vertically distracted fibula
|
|
|
- Edgar Grant
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Feng Wang* Wei Huang* Chenping Zhang Jian Sun Darnell Kaigler Yiqun Wu Comparative analysis of dental implant treatment outcomes following mandibular reconstruction with double-barrel fibula bone grafting or vertical distraction osteogenesis fibula: a retrospective study Authors affiliations: Feng Wang, Wei Huang, Yiqun Wu, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Implantology, Ninth People s Hospital Affiliated with Shanghai Jiao Tong University, School of Medicine, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Shanghai, China Chenping Zhang, Jian Sun, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Ninth People s Hospital Affiliated with Shanghai Jiao Tong University, School of Medicine, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Shanghai, China Darnell Kaigler, Department of Periodontics and Oral Medicine and Biomedical Engineering, University of Michigan, Michigan Center of Oral Health Research, Ann Arbor, MI, USA Corresponding author: Prof. Yiqun Wu Ninth People s Hospital Affiliated with Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine Shanghai China Tel.: ext5299 Fax: yiqunwu@hotmail.com Key words: clinical parameters, dental implants, double-barrel fibula, mandibular reconstruction, vertically distracted fibula Abstract Purpose: The purpose of this study was twofold: (i) to compare vertical bone height (VBH) after tumor resection through grafting with either a double-barrel fibula (DBF) technique or vertical distraction osteogenesis of the fibula (VDOF); (ii) to compare the performance of loaded dental implants following either DBF or VDOF with special focus on implant survival, implant success, and bone resorption. Materials and methods: This retrospective clinical study involved 19 patients who underwent implant placement following DBF (group A, n = 9) or VDOF (group B, n = 10) for mandibular reconstruction from March 2006 to May Clinical and radiographic assessments, including VBH, modified Plaque Index (mpi), modified Sulcus Bleeding Index (msbi), and marginal bone level (MBL), were taken for both groups after delivery of the final prostheses and annually thereafter. Results: Nine patients underwent DBF with 24 implants placed and 10 patients underwent VDOF with 27 implants placed for mandibular reconstruction after tumor resection. Overall, all DBF and VDOF procedures were successful for group A and group B. VBH for group A and group B were 20 and 17 mm. There was no statistically significant difference of msbi scores between group A and group B in the 3-year follow-up (P = 0.40). In four cases with eight implants of group A and two cases with three implants of group B, granulomatous soft tissue grew. There was no statistically significant differences of MBL between group A and group B in the 3-year follow-up (p = 0.7). The cumulative survival and success rates of implants for group A were 100% and 87.5%, and for group B were 100% and 85.2% in 3-year follow-up, respectively. Conclusions: On the basis of the study of 19 patients who received a total of 51 implants, reconstruction of the mandible with DBF flap or VDOF flap, combined with dental implant therapy, was considered a predictable option. Compared with implants placed in VDOF bone, implants placed in DBF bone had a relative higher incidence of associated gingival inflammation. The DBF bone seems more resistant to peri-implant resorption processes than VDOF bone during functional loading. *These authors contributed equally to this work. Date: Accepted 25 October 2013 To cite this article: Wang F, Huang W, Zhang C, Sun J, Kaigler D, Wu Y. Comparative analysis of dental implant treatment outcomes following mandibular reconstruction with double-barrel fibula bone grafting or vertical distraction osteogenesis fibula: a retrospective study. Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 26, 2015, doi: /clr Over the past 20 years, the fibular free flap technique has become a routine procedure for the functional reconstruction of the mandible to correct mandibular continuity defects that are caused by tumors resection (Sieg et al. 2002). The most common problem encountered with this method is the insufficient bone height of the fibula, which results in a gap between the bone margin and the occlusal plane, in particular, in patients treated by partial resection of the mandible with residual dentition on the healthy side (Frodel et al. 1993; Moscoso et al. 1994; Matsuura et al. 1999; Anne-Ga elle et al. 2011). The height discrepancy between native bone and graft fibula makes it less likely for 2013 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd 157
2 prostheses to achieve a desirable implant-tocrown ratio and increases the difficulty in maintaining adequate oral hygiene and negatively affects the profile of the lower border of the reconstructed mandible (Chiapasco et al. 2006). Various methods, such as the double-barrel fibula (DBF) technique, on lay grafting and distraction osteogenesis (DO), have been introduced to address this problem (Levin et al. 2003; Bilbao et al. 2009). The vascularized DBF technique was first used by B ahr et al. in 1998; and this technique achieved greater bone height and shortened the vertical distance to the occlusal plane. Mandibular defects shorter than 9.0 cm can be bridged by the double-barrel technique with the available fibula length (B ahr et al. 1998; Guerra et al. 2000; He et al. 2011). Additionally, limited studies report positive results of placing dental implants in vascularized DBF bone to achieve functional mandibular reconstruction (Chang et al. 2008, 2011; He et al. 2011). DO was another alternative to increase bone height by the creation of neoformed bone and adjacent soft tissue and was initially used in cases of vertical defect of edentulous jaws to improve bone volume for dental implant placement in 1996 (Chin & Toth 1996). It has become a widely known and effective technique to gain sufficient alveolar bone height in alveolar ridge atrophy. With this approach, bone gain in different parts of the jaws can be achieved from 8 to 10 mm (Rocchietta et al. 2008). Because of the predictable performance of DO in native bone, a few studies have focused on vertical distraction osteogenesis of fibula (VDOF) for attaining sufficient alveolar bone height before implant therapy; positive results were achieved in optimizing the implant position for ideal prosthetic rehabilitation (Siciliano et al. 1998; Chiapasco et al. 2000; Nocini et al. 2000; Marchetti et al. 2002). Although clinical data have demonstrated that bone grafting and placement of dental endosseous implants are widely accepted therapeutic options for reconstructing edentulous areas of the jaw following resective jaw surgery, there is limited information available on the clinical outcomes of dental implants in DBF and VDOF for mandibular reconstruction. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of DBF and VDOF associated with dental implant treatment for mandibular reconstruction after tumor resection. Implants were restored, and treatment outcomes were measured through implant survival, implant success, bone resorption, and complications associated with DBF and VDOF. Material and methods Patients The medical charts of patients who had been treated between March 2006 and May 2008 were reviewed. Patients were selected to participate if their clinical condition met the following inclusion criteria: (i) diagnosis of mandibular cyst or benign tumor, (ii) the presence of mandibular defect <9 cm in length; (iii) good oral hygiene without active periodontal disease; (iv) desire to have implant-supported fixed prostheses. Patients were excluded from participating if the following criteria were met: (i) overall general poor prognosis or systematically compromised health; (ii) current heavy smoker (>15 cigarettes per day); (iii) uncontrolled diabetes. The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee of the Ninth People s Hospital affiliated with Shanghai Jiao Tong University, School of Medicine. : surgery and implant treatment for DBF patients Reconstruction was performed for patients during the same surgery after a resection of the tumor in the mandible under general anesthesia. Fibula flap harvest proceeded simultaneously with the resection procedure as described previously by (He et al. 2011; Shen et al. 2012). The harvested fibula was then osteotomized into several segments to fit the mandibular defect. Before the surgery, a resin template had been made based on computerized tomographic data. The original mandibular contour was maintained by a reconstruction plate system (Synthes, Bettlach, Switzerland) according to the template; the lower layer of the fibula was fixed by the reconstruction plate to the lower border of the residual mandible, and miniplates were used for osteosynthesis between the upper layer of the fibula segments and the upper border of the residual mandible. Microvascular anastomoses were performed by magnifying optics. Dental implants (Straumann, Basel, Switzerland) were placed in DBF bone under local anesthesia by one clinician after the healing of revascularized DBF flap. Panoramic radiographs and/or computed tomographic (CT) scans were taken before implant placement. Anti-inflammatory agents, amoxicillin (500 mg, four times a day for 7 days), and metronidazole (400 mg, three times a day for 7 days) were prescribed post-operatively. A 0.12% chlorhexidine oral rinse was also prescribed for 60 s with a frequency of 5 6 times a day for 14 days. All of the implants were observed for a healing period of 3 5 months before impressions were taken. Dental implants were restored with screw-retained fixed metal ceramic prostheses (Fig. 1). : surgery and implant treatment for VDOF patients Patients were treated by resection of the tumor in the mandible under general anesthesia. Reconstruction was performed simultaneously in the operation with a free revascularized fibular flap. After anastomosis, the fibular bone was segmentalized vertically to follow the contour of the mandible and was fixed with titanium plates. Following the contour of the mandible, some patients underwent DO device fixation procedures at the same surgery. The bone segment to be vertically distracted was completely separated from the basal bone. The bone pedicle was connected to the lingual vessel-periosteum after horizontal osteotomy of the fibula. The DO devices (Cibei Medical Corporation, Ningbo, China; Yinghao Timing, Shanghai, China) were fixed to both the basal bone and the osteotomized segments by microplates and screws. The number of DO devices was determined by the size of defect, in general for partial mandible with deficiency distance of <10 mm, two sets of DO were used. Closure of intra- and extraoral wounds was then performed. After a 7-day period, the distraction was activated at a rate of 0.7 mm per day. After 14 days, the desired bone height (approximately 10 mm) was obtained. A solidation period of 8 12 weeks followed to obtain adequate maturation of the callus formed between the basal bone and the distracted segment (Zhang et al. 2012). Panoramic radiographs and/or computed tomography (CT) scans were taken after the consolidation period to ensure that an adequate quality and quantity of bone was available for dental implant placement. The implants were placed in these distracted areas under local anesthesia by one clinician after a consolidation period for the DO procedure. The post-operative medications for patients in group B were the same as for group A patients. After osseointegration was achieved, the same procedures for prostheses delivery described for group A were followed. The DO devices with osseointegration were left as implants to support fixed prostheses (Fig. 2). All patients of group A and group B were instructed to use a sonic toothbrush (sonic toothbrush; Philips, Bothell, WA, USA) and a dental water jet to maintain adequate oral hygiene. Outcome assessment The follow-up examination was performed according to a standardized protocol, which 158 Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 26, 2015 / John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd
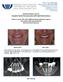
3 (a) (c) (b) (d) margin of the alveolar ridge and the lower aspect of basal bone were measured around each implant. Dimensional distortion between the different panoramic radiographs was corrected with the actual implant dimensions. Vertical bone height for group B was measured on panoramic radiographs immediately after the end of the distraction procedure. The linear measurements between the upper margin of the alveolar ridge and the lower aspect of basal bone were taken from panoramic radiographs. Measurements were performed mesial and distal to the implants in group A and distraction devices in group B. These measurements were performed twice by one observer. (e) (g) (f) (h) Peri-implant clinical parameters Modified Plaque Index (mpi) was measured at four points around the implants according to the following scale: 0, no plaque; 1, plaque on probing; 2, visible plaque; and 3, abundant plaque. For each implant, one MPI value was calculated based on the average of the four obtained values (Mombelli & Lang 1994). Modified Sulcus Bleeding Index (msbi) was measured at four surfaces around the implants. The msbi was scored as follows: 0 = no bleeding when a periodontal probe was passed along the gingival margin adjacent to the implant, 1 = visible, isolated bleeding spots, 2 = blood formed a confluent red line on the margin, and 3 = heavy or profuse bleeding. For each implant, one msbi value was calculated based on the average of the four obtained values ((Mombelli & Lang 1994). Modified Plaque Index and msbi measurements were recorded by a single experienced clinician using a plastic probe with a standardized probing force of 0.2 N. Fig. 1. (a) Panoramic radiograph showing the lesion affecting the mandibular body and the left ramus; (b) Panoramic radiograph after the tumor resection and reconstruction with DBF graft; (c) Adequate occlusal space and uneventful soft tissue healing available before implant placement; (d) Two Straumann implants were placed; (e) Panoramic radiograph immediately after implant placement; (f) The clinical status showing favorable soft tissue healing at the time of impression taken; (g) Buccal view of the prostheses; (h) Panoramic radiograph after 12 months of loading with limited peri-implant bone resorption. DBF, double-barrel fibula. included a clinical examination and radiographic evaluations (panoramic radiographs) after delivery of the final prosthesis and annually thereafter. Implant stability quotient After the implants were placed, resonance frequency analysis (RFA, Osstell, Integration Diagnostics, Savadaled, Sweden) was used to measure the implant stability quotient (ISQ; Glauser et al. 2004). The transducer was handscrewed into the implant body, as recommended by the manufacturer. Each measurement was taken twice (at the mesial, distal, buccal, and lingual aspects). These measurements were repeated when the impressions were taken and were performed by one observer. Vertical bone height Vertical bone height (VBH) for group A was taken from panoramic radiographs after implant placement. The distance between the upper Radiographic assessment of peri-implant bone resorption Peri-implant bone resorption was recorded by comparing panoramic radiographs taken after implant placement, at the time of prosthesis delivery, and at the follow-up. All of the panoramic images were scanned by one operator and transferred to a computer with an image analysis programme (GE Healthcare Centricity@ v3.0, Pitttsburgh, PA, USA). To perform accurate measurements and minimize the magnification factor inherent within panoramic radiographs, a calibration procedure based on the known implant length was performed prior to measurements being taken. Measurements between the top of the implant head shoulder and the most coronal level of the direct bone-to-implant contact were made mesial and distal to each implant. Finally, the vertical peri-implant 2013 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd 159 Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 26, 2015 /
4 (a) (b) of mobility, the absence of paresthesia and/or pain, the absence of peri-implant pathosis or radiographic radiolucencies, and marginal bone loss <1 mm during the first year and <0.2 mm/year in the following years (Albrektsson et al. 1986). (c) (e) (d) (f) Statistical analysis Statistical analysis was performed by means of a SAS statistical package (SAS 9.3, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). Descriptive statistical analyses of peri-implant hygienic parameters and marginal bone level (MBL) were performed using the mean of the distribution, the standard deviation, the median, the minimum and the maximum. The normal distribution of the data was tested. A nonparametric mixed model was applied to compare the quantitative dependant variables (ISQ, MBL) and categorical-dependant data (mpi, msbi) in the study. The level of statistical significance was set at P = Results (g) Fig. 2. (a) Panoramic radiograph showing the lesion affecting the mandibular body; (b) Panoramic radiograph right after fibular flap transfer and distraction device fixation; (c) Three-dimensional CT scan immediately after completing the VDOF procedure; (d) Panoramic radiography showing adequate bone available after the VDOF procedure; (e) Dental implants placement in VDOF bone and uneventful soft tissue healing available around implants; (f) Panoramic radiograph at the time of impression taken, showing good osseointegration of the two implants; (g) Buccal view of the prostheses, one of the DO devices with osseointegration combined with implants to withstand denture force; (h) Panoramic radiograph after 12 months of loading with limited peri-implant bone resorption. VDOF, vertical distraction osteogenesis of fibula; DO, distraction osteogenesis; CT, computed tomographic. bone resorption values were calculated as follows: (Perez-Sayans et al. 2008) Actual implant length Radiologic bone deficit Real bone deficit ¼ Radiologic implant length The measurements were taken by two examiners, and the interexaminer reliability (h) was assessed to ensure the accuracy of the measurements using intraclass correlation coefficient correlation test. Implant success rates The implant prognostic criteria were previously described by Albrektsson and Zarb. Briefly, implants were termed successful if the following criteria were met: the absence In a 3-year period ( ), nine patients (six men and three women, aged between 28 and 55 years, mean age years) received DBF, and 10 patients (six men and four women, aged between 28 and 53 years, mean age years) received VDOF for mandibular reconstruction after tumor resection. Eight patients were enrolled who had either recurrent keratocysts after initial curettage therapy or keratocysts with soft tissue infiltration. The mean follow-up is months after final prosthesis delivery. The final implant-supported prostheses were restored at the Unit of Oral-maxillofacial Surgery and the Unit of Oral Implantology, Shanghai 9th People s Hospital, China. In all patients in groups A and B, microvascular fibula transfers were successful. In group A, a total of 24 implants were placed in DBF bone (Table 1). One patient (No. 2) received four implants simultaneously at the time of the reconstruction surgery. The other 20 implants were placed in eight patients using a two-staged procedure whereby implants were placed following adequate healing (4 7 months, average 5.3 months) from the initial reconstructive surgery. One of the implants in patient No. 2 was left to sleep and not restored due to it being malpositioned buccally. In group B, following the contour of the mandible in reconstructive surgery, eight patients underwent VDOF procedures. The other three patients received DO procedures after tumor resection and simultaneous 160 Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 26, 2015 / John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd
5 Table 1. Clinical features of patients Patient no. Sex Age Tumor type reconstructive surgery. The mean interval between the reconstruction and DO fixation surgery was 7 months (5 11 months). Major complications associated with DO procedures did not occur in group B. However, a few complications were observed in the DO procedure. Patient No. 2 had lingual tilting of the distracted segment. The transport segment was mobilized, and the distraction vector of the distraction rod was realigned under local anesthesia. In patient no. 3 of group B, Surgery site No. of inserted implants 1 M 32 Ameloblastoma M 38 Ameloblastoma M 45 Keratocyst M 52 Ameloblastoma Implant site Implant dimensions 5 F 43 Ameloblastoma M 55 Ameloblastoma M 40 Keratocyst F 37 Keratocyst F 28 Keratocyst Mean SD F 48 Ameloblastoma M 45 Keratocyst M 53 Ameloblastoma F 28 Keratocyst M Ameloblastoma F 45 Keratocyst M 43 Keratocyst M 52 Ameloblastoma F 43 Ameloblastoma M 41 Ameloblastoma Mean SD wound dehiscence developed 8 days after surgery. The patient was then put on a regimen of rinsing with a chlorhexidaine four times a day until the dehiscence healed within 2 weeks. Distraction was continued in these two patients with no compromise of bone regeneration. A total of 27 implants were placed in vertical DO bone following a healing (4 6 months, average 5.1 months) after solidation period (Table 1). One patient was restored by combining two implants in the DO bone with two implants in the native bone. Ten sets of DO devices for which there was no detectable clinical mobility or bone resorption were kept in place. These were combined with regular implants to withstand denture force. After implant placement surgery, in all patients of group A and group B, healing proceeded without complications and with minimal post-operative discomfort. During 3 years of the clinical evaluation, there were no patients lost to follow-up. ISQ The RFA at implant placement for group A showed a mean ISQ of After the osseointegration period, all implants were stable, and the mean ISQ was for the implants. There was no significant difference in the ISQ values between the time of implant insertion and following the integration period, when impressions were made (P = 0.51). For patients in group B, the mean ISQ at the time of implant placement was Following the osseointegration period, the mean ISQ values increased to There was a significant difference in the RFA measurements between the time of implant insertion and when the impressions were made (P < 0.01). Although ISQ values recorded immediately after implant placement for both groups A and B indicate good primary stability of implants, there was a significant difference between implants placed in group A (DBF bone) relative to that in group B (VDOF bone; P < 0.01). Additionally, following the osseointegration period, the ISQ was higher for group A than group B and had statistically significant difference (P < 0.01). Vertical bone gained (VBH) The average VBH was 20 mm (18 23 mm) for group A and was 17 mm (16 20 mm) for group B. The measurement of VBH for group B could not be performed in three patients due to superimposition of the titanium plates, and DO devices seen on the images from the panoramic radiographs. Overall, there was a stable increase in VBH in both groups that enabled placement of dental implants. Peri-implant clinical parameters mpi Table 2 shows the mean, the median, the minimum, and the maximum of mpi (%) values at prosthesis delivery and at 1-, 2-, and 3-year follow-ups for groups A and B. The mean mpi (%) values at 1 and 3 years after prosthesis 2013 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd 161 Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 26, 2015 /
6 Table 2. Peri-implant hygienic parameters (group A and group B) at prosthesis delivery and follow-up Prosthesis delivery 1 year 2 year 3 year delivery were 13.0 and 14.8, respectively, in group A and 12.5 and 25.0, respectively, in group B. A P value of 0.06 was detected within group A and group B in 1-year and 3-year follow-ups. msbi In groups A and B, the peri-implant soft tissues appeared healthy which corresponded with mean msbi values of 0.2 and 0.4, respectively, at the time of prosthesis delivery. The mean msbi values at 1-, 2-, and 3- year follow-ups were 0.5, 1.0, and 1.2, respectively, in group A. There was a significant difference in the msbi between 1- and 3-year follow-ups in group A (P <0.01). In group B, the mean msbi was 0.7 at 1- year follow-up and at the end of the 3-year follow-up period, the mean msbi was 0.8. No significant difference in the msbi was observed during the follow-up period (P = 0.71). There was no significant difference in msbi scores between groups A and B in the 3-year follow-up period (P = 0.40; Table 2). In four cases with eight implants of group A and two cases with three implants of group B, granulomatous soft tissue was present and associated with bleeding and pain at the 1- and 2-year follow-ups. The soft tissue was removed around these 11 implants with an Er/YAG laser (Key Laser 3 Perio, KaVo, Biberach, Germany) under local anesthesia. Following this treatment, patients received individualized oral hygiene instructions. However, the granulomatous tissue of five implants in group A and 2 implants in group B reappeared 5 8 months later. In these cases, degranulation of this tissue was again performed around the implants in conjunction with free gingival grafts from tissue harvested from the palate. At the last clinical examination, there were no signs of mobility, suppuration or active peri-implant lesions around these implants. Radiographic assessment of peri-implant bone resorption Table 3 shows the peri-implant bone resorption for the subjects of group A and group B at the follow-up appointments. When the peri-implant bone loss data were analyzed for group A and group B, significant differences were detected between years 1 and year 3 for both groups (P = 0.022). No statistically significant differences were found in this study between groups A and B (P = 0.7). Table 4 shows the frequency distribution of the peri-implant bone changes around the implants. Three of 24 implants in group A and four of 27 implants in group B presented periimplant bone resorption values higher than standard values used as criteria for implant success. Thus, cumulative survival and success rates of implants placed in group A at the end of the follow-up period were 100% and 87.5%, respectively. In group B, survival and success rates were 100% and 85.2%, respectively. There was no difference in implant success rates between groups A and B. Discussion mpi (%) Mean Median Min Max msbi Mean Median Min Max Oral rehabilitation using dental implants in fibula transplants has been frequently used following reconstruction of the lower jaw and has proven to be a reliable method (Taylor et al. 1989; Hidalgo 1989). However, this method may produce a height discrepancy between the native mandible and the grafted bone that leads to subsequent problems such as facial esthetics and denture rehabilitation (Frodel et al. 1993; Moscoso et al. 1994). As the longest bone that can be transferred by microsurgical techniques, the fibula has the advantage of periosteal blood supply that makes it possible for several osteotomies in the reconstruction surgery (Klesper et al. 2000). After the introduction of the technique of double-barrel fibula bone in 1990s, it was demonstrated to be a safe and reliable method to esthetically and functionally reconstruct mandibular defects following tumor resection (Chang et al. 2008, 2011; He et al. 2011)). However, it has been reported that bridging of mandibular defects longer than 9.0 cm is very challenging with the double-barrel technique due to the limitations of fibula length (B ahr et al. 1998; Guerra et al. 2000; Klesper et al. 2000; He et al. 2011). Distraction osteogenesis is defined as the creation of neoformed bone and adjacent soft tissue after the gradual and controlled displacement of a bone fragment obtained from a surgical osteotomy. Histologic results have demonstrated that DO enables the formation of adequate quality and quantity of bone tissue, which could provide primary stability for implants and allow the loaded implants to withstand their biomechanical demands (Siciliano et al. 1998; Raghoebar et al. 2002). Histologic analysis of bone core biopsies from vertically distracted fibula in mandibular reconstruction confirmed that the distracted area was filled with newly formed bony trabeculae between the transported fibula and the basal segments (Cheung et al. 2013). In our case series, DBF and VDOF were used in patients with multicystic ameloblastoma and keratocysts. Mandibular keratocysts, especially large keratocysts, were generally first treated with a less-invasive technique, such as marsupialization. However, for some ineffective or recurrent cases or with soft tissue infiltration, segmental mandibulectomy with DO reconstruction or DBF graft was performed. Table 3. Means, standard deviations, and ranges of peri-implant bone resorption (group A and group B) at follow-up Peri-implant bone resorption (mm) 1 year 2 year 3 year Mean SD Median Min Max Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 26, 2015 / John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd
7 Table 4. Frequency distribution of peri-implant bone resorption (group A and group B) at prosthesis delivery and follow-up Peri-implant bone resorption (mm) 1 year 2 year 3 year Resonance frequency analysis is a modality extensively used in clinical research to monitor implant stability due to its high reproducibility (Aparicio et al. 2006). In this study, implants in patients of group B showed ISQ values >64 at implant placement, indicative of good primary stability. Following the osseointegration phase of adaptative bone remodeling around the implants, the ISQ of in group B indicated that secondary stability was also achieved. In group A, the mean ISQ was at implant placement, which was significantly higher than that in group B. This could be explained in part due to 12 and 14 mm implants being placed which provides good anchorage in the grafted fibula bone. Chiapasco & Gatti (2004) reported in a case series that due to excellent primary stability for implants placed in grafted fibula bone, immediate loading of the implants was achievable. There was only 1 patient in group A who received implants placed simultaneously at the time of reconstructive surgery. Chang et al. (2003) pointed out that simultaneous placement of dental implants in fibula grafts at the time of microvascular free tissue transfer affords better flexibility for re-creating an accurate interarch relationship with a simplified technique. However, immediate placement of the implants may compromise bone viability, lengthen the operative procedure or result in implant malposition (Disa et al.1999). We found it was considerably difficult to place implants in an ideal position in grafted fibula bone during primary insertion, even with the use of a surgical template. Furthermore, because of the minor gap between native bone and the grafted fibular bone and fixation plates, some implants could not be positioned with the ideal spacing in proximity to adjacent natural teeth, leading to long cantilevers as part of the prosthesis. In the present study, the keratinized attached mucosa was removed after the tumor resection for both groups. The skin paddle and oral mucosa were used to reconstruct < > the intraoral lining for group A patients. In two patients of group A, palatal mucosal grafts were utilized at the second-stage implant surgery to surround and seal the implants. The first measure to avoid hypertrophy is to thin the soft tissues of the flap during grafting (Anne-Ga elle et al. 2011). So we improved the design of the free vascularized fibula flap by not using a skin paddle and by decreasing the thickness of the soft tissue for six patients in group B. Oral hygiene instructions, which included the use of a sonic toothbrush and a dental water jet for daily maintenance, were given to all of the patients. Instead of using a traditional design, we used one that left sufficient space around the implants for the interdental brushes to provide effective plaque control in the marginal areas. At prosthesis delivery and 1-year follow-up, the low mean plaque levels (<20%) indicated a good level of oral hygiene for groups A and B. However, mpi and msbi of group A increased to 25% and 1.2 at 3-year follow-up. In 1- and 2-year follow-ups, we observed that four patients with eight implants in group A and two patients with three implants in group B exhibited an inflammatory response of the peri-implant mucosal tissue and formation of granulomatous tissue around the implants, particularly on the lingual surfaces. A similar tissue response in these types of cases has been described by others (Chang et al. 2008; Ciocca et al. 2008; Wu et al. 2008). It has been suggested that the extraoral derived soft tissues around these implants is not suitable and might respond adversely in the oral environment due to the inadequate integrity of the peri-implant attachment apparatus (Chiapasco et al. 2006; Chang et al. 2008). Other considerations include prosthetic designs and anatomical limitations created following these procedures (i.e., high level of the floor of the mouth), which could cause difficulties in maintaining adequate oral hygiene. Additionally, the soft tissue coverage of group A was often thicker (because of the fibula osteoseptocutaneous flap) leading to relatively deeper probing depths. The thick soft tissue around implants was very different than that of normal healthy gingiva and more mobile than the attached gingiva of the oral mucosa, proving less conducive to oral hygiene. For this reason, probing depths measures normally a part of any implant assessment were not used in the evaluation between group A and group B (Blake et al. 2008). Although the incidence of the peri-implant inflammatory response in group A (8/24) was higher than that in group B (3/27), there was no significant difference of marginal bone loss between groups A and B at 3-year follow-up. No implant was removed due to excessive bone loss. It has been demonstrated previously that the fibular bone graft can be resistant to bone resorption (Chiapasco et al. 2006; Gbara et al. 2007; Chang et al. 2008). In our study, despite having a higher incidence of a peri-implant inflammatory response, patients who received the double fibula graft (group A) were more resistant to crestal bone resorption over time. An important consideration of our study is that due to anatomical limitations post-resective and recontructive surgery (i.e., high floor of the mouth), standardized periapical radiographs could not be obtained in the majority of patients, As such, we used panoramic radiographs to assess peri-implant bone resorption, as has been described by others. To most accurately measure in this way, eliminating the magnification inherent within panoramic radiography, a calibration procedure based on the known implant length was performed (Gbara et al. 2007; Perez-Sayans et al. 2008). Nonetheless, measurement error from panoramic radiographs could still be a limitation of our evaluation. Conclusion On the basis of the study of 19 patients who received a total of 51 implants the following observations were made: The reconstruction of the mandible with DBF flap or VDOF flap, in combination with dental implant therapy, was considered a valuable and predictable treatment option for patients following tumor resective surgery. Compared with implants placed in VDOF bone, implants placed in DBF bone had a relative higher incidence of a peri-implant inflammatory response. Finally, DBF bone was more resistant to peri-implant bone resorption processes than VDOF bone during functional loading John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd 163 Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 26, 2015 /
8 Acknowledgements This study was supported by the Cross Research Fund of Biomedical Engineering of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Grant No. YG2012MS32), the National Natural Science Foundation of China ( ) and Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (13ZR ). We appreciate the statistical support from Pro. Naiqing Zhao (School of Public Health, FuDan University, China) for data management. References Albrektsson, T., Zarb, G., Worthington, P. & Eriksson, A.R. (1986) The long-term efficacy of currently used dental implants: a review and proposed criteria of success. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 1: Anne-Ga elle, B., Samuel, S., Julie, B., Renaud, L. & Pierre, B. (2011) Dental implant placement after mandibular reconstruction by microvascular free fibula flap: current knowledge and remaining questions. Oral Oncology 47: Aparicio, C., Lang, N.P. & Rangert, B. (2006) Validity and clinical significance of biomechanical testing of implant/bone interface. Clinical Oral Implants Research 17(Suppl 2): 2 7. B ahr, W., Stoll, P. & Wachter, R. (1998) Use of the double barrel free vascularized fibula in mandibular reconstruction. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery: Official Journal of the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 56: Bilbao, A., Oliveira, M.H., Varela-Centelles, P.I. & Seoane, J. (2009) Assessment of dental implant stability in osseodistraction-generated bone: a resonance frequency analysis. Clinical Oral Implants Research 20: Blake, F., Bubenheim, M., Heiland, M., Pohlenz, P., Schmelzle, R. & Gbara, A. (2008) Retrospective assessment of the peri-implant mucosa of implants inserted in reanastomosed or free bone grafts from the fibula or iliac crest. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 23: Chang, Y.M., Chana, J.S., Wei, F.C., Shen, Y.F., Chan, C.P. & Tsai, C.Y. (2003) Use of waxing screws for accurate primary placement of endosteal implants in the vascularized fibular bone-reconstructed mandible. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 111: Chang, Y.M., Tsai, C.Y. & Wei, F.C. (2008) Onestage, double-barrel fibula osteoseptocutaneous flap and immediate dental implants for functional and aesthetic reconstruction of segmental mandibular defects. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 122: Chang, Y.M., Wallace, C.G., Tsai, C.Y., Shen, Y.F., Hsu, Y.M. & Wei, F.C. (2011) Dental implant outcome after primary implantation into double-barreled fibula osteoseptocutaneous free flap-reconstructed mandible. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 128: Cheung, L.K., Chua, H.D.P., Hariri, F., Pow, E.H.N. & Zheng, L. (2013) Alveolar distraction osteogenesis for dental implant rehabilitation following fibular reconstruction: a case series. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery: Official Journal of the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 71: Chiapasco, M., Biglioli, F., Autelitano, L., Romeo, E. & Brusati, R. (2006) Clinical outcome of dental implants placed in fibula-free flaps used for the reconstruction of maxillo-mandibular defects following ablation for tumors or osteoradionecrosis. Clinical Oral Implants Research 17: Chiapasco, M., Brusati, R. & Galioto, S. (2000) Distraction osteogenesis of a fibular revascularized flap for improvement of oral implant positioning in a tumor patient: a case report. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery: Official Journal of the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 58: Chiapasco, M. & Gatti, C. (2004) Immediate loading of dental implants placed in revascularized fibula free flaps: a clinical report on 2 consecutive patients. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 19: Chin, M. & Toth, B.A. (1996) Distraction osteogenesis in maxillofacial surgery using internal devices: review of five cases. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery: Official Journal of the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 54: 45 53; discussion 54. Ciocca, L., Corinaldesi, G., Marchetti, C. & Scotti, R. (2008) Gingival hyperplasia around implants in the maxilla and jaw reconstructed by fibula free flap. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 37: Disa, J., Hidalgo, D., Cordeiro, P., Winter, R. & Thaler, H. (1999) Evaluation of bone height in osseous free flap mandible reconstruction: an indirect measure of bone mass. Plastic Reconstructive Surgery 103: Frodel, J.L. Jr, Funk, G.F., Capper, D.T., Fridrich, K.L., Blumer, J.R., Haller, J.R. & Hoffman, H.T. (1993) Osseointegrated implants: a comparative study of bone thickness in four vascularized bone flaps. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 92: ; discussion Gbara, A., Darwich, K., Li, L., Schmelzle, R. & Blake, F. (2007) Long-term results of jaw reconstruction with microsurgical fibula grafts and dental implants. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery: Official Journal of the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 65: Glauser, R., Sennerby, L., Meredith, N., Ree, A., Lundgren, A., Gottlow, J. & Hammerle, C.H. (2004) Resonance frequency analysis of implants subjected to immediate or early functional occlusal loading. Successful vs. failing implants. Clinical Oral Implants Research 15: Guerra, M.F., Gias, L.N., Campo, F.J., Perez, J.S., de Artinano, FO &, Gonzalez, FJ. (2000) The partial double-barrel free vascularized fibular graft: a solution for long mandibular defects. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 105: He, Y., Zhang, Z.Y., Zhu, H.G., Wu, Y.Q. & Fu, H.H. (2011) Double-barrel fibula vascularized free flap with dental rehabilitation for mandibular reconstruction. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery: Official Journal of the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 69: Hidalgo, D.A. (1989) Fibula free flap: a new method of mandible reconstruction. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 84: Klesper, B., Wahn, J. & Koebke, J. (2000) Comparisons of bone volumes and densities relating to osseointegrated implants in microvascularly reconstructed mandibles: a study of cadaveric radius and fibula bones. Journal of cranio-maxillo-facial surgery: official publication of the European Association for Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surgery 28: Levin, L., Carrasco, L., Kazemi, A. & Chalian, A. (2003) Enhancement of the fibula free flap by alveolar distraction for dental implant restoration: report of a case. Facial Plastic Surgery: FPS 19: Marchetti, C., Degidi, M., Scarano, A. & Piattelli, A. (2002) Vertical distraction osteogenesis of fibular free flap in mandibular prosthetic rehabilitation: a case report. The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 22: Matsuura, M., Ohno, K., Michi, K., Egawa, K. & Takiguchi, R. (1999) Clinicoanatomic examination of the fibula: anatomic basis for dental implant placement. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 14: Mombelli, A. & Lang, N.P. (1994) Clinical parameters for the evaluation of dental implants. Periodontology : Moscoso, J.F., Keller, J., Genden, E., Weinberg, H., Biller, H.F., Buchbinder, D. & Urken, M.L. (1994) Vascularized bone flaps in oromandibular reconstruction. A comparative anatomic study of bone stock from various donor sites to assess suitability for enosseous dental implants.. Archives of Otolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery 120: 43. Nocini, P.F., Wangerin, K., Albanese, M., Kretschmer, W. & Cortelazzi, R. (2000) Vertical distraction of a free vascularized fibular flap in a reconstructed hemimandible: case report. Journal of Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surgery: Official Publication of the European Association for Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surgery 28: Perez-Sayans, M., Fernandez-Gonzalez, B., Somoza- Martin, M., Gandara-Rey, J.M. & Garcia-Garcia, A. (2008) Peri-implant bone resorption around implants placed in alveolar bone subjected to distraction osteogenesis. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery: Official Journal of the American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 66: Raghoebar, G.M., Liem, R.S. & Vissink, A. (2002) Vertical distraction of the severely resorbed edentulous mandible: a clinical, histological and electron microscopic study of 10 treated cases. Clinical Oral Implants Research 13: Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 26, 2015 / John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd
9 Rocchietta, I., Fontana, F. & Simion, M. (2008) Clinical outcomes of vertical bone augmentation to enable dental implant placement: a systematic review. Journal of Clinical Periodontology : Shen, Y., Sun, Jian., Li, J., Shi, J. & Ow, A. (2012) Long-term results of partial double-barrel vascularized fibula graft in symphysis for extensive mandibular reconstruction. Journal of Oral Maxillofacial Surgery 70: Siciliano, S., Lengele, B. & Reychler, H. (1998) Distraction osteogenesis of a fibula free flap used for mandibular reconstruction: preliminary report. Journal of cranio-maxillo-facial surgery: official publication of the European Association for Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surgery 26: Sieg, P., Zieron, J.O., Bierwolf, S. & Hakim, S.G. (2002) Defect-related variations in mandibular reconstruction using fibula grafts. A review of 96 cases. The British Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery 40: Taylor, T.D. (1989) Osteogenesis of the mandible associated with implant reconstruction: a patient report. International Journal of Oral Maxillofacial Implants 4: Wu, Y.Q., Huang, W., Zhang, Z.Y., Zhang, Z.Y., Zhang, C.P. & Sun, J. (2008) Clinical outcome of dental implants placed in fibula-free flaps for orofacial reconstruction. Chinese Medical Journal 121: Zhang, C.P., Ruan, Min., Xu, L.Q., Hu, Y.J., Yang, W.J., Ji, T., Qu, X.Z., Li, S.Y., Ow, A., Ma, J.Z. & Wu, Y.Q. (2012) Dental implant distractor combined with free fibular flap: a new design for simultaneous functional mandibular reconstruction. Journal of Oral Maxillofacial Surgery 70: John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd 165 Clin. Oral Impl. Res. 26, 2015 /
Placement of implants in the mandible reconstructed with free vascularized fibula flap: comparison of 2 cases
 Placement of implants in the mandible reconstructed with free vascularized fibula flap: comparison of 2 cases Mehmet Kürkcü, DDS, MSc, PhD, a Mehmet Emre Benlidayı, DDS, b Cem Kurtoğlu, DDS, PhD, c and
Placement of implants in the mandible reconstructed with free vascularized fibula flap: comparison of 2 cases Mehmet Kürkcü, DDS, MSc, PhD, a Mehmet Emre Benlidayı, DDS, b Cem Kurtoğlu, DDS, PhD, c and
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
BUILDING A. Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation. 70 OCTOBER 2016 // dentaltown.com
 BUILDING A MANDI Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation by Dr. Fayette C. Williams Fayette C. Williams, DDS, MD, FACS, is clinical faculty at John Peter Smith Hospital in Fort Worth, Texas,
BUILDING A MANDI Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation by Dr. Fayette C. Williams Fayette C. Williams, DDS, MD, FACS, is clinical faculty at John Peter Smith Hospital in Fort Worth, Texas,
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/31632 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mensink, Gertjan Title: Bilateral sagittal split osteotomy by the splitter-separator
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/31632 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mensink, Gertjan Title: Bilateral sagittal split osteotomy by the splitter-separator
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This
 1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery. Dr.maryam khosravi
 Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space
 Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE
 INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE Joint Degree Master Program: Implantology and Dental Surgery (M.Sc.) Specialized Modules: List of individual modules Specialized Module 1 Basic principles of implantology
INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE Joint Degree Master Program: Implantology and Dental Surgery (M.Sc.) Specialized Modules: List of individual modules Specialized Module 1 Basic principles of implantology
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/24/14 REVISED DATE: 04/23/15, 04/28/16, 06/22/17, 06/28/18 POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Dental
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
Straumann SmartOne. Stage 4 Af terc are and maintenance. Step 2 Maintenance visit
 Stage 4 Af terc are and maintenance Step 2 Maintenance visit Overview Assessment and treatment planning Step 1 Patient's expectations, history and examination Step 2 Treatment planning Step 3 Consultation
Stage 4 Af terc are and maintenance Step 2 Maintenance visit Overview Assessment and treatment planning Step 1 Patient's expectations, history and examination Step 2 Treatment planning Step 3 Consultation
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Reconstruction of a Mandibular Osteoradionecrotic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap.
 Case Report Reconstruction of a Mandibular Osteoradionecrotic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap. Using Synthes ProPlan CMF, Patient Specific Plate Contouring (PSPC) and the MatrixMANDIBLE Plating
Case Report Reconstruction of a Mandibular Osteoradionecrotic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap. Using Synthes ProPlan CMF, Patient Specific Plate Contouring (PSPC) and the MatrixMANDIBLE Plating
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note
 Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Osseointegrated implant-supported
 CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
 Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
Screw hole-positioning guide and plate-positioning guide: A novel method to assist mandibular reconstruction
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2012) 7, 301e305 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com CASE REPORT Screw hole-positioning guide and plate-positioning guide: A novel method
Journal of Dental Sciences (2012) 7, 301e305 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com CASE REPORT Screw hole-positioning guide and plate-positioning guide: A novel method
Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System)
 Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System) Mucosa-supported complete prostheses with poor fit greatly reduce people's quality of life. This is why the importance of implant-supported
Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System) Mucosa-supported complete prostheses with poor fit greatly reduce people's quality of life. This is why the importance of implant-supported
Intraosseous dental implants fixed on mandibular autogenous bone transplants
 VARIA Intraosseous dental implants fixed on mandibular autogenous bone transplants Anton Iordanov Djorov Sofia, Bulgaria Summary We present our experience of one-time and secondary free bone plastic surgery
VARIA Intraosseous dental implants fixed on mandibular autogenous bone transplants Anton Iordanov Djorov Sofia, Bulgaria Summary We present our experience of one-time and secondary free bone plastic surgery
ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12 Accepted on:22/05/12
 SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants. by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD
 Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Surgical Therapy. Tuesday, April 2, 13. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS
 Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
An Introduction to Dental Implants
 An Introduction to Dental Implants Aims: This article provides an introduction to dental implants, outlining the categories of dental implants, the phases involved in implant dentistry and assessing a
An Introduction to Dental Implants Aims: This article provides an introduction to dental implants, outlining the categories of dental implants, the phases involved in implant dentistry and assessing a
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel
 PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of
 Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Long-term success of osseointegrated implants
 Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Basic information on the. Straumann Pro Arch TL. Straumann Pro Arch TL
 Basic information on the Straumann Pro Arch TL Straumann Pro Arch TL Contents 1. Introduction 2 1.1 Discover more treatment options with the 4 mm Short Implant 2 2. Technical information 3 3. Step-by-step
Basic information on the Straumann Pro Arch TL Straumann Pro Arch TL Contents 1. Introduction 2 1.1 Discover more treatment options with the 4 mm Short Implant 2 2. Technical information 3 3. Step-by-step
Diagnostics and treatment planning. Dr. Attila Szűcs DDS
 Diagnostics and treatment planning. Dr. Attila Szűcs DDS Considering both surgical Aim and prosthetic aspects in the planning of implant prosthetics Arrangements for implant therapy Preliminary examinations
Diagnostics and treatment planning. Dr. Attila Szűcs DDS Considering both surgical Aim and prosthetic aspects in the planning of implant prosthetics Arrangements for implant therapy Preliminary examinations
Oral Health and Dentistry
 Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Featured Patient Case #1: Complete Mouth Reconstruction with Hybrid Restorations
 Philip L. Fava II, DMD, MDSc Robert A. Levine, DDS, FCPP, FISPPS 9880 Bustleton Ave, Suite 211 Philadelphia, PA 19115 PADentalImplants.com 215-677-8686 Featured Patient Case #1: Complete Mouth Reconstruction
Philip L. Fava II, DMD, MDSc Robert A. Levine, DDS, FCPP, FISPPS 9880 Bustleton Ave, Suite 211 Philadelphia, PA 19115 PADentalImplants.com 215-677-8686 Featured Patient Case #1: Complete Mouth Reconstruction
A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material
 74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
MODIFIED SINGLE ROLL FLAP APPROACH FOR SIMULTANEOUS IMPLANT PLACEMENT AND GINGIVAL AUGMENTATION
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement
 Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
SCD Case Study. Implant-supported overdentures
 SCD Case Study Implant-supported overdentures An implant-retained overdenture may be indicated in patients with changed anatomy, neuromuscular disorders, significant gag reflex or considerable ridge resorption
SCD Case Study Implant-supported overdentures An implant-retained overdenture may be indicated in patients with changed anatomy, neuromuscular disorders, significant gag reflex or considerable ridge resorption
Specialty Dentistry. Dentistry has nine specialty fields recognized by the American Dental Association
 Specialty Dentistry Dentistry has nine specialty fields recognized by the American Dental Association Dental Public Health Endodontics Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology
Specialty Dentistry Dentistry has nine specialty fields recognized by the American Dental Association Dental Public Health Endodontics Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology
GuidedService. The ultimate guide for precise implantations
 GuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations ABGuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations At A.B. Dental we've brought implantology into the future with a 3D digitally planned
GuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations ABGuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations At A.B. Dental we've brought implantology into the future with a 3D digitally planned
Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment
 Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment Complete dentures have largely become the domain of the denturist due to the dissatisfaction general dentists feel with this treatment. Multiple visits,
Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment Complete dentures have largely become the domain of the denturist due to the dissatisfaction general dentists feel with this treatment. Multiple visits,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1.
 Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Reconstruction of large mandibular defects
 Immediate Reconstruction of a Large Mandibular Defect of Locally Invasive Benign Lesions (A New Method) Gholamreza Shirani, OMFS, DDS, MS,* Mahnaz Arshad, DDS, 1 Farnoush Mohammadi, OMFS, DDS, MS* Tehran,
Immediate Reconstruction of a Large Mandibular Defect of Locally Invasive Benign Lesions (A New Method) Gholamreza Shirani, OMFS, DDS, MS,* Mahnaz Arshad, DDS, 1 Farnoush Mohammadi, OMFS, DDS, MS* Tehran,
DETAILING THE SOFTWARE AIDED DESIGNING OF 3-D MODEL FOR MANDIBULAR RECONSTRUCTION: A CASE REPORT
 Oral Surgery Case Report International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 6, Issue 4, July-Aug 2018 DETAILING THE SOFTWARE AIDED DESIGNING OF 3-D MODEL FOR MANDIBULAR RECONSTRUCTION:
Oral Surgery Case Report International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 6, Issue 4, July-Aug 2018 DETAILING THE SOFTWARE AIDED DESIGNING OF 3-D MODEL FOR MANDIBULAR RECONSTRUCTION:
Contemporary Periodontal Surgery
 Contemporary Periodontal Surgery Chris van Kesteren, D.D.S. CPCC Dental Hygiene Program October 18, 2011 Surgical Management of Periodontitis Periodontal Plastic Surgery Soft tissue and esthetics Dental
Contemporary Periodontal Surgery Chris van Kesteren, D.D.S. CPCC Dental Hygiene Program October 18, 2011 Surgical Management of Periodontitis Periodontal Plastic Surgery Soft tissue and esthetics Dental
Reconstruction of a Maxillary Oncologic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap. Using Synthes ProPlan CMF and the MatrixMIDFACE Plating System.
 Case Report Reconstruction of a Maxillary Oncologic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap. Using Synthes ProPlan CMF and the MatrixMIDFACE Plating System. Reconstruction of a Maxillary Oncologic Defect
Case Report Reconstruction of a Maxillary Oncologic Defect with a Fibula Osteocutaneous Flap. Using Synthes ProPlan CMF and the MatrixMIDFACE Plating System. Reconstruction of a Maxillary Oncologic Defect
Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants
 Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
The advantages of the free vascularized fibular
 Clinicoanatomic Examination of the Fibula: Anatomic Basis for Dental Implant Placement Mitsuhiro Matsuura, DDS, PhD*/Kohsuke Ohno, DDS, PhD**/ Ken-ichi Michi, DDS, PhD***/Kaoru Egawa, PhD****/Reiji Takiguchi,
Clinicoanatomic Examination of the Fibula: Anatomic Basis for Dental Implant Placement Mitsuhiro Matsuura, DDS, PhD*/Kohsuke Ohno, DDS, PhD**/ Ken-ichi Michi, DDS, PhD***/Kaoru Egawa, PhD****/Reiji Takiguchi,
Ridge Split Procedure
 Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Abstract Purpose: Materials and methods Results:
 Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter
 THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter Periodontal aspects of implant therapy 1) Comprehensive perioprosthodontic treatment by utilizing implants on perio-patients. 2) Anatomical
THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter Periodontal aspects of implant therapy 1) Comprehensive perioprosthodontic treatment by utilizing implants on perio-patients. 2) Anatomical
What You Should Know About Dental Implants: The Process of Care Applies
 Learn how the process of care model can apply to dental implants and empower decisions for providing quality care for clients. Starting with assessing the need for implants, the process covers documentation,
Learn how the process of care model can apply to dental implants and empower decisions for providing quality care for clients. Starting with assessing the need for implants, the process covers documentation,
Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
TOPICS. T O P I C S Day 2. Introduction Surgical challenges to treat esthetic implant failures Treatment options & case reports Conclusions
 T O P I C S Day 2 Implant placement post extraction with simultaneous contour augmentation using GBR: When immediate, when early, when late? CAD-CAM technology and zirconia: new opportunities for esthetic
T O P I C S Day 2 Implant placement post extraction with simultaneous contour augmentation using GBR: When immediate, when early, when late? CAD-CAM technology and zirconia: new opportunities for esthetic
Case Presentation. Overall Health. Oral Hygiene. Chief Complaint. I hate my upper denture. I can t taste food. I want an implant solution
 Case Presentation Medical History Age & Gender 62 years old female Peri-implant Osteitis Overall Health Good Hx of Smoking 5 cigarets per day (Peri-implantitis) Oral Hygiene Fair Systemic Disease Osteoarthritis
Case Presentation Medical History Age & Gender 62 years old female Peri-implant Osteitis Overall Health Good Hx of Smoking 5 cigarets per day (Peri-implantitis) Oral Hygiene Fair Systemic Disease Osteoarthritis
Large Dentigerous Cyst
 Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
Volume 16.2.1 Feb 2016 This Lecture Series qualifies for 0.5 Informal CPD Learning Hours Large Dentigerous Cyst By Dr Hassem Geha A 55 year-old male presented with a painless swelling in the right mandible.
The Original remains unique.
 The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Diagnosis. overt Examination. Definitive Examination. History. atient interview. Personal History. Clinical Examination.
 Diagnosis overt Examination History Definitive Examination atient interview Personal History Mental Attitude Medical History Dental History Clinical Examination Extra Oral Oral Radiographic Evaluation
Diagnosis overt Examination History Definitive Examination atient interview Personal History Mental Attitude Medical History Dental History Clinical Examination Extra Oral Oral Radiographic Evaluation
synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions
 synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions INTRODUCTION synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations 1 The synocta Meso abutments, available
synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions INTRODUCTION synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations 1 The synocta Meso abutments, available
A PERIO-PROSTHETIC. with the BIO-GLASS. DR. Mirko Paoli (DDS) DT. Roberto Fabris ABUTMENT SYSTEM
 A PERIO-PROSTHETIC with the TREATMENT use of ABUTMENT SYSTEM BIO-GLASS DR. Mirko Paoli (DDS) DT. Roberto Fabris 110 SUMMER 2015 The implant therapy in dentistry has allowed the modification of prosthetic
A PERIO-PROSTHETIC with the TREATMENT use of ABUTMENT SYSTEM BIO-GLASS DR. Mirko Paoli (DDS) DT. Roberto Fabris 110 SUMMER 2015 The implant therapy in dentistry has allowed the modification of prosthetic
Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up
 Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up Dr. Salah Huwais discusses how osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability Introduction
Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up Dr. Salah Huwais discusses how osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability Introduction
The Brånemark osseointegration method, using titanium dental implants (fixtures)
 Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Pre op Failed endodontic treatment with sinus involvement.
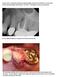 Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
Exclusion Criteria. Subjects were excluded if they were smokers and if they had residual mandible height after
 Stability of Implants Placed in Augmented Posterior Mandible after Alveolar Osteotomy Using Resorbable Nonceramic Hydroxyapatite or Intraoral Autogenous Bone: 12-Month Follow-Up Alexandre M. Dottore, DDS;*
Stability of Implants Placed in Augmented Posterior Mandible after Alveolar Osteotomy Using Resorbable Nonceramic Hydroxyapatite or Intraoral Autogenous Bone: 12-Month Follow-Up Alexandre M. Dottore, DDS;*
PDF of Trial CTRI Website URL -
 Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Sat, 07 Jul 2018 14:19:46 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 04/07/2012 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Sat, 07 Jul 2018 14:19:46 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 04/07/2012 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla
 CASE REPORT Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla Alberto Monje,* Florencio Monje, Fernando Suarez,* Raúl González-García, Laura Villanueva-Alcojol,
CASE REPORT Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla Alberto Monje,* Florencio Monje, Fernando Suarez,* Raúl González-García, Laura Villanueva-Alcojol,
A Technique for Utilizing Upper Lid Blepharoplasty Full thickness Skin for Peri-Implant Keratinized Tissue Grafting *,y
 A Technique for Utilizing Upper Lid Blepharoplasty Full thickness Skin for Peri-Implant Keratinized Tissue Grafting *,y George R. Deeb D.D.S., M.D. i, Bach T. Le D.D.S., M.D. ii, Brett A. Ueeck D.M.D iii,
A Technique for Utilizing Upper Lid Blepharoplasty Full thickness Skin for Peri-Implant Keratinized Tissue Grafting *,y George R. Deeb D.D.S., M.D. i, Bach T. Le D.D.S., M.D. ii, Brett A. Ueeck D.M.D iii,
CDT CODE** DOCUMENTATION GUIDELINES COVERAGE GUIDELINES* Restorative D2929-D2390 D2542-D2544 D2642-D2644 D2662-D2664 D2710-D2799 D2930 D2960-D2962
 DENTAL AND ORAL SURGERY CLAIM DOCUMENTATION GUIDELINES Each benefits plan defines which services are covered, excluded and subject to dollar caps or other limits. Members and their dentists will need to
DENTAL AND ORAL SURGERY CLAIM DOCUMENTATION GUIDELINES Each benefits plan defines which services are covered, excluded and subject to dollar caps or other limits. Members and their dentists will need to
Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis
 Martin Saaby Eva Karring Søren Schou Flemming Isidor Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis Authors affiliations: Martin Saaby, Søren Schou, Section for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Oral
Martin Saaby Eva Karring Søren Schou Flemming Isidor Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis Authors affiliations: Martin Saaby, Søren Schou, Section for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Oral
Case Report Alveolar Ridge Augmentation using Subepithelial Connective Tissue Grafts: A Case report
 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation using Subepithelial Connective Tissue Grafts: A Case report Po-Yu Lai, DDS, MS School of Dentistry, National Yang-Ming University Shing-Wai Yip, DDS, MS, DScD Prosthodontics
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation using Subepithelial Connective Tissue Grafts: A Case report Po-Yu Lai, DDS, MS School of Dentistry, National Yang-Ming University Shing-Wai Yip, DDS, MS, DScD Prosthodontics
University of Groningen. Dental implants in maxillofacial prosthodontics Korfage, Anke
 University of Groningen Dental implants in maxillofacial prosthodontics Korfage, Anke DOI: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2014.05.013 10.1016/j.ijom.2013.04.003 10.1002/hed.24053 IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult
University of Groningen Dental implants in maxillofacial prosthodontics Korfage, Anke DOI: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2014.05.013 10.1016/j.ijom.2013.04.003 10.1002/hed.24053 IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration. Ph.D. Thesis. Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban
 Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
botiss dental bone & tissue regeneration biomaterials mucoderm 3D-Regenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic
 dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials 3DRegenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic mucoderm Soft Tissue Graft Indications mucoderm is a collagen tissue matrix derived of animal dermis
dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials 3DRegenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic mucoderm Soft Tissue Graft Indications mucoderm is a collagen tissue matrix derived of animal dermis
RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS. The unique collagenase-resistant membrane protects bone graft and supports treatment success even when exposed 4
 RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS 1 RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS RESISTANT TO EXPOSURE The unique collagenase-resistant membrane protects bone graft and supports treatment success even when exposed 4 RELIABLE BARRIER
RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS 1 RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS RESISTANT TO EXPOSURE The unique collagenase-resistant membrane protects bone graft and supports treatment success even when exposed 4 RELIABLE BARRIER
Alveolar Ridge Preservation:
 Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Maxillary Reconstruction with the Free Fibula Flap
 Maxillary Reconstruction with the Free Fibula Flap Xin Peng, D.D.S., Ph.D., Chi Mao, D.D.S., Ph.D., Guang-yan Yu, D.D.S., Ph.D., Chuan-bin Guo, D.D.S., Ph.D., Min-xian Huang, D.D.S., and Yi Zhang, D.D.S.,
Maxillary Reconstruction with the Free Fibula Flap Xin Peng, D.D.S., Ph.D., Chi Mao, D.D.S., Ph.D., Guang-yan Yu, D.D.S., Ph.D., Chuan-bin Guo, D.D.S., Ph.D., Min-xian Huang, D.D.S., and Yi Zhang, D.D.S.,
Sandwich osteotomy of the atrophic posterior mandible prior to implant placement
 CASE REPORT Sandwich osteotomy of the atrophic posterior mandible prior to implant placement Luan Mavriqi 1, Egresa Baca 2 & Ariona Demiraj 3 1 Departament of Periodontology, Albanian University and Private
CASE REPORT Sandwich osteotomy of the atrophic posterior mandible prior to implant placement Luan Mavriqi 1, Egresa Baca 2 & Ariona Demiraj 3 1 Departament of Periodontology, Albanian University and Private
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Vertical Augmentation
 Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
Implantology without Periodontology is like Yin without Yang.
 Implantology without Periodontology is like Yin without Yang. NIWOP: The systematic and evidence-based workflow #niwop wh.com No Implantology without Periodontology NIWOP 1 Pretreatment Optimal periodontal
Implantology without Periodontology is like Yin without Yang. NIWOP: The systematic and evidence-based workflow #niwop wh.com No Implantology without Periodontology NIWOP 1 Pretreatment Optimal periodontal
Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior Region Along with Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting- A Case Report.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
CHAPTER. 1. Uncontrolled systemic disease 2. Retrognathic jaw relationship
 CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
