Morphometric study of the Axis vertebra
|
|
|
- Randall Lucas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Eur J Anat, 16 (2): (2012) Morphometric study of the Axis vertebra Shilpa Gosavi 1, Vatsala Swamy 2 1- Dept. of Anatomy, Padmashree Dr.Vitthalrao Vikhe Patil Foundation s Medical College, Ahmednagar, Maharashtra, India 2- Dept. of Anatomy, Padmashree Dr. D.Y. Patil Medical College, Pimpri, Pune, Maharashtra, India SUMMARY The axis (second cervical vertebra) is unique in possessing the dens or odontoid process and very specialized superior articular facets. The study was carried out to gather the metrical data of this atypical cervical vertebra. A hundred dried intact human axis vertebrae were measured using digital vernier caliper accurate up to 0.01 mm and a goniometer. Various linear and angular measurements of body, dens, lateral mass, pedicles, superior and inferior articular facets, lamina and spine were studied. The mean antero-posterior diameter of body of axis vertebra was ± 1.73 mm. The external height of lateral mass on the right side was 8.77 ± 1.43 mm and 8.28 ± 1.26 mm on the left side. The height of dens was ± 1.54 mm and the average transverse diameter was 9.28 mm. All the measurements, namely length, thickness and height of lamina were observed to be more on the right side than on the left, and all these differences were statistically significant. (P < ) The data in this study should be useful to surgeons while working around the second cervical vertebra to avoid injury to the vital structures. Key words: Axis Dens Morphometry INTRODUCTION The axis (second cervical vertebra) is unique in possessing a dens or odontoid process and very specialized superior articular facets. It acts as an axle for rotation of the atlas and the head around the strong dens which projects cranially from the superior surface of the body (Standring, 2008). A good understanding of the exact dimensions and shape of this bone is necessary for the evaluation of many clinical problems (Doherty and Heggeness, 1995). Several surgical techniques, such as interlaminar clamping, interspinous wiring, plate and screw fixation, have been employed to correct the instability of the atlanto-axial complex or occipito-cervical junction caused by numerous traumatic and non-traumatic conditions. In spite of the benefits conferred by transpedicular screw fixation in the cervical column, controversy exists regarding its potential risk. Incorrect insertion of a pedicle screw can cause damage to adjacent vital structures such as the spinal cord, nerve roots, cranial nerves and vertebral arteries (Senegul and Kodiglu, 2006). As new internal fixation methods evolve, a better understanding of the geometry and dimensions of the bone in ques- Submitted: February 22, 2012 Accepted: March 28, 2012 Corresponding author: Dr. Shilpa Gosavi N. Department of Anatomy, Padmashree Dr.Vitthalrao Vikhe Patil Foundation s Medical College, Vilad ghat, MIDC, Ahmednagar. Maharashtra, India Phone: sngosavi@yahoo.com 98
2 Morphometric study of the Axis vertebra tion is clearly indicated (Doherty and Heggeness, 1995). This study reports a detailed quantitative evaluation of several dimensions of one hundred human axis vertebrae. MATERIALS AND METHODS One hundred dried human axis vertebrae of unknown sex collected from the Departments of Anatomy of five medical colleges were examined. Only intact vertebrae, free from any osteophytes or metastatic tumors, were included in the study. All the linear parameters were measured using a digital vernier caliper accurate to 0.01 mm. The caliper had a depth gauge, which was used to measure the height of foramen transversarium accurately. The angular measurements were made using a standard goniometer. All measurements were made by a single observer. All symmetrical structures were measured bilaterally. The following parameters were measured for each axis. The body was measured for the antero posterior (A-P) diameter and transverse diameter of the body at the base of the vertebra. Anterior vertebral body height was measured at the anterior midline of the body from the inferior edge to the superior border, which was defined by a line drawn at the superior aspect of the superior articular processes (Fig. 1). Posterior vertebral body height was measured at the posterior midline of the body of the vertebra from the posterior inferior edge to the superior border. The end plate lip height was calculated as the difference between the anterior body height and the posterior body height (Doherty and Heggeness, 1995). The height of the dens was measured from the superior border of the superior articular facets to the tip of the dens. The maximum and minimum transverse diameter and the antero-posterior diameter were measured. The vertical angle of the dens was determined as an angle between the inferior surface of the vertebral body and the vertical axis of the dens. The height and transverse diameter of the articular surface on the anterior surface of the dens was measured. The length, height and thickness of the lamina were measured. We also noted the height of the bifid spine and the distance between its two parts. The total height of the vertebra was measured as the distance from the inferior edge of the body in the anterior midline to the tip of the odontoid process (Fig. 1). The length of the pedicle from the anterior-most point of the pedicle (anterior-most point on the superior articular facet) to the posterior edge of the inferior articular facet on the inferior aspect of the vertebra was measured. Pedicle width was measured as the distance from the external surface of pedicle to its internal surface at the level of foramen transversarium. Pedicle height was measured from the superior surface of the pedicle to its inferior surface. The median angle of the pedicle was measured as the angle between the axis of the pedicle and the median sagittal line of the bone (Fig. 2). The shape, the antero-posterior and transverse diameter of the superior and the inferior articular facets were measured. The superior facet angle relative to the axis of the facet and the sagittal plane was measured on both sides. The antero-posterior diameter of the vertebral foramen was measured at the inlet and outlet of the foramen at the midline. Its maximum transverse diameter was also measured (Fig. 3). The length, height and thickness of the lamina were measured. We also noted the height of the bifid spine and the distance between its two parts. The measurements of the lateral mass included its external height from the mid- Fig. 1. Lateral view of the axis. TH total height; ABH anterior body height; VAOD vertical angle of dens. 99
3 Shilpa Gosavi, Vatsala Swamy Fig. 2. Superior view of the axis. MAOP median angle of pedicle. Fig. 3.- Superior view of the axis. VFAP Vertebral foramen antero-posterior diameter; VFTD vertebral foramen transverse diameter; SAP superior articular facet antero-posterior diameter; STD superior articular facet transverse diameter. point of the superior articular facet to the lower-most point on its inferior surface. The height of the foramen transversarium was measured at the maximal vertical diameter and its width at the maximal horizontal diameter (Madawi et al., 1997). The data were analyzed statistically and the Z test was applied, using SPSS software. RESULTS The findings are shown in tables 1, 2 and 3. The width of the pedicle was less on the right side and greater on the left, and this difference was statistically significant. However, the difference in the length of the pedicles was not significant. The superior articular facets were large, flat or slightly convex and were directed laterally. It was observed that 63% of these were oval in shape and 37% were circular. The shape of the inferior articular facets was not different from the superior articular facets and 88% of the inferior articular facets were circular in shape while the remaining 22% were oval. There was no difference in the diameters of the superior and inferior articular facets on the two sides. The external height of the lateral mass was greater on the right side -i.e ± 1.43 mm- than on the left side - i.e., 8.28 ± 1.26 mm. This difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). All the dimensions of the lamina of the axis showed a significant bilateral difference, being more pronounced on the right side. DISCUSSION Metrical details of the axis vertebra are important for several surgical procedures. Table 4 gives a comparison between the different parameters of the axis in the present study and those reported in previous studies by other authors. The variations seen in the different parameters are perhaps due to the difference in the ethnicities to which these vertebrae belonged in various studies. If transpedicular screw placement were desirable in order to stabilize a fracture line through the axis pedicle, detailed knowledge of the pedicle would be essential (Xu et al., 1995). Table 5 compares our measurements of the pedicle with those of other authors. Gupta and Goel (2000) reported that the mean screwable thickness of the pedicle of the axis was 7.8 mm. In the present study, pedicle width ranged from 3.91 to mm. Senegul and Kodiglu (2006) found that 7.5% of the specimens had an isthmus width less than 5 mm, while in the present study 4% of the specimens showed a width of less than 5 mm. 100
4 Morphometric study of the Axis vertebra Table 1. Measurements of unpaired parameters of axis. Nº Parameter Range(mm) Mean ± SD (n=100) (mm) 1 Body A-P diameter ± 1.73 Transverse diameter ± 2.12 Anterior body height ± 2.25 Posterior body height ± 2.11 End plate lip height ± Vertebral foramen Transverse diameter ± 1.77 A-P diameter at inlet ± 1.68 A P diameter at outlet ± Dens Height ± 1.54 A-P diameter ± 0.94 Maximum width ± 1.07 Minimum width ± 0.88 Vertical angle of dens ± 6.55 Total height ± 3.21 Articular Vertical diameter ± 1.95 facet Transverse diameter ± 1.29 The superior articular facets of the axis vertebra differ from the facets of all other cervical vertebrae in two important ways, which make this region especially prone to vertebral artery injury during screw fixation. First, these facets in the axis are present in the proximity of the body when compared with vertebrae where they are located close to the lamina. Second, the foramen transversarium of the axis is partially or completely present on the inferior surface of the superior articular facet, while in other cervical vertebrae this foramen is very closely related to the transverse process (Cacciola et al., 2004). In the present study, 63% of the superior articular facets were oval and 37% were circular. In the oval facets, the A-P diameter was longer than the transverse diameter in all except one. Cacciola et al. (2004) observed that in 54% of the superior articular facets the A-P diameter was longer than the transverse Table 2. Measurements of paired parameters of pedicle and articular facets. Nº Parameter Range(mm) Mean ± SD (n=100) (mm) Rt.* Lt. Rt. Lt. 1 Pedicle Length ± ± 3.72 Width ± ± 1.65 Height ± ± 7.67 Median angle 40 75º 40 75º 8.20 ± ± Superior articular facet A-P diameter ± ± 1.76 Trans. diameter ± ± 1.42 Superior angle of SAF 60 90º 60 90º ± 5.73º ± 5.67º 3 Inferior articular facet A P diameter ± ± 1.79 Trans. Diameter ± ± Lateral mass External height ± ± Foramen transversarium Height ± ± 1.14 Width ± ± Lamina Length ± ± 3.19 Height ± ± 3.16 Thickness ± ± 1.16 * - Right, - Left, Trans. Transverse, SAF Superior articular facet Table 3. Measurements of some parameters of the axis. Nº Parameter Range (mm) Mean ± SD (n=100) (mm) Rt. Lt. Rt. Lt. 1 Dist. between SAF and midline ± ± Dist. between tip of TP and midline ± ± Height of spine ± ± Distance between limbs of the bifid spine ± 2.90 * - Right, - Left, SAF superior articular facet, TP transverse process 101
5 Shilpa Gosavi, Vatsala Swamy diameter and in 27% the transverse diameter was greater than A-P, whereas only 19% were circular. The mean antero-posterior diameter of the superior articular facet in the present study was mm. Xu et al. (1995) reported lengths of 18.2 mm in males and 17.1 mm in females, while Senegul and Kodiglu (2006) reported 17.5 ± 1.5 mm; they also observed the width of the superior facet to be 14 ± 1.5 mm, and Xu et al. (1995) reported it as 17.6 mm and 16.9 mm in males and females respectively. We found it to be 14.5 mm. Hence, our figures match with those of Senegul and Kodiglu (2006). The angle between the long axis of the superior facet and the sagittal plane in our study was 79.5º, while Xu et al. (1995) reported it as 66.3º in males and 68.4º in females. The shape of the inferior articular facet was circular in most (88%) of the vertebrae and oval in 12%, while Senegul and Kodiglu (2006) reported that these facets were circular in 96% and ovoid in 4%. They also observed that, in ovoid facets the transverse diameter was longer than the antero-posterior diameter. In our study, in nine facets the transverse diameter was longer than the antero-posterior diameter, but in three the A-P diameter was longer than the transverse diameter. In the present study, the mean antero-posterior diameter of the inferior articular facet was 9.74 mm and the width was 9.9 mm. Senegul and Kodiglu (2006) observed that the mean A-P dimension was 11.6 mm and the mean transverse dimension was 9.5 mm. Lu et al. (1998) determined the length of the inferior articular facet as 20 mm in males and 19 mm in females, while the width was 20 mm in males and 18 mm in females. In the present study, the various dimensions of the dens, such as length, the anteroposterior diameter, and minimum and maximum width were comparable to those reported in previous studies (Table 4). Nucci et al. (1995) found that the crucial transverse outer diameter for the emplacement of two 3.5 mm cortical screws with tapping in the dens was 9 mm. They observed that in 95% of cases the diameter was more than 9 mm. In the present study only 58% had a diameter of the dens greater than 9 mm. The vertical angle of the dens in the present study was 53.6º, whereas Table 4. Comparison of some Axis parameters in different studies. Parameters Xu et al. Doherty & Senegul & Lang Lu et al. Present (1995) Heggeness (1995) Kodiglu (2006) (1995) (1998) study A-P diameter Trans diameter Body Ant. Body height* Post. body height Lip height Height Dens A-P diameter Max. width Trans. diameter Vertebral foramen A-P inlet * - Ant. Anterior, Post. - Posterior A-P outlet Table 5. Comparison of parameters of pedicle of Axis in different studies. Parameter Present Xu et al. Madawi study (1995) et al. (1997) Length Width Height
6 Morphometric study of the Axis vertebra Xu et al. (1995) measured it as 64.1º. The total height of the axis vertebra was mm in our study and Doherty and Heggeness (1995) reported it as 39.9 ± 3mm. In the present study the articular facet on the anterior surface of the dens had a mean vertical diameter of 9.39 mm and a mean width of 7.47 mm. Doherty and Heggeness (1995) reported the vertical diameter of the articular facet of dens as 15.5 mm. Madawi et al. (1997) studied the different dimensions of the lateral mass of the axis. They observed the external height of lateral mass to be 8.6 mm, whereas in the present study it was 8.77 ± 1.43 mm on the right side and 8.28 ± 1.26 mm on the left side. The bilateral difference was statistically significant.(p<0.05) The mean transverse diameter of foramen transversaria was 5.43 mm in the present study while Madawi et al. (1997) measured it as 5.6 mm. The mean height of the foramen transversaria in the present study was 6.31 mm whereas according to Madawi et al. (1997) it was 5.7 mm. Hence these findings match each other. The length, thickness and the height of the lamina were higher on the right side as compared to the left and this difference was statistically significant. Here, the mean distance of the outer border of the superior articular facet from the midline on the right side was ± 2.23 mm and on the left side it was ± 2.23 mm. Senegul and Kodiglu (2006) observed it as 21.3 ± 2.8 mm on the right side and 21.9 ± 2.3 mm on the left side. The bilateral difference in the present study was not statistically significant. The mean distance from the tip of the transverse process to the midline in the present study was ± 2.54 mm on the right side and ± 2.86 mm on the left side while Senegul and Kodiglu (2006) measured it as 27.3 ± 2.8 mm on the right side and 27.2 ± 2.8 mm on the left side. The spinous process of the axis is large with a bifid tip and a broad base, which is concave inferiorly. We observed the height and the distance between the two limbs of the bifid spine. The height was mm on the right and mm on the left side. Marked variation was observed in the distance between the limbs of the bifid spine, ranging from 0.51 mm to mm, with a mean value of mm. The dimensions reported in the present study should be useful for the surgeons while working around the axis vertebra to avoid injury to vital structures. It can also be also useful to devise new methods of fixation of the fractured odontoid process or axis pedicles. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We are grateful to Dr. B.R. Zambare, Head of the Department, Dept. of Anatomy, P.D.V.V.P.F. Medical College, Ahmednagar, for his continuous support and encouragement during the present study. We are also very grateful to Dr. V.R. Mysorerkar, Ex-Professor & Head of the Department of Anatomy at various medical colleges for his valuable suggestions and guidance in the preparation of this paper. Sources of support: Department of Anatomy, P.D.V.V.P.F. Medical College, Ahmednagar, AFMC Pune, Dr. D.Y. Patil Medical College, Pune, B.J. Medical College, Pune, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College, Pune. REFERENCES CACCIOLA F, PHALKE U, GOEL A (2004) Vertebral artery in relationship with C1-C2 vertebra: An anatomical study. Neurol India [serial online], 52: DOHERTY BJ, HEGGENESS MH (1995) Quantitative anatomy of second cervical vertebra. Spine, 20: GUPTA S, GOEL A. (2000) Quantitative anatomy of lateral masses of atlas and axis vertebra. Neurol India, 48: LANG J, Editor (1995) Skull Base and Related structures. Schattauer, Stuttgart. LU J, EBRAHEIM NA, YANG H, HECK BE, YEASTING RA (1998) Anatomic considerations of anterior transarticular screw fixation for atlantoaxial instability. Spine, 23: MADAWI AA, SOLANKI G. CASEY ATH, CROCKRAL HA (1997) Variation of the groove in the axis vertebra for the vertebral artery. J Bone Joint Surg, 79 (B): NUCCI RC, SEIGAL S, MEROLA AA, GORUP J, MROCZEK KJ, DRYER J, ZIPNICK RI, HAHER TR (1995) Computed tomographic evaluation of the normal adult odontoid. Implications for internal fixation. Spine, 20: SENEGUL G, KODIGLU HH (2006) Morphometric anatomy of atlas and axis vertebra. Turkish neurosurgery, 16 (2): STANDRING S, Editor, (2008) Gray s anatomy: The Anatomical basis of Clinical practice. Edition 40 th, Churchill Livingstone, London, UK. XU R, NADAUD MC, EBRAHEIM NA, YEASTING RA (1995) Morphology of the second cervical vertebra and the posterior projection of the C2 pedicle axis. Spine, 20:
Morphometric Anatomy of the Atlas and Axis Vertebrae
 Original Article Morphometric Anatomy of the Atlas and Axis Vertebrae Gökflin fiengül Hakan Hadi KADIO LU ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: In this study, forty dried specimens of atlas and axis vertebrae were examined
Original Article Morphometric Anatomy of the Atlas and Axis Vertebrae Gökflin fiengül Hakan Hadi KADIO LU ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: In this study, forty dried specimens of atlas and axis vertebrae were examined
A morphometric study of the Pedicles of dry human typical lumbar vertebrae
 Original article: A morphometric of the Pedicles of dry human typical lumbar vertebrae Dhaval K. Patil 1 *, Pritha S. Bhuiyan 2 1Resident, Department of Anatomy, Seth G S Medical College, Parel, Mumbai-400012,
Original article: A morphometric of the Pedicles of dry human typical lumbar vertebrae Dhaval K. Patil 1 *, Pritha S. Bhuiyan 2 1Resident, Department of Anatomy, Seth G S Medical College, Parel, Mumbai-400012,
Any of the vertebra in the cervical (neck) region of the spinal column. The cervical vertebra are the smallest vertebra in the spine, reflective of th
 Any of the vertebra in the cervical (neck) region of the spinal column. The cervical vertebra are the smallest vertebra in the spine, reflective of the fact that they support the least load. In humans,
Any of the vertebra in the cervical (neck) region of the spinal column. The cervical vertebra are the smallest vertebra in the spine, reflective of the fact that they support the least load. In humans,
THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE
 THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE Osteology of the Vertebral Column Bone Description vertebra Notes a vertebra
THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE Osteology of the Vertebral Column Bone Description vertebra Notes a vertebra
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN. Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms.
 THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics. Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6. Typical Cervical Vertebra Anterior 10/5/2017
 Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6 Small, relatively broad body Bifid SpinousProcess Long and narrow laminae Spinal Canal: large, triangular; remarkably consistent dimensions
Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6 Small, relatively broad body Bifid SpinousProcess Long and narrow laminae Spinal Canal: large, triangular; remarkably consistent dimensions
VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL COLUMN
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
The sacrum is a complex anatomical structure.
 A Review Paper Rongming Xu, MD, Nabil A. Ebraheim, MD, and Nicholas K. Gove, MD Abstract Treatment in spinal disorders, sacroiliac joint disruption, and sacral fractures may involve instrumentation of
A Review Paper Rongming Xu, MD, Nabil A. Ebraheim, MD, and Nicholas K. Gove, MD Abstract Treatment in spinal disorders, sacroiliac joint disruption, and sacral fractures may involve instrumentation of
International J. of Healthcare & Biomedical Research, Volume: 1, Issue: 4, July 2013, Pages
 Original article: Morphometry of first pedicle of sacrum and its clinical relevance Sinha Manisha B, Rathore Mrithunjay, Trivedi Soumitra, Siddiqui A U Department of Anatomy, All India Institute of Medical
Original article: Morphometry of first pedicle of sacrum and its clinical relevance Sinha Manisha B, Rathore Mrithunjay, Trivedi Soumitra, Siddiqui A U Department of Anatomy, All India Institute of Medical
Cervical Cooled RF Training Presentation
 Cervical Cooled RF Training Presentation Agenda Patient Selection Considerations Diagnostic Block General Considerations COOLIEF* Cooled RF Technique Posterior Lateral Precautions Summary Appendix 2 Disclaimer
Cervical Cooled RF Training Presentation Agenda Patient Selection Considerations Diagnostic Block General Considerations COOLIEF* Cooled RF Technique Posterior Lateral Precautions Summary Appendix 2 Disclaimer
2. The vertebral arch is composed of pedicles (projecting from the body) and laminae (uniting arch posteriorly).
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
human anatomy 2015 lecture four Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure Sectioned spinous process. Interspinous.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
A Morphometric study of lamina of lumbar vertebrae: A dry bone study conducted in RIMS, Imphal
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 11 Ver. 4 (November. 2018), PP 35-39 www.iosrjournals.org A Morphometric study of lamina of
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 11 Ver. 4 (November. 2018), PP 35-39 www.iosrjournals.org A Morphometric study of lamina of
Vertebral Column. Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions. Cervical
 Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D.
 Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
Ligaments of the vertebral column:
 In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
Research article - Basic and applied anatomy Morphometric study of cervical vertebrae C3-C7 in South Indian population A clinico-anatomical approach
 IJAE Vol. 122, n. 1: 49-57, 2017 ITALIAN JOURNAL OF ANATOMY AND EMBRYOLOGY Research article - Basic and applied anatomy Morphometric study of cervical vertebrae C3-C7 in South Indian population A clinico-anatomical
IJAE Vol. 122, n. 1: 49-57, 2017 ITALIAN JOURNAL OF ANATOMY AND EMBRYOLOGY Research article - Basic and applied anatomy Morphometric study of cervical vertebrae C3-C7 in South Indian population A clinico-anatomical
You have 24 vertebrae in your spinal column. Two are special enough to be individually named.
 You have 24 vertebrae in your spinal column. Two are special enough to be individually named. Your atlas (C01) and axis (C02) are very important vertebrae. Without them, head and neck movement would be
You have 24 vertebrae in your spinal column. Two are special enough to be individually named. Your atlas (C01) and axis (C02) are very important vertebrae. Without them, head and neck movement would be
Department of Anatomy, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Rishikesh, Uttarakhand, India.
 Original Research Article A Study on the Morphometric Asymmetry of Atlas Vertebrae Mohd Salahuddin A ( ), Mukesh S, Binaya KB, Nilotpal C Department of Anatomy, All India Institute of Medical Sciences,
Original Research Article A Study on the Morphometric Asymmetry of Atlas Vertebrae Mohd Salahuddin A ( ), Mukesh S, Binaya KB, Nilotpal C Department of Anatomy, All India Institute of Medical Sciences,
ASJ. Cervical Pedicle Screw Fixation: Anatomic Feasibility of Pedicle Morphology and Radiologic Evaluation of the Anatomical Measurements
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2014;8(3):273-280 Cervical http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.3.273 pedicle screw fixation 273 Cervical Pedicle Screw Fixation: Anatomic
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2014;8(3):273-280 Cervical http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.3.273 pedicle screw fixation 273 Cervical Pedicle Screw Fixation: Anatomic
A STUDY OF MORPHOMETRY OF SUPERIOR ARTICULAR FACET OF ATLAS AND ITS CLINICAL IMPLICATION IN CENTRAL INDIA
 Original Research Article A STUDY OF MORPHOMETRY OF SUPERIOR ARTICULAR FACET OF ATLAS AND ITS CLINICAL IMPLICATION IN CENTRAL INDIA Ashita Kaore * 1, Ashish U Kamdi 2, A.P. Kasote 3, N.Y.Kamdi 4, M.P.Fulpatil
Original Research Article A STUDY OF MORPHOMETRY OF SUPERIOR ARTICULAR FACET OF ATLAS AND ITS CLINICAL IMPLICATION IN CENTRAL INDIA Ashita Kaore * 1, Ashish U Kamdi 2, A.P. Kasote 3, N.Y.Kamdi 4, M.P.Fulpatil
Involvement of the spine is common in rheumatoid. Incidence been reported to be 85% radiologically but only 30% have neurological signs and symptoms.
 RHEUMATOID SPINE Involvement of the spine is common in rheumatoid. Incidence been reported to be 85% radiologically but only 30% have neurological signs and symptoms. When neurology is present it may manifest
RHEUMATOID SPINE Involvement of the spine is common in rheumatoid. Incidence been reported to be 85% radiologically but only 30% have neurological signs and symptoms. When neurology is present it may manifest
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
Lauren M. Burke, Warren D. Yu, Anthony Ho, Timothy Wagner, Joseph R. O Brien. Department of Orthopaedic Surgery George Washington University
 Lauren M. Burke, Warren D. Yu, Anthony Ho, Timothy Wagner, Joseph R. O Brien Department of Orthopaedic Surgery George Washington University O Brien: Consultant for Globus, Relivant, Stryker. Royalties:
Lauren M. Burke, Warren D. Yu, Anthony Ho, Timothy Wagner, Joseph R. O Brien Department of Orthopaedic Surgery George Washington University O Brien: Consultant for Globus, Relivant, Stryker. Royalties:
Dorsal Cervical Surgeries and Techniques
 Dorsal Cervical Approaches Dorsal Cervical Surgeries and Techniques Gregory R. Trost, MD Professor and Vice Chair of Neurological Surgery University of Wisconsin-Madison Advantages Straightforward Easily
Dorsal Cervical Approaches Dorsal Cervical Surgeries and Techniques Gregory R. Trost, MD Professor and Vice Chair of Neurological Surgery University of Wisconsin-Madison Advantages Straightforward Easily
MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF TYPICAL CERVICAL VERTEBRAE AND THEIR CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS: A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY
 Original Research Article MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF TYPICAL CERVICAL VERTEBRAE AND THEIR CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS: A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY Ephraim Vikram Rao. K * 1, B Sadananda Rao 2, B H Shiny Vinila 3.
Original Research Article MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF TYPICAL CERVICAL VERTEBRAE AND THEIR CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS: A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY Ephraim Vikram Rao. K * 1, B Sadananda Rao 2, B H Shiny Vinila 3.
Chest cavity, vertebral column and back muscles. Respiratory muscles. Sándor Katz M.D., Ph.D.
 Chest cavity, vertebral column and back muscles. Respiratory muscles. Sándor Katz M.D., Ph.D. Chest cavity - bony structures Chest cavity- bony structures Sternum Ribs True ribs: first seven pairs connect
Chest cavity, vertebral column and back muscles. Respiratory muscles. Sándor Katz M.D., Ph.D. Chest cavity - bony structures Chest cavity- bony structures Sternum Ribs True ribs: first seven pairs connect
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Morphometric Study of Atlas Vertebrae in South Indian Population Yogesh M 1, Hemanth Raj M
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Morphometric Study of Atlas Vertebrae in South Indian Population Yogesh M 1, Hemanth Raj M
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW
 INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW CDC REPORT - CAUSES OF DISABILITY, 2005 REVIEW QUESTIONS ABOUT DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL
INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW CDC REPORT - CAUSES OF DISABILITY, 2005 REVIEW QUESTIONS ABOUT DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL
Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh. Razi kittaneh. Maher hadidi
 1 Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh Razi kittaneh Maher hadidi LECTURE 10 THORAX The thorax extends from the root of the neck to the abdomen. The thorax has a Thoracic wall Thoracic cavity and it is divided
1 Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh Razi kittaneh Maher hadidi LECTURE 10 THORAX The thorax extends from the root of the neck to the abdomen. The thorax has a Thoracic wall Thoracic cavity and it is divided
Technique Guide. C1/C2 Access System. Percutaneous transarticular screw fixation.
 Technique Guide C1/C2 Access System. Percutaneous transarticular screw fixation. C1/C2 Access System Table of Contents General introduction 2 Indications/Contraindications 2 Image intensifier-assisted
Technique Guide C1/C2 Access System. Percutaneous transarticular screw fixation. C1/C2 Access System Table of Contents General introduction 2 Indications/Contraindications 2 Image intensifier-assisted
ANATOMIC REPORT. Surgical Anatomic Evaluation of the Cervical Pedicle and Adjacent Neural Structures
 ANATOMIC REPORT Surgical Anatomic Evaluation of the Cervical Pedicle and Adjacent Neural Structures Hasan Çağlar Uğur, M.D., Ayhan Attar, M.D., Aysun Uz, M.D., İbrahim Tekdemir, M.D., Nihat Egemen, M.D.,
ANATOMIC REPORT Surgical Anatomic Evaluation of the Cervical Pedicle and Adjacent Neural Structures Hasan Çağlar Uğur, M.D., Ayhan Attar, M.D., Aysun Uz, M.D., İbrahim Tekdemir, M.D., Nihat Egemen, M.D.,
Study of Lumbar Vertebrae with respect to the dimensions of the pedicle in South Indian population
 Original article Study of Lumbar Vertebrae with respect to the dimensions of the pedicle in South Indian population 1 Dr.Sreevidya.J, 2 Dr.Dharani.V, 3 Dr.Savithri.K, 4 Dr.Sudha Seshayyan 1Senior Assistant
Original article Study of Lumbar Vertebrae with respect to the dimensions of the pedicle in South Indian population 1 Dr.Sreevidya.J, 2 Dr.Dharani.V, 3 Dr.Savithri.K, 4 Dr.Sudha Seshayyan 1Senior Assistant
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax
 Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM
 AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
Why does sideflexion increase ipsilateral vertebral artery occlusion with contralateral atlanto-axial rotation? Thomas Langer
 Why does sideflexion increase ipsilateral vertebral artery occlusion with contralateral atlanto-axial rotation? Thomas Langer 1 Introduction When the head and neck are placed in the premanipulative position
Why does sideflexion increase ipsilateral vertebral artery occlusion with contralateral atlanto-axial rotation? Thomas Langer 1 Introduction When the head and neck are placed in the premanipulative position
Anatomy and Physiology II. Spine
 Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
Structure and Function of the Vertebral Column
 Structure and Function of the Vertebral Column Posture Vertebral Alignment Does it really matter? Yes it does! Postural Curves The vertebral column has a series of counterbalancing curves posterior anterior
Structure and Function of the Vertebral Column Posture Vertebral Alignment Does it really matter? Yes it does! Postural Curves The vertebral column has a series of counterbalancing curves posterior anterior
Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam
 Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam Main Menu Introduction Clinical clearance of C-SpineC Radiographic evaluation Norms for C-spineC Triggers for CT exam: Odontoid Lateral view
Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam Main Menu Introduction Clinical clearance of C-SpineC Radiographic evaluation Norms for C-spineC Triggers for CT exam: Odontoid Lateral view
Outline. Epidemiology Indications for C-spine imaging Modalities Interpretation Types of fractures
 C-Spine Plain Films Outline Epidemiology Indications for C-spine imaging Modalities Interpretation Types of fractures Epidemiology 7000-10000 c-spine injuries treated each year Additional 5000 die at the
C-Spine Plain Films Outline Epidemiology Indications for C-spine imaging Modalities Interpretation Types of fractures Epidemiology 7000-10000 c-spine injuries treated each year Additional 5000 die at the
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Single-Thread Screw Available in 25-45mm lengths (5mm Increments) Dual-Thread Screw Available in 30-45mm lengths (5mm Increments)
 Single-Thread Screw Available in 25-45mm lengths (5mm Increments) Dual-Thread Screw Available in 30-45mm lengths (5mm Increments) 4.5mm diameter screws All screws cannulated 12mm percutaneous incision
Single-Thread Screw Available in 25-45mm lengths (5mm Increments) Dual-Thread Screw Available in 30-45mm lengths (5mm Increments) 4.5mm diameter screws All screws cannulated 12mm percutaneous incision
Morphometric characteristic of thyroid cartilage in Gujarat region: A cadaveric study
 Original Article Morphometric characteristic of thyroid cartilage in Gujarat region: A cadaveric study Shital Patel, Rashmi Bhardwaj, Priyanka Parmar, Vasant H Vaniya Department of Anatomy, Government
Original Article Morphometric characteristic of thyroid cartilage in Gujarat region: A cadaveric study Shital Patel, Rashmi Bhardwaj, Priyanka Parmar, Vasant H Vaniya Department of Anatomy, Government
Posterior Cervical Arthrodesis by Lateral Mass Screws Fixation A Long term Follow-up Study
 Original Article Posterior Cervical Arthrodesis by Lateral Mass Screws Fixation A Long term Follow-up Study Bhaskar G 1, Sharath Kumar Maila 2, Lakshman Rao A 3, Mastan Reddy A 4 1 Professor I/C 2, 3 Assistant
Original Article Posterior Cervical Arthrodesis by Lateral Mass Screws Fixation A Long term Follow-up Study Bhaskar G 1, Sharath Kumar Maila 2, Lakshman Rao A 3, Mastan Reddy A 4 1 Professor I/C 2, 3 Assistant
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences
 Original Research Article Anatomy and Allied sciences International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 SCREENING FOR ANOMALIES IN OCCIPITO-CERVICAL JUNCTION USING CRANIOMETRY IN COMPUTED
Original Research Article Anatomy and Allied sciences International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 SCREENING FOR ANOMALIES IN OCCIPITO-CERVICAL JUNCTION USING CRANIOMETRY IN COMPUTED
Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Anatomy.
 Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Anatomy www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Thoracic Vertebrae Bodies Pedicles Laminae Spinous Processes Transverse Processes Inferior & Superior Facets Distinguishing Feature Costal Fovea
Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Anatomy www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Thoracic Vertebrae Bodies Pedicles Laminae Spinous Processes Transverse Processes Inferior & Superior Facets Distinguishing Feature Costal Fovea
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
It consist of two components: the outer, laminar fibrous container (or annulus), and the inner, semifluid mass (the nucleus pulposus).
 Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Quantitative Anatomic Evaluation of Cervical Lateral Mass Fixation With a Comparison of the Roy-Camille and the Magerl Screw Techniques
 Quantitative Anatomic Evaluation of Cervical Lateral Mass Fixation With a Comparison of the Roy-Camille and the Magerl Screw Techniques SPINE Volume 30, Number 6, pp E140 E147 2005, Lippincott Williams
Quantitative Anatomic Evaluation of Cervical Lateral Mass Fixation With a Comparison of the Roy-Camille and the Magerl Screw Techniques SPINE Volume 30, Number 6, pp E140 E147 2005, Lippincott Williams
The craniocervical junction
 Anver Jameel, MD The craniocervical junction A biomechanical and anatomical unit that extends from the skull base to C2 Includes the clivus, foramen magnum and contiguous occipital bone, the occipital
Anver Jameel, MD The craniocervical junction A biomechanical and anatomical unit that extends from the skull base to C2 Includes the clivus, foramen magnum and contiguous occipital bone, the occipital
THE STUDY OF CERVICAL VERTEBRAE SHOWING VARIATIONAL PRESENTATION OF FORAMEN TRANSVERSARIUM
 Original Article THE STUDY OF CERVICAL VERTEBRAE SHOWING VARIATIONAL PRESENTATION OF FORAMEN TRANSVERSARIUM M.Y Dofe * 1, A.P Kasote 2, M.M Meshram 3. *1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Professor
Original Article THE STUDY OF CERVICAL VERTEBRAE SHOWING VARIATIONAL PRESENTATION OF FORAMEN TRANSVERSARIUM M.Y Dofe * 1, A.P Kasote 2, M.M Meshram 3. *1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor, 3 Professor
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion. Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD. Date Created: March 27 th, Last Updated:
 Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD Date Created: March 27 th, 2011 Last Updated: Summary: Students will perform a single level lumbar spine fusion to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD Date Created: March 27 th, 2011 Last Updated: Summary: Students will perform a single level lumbar spine fusion to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
Skeletal System. Axial Division
 Skeletal System Axial Division The Axial Skeleton You will see that each bone has special features (overviewed in section I below) that provide Sites of Attachment (for muscles, ligaments, tendons, etc.)
Skeletal System Axial Division The Axial Skeleton You will see that each bone has special features (overviewed in section I below) that provide Sites of Attachment (for muscles, ligaments, tendons, etc.)
Dorsal Fixation of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Techniques
 Pedicle, Facet, Cortical, and Translaminar Screw Techniques Gregory R. Trost, MD Professor and Vice Chair of Neurological Surgery University of Wisconsin-Madison Dorsal Fixation of the Thoracic and Lumbar
Pedicle, Facet, Cortical, and Translaminar Screw Techniques Gregory R. Trost, MD Professor and Vice Chair of Neurological Surgery University of Wisconsin-Madison Dorsal Fixation of the Thoracic and Lumbar
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants
 1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
Morphometric study of axis vertebra in subjects of Indian origin Kaur J 1, Kaur K 2, Singh P 3, Kumar A 4
 Morphometric study of axis vertebra in subjects of Indian origin Kaur J 1, Kaur K 2, Singh P 3, Kumar A 4 1 Dr Jasveen Kaur Assistant Professor jsvn.kr@gmail.com 2 Dr Kamaljeet Kaur Assistant Professor
Morphometric study of axis vertebra in subjects of Indian origin Kaur J 1, Kaur K 2, Singh P 3, Kumar A 4 1 Dr Jasveen Kaur Assistant Professor jsvn.kr@gmail.com 2 Dr Kamaljeet Kaur Assistant Professor
The Relationship amongst Intervertebral Disc Vertical Diameter, Lateral Foramen Diameter and Nerve Root Impingement in Lumbar Vertebra
 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1803.004 The Relationship amongst Intervertebral Disc Vertical Diameter, Lateral Foramen Diameter and Nerve Root Impingement in Lumbar Vertebra Yusof MI, MMed Orth, Hassan
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1803.004 The Relationship amongst Intervertebral Disc Vertical Diameter, Lateral Foramen Diameter and Nerve Root Impingement in Lumbar Vertebra Yusof MI, MMed Orth, Hassan
Craniovertebral Junction Embryology and Anatomy. Presented by: Amandeep Moderators: S.S.Kale G.D.Satyarthi. CVJ-Embryology & Anatomy
 Craniovertebral Junction Embryology and Anatomy Presented by: Amandeep Moderators: S.S.Kale G.D.Satyarthi CVJ-Embryology & Anatomy CVJ-Embryology SOMITE-The building block of vertebrae, skeletal muscle
Craniovertebral Junction Embryology and Anatomy Presented by: Amandeep Moderators: S.S.Kale G.D.Satyarthi CVJ-Embryology & Anatomy CVJ-Embryology SOMITE-The building block of vertebrae, skeletal muscle
Posterior surgical procedures are those procedures
 9 Cervical Posterior surgical procedures are those procedures that have been in use for a long time with established efficacy in the treatment of radiculopathy and myelopathy caused by pathologies including
9 Cervical Posterior surgical procedures are those procedures that have been in use for a long time with established efficacy in the treatment of radiculopathy and myelopathy caused by pathologies including
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Spinal Dynamics I: The Axio-atlanto-occipital Assemblage
 Spinal Dynamics I: The Axio-atlanto-occipital Assemblage Bones interact through joints. The relative placements of bones across joints determine how they move in space. In this section we will consider
Spinal Dynamics I: The Axio-atlanto-occipital Assemblage Bones interact through joints. The relative placements of bones across joints determine how they move in space. In this section we will consider
Transitioning to the Suboccipital Triangle. Suboccipital Triangle
 Transitioning to the Suboccipital Triangle Syllabus p. 14-15 Suboccipital Triangle Borders -Rectus capitis posterior major -Obliquus capitis superior -Obliquus capitis inferior Contents -Vertebral artery
Transitioning to the Suboccipital Triangle Syllabus p. 14-15 Suboccipital Triangle Borders -Rectus capitis posterior major -Obliquus capitis superior -Obliquus capitis inferior Contents -Vertebral artery
Morphometric Characteristics of C1-C2 Vertebrae to Perform Anterior Transarticular Crossing Screw Fixation
 DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.18971-16.1 Received: 01.09.2016 / Accepted: 21.11.2016 Published Online: 12.12.2016 Original Investigation Morphometric Characteristics of C1-C2 Vertebrae to Perform Anterior
DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.18971-16.1 Received: 01.09.2016 / Accepted: 21.11.2016 Published Online: 12.12.2016 Original Investigation Morphometric Characteristics of C1-C2 Vertebrae to Perform Anterior
Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine. Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University
 Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University Objective Anatomy Mechanism and type of injury PE.and radiographic evaluation
Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University Objective Anatomy Mechanism and type of injury PE.and radiographic evaluation
The Anatomy of the Atlantoaxial Complex
 The Anatomy of the Atlantoaxial Complex T. GLENN PAIT, M.D., KENAN 1. ARNAUTOVIC, M.D., and LUIS A.B. BORBA, M.D. Operating on the atlantoaxial complex has always posed a challenge to the surgeon because
The Anatomy of the Atlantoaxial Complex T. GLENN PAIT, M.D., KENAN 1. ARNAUTOVIC, M.D., and LUIS A.B. BORBA, M.D. Operating on the atlantoaxial complex has always posed a challenge to the surgeon because
The indications of upper cervical fusion include. Posterior fixation and fusion with atlas pedicle screw system for upper cervical diseases
 Chinese Journal of Traumatology 2008; 11(6):323-328.. Original articles Posterior fixation and fusion with atlas pedicle screw system for upper cervical diseases LI Lei *, ZHOU Feng-hua, WANG Huan, and
Chinese Journal of Traumatology 2008; 11(6):323-328.. Original articles Posterior fixation and fusion with atlas pedicle screw system for upper cervical diseases LI Lei *, ZHOU Feng-hua, WANG Huan, and
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS
 LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS Always occurs in the mobile segment. Factors play role in Stenosis Pre existing congenital or developmental narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal Translation of one anatomic segment
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS Always occurs in the mobile segment. Factors play role in Stenosis Pre existing congenital or developmental narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal Translation of one anatomic segment
Pedicle screw placement accuracy in thoracic and lumbar spinal surgery with a patient-matched targeting guide: A cadaveric study
 Pedicle screw placement accuracy in thoracic and lumbar spinal surgery with a patient-matched targeting guide: A cadaveric study [ based on the homonymous paper from Prof.Lamartina et al. Anticipated publication
Pedicle screw placement accuracy in thoracic and lumbar spinal surgery with a patient-matched targeting guide: A cadaveric study [ based on the homonymous paper from Prof.Lamartina et al. Anticipated publication
Inter- and intraobserver reliability assessment of computed tomographic 3D measurement of pedicles in scoliosis and size matching with pedicle screws
 Eur Spine J (2011) 20:1771 1779 DOI 10.1007/s00586-011-1908-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Inter- and intraobserver reliability assessment of computed tomographic 3D measurement of pedicles in scoliosis and size matching
Eur Spine J (2011) 20:1771 1779 DOI 10.1007/s00586-011-1908-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Inter- and intraobserver reliability assessment of computed tomographic 3D measurement of pedicles in scoliosis and size matching
Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar
 BIOMECHANICS OF SPINE Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar What is biomechanics? Biomechanics is the study of the consequences of application of external force on the spine Primary
BIOMECHANICS OF SPINE Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar What is biomechanics? Biomechanics is the study of the consequences of application of external force on the spine Primary
Mechanism of change in the orientation of the articular process of the zygapophyseal joint at the thoracolumbar junction
 J. Anat. (1999) 195, pp. 199 209, with 9 figures Printed in the United Kingdom 199 Mechanism of change in the orientation of the articular process of the zygapophyseal joint at the thoracolumbar junction
J. Anat. (1999) 195, pp. 199 209, with 9 figures Printed in the United Kingdom 199 Mechanism of change in the orientation of the articular process of the zygapophyseal joint at the thoracolumbar junction
Surgical Anatomy of the Uncinate Process and Transverse Foramen Determined by Computed Tomography
 THIEME GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL Original Article 383 Surgical Anatomy of the Uncinate Process and Transverse Foramen Determined by Computed Tomography Moon Soo Park 1 Seong-Hwan Moon 2 Tae-Hwan Kim 1 Jae Keun
THIEME GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL Original Article 383 Surgical Anatomy of the Uncinate Process and Transverse Foramen Determined by Computed Tomography Moon Soo Park 1 Seong-Hwan Moon 2 Tae-Hwan Kim 1 Jae Keun
Inferior view of the skull showing foramina (Atlas of Human Anatomy, 5th edition, Plate 12)
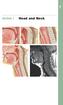 Section 1 Head and Neck Skull, Basal View Incisive foramen Choanae Foramen ovale Foramen lacerum Foramen spinosum Carotid canal Jugular fossa Mastoid process Inferior view of the skull showing foramina
Section 1 Head and Neck Skull, Basal View Incisive foramen Choanae Foramen ovale Foramen lacerum Foramen spinosum Carotid canal Jugular fossa Mastoid process Inferior view of the skull showing foramina
Definition of Anatomy. Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts.
 Definition of Anatomy Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts. Basic Anatomical Terms Anatomical terms for describing positions: Anatomical position: Supine position:
Definition of Anatomy Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts. Basic Anatomical Terms Anatomical terms for describing positions: Anatomical position: Supine position:
An anatomic consideration of C2 vertebrae artery groove variation for individual screw implantation in axis
 Eur Spine J (2013) 22:1547 1552 DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-2779-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE An anatomic consideration of C2 vertebrae artery groove variation for individual screw implantation in axis Janhua Wang Hong
Eur Spine J (2013) 22:1547 1552 DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-2779-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE An anatomic consideration of C2 vertebrae artery groove variation for individual screw implantation in axis Janhua Wang Hong
Occipital-Cervical-Thoracic Fixation Techniques
 Occipital-Cervical-Thoracic Fixation Techniques Neill M. Wright, M.D. Herbert Lourie Professor of Neurological Surgery Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Washington University School of Medicine Disclosures
Occipital-Cervical-Thoracic Fixation Techniques Neill M. Wright, M.D. Herbert Lourie Professor of Neurological Surgery Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Washington University School of Medicine Disclosures
Flexion Distraction Injuries in the Thoracolumbar Spine: An In Vitro Study of the Relation Between Flexion Angle and the Motion Axis of Fracture
 Journal of Spinal Disorders & Techniques Vol. 15, No. 2, pp. 139 143 2002 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Flexion Distraction Injuries in the Thoracolumbar Spine: An In Vitro Study of
Journal of Spinal Disorders & Techniques Vol. 15, No. 2, pp. 139 143 2002 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Flexion Distraction Injuries in the Thoracolumbar Spine: An In Vitro Study of
Cervical Spine: Pearls and Pitfalls
 Cervical Spine: Pearls and Pitfalls Presenters Dr. Rob Donkin Functional Anatomy Current research Cervical Radiculopathy Dr. Gert Ferreira Red flags Case Study Kinesio Taping Chris Neethling Gonstead adjusting
Cervical Spine: Pearls and Pitfalls Presenters Dr. Rob Donkin Functional Anatomy Current research Cervical Radiculopathy Dr. Gert Ferreira Red flags Case Study Kinesio Taping Chris Neethling Gonstead adjusting
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences
 Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Morphometric Analysis of Internal Acoustic Meatus and Its Surgically Relevant Relations in Human Temporal Bones. Rajanigandha Vadagaonkar
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences Morphometric Analysis of Internal Acoustic Meatus and Its Surgically Relevant Relations in Human Temporal Bones. Rajanigandha Vadagaonkar
The Back. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article A Study on the Foramen Transversarium in Cervical Vertebrae Kalpana Ramachandran 1, Parvathavarthine
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article A Study on the Foramen Transversarium in Cervical Vertebrae Kalpana Ramachandran 1, Parvathavarthine
Anatomy Lecture #19 AN INTRODUCTION TO THE THORAX April 3, 2012
 Page 1 بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم The Thoracic Wall Firstly, when we talk about thorax, we should begin with the thorax wall which means not only bones that construct the thorax but also the muscles which
Page 1 بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم The Thoracic Wall Firstly, when we talk about thorax, we should begin with the thorax wall which means not only bones that construct the thorax but also the muscles which
Exercise 10. The Axial Skeleton
 Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs
 locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
Anatomy of the Thorax
 Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
TSLP Thoracolumbar Spine Locking Plate
 Anterior thoracolumbar spine locking plate TSLP Thoracolumbar Spine Locking Plate Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use
Anterior thoracolumbar spine locking plate TSLP Thoracolumbar Spine Locking Plate Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use
Morphometric study of acromion process in scapula of north Indian population
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Singroha R et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2017 Nov;5(11):4965-4969 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20174953
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Singroha R et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2017 Nov;5(11):4965-4969 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20174953
Analysis of anatomic morphometry of the pedicles and the safe zone for through-pedicle procedures in the thoracic and lumbar spine
 Eur Spine J (27) 16:121 1222 DOI.7/s86-6-24-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Analysis of anatomic morphometry of the pedicles and the safe zone for through-pedicle procedures in the thoracic and lumbar spine Shiu-Bii
Eur Spine J (27) 16:121 1222 DOI.7/s86-6-24-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Analysis of anatomic morphometry of the pedicles and the safe zone for through-pedicle procedures in the thoracic and lumbar spine Shiu-Bii
The vault bones Frontal Parietals Occiput Temporals Sphenoid Ethmoid
 The Vertebral Column Head, Neck and Spine Bones of the head Some consider the bones of the head in terms of the vault bones and the facial bones hanging off the front of them The vault bones Frontal Parietals
The Vertebral Column Head, Neck and Spine Bones of the head Some consider the bones of the head in terms of the vault bones and the facial bones hanging off the front of them The vault bones Frontal Parietals
Original article Morphometric analysis of the cervical spine of Indian population by using computerized tomography
 J M e d A l l i e d S c i 2 0 1 2 ; 2 ( 2 ) : 66-76 w w w. j m a s. i n P r i n t I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 6 9 6 O n l i n e I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 7 0 X Journal of Medical & Allied Sciences Original article Morphometric
J M e d A l l i e d S c i 2 0 1 2 ; 2 ( 2 ) : 66-76 w w w. j m a s. i n P r i n t I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 6 9 6 O n l i n e I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 7 0 X Journal of Medical & Allied Sciences Original article Morphometric
Anatomy and Physiology II. Review Spine and Neck
 Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
