Six cases report of differential diagnosis of periapical diseases
|
|
|
- Harvey Todd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Oral Sci (2011) 3: CLINICAL ARTICLE Six cases report of differential diagnosis of periapical diseases Wen-wei Xia, Ya-qin Zhu, Xiao-yi Wang* Department of Endodontics and Operative Dentistry, Shanghai Ninth People s Hospital Affiliated Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai , China The distinction of some particular forms of periapical area, involving diseases from regular periapical disease, is a matter of considerable importance when choosing a correct treatment. The aim of this study is to describe the differential diagnosis of periapical diseases from six rare cases in clinical practice. The six rare cases are examples of situations where it is difficult to make a differential diagnosis in clinical practice. By retrospective surveys on the clinical examination, radiographs and pathological results, six patients referred to endodontic treatment in our department were analyzed for the accuracy of diagnosis and therapy. The pathoses of the six cases included two atypical radical cysts, periapical cemental dysplasia, cemento-ossifying fibroma, thymus cancer metastasis in the periapical site and tuberculosis. This report indicates that endodontists should be cognizant of a few particular circumstances when clinically treating periapical diseases. Keywords: periapical diseases; differential diagnosis; endodontic International Journal of Oral Science (2011) 3: doi: /IJOS11055 Introduction The periapical disease is one of the most prevalent diseases in general dental practice. However, because the clinical diagnosis and treatment of periapical diseases is quite straightforward, there are few descriptions on differential diagnosis of periapical diseases in either textbooks or reference books. More attention has been paid to periapical diseases, such as periapical abscesses [1], periapical granuloma, and periapical cysts [2]. In practice, a patient who has problems similar to periapical diseases, such as radical cysts, cemento-osseous dysplasia, or tumors, will also be presented to an endodontist for treatment. Moreover, it has been suggested that the associated symptoms of maxillofacial cancer [3] as well as some systemic diseases such as tuberculosis [4] may *Correspondence: Xiao-yi Wang Tel: ; Fax: xwwall@sina.com Received 27 December 2010; Accepted 13 January 2011 appear initially as periapical signs. Thus, early correct diagnosis of such patients was crucial for treatment and subsequent prevention of advanced pathological process. The aim of this study is to describe the differential diagnosis on periapical diseases based on six rare cases. We hope the cases presented here may be helpful in avoiding the risk of initial endodontic treatment in patients who do not have a periapical pathosis origin. Case Reports The six cases reported in this study are from patients who were diagnosed between 2000 and 2004 at the Department of Endodontics and Operative Dentistry, Shanghai Ninth People s Hospital Affiliated Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine. Case 1 A 72-year-old female patient experiencing toothache with right lower gum swelling for 3 weeks attended the endodontic clinic. The pathological diagnosis was inf-
2 Differential diagnosis of periapical diseases 154 lammation by biopsy in another hospital before the patient was referred to our department. On clinical examination, it was observed that the bone of teeth 44 and 45 expanded to buccal side without loosing teeth or knocking pain. The tooth 46 was a residual crown. Radiographic examination showed periapical radiolucence of 44 and 45 without obvious white osseous response lines. The alveolar bone resorption of tooth 44 almost reached the apex and tooth 45 reached 1/2 length of the root (Figure 1A). The pulp did not respond Figure 1 A typical radical cyst. (A) Radiographic image of case 1. Arrows indicate that the shadow of bone absorption reached mental foramen. (B) Histotolgical examination of the biopsy. H&E stainning, 200. (C) Histotolgical examination of the biopsy. H&E stainning, 400. to electric vital test. The patient therefore diagnosed was referred to Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery in our hospital to extract teeth 46, 45, 44. Upon the surgery, large amount of granulation tissue was resected from the periapical area and a biopsy was taken. The wound healed smoothly 3 weeks post-surgery. The pathological examination showed atypical radical cyst with reactive osseous proliferation (Figure 1B). Case 2 A 54-year-old female patient suffering from left upper lip swelling without relief by local anti-inflammatory therapy in other hospitals was referred to our department. On clinical examination, it was observed that the labial gingival and mucosal tissues above the left maxillary lateral incisor were swelling with undulation feeling in palpation. This tooth was intact without caries and responded to the vital pulp test. The labial abscess of tooth 22 was incised and the drainage was kept for 3 days. After the acute inflammation subsided, root canal therapy was performed and the pulp was observed to be intact. Radiographic examination showed a 1 cm 1.5 cm radiolucent lesion in the apical area of 22 with smooth, corticated borders indicating a cyst (Figure 2A). The cyst was removed 3 days after the root canal being filled. During the surgery, a small perforation of palatal osseous lamella was observed and most of the granulation tissue was in the palatal side of tooth 22. At 3 months postsurgery, X-ray examination showed that the destruction of the apical area had been recovered together with the formation of new tissue (Figure 2B). Histopathological examination of the biopsy showed a structure of typical radical cyst (Figure 2C). Case 3 A 71-year-old male patient experienced intermittent pain and swelling in right lower molars for more than 2 years. Since root canal therapy was not effective, the tooth was extracted one year prior. However, the extraction inhibited the healing and relief of pain. The patient was then referred to our department and a radiographic examination was performed. Radiographic images showed a high density lesion in either right or left molar areas. A diagnosis of periapical cemental dysplasia of bilateral molars was then made (Figure 3A). The patient was then referred to Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery. During the surgery, teeth 46, 44, 24, 25 were extracted and it was found that roots of these teeth were grossly enlarged and ossified. Histologically, maxilla and mandible cemental proliferation in bilateral periapical areas was observed (Figure 3B). Thus, final diagnosis was made as multiple periapical cemental dysplasia. International Journal of Oral Science Vol 3 No 3 July 2011
3 Wen-wei Xia et al. 155 Case 4 A 50-year-old female patient experiencing discomfort in the 36 area was referred to our department. Upon examination, a fixed cantilever bridge was found in teeth 36, 37, 38. No obvious pain on percussion was observed on tooth 36. Radiographic examination showed a 1.5 cm 1.5 cm lesion images at the apical area of the left side molar and a small isolated bone was observed in the center of the lesion. In consideration of the fact that the lesion was near to the apex of 36, a diagnosis of apical periodontitis with local bone necrosis was made (Figure 4A). The cantilever bridge was removed and the pulp was still alive. The tooth 36 was treated by root canal therapy and a biopsy was taken. Histopathological examination revealed a typical cemento-ossifying fibroma (Figure 4B). Figure 2 Typical radical cyst. (A) 22 Cyst of the incisive canal (1.0 cm 1.5 cm radiolucence lesion in the apical area of 22 ). (B) 22 Cyst of the incisive canal (The destruction of the apical area recovered after 3 months). (C) Histology observation of biopsy tissue in surgery. Staining, 200. Figure 4 Cemento-ossifying fibroma. (A) Radiogram showed 1.5 cm 1.5 cm lesion at the apical area of the left molar. (B) Histology examination of cementoossifying fibroma. H&E staining, 200. Figure 3 Multiple periapical cemental dysplasis. (A) Radiogram showed high dense radiopacity in bilateral molars. (B) Cemental proliferation in bilateral periapical areas was detected. H&E staining, 200. Case 5 A 32-year-old female patient experiencing tooth 47 pain unrelieved by root canal therapy, was referred to our department. On clinical examination, it was found that 47 had pain on percussion and displayed slight local swelling of buccal side. Radiographic examination showed a sparse distribution of bone trabecula, which was speculated as a result of bone resorption, at apical area of 47, International Journal of Oral Science
4 Differential diagnosis of periapical diseases The tooth of 48 was impacted (Figure 5A). When closely questioned the patient s medical history, it was discovered that she had received a thymusectomy because of the thymus cancer one year ago. Therefore, a suspicious diagnosis of cancer metatasis was made and the patient was referred to emission computed tomograpy (ECT) examination. Images of ECT examination showed exceptionally high density radioactivity in the right mandible, left anterior superior iliac spine, and left hip joint, indicating tumor metastasis (Figures 5B, 5C). The patient then received chemotherapy. Case 6 A 48-year-old female patient experiencing localized swelling and pain in the right lower molar area for 2 months, diagnosed with apical periodontitis in other hospitals, was referred to our department. On examination, the gums of teeth 47 and 43 were swolled, 45, 44 were lost, and tooth 46 was a residual crown with inflammatory granulation tissue in the mesial gingiva. The patient received anti-inflammation therapy in our department for one month but the swelling and toothache was not relieved. Thus, a biopsy was taken from the mesial side of tooth 46 at which inflammation resulting from tuberculosis was indicated. Radiographic examination showed obvious bone resorption at the furcation of tooth 46 (Figure 6A). Through further clinical examination, we found that the bilateral submandibular lymph nodes were tumescent with the quality of medium to hard. To make a definitive diagnosis, a biopsy was Figure 5 Thymus cancer metastasis. (A) Bone absorption characterized by sparse distribution of bone trabecula at apical area of 47, 48. (B) ECT images of cancer metastasis in right mandible (C) as well as in left anterior iliac and hip joint. Figure 6 The jaw bone tuberculosis. (A) X-ray images showed bone absorption at furcation of tooth 46. (B) Histology examination displayed tuberculosis. (C) After 4 months of anti-tuberculosis treatment, radiograms showed regeneration of bone (D) as well as healing of the wound resulted from tooth extraction. International Journal of Oral Science Vol 3 No 3 July 2011
5 collected from the right submandibular lymph node by aspiration. According to the histopathological examination, distribution of epithelial cells, multinuclear giant cells and lymphocytes were observed, indicating the strong possibility of tuberculosis (Figure 6B). Therefore, anti-tuberculosis treatment was carried out. After 3 months of treatment, the size of tumescent submandibular lymph node reduced remarkably. The granulation tissue in mesial gum and the swelling vanished. In the process of anti-tuberculosis treatment, 46 remnant coronal was broken off and only the remnant root was left. The radiographic image showed that the apical bone was repaired. 46 remnant root was then extracted and the anti-tuberculosis treatment was continued. After 4 months, a follow-up visit was made. The extraction wound was well healed, and the bone was well repaired (Figures 6C, 6D). Discussion The diagnosis of periapical lesions of different origin remains a crucial issue for endodontists because the correct diagnosis has a decisive influence on the subsequent choice of clinical interventional approaches and the resulting success of treatment. However, in some circumstances, it is difficult to identify the periapical diseases from other periapical area-related diseases derived either systemically or locally. Therefore, clear differential diagnosis of periapical lesions is also fundamental for successful treatment of patients experiencing periapical lesions. The diagnosis of radical cysts mainly depends on radiological examinations. The circular radiolucencies shadow with clear boundary in the periapex of the tooth, sometimes with the white osseous response line peripherally, remains the classical diagnostic standard for radical cyst. However, the identification of radical cysts, especially in cases which the radiographic images of apical area appeared atypically, can not be made merely by radiological examination. The main difference between atypical radical cysts and typical radical cysst is that there is no radiopaque line at the apical lesion and the boundary is fuzzy on X-ray film. However, the clinical signs of atypical cysts are similar to that of typical cysts. Therefore, in differential diagnosis, clinical signs and X-ray should be taken into consideration together. The distinction of radical cysts from tumor may be confusing if the diagnosis was made only on radiographic examination. In addition, the correct diagnosis was still difficult even integrating with clinical examination. The periapical radiographic image of case 1 showed irregular, burrow-like bone absorption without Wen-wei Xia et al. 157 obvious osseous response line near the mental foramen. Clinical examination indicated: the teeth 45 and 44 were not obviously loose; there was no pain on percussion; the bone was expended on buccal side. Thus, endodontists may make a diagnosis of tumor. However, the result of pathology of the biopsy demonstrated that it was a radical cyst with reactive osseous proliferation. The massive granulation tissue seen in the surgery indicated that the long lasting heavy inflammation reaction may be responsible for the non-typical X-ray image which caused endodontists to make an incorrect diagnosis of tumor. The identification of radical cysts from other odontogenic cysts and non-odontogenic cysts, which were classified as jaw cysts, remains another challenge to endodontists. Jaw cysts includes odontogenic cysst, nonodontogenic cysts (such as globlo-maxillary cysts, nasopalatine duct cysst, median cysts, nasolabial cysts), extravasation cysts, and traumatic bone cysts. Among non-odontogenic cysts, nasolabial cysts and cysts of the incisive canal (also named nasopalatine duct cysts) are more easily confused with radical cysts. Anatomical localization and pulp vigor are main points for differential diagnosis of odontogenic cyst and non-odontogenic cysts. The diagnosis of radical cysts for the case 2 is untenable because the pulp was alive. The diagnosis of globlo-maxillary cyst also is excluded for this case because X-ray showed the cyst was at the apical area of tooth 22 but not between teeth 22 and 23. Thus, the final diagnosis should be a cyst of the incisive canal. The reason is that incisive hole often appears as a boundary clear circular or elliptic lower density image on X-ray images. Anatomically, the incisive canal originates from lower incisive foramen and stops at upper incisive hole bilaterally. The positions of the incisive canal lower foramen are between the incisors, and near alveolar crest or at the apical level which can be seen on radiograph at incisor apical area. The incisive canal upper foramen located at the front of nose and the bottom of lip, near nasal septum. On the radiographic image of apical area, the incisive canal upper foramen could project to any incisor s apical area. Thus, sometimes it is recognized as periapical disease by mistake. The main distinction between apical periodontitis and periapical cemental dysplasia is that the necrosis in former is caused by pulpitis, while the latter is caused by a primarily pathological process of cementum [5]. By radiographic examination, the clinical process of the periapical cemental dysplasia was characterized by three different periods including normal alveolus, bone fibrosis and density, and atypical remineralization of bone. However, clinically, the pulp is always alive in any of International Journal of Oral Science
6 Differential diagnosis of periapical diseases 158 the three circumstances mentioned above and the mineralization of the apical area could be cementum, bone, or mixture of both. The pathological change in periapical cemental dysplasia would cause cortex expansion, mucosal ulcer, secondary infection, even reverse pulpitis and necrosis probably. The failed distinction of apical periodontitis from periapical cemental dysplasia was responsible for the inefficient relief of toothache of patient in case 3 who had an unnecessary root canal therapy experience. In fact, all three different processes of periapical cemental dysplasia, but mainly the mature stage, were observed by radiology in case 3 of this study. More importantly, the pulp in this case is alive. The reason why a correct differential diagnosis in this case was not made lies on the fact that the diagosis was based mainly on the periapical X-ray image. Thus, pantomography is the key for diagnosis of this case. Cemento-ossifying fibroma, which was once called cementifying fibroma and classified as a subtype of cementoma, is the pathological change of fibro-osseous tissues. As the cementum is histologically similar to the texture of bone tissue, it is very difficult to distinguish the cemento-ossifying fibroma from ossifying fibroma pathologically. Therefore, the classification of these two diseases had been listed as one which named as Cementoossifying fibroma according to the WHO revised classification since the year of 1992 [6]. The morbility of cemento-ossifying fibroma is rare in clinical practice. Most of cemento-ossifying fibroma occurs in the root of a tooth, forming not only bone trabecula but also cemental tissue. Thus, it is also classified as an odontogenic tumor. In most circumstances, cemento-ossifying fibroma is easily confused with periapical diseases at the early stage when the pathological lesion is limited within the jaw bone. The basic manifestation of cemento-ossifying fibroma in radiographic examination includes multiple cysts, ossification and osteopenia. However, according to our experience, the key point of differential diagnosis of cemento-ossifying fibroma with apical periodontitis is that the pulp is alive in cemento-ossifying fibroma but not in apical periodontitis. This is consistent with what had happened in the patient of case 4. In this patient, the chronic apical periodentitis was wrong diagnosed by the fact that tooth 36 had received crown repair without root canal therapy in other hospital. On the basis of this diagnosis, the small calcified shadow with bone-like density in X-ray images was neglected and suspected as the dead bone remnant caused by inflammation. However, the diagnosis of apical periodontitis was denied and a diagnosis of cemento-ossifying frbroma was made in our department. Tumorigenesis of jaw bone is usually the result of metastasis of cancer originally derived from breast [7], lung [8] as well as prostate [9], as previously reported. To our knowledge, no report has been found about the jaw metastasis of cancer originating from thymus, which is extremely rare in clinical practice. Unawareness of the thymus cancer metastasis as well as an insufficiently detailed medical history inquiry may be responsible for the misdiagnosis of periapical endodontitis and subsequent nonessential root canal therapy in this patient of case 5. Oral tuberculosis which is not a common disease in clinic may be located in soft tissue of oral cavity, or osseous-tissue in the jaw. Symptoms of oral soft tissue tuberculosis may typically be shown as latent mucosa ulcer and severe pain [4]. However, it is interesting to notice that the oral tuberculosis without pain occurred in the patient of case 6. Together with the observation of nonvital of 46, a misdiagnosis of periapical disease was made and a subsequent non-effective periapical therapy was carried out for 2 months before the patient was referred to our department. A final correct diagnosis of tuberculosis was made based on the histopathologic examination in combination with ineffective anti-inflammation therapy. Therefore, a proper diagnosis of periapical disease should not merely be based on examination of tooth and alveolous area, while comprehensive examination of the whole oral cavity and maxillofacial issues was also important. In conclusion, the diagnosis for periapical diseases in general is quite straightforward. However, in some peculiar circumstances, endodontists should be cautious to avoid the confusion of the apical diseases with other periapical-related diseases in clinical practice. The key point of differential diagnosis is that the pulps of periapical diseases are usually not viable, whereas the pulp is often alive in apical area related jaw diseases and system disease. Meanwhile, the history of system disease and clinical signs may also exist. Hence, prior to initiating any treatment, vital pulp test, a comprehensive examination in oral cavity as well as maxillofacial area not only limited to apical site, and when necessary, localized radiographic examination, pantomography, even CT or other general physical examination should all be taken into consideration. Acknowledgements We thank Pro. Wei-liu Qiu for his revision of this manuscript and Dr. Li-zhen Wang for her help in histological examination. This study was supported by International Journal of Oral Science Vol 3 No 3 July 2011
7 Science and Technology committee of Shanghai (10JC ). Reference 1 Huang CH, Brunsvold MA. Maxillary sinusitis and periapical abscess following periodontal therapy: a case report using three-dimensional evaluation. J Periodontol 2006; 77: Rózyło-Kalinowska I. Digital radiography density measurements in differentiation between periapical granulomas and radicular cysts. Med Sci Monit 2007; 13: Martins MD, Taghloubi SA, Bussadori SK, et al. Intraosseous schwannoma mimicking a periapical lesion on the adjacent tooth: case report. Int Endod J 2007; 40: Ertas U, Tozoglu S, Uyanik MH. Submandibular tuberculous lymphadenitis after endodontic treatment of the mandibular first premolar tooth: report of a case. J Endod Wen-wei Xia et al ; 32: Dunfee BL, Sakai O, Pistey R, Gohel A. Radiologic and pathologic characteristics of benign and malignant lesions of the mandible. Radiographics 2006; 26: Kramer IR, Pindborg JJ, Shear M. The World Health Organization histological typing of odontogenic tumours. Introducing the second edition. Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol 1993; 29B: Dib LL, Soares AL, Sandoval RL, Nannmark U. Breast metastasis around dental implants: a case report. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2007; 9: Park JY, Kim HS, Zo JI. Initial presentation of lung sarcomatoid carcinoma as a metastatic lesion in the mandibular gingiva. J Periodontol 2006; 77: Reyes Court D, Encina S, Levy I. Prostatic adenocarcinoma with mandibular metastatic lesion: case report. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2007; 12: E424 E International Journal of Oral Science
Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst
 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
Large Dentigerous Cyst
 Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki
 Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Disclosure. Educational Objectives. Terminology. Odontogenic Cysts. Terminology
 Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Disclosure Lisa J. Koenig BChD, DDS, MS Professor & Program Director, Oral Medicine and Oral Radiology Marquette University School of Dentistry Consultant to Soredex for the Scanora 3D and 3Dx Author/Editor
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter. Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July Volume 2
 Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
Examination of teeth and gingiva
 Examination of teeth and gingiva Siriporn Chattipakorn, DDS, PhD. SUBJECTIVE HISTORY Chief complaint In patient s own words My tooth hurts when I chew hard foods I can t drink cold drink I have bad breath
Examination of teeth and gingiva Siriporn Chattipakorn, DDS, PhD. SUBJECTIVE HISTORY Chief complaint In patient s own words My tooth hurts when I chew hard foods I can t drink cold drink I have bad breath
IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman
 IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman This is an area where radiology plays an important role in assisting with the diagnosis, determining the size of the lesion and the relationship to adjacent
IMAGING OF CYSTS OF THE JAWS July 2002 N. Serman This is an area where radiology plays an important role in assisting with the diagnosis, determining the size of the lesion and the relationship to adjacent
DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION
 DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry www.vetdentaltraning.com www.vetdentalrad.com Interpreting dental
DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry www.vetdentaltraning.com www.vetdentalrad.com Interpreting dental
Common/Important Radiolucencies. B. Most Common Location Apex of permanent first molar, rare in primary teeth.
 Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
Cincinnati Dental Association Breakfast at Tiffany s: The Jewels and Gems of Oral Pathology November 17, 2010 John A. Svirsky, DDS, MEd Virginia Commonwealth University 804-828-0547 FAX: 804-828-6234 EMAIL:
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts. SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST
 The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
The clinical appearance and diagnosis of odontogenic cysts SE Arc-Állcsont-Szájsebészeti és Fogászati Klinika BUDAPEST DEFINITION A cyst is a sac with walls of connective tissue, lined by epithelium, containing
The future of health is digital
 Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Squamous cell carcinoma of the maxillary sinus mimicking periodontitis
 Squamous cell carcinoma of the maxillary sinus mimicking periodontitis 저자저널명발행기관 NDSL URL Na, Ji Yeon ; Kang, Joo Hyun ; Choi, Seong-Ho ; Jeong, Ho-Gul ; Han, Sang-Sun 大韓齒科醫師協會誌 = The journal of the Korean
Squamous cell carcinoma of the maxillary sinus mimicking periodontitis 저자저널명발행기관 NDSL URL Na, Ji Yeon ; Kang, Joo Hyun ; Choi, Seong-Ho ; Jeong, Ho-Gul ; Han, Sang-Sun 大韓齒科醫師協會誌 = The journal of the Korean
Large periapical lesion: Healing without knife and incision
 Large periapical lesion: Healing without knife and incision Ridhima Suneja College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, UAE ABSTRACT Three dimensional obturation of root space has always yielded
Large periapical lesion: Healing without knife and incision Ridhima Suneja College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, UAE ABSTRACT Three dimensional obturation of root space has always yielded
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION. By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur
 COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position
 A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
Principles of diagnosis in Endodontics. Pain History. Patient Assessment. Examination. Examination 11/07/2014
 Principles of diagnosis in Endodontics Diagnosis, pulpitis, perio-endo. Treatment planning & case selection Patients assessment Special tests which help us diagnose pulpal disease How reliable are they?
Principles of diagnosis in Endodontics Diagnosis, pulpitis, perio-endo. Treatment planning & case selection Patients assessment Special tests which help us diagnose pulpal disease How reliable are they?
Vascular. Extravasated blood. Melanocytic. Tattoo. Epidermolysis bullosa. Lichen planus. Pemphigoid Pemphigus Lupus. Candidosis. Surface Epithelial
 Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
Oral Soft Tissue Pathology Epithelial Thickening (white) Combination Erythema migrans Epithelial atrophy (red) Surface Lesions Clinical Impression Enlargements Surface Debris Pigmented Vesicular Ulcerated
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology. & supporting structures. Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej
 Radiology Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej & supporting structures A radiograph is only one part of the diagnostic process. Usually one does NOT make a diagnosis solely from a radiograph. A diagnosis
Radiology Lec. 14 Common diseases of teeth Dr. Areej & supporting structures A radiograph is only one part of the diagnostic process. Usually one does NOT make a diagnosis solely from a radiograph. A diagnosis
2018 Dental Code Set For dates of service from 1/1/ /31/2018
 D0120 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION - ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0140 LIMITED ORAL EVALUATION - PROBLEM FOCUSED D0150 COMPREHENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION - NEW OR ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0160 DETAILED AND EXTENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION
D0120 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION - ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0140 LIMITED ORAL EVALUATION - PROBLEM FOCUSED D0150 COMPREHENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION - NEW OR ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0160 DETAILED AND EXTENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION
2018 Dental Code Set
 D0120 D0140 D0150 D0160 D0180 D0210 D0220 D0230 D0240 D0250 D0251 D0270 D0272 D0273 D0274 D0277 D0290 D0310 D0330 D0340 D0350 D0393 D0470 D0502 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION ESTABLISHED PATIENT LIMITED ORAL
D0120 D0140 D0150 D0160 D0180 D0210 D0220 D0230 D0240 D0250 D0251 D0270 D0272 D0273 D0274 D0277 D0290 D0310 D0330 D0340 D0350 D0393 D0470 D0502 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION ESTABLISHED PATIENT LIMITED ORAL
4/2/17. Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology. Composite of in-focused and blurred images. It s a type of Tomogram.
 Fundamentals Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology It s a type of Tomogram Jimmie L. Harper D.D.S., M.S. Cincinnati Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inc. Volunteer Assistant Professor, Division
Fundamentals Panoramic Radiography: Normal Variants and Pathology It s a type of Tomogram Jimmie L. Harper D.D.S., M.S. Cincinnati Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inc. Volunteer Assistant Professor, Division
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例
 高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
高雄醫學大學 口腔醫學院 口腔病理影像科 牙科 X 光影像判讀 教學範例 Content Image No. 001 Dentigerous cyst over left upper embedded canine--------------------- 頁 1 Image No. 002---------------------------------------------------------------
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses. Gingival Lesions
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Central Area
 VARIA Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Central Area Carmen Elena Georgescu 1, Gabriela Tãnase 2, Augustin Mihai 3 Bucharest, Romania Summary The radiopgraphic recognition of disease requires knowledge
VARIA Normal Radiographic Anatomy Maxillary Central Area Carmen Elena Georgescu 1, Gabriela Tãnase 2, Augustin Mihai 3 Bucharest, Romania Summary The radiopgraphic recognition of disease requires knowledge
CHAPTER 3 - DEFINITION, SCOPE, AND INDICATIONS FOR ENDODONTIC THERAPY ARNALDO CASTELLUCCI
 Contents Volume I CHAPTER 1 - A BRIEF HISTORY OF ENDODONTICS CHAPTER 2 - EMBRYOLOGY Crown formation Root formation Single- and multiple-root formation The formation of lateral canals Exposed dentin and
Contents Volume I CHAPTER 1 - A BRIEF HISTORY OF ENDODONTICS CHAPTER 2 - EMBRYOLOGY Crown formation Root formation Single- and multiple-root formation The formation of lateral canals Exposed dentin and
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. ADENOMATOID ODONTOGENIC TUMOR WITH RARE
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies
 Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve involvement
 Yadegari A,et al J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci e(issn): 2383-2754 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve
Yadegari A,et al J Res Dentomaxillofac Sci e(issn): 2383-2754 Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences Surgical management of Ossifying Fibroma of the mandible with inferior alveolar nerve
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Only 40% of the Story
 X-RAY, X-RAY, READ ALL ABOUT IT! The Use and Utility of Dental Radiographs in Practice Lisa Fink, DVM, DAVDC Dentistry & Oral Surgery Service October 4, 2015 Only 40% of the Story Radiographs of teeth
X-RAY, X-RAY, READ ALL ABOUT IT! The Use and Utility of Dental Radiographs in Practice Lisa Fink, DVM, DAVDC Dentistry & Oral Surgery Service October 4, 2015 Only 40% of the Story Radiographs of teeth
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
A case report of cemento-ossifying fibroma presenting as a mass of. the ethmoid sinus
 Received: 27.3.2010 Accepted: 1.8.2010 Case Report A case report of cemento-ossifying fibroma presenting as a mass of the ethmoid sinus Ali Hekmatnia a, Amirhossein Ghazavi* b, Masih Saboori c, Parvin
Received: 27.3.2010 Accepted: 1.8.2010 Case Report A case report of cemento-ossifying fibroma presenting as a mass of the ethmoid sinus Ali Hekmatnia a, Amirhossein Ghazavi* b, Masih Saboori c, Parvin
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Ossifying Fibroma of Jaw: A Clinico-Radiographic Case Series Dr Satyapal Johaley 1, Dr Freny R Karjodkar
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Ossifying Fibroma of Jaw: A Clinico-Radiographic Case Series Dr Satyapal Johaley 1, Dr Freny R Karjodkar
Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases
 (2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
(2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
2016 Dental Code Set For dates of service from 1/1/16-12/31/16
 HCPCS DESCRIPTIONS D0120 D0140 D0150 D0160 D0180 D0210 D0220 D0230 D0240 D0250 D0260 D0270 D0272 D0273 D0274 D0277 D0290 D0310 D0330 D0340 D0350 D0470 D0502 D1110 D1206 D1208 D1352 D2140 D2150 D2160 D2161
HCPCS DESCRIPTIONS D0120 D0140 D0150 D0160 D0180 D0210 D0220 D0230 D0240 D0250 D0260 D0270 D0272 D0273 D0274 D0277 D0290 D0310 D0330 D0340 D0350 D0470 D0502 D1110 D1206 D1208 D1352 D2140 D2150 D2160 D2161
MAXILLARY INJECTION TECHNIQUE. Chinthamani Laser Dental Clinic
 MAXILLARY INJECTION TECHNIQUE Chinthamani Laser Dental Clinic Introduction A number of injection techniques are available to aid in providing clinically adequate anesthesia of the teeth and soft and hard
MAXILLARY INJECTION TECHNIQUE Chinthamani Laser Dental Clinic Introduction A number of injection techniques are available to aid in providing clinically adequate anesthesia of the teeth and soft and hard
6610 NE 181st Street, Suite #1, Kenmore, WA
 660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
LIST OF COVERED DENTAL SERVICES
 LIST OF COVERED DENTAL SERVICES The following is a complete list of those dental Services which will be considered for payment by Constitution Life Insurance Company after the expiration of any applicable
LIST OF COVERED DENTAL SERVICES The following is a complete list of those dental Services which will be considered for payment by Constitution Life Insurance Company after the expiration of any applicable
FOCAL CEMENTO-OSSEOUS DYSPLASIA OF LOWER JAW IN AN ELDERLY WOMAN: CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL FEATURES AND MANAGEMENT IN A CASE REPORT
 www.djas.co.in ISSN No-31-148 DJAS 4(III), 08-1, 016 All rights are reserved CASE REPORT Dental JOURNAL of Advance Studies FOCAL CEMENTO-OSSEOUS DYSPLASIA OF LOWER JAW IN AN ELDERLY WOMAN: CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL
www.djas.co.in ISSN No-31-148 DJAS 4(III), 08-1, 016 All rights are reserved CASE REPORT Dental JOURNAL of Advance Studies FOCAL CEMENTO-OSSEOUS DYSPLASIA OF LOWER JAW IN AN ELDERLY WOMAN: CLINICOPATHOLOGICAL
Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. V. (Mar. 2014), PP 26-30 Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report Dr. Sahana Srinath
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. V. (Mar. 2014), PP 26-30 Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report Dr. Sahana Srinath
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions. An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling. John L. Alonge, MS, DDS
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling John L. Alonge, MS, DDS Goals 1. Review the diagnostic process needed to formulate a differential diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling John L. Alonge, MS, DDS Goals 1. Review the diagnostic process needed to formulate a differential diagnosis
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis
 RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis MODULE 1: The Introduction. Chief complaint Demographics Age Sex Race Historical findings Physical findings Clinical Radiographic Location Maxilla/mandible
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Differential Diagnosis MODULE 1: The Introduction. Chief complaint Demographics Age Sex Race Historical findings Physical findings Clinical Radiographic Location Maxilla/mandible
TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES
 Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
You know you would like to stop swearing at the computer after each shot. Troubleshooting oral radiography
 You know you would like to stop swearing at the computer after each shot Troubleshooting oral radiography Goals of oral radiology Achieve diagnostic images of the teeth and surrounding bone. Images should
You know you would like to stop swearing at the computer after each shot Troubleshooting oral radiography Goals of oral radiology Achieve diagnostic images of the teeth and surrounding bone. Images should
IMPACTED CANINES. Unfortunately, this important tooth is the second most common tooth to be impacted after third molars
 IMPACTED CANINES After we talked about impacted third molars, today we ll discuss about maxillary impacted canines in upper dental arch, how to manage these cases as a dental surgeon. You will study about
IMPACTED CANINES After we talked about impacted third molars, today we ll discuss about maxillary impacted canines in upper dental arch, how to manage these cases as a dental surgeon. You will study about
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adult performance horse dental care in, 505 519 bit seat reduction in, 514 515 canine teeth disorders, 515 diagnostic nerve blocks in,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adult performance horse dental care in, 505 519 bit seat reduction in, 514 515 canine teeth disorders, 515 diagnostic nerve blocks in,
Pre-reading - radiolucencies
 Pre-reading - radiolucencies Multiple radiolucencies o Suggests a systemic cause o Most likely: cherubism or KCOT s of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome o Sometimes: florid osseous dysplasia (if limited
Pre-reading - radiolucencies Multiple radiolucencies o Suggests a systemic cause o Most likely: cherubism or KCOT s of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome o Sometimes: florid osseous dysplasia (if limited
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors
 Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
[ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018
![[ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018 [ 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha India Abstract: Keywords ARTICLE 20/07/ /09/2018](/thumbs/87/95905171.jpg) Dentigerous Cyst Associated with an Impacted Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature [PP: 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha, Department of
Dentigerous Cyst Associated with an Impacted Mesiodens: A Rare Case Report with Review of Literature [PP: 06-10] Dr. B. Siva Reddy, Dr. B. Ajay Reginald, Dr. D. Sireesha, Dr. Meda Samatha, Department of
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours
 Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
Odontomes and Odontogenic tumours Odontomes Developmental hamartoma Hamartoma: normal tissue in abnormal location Any cells to be neoplastic it must be able to replicate, which is not seen in hamartoma
Case Report A Review and Report of Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma in a 4-Year-Old Child
 Volume 2016, Article ID 7536304, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7536304 Case Report A Review and Report of Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma in a 4-Year-Old Child Afsaneh Nekouei, Alireza Eshghi,
Volume 2016, Article ID 7536304, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7536304 Case Report A Review and Report of Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma in a 4-Year-Old Child Afsaneh Nekouei, Alireza Eshghi,
DISEASES OF THE JAWS I
 DISEASES OF THE JAWS I ODONTOGENIC AND PERIODONTAL INFECTIONS ODONTOGENIC INFECTIONS PERIAPICAL GRANULOMA PERIAPICAL ABSCESS APICAL PERIODONTAL CYST PHOENIX ABSCESS FISTULA, DRAINING SINUS SPACE INFECTIONS
DISEASES OF THE JAWS I ODONTOGENIC AND PERIODONTAL INFECTIONS ODONTOGENIC INFECTIONS PERIAPICAL GRANULOMA PERIAPICAL ABSCESS APICAL PERIODONTAL CYST PHOENIX ABSCESS FISTULA, DRAINING SINUS SPACE INFECTIONS
INTERPRETATION RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION. Law of Symmetry. We will be reviewing: 7/30/16
 RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Pam Wood, CDA, RDH, M.Ed, CAGS Community College of Rhode Island pwood@ccri.edu INTERPRETATION the ability to read what is revealed on a dental radiograph any dental professional
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION Pam Wood, CDA, RDH, M.Ed, CAGS Community College of Rhode Island pwood@ccri.edu INTERPRETATION the ability to read what is revealed on a dental radiograph any dental professional
Senior Dental Insurance Scheduled Allowance
 Senior Dental Insurance Scheduled Allowance LIST OF COVERED DENTAL SERVICES The following is a complete list of those dental services which will be considered for payment by The American Progressive Life
Senior Dental Insurance Scheduled Allowance LIST OF COVERED DENTAL SERVICES The following is a complete list of those dental services which will be considered for payment by The American Progressive Life
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS
 MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS MALIGNANT TUMOURS OF THE JAWS Squamous cell carcinoma Osteogenic sarcoma Chondrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Malignant lymphomas (incl. Burkitt s) Multiple myeloma Ameloblastoma Secondary
Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs
 Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs http://www.medispainstitute.com/menu_laser_tattoo.html http://www.life123.com/bm.pix/bigstockphoto_close_up_of_eye_surgery_catar_2264267.s600x600.jpg
Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs http://www.medispainstitute.com/menu_laser_tattoo.html http://www.life123.com/bm.pix/bigstockphoto_close_up_of_eye_surgery_catar_2264267.s600x600.jpg
ENDODONTIC PAIN CONTROL. Dr. Ameer H. AL-Ameedee Ph.D in Operative and Esthetic Dentistry
 ENDODONTIC PAIN CONTROL Dr. Ameer H. AL-Ameedee Ph.D in Operative and Esthetic Dentistry ENDODONTIC EMERGENCIES ARE CHALLENGE IN BOTH DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT -EVERY CASE IS A COMPLETE SEPARATE STORY Diagnostic
ENDODONTIC PAIN CONTROL Dr. Ameer H. AL-Ameedee Ph.D in Operative and Esthetic Dentistry ENDODONTIC EMERGENCIES ARE CHALLENGE IN BOTH DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT -EVERY CASE IS A COMPLETE SEPARATE STORY Diagnostic
Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family
 ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2014 Jan-Mar;11(1):88-92 Case Report Article Unusual transmigration of canines report of two cases in a family Sulabha A. Narsapur 1 Sameer Choudhari 2 Shrishal
The. Cone Beam. Conversation. A Townie endodontist shares 5 reasons she s sold on CBCT
 The Cone Beam Conversation A Townie endodontist shares 5 reasons she s sold on CBCT by Dr. Sonia Chopra Dr. Sonia Chopra is a practicing endodontist with 10 years of experience who currently practices
The Cone Beam Conversation A Townie endodontist shares 5 reasons she s sold on CBCT by Dr. Sonia Chopra Dr. Sonia Chopra is a practicing endodontist with 10 years of experience who currently practices
22 yo female presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #24
 Erick Sato Case Report Non-Surgical Root Canal Therapy #24 22 yo female presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #24 Subjective: Chief Complaint: My tooth is dark, and my dentist referred me for
Erick Sato Case Report Non-Surgical Root Canal Therapy #24 22 yo female presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #24 Subjective: Chief Complaint: My tooth is dark, and my dentist referred me for
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH
 FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
Let s start from the basics for a little review. The Mouth Is Like a Black Hole. But he s friendly at home. Always Wear Gloves!
 The Mouth Is Like a Black Hole Seek and ye shall find: Recognition of Oral Lesions in the Exam Room Lisa Fink, DVM, DAVDC Dentistry & Oral Surgery Service October 4, 2015 But he s friendly at home Part
The Mouth Is Like a Black Hole Seek and ye shall find: Recognition of Oral Lesions in the Exam Room Lisa Fink, DVM, DAVDC Dentistry & Oral Surgery Service October 4, 2015 But he s friendly at home Part
 www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
Principles of endodontic surgery
 Principles of endodontic surgery Note: the doctor said that this lecture mainly contain notes, so we should study it from the book for further information (chapter 18) principles of endodontic surgery.
Principles of endodontic surgery Note: the doctor said that this lecture mainly contain notes, so we should study it from the book for further information (chapter 18) principles of endodontic surgery.
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. CASE REPORT RADICULAR CYST: A CASE REPORT
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. CASE REPORT RADICULAR CYST: A CASE REPORT
Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
Case Presentation: Figure 1. Palatal lesion. Figure 2. Panoramic xray
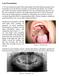 Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
INDEX. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. DENTISTRY
 DENTISTRY INDEX Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. Acquired brachygnathia, 302-303 Acquired dental diseases, 291-307. See also Dental diseases, acquired. Adamantinoma(s), 303-305
DENTISTRY INDEX Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. Acquired brachygnathia, 302-303 Acquired dental diseases, 291-307. See also Dental diseases, acquired. Adamantinoma(s), 303-305
Pre op Failed endodontic treatment with sinus involvement.
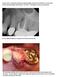 Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
Index. oralmaxsurgery.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, pediatric, 50 51 Ameloblastic carcinoma, pediatric, 17, 49 Ameloblastic fibro-odontoma, pediatric, 54 Ameloblastic
Jaws: Cysts and Odontogenic Neoplasms
 Topic 10: Jaw Cysts General Features of Jaw Cysts Sources of Epithelium in Cysts Radiographic Features of Jaw Cysts Microscopic Features of Jaw Cysts Treatment and Prognosis of Jaw Cysts Classification
Topic 10: Jaw Cysts General Features of Jaw Cysts Sources of Epithelium in Cysts Radiographic Features of Jaw Cysts Microscopic Features of Jaw Cysts Treatment and Prognosis of Jaw Cysts Classification
Focus On: Mandibular Fractures
 Focus On: Mandibular Fractures Fracture of the mandibles is a common injury in dogs and cats and can arise from a variety of situations. How to manage these fractures will be the subject of this article.
Focus On: Mandibular Fractures Fracture of the mandibles is a common injury in dogs and cats and can arise from a variety of situations. How to manage these fractures will be the subject of this article.
Case Report Aberrant Anatomical Variation of Maxillary Sinus Mimicking Periapical Cyst: A Report of Two Cases and Role of CBCT in Diagnosis
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 757645, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/757645 Case Report Aberrant Anatomical Variation of Maxillary Sinus Mimicking Periapical Cyst: A Report
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 757645, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/757645 Case Report Aberrant Anatomical Variation of Maxillary Sinus Mimicking Periapical Cyst: A Report
Employee Benefit Fund July 2018 ADA Codes and Plan Fees
 CSEA Employee Benefit Fund July 2018 ADA Codes and Plan Fees DIAGNOSTIC D0120 periodic oral examination 40 34 42 45 48 38 30 32 31 D0140 limited oral examination (Does not look at 9110) 40 34 42 45 48
CSEA Employee Benefit Fund July 2018 ADA Codes and Plan Fees DIAGNOSTIC D0120 periodic oral examination 40 34 42 45 48 38 30 32 31 D0140 limited oral examination (Does not look at 9110) 40 34 42 45 48
Everything You Wanted to Know About Extractions but Were Afraid to Ask
 Everything You Wanted to Know About Extractions but Were Afraid to Ask Tooth extraction is a surgical procedure with serious potential complications and should only be performed by a trained veterinarian.
Everything You Wanted to Know About Extractions but Were Afraid to Ask Tooth extraction is a surgical procedure with serious potential complications and should only be performed by a trained veterinarian.
An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report
 J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
THE GENERAL DENTIST AND TIMELY REFERRAL TO THE ENDODONTIST
 CLINICAL THE GENERAL DENTIST AND TIMELY REFERRAL TO THE ENDODONTIST Andrei Berdichewsky, DDS 1 The use of endodontic treatment to solve problems related to pulpal and periapical pathologies is extremely
CLINICAL THE GENERAL DENTIST AND TIMELY REFERRAL TO THE ENDODONTIST Andrei Berdichewsky, DDS 1 The use of endodontic treatment to solve problems related to pulpal and periapical pathologies is extremely
Recurrent symptomatic cemento-osseous dysplasia: A case report
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2018; 48: 131-7 https://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2018.48.2.131 Recurrent symptomatic cemento-osseous dysplasia: A case report Chang-Ki Min 1, Kwang-Joon Koh 1, Kyoung-A Kim 1, *
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2018; 48: 131-7 https://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2018.48.2.131 Recurrent symptomatic cemento-osseous dysplasia: A case report Chang-Ki Min 1, Kwang-Joon Koh 1, Kyoung-A Kim 1, *
Clinical details: Details of scan: CONE BEAM CT REPORT: Name: H. B. Gender: Reason for referral: Referred by:
 Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth
 New Edition Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth A Decision Guide American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/treatmentoptions TREATMENT PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS The Treatment Options for the
New Edition Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth A Decision Guide American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/treatmentoptions TREATMENT PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS The Treatment Options for the
Ameloblastic Carcinoma of the Mandible: a Rare Case Report
 IBIMA Publishing Journal of Research and Practice in Dentistry http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/dent/dent.html Vol. 2015 (2015), Article ID 672596, 6 pages DOI: 10.5171/2015.672596 Case Report Ameloblastic
IBIMA Publishing Journal of Research and Practice in Dentistry http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/dent/dent.html Vol. 2015 (2015), Article ID 672596, 6 pages DOI: 10.5171/2015.672596 Case Report Ameloblastic
Complex Odontome: A Review & Case Report Saxena Vasu Siddhartha 1, Karjodkar Freny 2
 Complex Odontome: A Review & Saxena Vasu Siddhartha 1, Karjodkar Freny 2 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Professor & Head 1 Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Career Post Graduate Institute of Dental Sciences
Complex Odontome: A Review & Saxena Vasu Siddhartha 1, Karjodkar Freny 2 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Professor & Head 1 Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Career Post Graduate Institute of Dental Sciences
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare case report
 Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Case Report Soft Tissue Reconstruction with Free Gingival Graft Technique following Excision of a Fibroma
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 248363, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/248363 Case Report Soft Tissue Reconstruction with Free Gingival Graft Technique following Excision of a
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 248363, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/248363 Case Report Soft Tissue Reconstruction with Free Gingival Graft Technique following Excision of a
INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report
 Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Case Report INFECTED DENTIGEROUS CYST IN IMPACTED CANINE- A case report Gazala Fatima Parveen, M.D. Akheel 1 Department of oral & maxillofacial surgery, MCDRC Lucknow, U.P.,India 1-Department of Oral &
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws
 Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
BOSTON TEACHERS UNION PARAPROFESSIONAL HEALTH AND WELFARE FUND Schedule of Covered Dental Procedures for the Dental Plan - Effective January 1, 2009
 TYPE 1 D0120 Periodic oral evaluation 27.81 D0140 Limited oral evaluation - problem focused 43.15 D0145 Oral evaluation for a patient under three years of age and 22.20 counseling with primary caregiver
TYPE 1 D0120 Periodic oral evaluation 27.81 D0140 Limited oral evaluation - problem focused 43.15 D0145 Oral evaluation for a patient under three years of age and 22.20 counseling with primary caregiver
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT
 Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Maxilla and mandible benign lesions: Radiologic Findings and Differential Diagnosis in CT Poster No.: C-0964 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Lopez 1, E. Marcos Naranjo 2, M. D.
Pictorial Essay. CT of Calcifying Jaw Bone Diseases
 Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
Pictorial Essay CT of Calcifying Jaw one Diseases Koichi Yonetsu 1 and Takashi Nakamura Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.204.207 on 01/08/18 from IP address 46.3.204.207. Copyright RRS. For personal
INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS
 INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS PROVIDER CODE TABLES Note: Due to possible changes in Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP) policy or national coding updates, inclusion of a code on the code tables
INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS PROVIDER CODE TABLES Note: Due to possible changes in Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP) policy or national coding updates, inclusion of a code on the code tables
Here are some frequently asked questions about Endodontic treatment:
 Here are some frequently asked questions about Endodontic treatment: What is an "Endodontist"? Endodontists are dentists who specialize in treating the soft inner tissue of your tooth's roots. After they
Here are some frequently asked questions about Endodontic treatment: What is an "Endodontist"? Endodontists are dentists who specialize in treating the soft inner tissue of your tooth's roots. After they
NC Medicaid Dental Reimbursement Rates General Dentist, Oral Surgeon, Pediatric Dentist, Periodontist, & Orthodontist Effective Date: January 1, 2017
 NC Dental Reimbursement s Refer to the NC and Health Choice Clinical Coverage Policies on the DMA website. D0120 Periodic oral evaluation 24.51 D0140 Limited oral evaluation - problem focused 34.94 D0145
NC Dental Reimbursement s Refer to the NC and Health Choice Clinical Coverage Policies on the DMA website. D0120 Periodic oral evaluation 24.51 D0140 Limited oral evaluation - problem focused 34.94 D0145
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 ORAL SURGERY TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION
 TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL 6010.47-M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 Issue Date: October 8, 1986 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(e)(10) I. DESCRIPTION There are certain oral surgical
TRICARE/CHAMPUS POLICY MANUAL 6010.47-M DEC 1998 SPECIAL BENEFIT INFORMATION CHAPTER 8 SECTION 1.4 Issue Date: October 8, 1986 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(e)(10) I. DESCRIPTION There are certain oral surgical
Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma
 Case Report Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma Zahra Dalili 1, Somayeh Nemati 2, Fatemeh Shahsavari 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Maxillofacial Radiology, Guilan University
Case Report Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma A Radiographic Diagnostic Dilemma Zahra Dalili 1, Somayeh Nemati 2, Fatemeh Shahsavari 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Maxillofacial Radiology, Guilan University
Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report
 457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
