Lesson Seven Paleoecology: Determining the Diet of Ancient Animals
|
|
|
- Brent Tate
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lesson Seven Paleoecology: Determining the Diet of Ancient Animals Summary Paleoecology, or the study of ancient ecosystems and how plants and animals interacted, includes many disciplines. One component of paleoecology that is easily understood by students is diet. Organisms must regularly acquire energy from their environment to support growth and development, which is in turn key to survival and reproduction. For animals, this energy comes in the form of food sources from their environment. Most vertebrates mechanically break down food in their mouth, then break it down further using enzymes and acids in their gut (stomach and small intestines), absorb the nutrients into the bloodstream, and finally transport them to the cells, where they are converted into energy that can be used. Over generations, the evolutionary process of natural selection has shaped this process, such that vertebrates efficiently acquire and process their food. Teeth are directly involved in the mechanical break down of food and thus, fossil teeth provide paleontologists a window into the diet of extinct vertebrates. The diets of vertebrates in a fossil assemblage can then be used to reconstruct the food web (what eats what) of an ecosystem, showing the ecological relationships between once-living beings. Teeth are composed of a wear-resistant and chemical-resistant mineral called apatite (calcium fluorophosphate) with an inner pulp cavity surrounded by a softer dentine and a harder outermost layer, enamel. Teeth are affixed to the jaws of vertebrates in different ways from sitting in deep sockets in mammals to be fused to the bone. Because enamel is the hardest mineral in the body, teeth tend to fossilize more readily than other body parts. They commonly survive scavenging and stream transport that can destroy other skeletal elements. And because animals tend to have many teeth, they have a higher chance of being preserved compared to some other parts. In addition, because we have modern teeth to study, we can compare the teeth of extinct fossil species with the teeth of living species and often identify the species, infer the types of foods that the extinct species ate, as well as determine the animal s size. Paleontologists may also be able to approximate the ancient food web in which the animal lived even going so far as to reconstruct
2 an ancient ecosystem from evidence provided by little more than fossil teeth preserved in a geologic deposit. In this lesson, students will work with teeth from animals from the Hell Creek Formation. They will use them to better understand how paleontologists use fossils to help bring an extinct animal to life. (This lesson adapted from ones developed by David Davies at Centenary College of Louisiana ( and James Westgate at Lamar University ( Objectives Students will be able to: 1. Explain the relationship between the shape of a tooth and the animal's diet (carnivore, herbivore, etc.). 2. Show how tooth shapes are correlated with specific ways of obtaining and processing food items. 3. Recognize the dietary habits of living animal species through the examination of their teeth. 4. Hypothesize what the diets of extinct animals were through the examination of their fossil teeth. 5. Discuss how understanding an animal s diet can illustrate how it fits into an ecosystem. 6. Explain the difference between the teeth of mammals and other groups such as reptiles and amphibians. Estimated teaching time One class session. Groups Students will work in groups. Materials At least one replica of teeth/jaw of each of the following animals: meat eater, insectivore, fish eater, plant eater (grinder), plant eater (scissoring) Photograph of tools equivalent to types of diet (five photographs in total) DVD with images of teeth, to be used during assessment Teacher background See handout on teeth. Student background None specifically required. Set up Have projector ready for PowerPoint presentation. This activity can be done in the classroom.
3 Introducing the activity 1. Explain to the class that today they will be focusing on one way that paleontologists reconstruct the life (i.e. ecology) of an extinct animal,. Ask students if they know what a food web is? Ask students how they would reconstruct a food web, or the trophic interactions between animals? How would they reconstruct a food web that includes dinosaurs and/or animals that lived at the same time and in the same ecosystem as dinosaurs? What evidence would they look for? 2. Now tell them that they will be focusing on teeth and what can be learned from studying teeth. First, find out what the students know. What do you eat? Describe the four different types of teeth that mammals (including humans) have: incisor, canine, premolar, and molar. What is the function of each tooth? How many teeth of each type do they have? What about adults (or children)? Which teeth do you use for which type of food, such as meat and plants? (Humans use all of their teeth no matter what they are eating but the point here is to get students to think about how they use some teeth primarily for cutting and some primarily for grinding. Mammals are unusual in that we have different types of teeth in our mouths, whereas other groups have just one type depending on whether they are a carnivore or herbivore.) Do all animals have the same type and number of teeth? What are some differences/similarities? Do all animals chew their food? 3. Using this information you are now going to work with a variety of teeth to try to understand the diet of the animals that lived at the end of the Cretaceous. All of the animals ate at least one of five types of food: meat; fish; insects; woody vegetation; or soft vegetation. Ask the students what they think are advantages and disadvantages of the four food types?! Meat is easily digested and very nutritious; prey must be caught (which may be difficult) and cut into chunks to be swallowed.! Fishes are also easily digested and very nutritious; however, slippery fishes live in water and are hard to grasp and swallow, typically whole.! Insects are nutritious, have high protein, some are squishy, others are crunchy; they are hard to find enough of at one spot for eating if you are large animal so insectivores tend to be small.! Woody plants are plentiful, but they have tough leaves and stems, which are difficult to chew; the high cellulose content also makes them the most difficult food to digest in the gut. They must be cut and crushed into very small pieces to be swallowed so that they can be digested.! Small herbs and fruit are easier to digest than woody plants or plant parts; however, they are harder to obtain in large quantities. Also explain how plants, which some students at first might think of as being very soft, can be
4 very abrasive. For example, when you run a blade of grass through your hand you can get a painful cut. This cut is from the glass-like minerals (phytoliths) incorporated into blades of grass and other leaves. Horses, which eat grasses for a living, have very tall teeth that are not completely worn down or eroded by the phytoliths in their diet of grasses. 4. Now show the PowerPoint (or laminated pictures) of five food and tools to see if the students can figure which type of tool works best for processing different types of food. Start by showing each food item and address the differences as described above. Examples of tools are listed below. A central point to make is to get students to think about the idea that a tooth is really a tool that breaks down food items. FOOD FOOD PROCESSOR MODEL Meat Fish Insects Woody Vegetation Softer Vegetation Piercing, slashing, and cutting teeth with tall blades Pointed, piercing teeth curved toward the back of the mouth to grasp and hold slippery prey Individual teeth have multiple levels for punching through exoskeleton or cutting through grubs then for chomping Battery of teeth with broad grinding surface and low cutting ridges Battery of teeth with low rounded bumps (cusps) and opposing basins for crushing and grinding soft material Serrated knife Fish Gig Scissors Washboard Mortar and Pestle 5. Teeth can also provide some insights into the size of the animal. Using the different teeth provided in the box, ask the students to think about how big an animal is, based simply on its teeth. You may want them to get to think about animals that they are familiar with and how big their teeth are. However, note that this can be tricky depending on how many teeth are in the mouth. Facilitating the activity 1. Divide the students into five groups and have them analyze the teeth provided in the box. Have them draw and write a description of each tooth (how are they shaped, what size are they, what fine structures, such as points, ridges, serrations, and bumps, are on the teeth). Have the students decide, based on their description and what the tooth looks like, whether the tooth's owner was big or small, what the animal ate (from the five choices), and whether it was more likely to chew its food or swallow it immediately. 2. Allow the students to work for five minutes or so on each tooth then pass the tooth to the next group. After each period is up have the students pass their tooth to the next group, until all groups have seen all teeth.
5 Assessment Show them Powerpoint of images of teeth and ask students to state what type of diet the animals have. Going further Have the students choose a contemporary animal and write a short description of what teeth it is likely to have, based on its diet, and why. The students might also look at other structures or adaptations that make this animal particularly good at obtaining its meals (for example, claws to apprehend vertebrate prey). They may also want to reflect or examine animals with unusual diets or teeth (or lack thereof), such as anteaters, polar bears, baleen whales, and vampire bats, as a way to think about natural selection and evolution. References NA Teaching standards Science Content Standard 1 - Students, through the inquiry process, demonstrate the ability to design, conduct, evaluate, and communicate results and reasonable conclusions of scientific investigations. Benchmark End of Grade 4, Number 1 - Develop the abilities necessary to safely conduct scientific inquiry, including (a step-by- step sequence is not implied): (a) asking questions about objects, events, and organisms in the environment, (b) planning and conducting simple investigations Glossary Browser An animal that feeds on leaves, buds, and green stems. These types of food are easier to digest, so that the digestive system does not need to be quite so big. Canine Pointed teeth towards the front of the mouth (think Dracula fangs); usually used for piercing food or firmly holding food in order to tear it apart, and occasionally used as weapons or display Carnivore An animal whose diet consists of animals (meat, fish, insects, other invertebrates) Grazer An animal that feeds primarily on grasses. Herbivore An animal whose diet consists of plant parts (leaves, bark, roots, fruits, seeds) Incisor Simple teeth in the very front of the mouth of mammals, primarily used for nipping or cutting Molar More complex teeth in rear of the mouth of mammals, used primarily for crushing and grinding (chewing) Premolar Somewhat complex teeth located between canines and molars in mammals; they help in the puncturing function of the canines and the crushing function of molars
Fossil Kit Laboratory Investigation 5: Fossil Teeth. Desired Results
 Fossil Kit Laboratory Investigation 5: Fossil Teeth Investigation Summary: Students examine and compare fossil and modern teeth. Students use properties of tooth shape and size to identify and interpret
Fossil Kit Laboratory Investigation 5: Fossil Teeth Investigation Summary: Students examine and compare fossil and modern teeth. Students use properties of tooth shape and size to identify and interpret
Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating
 Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating Types of teeth Preventing tooth decay Dentition of other animals Digestive system By the end of this unit you should: Know the structure, function and care of the human teeth.
Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating Types of teeth Preventing tooth decay Dentition of other animals Digestive system By the end of this unit you should: Know the structure, function and care of the human teeth.
Structure of an Incisor
 MAMMALIAN TEETH Mammals have different types and shapes of teeth and they are thus termed Heterodonts. Those which have teeth of the same size and shapes are termed as Homodonts. In mammals teeth consist
MAMMALIAN TEETH Mammals have different types and shapes of teeth and they are thus termed Heterodonts. Those which have teeth of the same size and shapes are termed as Homodonts. In mammals teeth consist
EUTHERIAN MAMMALS. Eutherian Mammals are classified into orders on the basis of dentition. It does not involve phylogeny.
 EUTHERIAN MAMMALS Eutherian Mammals are classified into orders on the basis of dentition. It does not involve phylogeny. Dinosaurs..? TROPHIC TYPES FOUND AMONG EUTHERIAN MAMMALS Predators Flesh eaters
EUTHERIAN MAMMALS Eutherian Mammals are classified into orders on the basis of dentition. It does not involve phylogeny. Dinosaurs..? TROPHIC TYPES FOUND AMONG EUTHERIAN MAMMALS Predators Flesh eaters
ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013
 ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Look at nutrition in various animals o Herbivores, Carnivores and Omnivores Study the structure of the human digestive system Look
ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Look at nutrition in various animals o Herbivores, Carnivores and Omnivores Study the structure of the human digestive system Look
Adaptation to diet. Different animals have different sets of teeth depending on the type of food that they eat:
 Adaptation to diet Different animals have different sets of teeth depending on the type of food that they eat: 1. Herbivore plants (teeth for grazing and grinding) 2. Carnivore animals/meat (teeth for
Adaptation to diet Different animals have different sets of teeth depending on the type of food that they eat: 1. Herbivore plants (teeth for grazing and grinding) 2. Carnivore animals/meat (teeth for
Digestion. Final Products of Digestion Carbohydrates Disaccharides (sucrose, maltose) Proteins Short polypeptides Individual amino acids
 Digestion Process has three stages: 1. Physical Digestion: mechanical process of breaking down the food. Knives and forks, teeth grinding and tearing 2. Chemical Digestion: enzymes and stomach acid breaks
Digestion Process has three stages: 1. Physical Digestion: mechanical process of breaking down the food. Knives and forks, teeth grinding and tearing 2. Chemical Digestion: enzymes and stomach acid breaks
Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
Adaptation of Gestation or Egg- laying in Species Depends on the Amount of Internal Heat Generated in Digesting the Food
 Adaptation of Gestation or Egg- laying in Species Depends on the Amount of Internal Heat Generated in Digesting the Food Karunakar Marasakatla *Correspondence to: kmarasakatla@gmail.com Abstract: Anatomically
Adaptation of Gestation or Egg- laying in Species Depends on the Amount of Internal Heat Generated in Digesting the Food Karunakar Marasakatla *Correspondence to: kmarasakatla@gmail.com Abstract: Anatomically
The Digestive System. Bringing it In and Taking it Out
 The Digestive System Bringing it In and Taking it Out Digestive System (on sheet, not notes ) Organ System Function Organs/Parts Digestive system To extract energy and nutrients from food To eliminate
The Digestive System Bringing it In and Taking it Out Digestive System (on sheet, not notes ) Organ System Function Organs/Parts Digestive system To extract energy and nutrients from food To eliminate
4th Grade. Slide 1 / 22. Slide 2 / 22. Slide 3 / 22. Bite into Structure and Function Activity. Animal Teeth
 Slide 1 / 22 Slide 2 / 22 4th Grade Bite into Structure and Function Activity 2015-08-27 www.njctl.org Animal Teeth Slide 3 / 22 Animal teeth are a good example of how structure fits function. Below is
Slide 1 / 22 Slide 2 / 22 4th Grade Bite into Structure and Function Activity 2015-08-27 www.njctl.org Animal Teeth Slide 3 / 22 Animal teeth are a good example of how structure fits function. Below is
Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
Medical NBDE-II. Dental Board Exams Part I.
 Medical NBDE-II Dental Board Exams Part I http://killexams.com/exam-detail/nbde-ii Question: 149 Anatomically, the term "clinical root" can be defined as which of the following: A. The space in the tooth
Medical NBDE-II Dental Board Exams Part I http://killexams.com/exam-detail/nbde-ii Question: 149 Anatomically, the term "clinical root" can be defined as which of the following: A. The space in the tooth
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
Introduction Evolution of Metabolism
 2 Introduction Evolution of Metabolism Activity for Our Cells, Our Selves Movie Goals Discover Darwin all over Pittsburgh in 2009 with Darwin 2009: Exploration is Never Extinct. Lesson plans, including
2 Introduction Evolution of Metabolism Activity for Our Cells, Our Selves Movie Goals Discover Darwin all over Pittsburgh in 2009 with Darwin 2009: Exploration is Never Extinct. Lesson plans, including
Characteristics of living organism
 At a glance : Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Living organisms are bundles of cells that carry out specialized functions. 1. Life is uncertain because Organic Matter is born, it Organic / Biotic Matter
At a glance : Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Living organisms are bundles of cells that carry out specialized functions. 1. Life is uncertain because Organic Matter is born, it Organic / Biotic Matter
2018 Teeth. DENTITION refers to the makeup of a set of teeth, including their type, number, and arrangement.
 2018 Teeth DENTITION refers to the makeup of a set of teeth, including their type, number, and arrangement. A dog's mouth is constructed for the diet of a carnivore, being able to stab, catch, and hold
2018 Teeth DENTITION refers to the makeup of a set of teeth, including their type, number, and arrangement. A dog's mouth is constructed for the diet of a carnivore, being able to stab, catch, and hold
2 days: 15- to 20-minute lessons. Day 1: Day 2
 2 days: 15- to 20-minute lessons Day 1: Teaching Guides Brushing, Flossing and Rinsing Children learn easy, everyday ways to prevent tooth decay Time to complete: 5 minutes Group size: Entire class Fluoride,
2 days: 15- to 20-minute lessons Day 1: Teaching Guides Brushing, Flossing and Rinsing Children learn easy, everyday ways to prevent tooth decay Time to complete: 5 minutes Group size: Entire class Fluoride,
4/8/16. Digestive System. When you are hungry it is because your brain receives a signal from your cells that they need energy
 When you are hungry it is because your brain receives a signal from your cells that they need energy Section 1 Digestive System A group of organs that work together to digest food so that it can be used
When you are hungry it is because your brain receives a signal from your cells that they need energy Section 1 Digestive System A group of organs that work together to digest food so that it can be used
The Anatomy of Eating by Cathy Marley.
 The Anatomy of Eating by Cathy Marley. As a faithful companion to humans for some 10,000 years, the trend to humanize our companion dogs comes as no surprise. Yet despite his long and close association
The Anatomy of Eating by Cathy Marley. As a faithful companion to humans for some 10,000 years, the trend to humanize our companion dogs comes as no surprise. Yet despite his long and close association
This is the knowledge that you should understand upon completing this section:
 MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS 5 SYLLABUS CHECKLIST This is the knowledge that you should understand upon completing this section: 5.1 CELLS, TISSUES, ORGANS AND SYSTEMS Multicellular organisms have a hierarchical
MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS 5 SYLLABUS CHECKLIST This is the knowledge that you should understand upon completing this section: 5.1 CELLS, TISSUES, ORGANS AND SYSTEMS Multicellular organisms have a hierarchical
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
1. Anterior-posterior movement of the mandible (APM):
 Dental Anatomy A. Terminology: Over the past few years there have been several acronyms introduced into the equine dentistry industry. These terms should help you describe and understand equine dental
Dental Anatomy A. Terminology: Over the past few years there have been several acronyms introduced into the equine dentistry industry. These terms should help you describe and understand equine dental
ANIMAL BITES. Lesson Plan. Skullduggery, Inc. 624 South B Street Tustin, CA (800) FAX (714)
 ANIMAL BITES Lesson Plan Skullduggery, Inc. 624 South B Street Tustin, CA 92680 (800) 336-7745 FAX (714) 832-1215 OBJECTIVE The Kit utilizes teeth and mandible fragment replicas to give students a unique
ANIMAL BITES Lesson Plan Skullduggery, Inc. 624 South B Street Tustin, CA 92680 (800) 336-7745 FAX (714) 832-1215 OBJECTIVE The Kit utilizes teeth and mandible fragment replicas to give students a unique
Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education Tata Institute of Fundamental Research V.N. Purav Marg, Mankhurd, Mumbai
 Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education Tata Institute of Fundamental Research V.N. Purav Marg, Mankhurd, Mumbai 400088 Sindhu Mathai PhD project on Visual and verbal literacies in the context of human
Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education Tata Institute of Fundamental Research V.N. Purav Marg, Mankhurd, Mumbai 400088 Sindhu Mathai PhD project on Visual and verbal literacies in the context of human
Dental disease in dogs
 Dental disease in dogs Dogs have 42 teeth in total - 12 incisors, 4 canines, 16 premolars and 10 molars Deciduous Teeth - also called milk teeth, usually erupt between 3-4 weeks of age. Teething begins
Dental disease in dogs Dogs have 42 teeth in total - 12 incisors, 4 canines, 16 premolars and 10 molars Deciduous Teeth - also called milk teeth, usually erupt between 3-4 weeks of age. Teething begins
Animal Nutrition. Chapter 41. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Our Teeth. History Of Equine Dentistry EQUINE DENTISTRY. Who Should Do Equine Dentistry? Some Facts To Know About Teeth
 EQUINE DENTISTRY Mike Black, DVM Nebraska Equine Veterinary Clinic Omaha NE History Of Equine Dentistry Some evidence of equine dentistry dates back to 2,000 B.C. Bit-Seats: Information on bit-seats dates
EQUINE DENTISTRY Mike Black, DVM Nebraska Equine Veterinary Clinic Omaha NE History Of Equine Dentistry Some evidence of equine dentistry dates back to 2,000 B.C. Bit-Seats: Information on bit-seats dates
Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41. Nutritional Requirements pp Essential Amino Acids p.939. Essential Fatty Acids p.
 Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41 Nutritional Requirements pp.939-941 Diets for animals must satisfy three needs : 1. Metabolic fuel Energy needed to do cellular work. E.g. glucose 2. Materials for
Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41 Nutritional Requirements pp.939-941 Diets for animals must satisfy three needs : 1. Metabolic fuel Energy needed to do cellular work. E.g. glucose 2. Materials for
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
Equine Dentistry Educating horse owners about the importance of proper equine dental care
 Equine Dentistry Educating horse owners about the importance of proper equine dental care From Ancient to Modern Horse Complex Oral Anatomy Equine Chewing Cycle Important Age- Related Facts The Basics
Equine Dentistry Educating horse owners about the importance of proper equine dental care From Ancient to Modern Horse Complex Oral Anatomy Equine Chewing Cycle Important Age- Related Facts The Basics
One Stop Shop For Educator
 One Stop Shop For Educator The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved
One Stop Shop For Educator The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved
Contents. Section 1: The Circulatory System. Section 2: The Digestive System. Section 3: The Excretory System. Section 4: The Endocrine System
 Contents Section 1: The Circulatory System 1. The Heart... 2 2. The Blood Vessels.... 6 3. The Blood.... 10 4. Quiz 1.... 14 Section 2: The Digestive System 5. The Mouth and Esophagus.... 15 6. The Stomach....
Contents Section 1: The Circulatory System 1. The Heart... 2 2. The Blood Vessels.... 6 3. The Blood.... 10 4. Quiz 1.... 14 Section 2: The Digestive System 5. The Mouth and Esophagus.... 15 6. The Stomach....
Bio 1M: The evolution of apes (complete) 1 Example. 2 Patterns of evolution. Similarities and differences. History
 Bio 1M: The evolution of apes (complete) 1 Example Humans are an example of a biological species that has evolved Possibly of interest, since many of your friends are probably humans Humans seem unique:
Bio 1M: The evolution of apes (complete) 1 Example Humans are an example of a biological species that has evolved Possibly of interest, since many of your friends are probably humans Humans seem unique:
7.4 Digestion. Highlight the definition of mechanical digestion.
 7.4 Digestion Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The large food molecules are starch,
7.4 Digestion Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The large food molecules are starch,
Heterodont animals *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m66060 1 Heterodont animals * Marcos Gridi-Papp This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 Abstract Mammals evolved a heterodont
OpenStax-CNX module: m66060 1 Heterodont animals * Marcos Gridi-Papp This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 Abstract Mammals evolved a heterodont
THE 'FIBREVORES' GUIDE FROM BURGESS PET CARE
 THE 'FIBREVORES' GUIDE FROM BURGESS PET CARE Essential facts for rabbits, guinea pigs & chinchillas. WHAT IS A 'FIBREVORE'? You'll be familiar with the words carnivore (a meat eater), omnivore (an eater
THE 'FIBREVORES' GUIDE FROM BURGESS PET CARE Essential facts for rabbits, guinea pigs & chinchillas. WHAT IS A 'FIBREVORE'? You'll be familiar with the words carnivore (a meat eater), omnivore (an eater
Animal Appetites. The following narrative was written by Alex, a 5th grader who raises livestock for 4-H.
 Animal Appetites The following narrative was written by Alex, a 5th grader who raises livestock for 4-H. This morning I woke up early because it was my turn to feed the animals my sister and I are raising
Animal Appetites The following narrative was written by Alex, a 5th grader who raises livestock for 4-H. This morning I woke up early because it was my turn to feed the animals my sister and I are raising
ANIMALS AND THEIR HABITATS: KS2 STUDENT RESOURCES
 ANIMALS AND THEIR HABITATS: KS2 STUDENT RESOURCES ANIMALS AND THEIR HABITATS (Lesson 1:1) Living things need Micro habitats Macro habitats Animals Difference? Plants Name: Class: Date: COMPARING ANIMALS
ANIMALS AND THEIR HABITATS: KS2 STUDENT RESOURCES ANIMALS AND THEIR HABITATS (Lesson 1:1) Living things need Micro habitats Macro habitats Animals Difference? Plants Name: Class: Date: COMPARING ANIMALS
Brookville Road Animal Hospital 8049 Brookville Road, Indianapolis, IN phone: (317)
 Brookville Road Animal Hospital 8049 Brookville Road, Indianapolis, IN 46239 phone: (317) 353-6143 Home Care Instructions The gums may be somewhat tender and sensitive for the next few days. Canned food
Brookville Road Animal Hospital 8049 Brookville Road, Indianapolis, IN 46239 phone: (317) 353-6143 Home Care Instructions The gums may be somewhat tender and sensitive for the next few days. Canned food
Structure and Function of Cells, Organs and Organ Systems 1
 I. Cell Structure and Function All living organisms are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry out the activities of life. These figures show some of the organelles and
I. Cell Structure and Function All living organisms are made up of one or more cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can carry out the activities of life. These figures show some of the organelles and
HEALTHY HABITS 45 Minute Health Lesson Science- to- Go! Program Grades: PreK- 1. Healthy Habits
 HEALTHY HABITS 45 Minute Health Lesson Science- to- Go! Program Grades: PreK- 1 TEACHER GUIDE Healthy Habits Description Explore nutrition, hygiene and exercise through hands- on, center- based activities.
HEALTHY HABITS 45 Minute Health Lesson Science- to- Go! Program Grades: PreK- 1 TEACHER GUIDE Healthy Habits Description Explore nutrition, hygiene and exercise through hands- on, center- based activities.
INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH
 INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH CLASS IV WORKSHEET- HALF YEARLY EXAM (2017-2018) E.V.S Lesson :5 Sources of water 1. is the purest form of natural water. 2. Higher parts of mountains are covered with.
INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH CLASS IV WORKSHEET- HALF YEARLY EXAM (2017-2018) E.V.S Lesson :5 Sources of water 1. is the purest form of natural water. 2. Higher parts of mountains are covered with.
The Digestive System Exam Questions
 The Digestive System Exam Questions 2012 - Higher Name an enzyme. Name the substrate that the enzyme you have named acts on. Name the product of the action of this enzyme. What reagent might you use, in
The Digestive System Exam Questions 2012 - Higher Name an enzyme. Name the substrate that the enzyme you have named acts on. Name the product of the action of this enzyme. What reagent might you use, in
Digestive System Practice Test
 Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
SECRETS FOR A HEALTHY LIFE 45 Minute Health Lesson Science-to-Go! Program Grades: PreK-1. Secrets for a Healthy Life
 SECRETS FOR A HEALTHY LIFE 45 Minute Health Lesson Science-to-Go! Program Grades: PreK-1 TEACHER GUIDE Secrets for a Healthy Life Description Jump into nutrition, hygiene and exercise to uncover the important
SECRETS FOR A HEALTHY LIFE 45 Minute Health Lesson Science-to-Go! Program Grades: PreK-1 TEACHER GUIDE Secrets for a Healthy Life Description Jump into nutrition, hygiene and exercise to uncover the important
We are an example of a biological species that has evolved
 Bio 1M: Primate evolution (complete) 1 Patterns of evolution Humans as an example We are an example of a biological species that has evolved Many of your friends are probably humans Humans seem unique:
Bio 1M: Primate evolution (complete) 1 Patterns of evolution Humans as an example We are an example of a biological species that has evolved Many of your friends are probably humans Humans seem unique:
TOOTH DECAY SESSION 1
 TOOTH DECAY SESSION 1 BSCS_flipchart_session1.indd 1 ANATOMY OF THE TOOTH Let s review the different parts of the teeth; we will use a tree to compare it to. Teeth are a live part of the body, just like
TOOTH DECAY SESSION 1 BSCS_flipchart_session1.indd 1 ANATOMY OF THE TOOTH Let s review the different parts of the teeth; we will use a tree to compare it to. Teeth are a live part of the body, just like
Congratulations! You really ARE amazing!
 Congratulations! You really ARE amazing! Make sure that you have written all your thoughts and emotional experiences in your journal. It can be a valid tool to look back at. Spend some time this next week
Congratulations! You really ARE amazing! Make sure that you have written all your thoughts and emotional experiences in your journal. It can be a valid tool to look back at. Spend some time this next week
1 The Digestive System
 CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
EXERCISE 3 Avian Organ & Organ System
 BI-160 LAB REPORT #3 NAME Introduction EXERCISE 3 Avian Organ & Organ System To investigate the major avian organs and organ systems used to sustain a bird and its active lifestyle, you will complete a
BI-160 LAB REPORT #3 NAME Introduction EXERCISE 3 Avian Organ & Organ System To investigate the major avian organs and organ systems used to sustain a bird and its active lifestyle, you will complete a
Biology: 4. The Digestive System
 Biology: 4. The Digestive System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB6 OB7 OB8 Syllabus Identify and locate the major parts of
Biology: 4. The Digestive System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB6 OB7 OB8 Syllabus Identify and locate the major parts of
The Digestive System. Parts and Functions
 The Digestive System Parts and Functions Mechanical Digestion A process of digestion in which food is cut, torn, mashed, and churned into smaller bits. This process starts in the mouth and ends in the
The Digestive System Parts and Functions Mechanical Digestion A process of digestion in which food is cut, torn, mashed, and churned into smaller bits. This process starts in the mouth and ends in the
INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL,RIYADH LESSON: 5 SOURCES OF WATER
 INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL,RIYADH CLASS-IV WORKSHEET-HALF YEARLY EXAM (2018-2019) EVS LESSON: 5 SOURCES OF WATER 1. is the purest form of natural water. 2. Oceans cover more than of the earth s surface.
INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL,RIYADH CLASS-IV WORKSHEET-HALF YEARLY EXAM (2018-2019) EVS LESSON: 5 SOURCES OF WATER 1. is the purest form of natural water. 2. Oceans cover more than of the earth s surface.
(producer) seeds (primary consumer) sparrow (secondary consumer) hawk
 What Are Some Parts of a Food Chain and a Food Web? Plants use light energy of the sun to make food. The food is stored in the cells of the plant. Plants are called producers because they make food. Some
What Are Some Parts of a Food Chain and a Food Web? Plants use light energy of the sun to make food. The food is stored in the cells of the plant. Plants are called producers because they make food. Some
*Digestive System Lesson* Big Idea for Unit: From small to BIG Liz Campbell 5 th Grade
 *Digestive System Lesson* Big Idea for Unit: From small to BIG Liz Campbell 5 th Grade I. Objectives A. Given the opportunity to explore and observe the digestive system through a hands-on, interactive
*Digestive System Lesson* Big Idea for Unit: From small to BIG Liz Campbell 5 th Grade I. Objectives A. Given the opportunity to explore and observe the digestive system through a hands-on, interactive
The Egyptian British international school Year 3 Science department Term 2. Final practice pack. Name:. Class:..
 Final practice pack Name:. Class:.. 1 Question 1: Materials have different properties. Here are six different materials. 1- Materials Cotton- metal- stone- rubber-fabrics-paper Name one property for each
Final practice pack Name:. Class:.. 1 Question 1: Materials have different properties. Here are six different materials. 1- Materials Cotton- metal- stone- rubber-fabrics-paper Name one property for each
Molecules. Background
 Background A molecule is a group of two or more atoms. Compounds are also two or more atoms. Compounds are made from different types of atoms. can be made of different types of atoms or can also be made
Background A molecule is a group of two or more atoms. Compounds are also two or more atoms. Compounds are made from different types of atoms. can be made of different types of atoms or can also be made
Human Body. Digestive. System and Nutrition
 Human Body Digestive System and Nutrition 1 Digestive System To stay alive, we need fuel. We get this fuel from the things we eat. Digestion is the process that changes the food you eat into fuel for your
Human Body Digestive System and Nutrition 1 Digestive System To stay alive, we need fuel. We get this fuel from the things we eat. Digestion is the process that changes the food you eat into fuel for your
A Study of the Predator-Prey Relationship
 Name: Block: v3/06 A Study of the Predator-Prey Relationship The predator-prey relationship is important to ecosystems. How can we measure that relationship? It would be difficult to follow a predator
Name: Block: v3/06 A Study of the Predator-Prey Relationship The predator-prey relationship is important to ecosystems. How can we measure that relationship? It would be difficult to follow a predator
The Digestive System. Chapter 23 Anatomy of the Digestive System Part 1
 The Digestive System Chapter 23 Anatomy of the Digestive System Part 1 Overview Organs: Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine Overview Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
The Digestive System Chapter 23 Anatomy of the Digestive System Part 1 Overview Organs: Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine Overview Accessory Organs Teeth, tongue,
Special Educational Needs (SEN) HANDS-ON REPTILES
 Special Educational Needs (SEN) HANDS-ON REPTILES General points about this talk: This is a fun interactive talk which includes the opportunity to touch some reptiles. This talk generally lasts 30 minutes
Special Educational Needs (SEN) HANDS-ON REPTILES General points about this talk: This is a fun interactive talk which includes the opportunity to touch some reptiles. This talk generally lasts 30 minutes
"The Digestive Process Begins" and "Final Digestion and Absorption" excerpts
 Read the following two passages about how the human digestive system processes food. Then answer the questions based on the text. "The Digestive Process Begins" and "Final Digestion and Absorption" excerpts
Read the following two passages about how the human digestive system processes food. Then answer the questions based on the text. "The Digestive Process Begins" and "Final Digestion and Absorption" excerpts
Phytoplankton Food for Thought
 Phytoplankton Food for Thought Developed by: Evan Smith Adapted from: Carrying Capacity and How Many Bears can Live in This Forest? Project WILD K-12 Curriculum & Activity Guide. Huston, TX: Council for
Phytoplankton Food for Thought Developed by: Evan Smith Adapted from: Carrying Capacity and How Many Bears can Live in This Forest? Project WILD K-12 Curriculum & Activity Guide. Huston, TX: Council for
TEST NAME:Cells and Health TEST ID: GRADE:08 - Eighth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: School Assessment
 TEST NAME:Cells and Health TEST ID:1326431 GRADE:08 - Eighth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: School Assessment Cells and Health Page 1 of 15 Student: Class: Date: 1. Which best
TEST NAME:Cells and Health TEST ID:1326431 GRADE:08 - Eighth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: School Assessment Cells and Health Page 1 of 15 Student: Class: Date: 1. Which best
Digestive System Lecture Notes Read Ch 14; review questions start on page 477 S/A # 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 16, 17, 19, 20, 21, 22, 26, 35
 The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
Materials Photo copied food labels and worksheet available Understanding Food Labels & Claims (take home handout)
 Reading Food Labels Grade Level: Grades 4-8 Objectives: Student will learn the key components of the food label Students will identify which nutrient values should be low and which values should be high
Reading Food Labels Grade Level: Grades 4-8 Objectives: Student will learn the key components of the food label Students will identify which nutrient values should be low and which values should be high
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that
 PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
Digestion is a process in which the complex food we eat is broken down in to simple, soluble, substances which our body is able to use.
 KEY POINTS We eat different kinds of food to get energy and to grow well. The food we eat cannot be used by the body as it is. It has to be broken down in to simpler and soluble from that the body can
KEY POINTS We eat different kinds of food to get energy and to grow well. The food we eat cannot be used by the body as it is. It has to be broken down in to simpler and soluble from that the body can
Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root. Tooth type and job. Why do humans have more than one type of tooth?
 Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
PREMATURE PRIMARY TOOTH LOSS
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your dental health. All decisions about the management of premature primary tooth loss must be made in conjunction
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your dental health. All decisions about the management of premature primary tooth loss must be made in conjunction
The Egyptian British international school Year 3 Science department Term 2. Final practice pack. Name:. Class:..
 Final practice pack Name:. Class:.. 1 Question 1: Materials have different properties. Here are six different materials. 1- Materials Cotton- metal- stone- rubber-fabrics-paper Name one property for each
Final practice pack Name:. Class:.. 1 Question 1: Materials have different properties. Here are six different materials. 1- Materials Cotton- metal- stone- rubber-fabrics-paper Name one property for each
Information for Parents/Carers SCIENCE TARGETS - A YEAR 1 SCIENTIST
 SCIENCE TARGETS - A YEAR 1 SCIENTIST Working scientifically (Y1 and Y2) I can ask simple scientific questions. I can use simple equipment to make observations. I can carry out simple tests. I can identify
SCIENCE TARGETS - A YEAR 1 SCIENTIST Working scientifically (Y1 and Y2) I can ask simple scientific questions. I can use simple equipment to make observations. I can carry out simple tests. I can identify
Introduction to Equine Dentistry Presented By Ulf Berglund, Iaed C/EqDT
 Introduction to Equine Dentistry Presented By Ulf Berglund, Iaed C/EqDT Hyoid apparatus PERFORMANCE EQUINE DENTISTRY Thanks Tony Basile M/EqDT Thomas J. Johnson, D.V.M. Technical Advisors Andy Dibbern
Introduction to Equine Dentistry Presented By Ulf Berglund, Iaed C/EqDT Hyoid apparatus PERFORMANCE EQUINE DENTISTRY Thanks Tony Basile M/EqDT Thomas J. Johnson, D.V.M. Technical Advisors Andy Dibbern
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013
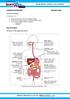 HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
Animal Nutrition Variations, Adaptations & Regulation
 Animal Nutrition Variations, Adaptations & Regulation This obese mouse (L) has defect in gene which normally produces leptin, an appetite-regulating protein. Many herbivores have diets deficient in mineral
Animal Nutrition Variations, Adaptations & Regulation This obese mouse (L) has defect in gene which normally produces leptin, an appetite-regulating protein. Many herbivores have diets deficient in mineral
Grass to Glass Amazing Dairy Cows
 Purpose: Students learn how the complex digestive system of dairy cows allows these animals to eat grass and other forages to produce milk for humans to drink. Time: 60 min Level: 3-6 Materials: Diagram
Purpose: Students learn how the complex digestive system of dairy cows allows these animals to eat grass and other forages to produce milk for humans to drink. Time: 60 min Level: 3-6 Materials: Diagram
The Importance of Maintaining the Health of Your Horse's Mouth
 Dental Care The Importance of Maintaining the Health of Your Horse's Mouth Routine dental care is essential to your horse's health. Periodic examination, correction s and regular maintenance, are especially
Dental Care The Importance of Maintaining the Health of Your Horse's Mouth Routine dental care is essential to your horse's health. Periodic examination, correction s and regular maintenance, are especially
Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Biology
 Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) Underline the correct answer: Part 1 1) Given below are some adapative features of plants: (i) It
Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) Underline the correct answer: Part 1 1) Given below are some adapative features of plants: (i) It
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
During the investigation the slugs moved towards the food. Two possible hypotheses for the movement of the slugs are:
 7. (a) An investigation was set up to examine the behaviour of slugs. Food During the investigation the slugs moved towards the food. (i) Two possible hypotheses for the movement of the slugs are: The
7. (a) An investigation was set up to examine the behaviour of slugs. Food During the investigation the slugs moved towards the food. (i) Two possible hypotheses for the movement of the slugs are: The
STEPS to better gut health
 5 STEPS to better gut health More than 2000 years ago, the renowned Greek Physician Hippocrates and Father of Medicine said... Let Food be Your Medicine & Medicine be Your Food. His words of wisdom are
5 STEPS to better gut health More than 2000 years ago, the renowned Greek Physician Hippocrates and Father of Medicine said... Let Food be Your Medicine & Medicine be Your Food. His words of wisdom are
DENTAL TRAUMA IN DECIDUOUS TEETH
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of Dental Trauma in Deciduous Teeth must be made in conjunction with
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of Dental Trauma in Deciduous Teeth must be made in conjunction with
Our Teeth. Word List: find each word from the list below in the table above (just circle each word on the table and cross it off from your list)
 Your Teeth Our Teeth B I L L E V Q I Z Q Q V E J E U Q A L P S Q A V S R Q E D Y E E G L E M A N E Y R V J R R G R L E A I Y T I V A C E B R A B Q O A C A P N C X M I L K T E E T H L M X O L M I Z T E
Your Teeth Our Teeth B I L L E V Q I Z Q Q V E J E U Q A L P S Q A V S R Q E D Y E E G L E M A N E Y R V J R R G R L E A I Y T I V A C E B R A B Q O A C A P N C X M I L K T E E T H L M X O L M I Z T E
DIGESTION. The What: Convert big food items into small molecules move them from gut to blood. The Where: In a long tube called the GI tract = gut.
 DIGESTION The What: Convert big food items into small molecules move them from gut to blood. The Where: In a long tube called the GI tract = gut. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MOUTH + GI TRACT + ACCESSORY ORGANS MOUTH
DIGESTION The What: Convert big food items into small molecules move them from gut to blood. The Where: In a long tube called the GI tract = gut. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MOUTH + GI TRACT + ACCESSORY ORGANS MOUTH
Name Date Class. 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Food is required for the body to. maintain homeostasis, keeping a steady internal state.
 CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
MARKING SCHEME - HALF-YEARLY EXAMS 2017/2018
 S E C O N D A R Y S C H O O L M R I E H E L ST THOMAS MORE COLLEGE SECONDARY SCHOOL ZEJTUN MARKING SCHEME - HALF-YEARLY EXAMS 2017/2018 YEAR 10 Biology Time: 2hrs NOTE: / indicates alternative answers.
S E C O N D A R Y S C H O O L M R I E H E L ST THOMAS MORE COLLEGE SECONDARY SCHOOL ZEJTUN MARKING SCHEME - HALF-YEARLY EXAMS 2017/2018 YEAR 10 Biology Time: 2hrs NOTE: / indicates alternative answers.
and Non-Human MODULE No.17: Structural Variation in Teeth- Human and Non-Human
 SUBJECT Paper No. and Title Module No. and Title Module Tag MODULE No.17: Structural Variation in Teeth- Human and FSC_P11_M17 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction 3. Structure of Human
SUBJECT Paper No. and Title Module No. and Title Module Tag MODULE No.17: Structural Variation in Teeth- Human and FSC_P11_M17 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction 3. Structure of Human
Equine Science & Technology. Unit Title: Health Management CIP:
 Equine Science & Technology Unit Title: Health Management CIP: 020221-07 Instructor: Objectives: After completing this unit of instruction, students will be able to: A. Discuss equine vaccination; B. List
Equine Science & Technology Unit Title: Health Management CIP: 020221-07 Instructor: Objectives: After completing this unit of instruction, students will be able to: A. Discuss equine vaccination; B. List
Identifying Fish Digestion and Feeding
 Lesson C3 4 Identifying Fish Digestion and Feeding Unit C. Animal Wildlife Management Problem Area 3. Fish Management Lesson 4. Identifying Fish Digestion and Feeding New Mexico Content Standard: Pathway
Lesson C3 4 Identifying Fish Digestion and Feeding Unit C. Animal Wildlife Management Problem Area 3. Fish Management Lesson 4. Identifying Fish Digestion and Feeding New Mexico Content Standard: Pathway
To power float or not to power float? A L L I S O N D O H E R T Y P O R T P E R R Y V E T E R I N A R Y S E R V I C E S
 To power float or not to power float? A L L I S O N D O H E R T Y P O R T P E R R Y V E T E R I N A R Y S E R V I C E S My horsey friends Photos courtesy of Kenzie Black An intro to the horse s mouth Most
To power float or not to power float? A L L I S O N D O H E R T Y P O R T P E R R Y V E T E R I N A R Y S E R V I C E S My horsey friends Photos courtesy of Kenzie Black An intro to the horse s mouth Most
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
Common Equine Dental Malocclusions Molars
 Common Equine Dental Malocclusions Molars CAUDAL HOOKS Definition - Dominant lower or upper last molar overhanging opposing molar. Etiology - Hereditary - May result from horse born with over or under
Common Equine Dental Malocclusions Molars CAUDAL HOOKS Definition - Dominant lower or upper last molar overhanging opposing molar. Etiology - Hereditary - May result from horse born with over or under
SRS Achievement Statements. Science
 SRS Achievement Statements Science Scales SRS Achievement Statements for Science 2018/19 2 Year 1 Achievement Statements Working Scientifically talk about what I see, hear, smell, taste or touch ask you
SRS Achievement Statements Science Scales SRS Achievement Statements for Science 2018/19 2 Year 1 Achievement Statements Working Scientifically talk about what I see, hear, smell, taste or touch ask you
Class Mammalia. Biology ~ Advanced Studies
 Class Mammalia Biology ~ Advanced Studies DOL 60-64 VI. Class Mammalia A. General characteristics 1. Hair on bodies 2. Females have mammary glands a. nourish young with milk 3. Breathe air with lungs 4.
Class Mammalia Biology ~ Advanced Studies DOL 60-64 VI. Class Mammalia A. General characteristics 1. Hair on bodies 2. Females have mammary glands a. nourish young with milk 3. Breathe air with lungs 4.
TRACKS Lesson Plan. Drinks and Calcium Rethink Your Drink Special Needs Students Any Grade
 TRACKS Lesson Plan Drinks and Calcium Rethink Your Drink Special Needs Students Any Grade I. Nutrition Education Goal & Objective: Goal 1: Students will comprehend concepts consistent with USDA guidance
TRACKS Lesson Plan Drinks and Calcium Rethink Your Drink Special Needs Students Any Grade I. Nutrition Education Goal & Objective: Goal 1: Students will comprehend concepts consistent with USDA guidance
Interactive Notebooks
 Grade 3 Interactive Notebooks CD-104907 Interactive Notebooks: Science Interactive notebooks are a fun new way to teach and reinforce effective note taking for students of all ages. Students are able to
Grade 3 Interactive Notebooks CD-104907 Interactive Notebooks: Science Interactive notebooks are a fun new way to teach and reinforce effective note taking for students of all ages. Students are able to
Lesson 24. Lesson Outline: Phylogenetic Trends in Digestive System Form and Function
 Lesson 24 Lesson Outline: Phylogenetic Trends in Digestive System Form and Function Objectives: Throughout the course what you need to master is an understanding of: 1) the form and function of structures,
Lesson 24 Lesson Outline: Phylogenetic Trends in Digestive System Form and Function Objectives: Throughout the course what you need to master is an understanding of: 1) the form and function of structures,
Year 6 (Entry into Year 7) 10 Hour Revision Course Biology
 Year 6 (Entry into Year 7) 10 Hour Revision Course Biology This page has been intentionally left blank Biology 4 Hours Life Processes (20 Minutes) There are 7 life processes carried out by all living things,
Year 6 (Entry into Year 7) 10 Hour Revision Course Biology This page has been intentionally left blank Biology 4 Hours Life Processes (20 Minutes) There are 7 life processes carried out by all living things,
