Morphological Variants of Ameloblastoma and Their Mimickers
|
|
|
- Dwayne Ward
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
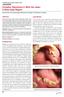
1 20 Jan 2012 Vol 5 No.1 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Review Morphological Variants of Ameloblastoma and Their Mimickers Khaled Shaikhi, BDS; 1 Mirdza Neiders, DDS, MS; 1 Frank Chen, MD, PhD; 2 Alfredo Aguirre, DDS, MS 1 * 1 Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology, Department of Oral Diagnostic Sciences, University at Buffalo, The State University of New York, Buffalo, NY 2 Department of Pathology, Buffalo General Hospital, The State University of New York, Buffalo, NY Ameloblastoma is the second most common intraosseous benign odontogenic tumor. This tumor exhibits a locally aggressive behavior. A number of morphological variants of ameloblastoma have been documented in the literature and at times, may pose a diagnostic challenge to the pathologist. The purpose of this paper is to discuss the spectrum of histopathological variants of ameloblastoma. Recognition of the subtypes of ameloblastoma is important, as it has been documented that some subtypes may exhibit a more aggressive biological behavior than the so-called conventional ameloblastoma. [N A J Med Sci. 2012;5(1):20-28.] Key Words: ameloblastoma, calcifying odontogenic cyst, squamous odontogenic tumor, ameloblastic fibroma, ameloblastic fibrosarcoma, odontogenic keratocyst INTRODUCTION Ameloblastoma is a tumor that arises from odontogenic epithelium with an estimated incidence in the population of approximately 0.5 per million.1 Ameloblastoma is a benign tumor that displays an insidious slow growth, and a locally invasive behavior with a high rate of recurrence. It is considered the most clinically significant odontogenic tumor. 2 The World Health Organization classifies ameloblastoma into four types: solid/multicystic; desmoplastic; unicystic, and extraosseous/peripheral types. 3 A review of 3677 cases of ameloblastoma in 1995 summarized the clinical features of this tumor. 4 The average age of ameloblastoma is 36. However, younger populations, particularly females, are identified in developing countries. The most common location of ameloblastoma is the posterior region of the mandible with a mandibular to maxillary ratio of 5 to 1. Many cases of ameloblastoma are asymptomatic and are found by routine radiographic examination. The most common clinical sign is swelling and expansion of the jaws. 5 Other clinical findings may include pain and delayed tooth eruption. Radiographically, amelobastoma is identified as a radiolucent lesion that presents either as a unilocular or multilocular lesion. In Reichart s study in 1995, a unilocular appearance was observed in 51% of the cases while a multilocular appearance was noted in 48.9%. 4 The unilocular pattern consists of a well-defined radiolucent lesion that may or may Received 12/14/2011; Revised 1/5/2012; Accepted 1/10/2012 Corresponding Author: Director, Advanced Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Program, Professor, Department of Oral Diagnostic Sciences, University at Buffalo, The State University of New York, 335 Squire Hall, 3435 Main Street, Buffalo, NY ( aguirr@buffalo.edu) not be associated with a tooth and cannot be radiographically differentiated from other common cystic lesions in the jaws, such as dentigerous cyst or odontogenic keratocyst. The multilocular lesions are commonly described as radiolucent lesions displaying a soap bubble or honeycomb appearance. 6 Ameloblastoma presents as a variety of histological types that may create diagnostic challenges. The purpose of this article is to present a comprehensive review of the histological types of ameloblastoma and to discuss its most common mimickers. HISTOLOGICAL FEATURES OF AMELOBLAS- TOMA Ameloblastoma consists of a proliferation of solid strands, cords and islands of odontogenic epithelium supported by connective tissue stroma. This proliferating epithelium can undergo cystic changes. Vickers and Gorlin in 1970 defined the histopathological features of ameloblastoma. 7 These features include hyperchromasia, palisading and reverse polarization of the basal nuclei of the epithelial cells with vacuolization of the cytoplasm. A variety of patterns are usually seen in ameloblastoma and they are described as follows: 1. Follicular ameloblastoma In a large case study of ameloblastomas, the follicular pattern was found in 28.2 % of the cases. The follicular ameloblastoma is characterized by the presence of follicles that resemble the developing enamel organ. These islands of cells are surrounded by connective tissue. The periphery of these islands is comprised of tall columnar cells reminiscent
2 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Jan 2012 Vol 5 No.1 21 of ameloblasts. These cells show reverse polarization of the nuclei. The central areas of the islands consist of loosely arranged cells resembling stellate reticulum. 7 It is not infrequent to observe squamous differentiation or microcystic changes in the central areas (Figures 1A and 1B). Figure 1. Follicular ameloblastoma. 1A. Follicles of ameloblastic epithelium displays squamous differentiation and microcystic formation (hematoxylin-eosin stain; original 1B. Higher magnification shows solid follicles with peripheral tall columnar basal cells displaying nuclear hyperchromatism, reverse polarization, palisading and a loose stellate-like reticulum in the center Figure 2. Plexiform amelobastoma. 2A. Anastamosing cords of ameloblastic epithelium supported by loose connective tissue stroma 2B. The cords are thin and contain small number of centrally located cells. Nuclear palisading, and reversed nuclear polarization of the peripheral cells, and basal cells are evident (hematoxylin-eosin stain; original Figure 3. Acanthomatous ameloblastoma. 3A. Ameloblastic follicles with central squamous metaplasia. 3B. A solid follicle demonstrates central squamous metaplasia with typical peripheral columnar to cuboidal basal cells with typical ameloblastic features. (hematoxylineosin x200). Figure 4. Keratoameloblastoma. 4A. This low magnification shows the presence of keratin masses in the ameloblastic tissue (hematoxylineosin 4B. Abrupt lamellar keratinization is seen within an ameloblastic follicle.
3 22 Jan 2012 Vol 5 No.1 North American Journal of Medicine and Science 2. Plexiform ameloblastoma The plexiform ameloblastoma is another common pattern seen in approximately 32.5% of cases. 4 This pattern consists of anastomosing strands and cords of ameloblastic epithelium. Similar to follicular ameloblastoma, the plexiform subtype presents peripheral basal cells that are tall and columnar with reverse polarity of the nuclei and cytoplasmic vacuolization. The central parts of the cords and strands are thin and contain loosely arranged cells. The stroma varies from dense to loose collagenous tissue (Figures 2A and 2B). 3. Acanthomatous ameloblastoma The acanthomatous ameloblastoma pattern is seen in approximately 12.1% of cases. 4 In this pattern, the stellar reticulum-like central area is replaced by squamous metaplasia with keratin pearl formation (Figures 3A and 3B). Histologically, acanthomatous ameloblastoma may be confused with keratoameloblastoma. What separates keratoameloblastoma from acanthomatous ameloblastoma is the presence of an abrupt ortho- and parakeratinization (Figures 4A and 4B) resulting in the accumnulation of keratin masses filling the center of the ameloblastic epithelial islands. 8 Figure 5. Granular cell ameloblastoma. 5A. Follicles of ameloblastic epithelium with central areas containing granular cells. (hematoxylin-eosin stain; original magnifycation 5B. In this field, numerous granular cells are seeing in the center of the follicles. In addition, the granular cells replace some of the basal peripheral cells. (hematoxylin-eosin x200). Figure 6. Desmoplastic ameloblastoma. 6A. Thin strands of epithelial cells compressed by desmoplastic connective tissue stroma. (hematoxylineosin 6B. Due to stromal compression, the nuclear palisading becomes less obvious. (hematoxylin-eosin stain; original 4. Granular cell ameloblastoma Approximately 4.28% of ameloblastomas show a granular cell pattern. 4 These granular cells display central vesicular nuclei with abundant cytoplasm containing eosinophilic granules that represent lysosomes under ultrastructural and histochemical examination. These granular cells may replace the central stellate reticulum-like areas and/or the basal peripheral cells (Figures 5A and 5B). 9,10 5. Desmoplastic ameloblastoma The desmoplastic ameloblastoma represents 4-13% of all ameloblastomas. 11 Two distinctive characteristics allow the segregation of this subtype of ameloblastoma. One of these features is of the presence of desmoplastic fibrous connective tissue that contains thin strands and nests of odontogenic epithelium. 12 The second feature is the almost complete absence of discernable basal cells with the typical nuclear palisading, reverse polarization and vacuolization of the cytoplasm. Occasionally, few strands will display the cellular features of ameloblastoma, suggesting an odontogenic derivation (Figures 6A and 6B), facilitating its identification as such. Otherwise, the identification of these strands as ameloblastic epithelium becomes a difficult task. 6. Basal cell ameloblastoma Basal cell ameloblastoma is the least common pattern comprising only 2.02% of all cases of ameloblastomas. 4 Basal cell ameloblastoma consists of nests of basaloid cells. The peripheral cells of the nests are cuboidal and may show reverse nuclear polarity. Usually, a net-like pattern of interconnecting nests is observed (Figures 7A and 7B). The central area of the nests does not display a stellate reticulum.
4 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Jan 2012 Vol 5 No.1 23 Figure 7. Basal cell ameloblastoma. 7A. Nests of interconnecting ameloblastic epithelium form a netlike pattern. (hematoxylin-eosin 7B. The peripheral cells of the interconnecting strands are cuboidal to columnar and show reverse nuclear polarization. (hematoxylineosin x200). 7. Unicystic ameloblastoma Unicystic ameloblastoma is a type of ameloblastoma seen in approximately 6% of all cases of ameloblastomas. 4 In contrast to the conventional ameloblastoma where the average age of presentation is the fourth decade of life, unicystic ameloblastoma is typically seen in young patients, around the second decade of life. Radiographically, the unilocular pattern is seen more often than the multilocular pattern, particularly when associated with an unerupted tooth. 13 Three subtypes of unicystic ameloblastoma are recognized. The first one is known as luminal unicystic ameloblastoma that consists of a cystic lesion lined by simple odontogenic epithelium demonstrating nuclear palisading and reverse polarization with cytoplasmic vacuolization of the basal cells. An overlying stellate reticulum-like area is present (Figure 8). The second subtype is called intraluminal unicystic ameloblastoma. This lesion consists of a cystic lesion showing an intraluminal plexiform proliferation of epithelium. In this pattern, the typical cytological features of ameloblastoma are not commonly observed, probably due to associated inflammatory changes. In areas where the inflammation is minimal, it is possible to note the typical ameloblastic changes. The third subtype is the mural unicystic ameloblastoma where the fibrous connective tissue cystic wall presents typical islands of plexiform or follicular ameloblastoma. 8. Peripheral ameloblastoma This extraosseous subtype represents approximately 2-10% of all cases of ameloblastomas. 14 Clinically, peripheral Figure 8. Unicystic ameloblastoma. Low magnification. The cyst is lined by odontogenic epithelium showing nuclear palisading, nuclear reverse polarization and cytoplasmic vacuolization of basal cells. The overlying epithelial cells resemble stellate reticulum. (hematoxylin-eosin stain; original magnification x100) ameloblastoma presents as a sessile or pedunculated gingival or alveolar mucosal lesion. In the majority of cases, there is no radiographically visible bone involvement. However, superficial alveolar bone erosion may be observed. Histologically, peripheral ameloblastoma shows islands of typical ameloblastic epithelium displaying follicular and/or plexiform patterns (Figures 9A and 9B). 15 Only 50% of peripheral ameloblastomas show a connection between the overlying mucosal epithelium and the ameloblastic proliferation. 6 Figure 9. Peripheral ameloblastoma. 9A. Low magnification shows islands of ameloblastic tissue connecting with the surface Epithetlium. The cellular phenotype resembles basal cell ameloblastoma 9B. Typical ameloblastic features (i.e., reverse nuclear polarization, nuclear palisading and cytoplasmic vacuolization of basal cells are evident. (hematoxylin-eosin stain; original
5 24 Jan 2012 Vol 5 No.1 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Figure 10. Ameloblastic carcinoma. 10A. Low magnification illustrates a tumor with central stellate reticulum and peripheral basal cells with malignant features. (hematoxylineosin 10B. Increased mitotic activity, cellular pleomorphism and disarray of the basal cells are observed. Figure 11. Odontogenic keratocyst. 11A. Corrugated surface of the cystic stratified squamous epithetlium shows parakeratosis. 11B. The cyst wall which is composed of squamous epithelium and fibrous connective tissue show palisading of the basal cells and parakeratinization epithelium without inflammation. (hematoxylineosin x200). Figure 12. Calcifying odontogenic cyst. 12A. Superficial formation of ghost cells is noted. (hematoxylin-eosin 12B. Calcification of ghost cells and palisading of basal cells is observed in this microscopic field. LESIONS MIMICKING AMELOBLASTOMA There are a number of lesions that can be confused with ameloblastoma. Their proper identification is important because there are significant differences in the clinical biological behavior of these entities. 1. Ameloblastic carcinoma Ameloblastic carcinoma is a rare malignant odontogenic tumor that shows clear cytological features of malignancy. 16 It occurs at a later age than ameloblastoma and it is locally much more aggressive. 17 It is more common in the mandible and shows a high propensity to recur. Histologic examination reveals malignant features that include cellular pleomorphism, nuclear hyperchromatism and high mitotic activity (Figures 10A and 10B). Some histologic features reminiscent of conventional ameloblastoma, such as a hint of nuclear palisading and reverse polarization, are also present (Figure 10B). About 22% of ameloblastic carcinomas produce metastases that show the same histopathological features as those of the malignant primary tumor. 17 Metastatic ameloblastomas with histological features of conventional ameloblastoma (i.e., bland cytological features with nuclear palisading, reverse polarization if the nuclei and vacuolization of the cytoplasm) have also been described. In these cases, the term malignant ameloblastoma is used Odontogenic keratocyst Odontogenic keratocyst (OKC) is a controversial lesion that some pathologists classify as a cyst while others believe that it represents a benign tumor. 19,20 This lesion has a high recurrence rate and aggressive behavior. 21 Although OKC may occur at any age, but most cases are seen in the third decade of life. 21 It is seen most frequently in the mandible with clinical symptoms present in 50%-80% of the cases. 21,22 Multiple odontogenic keratocyst are associated with nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. 21 The radiographs findings are not pathognomonic and may simulate other conditions, such as ameloblastoma, dentigerous cyst or other dental cysts.
6 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Jan 2012 Vol 5 No.1 25 The microscopic findings of OKC consist of a cystic wall lined by parakeratinized-stratified squamous epithelium with palisading of basal cell nuclei (Figures 11A and 11B). A frequent finding is the detachment of the cystic lining from the connective tissue wall as well as the absence of rete pegs. In contrast to other dental cysts, there is an absence of inflammation in the connective tissue of cyst wall. In cases where inflammation is present in the cyst wall, the classic phenotype of odontogenic keratocyst is lost and conventional stratified squamous epithelium is found. The high rate of recurrence (up to 60%) is thought to be due to the presence of satellite cysts due to budding of the basal cell layer of the cystic epithelium. 21 Odontogenic keratocyst is usually confused with unicystic ameloblastoma on clinical, radiographic and histologic appearance. Treatment consists in enucleation of the lesion with vigorous curettage and close follow-up. In large cystic lesions, marsupialization of an odontogenic keratocyst can be performed, reducing the morbidity associated with this lesion. Repeated, periodic surgical interventions are not rare for this lesion Calcifying odontogenic cyst Calcifying odontogenic cyst (COC) was first described by Gorlin et al in The mean age of this lesion is An extraosseous location for this typically intraosseous cyst has been documented in gingival tissues. 26 Radiographically, this lesion appears radiolucent. However, radiopaque structures may also be present. Microscopically, COC consists of cystic odontogenic epithelium displaying palisading of basal cell nuclei with adjacent spinous keratinocytes resembling stellate reticulum. In addition, ghost cells, some of them showing different levels of calcification are seen in the cystic epithelium (Figures 12A and 12B). COC may be confused with unicystic ameloblastoma because of the nuclear palisading and the presence of tissue resembling stellate reticulum. COC has a good prognosis. Local curettage for intraosseous COC and conservative excision for peripheral COC are curative and only few recurrences have been reported Squamous odontogenic tumor Squamous odontogenic tumor (SOT) is a rare benign odontogenic neoplasm. It was first described as a separate entity in This lesion is seen with similar incidence in the mandible and the maxilla at a mean age of 38. At the microscopic level, SOT closely resembles acanthomatous ameloblastoma with islands of benign appearing squamous epithelium. The main feature that allows the distinction between SOT and ameloblastoma is the fact that in SOT, reverse polarization and palisading of the nuclei of keratinocytes is absent. Some islands may show the development of microcysts and/or intraepithelial dystrophic calcifications (Figures 13A and 13B). SOT has a good prognosis as its biological behavior is not linked to recurrences and conservative surgical intervention is curative Ameloblastic fibroma Ameloblastic fibroma is a rare odontogenic tumor that is usually diagnosed in the first decade of life. 30 The posterior mandible is the most common site where it presents as an asymptomatic slowly growing tumor. 31 Radiographically, this lesion shows either a unilocular or multilocular radiolucencies associated with an unerupted tooth. 32 Figure 13. Squamous odontogenic tumor. 13A. Islands of bland-appearing epithelial cells arranged in ovoid to elongated strands. (hematoxylineosin 13B. Absence of reverse polarization of basal cells and conspicuous intraepithelial calcifycations are typically noted. (hematoxylin-eosin x200). Figure 14. Ameloblastic fibroma. 14A. Cords, strands and buds of odontogenic epithelium amidst an hypercellular connective tissue stroma. (hematoxylin-eosin stain; original magnification x10). 14B. Zones of hyalinization around the epithelial buds are observed.
7 26 Jan 2012 Vol 5 No.1 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Histologically, the tumor is composed of islands, cords, and strands of odontogenic epithelium amidst a hypercellular connective tissue stroma that resembles primitive dental papillae (Figures 14A and 14B). At times, areas of hyalinization may be found at epithelial-mesenchymal interfaces. 31 This lesion may be confused with follicular ameloblastoma. However, follicular ameloblastoma lacks the stromal hypercellularity of spindle cells that are characteristic of ameloblastic fibroma. Conservative surgical excision and regular follow-ups are indicated for primary lesions. Wider and more aggressive surgical excision is indicated for recurrences because one third of ameloblastic fibrosarcoma cases arise from recurrent ameloblastic fibromas. 6,33 6. Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma is often diagnosed during the first and second decades of life. Ameloblastic fibroodontoma is usually asymptomatic and may prevent a tooth from erupting or may displace adjacent teeth. Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma represents an ameloblastic fibroma with varying amounts of soft and calcified dental tissues. 34 If there is sufficient calcification of the enamel and dental matrix, the lesion shows radiopaque areas on radiographic films. The hard tissues may be minimal or extensive (Figures 15A and 15B). Confusion with ameloblastic fibroma may occur if the amount of dental tissues is minimal. 7. Ameloblastic fibrosarcoma Ameloblastic fibrosarcoma is a very rare odontogenic malignancy (Figures 16A and 16B), in which the connective tissue shows microscopic features reminiscent of fibrosarcoma. 35,36 Some of these cases arise de novo, but about half of them may arise from a preexisting ameloblastic fibroma. 35 Ameloblastic fibrosarcoma is a locally aggressive tumor and radical resection is indicated. Metastases are not unusual. This tumor can be confused with ameloblastic fibroma and/or ameloblastoma. However, the distinction is easily done by paying attention to the cytological characteristics of the malignant mesenchymal spindle cells of ameloblastic fibrosarcoma that show frequent mitotic figures. Some of them also show aberrant, variation in nuclear chromatism and anisonucleosis. 8. Craniopharyngioma Craniopharyngioma is a rare epithelial tumor that is identical to ameloblastoma with basal cells showing nuclear palisading, areas of stellate reticulum, keratinization and calcifications. Clinical information is crucial to render the proper diagnosis since craniopharyngioma is located in sellar and suprasellar regions of the sphenoid bone, sites that preclude a diagnosis of ameloblastoma Adamantinoma Another lesion that may mimic ameloblastoma histologically is the adamantinoma of long bones. While these two lesions have similar histological appearance, there is no evidence that supports the notion of a common histogenesis. 38 Adamantinoma is considered a low-grade malignant tumor of long bones (tibia or fibula) and the information on the location allows an easy separation of this tumor from ameloblastoma. Figure 15. Ameloblastic fibroodontoma. 15A. Dental structures with a haphazards configuration are present (hematoxylin-eosin stain; original 15B. Enamel matrix (honeycomb appearance) is seen surrounding dentin, predentin and pulp tissues in the odontoma portion of an ameloblastic fibro-odontoma. Figure 16. Ameloblastic fibrosarcoma. 16A. Low power view of this tumor suggests a diagnosis of ameloblastic fibroma. (hematoxylin-eosin stain; original magnification x10). 16B. High power view reveals the presence of nuclear pleomorphism and abundant mitotic figures of the malignant stromal cells.
8 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Jan 2012 Vol 5 No.1 27 Table 1. Subtypes of Ameloblastoma and Its Mimickers. Variant Morphological Features Mimickers Follicular ameloblastoma Plexiform ameloblastoma Acanthomatous ameloblastoma Granular cell ameloblastoma Desmoplastic ameloblastoma Basal cell ameloblastoma Unicystic ameloblastoma Peripheral ameloblastoma Multiple islands of odontogenic epithelium exhibiting peripheral nuclear palisading with reverse polarization. Central areas resemble stellate reticulum Anastomosing cords of odontogenic epithelium exhibiting peripheral nuclear palisading with reverse polarization. Areas resembling stellate reticulum mostly absent Islands of odontogenic epithelium exhibiting peripheral nuclear palisading with reverse polarization and conspicuous central squamous differentiation Island of odontogenic epithelium demonstrating basal and /or central cells with prominent granular cytoplasm Thin cords of ameloblastic epithelium within a dense fibrous connective tissue stroma. Nuclear palisading of basal cells is tenuous to absent Islands of hyperchromatic basaloid cells with peripheral nuclear palisading The cyst is lined by ameloblastic basal cells. The overlying epithelial cells are loosely cohesive and resemble stellate reticulum Interconnecting cords and islands of ameloblastic epithelium. Only 50% of cases show origin from overlying mucosal epithelium Ameloblastic fibroma Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma Ameloblastic fibrosarcoma Ameloblastic carcinoma Craniopharyngioma Adamantinoma Craniopharyngioma Squamous odontogenic tumor (SOT) Adamantinoma Adamantinoma Odontogenic keratocyst (OKC) Calcifying odontogenic cyst (COC) Ameloblastoma SUMMARY Ameloblastoma is a benign neoplasm that arises from odontogenic epithelium residing in the mandible and to a lesser extent, in the maxilla. This neoplasm shows a wide variety of histological patterns. The main distinctive features of these variants are summarized in Table 1. Follicular and plexiform ameloblastomas are the most common variants. A number of benign and malignant neoplasms as well as cystic lesions may mimic the histological appearance of ameloblastoma. It is important to establish the precise diagnosis of these lesions since the biological behavior and treatment varies according to the diagnosis. CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors have no conflict of interest to declare. REFERENCES 1. Gomes CC, Duarte AP, Diniz MG, Gomez RS. Review article: Current concepts of ameloblastoma pathogenesis. J Oral Pathol Med. 2010;39(8): Gardner DG, Pecak AM. The treatment of ameloblastoma based on pathologic and anatomic principles. Cancer. 1980;46(11): Gardner DG HK, Shear M et al. In: Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P, Sidransky D, editors. World Health Organization classification of tumor: pathology and genetics, head and neck tumors. Lyon: IARC Press. 2005; Reichart PA, Philipsen HP, Sonner S. Ameloblastoma: biological profile of 3677 cases. Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol. 1995;31B(2): Junquera L, Ascani G, Vicente JC, Garcia-Consuegra L, Roig P. Ameloblastoma revisited. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2003;112(12): Neville BW DD, Allen CM, Bouquot JE. Odontogenic cysts and tumors. In: Oral and maxillofacial pathology, 3rd edition. Missouri: Saunders Elsevier;
9 28 Jan 2012 Vol 5 No.1 North American Journal of Medicine and Science 7. Vickers RA, Gorlin RJ. Ameloblastoma: Delineation of early histopathologic features of neoplasia. Cancer. 1970;26(3): Pindborg JJ, eds. Pathology of the dental hard tissues. 1st ed. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders; Hartman KS. Granular-cell ameloblastoma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1974;38(2): Takeda Y. Intracytoplasmic crystalloids in granular cell ameloblastoma. J Oral Pathol. 1986;15(6): Philipsen HP, Reichart PA, Takata T. Desmoplastic ameloblastoma (including "hybrid" lesion of ameloblastoma). Biological profile based on 100 cases from the literature and own files. Oral Oncol. 2001;37(5): Sun ZJ, Wu YR, Cheng N, Zwahlen RA, Zhao YF. Desmoplastic ameloblastoma - A review. Oral Oncol. 2009;45(9): Philipsen HP, Reichart PA. Unicystic ameloblastoma. A review of 193 cases from the literature. Oral Oncol. 1998;34(5): Philipsen HP, Reichart PA, Nikai H, Takata T, Kudo Y. Peripheral ameloblastoma: biological profile based on 160 cases from the literature. Oral Oncol. 2001;37(1): Vanoven BJ, Parker NP, Petruzzelli GJ. Peripheral ameloblastoma of the maxilla: a case report and literature review. Am J Otolaryngol. 2008;29(5): Akrish S, Buchner A, Shoshani Y, Vered M, Dayan D. Ameloblastic carcinoma: report of a new case, literature review, and comparison to ameloblastoma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;65(4): Yoon HJ, Hong SP, Lee JI, Lee SS, Hong SD. Ameloblastic carcinoma: an analysis of 6 cases with review of the literature. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009;108(6): Cardoso A, Lazow SK, Solomon MP, Berger JR, Rock A. Metastatic ameloblastoma to the cervical lymph nodes: a case report and review of literature. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;67(6): Shear M. The aggressive nature of the odontogenic keratocyst: is it a benign cystic neoplasm? Part 1. Clinical and early experimental evidence of aggressive behaviour. Oral Oncol. 2002;38(3): Philipsen HP. Keratocystic odontogenic tumor. In: Barnes L EJ, Reichart P, Sidransky D, eds. World Health Organization classification of tumor: pathology and genetics, head and neck tumors. Lyon: IARC Press. 2005; Myoung H, Hong SP, Hong SD, et al. Odontogenic keratocyst: Review of 256 cases for recurrence and clinicopathologic parameters. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2001;91(3): Brannon RB. The odontogenic keratocyst. A clinicopathologic study of 312 cases. Part I. Clinical features. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1976;42(1): Zhao Y, Liu B, Han QB, Wang SP, Wang YN. Changes in bone density and cyst volume after marsupialization of mandibular odontogenic keratocysts (keratocystic odontogenic tumors). J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;69(5): Gorlin RJ, Pindborg JJ, Odont, Clausen FP, Vickers RA. The calcifying odontogenic cyst--a possible analogue of the cutaneous calcifying epithelioma of Malherbe. An analysis of fifteen cases. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1962;15: Hong SP, Ellis GL, Hartman KS. Calcifying odontogenic cyst. A review of ninety-two cases with reevaluation of their nature as cysts or neoplasms, the nature of ghost cells, and subclassification. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1991;72(1): Praetorius F, Hjorting-Hansen E, Gorlin RJ, Vickers RA. Calcifying odontogenic cyst. Range, variations and neoplastic potential. Acta Odontol Scand. 1981;39(4): Lin GC, Qiu WL, Wang Y. [The management of the treatment and diagnosis for the calcifying odontogenic cyst]. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 1996;5(3): Pullon PA, Shafer WG, Elzay RP, Kerr DA, Corio RL. Squamous odontogenic tumor. Report of six cases of a previously undescribed lesion. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1975;40(5): Haghighat K, Kalmar JR, Mariotti AJ. Squamous odontogenic tumor: diagnosis and management. J Periodontol. 2002;73(6): Kramer IRH PJ, Shear M. Histological typing of odontogenic tumors. 2nd ed. World Health Organization international histological classification of tumors. Berlin: Springer Verlag. 1992; Chen Y, Li TJ, Gao Y, Yu SF. Ameloblastic fibroma and related lesions: a clinicopathologic study with reference to their nature and interrelationship. J Oral Pathol Med. 2005;34(10): Dallera P, Bertoni F, Marchetti C, Bacchini P, Campobassi A. Ameloblastic fibroma: a follow-up of six cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1996;25(3): Kobayashi K, Murakami R, Fujii T, Hirano A. Malignant transformation of ameloblastic fibroma to ameloblastic fibrosarcoma: case report and review of the literature. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2005;33(5): De Riu G, Meloni SM, Contini M, Tullio A. Ameloblastic fibroodontoma. Case report and review of the literature. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2010;38(2): Muller S, Parker DC, Kapadia SB, Budnick SD, Barnes EL. Ameloblastic fibrosarcoma of the jaws. A clinicopathologic and DNA analysis of five cases and review of the literature with discussion of its relationship to ameloblastic fibroma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1995;79(4): Bregni RC, Taylor AM, Garcia AM. Ameloblastic fibrosarcoma of the mandible: report of two cases and review of the literature. J Oral Pathol Med. 2001;30(5): Fernandez-Miranda JC, Gardner PA, Snyderman CH, et al. Craniopharyngioma: A pathologic, clinical, and surgical review. Head Neck. 2011;16(10): Papagelopoulos PJ, Mavrogenis AF, Galanis EC, Savvidou OD, Inwards CY, Sim FH. Clinicopathological features, diagnosis, and treatment of adamantinoma of the long bones. Orthopedics. 2007;30(3):
Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst
 319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
319 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 319-323, 2007 Case Report Ameloblastomatous Gorlin s cyst Mala Kamboj 1) and Manish Juneja 2) 1) Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, U.P. King George
SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE
 African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
Problem diagnoses. Current issues in Anatomic pathology. Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity 5/29/2009
 Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours
 Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts
 77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
 Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 3089540, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3089540 Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
Case Reports in Pathology Volume 2016, Article ID 3089540, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3089540 Case Report Unicystic Ameloblastoma with Mural Proliferation Managed by Conservative Treatment
Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst with Complex Odontoma: Histological and Immunohistochemical Features
 Case Report Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst with Complex Odontoma: Histological and Immunohistochemical Features Nooshin Mohtasham 1, Amin Rahpeyma 2, Saeedeh Khajeh Ahmadi 3, Mohsen Merati 4 1 Oral and Maxillofacial
Case Report Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst with Complex Odontoma: Histological and Immunohistochemical Features Nooshin Mohtasham 1, Amin Rahpeyma 2, Saeedeh Khajeh Ahmadi 3, Mohsen Merati 4 1 Oral and Maxillofacial
IN THE NAME OF GOD. Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND TUMORS Chapter 15 I. DENTIGEROUS CYST II. III. IV. ERUPTION CYST ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST Orthokeratinized
Case Report The Onset of a Peripheral Ameloblastoma
 Volume 2012, Article ID 729467, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/729467 Case Report The Onset of a Peripheral Ameloblastoma Kellen Cristine Tjioe, 1 José Humberto Damante, 1 anddenisetostesoliveira 2, 3 1 Department
Volume 2012, Article ID 729467, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/729467 Case Report The Onset of a Peripheral Ameloblastoma Kellen Cristine Tjioe, 1 José Humberto Damante, 1 anddenisetostesoliveira 2, 3 1 Department
Histologic Variants of Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst: A Study of 52 Cases
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2108 Histologic Variants of Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst: A Study of 52 Cases 1 Soussan Irani, 2 Forough Foroughi ABSTRACT Aim: This study aimed at evaluating
ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2108 Histologic Variants of Calcifying Odontogenic Cyst: A Study of 52 Cases 1 Soussan Irani, 2 Forough Foroughi ABSTRACT Aim: This study aimed at evaluating
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors
 Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare case report
 Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 187820, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187820 Case Report Basal Cell Ameloblastoma of Mandible: A Rare Case Report with Review Hemant Shakya, 1
Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: Case Report
 Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: Case Report Corresponding Author: Prof. Sergio E Cury, DDS PhD, Oral Pathology - UniFOA - University of Volta Redonda, 27.310-060 - Brazil
Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: Case Report Corresponding Author: Prof. Sergio E Cury, DDS PhD, Oral Pathology - UniFOA - University of Volta Redonda, 27.310-060 - Brazil
Educational Cases EQA November T.J. Palmer Raigmore Hospital Inverness
 Educational Cases EQA November 2013 T.J. Palmer Raigmore Hospital Inverness Case 2 Clinical Details Dob 11 February 1951 PMH: 1964 Extraction of 45 aet 13 yr 1966 Cyst between 44 and 46 enucleated 1973
Educational Cases EQA November 2013 T.J. Palmer Raigmore Hospital Inverness Case 2 Clinical Details Dob 11 February 1951 PMH: 1964 Extraction of 45 aet 13 yr 1966 Cyst between 44 and 46 enucleated 1973
Histopathologic Diversity of Gorlin s Cyst: A Study of Four Cases and Review of Literature
 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1065 Kishore Sonawane et al CASE REPORT Histopathologic Diversity of Gorlin s Cyst: A Study of Four Cases and Review of Literature Kishore Sonawane, Medhini Singaraju, Indra Gupta,
10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1065 Kishore Sonawane et al CASE REPORT Histopathologic Diversity of Gorlin s Cyst: A Study of Four Cases and Review of Literature Kishore Sonawane, Medhini Singaraju, Indra Gupta,
Case Report Ameloblastic Fibroodontoma of the Mandible with Normal Karyotype in a Pediatric Patient
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 969687, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/969687 Case Report Ameloblastic Fibroodontoma of the Mandible with Normal Karyotype in a Pediatric Patient Esther Manor,
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 969687, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/969687 Case Report Ameloblastic Fibroodontoma of the Mandible with Normal Karyotype in a Pediatric Patient Esther Manor,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Case Report- A Milder Variant of OKC or an Independent Entity Mariyam
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Case Report- A Milder Variant of OKC or an Independent Entity Mariyam
A COMPARATIVE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF EPITHELIAL linings OF ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND UNICYSTIC AMElOBlASTOMAS
 A COMPARATIVE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF EPITHELIAL linings OF ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND UNICYSTIC AMElOBlASTOMAS J Sudiono, RB Zain. A Comparative Histopathological Study of Epithelial Linings of Odontogenic
A COMPARATIVE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF EPITHELIAL linings OF ODONTOGENIC CYSTS AND UNICYSTIC AMElOBlASTOMAS J Sudiono, RB Zain. A Comparative Histopathological Study of Epithelial Linings of Odontogenic
AMELOBLASTIC CARCINOMA OF
 AMELOBLASTIC CARCINOMA OF MANDIBLE- A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature Mubeen K (1), Shakya HK (2), Jigna VR (3) (1) MDS, Professor and Head of Department, Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology,
AMELOBLASTIC CARCINOMA OF MANDIBLE- A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature Mubeen K (1), Shakya HK (2), Jigna VR (3) (1) MDS, Professor and Head of Department, Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology,
Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. V. (Mar. 2014), PP 26-30 Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report Dr. Sahana Srinath
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. V. (Mar. 2014), PP 26-30 Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report Dr. Sahana Srinath
Disclosure. Educational Objectives. Terminology. Odontogenic Cysts. Terminology
 Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST (OKC) AND THE ROLE OF AgNORs IN CELL PROLIFERATION
 A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST (OKC) AND THE ROLE OF AgNORs IN CELL PROLIFERATION * Vindhya Savithri **Sudha S ***Shameena P.M ****Ipe Varghese Abstract : The histologic pattern of
A CLINICOPATHOLOGIC STUDY OF ODONTOGENIC KERATOCYST (OKC) AND THE ROLE OF AgNORs IN CELL PROLIFERATION * Vindhya Savithri **Sudha S ***Shameena P.M ****Ipe Varghese Abstract : The histologic pattern of
Ameoblastic carcinoma of mandible - A rare case report with review of literature
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case report doi:10.4317/jced.2.e100 Ameoblastic carcinoma of mandible - A rare case report with review of literature K Mubeen 1, Hemant Kumar
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case report doi:10.4317/jced.2.e100 Ameoblastic carcinoma of mandible - A rare case report with review of literature K Mubeen 1, Hemant Kumar
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies
 Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Fine Needle Aspiration Findings in Malignant Ameloblastoma:
 BRIEF REPORTS Fine Needle Aspiration Findings in Malignant Ameloblastoma: A Case Report and Differential Diagnosis Michelle Reid-Nicholson, M.B.B.S., 1 * Daniel Teague, M.D., 1 Barry White, M.D., 1 Preetha
BRIEF REPORTS Fine Needle Aspiration Findings in Malignant Ameloblastoma: A Case Report and Differential Diagnosis Michelle Reid-Nicholson, M.B.B.S., 1 * Daniel Teague, M.D., 1 Barry White, M.D., 1 Preetha
Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
http://dx.doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2013.40.4.321 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 Successful Conservative Surgical Treatment of Ameloblastic Fibroma in the Posterior Maxilla : A Case Report Youngeun Lee 1, Hyojung
Case Report Intraosseous Follicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour A Case Report
 International Dentistry Volume 2009, Article ID 597483, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/597483 Case eport Intraosseous Follicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour A Case eport Farhan Durrani 1 and oyana Singh 2
International Dentistry Volume 2009, Article ID 597483, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/597483 Case eport Intraosseous Follicular Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour A Case eport Farhan Durrani 1 and oyana Singh 2
Ameloblastic Carcinoma of the Mandible: a Rare Case Report
 IBIMA Publishing Journal of Research and Practice in Dentistry http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/dent/dent.html Vol. 2015 (2015), Article ID 672596, 6 pages DOI: 10.5171/2015.672596 Case Report Ameloblastic
IBIMA Publishing Journal of Research and Practice in Dentistry http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/dent/dent.html Vol. 2015 (2015), Article ID 672596, 6 pages DOI: 10.5171/2015.672596 Case Report Ameloblastic
Annals and Essences of Dentistry
 aedj.2014.6.3.2.4 Central Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Of Mandible A Case Report 1 Rajasekhar Gali 2 Madan Mohan Reddy 3 Vandana Raghunath 4 Sajan Anand 1 Associate Professor 2 Reader 3 Professor
aedj.2014.6.3.2.4 Central Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Of Mandible A Case Report 1 Rajasekhar Gali 2 Madan Mohan Reddy 3 Vandana Raghunath 4 Sajan Anand 1 Associate Professor 2 Reader 3 Professor
JOURNAL TAOMFR Mandiblular Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma
 Ameloblastic Fibro-Odontoma of the Mandible with Emphasis on Evaluation Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Jing-Yi Chen 1, Frank Lei 2, Yu-Fong Chen 3,4 * Divisions of 1 Oral Pathology, 2 Periodotology,
Ameloblastic Fibro-Odontoma of the Mandible with Emphasis on Evaluation Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Jing-Yi Chen 1, Frank Lei 2, Yu-Fong Chen 3,4 * Divisions of 1 Oral Pathology, 2 Periodotology,
Ameloblastic Carcinoma: Case Report and Literature Review
 C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E Ameloblastic Carcinoma: Case Report and Literature Review Sylvie Louise Avon, DMD, MSc John McComb, DDS, MSc, FRCD(C) Cameron Clokie, DDS, PhD, FRCD(C) A b s t r a c t Ameloblastic
C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E Ameloblastic Carcinoma: Case Report and Literature Review Sylvie Louise Avon, DMD, MSc John McComb, DDS, MSc, FRCD(C) Cameron Clokie, DDS, PhD, FRCD(C) A b s t r a c t Ameloblastic
Odontogenic Keratocyst Masquerading as a Dentigerous Cyst in the Maxilla: A Case Report of an Unusual Presentation
 European Journal of Therapeutics DOI: 10.5152/EurJTher.2018.496 Case Report Odontogenic Keratocyst Masquerading as a Dentigerous Cyst in the Maxilla: A Case Report of an Unusual Presentation Arvind Karikal
European Journal of Therapeutics DOI: 10.5152/EurJTher.2018.496 Case Report Odontogenic Keratocyst Masquerading as a Dentigerous Cyst in the Maxilla: A Case Report of an Unusual Presentation Arvind Karikal
Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor associated with odontoma: a case report and critical review of the literature
 Gomez et al. Head & Face Medicine 2013, 9:20 HEAD & FACE MEDICINE CASE REPORT Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor associated with odontoma: a case report and critical review of the literature Open Access Ricardo
Gomez et al. Head & Face Medicine 2013, 9:20 HEAD & FACE MEDICINE CASE REPORT Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor associated with odontoma: a case report and critical review of the literature Open Access Ricardo
Management of ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in a 6-year-old girl preserving the associated impacted permanent tooth
 331 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 331-335, 2007 Case Report Management of ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in a 6-year-old girl preserving the associated impacted permanent tooth Sílvia R. A. Reis
331 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 49, No. 4, 331-335, 2007 Case Report Management of ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in a 6-year-old girl preserving the associated impacted permanent tooth Sílvia R. A. Reis
Epithelial Sources. Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa
 ODONTOGENIC CYSTS Epithelial Sources Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa Epithelial Sources Surface Epithelium Rests of Serres Reduced Enamel Epithelium Rests of
ODONTOGENIC CYSTS Epithelial Sources Rests of Serres Rests of Malassez Reduced Enamel Epithelium Surface Mucosa Epithelial Sources Surface Epithelium Rests of Serres Reduced Enamel Epithelium Rests of
Glandular odontogenic cyst associated with ameloblastoma: Case report and review of the literature
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/jced.53775 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53775 : Case report and review of the literature Timothée Cousin 1, Samuel
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/jced.53775 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53775 : Case report and review of the literature Timothée Cousin 1, Samuel
Ameloblastic Carcinoma-Secondary Type,A Rare Case Report and Distinction from Malignant Ameloblastoma
 Ameloblastic Carcinoma-Secondary Type,A Rare Case Report and Distinction from Malignant Ameloblastoma Rajesh B Dhirawani, Sumit Asrani, Anshalika Agrawal, Sauvik Singha* and Kshitij Aggarwal Department
Ameloblastic Carcinoma-Secondary Type,A Rare Case Report and Distinction from Malignant Ameloblastoma Rajesh B Dhirawani, Sumit Asrani, Anshalika Agrawal, Sauvik Singha* and Kshitij Aggarwal Department
WHO Histological typing of odontogenic tumors, A. Epithelial Odontogenic Tumors
 Cheng-Chung Lin, Prof. in Oral Pathology College of Dental Medicine, KMU 2007 Classification: The following classification is based upon the inductive effect of one dental tissue upon another. In normal
Cheng-Chung Lin, Prof. in Oral Pathology College of Dental Medicine, KMU 2007 Classification: The following classification is based upon the inductive effect of one dental tissue upon another. In normal
Ameloblastic fibroma and related lesions: a clinicopathologic study with reference to their nature and interrelationship
 J Oral Pathol Med (2005) 34: 588 95 ª Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Æ All rights reserved www.blackwellmunksgaard.com/jopm Ameloblastic fibroma and related lesions: a clinicopathologic study with reference
J Oral Pathol Med (2005) 34: 588 95 ª Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Æ All rights reserved www.blackwellmunksgaard.com/jopm Ameloblastic fibroma and related lesions: a clinicopathologic study with reference
MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT
 International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
International Journal of Advancements in Research & Technology, Volume 2, Issue2, February-2013 1 MULTILOCULAR AMELOBLASTOMA OF MANDIBLE-A CASE REPORT DR SANTOSH KUMAR SUBUDHI*, DR SUMIT DASH**, DR.K..PREMANANDA***,
Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience
 wjd Parveen Akhter Lone et al Original Research 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1344 Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience 1 Parveen Akhter Lone, 2 Mohan Singh,
wjd Parveen Akhter Lone et al Original Research 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1344 Treatment Modalities of Odontogenic Keratocyst of Maxilla and Mandible: Our Experience 1 Parveen Akhter Lone, 2 Mohan Singh,
Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in a 9-year-old boy
 Okui et al. Stomatological Dis Sci 2018;2:7 DOI: 10.20517/2573-0002.2017.23 Stomatological Disease and Science Case Report Open Access Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in a 9-year-old boy Tatsuo Okui 1, Soichiro
Okui et al. Stomatological Dis Sci 2018;2:7 DOI: 10.20517/2573-0002.2017.23 Stomatological Disease and Science Case Report Open Access Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma in a 9-year-old boy Tatsuo Okui 1, Soichiro
Odontogenic tumors: a review
 Periodontology 2000, Vol. 57, 2011, 160 176 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Ó 2011 John Wiley & Sons A/S PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Odontogenic tumors: a review PETER R. MORGAN Odontogenic tumors comprise
Periodontology 2000, Vol. 57, 2011, 160 176 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Ó 2011 John Wiley & Sons A/S PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Odontogenic tumors: a review PETER R. MORGAN Odontogenic tumors comprise
Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Arising from Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: A Case Report
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2012; 46: 478-482 CASE REPORT Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Arising from Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: A Case Report Zhi-Yu Zhu Zhi-Gang Chu 1 Yu Chen Wei-Ping
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2012; 46: 478-482 CASE REPORT Ghost Cell Odontogenic Carcinoma Arising from Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor: A Case Report Zhi-Yu Zhu Zhi-Gang Chu 1 Yu Chen Wei-Ping
Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case Report
 Phulambrikar T., et al. Dent Shiraz Univ Med Sci., December 2015; 16(4): 374-379. Case Report Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case
Phulambrikar T., et al. Dent Shiraz Univ Med Sci., December 2015; 16(4): 374-379. Case Report Cone Beam Computed Tomography Findings in Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor Associated with Odontome: A Case
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position
 A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
Squamous odontogenic tumor: with recurrence and 12 years of follow-up
 SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOR 51 RELATO DE CASO Squamous odontogenic tumor: with recurrence and 12 years of follow-up Tumor odontogênico escamoso: com recidiva e doze anos de acompanhamento Márcia Gaiger
SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOR 51 RELATO DE CASO Squamous odontogenic tumor: with recurrence and 12 years of follow-up Tumor odontogênico escamoso: com recidiva e doze anos de acompanhamento Márcia Gaiger
An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report
 J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report
 SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
SmyrnaMed Case 2018;2(1): 1-5 ISSN (Online): 2564-6869 www.smyrnamed.com Glandular Odontogenic Cyst Coexisting with a Dentigerous Cyst: Case Report Assist.Prof.Dr. Serap Keskin Tunç 1, Dt. Erkan Feslihan
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws
 Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Management of Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year old female: A Case Report
 Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 Management of Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year old female: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Sheeraz Badal, Senior Lecturer, Dept of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, MIDSR,
Article ID: ISSN 2046-1690 Management of Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year old female: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Sheeraz Badal, Senior Lecturer, Dept of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, MIDSR,
Low-grade spindle-cell ameloblastic carcinoma: report of an unusual case with immunohistochemical findings and review of the literature
 JINDAL et al. C A S E R E P O R T Low-grade spindle-cell ameloblastic carcinoma: report of an unusual case with immunohistochemical findings and review of the literature C. Jindal m d s,* S. Palaskar m
JINDAL et al. C A S E R E P O R T Low-grade spindle-cell ameloblastic carcinoma: report of an unusual case with immunohistochemical findings and review of the literature C. Jindal m d s,* S. Palaskar m
Management of Unicystic Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year Old Female: Report of a Case
 Article ID: WMC002613 2046-1690 Management of Unicystic Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year Old Female: Report of a Case Corresponding Author: Dr. Sheeraz Badal, Senior Lecturer, Dept of Oral & Maxillofacial
Article ID: WMC002613 2046-1690 Management of Unicystic Plexiform Ameloblastoma in a 12 year Old Female: Report of a Case Corresponding Author: Dr. Sheeraz Badal, Senior Lecturer, Dept of Oral & Maxillofacial
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor (KCOT) in Maxillary Sinus arising from an Infected Dentigerous Cyst
 Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor (KCOT) in Maxillary Sinus arising from an Infected Dentigerous Cyst N R Chourasia, Abhishek Singh Payak, Preeti Bhadouria Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rishiraj
Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor (KCOT) in Maxillary Sinus arising from an Infected Dentigerous Cyst N R Chourasia, Abhishek Singh Payak, Preeti Bhadouria Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rishiraj
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences
 Case report Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 VARIATIONS IN THE BIOLOGICAL BEHAVIOR OF CALCIFYING ODONTOGENIC CYST TO CALCIFYING CYSTIC ODONTOGENIC TUMOR: A CASE
Case report Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 VARIATIONS IN THE BIOLOGICAL BEHAVIOR OF CALCIFYING ODONTOGENIC CYST TO CALCIFYING CYSTIC ODONTOGENIC TUMOR: A CASE
A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 1 A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur Citation D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 1 A Radiographic technique for differentiating enamel and dentin in odontogenic tumors D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur Citation D Shetty, A Urs, R Kaur.
Erupted odontomas: a report of two unusual cases
 ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Apr-Jun;9(2):199-203 Case Report Article Erupted odontomas: a report of two unusual cases Santosh Patil¹ Farzan Rahman² Shoaib
ISSN: Printed version: 1806-7727 Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2012 Apr-Jun;9(2):199-203 Case Report Article Erupted odontomas: a report of two unusual cases Santosh Patil¹ Farzan Rahman² Shoaib
Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour: A Case Report and Review of Literature Sunil S, Nivia M, Devi Gopakumar
 International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology. 2012;3(4):52-56 ISSN 2231 2250 Available online at http://www.journalgateway.com or www.ijomp.org Case Report Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour: A
International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology. 2012;3(4):52-56 ISSN 2231 2250 Available online at http://www.journalgateway.com or www.ijomp.org Case Report Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumour: A
Jaws: Cysts and Odontogenic Neoplasms
 Topic 10: Jaw Cysts General Features of Jaw Cysts Sources of Epithelium in Cysts Radiographic Features of Jaw Cysts Microscopic Features of Jaw Cysts Treatment and Prognosis of Jaw Cysts Classification
Topic 10: Jaw Cysts General Features of Jaw Cysts Sources of Epithelium in Cysts Radiographic Features of Jaw Cysts Microscopic Features of Jaw Cysts Treatment and Prognosis of Jaw Cysts Classification
Case Report A Conservative Approach to a Peripheral Ameloblastoma
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 8254571, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8254571 Case Report A Conservative Approach to a Peripheral Ameloblastoma Rocco Borrello, 1 Elia Bettio,
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 8254571, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8254571 Case Report A Conservative Approach to a Peripheral Ameloblastoma Rocco Borrello, 1 Elia Bettio,
Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report
 457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
Orthokeratinized Odontogenic Cyst: A Rarity
 aijoc AIJOC Case Report 1 Heena Sonawane, 2 Freny R Karjodkar, 3 Kaustubh Sansare, 4 Nimish Prakash ABSTRACT Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst (OOC) was first identified as the rare variant of keratocystic
aijoc AIJOC Case Report 1 Heena Sonawane, 2 Freny R Karjodkar, 3 Kaustubh Sansare, 4 Nimish Prakash ABSTRACT Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst (OOC) was first identified as the rare variant of keratocystic
Granular cell Ameloblastoma of the mandible A rare case report with brief review of literature
 Case Report Granular cell Ameloblastoma of the mandible A rare case report with brief review of literature Vandana Reddy 1, Vishal Bansal 2, Vijay Wadhwan 3, Arvind Venkatesh 4 1. Reader, Oral & Maxillofacial
Case Report Granular cell Ameloblastoma of the mandible A rare case report with brief review of literature Vandana Reddy 1, Vishal Bansal 2, Vijay Wadhwan 3, Arvind Venkatesh 4 1. Reader, Oral & Maxillofacial
Salivary gland tumor cytologic and histologic correlation: Algorithmic and risk stratification based approaches
 Salivary gland tumor cytologic and histologic correlation: Algorithmic and risk stratification based approaches Christopher C. Griffith, MD, PhD Raja R. Seethala, MD 1. Salivary gland tumor cytology: A
Salivary gland tumor cytologic and histologic correlation: Algorithmic and risk stratification based approaches Christopher C. Griffith, MD, PhD Raja R. Seethala, MD 1. Salivary gland tumor cytology: A
Simultaneous Occurrence of Central Giant Cell Granuloma and Odontogenic Keratocyst in Mandible
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 171 175 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0018 Simultaneous Occurrence of Central Giant Cell Granuloma and Odontogenic Keratocyst in Mandible Bruna da Fonseca
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 171 175 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0018 Simultaneous Occurrence of Central Giant Cell Granuloma and Odontogenic Keratocyst in Mandible Bruna da Fonseca
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses. Gingival Lesions
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: GROSS AND HISTOLOGICAL EXAMINATION OF 45 CASES
 SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: GROSS AND HISTOLOGICAL EXAMINATION OF 45 CASES CH Siar KHNg P Murugasu SYNOPSIS This paper represents a reappraisal of the gross and histological
SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: GROSS AND HISTOLOGICAL EXAMINATION OF 45 CASES CH Siar KHNg P Murugasu SYNOPSIS This paper represents a reappraisal of the gross and histological
Ortho keratinized Odontogenic Cyst of Mandible: A Rare Case Report
 Journal of Dental School 2015; 33(3): 233-237 Case Report Ortho keratinized Odontogenic Cyst of Mandible: A Rare Case Report 1 Soudabeh Sargolzaei 1 Fatemeh Mashhadi Abbas *2 Leila Hesami Moghadam 3 Sanaa
Journal of Dental School 2015; 33(3): 233-237 Case Report Ortho keratinized Odontogenic Cyst of Mandible: A Rare Case Report 1 Soudabeh Sargolzaei 1 Fatemeh Mashhadi Abbas *2 Leila Hesami Moghadam 3 Sanaa
Calcifying Cystic Odontogenic Tumor A Case Report and Review on Diverse Presentation of the Tumor
 : J Dentistry and Otolaryngology Volume 14 Issue 3 Version 1.0 Year 2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618 & Print
: J Dentistry and Otolaryngology Volume 14 Issue 3 Version 1.0 Year 2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618 & Print
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA--CASE REPORT
 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA--CASE REPORT J. R. TROTT, M.D.S.(Adelaide) Associate Professor of Oral Pathology, University of Manitoba, Faculty of Dentistry, Winnipeg 3, Canada INTRODUCTION NEOPLASIA of the odontogenic
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA--CASE REPORT J. R. TROTT, M.D.S.(Adelaide) Associate Professor of Oral Pathology, University of Manitoba, Faculty of Dentistry, Winnipeg 3, Canada INTRODUCTION NEOPLASIA of the odontogenic
Soft tissue recurrent ameloblastomas also show some malignant features: A clinicopathological study of a 15-year database
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.20276 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.20276 Soft tissue recurrent ameloblastomas also show some malignant features: A
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.20276 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.20276 Soft tissue recurrent ameloblastomas also show some malignant features: A
Basal cell carcinoma 5/28/2011
 Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma : A Case Report
 Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma : A Case Report Vinayak V Meharwade 1, Vidya V Meharwade 2 1- Assistant Professor, Department of Periodontology, Sinhgad Dental College and Hospital, Pune, Maharashtra, India.
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma : A Case Report Vinayak V Meharwade 1, Vidya V Meharwade 2 1- Assistant Professor, Department of Periodontology, Sinhgad Dental College and Hospital, Pune, Maharashtra, India.
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Update in Salivary Gland Pathology. Benjamin L. Witt University of Utah/ARUP Laboratories February 9, 2016
 Update in Salivary Gland Pathology Benjamin L. Witt University of Utah/ARUP Laboratories February 9, 2016 Objectives Review the different appearances of a selection of salivary gland tumor types Establish
Update in Salivary Gland Pathology Benjamin L. Witt University of Utah/ARUP Laboratories February 9, 2016 Objectives Review the different appearances of a selection of salivary gland tumor types Establish
Unicystic Ameloblastoma: Implant- supported Reconstruction and Long-Term Follow-up
 OLGU RAPORU (Case Report) Hacettepe Dişhekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi Cilt: 31, Sayı: 2, Sayfa: 49-53, 2007 Unicystic Ameloblastoma: Implant- supported Reconstruction and Long-Term Follow-up Unikistik Ameloblastoma:
OLGU RAPORU (Case Report) Hacettepe Dişhekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi Cilt: 31, Sayı: 2, Sayfa: 49-53, 2007 Unicystic Ameloblastoma: Implant- supported Reconstruction and Long-Term Follow-up Unikistik Ameloblastoma:
Odontogenic tumours: A review of 266 cases
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.50949 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.50949 Odontogenic tumours: A review of 266 cases Ahmed O. Lawal 1, Akinyele
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.50949 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.50949 Odontogenic tumours: A review of 266 cases Ahmed O. Lawal 1, Akinyele
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH e-issn - 2348-2184 Print ISSN - 2348-2176 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajbpr SOLID AND MULTICYSTIC FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA - A CASE
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH e-issn - 2348-2184 Print ISSN - 2348-2176 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajbpr SOLID AND MULTICYSTIC FOLLICULAR AMELOBLASTOMA - A CASE
Unicystic Ameloblastoma of mandible. Aggresive treatment A myth or a need. Case report and Extensive review of literature
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 12, Issue 2 (Nov.- Dec. 2013), PP 26-31 Unicystic Ameloblastoma of mandible. Aggresive treatment A myth
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 12, Issue 2 (Nov.- Dec. 2013), PP 26-31 Unicystic Ameloblastoma of mandible. Aggresive treatment A myth
International Journal of Scientific Research and Innovative Technology ISSN: Vol. 4 No. 4; April 2017
 Frequency of Lesions Associated with Impacted Teeth in Patients Referring to the Department of Oral Pathology, Tabriz Faculty of Dentistry from 2004 to 2013 and Its Relationship with Age, Gender, Location
Frequency of Lesions Associated with Impacted Teeth in Patients Referring to the Department of Oral Pathology, Tabriz Faculty of Dentistry from 2004 to 2013 and Its Relationship with Age, Gender, Location
Complex Odontoma in Both the Jaws: A Rare Case Report
 10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1013 Adit Srivastava et al CASE REPORT Complex Odontoma in Both the Jaws: A Rare Case Report Adit Srivastava, AG Annaji, Sanjay B Nyamati, Govind Singh, GC Shivakumar, S Sahana
10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1013 Adit Srivastava et al CASE REPORT Complex Odontoma in Both the Jaws: A Rare Case Report Adit Srivastava, AG Annaji, Sanjay B Nyamati, Govind Singh, GC Shivakumar, S Sahana
Diagnosing the most common odontogenic cystic and osseous lesions of the jaws for the practicing pathologist
 S96 2017 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/17 $32.00 Diagnosing the most common odontogenic cystic and osseous lesions of the jaws for the practicing pathologist Robert A Robinson Department of
S96 2017 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/17 $32.00 Diagnosing the most common odontogenic cystic and osseous lesions of the jaws for the practicing pathologist Robert A Robinson Department of
Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown
 Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
Imaging Science in entistry 2013; 43: 295-301 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2013.43.4.295 Pericoronal radiolucency associated with incomplete crown Kyung-Soo Nah 1, * 1 epartment of Oral and Maxillofacial
A case of orthokeratinized odontoge Title suspected to be a radicular cyst
 A case of orthokeratinized odontoge Title suspected to be a radicular cyst Onuki, M; Saito, A; Hosokawa, S; Oh Author(s) Hayakawa, H; Seta, S; Muramatsu, T; Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5
A case of orthokeratinized odontoge Title suspected to be a radicular cyst Onuki, M; Saito, A; Hosokawa, S; Oh Author(s) Hayakawa, H; Seta, S; Muramatsu, T; Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5
Recurrent odontogenic ghost cell carcinoma (OGCC) at a reconstructed fibular flap: A case report with immunohistochemical findings
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/medoral.17207 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17207 at a reconstructed fibular flap: A case report with immunohistochemical
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Case Report doi:10.4317/medoral.17207 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17207 at a reconstructed fibular flap: A case report with immunohistochemical
An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report.
 RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report. Nasib Chand Khabra 1, Ish Pandhi 1 *, Kiran DN 2, Sunil Alipuria 1, Bhawna Gulati 1, and
RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES An Expansile Large Odontogenic Keratocyst Maxilla: A Case Report. Nasib Chand Khabra 1, Ish Pandhi 1 *, Kiran DN 2, Sunil Alipuria 1, Bhawna Gulati 1, and
Case Report A Giant Cell Fibroma and Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia in a Young Child: A Case Report
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 370242, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/370242 Case Report A Giant Cell Fibroma and Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia in a Young Child:
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 370242, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/370242 Case Report A Giant Cell Fibroma and Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia in a Young Child:
Ameloblastomas: Clinicopathological features from 70 cases diagnosed in a single Oral Pathology service in an 8-year period
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.19802 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.19802 Ameloblastomas: Clinicopathological features from 70 cases
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.19802 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.19802 Ameloblastomas: Clinicopathological features from 70 cases
Odontogenic tumors: a retrospective clinicopathological study from two Italian centers
 PATHOLOGICA 2017;109:35-46 Review - Study Group GIPaTeC Odontogenic tumors: a retrospective clinicopathological study from two Italian centers C. RUBINI 1, M. MASCITTI 2, A. SANTARELLI 2, A. TEMPESTA 3,
PATHOLOGICA 2017;109:35-46 Review - Study Group GIPaTeC Odontogenic tumors: a retrospective clinicopathological study from two Italian centers C. RUBINI 1, M. MASCITTI 2, A. SANTARELLI 2, A. TEMPESTA 3,
Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor a rare case report with review of literature
 Case Report Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor a rare case report with review of literature Yash Agrawal 1, Giridhar S. Naidu 1, Ramanpal Singh Makkad 1, Ravleen Nagi 1, Supreet Jain 1, Dilip R. Gadewar 1,
Case Report Dentinogenic ghost cell tumor a rare case report with review of literature Yash Agrawal 1, Giridhar S. Naidu 1, Ramanpal Singh Makkad 1, Ravleen Nagi 1, Supreet Jain 1, Dilip R. Gadewar 1,
Diagnostic value of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for unilocular cystic-type
 Diagnostic value of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for unilocular cystic-type ameloblastomas with homogeneously bright high signal intensity on T2-weighted or STIR MR images Miki Hisatomi a, Yoshinobu Yanagi
Diagnostic value of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for unilocular cystic-type ameloblastomas with homogeneously bright high signal intensity on T2-weighted or STIR MR images Miki Hisatomi a, Yoshinobu Yanagi
Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor hamartoma or true neoplasm: a case report
 155 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 1, 155-159, 2009 Case Report Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor hamartoma or true neoplasm: a case report Deepti Garg, Sangeeta Palaskar, V. P. Shetty and Anju Bhushan
155 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 1, 155-159, 2009 Case Report Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor hamartoma or true neoplasm: a case report Deepti Garg, Sangeeta Palaskar, V. P. Shetty and Anju Bhushan
INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 03 INFLAMMATORY DENTIGEROUS CYST OR INFLAMMATORY CYSTIC LESIONS OF MIXED DENTITION?: A REPORT OF THREE CASES Pritam K Mankapure
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT
 Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.

 0/ *56:**7B:A9'?)2@9-: ;
0/ *56:**7B:A9'?)2@9-: ;