DENTAL EXTRACTIONS MADE EASIER. Brook A. Niemiec, DVM
|
|
|
- Blake Miles Hancock
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DENTAL EXTRACTIONS MADE EASIER Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Diplomate, European Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry San Diego Vet Dental Training Center Step 1: OBTAIN CONSENT NEVER extract teeth without owner consent (preferably written), no matter how bad the problem, or how obvious the decision is. Make sure that you have a valid daytime number (or numbers) for the client and inform them they must be available during surgery hours. Consider loaning pagers to clients for the day, as this author has found this to be a very effective means to contact clients. If the client cannot be reached and prior consent was not obtained, DO NOT PULL THE TOOTH. Document the problem, recover the patient, and reschedule the work. Remember, the tooth can always be extracted later, but it cannot be put back in! Step 2: DENTAL RADIOGRAPHS Dental radiographs should be exposed on all teeth prior to extraction. Dental radiographs are invaluable resources for the practiconer. Radiographs allow the practitioner to determine the amount of disease present, any root abnormalities or ankylosis. Help with radiographic interpretation is available while the patient is under anesthesia at In addition, the radiographs will serve as evidence for the extraction in the medical record. Radiographs should also be exposed postextraction to document complete removal of the tooth. Step 3: OBTAIN PROPER VISABILITY AND ACCESSABILITY The patient should be positioned in such a way as to allow maximum visibility of the area as well as make the surgeon most comfortable. Note that during the extraction procedure the ideal position may change and the patient should be adjusted appropriately. The lighting should be bright and focusable on the surgical field. Suction, air/water syringes, and gauze should be utilized continually to keep the surgical field clear, and mouth gags can be used to hold the mouth in proper position for surgery. Finally, magnification may help the surgeon locate furcations or retained root tips. Step 4: PAIN MANAGEMENT Extractions are surgical procedures and are moderately to severely painful for the patient. Depending on patient health, a multimodal approach (combination of opioids, NSAIDs, local anesthetics, and dissociative) should be employed, as this provides superior analgesia. Preemptive analgesia is proven to be more effective than postoperative, and it is therefore important to administer the drugs BEFORE the painful procedure.
2 SINGLE ROOT EXTRACTIONS Step 5: INCISE THE GINGIVAL ATTACHMENT This is accomplished with a scalpel blade (number 11 or 15), elevator, or luxator. The selected instrument is placed into the gingival sulcus with the tip of the blade angled toward the tooth (this will help avoid going outside the bone and creating a defect or cutting through the gingiva). The blade is then advanced apically to the level of the alveolar bone, and the instrument is carefully worked around the entire tooth circumference. This step is very helpful as the gingival attachment contributes approximately15% of the retentive strength of the periodontal apparatus. More importantly, however, this procedure will keep the gingiva from tearing during the extraction procedure. This is most important with mobile teeth where little elevation is needed, but one edge is still attached. Gingival tearing can cause defects that require closure or can make a planned closure more difficult. Step 6: ELEVATE THE TOOTH Elevation is the most dangerous step in the extraction procedure. Remember that you are holding a sharp surgical instrument and working in an area of numerous critical and delicate structures. There have been many reports of eyes that have been gouged and lost by extraction instruments as well as at least one confirmed fatality due to an elevator puncturing a patient s brain. The index finger is placed near the tip of the instrument to avoid causing iatrogenic trauma in the event of instrument slippage or encountering diseased bone. In addition, the jaw should be gently held with the opposite hand to provide stability and avoid mandibular fracture. First, select an instrument which matches the curvature and size of the root. There are numerous instruments available including the classic elevator, the luxating elevator, and the winged elevators. Classic elevators and winged elevators are used in an insert and twist motion to tear the periodontal ligament, whereas luxators are used in a rocking motion during insertion to fatigue as well as cut the periodontal ligament. Luxators can be GENTLY twisted for elevation, but they are not designed for this and can be easily damaged when used in this manner. Elevation is initiated by inserting the elevator or luxator firmly yet gently into the periodontal space. The insertion should be performed while keeping the instrument at about a 10 to 20 degree angle toward the tooth, to avoid slippage. Once in the space between the bone and the tooth, the instrument is gently twisted with two-finger pressure. This is not to say that the instrument should be held with two fingers, rather the entire hand should be used to hold the instrument. Twist only with the force that you could generate when holding with two fingers. Hold the position for seconds to fatigue and tear the periodontal ligament. It is important to note that the periodontal ligament is very effective in resisting intense, short forces. It is only by the exertion of prolonged force (i.e seconds) that the ligament will become weakened. Heavy stresses only serve to put pressure on the alveolar bone and tooth which can result in the fracture of one of these structures, so it is important not to use too much force. After holding for 10 to 30 seconds, reposition the instrument about 1/8 of the way around the tooth and repeat the above step. Continue this procedure 360 degrees around the tooth, each time moving the elevator apically as much as possible. Depending
3 on the level of disease and the size of the tooth, a few to several rotations of the tooth may be necessary. The key point to successful elevation is PATIENCE. Only by slow, consistent elevation will the root loosen without breaking. It is always easier to extract an intact root than to remove fractured root tips. Step 7: EXTRACT THE TOOTH: Removing the tooth should only be attempted after the tooth is very mobile and loose. This is accomplished by grasping the tooth with the extraction forceps and gently pulling the tooth from the socket. Do NOT apply undue pressure as this may result in root fracture. In many cases, especially with premolars, the roots are round in shape and will respond favorably to gentle twisting and holding of the tooth while applying traction. This should not be performed if there are root abnormalities (significant curves, weakening) seen on the pre-operative radiograph. It is helpful to think of the extraction forceps as an extension of your fingers. Undue pressure should not be applied. If the tooth does not come out easily, more elevation is necessary. Start elevation again until the tooth is loose enough to be easily removed from the alveolus. Step 8: AVELOPLASTY This step is performed to remove diseased tissue or bone, as well as rough boney edges that could irritate the gingiva and delay healing. Diseased tissue can be removed by hand with a curette. Bone removal and smoothing is best performed with a carbide, or preferably a coarse diamond bur on a water-cooled high-speed air driven hand-piece. Alternatively, ronguers or bone files may be used if a high-speed dental unit is unavailable. Next, the alveolus should be gently flushed with a 0.12% chlorhexidine solution to decrease bacterial contamination. After the alveolus is cleaned, it may be packed with an osseopromotive substance. Step 9: CLOSURE OF THE EXTRACTION SITE: This is a controversial subject among veterinary dentists, and thus some texts recommend suturing only in large extractions, other authors (including this one) recommend suturing almost all extraction sites. Closure of the extraction site promotes hemostasis and improve post-operative discomfort and aesthetics. It is always indicated in cases of larger teeth (e.g. canines, carnassials), or any time that a gingival flap is created to allow for easier extraction. This is best accomplished with size 3/0 to 5/0 absorbable sutures on a reverse cutting needle. Closure is performed with a simple interrupted pattern with sutures placed 2 to 3 mm apart. It is further recommended to utilize one additional throw over manufacturer s recommendations to counteract tongue action. In regards to flap closure, there are several key points associated with successful healing. The first and most important is that there must be no tension on the incision line. If there is any tension on the suture line, it will not heal. Tension can be removed by extending the gingival incision along the arcade (called an envelope flap) or by creating vertical releasing incisions and fenestrating the periosteum. The periosteum is a very thin fibrous tissue which attaches the buccal mucosa to the underlying bone. Since it is
4 fibrotic, it is inflexible and will interfere with the ability to close the defect without tension. The buccal mucosa is very flexible and therefore will stretch to cover large defects. If there is no tension, the flap should stay in position without sutures. If at all possible, the suture line should not be made over a void. If sufficient tissue is present, consider removing some on the attached side to make the suture line over bone. Always suture from the unattached (flap side) to the attached tissue, because this avoids tearing the flap as the needle dulls. Finally, ensure that all tissue edges have been thoroughly debrided as intact epithelial tissues will not heal. EXTRACTION OF MULTI ROOTED TEETH: Section all multi-rooted teeth into single rooted pieces. The roots of almost all multi-rooted teeth are divergent and this will cause the root tips to break off if extractions are attempted in one piece. Root fracture can occur even if a tooth is relatively mobile to start with. With mobile teeth, the sectioning step alone often allows for simple extraction. The best tool for sectioning teeth is a bur on a high-speed air driven hand piece. Besides being the quickest and most efficient tool for the job, it also has air and water coolant that will avoid overheating the tooth. Many different styles of burs are available, however this author prefers a cross-cut taper fissure bur (699 for cats and small dogs, 701 for medium dogs and 702 for large breeds). The best way to section the teeth is to start at the furcation and work towards the crown of the tooth. This method is used for two major reasons. First, it avoids the possibility of missing the furcation and cutting down into a root, which subsequently weakens the root and increases the risk of root fracture. In addition, this method avoids the possibility of cutting through the tooth and inadvertently damaging the gingiva or alveolar bone. After the tooth has been properly sectioned, follow the above steps for each single rooted piece. In some cases, the individual tooth pieces can be carefully elevated against each other to gain purchase.
5 SURGICAL EXTRACTIONS The more difficult extractions are best performed via a surgical approach. This includes canine and carnassial (maxillary fourth premolar and mandibular first molar) teeth, as well as teeth with root malformations or pathology, and finally retained roots. A surgical approach allows the practitioner to remove a small amount of buccal cortical bone, promoting an easier extraction process. A surgical extraction is initiated by creating a gingival flap. This can be a horizontal flap along the arcade (an envelope flap) or a flap with vertical releasing incisions (a full flap). An envelope flap is created by releasing the gingival attachment with a periosteal elevator along the arcade including one to several teeth on either side of the tooth or teeth to be extracted. The gingiva along the arcade is released to or below the level of the mucogingival junction (MGJ) and the flap is connected by incising the gingiva in the interdental spaces. The advantage to this flap is that the blood supply is not interrupted and there is less suturing. The more commonly used flap includes one or more vertical releasing incisions. This method allows for a much larger flap to be created, which (if handled properly) will increase the defects which can be covered. The vertical incisions are created at the line angle of the target tooth, or one tooth mesial and distal to the target tooth. The incisions should be made slightly apically divergent (wider at the base than at the gingival margin). Furthermore, it is important that the incisions be created full thickness, in one motion (rather than slow and choppy). A full thickness incision is created by incising all the way to the bone, and the periosteum is thus kept with the flap. Once created, the entire flap is gently reflected with a periosteal elevator. Care must be taken not to tear the flap, especially at the muco-gingival junction. Following the flap elevation, a small amount of buccal bone should be removed (approximately 1/3 to ½ of the root length depending on the situation) to the depth of the root. This should only be performed on the buccal side. Next, the teeth should be sectioned if multirooted and the teeth then extracted as described above. After the roots are removed the alveolar bone should be smoothed and the defect closed. Closure is initiated with a procedure called fenestrating the periosteum. The periosteum is a very thin fibrous tissue which attaches the buccal mucosa to the underlying bone. Since the periosteum is fibrotic, it is inflexible and will interfere with the ability to close the defect without tension. The buccal mucosa however, is very flexible and will stretch to cover large defects. Consequently, incising the periosteum takes advantage of this attribute. The fenestration should be performed at the base of the flap, and must be very shallow as the periosteum is very thin. This step requires careful attention, as to not cut through or cut off the entire flap. After fenestration, the flap should stay in desired position without sutures. If this is not the case, then tension is still present and further release is necessary prior to closure. Once the release is accomplished, the flap is sutured normally.
Everything You Wanted to Know About Extractions but Were Afraid to Ask
 Everything You Wanted to Know About Extractions but Were Afraid to Ask Tooth extraction is a surgical procedure with serious potential complications and should only be performed by a trained veterinarian.
Everything You Wanted to Know About Extractions but Were Afraid to Ask Tooth extraction is a surgical procedure with serious potential complications and should only be performed by a trained veterinarian.
Elevators. elevators:- There are three major components of the elevator are:-
 Elevators Elevators:- Are exo-levers, instrument designed to elevate or luxate the teeth or roots from their bony socket in close or surgical method of extraction to force a tooth or root along the line
Elevators Elevators:- Are exo-levers, instrument designed to elevate or luxate the teeth or roots from their bony socket in close or surgical method of extraction to force a tooth or root along the line
Surgical removal of wisdom teeth
 Oral surgery/dr.hazem Lecture #8 Rand Herzallah Surgical removal of wisdom teeth Wisdom teeth extraction is harder than the extraction of any other teeth; because of: 1) The anatomical location of the
Oral surgery/dr.hazem Lecture #8 Rand Herzallah Surgical removal of wisdom teeth Wisdom teeth extraction is harder than the extraction of any other teeth; because of: 1) The anatomical location of the
Surgical Therapy. Tuesday, April 2, 13. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS
 Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Complex Exodontia. Jone Kim, DDS, MS
 Complex Exodontia Jone Kim, DDS, MS Diplomate, American Board of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Lecturer, UCLA School of Dentistry, Dept. of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Principle of Complex Exodontia Principle
Complex Exodontia Jone Kim, DDS, MS Diplomate, American Board of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Lecturer, UCLA School of Dentistry, Dept. of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Principle of Complex Exodontia Principle
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Detecting a sinus perforation.
 Extractions and the Sinus Dentistry s Black Hole. Detecting a sinus perforation. How to know when you have a small perforation? Need: Adequate light (headlight preferred) Small suction tip (2 mm diameter)
Extractions and the Sinus Dentistry s Black Hole. Detecting a sinus perforation. How to know when you have a small perforation? Need: Adequate light (headlight preferred) Small suction tip (2 mm diameter)
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior
 Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION
 DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry www.vetdentaltraning.com www.vetdentalrad.com Interpreting dental
DENTAL RADIOGRAPH INTERPRETATION Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry www.vetdentaltraning.com www.vetdentalrad.com Interpreting dental
Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the. Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System
 Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System 1 Introduction This presentation familiarizes you with the basic steps how to use the Inion GTR membrane
Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System 1 Introduction This presentation familiarizes you with the basic steps how to use the Inion GTR membrane
10 steps to a healthy mouth
 Dentistry at Four Paws Veterinary Center Did you know that 80% of animals over 5 years of age have some form of dental disease? At Four Paws, we use the latest techniques and modern equipment to provide
Dentistry at Four Paws Veterinary Center Did you know that 80% of animals over 5 years of age have some form of dental disease? At Four Paws, we use the latest techniques and modern equipment to provide
Educational Training Document
 Educational Training Document Table of Contents Part 1: Resource Document Disclaimer Page: 2 Part 2: Line Item Grade Sheets Page: 3 Release: 11/2016 Page 1 of 6 Part 1: Resource Document Disclaimer The
Educational Training Document Table of Contents Part 1: Resource Document Disclaimer Page: 2 Part 2: Line Item Grade Sheets Page: 3 Release: 11/2016 Page 1 of 6 Part 1: Resource Document Disclaimer The
FS MTS. Micro Periodontal Tissue Scissors
 FEATHERLITE SCISSORS Our patented Flex Series Scissors are designed to have a 300% increase in its shearing angulation compared to conventional scissors. The result is that, no mater what is being cut,
FEATHERLITE SCISSORS Our patented Flex Series Scissors are designed to have a 300% increase in its shearing angulation compared to conventional scissors. The result is that, no mater what is being cut,
Luxator. Design By Dentists. By DIRECTA
 Luxator By DIRECTA Directa s products are developed, tested and evaluated by our elected team of highly-qualified and renowned Swedish and international dentists with the aim of making life easier for
Luxator By DIRECTA Directa s products are developed, tested and evaluated by our elected team of highly-qualified and renowned Swedish and international dentists with the aim of making life easier for
,5 mm mm
 Mini luxators These mini luxators have an anatomically curved blade to adapt to the tooth root. Through a slight rotating movement the periodontal ligaments can be cut cleanly, at the same time dilating
Mini luxators These mini luxators have an anatomically curved blade to adapt to the tooth root. Through a slight rotating movement the periodontal ligaments can be cut cleanly, at the same time dilating
Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques
 I J Pre Clin Dent Res 2014;1(2):49-53 April-June All rights reserved International Journal of Preventive & Clinical Dental Research Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and
I J Pre Clin Dent Res 2014;1(2):49-53 April-June All rights reserved International Journal of Preventive & Clinical Dental Research Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
botiss dental bone & tissue regeneration biomaterials mucoderm 3D-Regenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic
 dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials 3DRegenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic mucoderm Soft Tissue Graft Indications mucoderm is a collagen tissue matrix derived of animal dermis
dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials 3DRegenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic mucoderm Soft Tissue Graft Indications mucoderm is a collagen tissue matrix derived of animal dermis
TOP 5 COMPLICATIONS OF TOOTH EXTRACTIONS
 TOP 5 TOP 5 COMPLICTIONS OF TOOTH EXTRCTIONS Kendall Taney, DVM, DVDC, FVD Center for Veterinary Dentistry and Oral Surgery Gaithersburg, Maryland ecause of the prevalence of periodontal disease in companion
TOP 5 TOP 5 COMPLICTIONS OF TOOTH EXTRCTIONS Kendall Taney, DVM, DVDC, FVD Center for Veterinary Dentistry and Oral Surgery Gaithersburg, Maryland ecause of the prevalence of periodontal disease in companion
IMPACTED CANINES. Unfortunately, this important tooth is the second most common tooth to be impacted after third molars
 IMPACTED CANINES After we talked about impacted third molars, today we ll discuss about maxillary impacted canines in upper dental arch, how to manage these cases as a dental surgeon. You will study about
IMPACTED CANINES After we talked about impacted third molars, today we ll discuss about maxillary impacted canines in upper dental arch, how to manage these cases as a dental surgeon. You will study about
14/09/15. Assessment of Periodontal Disease. Outline. Why is Periodontal assessment needed? The Basics of Periodontal assessment
 Assessment of Periodontal Disease Dr Wendy Turner Outline Why is Periodontal assessment needed? The Basics of Periodontal assessment Probing: Basic Periodontal Examination for adults and children. Detailed
Assessment of Periodontal Disease Dr Wendy Turner Outline Why is Periodontal assessment needed? The Basics of Periodontal assessment Probing: Basic Periodontal Examination for adults and children. Detailed
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery. Dr.maryam khosravi
 Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
Small Animal Dentistry. Presented by: Rebecca Dodge, CVT
 Small Animal Dentistry Presented by: Rebecca Dodge, CVT Topics to be discussed Anatomy and oral examination Common dental problems for canines and felines Client knowledge and prevention tips Anatomy Dog
Small Animal Dentistry Presented by: Rebecca Dodge, CVT Topics to be discussed Anatomy and oral examination Common dental problems for canines and felines Client knowledge and prevention tips Anatomy Dog
You know you would like to stop swearing at the computer after each shot. Troubleshooting oral radiography
 You know you would like to stop swearing at the computer after each shot Troubleshooting oral radiography Goals of oral radiology Achieve diagnostic images of the teeth and surrounding bone. Images should
You know you would like to stop swearing at the computer after each shot Troubleshooting oral radiography Goals of oral radiology Achieve diagnostic images of the teeth and surrounding bone. Images should
Principles of endodontic surgery
 Principles of endodontic surgery Note: the doctor said that this lecture mainly contain notes, so we should study it from the book for further information (chapter 18) principles of endodontic surgery.
Principles of endodontic surgery Note: the doctor said that this lecture mainly contain notes, so we should study it from the book for further information (chapter 18) principles of endodontic surgery.
Dentistry at Willow Mill Veterinary Hospital. Importance of Good Oral Hygiene. Steps for a Healthy Mouth
 Willow Mill Veterinary Hospital 11 Willow Mill Park Road Mechanicsburg, PA 17050 www.willowmillvet.com Phone: (717)766-7981 Fax: (717) 766-6727 Email:willowmillvethosp@gmail.com Mon-Fri: 8AM-7PM, Sat:
Willow Mill Veterinary Hospital 11 Willow Mill Park Road Mechanicsburg, PA 17050 www.willowmillvet.com Phone: (717)766-7981 Fax: (717) 766-6727 Email:willowmillvethosp@gmail.com Mon-Fri: 8AM-7PM, Sat:
Gum Graft? Patient Need a. Does My. 66 JANUARY 2017 // dentaltown.com. by Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky
 by Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky was born in Dallas and attended college at the University of Texas at Austin. He continued his education at Baylor College of Dentistry in Dallas, where he
by Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky was born in Dallas and attended college at the University of Texas at Austin. He continued his education at Baylor College of Dentistry in Dallas, where he
Focus On: Mandibular Fractures
 Focus On: Mandibular Fractures Fracture of the mandibles is a common injury in dogs and cats and can arise from a variety of situations. How to manage these fractures will be the subject of this article.
Focus On: Mandibular Fractures Fracture of the mandibles is a common injury in dogs and cats and can arise from a variety of situations. How to manage these fractures will be the subject of this article.
DF1 Case Studies Surgical Case Michael Hicks
 DF1 Case Studies Surgical Case Michael Hicks North Western Deanery Background Miss M attended as a new patient requiring treatment. She was a nervous patient and required basic periodontal therapy, an
DF1 Case Studies Surgical Case Michael Hicks North Western Deanery Background Miss M attended as a new patient requiring treatment. She was a nervous patient and required basic periodontal therapy, an
MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF UKRAINE Higher medical educational institution of Ukraine "Ukrainian medical stomatological academy"
 MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF UKRAINE Higher medical educational institution of Ukraine "Ukrainian medical stomatological academy" Approved On the meeting chair Of Pediatric Surgical Stomatology and Propaedeutics
MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF UKRAINE Higher medical educational institution of Ukraine "Ukrainian medical stomatological academy" Approved On the meeting chair Of Pediatric Surgical Stomatology and Propaedeutics
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
ORTHODONTIC BANDING AND CEMENTATION. Materials
 ORTHODONTIC BANDING AND CEMENTATION Materials Required Materials for fitting bands: 1. Selection of bands of different sizes for the teeth to which you are fitting bands 2. Tweezers to take the bands out
ORTHODONTIC BANDING AND CEMENTATION Materials Required Materials for fitting bands: 1. Selection of bands of different sizes for the teeth to which you are fitting bands 2. Tweezers to take the bands out
Structure of an Incisor
 MAMMALIAN TEETH Mammals have different types and shapes of teeth and they are thus termed Heterodonts. Those which have teeth of the same size and shapes are termed as Homodonts. In mammals teeth consist
MAMMALIAN TEETH Mammals have different types and shapes of teeth and they are thus termed Heterodonts. Those which have teeth of the same size and shapes are termed as Homodonts. In mammals teeth consist
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Bridge Flap: A Sine Qua Non For Mucogingival Deformities Debajyoti Mondal, Anju L, Rajul Choradia, Somen
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Bridge Flap: A Sine Qua Non For Mucogingival Deformities Debajyoti Mondal, Anju L, Rajul Choradia, Somen
Chapter 13. Tartar Scrapers - Various 13 DENTAL HAND INSTRUMENTS. Hoe Scaler. Explorer / Measuring Probe. Double-ended Scraper
 Chapter 13 Explorer / Measuring Probe Hoe Scaler Useful for removal of large areas of tartar and plaque from flat tooth surfaces. Double ended scaler. HOE SCALER 012110 Hoe Scaler (double ended) 165mm
Chapter 13 Explorer / Measuring Probe Hoe Scaler Useful for removal of large areas of tartar and plaque from flat tooth surfaces. Double ended scaler. HOE SCALER 012110 Hoe Scaler (double ended) 165mm
Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques
 Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques Mohammad Assaf Assistant Professor, Faculty of Dentistry, Al-Quds University, Jerusalem, Palestine. ABSTRACT Correspondence
Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques Mohammad Assaf Assistant Professor, Faculty of Dentistry, Al-Quds University, Jerusalem, Palestine. ABSTRACT Correspondence
TASKS. 2. Apply a disclosing agent to make the plaque visible.
 TASKS EQUIPMENT AND MATERIALS Personal protective equipment Assortment of nylon, soft-bristled toothbrushes Assortment of dental Floss, waxed and nonwaxed Disclosing solution Face mirror 3. Demonstrate
TASKS EQUIPMENT AND MATERIALS Personal protective equipment Assortment of nylon, soft-bristled toothbrushes Assortment of dental Floss, waxed and nonwaxed Disclosing solution Face mirror 3. Demonstrate
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera
 PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera Operator Name Total 0-49, Passing 39 Your Score Patient Name Date of Series Instructions: Evaluate your Series of photographs first.
PH-04A: Clinical Photography Production Checklist With A Small Camera Operator Name Total 0-49, Passing 39 Your Score Patient Name Date of Series Instructions: Evaluate your Series of photographs first.
9-2 cover.qxd 7/13/ :58 AM Page 1 $20.00 (US)
 $20.00 (US) SPECIAL FEATURE Ferret Dental Disorders: Pictorial of Common Clinical Presentations Cathy A. Johnson-Delaney, DVM, Dipl ABVP-Avian Practice Cathy A. Johnson-Delaney, DVM, Dipl ABVP-Avian Practice
$20.00 (US) SPECIAL FEATURE Ferret Dental Disorders: Pictorial of Common Clinical Presentations Cathy A. Johnson-Delaney, DVM, Dipl ABVP-Avian Practice Cathy A. Johnson-Delaney, DVM, Dipl ABVP-Avian Practice
Your Pet s Dentistry Procedure
 Your Pet s Dentistry Procedure Does your pets breath smell? Periodontal disease is the most common disease in dogs and cats. Without adequate care and attention, periodontal disease can result in pain,
Your Pet s Dentistry Procedure Does your pets breath smell? Periodontal disease is the most common disease in dogs and cats. Without adequate care and attention, periodontal disease can result in pain,
Maintain Your Edge. Instrumental in the preservation of the environment and each other
 Maintain Your Edge Instrumental in the preservation of the environment and each other Thank you. To Toronto Academy of Dentistry To D-Sharp and rdhu Today we will 1. 2. 3. 4. Discuss the benefits of sharpening
Maintain Your Edge Instrumental in the preservation of the environment and each other Thank you. To Toronto Academy of Dentistry To D-Sharp and rdhu Today we will 1. 2. 3. 4. Discuss the benefits of sharpening
أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل CROWN AND BRIDGE جامعة تكريت كلية. Lec. (2) طب االسنان
 Lec. (2) CROWN AND BRIDGE أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل Patient selection and examination A thorough diagnosis must first be made of the patient's dental condition, considering both hard and soft tissues. this
Lec. (2) CROWN AND BRIDGE أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل Patient selection and examination A thorough diagnosis must first be made of the patient's dental condition, considering both hard and soft tissues. this
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Principles of Complicated Exodontia
 Principles of Complicated Exodontia Larry J. Peterson CHAPTER CHAPTER OUTLINE PRINCIPLES OF FLAP DESIGN, DEVELOPMENT, AND MANAGEMENT Design Parameters for Soft Tissue Flaps Types of Mucoperiosteal Flaps
Principles of Complicated Exodontia Larry J. Peterson CHAPTER CHAPTER OUTLINE PRINCIPLES OF FLAP DESIGN, DEVELOPMENT, AND MANAGEMENT Design Parameters for Soft Tissue Flaps Types of Mucoperiosteal Flaps
Maxillary LA: Techniques. Ra ed Salma BDS, MSc, JBOMFS, MFDRCSI
 Maxillary LA: Techniques Ra ed Salma BDS, MSc, JBOMFS, MFDRCSI dr.raedsalma@riyadh.edu.sa https://sites.google.com/a/riyadh.edu.sa/raed/ LA Options for the Maxilla Infiltration Submucosal Supraperiosteal
Maxillary LA: Techniques Ra ed Salma BDS, MSc, JBOMFS, MFDRCSI dr.raedsalma@riyadh.edu.sa https://sites.google.com/a/riyadh.edu.sa/raed/ LA Options for the Maxilla Infiltration Submucosal Supraperiosteal
Double Papillary Flap - A Treatment for Gingival Recession
 World Journal of Medical Sciences 10 (2): 117-121, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.10.2.82175 Double Papillary Flap - A Treatment for Gingival Recession 1 1 1
World Journal of Medical Sciences 10 (2): 117-121, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.10.2.82175 Double Papillary Flap - A Treatment for Gingival Recession 1 1 1
1984 Lubow et al Endodontic flap design: analysis and recommendations for current usage
 Surgical Endodontics Endodontic flap design 1984 Lubow et al Endodontic flap design: analysis and recommendations for current usage Most important factor in flap design is blood supply therefore widest
Surgical Endodontics Endodontic flap design 1984 Lubow et al Endodontic flap design: analysis and recommendations for current usage Most important factor in flap design is blood supply therefore widest
Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation
 Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation Historical Background Guided tissue regeneration is a well established concept in the repair of oral bone defects. The exclusion of soft tissue epithelial
Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation Historical Background Guided tissue regeneration is a well established concept in the repair of oral bone defects. The exclusion of soft tissue epithelial
Textbook of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. Gustav O Kruger. (The C V Mosby Company, St Louis, Toronto, London, 1979) Fifth Edition.
 Textbook of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Gustav O Kruger (The C V Mosby Company, St Louis, Toronto, London, 1979) Fifth Edition Chapter 5 Complicated exodontics Gustav O Kruger Alveoloplasty Alveoloplasty
Textbook of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Gustav O Kruger (The C V Mosby Company, St Louis, Toronto, London, 1979) Fifth Edition Chapter 5 Complicated exodontics Gustav O Kruger Alveoloplasty Alveoloplasty
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations The outline form
 Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
1. Rotosonic burs have 6 sides with non-cutting edge and will not injure soft and hard tissue.
 Rotosonic Scaler bur Rotosonic scaler bur are manufactured in two shape. One is perio type and the other is flame type. Perio type is made of stainless steel but flame type is made of carbide. Characteristics
Rotosonic Scaler bur Rotosonic scaler bur are manufactured in two shape. One is perio type and the other is flame type. Perio type is made of stainless steel but flame type is made of carbide. Characteristics
Minimal-invasive extraction and Surgical extrusion Application of the vertical extraction System Benex
 Minimal-invasive extraction and Surgical extrusion Application of the vertical extraction System Benex Dr. med. et. med. dent. Benno Syfrig Tooth extraction is one of the oldest and most commonly performed
Minimal-invasive extraction and Surgical extrusion Application of the vertical extraction System Benex Dr. med. et. med. dent. Benno Syfrig Tooth extraction is one of the oldest and most commonly performed
Focus Meeting on Dentistry Charlotte, NC, USA Aug. 4-6, 2013
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the American Association of Equine Practitioners Focus Meeting on Dentistry Charlotte, NC, USA Aug. 4-6, 2013 Next Meeting: Annual Convention Dec. 7-11, 2013 - Nashville, TN,
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the American Association of Equine Practitioners Focus Meeting on Dentistry Charlotte, NC, USA Aug. 4-6, 2013 Next Meeting: Annual Convention Dec. 7-11, 2013 - Nashville, TN,
CLASS II CAVITY PREPARATION CHARACTERISTICS OF AN IDEAL CLASS II
 CLASS II CAVITY PREPARATION CHARACTERISTICS OF AN IDEAL CLASS II Contact area carious lesion Proximal view Vertical section - Buccal view Class II carious lesions are diagnosed using bitewing radiographs.
CLASS II CAVITY PREPARATION CHARACTERISTICS OF AN IDEAL CLASS II Contact area carious lesion Proximal view Vertical section - Buccal view Class II carious lesions are diagnosed using bitewing radiographs.
For more information on why AVDC does not recommend Non-anesthetic (Anesthesia-free) Dentistry, click this link:
 In the United States and Canada, only licensed veterinarians can practice veterinary medicine. Veterinary medicine includes veterinary surgery, medicine and dentistry. Anyone providing dental services
In the United States and Canada, only licensed veterinarians can practice veterinary medicine. Veterinary medicine includes veterinary surgery, medicine and dentistry. Anyone providing dental services
Proceedings of the American Association of Equine Practitioners - Focus Meeting. Focus on Dentistry. Albuquerque, NM, USA 2011
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the American Association of Equine Practitioners - Focus Meeting Focus on Dentistry Albuquerque, NM, USA 2011 Next Focus Meetings: July 22-24, 2012 - Focus on Hind Limb Lameness
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the American Association of Equine Practitioners - Focus Meeting Focus on Dentistry Albuquerque, NM, USA 2011 Next Focus Meetings: July 22-24, 2012 - Focus on Hind Limb Lameness
Principles of Exodontia
 Principles of Exodontia *This lecture will help you selecting properly patients to do extraction for.. First of all and before extraction you have to deal with: # Pain management and anxiety control, by
Principles of Exodontia *This lecture will help you selecting properly patients to do extraction for.. First of all and before extraction you have to deal with: # Pain management and anxiety control, by
Dental disease in dogs
 Dental disease in dogs Dogs have 42 teeth in total - 12 incisors, 4 canines, 16 premolars and 10 molars Deciduous Teeth - also called milk teeth, usually erupt between 3-4 weeks of age. Teething begins
Dental disease in dogs Dogs have 42 teeth in total - 12 incisors, 4 canines, 16 premolars and 10 molars Deciduous Teeth - also called milk teeth, usually erupt between 3-4 weeks of age. Teething begins
PRE-OP and POST-OP SURGICAL CONSIDERATIONS
 PRE-OP and POST-OP SURGICAL CONSIDERATIONS Darlene Sorrell, DMD, is not an oral surgeon. AIDC is an out-patient facility. 29 years of experience in IHS. Advanced General Practice Residency. No access
PRE-OP and POST-OP SURGICAL CONSIDERATIONS Darlene Sorrell, DMD, is not an oral surgeon. AIDC is an out-patient facility. 29 years of experience in IHS. Advanced General Practice Residency. No access
immediate implantation and loading with Paltop Osteotomes for bone expansion Case Study
 immediate implantation and loading with Paltop Osteotomes for bone expansion Case Study Osteotomes for bone expansion 2 This 55-year-old female patient presents with a failing maxillary cuspid. 3 A fistula
immediate implantation and loading with Paltop Osteotomes for bone expansion Case Study Osteotomes for bone expansion 2 This 55-year-old female patient presents with a failing maxillary cuspid. 3 A fistula
Free Gingival Autograft: A Case Report
 CASE REPORT Free Gingival Autograft: A Case Report Veena Ashok. P. MDS, Bhargav Neetha BDS Abstract: Gingival recession is defined as Displacement of soft tissue margin apical to the cemento-enamel junction
CASE REPORT Free Gingival Autograft: A Case Report Veena Ashok. P. MDS, Bhargav Neetha BDS Abstract: Gingival recession is defined as Displacement of soft tissue margin apical to the cemento-enamel junction
Technique Guide. Rapid IMF Device. Temporary mandibular fixation device.
 Technique Guide Rapid IMF Device. Temporary mandibular fixation device. Indications Rapid IMF is an adjustable flexible plastic band that wraps around a tooth to create an anchorage point for temporary
Technique Guide Rapid IMF Device. Temporary mandibular fixation device. Indications Rapid IMF is an adjustable flexible plastic band that wraps around a tooth to create an anchorage point for temporary
MAXILLARY INJECTION TECHNIQUE. Chinthamani Laser Dental Clinic
 MAXILLARY INJECTION TECHNIQUE Chinthamani Laser Dental Clinic Introduction A number of injection techniques are available to aid in providing clinically adequate anesthesia of the teeth and soft and hard
MAXILLARY INJECTION TECHNIQUE Chinthamani Laser Dental Clinic Introduction A number of injection techniques are available to aid in providing clinically adequate anesthesia of the teeth and soft and hard
Scoring the Full Extent of Periodontal Disease in the Dog: Development of a Total Mouth Periodontal Score (TMPS) System
 Scoring the Full Extent of Periodontal Disease in the Dog: Development of a Total Mouth Periodontal Score (TMPS) System Colin E. Harvey, Larry Laster, Frances Shofer, Bonnie Miller Summary: The development
Scoring the Full Extent of Periodontal Disease in the Dog: Development of a Total Mouth Periodontal Score (TMPS) System Colin E. Harvey, Larry Laster, Frances Shofer, Bonnie Miller Summary: The development
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association
 All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
6610 NE 181st Street, Suite #1, Kenmore, WA
 660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Stainless Steel Crowns
 Stainless Steel Crowns Objectives Indications for use of stainless steel crowns Technique used in preparing and placing a stainless steel crown restoration on a primary molar. Indications for SSC Restoration
Stainless Steel Crowns Objectives Indications for use of stainless steel crowns Technique used in preparing and placing a stainless steel crown restoration on a primary molar. Indications for SSC Restoration
Swissfloat User Manual
 Swissfloat User Manual Swissvet Veterinary Products 2010 for questions or comments please contact swissvet veterinary products 877 794 7735 - www.swissvet.com 2010 SWISSVET General information: Swissfloat
Swissfloat User Manual Swissvet Veterinary Products 2010 for questions or comments please contact swissvet veterinary products 877 794 7735 - www.swissvet.com 2010 SWISSVET General information: Swissfloat
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATISED INCISORS
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATISED INCISORS Dentists need to understand that the decision to remove or not reimplant an avulsed incisor must be made very carefully. The loss of such a tooth in
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATISED INCISORS Dentists need to understand that the decision to remove or not reimplant an avulsed incisor must be made very carefully. The loss of such a tooth in
BRITISH BIOMEDICAL BULLETIN
 Journal Home Page www.bbbulletin.org BRITISH BIOMEDICAL BULLETIN Case Report Hemisection- A Baton for Extracting Teeth Savita S, R S Senthil Rajan, Ambica *, Krishna Kripal, Poorna Prakash and Sachidananda
Journal Home Page www.bbbulletin.org BRITISH BIOMEDICAL BULLETIN Case Report Hemisection- A Baton for Extracting Teeth Savita S, R S Senthil Rajan, Ambica *, Krishna Kripal, Poorna Prakash and Sachidananda
Socket grafting and ridge preservation using Bond Apatite. Cases 1. Surgery Dr. David Baranes D.M.D
 Socket grafting and ridge preservation using Bond Apatite Cases 1 Case 1 description In this case the two inferiors hopeless molars 37 38 was removed.the socket and the ridge was preserve by augmenting
Socket grafting and ridge preservation using Bond Apatite Cases 1 Case 1 description In this case the two inferiors hopeless molars 37 38 was removed.the socket and the ridge was preserve by augmenting
Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations:
 1 Lec.7 د.عبد املنعم اخلفاجي CLASS V CAVITY PREPARATION FOR AMAGLAM Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations: 1- Caries:
1 Lec.7 د.عبد املنعم اخلفاجي CLASS V CAVITY PREPARATION FOR AMAGLAM Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations: 1- Caries:
Oral Surgery. Basic Techniques of Dental Local Anesthesia. A variety of techniques used in administration and deposition of local anesthesia:
 Oral Surgery Lecture: 9 Dr. Saif Saadedeen Basic Techniques of Dental Local Anesthesia A variety of techniques used in administration and deposition of local anesthesia: 1. Topical anesthesia 2. Infiltration
Oral Surgery Lecture: 9 Dr. Saif Saadedeen Basic Techniques of Dental Local Anesthesia A variety of techniques used in administration and deposition of local anesthesia: 1. Topical anesthesia 2. Infiltration
Minimally invasive techniques for periodontal regeneration
 2016; 2(12): 230-234 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2016; 2(12): 230-234 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 04-10-2016 Accepted: 05-11-2016 Dr. Rizwan M Sanadi Professor,
2016; 2(12): 230-234 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2016; 2(12): 230-234 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 04-10-2016 Accepted: 05-11-2016 Dr. Rizwan M Sanadi Professor,
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH
 FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
ARAB AMERICAN UNIVERSITY. Lab. Manual. Prosthetic Dentistry1; Removable Prosthodontics. 3 rd year
 ARAB AMERICAN UNIVERSITY Lab. Manual Prosthetic Dentistry1; Removable Prosthodontics 3 rd year Department of Fixed and removable prosthetic Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry 2012/2013 Course Instructor Dr.
ARAB AMERICAN UNIVERSITY Lab. Manual Prosthetic Dentistry1; Removable Prosthodontics 3 rd year Department of Fixed and removable prosthetic Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry 2012/2013 Course Instructor Dr.
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Buccal approach in surgical removal of lingually embedded teeth: a report of 2 cases
 Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Case report Buccal approach in surgical removal of lingually embedded teeth: a report of 2 cases Thatsanai Tangmankongworakoon 1, Nattamet Wongsirichat 2 1 Lad Yao
Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Case report Buccal approach in surgical removal of lingually embedded teeth: a report of 2 cases Thatsanai Tangmankongworakoon 1, Nattamet Wongsirichat 2 1 Lad Yao
THE GENERAL DENTIST AND TIMELY REFERRAL TO THE ENDODONTIST
 CLINICAL THE GENERAL DENTIST AND TIMELY REFERRAL TO THE ENDODONTIST Andrei Berdichewsky, DDS 1 The use of endodontic treatment to solve problems related to pulpal and periapical pathologies is extremely
CLINICAL THE GENERAL DENTIST AND TIMELY REFERRAL TO THE ENDODONTIST Andrei Berdichewsky, DDS 1 The use of endodontic treatment to solve problems related to pulpal and periapical pathologies is extremely
BOCL-01: Bonding Materials Checklist
 Task 19: Gather materials to bond partner using toothpaste as etchant Take a photo of gathered materials and submit with this completed checklist BOCL-01: Bonding Materials Checklist Date: Patient: Operator:
Task 19: Gather materials to bond partner using toothpaste as etchant Take a photo of gathered materials and submit with this completed checklist BOCL-01: Bonding Materials Checklist Date: Patient: Operator:
Extractions and the Maxillary Sinus
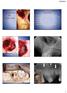 Extractions and the Maxillary Sinus Four levels of sinus membrane involvement: Level One: Sinus membrane showing within the socket after an extraction. Not perforated. Level Two: 1-2mm tear. Level three:
Extractions and the Maxillary Sinus Four levels of sinus membrane involvement: Level One: Sinus membrane showing within the socket after an extraction. Not perforated. Level Two: 1-2mm tear. Level three:
502 Jefferson Highway N. Champlin, MN Saving Your Teeth with ROOT CANAL THERAPY
 502 Jefferson Highway N. Champlin, MN 55316 763 427-1311 www.moffittrestorativedentistry.com Saving Your Teeth with ROOT CANAL THERAPY YOUR TOOTH NEEDS THERAPY: ENDODONTICS If you have a tooth whose internal
502 Jefferson Highway N. Champlin, MN 55316 763 427-1311 www.moffittrestorativedentistry.com Saving Your Teeth with ROOT CANAL THERAPY YOUR TOOTH NEEDS THERAPY: ENDODONTICS If you have a tooth whose internal
Management of dental disease in the canine and feline patient
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Management of dental disease in the canine and feline patient Author : Michelle Donovan Categories : RVNs Date : October 1,
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Management of dental disease in the canine and feline patient Author : Michelle Donovan Categories : RVNs Date : October 1,
A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material
 74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
THE INDICATIONS FOR THE TRANSPLANTATION OF MAXILLARY CANINES IN THE LIGHT OF 100 CASES. J. I. Moss, PhD.(Lond.), B.D.S., F.D.S., R.C.S.(Eng.
 British Journal of Oral surgery (1975), 12, 268-274 THE INDICATIONS FOR THE TRANSPLANTATION OF MAXILLARY CANINES IN THE LIGHT OF 100 CASES J. I. Moss, PhD.(Lond.), B.D.S., F.D.S., R.C.S.(Eng.) University
British Journal of Oral surgery (1975), 12, 268-274 THE INDICATIONS FOR THE TRANSPLANTATION OF MAXILLARY CANINES IN THE LIGHT OF 100 CASES J. I. Moss, PhD.(Lond.), B.D.S., F.D.S., R.C.S.(Eng.) University
Common Equine Dental Malocclusions Molars
 Common Equine Dental Malocclusions Molars CAUDAL HOOKS Definition - Dominant lower or upper last molar overhanging opposing molar. Etiology - Hereditary - May result from horse born with over or under
Common Equine Dental Malocclusions Molars CAUDAL HOOKS Definition - Dominant lower or upper last molar overhanging opposing molar. Etiology - Hereditary - May result from horse born with over or under
Contemporary Atraumatic Oral Surgery for General Dentists. Getting it Right, So Things Don t Go Wrong
 Contemporary Atraumatic Oral Surgery for General Dentists Getting it Right, So Things Don t Go Wrong Alan Jeroff DMD ajeroff@dentistry.ubc.ca Patient Evaluation Medical Clinical Record Keeping Dentoalveolar
Contemporary Atraumatic Oral Surgery for General Dentists Getting it Right, So Things Don t Go Wrong Alan Jeroff DMD ajeroff@dentistry.ubc.ca Patient Evaluation Medical Clinical Record Keeping Dentoalveolar
Chapter 14. Anatomy and Function of a Table Top Gag 14 RODENT DENTISTRY. Adjusting the Gag for use. How to assemble the Table Top Gag
 Chapter 14 Anatomy and Function of a Table Top Gag Adjusting the Gag for use. Access to the cheek teeth of rabbits is a problem recognised by all involved in their dental care. A combination of the diets
Chapter 14 Anatomy and Function of a Table Top Gag Adjusting the Gag for use. Access to the cheek teeth of rabbits is a problem recognised by all involved in their dental care. A combination of the diets
Ankylosed primary teeth with no permanent successors: What do you do? -- Part 1
 Ankylosed primary teeth with no permanent successors: What do you do? -- Part 1 March 3, 2015 By David M. Sarver, DMD, MS The clinical problem You have a seven-year-old patient who comes to your office
Ankylosed primary teeth with no permanent successors: What do you do? -- Part 1 March 3, 2015 By David M. Sarver, DMD, MS The clinical problem You have a seven-year-old patient who comes to your office
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION. By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur
 COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
Patellar Ligament Disease.
 Patellar Ligament Disease. The patellar ligament disease is a condition of the stifle where the cartilage keeping the patella in place over knee joint is weakened or damaged. The patella is held in place
Patellar Ligament Disease. The patellar ligament disease is a condition of the stifle where the cartilage keeping the patella in place over knee joint is weakened or damaged. The patella is held in place
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
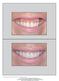 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 433 Lip Repositioning for Reduction of Excessive Gingival Display: A Clinical Report Ari Rosenblatt, DMD, DDS* Ziv Simon, DMD, MSc* Excessive
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 433 Lip Repositioning for Reduction of Excessive Gingival Display: A Clinical Report Ari Rosenblatt, DMD, DDS* Ziv Simon, DMD, MSc* Excessive
Use of elevator instruments when luxating and extracting teeth in dentistry: clinical techniques
 TECHNICAL NOTE https://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2017.43.3.204 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Use of elevator instruments when luxating and extracting teeth in dentistry: clinical techniques John Mamoun
TECHNICAL NOTE https://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2017.43.3.204 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Use of elevator instruments when luxating and extracting teeth in dentistry: clinical techniques John Mamoun
Concepts of occlusion Balanced occlusion. Monoplane occlusion. Lingualized occlusion. Figure (10-1)
 Any contact between teeth of opposing dental arches; usually, referring to contact between the occlusal surface. The static relationship between the incising or masticatory surfaces of the maxillary or
Any contact between teeth of opposing dental arches; usually, referring to contact between the occlusal surface. The static relationship between the incising or masticatory surfaces of the maxillary or

