Comparison of Dimensional Accuracy of Four Different Die Materials before and after Disinfection of the Impression: An in vitro Study
|
|
|
- Jonas Grant
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 /jp-journals Yamini Nandini et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Comparison of Dimensional Accuracy of Four Different Die Materials before and after Disinfection of the Impression: An in vitro Study Yamini Nandini, KB Vinitha, Supriya Manvi, M Smitha ABSTRACT Background: This study was conducted to compare the linear dimensional accuracy of die materials before and after disinfection of the impression. Type IV and V conventional dental stone, type IV-resin impregnated and copper-plated die materials were studied. Materials and methods: A stainless-steel master die analogs to a complete veneer crown preparation with three scribed lines (I: vertical, II and III: horizontal) was machined and measurements were made from these scribed reference lines. Impressions were made with monophase addition silicone impression material for each of the specimens. 2% glutaraldehyde was used as a disinfectant. The fabricated dies were measured to the nearest mm. ANOVA and post hoc was carried out using Scheffe multiple comparison test at significance level of Results: Type IV resin-impregnated dental stone and copperplated dies approximated the dimensions of the master die. Type IV and V conventional dental stone dies showed greater variation in measurements. Statistically significant differences were observed for type IV resin-impregnated and copper-plated dies in dimension I and III. For dimension II no significant differences were found for dies fabricated from four die materials. A one-way analysis of variance indicated no statistical significant differences among the two groups of dies fabricated from disinfectant treated impressions and those fabricated from nondisinfectant treated impressions. Conclusion: Type IV resin-impregnated dental stone and copper-plated dies are dimensionally more accurate than type IV and V conventional dental stone die materials. No significant linear distortion in the dies fabricated from the disinfected impressions was observed. Keywords: Die materials, Dimensional accuracy, Disinfection. How to cite this article: Nandini Y, Vinitha KB, Manvi S, Smitha M. Comparison of Dimensional Accuracy of Four Different Die Materials before and after Disinfection of the Impression: An in vitro Study. J Contemp Dent Pract 2013;14(4): Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None declared INTRODUCTION The accurate duplication of prepared teeth is essential for the fabrication of fixed prosthesis. 1 The fit and ultimate clinical success of cast dental restorations depends upon the accuracy, completeness of die reproduction and durability of the resultant die, which is subject to possible deformation during the process of fabrication used to construct a cast restoration. 2 Improved dental stones are used for producing dies for the fabrication of restorations due to the perceived dimensional accuracy, low cost and ease of use. But they have less than ideal abrasion resistance, strength and detail reproduction. These properties render a die susceptible to dimensional change during laboratory procedures. Alternative die materials such as copper-plated and resin-impregnated gypsum have been shown to possess superior abrasion resistance, strength and detail reproduction. Some investigators have found electroplated dies to be more dimensionally accurate than stone dies while others have demonstrated otherwise. 3 The awareness of infectious diseases and the recognition of the potential for transmission of infection during dental procedures have increased concern and attention to infection control in dental practice. 4 Disinfection provides a method of preventing the transmission of these microorganisms from the patient to dental personnel who handle the impression or stone cast. 5 It is conceived that chemical solutions may adversely affect detail reproduction or dimensional stability of the impression material. 6 Hence, this study was undertaken to compare the linear dimensional accuracy of four different die materials including type IV, type IV-resin impregnated, type V and copper-plated die materials before and after disinfection of the impression. 668
2 JCDP Comparison of Dimensional Accuracy of Four Different Die Materials before and after Disinfection of the Impression MATERIALS AND METHODS A stainless steel master die analogs to a complete veneer crown preparation was machined to the specifications originally described by Bailey et al 7 with a vertical dimension of 12 mm from the cavosurface line angle to the occlusoaxial line angle, diameter of 13 mm at the cavosurface line angle with convergence angle of 5 providing a diameter of 9 mm at the occlusal end of the die and the shoulder width of 1.5 mm wide. Two mutually perpendicular lines intersecting at the center of the occlusal surface were scribed. With the intersection of these two scribed lines as its center, a 3.5 mm circle was scribed. On the occlusal surface, the four points at which the circle intersected the scribed lines were used to record dimensions by measuring the distance between the two points along each scribed line. Two lines each in a plane perpendicular to the long axis of the die were scribed circumferentially onto the surface of the axial wall of the die, one line located 1mm gingivally from the occlusoaxial line angle and other 1mm occlusally from the axiogingival line angle. Another line was scribed along the vertical axis of the die. The measurement between the circumferential lines at the vertical axis line (Point A-Point B) was referred to as dimension I. The occlusal line intersecting the vertical axis line (Point C-Point D) was referred to as dimension II. The occlusal line perpendicular to dimension II (Point E-Point F) was referred to as dimension III (Figs 1A to C). Two millimeters of relief was provided over the master die for the impression material and a stainless steel tray was made over the die to make the impressions. Alignment guide and stop were made on the tray and die for proper positioning of the tray on the die (Fig. 2). A total of 128 impressions were made with monophase addition silicone impression material with adhesive retention used within the tray. The impressions were allowed to set as per the manufacturer s recommended time (Fig. 3). Those impressions which were to be disinfected were immersed in 2% glutaraldehyde for 30 minutes. Fig. 2: Machined stainless steel master die analogs to a complete veneer crown preparation Fabrication of Dies Fig. 3: Impression of the die Thirty two dies were made from each of the three gypsum based die materials: type IV and V conventional dental stone and type IV resin-impregnated dental stone. The die materials were proportioned and hand mixed following the manufacturer s recommended water: powder ratio (Table 1). The stone was vibrated into the impression and allowed to set for 1 hour at room temperature, following which the dies were recovered from the impressions for measurement. Another set of 32 electroplated dies were fabricated using copper plating apparatus. The composition of the copper plating solution consisted of copper sulfate (crystals) 200 mg, sulfuric acid 30 ml, phenolsulfonic acid 2 ml and distilled water 1000 ml. 8 A B C Figs 1A to C: Diagrammatic representations of the master die with its dimensions: (A) Lateral view, (B) End-on view and (C) 3- dimensional view Table 1: Die materials tested and mixing proportions Product Type Manufacturer H 2 O/ claimed powder expansion (in %) ratio Kalrock Type IV 0.10% 23 cc/100 gm Hard rock Type V 0.25% 21 ml/100 gm Resin rock Type IV resin-impregnated 0.14% 20 ml/100 gm The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice, July-August 2013;14(4):
3 Yamini Nandini et al The impression surfaces were made conductive by the application of a thin layer of silver paste using a fine bristle brush and allowed to dry. A copper wire was connected to the impression was then connected to the negative terminal of the power source. The impression was placed in the electroplating solution. The platinum anode was connected to the positive terminal of the power source. Current was set at 15 ma for 1 hour and then increased to 45 ma for next 12 hours. All impressions were electroplated individually. Following electroplating, the impressions were rinsed with water, dried and poured up with die stone (Fig. 4). The die stone was allowed to set for 1 hour, following which the dies were recovered from the impressions for measurement. Grouping of Dies A total of 128 dies were fabricated. They were divided in to 8 groups, each consisting of 16 dies as follows: Group A: Type IV conventional dental stone dies fabricated from nondisinfectant treated impressions. Group B: Type IV resin-impregnated dies fabricated from nondisinfectant treated impressions. Group C: Type V conventional dental stone dies fabricated from nondisinfectant treated impressions. Group D: Copper-plated dies fabricated from nondisinfectant treated impressions. Group 1: Type IV conventional dental stone dies fabricated from disinfectant treated impressions. Group 2: Type IV resin-impregnated dies fabricated from disinfectant treated impressions. Group 3: Type V conventional dental stone dies fabricated from disinfectant treated impressions. Group 4: Copper-plated dies fabricated from disinfectant treated impressions. Evaluation of Dimensional Accuracy Dimensional accuracy was evaluated by measuring dimension I, II and III in all the dies. The master die measurements was arrived at from mean of four measurements taken for each of the three dimensions to the nearest mm, at the original magnification of 50 using video vision measuring microscope (Fig. 5). All the 128 dies were measured in the same manner as the master die. The 3 measured dimensions were averaged and compared with the measurements of dimensions on the metal master die. STATISTICAL ANALYSIS Statistical analysis (ANOVA) was performed to determine the significance between the dimensions and types of materials. The difference in mean dimensional change along with the types of material was evaluated using one-way analysis of variance and post hoc test was conducted using Scheffe multiple comparison test. p-value 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. Comparison of mean values between the two groups of dies fabricated from disinfectant treated impressions and those fabricated from nondisinfectant treated impressions was conducted using one-way ANOVA. RESULTS The master die measurements, mean values and standard deviation for all dimensions for each of the die material are presented in the Table 2 (dies fabricated from nondisinfectant treated impressions) and Table 5 (dies fabricated from disinfectant treated impressions). The dimensional differences (in percentage) from the master die for each material are shown in Tables 3 and 6. Type IV resinimpregnated and copper-plated dies most closely approximated the dimensions of the master die. Type IV and V conventional dental stone dies recorded the greatest variation in dimensions. Tables 4 and 7 shows the results Fig. 4: Copper plated impression Fig. 5: Video vision measuring microscope and the observed microscopic image at Point A of the die 670
4 JCDP Comparison of Dimensional Accuracy of Four Different Die Materials before and after Disinfection of the Impression Table 2: Master die measurements, mean values and standard deviation for dies fabricated from nondisinfectant treated impressions Die Dimension I Dimension II Dimension III AB SD CD SD EF SD Master die Group A: Type IV (Kalrock) Group B: Type IV resin impregnated (Resin rock) Group C: Type V (Hard rock) Group D: Copper-plated die Measurements in millimeters Table 3: Dimensional differences from master die in percent Material Dimension I change Dimension II change Dimension III change Group A: Type IV (Kalrock) dies % % % Group B: Type IV resin impregnated (Resin rock) dies % % % Group C: Type V (Hard rock) dies % % % Group D: Copper-plated dies % % % Table 4: Results of statistical analysis Variable Difference Mean dimensional change (Dimension I) RI, CP < Type V, Type IV Mean dimensional change (Dimension II) No statistical significance Mean dimensional change (Dimension III) RI, CP < Type V, Type IV < denotes statistically significant difference (Results of Scheffe post hoc test with significance level 0.05) Table 5: Master die measurements, mean values and standard deviation for dies fabricated from disinfectant treated impressions Die Dimension I Dimension II Dimension III AB SD CD SD EF SD Master die Group 1: Type IV (Kalrock) Group 2: Type IV resin impregnated (Resin rock) Group 3: Type V (Hard rock) Group 4: Copper-plated die Table 6: Dimensional differences from master die in percent Material Dimension I change Dimension II change Dimension III change Group 1: Type IV (Kalrock) dies % % % Group 2: Type IV resin impregnated (Resin rock) dies % % % Group 3: Type V (Hard rock) dies % % % Group 4: Copper-plated dies % % % of the statistical analysis (Scheffe post hoc test with significance level 0.05). Statistical differences were observed for type IV resin-impregnated and copper-plated dies in dimension I and III, compared to type IV and V conventional dental stone dies fabricated from disinfectant treated and nondisinfectant treated impressions. For dimension II no significant differences were found for dies fabricated from four die materials. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) indicated no significant differences among the two groups of dies fabricated from disinfectant treated impressions and those fabricated from nondisinfectant treated impressions (Table 8). DISCUSSION The dimensional accuracy of the die material is important for accurate final restoration. The different die materials available for the fabrication of dies in fixed prosthodontics include the type IV and V conventional dental stone, type IV resin-impregnated dental stone, epoxy resin and electroplated dies. Toreskog et al tested eight different classes of die materials and concluded that no material was superior. 9 Newman and Williams also concluded that an ideal universal die material is yet to be produced. 10 Gypsum die materials have been reported to exhibit a setting expansion of 0.01 to 0.1%. This minimal expansion The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice, July-August 2013;14(4):
5 Yamini Nandini et al Variable Mean dimensional change (Dimension I) Mean dimensional change (Dimension II) Mean dimensional change (Dimension III) Table 7: Results of statistical analysis Difference < denotes statistically significant difference (Results of Scheffe Post hoc test with significance level 0.05). RI, CP < Type V,Type IV No statistical significance RI, CP < Type V,Type IV Table 8: Comparison of mean values among the two groups dies fabricated from disinfectant treated (DT) impressions and from nondisinfectant treated (NDT) impressions Dimension I Dimension II Dimension III Type IV Kalrock dies Group 1 Group A Group 1 Group A Group 1 Group A Mean SD F p-value Type IV Resin rock dies Group 2 Group B Group 2 Group B Group 2 Group B Mean SD F p-value Type V Hard rock dies Group 3 Group C Group 3 Group C Group 3 Group C Mean SD F p-value Copper-plated dies Group 4 Group D Group 4 Group D Group 4 Group D Mean SD F p-value Any p-value 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant has been said to compensate for the dimensional changes inherent in the fabrication process of an indirect restoration. There are several disadvantages to its use in the fabrication of dies due to its poor abrasion resistance, potential variability in fine detail reproduction and inadequate tensile strength which are necessary for the production of certain restorations such as all porcelain margins, long and narrow preparations. 11 The use of resin die materials which contains incorporation of hydrocarbon-based polymers as a noncovalent composite (nonbonding) filler to reduce the brittle nature of gypsum die material 12 and resin coatings on gypsum dies has been investigated. In another study, the linear dimensional change, detail reproduction, surface hardness, abrasion resistance and transverse strength of resin-modified gypsum die materials (Resin rock and Mile stone), epoxy resin die material (Epoxy-die) and 2 conventional type IV gypsum die materials (Silky rock and Die-Stone) were evaluated. All gypsum products expanded, whereas the epoxy resin material contracted during setting. The resin modified gypsum products were not significantly superior to the conventional type IV gypsum die materials Cassimatey found electroplated dies to be more dimensionally accurate than stone dies. 14 Bailey et al showed that improved dental stone dies had the greatest variation in measurements of the 3 die systems examined, epoxy resin dies were next and silver plated dies showed the least variation. 7 In this study the type IV resin-impregnated and copperplated dies most closely approximated the master die with respect to the three-dimensions measured. In previous studies statistical differences were observed for type IV resin-impregnated and copper-plated dies in dimension I only compared to the other five die materials. In our study statistical differences were observed for type IV resinimpregnated and copper-plated dies in dimension I and III compared to type IV and V conventional dental stone dies. No significant differences were found for dies fabricated from nondisinfectant treated impressions along dimension II. The fit and ultimate clinical success of a cast dental restoration depends on an accurate, strong, abrasion resistant die material with good detail reproduction. The use of dimensionally accurate materials such as type IV resin-
6 JCDP Comparison of Dimensional Accuracy of Four Different Die Materials before and after Disinfection of the Impression impregnated and copper-plated dies should result in the development of a crown margin that lies in more intimate contact with the finish line of the tooth preparation, given that the dimensional changes of the wax pattern, alloy and investment are carefully matched. 3 Type IV and V gypsum dies recorded the greatest variation in dimensions than the other die materials examined. The minimal setting expansion of conventional type IV and V dental stone should result in the fabrication of satisfactory crown margins and provide enough space between the casting and the tooth to allow complete seating without binding and space for a film of cement. 3 The poor strength and abrasion resistance of conventional type IV and V dental stone become more significant in complex fixed prosthodontics, when transfer copings are necessary or when fabricating all porcelain margins. Of the tested materials, type IV resin-impregnated and copper-plated dies are recommended for these cases because of their strength, abrasion resistance and dimensional accuracy. If maximum strength and abrasion resistance are required, copper-plated dies could be used. If less abrasion resistance is needed or ease of construction is essential, type IV resin-impregnated dies is recommended. Though copper-plated dies are considered to be dimensionally accurate convenience is not one of the positive characteristics of the copper electroplating technique. It involves special equipment, materials and more number of steps requiring 10 to 15 hours until it is ready for use and is incompatible with many impression materials. In addition, the fabrication of copper-plated dies can be more technique sensitive compared with other die materials. The impression surfaces must be delicately coated with a thin layer of silver paste to achieve an accurate, smooth, even layer of plated metal with good detail. The sectioning and trimming of copper plated dies must be performed carefully to avoid damaging the margin or adjacent proximal contacts. 3 The prevalence of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and other infectious diseases in blood and other body fluids has influenced the necessity for personal protection and the prevention of disease transmission. Dental impressions contact saliva and blood, immersion disinfection is used as a method of preventing microorganism transmission from the patient to dental personnel. Several studies have reported that elastomeric impressions disinfected by immersion exhibited no detrimental, clinically significant results relative to the accuracy of the impression or subsequent stone cast. 15 Toh et al found that polyvinyl siloxane exhibited dimensional changes after a 30-minute immersion in iodophor or glutaraldehyde, whereas Merchant et al noted no change. 6 In this study comparison of dimensional accuracy of four different die materials fabricated from impressions which were disinfected was done. The type IV resinimpregnated and copper-plated dies most closely approximated the master die with respect to the three dimensions measured. Statistical differences were observed for type IV resin-impregnated and copper-plated dies in dimension I and III compared to type IV and V conventional dental stone dies. For dimension II no significant differences was found for dies fabricated from disinfectant treated impressions. Greater magnitude dimensional differences from the master die was observed for type IV and V conventional dental stone dies fabricated from disinfected treated impressions. CONCLUSION Type IV resin-impregnated dental stone and copper-plated dies fabricated from both disinfectant treated and nondisinfectant treated impressions was more dimensionally accurate than the other die materials examined. Type IV and V conventional dental stone dies fabricated from both disinfectant treated and nondisinfectant treated impressions had the greater variation in measurements of the four die materials examined. No statistically significant differences were found in the accuracy among the two groups of dies fabricated from both disinfectant treated and nondisinfectant treated impressions. This study shows that immersion disinfection of the rubber impression materials does not cause distortion of the impression that would therefore result in an unacceptable die. It provides research support for the ADA recommendation that rubber impressions be disinfected by immersion in glutaraldehyde. REFERENCES 1. Bloem TJ, Czerniawski B, Luke J, Lang BR. Determination of the accuracy of three die systems. J Prosthet Dent 1991;65: James Ragain C, Mark Groskko L, Raj M, Thomas Ryan N, William Johnston M. Detail reproduction, contact angles and die hardness of elastomeric impression and gypsum die material combinations. Int J Prosthodont 2000;13: Kenyon BJ, Hagge MS, Leknius C, Daniels WC, Weed ST. Dimensional accuracy of 7 die materials. J Prosthet Dent 2005;14: Peter Owen C, Goolam R. Disinfection of impression materials to prevent viral cross contamination: a review and a protocol. Int J Prosthodont 1993;6: Drennon DG, Johnson GH, Lynn Powell G. The accuracy and efficacy of disinfection by spray atomization on elastomeric impressions. J Prosthet Dent 1989;62: Toh CG, Setcos JC, Palenik CJ, Williams KJ, Phillips RW. Influence of disinfectants on polyvinylsiloxane impression material. J Dent Res 1987;66:133. The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice, July-August 2013;14(4):
7 Yamini Nandini et al 7. Bailey JH, Donovan TE, Preston. The dimensional accuracy of improved dental stone, silver plated and epoxy resin die materials. J Prosthet Dent 1988;59: Craig RG. Impression materials. In: Restorative dental materials. 10th ed. Mosby 1997; Toreskog S, Phillips RW, Schnell RJ. Properties of die materials: a comparative study. J Prosthet Dent 1966;16: Newman A, Williams JD. Die materials for inlay, crown and bridge work. Br Dent J 1969;115: Chaffee NR, Bailey JH, Sherrard DJ. Dimensional accuracy of improved dental stone and epoxy resin die materials. Part I: single die. J Prosthet Dent 1997;77: Stackhouse JA. Impression materials and electrodeposits. Part I: Impression materials. J Prosthet Dent 1981;45: Duke P, Moore K, Haug SP, Carl J. Andres. Study of the physical properties of type IV gypsum, resin-containing, and epoxy die materials. J Prosthet Dent 2000;83: Cassimaty EM, Walton TR. Effect of three variables on the accuracy and variability of electroplated copper dies. Int J Prosthodont 1996;9: Drennon DG, Johnson GH. The effect of immersion disinfection of elastomeric impressions on the surface detail reproduction of improved gypsum casts. J Prosthet Dent 1990; 63: ABOUT THE AUTHORS Yamini Nandini Reader, Department of Prosthodontics, KLE Society s Institute of Dental Sciences, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India Correspondence Address: KLE Society s Institute of Dental Sciences No. 20, Yeshwanthpur Suburb, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India Phone: , dryamini_nandini07@yahoo.co.in KB Vinitha Reader, Department of Prosthodontics, Vydehi Institute of Dental Sciences, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India Supriya Manvi Professor, Department of Prosthodontics, KLE Society s Institute of Dental Sciences, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India M Smitha Professor, Department of Prosthodontics, NSVK Sri Venkateshwara Dental College and Hospital, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India 674
Acknowledgments Introduction p. 1 Objectives p. 1 Goals p. 2 History of Dental Materials p. 3 The Oral Environment p. 4 Characteristics of the Ideal
 Preface p. v Acknowledgments p. vii Introduction p. 1 Objectives p. 1 Goals p. 2 History of Dental Materials p. 3 The Oral Environment p. 4 Characteristics of the Ideal Dental Material p. 5 Quality Assurance
Preface p. v Acknowledgments p. vii Introduction p. 1 Objectives p. 1 Goals p. 2 History of Dental Materials p. 3 The Oral Environment p. 4 Characteristics of the Ideal Dental Material p. 5 Quality Assurance
Double-casting method for fixed prosthodontics with functionally generated path
 Double-casting method for fixed prosthodontics with functionally generated path Shogo Minagi, DDS, PhD, a Toshiyuki Tanaka, DDS, b Takashi Sato, DDS, PhD, c and Tadashi Matsunaga, DDS, PhD d Department
Double-casting method for fixed prosthodontics with functionally generated path Shogo Minagi, DDS, PhD, a Toshiyuki Tanaka, DDS, b Takashi Sato, DDS, PhD, c and Tadashi Matsunaga, DDS, PhD d Department
An in vitro study to evaluate the effect on dimensional changes of elastomers during cold sterilization
 Original Article An in vitro study to evaluate the effect on dimensional changes of elastomers during cold sterilization Poonam K. Khinnavar, B. H. Dhanya Kumar, D. B. Nandeeshwar Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article An in vitro study to evaluate the effect on dimensional changes of elastomers during cold sterilization Poonam K. Khinnavar, B. H. Dhanya Kumar, D. B. Nandeeshwar Department of Prosthodontics,
Al-Qarni AA. Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from
 IJopRD IJOPRD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from Different 10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1155 Elastomer Impression Techniques Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from Different
IJopRD IJOPRD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from Different 10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1155 Elastomer Impression Techniques Dimensional Accuracy of Multiple Pour Cast from Different
Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect and Dimensional Stability of Self-disinfecting Irreversible Hydrocolloid: An in vitro Study
 JCDP Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect and Dimensional Stability of Self-disinfecting 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2144 Irreversible Hydrocolloid ORIGINAL RESEARCH Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect and
JCDP Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect and Dimensional Stability of Self-disinfecting 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2144 Irreversible Hydrocolloid ORIGINAL RESEARCH Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect and
Evaluating the Effect of a Sloping Shoulder and a Shoulder Bevel on the Marginal Integrity of Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) Veneer Crowns
 Evaluating the Effect of a Sloping Shoulder and a Shoulder Bevel on the Marginal Integrity of Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) Veneer Crowns Abstract Aim: A porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) veneer crown restoration
Evaluating the Effect of a Sloping Shoulder and a Shoulder Bevel on the Marginal Integrity of Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) Veneer Crowns Abstract Aim: A porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) veneer crown restoration
CASE REPORT ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION. AIMS AND OBJECTIVES Aims
 An in vitro Study to Compare the Accuracy of Master Cast Fabricated by Three Different 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1143 Transfer Techniques for Single Tooth CASE REPORT An in vitro Study to Compare the Accuracy
An in vitro Study to Compare the Accuracy of Master Cast Fabricated by Three Different 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1143 Transfer Techniques for Single Tooth CASE REPORT An in vitro Study to Compare the Accuracy
FR Attachment Instructions Removable Partial Dentures
 www.preat.com 800-232-7732 FR Attachment Instructions Removable Partial Dentures 1 2 Adjust the master cast on mounting platform of the surveyor to the chosen angle of insertion. Check to be sure the tooth
www.preat.com 800-232-7732 FR Attachment Instructions Removable Partial Dentures 1 2 Adjust the master cast on mounting platform of the surveyor to the chosen angle of insertion. Check to be sure the tooth
Evaluation of the Effect of Temperature Changes on the Dimensional Stability of poly (Vinyl Siloxane) Impression Material.
 IOR Journal of Dental and Medical ciences (IOR-JDM e-in: 2279-0853, p-in: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. VIII (Dec. 2017, PP 10-15 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of the Effect of Temperature Changes
IOR Journal of Dental and Medical ciences (IOR-JDM e-in: 2279-0853, p-in: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. VIII (Dec. 2017, PP 10-15 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of the Effect of Temperature Changes
The full veneer crown is one of the most important
 CLASSIC ARTICLE The effect of various finish line preparations on the marginal seal and occlusal seat of full crown preparations J. R. Gavelis, DMD, a J. D. Morency, DMD, b E. D. Riley, DMD, c and R. B.
CLASSIC ARTICLE The effect of various finish line preparations on the marginal seal and occlusal seat of full crown preparations J. R. Gavelis, DMD, a J. D. Morency, DMD, b E. D. Riley, DMD, c and R. B.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE DENTIST. synocta impression procedure, Screw-retained and Snap-on. Screw-retained (Open tray) Snap-on (Closed tray)
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE DENTIST synocta impression procedure, Screw-retained and Snap-on Screw-retained (Open tray) Snap-on (Closed tray) click 1. Attach synocta Impression caps to implants. Hand-tighten
INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE DENTIST synocta impression procedure, Screw-retained and Snap-on Screw-retained (Open tray) Snap-on (Closed tray) click 1. Attach synocta Impression caps to implants. Hand-tighten
Removable Partial Dentures
 Removable Partial Dentures Replacement of missing teeth Fixed partial denture Removable partial denture Complete removable Transitional denture Partial removable Implant retained prosthodontics No prosthetic
Removable Partial Dentures Replacement of missing teeth Fixed partial denture Removable partial denture Complete removable Transitional denture Partial removable Implant retained prosthodontics No prosthetic
Dowel restorations Treatment with a post and core
 Dowel restorations Treatment with a post and core A post and core is a dental restoration used to sufficiently buildup tooth structure for future restoration with a crown when there is not enough tooth
Dowel restorations Treatment with a post and core A post and core is a dental restoration used to sufficiently buildup tooth structure for future restoration with a crown when there is not enough tooth
Rahul Nagrath Manesh Lahori Manjari Agrawal
 J Indian Prosthodont Soc (December 2014) 14(Suppl. 1):S59 S66 DOI 10.1007/s13191-014-0365-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Comparative Evaluation of Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Detail Reproduction of Four Hydrophilic
J Indian Prosthodont Soc (December 2014) 14(Suppl. 1):S59 S66 DOI 10.1007/s13191-014-0365-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Comparative Evaluation of Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Detail Reproduction of Four Hydrophilic
أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل CROWN AND BRIDGE جامعة تكريت كلية. Lec. (2) طب االسنان
 Lec. (2) CROWN AND BRIDGE أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل Patient selection and examination A thorough diagnosis must first be made of the patient's dental condition, considering both hard and soft tissues. this
Lec. (2) CROWN AND BRIDGE أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل Patient selection and examination A thorough diagnosis must first be made of the patient's dental condition, considering both hard and soft tissues. this
synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions
 synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions INTRODUCTION synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations 1 The synocta Meso abutments, available
synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions INTRODUCTION synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations 1 The synocta Meso abutments, available
Hex-Lock Abutment System. Restorative Manual
 System Restorative Manual 32 Restorative options with s s are manufactured from titanium alloy and used as the support foundation for single- or multiple-unit cement-retained, partially edentulous fixed
System Restorative Manual 32 Restorative options with s s are manufactured from titanium alloy and used as the support foundation for single- or multiple-unit cement-retained, partially edentulous fixed
Shadeguides Ceramic Veneers: Tooth Preparation for Enamel Preservation
 Ajay Juneja Shadeguides Ceramic Veneers: Tooth Preparation for Enamel Preservation 1 Feb 2016 The rationale of having minimal preparation and having ceramic veneers cemented to enamel in order for the
Ajay Juneja Shadeguides Ceramic Veneers: Tooth Preparation for Enamel Preservation 1 Feb 2016 The rationale of having minimal preparation and having ceramic veneers cemented to enamel in order for the
US Implant System 2013 PROSTHETIC PROCEDURE
 US Implant System 2013 PROSTHETIC PROCEDURE Contents TS Implant System Cement retained restoration 06 Cement retained bridges with the Cement abutment system 18 Cement retained crown with the Angled abutment
US Implant System 2013 PROSTHETIC PROCEDURE Contents TS Implant System Cement retained restoration 06 Cement retained bridges with the Cement abutment system 18 Cement retained crown with the Angled abutment
CROWN AND BRIDGE RESTORATIONS WITH THE SYNOCTA PROSTHETIC SYSTEM
 CROWN AND BRIDGE RESTORATIONS WITH THE SYNOCTA PROSTHETIC SYSTEM Straumann is the industrial partner of the ITI (International Team for Implantology) in the areas of research, development, and education.
CROWN AND BRIDGE RESTORATIONS WITH THE SYNOCTA PROSTHETIC SYSTEM Straumann is the industrial partner of the ITI (International Team for Implantology) in the areas of research, development, and education.
Department of Prosthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand
 Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Dimensional stability of compression and injection molding denture bases in long and short curing procedures Noppavan Nagaviroj, Krantarat Wanitchanont,
Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Dimensional stability of compression and injection molding denture bases in long and short curing procedures Noppavan Nagaviroj, Krantarat Wanitchanont,
cement-retained single crowns using cementable abutments
 cement-retained single crowns using cementable abutments cement-retained restorations cement-retained single crowns using cementable abutments Cement-retained implant restorations are similar to conventional
cement-retained single crowns using cementable abutments cement-retained restorations cement-retained single crowns using cementable abutments Cement-retained implant restorations are similar to conventional
Construction of Removable Partial Denture
 Construction of Removable Partial Denture Peter Hermann Department of Prosthodontics Semmelweis University Treatment options for edentulous spaces Fixed prosthodontics (crowns/bridges) Removable prosthodontics
Construction of Removable Partial Denture Peter Hermann Department of Prosthodontics Semmelweis University Treatment options for edentulous spaces Fixed prosthodontics (crowns/bridges) Removable prosthodontics
CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: ABSTRACT
 EVALUATION OF EFFECTS OF PORCELAIN FIRING ON THE MARGINAL FIT CHANGES OF PORCELAIN-FUSED-TO -METAL CROWN FABRICATED UTILIZING TWO DIFFERENT MARGIN DESIGNS AND TWO COMMERCIALLY AVAILABLE BASE METAL ALLOYS
EVALUATION OF EFFECTS OF PORCELAIN FIRING ON THE MARGINAL FIT CHANGES OF PORCELAIN-FUSED-TO -METAL CROWN FABRICATED UTILIZING TWO DIFFERENT MARGIN DESIGNS AND TWO COMMERCIALLY AVAILABLE BASE METAL ALLOYS
B U J O D. Invited Review IMPLANT IMPRESSIONS SIMPLIFIED. Reddy et al. Vol. 2 Issue-3 Sept
 Invited Review IMPLANT IMPRESSIONS SIMPLIFIED AUTHORS: Vahini Reddy*, Venkateswara Allu Reddy**, Sadhvi K.V*** Introduction It is said that you never get a second chance to make a first impression but
Invited Review IMPLANT IMPRESSIONS SIMPLIFIED AUTHORS: Vahini Reddy*, Venkateswara Allu Reddy**, Sadhvi K.V*** Introduction It is said that you never get a second chance to make a first impression but
Comparison between Acetal Resin and Cobalt-Chromium. Removable Partial Denture Clasp Retention: An in vitro Study.
 10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1076 Tarek ORIGINAL Mohamed RESEARCH et al Comparison between Acetal Resin and Cobalt-Chromium Removable Partial Denture Clasp Retention: An in vitro Study Tarek Mohamed, Osama
10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1076 Tarek ORIGINAL Mohamed RESEARCH et al Comparison between Acetal Resin and Cobalt-Chromium Removable Partial Denture Clasp Retention: An in vitro Study Tarek Mohamed, Osama
ACOMPARATIVEEVALUATIONOFEASY REMOVALOFDENTALCASTSFROMALGINATE IMPRESSIONSUSINGDIFFERENTBRANDSOF DENTALSTONE-ANINVITROSTUDY
 ORIGINALRESEARCHARTICLE ACOMPARATIVEEVALUATIONOFEASY REMOVALOFDENTALCASTSFROMALGINATE IMPRESSIONSUSINGDIFFERENTBRANDSOF DENTALSTONE-ANINVITROSTUDY ABSTRACT: Background: The fracture of teeth on removal
ORIGINALRESEARCHARTICLE ACOMPARATIVEEVALUATIONOFEASY REMOVALOFDENTALCASTSFROMALGINATE IMPRESSIONSUSINGDIFFERENTBRANDSOF DENTALSTONE-ANINVITROSTUDY ABSTRACT: Background: The fracture of teeth on removal
Predictable Real World Aesthetics. The Key to Success with Natural Restorations
 The Insiders Guide to Quality Dentistry Predictable Real World Aesthetics The Key to Success with Natural Restorations ISUS CAD/CAM Implant Supra-Structures: Accuracy, durability and precision Conscious
The Insiders Guide to Quality Dentistry Predictable Real World Aesthetics The Key to Success with Natural Restorations ISUS CAD/CAM Implant Supra-Structures: Accuracy, durability and precision Conscious
Chapter 12. Prosthodontics
 Chapter 12 Prosthodontics Golbarg Kolahi 1 Prosthesis [prahs-thee-sis] A replacement for a missing body part Golbarg Kolahi 2 Prosthesis In the dental field, it is a fixed or removable appliance replacing
Chapter 12 Prosthodontics Golbarg Kolahi 1 Prosthesis [prahs-thee-sis] A replacement for a missing body part Golbarg Kolahi 2 Prosthesis In the dental field, it is a fixed or removable appliance replacing
TOOTH PREPARATION. (Boucher's Clinical Dental Terminology, 4th ed, p239)
 Budapest, 2017 TOOTH PREPARATION The selected form given to a natural tooth when it is reduced by instrumentation to receive a prosthesis (e.g. artificial crown or a retainer for a fixed or removable prosthesis)
Budapest, 2017 TOOTH PREPARATION The selected form given to a natural tooth when it is reduced by instrumentation to receive a prosthesis (e.g. artificial crown or a retainer for a fixed or removable prosthesis)
Journal of Clinical and Translational Research; 2018; 4(1): xxx-xxx
 Journal of Clinical and Translational Research; 2018; 4(1): xxx-xxx ORINIAL ARTICLE Viscosity effects of polyvinyl siloxane impression materials on the accuracy of the stone die produced Warren Ho 1, Liang
Journal of Clinical and Translational Research; 2018; 4(1): xxx-xxx ORINIAL ARTICLE Viscosity effects of polyvinyl siloxane impression materials on the accuracy of the stone die produced Warren Ho 1, Liang
INTRODUCTION TO NON-METALLIC DENTAL MATERIALS. Office Hours Room P- 409 TBD Phone (718) Fax (718)
 NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK DEPARTMENT OF RESTORATIVE DENTISTRY DEPARTMENT: COURSE CODE: COURSE TITLE: CONTACT INFORMATION: COURSE DESCRIPTION: CLASS HOURS & CREDITS:
NEW YORK CITY COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY THE CITY UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK DEPARTMENT OF RESTORATIVE DENTISTRY DEPARTMENT: COURSE CODE: COURSE TITLE: CONTACT INFORMATION: COURSE DESCRIPTION: CLASS HOURS & CREDITS:
Surveying. 3rd year / College of Dentistry/University of Baghdad ( ) Page 1
 د. فائزة Lec.3 Prosthodontics Surveying The ideal requirements for successful removable partial denture are: 1. Be easily inserted and removed by the patient. 2. Resist dislodging forces. 3. It should
د. فائزة Lec.3 Prosthodontics Surveying The ideal requirements for successful removable partial denture are: 1. Be easily inserted and removed by the patient. 2. Resist dislodging forces. 3. It should
The LOCATOR concept. Simplicity and versatility for prosthesis fixation
 The concept Simplicity and versatility for prosthesis fixation The concept Experience the freedom in prosthesis fixation Simple and secure fixation of implant-supported prostheses is essential for successful
The concept Simplicity and versatility for prosthesis fixation The concept Experience the freedom in prosthesis fixation Simple and secure fixation of implant-supported prostheses is essential for successful
All Ceramic Inlays - Coming of Age
 CASE REPORT All Ceramic Inlays - Coming of Age Ahmad Naeem 1 & Bashir Taseer 2 Quick Response Code ABSTRACT: In the past decade and a half there has been an explosion in the introduction of restorative
CASE REPORT All Ceramic Inlays - Coming of Age Ahmad Naeem 1 & Bashir Taseer 2 Quick Response Code ABSTRACT: In the past decade and a half there has been an explosion in the introduction of restorative
SURVEYING OF REMOVABLE PARITAL DENTURES FEB, 11, 2015
 SURVEYING OF REMOVABLE PARITAL DENTURES FEB, 11, 2015 Dental Surveyor: It is a mechanical device used to determine the relative parallelism of the teeth surfaces and the undercuts areas in relation to
SURVEYING OF REMOVABLE PARITAL DENTURES FEB, 11, 2015 Dental Surveyor: It is a mechanical device used to determine the relative parallelism of the teeth surfaces and the undercuts areas in relation to
Professor Dept. of Prosthodontics, Crown and Bridge, Sri Aurobindo College of Dentistry, Indore M.P.
 A COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF DIMENSIONAL STABILITY OF POLYVINYL SILOXANE IMPRESSION MATERIAL FOLLOWINGDISINFECTION WITH 2% GLUTARALDEHYDE AND U.V. RAYS USING THREE DIMENSIONAL OPTICAL DIGITIZATION. 1 Kavita
A COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF DIMENSIONAL STABILITY OF POLYVINYL SILOXANE IMPRESSION MATERIAL FOLLOWINGDISINFECTION WITH 2% GLUTARALDEHYDE AND U.V. RAYS USING THREE DIMENSIONAL OPTICAL DIGITIZATION. 1 Kavita
OT EQUATOR CASTABLE Single Attachment for Overdentures
 OT EQUATOR CASTABLE Single Attachment for Overdentures pick-up impression OT EQUATOR PROFILE CASTABLE MALE ATTACHMENT individual tray RETENTIVE CAPS OT EQUATOR HOUSING VIOLET CAP RIGID RETENTION (2.7Kg)
OT EQUATOR CASTABLE Single Attachment for Overdentures pick-up impression OT EQUATOR PROFILE CASTABLE MALE ATTACHMENT individual tray RETENTIVE CAPS OT EQUATOR HOUSING VIOLET CAP RIGID RETENTION (2.7Kg)
IMPRESSION MATERIALS
 IMPRESSION MATERIALS Function of Impression Materials To make a negative copy of an oral structure single tooth, quadrant, or arch edentulous or dentulous Negative copy must be accurate to produce an accurate
IMPRESSION MATERIALS Function of Impression Materials To make a negative copy of an oral structure single tooth, quadrant, or arch edentulous or dentulous Negative copy must be accurate to produce an accurate
The Reinforced Removable Retainer
 The Reinforced Removable Retainer Abstract The aim of this paper is to present a new type of orthodontic removable retainer, which is of great help to the orthodontist as well as to the patient. The procedures
The Reinforced Removable Retainer Abstract The aim of this paper is to present a new type of orthodontic removable retainer, which is of great help to the orthodontist as well as to the patient. The procedures
ACCREDITATION STANDARDS FOR DENTAL LABORTATORY TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION PROGRAMS Frequency of Citings Based on Required Areas of Compliance
 Page 1 ACCREDITATION STANDARDS FOR DENTAL LABORTATORY TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION PROGRAMS Frequency of Citings Based on Required Areas of Compliance Total Number of Programs Evaluated: 10 January 1, 2014 through
Page 1 ACCREDITATION STANDARDS FOR DENTAL LABORTATORY TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION PROGRAMS Frequency of Citings Based on Required Areas of Compliance Total Number of Programs Evaluated: 10 January 1, 2014 through
A comparative evaluation of the marginal accuracy of crowns fabricated from four commercially available provisional materials: An in vitro study
 A comparative evaluation of the marginal accuracy of crowns fabricated from four commercially available provisional materials: An in vitro study Bhavya Mohandas Amin, Meena Ajay Aras, Vidya Chitre Abstract
A comparative evaluation of the marginal accuracy of crowns fabricated from four commercially available provisional materials: An in vitro study Bhavya Mohandas Amin, Meena Ajay Aras, Vidya Chitre Abstract
Annotation to the lesson 21 Topic: Methods of provisory crowns fabrication. Chair-side technique. Evaluation of
 Annotation to the lesson 21 Topic: Methods of provisory crowns fabrication. Chair-side technique. Evaluation of crown fitting quality Contemporary methods of restoration of tooth tissues pathology, using
Annotation to the lesson 21 Topic: Methods of provisory crowns fabrication. Chair-side technique. Evaluation of crown fitting quality Contemporary methods of restoration of tooth tissues pathology, using
Lect. Pre. Clin
 FIXED PROSTHODONTICS ( OMR 534 ) Course No. Course Title Unit OMR 534 Fixed Prosthodontics Lect. Pre. Clin. 1 1 3 Objectives: Summary of main learning outcomes for students enrolled in the course. At the
FIXED PROSTHODONTICS ( OMR 534 ) Course No. Course Title Unit OMR 534 Fixed Prosthodontics Lect. Pre. Clin. 1 1 3 Objectives: Summary of main learning outcomes for students enrolled in the course. At the
SCD Case Study. Attachments in Prosthodontics
 SCD Case Study Attachments in Prosthodontics Precision attachments are retention units milled out of alloy. They have male and female parts that fit together with tolerances of 10 microns. It is important
SCD Case Study Attachments in Prosthodontics Precision attachments are retention units milled out of alloy. They have male and female parts that fit together with tolerances of 10 microns. It is important
Virtual The hydrophilic precision impression material
 Impressive Impressions The hydrophilic precision impression material Hydrophilic: exactly where you need it Single-phase impressions with Hydrophilicity and contact angle Excellent wettability Excellent
Impressive Impressions The hydrophilic precision impression material Hydrophilic: exactly where you need it Single-phase impressions with Hydrophilicity and contact angle Excellent wettability Excellent
A comparative evaluation of three different techniques for single step border molding
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A comparative evaluation of three different techniques for single step border molding Kheur M 1, Jambhekar S 2, Sethi T 3, Kheur S 4 1Professor, 3 PG student, Dept. of Prosthodontics,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A comparative evaluation of three different techniques for single step border molding Kheur M 1, Jambhekar S 2, Sethi T 3, Kheur S 4 1Professor, 3 PG student, Dept. of Prosthodontics,
Complete denture impressions
 Lec.5 Complete denture impressions د. غسان الطائي Dental Impression: a negative imprint of an oral structure used to produce a positive replica of the structure to be used as a permanent record or in the
Lec.5 Complete denture impressions د. غسان الطائي Dental Impression: a negative imprint of an oral structure used to produce a positive replica of the structure to be used as a permanent record or in the
ACCREDITATION STANDARDS FOR DENTAL LABORATORY TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION PROGRAMS Frequency of Citings Based on Required Areas of Compliance
 Page 1 ACCREDITATION STANDARDS FOR DENTAL LABORATORY TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION PROGRAMS Based on Required Areas of Compliance Total Number of Programs Evaluated: 13 July 2009 through December 2013 STANDARD
Page 1 ACCREDITATION STANDARDS FOR DENTAL LABORATORY TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION PROGRAMS Based on Required Areas of Compliance Total Number of Programs Evaluated: 13 July 2009 through December 2013 STANDARD
INDICATIONS. Fixed Appliances are indicated when precise tooth movements are required
 DEFINITION Fixed Appliances are devices or equipments that are attached to the teeth, cannot be removed by the patient and are capable of causing tooth movement. INDICATIONS Fixed Appliances are indicated
DEFINITION Fixed Appliances are devices or equipments that are attached to the teeth, cannot be removed by the patient and are capable of causing tooth movement. INDICATIONS Fixed Appliances are indicated
The Effect of Outdoor Weathering on Color Stability of Silicone and Acrylic Resin, Pigments A Comparative Evaluation: An in vitro Study
 The Effect of Outdoor Weathering on Color Stability of Silicone and Acrylic Resin, 10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1135 Pigments A Comparative Evaluation ORIGINAL RESEARCH The Effect of Outdoor Weathering on
The Effect of Outdoor Weathering on Color Stability of Silicone and Acrylic Resin, 10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1135 Pigments A Comparative Evaluation ORIGINAL RESEARCH The Effect of Outdoor Weathering on
MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary Vol.:9 No.:2 2012
 MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary fillings on shear bond strength of composite restoration Dr. Farid G. Numan B.D.S., M.Sc Abstract The purpose of this in-vitro study was to evaluate
MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary fillings on shear bond strength of composite restoration Dr. Farid G. Numan B.D.S., M.Sc Abstract The purpose of this in-vitro study was to evaluate
SS Implant System 2013 PROSTHETIC PROCEDURE
 SS Implant System 2013 PROSTHETIC PROCEDURE Contents TS Implant System Cement retained restoration 06 Cement-retained bridges with the Solid abutment system (non-modified abutment) 16 Cement-retained bridges
SS Implant System 2013 PROSTHETIC PROCEDURE Contents TS Implant System Cement retained restoration 06 Cement-retained bridges with the Solid abutment system (non-modified abutment) 16 Cement-retained bridges
Straumann synocta Prosthetic System Basic Information. Technical Information
 Straumann synocta Prosthetic System Basic Information Technical Information About this guide The Basic Information on the Straumann synocta Prosthetic System provide dental practitioners and related specialists
Straumann synocta Prosthetic System Basic Information Technical Information About this guide The Basic Information on the Straumann synocta Prosthetic System provide dental practitioners and related specialists
Color stability and colorant effect on maxillofacial elastomers. Part I: Colorant effect on physical properties
 Color stability and colorant effect on maxillofacial elastomers. Part I: Colorant effect on physical properties Steven P. Haug, DDS, MSD, a Carl J. Andres, DDS, MSD, a and B. Keith Moore, PhD b Indiana
Color stability and colorant effect on maxillofacial elastomers. Part I: Colorant effect on physical properties Steven P. Haug, DDS, MSD, a Carl J. Andres, DDS, MSD, a and B. Keith Moore, PhD b Indiana
King Saud University College of Dentistry Department of Prosthetic Dental Sciences DR. EMAN ALHAMDAN. Course Director - MUC DR.
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Department of Prosthetic Dental Sciences DR. EMAN ALHAMDAN Course Director - MUC DR. SARA ALTAWEEL Course Co-Director-MUC ACADEMIC YEAR 1433 /1434H (2012/2013G)
King Saud University College of Dentistry Department of Prosthetic Dental Sciences DR. EMAN ALHAMDAN Course Director - MUC DR. SARA ALTAWEEL Course Co-Director-MUC ACADEMIC YEAR 1433 /1434H (2012/2013G)
Evaluation of Bond Strength of Silicone and Acrylic Resin Based Resilient Denture Liners Over A Period of Storage in Water.
 DOI: 0.2276/aimdr.208.4..DE4 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-284 Evaluation of Bond Strength of Silicone and Acrylic Resin Based Resilient Denture Liners Over A Period of Storage in
DOI: 0.2276/aimdr.208.4..DE4 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-284 Evaluation of Bond Strength of Silicone and Acrylic Resin Based Resilient Denture Liners Over A Period of Storage in
Impression for crown and bridge work
 Lec.9 Crown & Bridge ims Impression for crown and bridge work Definition: an impression is a negative reproduction or likeness of an object, from which, a positive reproduction (or cast) could be obtained.
Lec.9 Crown & Bridge ims Impression for crown and bridge work Definition: an impression is a negative reproduction or likeness of an object, from which, a positive reproduction (or cast) could be obtained.
The effect of immersion disinfection procedures on dimensional stability of two elastomeric impression materials
 441 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 50, No. 4, 441-446, 2008 Original The effect of immersion disinfection procedures on dimensional stability of two elastomeric impression materials Dario Melilli, Antonio
441 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 50, No. 4, 441-446, 2008 Original The effect of immersion disinfection procedures on dimensional stability of two elastomeric impression materials Dario Melilli, Antonio
Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland School of Dentistry
 Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry-Biomaterials Structures, chemical properties, physical properties BASIC CONCEPTS ON HOW DENTAL MATERIALS WORK! Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry-Biomaterials Structures, chemical properties, physical properties BASIC CONCEPTS ON HOW DENTAL MATERIALS WORK! Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland
VIP Partner Laboratory (PL) Process Flow
 VIP Partner Laboratory (PL) Process Flow 1. VIP Software 2. CT Scan Appliance 3. CT Scan Clinician purchases VIP for PL fabricates CT Scan Appliance Patient submitted for scans treatment planning purposes
VIP Partner Laboratory (PL) Process Flow 1. VIP Software 2. CT Scan Appliance 3. CT Scan Clinician purchases VIP for PL fabricates CT Scan Appliance Patient submitted for scans treatment planning purposes
UDELL DENTAL LABORATORY Instructions for Use
 DALLA BONA Summary Cylindrical Dalla Bona Rigid precision attachment. Radicular telescopic stud. Adjustable frictional retention. Gold alloy male (Elitor) and female (OSV). Fixation: Male - soldered to
DALLA BONA Summary Cylindrical Dalla Bona Rigid precision attachment. Radicular telescopic stud. Adjustable frictional retention. Gold alloy male (Elitor) and female (OSV). Fixation: Male - soldered to
COURSE CURRICULUM FOR AESTHETIC DENTISTRY
 COURSE CURRICULUM FOR AESTHETIC DENTISTRY Esthetic Dentistry is actually the fourth dimension in clinical dentistry. In addition to biologic, Physiologic, and mechanical factors, all of which must be understood
COURSE CURRICULUM FOR AESTHETIC DENTISTRY Esthetic Dentistry is actually the fourth dimension in clinical dentistry. In addition to biologic, Physiologic, and mechanical factors, all of which must be understood
Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama
 Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Principles of Removable Partial Denture Design Difference in Prosthesis Support and Influence on Design: For a tooth-supported prosthesis, the movement potential is less
Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Principles of Removable Partial Denture Design Difference in Prosthesis Support and Influence on Design: For a tooth-supported prosthesis, the movement potential is less
Abutment level impression Ⅰ. Combi abutment/dual abutment Multi units
 Pr osthetic par t Abutment level impression Ⅰ Combi abutment/dual abutment Multi units Prosthetic part Remove Cover screw Prosthetic part Remove Healing abutment Prosthetic part Select suitable Combi abutment,
Pr osthetic par t Abutment level impression Ⅰ Combi abutment/dual abutment Multi units Prosthetic part Remove Cover screw Prosthetic part Remove Healing abutment Prosthetic part Select suitable Combi abutment,
This PDF is available for free download from a site hosted by Medknow Publications
 CMYK115 Review Article 12-06 CEREC - The power of technology I. Kaur, K. Datta Department of Prosthodontics, Pb Govt. Dental College and Hospital, Amritsar, Punjab, India For correspondence Inderpreet
CMYK115 Review Article 12-06 CEREC - The power of technology I. Kaur, K. Datta Department of Prosthodontics, Pb Govt. Dental College and Hospital, Amritsar, Punjab, India For correspondence Inderpreet
What are the advantages and disadvantages of an inlay or onlay?
 Problems Solvers 50 Inlays, Onlays and ¾ crowns Oh My! Synonyms: Inlays, Onlays, ¾ Crowns, 7/8 crowns When people have a cavity or a large filling there are times when a full crown is not the best choice
Problems Solvers 50 Inlays, Onlays and ¾ crowns Oh My! Synonyms: Inlays, Onlays, ¾ Crowns, 7/8 crowns When people have a cavity or a large filling there are times when a full crown is not the best choice
The width of the MCXL step bur is 1.4 mm wide and has a blunt end. As the bur approaches the inside of
 As I teach first year dental students how to prep a tooth for a full gold crown, get an impression, pour and mount models, wax-up, cast and polish, they are almost always amazed at all the required steps
As I teach first year dental students how to prep a tooth for a full gold crown, get an impression, pour and mount models, wax-up, cast and polish, they are almost always amazed at all the required steps
DURATEMP Temporary Crown & Bridge Material. Temrex Corporation October 2009
 DURATEMP Temporary Crown & Bridge Material Temrex Corporation October 2009 DURATEMP Temporary Crown & Bridge Material Overview Product Characteristics Physical Properties Case Report Instructions Ordering
DURATEMP Temporary Crown & Bridge Material Temrex Corporation October 2009 DURATEMP Temporary Crown & Bridge Material Overview Product Characteristics Physical Properties Case Report Instructions Ordering
Using technology to create the perfect impression
 The take-aways ȜȜ ȜȜ Taking impressions with traditional stock impress trays and many closed bite systems can be challenging. Clinician s Choice HeatWave system offers an accurate fit out of the box, allowing
The take-aways ȜȜ ȜȜ Taking impressions with traditional stock impress trays and many closed bite systems can be challenging. Clinician s Choice HeatWave system offers an accurate fit out of the box, allowing
DENTAL MATERIALS STUDY GUIDE
 DENTAL MATERIALS STUDY GUIDE WORKSHEET Dentalelle Tutoring www.dentalelle.com Study Guide for Dental Materials Dentalelle Tutoring 1. When completing a large composite restoration, how should the composite
DENTAL MATERIALS STUDY GUIDE WORKSHEET Dentalelle Tutoring www.dentalelle.com Study Guide for Dental Materials Dentalelle Tutoring 1. When completing a large composite restoration, how should the composite
Psychological Impact of Communication
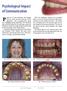 Psychological Impact of Communication Patient is a 47 year old female was unhappy with her smile and self conscience of her appearance. She is missing teeth, which was impinging during mastication. The
Psychological Impact of Communication Patient is a 47 year old female was unhappy with her smile and self conscience of her appearance. She is missing teeth, which was impinging during mastication. The
Comparison of Flexural Strength of two Provisional Materials Used In Fixed Prosthodontics -An in Vitro Study.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. XII (September). 2016), PP 54-58 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of Flexural Strength
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. XII (September). 2016), PP 54-58 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of Flexural Strength
International J. of Healthcare and Biomedical Research, Volume: 04, Issue: 03, April 2016, 83-92
 Original article: Impression materials and techniques used and followed for the fixed partial denture treatment by private dental practitioners in Maharashtra state: A questionnaire study 1Dr.Amruta P.
Original article: Impression materials and techniques used and followed for the fixed partial denture treatment by private dental practitioners in Maharashtra state: A questionnaire study 1Dr.Amruta P.
Original Research. Absorption of soft lining materials Kumar SK et al
 Absorption of soft lining materials Kumar SK et al Journal of International Oral Health 2015; 7(11):47-52 Received: 07 th June 2015 Accepted: 13 th September 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of
Absorption of soft lining materials Kumar SK et al Journal of International Oral Health 2015; 7(11):47-52 Received: 07 th June 2015 Accepted: 13 th September 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of
Nagri D et al. Linear occlusion and Neutral Zone recording for severely resorbed ridges
 Doi:10.21276/ledent.2018.02.01.02 Case Report LINEAR OCCLUSION AND NEUTRAL ZONE RECORDING USING TISSUE CONDITIONER REPORT OF A SEVERELY RESORBED RIDGE Divya Nagri, 1Ashish Kakkar, 2Neeraj Mittal, 3Lovely
Doi:10.21276/ledent.2018.02.01.02 Case Report LINEAR OCCLUSION AND NEUTRAL ZONE RECORDING USING TISSUE CONDITIONER REPORT OF A SEVERELY RESORBED RIDGE Divya Nagri, 1Ashish Kakkar, 2Neeraj Mittal, 3Lovely
Stainless Steel Crowns
 Stainless Steel Crowns Objectives Indications for use of stainless steel crowns Technique used in preparing and placing a stainless steel crown restoration on a primary molar. Indications for SSC Restoration
Stainless Steel Crowns Objectives Indications for use of stainless steel crowns Technique used in preparing and placing a stainless steel crown restoration on a primary molar. Indications for SSC Restoration
Impressions in fixed partial denture: A review update
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2015, 5(12):1-5 Impressions in fixed partial denture: A review update ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Yeshwante
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2015, 5(12):1-5 Impressions in fixed partial denture: A review update ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Yeshwante
Tooth preparation for posterior fi xed partial denture (FPD) Tooth preparation for anterior fi xed partial denture (FPD)
 CHAPTER 17 Tooth preparation for posterior fi xed partial denture (FPD) 1 Defi nition and feature of FPD 2 Actual sequence of tooth preparation for posterior FPD Verify abutment teeth Occlusal guide groove
CHAPTER 17 Tooth preparation for posterior fi xed partial denture (FPD) 1 Defi nition and feature of FPD 2 Actual sequence of tooth preparation for posterior FPD Verify abutment teeth Occlusal guide groove
Essentials of. Dental Assisting. Edition 6. Debbie S. Robinson Doni L. Bird
 Essentials of Dental Assisting Edition 6 Debbie S. Robinson Doni L. Bird CHAPTER21 Restorative Procedures http://evolve.elsevier.com/robinson/essentials/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES KEY TERMS 1. Pronounce, define,
Essentials of Dental Assisting Edition 6 Debbie S. Robinson Doni L. Bird CHAPTER21 Restorative Procedures http://evolve.elsevier.com/robinson/essentials/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES KEY TERMS 1. Pronounce, define,
Cast Partial Denture Improving Emergence and Masticatory Function - A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. VI (Sep. 2015), PP 51-56 www.iosrjournals.org Cast Partial Denture Improving Emergence
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. VI (Sep. 2015), PP 51-56 www.iosrjournals.org Cast Partial Denture Improving Emergence
Original Research. Matrix impression system Kumar MP et al
 Received: 08 th January 2015 Accepted: 03 rd April 2014 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research A Comparison of Accuracy of Matrix Impression System with Putty Reline Technique
Received: 08 th January 2015 Accepted: 03 rd April 2014 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research A Comparison of Accuracy of Matrix Impression System with Putty Reline Technique
Effect of Intermixing Brands on the Dimensional Accuracy of Master Cast using Putty-wash Impression Technique
 Mohammed E Sayed et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1921 Effect of Intermixing Brands on the Dimensional Accuracy of Master Cast using Putty- Impression Technique 1 Mohammed E Sayed, 2 Bandar
Mohammed E Sayed et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1921 Effect of Intermixing Brands on the Dimensional Accuracy of Master Cast using Putty- Impression Technique 1 Mohammed E Sayed, 2 Bandar
Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2016, vol. 22, issue 3
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X http://dx.doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2016223.1296 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2016, vol. 22, issue 3 COMPARISON OF INTERFACIAL SURFACE TENSION AND
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X http://dx.doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2016223.1296 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2016, vol. 22, issue 3 COMPARISON OF INTERFACIAL SURFACE TENSION AND
Fixed Partial Denture
 University of Minnesota School of Dentistry Fixed Partial Denture Self-guided Instructional Material for Dental Students Authors Ranier M. Adarve, DMD, MS, MHPE Lisa Fedor James, DDS, Cert. Pros. Fixed
University of Minnesota School of Dentistry Fixed Partial Denture Self-guided Instructional Material for Dental Students Authors Ranier M. Adarve, DMD, MS, MHPE Lisa Fedor James, DDS, Cert. Pros. Fixed
Rehabilitation of Resorbed Mandibular Ridge with Implant Supported Overdenture- A Clinical Report
 Rehabilitation of Resorbed Mandibular Ridge with Implant Supported Overdenture- A Clinical Report 1 2 1 1 Mittal R, Saxena D, Rao S, Kumar M Abstract: Statement of Problem: Complete denture rehabilitation
Rehabilitation of Resorbed Mandibular Ridge with Implant Supported Overdenture- A Clinical Report 1 2 1 1 Mittal R, Saxena D, Rao S, Kumar M Abstract: Statement of Problem: Complete denture rehabilitation
SimpleLine II Surgical / Prosthesis Manual
 SimpleLine II Surgical / Prosthesis Manual SimpleLine II SURGICAL MANUAL Surgical Drill Sequence 04 Fixture Installation 05 Fixture Connection 06 Surgical Kit Maintenance 08 Warnings 09 04 SimpleLine ll
SimpleLine II Surgical / Prosthesis Manual SimpleLine II SURGICAL MANUAL Surgical Drill Sequence 04 Fixture Installation 05 Fixture Connection 06 Surgical Kit Maintenance 08 Warnings 09 04 SimpleLine ll
Rejuvenating the Ovate Pontic
 10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1095 Mohsin CASE REPORT Atibuddin Quazi et al Mohsin Atibuddin Quazi, Jaykumar Gade, Krishnakumar Lahoti, Vandana Gade ABSTRACT The restoration of esthetics along with maintenance
10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1095 Mohsin CASE REPORT Atibuddin Quazi et al Mohsin Atibuddin Quazi, Jaykumar Gade, Krishnakumar Lahoti, Vandana Gade ABSTRACT The restoration of esthetics along with maintenance
illustrated technique guide
 DENTSPLY Caulk 38 West Clarke Avenue Milford, DE 9963 www.dentsply.com www.caulk.com -302-422-45 In Canada call -800-263-437 illustrated technique guide Complete Luting System for: 2006 DENTSPLY International.
DENTSPLY Caulk 38 West Clarke Avenue Milford, DE 9963 www.dentsply.com www.caulk.com -302-422-45 In Canada call -800-263-437 illustrated technique guide Complete Luting System for: 2006 DENTSPLY International.
Restoration of the worn dentition
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:4 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0003-3 TREATMENT Restoration of the worn dentition Paul King 1 Received: 16 March 2017 / Accepted: 31 May 2017 / Published online: 30 June 2017
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:4 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0003-3 TREATMENT Restoration of the worn dentition Paul King 1 Received: 16 March 2017 / Accepted: 31 May 2017 / Published online: 30 June 2017
Comparison of the accuracy and dimensional stability of interocclusal recording materials - An in- vitro study.
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 7, July 2015 1 Comparison of the accuracy and dimensional stability of interocclusal recording materials - An in- vitro study.
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 7, July 2015 1 Comparison of the accuracy and dimensional stability of interocclusal recording materials - An in- vitro study.
2. Gap closure and replacement of the missing tooth 35 with directly modelled bridge region 34-36
 GrandTEC Test Kit Dear User, This Test Kit has been put together to enable you to test GrandTEC on the model before using it in a clinical situation. GrandTEC is a resin-impregnated glass fibre strip.
GrandTEC Test Kit Dear User, This Test Kit has been put together to enable you to test GrandTEC on the model before using it in a clinical situation. GrandTEC is a resin-impregnated glass fibre strip.
PROSTHODONTICS 525P CLINICAL PREPARATORY COURSE IN REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURES. Spring Quarter 2008
 PROSTHODONTICS 525P CLINICAL PREPARATORY COURSE IN REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURES & MANAGEMENT OF THE IMMEDIATE DENTURE PATIENT Spring Quarter 2008 Course Director: Assistant Course Director: Faculty: Dr.
PROSTHODONTICS 525P CLINICAL PREPARATORY COURSE IN REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURES & MANAGEMENT OF THE IMMEDIATE DENTURE PATIENT Spring Quarter 2008 Course Director: Assistant Course Director: Faculty: Dr.
Prosthetic V. Removable dentures I.
 Prosthetic V. Removable dentures I. Removable dentures Partial Complete (full) lenka.roubalikova@tiscali.cz 2 Prosthetic dentistry replacement of Damaged teeth reconstruction of the crown (inlays, crowns)
Prosthetic V. Removable dentures I. Removable dentures Partial Complete (full) lenka.roubalikova@tiscali.cz 2 Prosthetic dentistry replacement of Damaged teeth reconstruction of the crown (inlays, crowns)
Effect of Thickness and Recycling on Transverse Strength of Relined Acrylic Resin Denture
 ISSN: 1812 1217 Effect of Thickness and Recycling on Transverse Strength of Relined Acrylic Resin Denture Base. Nadira A Hatim BDS, MSc ( Prof) Aliaa W AL-Omari BDS, MSc (Asst Lec) Department of Prosthetic
ISSN: 1812 1217 Effect of Thickness and Recycling on Transverse Strength of Relined Acrylic Resin Denture Base. Nadira A Hatim BDS, MSc ( Prof) Aliaa W AL-Omari BDS, MSc (Asst Lec) Department of Prosthetic
Comparative Investigation of the Fracture Strengths of Crowns of Three Different Non-metal Materials
 Comparative Investigation of the Fracture Strengths of Crowns of Three Different Non-metal Materials Danijel Fiket 1 Adnan Ćatović 1 Mladen Franz 2 Davor Seifert 1 1 Department of Dental Prosthetics School
Comparative Investigation of the Fracture Strengths of Crowns of Three Different Non-metal Materials Danijel Fiket 1 Adnan Ćatović 1 Mladen Franz 2 Davor Seifert 1 1 Department of Dental Prosthetics School
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations The outline form
 Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
Comparative Evaluation of Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Detail Reproduction of Elastomeric Impression Material when Treated
 Comparative Evaluation of Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Detail Reproduction of Elastomeric Impression Material when Treated with Three Retraction Cord Medicaments : An In Vitro Study Pravin Raipure
Comparative Evaluation of Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Detail Reproduction of Elastomeric Impression Material when Treated with Three Retraction Cord Medicaments : An In Vitro Study Pravin Raipure
AFFINIS Sys360 putty maximum precision and easy to use
 AFFINIS Sys360 putty maximum precision and easy to use Dr. RALPH SCHÖNEMANN, November 2010 Dentists can now select from a wide range of very different impression materials supplied by a large number of
AFFINIS Sys360 putty maximum precision and easy to use Dr. RALPH SCHÖNEMANN, November 2010 Dentists can now select from a wide range of very different impression materials supplied by a large number of
Administrative - Master Syllabus COVER SHEET
 Administrative - Master Syllabus COVER SHEET Purpose: It is the intention of this to provide a general description of the course, outline the required elements of the course and to lay the foundation for
Administrative - Master Syllabus COVER SHEET Purpose: It is the intention of this to provide a general description of the course, outline the required elements of the course and to lay the foundation for
