The Open Dentistry Journal
|
|
|
- Victoria Stone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Send Orders for Reprints to The Open Dentistry Journal, 2017, 11, The Open Dentistry Journal Content list available at: DOI: / CASE REPORT Alveolar Ridge Preservation After Tooth Extraction with DFDBA and Platelet Concentrates: A Radiographic Retrospective Study Behrang Baniasadi * and Laurence Evrard Department of Maxillofacial Surgery and Dentistry, Erasme Hospital, Université libre de Bruxelles, Brussels, Belgium Received: November 12, 2016 Revised: January 06, 2017 Accepted: January 11, 2017 Abstract: Objectives: The purpose of this study was to evaluate vertical alveolar bone loss after tooth extraction when a technique of ridge preservation was applied using a particulate demineralized freeze-dried bone allograft µm associated with platelet concentrates (platelet-rich-fibrin) in the form of gel and membranes. Material and Methods: A retrospective radiological clinical study was conducted on 56 patients for whom 95 extractions had been performed immediately followed by alveolar filling. Among the patients, 17 were smokers and 16 were provided with an immediate removable temporary prosthesis after extractions. Vertical bone loss was measured radiologically by panoramic X-ray before extractions and by a computed tomography scan after, at the level of mid-buccal bone wall, by two independent observers. For statistical analysis, Student s t-test was performed to compare the mean bone loss between mono- and pluri-radicular teeth and to compare the mean bone loss between tobacco users versus non users and finally to compare the mean bone loss between individuals that had provisional removable prosthesis and those that had not. Results: Three months after tooth extraction, the mean of vertical loss of the mid-buccal bone wall was 0.72 (SD 0.71) mm (5.53% SD 5.19). No significant difference between bone loss at mono-radicular and pluri-radicular teeth (P = 0.982) was observed. There was no significant correlation between tobacco habits and bone loss (P = 0.2), nor between provisional removable prosthesis and bone loss (P = 0.786). Conclusion: These results indicate a good potential for the technique using Demineralized Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft µm and platelet concentrates in alveolar bone preservation. Keywords: Allografts, Alveolar bone loss, Extraction socket, Platelet rich fibrin, Ridge preservation, Socket preservation, Tissue regeneration. INTRODUCTION Post-extraction bone resorption is a progressive and irreversible process that has been well described in the scientific literature. A physiological alveolar bone resorption may reach up to 40% in height and 60% in width, with the gross loss being reached within after extraction [1]. Insufficient bone may compromise dental implant treatment with a risk of injuring the anatomical structures. Therefore, adequate alveolar ridge preservation is essential * Address correspondence to this author at the Department of Maxillofacial Surgery and Dentistry, Erasme Hospital, Université libre de Bruxelles, 808 Route de Lennik 1070 Brussels, Belgium, Tel: , Fax: , behrang.baniasadi@ulb.ac.be / Bentham Open
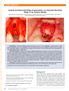
2 100 The Open Dentistry Journal, 2017, Volume 11 Baniasadi and Evrard for an esthetical outcome and correct implant placement [2, 3]. Among the biomaterials used for post-extraction alveolar filling, allogenic bone has been described as a suitable material [4-7]. In particulate form, freeze dried bone allograft (FDBA) and demineralized freeze-dried bone allograft (DFDBA) are used in dental surgery and alveolar ridge preservation techniques [8-11]. It has been shown that when used in post-extraction sockets, allografts have a positive effect on height preservation [8]. In a histological study on alveolar preservation, it was shown that DFBDA leads to a statistically significant greater mean percentage of newly formed vital bone than FDBA [10]. The platelet concentrates (platelet-rich-fibrin) are obtained by blood centrifugation, following a method first described by Choukroun et al. [12]. The platelet concentrates contain a high concentration of growth factors (PDGF, TGF-β, IGF and VEGF) and anti-inflammatory molecules (IL-1β, IL-4, IL-6 and TNF-α) and enhance the healing process [13, 14]. This may lead to better bone repair and regeneration [14, 15]. It has been shown that platelet concentrates accelerate the healing of dermal soft tissue and of the oral mucosa in cases of dental extraction [16-18]. It is still unclear if platelet concentrates are able to accelerate bone healing and influence bone quality, although it has been suggested to occur in some studies related to extraction socket healing [19, 20]. In oral surgery, the clinical benefits of platelet concentrates, when combined with DFDBA in bone regeneration, have been suggested for the treatment of intrabony periodontal defects [21]. The aim of our study was to evaluate the potential benefits of a combination of DFDBA and platelet concentrates in alveolar preservation, measuring the amount of bone loss after extractions, in a great number of patients to compare with results obtained from other techniques. MATERIAL AND METHODS The protocol of our study was accepted by the Ethical Committee of Erasme Hospital, (Université libre de Bruxelles, Brussels, Belgium) (P 2013/069). A retrospective radiological clinical study was designed. The inclusion criteria were patients older than 18 years who had undergone dental extractions prior to implant treatment in our department. Their teeth had been extracted due to severe dental decay, fractures or periodontal disease. Fig. (1). Platelets concentrates (platelet-rich-fibrin) were obtained by centrifugation of blood samples.
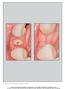
3 Alveolar Ridge Preservation After Tooth Extraction The Open Dentistry Journal, 2017, Volume No exclusion criteria were defined. Fifty-six patients were included in the study. The average age was 51-years-old, from 22 years and 84 years. Seventeen patients (30%) were smokers (> 10 cigarettes a day), and 16 patients (28%) were provided with a provisional removable prosthesis after extraction. Ninety-five extractions were performed: 72 extractions of uni-radicular teeth (76%) and 23 extractions of pluriradicular teeth (24%). At the beginning of surgery, platelet concentrates (platelet-rich-fibrin) were obtained by centrifuging patient blood samples in 10-ml tubes with no anticoagulant adjuvant at 3000 rpm for 10 minutes following a protocol described previously [22]. A portion of the centrifuged blood rich in platelets (named buffy-coats) was cut and mixed with particulate DFDBA (produced in Hôpital Erasme- ULB- Brussels) µm (Figs. 1 and 2). A portion rich in fibrin was pressed manually between gauze to obtain autologous rich-in-fibrin membranes (Fig. 3). Atraumatic extractions were realized, and immediately after extraction, the socket was filled with a mixture of DFDBA and platelet concentrates. Closure of the sockets was realized using an autologous fibrin membrane to cover the filled socket and a polyglactin absorbable suture to close the socket (Fig. 4). Fig. (2). Demineralized freeze dried bone allograft µm. For ethical reasons, no control group was used in this study, because no alveolar preservation leads to consequent bone loss [1-3]. In the post-operative period, ibuprofen 600 mg three times a day and paracetamol 500 mg were taken by the patients in case of pain. All patients received 1 gr of Amoxicillin twice a day for 4 days post-operatively, or in case of a penicillin allergy, they received clindamycin 300 mg three times a day for 4 days. The pre- and post-operative alveolar ridge heights were measured by two independent observers. A panoramic radiograph of each patient was taken preoperatively. The panoramic radiographs were taken with Planmeca ProMax (precision = 0.1 mm) and analyzed with ROMEXIS software. For each tooth, we measured the preoperative socket height as the distance between the apex and lowest visible crestal point (Fig. 5).
4 102 The Open Dentistry Journal, 2017, Volume 11 Baniasadi and Evrard Fig. (3). Parts rich in fibrin were pressed manually between gauzes in order to obtain autologous rich-in-fibrin membranes. Fig. (4). Closure of the sockets was realized using autologous fibrin membrane after filling the socket with a mixture of Demineralized freeze dried bone allograft. A polyglactin absorbable suture is used to close the socket.
5 Alveolar Ridge Preservation After Tooth Extraction The Open Dentistry Journal, 2017, Volume A computed tomography (CT) scan, Siemens Somatom Emotion (precision = 0.1 mm), was performed after the extractions for pre-implant planning. All of the CT scans were performed at Erasme hospital. For each socket, a measurement was performed between the apex and lowest visible crestal point (Fig. 6). Fig. (5). Pre-operative socket height is evaluated as the distance between apex and lowest crestal visible point on a panoramic radiography. Because of a panoramic radiography deformity and the fact that the pre- and post-extraction imaging techniques were different, a calibration was performed for each measure based on a three-rule using clear anatomical landmarks (adjacent tooth, or mandibular nerve). With the help of this calibration, the alveolar ridge preservation was measured between the apex of the socket and the lowest point of the alveolar crest of the socket at the crestal level. Statistical Analysis The observed data were statistically analyzed using a Student s t test for continuous (horizontal measurements) variable and Student s t test for categorical (mono- or pluri-radicular teeth, smoking habits and immediate prosthesis) variables to assess bone loss after surgery. The measurements are presented as an average with a 95% standard deviation. Statistical significance level was defined at P = A correlation test was applied for inter-observer measurements.
6 104 The Open Dentistry Journal, 2017, Volume 11 Baniasadi and Evrard Fig. (6). Three months after extraction, height is evaluated as the distance between apex and lowest crestal visible point on the postoperative CT Scan. RESULTS The correlation coefficient between the two observers was r = , with a 2-sided P-value of < This was considered to be a significant correlation. A mean average height loss of 0.72 mm (SD 0.71) (5.53% SD 5.19) was measured for all 95 extractions. No statistically significant difference in height loss (P = 0.982) was found between mono-radicular and pluri-radicular teeth (Table 1). Table 1. Mean bone loss in height after dental extraction. N Mean (SD) height loss after extraction (mm) Mean height loss after extraction (%) Mono-radicular teeth (0.61) 5.45 (4.41) Pluri-radicular teeth (0.74) 5.64 (5.42) Total (0.71) 5.53 (5.19) a Statistical significance level was defined at P = N = total number of tooth extracted, with mono-radicular and pluri-radicular teeth. t-test was performed to compare the mean bone loss between mono- and pluri-radicular teeth. P-value a Table 2 presents the bone loss measurements related to the type of teeth extracted. The mean difference in height before and after the extractions ranged from 0.6 to 0.8 mm. The highest alveolar height loss was measured for the upper canine (N = 12) (7.19% SD 6.80 bone loss), and the lowest height loss was observed for the lower incisors (N = 8) (4.17% SD 1.55 bone loss). Table 2. Mean bone loss in height related to the type of tooth Number of teeth extracted Mean (SD) height loss after extraction (mm) Mean (SD)height loss after extraction (%) Upper incisor (0.61) 6.3 (5.06) Upper canine (0.73) 7.19 (6.80)
7 Alveolar Ridge Preservation After Tooth Extraction The Open Dentistry Journal, 2017, Volume (Table ) contd... Number of teeth extracted Mean (SD) height loss after extraction (mm) Mean (SD)height loss after extraction (%) Upper premolar (1.11) 5.91 (6.71) Upper molar (0.74) 5.38 (5.42) Lower incisor (0.17) 4.17 (1.55) Lower canine (0.07) 4.57 (0.61) Lower premolar (0.51) 4.28 (6.47) Lower molar (0.84) 5.9 (6.07) SD = standard deviation. Mean bone loss for each type of teeth. The measurements are presented as an average with a 95% standard deviation. The average height loss after was 0.39 mm (SD 0.68) for patients who were smokers (N = 17) compared with 0.84 mm (SD 0.59) for non-smokers (N = 39). There was no statistically significant difference between smokers and non-smokers (P = 0.2). The average height loss after was 0.85 mm (SD 0.56) for patients who received an immediate prosthesis (N = 16) compared with 0.67 mm (SD 0.62) for those patients who did not receive an immediate prosthesis (N = 40) (P = 0.786), which was not statistically significant Table 3. Table 3. Bone loss in height after dental extraction according to smoking habit or provisional prosthesis. Number of teeth extracted Mean (SD) height loss after extraction (mm) Mean height loss after extraction (%) Smokers (0.68) 4.06 (6.51) Non smokers (0.59) 6.23 (5.49) Immediate prosthesis (0.56) 5.18 (3.17) No immediate prosthesis (0.62) 6.53 (6.47) a Statistical significance level was defined at P = Number of teeth extracted for each categories of patient, and the mean bone loss according to the smoking habit or provisional prosthesis. Student s t test was performed to determine if tobacco use or the provisional removable prosthesis had any effect on bone loss. DISCUSSION P-value a This study aimed at evaluating alveolar bone loss in the vertical dimension after tooth extraction when a mix of a particulate DFDBA µm and platelet concentrates in the form of a gel was used as the filling material of the socket and an autologous fibrin membrane was used as a covering material. For ethical reasons, no control group was used in this study, because alveolar ridge preservation was necessary in order to ensure adequate bone volume for implants [1-3]. Previous studies have shown that using height measurements to evaluate bone loss is possible by comparing preand post-operative standard radiographs [23, 24]. One of the restraints is that this does not authorize the evaluation of width loss. To measure height and width loss, pre- and post-extraction CT scans or cone beam CT should be performed, but there is an ethical restriction because of the radiation risks. The measurements of the bone height in our study were made on pre-extraction panoramic radiographs and 3-month post-extraction pre-implantation CT scans. To avoid any deformity in measurement, a three-rule calibration between the two types of radiographs was performed by the two independent operators for each measure, using anatomical landmarks. In this study, focusing on 95 extractions, we observed a mean bone height loss of 0.72 mm (SD 0.71) after three months. For single rooted teeth (N = 72), this loss was, on average, 0.72 mm (SD 0.61), while for pluri-radicular teeth (N = 23), the loss was 0.73 mm (SD 0.74) (Table 1). In a systematic review, it was shown that the crestal height loss as assessed on the radiographs ranged from 0.8 to 3.6 mm, 3 to 6 months after tooth extraction if preservation techniques are not applied [5]. There is a great variability in the techniques, materials, and methods of measurement used in studies related to alveolar bone preservation, which renders it difficult to compare the results from different studies. A systematic review reported a 1.67 mm bone loss after a period of 3 to 12 months if an alveolar filling was applied, independent of the biomaterial used [1]. Another systematic review showed a statistically significant greater ridge reduction in bone height in a control group compared to the socket preservation group, with a weighted mean difference of 1.47 mm [4]. All of these studies concluded that the benefits of socket preservation therapies were demonstrated
8 106 The Open Dentistry Journal, 2017, Volume 11 Baniasadi and Evrard DFDBA in particulate form has been proposed as a suitable biomaterial in socket preservation [8-11]. In a histological study, it was demonstrated that DFBDA led to a statistically significant greater mean percentage of newly formed vital bone than FDBA [11]. The combination of DFDBA and platelet concentrates has been proven to be effective in the treatment of periodontal defects, but has never been evaluated in oral surgery in a large cohort group [25, 26]. In a RCT, the alveolar ridge height loss 4 months after extraction of intercalate anterior teeth was compared using pre- and post-extraction panoramic X-rays between 6 teeth that were DFDBA filled and 6 teeth that were DFDBA filled and covered by a palatal connective tissue [8]. In the DFDBA only group, a 0.72 mm height loss was observed compared with 0.86 mm in the DFDBA plus connective tissue group. These results are difficult to compare with our results because of the heterogeneity in study characteristics, differences in measurement techniques and socket covering, and the fact that the study had a small number of extractions. Our study included 95 extractions, and contrary to the previous study, we did not apply any exclusion criteria, except for the necessity to be over the age of 18 years. This suggests that the results gained with the technique of filling the extraction socket with a mix of particulate DFDBA µm and platelet concentrates and covering it with an autologous fibrin membrane leads to an advantage in terms of the conservation of bone height. This is consistent with what the results of a clinical study, in which the mean height resorption 4 months after extraction and filling with platelet-rich-fibrin alone was 7.13% [18], which represents two percent greater loss than in our study. The more favourable results from our study could be because the platelet concentrates in the form of a gel and membrane could have acted via quicker healing of the overlaying gingival mucosa and hence may have secondarily preserved the filling mixture, which could explain the beneficial effects. Consistent with our results, in a recent systematic review, a meta-analysis was suggestive for a positive effect of platelet concentrates on bone formation in post-extraction sockets [19]. The beneficial effects of platelet concentrates are theoretically due to the high concentration of multiple growth factors that, as suggested in the literature, could remain active for more than 7 days in their fibrin matrix [12-14]. These growth factors are known to be essential for the regulation and stimulation of healing of soft and hard tissues by regulating cellular processes, such as mitogenesis, chemotaxis, and differentiation [12-14]. In a RCT of premolar extractions in 33 patients aimed at evaluating the impact of platelet-rich-fibrin on the quality of alveolar bone, it was shown that socket filling with a platelet concentrate led to better bone healing and quality in a statistically significant fashion [20]. In addition, it has been shown that platelet concentrates accelerated the healing of dermal soft tissue in a statistically significant fashion and that they had a strong stimulant effect on capillary regeneration in oral wound healing during the early stages of wound healing [16, 27]. In our study, the average height loss after was 0.39 mm (SD 0.68) for patients who were smokers (N = 17) compared with 0.84 mm (SD 0.59) for non-smokers (N = 39), which was not statistically significant (P = 0.2). Although the relationship between tobacco use and post-extraction alveolar height loss has not been proven, it has been suggested that smoking habits may adversely affect wound healing and lead to a higher degree of complications, such as alveolitis or infections [28]. In our study, the socket filling material was protected by a fibrin membrane at the time of the early healing period, which could have contributed to the good results, as well as the degree of accelerated soft tissue healing due to the platelet concentrates. We did not find any significant difference in height loss between patients who received an immediate prosthesis (N = 16) or who did not receive an immediate prosthesis (N = 40) (P = 0.786). Those who received prostheses lost 0.85 mm (SD 0.56) on average, and those who did not receive prostheses lost 0.67 mm (SD 0.62). There is no evidence in the literature as to the effect of immediate provisional prostheses on extraction socket healing. We can assume that when a removable prosthesis is delivered immediately after extractions, it may have a role in soft tissue protection, which may contribute to a good result in terms of height bone preservation, but on the contrary, it may constitute a factor of mechanical restriction for soft and hard tissue healing. Further studies would be needed to answer this question. CONCLUSION This clinical radiological retrospective study aimed at evaluating the height of bone loss in the vertical dimension 3 months after extractions after use of a technique for alveolar preservation using a mix of a particulate demineralized freeze-dried bone allograft µm and platelet-rich-fibrin in the form of gel to fill the socket and an autologous platelet-rich-fibrin membrane to cover it. The mean average height loss is 0.72 mm (SD 0.71), which represents 5.53% (SD 5.19) of the initial height, with no significant influence for tobacco or provisional prosthesis. There is a good potential for the use of particulate demineralized freeze-dried bone allograft µm
9 Alveolar Ridge Preservation After Tooth Extraction The Open Dentistry Journal, 2017, Volume associated with platelet concentrates in the form of a gel and membranes in alveolar bone preservation. Further clinical prospective studies should be conducted to better evaluate the potential benefits of this technique. CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors confirm that this article content has no conflict of interest. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS Declared none. REFERENCES [1] Araújo MG, Lindhe J. Socket grafting with the use of autologous bone: an experimental study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res 2011; 22(1): [ [PMID: ] [2] Horváth A, Mardas N, Mezzomo LA, Needleman IG, Donos N. Alveolar ridge preservation. A systematic review. Clin Oral Investig 2013; 17(2): [ [PMID: ] [3] Vignoletti F, Matesanz P, Rodrigo D, Figuero E, Martin C, Sanz M. Surgical protocols for ridge preservation after tooth extraction. A systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res 2012; 23(5)(Suppl. 5): [ [PMID: ] [4] Baeyens W, Glineur R, Evrard L. The use of platelet concentrates: platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) in bone reconstruction prior to dental implant surgery. Rev Med Brux 2010; 31(6): [PMID: ] [5] Ten Heggeler JM, Slot DE, Van der Weijden GA. Effect of socket preservation therapies following tooth extraction in non-molar regions in humans: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res 2011; 22(8): [ [PMID: ] [6] Van der Weijden F, DellAcqua F, Slot DE. Alveolar bone dimensional changes of post-extraction sockets in humans: a systematic review. J Clin Periodontol 2009; 36(12): [ [PMID: ] [7] Darby I, Chen ST, Buser D. Ridge preservation techniques for implant therapy. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2009; 24(Suppl.): [PMID: ] [8] Fugazzotto PA. Treatment options following single-rooted tooth removal: a literature review and proposed hierarchy of treatment selection. J Periodontol 2005; 76(5): [ [PMID: ] [9] Misch CE, Dietsh-Misch F, Misch CM. A modified socket seal surgery with composite graft approach. J Oral Implantol 1999; 25(4): [ [PMID: ] [10] Bader H. Immediate extraction site grafting: materials and clinical objectives. Dent Today 2005; 24(7): [PMID: ] [11] Tischler M, Misch CE. Extraction site bone grafting in general dentistry. Review of applications and principles. Dent Today 2004; 23(5): [PMID: ] [12] Choukroun J, Diss A, Simonpieri A, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part V: histologic evaluations of PRF effects on bone allograft maturation in sinus lift. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2006; 101(3): [ [PMID: ] [13] Simon BI, Zatcoff AL, Kong JJ, OConnell SM. Clinical and histological comparison of extraction socket healing following the use of autologous platelet-rich fibrin matrix (PRFM) to ridge preservation procedures employing demineralized freeze dried bone allograft material and membrane. Open Dent J 2009; 3: [ [PMID: ] [14] Plachokova AS, Nikolidakis D, Mulder J, Jansen JA, Creugers NH. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on bone regeneration in dentistry: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res 2008; 19(6): [ [PMID: ] [15] Lindeboom JA, Mathura KR, Aartman IH, Kroon FH, Milstein DM, Ince C. Influence of the application of platelet-enriched plasma in oral mucosal wound healing. Clin Oral Implants Res 2007; 18(1): [ [PMID: ] [16] Choukroun J, Diss A, Simonpieri A, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part IV: clinical effects on tissue healing. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2006; 101(3): e [ [PMID: ]
10 108 The Open Dentistry Journal, 2017, Volume 11 Baniasadi and Evrard [17] Dohan DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part III: leucocyte activation: a new feature for platelet concentrates? Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2006; 101(3): e51-5. [ [PMID: ] [18] Dohan DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part I: technological concepts and evolution. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2006; 101(3): e [ [PMID: ] [19] Brown LF, Lanir N, McDonagh J, Tognazzi K, Dvorak AM, Dvorak HF. Fibroblast migration in fibrin gel matrices. Am J Pathol 1993; 142(1): [PMID: ] [20] Moghaddas H, Amjadi MR, Naghsh N. Clinical and biometrical evaluation of socket preservation using demineralized freeze-dried bone allograft with and without the palatal connective tissue as a biologic membrane. Dent Res J (Isfahan) 2012; 9(6): [PMID: ] [21] Marx RE, Carlson ER, Eichstaedt RM, Schimmele SR, Strauss JE, Georgeff KR. Platelet-rich plasma: Growth factor enhancement for bone grafts. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1998; 85(6): [ [PMID: ] [22] Prakash S, Thakur A. Platelet concentrates: past, present and future. J Maxillofac Oral Surg 2011; 10(1): [ [PMID: ] [23] Kaur P, Maria A. Efficacy of platelet rich plasma and hydroxyapatite crystals in bone regeneration after surgical removal of mandibular third molars. J Maxillofac Oral Surg 2013; 12(1): [ [PMID: ] [24] Girish Rao S, Bhat P, Nagesh KS, et al. Bone regeneration in extraction sockets with autologous platelet rich fibrin gel. J Maxillofac Oral Surg 2013; 12(1): [ [PMID: ] [25] Pelegrine AA, da Costa CE, Correa ME, Marques JF Jr. Clinical and histomorphometric evaluation of extraction sockets treated with an autologous bone marrow graft. Clin Oral Implants Res 2010; 21(5): [ [PMID: ] [26] Crespi R, Capparè P, Gherlone E. Magnesium-enriched hydroxyapatite compared to calcium sulfate in the healing of human extraction sockets: radiographic and histomorphometric evaluation at. J Periodontol 2009; 80(2): [ [PMID: ] [27] Barone A, Aldini NN, Fini M, Giardino R, Calvo Guirado JL, Covani U. Xenograft versus extraction alone for ridge preservation after tooth removal: a clinical and histomorphometric study. J Periodontol 2008; 79(8): [ [PMID: ] [28] Hom DB, Linzie BM, Huang TC. The healing effects of autologous platelet gel on acute human skin wounds. Arch Facial Plast Surg 2007; 9(3): [ [PMID: ] 2017 Baniasadi and Evrard This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Public License (CC-BY 4.0), a copy of which is available at: This license permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
ALVEOLAR RIDGE AUGMENTATION UTILIZING PLATELET RICH FIBRIN IN COMBINATION WITH DEMINERALIZED FREEZE-DRIED BONE ALLOGRAFT A CASE REPORT
 ALVEOLAR RIDGE AUGMENTATION UTILIZING PLATELET RICH FIBRIN IN COMBINATION WITH DEMINERALIZED FREEZE-DRIED BONE ALLOGRAFT A CASE REPORT * Mishal Piyush Shah 1 and Sheela Kumar Gujjari 2 1 Department of
ALVEOLAR RIDGE AUGMENTATION UTILIZING PLATELET RICH FIBRIN IN COMBINATION WITH DEMINERALIZED FREEZE-DRIED BONE ALLOGRAFT A CASE REPORT * Mishal Piyush Shah 1 and Sheela Kumar Gujjari 2 1 Department of
Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques
 Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
SOCKET WHETHER TO PRESERVE IT NOW OR TO CREATE LATER? - A CASE REPORT
 MAVEN CASE REPORT SOCKET WHETHER TO PRESERVE IT NOW OR TO CREATE LATER? - A CASE REPORT Dr. Parthasarathi Biswas 1, Dr. Debajyoti Mondal 1, Dr. B Praveena Devi 1, Dr. Indrasri Das 2, Dr. Somen Bagchi 3,
MAVEN CASE REPORT SOCKET WHETHER TO PRESERVE IT NOW OR TO CREATE LATER? - A CASE REPORT Dr. Parthasarathi Biswas 1, Dr. Debajyoti Mondal 1, Dr. B Praveena Devi 1, Dr. Indrasri Das 2, Dr. Somen Bagchi 3,
Extraction socket preservation using β tricalcium phosphate bone graft plug and platelet rich fibrin membrane A case series
 2014; 1(1): 39-43 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2014; 1(1): 39-43 2014 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 02-01-2015 Accepted: 07-02-2015 Shantipriya Reddy Prof and Head, department
2014; 1(1): 39-43 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2014; 1(1): 39-43 2014 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 02-01-2015 Accepted: 07-02-2015 Shantipriya Reddy Prof and Head, department
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation. Sanju P. Jose
 Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation by Sanju P. Jose B.S., University of Maryland Baltimore County, 2008 D.D.S., University of Maryland School
Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation by Sanju P. Jose B.S., University of Maryland Baltimore County, 2008 D.D.S., University of Maryland School
PRP Usage in Today's Implantology
 Volume 1, December 2004 www.implant.co.il PRP Usage in Today's Implantology by Dr. R. Shapira Introduction: Treating patients suffering from hematological disorders or using anticoagulant medications always
Volume 1, December 2004 www.implant.co.il PRP Usage in Today's Implantology by Dr. R. Shapira Introduction: Treating patients suffering from hematological disorders or using anticoagulant medications always
More than bone regeneration. A total solution.
 More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
The effect of concentrated growth factors on ridge augmentation
 USERREPORT The effect of concentrated growth factors on ridge augmentation 34 Introduction The bony defects can be developed by periodontal disease, tooth loss, trauma and infection. Guided bone generation(gbr)
USERREPORT The effect of concentrated growth factors on ridge augmentation 34 Introduction The bony defects can be developed by periodontal disease, tooth loss, trauma and infection. Guided bone generation(gbr)
Platelet-rich fibrin membrane in immediate dental implant loading
 original article Platelet-rich fibrin membrane in immediate dental implant loading Carlos Fernando de Almeida Barros MOURÃO 1, Natália Belmock Mascarenhas Freitas MOURÃO 2 104 Abstract / Introduction:
original article Platelet-rich fibrin membrane in immediate dental implant loading Carlos Fernando de Almeida Barros MOURÃO 1, Natália Belmock Mascarenhas Freitas MOURÃO 2 104 Abstract / Introduction:
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report
 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants
 Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up
 643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
CLOSURE OF OROANTRAL COMMUNICATION WITH PLATELET-RICH FIBRIN
 Original rticle International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03,Issue 05 CLOSURE OF ORONTRL COMMUNICTION WITH PLTELET-RICH FIRIN Waseem itar 1, Mounzer ssad 2 1. MSc, Department of oral and
Original rticle International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03,Issue 05 CLOSURE OF ORONTRL COMMUNICTION WITH PLTELET-RICH FIRIN Waseem itar 1, Mounzer ssad 2 1. MSc, Department of oral and
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
01/05/2014. Background. Minimally invasive tooth extraction. Thomas Dietrich Professor of Oral Surgery University of Birmingham, School of Dentistry
 Background Remodelling of alveolar bone following extraction Minimally invasive tooth extraction Thomas Dietrich Professor of Oral Surgery University of Birmingham, School of Dentistry 2 weeks 4 weeks
Background Remodelling of alveolar bone following extraction Minimally invasive tooth extraction Thomas Dietrich Professor of Oral Surgery University of Birmingham, School of Dentistry 2 weeks 4 weeks
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
MODIFIED SINGLE ROLL FLAP APPROACH FOR SIMULTANEOUS IMPLANT PLACEMENT AND GINGIVAL AUGMENTATION
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants
 Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Immediate Implant Placement Along With Guided Bone Regeneration In Mandibular Anterior Region A Case Report.
 IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Dental Research Journal
 Dental Research Journal Original Article Clinical and biometrical evaluation of socket preservation using demineralized freeze dried bone allograft with and without the palatal connective tissue as a biologic
Dental Research Journal Original Article Clinical and biometrical evaluation of socket preservation using demineralized freeze dried bone allograft with and without the palatal connective tissue as a biologic
Pattern of bone resorption after extraction
 Teeth loss Pattern of bone resorption after extraction 50% in 1st year 2/ 3 in first 3 months Reich KM, Huber CD, Lippnig WR, Um C, Watzek G, Tangl S. (2011, 17). Atrophy of Residual Alveolar Ridge following
Teeth loss Pattern of bone resorption after extraction 50% in 1st year 2/ 3 in first 3 months Reich KM, Huber CD, Lippnig WR, Um C, Watzek G, Tangl S. (2011, 17). Atrophy of Residual Alveolar Ridge following
Is alveolar ridge preservation (socket grafting) an effective therapy to preserve physiologic bone loss after tooth extraction?
 C L I N I C A L Is alveolar ridge preservation (socket grafting) an effective therapy to preserve physiologic bone loss after tooth extraction? Johan Hartshorne 1 Summary Systematic review conclusion:
C L I N I C A L Is alveolar ridge preservation (socket grafting) an effective therapy to preserve physiologic bone loss after tooth extraction? Johan Hartshorne 1 Summary Systematic review conclusion:
The Clinical Application of Platelet-Rich Fibrin (Prf) and Allograft In Treatment Of Bony Defect - A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 12 Ver. IX (Dec. 2015), PP 16-20 www.iosrjournals.org The Clinical Application of Platelet-Rich
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 12 Ver. IX (Dec. 2015), PP 16-20 www.iosrjournals.org The Clinical Application of Platelet-Rich
REFERENCES for PLATELET RICH PLASMA (PRP)
 REFERENCES for PLATELET RICH PLASMA (PRP) Daif ET. Autologous blood injection as a new treatment modality for chronic recurrent temporomandibular joint dislocation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
REFERENCES for PLATELET RICH PLASMA (PRP) Daif ET. Autologous blood injection as a new treatment modality for chronic recurrent temporomandibular joint dislocation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
Conventional immediate implant placement and immediate placement with socket-shield technique Which is better
 International Journal of Clinical Medicine Research 2014; 1(5): 176-180 Published online December 30, 2014 (http://www.aascit.org/journal/ijcmr) ISSN: 2375-3838 Conventional immediate implant placement
International Journal of Clinical Medicine Research 2014; 1(5): 176-180 Published online December 30, 2014 (http://www.aascit.org/journal/ijcmr) ISSN: 2375-3838 Conventional immediate implant placement
Clinical and histologic evaluations of healing in an extraction socket filled with platelet-rich fibrin
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2011) 6, 116e122 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com Case Report Clinical and histologic evaluations of healing in an extraction socket filled
Journal of Dental Sciences (2011) 6, 116e122 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com Case Report Clinical and histologic evaluations of healing in an extraction socket filled
Clinical cases by Dr. Fernando Rojas-Vizcaya. botiss. dental bone & tissue regeneration. biomaterials. strictly biologic
 Clinical cases by Dr. Fernando Rojas-Vizcaya dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials strictly biologic botiss BTR system: BONE biologic potential bovine block & granules: pure bone mineral
Clinical cases by Dr. Fernando Rojas-Vizcaya dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials strictly biologic botiss BTR system: BONE biologic potential bovine block & granules: pure bone mineral
The Original remains unique.
 The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
Hyun-Jae Cho, Kun-Soo Jang, Ki-Hyun Jeong, Jae-Yun Jeon, Kyung-Gyun Hwang, Chang-Joo Park
 Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Socket Treatment. Procedure Guide
 Socket Treatment Procedure Guide www.implantdirect.com 888.649.6425 Extraction Healing and Ridge Resorption The Why Working with patients to educate them on the benefits of bone maintenance post extraction
Socket Treatment Procedure Guide www.implantdirect.com 888.649.6425 Extraction Healing and Ridge Resorption The Why Working with patients to educate them on the benefits of bone maintenance post extraction
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
SOCKET PRESERVATION AND TECHNIQUES AN EVALUATION OF THE LITERATURE
 SOCKET PRESERVATION AND TECHNIQUES AN EVALUATION OF THE LITERATURE Raghav Khandelwal, DMD Highland General Hospital Assistant Program Director: Ben Shimel, DDS Program Director/Chair: Chan Park, DDS,MD
SOCKET PRESERVATION AND TECHNIQUES AN EVALUATION OF THE LITERATURE Raghav Khandelwal, DMD Highland General Hospital Assistant Program Director: Ben Shimel, DDS Program Director/Chair: Chan Park, DDS,MD
A WIDE RANGE OF REGENERATIVE SOLUTIONS
 A WIDE RANGE OF REGENERATIVE SOLUTIONS INDICATIONS: 1/ SOCKET AND RIDGE PRESERVATION 2/ FILLING OF EXTRACTION SOCKETS Biomaterials offers portfolio of regenerative materials for implantology, aimed at
A WIDE RANGE OF REGENERATIVE SOLUTIONS INDICATIONS: 1/ SOCKET AND RIDGE PRESERVATION 2/ FILLING OF EXTRACTION SOCKETS Biomaterials offers portfolio of regenerative materials for implantology, aimed at
Working together as a team, the periodontist
 The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
(Images are at the end of article)
 Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Years of research and advancement in
 Immediate Implants with Guided Bone Regeneration Using Titanium Mesh and Alloplast in an Infected Site: A Case Report Mahesh et al Dr. Lanka Mahesh 1 Dr. Ajay Bibra 2 Dr. Vishal Gupta 3 Abstract Years
Immediate Implants with Guided Bone Regeneration Using Titanium Mesh and Alloplast in an Infected Site: A Case Report Mahesh et al Dr. Lanka Mahesh 1 Dr. Ajay Bibra 2 Dr. Vishal Gupta 3 Abstract Years
COMBINATION OF PLATELET RICH FIBRIN MEMBRANE WITH CORONALLY ADVANCED FLAP IN TREATMENT OF GINGIVAL RECESSION: A CASE REPORT
 ISSN No: 2455-7803 CASE REPORT COMBINATION OF PLATELET RICH FIBRIN MEMBRANE WITH CORONALLY ADVANCED FLAP IN TREATMENT OF GINGIVAL RECESSION: A CASE REPORT Prabhjeeet Singh 1, Rashmi Thakral 2, Manveen
ISSN No: 2455-7803 CASE REPORT COMBINATION OF PLATELET RICH FIBRIN MEMBRANE WITH CORONALLY ADVANCED FLAP IN TREATMENT OF GINGIVAL RECESSION: A CASE REPORT Prabhjeeet Singh 1, Rashmi Thakral 2, Manveen
Coronally advanced flap with Platelet Rich Fibrin- An effective mode of treating gingival recession: A case report
 Case Report Coronally advanced flap with Platelet Rich Fibrin- An effective mode of treating gingival recession: A case report Vijendra Pal Singh 1,*, Sangeeta Umesh Nayak 2, Dipen Shah 3 1 Associate Professor,
Case Report Coronally advanced flap with Platelet Rich Fibrin- An effective mode of treating gingival recession: A case report Vijendra Pal Singh 1,*, Sangeeta Umesh Nayak 2, Dipen Shah 3 1 Associate Professor,
Pressure Bearing Device Affects Extraction Socket Remodeling of Maxillary Anterior Tooth. A Prospective Clinical Trial
 Pressure Bearing Device Affects Extraction Socket Remodeling of Maxillary Anterior Tooth. A Prospective Clinical Trial Xi Jiang, DMD;* Yu Zhang, DMD; Bo Chen, DMD; Ye Lin, DMD ABSTRACT Background: Extraction
Pressure Bearing Device Affects Extraction Socket Remodeling of Maxillary Anterior Tooth. A Prospective Clinical Trial Xi Jiang, DMD;* Yu Zhang, DMD; Bo Chen, DMD; Ye Lin, DMD ABSTRACT Background: Extraction
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 07 Page July 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i7.101 Immediate Implant Following
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i7.101 Immediate Implant Following
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
Leukocyte - Platelet Rich Fibrin
 INTRA-LOCK Leukocyte - Platelet Rich Fibrin L-PRF is a 3-D autogenous combination of Platelet Rich Fibrin derived from the patient s blood 1. A simplifi ed chairside procedure results in the production
INTRA-LOCK Leukocyte - Platelet Rich Fibrin L-PRF is a 3-D autogenous combination of Platelet Rich Fibrin derived from the patient s blood 1. A simplifi ed chairside procedure results in the production
L-PRF Leukocyte-Platelet Rich Fibrin
 Patient information bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials L-PRF Leukocyte-Platelet Rich Fibrin innovative How to naturally support wound healing safe natural Wound healing What happens when a
Patient information bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials L-PRF Leukocyte-Platelet Rich Fibrin innovative How to naturally support wound healing safe natural Wound healing What happens when a
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
Computer-guided implant therapy and soft- and hard-tissue aspects. The Third EAO Consensus Conference 2012
 Alberto Sicilia Daniele Botticelli on behalf of Working Group 3 Computer-guided implant therapy and soft- and hard-tissue aspects. The Third EAO Consensus Conference 2012 Authors affiliations: Alberto
Alberto Sicilia Daniele Botticelli on behalf of Working Group 3 Computer-guided implant therapy and soft- and hard-tissue aspects. The Third EAO Consensus Conference 2012 Authors affiliations: Alberto
Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Alveolar Ridge Preservation:
 Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry
 Group 1 and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry Michael M. Bornstein, PD Dr Med Dent 1 /Bilal Al-Nawas, Prof Dr Med, Dr Med
Group 1 and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry Michael M. Bornstein, PD Dr Med Dent 1 /Bilal Al-Nawas, Prof Dr Med, Dr Med
Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla
 CASE REPORT Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla Alberto Monje,* Florencio Monje, Fernando Suarez,* Raúl González-García, Laura Villanueva-Alcojol,
CASE REPORT Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla Alberto Monje,* Florencio Monje, Fernando Suarez,* Raúl González-García, Laura Villanueva-Alcojol,
Redefining Regeneration
 Redefining Regeneration Taking Volume to the MAX One Product, One Treatment, Real VOLUME Buccal Bone Loss Socket Preservation Lateral / Vertical Augmentation Grafting Material Scaffold Barrier (4-6 months)
Redefining Regeneration Taking Volume to the MAX One Product, One Treatment, Real VOLUME Buccal Bone Loss Socket Preservation Lateral / Vertical Augmentation Grafting Material Scaffold Barrier (4-6 months)
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
International Journal of Implant Dentistry. Julia Hehn 1*, Thomas Schwenk 2, Markus Striegel 2 and Markus Schlee 3
 Hehn et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2016) 2:13 DOI 10.1186/s40729-016-0044-4 International Journal of Implant Dentistry RESEARCH The effect of PRF (platelet-rich fibrin) inserted with
Hehn et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2016) 2:13 DOI 10.1186/s40729-016-0044-4 International Journal of Implant Dentistry RESEARCH The effect of PRF (platelet-rich fibrin) inserted with
DDS, resident of Periodontology, School of Dentistry, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran INTRODUCTION
 A comparative study of ridge preservation using calcium sulfate and collagen membrane with and without freeze-dried bone allograft following tooth extraction REZA AMIRZARGAR 1, GHOLAMREZA SHIRANI 2, HAMID
A comparative study of ridge preservation using calcium sulfate and collagen membrane with and without freeze-dried bone allograft following tooth extraction REZA AMIRZARGAR 1, GHOLAMREZA SHIRANI 2, HAMID
Diagnostics and treatment planning. Dr. Attila Szűcs DDS
 Diagnostics and treatment planning. Dr. Attila Szűcs DDS Considering both surgical Aim and prosthetic aspects in the planning of implant prosthetics Arrangements for implant therapy Preliminary examinations
Diagnostics and treatment planning. Dr. Attila Szűcs DDS Considering both surgical Aim and prosthetic aspects in the planning of implant prosthetics Arrangements for implant therapy Preliminary examinations
Buasod.K 1, Suttapreyasri.S 1, Leepong.N 1, Pripatnanont.P 1. Abstract. *Corresponding author.
 Dimensional ridge preservation using epithelialized palatal free graft or platelet rich fibrin following tooth extraction: An experimental study in minipigs Buasod.K 1, Suttapreyasri.S 1, Leepong.N 1,
Dimensional ridge preservation using epithelialized palatal free graft or platelet rich fibrin following tooth extraction: An experimental study in minipigs Buasod.K 1, Suttapreyasri.S 1, Leepong.N 1,
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94
 ( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
Dr. Muhannad Abdulrhman Muhammed Halwani, Rakan Saed Safar Al Thobaiti and Abdallah Ali M Asker
 2018; 4(3): 276-280 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2018; 4(3): 276-280 2018 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 01-05-2018 Accepted: 05-06-2018 Dr. Muhannad Abdulrhman Muhammed Halwani
2018; 4(3): 276-280 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2018; 4(3): 276-280 2018 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 01-05-2018 Accepted: 05-06-2018 Dr. Muhannad Abdulrhman Muhammed Halwani
The treatment protocol for replacing
 RESEARCH Detection of the Mandibular Canal and the Mental Foramen in Panoramic Radiographs: Intraexaminer Agreement Jamil A. Shibli, DDS, PhD 1 Marília C. Martins, DDS, PhD 2 Leonor C. M. Loffredo, PhD
RESEARCH Detection of the Mandibular Canal and the Mental Foramen in Panoramic Radiographs: Intraexaminer Agreement Jamil A. Shibli, DDS, PhD 1 Marília C. Martins, DDS, PhD 2 Leonor C. M. Loffredo, PhD
Identification and Efficacy Ranking of Allograft and Xenograft for Extraction and Ridge Preservation Procedures
 e253 Identification and Efficacy Ranking of and for and Ridge Preservation Procedures 1 Department of Dental Public Health, Faculty of Dentistry, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Zuhair
e253 Identification and Efficacy Ranking of and for and Ridge Preservation Procedures 1 Department of Dental Public Health, Faculty of Dentistry, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Zuhair
Sinus Augmentation Studies Methods and Definition
 FDA approved indications for Infuse Bone Graft in the Maxillofacial Skeleton Alveolar Ridge Augmentation (Buccal Wall Defects) in the Maxilla Maxillary Sinus Floor augmentation Sinus Augmentation Studies
FDA approved indications for Infuse Bone Graft in the Maxillofacial Skeleton Alveolar Ridge Augmentation (Buccal Wall Defects) in the Maxilla Maxillary Sinus Floor augmentation Sinus Augmentation Studies
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
A Retrospective Analysis of Maxillary Sinuses and Implant Survival after Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation. Marlon Foote, DDS Periodontics
 A Retrospective Analysis of Maxillary Sinuses and Implant Survival after Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation Marlon Foote, DDS Periodontics Boyne, 1980 Maxillary Sinus Augmentations Maxillary sinus augmentation,
A Retrospective Analysis of Maxillary Sinuses and Implant Survival after Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation Marlon Foote, DDS Periodontics Boyne, 1980 Maxillary Sinus Augmentations Maxillary sinus augmentation,
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) The Research Progress of Platelet-Rich Fibrin Applications in the Orthodontic Treatment Yuanqian Chea, Peirong Li,
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) The Research Progress of Platelet-Rich Fibrin Applications in the Orthodontic Treatment Yuanqian Chea, Peirong Li,
Study Cases: Ride Augmentation Bone by Grafting and PRP/Preparation for Dental Implants Placement
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Case Report Study Cases: Ride Augmentation Bone by Grafting and PRP/Preparation for Dental Implants Placement Farzat Alksiri* Implantologist, German Board of Oral
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Case Report Study Cases: Ride Augmentation Bone by Grafting and PRP/Preparation for Dental Implants Placement Farzat Alksiri* Implantologist, German Board of Oral
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Socket preservation using deproteinized horsederived
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2010;40:227-231 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2010.40.5.227 Socket preservation using deproteinized horsederived bone mineral Jang-Yeol Park, Ki-Tae Koo, Tae-Il Kim, Yang-Jo
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2010;40:227-231 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2010.40.5.227 Socket preservation using deproteinized horsederived bone mineral Jang-Yeol Park, Ki-Tae Koo, Tae-Il Kim, Yang-Jo
Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 219-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.219 Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 219-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.219 Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1.
 Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
High Crown to Implant Ratio as Stress Factor in Short Implants Therapy
 10.1515/bjdm-2016-0015 BALKAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL MEDICINE ISSN 2335-0245 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY High Crown to Implant Ratio as Stress Factor in Short Implants Therapy SUMMARY Background/Aim: The purpose
10.1515/bjdm-2016-0015 BALKAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL MEDICINE ISSN 2335-0245 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY High Crown to Implant Ratio as Stress Factor in Short Implants Therapy SUMMARY Background/Aim: The purpose
Ridge preservation in a case of severe periodontitis
 Ridge preservation in a case of severe periodontitis Roberto Rossi, Ulf Nannmark, Andrea Pilloni and Nino Squadrito demonstrate how to preserve and condition the soft tissue with a combined approach Periodontal
Ridge preservation in a case of severe periodontitis Roberto Rossi, Ulf Nannmark, Andrea Pilloni and Nino Squadrito demonstrate how to preserve and condition the soft tissue with a combined approach Periodontal
Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 15 No. 03 July 16
 Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 5 No. 03 July 6 Original article Dimensional changes of hard and soft tissue after immediate implantation in comparison with conventional tooth extraction Radvar
Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 5 No. 03 July 6 Original article Dimensional changes of hard and soft tissue after immediate implantation in comparison with conventional tooth extraction Radvar
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry
 Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Our ultimate goal is to provide you and your patients with the highest standards in implant case planning
Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Our ultimate goal is to provide you and your patients with the highest standards in implant case planning
The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting
 44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
Abstract. Introduction. Case Report
 Chettinad Health City Medical Journal Case Report Ridge using Titanium Mesh, PRF and Autogenous Bone Graft with Implant Placement Dr.Vinayak S Gowda*, Dr.B.Meena Priya** *Professor, Department of Periodontics,
Chettinad Health City Medical Journal Case Report Ridge using Titanium Mesh, PRF and Autogenous Bone Graft with Implant Placement Dr.Vinayak S Gowda*, Dr.B.Meena Priya** *Professor, Department of Periodontics,
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits. Your combination for success
 Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Management Of Multiple Gingival Recession Defect Using Coronally Advanced Flap Alone Or With PRF Membrane
 CASE REPORT Management Of Multiple Gingival Recession Defect Using Coronally Advanced Flap Alone Or With PRF Membrane Neetu Rani 1, Surendra Singh 2, Rachita Arora 3, Nandlal 4, Amitabh Srivastava 5 1
CASE REPORT Management Of Multiple Gingival Recession Defect Using Coronally Advanced Flap Alone Or With PRF Membrane Neetu Rani 1, Surendra Singh 2, Rachita Arora 3, Nandlal 4, Amitabh Srivastava 5 1
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
REASONS TO USE R.T.R.
 3 REASONS TO USE R.T.R. AFTER EACH EXTRACTION Fully resorbable ß-TCP material RTR 3raisons 120x280.indd 1 16/06/15 10:52 1AVOID SPONTANEOUS RIDGE RESORPTION After tooth extraction, spontaneous healing
3 REASONS TO USE R.T.R. AFTER EACH EXTRACTION Fully resorbable ß-TCP material RTR 3raisons 120x280.indd 1 16/06/15 10:52 1AVOID SPONTANEOUS RIDGE RESORPTION After tooth extraction, spontaneous healing
Evaluation of proximity of the floor of the maxillary. Zanco J. Med. Sci., Vol. 16, No. (2), 2012
 Evaluation of proximity of the floor of the maxillary sinus to the alveolar bone crest, using digital panoramic imaging system, in Erbil city Received: 10/2/2011 Accepted: 13/9/2011 Sarkawt H. Ali* Saeed
Evaluation of proximity of the floor of the maxillary sinus to the alveolar bone crest, using digital panoramic imaging system, in Erbil city Received: 10/2/2011 Accepted: 13/9/2011 Sarkawt H. Ali* Saeed
CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature:
 CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature: CF Hoogendijk Maxillo- facial and Oral surgery: Trauma: 1. Facial trauma for the confirmation or exclusion of fractures
CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature: CF Hoogendijk Maxillo- facial and Oral surgery: Trauma: 1. Facial trauma for the confirmation or exclusion of fractures
The healthy natural tooth AMODIFIED SOCKET SEAL SURGERY WITH COMPOSITE GRAFT APPROACH CLINICAL
 CLINICAL fil AMODIFIED SOCKET SEAL SURGERY WITH COMPOSITE GRAFT APPROACH Carl E. Misch, DDS, MDS Francine Dietsh-Misch, DDS, MDS Craig M. Misch, DDS, MDS KEY WORDS Bone contour Socket seal Composite graft
CLINICAL fil AMODIFIED SOCKET SEAL SURGERY WITH COMPOSITE GRAFT APPROACH Carl E. Misch, DDS, MDS Francine Dietsh-Misch, DDS, MDS Craig M. Misch, DDS, MDS KEY WORDS Bone contour Socket seal Composite graft
Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
World Congress of Ultrasonic Piezoelectric Bone Surgery 2015, Busan Korea, May Pre-Congress Workshop 1
 World Congress of Ultrasonic Piezoelectric Bone Surgery 2015, Busan Korea, May 01-03 Pre-Congress Workshop 1 Course Director Prof. Dong-Seok Sohn S-dental Date May 1(Fri) 2015, 9:00 AM to 5:00 PM $800
World Congress of Ultrasonic Piezoelectric Bone Surgery 2015, Busan Korea, May 01-03 Pre-Congress Workshop 1 Course Director Prof. Dong-Seok Sohn S-dental Date May 1(Fri) 2015, 9:00 AM to 5:00 PM $800
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Immediate Implant Placement:
 Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
