Pre-reading - radiolucencies
|
|
|
- Virgil Lyons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pre-reading - radiolucencies Multiple radiolucencies o Suggests a systemic cause o Most likely: cherubism or KCOT s of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome o Sometimes: florid osseous dysplasia (if limited to alveolar process) Odontogenic neoplasms o Mainly benign, but have the potential to be malignant o Have the tendency to recur o Includes ameloblastomas, keratocystic odontogenic tumors, odontogenic myxomas, and glandular odontogenic cysts Cherubism -Pan reconstruction of a CBCT -Bilateral RL on posterior mandible and on left posterior maxilla -A RL like this would prompt one to think ameloblastoma -If there is little evidence of B-L expansion, then think KCOT -Palmar pitting can be checked to see if it is multiple KCOT s due to NBCC -Also, ameloblastomas do not cross the midline unlike cherubism -Autosomal dominant genetic disorder -During earliest and active stage, cherubism lesions contain giant cells -When cherubism inactivates, the lesions is replaced with woven bone first ( sketch line appearance ) then back to lamellar bone (normal bone) -Earlier the onset, earlier the involution to normal bone -Europeans = onset in earlier 1 st decade -East Asians = onset in later 1 st decade -Could permanently affect tooth development, even after active phase is over -Bilateral swollen cheeks -Tooth germs in affected areas are destroyed, already developed teeth are displaced -Could affect the airway, blockage of nasal passage, or even affect the orbits -Radiolucency -Multilocular -Usually bilateral and almost symmetrical -Almost always the posterior mandible -Frequently the maxilla -Rarely affects the eyes -Variable -Corticated borders around radiolucent lesion -Possible displacement of teeth 1
2 . Charles Kim Periapical radiolucency of inflammatory origin (PRIO). -Axial view and sectional coronal view -Unilocular RL on patient s RIGHT side -Erosion of the lingual cortex and buccal cortex -Buccal cortex erosion is due to a fistula -Root resorption visible -DDx: radicular cyst, ameloblastoma, KCOT -Draining fistula makes it likely a lesion of inflammatory origin, but should never rule out ameloblastoma -Sagittal view and axial view -Lesion is not due to the nasopalatine duct, as it can be seen on the right image -Radiopacity on midline of right image is a maxillary torus -Vitality testing can help differentiate between NPDC (vital) and PRIO (non vital) -If a PRIO, would be a radicular cyst due to size and tooth being previously RCT ed -KCOT would also be on the differential (commonly in maxillary canine/lateral area) -Represents 3 histological diagnoses: granuloma, radicular cyst, and abscess -Happens to a tooth when there is caries or trauma -After RCT, most resolve within a year. If there is no resolution, likely a radicular cyst that is self sustaining regardless of infection -Varies depending on histological diagnosis, but all associated with a non vital tooth -Toothache, tenderness on biting/percussion -Unilocular -Associated with a tooth apex -Any PRIO larger than 1.5cm is considered to be a radicular cyst Nasopalatine duct cyst (NPDC) -Panoramic reconstruction and sagittal view -Well defined unilocular RL in anterior maxilla -Teeth are not seen in pano due to narrow width used on reconstruction -Enucleation of NDPC s can be difficult due to proximity to the nasal mucosa -Adjacent teeth are usually vital -Unilocular -Anterior maxilla on/near midline -Nasal mucosa superiorly, roots of maxillary anterior teeth laterally -In the image above, a communication with the oral cavity can be seen in the panoramic image and a communication can be seen with the nasal cavity in the sagittal image -Enlargement of the nasopalatine duct, duct not visible elsewhere 2
3 Keratocystic odontogenic tumor -Pan reconstruction and transaxial sections -Multilocular radiolucency extending from the canine to the site of the 3 rd molar -Transaxial sections below show a little displacement and erosion of the lingual cortex -Left canine has some root resorption on the apex -No B-L expansion -Axial view and sagittal view -Well defined RL lesion extending from anterior midline to first molar site -Displaced and eroded anterior wall of the maxillary sinus -Infiltrating the lumen of the sinus -B-L expansion is half of M-D expansion -Unerupted tooth is seen (blue arrow) -Provisional diagnosis is KCOT, as it commonly starts at the lateral/canine region -Panoramic reconstruction of a CBCT -Floor of maxillary sinus elevated -Growth is much less restricted in the maxilla due to thin bone and less cortical bone -Although this is KCOT, it may present with large B-L expansion in the softer maxillary bone -Mean presentation age is 38 years -Used to be called odontogenic keratocyst which encompassed para-keratotic and ortho-keratotic lesions -Now, para-keratotic lesions are called KCOT s as they are neoplastic -Also, ortho-keratotic lesions are called OOC s as they are a true cyst -OOC s are unique radiographically. They have huge B-L expansion and no root resorption -Mixed ortho/para keratotic lesions are treated as if they were KCOT s -Global recurrence rate of 28%. Anterior, smaller lesions are more likely to recur because they are thought to be non-neoplastic and enucleated conservatively by surgeons -Presents with swelling, pain (1/3 of pts) -2/3 are well defined and unilocular -Older lesions are more likely to be multilocular and expand M-D -3/4 occurs in the mandible, overwhelmingly in ramus and posterior sextant -1/4 occurs in the maxilla, of which 2/3 is between the canine and lateral, and 1/3 is in anterior sextant -Spreads easier in the maxilla, likely due to less cortical bone -Like ameloblastoma, 1/4 of KCOT s cause root resorption but to a lesser degree -2/3 had some fusiform B-L expansion, but nowhere near the extent of an ameloblastoma 3
4 Nevoid basal cell carcinomas -Left is axial view, middle is coronal view, right is sagittal view -Lateral wall of sinus in coronal view: missing bone due to biopsy taken prior to radiograph -Multiple radiolucencies resembling KCOTs -A multi system disorder requiring treatment from maxillofacial + head + neck specialties -NBCCs involve basal cell carcinomas, multiple KCOT s, and 4 other major criteria -Most frequent in North Europeans -Less frequent in East Asians (darker skin), but more frequently present with multiple KCOT s -Syndromic KCOT s usually presents in 2 nd ~3 rd decade, non syndromic KCOT s 3 rd ~4 th decade -Syndromic KCOT s are more likely to recur after surgery than non syndromic -Swelling, pain -Maxilla: usually unilocular, small, and round -Mandible: usually unilocular +/- scalloped margins. Could be multilocular -Minimal B-L expansion (as seen in left image) -Corticated borders around lesion -In the middle and right image, the lesion has infiltrated the right maxillary sinus -Buccal wall of sinus is missing as radiograph was taken AFTER the biopsy (don t do this!) Dentigerous cyst -Most commonly seen with unerupted 3 rd molars -Also possibly seen on maxillary anteriors, supernumerary teeth, and premolars -False myth: ameloblastomas arise from untreated dentigerous cysts -Most common in white south Africans -Unilocular -Pericoronal with attachments to the CEJ of an unerupted tooth -Lingual cortex becoming eroded, hence reducing density -In the image, we see a displacement of the lingual cortex and some erosion 4
5 Ameloblastoma -Coronal and axial reconstruction of a CBCT -Unicystic ameloblastoma -Eroded lingual cortex is visible -Extension beyond lower border of the mandible is unique to ameloblastomas -Axial reconstruction of a CBCT -Large unilocular RL with extreme B-L expansion -Septae are visible in lesion -Solid ameloblastoma -Sagittal reconstruction of a CBCT -Desmoplastic ameloblastoma -Root resorption can be seen -Usually presents before 25 years old -Ameloblastomas arising from the jaw bones are classified as: solid (multilocular), unicystic, or desmoplastic -Most ameloblastomas in Western countries are solid. Mostly treated by resection -Most ameloblastomas in Chinese are unicystic. Mostly treated by enucleation, Carnoy s, small surgery -Expansion of jaw -Unicystic may appear unilocular -Solid is usually multilocular -Unilocular usually affects the ramus and posterior sextant of the mandible -Solid usually affects the anterior sextant of the mandible -Can cause root resorption -Ball-like bucco-lingual expansion of the mandible 5
6 Odontogenic myxoma -Took a random picture off google for sake of consistency -First presents around 30 years -Cells infiltrate the bone around the lesion, so 1cm margins are recommended when resecting -1/2 present with swelling and/or pain septae -Multilocular tennis racket pattern is only seen in a minority of myxomas -Mainly in the posterior sextants of max/mand -Only well defined half the time -Suggests that this lesion does not contain a capsule -Fusiform B-L expansion in the body of the mandible -Will displace into the lumen of the sinus nearly every time it s near the sinus Brown tumor -Axial, coronal, and sagittal views -Unilocular RL affecting the anterior mandible -Erosion of B+L cortices -B-L expansion -Highest on the differential would be a solid ameloblastoma (solid because it is unilocular) -Surprise: CT scan showed calcifying arteries everywhere (calcified carotid can be seen on axial) -Pt had chronic renal failure and hyperparathyroidism -Lesion involuted after kidney transplant -Real Dx is actually a brown tumor due to hyperparathyroidism -Histologically will show giant cells, not ameloblastic cells 6
7 Lingual bone defect (Stafne s bone cyst) -Must weaken the mandible, but no pathologic fractures have been reported -Likely because it is mostly found in older adults (~50), who rarely participate in contact sports -Asymptomatic -Ovoid -Basal process of the posterior mandible -In relation to the submandibular gland or below the mandibular canal -Corticated, radiopaque -Could erode the buccal cortex Simple bone cyst (traumatic, idiopathic, hemorrhagic bone cyst) - Panoramic reconstruction of a CBCT -No displacement, resorption -Scalloped borders -Happens mostly in children, possibly related to orthodontics -Contains no epithelium, only lined with thin CT -Will yield no findings on an aspiration -Usually asymptomatic -Affected teeth remain vital -Unilocular -May reach significant M-D dimensions, but very small B-L -Scalloping around roots -Well corticated borders -Filled with nothing or blood 7
8 Glandular odontogenic cyst -Poorly defined unilocular RL -Root resorption of the 5 -Some B-L expansion -IAN displaced inferiorly (yellow arrow), basal process affected -Superior cortex eroded -It is a GOC, but may be KCOT until proven otherwise -Axial, 3D, coronal, and sagittal views -Unilocular well defined radiolucency -No B-L expansion -Some extension into the basal process -Mandibular canal slightly placed downward -Root resorption visible -Mean presentation age is 46 for westerners, decade earlier for East Asians + Africans -Can appear like an innocent dentigerous cyst to a well defined mucoepidermoid carcinoma -Wide range of radiological and histological presentations: we don t know enough about it yet, and it could even be a collection of unidentified lesions -Multilocular + root resorption should be treated as if it were neoplastic -90% have swelling, 33% with pain, 15% with numbness -Varies from unilocular (small) to multilocular (large) -80% in the mandible, nearly always in the anterior sextant -1/3 have root resorption -1/2 have tooth displacement -Minimal B-L expansion - of IAN (seen in picture above) 8
9 Pre-reading Radiopacities Fibrous dysplasia -Poorly defined radiopacity resembling a ground glass appearance on the posterior sextant of the left mandible -Cortex surrounding the IAN on right side has been eroded -Little B-L expansion -Diagnosed as fibrous dysplasia -Pan reconstruction of a CBCT (scale on the bottom, no superimposition of other structures, slightly worse resolution than a regular pan) -Ground glass radiopacity in the posterior sextant of the right maxilla -Poorly defined - of the floor of the sinus is seen -Dx: monostotic fibrous dysplasia -Note: this is same patient as above -Coronal reconstruction of a CBCT -Appears to be somewhat well defined FD in the jaw is poorly defined, but in other bones it is well defined. Possibly due to difference in embryonic bone formation -Appears to stop right at the zygoma only one bone affected -Blue arrow points to the nasopalatine duct -Dx: monostotic fibrous dysplasia -Radiopacity resembling ground glass seen on mandible, maxilla, zygoma, and sphenoid -Maxillary antrum has been completely obturated -Buccal expansion of the zygoma -Medially directed expansion of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity -Substantial B-L expansion of the mandible 9
10 -Benign, non inheritable disease affecting 1:30,000 individuals -Overall, FD is seen on average at 15 years, but 25 years in the jaw -Can be a local lesion (monostotic, 93%) or systemic lesion (polyostotic, 7%) -Polyostotic + hormonal disorder + café au lait spots = McCune Albright syndrome -Hormonal disorders: precocious puberty, ovarian follicular cysts -Believed that all FD s arise in childhood, but remain undetected until it reactivates later in life -Earlier the mutation starts, the more severe the s -If monostotic, not necessary to treat unless evident deformity or threat to vision -Can remain dormant after childhood, and reactivate during pregnancy -Monitor for reactivation or possible associated lesions (aneurysmal bone cyst, osteosarcoma) -Monostotic: affects one bone -Polyostotic: affects multiple bones throughout the body -90% presents with swelling, but only 18% reported pain -Radiopaque -Ground glass appearance (seen 38% of the time on normal radiographs, 100% on CT) -58% in maxilla, 42% in mandible, overwhelmingly in the posterior sextants -Poorly defined with a 1mm zone of transition -This zone of transition is only found in jaw-related FD s, not FD s on other bones -Root resorption is rare -Sometimes see thinning of the lower border of the mandible -Possible loss of lamina dura of affected teeth -Maxillary sinus is completely or partially obturated in nearly every case of maxillary FD -Expansion seen (enlargement in maxilla, fusiform expansion in mandible) -Teeth were displaced in 35% of cases Dense bone island -Well defined RO at apex of 47 -Could be cementoblastoma, condensing osteitis, or a dense bone island -Could also be osteomyelitis if it extended below IAN -No RL border = less likely cementoblastoma -PDL space visible throughout the root = less likely cementoblastoma -No B-L expansion = less likely cementoblastoma -Tooth is vital = cannot be condensing osteitis -More prevalent in areas of high [F] in water -Seeing 5+ DBI s suspect Gardner s syndrome -If associated with an infected, non vital tooth it is called condensing osteitis -Does not regress -No symptoms -Radiopacity -Most common in posterior mandible 10
11 Ossifying fibroma o FD can be distinguished from OF based on their margins, which are poorly defined for FD and well defined for OF -Well defined ground glass radiopacity -Can trace the thin radiolucent outline (capsule) on A -Rounded B-L expansion is seen on B and C -Buccal and lingual corticies are thinned on B and C -If it was the juvenile type of OF, it would not have a capsule -The B-L expansion and displacement of the teeth make it less likely to be osseous dysplasia -Usually seen in female (71%) adults (mean 31 yo) in teeth bearing jaws -Overall recurrence rate is 12% after careful surgery -Can re-activate or accelerate in growth at the onset of menopause -Secreting carcinoma is the underlying cause of OF s in 10~15%. An example of this is familial hyperparathyroidism (autosomal dominant disorder) -31% of OF s are incidental findings, 66% present with swelling, 16% with pain -Ground glass radiopacity -Mandible is affected 75% of the time -Even distribution of anterior or posterior segments -Has an observable capsule (shell of radiolucency around lesion) most of the time - Radiopacity within a radiolucency -16% of the time, it is completely radiopaque -20% have root resorption -84% present with B-L expansion -27% have teeth displacement -If arising in the maxilla, the sinus is affected 90% of the time MRONJ/osteomyelitis -2 dots in the center = genial tubercles -Happens on patients taking bisphosphonates -MRONJ and osteomyelitis often come hand in hand, and appear very similar -Visible necrotic bone -Fever, pain -Necrotic bone with concurrent infection (osteomyelitis) can appear RL, RO, or both -Usually appears radiopaque and laminated -Spreads from alveolar process to basal process -Expands the bone, similar to the way fibrous dysplasia does -Coronal and axial reconstructions -Unilocular radiopacity surrounded by a radiolucent line on the right mandible -Erosion of buccal and lingual walls 11
12 Osseous dysplasia o A tooth with a periapical radiolucency but tests vital may be a focal osseous dysplasia o Florid and focal osseous dysplasias are monitored and removed only if causing symptoms o Expansive osseous dysplasias need to be removed due to their aggressive nature -A: Multiple well defined radiopacities in the alveolus of the mandible -B: Axial reconstruction show no B-L expansion -C: There is a clear boundary between dysplastic tissues and normal bone. All the dysplastic tissues are situated in the alveolus -Lesion is situated above the mandibular canal -Dx: florid osseous dysplasia -A: Axial view presenting bilateral multilocular radiolucencies in posterior sextant of the mandible. There is significant M-D expansion but minimal B-L expansion. Cortices are eroded but intact. Radiopacities are seen within the radiolucencies, but it may also be a tooth root -C: Sagittal view or reconstructed transaxial image. one lesion also in the anterior sextant with a well defined radiopacity at the apex. Texture is ground glass -B: radiopacities are seen at the apices of the molars. This medium FOV cannot image the PDL, but small FOV s can. -Dx: florid osseous dysplasia -DDx: KCOT (2x), fibrous dysplasia, osseous dysplasia, ossifying fibroma -A: Axial view showing unilocular radiopaque lesion with radiolucent border affecting left mandible. There is no B- L expansion -B: Sagittal view showing lesion is at the apex of 35/36, and no RR is seen -C: Coronal view, no RR is seen. 46 has some hypercementosis, but is unrelated to the lesion -Dx: focal osseous dysplasia -RCT on 46 was likely done when FocOD was in early stages and looked like a PARL -Anterior sextant of the mandible -Multiple radiolucencies at the apices of the teeth -Depending on the view, it is evident that there are radiopacities within each radiolucency -Teeth were diagnosed as vital -Slight internal root resorption can be seen (irregular pulp outlines) -Dx: periapical osseous dysplasia 12
13 Florid osseous dysplasia Focal osseous dysplasia Expansive osseous dysplasia -Confined to the alveolar process (above mandibular canal, below junction of hart palate), but are generally not considered to be odontogenic -Females affected 97% of the time -Females affected 88% -Expansion affects alveolar -Mean age 49 years old -Mean age 41 and basal processes -50% are incidental findings, 31% swelling, 30% -64% incidental, 25% -Affects males and females drainage or fistula swelling, 28% pain, 17% evenly numbness -Presents in young ages -Can be just a radiolucency or a radiolucency with >1 central radiopacities -More than 1 sextant needs to be affected to be considered FOD -Presentation is usually bilateral -Mandible affected in 100%, maxilla affected in 67% -Osseous dysplastic tissues (radiopacities) are positioned centrally within the lesion on CT -Radiolucency (31%) -Radiopacity within radiolucency (37%) -Complete radiopacity (32%) -Confined to a single sextant -Can be a single lesion or a group of juxtaposed lesions -85% in mandible -Posterior sextants more common -53% well defined -40% sclerotic periphery -Extensive B-L expansion 13
Disclosure. Educational Objectives. Terminology. Odontogenic Cysts. Terminology
 Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例
 高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
Large Dentigerous Cyst
 Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis
 RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis MODULE 1: The Introduction. Chief complaint Demographics Age Sex Race Historical findings Physical findings Clinical Radiographic Location Maxilla/mandible
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis MODULE 1: The Introduction. Chief complaint Demographics Age Sex Race Historical findings Physical findings Clinical Radiographic Location Maxilla/mandible
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws
 Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Common/Important Radiolucencies. B. Most Common Location Apex of permanent first molar, rare in primary teeth.
 Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position
 A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki
 Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Charles Kim, Brianne Henderson, Calvin Biddle. Introduction
 Introduction What is conventional imaging? List its pros/cons o Panoramic radiographs, intra-oral radiographs, lateral cephalometrics o Advantages: superior spatial resolution, low cost, easy access (readily
Introduction What is conventional imaging? List its pros/cons o Panoramic radiographs, intra-oral radiographs, lateral cephalometrics o Advantages: superior spatial resolution, low cost, easy access (readily
Problem diagnoses. Current issues in Anatomic pathology. Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity 5/29/2009
 Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Vascular. Extravasated blood. Melanocytic. Tattoo. Epidermolysis bullosa. Lichen planus. Pemphigoid Pemphigus Lupus. Candidosis. Surface Epithelial
 Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman
 IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman This is an area where radiology plays an important role in assisting with the diagnosis, determining the size of the lesion and the relationship to adjacent
IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman This is an area where radiology plays an important role in assisting with the diagnosis, determining the size of the lesion and the relationship to adjacent
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts. SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST
 The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions
 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions Plus Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. Jonathan Swift 1667-1745 Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions A group of lesions
Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions Plus Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. Jonathan Swift 1667-1745 Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions A group of lesions
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT
 Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies
 Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Inherited & developmental disorders:
 Inherited & developmental disorders: Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Excessive fragility of bone Defect in synthesis of type I collagen Inadequate formation of bone generalized osteoporosis Slender and fracture
Inherited & developmental disorders: Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Excessive fragility of bone Defect in synthesis of type I collagen Inadequate formation of bone generalized osteoporosis Slender and fracture
Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Rarity
 aijoc AIJOC Case Report 1 Heena Sonawane, 2 Freny R Karjodkar, 3 Kaustubh Sansare, 4 Nimish Prakash ABSTRACT Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst (OOC) was first identified as the rare variant of keratocystic
aijoc AIJOC Case Report 1 Heena Sonawane, 2 Freny R Karjodkar, 3 Kaustubh Sansare, 4 Nimish Prakash ABSTRACT Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst (OOC) was first identified as the rare variant of keratocystic
TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES
 Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Pictorial Essay. CT of Calcifying Jaw Bone Diseases
 Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
Radiology. & supporting structures. Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej
 Radiology Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej & supporting structures A radiograph is only one part of the diagnostic process. Usually one does NOT make a diagnosis solely from a radiograph. A diagnosis
Radiology Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej & supporting structures A radiograph is only one part of the diagnostic process. Usually one does NOT make a diagnosis solely from a radiograph. A diagnosis
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors
 Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
Index. oralmaxsurgery.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report
 SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
The future of health is digital
 Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
IN THE NAME OF GOD. Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
Arun V Subramaniam et al. / International Journal of Biopharmaceutics. 2014; 5(3): International Journal of Biopharmaceutics
 225 e- ISSN 0976-1047 Print ISSN 2229-7499 International Journal of Biopharmaceutics Journal homepage: www.ijbonline.com IJB ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYSTS: VARIOUS RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCES Arun Subramaniam*
225 e- ISSN 0976-1047 Print ISSN 2229-7499 International Journal of Biopharmaceutics Journal homepage: www.ijbonline.com IJB ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYSTS: VARIOUS RADIOGRAPHIC APPEARANCES Arun Subramaniam*
10/23/2014. features to image interpretation what to look for and what it means. interpretation vs. diagnosis. science or art? image investigation
 features to image interpretation what to look for and what it means interpretation vs. diagnosis ERNEST LAM, DMD, MSc, PhD, FRCD(C) PROFESSOR AND THE DR. LLOYD & MRS. KAY CHAPMAN CHAIR IN CLINICAL SCIENCES
features to image interpretation what to look for and what it means interpretation vs. diagnosis ERNEST LAM, DMD, MSc, PhD, FRCD(C) PROFESSOR AND THE DR. LLOYD & MRS. KAY CHAPMAN CHAIR IN CLINICAL SCIENCES
Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws. Cyst. Effects on adjacent structures. Types. Odontogenic Cysts. Non-Odontogenic cysts
 Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws Cyst A Cyst is a benign pathologic cavity filled with fluid, lined by epithelium, and surrounded by a connective tissue wall Steven R. Singer,
Radiographic features of cysts and benign tumors of the jaws Cyst A Cyst is a benign pathologic cavity filled with fluid, lined by epithelium, and surrounded by a connective tissue wall Steven R. Singer,
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
4/2/17. Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology. Composite of in-focused and blurred images. It s a type of Tomogram.
 Fundamentals Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology It s a type of Tomogram Jimmie L. Harper D.D.S., M.S. Cincinnati Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inc. Volunteer Assistant Professor, Division
Fundamentals Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology It s a type of Tomogram Jimmie L. Harper D.D.S., M.S. Cincinnati Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inc. Volunteer Assistant Professor, Division
Clinical details: Details of scan: CONE BEAM CT REPORT: Name: H. B. Gender: Reason for referral: Referred by:
 Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases
 (2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
(2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
This lecture is sponsored by a grant from the Delta Dental of Iowa Foundation IDA Annual Conference Guest Lecture Series.
 This lecture is sponsored by a grant from the Delta Dental of Iowa Foundation IDA Annual Conference Guest Lecture Series. Radiology: Back to the Classroom! Juan F. Yepes DDS, MD, MPH, MS, DrPH Associate
This lecture is sponsored by a grant from the Delta Dental of Iowa Foundation IDA Annual Conference Guest Lecture Series. Radiology: Back to the Classroom! Juan F. Yepes DDS, MD, MPH, MS, DrPH Associate
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know?
 Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor : What radiologist needs to know? Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit K. El Karzazi, J. M. Villanueva Rincón, R. Corrales,
Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours
 Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 18/May 05, 2014 Page 4859
 CYSTIC DEGENERATION IN FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA: A CASE REPORT Neeraj Kumar 1, Niharika Rathore 2, Hemant Shakya 3, Anshuman Jamdade 4, Puneet Chitlangia 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Neeraj Kumar, Niharika
CYSTIC DEGENERATION IN FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA: A CASE REPORT Neeraj Kumar 1, Niharika Rathore 2, Hemant Shakya 3, Anshuman Jamdade 4, Puneet Chitlangia 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Neeraj Kumar, Niharika
INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report
 Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions. An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling. John L. Alonge, MS, DDS
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling John L. Alonge, MS, DDS Goals 1. Review the diagnostic process needed to formulate a differential diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling John L. Alonge, MS, DDS Goals 1. Review the diagnostic process needed to formulate a differential diagnosis
Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown
 Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report.
 RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report. Nasib Chand Khabra 1, Ish Pandhi 1 *, Kiran DN 2, Sunil Alipuria 1, Bhawna Gulati 1, and
RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report. Nasib Chand Khabra 1, Ish Pandhi 1 *, Kiran DN 2, Sunil Alipuria 1, Bhawna Gulati 1, and
INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
Case Report An Extrafollicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor Mimicking a Periapical Cyst
 Hindawi Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2018, Article ID 6987050, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6987050 Case Report An Extrafollicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor Mimicking a Periapical Cyst
Hindawi Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2018, Article ID 6987050, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6987050 Case Report An Extrafollicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor Mimicking a Periapical Cyst
Study of maxillary and mandibular cystic lesions
 Study of maxillary and mandibular cystic lesions Poster No.: C-1428 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. L. Rozas Rodríguez, M. E. Banegas Illescas, M. Y. Torres Sousa, R. M. Fernández
Study of maxillary and mandibular cystic lesions Poster No.: C-1428 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. L. Rozas Rodríguez, M. E. Banegas Illescas, M. Y. Torres Sousa, R. M. Fernández
The resident will be assigned to be on call with the Oral and Maxillofacial service. Call will be set according to PARO guidelines.
 Goals and Objectives for the Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Resident on the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (OMFS) Rotation St. Catharines General Hospital (1 four-week rotational block) During the second year
Goals and Objectives for the Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Resident on the Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (OMFS) Rotation St. Catharines General Hospital (1 four-week rotational block) During the second year
Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family
 ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
Incidental finding of dentigerous cyst - a case report
 Case Report Incidental finding of dentigerous cyst - a case report Pulivarthi Sushma 1, Sowbhagya M.B 2, Balaji P 3, Mahesh Kumar T.S 4 1 Postgraduate, 2 Reader, 3 Professor and Head of department, 4 Senior
Case Report Incidental finding of dentigerous cyst - a case report Pulivarthi Sushma 1, Sowbhagya M.B 2, Balaji P 3, Mahesh Kumar T.S 4 1 Postgraduate, 2 Reader, 3 Professor and Head of department, 4 Senior
An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report
 J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
Advanced radiographic techniques for the detection of lesions in bone
 Endodontic Topics 2004, 7, 52 72 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard ENDODONTIC TOPICS 2004 Advanced radiographic techniques for the detection of lesions in bone ELISABETTA
Endodontic Topics 2004, 7, 52 72 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard ENDODONTIC TOPICS 2004 Advanced radiographic techniques for the detection of lesions in bone ELISABETTA
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Ossifying Fibroma of Jaw: A Clinico-Radiographic Case Series Dr Satyapal Johaley 1, Dr Freny R Karjodkar
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Ossifying Fibroma of Jaw: A Clinico-Radiographic Case Series Dr Satyapal Johaley 1, Dr Freny R Karjodkar
Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst
 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
INTERPRETATION RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION. Law of Symmetry. We will be reviewing: 7/30/16
 RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Pam Wood, CDA, RDH, M.Ed, CAGS Community College of Rhode Island pwood@ccri.edu INTERPRETATION the ability to read what is revealed on a dental radiograph any dental professional
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Pam Wood, CDA, RDH, M.Ed, CAGS Community College of Rhode Island pwood@ccri.edu INTERPRETATION the ability to read what is revealed on a dental radiograph any dental professional
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses. Gingival Lesions
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1
 Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1 Min Seok Kang, M.D., Hak Jin Kim, M.D. Multifocal central giant cell granulomas (CGCG) in the maxillofacial
Multiple Synchronous Central Giant Cell Granulomas of the Maxillofacial Region: A Case Report 1 Min Seok Kang, M.D., Hak Jin Kim, M.D. Multifocal central giant cell granulomas (CGCG) in the maxillofacial
[ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018
![[ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018 [ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018](/thumbs/87/95905171.jpg) Dentigerous Cyst Associated with an Impacted Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature [PP: 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha, Department of
Dentigerous Cyst Associated with an Impacted Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature [PP: 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha, Department of
Only 40% of the Story
 X-RAY, X-RAY, READ ALL ABOUT IT! The Use and Utility of Dental Radiographs in Practice Lisa Fink, DVM, DAVDC Dentistry & Oral Surgery Service October 4, 2015 Only 40% of the Story Radiographs of teeth
X-RAY, X-RAY, READ ALL ABOUT IT! The Use and Utility of Dental Radiographs in Practice Lisa Fink, DVM, DAVDC Dentistry & Oral Surgery Service October 4, 2015 Only 40% of the Story Radiographs of teeth
Malignant Lesions Steven R. Singer, DDS
 Definitions Malignant Lesions Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Malignancies are uncontrolled growths of tissue Primary tumors represent de novo tumors in their initial site Metastatic
Definitions Malignant Lesions Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Malignancies are uncontrolled growths of tissue Primary tumors represent de novo tumors in their initial site Metastatic
Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve involvement
 Yadegari A,et al J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci e(issn): 2383-2754 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve
Yadegari A,et al J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci e(issn): 2383-2754 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve
University of Palestine. Final Exam 2 ed Semester 2014/2015 Total Grade: 60
 Question One: MCQ: 1- Dens in dent occurs most commonly in the : A- Maxillary canines B- Mandibular premolars C- Mandibular second molars D- Maxillary lateral incisors 2- A cyst occurring under the tongue
Question One: MCQ: 1- Dens in dent occurs most commonly in the : A- Maxillary canines B- Mandibular premolars C- Mandibular second molars D- Maxillary lateral incisors 2- A cyst occurring under the tongue
Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
Jaws: Cysts and Odontogenic Neoplasms
 Topic 10: Jaw Cysts General Features of Jaw Cysts Sources of Epithelium in Cysts Radiographic Features of Jaw Cysts Microscopic Features of Jaw Cysts Treatment and Prognosis of Jaw Cysts Classification
Topic 10: Jaw Cysts General Features of Jaw Cysts Sources of Epithelium in Cysts Radiographic Features of Jaw Cysts Microscopic Features of Jaw Cysts Treatment and Prognosis of Jaw Cysts Classification
Case Report An Unusual Case of Tooth in the Floor of the Orbit: The Libyan Experience
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 954789, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/954789 Case Report An Unusual Case of Tooth in the Floor of the Orbit: The Libyan Experience Y. Naresh Shetty, Irfan Adil
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 954789, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/954789 Case Report An Unusual Case of Tooth in the Floor of the Orbit: The Libyan Experience Y. Naresh Shetty, Irfan Adil
Glandular odontogenic cyst associated with ameloblastoma: Case report and review of the literature
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/jced.53775 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53775 : Case report and review of the literature Timothée Cousin 1, Samuel
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/jced.53775 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53775 : Case report and review of the literature Timothée Cousin 1, Samuel
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present a case of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) arising from a mandibular residual cyst.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Arising in a Residual Cyst: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The purpose of this report is to present a case of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) arising from a mandibular residual cyst.
The. Cone Beam. Conversation. A Townie endodontist shares 5 reasons she s sold on CBCT
 The Cone Beam Conversation A Townie endodontist shares 5 reasons she s sold on CBCT by Dr. Sonia Chopra Dr. Sonia Chopra is a practicing endodontist with 10 years of experience who currently practices
The Cone Beam Conversation A Townie endodontist shares 5 reasons she s sold on CBCT by Dr. Sonia Chopra Dr. Sonia Chopra is a practicing endodontist with 10 years of experience who currently practices
 www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH e-issn - 2348-2184 Print ISSN - 2348-2176 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajbpr SOLID AND MULTICYSTIC FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA - A CASE
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH e-issn - 2348-2184 Print ISSN - 2348-2176 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajbpr SOLID AND MULTICYSTIC FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA - A CASE
Case Report Aberrant Anatomical Variation of Maxillary Sinus Mimicking Periapical Cyst: A Report of Two Cases and Role of CBCT in Diagnosis
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 757645, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/757645 Case Report Aberrant Anatomical Variation of Maxillary Sinus Mimicking Periapical Cyst: A Report
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 757645, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/757645 Case Report Aberrant Anatomical Variation of Maxillary Sinus Mimicking Periapical Cyst: A Report
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Actinomycosis, 200 201 Adenoid cystic carcinoma, 148 150 Adenomatoid odontogenic tumors, 134, 135 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, 134 Ameloblastoma,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Actinomycosis, 200 201 Adenoid cystic carcinoma, 148 150 Adenomatoid odontogenic tumors, 134, 135 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, 134 Ameloblastoma,
Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report
 Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report 1Dr Praveen Kumar, 2 Dr Balreddy P., 3 Dr Sridhar Reddy B., 4 Dr Sanjeev Naik, 5Dr. Sujitha Reddy Patil 1Post Graduate, Department of
Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report 1Dr Praveen Kumar, 2 Dr Balreddy P., 3 Dr Sridhar Reddy B., 4 Dr Sanjeev Naik, 5Dr. Sujitha Reddy Patil 1Post Graduate, Department of
Upper arch. 1Prosthodontics. Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi. Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth
 1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
Management of Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumour With Marsupialisation, Enucleation and Carnoy s Solution Application: A Case Report
 Management of Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumour With Marsupialisation, Enucleation and Carnoy s Solution Application: A Case Report Aydin Ozkan 1, Gurkan Rasit Bayar 2, Hasan Ayberk Altug 2, Metin Sencimen
Management of Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumour With Marsupialisation, Enucleation and Carnoy s Solution Application: A Case Report Aydin Ozkan 1, Gurkan Rasit Bayar 2, Hasan Ayberk Altug 2, Metin Sencimen
Role of MDCT and VR reconstructions in the diagnosis and characterization of maxillary cystic lesions.
 Role of MDCT and VR reconstructions in the diagnosis and characterization of maxillary cystic lesions. Poster No.: C-0704 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Coronella 1, P. V. Foti
Role of MDCT and VR reconstructions in the diagnosis and characterization of maxillary cystic lesions. Poster No.: C-0704 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Coronella 1, P. V. Foti
MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT
 International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 1 A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur Citation D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 1 A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur Citation D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur.
CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 ORAL SURGERY TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION
 TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL 6010.47-M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 Issue Date: October 8, 1986 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(e)(10) I. DESCRIPTION There are certain oral surgical
TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL 6010.47-M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 Issue Date: October 8, 1986 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(e)(10) I. DESCRIPTION There are certain oral surgical
Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
 Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 3089540, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3089540 Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 3089540, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3089540 Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
Bone tumors. RMG: jan
 Bone tumors RMG: jan 217. @Kijohs KIZZA JOHN KIJOHS Diseases arising in bone Lipoma Fibrous cortical defects Non-ossifying fibroma Bone island Benign simple cysts Enchondroma Osteochondroma Osteoid osteoma
Bone tumors RMG: jan 217. @Kijohs KIZZA JOHN KIJOHS Diseases arising in bone Lipoma Fibrous cortical defects Non-ossifying fibroma Bone island Benign simple cysts Enchondroma Osteochondroma Osteoid osteoma
Case Presentation: Figure 1. Palatal lesion. Figure 2. Panoramic xray
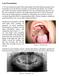 Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Annals and Essences of Dentistry
 doi: 10.5958/0976-156X.2014.00005.7 LARGE RADICULAR CYST OF THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA A CASE REPORT 1 Manoj Meena 2 Nigel R Figueiredo 3 Ajit D Dinkar 4 Ena Mathur 5 Arum Khatkar 6 Sonam Malik 1 Senior lecturer
doi: 10.5958/0976-156X.2014.00005.7 LARGE RADICULAR CYST OF THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA A CASE REPORT 1 Manoj Meena 2 Nigel R Figueiredo 3 Ajit D Dinkar 4 Ena Mathur 5 Arum Khatkar 6 Sonam Malik 1 Senior lecturer
Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 255-60 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.255 Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases Neha Khambete, Rahul Kumar*, Mukund
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 255-60 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.255 Dentigerous cyst associated with an impacted mesiodens: report of 2 cases Neha Khambete, Rahul Kumar*, Mukund
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS
 MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Central Area
 VARIA Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Central Area Carmen Elena Georgescu 1, Gabriela Tãnase 2, Augustin Mihai 3 Bucharest, Romania Summary The radiopgraphic recognition of disease requires knowledge
VARIA Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Central Area Carmen Elena Georgescu 1, Gabriela Tãnase 2, Augustin Mihai 3 Bucharest, Romania Summary The radiopgraphic recognition of disease requires knowledge
DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION
 DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry www.vetdentaltraning.com www.vetdentalrad.com Interpreting dental
DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry www.vetdentaltraning.com www.vetdentalrad.com Interpreting dental
Unicystic Ameloblastoma of mandible. Aggresive treatment A myth or a need. Case report and Extensive review of literature
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 12, Issue 2 (Nov.- Dec. 2013), PP 26-31 Unicystic Ameloblastoma of mandible. Aggresive treatment A myth
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 12, Issue 2 (Nov.- Dec. 2013), PP 26-31 Unicystic Ameloblastoma of mandible. Aggresive treatment A myth
Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case Report?
 Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
Epithelial Sources. Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa
 ODONTOGENIC CYSTS Epithelial Sources Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa Epithelial Sources Surface Epithelium Rests of Serres Reduced Enamel Epithelium Rests of
ODONTOGENIC CYSTS Epithelial Sources Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa Epithelial Sources Surface Epithelium Rests of Serres Reduced Enamel Epithelium Rests of
Squamous cell carcinoma of the maxillary sinus mimicking periodontitis
 Squamous cell carcinoma of the maxillary sinus mimicking periodontitis 저자저널명발행기관 NDSL URL Na, Ji Yeon ; Kang, Joo Hyun ; Choi, Seong-Ho ; Jeong, Ho-Gul ; Han, Sang-Sun 大韓齒科醫師協會誌 = The journal of the Korean
Squamous cell carcinoma of the maxillary sinus mimicking periodontitis 저자저널명발행기관 NDSL URL Na, Ji Yeon ; Kang, Joo Hyun ; Choi, Seong-Ho ; Jeong, Ho-Gul ; Han, Sang-Sun 大韓齒科醫師協會誌 = The journal of the Korean
Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report
 Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report Kiran Patel 1, Nishtha Patel 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3 1 Sr. Lecturer, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial
Management of a Dentigerous Cyst Associated with Inverted and Fused Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report Kiran Patel 1, Nishtha Patel 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3 1 Sr. Lecturer, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial
Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma
 Case Report Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma Zahra Dalili 1, Somayeh Nemati 2, Fatemeh Shahsavari 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Maxillofacial Radiology, Guilan University
Case Report Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma Zahra Dalili 1, Somayeh Nemati 2, Fatemeh Shahsavari 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Maxillofacial Radiology, Guilan University
Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case Report
 Phulambrikar T., et al. Dent Shiraz Univ Med Sci., December 2015; 16(4): 374-379. Case Report Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case
Phulambrikar T., et al. Dent Shiraz Univ Med Sci., December 2015; 16(4): 374-379. Case Report Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case
Glandular odontogenic cyst: A case report
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2014; 44: 75-9 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2014.44.1.75 Glandular odontogenic cyst: A case report Shahnaz S. Tambawala 1, *, Freny R. Karjodkar 1, Archana Yadav 2, Kaustubh
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2014; 44: 75-9 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2014.44.1.75 Glandular odontogenic cyst: A case report Shahnaz S. Tambawala 1, *, Freny R. Karjodkar 1, Archana Yadav 2, Kaustubh
