Gingival Recession and Various Root Coverage Procedures: A Review
|
|
|
- Barbra McKinney
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REVIEW ARTICLE and Various Root Coverage Procedures: A Review Mamta Singh 1, Kratee Sharma 2, Manvi Chandra Agarwal 3, Pranav Gupta 4 ABSTRACT Esthetics is of prime concern in today s sophisticated and modernised society. Esthetics is the science of beauty and encompasses almost every field of dentistry. Gingival recession is defined as the oral exposure of the root surface due to a displacement of the gingival margin apical to the cement-enamel junction and it is regularly linked to the deterioration of dental aesthetics. It has been associated with many factors such as inflammatory periodontal disease, developmental anatomic abnormalities (aberrant frenal attachment, thin bony plate), toothbrush injury, tooth malposition and iatrogenic factors. Apart from compromised esthetics, gingival recession also results in a variety of other problems such as root hypersensitivity, a higher incidence of root caries and diminished plaque control, thus necessitating treatment. Successful treatment of recession-type defects is based on the use of predictable periodontal plastic surgery (PPS) procedures. Keywords: Gingival recession, cemento-enamel junction, periodontal plastic surgery INTRODUCTION Gingival recession is the displacement of the gingival margin apical to the cemento-enamel junction (CEJ). 1 It is observed more frequently on the labial/buccal surfaces of the teeth and is probably one of the most common esthetic concerns associated with the periodontal tissues. Recession refers to the location of the gingiva, not its condition. Receded gingiva can be inflamed but may be normal except for their position. Recession may be localized to one tooth or a group of teeth, or it may be generalized throughout the mouth. 2 Apart from compromised esthetics, gingival recession often results in a variety of other problems as well such as root hypersensitivity, a higher incidence of root caries and diminished plaque control, thus necessitating treatment. ETIOLOGY OF GINGIVAL RECESSION 3 The cause of gingival recession whether localized or generalized is not always easy to determine but is essential prior to treatment planning. The following factors have been incriminated. - Inflammatory periodontal disease (considered as the principal etiologic factor), Ageing, Developmental anatomic abnormalities (dehiscences, thin bony plates, high frenum attachments), Malaligned tooth, Toothbrush trauma, Deleterious habits (pressure from foreign objects, fingernails, pencils, hairpins), Iatrogenic factors (orthodontic forces, pressure from bands, arch wires, clasps, subgingival restorations, post periodontal surgery). PATHOGENESIS The process of apical migration of marginal gingiva over the root surface results in the condition of gingival recession. The definition of the condition of gingival recession: Some slight apical shift of supra-crestal connective tissue attachment that is the cementum which is exposed and has already lost attachment to the collagenous gingival fibers which are found just coronal to the crest of the alveolar bone and just apical to the junctional epithelium. It is the continual apical migration of gingival fibers attachment and marginal gingiva which characterizes the process of recession. 4 Histologically, the destruction of gingival tissues, due to mechanical forces or related to inflammatory periodontal disease, is associated with loss of periodontal connective tissue fibers and alveolar bone. For gingival augmentation, the main objective is to increase width and thickness of the gingiva in areas where the amount of keratinized tissue is judged clinically inadequate. However, scientific data do not support the hypothesis that gingival tissue dimensions are critical to the prevention of gingival recession defects. 5,6 Nevertheless, gingival augmentation should be considered where a change in mucogingival morphology may facilitate plaque control and when alveolar bone dehiscence would be anticipated as a result of orthodontic tooth movement. 7 Ideally, surgical treatment of gingival recession defects should fully restore the anatomy of the mucogingival complex. However, aesthetic concerns are usually the reason to perform these procedures. This im- 1 Second year Post Graduate Student, 2 Third year Post Graduate Student, 3 Reader, Department of Periodontics, 4 Second year Post graduate student, Department of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry, Kothiwal Dental College and Research Centre, Mora Mustaqueem, Kanth Road, Moradabad, Uttar Pradesh, India Corresponding author: C/O Dr. Mamta Singh, Second Year Post Graduate Student, Room No.12 B, PG Girls Hostel, Kothiwal Dental College & Research Centre, Mora Mustaqueem, Kanth Road, Moradabad, Uttar Pradesh, India. How to cite this article: Mamta Singh, Kratee Sharma, Manvi Chandra Agarwal, Pranav Gupta. and Various Root Coverage Procedures: A Review. International Journal of Contemporary Medical Research 2016;3(1): Volume 3 Issue 1 January 2016 ISSN (Online): X; (Print):
2 plies regeneration of the attachment apparatus of the tooth, including cementum with inserting connective tissue fibers, and alveolar bone, as well as recreation of topographic relationships between the keratinized tissue and the alveolar mucosa that are functionally and aesthetically acceptable to the patient. 4 Certainly, the ultimate goal of periodontal therapy is regeneration. This involves the elimination of diseased state and replacement with a healthy state, in which all tissues that are originally found have been restored. Regeneration has been defined as The natural renewal of a structure, produced by growth and differentiation of new cells and intercellular substance to form new tissues or part. 8 INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE: Gorman 9 stated that recession increased in both numerical as well as linear dimension with age. The occurrence of recession was found to vary from 54.5% of all the subjects in the years of age group to 100 % in the years of age groups. The most pronounced increase was from years to the years of age groups. Males showed greater recession than females of the same groups. 9 Occurrence of recession can be seen as early as 15 years as per Guiha et al. 10 Woofter 11 showed that incidence varies from 8% in children to 100% after the age of 50 years. Yoneyama et al. 12 stated that, it is common in populations with good as well as poor oral hygiene. Buccal recession seems to be more common and more advanced at single rooted teeth than at molars. The attachment loss difference observed between different surfaces of a given tooth or a group of teeth. The data suggested that in younger subject groups, progression was confined to a subset of individuals, while in older age groups, more subjects and sites became involved. 14 A 3-year longitudinal study was conducted to find out the occurrence of gingival recession in mandibular incisors. 28 children aged 6-13 years, with gingival recession localized to mandibular incisors, were monitored longitudinally to evaluate any changes of the labial periodontal tissues. Gradual reductions in the amount of gingival recession and probing attachment levels took place in all children except for one of the subjects with one severely malpositioned tooth. Probing depths and widths of keratinized and attached gingiva remained relatively unchanged. This finding showed that, gingival recession in mandibular incisors in young children often improves over time which suggests that, preventive or reparative treatment in this part of the developing dentition may not be necessary. Decisions about such treatment should be postponed until any spontaneous improvement has taken place. 15 A study was carried out to assess the development of gingival recession in young adult smokers and nonsmokers. At the outset, 50% of subjects presented with gingival recession at one or more sites. There was no significant difference in the prevalence of gingival recession between non-smokers and smokers. The risk for recession development appeared not to be influenced by smoking status after adjusting for periodontal probing depth, recession at baseline, tooth brushing frequency, gender, jaw, tooth type and site. Their study did not support the hypothesis that, smokers are at an increased risk for the development of gingival recession. 13 CLASSIFICATION OF GINGIVAL RECESSION Several classification systems have been proposed in the literature in order to facilitate the diagnosis of gingival recession. Sullivan s and Atkins in 1968 classified recession into four categories. 16 Shallow Narrow. 2) Shallow Wide. 3) Deep Narrow, 4) Deep Wide Mlinek et al in 1973 classified recession as 4 1. Shallow-narrow clefts as being <3 mm in both dimensions. 2. Deep-wide defects as being >3 mm in both dimensions. Miller s classification of gingival recession 5 Four types of recession defects were categorized on the basis of evaluation of the soft and hard periodontal tissues. Class I Marginal tissue recession does not extend to the mucogingival junction (MGJ). There is no periodontal loss (bone or soft tissue) in the interdental area and 100% root coverage can be anticipated. Class II - Marginal tissue recession that extends to or beyond the MGJ. There is no periodontal loss (bone or soft tissue) in the interdental area and 100% root coverage can be anticipated. Class III - Marginal tissue recession that extends to or beyond the MGJ. Bone or soft tissue loss in the interdental area is present or there is malpositioning of the teeth, which prevents the attempting of 100% of root coverage. Partial root coverage can be anticipated. Class IV - Marginal tissue recession that extends to or beyond the MGJ. The bone or soft tissue loss in the interdental area and/or malpositioning of teeth is so severe that root coverage cannot be anticipated. Mahajan's modification of Miller's classification 7 1. Class I: Gingival tissue recession not extending to muco-gingival junction. 2. Class II: Gingival tissue recession extending to muco-gingival junction or beyond it. 3. Class III: Gingival tissue recession with bone or soft-tissue loss in interdental area up to cervical 1/3 of root surfaces and/or malpositioning of the teeth. 4. Class IV: Gingival tissue recession with severe bone or soft tissue loss in interdental area greater than cervical 1/3 of root surface and/or severe malpositioning of teeth. ISSN (Online): X; (Print): Volume 3 Issue 1 January
3 Prognosis according to Mahajan's modification BEST - Class I and Class II with thick gingival profile. GOOD - Class I and Class II with thin gingival profile. FAIR - Class III with thick gingival profile. POOR - Class III and Class IV with thin gingival profile. Cairo et al 7 taking into account the desirable characteristics of a classification system (usefulness, exhaustiveness, disjointness and simplicity) suggested by Murphy (1997), the following classification of gingival recession was then identified based on the assessment of clinical attachment level (CAL) at both buccal and interproximal sites Recession Type 1 (RT1): Gingival recession with no loss of interproximal attachment. Interproximal cementoenamel junction (CEJ) was clinically not detectable at both mesial and distal aspects of the tooth. 2. Recession Type 2 (RT2): Gingival recession associated with loss of interproximal attachment. The amount of interproximal attachment loss (measured from the interproximal CEJ to the depth of the interproximal pocket) was less than or equal to the buccal attachment loss (measured from the buccal CEJ to the depth of the buccal pocket). 3. Recession Type 3 (RT3): Gingival recession associated with loss of interproximal attachment. The amount of interproximal attachment loss (measured from the interproximal CEJ to the depth of the pocket) was higher than the buccal attachment loss (measured from the buccal CEJ to the depth of the buccal pocket). TREATMENT OF GINGIVAL RECESSION Compromised esthetics, root hypersensitivity, diminished plaque control, progression of defect; etc resulting from gingival recession may warrant its treatment. Investigation of etiologic factors and consideration of therapeutic options directed at minimizing the progression of apical migration of the marginal gingival tissue are the objectives for the treatment of gingival recession. Various mucogingival surgeries have been proposed for the purpose of root coverage Pedicle grafts: a. Rotational flaps. Laterally positioned flap. Obliquely rotated flap. Double papilla flap. b. Advanced flaps. Coronally positioned flap. Semilunar flap. 2. Free soft tissue grafts: a. Epithelialized (classical gingival graft). b. Non-epithelialized. 3. Combination grafts: 1-Stage procedure. Connective tissue graft plus pedicle graft. Biodegradable membrane barrier plus pedicle graft. 2-Stage procedure. Coronally positioned previously placed soft tissue graft. Non-biodegradable membrane barrier plus pedicle graft. TECHNIQUES FOR ROOT COVERAGE Rotational flap procedures The use of a laterally repositioned flap to cover areas with localized recession was introduced by Grupe and Warren 17 which was called the laterally sliding flap operation. In order to reduce the risk for recession on the donor tooth, Grupe 18 suggested that the marginal soft tissue should not be included in the flap. Staffileno 19 and Pfiefer & Heller 19 advocated the use of split thickness flap to minimize the potential risk for the development of dehiscence at the donor tooth. Laterally positioned flap Grupe & Warren 17 introduced contiguous soft tissue autografts to the literature under the term lateral sliding flap currently known as the laterally positioned pedicle graft. For successful root coverage using laterally positioned pedicle graft, these three criteria must be met. 1. Adequate donor tissue laterally. 2. Normal to deep vestibule. 3. Recession involving only one tooth. Double papilla repositioned flap Double papilla graft is the variation of the laterally positioned graft which was given by Cohen and Ross. 20 This procedure evolved in an attempt to use minimal amounts of gingiva for root coverage. It is indicated in where there is recession of labial or lingual gingiva, but destruction of the interdental papillae on either side of the denuded area has not occurred. Recession of this type is observed in areas where trauma from incorrect tooth brushing has destroyed the gingiva and cleft formation develops. This pattern of gingival recession is noted on the labial or buccal surfaces of roots where the involved tooth is in labial version to the approximating teeth. If the adjacent area to the recession is intact with no pocket formation or minimal in the proximal areas, then joining both papillae together to form a flap will repair the area of root exposure. The restoration of the gingival unit is advantageous not only from the cosmetic standpoint but also from a functional aspect. Covering the exposed root surface with gingiva has helped to reduce or eliminate the problem of hypersensitivity. This procedure may also permit the covering of the margin of a restoration which has been exposed by recession. Pedicle soft tissue graft procedures combined with membrane barriers: The use of membrane barrier, according to the principles of guided tissue regeneration (GTR), in conjunction with pedi- 36 Volume 3 Issue 1 January 2016 ISSN (Online): X; (Print):
4 cle soft tissue graft procedures was introduced as a treatment modality for root coverage. A membrane barrier is placed between the graft and the root in order to favor the regeneration of the periodontium. According to the concept of the GTR, a critical factor for the outcome of the treatment procedure is that a space for tissue formation is established between the facial root surface and the membrane and maintained during the healing. In order to create such a space, Pini Prato et al 21 suggested that extensive root planing should be carried out to produce a concave morphology. Specially designed membranes for the treatment of recession type defects are also available, such as non-absorbable titanium- reinforced expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (eptfe) membranes and a variety of bioabsorbable membranes but many of these may not be rigid enough for maintaining required space during healing. FREE SOFT TISSUE GRAFT PROCEDURES A free soft tissue of the masticatory mucosa is usually selected when, 1. There is no acceptable donor tissue present in the area adjacent to the recession defect. 2. Thicker marginal tissue is desirable. Epithelialized soft tissue graft The epithelialized free soft tissue graft procedure can be performed either as a two-step surgical technique, where an epithelialized free soft tissue graft is placed apical to the recession and following healing is coronally positioned over the denuded root, or as a one-step technique, in which the graft is placed directly over the root surface. The classic epithelialized palatal graft was originally presented by King and Pennel in 1964 as a gingival augmentation procedure with the following treatment goals: 1. To establish a soft tissue margin of keratinized tissue. 2. To prevent further recession. 3. To negate the effects of an aberrant frenum. 4. To produce a soft tissue margin that enables the patient to practice a high level of plaque removal without traumatizing the soft tissue. 5. To be used as an adjunctive treatment when margins of restorations must be placed in the gingival sulcus. Drawbacks of epithelialized palatal graft 1. The technique is difficult to perform. It is technically demanding from the suturing point of view. 2. The technique is time- consuming. 3. A blood supply to the graft is available on only one surface rather than two, as with the connective tissue graft, and so, more difficult to achieve and it is difficult to stabilize the epithelialized tissue. 4. The palatal wound (donor site) is more invasive, more prone to hemorrhage, and slower to heal. It is painful and ulcerated. Thus, it is more annoying to the patient during the healing phase. 5. When the epithelialized palatal graft is used for root coverage grafting, a functional result is produced, but the color match of the tissues is often less than ideal. On healing, the grafted palatal tissue tends to be lighter (whiter) and more opaque than gingiva. 6. Furthermore, one does not expect to see grafted masticatory mucosa extending deep into the vestibule. 7. Another problem in free grafting is the thickness of the tissue on healing. Often a slight abrasion of the healed graft is necessary to produce the most esthetic result. Although the subepithelial connective tissue graft has become increasingly popular for root coverage, the epithelialized palatal graft is still used for gingival augmentation when thicker tissue is desired, when esthetic is not a concern, when there is a need to deepen the vestibule, or when pinker tissue is required as in removing an amalgam tattoo. SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT (SCTG) According to Karring et al 14 gingival connective tissue is a viable source of cells for repopulating the epithelium. Free connective tissue graft was first used by Edel 22 to increase the width of keratinized gingiva. The use of connective tissue graft for treatment of gingival recession was first reported in 1985 by Langer and Langer, 23 who described the Subepithelial connective tissue graft procedure for covering gingival recession of single as well as multiple teeth. Raetzke 24 performed connective tissue grafting with an Envelope technique and achieved 80% root coverage. Various other modifications were proposed by Nelson 25, Harris 26, Blanes and Allen 27, Santerelli et al 28 and Tozum. 29,30 The SCTG is usually harvested from the palate. The thickest donor tissue can be harvested from the premolar region of the palate. If sufficient tissue cannot be obtained from one side, the contralateral side of the palate may be utilized simultaneously. Greater tissue availability is found with a high palatal vault than a low palatal vault. The height, length and thickness of donor tissue that can be obtained varies with the differing anatomic dimensions of the palatal vault. 29 CORONALLY ADVANCED FLAP TECHNIQUE 31 The coronally advanced flap (CAF) is a procedure frequently used in periodontal plastic surgery. The main objective of this surgical technique is to mobilize the gingival margin and reposition it at a level more coronal (incisal direction) than its original location. CAF is mainly used for the treatment of gingival recessions. The procedure was originally introduced by Allen & Miller in 1989, throughout time. Several authors proposed modifications to the original technique. Indications for Coronally Advanced Flap 31,32 1. Coverage of certain types of gingival recessions. ISSN (Online): X; (Print): Volume 3 Issue 1 January
5 2. Esthetic coverage of exposed roots. 3. For tooth sensitivity owing to gingival recession. Contraindications for Coronally Advanced Flap: 1. Lack of keratinized tissue. 2. Shallow vestibule. Evidence shows that a coronally advanced flap alone in many instances results in complete root coverage and is stable over time. A coronally advanced flap is less invasive for the patient, requires less chair-time and probably less surgical skill. It would therefore be desirable to use a coronally advanced flap approach when indicated. It has been hypothesized that a coronally advanced flap approach alone could be successfully applied when the residual gingiva is thick and wide. It can be used in treating single or multiple recession defects. In an attempt to obtain higher success rate of root coverage in aesthetic zone, combination of different procedures have been used. A recent innovation in dentistry is the use of Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF), a concentrated suspension of the Concentrated Growth Factors (CGF), along with the root coverage procedures in recession defects to enhance wound healing and tissue regeneration. CONCLUSION Among the various treatment modalities, root coverage with coronally advanced flap holds the most promising results. Studies have been done by using this technique and the results provided significant root coverage, clinical attachment level and keratinized tissue gain as compared to various other procedures and hence could be considered as the gold standard procedure in the treatment of gingival recession defects. REFERENCES 1. The American Academy of Periodontology. Glossary of periodontal terms, 4 th edition. Chicago IL: The American Academy of Periodontology 200: Deby Johnson. Perio Plastic Surgery Garant, Stern, Listgarten. Periodontics. 6th ed. Mosby; Mlinek A, Smukler H, Buchner A. The use of free gingival grafts for the coverage of denuded roots. J Periodontol 1973;44: Miller Jr PD. A classification of marginal tissue recession. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 1985;5: Smith RG. Gingival recession: reappraisal of an enigmatic condition and a new index for monitoring. J Clin Periodontol 1997;24: Mahajan A. Mahajan's Modification of the Miller s Classification for. Dental hypotheses 2010;1: Serino G, Wennstorm J, Lindhe J, Eneroth L. The prevalence and distribution of the gingival recession in subjects with a high standard of oral hygiene. J Clin Periodontol 1994;21: The American Academy of Periodontology. Consesus report. Mucogingival therapy. Ann Periodontol 1996;1: Guiha R, EL Khodeiry S, Mota L, Caffesse R. Histologic evaluation of healing and vascularization of subepithelial connective tissue graft. J Periodontol 2001;72: Woofter C. The prevalence and etiology of gingival recession. Periodontal Abstr 1969; 17: Yoneyama T, Okamolo H, Lindhe J, Socransky SS, Haffejee AD. Probing depth, attachment loss and gingival recession. J Clin Periodontol 1988;15: Muller HP, Stademann S, Heinecke A. Gingival recession in smokers and non smokers with minimal periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol 2002;29: Karring T, Ostergaard E and Loe H. Conservation of tissue specificity after heterotopic transplantation of gingiva and alveolar mucosa. J Periodontol Res 1971;6: Andlin-Sobocki A, Marcusson A, Persson M. 3-year observation on gingival recession in mandibular incisors in children. J Clin Periodontol 1991;18: Sullivan HC, Atkins JH. Free autogenous gingival grafts and utilization of grafts in the treatment of gingival recession. Perio 1968;6: Grupe H, Warren R. Repair of gingival defects by a sliding flap operation. J Periodontol 1956;27: Grupe H E. Modified technique for the sliding flap operation. J Periodontol 1966;37: Pfeifer JS, Heller R. Histologic evaluation of full and partial thickness lateral repositioned flaps. J Periodontol 1971;42: Cohen DW, Ross SE. The double papillae repositioned in periodontal therapy. J Periodontol 1968;39: Pini Prato G, G.P.Tinti, C, Vincenzi, G. Guided tissue regeneration versus mucogingival surgery in the treatment of human buccal gingival recession. J Periodontol 1992;63: Edel A. Clinical evaluation of free connective tissue grafts used to increase the width of keratinized gingiva. J Clin Periodontol 1974;1: Langer B and Langer L. Subepithelial Connective Tissue Graft Technique for Root Coverage. J Periodontol 1985;60: Raetzke PB. Covering Localized Areas of Root Exposure Employing the "Envelope" Technique. J Periodontol 1985;56: Nelson SW. The subpedicle connective tissue graft. A bilaminar reconstructive procedure for the coverage of denuded root surfaces. J Periodontol. 1987;58: Harris RJ. The connective tissue and partial thickness double pedicle graft: A predictable method of obtaining root coverage. J Periodontol 1992;63: Blanes RJ, Allen EP. The bilateral pedicle flap-tunnel technique: A new approach to cover connective tissue grafts. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 1999;19: Volume 3 Issue 1 January 2016 ISSN (Online): X; (Print):
6 27. Santarelli GA, Ciancaglini R, Campanari F, et al. Connective tissue grafting employing the tunnel technique: A case report of complete root coverage in the anterior maxilla. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2001;21: Tozum TF. A promising periodontal procedure for the treatment of gingival recession defects. J Can Dent Assoc 2003;69: Sedon CL, Breault LG, Covington LL, Bishop BG. The Subepithelial Connective Tissue Graft: Part I. Patient Selection and Surgical Techniques. J Contemp Dent Pract 2005;6: Alessandro Geminiani et al. Coronally Advanced Flap: How to achieve predictable root coverage. Love Perio Houston TX. Periodontics and Dental Implants, Houston, TX. September 24, Edward S Cohen. Atlas of cosmetic and reconstructive periodontal surgery 3 rd edition. Page no 283. Source of Support: Nil; Conflict of Interest: None Submitted: ; Published online: ISSN (Online): X; (Print): Volume 3 Issue 1 January
MUCOGINGIVAL THERAPY PERIODONTAL PLASTIC SURGERY
 MUCOGINGIVAL THERAPY PERIODONTAL PLASTIC SURGERY DR.H.Gharati Periodontist & Dental Implant Specialist Assistant Professor, School Of Dentistry Friedman(1957): DEFINITION Mucogingival surgery, Surgical
MUCOGINGIVAL THERAPY PERIODONTAL PLASTIC SURGERY DR.H.Gharati Periodontist & Dental Implant Specialist Assistant Professor, School Of Dentistry Friedman(1957): DEFINITION Mucogingival surgery, Surgical
RESEARCH REVIEW. Gingival recession: a proposal for a new classification ISSN :
 RESEARCH REVIEW Gingival recession: a proposal for a new classification Shantipriya Reddy, Sanjay Kaul, Prasad M.G.S., Jaya Agnihotri, Amudha D., Soumya Kambali ABSTRACT An accurate diagnosis is often
RESEARCH REVIEW Gingival recession: a proposal for a new classification Shantipriya Reddy, Sanjay Kaul, Prasad M.G.S., Jaya Agnihotri, Amudha D., Soumya Kambali ABSTRACT An accurate diagnosis is often
Many techniques have been proposed for root coverage:
 Case Series Localized Gingival Recessions Treated With the Original Envelope Technique: A Report of 50 Consecutive Patients Jaime A. Vergara* and Raul G. Caffesse Background: The surgical techniques used
Case Series Localized Gingival Recessions Treated With the Original Envelope Technique: A Report of 50 Consecutive Patients Jaime A. Vergara* and Raul G. Caffesse Background: The surgical techniques used
CITRIC ACID ROOT BIOMODIFICATION IN RECESSION COVERAGE WITH LATERAL PEDICLE FLAP TECHNIQUE- A CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 05 CITRIC ACID ROOT BIOMODIFICATION IN RECESSION COVERAGE WITH LATERAL PEDICLE FLAP TECHNIQUE- A CASE REPORT Mamta Singh
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 05 CITRIC ACID ROOT BIOMODIFICATION IN RECESSION COVERAGE WITH LATERAL PEDICLE FLAP TECHNIQUE- A CASE REPORT Mamta Singh
Classifications for Gingival Recession: A Mini Review
 Galore International Journal of Health Sciences and Research Vol.3; Issue: 1; Jan.-March 2018 Website: www.gijhsr.com Review Article P-ISSN: 2456-9321 Classifications for Gingival Recession: A Mini Review
Galore International Journal of Health Sciences and Research Vol.3; Issue: 1; Jan.-March 2018 Website: www.gijhsr.com Review Article P-ISSN: 2456-9321 Classifications for Gingival Recession: A Mini Review
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Management of miller class II gingival recession by laterally positioned pedicle flap revised technique
 Management of miller class II gingival by laterally positioned pedicle flap revised technique Received: 2/4/206 Accepted: 3/0/206 Dildar Abdullah Othman* Abstract Background and objective: Gingival is
Management of miller class II gingival by laterally positioned pedicle flap revised technique Received: 2/4/206 Accepted: 3/0/206 Dildar Abdullah Othman* Abstract Background and objective: Gingival is
Case Report Esthetic Root Coverage with Double Papillary Subepithelial Connective Tissue Graft: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 509319, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/509319 Case Report Esthetic Root Coverage with Double Papillary Subepithelial Connective Tissue Graft: A Case Report
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 509319, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/509319 Case Report Esthetic Root Coverage with Double Papillary Subepithelial Connective Tissue Graft: A Case Report
TWO-STEP SURGICAL PROCEDURE FOR ROOT COVERAGE (FREE GINGIVAL GRAFT AND CORONALLY POSITIONED FLAP) - A CASE REPORT
 TWO-STEP SURGICAL PROCEDURE FOR ROOT COVERAGE (FREE GINGIVAL GRAFT AND CORONALLY POSITIONED FLAP) - A CASE REPORT Dr Prashant Bhusari*, Dr Apoorva Saxena**, Dr Jaya Jain***,Dr Rashmi Rathore***, Dr Aditi
TWO-STEP SURGICAL PROCEDURE FOR ROOT COVERAGE (FREE GINGIVAL GRAFT AND CORONALLY POSITIONED FLAP) - A CASE REPORT Dr Prashant Bhusari*, Dr Apoorva Saxena**, Dr Jaya Jain***,Dr Rashmi Rathore***, Dr Aditi
The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato, Carlo Baldi, Roberto Rotundo, Debora Franceschi,
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato, Carlo Baldi, Roberto Rotundo, Debora Franceschi,
ELIMINATE POCKETS. Periodontal pocket is the consequence of periodontal infection But also a major risk factor for the further progression of disease
 ELIMINATE POCKETS Periodontal pocket is the consequence of periodontal infection But also a major risk factor for the further progression of disease CONSEQUENTLY Periodontal pockets should be eliminated
ELIMINATE POCKETS Periodontal pocket is the consequence of periodontal infection But also a major risk factor for the further progression of disease CONSEQUENTLY Periodontal pockets should be eliminated
Efficacy of Lateral Pedicle Graft in the Treatment of Isolated Gingival Recession Defects
 International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 3 Issue 1 January 2014 PP.46-50 Efficacy of Lateral Pedicle Graft in the Treatment of
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 3 Issue 1 January 2014 PP.46-50 Efficacy of Lateral Pedicle Graft in the Treatment of
Alarge number of sound clinical
 Volume 83 Number 5 Long-Term 8-Year Outcomes of Coronally Advanced Flap forrootcoverage Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato,* Debora Franceschi,* Roberto Rotundo,* Francesco Cairo,* Pierpaolo Cortellini, and Michele
Volume 83 Number 5 Long-Term 8-Year Outcomes of Coronally Advanced Flap forrootcoverage Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato,* Debora Franceschi,* Roberto Rotundo,* Francesco Cairo,* Pierpaolo Cortellini, and Michele
Rescuing Tooth with Regenerative Technique: A Case Report. Women,, Suraram Mainroad, Ghmc Quthbullapur, Hyderabad , Telangana.
 ISSN- O: 2458-868X, ISSN P: 2458 8687 Index Copernicus Value: 49. 23 PubMed - National Library of Medicine - ID: 101731606 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.956 International Journal of Medical Science and Innovative
ISSN- O: 2458-868X, ISSN P: 2458 8687 Index Copernicus Value: 49. 23 PubMed - National Library of Medicine - ID: 101731606 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.956 International Journal of Medical Science and Innovative
A Promising Periodontal Procedure for the Treatment of Adjacent Gingival Recession Defects. Tolga Fikret Tözüm, DDS, PhD
 C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E A Promising Periodontal Procedure for the Treatment of Adjacent Gingival Recession Defects Tolga Fikret Tözüm, DDS, PhD A b s t r a c t Various clinical reports on the reconstruction
C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E A Promising Periodontal Procedure for the Treatment of Adjacent Gingival Recession Defects Tolga Fikret Tözüm, DDS, PhD A b s t r a c t Various clinical reports on the reconstruction
Delta Dental of Virginia Clinical Policy # 402
 Delta Dental of Virginia Clinical Policy # 402 Subject Mucogingival Surgery and Soft Tissue Grafting Originating Department Clinical Professional Services Signature Authority Dental Director Type: New
Delta Dental of Virginia Clinical Policy # 402 Subject Mucogingival Surgery and Soft Tissue Grafting Originating Department Clinical Professional Services Signature Authority Dental Director Type: New
WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF WHAT WE DO? TEAM PERIODONTICS: WORKING TOGETHER TO IMPROVE PATIENT CARE YOU ARE THE PERIODONTISTS IN YOUR PRACTICE!
 Setter Periodontics 2075 SW 1 st Ave #2L Portland, OR 97201 503-222-9961 michael@setterperio.com WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF WHAT WE DO? Gum Gardeners Study Club 2.27.17 TEAM PERIODONTICS: WORKING TOGETHER
Setter Periodontics 2075 SW 1 st Ave #2L Portland, OR 97201 503-222-9961 michael@setterperio.com WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF WHAT WE DO? Gum Gardeners Study Club 2.27.17 TEAM PERIODONTICS: WORKING TOGETHER
SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT A PREDICTABLE INDICATOR FOR ROOT COVERAGE
 SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT A PREDICTABLE INDICATOR FOR ROOT COVERAGE Munishwar Singh* * 201 Military Dental Centre, C/o 99 APO, India Keywords: Gingival recession, Root coverage procedure, Connective
SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT A PREDICTABLE INDICATOR FOR ROOT COVERAGE Munishwar Singh* * 201 Military Dental Centre, C/o 99 APO, India Keywords: Gingival recession, Root coverage procedure, Connective
Townie Guest Editorial. Gingival Attachment Loss: Evaluation and Surgical Options. Daniel J. Melker, DDS. fig. 1
 Gingival Attachment Loss: Evaluation and Surgical Options Daniel J. Melker, DDS Attached connective tissue (a.k.a. attached tissue) in the simplest terms is the body s only barrier between the underlying
Gingival Attachment Loss: Evaluation and Surgical Options Daniel J. Melker, DDS Attached connective tissue (a.k.a. attached tissue) in the simplest terms is the body s only barrier between the underlying
Free Gingival Autograft: A Case Report
 CASE REPORT Free Gingival Autograft: A Case Report Veena Ashok. P. MDS, Bhargav Neetha BDS Abstract: Gingival recession is defined as Displacement of soft tissue margin apical to the cemento-enamel junction
CASE REPORT Free Gingival Autograft: A Case Report Veena Ashok. P. MDS, Bhargav Neetha BDS Abstract: Gingival recession is defined as Displacement of soft tissue margin apical to the cemento-enamel junction
Gum Graft? Patient Need a. Does My. 66 JANUARY 2017 // dentaltown.com. by Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky
 by Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky was born in Dallas and attended college at the University of Texas at Austin. He continued his education at Baylor College of Dentistry in Dallas, where he
by Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky was born in Dallas and attended college at the University of Texas at Austin. He continued his education at Baylor College of Dentistry in Dallas, where he
Research Article. ISSN (Print)
 Scholars Journal of Dental Sciences (SJDS) Sch. J. Dent. Sci., 15; 2(6):343-348 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources) www.saspublisher.com
Scholars Journal of Dental Sciences (SJDS) Sch. J. Dent. Sci., 15; 2(6):343-348 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources) www.saspublisher.com
Over the years, mucogingival surgery
 The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation and Root Coverage: A Case Series Saroff Stephen Andrew Saroff, DDS, MSD 1 Abstract Over the years, mucogingival surgery has developed
The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation and Root Coverage: A Case Series Saroff Stephen Andrew Saroff, DDS, MSD 1 Abstract Over the years, mucogingival surgery has developed
Management of millers class III marginal tissue recession associated with endodontic lesion: Report of two cases managed using second stage surgery
 CASE SERIES 1 OPEN ACCESS Management of millers class III marginal tissue recession associated with endodontic lesion: Report of two cases managed using second stage surgery Sangeeta ABSTRACT Introduction:
CASE SERIES 1 OPEN ACCESS Management of millers class III marginal tissue recession associated with endodontic lesion: Report of two cases managed using second stage surgery Sangeeta ABSTRACT Introduction:
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Connective Tissue Graft for Gingival Recession in Mandibular Incisor Area: A Case Report
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 155 162 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0038 Connective Tissue Graft for Gingival Recession in Mandibular Incisor Area: A Case Report Masahiro Egawa 1), Satoru
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 155 162 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0038 Connective Tissue Graft for Gingival Recession in Mandibular Incisor Area: A Case Report Masahiro Egawa 1), Satoru
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Bridge Flap: A Sine Qua Non For Mucogingival Deformities Debajyoti Mondal, Anju L, Rajul Choradia, Somen
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Bridge Flap: A Sine Qua Non For Mucogingival Deformities Debajyoti Mondal, Anju L, Rajul Choradia, Somen
Department of Periodontology & Oral Implantology, Genesis Institute of Dental Sciences and Research, Ferozepur, Punjab, India
 Original Article Comparison of semilunar coronally advanced flap alone and in combination with button technique in the treatment of Miller s Class I and II gingival recessions: A Pilot Study Ranjit Singh
Original Article Comparison of semilunar coronally advanced flap alone and in combination with button technique in the treatment of Miller s Class I and II gingival recessions: A Pilot Study Ranjit Singh
Surgical Therapy. Tuesday, April 2, 13. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS
 Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Free Gingival Graft as a Single Step Procedure for Treatment of Mandibular Miller Class I and II Recession Defects
 12 Gingival graft in mandibular defect Original Article Free Gingival Graft as a Single Step Procedure for Treatment of Mandibular Miller Class I and II Recession Defects Lata Goyal1*, Narender Dev Gupta2,
12 Gingival graft in mandibular defect Original Article Free Gingival Graft as a Single Step Procedure for Treatment of Mandibular Miller Class I and II Recession Defects Lata Goyal1*, Narender Dev Gupta2,
A Fantastic Aprroach for Multiple Recession Coverage: Vestibular Incision Subperiosteal Tunnel Access Technique (Vista)-A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. I (Feb. 2016), PP 52-56 www.iosrjournals.org A Fantastic Aprroach for Multiple Recession
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. I (Feb. 2016), PP 52-56 www.iosrjournals.org A Fantastic Aprroach for Multiple Recession
Clinical Application of Modified Apically Repositioned Flap in Class III/IV Gingival Recession Cases
 J Harjeet Singh et al SE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1200 linical pplication of Modified pically Repositioned Flap in lass III/IV Gingival Recession ases 1 Harjeet Singh, 2 Manab Kosala, 3 Vivek apurao
J Harjeet Singh et al SE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1200 linical pplication of Modified pically Repositioned Flap in lass III/IV Gingival Recession ases 1 Harjeet Singh, 2 Manab Kosala, 3 Vivek apurao
Prevalence of Gingival recession in Dental college students: A Clinical investigation
 American Journal of Advances in Medical Science www.arnaca.com eissn: 2347-2766 Original Research Article Prevalence of Gingival recession in Dental college students: A Clinical Ninad Moon 1, Prasant Pillai
American Journal of Advances in Medical Science www.arnaca.com eissn: 2347-2766 Original Research Article Prevalence of Gingival recession in Dental college students: A Clinical Ninad Moon 1, Prasant Pillai
AETIOLOGY AND SEVERITY OF GINGIVAL RECESSION AMONG YOUNG INDIVIDUALS IN BELGAUM DISTRICT IN INDIA
 AETIOLOGY AND SEVERITY OF GINGIVAL RECESSION AMONG YOUNG INDIVIDUALS IN BELGAUM DISTRICT IN INDIA V. Dodwad. Aetiology and severity of gingival recession among young individuals in Belgaum district in
AETIOLOGY AND SEVERITY OF GINGIVAL RECESSION AMONG YOUNG INDIVIDUALS IN BELGAUM DISTRICT IN INDIA V. Dodwad. Aetiology and severity of gingival recession among young individuals in Belgaum district in
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery. Dr.maryam khosravi
 Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF GINGIVAL RECESSION WITH SOFT TISSUE GRAFT PROCEDURE
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2018243.2149 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2018 Jul-Sep;24(3) Literature review
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2018243.2149 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2018 Jul-Sep;24(3) Literature review
Esthetic Crown Lengthening
 Esthetic Crown Lengthening Esthetic Crown Lengthening ACCELERATED OSTEOGENIC ORTHODOTNICS (WILKODONTICS) It is a technique developed by Wilko brothers. has roots in orthopedics, back to the early 1900s
Esthetic Crown Lengthening Esthetic Crown Lengthening ACCELERATED OSTEOGENIC ORTHODOTNICS (WILKODONTICS) It is a technique developed by Wilko brothers. has roots in orthopedics, back to the early 1900s
ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12 Accepted on:22/05/12
 SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation: A Case Series Dr. Stephen Saroff, DDS
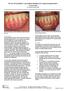 The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation: A Case Series Dr. Stephen Saroff, DDS LOCALIZED RECESSION ON TOOTH #25 DUE TO BONE RECESSION (PRE OP) Introduction Tissue grafting
The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation: A Case Series Dr. Stephen Saroff, DDS LOCALIZED RECESSION ON TOOTH #25 DUE TO BONE RECESSION (PRE OP) Introduction Tissue grafting
Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Contemporary Periodontal Surgery
 Contemporary Periodontal Surgery Chris van Kesteren, D.D.S. CPCC Dental Hygiene Program October 18, 2011 Surgical Management of Periodontitis Periodontal Plastic Surgery Soft tissue and esthetics Dental
Contemporary Periodontal Surgery Chris van Kesteren, D.D.S. CPCC Dental Hygiene Program October 18, 2011 Surgical Management of Periodontitis Periodontal Plastic Surgery Soft tissue and esthetics Dental
Avita Rath, 1 Smrithi Varma, 2 and Renny Paul Case Presentation. 1. Background
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 9289634, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9289634 Case Report Two-Stage Mucogingival Surgery with Free Gingival Autograft and Biomend Membrane and
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 9289634, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9289634 Case Report Two-Stage Mucogingival Surgery with Free Gingival Autograft and Biomend Membrane and
CLINICAL. Free gingival grafts to manage recession when and how? Matthew B M Thomas CLINICAL
 CLINICAL CLINICAL Free gingival grafts to manage recession when and how? Matthew B M Thomas Gingival recession results from displacement of the gingival margin below the cemento-enamel junction leading
CLINICAL CLINICAL Free gingival grafts to manage recession when and how? Matthew B M Thomas Gingival recession results from displacement of the gingival margin below the cemento-enamel junction leading
Michael K. McGuire* and Martha Nunn
 Volume 74 Number 8 Evaluation of Human Recession Defects Treated with Coronally Advanced Flaps and Either Enamel Matrix Derivative or Connective Tissue. Part 1: Comparison of Clinical Parameters Michael
Volume 74 Number 8 Evaluation of Human Recession Defects Treated with Coronally Advanced Flaps and Either Enamel Matrix Derivative or Connective Tissue. Part 1: Comparison of Clinical Parameters Michael
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association
 All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
Treatment of multiple gingival recessions using subepithelial connective tissue grafting with a single-incision technique
 317 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 2, 317-321, 2009 Case Report Treatment of multiple gingival recessions using subepithelial connective tissue grafting with a single-incision technique Jun-Beom
317 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 2, 317-321, 2009 Case Report Treatment of multiple gingival recessions using subepithelial connective tissue grafting with a single-incision technique Jun-Beom
Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report The Vestibular Incision Subperiosteal Tunnel Access (VISTA) for Treatment of Maxillary Anterior Gingival
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report The Vestibular Incision Subperiosteal Tunnel Access (VISTA) for Treatment of Maxillary Anterior Gingival
Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques
 I J Pre Clin Dent Res 2014;1(2):49-53 April-June All rights reserved International Journal of Preventive & Clinical Dental Research Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and
I J Pre Clin Dent Res 2014;1(2):49-53 April-June All rights reserved International Journal of Preventive & Clinical Dental Research Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and
A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran
 Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
Osseous surgery in periodontal treatment
 SCIENTIFIC SESSION Osseous surgery in periodontal treatment Essayist: Roberto Pontoriero Introduction In periodontally involved patients, periodontal therapy usually results in various degrees of soft-tissue
SCIENTIFIC SESSION Osseous surgery in periodontal treatment Essayist: Roberto Pontoriero Introduction In periodontally involved patients, periodontal therapy usually results in various degrees of soft-tissue
A 2-Year Follow-Up of Root Coverage Using Subpedicle Acellular Dermal Matrix Allografts and Subepithelial Connective Tissue Autografts
 J Periodontol August 2005 A 2-Year Follow-Up of Root Coverage Using Subpedicle Acellular Dermal Matrix Allografts and Subepithelial Connective Tissue Autografts A. Hirsch,* M. Goldstein,* J. Goultschin,*
J Periodontol August 2005 A 2-Year Follow-Up of Root Coverage Using Subpedicle Acellular Dermal Matrix Allografts and Subepithelial Connective Tissue Autografts A. Hirsch,* M. Goldstein,* J. Goultschin,*
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Coverage of gingival recession defe Titletissue regeneration with and withou enamel matrix derivative in
 Coverage of gingival recession defe Titletissue regeneration with and withou enamel matrix derivative in a dog m Author(s) Fujita, T; Yamamoto, S; Ota, M; Shi Alternative Yamada, S International journal
Coverage of gingival recession defe Titletissue regeneration with and withou enamel matrix derivative in a dog m Author(s) Fujita, T; Yamamoto, S; Ota, M; Shi Alternative Yamada, S International journal
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniel Gober Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option The Situation A 35 year old male presented in my practice with a
A Case Report by Dr. Daniel Gober Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option The Situation A 35 year old male presented in my practice with a
The Internatonal Journal of Periodontics & Restoraive Dentistry
 The Internatonal Journal of Periodontics & Restoraive Dentistry 3 Incisive Vessel Based Palatal Flap for the Reconstruction of Anterior Maxillary Soft Tissues [Au: Text has been edited heavily. Please
The Internatonal Journal of Periodontics & Restoraive Dentistry 3 Incisive Vessel Based Palatal Flap for the Reconstruction of Anterior Maxillary Soft Tissues [Au: Text has been edited heavily. Please
Periosteal fenestration: A single stage surgical procedure for root coverage along with vestibular deepening
 2017; 3(2): 14-18 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2017; 3(2): 14-18 2017 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 05-02-2017 Accepted: 06-03-2017 Dr. Hoti Lal Gupta MDS, Professor and Head
2017; 3(2): 14-18 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2017; 3(2): 14-18 2017 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 05-02-2017 Accepted: 06-03-2017 Dr. Hoti Lal Gupta MDS, Professor and Head
Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports
 0 Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports R.G. Caffesse, B.A. Smith/ B. Duff, E.C. Morrison, D. Merrill/ and W. Becker In the cases reported here, the response
0 Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports R.G. Caffesse, B.A. Smith/ B. Duff, E.C. Morrison, D. Merrill/ and W. Becker In the cases reported here, the response
Treatment of dental recessions in the esthetic zone by gingival and osseous recontouring. A multidisciplinary perio-prosthodontic case report.
 European International Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 6 No. 5 July 2017 Treatment of dental recessions in the esthetic zone by gingival and osseous recontouring. A multidisciplinary perio-prosthodontic
European International Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 6 No. 5 July 2017 Treatment of dental recessions in the esthetic zone by gingival and osseous recontouring. A multidisciplinary perio-prosthodontic
Double Papillary Flap - A Treatment for Gingival Recession
 World Journal of Medical Sciences 10 (2): 117-121, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.10.2.82175 Double Papillary Flap - A Treatment for Gingival Recession 1 1 1
World Journal of Medical Sciences 10 (2): 117-121, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.10.2.82175 Double Papillary Flap - A Treatment for Gingival Recession 1 1 1
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
GINGIVAL SURGICAL TECHNIQUES
 Gingival Surgical Procedures GINGIVAL SURGICAL TECHNIQUES! limited to the gingival and not involving underlying osseous structures! Gingival Curettage! Gingivectomy! Gingivoplasty! Gingival Flap Gingival
Gingival Surgical Procedures GINGIVAL SURGICAL TECHNIQUES! limited to the gingival and not involving underlying osseous structures! Gingival Curettage! Gingivectomy! Gingivoplasty! Gingival Flap Gingival
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Maintenance. Periodontics & Restorative. Naoshi Sato. A Clinical Atlas
 Naoshi Sato Periodontics & Restorative Maintenance A Clinical Atlas London, Berlin, Chicago, Tokyo, Barcelona, Beijing, Istanbul, Milan, Moscow, New Delhi, Paris, Prague, São Paulo, Seoul and Warsaw Preface
Naoshi Sato Periodontics & Restorative Maintenance A Clinical Atlas London, Berlin, Chicago, Tokyo, Barcelona, Beijing, Istanbul, Milan, Moscow, New Delhi, Paris, Prague, São Paulo, Seoul and Warsaw Preface
CASE REPORT MANAGEMENT OF MILLER S CLASS III GINGIVAL RECESSION USING FREE CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFTS - THE USE OF TWO DIFFERENT TECHNIQUES
 (e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599 Rao J et al. Free connective tissue grafts in Miller s class III defects. (p) ISSN Print: 2348-6805 CASE REPORT MANAGEMENT OF MILLER S CLASS III GINGIVAL RECESSION USING FREE
(e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599 Rao J et al. Free connective tissue grafts in Miller s class III defects. (p) ISSN Print: 2348-6805 CASE REPORT MANAGEMENT OF MILLER S CLASS III GINGIVAL RECESSION USING FREE
Gingival recession causes periodontal
 J Periodontol October 2005 Factors Affecting the Outcomes of Coronally Advanced Flap Root Coverage Procedure Lien-Hui Huang,* Rodrigo E.F. Neiva, and Hom-Lay Wang Background: The coronally advanced flap
J Periodontol October 2005 Factors Affecting the Outcomes of Coronally Advanced Flap Root Coverage Procedure Lien-Hui Huang,* Rodrigo E.F. Neiva, and Hom-Lay Wang Background: The coronally advanced flap
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
FRENECTOMY WITH LATERALLY DISPLACED FLAP: A CASE REPORT
 FRENECTOMY WITH LATERALLY DISPLACED FLAP: A CASE REPORT Dr. Minu.P. Mathew, Dr.R.Saravanakumar, Dr.Pratebha.B, Dr.Jannani.M, ABSTRACT An aberrant Maxillary labial frenum is capable of creating diastema
FRENECTOMY WITH LATERALLY DISPLACED FLAP: A CASE REPORT Dr. Minu.P. Mathew, Dr.R.Saravanakumar, Dr.Pratebha.B, Dr.Jannani.M, ABSTRACT An aberrant Maxillary labial frenum is capable of creating diastema
This document addresses Anthem s clinical policy for mucogingival surgery and soft tissue grafting.
 Clinical Guideline Subject: Mucogingival Surgery and Soft Tissue Grafting Guideline #: 04-204 Current Effective Date: 03/24/2017 Status: New Last Review Date: 07/10/2017 Description This document addresses
Clinical Guideline Subject: Mucogingival Surgery and Soft Tissue Grafting Guideline #: 04-204 Current Effective Date: 03/24/2017 Status: New Last Review Date: 07/10/2017 Description This document addresses
Pouch and tunnel technique: Minimally invasive periodontal plastic surgery for root coverage
 www.edoriumjournals.com case Series OPEN ACCESS Pouch and tunnel technique: Minimally invasive periodontal plastic surgery for root coverage Sangeeta Singh ABSTRACT Introduction: The indications for root
www.edoriumjournals.com case Series OPEN ACCESS Pouch and tunnel technique: Minimally invasive periodontal plastic surgery for root coverage Sangeeta Singh ABSTRACT Introduction: The indications for root
Over the years, mucogingival surgery
 The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation and Root Coverage: A Case Series Saroff Stephen Andrew Saroff, DDS, MSD 1 Abstract Over the years, mucogingival surgery has developed
The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation and Root Coverage: A Case Series Saroff Stephen Andrew Saroff, DDS, MSD 1 Abstract Over the years, mucogingival surgery has developed
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Changes of the Marginal Periodontium as a Result of
 Changes of the Marginal Periodontium as a Result of Labial Tooth Movement in Monkeys G. G. Steiner,* J. K. Pearson,f J. Ainamo^ Tooth position has been suggested to be an important factor in gingival recession.
Changes of the Marginal Periodontium as a Result of Labial Tooth Movement in Monkeys G. G. Steiner,* J. K. Pearson,f J. Ainamo^ Tooth position has been suggested to be an important factor in gingival recession.
Nicholas Caplanis DMD MS 6/13/2012
 Considerations In The Esthetic Zone Nick Caplanis DMD MS Private Practice Periodontics and Implant Surgery Mission Viejo, California Nick@drcaplanis.com Assistant Professor Loma Linda University Anatomic
Considerations In The Esthetic Zone Nick Caplanis DMD MS Private Practice Periodontics and Implant Surgery Mission Viejo, California Nick@drcaplanis.com Assistant Professor Loma Linda University Anatomic
Minimally invasive techniques for periodontal regeneration
 2016; 2(12): 230-234 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2016; 2(12): 230-234 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 04-10-2016 Accepted: 05-11-2016 Dr. Rizwan M Sanadi Professor,
2016; 2(12): 230-234 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2016; 2(12): 230-234 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 04-10-2016 Accepted: 05-11-2016 Dr. Rizwan M Sanadi Professor,
Gingival Unit Graft Versus Free Gingival Graft for Treatment of Gingival Recession: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
 Original Article Gingival Unit Graft Versus Free Gingival Graft for Treatment of Gingival Recession: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Niloofar Jenabian 1, Mohadese Yazdanpanah Bahabadi 2, Ali Bijani
Original Article Gingival Unit Graft Versus Free Gingival Graft for Treatment of Gingival Recession: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Niloofar Jenabian 1, Mohadese Yazdanpanah Bahabadi 2, Ali Bijani
Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the. Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System
 Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System 1 Introduction This presentation familiarizes you with the basic steps how to use the Inion GTR membrane
Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System 1 Introduction This presentation familiarizes you with the basic steps how to use the Inion GTR membrane
Gingival Recession: Short Literature Review on Etiology, Classifications and Various Treatment Options.
 Gingival Recession: Short Literature Review on Etiology, Classifications and Various Treatment Options. Swathi Ravipudi, Devapriya Appukuttan, P.S.G. Prakash, D.J. Victor Savitha Dental College and Hospitals,
Gingival Recession: Short Literature Review on Etiology, Classifications and Various Treatment Options. Swathi Ravipudi, Devapriya Appukuttan, P.S.G. Prakash, D.J. Victor Savitha Dental College and Hospitals,
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of
 Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
The Evaluation of Prevalence, Extension and Severity of Gingival Recession among Rural Nepalese Adults
 Original Article Interdisciplinary The Evaluation of Prevalence, Extension and Severity of Gingival Recession among Rural Nepalese Adults Dr Manoj Humagain, 1 Dr Dashrath Kafle 2 1 Asst Professor, Dept
Original Article Interdisciplinary The Evaluation of Prevalence, Extension and Severity of Gingival Recession among Rural Nepalese Adults Dr Manoj Humagain, 1 Dr Dashrath Kafle 2 1 Asst Professor, Dept
Vertical and/or horizontal alveolar
 CLINICAL Vascularized Connective Tissue Flap for Bone Graft Coverage Alan S. Herford, DDS, MD 1 * Todd C. Cooper, DDS 1 Carlo Maiorana, DDS, MD 2 Marco Cicciù, DDS, PhD 2 Alveolar defects are characterized
CLINICAL Vascularized Connective Tissue Flap for Bone Graft Coverage Alan S. Herford, DDS, MD 1 * Todd C. Cooper, DDS 1 Carlo Maiorana, DDS, MD 2 Marco Cicciù, DDS, PhD 2 Alveolar defects are characterized
Dental Policy. This document addresses Anthem s clinical policy for mucogingival surgery and soft tissue grafting.
 Dental Policy Subject: Mucogingival Surgery and Soft Tissue Grafting Guideline #: 04-204 Publish Date: 03/15/2018 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 02/06/2018 Description This document addresses Anthem
Dental Policy Subject: Mucogingival Surgery and Soft Tissue Grafting Guideline #: 04-204 Publish Date: 03/15/2018 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 02/06/2018 Description This document addresses Anthem
Aesthetic Periodontal Plastic Surgery a Case Report
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT Aesthetic Periodontal Plastic Surgery a Case Report José R. Gonzales, Joachim Klimek, Jörg Meyle A 46-year-old woman presented at the Department of Periodontology, University
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT Aesthetic Periodontal Plastic Surgery a Case Report José R. Gonzales, Joachim Klimek, Jörg Meyle A 46-year-old woman presented at the Department of Periodontology, University
PERIODONTAL/PROSTHETIC REHABILITATION OF DENTAL CARIES AND MUCOGINGIVAL DEFORMITIES USING AN OILY CALCIUM HYDROXID SUSPENSION
 C O N T I N U I N G E D U C A T I O N 3 PERIODONTAL/PROSTHETIC REHABILITATION OF DENTAL CARIES AND MUCOGINGIVAL DEFORMITIES USING AN OILY CALCIUM HYDROXID SUSPENSION Daniel Engler-Hamm, DDS, MSc* Hiroshi
C O N T I N U I N G E D U C A T I O N 3 PERIODONTAL/PROSTHETIC REHABILITATION OF DENTAL CARIES AND MUCOGINGIVAL DEFORMITIES USING AN OILY CALCIUM HYDROXID SUSPENSION Daniel Engler-Hamm, DDS, MSc* Hiroshi
Clinical applications of minimally invasive periodontal plastic surgery
 www.edoriumjournals.com CASE SERIES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Clinical applications of minimally invasive periodontal plastic surgery Sangeeta Singh, Saravanan SP, Devendra Srivastava, Raghvendra MH, A.
www.edoriumjournals.com CASE SERIES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Clinical applications of minimally invasive periodontal plastic surgery Sangeeta Singh, Saravanan SP, Devendra Srivastava, Raghvendra MH, A.
MODIFIED SINGLE ROLL FLAP APPROACH FOR SIMULTANEOUS IMPLANT PLACEMENT AND GINGIVAL AUGMENTATION
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques
 Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques Mohammad Assaf Assistant Professor, Faculty of Dentistry, Al-Quds University, Jerusalem, Palestine. ABSTRACT Correspondence
Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques Mohammad Assaf Assistant Professor, Faculty of Dentistry, Al-Quds University, Jerusalem, Palestine. ABSTRACT Correspondence
Gingivectomy, excision gingival, each quadrant Gingivoplasty, each quadrant
 Dental in Nature Oral Surgery Effective CDT D3410 surgery - anterior D3421 surgery bicuspid (first root) D3425 surgery molar (first root) D3426 D3427 surgery (each additional root) Periradicular surgery
Dental in Nature Oral Surgery Effective CDT D3410 surgery - anterior D3421 surgery bicuspid (first root) D3425 surgery molar (first root) D3426 D3427 surgery (each additional root) Periradicular surgery
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
A New Papilla Preservation Technique for Periodontal Regeneration of Severely Compromised Teeth. Jose A. Moreno Rodríguez and Raúl G.
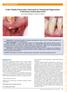 A New Papilla Preservation Technique for Periodontal Regeneration of Severely Compromised Teeth Jose A. Moreno Rodríguez and Raúl G. Caffesse Introduction: Periodontal regeneration of hopeless teeth represents
A New Papilla Preservation Technique for Periodontal Regeneration of Severely Compromised Teeth Jose A. Moreno Rodríguez and Raúl G. Caffesse Introduction: Periodontal regeneration of hopeless teeth represents
Dental Research Journal
 Dental Research Journal Case Report Treatment strategy for guided tissue regeneration in various class II furcation defect: Case series Pushpendra Kumar Verma 1, Ruchi Srivastava 1, K. K. Gupta 2, T. P.
Dental Research Journal Case Report Treatment strategy for guided tissue regeneration in various class II furcation defect: Case series Pushpendra Kumar Verma 1, Ruchi Srivastava 1, K. K. Gupta 2, T. P.
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
THE PREVALENCE OF GINGIVAL RECESSIONS IN A GROUP OF STUDENTS IN CLUJ-NAPOCA Daniela Condor 1, H. Colo[i 2, Alexandra Roman 3
 Periodontology THE PREVALENCE OF GINGIVAL RECESSIONS IN A GROUP OF STUDENTS IN CLUJ-NAPOCA Daniela Condor 1, H. Colo[i 2, Alexandra Roman 3 1 Assistant Professor, the Department of Periodontology, the
Periodontology THE PREVALENCE OF GINGIVAL RECESSIONS IN A GROUP OF STUDENTS IN CLUJ-NAPOCA Daniela Condor 1, H. Colo[i 2, Alexandra Roman 3 1 Assistant Professor, the Department of Periodontology, the
W J C C. World Journal of Clinical Cases. Gingival unit transfer using in the Miller Ⅲ recession defect treatment. Abstract INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 W J C C World Journal of Clinical Cases Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v3.i2.199 World J Clin Cases 2015 February
W J C C World Journal of Clinical Cases Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v3.i2.199 World J Clin Cases 2015 February
Biologic width: Understanding and its preservation Malathi K 1, Singh A 2
 Biologic width: Understanding and its preservation Malathi K 1, Singh A 2 Review Article 1 Dr K Malathi Professor & Head, Periodontics Government Dental college and Hospital Tamil Nadu, India 2 Dr Arjun
Biologic width: Understanding and its preservation Malathi K 1, Singh A 2 Review Article 1 Dr K Malathi Professor & Head, Periodontics Government Dental college and Hospital Tamil Nadu, India 2 Dr Arjun
Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants
 Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Findings and Conclusions: Clinical parameters mean at baseline at post-surgery were:
 Barros R, Novaes AB, Grisi M, et al. A 6 month comparative clinical study of a conventional and a new surgical approach for root coverage with acellular dermal matrix. J Periodontol 2004;75:1350-56. (29
Barros R, Novaes AB, Grisi M, et al. A 6 month comparative clinical study of a conventional and a new surgical approach for root coverage with acellular dermal matrix. J Periodontol 2004;75:1350-56. (29
Treatment of Altered Passive Eruption: Periodontal Plastic Surgery of the Dentogingival Junction
 CASE REPORT Publication Treatment of Altered Passive Eruption: Periodontal Plastic Surgery of the Dentogingival Junction Roberto Rossi, DDS, MScD Private Practice Genoa, Italy Remo Benedetti, MD, DDS Private
CASE REPORT Publication Treatment of Altered Passive Eruption: Periodontal Plastic Surgery of the Dentogingival Junction Roberto Rossi, DDS, MScD Private Practice Genoa, Italy Remo Benedetti, MD, DDS Private
