The notable success of dental implants. Relationship Between Smoking and Bleeding on Probing RESEARCH
|
|
|
- Derrick Mason
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RESEARCH Relationship Between Smoking and Bleeding on Probing João Gustavo Oliveira de Souza 1 Marco Aurélio Bianchini, PhD, MSc 2 Cimara Fortes Ferreira, PhD, MSc 3 * The objective of this study was to assess and compare bone loss (BL) around the dental implant platform as well as the presence of bacterial plaque (PBP), bleeding on probing (BOP), and periodontal probing depths (PD) of teeth and dental implants of smokers and nonsmokers. Three hundred forty-seven teeth and 98 implants of 20 randomly selected patients were assessed (12 smokers and 8 nonsmokers). The specimens were divided into 4 groups according to the site probed. Group 1 included smoker implant sites, group 2 included smoker tooth sites, group 3 included nonsmoker implant sites, and group 4 included nonsmoker tooth sites. The presence/ absence of visible bacterial plaque, presence/absence of BOP, PD 3 mm or.3 mm, and BL around the dental implant platform were the data assessed. The PBP and BL showed statistical significance between smokers and nonsmokers. Bleeding on probing and PD 3 mm showed statistical significance between groups 1, 3, and 4. Comparing sites with BOP and PD. 3 mm, there was no statistical significance except for group 1, which did not present sites with these characteristics. Comparing sites with BOP and PD 3 mm, there was statistical significance between group 2 and groups 3 and 4. When comparing the prevalence of sites without BOP and PD. 3 mm, there was statistical significance between groups 1, 3, and 4. Smoking promotes a greater BL around the dental implant platform and results in vasoconstriction of the peri-implant and periodontal tissues. Key Words: cigarette smoking, teeth, dental implants, bleeding on probing INTRODUCTION The notable success of dental implants showed increased use of this treatment modality for replacing missing teeth and resulted in an increased interest in identification of factors associated with its failures. The deleterious effects of smoking on wound healing and its association with low bone quality and periodontal disease are well documented. Therefore, a negative effect from smoking is expected when individuals are rehabilitated with dental implants. 2 Failure of dental implants can occur immediately after implant placement or after osseointegration has occurred. Early failure occurs especially because of lack of primary stability, resulting in fibrous tissue formation in the boneimplant interface. Delayed failures occur because of 1 Federal University of Santa Catarina, Florianopolis, Brazil. 2 Department of Periodontics, Federal University of Santa Catarina, Florianopolis, SC, Brazil. 3 University of Tennessee, Memphis, Tenn. * Corresponding author, cferreir@uthsc.edu DOI: /AAID-JOI-D loss of osseointegration from overload, infection, or from an association of both. 2 Studies demonstrate that systemic factors can compromise the intimate contact between implant and bone before they are exposed to the oral cavity. 1,3 However, the longevity of dental implants and the identification and action of these factors as time elapses remain unknown. Various studies were therefore developed to identify the factors that impair the host s response to peri-implant infection. 1 3 Smoking shows a strong association with the severity of periodontal diseases and with periimplant bone loss (BL). 2,4 6 Bacterial proliferation in epithelial cells is greater in smokers. In addition, the microorganisms involved in periodontal disease (Porphyromonas gingivalis, Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, Prevotella intermedia, Eikenella corrodens, Fusobacterium nucleatum, and Tannarella forsythensis) are the same that are related to periimplant diseases. 7 This could predispose to early dental implant loss because of the higher concentration of A actinomycetemcomitans, P gingivalis, and T forsythensis in smokers. 8 Journal of Oral Implantology 581
2 Relationship Between Smoking and Bleeding on Probing Nicotine is considered the most active pharmacological substance in cigarettes that is passively absorbed in the oral mucosa. 9 Nicotine acts directly in the capillaries and veins, causing vasoconstriction. 10 In addition to impeding wound healing, 11 vasoconstriction restricts identification of inflammation in areas with significant amounts of bacterial plaque, which can be assessed clinically by bleeding on probing (BOP). This masks the ability of the patient and less experienced dentists to identify disease, favoring the evolution of the disease. 12,13 In the short term, nicotine alone does not have any negative impact on osseointegration. 11 However, its action of vasoconstriction associated with the other substances present in the cigarette result in a 10% increase in the failure risk in mild and moderate smokers and a 30.8% failure risk in heavy smokers. Mild, moderate, and heavy smokers are classified as smoking fewer than 10 cigarettes per day, between 10 and 20 cigarettes per day, and more than 20 cigarettes per day, respectively. 5 The unfavorable outcome of dental implants in smokers is due to the alterations that occur in the immune system and the healing potential. Studies show that tobacco causes cytotoxic effects of fibroblast functions (adhesion and proliferation), interferes in chemotaxis and neutrophil phagocytosis, and negatively influences the lymphocytes immunoglobulin production. 14 Smoking also increases blood viscosity and the levels of carboxyhemoglobins, resulting in an alteration of connective tissue integrity and remodeling capability, arresting wound healing and host response to aggression. 15 This retrospective study aims at comparing periimplant BL to BL around teeth. In addition, the relationship between BOP and probing depth (PD) around teeth and dental implants of smokers and nonsmokers will be addressed. MATERIALS AND METHODS All of the individuals selected for this study were enrolled at the Center of Continuing Education and Research in Implant Dentistry at the Center of Health Sciences of the Federal University of Santa Catarina (CEPID-CCS-UFSC). The local Ethics Committee approved the study. Written consent was obtained from all subjects enrolled. Three hundred forty-seven teeth and 98 dental implants of 20 patients (8 smokers, 12 nonsmokers) who received dental implants between August 3, 2004, and August 3, 2006, with a mean age of 52 years (varying from 36 to 72 years) were randomly selected. This study comprised 5 male and 10 female patients. Information regarding the patient s medical health before chart analysis and after implant placement was registered. The patient s medical history needed to be noncontributory. All of the patients presented functional dental implants supporting provisional or final prostheses for at least 2 years. Any history of implant failure was related in the period. The specimens were divided into 4 groups according to the sites probed. In the smoker group, the groups were as follows: group 1, smoker implant sites (36 implants; n ¼ 216 sites); group 2, smoker tooth sites (150 implants; n ¼ 900 sites); group 3, nonsmoker implant sites (62 implants; n ¼ 372 sites); and group 4, nonsmoker tooth sites (197 implants; n ¼ 1182 sites). In the smoker groups, 2 patients smoked fewer than 10 cigarettes a day, 5 smoked from 10 to 20 cigarettes a day, and 1 smoked more than 20 cigarettes a day. In the smoker group, 13 implants in the mandible and 23 in the maxilla were assessed. In nonsmokers, 27 implants in the mandible and 35 in the maxilla were assessed. The data and measurements used in the analysis were as follows: 1. sites with BOP and PD 3 mm, 2. sites with BOP and PD. 3 mm, 3. sites without BOP and PD 3 mm, 4. sites without BOP and PD. 3 mm, 5. presence of bacterial plaque, 6. absence of bacterial plaque, and 7. BL around the dental implant platform. The bacterial plaque score implemented for this study was the one preconized by O Leary et al. 16 The patients and the radiographs were examined by only 1 periodontist previously calibrated, and the clinical findings were registered in the patient s chart. Presence of bacterial plaque was registered as present or absent by visual assessment during clinical examination. Clinical attachment level, BOP, PD, and suppuration measurements around teeth 582 Vol. XXXVIII / No. Five / 2012
3 de Souza et al TABLE 1 Visible Bacterial Plaque Group Absence Presence 1 2 (5.5%) a 34 (94.5%) 2 32 (21.3%) a 118 (78.7%) 3 27 (43.54%) b 35 (56.46%) 4 90 (45.48%) b 107 (54.52%) *Percentages followed by the same letters in columns do not differ statistically by the chi-square test (P..05). and dental implants were conducted in 6 sites (mesio-buccal, mid-buccal, distal-buccal, mesial-lingual, mid-lingual, distal-lingual). The PD assessment was conducted in teeth by means of a conventional periodontal probe (12 UNC Color-Coded Probe, Hu-Friedy Inc, Chicago, Ill), and for the dental implants, a Teflon probe was used (PCV12PT, Hu-Friedy Inc). The dental implant prosthesis were removed prior to conducting the examination in areas with difficult access. After the examination, prophylaxis was conducted and the prosthesis was readapted. Radiographic examinations (panoramic and periapical) were evaluated with the clinical findings for assessing the pattern of cervical alveolar bone resorption around dental implants. A cervical bone resorption was considered normal when it was 2 mm from the dental implant platform. The measures were obtained using a plastic ruler in the distal and mesial aspect of the implant. Data were submitted for statistical analysis. RESULTS Binary logistic regression was used for comparison among groups for the presence of visible bacterial plaque, BOP, PD, and BL (in millimeters). In this model, a chi-square was used to compare the groups 2 by 2, in order to verify which groups present statistical significance (P.05). Statistical analysis was conducted by using the software SAS for Windows version 8. No dental implant presented mobility, and patients did not experience pain. The total dental implant success rate was 100%. All dental implants were osseointegrated. Group 1 showed a prevalence of 7.91 and 8.26 times less presence of bacterial plaque compared with groups 3 and 4, respectively. When comparing presence of bacterial plaque for group 2, it showed a prevalence of 2.04 and 2.13 times less compared with the same groups (Table 1). In the sites presenting BOP and PD 3 mm, comparison of groups 3 (33% 8.8%) and 4 (149% 12.6%) with group 1 (6% 2.7%) showed a that the prevalence of sites with these characteristics are 4.66 times and 3.25 times higher for groups 4 and 3, respectively. When comparing sites with BOP and with PD. 3 mm, group 1 was not included in the statistical analysis because it did not show any site with those characteristics. Therefore, the prevalence of these sites in group 4 (37% 3.1%) was 15.5 times higher when compared with group 2 (2% 0.2%). Regarding the sites without BOP and PD 3 mm, groups 3 (314% 84.4%) and 4 (967% 81.8%) presented a slightly lower prevalence of sites when compared with groups 1 (190% 87.9%) and 2 (798% 88.6%). When comparing the prevalence of sites without BOP and with PD. 3 mm, group 1 (20% 9.2%) presented 3.83 times and 2.3 times higher prevalence when compared with groups 4 (29% 2.4%) and 3 (15% 4%), respectively (Table 2). When only BOP was compared between groups, not considering PD, there was an absence of statistical significance between groups 1 and 2. However, group 4 (186% 15.74%) presented 2.83 times higher prevalence of sites with BOP when compared with group 2 (50% 5.56%). The compar- TABLE 2 Logistic regression analysis for the comparison between Group BOP 3 mm BOP. 3 mm Without BOP 3 mm Without BOP. 3mm 1 6 (2.7%) a 0 (0) 190 (87.9%) ab 20 (9.2%) a 2 48 (5.3%) ac 2 (0.2%) a 798 (88.6%) a 52 (5.7%) ab 3 33 (8.8%) b 10 (2.6%) b 314 (84.4%) b 15 (4.0) b (12.6%) bc 37 (3.1%) c 967 (81.8%) b 29 (2.4%) b *Percentages followed by same letters in columns do not differ statistically by the chi-square test (P..05). BOP indicates bleeding on probing. Journal of Oral Implantology 583
4 Relationship Between Smoking and Bleeding on Probing TABLE 3 Group BOP Without BOP 1 6 (2.78%) a 210 (97.2%) 2 50 (5.56%) a 850 (94.4%) 3 43 (11.56%) b 329 (88.4%) (15.74%) c 996 (84.26%) *Percentages followed by same letters in columns do not differ statistically by the chi-square test (P..05). BOP indicates bleeding on probing. ison between group 3 (43% 11.56%) and group 1 (6% 2.78%) showed 4.15 times higher prevalence of sites with BOP than in group 3. The comparison between group 4 (186% 15.74%) and group 1 (6% 2.78%) showed a 5.6 times higher prevalence of these characteristics for group 4 (Table 3). When prevalence was compared in sites presenting BOP among smoker sites (n ¼ 56; 5.02%) and nonsmoker sites (n ¼ 229; 14.74%), the results showed that the nonsmoker sites had 2.9 times higher BOP when compared with the smoker sites (Table 4). The comparison between smokers and nonsmokers showed a presence of 2 mm alveolar BL in 19 sites (10 in maxilla and 9 in mandible) and 10 sites (4 in maxilla and 6 in mandible), respectively. This result showed that the smokers had 4.26 times higher sites with BL compared with the nonsmoker sites (Table 5). DISCUSSION Evidence-based dentistry introduced studies and methodologies to improve the availability of information and concepts that allow us to better select treatment alternatives for our patients. However, decisions regarding the treatment of patients with dental implants should be made with TABLE 4 Group BOP Without BOP 1 and 2 56 (5.02%) a and (14.74%) b 1325 *Percentages followed by same letters in columns do not differ statistically by the chi-square test (P..05). BOP indicates bleeding on probing. TABLE 5 Group BL Without BL Smokers 19 (35%) a 53 Nonsmokers 10 (8.2%) b 121 *Percentages followed by same letters in columns do not differ statistically by the chi-square test (P..05). BL indicates bone loss. the patient, informing them of all possible disadvantages, contraindications, and risk factors involved in each case. Smoking is seen as a general health risk factor, and it is responsible for 90% of lung cancers, 70% of chronic lung disorders, 80% of myocardium infarction before 50 years of age, and 30% of chronic heart diseases. There are about 1.3 billion smokers in the world, and 4.9 million deaths are from diseases related to tobacco use. 17 The results of the present study show that smoking does not impair osseointegration, which corroborates the findings of other studies. 6,7,18,19 However, many studies support smoking as a risk factor for dental implant loss and failure. 1,2,5,6,11,15,20 The authors suggest that further detailed research is needed to indicate the direct factors affecting osseointegration in smokers. The dental implant and teeth assessments of the study population of smokers and nonsmokers showed that the presence of visible bacterial plaque was less prevalent in smokers than in nonsmokers. This could be attributed to the oral hygiene instructions and awareness of the risk given by the dentists to the smokers. 21 When the prevalence of sites presenting BOP between smoker sites (n ¼ 56; 5.02%) and nonsmoker sites (n ¼ 229; 14.74%) was evaluated, the results showed that the prevalence of sites with BOP was 2.9 times higher in the nonsmoker group compared with smokers. This result shows that cigarette smoking and its components mask the main indicators of the presence of disease activity, the BOP When BOP was compared between groups, the results showed an absence of statistical significance with regard to prevalence of these sites around smoker dental implants and teeth. However, the comparison between nonsmoker and smoker periimplant tissues showed 4.15 times higher preva- 584 Vol. XXXVIII / No. Five / 2012
5 de Souza et al lence of BOP in sites around nonsmoker dental implant sites. Nonsmoker periodontal sites showed a 2.83 times higher prevalence of BOP when compared with smoker periodontal tissues, which concurs with results of studies showing vasoconstriction activity of tobacco. 3,4,7 In the comparison of BOP between smoker and nonsmoker sites with the peri-implant tissues of smokers, the results showed a 5.6 times higher prevalence in sites with BOP around nonsmoker teeth. Despite these results concurring with the literature, which shows the presence of a tissue with more collagen and less vascularization around dental implants, 22 the finding did not occur when comparing the BOP of peri-implant and periodontal tissues of smokers. In relation to BOP sites and PD 3 mm, results showed 4.66 and 3.25 higher prevalence in sites with these characteristics in nonsmoker teeth and dental implants, respectively, when compared with sites around smoker dental implants. In BOP sites, with PD. 3 mm, there was an absence of BOP in no sites around smoker dental implants. Despite the prevalence of these sites being 15.5 times higher in nonsmoker teeth when compared with smoker teeth, the sites comprised 3.1% and 0.2% of all the smoker and nonsmoker sites, respectively, which is low and should be interpreted with caution. When the prevalence of sites without BOP and with PD. 3 mm was compared, the prevalence of sites around the smoker implants was 3.83 and 2.3 times higher when compared with nonsmoker teeth and dental implant sites, respectively. These results suggest that smoking may result in a higher PD in peri-implant sites because of a more fragile periimplant mucosa due to the inflammatory process. 23,24 In addition, the higher prevalence of sites with increased PDs probably favors pathogenic bacteria colonization and consequently a higher BL around smoker dental implant platforms. In the present study, the BL was 4.26 higher in smokers compared with nonsmokers. The dental implants assessed in the present study showed a 100% success rate. 25 However, the sites showing the lowest levels of clinical attachment loss were related to smoker dental implants and with sites that did not present BOP. These results show that smoking makes it difficult for the assessment of BOP, which hinders the diagnosis for early treatment of peri-implantitis. 11,12 Although smoking is a risk factor for medical health and for osseointegration, the present study showed that dental implants can be a treatment option for smokers. Despite the low bacterial plaque score shown for the smokers in this study, the authors support their treatment protocol, which involves the following: (1) the patients are informed of their risk factor for loss of osseointegration, (2) oral hygiene instructions are reinforced at follow-up visits, and (3) maintenance visits are within shorter intervals. CONCLUSION This retrospective study suggests that smoking did not interfere with the clinical parameters of implant success despite promoting BL around the dental implant neck. In addition, the vasoconstriction effect of smoking in periodontal and peri-implant tissues hinders the main indicator of disease, BOP, especially in sites with lowest levels of clinical attachment. ABBREVIATIONS BL: bone loss BOP: bleeding on probing PBP: presence of bacterial plaque PD: probing depths REFERENCES 1. Feloutzis A, Lang NP, Tonetti MS, et al. IL-1 gene polymorphism and smoking as risk factors for periimplant bone loss in a well-maintained population. Clin Oral Implant Res. 2003;14: Alsaadi G, Quirynen M, Michiles K, Teughels W, Koma rek A, van Steenberghe D. Impact of local and systemic factors on the incidence of failures up to abutment connection with modified surface oral implants. J Clin Periodontol. 2008;35: Mombelli A, Gionca N. Systemic disease affecting osseointegration therapy. Clin Oral Implant Res. 2006;17: Macgregor IDM. Smoking and periodontal disease from drugs, diseases, and the periodontium. In: Seymour RA, Heasman PA, eds. Drugs, Diseases and the Periodontium. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; Sánchez-Pérez A, Moya-Villaescusa MJ, Caffesse RJ. Tobacco as a risk factor for survival of dental implants. J Periodontol. 2007; 78: Esposito M, Hirsch JM, Lekholm U, Thomsen P. Biological factors contributing to failures of osseointegrated oral implants (II). Etiopathogenesis. Eur J Oral Sci. 1998;106: Esposito M, Hirsch JM, Lekholm U, Thomsen P. Biological Journal of Oral Implantology 585
6 Relationship Between Smoking and Bleeding on Probing factors contributing to failures of osseointegrated oral implants (II). Etiopathogenesis. Eur J Oral Sci. 1998;106: Zambon JJ, Grossi SG, Machtei EE, Ho AW, Dunford R, Genco RJ. Cigarette smoking increases the risk for subgingival infection with periodontal pathogens. J Periodontol. 1996;67: Tonetti MS. Cigarette smoking and periodontal disease: etiology and management of disease. Ann Periodontol. 1998;3: Larson PS, Silvette H. Tobacco Experimental and Clinical Studies (Supplement III). Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins; Balatsouka D, Gotfredsen K, Lindh CH, Berglundh T. The impact of nicotine on osseointegration: an experimental study in the femur and tibia of rabbits. Clin Oral Implant Res. 2005;6: Bergström J, Floderus-Myrhed B. Co-twin control study of the relationship between smoking and some periodontal disease factors. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 1983;11: Trikilis N, Rawlinson A, Walsh TF. Periodontal probing depth and subgingival temperature in smokers and non-smokers. J Clin Periodontol. 1999;26: Raulin LA, McPherson JC III, McQuade MJ, Hanson BS. The effect of nicotine on the attachment of human fibroblasts to glass and human root surfaces in vitro. J Periodontol. 1988;59: Bain CA, Moy PK. The association between the failure of dental implants and cigarette smoking. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1993;8: O Leary TJ, Drake RB, Naylor JE. The plaque control record. J Periodontol. 1972;43: Strietzel FP, Reichart PA, Kale A, Kulkarni M, Wegner B, Küchler I. Smoking interferes with the prognosis of dental implant treatment: a systematic review and metaanalysis. J Clin Periodontol. 2007;34: Quirynen M, Peeters W, Naert I, Coucke W, van Steenberghe D. Peri-implant health around screw-shaped c. p. titaniummachined implants in partially edentulous patients with or without ongoing periodontitis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2001;12: Lambert PM, Morris HF, Ochi S. The influence of smoking on 3-year clinical success of osseointegrated dental implants. Ann Periodontol. 2000;5: Sweet JB. The relationship of cigarette smoking to impaired intra-oral wound healing: a review of evidence and implications for patient care. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1992;50: Schropp L, Isidor F, Kostopoulos L, Wenzel A. Patient experience of, and satisfaction with, delayed-immediate vs. delayed single-tooth implant placement. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004;15: Gerber JA, Tan WC, Balmer TE, Salvi GE, Lang NP. Bleeding on probing and pocket probing depth in relation to probing pressure and mucosal health around oral implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20: Abrahamsson I, Soldini C. Probe penetration in periodontal and peri-implant tissues: an experimental study in the beagle dog. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006;17: Albrektsson T, Zarb G, Worthington P, Eriksson AR. The long-term efficacy of currently used dental implants: a review and proposed criteria of success. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1986;1: Lang NP, Wetzel AC, Stich H, Caffesse RG. Histologic probe penetration in healthy and inflamed peri-implant tissues. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1994;5: Vol. XXXVIII / No. Five / 2012
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Abstract Purpose: Materials and methods Results:
 Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Please visit the C.E. Pavilion to validate your course attendance Or If There s a Line Go cdapresents.com
 UCLA Innovations 2016 CDA Presents in Anaheim Tara Aghaloo, DDS, MD, PhD Dean Ho, MS, PhD Jay Jayanetti Eric C. Sung, DDS David T. W. Wong, DMD, DMSc Benjamin M. Wu, DDS, PhD Saturday, May 14, 2016 8:00
UCLA Innovations 2016 CDA Presents in Anaheim Tara Aghaloo, DDS, MD, PhD Dean Ho, MS, PhD Jay Jayanetti Eric C. Sung, DDS David T. W. Wong, DMD, DMSc Benjamin M. Wu, DDS, PhD Saturday, May 14, 2016 8:00
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of
 Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
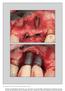 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 699 A Classification System for Peri-implant Diseases and Conditions Hector L. Sarmiento, DMD, MSc 1 Michael R. Norton, BDS, FDS, RCS(Ed)
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 699 A Classification System for Peri-implant Diseases and Conditions Hector L. Sarmiento, DMD, MSc 1 Michael R. Norton, BDS, FDS, RCS(Ed)
CEMENT-RETAINED PROSTHESES INCREASE RISK OF PERI-IMPLANTITIS WHEN COMPARED TO SCREW- RETAINED PROSTHESES
 Braz J Periodontol - September 2014 - volume 24 - issue 03 CEMENT-RETAINED PROSTHESES INCREASE RISK OF PERI-IMPLANTITIS WHEN COMPARED TO SCREW- RETAINED PROSTHESES Rachel de Queiroz Ferreira Rodrigues
Braz J Periodontol - September 2014 - volume 24 - issue 03 CEMENT-RETAINED PROSTHESES INCREASE RISK OF PERI-IMPLANTITIS WHEN COMPARED TO SCREW- RETAINED PROSTHESES Rachel de Queiroz Ferreira Rodrigues
THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter
 THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter Periodontal aspects of implant therapy 1) Comprehensive perioprosthodontic treatment by utilizing implants on perio-patients. 2) Anatomical
THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter Periodontal aspects of implant therapy 1) Comprehensive perioprosthodontic treatment by utilizing implants on perio-patients. 2) Anatomical
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
The Brånemark osseointegration method, using titanium dental implants (fixtures)
 Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Straumann SmartOne. Stage 4 Af terc are and maintenance. Step 2 Maintenance visit
 Stage 4 Af terc are and maintenance Step 2 Maintenance visit Overview Assessment and treatment planning Step 1 Patient's expectations, history and examination Step 2 Treatment planning Step 3 Consultation
Stage 4 Af terc are and maintenance Step 2 Maintenance visit Overview Assessment and treatment planning Step 1 Patient's expectations, history and examination Step 2 Treatment planning Step 3 Consultation
Risk of Implant Failure and Marginal Bone Loss in Subjects with a History of Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
 Risk of Implant Failure and Marginal Bone Loss in Subjects with a History of Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Syarida H. Safii, DDS [Correction added after online publication 1 June
Risk of Implant Failure and Marginal Bone Loss in Subjects with a History of Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Syarida H. Safii, DDS [Correction added after online publication 1 June
Detection of predominant subgingival periopathogens around submerged and non submerged hydroxy apatite implants
 [Downloaded free from http://www.jdionline.org on Sunday, January 26, 2014, IP: 201.22.186.203] Click here to download free Android application for this journa ORIGINAL ARTICLE Detection of predominant
[Downloaded free from http://www.jdionline.org on Sunday, January 26, 2014, IP: 201.22.186.203] Click here to download free Android application for this journa ORIGINAL ARTICLE Detection of predominant
The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up
 643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
As an increasing number of
 LITERATURE REVIEWS Understanding Peri-implantitis: A Strategic Review Preetinder Singh, MDS* The high survival rate of osseointegrated dental implants is well documented, but it is becoming increasingly
LITERATURE REVIEWS Understanding Peri-implantitis: A Strategic Review Preetinder Singh, MDS* The high survival rate of osseointegrated dental implants is well documented, but it is becoming increasingly
Amount of bone loss after maxillary dental implant loading in smoker and non-smoker patients
 Amount of bone loss after maxillary dental implant loading in smoker and non-smoker patients Taha Y. Hamad, B.D.S., H.D.D., M.Sc. (1) Background: Excessive crestal bone loss after dental implant occurs
Amount of bone loss after maxillary dental implant loading in smoker and non-smoker patients Taha Y. Hamad, B.D.S., H.D.D., M.Sc. (1) Background: Excessive crestal bone loss after dental implant occurs
The Influence of Controlled Occlusal Overload on Peri-implant Tissue. Part 3: A Histologic Study in Monkeys
 The Influence of Controlled Occlusal Overload on Peri-implant Tissue. Part 3: A Histologic Study in Monkeys Takashi Miyata, DDS, DDSc 1 /Yukinao Kobayashi, DDS 2 /Hisao Araki, DDS, DDSc 3 / Takaichi Ohto,
The Influence of Controlled Occlusal Overload on Peri-implant Tissue. Part 3: A Histologic Study in Monkeys Takashi Miyata, DDS, DDSc 1 /Yukinao Kobayashi, DDS 2 /Hisao Araki, DDS, DDSc 3 / Takaichi Ohto,
Interrelationship between Periodontitis and Peri-Implantitis: Myth or Reality?
 REVIEW ARTICLE Rashmi Paramashivaiah 1, *, Prabhuji M.L.V 2 1 Reader, 2 Professor& HOD, Krishnadevaraya College of Dental Sciences, Bangalore-562157 *Corresponding Author: Email: rashparams2005@yahoo.co.in
REVIEW ARTICLE Rashmi Paramashivaiah 1, *, Prabhuji M.L.V 2 1 Reader, 2 Professor& HOD, Krishnadevaraya College of Dental Sciences, Bangalore-562157 *Corresponding Author: Email: rashparams2005@yahoo.co.in
Periodontal conditions in patients Title dental implant treatment. Ito, T; Yasuda, M; Norizuki, Y; Sas Author(s) S; Furuya, Y; Kato, T; Yajima, Y
 Periodontal conditions in patients Title dental implant treatment. Ito, T; Yasuda, M; Norizuki, Y; Sas Author(s) S; Furuya, Y; Kato, T; Yajima, Y Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/2329
Periodontal conditions in patients Title dental implant treatment. Ito, T; Yasuda, M; Norizuki, Y; Sas Author(s) S; Furuya, Y; Kato, T; Yajima, Y Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/2329
Risk Factors and Early Survival Rate of Biomet 3i Dental Implants. A Retrospective Study
 Risk Factors and Early Survival Rate of Biomet 3i Dental Implants. A Retrospective Study Original Article Rasoul Heidary Postkan 1, Mina Kahyaie Aghdam 2, Ali Momen 3 1 Assisstant Professor,Department
Risk Factors and Early Survival Rate of Biomet 3i Dental Implants. A Retrospective Study Original Article Rasoul Heidary Postkan 1, Mina Kahyaie Aghdam 2, Ali Momen 3 1 Assisstant Professor,Department
Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study
 Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study Henny J. A. Meijer, DDS, PhD 1 /Rutger H. K. Batenburg, DDS,
Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study Henny J. A. Meijer, DDS, PhD 1 /Rutger H. K. Batenburg, DDS,
Case Presentation. Overall Health. Oral Hygiene. Chief Complaint. I hate my upper denture. I can t taste food. I want an implant solution
 Case Presentation Medical History Age & Gender 62 years old female Peri-implant Osteitis Overall Health Good Hx of Smoking 5 cigarets per day (Peri-implantitis) Oral Hygiene Fair Systemic Disease Osteoarthritis
Case Presentation Medical History Age & Gender 62 years old female Peri-implant Osteitis Overall Health Good Hx of Smoking 5 cigarets per day (Peri-implantitis) Oral Hygiene Fair Systemic Disease Osteoarthritis
The impact of smoking and previous periodontal disease on peri-implant microbiota and health: a retrospective study up to 7-year follow-up
 Original article The impact of smoking and previous periodontal disease on peri-implant microbiota and health: a retrospective study up to 7-year follow-up Alessandro Quaranta, DDS, PhD 1 Bartolomeo Assenza,
Original article The impact of smoking and previous periodontal disease on peri-implant microbiota and health: a retrospective study up to 7-year follow-up Alessandro Quaranta, DDS, PhD 1 Bartolomeo Assenza,
Bacterial colonization of the peri-implant sulcus in dentate patients: a prospective observational study
 Clin Oral Invest (2017) 21:717 724 DOI 10.1007/s00784-016-1941-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bacterial colonization of the peri-implant sulcus in dentate patients: a prospective observational study M. A. Stokman
Clin Oral Invest (2017) 21:717 724 DOI 10.1007/s00784-016-1941-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bacterial colonization of the peri-implant sulcus in dentate patients: a prospective observational study M. A. Stokman
Case study 2. A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant
 Case study 2 A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant Benny Karmon DMD, Jerry Kohen DMD, Ariel Lor DMD, Yiftach Gratciany DMD, Zvi Laster DMD, Gideon Hallel DMD MPA, Tsvia Karmon A Retrospective
Case study 2 A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant Benny Karmon DMD, Jerry Kohen DMD, Ariel Lor DMD, Yiftach Gratciany DMD, Zvi Laster DMD, Gideon Hallel DMD MPA, Tsvia Karmon A Retrospective
Predictors of Peri-implant Bone Loss During Long-Term Maintenance of Patients Treated with 10-mm Implants and Single Crown Restorations
 Predictors of Peri-implant Bone Loss During Long-Term Maintenance of Patients Treated with 10-mm Implants and Single Crown Restorations Manuel De la Rosa, DDS, MSc 1 /Angel Rodríguez, DDS 1 /Katia Sierra,
Predictors of Peri-implant Bone Loss During Long-Term Maintenance of Patients Treated with 10-mm Implants and Single Crown Restorations Manuel De la Rosa, DDS, MSc 1 /Angel Rodríguez, DDS 1 /Katia Sierra,
Longitudinal Supportive Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Furcation Involvement: A 12-year Follow-up Report
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2013) 54(4): 243 250 Case Report Longitudinal Supportive Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Furcation Involvement: A 12-year Follow-up Report Akiyo Komiya-Ito,
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2013) 54(4): 243 250 Case Report Longitudinal Supportive Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Furcation Involvement: A 12-year Follow-up Report Akiyo Komiya-Ito,
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
ARESTIN (minocycline hcl) subgingival powder
 ARESTIN (minocycline hcl) subgingival powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
ARESTIN (minocycline hcl) subgingival powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2014) 55(4): 217 224 Case Report Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report Takashi
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2014) 55(4): 217 224 Case Report Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report Takashi
Peri-implant marginal bone loss: What is the current concensus? an academic controversy or a clinical challenge?
 Peri-implant marginal bone loss; What is the current concensus? Bjorn.Klinge@mah.se Peri-implant marginal bone loss: an academic controversy or a clinical challenge? Björn Klinge Eur J Oral Implantol 2012;5
Peri-implant marginal bone loss; What is the current concensus? Bjorn.Klinge@mah.se Peri-implant marginal bone loss: an academic controversy or a clinical challenge? Björn Klinge Eur J Oral Implantol 2012;5
Associations of clinical characteristics and interval between maintenance visits with peri-implant pathology
 143 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 56, No. 2, 143-150, 2014 Original Associations of clinical characteristics and interval between maintenance visits with peri-implant pathology Miguel A. de Araújo Nobre
143 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 56, No. 2, 143-150, 2014 Original Associations of clinical characteristics and interval between maintenance visits with peri-implant pathology Miguel A. de Araújo Nobre
Over the past few decades, an improved
 RESEARCH SANDBLASTED/ACID-ETCHED VS SMOOTH- SURFACE IMPLANTS: IMPLANT MOBILITY AND CLINICAL REACTION TO EXPERIMENTALLY INDUCED PERI-IMPLANTITIS IN BEAGLE DOGS Rodrigo Tadashi Martines, DDS; Wilson Roberto
RESEARCH SANDBLASTED/ACID-ETCHED VS SMOOTH- SURFACE IMPLANTS: IMPLANT MOBILITY AND CLINICAL REACTION TO EXPERIMENTALLY INDUCED PERI-IMPLANTITIS IN BEAGLE DOGS Rodrigo Tadashi Martines, DDS; Wilson Roberto
Correlations between clinical parameters in implant maintenance patients: analysis among healthy and history-of-periodontitis groups
 Seki et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2017) 3:45 DOI 10.1186/s40729-017-0108-0 International Journal of Implant Dentistry RESEARCH Correlations between clinical parameters in implant
Seki et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2017) 3:45 DOI 10.1186/s40729-017-0108-0 International Journal of Implant Dentistry RESEARCH Correlations between clinical parameters in implant
Volume 2 Issue
 Volume 2 Issue 2 2017 Page 333 to 340 Research Article Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 The Anti-Inflammatory Actions of an Intra-Oral Adhesive Patch Containing Botanical Extracts Exert Inhibitory
Volume 2 Issue 2 2017 Page 333 to 340 Research Article Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 The Anti-Inflammatory Actions of an Intra-Oral Adhesive Patch Containing Botanical Extracts Exert Inhibitory
The clinical use of endosseous implants has
 A Prospective Multicenter Clinical Trial of 3i Machined-Surface Implants: Results After 6 Years of Follow-up Dietmar Weng, DDS, Dr Med Dent 1 /Zhimon Jacobson, DDS 2 /Dennis Tarnow, DDS 3 / Markus B. Hürzeler,
A Prospective Multicenter Clinical Trial of 3i Machined-Surface Implants: Results After 6 Years of Follow-up Dietmar Weng, DDS, Dr Med Dent 1 /Zhimon Jacobson, DDS 2 /Dennis Tarnow, DDS 3 / Markus B. Hürzeler,
Effect of thread size on the implant neck area: preliminary results at 1 year of function
 Young-Il Kang* Dong-Won Lee* Kwang-Ho Park Ik-Sang Moon Effect of thread size on the implant neck area: preliminary results at 1 year of function Authors affiliations: Young-Il Kang*, Dong-Won Lee*, Ik-Sang
Young-Il Kang* Dong-Won Lee* Kwang-Ho Park Ik-Sang Moon Effect of thread size on the implant neck area: preliminary results at 1 year of function Authors affiliations: Young-Il Kang*, Dong-Won Lee*, Ik-Sang
Endosseous dental implants initially showed very
 Five-mm-Diameter Implants without a Smooth Surface Collar: Report on 98 Consecutive Placements Franck Renouard, DDS*/Jean-Pierre Arnoux, DDS**/David P. Sarment, DDS*** In recent years, indications for
Five-mm-Diameter Implants without a Smooth Surface Collar: Report on 98 Consecutive Placements Franck Renouard, DDS*/Jean-Pierre Arnoux, DDS**/David P. Sarment, DDS*** In recent years, indications for
Multidisciplinary treatment planning for patients with severe periodontal disease
 Clinical Multidisciplinary treatment planning for patients with severe periodontal disease Josselin Lethuillier, 1 Sébastien Felenc, 2 Philippe Bousquet 3 Abstract Periodontally compromised patients usually
Clinical Multidisciplinary treatment planning for patients with severe periodontal disease Josselin Lethuillier, 1 Sébastien Felenc, 2 Philippe Bousquet 3 Abstract Periodontally compromised patients usually
The Endodontic / Implant Controversy
 The Endodontic / Implant Controversy Innovations in Endodontics Series Robert Handysides DDS Associate Professor and Chair Department of Endodontics Loma Linda University School of Dentistry Endodontic
The Endodontic / Implant Controversy Innovations in Endodontics Series Robert Handysides DDS Associate Professor and Chair Department of Endodontics Loma Linda University School of Dentistry Endodontic
Endosseous cylindric implants are well accepted
 Soft Tissue Exposure of Endosseous Implants Between Stage I and Stage II Surgery as a Potential Indicator of Early Crestal Bone Loss Joseph A. Toljanic, DDS*/Mark L. Banakis, DDS**/Leslee A. K. Willes,
Soft Tissue Exposure of Endosseous Implants Between Stage I and Stage II Surgery as a Potential Indicator of Early Crestal Bone Loss Joseph A. Toljanic, DDS*/Mark L. Banakis, DDS**/Leslee A. K. Willes,
Impact of Photodynamic Therapy Applied by FotoSan on Periodontal Tissues Clinical Parameters
 Impact of Photodynamic Therapy Applied by FotoSan on Periodontal Tissues Clinical Parameters REVIEWED PAPER Most patients visiting dental surgeries suffer from various types of periodontopathies. Since
Impact of Photodynamic Therapy Applied by FotoSan on Periodontal Tissues Clinical Parameters REVIEWED PAPER Most patients visiting dental surgeries suffer from various types of periodontopathies. Since
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
STABILITY OF IMPLANTS AND NATURAL TEETH MONTHS OF FUNCTION AS DETERMINED BY THE PERIOTEST OVER 60 CLINICAL
 CLINICAL STABILITY OF IMPLANTS AND NATURAL TEETH AS DETERMINED BY THE PERIOTEST OVER 60 MONTHS OF FUNCTION Sheldon Winkler, DDS Harold F. Morris, DDS, MS J. Robert Spray, DDS KEY WORDS Implant Natural
CLINICAL STABILITY OF IMPLANTS AND NATURAL TEETH AS DETERMINED BY THE PERIOTEST OVER 60 MONTHS OF FUNCTION Sheldon Winkler, DDS Harold F. Morris, DDS, MS J. Robert Spray, DDS KEY WORDS Implant Natural
Buccal Bone Resorption Around Posterior Implants After Surgery: A 1-Year Prospective Study
 Buccal Bone Resorption Around Posterior Implants After Surgery: A 1-Year Prospective Study Toshio Takuma, DDS 1,2 /Keiji Oishi, DDS, PhD 3 /Tomofusa Manabe, DT 2 / Satoshi Yoneda, DDS, PhD 4 /Toshihiko
Buccal Bone Resorption Around Posterior Implants After Surgery: A 1-Year Prospective Study Toshio Takuma, DDS 1,2 /Keiji Oishi, DDS, PhD 3 /Tomofusa Manabe, DT 2 / Satoshi Yoneda, DDS, PhD 4 /Toshihiko
Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Ankylos. Scientific Summary
 Ankylos Scientific Summary Implanting TissueCare For over 25 years, the Ankylos implant system stands for stable, long-term esthetics. The results from numerous publications and long-term clinical experience
Ankylos Scientific Summary Implanting TissueCare For over 25 years, the Ankylos implant system stands for stable, long-term esthetics. The results from numerous publications and long-term clinical experience
Case Report Immediate, Early, and Conventional Implant Placement in a Patient with History of Periodontitis
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 217895, 10 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/217895 Case Report Immediate, Early, and Conventional Implant Placement in a Patient with History of Periodontitis
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 217895, 10 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/217895 Case Report Immediate, Early, and Conventional Implant Placement in a Patient with History of Periodontitis
Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around Implants Placed in Healed Sockets: A Cross-sectional Study
 JDSOR ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1099 Implants Placed in Healed Sockets Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around Implants Placed
JDSOR ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1099 Implants Placed in Healed Sockets Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around Implants Placed
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis
 Martin Saaby Eva Karring Søren Schou Flemming Isidor Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis Authors affiliations: Martin Saaby, Søren Schou, Section for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Oral
Martin Saaby Eva Karring Søren Schou Flemming Isidor Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis Authors affiliations: Martin Saaby, Søren Schou, Section for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Oral
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel
 PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
Diabetes and Periodontal Disease. Brianne Neelis & Katie Torres. Literature Review 1 11/4/08
 1 Diabetes and Periodontal Disease Brianne Neelis & Katie Torres Literature Review 1 11/4/08 2 Introduction Diabetes is a cardiovascular condition that effects an estimated 20 million people in the United
1 Diabetes and Periodontal Disease Brianne Neelis & Katie Torres Literature Review 1 11/4/08 2 Introduction Diabetes is a cardiovascular condition that effects an estimated 20 million people in the United
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial
 Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
A study of the consequences of smoking on periodontal health
 A study of the consequences of smoking on periodontal health Cristina Gabriela Puscasu1, Irina Totolici 2, Anca Silvia Dumitriu 3, Dragos Totolici 4, Doru Petrovici 5 Constanta, Romania Abstract Background:
A study of the consequences of smoking on periodontal health Cristina Gabriela Puscasu1, Irina Totolici 2, Anca Silvia Dumitriu 3, Dragos Totolici 4, Doru Petrovici 5 Constanta, Romania Abstract Background:
The Effects of Anti-infective Preventive Measures on the Occurrence of Biologic Implant Complications and Implant Loss: A Systematic Review
 The Effects of Anti-infective Preventive Measures on the Occurrence of Biologic Implant Complications and Implant Loss: A Systematic Review Giovanni E. Salvi, DMD, Prof Dr Med Dent 1 /Nicola U. Zitzmann,
The Effects of Anti-infective Preventive Measures on the Occurrence of Biologic Implant Complications and Implant Loss: A Systematic Review Giovanni E. Salvi, DMD, Prof Dr Med Dent 1 /Nicola U. Zitzmann,
Periodontist-Dental Hygienist Collaboration in Periodontal Care for Chronic Periodontitis: An 11-year Case Report
 ull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 177 186 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0039 Periodontist-Dental Hygienist Collaboration in Periodontal Care for Chronic Periodontitis: An 11-year Case Report
ull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 177 186 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0039 Periodontist-Dental Hygienist Collaboration in Periodontal Care for Chronic Periodontitis: An 11-year Case Report
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
IMPLANTS. Guideline Number: DCG Effective Date: January 1, 2018
 IMPLANTS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG007.04 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1 COVERAGE RATIONALE...1
IMPLANTS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG007.04 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1 COVERAGE RATIONALE...1
What You Should Know About Dental Implants: The Process of Care Applies
 Learn how the process of care model can apply to dental implants and empower decisions for providing quality care for clients. Starting with assessing the need for implants, the process covers documentation,
Learn how the process of care model can apply to dental implants and empower decisions for providing quality care for clients. Starting with assessing the need for implants, the process covers documentation,
The effect of peri-implant bone exposure on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
INTRODUCTION TO DENTAL IMPLANTOLOGY HISTORY OF DENTAL IMPLANTS EUGENIA PROKOPETS, DDS LSU PERIODONTICS
 INTRODUCTION TO DENTAL IMPLANTOLOGY HISTORY OF DENTAL IMPLANTS EUGENIA PROKOPETS, DDS LSU PERIODONTICS Thank you Dr. Simmons BEFORE THE COMMON ERA 16TH AND 17TH CENTURIES Archeological records from China
INTRODUCTION TO DENTAL IMPLANTOLOGY HISTORY OF DENTAL IMPLANTS EUGENIA PROKOPETS, DDS LSU PERIODONTICS Thank you Dr. Simmons BEFORE THE COMMON ERA 16TH AND 17TH CENTURIES Archeological records from China
Many of the problems reported by conventional
 Maxillary Overdentures Retained by Splinted and Unsplinted Implants: A Retrospective Study Timo O. Närhi, DDS, PhD 1 /Miluska Hevinga, DDS 2 / Ralph A. C. A. Voorsmit, DDS, PhD 3 /Warner Kalk, DDS, PhD
Maxillary Overdentures Retained by Splinted and Unsplinted Implants: A Retrospective Study Timo O. Närhi, DDS, PhD 1 /Miluska Hevinga, DDS 2 / Ralph A. C. A. Voorsmit, DDS, PhD 3 /Warner Kalk, DDS, PhD
Effect of Systemically Administered Azithromycin in Early Onset Aggressive Periodontitis
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORTS Effect of Systemically Administered Azithromycin in Early Onset Aggressive Periodontitis Takeo Fujii, Pao-Li Wang, Yoichiro Hosokawa, Shinichi Shirai, Atsumu Tamura, Kazuhiro
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORTS Effect of Systemically Administered Azithromycin in Early Onset Aggressive Periodontitis Takeo Fujii, Pao-Li Wang, Yoichiro Hosokawa, Shinichi Shirai, Atsumu Tamura, Kazuhiro
THE EFFICIENCY OF INITIAL PHASE TREATMENT IN CHRONIC MARGINAL PERIODONTITIS
 THE EFFICIENCY OF INITIAL PHASE TREATMENT IN CHRONIC MARGINAL PERIODONTITIS Adriana Monea, Lecturer, DMD, PhD Department of Odontology and Periodontology Faculty of Dental Medicine, UMF Tîrgu-Mureş, Romania
THE EFFICIENCY OF INITIAL PHASE TREATMENT IN CHRONIC MARGINAL PERIODONTITIS Adriana Monea, Lecturer, DMD, PhD Department of Odontology and Periodontology Faculty of Dental Medicine, UMF Tîrgu-Mureş, Romania
The surgical placement of dental implants has
 Flapless Implant Surgery: A 10-year Clinical Retrospective Analysis Luis Dominguez Campelo, DDS 1 /Jose R. Dominguez Camara, MD, DDS 2 Purpose: This article is a retrospective clinical analysis of implants
Flapless Implant Surgery: A 10-year Clinical Retrospective Analysis Luis Dominguez Campelo, DDS 1 /Jose R. Dominguez Camara, MD, DDS 2 Purpose: This article is a retrospective clinical analysis of implants
Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports
 0 Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports R.G. Caffesse, B.A. Smith/ B. Duff, E.C. Morrison, D. Merrill/ and W. Becker In the cases reported here, the response
0 Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports R.G. Caffesse, B.A. Smith/ B. Duff, E.C. Morrison, D. Merrill/ and W. Becker In the cases reported here, the response
Outcome of dental implants in patients with a history of periodontitis
 Joint Degree Master Program of the International Medical College and the Universities Dresden, Essen, Saarland, Leipzig, Szeged and Bangkok Scientific director: Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. Dr. med. dent. Dr.
Joint Degree Master Program of the International Medical College and the Universities Dresden, Essen, Saarland, Leipzig, Szeged and Bangkok Scientific director: Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. Dr. med. dent. Dr.
JSS Medical and Dental College and Hospital, JSS University, Mysore, India *Author for Correspondence
 CLINICAL, MICROBIOLOGICAL AND MOLECULAR STUDY OF PORPHYROMONAS GINGIVALIS IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS *Mayuri Vajawat 1, Vijay Kumar 2, K.G. Rajeshwari 3 and P.C. Deepika 4 1&4 Department of
CLINICAL, MICROBIOLOGICAL AND MOLECULAR STUDY OF PORPHYROMONAS GINGIVALIS IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS *Mayuri Vajawat 1, Vijay Kumar 2, K.G. Rajeshwari 3 and P.C. Deepika 4 1&4 Department of
During the last 30 years, endosseous oral
 Influence of Variations in Implant Diameters: A 3- to 5-Year Retrospective Clinical Report Carl-Johan Ivanoff, DDS*/Kerstin Gröndahl, DDS, PhD**/Lars Sennerby, DDS, PhD***/ Christina Bergström, MSc****/Ulf
Influence of Variations in Implant Diameters: A 3- to 5-Year Retrospective Clinical Report Carl-Johan Ivanoff, DDS*/Kerstin Gröndahl, DDS, PhD**/Lars Sennerby, DDS, PhD***/ Christina Bergström, MSc****/Ulf
Materials and Methods: Literature review and Authors opinion.
 Haffajee AD, Bogren A, Hasturk H et al. Subgingival microbiota of chronic periodontitis subjects from different geographic locations. J Clin Periodontol 2004; 31:996-1002. Purpose: To compare the subgingival
Haffajee AD, Bogren A, Hasturk H et al. Subgingival microbiota of chronic periodontitis subjects from different geographic locations. J Clin Periodontol 2004; 31:996-1002. Purpose: To compare the subgingival
Periimplant diseases: where are we now? Consensus of the Seventh European Workshop on Periodontology
 Article Periimplant diseases: where are we now? Consensus of the Seventh European Workshop on Periodontology LANG, Niklaus P, BERGLUNDH, Tord, MOMBELLI, Andrea Abstract Peri-implant diseases present in
Article Periimplant diseases: where are we now? Consensus of the Seventh European Workshop on Periodontology LANG, Niklaus P, BERGLUNDH, Tord, MOMBELLI, Andrea Abstract Peri-implant diseases present in
There is overwhelming evidence that implant-retained
 CLINICAL Two-Year Success Rate of Implant-Retained Mandibular Overdentures by Novice General Dentistry Residents Hans Malmstrom, DDS 1 * Jin Xiao, DDS, MS, PhD 1 Georgios Romanos, DDS, PhD 1,2 Yan-Fang
CLINICAL Two-Year Success Rate of Implant-Retained Mandibular Overdentures by Novice General Dentistry Residents Hans Malmstrom, DDS 1 * Jin Xiao, DDS, MS, PhD 1 Georgios Romanos, DDS, PhD 1,2 Yan-Fang
Developing Keratinized Mucosa Around Nonsubmerged Dental Implants. Part I: The Use of Vascularized Flaps
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORTS Developing Keratinized Mucosa Around Nonsubmerged Dental Implants. Part I: The Use of Vascularized Flaps Jay R. Beagle Despite the continued debate regarding the need for
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORTS Developing Keratinized Mucosa Around Nonsubmerged Dental Implants. Part I: The Use of Vascularized Flaps Jay R. Beagle Despite the continued debate regarding the need for
Tooth Retained Implant: No More an Oxymoron
 بنام خدا بنام خدا OPEN ACCESS Freely Available Online Original Hypothesis Tooth Retained Implant: No More an Oxymoron Divya Bhat a Abstract a Department of Periodontics, D.A.P.M.R.V. Dental College, Karnataka,
بنام خدا بنام خدا OPEN ACCESS Freely Available Online Original Hypothesis Tooth Retained Implant: No More an Oxymoron Divya Bhat a Abstract a Department of Periodontics, D.A.P.M.R.V. Dental College, Karnataka,
Citation for published version (APA): de Waal, Y. C. M. (2015). Peri-implant infections [Groningen]: University of Groningen
![Citation for published version (APA): de Waal, Y. C. M. (2015). Peri-implant infections [Groningen]: University of Groningen Citation for published version (APA): de Waal, Y. C. M. (2015). Peri-implant infections [Groningen]: University of Groningen](/thumbs/82/86452679.jpg) University of Groningen Peri-implant infections de Waal, Yvonne IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Peri-implant infections de Waal, Yvonne IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Ucer, C; Wright, S; Scher E; West, N; Retzepi, M; Simpson, S; Slade, K; Donos, N
 ADI GUIDELINES On Peri-implant Monitoring and Maintenance Ucer, C; Wright, S; Scher E; West, N; Retzepi, M; Simpson, S; Slade, K; Donos, N Scope of the Problem: During the last two decades implant treatment
ADI GUIDELINES On Peri-implant Monitoring and Maintenance Ucer, C; Wright, S; Scher E; West, N; Retzepi, M; Simpson, S; Slade, K; Donos, N Scope of the Problem: During the last two decades implant treatment
PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1
 PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1 Overview A 32 year-old patient presented with generalized aggressive periodontitis. Treatment included non-surgical therapy with adjunctive antibiotics and surgical treatment.
PERIODONTAL CASE PRESENTATION - 1 Overview A 32 year-old patient presented with generalized aggressive periodontitis. Treatment included non-surgical therapy with adjunctive antibiotics and surgical treatment.
Microbial Complexes Detected in the Second/Third Molar Region in Patients With Asymptomatic Third Molars
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:1234-1240, 2002 Microbial Complexes Detected in the Second/Third Molar Region in Patients With Asymptomatic Third Molars Raymond P. White, Jr, DDS, PhD,* Phoebus N. Madianos,
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:1234-1240, 2002 Microbial Complexes Detected in the Second/Third Molar Region in Patients With Asymptomatic Third Molars Raymond P. White, Jr, DDS, PhD,* Phoebus N. Madianos,
Peri-implant diseases at a glance do we have all the answers?
 412 > http://dx.doi.org/10.17159/2519-0105/2018/v73no6a5 Peri-implant diseases at a glance do we have all the answers? 2018 Theme Article: Oral manifestations of systemic disease SADJ July 2018, Vol 73
412 > http://dx.doi.org/10.17159/2519-0105/2018/v73no6a5 Peri-implant diseases at a glance do we have all the answers? 2018 Theme Article: Oral manifestations of systemic disease SADJ July 2018, Vol 73
Implant osseointegration and successful restoration
 Prosthodontic Complications in a Prospective Clinical Trial of Single-stage Implants at 36 Months Jacqueline P. Duncan, DMD, MDSc 1 /Elena Nazarova, DMD, PhD 2 /Theodora Vogiatzi, DDS 1 / Thomas D. Taylor,
Prosthodontic Complications in a Prospective Clinical Trial of Single-stage Implants at 36 Months Jacqueline P. Duncan, DMD, MDSc 1 /Elena Nazarova, DMD, PhD 2 /Theodora Vogiatzi, DDS 1 / Thomas D. Taylor,
JOMI on CD-ROM, 1990 Mar ( ): The Applicability of Osseointegrated Oral Imp
 The Applicability of Osseointegrated Oral Implants in the Rehabilitation of Partial Edentulism: A Prospective Multicenter Study on 558 Fixtures Daniel van Steenberghe, MD, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS, PhD/Charles
The Applicability of Osseointegrated Oral Implants in the Rehabilitation of Partial Edentulism: A Prospective Multicenter Study on 558 Fixtures Daniel van Steenberghe, MD, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS, PhD/Charles
TwinLight TM Periodontal Treatment. Tomaž Lipoglavšek, DMD
 TwinLight TM Periodontal Treatment Tomaž Lipoglavšek, DMD REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE 2 The available evidence consistently shows that therapies intended to arrest and control periodontitis depend primarily
TwinLight TM Periodontal Treatment Tomaž Lipoglavšek, DMD REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE 2 The available evidence consistently shows that therapies intended to arrest and control periodontitis depend primarily
Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient. Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club
 Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club Periodontal Maintenance for Natural Teeth and Implants What is Periodontal Maintenance?
Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club Periodontal Maintenance for Natural Teeth and Implants What is Periodontal Maintenance?
Microbial and Genetic Testing in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease
 Microbial and Genetic Testing in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease Mr P.Renton-Harper Specialist in Periodontics prh@perio.co.uk www.perio.co.uk Periodontal Disease A bacterial infection in a susceptible
Microbial and Genetic Testing in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease Mr P.Renton-Harper Specialist in Periodontics prh@perio.co.uk www.perio.co.uk Periodontal Disease A bacterial infection in a susceptible
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
With the establishment of evaluation
 J Periodontol December 2009 Comparative Analysis of Peri-Implant Marginal Bone Loss Based on Microthread Location: A 1-Year Prospective Study After Loading Dong-Wook Song,* Dong-Won Lee,* Chong-Kwan Kim,
J Periodontol December 2009 Comparative Analysis of Peri-Implant Marginal Bone Loss Based on Microthread Location: A 1-Year Prospective Study After Loading Dong-Wook Song,* Dong-Won Lee,* Chong-Kwan Kim,
Failures in implant therapy. Biological and mechanical complications. Their prevention management. Dr. Katalin Csurgay Dr.
 Failures in implant therapy. Biological and mechanical complications. Their prevention management. Dr. Katalin Csurgay Dr. Tatiana Shkolnik Complications could be: Doctor related Patient related Early
Failures in implant therapy. Biological and mechanical complications. Their prevention management. Dr. Katalin Csurgay Dr. Tatiana Shkolnik Complications could be: Doctor related Patient related Early
BONE HEALING AT A FAILED IMPLANT SITE. HISTOLOGIC EVALUATIONS: ACASE REPORT Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD IN A TYPE II DIABETIC PATIENT: CLINICAL AND
 CLINICAL BONE HEALING AT A FAILED IMPLANT SITE IN A TYPE II DIABETIC PATIENT: CLINICAL AND HISTOLOGIC EVALUATIONS: ACASE REPORT Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD Placement of endosseous dental implants in diabetic
CLINICAL BONE HEALING AT A FAILED IMPLANT SITE IN A TYPE II DIABETIC PATIENT: CLINICAL AND HISTOLOGIC EVALUATIONS: ACASE REPORT Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD Placement of endosseous dental implants in diabetic
Periodontal Case Report
 Periodontal Case Report By Dan AlAhmed 431200041 Saleha AlZahrani 431200123 Raghad AlSaawy 431200297 Afnan AlAssiri 431200687 Mawadh Demyati 431200824 Hend Jaddoh 431201247 Alaa AlDoss 431201808 Rawan
Periodontal Case Report By Dan AlAhmed 431200041 Saleha AlZahrani 431200123 Raghad AlSaawy 431200297 Afnan AlAssiri 431200687 Mawadh Demyati 431200824 Hend Jaddoh 431201247 Alaa AlDoss 431201808 Rawan
GuidedService. The ultimate guide for precise implantations
 GuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations ABGuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations At A.B. Dental we've brought implantology into the future with a 3D digitally planned
GuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations ABGuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations At A.B. Dental we've brought implantology into the future with a 3D digitally planned
Citation for published version (APA): Hoeksema, A. (2016). Oral health in frail elderly [Groningen]: Rijksuniversiteit Groningen
![Citation for published version (APA): Hoeksema, A. (2016). Oral health in frail elderly [Groningen]: Rijksuniversiteit Groningen Citation for published version (APA): Hoeksema, A. (2016). Oral health in frail elderly [Groningen]: Rijksuniversiteit Groningen](/thumbs/87/96311633.jpg) University of Groningen Oral health in frail elderly Hoeksema, Albert IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the
University of Groningen Oral health in frail elderly Hoeksema, Albert IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the
Immediate implant placement in molar regions: risk factors for early failure
 Thomas Urban Lambros Kostopoulos Ann Wenzel Immediate implant placement in molar regions: risk factors for early failure Authors affiliations: Thomas Urban, Department of Oral Radiology and Department
Thomas Urban Lambros Kostopoulos Ann Wenzel Immediate implant placement in molar regions: risk factors for early failure Authors affiliations: Thomas Urban, Department of Oral Radiology and Department
Dent Clin N Am 49 (2005) Peri-implantitis
 Dent Clin N Am 49 (2005) 661 676 Peri-implantitis Bjo rn Klinge, DDS, Odont Dr a, *, Margareta Hultin, DDS, Odont Dr a, Tord Berglundh, DDS, Odont Dr b a Karolinska Institutet, Institute of Odontology,
Dent Clin N Am 49 (2005) 661 676 Peri-implantitis Bjo rn Klinge, DDS, Odont Dr a, *, Margareta Hultin, DDS, Odont Dr a, Tord Berglundh, DDS, Odont Dr b a Karolinska Institutet, Institute of Odontology,
Periodontal disease is characterized by progressive periodontal pathogens. It is known that coronary heart disease is
 ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com PREVALENCE OF PERIODONTAL DISEASES IN PATIENTS WITH CORONARY HEART DISEASE Niha Naveed* BDS student, Saveetha
ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com PREVALENCE OF PERIODONTAL DISEASES IN PATIENTS WITH CORONARY HEART DISEASE Niha Naveed* BDS student, Saveetha
FACULTY OF HEALTH SCIENCES INSTITUTE OF CLINICAL DENTISTRY
 Professor Gottfried Schmalz Editor-in-Chief Clinical Oral Investigations Universität Regensburg Fakultät für Medizin Poliklinik für Zahnerhatungskunde und Parodontologie Frans-Josef-Strauss-Allee 11 93053
Professor Gottfried Schmalz Editor-in-Chief Clinical Oral Investigations Universität Regensburg Fakultät für Medizin Poliklinik für Zahnerhatungskunde und Parodontologie Frans-Josef-Strauss-Allee 11 93053
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
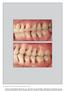 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 395 Clinical Case Report on Treatment of Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis: 5-Year Follow-up Kai-Fang Hu, DDS, MD 1 /Ya-Ping Ho, DDS,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 395 Clinical Case Report on Treatment of Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis: 5-Year Follow-up Kai-Fang Hu, DDS, MD 1 /Ya-Ping Ho, DDS,
