6) 70/03±(3/0) -1/07±(2/0) 0/06 *: significance level of 0.05; **: standard deviation Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science Vol. 6 Issue 2 March
5 Table 4: Linear regression models for linear variables Variable L1-NB U1-NA Co-Go Co-Gn Go-Me AFH PFH PFH/AFH LAFH LAFH/AFH ANS-PNS *: Significance level of P-value 0/415 0/724 0/192 0/780 0/510 *0/009 0/726 *0/006 0/201 *0/003 0/080 0/842 0/303 *0/002 0/449 *0/010 *0/028 0/984 0/116 0/458 0/453 0/557 Table 5: Linear regression models for angular variables Variable SNA SNB ANB IMPA U1-SN Interincisal angle Ar-Go-Me Y-Axis Significance level of 0.05 P-value 0/593 0/133 0/276 0/141 0/101 0/653 0/003 0/343 0/085 0/165 0/617 *0/004 0/054 0/146 0/427 0/323 Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science Vol. 6 Issue 2 March
6 DISCUSSION Main findings The results from this research revealed that twin block appliance is effective in correcting skeletal class II malocclusion both in normal and vertical growth pattern groups. This conclusion was achieved regarding a significant reduction in overjet and ANB at the end of treatment in both groups. Using twin block functional appliance separately in both groups induced a number of dentoskeletal changes in relation to mandible and maxilla. Most of these changes including all of the changes in relation to mandibular skeleton and dental changes were in the same direction in both groups, however, there were differences in significance in some of those variables. It should be noted that after data analysis no significant difference was found in size of variables after treatment between two groups (with modulation the size of variables before treatment). Skeletal changes in mandible In this study findings revealed a forward movement and/or an increase in mandibular length and ramus height in both groups. However, in vertical group these findings showed a significant and more increase in total mandibular length, ramus height and forward movement of mandible. The means of results indicate that in normal growth pattern group, mandibular skeletal changes happened less, that is also not statistically significant. The findings in relation with mandibular length increase were in consistent with other studies [5-13]. Burhan et al [14], Lau Ey et al [11] and Schaefer et al [13] also found ramus height increase as a result of treatment with twin block. It should be noticed that till now no research has studied the patients separately in different growth patterns. Maxillary skeletal changes These findings show slight and different changes in size and direction of maxillary growth regarding the points S, N & A in both groups; In a way that in normal group a slight reduction in SNA(-2.8±0.85) was seen. Although, this reduction was not clinically noticeable and statistically significant, but in Lunda & Sandler's view, claiming that retroclination of maxillary incisors and labial tipping of the roots cause remodeling of point A to a forward position and hiding the headgear effect on maxilla, this slight reduction in SNA could show the headgear effect of the appliance and growth restriction of maxilla in normal group. But significantly, this growth restriction was not seen in any group, which is in agreement with Lunda and Sandler [12], Dauravu et al [15] and several other studies [8, 16]. However, some studies [7, 17, 18] suggest significant headgear effect in treatment with twin block appliance regarding SNA angle. As another difference between these two groups about maxillary skeletal changes, slight but significant increase in maxillary length in vertical group can be mentioned. These cephalometric findings which are exclusively seen in vertical growth pattern group, in addition to those related to SNA angle, can show the inability of this kind of functional therapy in modification of maxillary skeletal growth in this group. Dentoalveolar changes Dentoalveolar changes in this study, the same as in other past studies [5, 7, 8, 14, 16], showed significant mandibular incisor protrusion and maxillary incisor retrusion. When evaluating this factor separately in two groups, dentoalveolar changes of both arches were more noticeable in vertical group. Skeletal class II correction According to the changes mentioned in previous parts, the correction of maxillomandibular sagital relationship in both groups has happened with this functional appliance; although, when dividing groups, it seems that this amount of overjet correction in normal group was dominantly because of dentoalveolar changes (and a slight but not significant restriction of maxillary growth). These findings are consistent with those of Lunda & Sandler [14] and O'Brien et al., [19] about the dominant and significant effects of dentoalveolar changes on class II correction. According to the results, displayed in Tables 2 & 3, the correction of maxillomandibular relationship in patients with vertical growth pattern has been achieved differently from normal group, by dominant effects of skeletal changes in mandibular length and height. Studies of Bacceti et al [20], Jenna et al [16] and Mills and Mc Culloach [17] were also in agreement with this study; however, Jenna had considered this amount of skeletal changes in his sample due to treatment time because they were all in their pubertal growth spurts. O'Brien [19] also argues that most of the studies that have reported significant skeletal improvements were retrospective and Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science Vol. 6 Issue 2 March
7 therefore exposed to selection bias, resulting in overestimated treatment effects. So, this study was designed prospectively with no significant difference in the average of age between two groups. Vertical dimension Regarding the results, the mandibular plan has not been affected significantly during treatment, just the same as what Lunda [14] and Mc Culloach [17] mentioned. However, a slight but significant increase in gonial angle occurred in patients with vertical growth pattern. About the changes of vertical dimension, although we saw an increase in anterior facial height in both groups, but the same as Sidlauskas [18] study, we found that since the lower anterior facial height to total anterior facial height ratio did not change, the proportionality of upper and lower anterior face height was not affected. So, this finding can be indicative of normal growth and also the ability of twin block appliance in controlling vertical dimensions in both groups. As the most prominent finding of changes in vertical dimension, a significant increase in posterior facial height and the ratio of posterior facial height to the anterior facial height in vertical group can be mentioned. Burhan et al [14] and Scheafer et al [13] noted the increase of posterior facial height as a significant finding in their studies, but none of them evaluate the ratio of posterior height changes to the anterior. So, this study suggests that, in addition to a vertical dimension control, treatment with twin block appliance can modulate the pattern of vertical growth significantly by stimulating ramus growth and increasing the posterior facial height in patients with vertical growth pattern. The effects of different growth patterns on treatment results According to the results from ANKOVA analysis displayed in Tables 4 & 5, after modulating the effects of variable size before treatment, "group" has no significant effect on any variable size after treatment. CONCLUSIONS Twin block appliance is effective on correcting skeletal class II in both normal and vertical growth patterns, and there is statistically no significant difference in size of variables after treatment between two groups. The correction of maxillomandibular Sagital relationship is achieved due to reduction in overjet an ANB angle. In patients with vertical growth pattern, there are significant skeletal changes in mandibular length and ramus height which cause an increase in posterior facial height and modulation of vertical pattern of growth consequently. Dentoalveolar changes including mandibular incisors protrusion and maxillary incisors retrusion are the most common findings of both groups that seem to have the most dominant effect on skeletal class II correction in patients with normal growth pattern. Acknowledgments We would like to thank Vic-Chancellor of education as well as Vic-Chancellor of research and technology for financial support of this study. REFERENCES 1. Jena AK, Duggal R, Parkash H. Skeletal and dentoalveolar effects of Twin-block and bionator appliances in the treatment of Class II malocclusion: a comparative study. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics. 2006; 130(5): Ali B, Shaikh A, Fida M. Effect of Clark s twin-block appliance (CTB) and nonextraction fixed mechano-therapy on the pharyngeal di mensions of growing children. Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics. 2015; 20(6): Khoja A, Fida M, Shaikh A. Cephalometric evaluation of the effects of the Twin Block appliance in subjects with Class II, Division 1 malocclusion amongst different cervical vertebral maturation stages. Dental Press Journal of Orthodontics. 2016; 21(3): Proffit. cotemporary orthodontics. 5, editor: Elsevier, 2013: Franchi L, Baccetti T. Prediction of individual mandibular changes induced by functional jaw orthopedics followed by fixed appliances in Class II patients. The Angle Orthodontist. 2006; 76(6): Tweed CH. The Frankfort-mandibular plane angle in orthodontic diagnosis, classification, 7. treatment planning, and prognosis. American Journal of Orthodontics and Oral Surgery. 1946; 32(4): Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science Vol. 6 Issue 2 March
8 8. Braun S, Diers NR, Engel G, Wojtkiewicz P, Ewing SK. The effect of Frankel II and modified twin block appliances on the'c'- axis: the growth vector of the dentomaxillary complex. The Angle Orthodontist. 2004; 74(6): Jena AK, Duggal R. Treatment effects of twin-block and mandibular protraction appliance-iv in the correction of class II malocclusion. Angle Orthodontist. 2010; 80(3): Toth LR, McNamara JA. Treatment effects produced by the Twin-block appliance and the FR-2 appliance of Frankel compared with an untreated Class II sample. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics. 1999; 116(6): Lau EY, Sampson WJ, Townsend GC, Hughes T. An evaluation of maxillary and mandibular rotational responses with the Clark twin block appliance. Australian Orthodontic Journal. 2009; 25(1): Siara-Olds NJ, Pangrazio-Kulbersh V, Berger J, Bayirli B. Long-term dentoskeletal changes with the Bionator, Herbst, Twin Block, and MARA functional appliances. The Angle Orthodontist. 2010; 80(1): Freeman CS, McNamara JA, Baccetti T, Franchi L, Graff TW. Treatment effects of the bionator and high-pull facebow combination followed by fixed appliances in patients with increased vertical dimensions. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics. 2007; 131(2): Schaefer AT, McNamara JA, Franchi L, Baccetti T. A cephalometric comparison of treatment with the Twin-block and stainless steel crown Herbst appliances followed by fixed appliance therapy. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics. 2004; 126(1): Lund DI, Sandler PJ. The effects of Twin Blocks: a prospective controlled study. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics. 1998; 113(1): Dauravu LM, Vannala V, Arafath M, Singaraju GS, Cherukuri SA, Mathew A. The Assessment of sagittal changes with twin block appliance in patients with decelerating growth phase. Journal of clinical and diagnostic research: JCDR. 2014;8(12):ZC Lagravere MO, Major PW, Flores-Mir C. Long-term skeletal changes with rapid maxillary expansion: a systematic review. The Angle Orthodontist. 2005; 75(6): Mills CM, McCulloch KJ. Posttreatment changes after successful correction of Class II malocclusions with the twin block appliance. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics. 2000; 118(1): Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science Vol. 6 Issue 2 March
Class II Correction using Combined Twin Block and Fixed Orthodontic Appliances: A Case Report
 Case Report Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/506 Class II Correction using Combined Twin Block and Fixed Orthodontic Appliances: A Case Report Ahmed Alassiry Assistant
Case Report Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/506 Class II Correction using Combined Twin Block and Fixed Orthodontic Appliances: A Case Report Ahmed Alassiry Assistant
A Cephalometric Comparison of Twin Block and Bionator Appliances in Treatment of Class II Malocclusion
 Journal section: Orthodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.53031 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53031 A Cephalometric Comparison of Twin Block and Bionator Appliances in Treatment of Class
Journal section: Orthodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.53031 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53031 A Cephalometric Comparison of Twin Block and Bionator Appliances in Treatment of Class
Skeletal And DentoalveolarChanges Seen In Class II Div 1 Mal- Occlusion Cases Treated With Twin Block Appliance- A Cephalometric Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 1, Ver. VIII (Feb. 2014), PP 05-09 Skeletal And DentoalveolarChanges Seen In Class II Div 1
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 1, Ver. VIII (Feb. 2014), PP 05-09 Skeletal And DentoalveolarChanges Seen In Class II Div 1
Correction of Class II Division 2 Malocclusion by Fixed Functional Class II Corrector Appliance: Case Report
 Case Report To cite: Kumar M, Sharma H, Bohara P. Correction of class II division 2 malocclusion by fixed functional class II corrector appliance: case report. Journal of contemporary orthodontics, February
Case Report To cite: Kumar M, Sharma H, Bohara P. Correction of class II division 2 malocclusion by fixed functional class II corrector appliance: case report. Journal of contemporary orthodontics, February
Several studies have shown that a Twin-block appliance
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of 2 modifications of the Twinblock appliance in matched Class II samples Nicola Ann Parkin, BDS, MMedSci, FDS RCS(Eng), M Orth RCS(Eng), a Helen Fiona McKeown, BDS, MMedSci,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of 2 modifications of the Twinblock appliance in matched Class II samples Nicola Ann Parkin, BDS, MMedSci, FDS RCS(Eng), M Orth RCS(Eng), a Helen Fiona McKeown, BDS, MMedSci,
The Modified Twin Block Appliance in the Treatment of Class II Division 2 Malocclusions
 Journal of Orthodontics/Vol. 28/2001/271 280 The Modified Twin Block Appliance in the Treatment of Class II Division 2 Malocclusions F. M. V. DYER H. F. MCKEOWN P. J. SANDLER Department of Orthodontics,
Journal of Orthodontics/Vol. 28/2001/271 280 The Modified Twin Block Appliance in the Treatment of Class II Division 2 Malocclusions F. M. V. DYER H. F. MCKEOWN P. J. SANDLER Department of Orthodontics,
OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS
 EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS CANDIDATE NUMBER: KDr. KP. kanarelis CASE NUMBER: 1 Year: 2010 WBLO 01 RESUME OF CASE 1 CASE CATEGORY: ADULT MALOCCLUSION NAME : IOANNIS.G BORN: 03.01.1989 SEX:
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS CANDIDATE NUMBER: KDr. KP. kanarelis CASE NUMBER: 1 Year: 2010 WBLO 01 RESUME OF CASE 1 CASE CATEGORY: ADULT MALOCCLUSION NAME : IOANNIS.G BORN: 03.01.1989 SEX:
OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS
 EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS CANDIDATE NUMBER: KDr. KP. kanarelis CASE NUMBER: 2 Year: 2010 WBLO 01 RESUME OF CASE 2 CASE CATEGORY: ADULT MALOCCLUSION NAME : MARIA A. BORN: 18.04.1983 SEX:
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS CANDIDATE NUMBER: KDr. KP. kanarelis CASE NUMBER: 2 Year: 2010 WBLO 01 RESUME OF CASE 2 CASE CATEGORY: ADULT MALOCCLUSION NAME : MARIA A. BORN: 18.04.1983 SEX:
Early Mixed Dentition Period
 REVIEW ARTIC CLE AODMR The Effects of a Prefabricated Functional Appliance in Early Mixed Dentition Period Toshio Iwata 1, Takashi Usui 2, Nobukazu Shirakawa 2, Toshitsugu Kawata 3 1 Doctor of Philosophy
REVIEW ARTIC CLE AODMR The Effects of a Prefabricated Functional Appliance in Early Mixed Dentition Period Toshio Iwata 1, Takashi Usui 2, Nobukazu Shirakawa 2, Toshitsugu Kawata 3 1 Doctor of Philosophy
UNILATERAL UPPER MOLAR DISTALIZATION IN A SEVERE CASE OF CLASS II MALOCCLUSION. CASE PRESENTATION. 1*
 UNILATERAL UPPER MOLAR DISTALIZATION IN A SEVERE CASE OF CLASS II MALOCCLUSION. CASE PRESENTATION. 1* Department of Orthodontics and Pedodontics 1 Faculty of Dental Medicine, University of Medicine and
UNILATERAL UPPER MOLAR DISTALIZATION IN A SEVERE CASE OF CLASS II MALOCCLUSION. CASE PRESENTATION. 1* Department of Orthodontics and Pedodontics 1 Faculty of Dental Medicine, University of Medicine and
The most common maxillary characteristics of
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment effects of the bionator and high-pull facebow combination followed by fixed appliances in patients with increased vertical dimensions Christopher S. Freeman, a James A. McNamara,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment effects of the bionator and high-pull facebow combination followed by fixed appliances in patients with increased vertical dimensions Christopher S. Freeman, a James A. McNamara,
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTISTS
 EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTISTS CANDIDATE NUMBER:44 CASE NUMBER: 2 Year: 2010 ESLO 01 RÉSUMÉ OF CASE 5 CASE CATEGORY: CLASS II DIVISION 1 MALOCCLUSION A MALOCCLUSION WITH SIGNIFICANT MANDIBULAR
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTISTS CANDIDATE NUMBER:44 CASE NUMBER: 2 Year: 2010 ESLO 01 RÉSUMÉ OF CASE 5 CASE CATEGORY: CLASS II DIVISION 1 MALOCCLUSION A MALOCCLUSION WITH SIGNIFICANT MANDIBULAR
Maxillary Growth Control with High Pull Headgear- A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. X January. (2018), PP 09-13 www.iosrjournals.org Maxillary Growth Control with High
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. X January. (2018), PP 09-13 www.iosrjournals.org Maxillary Growth Control with High
Angle Class II, division 2 malocclusion with deep overbite
 BBO Case Report Angle Class II, division 2 malocclusion with deep overbite Arno Locks 1 Angle Class II, division 2, malocclusion is characterized by a Class II molar relation associated with retroclined
BBO Case Report Angle Class II, division 2 malocclusion with deep overbite Arno Locks 1 Angle Class II, division 2, malocclusion is characterized by a Class II molar relation associated with retroclined
TWO PHASE FOR A BETTER FACE!! TWIN BLOCK AND HEADGEAR FOLLOWED BY FIXED THERAPY FOR CLASS II CORRECTION
 Case Report NUJHS Vol. 5, No.2, June 2015, ISSN 2249-7110 TWO PHASE FOR A BETTER FACE!! TWIN BLOCK AND HEADGEAR FOLLOWED BY FIXED THERAPY FOR CLASS II CORRECTION 1 2 3 4 U S Krishna Nayak, Ashutosh Shetty,
Case Report NUJHS Vol. 5, No.2, June 2015, ISSN 2249-7110 TWO PHASE FOR A BETTER FACE!! TWIN BLOCK AND HEADGEAR FOLLOWED BY FIXED THERAPY FOR CLASS II CORRECTION 1 2 3 4 U S Krishna Nayak, Ashutosh Shetty,
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTISTS
 EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTISTS Dr. Masatoshi Sana Year: ESLO 01 RÉSUMÉ OF CASE 8 CASE CATEGORY: TRANS / VERTICAL DISCREPANCY NAME: Akiko T. BORN : 15/03/1973 SEX: F PRE-TREATMENT RECORDS: AGE:
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTISTS Dr. Masatoshi Sana Year: ESLO 01 RÉSUMÉ OF CASE 8 CASE CATEGORY: TRANS / VERTICAL DISCREPANCY NAME: Akiko T. BORN : 15/03/1973 SEX: F PRE-TREATMENT RECORDS: AGE:
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTISTS
 EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTISTS CANDIDATE NUMBER : 13 Dr. Masatoshi Sana CASE NUMBER : Year : ESLO 01 RÉSUMÉ OF CASE 2 CASE CATEGORY: CLASS I MALOCCLUSION NAME: BORN: SEX: Yukari K. 08/03/1979
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTISTS CANDIDATE NUMBER : 13 Dr. Masatoshi Sana CASE NUMBER : Year : ESLO 01 RÉSUMÉ OF CASE 2 CASE CATEGORY: CLASS I MALOCCLUSION NAME: BORN: SEX: Yukari K. 08/03/1979
Non extraction treatment of growing skeletal class II malocclusion with Forsus Fatigue Resistant Appliance- A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 9 Ver. X (Sep. 2017), PP 23-31 www.iosrjournals.org Non extraction treatment of growing skeletal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 9 Ver. X (Sep. 2017), PP 23-31 www.iosrjournals.org Non extraction treatment of growing skeletal
Maxillary Expansion and Protraction in Correction of Midface Retrusion in a Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Patient
 Case Report Maxillary Expansion and Protraction in Correction of Midface Retrusion in a Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Patient Masayoshi Kawakami, DDS, PhD a ; Takakazu Yagi, DDS, PhD b ; Kenji
Case Report Maxillary Expansion and Protraction in Correction of Midface Retrusion in a Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Patient Masayoshi Kawakami, DDS, PhD a ; Takakazu Yagi, DDS, PhD b ; Kenji
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTISTS
 EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTISTS CANDIDATE NUMBER: 44 CASE NUMBER: 1 Year: ESLO 01 RÉSUMÉ OF CASE 1 CASE CATEGORY: ADULT MALOCCLUSION NAME: K.N BORN: 03/03/1980 SEX: Male PRE-TREATMENT RECORDS:
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTISTS CANDIDATE NUMBER: 44 CASE NUMBER: 1 Year: ESLO 01 RÉSUMÉ OF CASE 1 CASE CATEGORY: ADULT MALOCCLUSION NAME: K.N BORN: 03/03/1980 SEX: Male PRE-TREATMENT RECORDS:
Case Report: Long-Term Outcome of Class II Division 1 Malocclusion Treated with Rapid Palatal Expansion and Cervical Traction
 Case Report Case Report: Long-Term Outcome of Class II Division 1 Malocclusion Treated with Rapid Palatal Expansion and Cervical Traction Roberto M. A. Lima, DDS a ; Anna Leticia Lima, DDS b Abstract:
Case Report Case Report: Long-Term Outcome of Class II Division 1 Malocclusion Treated with Rapid Palatal Expansion and Cervical Traction Roberto M. A. Lima, DDS a ; Anna Leticia Lima, DDS b Abstract:
Treatment Effects of Twin-Block and Mandibular Protraction Appliance-IV in the Correction of Class II Malocclusion
 Original Article Treatment Effects of Twin-Block and Mandibular Protraction Appliance-IV in the Correction of Class II Malocclusion Ashok Kumar Jena a ;Ritu Duggal b ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate the
Original Article Treatment Effects of Twin-Block and Mandibular Protraction Appliance-IV in the Correction of Class II Malocclusion Ashok Kumar Jena a ;Ritu Duggal b ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate the
The Effect of Frankel II and Modified Twin Block Appliances on the C -axis: The Growth Vector of the Dentomaxillary Complex
 Original Article The Effect of Frankel II and Modified Twin Block Appliances on the C -axis: The Growth Vector of the Dentomaxillary Complex Stanley Braun, DDS, MME, PE a ; Nelson R. Diers, DDS b ; Gabriel
Original Article The Effect of Frankel II and Modified Twin Block Appliances on the C -axis: The Growth Vector of the Dentomaxillary Complex Stanley Braun, DDS, MME, PE a ; Nelson R. Diers, DDS b ; Gabriel
Semilongitudinal cephalometric study of craniofacial growth in untreated Class III malocclusion
 ONLINE ONLY Semilongitudinal cephalometric study of craniofacial growth in untreated Class III malocclusion Ann E. Zionic Alexander, a James A. McNamara, Jr, b Lorenzo Franchi, c and Tiziano Baccetti c
ONLINE ONLY Semilongitudinal cephalometric study of craniofacial growth in untreated Class III malocclusion Ann E. Zionic Alexander, a James A. McNamara, Jr, b Lorenzo Franchi, c and Tiziano Baccetti c
Mandibular Cervical Headgear vs Rapid Maxillary Expander and Facemask for Orthopedic Treatment of Class III Malocclusion
 Original Article Mandibular Cervical Headgear vs Rapid Maxillary Expander and Facemask for Orthopedic Treatment of Class III Malocclusion Tiziano Baccetti a ; Diego Rey b ; David Angel c ; Giovanni Oberti
Original Article Mandibular Cervical Headgear vs Rapid Maxillary Expander and Facemask for Orthopedic Treatment of Class III Malocclusion Tiziano Baccetti a ; Diego Rey b ; David Angel c ; Giovanni Oberti
Nonsurgical Treatment of Adult Open Bite Using Edgewise Appliance Combined with High-Pull Headgear and Class III Elastics
 Case Report Nonsurgical Treatment of Adult Open Bite Using Edgewise Appliance Combined with High-Pull Headgear and Class III Elastics Isao Saito, DDS, PhD a ; Masaki Yamaki, DDS, PhD b ; Kooji Hanada,
Case Report Nonsurgical Treatment of Adult Open Bite Using Edgewise Appliance Combined with High-Pull Headgear and Class III Elastics Isao Saito, DDS, PhD a ; Masaki Yamaki, DDS, PhD b ; Kooji Hanada,
Comparison of Skeletal Changes between Female Adolescents and Adults with Hyperdivergent Class II Division 1 Malocclusion after Orthodontic Treatment
 Comparison of Skeletal Changes between Female Adolescents and Adults with Hyperdivergent Class II Division 1 Malocclusion after Orthodontic Treatment Yun DING 1, Jian Hui ZHAO 2, Jin Rong DENG 1, Xiu Jing
Comparison of Skeletal Changes between Female Adolescents and Adults with Hyperdivergent Class II Division 1 Malocclusion after Orthodontic Treatment Yun DING 1, Jian Hui ZHAO 2, Jin Rong DENG 1, Xiu Jing
Treatment of a severe class II division 1 malocclusion with twin-block appliance
 2018; 4(5): 167-171 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2018; 4(5): 167-171 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 27-03-2018 Accepted: 28-04-2018 Dr. Sheetal Bohra Resident
2018; 4(5): 167-171 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2018; 4(5): 167-171 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 27-03-2018 Accepted: 28-04-2018 Dr. Sheetal Bohra Resident
Premolar extraction in orthodontics: Does it have any effect on patient s facial height?
 Original Article Premolar extraction in orthodontics: Does it have any effect on patient s facial height? Abdol-Hamid Zafarmand, Mohamad-Mahdi Zafarmand 1 Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry,
Original Article Premolar extraction in orthodontics: Does it have any effect on patient s facial height? Abdol-Hamid Zafarmand, Mohamad-Mahdi Zafarmand 1 Department of Orthodontics, School of Dentistry,
The ASE Example Case Report 2010
 The ASE Example Case Report 2010 The Requirements for Case Presentation in The Angle Society of Europe are specified in the Appendix I to the Bylaws. This example case report exemplifies how these requirements
The ASE Example Case Report 2010 The Requirements for Case Presentation in The Angle Society of Europe are specified in the Appendix I to the Bylaws. This example case report exemplifies how these requirements
Case Report: Early Correction of Class III Malocclusion with alternate Rapid Maxillary Expansion And Constriction (Alt-RAMEC) and Face Mask Therapy
 Case Report: Early Correction of Class III Malocclusion with alternate Rapid Maxillary Expansion And Constriction (Alt-RAMEC) and Face Mask Therapy Dr. Falguni Mehta 1, Dr. Shivam Mehta 2, Dr. Manop Agrawal
Case Report: Early Correction of Class III Malocclusion with alternate Rapid Maxillary Expansion And Constriction (Alt-RAMEC) and Face Mask Therapy Dr. Falguni Mehta 1, Dr. Shivam Mehta 2, Dr. Manop Agrawal
The effect of tooth agenesis on dentofacial structures
 European Journal of Orthodontics 19 (1997) 71 78 9 1997 European Orthodontic Society The effect of on dentofacial structures Sema Yª and Tuba Department of Orthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Gazi University,
European Journal of Orthodontics 19 (1997) 71 78 9 1997 European Orthodontic Society The effect of on dentofacial structures Sema Yª and Tuba Department of Orthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Gazi University,
CASE: EXTRACTION Dr. TRAINING M (CA) Caucasian AGE: 8.6 VISUAL NORMS RMO X: 02/06/ R: 02/21/2003 MISSING PERMANENT TEETH RMO 2003
 O C RMO CASE: EXTRACTION Dr. TRAINING M (CA) Caucasian AGE:. X: // - R: // MISSING PERMANENT TEETH VISUAL NORMS RMO R L RMO Diagnostic Services RMO, Inc. ()- Post Office Box ()- Canoga Park, CA - EXTRACTION
O C RMO CASE: EXTRACTION Dr. TRAINING M (CA) Caucasian AGE:. X: // - R: // MISSING PERMANENT TEETH VISUAL NORMS RMO R L RMO Diagnostic Services RMO, Inc. ()- Post Office Box ()- Canoga Park, CA - EXTRACTION
Treatment effects produced by the Twin-block appliance and the FR-2 appliance of Fränkel compared with an untreated Class II sample
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment effects produced by the Twin-block appliance and the FR-2 appliance of Fränkel compared with an untreated Class II sample Linda Ratner Toth, DDS, MS, a and James A. McNamara,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment effects produced by the Twin-block appliance and the FR-2 appliance of Fränkel compared with an untreated Class II sample Linda Ratner Toth, DDS, MS, a and James A. McNamara,
Long-term skeletal effects of high-pull headgear plus fixed appliances: a cephalometric study
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Spring 2014 Long-term skeletal effects of high-pull headgear plus fixed appliances: a cephalometric study Eve Erin Bilbo University of Iowa
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Spring 2014 Long-term skeletal effects of high-pull headgear plus fixed appliances: a cephalometric study Eve Erin Bilbo University of Iowa
Removable appliances
 Removable appliances Melinda Madléna DMD, PhD associate professor Department of Pedodontics and Orthodontics Faculty of Dentistry Semmelweis University Budapest Classification of the orthodontic anomalies
Removable appliances Melinda Madléna DMD, PhD associate professor Department of Pedodontics and Orthodontics Faculty of Dentistry Semmelweis University Budapest Classification of the orthodontic anomalies
Different Non Surgical Treatment Modalities for Class III Malocclusion
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 9, Issue 6 (Sep.- Oct. 2013), PP 48-52 Different Non Surgical Treatment Modalities for Class III Malocclusion
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 9, Issue 6 (Sep.- Oct. 2013), PP 48-52 Different Non Surgical Treatment Modalities for Class III Malocclusion
Treatment of Angle Class III. Department of Paedodontics and Orthodontics Dr. habil. Melinda Madléna associate professor
 Department of Paedodontics and Orthodontics Dr. habil. Melinda Madléna associate professor Disorders in Angle Class III The position of the lower jaw is foreward regarding to the upper jaw Mesialocclusion
Department of Paedodontics and Orthodontics Dr. habil. Melinda Madléna associate professor Disorders in Angle Class III The position of the lower jaw is foreward regarding to the upper jaw Mesialocclusion
2008 JCO, Inc. May not be distributed without permission. Correction of Asymmetry with a Mandibular Propulsion Appliance
 2008 JCO, Inc. May not be distributed without permission. www.jco-online.com CASE REPORT Correction of Asymmetry with a Mandibular Propulsion Appliance JOSÉ AUGUSTO MENDES MIGUEL, DDS, MSC, PHD GUSTAVO
2008 JCO, Inc. May not be distributed without permission. www.jco-online.com CASE REPORT Correction of Asymmetry with a Mandibular Propulsion Appliance JOSÉ AUGUSTO MENDES MIGUEL, DDS, MSC, PHD GUSTAVO
Class II malocclusions are observed commonly in
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improving Class II malocclusion as a side-effect of rapid maxillary expansion: A prospective clinical study Susan S. Guest, a James A. McNamara, Jr., b Tiziano Baccetti, c and Lorenzo
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improving Class II malocclusion as a side-effect of rapid maxillary expansion: A prospective clinical study Susan S. Guest, a James A. McNamara, Jr., b Tiziano Baccetti, c and Lorenzo
Case Report Diagnosis and Treatment of Pseudo-Class III Malocclusion
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 652936, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/652936 Case Report Diagnosis and Treatment of Pseudo-Class III Malocclusion Ariel Reyes, 1 Luis Serret, 2,3 Marcos Peguero,
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 652936, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/652936 Case Report Diagnosis and Treatment of Pseudo-Class III Malocclusion Ariel Reyes, 1 Luis Serret, 2,3 Marcos Peguero,
Surgical-Orthodontic Treatment of Gummy Smile with Vertical Maxillary Excess
 Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10021-1219 Surgical-Orthodontic Treatment of Gummy Smile with Vertical Maxillary Excess 1 Sumit Kumar Yadav, 2 Vikas Sehgal, 3 Sanjay Mittal ABSTRACT Vertical maxillary
Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10021-1219 Surgical-Orthodontic Treatment of Gummy Smile with Vertical Maxillary Excess 1 Sumit Kumar Yadav, 2 Vikas Sehgal, 3 Sanjay Mittal ABSTRACT Vertical maxillary
RMO VISUAL NORMS. CASE: CHINESE SAMPLE Dr. TRAINING F (CH) Chinese AGE: 12.4 X: 09/30/ R: 02/21/2003 MISSING PERMANENT TEETH
 O C RMO CASE: CHINESE SAMPLE Dr. TRAINING F (CH) Chinese AGE:. X: // - R: // MISSING PERMANENT TEETH VISUAL NORMS RMO R L RMO Diagnostic Services RMO, Inc. ()- Post Office Box ()- Canoga Park, CA - CHINESE
O C RMO CASE: CHINESE SAMPLE Dr. TRAINING F (CH) Chinese AGE:. X: // - R: // MISSING PERMANENT TEETH VISUAL NORMS RMO R L RMO Diagnostic Services RMO, Inc. ()- Post Office Box ()- Canoga Park, CA - CHINESE
SURGICAL - ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT OF CLASS II DIVISION 1 MALOCCLUSION IN AN ADULT PATIENT: A CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 02 SURGICAL - ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT OF CLASS II DIVISION 1 MALOCCLUSION IN AN ADULT PATIENT: A CASE REPORT Amit Dahiya 1,Minakshi
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 02 SURGICAL - ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT OF CLASS II DIVISION 1 MALOCCLUSION IN AN ADULT PATIENT: A CASE REPORT Amit Dahiya 1,Minakshi
The clinical management of malocclusions characterized
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment timing for an orthopedic approach to patients with increased vertical dimension Tiziano Baccetti, a Lorenzo Franchi, a Scott O. Schulz, b and James A. McNamara, Jr c Florence,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment timing for an orthopedic approach to patients with increased vertical dimension Tiziano Baccetti, a Lorenzo Franchi, a Scott O. Schulz, b and James A. McNamara, Jr c Florence,
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS
 EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS CANDIDATE NUMBER: Dr. Stefan Blasius Year: 2010 WBLO 01 EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS CANDIDATE NUMBER: Dr. Stefan Blasius Year: 2010 WBLO 01 RÉSUMÉ
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS CANDIDATE NUMBER: Dr. Stefan Blasius Year: 2010 WBLO 01 EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS CANDIDATE NUMBER: Dr. Stefan Blasius Year: 2010 WBLO 01 RÉSUMÉ
A Modified Three-piece Base Arch for en masse Retraction and Intrusion in a Class II Division 1 Subdivision Case
 Dhaval Ranjitbhai Lekhadia, Gautham Hegde RESEARCH ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1149 A Modified Three-piece Base Arch for en masse Retraction and Intrusion in a Class II Division 1 Subdivision Case
Dhaval Ranjitbhai Lekhadia, Gautham Hegde RESEARCH ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1149 A Modified Three-piece Base Arch for en masse Retraction and Intrusion in a Class II Division 1 Subdivision Case
Treatment of Long face / Open bite
 In the name of GOD Treatment of Long face / Open bite in preadolescent children Presented by: Dr Somayeh Heidari Orthodontist Reference: Contemporary Orthodontics Chapter 13 William R. Proffit, Henry W.
In the name of GOD Treatment of Long face / Open bite in preadolescent children Presented by: Dr Somayeh Heidari Orthodontist Reference: Contemporary Orthodontics Chapter 13 William R. Proffit, Henry W.
Comparison between conventional Twin block and a modified Essix twin block in adolescents with Class II malocclusion
 International Journal of Dentistry Research 2016; 1(1): 1-5 Research Article IJDR 2016; 1(1): 1-5 December 2017, All rights reserved www.dentistryscience.com Comparison between conventional Twin block
International Journal of Dentistry Research 2016; 1(1): 1-5 Research Article IJDR 2016; 1(1): 1-5 December 2017, All rights reserved www.dentistryscience.com Comparison between conventional Twin block
Mesial Step Class I or Class III Dependent upon extent of step seen clinically and patient s growth pattern Refer for early evaluation (by 8 years)
 Orthodontics and Dentofacial Development Overview Development of Dentition Treatment Retention and Relapse Growth of Naso-Maxillary Complex Develops postnatally entirely by intramenbranous ossification
Orthodontics and Dentofacial Development Overview Development of Dentition Treatment Retention and Relapse Growth of Naso-Maxillary Complex Develops postnatally entirely by intramenbranous ossification
Correction of Crowding using Conservative Treatment Approach
 Case Report Correction of Crowding using Conservative Treatment Approach Dr Tapan Shah, 1 Dr Tarulatha Shyagali, 2 Dr Kalyani Trivedi 3 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Professor, Department of Orthodontics, Darshan
Case Report Correction of Crowding using Conservative Treatment Approach Dr Tapan Shah, 1 Dr Tarulatha Shyagali, 2 Dr Kalyani Trivedi 3 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Professor, Department of Orthodontics, Darshan
Class III malocclusions are complex to MANDIBULAR CERVICAL HEADGEAR IN ORTHOPEDIC AND ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT OF CLASS III CASES
 Diego Rey, DDS, Cert Ortho 1 Juan Fernando Aristizabal, DDS, Cert Ortho 2 Giovanni Oberti, DDS, Cert Ortho 3 David Angel, DDS, Cert Ortho 4 MANDIBULAR CERVICAL HEADGEAR IN ORTHOPEDIC AND ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT
Diego Rey, DDS, Cert Ortho 1 Juan Fernando Aristizabal, DDS, Cert Ortho 2 Giovanni Oberti, DDS, Cert Ortho 3 David Angel, DDS, Cert Ortho 4 MANDIBULAR CERVICAL HEADGEAR IN ORTHOPEDIC AND ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT
Comparative Study of Tweed Triangle in Angle Class II Division 1 Malocclusion between Nepalese and Chinese Students
 GENERAL SECTION Bishnu Prasad Sharma: Comparative Study of Tweed Triangle in Nepali and Chinese ORGINAL ARTICLE Comparative Study of Tweed Triangle in Angle Class II Division 1 Malocclusion between Nepalese
GENERAL SECTION Bishnu Prasad Sharma: Comparative Study of Tweed Triangle in Nepali and Chinese ORGINAL ARTICLE Comparative Study of Tweed Triangle in Angle Class II Division 1 Malocclusion between Nepalese
ACTIVATOR: SIMPLE YET EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONAL APPLIANCE FOR SKELETAL CLASS II CORRECTION: CASE REPORT... ABSTRACT:...
 ACTIVATOR: SIMPLE YET EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONAL APPLIANCE FOR SKELETAL CLASS II CORRECTION: CASE REPORT 1Dr. Falguni Mehta *, 2 Dr. Dolly Patel, 3 Dr. Nishit Mehta 1Professor, Dept of orthodontics & Dentofacial
ACTIVATOR: SIMPLE YET EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONAL APPLIANCE FOR SKELETAL CLASS II CORRECTION: CASE REPORT 1Dr. Falguni Mehta *, 2 Dr. Dolly Patel, 3 Dr. Nishit Mehta 1Professor, Dept of orthodontics & Dentofacial
Arch dimensional changes following orthodontic treatment with extraction of four first premolars
 Received: 14 June. 2015 Accepted: 7 Dec. 2015 Arch dimensional changes following orthodontic treatment with extraction of four first premolars Abstract Asghar Ebadifar DDS, MSc 1, Mohammad Hossien Shafazand
Received: 14 June. 2015 Accepted: 7 Dec. 2015 Arch dimensional changes following orthodontic treatment with extraction of four first premolars Abstract Asghar Ebadifar DDS, MSc 1, Mohammad Hossien Shafazand
Nonextraction Management of Class II Malocclusion Using Powerscope: A Case Report
 Case Report To cite: Paul R, Mattu N, Golchha V, Yadav D, Gupta M. Nonextraction Management of Class II Malocclusion Using Powerscope: A Case Report. Journal of Contemporary Orthodontics, February 2018,
Case Report To cite: Paul R, Mattu N, Golchha V, Yadav D, Gupta M. Nonextraction Management of Class II Malocclusion Using Powerscope: A Case Report. Journal of Contemporary Orthodontics, February 2018,
Skeletal changes of maxillary protraction without rapid maxillary expansion
 Original Article Skeletal changes of maxillary protraction without rapid maxillary expansion A comparison of the primary and mixed dentition Dong-Yul Lee a ; Eun-Soo Kim b ; Yong-Kyu Lim a ; Sug-Joon Ahn
Original Article Skeletal changes of maxillary protraction without rapid maxillary expansion A comparison of the primary and mixed dentition Dong-Yul Lee a ; Eun-Soo Kim b ; Yong-Kyu Lim a ; Sug-Joon Ahn
Chin cup effects using two different force magnitudes in the management of Class III malocclusions
 Original Article Chin cup effects using two different force magnitudes in the management of Class III malocclusions Yasser L. Abdelnaby a ; Essam A. Nassar b ABSTRACT Objectives: To evaluate the dental
Original Article Chin cup effects using two different force magnitudes in the management of Class III malocclusions Yasser L. Abdelnaby a ; Essam A. Nassar b ABSTRACT Objectives: To evaluate the dental
Non Extraction philosophy: Distalization using Jone s Jig appliance- a case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. IV (Sep. 2014), PP 36-41 Non Extraction philosophy: Distalization using Jone s Jig appliance-
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. IV (Sep. 2014), PP 36-41 Non Extraction philosophy: Distalization using Jone s Jig appliance-
The literature contains evidence that subjects
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dentofacial growth changes in subjects with untreated I malocclusion from late puberty through young adulthood Tiziano Baccetti, a Franka Stahl, b and James A. McNamara, Jr c Florence,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dentofacial growth changes in subjects with untreated I malocclusion from late puberty through young adulthood Tiziano Baccetti, a Franka Stahl, b and James A. McNamara, Jr c Florence,
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS
 EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS KANARELIS PANAGIOTIS (TAKIS) CASE NUMBER: 1 Year: 2012 WBLO 1 RÉSUMÉ OF CASE 1 CASE CATEGORY: ADULT MALOCCLUSION NAME:
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTICS KANARELIS PANAGIOTIS (TAKIS) CASE NUMBER: 1 Year: 2012 WBLO 1 RÉSUMÉ OF CASE 1 CASE CATEGORY: ADULT MALOCCLUSION NAME:
Treatment of Developing Skeletal Class iii Malocclusion, Using fr-iii Appliance: A Case Report
 CASE REPORT Treatment of Developing Skeletal Class iii Malocclusion, Using fr-iii Appliance: A Case Report Saveen. N.S, Rosaline Tina Paul, Jerun Jose, Deepak. P.R, Drisya S, Lakshmanan L Royal dental
CASE REPORT Treatment of Developing Skeletal Class iii Malocclusion, Using fr-iii Appliance: A Case Report Saveen. N.S, Rosaline Tina Paul, Jerun Jose, Deepak. P.R, Drisya S, Lakshmanan L Royal dental
CASE: HISPANIC SAMPLE Dr. TRAINING F (LA) Latin AGE: 10.5 VISUAL NORMS RMO X: 06/23/ R: 02/21/2003 MISSING PERMANENT TEETH RMO 2003
 O C RMO CASE: HISPANIC SAMPLE Dr. TRAINING F (LA) Latin AGE:. X: // - R: // MISSING PERMANENT TEETH VISUAL NORMS RMO R L RMO Diagnostic Services RMO, Inc. ()- Post Office Box 7 ()7- Canoga Park, CA -7
O C RMO CASE: HISPANIC SAMPLE Dr. TRAINING F (LA) Latin AGE:. X: // - R: // MISSING PERMANENT TEETH VISUAL NORMS RMO R L RMO Diagnostic Services RMO, Inc. ()- Post Office Box 7 ()7- Canoga Park, CA -7
Non-surgical management of skeletal malocclusions: An assessment of 100 cases
 Non-surgical management of skeletal malocclusions: An assessment of 100 cases In early 1970 s reduced risks associated with surgical procedures allowed the treatment planning process for skeletal malocclusions
Non-surgical management of skeletal malocclusions: An assessment of 100 cases In early 1970 s reduced risks associated with surgical procedures allowed the treatment planning process for skeletal malocclusions
Case Report n 2. Patient. Age: ANB 8 OJ 4.5 OB 5.5
 Case Report n 2 Patient Age: 12.11 Diagnosis Angle cl.ii div.2 ANB 8 OJ 4.5 OB 5.5 Author: Dr. Case History The patient is a thirteen year old girl who exhibits delayed development, both physically and
Case Report n 2 Patient Age: 12.11 Diagnosis Angle cl.ii div.2 ANB 8 OJ 4.5 OB 5.5 Author: Dr. Case History The patient is a thirteen year old girl who exhibits delayed development, both physically and
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Orthodontic Camouflage of Skeletal Class I, Class II and Class III Malocclusion in Borderline Cases Report of Three Cases Dr. Seema Kapil Lahoti 1 *, Dr.
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Orthodontic Camouflage of Skeletal Class I, Class II and Class III Malocclusion in Borderline Cases Report of Three Cases Dr. Seema Kapil Lahoti 1 *, Dr.
An Effectiv Rapid Molar Derotation: Keles K
 An Effectiv ective e and Precise Method forf Rapid Molar Derotation: Keles K TPA Ahmet Keles, DDS, DMSc 1 /Sedef Impar, DDS 2 Most of the time, Class II molar relationships occur due to the mesiopalatal
An Effectiv ective e and Precise Method forf Rapid Molar Derotation: Keles K TPA Ahmet Keles, DDS, DMSc 1 /Sedef Impar, DDS 2 Most of the time, Class II molar relationships occur due to the mesiopalatal
Racial Variations in Cephalometric Analysis between Whites and Kuwaitis
 Original Article Racial Variations in Cephalometric Analysis between Whites and Kuwaitis Faraj Behbehani a ; E. Preston Hicks b ; Cynthia Beeman c ; G. Thomas Kluemper d ; Mary K. Rayens e Abstract: The
Original Article Racial Variations in Cephalometric Analysis between Whites and Kuwaitis Faraj Behbehani a ; E. Preston Hicks b ; Cynthia Beeman c ; G. Thomas Kluemper d ; Mary K. Rayens e Abstract: The
EUROPEAN BOARD OF ORTHODONTISTS APPENDIX 1 CASE PRESENTATION 2005
 EUROPEAN BOARD OF ORTHODONTISTS APPENDIX 1 CASE PRESENTATION 2005 This appendix contains all the pre-printed forms to produce the 8 case presentations. EUROPEAN BOARD OF ORTHODONTISTS CASE NUMBER: 2005
EUROPEAN BOARD OF ORTHODONTISTS APPENDIX 1 CASE PRESENTATION 2005 This appendix contains all the pre-printed forms to produce the 8 case presentations. EUROPEAN BOARD OF ORTHODONTISTS CASE NUMBER: 2005
Management of severe Class II malocclusion with sequential removable functional and orthodontic appliances: a case for MorthRCSEd examination
 Title Management of severe Class II malocclusion with sequential removable functional and orthodontic appliances: a case for MorthRCSEd examination Author(s) Li, LCF; Wong, RWK Citation Dental Press Journal
Title Management of severe Class II malocclusion with sequential removable functional and orthodontic appliances: a case for MorthRCSEd examination Author(s) Li, LCF; Wong, RWK Citation Dental Press Journal
Effects of camouflage treatment on dentofacial structures in Class II division 1 mandibular retrognathic patients
 European Journal of Orthodontics 27 (2005) 524 531 doi:10.1093/ejo/cji046 Advance Access publication 27 July 2005 The Author 2005. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Orthodontics
European Journal of Orthodontics 27 (2005) 524 531 doi:10.1093/ejo/cji046 Advance Access publication 27 July 2005 The Author 2005. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Orthodontics
Combined Orthodontic And Surgical Correction Of An Adolescent Patient With Thin Palatal Cortex And Vertical Maxillary Excess
 Combined Orthodontic And Surgical Correction Of An Adolescent Patient With Thin Palatal Cortex And Vertical Maxillary Excess Hegde M, 1 Hegde C, 2 Parajuli U, 3 Kamath P, 4 MR D 1 Department of orthodontics
Combined Orthodontic And Surgical Correction Of An Adolescent Patient With Thin Palatal Cortex And Vertical Maxillary Excess Hegde M, 1 Hegde C, 2 Parajuli U, 3 Kamath P, 4 MR D 1 Department of orthodontics
Skeletal and Dental Components of Class II Division 1 Correction with the MARA Compared to the Standard Edgewise Appliance
 University of Tennessee Health Science Center UTHSC Digital Commons Theses and Dissertations (ETD) College of Graduate Health Sciences 5-2012 Skeletal and Dental Components of Class II Division 1 Correction
University of Tennessee Health Science Center UTHSC Digital Commons Theses and Dissertations (ETD) College of Graduate Health Sciences 5-2012 Skeletal and Dental Components of Class II Division 1 Correction
Orthodontic mini-implants have revolutionized
 CASE REPORT Correction of deep overbite and gummy smile by using a mini-implant with a segmented wire in a growing Class II Division 2 patient Tae-Woo Kim, a Hyewon Kim, b and Shin-Jae Lee c Seoul, South
CASE REPORT Correction of deep overbite and gummy smile by using a mini-implant with a segmented wire in a growing Class II Division 2 patient Tae-Woo Kim, a Hyewon Kim, b and Shin-Jae Lee c Seoul, South
Vertical changes during Begg s and PEA-A Comparative Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 9, Issue 4 (Sep.- Oct. 2013), PP 48-53 Vertical changes during Begg s and PEA-A Comparative Study Dr.
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 9, Issue 4 (Sep.- Oct. 2013), PP 48-53 Vertical changes during Begg s and PEA-A Comparative Study Dr.
Class III malocclusion occurs in less than 5%
 CDABO CASE REPORT Orthodontic correction of a Class III malocclusion in an adolescent patient with a bonded RPE and protraction face mask Steven W. Smith, DDS, a and Jeryl D. English, DDS, MS b Dallas,
CDABO CASE REPORT Orthodontic correction of a Class III malocclusion in an adolescent patient with a bonded RPE and protraction face mask Steven W. Smith, DDS, a and Jeryl D. English, DDS, MS b Dallas,
EXPANSION. Effective Management of Transverse Problems in the Growing Patient: Evidence-based Approach
 Effective Management of Transverse Problems in the Growing Patient: Evidence-based Approach Lorenzo Franchi, DDS, PhD The transverse deficiency of the maxillary arch is the most common occlusal problem
Effective Management of Transverse Problems in the Growing Patient: Evidence-based Approach Lorenzo Franchi, DDS, PhD The transverse deficiency of the maxillary arch is the most common occlusal problem
ASSESSMENT OF MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR ROTATION IN SKELETAL CLASS II, AND THEIR COMPARISON WITH CLASS I AND CLASS III SUBJECTS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ASSESSMENT OF MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR ROTATION IN SKELETAL CLASS II, AND THEIR COMPARISON WITH CLASS I AND CLASS III SUBJECTS ABSTRACT FARHAT AMIN, BDS, MCPS, FCPS Mesial rotation of maxillary
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ASSESSMENT OF MAXILLARY FIRST MOLAR ROTATION IN SKELETAL CLASS II, AND THEIR COMPARISON WITH CLASS I AND CLASS III SUBJECTS ABSTRACT FARHAT AMIN, BDS, MCPS, FCPS Mesial rotation of maxillary
Cephalometric Analysis for Diagnosis and Treatment of Orthodontic Patients
 Journal of Oral Health & Community Dentistry ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cephalometric Analysis for Diagnosis and Treatment of Orthodontic Patients Agrawal D 1 ABSTRACT Cephalometric analysis for diagnosis and treatment
Journal of Oral Health & Community Dentistry ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cephalometric Analysis for Diagnosis and Treatment of Orthodontic Patients Agrawal D 1 ABSTRACT Cephalometric analysis for diagnosis and treatment
A correlation between a new angle (S-Gn-Go angle) with the facial height
 A correlation between a new angle (S-Gn-Go angle) with the facial height Esraa S. Jassim B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Marwan S. Al-Daggistany B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Jinan E. Saloom B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) ABSTRACT Background:
A correlation between a new angle (S-Gn-Go angle) with the facial height Esraa S. Jassim B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Marwan S. Al-Daggistany B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Jinan E. Saloom B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) ABSTRACT Background:
Crowded Class II Division 2 Malocclusion
 Class II Division 2 Malocclusion Crowded Class II Division 2 Malocclusion Clinicians: Drs. Chris Chang, Hsin-Yin Yeh, Sophia Pei-Wen Shu, W. Eugene Roberts Patient: Miss Jhan Pre-treatment Diagnosis An
Class II Division 2 Malocclusion Crowded Class II Division 2 Malocclusion Clinicians: Drs. Chris Chang, Hsin-Yin Yeh, Sophia Pei-Wen Shu, W. Eugene Roberts Patient: Miss Jhan Pre-treatment Diagnosis An
Therapeutic Effect of Face Mask with Two Different Retention Plaques in Class III Children
 Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science 2018, Volume 6, Issue 5, Page No: 335-342 Copyright CC BY-NC 4.0 Available Online at: www.jrmds.in eissn No. 2347-2367: pissn No. 2347-2545 Therapeutic
Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science 2018, Volume 6, Issue 5, Page No: 335-342 Copyright CC BY-NC 4.0 Available Online at: www.jrmds.in eissn No. 2347-2367: pissn No. 2347-2545 Therapeutic
The treatment of patients with increased vertical
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment effects of bonded RME and verticalpull chincup followed by fixed appliance in patients with increased vertical dimension Scott O. Schulz, a James A. McNamara, Jr, b Tiziano Baccetti,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment effects of bonded RME and verticalpull chincup followed by fixed appliance in patients with increased vertical dimension Scott O. Schulz, a James A. McNamara, Jr, b Tiziano Baccetti,
An orthopaedic approach to the treatment of Class III malocclusions in the early mixed dentition
 European Journal of Orthodontics 26 (2004) 191 199 European Journal of Orthodontics vol. 26 no. 2 European Orthodontic Society 2004; all rights reserved. An orthopaedic approach to the treatment of Class
European Journal of Orthodontics 26 (2004) 191 199 European Journal of Orthodontics vol. 26 no. 2 European Orthodontic Society 2004; all rights reserved. An orthopaedic approach to the treatment of Class
Management of Severe Class II Division 1 Malocclusion with Hybrid Functional Appliance by Double Advancement A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 2 Ver. IV (February. 2017), PP 83-88 www.iosrjournals.org Management of Severe Class II Division
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 2 Ver. IV (February. 2017), PP 83-88 www.iosrjournals.org Management of Severe Class II Division
Original Article. Sayeh Ehsani a ; Brian Nebbe b ; David Normando c ; Manuel O. Lagravere d ; Carlos Flores-Mir e
 Original Article Dental and skeletal changes in mild to moderate Class II malocclusions treated by either a Twin-block or Xbow appliance followed by full fixed orthodontic treatment Sayeh Ehsani a ; Brian
Original Article Dental and skeletal changes in mild to moderate Class II malocclusions treated by either a Twin-block or Xbow appliance followed by full fixed orthodontic treatment Sayeh Ehsani a ; Brian
Twin Block appliance. A Systematic Review.
 Article ID: WMC005372 ISSN 2046-1690 Twin Block appliance. A Systematic Review. Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Martina Mezio, Submitting Author: Dr. Martina Mezio, Other Authors: Dr.
Article ID: WMC005372 ISSN 2046-1690 Twin Block appliance. A Systematic Review. Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Martina Mezio, Submitting Author: Dr. Martina Mezio, Other Authors: Dr.
An open bite develops from a combination of
 CASE REPORT Treatment of skeletal open-bite malocclusion with lymphangioma of the tongue Chooryung J. Chung, a Soonshin Hwang, b Yoon-Jeong Choi, c and Kyung-Ho Kim d Seoul, Korea Lymphangioma of the tongue
CASE REPORT Treatment of skeletal open-bite malocclusion with lymphangioma of the tongue Chooryung J. Chung, a Soonshin Hwang, b Yoon-Jeong Choi, c and Kyung-Ho Kim d Seoul, Korea Lymphangioma of the tongue
Mx1 to NA = 34 & 10 mm. Md1 to NB = 21 & 3 mm.
 Chapter 16 Clinical cases: mixed dentition and adolescent, CLII non-extraction 219 Full CLII div I OJ = 15 OB = 8 SNA = 82 SNB = 75 Mx1 to NA = 34 & 10 mm. Md1 to NB = 21 & 3 mm. Md1 to A-pog = -2 GO-GN
Chapter 16 Clinical cases: mixed dentition and adolescent, CLII non-extraction 219 Full CLII div I OJ = 15 OB = 8 SNA = 82 SNB = 75 Mx1 to NA = 34 & 10 mm. Md1 to NB = 21 & 3 mm. Md1 to A-pog = -2 GO-GN
Comparison of craniofacial characteristics of typical Chinese and Caucasian young adults
 European Journal of Orthodontics 33 (2011) 205 211 doi:10.1093/ejo/cjq054 Advance Access Publication 13 August 2010 The Author 2010. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Orthodontic
European Journal of Orthodontics 33 (2011) 205 211 doi:10.1093/ejo/cjq054 Advance Access Publication 13 August 2010 The Author 2010. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Orthodontic
Dr Robert Drummond. BChD, DipOdont Ortho, MChD(Ortho), FDC(SA) Ortho. Canad Inn Polo Park Winnipeg 2015
 Dr Robert Drummond BChD, DipOdont Ortho, MChD(Ortho), FDC(SA) Ortho Canad Inn Polo Park Winnipeg 2015 Severely compromised FPM with poor prognosis Children often present with a developing dentition affected
Dr Robert Drummond BChD, DipOdont Ortho, MChD(Ortho), FDC(SA) Ortho Canad Inn Polo Park Winnipeg 2015 Severely compromised FPM with poor prognosis Children often present with a developing dentition affected
Evaluation of Correlation between Wits Appraisal and a New Method for Assessment of Sagittal Relationship of Jaws
 Original Article Evaluation of Correlation between Wits Appraisal and a New Method for Assessment of Sagittal Relationship of Jaws Z. Hedayati 1, S. Heidari 2, F. Khaje 3 1 Orthodontic Research Center,
Original Article Evaluation of Correlation between Wits Appraisal and a New Method for Assessment of Sagittal Relationship of Jaws Z. Hedayati 1, S. Heidari 2, F. Khaje 3 1 Orthodontic Research Center,
Correlation Between Naso Labial Angle and Effective Maxillary and Mandibular Lengths in Untreated Class II Patients
 9 International Journal of Interdisciplinary and Multidisciplinary Studies,2014,Vol 1,No.3,9-14. Available online at httt://www.ijims.com ISSN: 2348 0343 Correlation Between Naso Labial Angle and Effective
9 International Journal of Interdisciplinary and Multidisciplinary Studies,2014,Vol 1,No.3,9-14. Available online at httt://www.ijims.com ISSN: 2348 0343 Correlation Between Naso Labial Angle and Effective
The Herbst appliance was introduced in the early
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment effects of the edgewise Herbst appliance: A cephalometric and tomographic investigation Ryan VanLaecken, a Chris A. Martin, b Terry Dischinger, c Thomas Razmus, d and Peter Ngan
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment effects of the edgewise Herbst appliance: A cephalometric and tomographic investigation Ryan VanLaecken, a Chris A. Martin, b Terry Dischinger, c Thomas Razmus, d and Peter Ngan
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
One of the greatest challenges in contemporary
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment and posttreatment craniofacial changes after rapid maxillary expansion and facemask therapy Tiziano Baccetti, DDS, PhD, a Lorenzo Franchi, DDS, PhD, b and James A. McNamara,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment and posttreatment craniofacial changes after rapid maxillary expansion and facemask therapy Tiziano Baccetti, DDS, PhD, a Lorenzo Franchi, DDS, PhD, b and James A. McNamara,
Orthodontic and Orthognathic Surgical Correction of a Skeletal Class III Malocclusion
 Dental Medicine Research 30 2) 161 166, 2010 161 Case Report Orthodontic and Orthognathic Surgical Correction of a Skeletal Class III Malocclusion Tetsutaro Yamaguchi, Yoko Tomoyasu, Tatsuo Shirota*, Masashi
Dental Medicine Research 30 2) 161 166, 2010 161 Case Report Orthodontic and Orthognathic Surgical Correction of a Skeletal Class III Malocclusion Tetsutaro Yamaguchi, Yoko Tomoyasu, Tatsuo Shirota*, Masashi
Early Treatment of Class III Patients To Improve Facial Aesthetics and Predict Future Growth
 CLINICAL ARTICLES Hong Kong Dental Journal 2004; 1: 24-30 Early Treatment of Class III Patients To Improve Facial Aesthetics and Predict Future Growth Peter Ngan*, DMD, DABOrtho, DABPedD Stephen Hon-Yin
CLINICAL ARTICLES Hong Kong Dental Journal 2004; 1: 24-30 Early Treatment of Class III Patients To Improve Facial Aesthetics and Predict Future Growth Peter Ngan*, DMD, DABOrtho, DABPedD Stephen Hon-Yin
A SERIOUS CHALLENGE IN DENTOFACIAL ORTHOPEDICS
 New perspectives in the orthopedic approach to Class III treatment Lorenzo Franchi, DDS, PhD Department of Orthodontics, The University of Florence, Italy, and T.M. Graber Visiting Scholar Department of
New perspectives in the orthopedic approach to Class III treatment Lorenzo Franchi, DDS, PhD Department of Orthodontics, The University of Florence, Italy, and T.M. Graber Visiting Scholar Department of
The conservative treatment of Class I malocclusion with maxillary transverse deficiency and anterior teeth crowding
 B B O C a s e R e p o r t The conservative treatment of Class I malocclusion with maxillary transverse deficiency and anterior teeth crowding Lincoln I. Nojima* Abstract This report describes the treatment
B B O C a s e R e p o r t The conservative treatment of Class I malocclusion with maxillary transverse deficiency and anterior teeth crowding Lincoln I. Nojima* Abstract This report describes the treatment
