Nasolabial Flap Reconstruction of Oral Cavity Defects: A Report of 18 Cases
|
|
|
- Meredith James
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 58: , 2000 Nasolabial Flap Reconstruction of Oral Cavity Defects: A Report of 18 Cases Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCS (C),* and Mark Burye, DDS Purpose: This article describes the successful use of pedicled nasolabial flaps in the reconstruction of various oral cavity defects with or without adjunctive microvascular free tissue transfer. Patients and Methods: Twenty-eight flaps were performed in 18 patients, for a variety of oral cavity defects. Results: All flaps healed without evidence of necrosis, infection, or dehiscence. Patient satisfaction with this procedure was high. The use of the nasolabial flap appears to provide an improvement in overall functional outcome. Conclusions: The inferiorly based nasolabial flap provides reliable coverage of intermediate-sized oral cavity defects when used alone. It can improve mastication and speech when used in conjunction with microvascular free tissue transfer for the reconstruction of large combined defects of the tongue and floor of mouth American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons With the increasingly widespread application of reliable microvascular free tissue transfer techniques for oral cavity reconstruction, the routine need for a variety of local and regional flaps has decreased. However, a number of such flaps remain quite useful and should be included in the modern armamentarium of the reconstructive surgeon. Often, a combination of local and distant flaps is required to optimize the functional outcome after oral reconstruction. In this article, the focus is on the utility of the pedicled nasolabial flap to achieve this goal. The subcutaneous pedicled nasolabial flap appears to have been originally described in the works of Sushruta in 600 BC. 1 For centuries thereafter it was used primarily in external nasal reconstruction. Thiersch 2 was the first to use a transbuccal transfer of this flap for closure of an oral cavity defect. Subsequently, Esser 3 reported use of a cutaneous nasolabial flap transferred in 2 stages to increase its reliability. Wallace 4 and Rose 5 later reported modifications of the basic flap, allowing for single-stage transfer. Several * Assistant Professor, Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery at the University of Texas South Western Medical Center, Dallas, TX and Director, Division of Otolaryngology and Facial Plastic Surgery, John Peter Smith Hospital, Fort Worth, TX. Resident, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, John Peter Smith Hospital, Ft Worth, TX. Address correspondence and reprint requests to Dr Ducic: Director, Otolaryngology and Facial Plastic Surgery, 1500 S Main St, Fort Worth, TX 76092; yducic@aol.com 2000 American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons /00/ $3.00/0 doi: /joms authors have reported favorable outcomes when this flap was used to cover various oral cavity defects. 6-9 However, none has reported its adjunctive role with simultaneous free tissue transfer for oral cavity reconstruction. In this article, an overview of a favorable experience with the use of the nasolabial flap for closure of oral cavity defects is presented. When these flaps should be transferred as a single stage, under what circumstances a second stage will be required, and the adjunctive role of these flaps in microvascular oromandibular reconstruction is also discussed. Technique For oral cavity reconstruction, the use of an inferiorly based nasolabial flap is preferred. The medial incision line precisely follows the nasofacial fold in its superior two thirds (Fig 1) and is located 3 to 4 mm medial to the nasolabial fold in its inferior third (Fig 2). This will cause less distortion after flap transfer and allow for an improved arc of rotation. The base of the flap should be 1.5 to 2.5 cm in width (Fig 3). Flaps of greater width are difficult to effectively rotate into position, whereas flaps with a narrower base may have a compromised blood supply and will provide only a limited amount of tissue for transfer. The medial and lateral limbs of the incision taper together superiorly approximately 0.5 to 0.75 cm anterior to the medial canthus. The inferior limit of the flap is at the level of the oral commissure. When coverage for lateral oral cavity defects (lateral one third of the palate, alveolus, floor of mouth, and retromolar trigone) is required, a 1104
2 DUCIC AND BURYE 1105 aspect of the dissection. The transbuccal tunnel is made next according to the site of the defect in the oral cavity as described previously. The tunnel should be large enough to easily accommodate 1 or 2 fingers (1.5 to 2.0 cm). The flap is then transferred into the oral cavity in a tension-free manner and inset with a series of interrupted 3-0 absorbable sutures. Generous undermining of the donor site is performed in the subcutaneous plane as for a skin-lift rhytidectomy. Layered closure of the donor defect is then performed (Fig 5). An attempt is made to evert the skin along the nasofacial portion of the incision to achieve a flat scar once healing is completed. However, along the nasolabial fold, a slightly depressed scar (hence, minimal eversion at the time of closure) results in a more natural appearance. In cases in which a second stage is required, division and inset of the flap is generally performed 3 weeks after the initial procedure. Most patients are able to tolerate a soft diet during this period. During flap division, it is important to remove all of the transbuccal component of the flap rather than to FIGURE 1. Initial presurgical planning with proposed incision line precisely following the nasolabial fold. single-stage nasolabial flap can be used. The inferior 2 to 2.5 cm of the flap is deepithelialized with a no. 15 scalpel blade (Fig 4). For defects of the palate, upper alveolus, and retromolar trigone, a transbuccal tunnel is fashioned with Metzenbaum scissors at the posterior aspect of the upper gingivobuccal sulcus. To accomplish a single-stage closure of defects of the lateral one third of the floor of mouth and lower alveolus, the transbuccal tunnel is made at the posterior aspect of the lower gingivobuccal sulcus. If the defect is in the central one third of the oral cavity (central palate, floor of mouth, upper and lower alveolus) or anterior tongue, a 2-stage nasolabial flap will be required, and the necessity for bilateral flap harvest is significantly increased. Hence, only the inferior 1 to 1.5 cm of the flap is deepithelialized. A transbuccal tunnel is fashioned at the level of the posterior bite margin to facilitate transfer. With the planning completed, the flap is raised from superior to inferior in a supramuscular plane by using dissecting scissors. The angular branch of the facial artery often needs to be tied off in the superior FIGURE 2. Placing the inferior one third to one half of the nasolabial portion of the incision medial to the fold will allow for an improved arc of rotation and aesthetic result.
3 1106 NASOLABIAL FLAP RECONSTRUCTION OF THE ORAL CAVITY tongue, with the microvascular flap providing for reconstruction of other areas of the oral cavity. In this subset of oromandibular reconstructions, all were able to maintain their weight with a soft diet. This is remarkable in that each of these patients had large combined defects of the oral cavity. All flaps healed without any evidence of necrosis. Discussion Even relatively small defects of the oral cavity often require reconstruction to avoid anatomic distortion and subsequent limitation of function. This is especially important in reconstruction of combined defects of the anterolateral tongue and floor of mouth. We believe that, although simple to perform, splitthickness graft reconstruction of these defects or the use of a single cutaneous paddle from a microvascular free tissue transfer, frequently will not provide optimal functional restoration after oncologic resection. In fact, in this series, 3 patients underwent reversal of tethering of the tongue by incision, release, and interposition of pedicled nasolabial flaps. All of them had FIGURE 3. Presurgical markings completed. The base of the flap is 2 cm wide in this patient. simply divide it flush with the cheek tissue on the oral cavity side. Failure to do so will invariably result in the presence of a visible long-term fullness at the level of the lateral commissure. Results A total of 28 flaps were performed in 18 patients by the senior author (Y.D.). One patient underwent a repeated bilateral nasolabial flap harvest. The most common defect site in the oral cavity was the anterolateral tongue (Tables 1, 2). Three patients underwent secondary reconstruction to release tongues that were functionally tethered anteriorly. All of this subset of patients had significant improvement in speech clarity and masticatory capacity, and there was a reversal of chronic aspiration in 1 case. Five patients with complex combined defects of the oral cavity (9 nasolabial flaps) underwent simultaneous microvascular free tissue transfer (3 radial forearm fasciocutaneous flaps, 2 fibula osteomusculocutaneous flaps). In each case, the nasolabial flaps were used to provide independent reconstruction for the anterolateral FIGURE 4. Flap raised in a supramuscular plane of dissection and the inferior 2 cm deepithelialized in preparation for single-stage transfer.
4 DUCIC AND BURYE 1107 Table 2. CAUSE OF ORAL CAVITY DEFECTS Squamous Cell Carcinoma Osteoradionecrosis Wound Breakdown Tethered Tongue From Previous Surgery FIGURE 5. View of the donor site closure. previously undergone single modality reconstruction of the tongue and floor of mouth, and they now showed significant improvement in mastication, clarity of speech, and tongue mobility postoperatively. Performing primary nasolabial flap reconstruction of anterolateral tongue defects in conjunction with microvascular reconstruction of large floor of mouth and mandible defects appears to be safe, does not add significantly to the length of the procedure, and is associated with a significant improvement in functional outcome. The decision as to whether unilateral or bilateral flaps are required, or whether they may be safely and effectively transferred in 1 or 2 stages, should be based primarily on the size and location of the defect, as previously discussed. Generally, defects up to 4 Table 1. DEFECT SITES Anterior Tongue Lateral FOM Midline FOM Lateral Palate Midline Palate Retromolar Trigone Abbreviation: FOM, floor of mouth. 5 cm can be satisfactorily closed by using this technique. There has been some controversy over the nature of the blood supply to the inferiorly based nasolabial flap. 10,11 Some authors have even advocated performing nasolabial flaps on the side contralateral to a radical neck dissection to avoid basing the flap on a potentially compromised facial artery. We believe that the inferiorly based nasolabial flap can be raised as a random pattern flap, as evidenced by its viability in the face of transected ipsilateral facial arteries and the ability to raise a second (bilateral) set of nasolabial flaps in a single patient. We have performed 4 radical neck dissections ipsilateral to a nasolabial flap harvest at the same setting and have encountered no adverse effects. The nasolabial flap is generally outside of the radiation therapy portals used in combined modality therapy for oral cavity squamous cell carcinomas. Thus, its vascularity is generally not compromised in this patient population. The administration of planned postoperative external beam radiation therapy may, in fact, be beneficial, especially in males, because it limits subsequent hair growth along the flap and, thus, obviates the need for epilation. The nasolabial flap is a simple, effective, and safe flap with a low complication rate. Although not encountered in this series of patients, other authors have reported complications (infection, minor or major flap necrosis, wound dehiscence) occurring in a small minority of their patients. 12 Donor site morbidity is negligible in cases in which bilateral flaps have been raised. Asymmetry at the level of the nasolabial fold is noted in unilateral cases. The degree of asymmetry is lessened by broad undermining at the donor site. References 1. Pers M: Cheek flaps in partial rhinoplasty. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg 1:37, Thiersch C: Verschluss eines loches im harten gaumen durch dic weichtheile der wange. Arch Heilkunde 9:159, Esser JFS: Deckung von gaumendefekten mittels gestielter naso-labial-haultlappen. Deutsch Zeitschrift fur Chirurgie 147: 128, Wallace AF: Esser s skin flap for closing large palatal fistulae. Br J Plast Surg 19:322, Rose EH: One staged arterialised nasolabial island flap for floor of mouth reconstruction. Ann Plast Surg 6:71, 1981
5 Morgan RF, Chambers RG, Jaques DA, et al: Nasolabial flap in intraoral reconstruction. Am J Surg 142:448, Gewirtz HS, Eilber FR, Zaram HA: Use of the nasolabial flap for reconstruction of the floor of the mouth. Am J Surg 136:508, Ioannides C, Fossion E: Nasolabial flap for the reconstruction of defects of the floor of mouth. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 20:40, Mutimer KL, Poole MD: A review of nasolabial flaps for intraoral defects. Br J Plast Surg 40:472, Hynes B, Boyd BB: The nasolabial flap: Axial or random? Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 114:1389, Herbert DC, Harrison RG: Nasolabial subcutaneous pedicle flaps. Br J Plast Surg 28:85, Ioannides C, Fossion E: Nasolabial flap for the reconstruction of defects of the floor of the mouth. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 20:40, 1991
Nasolabial flap reconstruction in oral cancer
 Singh et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2012, 10:227 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Nasolabial flap reconstruction in oral cancer Seema Singh, Rajesh Kumar Singh and Manoj
Singh et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2012, 10:227 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Nasolabial flap reconstruction in oral cancer Seema Singh, Rajesh Kumar Singh and Manoj
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY NASOLABIAL FLAP FOR ORAL CAVITY RECONSTRUCTION Harry Wright, Scott Stephan, James Netterville Designed as a true myocutaneous flap pedicled
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY NASOLABIAL FLAP FOR ORAL CAVITY RECONSTRUCTION Harry Wright, Scott Stephan, James Netterville Designed as a true myocutaneous flap pedicled
TitleNasolabial flap reconstruction of f. Ikeda, C; Katakura, A; Yamamoto, N; Author(s) Shibahara, T; Onoda, N; Tamura, H
 TitleNasolabial flap reconstruction of f Ikeda, C; Katakura, A; Yamamoto, N; Author(s) Shibahara, T; Onoda, N; Tamura, H Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/415
TitleNasolabial flap reconstruction of f Ikeda, C; Katakura, A; Yamamoto, N; Author(s) Shibahara, T; Onoda, N; Tamura, H Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/415
ALTHOUGH FIRST described
 The Cervicodeltopectoral Flap for Single-Stage Resurfacing of Anterolateral Defects of the Face and Neck Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCSC; Jesse E. Smith, MD SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Objective: To evaluate prospectively
The Cervicodeltopectoral Flap for Single-Stage Resurfacing of Anterolateral Defects of the Face and Neck Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCSC; Jesse E. Smith, MD SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Objective: To evaluate prospectively
Primary closure of the deltopectoral flap-donor site without skin grafting
 Primary closure of the deltopectoral flap-donor site without skin grafting Received: 4/3/2013 Accepted: 14/5/2013 Introduction Reliable and simultaneous reconstruction of head-and-neck defects has been
Primary closure of the deltopectoral flap-donor site without skin grafting Received: 4/3/2013 Accepted: 14/5/2013 Introduction Reliable and simultaneous reconstruction of head-and-neck defects has been
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 258 262 CASE REPORTS Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects Kenji Yano*, Ko Hosokawa, Tateki Kubo Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 258 262 CASE REPORTS Combined tongue flap and V Y advancement flap for lower lip defects Kenji Yano*, Ko Hosokawa, Tateki Kubo Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty
 CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
CASE REPORT Reconstruction and Characterization of Composite Mandibular Defects Requiring Double Skin Paddle Fibular Free Flaps
 CASE REPORT Reconstruction and Characterization of Composite Mandibular Defects Requiring Double Skin Paddle Fibular Free Flaps Austin M. Badeau, BA, a and Frederic W.-B. Deleyiannis, MD, MPhil, MPH b
CASE REPORT Reconstruction and Characterization of Composite Mandibular Defects Requiring Double Skin Paddle Fibular Free Flaps Austin M. Badeau, BA, a and Frederic W.-B. Deleyiannis, MD, MPhil, MPH b
An island flap based on the anterior branch of the superficial temporal artery for perioral defects
 Free full text on www.ijps.org Original Article An island flap based on the anterior branch of the superficial temporal artery for perioral defects V. Bhattacharya, Ganji Raveendra Reddy, Sheikh Adil Bashir,
Free full text on www.ijps.org Original Article An island flap based on the anterior branch of the superficial temporal artery for perioral defects V. Bhattacharya, Ganji Raveendra Reddy, Sheikh Adil Bashir,
Oral functional outcome after intraoral reconstruction with nasolabial flaps
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 150 155 Oral functional outcome after intraoral reconstruction with nasolabial flaps E.I. Hofstra a, S.O.P. Hofer b, *, J.M. Nauta c, J.L.N. Roodenburg
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 150 155 Oral functional outcome after intraoral reconstruction with nasolabial flaps E.I. Hofstra a, S.O.P. Hofer b, *, J.M. Nauta c, J.L.N. Roodenburg
The Versatile Naso-Labial Flaps in Facial Reconstruction
 Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 17, No. 4, December: 245-250, 2005 The Versatile Naso-Labial Flaps in Facial Reconstruction HAMDY H. EL-MARAKBY, M.D., F.R.C.S. The Departments of National
Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 17, No. 4, December: 245-250, 2005 The Versatile Naso-Labial Flaps in Facial Reconstruction HAMDY H. EL-MARAKBY, M.D., F.R.C.S. The Departments of National
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY PARAMEDIAN FOREHEAD FLAP NASAL RECONSTRUCTION SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Brian Cervenka, Travis Tollefson, Patrik Pipkorn The paramedian forehead
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY PARAMEDIAN FOREHEAD FLAP NASAL RECONSTRUCTION SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Brian Cervenka, Travis Tollefson, Patrik Pipkorn The paramedian forehead
Kevin T. Kavanagh, MD
 Kevin T. Kavanagh, MD Axial Based upon a named artery. Survival length depends upon the artery not the width of the flap. Random Has random unnamed vessels supplying it. Survival length is directly proportional
Kevin T. Kavanagh, MD Axial Based upon a named artery. Survival length depends upon the artery not the width of the flap. Random Has random unnamed vessels supplying it. Survival length is directly proportional
Versatility of nasolabial flaps in oral cavity reconstructions
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Review doi:10.4317/medoral.19376 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.19376 Versatility of nasolabial flaps in oral cavity reconstructions Estefanía Alonso-Rodríguez
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Review doi:10.4317/medoral.19376 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.19376 Versatility of nasolabial flaps in oral cavity reconstructions Estefanía Alonso-Rodríguez
THE SUBMENTAL ISLAND FLAP IN HEAD AND NECK RECONSTRUCTION
 THE SUBMENTAL ISLAND FLAP IN HEAD AND NECK RECONSTRUCTION Emre Vural, MD, James Y. Suen, MD Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, 4301 West Markham,
THE SUBMENTAL ISLAND FLAP IN HEAD AND NECK RECONSTRUCTION Emre Vural, MD, James Y. Suen, MD Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, 4301 West Markham,
Disclosures. The Expanding Role of Microvascular Reconstruction. Overview. Things they are a Changing. Surgical Advisory Board, Genentech Corp
 Disclosures Surgical Advisory Board, Genentech Corp The Expanding Role of Microvascular Reconstruction P. Daniel Knott, MD FACS Associate Professor Director, Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery UCSF
Disclosures Surgical Advisory Board, Genentech Corp The Expanding Role of Microvascular Reconstruction P. Daniel Knott, MD FACS Associate Professor Director, Facial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery UCSF
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Reconstruction of the Nasal Columella. David A. Sherris, MD; Jon Fuerstenberg, MD; Daniel Danahey, MD, PhD; Peter A.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reconstruction of the Nasal Columella David A. Sherris, MD; Jon Fuerstenberg, MD; Daniel Danahey, MD, PhD; Peter A. Hilger, MD Objective: To report techniques successful for nasal columella
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reconstruction of the Nasal Columella David A. Sherris, MD; Jon Fuerstenberg, MD; Daniel Danahey, MD, PhD; Peter A. Hilger, MD Objective: To report techniques successful for nasal columella
Fascia Lata Free Flap Reconstruction of Limited Hard Palate Defects
 Open Access Original Article DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2356 Fascia Lata Free Flap Reconstruction of Limited Hard Palate Defects Rhorie P. Kerr 1, Andrea Hanick 1, Michael A. Fritz 1 1. Head and Neck Institute,
Open Access Original Article DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2356 Fascia Lata Free Flap Reconstruction of Limited Hard Palate Defects Rhorie P. Kerr 1, Andrea Hanick 1, Michael A. Fritz 1 1. Head and Neck Institute,
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5. Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. JPRAS Open. journal homepage:
 JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
FOLLOWING INTRODUCTION OF
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Alternative 1-Step Nasal Reconstruction Technique Kazuo Kishi, MD, PhD; Nobuaki Imanishi, MD, PhD; Yusuke Shimizu, MD; Ruka Shimizu, MD, PhD; Keisuke Okabe, MD; Hideo Nakajima, MD, PhD
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Alternative 1-Step Nasal Reconstruction Technique Kazuo Kishi, MD, PhD; Nobuaki Imanishi, MD, PhD; Yusuke Shimizu, MD; Ruka Shimizu, MD, PhD; Keisuke Okabe, MD; Hideo Nakajima, MD, PhD
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. The Palatal Island Flap for Reconstruction of Palatal and Retromolar Trigone Defects Revisited. decades, the range of reconstructive
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Palatal Island Flap for Reconstruction of Palatal and Retromolar Trigone Defects Revisited Eric M. Genden, MD; Bryant B. Lee, MD; Mark L. Urken, MD Background: Although a host of local
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Palatal Island Flap for Reconstruction of Palatal and Retromolar Trigone Defects Revisited Eric M. Genden, MD; Bryant B. Lee, MD; Mark L. Urken, MD Background: Although a host of local
McGregor Flap Reconstruction of Extensive Lower Lip Defects Following Excision of Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 12, NO 2 May 2011 27 McGregor Flap Reconstruction of Extensive Lower Lip Defects Following Excision of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mohamed A. Albadawy, MD and Bassem M.
Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 12, NO 2 May 2011 27 McGregor Flap Reconstruction of Extensive Lower Lip Defects Following Excision of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mohamed A. Albadawy, MD and Bassem M.
Reconstruction of a Mandibular Osteoradionecrotic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap.
 Case Report Reconstruction of a Mandibular Osteoradionecrotic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap. Using Synthes ProPlan CMF, Patient Specific Plate Contouring (PSPC) and the MatrixMANDIBLE Plating
Case Report Reconstruction of a Mandibular Osteoradionecrotic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap. Using Synthes ProPlan CMF, Patient Specific Plate Contouring (PSPC) and the MatrixMANDIBLE Plating
Large full-thickness nasal tip defects after Mohs
 RECONSTRUCTIVE CONUNDRUM Repair of a Large, Exposed-Cartilage Nasal Tip Defect Using Nasalis-Based Subcutaneous Pedicle Flaps and Full-Thickness Skin Grafting DIEGO E. MARRA, MD, EDGAR F. FINCHER, MD,
RECONSTRUCTIVE CONUNDRUM Repair of a Large, Exposed-Cartilage Nasal Tip Defect Using Nasalis-Based Subcutaneous Pedicle Flaps and Full-Thickness Skin Grafting DIEGO E. MARRA, MD, EDGAR F. FINCHER, MD,
Lateral Oropharyngeal Wall Coverage with Buccinator Myomucosal and Buccal Fat Pad Flaps
 Lateral Oropharyngeal Wall Coverage with Buccinator Myomucosal and Buccal Fat Pad Flaps Bok Ki Jung 1, Seung Yong Song 1, Se-Heon Kim 2, Young Seok Kim 3, Won Jai Lee 1, Jong Won Hong 1, Tai Suk Roh 3,
Lateral Oropharyngeal Wall Coverage with Buccinator Myomucosal and Buccal Fat Pad Flaps Bok Ki Jung 1, Seung Yong Song 1, Se-Heon Kim 2, Young Seok Kim 3, Won Jai Lee 1, Jong Won Hong 1, Tai Suk Roh 3,
THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction
 THE PEDICLE!) SKIN FLAP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction of skin and soft tissue defects, differs from the
THE PEDICLE!) SKIN FLAP ROBIN ANDERSON, M.D. Department of Plastic Surgery THE pedicled flap, commonly used by the plastic surgeon in the reconstruction of skin and soft tissue defects, differs from the
cally, a distinct superior crease of the forehead marks this spot. The hairline and
 4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
Closure of Palatal Fistula with Bucco-labial Myomucosal Pedicled Flap
 Annals of Pediatric Surgery, Vol 5, No 2, April 2009, PP 104-108 Original Article Closure of Palatal Fistula with Bucco-labial Myomucosal Pedicled Flap Mohamed M. EL-Leathy* and Mohamed F. Attia** Pediatric
Annals of Pediatric Surgery, Vol 5, No 2, April 2009, PP 104-108 Original Article Closure of Palatal Fistula with Bucco-labial Myomucosal Pedicled Flap Mohamed M. EL-Leathy* and Mohamed F. Attia** Pediatric
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY INFERIOR MAXILLECTOMY Tumours of the hard palate and superior alveolus may be resected by inferior maxillectomy (Figure 1). A Le Fort
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY INFERIOR MAXILLECTOMY Tumours of the hard palate and superior alveolus may be resected by inferior maxillectomy (Figure 1). A Le Fort
Our Experience with Endoscopic Brow Lifts
 Aesth. Plast. Surg. 24:90 96, 2000 DOI: 10.1007/s002660010017 2000 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. Our Experience with Endoscopic Brow Lifts Ozan Sozer, M.D., and Thomas M. Biggs, M.D. İstanbul, Turkey and
Aesth. Plast. Surg. 24:90 96, 2000 DOI: 10.1007/s002660010017 2000 Springer-Verlag New York Inc. Our Experience with Endoscopic Brow Lifts Ozan Sozer, M.D., and Thomas M. Biggs, M.D. İstanbul, Turkey and
Repair of scalp defect using a superficial temporal fascia pedicle VY advancement scalp flap *
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 676 680 Repair of scalp defect using a superficial temporal fascia pedicle VY advancement scalp flap * Kiyoshi Onishi a, *, Yu Maruyama b, Akiteru Hayashi
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 676 680 Repair of scalp defect using a superficial temporal fascia pedicle VY advancement scalp flap * Kiyoshi Onishi a, *, Yu Maruyama b, Akiteru Hayashi
Survey of Laryngeal Cancer at SBUH comparing 108 cases seen here from to the NCDB of 9,256 cases diagnosed nationwide in 2000
 Survey of Laryngeal Cancer at comparing 108 cases seen here from 1998 2002 to the of 9,256 cases diagnosed nationwide in 2000 Stony Brook University Hospital Cancer Program Annual Report 2002-2003 Gender
Survey of Laryngeal Cancer at comparing 108 cases seen here from 1998 2002 to the of 9,256 cases diagnosed nationwide in 2000 Stony Brook University Hospital Cancer Program Annual Report 2002-2003 Gender
Vertical mammaplasty has been developed
 BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
The Role of the Lip Adhesion Procedure. in Cleft Lip Repair*
 The Role of the Lip Adhesion Procedure in Cleft Lip Repair* RALPH HAMILTON, M.D. WILLIAM P. GRAHAM, III, M.D. PETER RANDALL, M.D. Philadelphia, Pa. 19104 Introduction A lip adhesion procedure utilizing
The Role of the Lip Adhesion Procedure in Cleft Lip Repair* RALPH HAMILTON, M.D. WILLIAM P. GRAHAM, III, M.D. PETER RANDALL, M.D. Philadelphia, Pa. 19104 Introduction A lip adhesion procedure utilizing
Mc Gregor Flap for Lower Eyelid Defect
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 4 Ver. V (April. 2017), PP 69-74 www.iosrjournals.org Mc Gregor Flap for Lower Eyelid Defect
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 4 Ver. V (April. 2017), PP 69-74 www.iosrjournals.org Mc Gregor Flap for Lower Eyelid Defect
New 2010 CPT Codes (italic font represents a new or revised code/description)
 New 2010 CPT Codes (italic font represents a new or revised code/description) 14301 Adjacent tissue transfer or rearrangement, any area; defect 30.1 sq cm to 60.0 sq cm 14302 each additional 30.0 sq cm,
New 2010 CPT Codes (italic font represents a new or revised code/description) 14301 Adjacent tissue transfer or rearrangement, any area; defect 30.1 sq cm to 60.0 sq cm 14302 each additional 30.0 sq cm,
BUILDING A. Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation. 70 OCTOBER 2016 // dentaltown.com
 BUILDING A MANDI Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation by Dr. Fayette C. Williams Fayette C. Williams, DDS, MD, FACS, is clinical faculty at John Peter Smith Hospital in Fort Worth, Texas,
BUILDING A MANDI Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation by Dr. Fayette C. Williams Fayette C. Williams, DDS, MD, FACS, is clinical faculty at John Peter Smith Hospital in Fort Worth, Texas,
Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 170 174 Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap Arif Turkmen*, A. Graeme B. Perks Plastic Surgery Department, Nottingham City
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 170 174 Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap Arif Turkmen*, A. Graeme B. Perks Plastic Surgery Department, Nottingham City
Interesting Case Series. Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle
 Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
Kuwabara, Kaoru; Nonaka, Takashi; H. Citation Journal of Clinical Urology, 7(5),
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Gluteal-fold adipofascial perforato fistula reconstruction Fujioka, Masaki; Hayashida, Kenji; Kuwabara, Kaoru; Nonaka, Takashi; H Citation Journal of Clinical
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Gluteal-fold adipofascial perforato fistula reconstruction Fujioka, Masaki; Hayashida, Kenji; Kuwabara, Kaoru; Nonaka, Takashi; H Citation Journal of Clinical
Principles of flap reconstruction in ORL-HN defects. O.M. Oluwatosin Department of Surgery
 Principles of flap reconstruction in ORL-HN defects O.M. Oluwatosin Department of Surgery Nasal defects and deformities Cleft palate and Velopharyngeal incompetence Pharyngeal and oesophageal defects Pinnal
Principles of flap reconstruction in ORL-HN defects O.M. Oluwatosin Department of Surgery Nasal defects and deformities Cleft palate and Velopharyngeal incompetence Pharyngeal and oesophageal defects Pinnal
Management of Complex Avulsion Injuries of the Dorsum of the Foot and Ankle in Pediatric Patients by Using Local Delayed Flaps and Skin Grafts
 Management of Complex Avulsion Injuries of the Dorsum of the Foot and Ankle in Pediatric Patients by Using Local Delayed Flaps and Skin Grafts Ahmed Elshahat, MD Plastic Surgery Department, Ain Shams University,
Management of Complex Avulsion Injuries of the Dorsum of the Foot and Ankle in Pediatric Patients by Using Local Delayed Flaps and Skin Grafts Ahmed Elshahat, MD Plastic Surgery Department, Ain Shams University,
MEDIAL SURAL ARTERY PERFORATOR FLAP FOR TONGUE AND FLOOR OF MOUTH RECONSTRUCTION. Adequate speech and swallowing are dependent
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE MEDIAL SURAL ARTERY PERFORATOR FLAP FOR TONGUE AND FLOOR OF MOUTH RECONSTRUCTION Shao-Liang Chen, MD, 1 Tim-Mo Chen, MD, 1 Niann-Tzyy Dai, MD, 1 Yi-Jan Hsia, DDS, MDSC, 2 Yaoh-Shiang Lin,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE MEDIAL SURAL ARTERY PERFORATOR FLAP FOR TONGUE AND FLOOR OF MOUTH RECONSTRUCTION Shao-Liang Chen, MD, 1 Tim-Mo Chen, MD, 1 Niann-Tzyy Dai, MD, 1 Yi-Jan Hsia, DDS, MDSC, 2 Yaoh-Shiang Lin,
(loco-regional disease)
 (loco-regional disease) (oral cavity) (circumvillae papillae) (subsite) A (upper & lower lips) B (buccal membrane) C (mouth floor) D (upper & lower gingiva) E (hard palate) F (tongue -- anterior 2/3 rds
(loco-regional disease) (oral cavity) (circumvillae papillae) (subsite) A (upper & lower lips) B (buccal membrane) C (mouth floor) D (upper & lower gingiva) E (hard palate) F (tongue -- anterior 2/3 rds
SCOPE OF PRACTICE PGY-6 PGY-7 PGY-8
 PGY-6 Round on all plastic surgery inpatients every day. Assess progress of patients and identify real or potential problems. Review patients progress with attending physicians daily and participate in
PGY-6 Round on all plastic surgery inpatients every day. Assess progress of patients and identify real or potential problems. Review patients progress with attending physicians daily and participate in
Reconstruction of a Maxillary Oncologic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap. Using Synthes ProPlan CMF and the MatrixMIDFACE Plating System.
 Case Report Reconstruction of a Maxillary Oncologic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap. Using Synthes ProPlan CMF and the MatrixMIDFACE Plating System. Reconstruction of a Maxillary Oncologic Defect
Case Report Reconstruction of a Maxillary Oncologic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap. Using Synthes ProPlan CMF and the MatrixMIDFACE Plating System. Reconstruction of a Maxillary Oncologic Defect
A Study of Classification Systems for Maxillectomy Defects
 A Study of Classification Systems for Maxillectomy Defects Zubair Durrani FFDRCS, FRCS, FRCS (OMFS)* Syed Ghazanfar Hassan FFDRCS** Shomaila Ameer Alam BDS*** * Associate Professor & Consultant Oral and
A Study of Classification Systems for Maxillectomy Defects Zubair Durrani FFDRCS, FRCS, FRCS (OMFS)* Syed Ghazanfar Hassan FFDRCS** Shomaila Ameer Alam BDS*** * Associate Professor & Consultant Oral and
Extended Bilaminar Forehead Flap With Cantilevered Bone Grafts for Reconstruction of Full-Thickness Nasal Defects
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63:566 570, 2005 Extended Bilaminar Forehead Flap With Cantilevered Bone Grafts for Reconstruction of Full-Thickness Nasal Defects Jason K. Potter, DDS, MD,* Yadranko Ducic, MD,
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63:566 570, 2005 Extended Bilaminar Forehead Flap With Cantilevered Bone Grafts for Reconstruction of Full-Thickness Nasal Defects Jason K. Potter, DDS, MD,* Yadranko Ducic, MD,
Stanford University School of Medicine, Department of Surgery, Stanford, California
 THE RESTRICTIVE PHARYNGEAL FLAP By JAROY WEBER, Jr., M.D., ROBERT A. CHASE, M.D. and RICHARD P. JOBE, M.D. Stanford University School of Medicine, Department of Surgery, Stanford, California THE historical
THE RESTRICTIVE PHARYNGEAL FLAP By JAROY WEBER, Jr., M.D., ROBERT A. CHASE, M.D. and RICHARD P. JOBE, M.D. Stanford University School of Medicine, Department of Surgery, Stanford, California THE historical
Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
Scientific Forum. Nostrilplasty: Raising, Lowering, Widening, and Symmetry Correction of the Alar Rim
 Nostrilplasty: Raising, Lowering, Widening, and Symmetry Correction of the lar Rim Richard Ellenbogen, MD; and Greg azell, MD ackground: lthough the alar rim has frequently been neglected in correction
Nostrilplasty: Raising, Lowering, Widening, and Symmetry Correction of the lar Rim Richard Ellenbogen, MD; and Greg azell, MD ackground: lthough the alar rim has frequently been neglected in correction
Cleft lip is the most common craniofacial
 Ideas and Innovations Fat Grafting in Primary Cleft Lip Repair Elizabeth Gordon Zellner, M.D. Miles J. Pfaff, M.D. Derek M. Steinbacher, M.D., D.M.D. New Haven, Conn. Summary: The goal of primary cleft
Ideas and Innovations Fat Grafting in Primary Cleft Lip Repair Elizabeth Gordon Zellner, M.D. Miles J. Pfaff, M.D. Derek M. Steinbacher, M.D., D.M.D. New Haven, Conn. Summary: The goal of primary cleft
Use of the Teres Major Muscle in Chimeric Subscapular System Free Flaps for Head and Neck Reconstruction
 Research Original Investigation Use of the Teres Major Muscle in Chimeric Sub System Free Flaps for Head and Neck Reconstruction Andrew R. Tomlinson, MD; Mark J. Jameson, MD, PhD; Nitin A. Pagedar, MD,
Research Original Investigation Use of the Teres Major Muscle in Chimeric Sub System Free Flaps for Head and Neck Reconstruction Andrew R. Tomlinson, MD; Mark J. Jameson, MD, PhD; Nitin A. Pagedar, MD,
Learning Objectives. Head and Neck Cancer: Post-Treatment Changes. Neck Dissection Classification * Radical neck dissection. Radical Neck Dissection
 Head and Neck Cancer: Post-Treatment Changes Daniel W. Williams III, MD Learning Objectives In patients treated for H/N Cancer: Describe the various types of neck dissections Explain reconstruction techniques
Head and Neck Cancer: Post-Treatment Changes Daniel W. Williams III, MD Learning Objectives In patients treated for H/N Cancer: Describe the various types of neck dissections Explain reconstruction techniques
Sure closure skin stretching system, our clinical experience
 Free full text on www.ijps.org Original Article Sure closure skin stretching system, our clinical experience K. I. Subramania, S. Mohit, P. R. Sasidharan, M. K. Abraham, P. Arun, V. Kekatpure Department
Free full text on www.ijps.org Original Article Sure closure skin stretching system, our clinical experience K. I. Subramania, S. Mohit, P. R. Sasidharan, M. K. Abraham, P. Arun, V. Kekatpure Department
Construction of the congenitally missing columella in midline clefts
 Construction of the congenitally missing columella in midline clefts Kurt-Wilhelm BÜTOW Department of Maxillo-Facial and Oral Surgery (Head: Prof. Kurt-W. Bütow, MChD(OMFSurg), DMD, PhD, DSc(Odont), FCMFOS),
Construction of the congenitally missing columella in midline clefts Kurt-Wilhelm BÜTOW Department of Maxillo-Facial and Oral Surgery (Head: Prof. Kurt-W. Bütow, MChD(OMFSurg), DMD, PhD, DSc(Odont), FCMFOS),
Robot-Assisted Free Flap in Head and Neck Reconstruction
 Robot-ssisted Free Flap in Head and Neck Reconstruction Han Gyeol Song, In Sik Yun, Won Jai Lee, Dae Hyun Lew, Dong Kyun Rah Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Institute for Human Tissue
Robot-ssisted Free Flap in Head and Neck Reconstruction Han Gyeol Song, In Sik Yun, Won Jai Lee, Dae Hyun Lew, Dong Kyun Rah Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Institute for Human Tissue
Versatility of Reverse Sural Artery Flap for Heel Reconstruction
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck reconstruction
 European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck diseases (2012) 129, 167 171 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com TECHNICAL NOTE The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck
European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck diseases (2012) 129, 167 171 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com TECHNICAL NOTE The free thoracodorsal artery perforator flap in head and neck
Evaluation of the donor site after the median forehead flap
 Evaluation of the donor site after the median forehead flap June Seok Choi 1, Yong Chan Bae 1,2, Soo Bong Nam 1, Seong Hwan Bae 1, Geon Woo Kim 1 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Pusan
Evaluation of the donor site after the median forehead flap June Seok Choi 1, Yong Chan Bae 1,2, Soo Bong Nam 1, Seong Hwan Bae 1, Geon Woo Kim 1 1 Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Pusan
Principles of Facial Reconstruction After Mohs Surgery
 Objectives Principles of Facial Reconstruction After Mohs Surgery Identify important functional anatomy and aesthetic units of the face. Describe techniques used in facial reconstruction. Discuss postoperative
Objectives Principles of Facial Reconstruction After Mohs Surgery Identify important functional anatomy and aesthetic units of the face. Describe techniques used in facial reconstruction. Discuss postoperative
Use of cervicopectoral flap as an access for radical neck dissection and reconstruction of facial defects
 Use of cervicopectoral flap as an access for radical neck dissection and reconstruction of facial defects Balsam S. abdulhamed, B.D.S., F.I.C.M.S., H.D.L. (1) Bassem T. Merry, B.D.S. (2) ABSTRACT Background:
Use of cervicopectoral flap as an access for radical neck dissection and reconstruction of facial defects Balsam S. abdulhamed, B.D.S., F.I.C.M.S., H.D.L. (1) Bassem T. Merry, B.D.S. (2) ABSTRACT Background:
Surgical treatment of non-melanoma skin cancer of the head and neck: expanding reconstructive options van der Eerden, P.A.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Surgical treatment of non-melanoma skin cancer of the head and neck: expanding reconstructive options van der Eerden, P.A. Link to publication Citation for published
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Surgical treatment of non-melanoma skin cancer of the head and neck: expanding reconstructive options van der Eerden, P.A. Link to publication Citation for published
The bi-pedicle post-auricular tube flap for reconstruction of partial ear defects
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 593 598 The bi-pedicle post-auricular tube flap for reconstruction of partial ear defects Mohammed G. Ellabban*, Maamoun I. Maamoun, Moustafa Elsharkawi
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 593 598 The bi-pedicle post-auricular tube flap for reconstruction of partial ear defects Mohammed G. Ellabban*, Maamoun I. Maamoun, Moustafa Elsharkawi
Radial Artery Pedicle Flap To Cover Exposed Mesh After Abdominal Wound Dehiscence-An Easy Solution To A Difficult Problem
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Radial Artery Pedicle Flap To Cover Exposed Mesh After Abdominal Wound Dehiscence-An Easy Solution To A Difficult Problem S Tripathy,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Plastic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Radial Artery Pedicle Flap To Cover Exposed Mesh After Abdominal Wound Dehiscence-An Easy Solution To A Difficult Problem S Tripathy,
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Reverse Adipofascial Radial Forearm Flap Surgery for Soft-Tissue Reconstruction of Hand Defects
 Reverse Adipofascial Radial Forearm Flap Surgery for Soft-Tissue Reconstruction of Hand Defects Osman Akdag, MD, a Mehtap Karamese, MD, a Muhammed NebilSelimoglu, MD, a Ahmet Akatekin, MD, a Malik Abacı,
Reverse Adipofascial Radial Forearm Flap Surgery for Soft-Tissue Reconstruction of Hand Defects Osman Akdag, MD, a Mehtap Karamese, MD, a Muhammed NebilSelimoglu, MD, a Ahmet Akatekin, MD, a Malik Abacı,
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Reconstruction for Oral Neoplasms in Indian Setup: Redebating the Utility of Radial Artery Free Flaps
 World Articles of Ear, Nose and Throat ---------------------Page 1 Reconstruction for Oral Neoplasms in Indian Setup: Redebating the Utility of Radial Artery Free Flaps Authors: Ranjan G Aiyer*, Rahul
World Articles of Ear, Nose and Throat ---------------------Page 1 Reconstruction for Oral Neoplasms in Indian Setup: Redebating the Utility of Radial Artery Free Flaps Authors: Ranjan G Aiyer*, Rahul
BONE GRAFTING IN TREATMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE 337
 PRIMARY BONE GRAFTING IN THE TREATMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO ALVEOLAR COLLAPSE By FRANK ROBINSON, F.R.C.S., and BARRIE WOOD, L.D.S. Burns and Plastic Surgery Unit, Booth Hall
PRIMARY BONE GRAFTING IN THE TREATMENT OF CLEFT LIP AND PALATE WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO ALVEOLAR COLLAPSE By FRANK ROBINSON, F.R.C.S., and BARRIE WOOD, L.D.S. Burns and Plastic Surgery Unit, Booth Hall
UCL Repair: Emphasis on Muscle Dissection and Reconstruction
 UCL Repair: Emphasis on Muscle Dissection and Reconstruction Unilateral cleft lip repair is performed using rotation-advancement technique. Markings are made on columella base, redlines, Cupid s bow on
UCL Repair: Emphasis on Muscle Dissection and Reconstruction Unilateral cleft lip repair is performed using rotation-advancement technique. Markings are made on columella base, redlines, Cupid s bow on
Cancer of the Oral Cavity
 The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies Current Concepts in Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology Cancer of the Oral Cavity Ashok Shaha Principals of Management of Oral Cancer A)
The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies Current Concepts in Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology Cancer of the Oral Cavity Ashok Shaha Principals of Management of Oral Cancer A)
Expanded Transposition Flap Technique for Total and Subtotal Resurfacing of the Face and Neck
 Expanded Transposition Flap Technique for Total and Subtotal Resurfacing of the Face and Neck Robert J. Spence, MD, FACS Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD Correspondence: rspence@jhmi.edu
Expanded Transposition Flap Technique for Total and Subtotal Resurfacing of the Face and Neck Robert J. Spence, MD, FACS Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD Correspondence: rspence@jhmi.edu
Reconstructive surgeries in oral cancers
 International Journal of A J Institute of Medical Sciences 1 (2012) 47-54 Original Research Article Reconstructive surgeries in oral cancers Rithin Suvarna, 1 Aravind Pallipady, 2 Ranjith Rao, 3 Ashok
International Journal of A J Institute of Medical Sciences 1 (2012) 47-54 Original Research Article Reconstructive surgeries in oral cancers Rithin Suvarna, 1 Aravind Pallipady, 2 Ranjith Rao, 3 Ashok
Columella Lengthening with a Full-Thickness Skin Graft for Secondary Bilateral Cleft Lip and Nose Repair
 Original Article Columella Lengthening with a Full-Thickness Skin Graft for Secondary Bilateral Cleft Lip and Nose Repair Yoon Seok Lee 1, Dong Hyeok Shin 1, Hyun Gon Choi 1, Jee Nam Kim 1, Myung Chul
Original Article Columella Lengthening with a Full-Thickness Skin Graft for Secondary Bilateral Cleft Lip and Nose Repair Yoon Seok Lee 1, Dong Hyeok Shin 1, Hyun Gon Choi 1, Jee Nam Kim 1, Myung Chul
Perichondrial Cutaneous Grafts in Facial Reconstruction
 IJHNS Jamie G Bizzell, Jennings R Boyette ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10001-1285 1 Jamie G Bizzell, 2 Jennings R Boyette ABSTRACT Aim: The purpose of this study is to review the indications, techniques,
IJHNS Jamie G Bizzell, Jennings R Boyette ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10001-1285 1 Jamie G Bizzell, 2 Jennings R Boyette ABSTRACT Aim: The purpose of this study is to review the indications, techniques,
Center for Reconstructive Urethral Surgery Guido Barbagli Center for Reconstructive Urethral Surgery Arezzo - Italy
 Guido Barbagli Arezzo - Italy E-mail: info@urethralcenter.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it SHANGHAI February 6 8, 2009 Prof. Qiang FU Professor FU day Professor FU and night Anterior urethroplasty using
Guido Barbagli Arezzo - Italy E-mail: info@urethralcenter.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it SHANGHAI February 6 8, 2009 Prof. Qiang FU Professor FU day Professor FU and night Anterior urethroplasty using
be very thin and variable. Facial nerve branches that exit the parotid gland are deep to the SMAS.
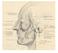 The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DISTALLY BASED PERONEUS BREVIS MUSCLE FLAP FOR DISTAL LEG DEFECTS
 DISTALLY BASED PERONEUS BREVIS MUSCLE FLAP FOR DISTAL LEG DEFECTS Peddi Manjunath 1, Ramesha K.T 2, Smitha S Segu 3, Jainath 4, Shankarappa M 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Peddi Manjunath, Ramesha KT, Smitha
DISTALLY BASED PERONEUS BREVIS MUSCLE FLAP FOR DISTAL LEG DEFECTS Peddi Manjunath 1, Ramesha K.T 2, Smitha S Segu 3, Jainath 4, Shankarappa M 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Peddi Manjunath, Ramesha KT, Smitha
A TECHNIQUE FOR ONE STAGE REPAIR OF COMPLETE PALATAL CLEFT
 A TECHNIQUE FOR ONE STAGE REPAIR OF COMPLETE PALATAL CLEFT Pages with reference to book, From 105 To 107 Iftikhar Ahmad, M. Rafiq Khan, Abdullah Jan, Abdur Rasheed ( Department of E.N.T. and Head and Neck
A TECHNIQUE FOR ONE STAGE REPAIR OF COMPLETE PALATAL CLEFT Pages with reference to book, From 105 To 107 Iftikhar Ahmad, M. Rafiq Khan, Abdullah Jan, Abdur Rasheed ( Department of E.N.T. and Head and Neck
Multi-dimensional analysis of oral cavity and oropharyngeal defects following cancer extirpation surgery, a cadaveric study
 Idris et al. Journal of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery (2018) 47:27 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40463-018-0276-9 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Multi-dimensional analysis of oral cavity and
Idris et al. Journal of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery (2018) 47:27 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40463-018-0276-9 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Multi-dimensional analysis of oral cavity and
ORIGINAL ARTICLE TEMPORALIS MUSCLE FLAP FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF SKULL BASE DEFECTS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TEMPORALIS MUSCLE FLAP FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF SKULL BASE DEFECTS Jesse E. Smith, MD, 1,2 Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCS(C), 1,2,3 Robert T. Adelson, MD 4 1 Department of Otolaryngology-Head and
ORIGINAL ARTICLE TEMPORALIS MUSCLE FLAP FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF SKULL BASE DEFECTS Jesse E. Smith, MD, 1,2 Yadranko Ducic, MD, FRCS(C), 1,2,3 Robert T. Adelson, MD 4 1 Department of Otolaryngology-Head and
Septic Bone and Joint Surgery
 Septic Bone and Joint Surgery Bearbeitet von Reinhard Schnettler 1. Auflage 2010. Buch. 328 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 13 149031 5 Format (B x L): 19,5 x 27 cm Weitere Fachgebiete > Medizin > Chirurgie >
Septic Bone and Joint Surgery Bearbeitet von Reinhard Schnettler 1. Auflage 2010. Buch. 328 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 13 149031 5 Format (B x L): 19,5 x 27 cm Weitere Fachgebiete > Medizin > Chirurgie >
Use of Buccal Fat Pad for Treatment of Oral Submucous Fibrosis
 Use of Buccal Fat Pad for Treatment of Oral Submucous Fibrosis Rohit Sharma, MDS,* G. K. Thapliyal, MDS, FIBOMS, Ramen Sinha, MDS, FIBOMS, and P. Suresh Menon, MDS, FIBOMS J Oral Maxillofac Surg xx:xxx,
Use of Buccal Fat Pad for Treatment of Oral Submucous Fibrosis Rohit Sharma, MDS,* G. K. Thapliyal, MDS, FIBOMS, Ramen Sinha, MDS, FIBOMS, and P. Suresh Menon, MDS, FIBOMS J Oral Maxillofac Surg xx:xxx,
OF CONCHA-HELIX DEFECTS. BY JAMES K. MASSON, M.D. Mayo Clinic and Mayo Foundation, Rochester, Minnesota
 British Journal qf Plastic Surgery (x97z), 7,5, 399-403 A SIMPLE ISLAND FLAP FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF CONCHA-HELIX DEFECTS BY JAMES K. MASSON, M.D. Mayo Clinic and Mayo Foundation, Rochester, Minnesota AFTER
British Journal qf Plastic Surgery (x97z), 7,5, 399-403 A SIMPLE ISLAND FLAP FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF CONCHA-HELIX DEFECTS BY JAMES K. MASSON, M.D. Mayo Clinic and Mayo Foundation, Rochester, Minnesota AFTER
Case Report Dorsalis Pedis Free Flap: The Salvage Option following Failure of the Radial Forearm Flap in Total Lower Lip Reconstruction
 Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 458286, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/458286 Case Report Dorsalis Pedis Free Flap: The Salvage Option following Failure of the Radial Forearm Flap in Total
Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 458286, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/458286 Case Report Dorsalis Pedis Free Flap: The Salvage Option following Failure of the Radial Forearm Flap in Total
Interesting Case Series. Reconstruction of Dorsal Wrist Defects
 Interesting Case Series Reconstruction of Dorsal Wrist Defects Maelee Yang, BS, and Joseph Meyerson, MD The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus Correspondence: maelee.yang@osumc.edu Keywords:
Interesting Case Series Reconstruction of Dorsal Wrist Defects Maelee Yang, BS, and Joseph Meyerson, MD The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus Correspondence: maelee.yang@osumc.edu Keywords:
Reconstruction of axillary scar contractures retrospective study of 124 cases over 25 years
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2003), 56, 100 105 q 2003 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(03)00035-3 Reconstruction
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2003), 56, 100 105 q 2003 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s0007-1226(03)00035-3 Reconstruction
PECTORALIS MAJOR MYOCUTAJNEUUS FLAP FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF DEFECTS FOLLOWING RESECTIONS IN HEAD AND NECK AREA
 PECTORALIS MAJOR MYOCUTAJNEUUS FLAP FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF DEFECTS FOLLOWING RESECTIONS IN HEAD AND NECK AREA Pages with reference to book, From 72 To 76 Mohammad Arshad Cheema ( Department of Surgery,
PECTORALIS MAJOR MYOCUTAJNEUUS FLAP FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF DEFECTS FOLLOWING RESECTIONS IN HEAD AND NECK AREA Pages with reference to book, From 72 To 76 Mohammad Arshad Cheema ( Department of Surgery,
RECONSTRUCTION of large surgical
 Triple-Flap Technique for Reconstruction of Large Nasal Defects Timothy W. Wild, MD, DDS; C. Patrick Hybarger, MD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Objective: To determine the usefulness of a triple-flap technique for
Triple-Flap Technique for Reconstruction of Large Nasal Defects Timothy W. Wild, MD, DDS; C. Patrick Hybarger, MD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Objective: To determine the usefulness of a triple-flap technique for
Naso-Orbital Complex Reconstruction with Titanium Mesh and Canthopexy
 Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com DOI: 10.4172/2472-1905.100011 Naso-Orbital Complex Reconstruction with Titanium Mesh and Canthopexy Abstract Context: We are introducing the reconstruction
Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com DOI: 10.4172/2472-1905.100011 Naso-Orbital Complex Reconstruction with Titanium Mesh and Canthopexy Abstract Context: We are introducing the reconstruction
1 The nasal bones are deeper and are therefore MATERIAL AND METHODS. At the Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
 Technical Experiences Reconstruction of the Nasal Tip Valerio Cervelli, MD, DJ Bottini, PhD, Pietro Gentile, MD Rome, Italy Defects of the nasal tip present complex problems in terms of reconstruction,
Technical Experiences Reconstruction of the Nasal Tip Valerio Cervelli, MD, DJ Bottini, PhD, Pietro Gentile, MD Rome, Italy Defects of the nasal tip present complex problems in terms of reconstruction,
PEDICLED BUCCAL PAD OF FAT: A TRUSTWORTHY ADJUNCT IN PRIMARY PALATOPLASTY- A CASE REPORT
 Case Report PEDICLED BUCCAL PAD OF FAT: A TRUSTWORTHY ADJUNCT IN PRIMARY PALATOPLASTY- A CASE REPORT Authors: Ashok Kumar Gupta*, Rupinder Sandhu**, Anantpreet Singh***,Vivek Prabhu****, Jay prakash Narayan*****.
Case Report PEDICLED BUCCAL PAD OF FAT: A TRUSTWORTHY ADJUNCT IN PRIMARY PALATOPLASTY- A CASE REPORT Authors: Ashok Kumar Gupta*, Rupinder Sandhu**, Anantpreet Singh***,Vivek Prabhu****, Jay prakash Narayan*****.
Use of tent-pole graft for setting columella-lip angle in rhinoplasty
 Agrawal et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2018;5:13 DOI: 10.20517/2347-9264.2018.17 Plastic and Aesthetic Research Letter to Editor Open Access Use of tent-pole graft for setting columella-lip angle in rhinoplasty
Agrawal et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2018;5:13 DOI: 10.20517/2347-9264.2018.17 Plastic and Aesthetic Research Letter to Editor Open Access Use of tent-pole graft for setting columella-lip angle in rhinoplasty
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and surgical delay improve flap survival of reverse pedicle flaps for lower third leg and foot reconstruction
 Original Article Plastic and Aesthetic Research Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and surgical delay improve flap survival of reverse pedicle flaps for lower third leg and foot reconstruction Pradeoth Mukundan
Original Article Plastic and Aesthetic Research Hyperbaric oxygen therapy and surgical delay improve flap survival of reverse pedicle flaps for lower third leg and foot reconstruction Pradeoth Mukundan
ONCOPLASTIC SURGERY. Dr. Sadir Alrawi Director of Surgical Oncology Services. Dr. Humaa Darr Surgical Oncology Fellow
 Hessa St ONCOPLASTIC SURGERY Dr. Sadir Alrawi Director of Surgical Oncology Services Dr. Humaa Darr Surgical Oncology Fellow Al Sufouh Rd AL SUFOUH AL SUFOUH Sharaf DG Mall of the Emirates Mall Of the
Hessa St ONCOPLASTIC SURGERY Dr. Sadir Alrawi Director of Surgical Oncology Services Dr. Humaa Darr Surgical Oncology Fellow Al Sufouh Rd AL SUFOUH AL SUFOUH Sharaf DG Mall of the Emirates Mall Of the
Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect of Upper and Middle Third Leg
 Downloaded from wjps.ir at 22:25 +0330 on Sunday November 18th 28 314 Gastrocnemius flap for coverage of leg defects Original Article Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect
Downloaded from wjps.ir at 22:25 +0330 on Sunday November 18th 28 314 Gastrocnemius flap for coverage of leg defects Original Article Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect
Buccal Corticotomy for Closure of Oroantral Openings: Case Report
 Turk J Med Sci 34 (2004) 409-414 TÜB TAK SHORT REPORT Buccal Corticotomy for Closure of Oroantral Openings: Case Report Bedrettin Cem fiener, Hasan GAR P, Faysal U URLU, Kamil GÖKER Department of Oral
Turk J Med Sci 34 (2004) 409-414 TÜB TAK SHORT REPORT Buccal Corticotomy for Closure of Oroantral Openings: Case Report Bedrettin Cem fiener, Hasan GAR P, Faysal U URLU, Kamil GÖKER Department of Oral
Case Report Maintenance of Increased Mouth Opening in Oral Submucous Fibrosis Patient Treated with Nasolabial Flap Technique
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 842578, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/842578 Case Report Maintenance of Increased Mouth Opening in Oral Submucous Fibrosis Patient Treated with Nasolabial
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 842578, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/842578 Case Report Maintenance of Increased Mouth Opening in Oral Submucous Fibrosis Patient Treated with Nasolabial
