Cutting instruments. Instruments
|
|
|
- Sophie Davidson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Instruments أﻧﺲ اﻟﻌﺒﯿﺪي. د The removal and shaping of tooth structure are essential aspects of restorative dentistry. Initially this was a difficult process accomplished entirely by the use of - Hand instruments. - Rotary, powered cutting instruments. Hand instruments Black organized not only the classification of cavity but the naming and the numbering of hand instruments. For many years, carbon steel was the primary material used in hand instruments because they were harder and maintained sharpness better than stainless steel. Stainless steel is now the preferred material because stainless steel instruments remain bright with steam or dry heat sterilization, and because the properties of stainless steel have improved by incorporating a significant amount of chromium imparts corrosion resistance and carbon imparts hardness. Hand instruments used in operative dentistry may be categorized as: cutting instruments and non cutting instruments. Cutting instruments These instruments are used to cut hard or soft tissue of the mouth. Hand cutting instruments are composed of three parts: handle, shank and blade (Fig 1). For non cutting instrument; the part corresponding to the blade is termed the nib or working end. Fig. (1) Double-ended instrument illustrating three component parts of hand instruments: blade (a), shank (b), and handle (c) 1
2 The blade or nib; is the working end of the instrument and is connected to the shank. Some instruments have a blade on both ends of the handle and are known as double ended instruments. The blades have many designs and sizes, depending on the function they are to perform. Shank serves to connect the handle to the blade of the instrument. The shank may be straight, monoangle(with one angle), biangle (with two angles), triangle (three angles), or quadangle (four angles) as in Fig(3&4&5). The term contra-angle refers to shank in which two or more angles are present. The angles in the shank are important to keep the blade edge within 1-2 mm to the long axis of the instruments. This is a basic factor to concentrate the force onto the blade for balancing the instrument during use and prevent its rotation Handle is the part that is grasped by the operator hand while he is using the instrument. Operative cutting instrument formula Cutting instruments have numeric formula describing the dimensions and angles of the working ends. These are placed on the handles using a code of three to four numbers separated by dashes or spaces (e.g ) as in Fig. (2). The first number indicates the width of the blade or primary cutting edge in tenths of a millimeter (0.1 mm) (e.g. 10=1.0mm). The second number of a four number code indicates the primary cutting edge angle measured from a line parallel to the long axis of the instruments handle in clockwise centigrades (angle expressed as a percent of 360 degrees). If the edge is locally perpendicular to the blade then this number is normally omitted resulting in a three numbers code. The third number (second number in three numbers code) indicates the blade length in millimeters (1.0mm). The forth number (third number in three number code) indicates the blade angle relative to the long axis of the handle in clockwise centigrades. In Fig (3&4&5) some of the cutting instruments with their formulas indicated 2
3 Fig. (2) Instrument shank and blade design (with primary cutting edge positioned close to handle axis to produce balance). The complete instrument formula (four numbers) is expressed as the blade width (1) in 0.1-mm increments, cutting edge angle (2) in centigrades, blade length (3) in millimeters, and blade angle (4) in centigrades. Examples of the cutting instruments are: 1. Chisel: - either has a straight shank or with slight angle, and the blade has bevel only on one side of the edge. Its cutting edge is perpendicular to the axis of the handle. The chisels are used for cutting enamel and dentin with pushing motion. (Fig. 3 A) 2. Hoe: - It is like chisel with cutting edge is perpendicular to the axis of the handle (Fig 3C), however its blade has a greater angle from the long axis of the handle than does that of the chisel. It has the same uses of the chisel. 3. Hatchet: - also called enamel hatchet. The cutting edge of the hatchet is parallel to the long axis of the handle and beveled only from one side (Fig. 4 A). It is used for cutting enamel and dentin and comes as right or left types for using on opposite sides of the cavity. 3
4 4. Gingival margin trimmer: - This instrument is used for beveling of the gingival enamel margin of proximo-occlusal preparations. Also it is using for beveling of axiopulpal line angle of two surface preparation as in class II cavities. It is similar in design to the hatchet, except the blade is curved, and cutting edge is at an angle (other than perpendicular) to the long axis of the blade (Fig. 4, B and C). It is made as right and left types. Also it is made so a right and left pair is either a mesial pair or a distal pair. When the second number in the formula it 90 to 100, the pair is used on the distal gingival margin. When this number is 85 to 75, the pair is used to bevel the mesial margin. 5. Spoon excavator:- The blade is curved and the cutting edge at the end of the blade is in the form of a semicircle. This gives the instrument an outer convexity and inner concaving that makes it looks like a spoon Fig. (5). Like the hatchet the cutting edge at the end of the blade is parallel to the handle, therefore there are left cutting and right cutting spoons. The shank of some spoons holds a small circular (disk blade) or claw like blade at its end. The disk blade is known as a discoid, where the claw like blade is termed a cleoid (Fig 6, A and B). Fig. (3) Examples of hand instruments called chisels (with corresponding instrument formulas). A, Straight (12-7-0). B, Wedelstaedt (11'/2-15-3). C, Bin-angle (107-8). 4
5 Fig.(4) Examples of hand cutting instruments (with corresponding instrument formulas). A, Enamel hatchet ( ). B, Gingival margin trimmer (12 1/ ). C, Gingival margin trimmer (12'/ ). Fig. (5) Examples of hand instruments called spoon excavators (with corresponding instrument formulas). A, Binangle spoon ( ). B, Triple-angle spoon ( ). C, Spoon ( ). 5
6 Fig. (6) Examples of other hand instruments for cutting (spoons) 1st picture is Cleoid blade. 2nd picture is Discoid blade carving amalgam. Hand instrument grasping 1. Pen grasp: - as implies, it is similar to that used in holding a pen. Pads of the thumb, index and middle fingers hold the instrument, while the tip of the ring finger, or tips of ring and little fingers, is placed on a nearby tooth surface of the same arch as arrest. The palm of the hard generally is facing away from the operator. (Fig 7, B) 2. Inverted pen grasp: - the finger position are the same as of pen grasp, but the hand is rotated so that the palm more toward the operator. This grasping is used mostly for preparing of upper teeth with indirect viewing technique. (Fig 7, C) 3. Palm and thumb grasp: - the handle of the instrument is placed in the palm of the hand and grasped by all fingers, while the thumb is free of the instrument and used for resting on a nearby tooth of the same arch (Fig 7, D). * A proper instrument grasp must include a firm rest to steady the hand during operating procedures. The closer the rest areas are to the operating area, the more reliable they are. A B C D Fig.(7) Instrument grasping A, grasping of ordinary pen. B, pen grasping of hand instrument with correct position of middle finger is near the "topside" of the instrument for good control and cutting pressure. The rest is tip(s) of ring finger (ring and little fingers) on tooth (teeth) of same arch. C, Inverted pen grasp, palm faces more toward operator. D, Palm-and-thumb grasp. This grasp has limited use, such as preparing incisal retention in a Class III preparation on a maxillary incisor. The rest is tip of thumb on tooth in same arch. 6
7 Non cutting instruments: In these instruments the blade is replaced by a nib or point. These are divided according to function into:- I. Diagnostic instruments:- These are basic instruments that will be needed during each appointment for diagnosis and treatment (Fig. 8), including. 1- Mirror:- used for indirect visualization of any tooth surface that cannot be seen by the eye, also reflection of light into the area being examined or treated. The mirror also served as a retractor of soft tissue (tongue, cheek and lip) to aid access and visualization. 2- Probe or explorer:- pointed instruments used to feel tooth surface for irregularities and to determine the hardness of exposed dentin and caries detection. Probes have different shapes either sickle, straight or angled as appear in Fig. (8). 3- Tweezer or cotton forceps:- used for aiding the operator to carrying small items to the mouth of the patient. Fig. (8) Diagnostic instruments (from left to right) showing tweezer, mirror, and three types of probes (straight, angled, and sickle). II. Plastic instruments:or plastic filling instrument are used to carry and shape tooth colored restorative material such as composite resin and glass ionomer, or for packing temporary filling material inside unfilled cavies preparation, or for placing of basing and lining material into the cavities. In past these instruments are made of plastic, but now are available in either hard plastic or metal. Ash 6 is one of plastic instrument similar to carver but the margin of its working end is not sharp (Fig. 9B). Ash 49 is double ended instrument with cylindrical nibs and rounded ends (Fig.9A). Dycal applicator is small hand instrument with small round nib used for mixing and placing dycal lining material in the cavity (Fig.9C). Cement spatula: - it is used for mixing variety of material which required mixing (such as cement or temporary filling material) on glass or on a paper pad (Fig.9 D). Fig. (9), some of plastic instrument. A, ash49 B,ash6 C,dycal applicator D, cement spatula. 7
8 III. Amalgam instruments:those instruments used to place dental amalgam, and to a certain extent, resin composite restorative material. 1- Condensers:- condensers are used to compress the amalgam into all areas of the prepared cavity. The working end or nib of the condenser is usually round with flat end (face), but also the nibs may have different shapes as triangular, rectangular or diamond shape ends (Fig.10). Condenser may also be used to place resin composite material by pushing or patting into the prepared cavity. 2- Burnisher:- burnishers have different nib shapes which may be round, oral or rounded cone shapes (Fig. 11), also with different sizes. Burnishers are used for several functions such as; burnishing of the amalgam on the margins of the cavity, and also smoothing of the carved amalgam surface. Burnishers also used for shaping metal matrix band to have more desirable contours for restoration. Other uses of the burnishers are to bend cast gold restoration (inlay or onlay) near the margin of the prepared cavity to narrow the gap between gold and the tooth. 3- Carver:- carvers are used to shape amalgam or resin composites (tooth colored) material after they have been placed in the tooth preparations. Carvers have many shapes but usually the nibs are flat with sharp margins for carving as in Fig. (12). 4- Amalgam carrier:- used to carry the amalgam and place into the prepared cavities. Fig (10) Different shapes of condensers. Fig. (11) Different types of burnishers A,round B,oval C,rounded cone shape. Fig. (12) Different shapes of amalgam carvers. 8
9 Rotary instruments:handpieces:two basic types of handpieces, the straight handpiece and contra angle handpiece. The straight is used more frequently for laboratory work, while contra angle used in the mouth. The contra angle handpiece are classified according to their speed of rotation into:low speed handpiece:- these handpiece have atypical free running speed range from 500 to 15,000 rpm (revolution per minute). High speed handpiece: - have a free running speed above 160,000 rpm and some have speed up to 500,000 rpm. High speed techniques are generally preferred for cutting enamel and dentin. Penetration through enamel and extension of the cavities outline are more efficient at high speed. Small diameter burs should be used in the high speed handpiece. High speed generates considerable heat during cutting, even with small diameter burs and should be used with water coolant and high efficiency evacuation. Low speed contra angle handpiece, with round bur rotating slowly, are used for removal of carious dentin. Also low speed handpiece may be used with different bur shapes to finish the prepared cavity (e.g. rounding of sharp edges, or flatting of the floor), and used in finishing and polishing of restorations. Burs:A group of instruments that can turn on an axis with different speed of rotation to perform different types of work. The characteristics of this work are either cutting, abrasive, finishing or polishing. Burs used for cutting are manufactured from different materials, which may be stainless steel, carbide or diamond. Each bur consist of three parts: shank, neck, and head (Fig. 13). Shank is the part that fit into the handpiece, accepts the rotation motion from handpiece, and which the bur is locked inside the handpiece head. Neck is the part of the bur that connects the head to the shank. Head is the working part of the bur which contains the cutting edges or points, and burs are classified according to the shapes of their heads. The burs have hundreds of shapes and sizes. The basic bur shapes are round, inverted cone or fissure burs. Fig. (14). Round bur: the head is spherical so it is used for initial entry into the tooth, preparation of retentive holes or for removal of caries dentin. Inverted cone bur: the head is a cone shape with the apex of cone directed toward the bur shank. This bur is used for flatting the floor of the cavity, increasing the depth of cavity or for providing undercuts in cavities preparation. Straight fissure bur: - is an elongated cylindrical head bur used for obtaining the outline form of the cavity and to cut walls, floor, or margins of the cavity. 9
10 Fig. (13) Normal designation of three parts of rotary cutting instruments. Fig.(14) Basic bur head shapes. 10
Preclinical Dentistry. I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects. Lenka Roubalíková
 Preclinical Dentistry I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects Lenka Roubalíková Understanding dental caries crown pulp chamber neck root canal root Dental
Preclinical Dentistry I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects Lenka Roubalíková Understanding dental caries crown pulp chamber neck root canal root Dental
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations The outline form
 Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
CLASS II AMALGAM RESTORATIONS. Amalgam restorations that restore one or both of the proximal surfaces of the tooth
 CLASS II AMALGAM RESTORATIONS Amalgam restorations that restore one or both of the proximal surfaces of the tooth Initial Tooth Preparation Occlusal outline form (occlusal step).the occlusal outline form
CLASS II AMALGAM RESTORATIONS Amalgam restorations that restore one or both of the proximal surfaces of the tooth Initial Tooth Preparation Occlusal outline form (occlusal step).the occlusal outline form
CLASS II AMALGAM RESTORATION 36MO
 INTERNATIONAL PEER REVIEW CLASS II AMALGAM RESTORATION 36MO Leung Kwan Yu, Steve BDS II - Class 2019, The University of Hong Kong instruments Mirror Periodontal probe Hatchets Gingival margin trimmers
INTERNATIONAL PEER REVIEW CLASS II AMALGAM RESTORATION 36MO Leung Kwan Yu, Steve BDS II - Class 2019, The University of Hong Kong instruments Mirror Periodontal probe Hatchets Gingival margin trimmers
ASSIGNMENT 16. Book Assignment: Operative Dentistry, pages 16-1 to 16-33
 ASSIGNMENT 16 Book Assignment: Operative Dentistry, pages 16-1 to 16-33 16-1. Operative dentistry is concerned with the prevention and treatment of defects of what tooth surfaces? 1. Enamel and cementum
ASSIGNMENT 16 Book Assignment: Operative Dentistry, pages 16-1 to 16-33 16-1. Operative dentistry is concerned with the prevention and treatment of defects of what tooth surfaces? 1. Enamel and cementum
Preclinical Dentistry. I. Dental Caries. defects. Lenka Roubalíková. 1
 Preclinical Dentistry I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: : trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects Lenka Roubalíková lenka.roubalikova@tiscali.cz 1 Understanding dental caries lenka.roubalikova@tiscali.cz
Preclinical Dentistry I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: : trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects Lenka Roubalíková lenka.roubalikova@tiscali.cz 1 Understanding dental caries lenka.roubalikova@tiscali.cz
CLASS II CAVITY PREPARATION CHARACTERISTICS OF AN IDEAL CLASS II
 CLASS II CAVITY PREPARATION CHARACTERISTICS OF AN IDEAL CLASS II Contact area carious lesion Proximal view Vertical section - Buccal view Class II carious lesions are diagnosed using bitewing radiographs.
CLASS II CAVITY PREPARATION CHARACTERISTICS OF AN IDEAL CLASS II Contact area carious lesion Proximal view Vertical section - Buccal view Class II carious lesions are diagnosed using bitewing radiographs.
DENTAL CARIES CARACTERISTICS, HANDPIECES, HAND INSTRUMENTS, (USED IN PHANTOM LAB) HYSTOPATHOLOGY. BURS. 3rd year, 1st semester
 DENTAL CARIES CARACTERISTICS, HYSTOPATHOLOGY. HANDPIECES, HAND INSTRUMENTS, BURS. (USED IN PHANTOM LAB) 3rd year, 1st semester DENTAL CARIES CARIES Dental caries is a multifactorial chronic, irreversible
DENTAL CARIES CARACTERISTICS, HYSTOPATHOLOGY. HANDPIECES, HAND INSTRUMENTS, BURS. (USED IN PHANTOM LAB) 3rd year, 1st semester DENTAL CARIES CARIES Dental caries is a multifactorial chronic, irreversible
Essentials of. Dental Assisting. Edition 6. Debbie S. Robinson Doni L. Bird
 Essentials of Dental Assisting Edition 6 Debbie S. Robinson Doni L. Bird CHAPTER21 Restorative Procedures http://evolve.elsevier.com/robinson/essentials/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES KEY TERMS 1. Pronounce, define,
Essentials of Dental Assisting Edition 6 Debbie S. Robinson Doni L. Bird CHAPTER21 Restorative Procedures http://evolve.elsevier.com/robinson/essentials/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES KEY TERMS 1. Pronounce, define,
Jet Carbides. Enduring esthetics. Effortless efficiency. Precisely.
 Jet Carbides Enduring esthetics. Effortless efficiency. Precisely. Your practice inspires Kerr to bring the highest quality, most innovative products to the dental community. Shank Type Code Shank Type
Jet Carbides Enduring esthetics. Effortless efficiency. Precisely. Your practice inspires Kerr to bring the highest quality, most innovative products to the dental community. Shank Type Code Shank Type
Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations:
 1 Lec.7 د.عبد املنعم اخلفاجي CLASS V CAVITY PREPARATION FOR AMAGLAM Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations: 1- Caries:
1 Lec.7 د.عبد املنعم اخلفاجي CLASS V CAVITY PREPARATION FOR AMAGLAM Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations: 1- Caries:
Dr.Zainab. second. step): The. proximal
 Class II Amalgam Restorations Dr.Zainab This section introduces the principles and techniques of a Class II tooth preparation for an amalgam restoration involving a carious lesion on one proximal surface.
Class II Amalgam Restorations Dr.Zainab This section introduces the principles and techniques of a Class II tooth preparation for an amalgam restoration involving a carious lesion on one proximal surface.
Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor
 Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor Generally The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 3 18 months of age, with 6 months being the average and is replaced by the permanent tooth around 7 8 years of
Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor Generally The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 3 18 months of age, with 6 months being the average and is replaced by the permanent tooth around 7 8 years of
ORTHODONTIC BANDING AND CEMENTATION. Materials
 ORTHODONTIC BANDING AND CEMENTATION Materials Required Materials for fitting bands: 1. Selection of bands of different sizes for the teeth to which you are fitting bands 2. Tweezers to take the bands out
ORTHODONTIC BANDING AND CEMENTATION Materials Required Materials for fitting bands: 1. Selection of bands of different sizes for the teeth to which you are fitting bands 2. Tweezers to take the bands out
Principles of Periodontal Instrumentation. Periodontology I - 4th year 23/2/2012 Dr. Murad Shaqman
 Principles of Periodontal Instrumentation Periodontology I - 4th year 23/2/2012 Dr. Murad Shaqman Outline Classification of periodontal instruments General principles of instrumentation Principles of scaling
Principles of Periodontal Instrumentation Periodontology I - 4th year 23/2/2012 Dr. Murad Shaqman Outline Classification of periodontal instruments General principles of instrumentation Principles of scaling
روپ قداص رتکد ناشخرد یاھدادعتسا رتفد
 CLASS II (pp 658-664 664, 696-708 708) دکتر صادق پور دفتر استعدادھای درخشان Seven Steps of Cavity Preparation 1) Establish the outline form 2) Establish resistance form 3) Establish retention form 4) Provide
CLASS II (pp 658-664 664, 696-708 708) دکتر صادق پور دفتر استعدادھای درخشان Seven Steps of Cavity Preparation 1) Establish the outline form 2) Establish resistance form 3) Establish retention form 4) Provide
International Dentist Program (IDP) Admissions Cycle Bench Test Guidelines
 International Dentist Program (IDP) 2018-2019 Admissions Cycle Bench Test Guidelines Prepared by Dr. Lata Shenoy The purpose of this document and its associated attachments is to explain what will occur
International Dentist Program (IDP) 2018-2019 Admissions Cycle Bench Test Guidelines Prepared by Dr. Lata Shenoy The purpose of this document and its associated attachments is to explain what will occur
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry. Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer)
 Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer) Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland Dental School With special acknowledgements
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer) Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland Dental School With special acknowledgements
Implant Maintenance HYGIENE INSTRUMENTS. IMPLA-MATE Universal Curette/Langer 1-2. IMPLA-MATE Universal Curette/Langer 3-4
 HYGIENE Implant Maintenance each $39.95 Introducing ImplaMate The Ultimate in Implant Scaler Technology! Until now clinicians have relied on a limited selection of instruments with thick plastic tips to
HYGIENE Implant Maintenance each $39.95 Introducing ImplaMate The Ultimate in Implant Scaler Technology! Until now clinicians have relied on a limited selection of instruments with thick plastic tips to
Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV.
 Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV. Class V. Cervical defects - Dental caries - Non carious lesions (erosion, abrasion, V shaped defects) Types of defects Caries Erosion Abrasion V shaped
Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV. Class V. Cervical defects - Dental caries - Non carious lesions (erosion, abrasion, V shaped defects) Types of defects Caries Erosion Abrasion V shaped
Amalgam restoration of posterior proximal cavities with deep and concave gingival outlines
 Amalgam restoration of posterior proximal cavities with deep and concave gingival outlines M. Darveniza, MDSc, FRACDS* Abstract A technique for making a matrix and wedges for amalgam restoration of deep
Amalgam restoration of posterior proximal cavities with deep and concave gingival outlines M. Darveniza, MDSc, FRACDS* Abstract A technique for making a matrix and wedges for amalgam restoration of deep
Stainless Steel Crowns
 Stainless Steel Crowns Objectives Indications for use of stainless steel crowns Technique used in preparing and placing a stainless steel crown restoration on a primary molar. Indications for SSC Restoration
Stainless Steel Crowns Objectives Indications for use of stainless steel crowns Technique used in preparing and placing a stainless steel crown restoration on a primary molar. Indications for SSC Restoration
Restorative Dentistry for the Primary Dentition. References : pinkham, chapter 21
 In The Name Of God Restorative Dentistry for the Primary Dentition References : pinkham, chapter 21 INSTRUMENTATION High speed Handpiece(100,000 to 300,000 rpm) Low speed handpiece(500 to 15,000 rpm) hand
In The Name Of God Restorative Dentistry for the Primary Dentition References : pinkham, chapter 21 INSTRUMENTATION High speed Handpiece(100,000 to 300,000 rpm) Low speed handpiece(500 to 15,000 rpm) hand
HOW TO USE THIS BOOK. The instruments in this guide are not to scale, and during photography some colours may have been altered.
 SBGPR 3/25/06 9:35 AM Page vi HOW TO USE THIS BOOK As the dental profession evolves, there is an increasing demand for supplementary material that can keep up with advancing trends. Hands on practical
SBGPR 3/25/06 9:35 AM Page vi HOW TO USE THIS BOOK As the dental profession evolves, there is an increasing demand for supplementary material that can keep up with advancing trends. Hands on practical
KaVo Kerr Carbides Comprehensive Portfolio of Operative, Trimming & Finishing and Specialty Carbides
 Rotary KaVo Kerr Carbides Comprehensive Portfolio of Operative, Trimming & Finishing and Specialty Carbides PRECISION. QUALITY. VALUE. KaVo Kerr knows we ve designed our Carbide burs to bridge the gap
Rotary KaVo Kerr Carbides Comprehensive Portfolio of Operative, Trimming & Finishing and Specialty Carbides PRECISION. QUALITY. VALUE. KaVo Kerr knows we ve designed our Carbide burs to bridge the gap
,5 mm mm
 Mini luxators These mini luxators have an anatomically curved blade to adapt to the tooth root. Through a slight rotating movement the periodontal ligaments can be cut cleanly, at the same time dilating
Mini luxators These mini luxators have an anatomically curved blade to adapt to the tooth root. Through a slight rotating movement the periodontal ligaments can be cut cleanly, at the same time dilating
BOCL-01: Bonding Materials Checklist
 Task 19: Gather materials to bond partner using toothpaste as etchant Take a photo of gathered materials and submit with this completed checklist BOCL-01: Bonding Materials Checklist Date: Patient: Operator:
Task 19: Gather materials to bond partner using toothpaste as etchant Take a photo of gathered materials and submit with this completed checklist BOCL-01: Bonding Materials Checklist Date: Patient: Operator:
Central Incisor DR.Ahmed Al-Jobory B.D.S.,M.Sc. Conservative Department
 Dental Anatomy Lecture 3 Central Incisor DR.Ahmed Al-Jobory B.D.S.,M.Sc. Conservative Department The permanent maxillary Incisors Maxillary incisor are four in number. The maxillary central incisor is
Dental Anatomy Lecture 3 Central Incisor DR.Ahmed Al-Jobory B.D.S.,M.Sc. Conservative Department The permanent maxillary Incisors Maxillary incisor are four in number. The maxillary central incisor is
Elevators. elevators:- There are three major components of the elevator are:-
 Elevators Elevators:- Are exo-levers, instrument designed to elevate or luxate the teeth or roots from their bony socket in close or surgical method of extraction to force a tooth or root along the line
Elevators Elevators:- Are exo-levers, instrument designed to elevate or luxate the teeth or roots from their bony socket in close or surgical method of extraction to force a tooth or root along the line
DENTAL MATERIALS STUDY GUIDE
 DENTAL MATERIALS STUDY GUIDE WORKSHEET Dentalelle Tutoring www.dentalelle.com Study Guide for Dental Materials Dentalelle Tutoring 1. When completing a large composite restoration, how should the composite
DENTAL MATERIALS STUDY GUIDE WORKSHEET Dentalelle Tutoring www.dentalelle.com Study Guide for Dental Materials Dentalelle Tutoring 1. When completing a large composite restoration, how should the composite
Class I Cavity Preparation. Alaa Sabrah, BDS, MSD, PhD Nov,
 بسم اهلل الرحمن الرحيم Class I Cavity Preparation Alaa Sabrah, BDS, MSD, PhD Nov, 2015 15 Goals and Objectives?Define class I carious lesion.1 Describe the clinical technique for treating class I?carious
بسم اهلل الرحمن الرحيم Class I Cavity Preparation Alaa Sabrah, BDS, MSD, PhD Nov, 2015 15 Goals and Objectives?Define class I carious lesion.1 Describe the clinical technique for treating class I?carious
PLATE 1. Outline Form
 PLATE 1 Outline Form A. A standard radiograph (left) in buccolingual projection provides only a two-dimensional view of what is actually a three-dimensional problem. If a mesiodistal x-ray projection could
PLATE 1 Outline Form A. A standard radiograph (left) in buccolingual projection provides only a two-dimensional view of what is actually a three-dimensional problem. If a mesiodistal x-ray projection could
UDELL DENTAL LABORATORY Instructions for Use PREAT Precision Attachments
 Indications Instructions The Locator Root Attachment is designed for use with overdentures or partial dentures, retained in whole or in part by endodontically treated roots in the mandibular or maxilla.
Indications Instructions The Locator Root Attachment is designed for use with overdentures or partial dentures, retained in whole or in part by endodontically treated roots in the mandibular or maxilla.
PEER Surgical Ltd. Dental Instruments.
 PEER Surgical Ltd. Dental Instruments. www.peersurgical.com info@peersurgical.com Table of Contents 01 Tooth Extracting Forceps 04-53 02 Root Elevators 04-73 03 Scalpel Handles, Handles, Moth Mirrors,
PEER Surgical Ltd. Dental Instruments. www.peersurgical.com info@peersurgical.com Table of Contents 01 Tooth Extracting Forceps 04-53 02 Root Elevators 04-73 03 Scalpel Handles, Handles, Moth Mirrors,
PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera
 PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera Operator Name Total 0-49, Passing 39 Your Score Patient Name Date of Series Instructions: Evaluate your Series of photographs first.
PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera Operator Name Total 0-49, Passing 39 Your Score Patient Name Date of Series Instructions: Evaluate your Series of photographs first.
DENTATUS PROFIN DIRECTIONAL SYSTEM
 DENTATUS PROFIN DIRECTIONAL SYSTEM THE DENTATUS PROFIN RANGE OF PRODUCTS 1. Proin PDX Handpiece 2. Proin PDH Hand Instrument for Manual Finishing 3. Proin Lamineer Tips for all Proin/EVA Handpieces 4.
DENTATUS PROFIN DIRECTIONAL SYSTEM THE DENTATUS PROFIN RANGE OF PRODUCTS 1. Proin PDX Handpiece 2. Proin PDH Hand Instrument for Manual Finishing 3. Proin Lamineer Tips for all Proin/EVA Handpieces 4.
griplite s 6 instruments
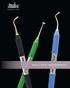 griplite s 6 instruments griplite s 6 Miltex griplite S 6 hand instruments The Miltex GripLite S 6 hand instruments are designed with the dentist in mind. These high quality instruments feature a lightweight
griplite s 6 instruments griplite s 6 Miltex griplite S 6 hand instruments The Miltex GripLite S 6 hand instruments are designed with the dentist in mind. These high quality instruments feature a lightweight
Chapter 14. Anatomy and Function of a Table Top Gag 14 RODENT DENTISTRY. Adjusting the Gag for use. How to assemble the Table Top Gag
 Chapter 14 Anatomy and Function of a Table Top Gag Adjusting the Gag for use. Access to the cheek teeth of rabbits is a problem recognised by all involved in their dental care. A combination of the diets
Chapter 14 Anatomy and Function of a Table Top Gag Adjusting the Gag for use. Access to the cheek teeth of rabbits is a problem recognised by all involved in their dental care. A combination of the diets
A Systematic Technique for Carving Amalgam and Composite Restorations
 Ó Operative Dentistry, 2011, 36-3, 335-339 Clinical Technique/Case Report A Systematic Technique for Carving Amalgam and Composite Restorations A Kilistoff Clinical Relevance The purpose of this technique
Ó Operative Dentistry, 2011, 36-3, 335-339 Clinical Technique/Case Report A Systematic Technique for Carving Amalgam and Composite Restorations A Kilistoff Clinical Relevance The purpose of this technique
Award Matrix HPVC Dental Consumables
 Award Matrix HPVC2017-123 Dental Consumables Effective 1st March 2017 3M Australia Pty Ltd Product Sub Category Number & 1 BURS 1.01 BURS DIAMOND FINISHING AND POLISHING A A A A A A A 1 BURS 1.02 BURS
Award Matrix HPVC2017-123 Dental Consumables Effective 1st March 2017 3M Australia Pty Ltd Product Sub Category Number & 1 BURS 1.01 BURS DIAMOND FINISHING AND POLISHING A A A A A A A 1 BURS 1.02 BURS
1. Rotosonic burs have 6 sides with non-cutting edge and will not injure soft and hard tissue.
 Rotosonic Scaler bur Rotosonic scaler bur are manufactured in two shape. One is perio type and the other is flame type. Perio type is made of stainless steel but flame type is made of carbide. Characteristics
Rotosonic Scaler bur Rotosonic scaler bur are manufactured in two shape. One is perio type and the other is flame type. Perio type is made of stainless steel but flame type is made of carbide. Characteristics
CARIES STABILIZATION AND TEMPORARY RESTORATION
 CARIES STABILIZATION AND TEMPORARY RESTORATION LEARNING OUTCOMES Justify the importance of caries stabilisation procedure in operative care. List and discuss the methods to stabilise caries ( include preventive
CARIES STABILIZATION AND TEMPORARY RESTORATION LEARNING OUTCOMES Justify the importance of caries stabilisation procedure in operative care. List and discuss the methods to stabilise caries ( include preventive
Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control
 Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control REST 528A
Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control REST 528A
M. Molitor REMOVAL OF ORTHODONTIC BANDS AND CEMENT REMOVAL WITH A HAND INSTRUMENT
 M. Molitor REMOVAL OF ORTHODONTIC BANDS AND CEMENT REMOVAL WITH A HAND INSTRUMENT REMOVAL OF ORTHODONTIC BANDS AND CEMENT REMOVAL WITH A HAND INSTRUMENT COURSE OUTLINE, ACTIVITIES AND HOUR BREAKDOWN 1.
M. Molitor REMOVAL OF ORTHODONTIC BANDS AND CEMENT REMOVAL WITH A HAND INSTRUMENT REMOVAL OF ORTHODONTIC BANDS AND CEMENT REMOVAL WITH A HAND INSTRUMENT COURSE OUTLINE, ACTIVITIES AND HOUR BREAKDOWN 1.
Advance Dental Simulation Module on Crown Preparation
 Advance Dental Simulation Module on Crown Preparation Ranier M. Adarve, DMD, MS, MHPE Prosthodontist and Instructional Designer Introduction Welcome! This module is developed to guide dental students in
Advance Dental Simulation Module on Crown Preparation Ranier M. Adarve, DMD, MS, MHPE Prosthodontist and Instructional Designer Introduction Welcome! This module is developed to guide dental students in
Advancing the Art of Freehand Cosmetic Contouring
 Advancing the Art of Freehand Cosmetic Goldfogel Instruments Goldfogel XTS Instruments Goldfogel Anterior Instruments Created by Dr. Michael Goldfogel, the XTS Instruments represent an important step forward
Advancing the Art of Freehand Cosmetic Goldfogel Instruments Goldfogel XTS Instruments Goldfogel Anterior Instruments Created by Dr. Michael Goldfogel, the XTS Instruments represent an important step forward
IFURH0017.V04 NOV2017 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE CLINICAL PROCEDURE
 IFURH0017.V04 NOV2017 H Y B R I D INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE CLINICAL PROCEDURE OVC PROCEDURE 1. OVC Selection Determine the mesial-distal (M-D) distance of the affected tooth using the appropriate Selector
IFURH0017.V04 NOV2017 H Y B R I D INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE CLINICAL PROCEDURE OVC PROCEDURE 1. OVC Selection Determine the mesial-distal (M-D) distance of the affected tooth using the appropriate Selector
For the Perfect Class V and All Cervical Area Gingival Margins when Placing Direct Composites, Create an Injection Molding Matrix
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Case Report For the Perfect Class V and All Cervical Area Gingival Margins when Placing Direct Composites, Create an Injection Molding Paul C Belvedere* Adjunct Professor,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Case Report For the Perfect Class V and All Cervical Area Gingival Margins when Placing Direct Composites, Create an Injection Molding Paul C Belvedere* Adjunct Professor,
FS MTS. Micro Periodontal Tissue Scissors
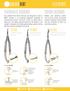 FEATHERLITE SCISSORS Our patented Flex Series Scissors are designed to have a 300% increase in its shearing angulation compared to conventional scissors. The result is that, no mater what is being cut,
FEATHERLITE SCISSORS Our patented Flex Series Scissors are designed to have a 300% increase in its shearing angulation compared to conventional scissors. The result is that, no mater what is being cut,
Tungsten Carbide Catalog1
 Tungsten Carbide Catalog1 2 Turning Precision into Value Strauss high precision Carbides Introduction Strauss offers highly accurate, One-piece FG tungsten carbide bur: n Highest quality raw materials:
Tungsten Carbide Catalog1 2 Turning Precision into Value Strauss high precision Carbides Introduction Strauss offers highly accurate, One-piece FG tungsten carbide bur: n Highest quality raw materials:
Metal-Free Restorations PROCEDURES FOR POSTERIOR DIRECT & SEMI-DIRECT COMPOSITE RESTORATIONS D I D I E R D I E T S C H I. For.
 PROCEDURES FOR POSTERIOR DIRECT & SEMI-DIRECT COMPOSITE RESTORATIONS Metal-Free Restorations D I D I E R D I E T S C H I The Geneva Smile Center D.M.D, PhD, Privat-Docent 2, Quai Gustave Ador 1207 Geneva
PROCEDURES FOR POSTERIOR DIRECT & SEMI-DIRECT COMPOSITE RESTORATIONS Metal-Free Restorations D I D I E R D I E T S C H I The Geneva Smile Center D.M.D, PhD, Privat-Docent 2, Quai Gustave Ador 1207 Geneva
Contouring vs. Orthodontics. Contouring to Eliminate Fractures and Enhance Proportions
 Contouring vs. Orthodontics Photo 1 Maxillary central incisors are overlapped. Patient chose rapid tooth movement instead of contouring. Photo 2 Maxillary central incisors after six months of orthodontic
Contouring vs. Orthodontics Photo 1 Maxillary central incisors are overlapped. Patient chose rapid tooth movement instead of contouring. Photo 2 Maxillary central incisors after six months of orthodontic
Hands-on Posterior Tooth Preparation. Practical Skills Courses, SWL, 25/11/2016
 Hands-on Posterior Tooth Preparation Practical Skills Courses, SWL, 25/11/2016 Hands-On Didactic Teaching A Tooth-Friendly-Approach - Hands-on Tooth Preparation Course - Dental Simulation to include: Posterior
Hands-on Posterior Tooth Preparation Practical Skills Courses, SWL, 25/11/2016 Hands-On Didactic Teaching A Tooth-Friendly-Approach - Hands-on Tooth Preparation Course - Dental Simulation to include: Posterior
Full Arch Hygiene Protocol
 Full Arch Hygiene Protocol Patients should be evaluated and categorized into 3 different Recall Frequency Groups (RFG s). An evaluation of homecare should be made during the prosthetic phase of treatment
Full Arch Hygiene Protocol Patients should be evaluated and categorized into 3 different Recall Frequency Groups (RFG s). An evaluation of homecare should be made during the prosthetic phase of treatment
Hex-Lock Abutment System. Restorative Manual
 System Restorative Manual 32 Restorative options with s s are manufactured from titanium alloy and used as the support foundation for single- or multiple-unit cement-retained, partially edentulous fixed
System Restorative Manual 32 Restorative options with s s are manufactured from titanium alloy and used as the support foundation for single- or multiple-unit cement-retained, partially edentulous fixed
LMArte. Sculpt masterpieces
 LMArte Sculpt masterpieces LMArte LMArte by Style Italiano Designed by Walter Devoto DDS and Angelo Putignano MD, DDS. Esthetic layering - succeed with LM-Arte LM-Arte is a set of innovative instruments
LMArte Sculpt masterpieces LMArte LMArte by Style Italiano Designed by Walter Devoto DDS and Angelo Putignano MD, DDS. Esthetic layering - succeed with LM-Arte LM-Arte is a set of innovative instruments
Clinical report. Drs Paul and Alexandre MIARA and F. CONNOLLY COMPOSITE POSTERIOR FILLINGS. How to control. layering? 8 - Dentoscope n 124
 COMPOSITE POSTERIOR FILLINGS How to control layering? 8 - Dentoscope n 124 CV FLASH Dr Paul MIARA Dental surgeon Dr Alexandre MIARA Dental surgeon Dr F. CONNOLLY Dental surgeon Thanks to continuous improvements
COMPOSITE POSTERIOR FILLINGS How to control layering? 8 - Dentoscope n 124 CV FLASH Dr Paul MIARA Dental surgeon Dr Alexandre MIARA Dental surgeon Dr F. CONNOLLY Dental surgeon Thanks to continuous improvements
Use and description of endodontic instruments
 Use and description of endodontic instruments Today s lecture is on the endodontic tools that we re going to use in the root canal therapy. As we already know all of the steps of root canal therapy beginning
Use and description of endodontic instruments Today s lecture is on the endodontic tools that we re going to use in the root canal therapy. As we already know all of the steps of root canal therapy beginning
PROPORTION GAUGE T-BAR TIP
 Proportion PROPORTION GAUGE The Proportion Gauge has the T-bar tip on one end and an In-line tip on the opposite end. The T-bar tip is used on teeth with normal alignment and the In-line tip is used for
Proportion PROPORTION GAUGE The Proportion Gauge has the T-bar tip on one end and an In-line tip on the opposite end. The T-bar tip is used on teeth with normal alignment and the In-line tip is used for
Operative dentistry. Lec: 10. Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE):
 Operative dentistry Lec: 10 د.عبذالمنعم الخفاجي Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE): There are 2 types: 1) Unreinforced ZOE (ordinary type): supplied as powder (zinc oxide + some additives like zinc acetate, white
Operative dentistry Lec: 10 د.عبذالمنعم الخفاجي Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE): There are 2 types: 1) Unreinforced ZOE (ordinary type): supplied as powder (zinc oxide + some additives like zinc acetate, white
أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل CROWN AND BRIDGE جامعة تكريت كلية. Lec. (2) طب االسنان
 Lec. (2) CROWN AND BRIDGE أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل Patient selection and examination A thorough diagnosis must first be made of the patient's dental condition, considering both hard and soft tissues. this
Lec. (2) CROWN AND BRIDGE أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل Patient selection and examination A thorough diagnosis must first be made of the patient's dental condition, considering both hard and soft tissues. this
NATIONAL EXAMINING BOARD FOR DENTAL NURSES
 NATIONAL EXAMINING BOARD FOR DENTAL NURSES NATIONAL DIPLOMA EXAMINATION DENTAL CHARTING NEBDN is a limited company registered in England & Wales No. 5580200 Registered with the Charity Commisioners No.
NATIONAL EXAMINING BOARD FOR DENTAL NURSES NATIONAL DIPLOMA EXAMINATION DENTAL CHARTING NEBDN is a limited company registered in England & Wales No. 5580200 Registered with the Charity Commisioners No.
2. Gap closure and replacement of the missing tooth 35 with directly modelled bridge region 34-36
 GrandTEC Test Kit Dear User, This Test Kit has been put together to enable you to test GrandTEC on the model before using it in a clinical situation. GrandTEC is a resin-impregnated glass fibre strip.
GrandTEC Test Kit Dear User, This Test Kit has been put together to enable you to test GrandTEC on the model before using it in a clinical situation. GrandTEC is a resin-impregnated glass fibre strip.
Scaler Periodontal Curette Explorer Root Planing Check Scaler Sharpening Product Periodontal Probe Resin Color Probe Medicine Applicator
 Scaler Periodontal Curette Explorer Root Planing Check Scaler Sharpening Product Periodontal Probe Resin Color Probe Medicine Applicator 14 20 24 24 25 29 31 32 13 Scaler -Single End- -Pair- *Efficiently
Scaler Periodontal Curette Explorer Root Planing Check Scaler Sharpening Product Periodontal Probe Resin Color Probe Medicine Applicator 14 20 24 24 25 29 31 32 13 Scaler -Single End- -Pair- *Efficiently
Lec11 يجافخلا معنملاذبع د 0 Dental Amalgam:- Advantages:- Disadvantages:- Composition: -
 Operative dentistry Lec11 د 0 عبذالمنعم الخفاجي Dental Amalgam:-Is a union of mercury (liquid) with amalgam alloys (powder) to give a plastic mass, which, hardens in the cavity. Amalgam alloy:- Is a combination
Operative dentistry Lec11 د 0 عبذالمنعم الخفاجي Dental Amalgam:-Is a union of mercury (liquid) with amalgam alloys (powder) to give a plastic mass, which, hardens in the cavity. Amalgam alloy:- Is a combination
SURVEYING OF REMOVABLE PARITAL DENTURES FEB, 11, 2015
 SURVEYING OF REMOVABLE PARITAL DENTURES FEB, 11, 2015 Dental Surveyor: It is a mechanical device used to determine the relative parallelism of the teeth surfaces and the undercuts areas in relation to
SURVEYING OF REMOVABLE PARITAL DENTURES FEB, 11, 2015 Dental Surveyor: It is a mechanical device used to determine the relative parallelism of the teeth surfaces and the undercuts areas in relation to
4766 Research Dr. San Antonio, TX insightdentalsystems.com
 OVERVIEW OF THE INSIGHT DENTAL IMPLANT DELIVERY SYSTEM The IDS system comes in a unit dose implant system where its advantage provides sterile instrumentation in one single-use kit. It is organized to
OVERVIEW OF THE INSIGHT DENTAL IMPLANT DELIVERY SYSTEM The IDS system comes in a unit dose implant system where its advantage provides sterile instrumentation in one single-use kit. It is organized to
Invisible Retainer with Single-Tooth Pontic Fabrication Technique (Multi-Tooth Pontic Procedure also available)
 Invisible Retainer with Single-Tooth Pontic Fabrication Technique (Multi-Tooth Pontic Procedure also available) Safety glasses should be worn for all lab procedures as well as gloves when handling acrylics.
Invisible Retainer with Single-Tooth Pontic Fabrication Technique (Multi-Tooth Pontic Procedure also available) Safety glasses should be worn for all lab procedures as well as gloves when handling acrylics.
A SIMPLIFIED INSTRUMENTATION APPROACH TO ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT Hands On Workshop
 A SIMPLIFIED INSTRUMENTATION APPROACH TO ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT Hands On Workshop 2014 Kentucky Dental Association Louisville, KY Friday, March 14, 2014 2:00 p.m. 5:00 p.m. A Simplified Instrumentation
A SIMPLIFIED INSTRUMENTATION APPROACH TO ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT Hands On Workshop 2014 Kentucky Dental Association Louisville, KY Friday, March 14, 2014 2:00 p.m. 5:00 p.m. A Simplified Instrumentation
Dispensary Kit Inventory
 Dispensary Kit Inventory Clinic 1 Acrylic Bur Block Adams Pliers Air/Water Tip Alginate Impression Tray Amalgam Back Action Kit Amalgam Carrier Double Ended Amalgam Carrier Single Ended Amalgam Sho-Fu
Dispensary Kit Inventory Clinic 1 Acrylic Bur Block Adams Pliers Air/Water Tip Alginate Impression Tray Amalgam Back Action Kit Amalgam Carrier Double Ended Amalgam Carrier Single Ended Amalgam Sho-Fu
Ceramic Based Aesthetic CAD/CAM Restorative
 Ceramic Based Aesthetic CAD/CAM Restorative Create Natural Aesthetics with High-Strength Materials SHOFU Block HC and Disk HC are the latest generation of hybrid-ceramic restorative materials for use with
Ceramic Based Aesthetic CAD/CAM Restorative Create Natural Aesthetics with High-Strength Materials SHOFU Block HC and Disk HC are the latest generation of hybrid-ceramic restorative materials for use with
Principles of. By: Dr. Ahmad Rabah
 Principles of By: Dr. Ahmad Rabah 1. Utilize what's present: Whenever possible, select a design that fits the teeth and soft tissues, rather than choosing one that requires tissue alteration. When minimal
Principles of By: Dr. Ahmad Rabah 1. Utilize what's present: Whenever possible, select a design that fits the teeth and soft tissues, rather than choosing one that requires tissue alteration. When minimal
KaVo SONICflex Tips KaVo SONICflex tips
 KaVo SONICflex Tips KaVo SONICflex tips KaVo SONICflex tips overview SONICflex handpiece overview MASTER SERIES EXPERT SERIES Fast and comfortable change of tips - only one turn 3 VARIETY DEVELOPED TO
KaVo SONICflex Tips KaVo SONICflex tips KaVo SONICflex tips overview SONICflex handpiece overview MASTER SERIES EXPERT SERIES Fast and comfortable change of tips - only one turn 3 VARIETY DEVELOPED TO
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Filling materials are used to replace missing parts of the tooth.
 Filling materials are used to replace missing parts of the tooth. 1- Dental caries. 2- Trauma. 3- Abrasion. Parts of teeth which require replacement by restorative materials vary in size of cavity, shape,
Filling materials are used to replace missing parts of the tooth. 1- Dental caries. 2- Trauma. 3- Abrasion. Parts of teeth which require replacement by restorative materials vary in size of cavity, shape,
The width of the MCXL step bur is 1.4 mm wide and has a blunt end. As the bur approaches the inside of
 As I teach first year dental students how to prep a tooth for a full gold crown, get an impression, pour and mount models, wax-up, cast and polish, they are almost always amazed at all the required steps
As I teach first year dental students how to prep a tooth for a full gold crown, get an impression, pour and mount models, wax-up, cast and polish, they are almost always amazed at all the required steps
Dr.Adel F.Ibraheem Partial Veneer Crown(Three quarter crown) Three quarter (¾ )crown: Uses: Indications ---- For posterior teeth ;
 Lecture.9 Dr.Adel F.Ibraheem Partial Veneer Crown(Three quarter crown) *It is a cast metal crown restoration that cover only a part of the clinical crown, most commonly used type of partial veneer crown
Lecture.9 Dr.Adel F.Ibraheem Partial Veneer Crown(Three quarter crown) *It is a cast metal crown restoration that cover only a part of the clinical crown, most commonly used type of partial veneer crown
Direct composite restorations for large posterior cavities extended range of applications for high-performance materials
 Direct composite restorations for large posterior cavities extended range of applications for high-performance materials A case study by Ann-Christin Meier, Dr. med. dent., Stapelfeld, Germany When large
Direct composite restorations for large posterior cavities extended range of applications for high-performance materials A case study by Ann-Christin Meier, Dr. med. dent., Stapelfeld, Germany When large
Invisible Retainer with Multi-Tooth Pontic Fabrication Technique (Single-Tooth Pontic Procedure also available)
 Invisible Retainer with Multi-Tooth Pontic Fabrication Technique (Single-Tooth Pontic Procedure also available) Safety glasses should be worn for all lab procedures as well as gloves when handling acrylics.
Invisible Retainer with Multi-Tooth Pontic Fabrication Technique (Single-Tooth Pontic Procedure also available) Safety glasses should be worn for all lab procedures as well as gloves when handling acrylics.
Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location
 Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
Kois Dento-Facial Analyzer System Instructions
 These instructions apply to the following items: M Panadent Corporation 580 S. Rancho Avenue Colton, California 92324, USA Tel: (909) 783-1841 USA & Canada (800) 368-9777 Kois Dento-Facial Analyzer System
These instructions apply to the following items: M Panadent Corporation 580 S. Rancho Avenue Colton, California 92324, USA Tel: (909) 783-1841 USA & Canada (800) 368-9777 Kois Dento-Facial Analyzer System
Jordi Manauta. Shadeguides Composite onlays. Page 1 of Apr 2012
 Jordi Manauta Shadeguides Composite onlays 25 Apr 2012 Indirect composite restorations in posterior teeth give us advantages to enhance the quality, durability and supreme aesthetics. An Article byâ Jordi
Jordi Manauta Shadeguides Composite onlays 25 Apr 2012 Indirect composite restorations in posterior teeth give us advantages to enhance the quality, durability and supreme aesthetics. An Article byâ Jordi
Dowel restorations Treatment with a post and core
 Dowel restorations Treatment with a post and core A post and core is a dental restoration used to sufficiently buildup tooth structure for future restoration with a crown when there is not enough tooth
Dowel restorations Treatment with a post and core A post and core is a dental restoration used to sufficiently buildup tooth structure for future restoration with a crown when there is not enough tooth
Introduction to Layering with Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative. Filtek. Supreme Plus Universal Restorative
 Introduction to Layering with Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative Introduction to Layering with Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative TM. Multishade
Introduction to Layering with Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative Introduction to Layering with Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative TM. Multishade
CEREC 3D Preparation Guideline
 CEREC 3D Preparation Guideline Before knowing exactly what the preparation guidelines are for CEREC 3D R1000, we must first understand how the milling instruments work and what we can do with them. Let
CEREC 3D Preparation Guideline Before knowing exactly what the preparation guidelines are for CEREC 3D R1000, we must first understand how the milling instruments work and what we can do with them. Let
PERMANENT MANDIBULAR INCISORS
 PERMANENT MANDIBULAR INCISORS (Central and Lateral) DR.AHMED AL-JOBORY LEC. 5 PERMANENT MANDIBULAR INCISORS ARE 4 IN NUMBER : 2 CENTRAL (RIGHT &LEFT) AND 2 LATERAL INCISORS (RIGHT &LEFT). CHARACTERISTIC
PERMANENT MANDIBULAR INCISORS (Central and Lateral) DR.AHMED AL-JOBORY LEC. 5 PERMANENT MANDIBULAR INCISORS ARE 4 IN NUMBER : 2 CENTRAL (RIGHT &LEFT) AND 2 LATERAL INCISORS (RIGHT &LEFT). CHARACTERISTIC
A Step-by-Step Approach to
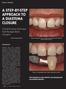 A Step-by-Step Approach to a Diastema Closure A Dual-Purpose Technique that Manages Black Triangles Marcos Vargas, DDS, MS Figure 1: Preoperative view of a patient who presented with a diastema between
A Step-by-Step Approach to a Diastema Closure A Dual-Purpose Technique that Manages Black Triangles Marcos Vargas, DDS, MS Figure 1: Preoperative view of a patient who presented with a diastema between
Note: The short arm of the BLPG tip is of the same length and measurement as the long arm of the T-bar and the Inline tip.
 Crown Lengthening CROWN LENGTHENING (CL) GAUGE: The Crown Lengthening Gauge has the Biologic Periogauge (BLPG) tip on one end and the Papilla tip on the opposite end. The BLPG tip is used to achieve the
Crown Lengthening CROWN LENGTHENING (CL) GAUGE: The Crown Lengthening Gauge has the Biologic Periogauge (BLPG) tip on one end and the Papilla tip on the opposite end. The BLPG tip is used to achieve the
Protemp Crown Temporization Material
 Clinical Case Studies Introduction from 3M ESPE is the world s first preformed, malleable temporary crown, providing speed and simplicity in temporization like never before. With this revolutionary light-curable
Clinical Case Studies Introduction from 3M ESPE is the world s first preformed, malleable temporary crown, providing speed and simplicity in temporization like never before. With this revolutionary light-curable
Top Finisher System Instructions for Use
 POLISHING AMALGAM OR GOLD 1 Prepolish with method of choice. 2 Follow with discs, cups and points where needed. 3 To achieve a final polish, use Enamelize on FlexiBuff and prophy cup. The shine will amaze
POLISHING AMALGAM OR GOLD 1 Prepolish with method of choice. 2 Follow with discs, cups and points where needed. 3 To achieve a final polish, use Enamelize on FlexiBuff and prophy cup. The shine will amaze
Set for tunneling technique, consisting of 1/3 washtray, tunneling instruments # 1 upper jaw, # 2 lower jaw, # 3 upper / lower jaw combination
 All CE marked products according to the Medical Device Directive 93/42/EEC Microsurgery zepf-dental.com 08-01 08 Instruments for the modified Tunneling Technique 46.040.00 Tunneling Instrument, # 1, for
All CE marked products according to the Medical Device Directive 93/42/EEC Microsurgery zepf-dental.com 08-01 08 Instruments for the modified Tunneling Technique 46.040.00 Tunneling Instrument, # 1, for
Efficient Bonding Protocol for the Insignia Custom Bracket System
 Efficient Bonding Protocol for the Insignia Custom Bracket System Abstract The Insignia appliance is reverse-engineered from a digital set-up of the prescribed dental alignment. Each bracket configuration,
Efficient Bonding Protocol for the Insignia Custom Bracket System Abstract The Insignia appliance is reverse-engineered from a digital set-up of the prescribed dental alignment. Each bracket configuration,
TUBES, LINGUAL ATTACHMENTS AND BANDS. tportho.com cosmeticbraces.com. POD_TPOC_04_Tubes_Linguals_Bands_2017, Rev. 1
 4 TUBES, LINGUAL ATTACHMENTS AND BANDS tportho.com cosmeticbraces.com POD_TPOC_04_Tubes_Linguals_Bands_2017, Rev. 1 TUBES, LINGUALS AND BANDS First Molar Tubes Ultra Low Profile Big Foot and Small Foot
4 TUBES, LINGUAL ATTACHMENTS AND BANDS tportho.com cosmeticbraces.com POD_TPOC_04_Tubes_Linguals_Bands_2017, Rev. 1 TUBES, LINGUALS AND BANDS First Molar Tubes Ultra Low Profile Big Foot and Small Foot
Device Technical File
 Device Technical File ContactPro Matrix System Instructions for Use 1.0 Product Description A. For placement of restorations in the posterior area of the oral cavity, the Microbrush ContactPro Sectional
Device Technical File ContactPro Matrix System Instructions for Use 1.0 Product Description A. For placement of restorations in the posterior area of the oral cavity, the Microbrush ContactPro Sectional
CAREFULLY READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS PRIOR TO USE
 CAREFULLY READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS PRIOR TO USE INDICATIONS FOR USE The LATERA Absorbable Nasal Implant is indicated for supporting upper and lower lateral nasal cartilage. CAUTION: Federal law restricts
CAREFULLY READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS PRIOR TO USE INDICATIONS FOR USE The LATERA Absorbable Nasal Implant is indicated for supporting upper and lower lateral nasal cartilage. CAUTION: Federal law restricts
Parallel-Axis Gear Terminology
 Parallel-Axis Gear Terminology For more detailed coverage of this subject, consult ANSI/AGMA Standard 1012-F90; Gear Nomenclature, Definitions with Terms and Symbols Active Profile- that part of the gear
Parallel-Axis Gear Terminology For more detailed coverage of this subject, consult ANSI/AGMA Standard 1012-F90; Gear Nomenclature, Definitions with Terms and Symbols Active Profile- that part of the gear
DH220 Dental Materials
 DH220 Dental Materials Lecture #5 Prof. Lamanna RDH, MS Restorative Dentistry: Glass Ionomer Bird & Robinson p.740-741 I. Use Liner Base Luting agent Restorative material: Class III, V, & eroded/abraded
DH220 Dental Materials Lecture #5 Prof. Lamanna RDH, MS Restorative Dentistry: Glass Ionomer Bird & Robinson p.740-741 I. Use Liner Base Luting agent Restorative material: Class III, V, & eroded/abraded
Acknowledgments Introduction p. 1 Objectives p. 1 Goals p. 2 History of Dental Materials p. 3 The Oral Environment p. 4 Characteristics of the Ideal
 Preface p. v Acknowledgments p. vii Introduction p. 1 Objectives p. 1 Goals p. 2 History of Dental Materials p. 3 The Oral Environment p. 4 Characteristics of the Ideal Dental Material p. 5 Quality Assurance
Preface p. v Acknowledgments p. vii Introduction p. 1 Objectives p. 1 Goals p. 2 History of Dental Materials p. 3 The Oral Environment p. 4 Characteristics of the Ideal Dental Material p. 5 Quality Assurance
DENTAL ASST: DENTAL SCIENCE II (721)
 DESCRIPTION The second assessment in a series, Dental Assistant II prepares students to assist a dentist or dental hygienist performing the functions of a dental practice. Topics include: chair-side assisting,
DESCRIPTION The second assessment in a series, Dental Assistant II prepares students to assist a dentist or dental hygienist performing the functions of a dental practice. Topics include: chair-side assisting,
