Clinical Study Implant Restoration of Edentulous Jaws with 3D Software Planning, Guided Surgery, Immediate Loading, and CAD-CAM Full Arch Frameworks
|
|
|
- Augustine Newman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID , 7 pages Clinical Study Implant Restoration of Edentulous Jaws with 3D Software Planning, Guided Surgery, Immediate Loading, and CAD-CAM Full Arch Frameworks Silvio Mario Meloni, 1,2 Giacomo De Riu, 1 Milena Pisano, 1 Francesco Maria Lolli, 2 Alessandro Deledda, 2 Guglielmo Campus, 2 and Antonio Tullio 1 1 Maxillofacial Surgery Unit, University Hospital of Sassari, Sassari, Italy 2 Dentistry Unit, University Hospital of Sassari, Sassari, Italy Correspondence should be addressed to Silvio Mario Meloni; melonisilviomario@yahoo.it Received 25 March 2013; Revised 2 June 2013; Accepted 25 June 2013 Academic Editor: Dimitris N. Tatakis Copyright 2013 Silvio Mario Meloni et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Purpose. The aim of this study was to analyze the clinical and radiographic outcomes of 23 edentulous jaws treated with 3D software planning, guided surgery, and immediate loading and restored with CAD-CAM full arch frameworks. Materials and Methods. This work was designed as a prospective case series clinical study. Twenty patients have been consecutively rehabilitated with an immediately loaded implant supported fixed full prosthesis. A total of 120 fixtures supporting 23 bridges were placed. 117 out of 120 implants were immediately loaded. Outcome measures were implants survival, radiographic marginal bone levels and remodeling, soft tissue parameters, and complications. Results. 114 of 117 implants reached a 30 months follow-up, and no patients dropped out fromthestudy.thecumulativesurvivalratewas97.7%;after30months,meanmarginalbonelevelwas1.25 ± 0.31 mm, mean marginal bone remodeling value was 1.08 ± 0.34, mean PPD value was 2.84 ± 0.55 mm,andmeanbopvaluewas4%± 2.8%. Only minor prosthetic complications were recorded. Conclusion. Within the limitations of this study, it can be concluded that computerguided surgery and immediate loading seem to represent a viable option for the immediate rehabilitations of completely edentulous jaws with fixed implant supported restorations. This trial is registered with Clinicaltrials.gov NCT Introduction The standard surgical protocol for guided implant placement comprises a diagnostic step, (clinical and radiographic examination), a planning step, and a surgical step, where the surgeon implements what was planned [1]. The growing interest in minimally invasive surgery, together with the possibility of fitting prostheses with immediatefunction,hasledtothedevelopmentofsoftwareand digital workflows allowing for the planning and manufacturing of a surgical guide and provisional prosthesis that can be inserted immediately after the implant surgery step [2 5]. The typical dental implant surgical approach that was introduced in the early 1980s requires two steps [6] andthe use of a removable bridge or denture during the healing period. In the 1990s, [7] itwasfirstshownthatimplants could be placed and restored in a single visit: this procedure, known as immediate loading, needed a full day of coordinated surgical, restorative, and dental laboratory interaction. Advancements in computerized tomography (CT) scans, [8] coupled with computer-assisted treatment planning [9] and a double CT scan approach [3, 10], allowed for the virtual planning of placement of implants in 3-dimensional (3D) orientation relative to the bone, soft tissue, and final planned prosthesis. In 2002, the concept of software planning and surgically guided techniques combined with immediate loading was clinically introduced in Leuven, Belgium [11]. These early treatments were limited to the edentulous maxilla and required a full-thickness flap. Later, the procedure was refined to include flapless implant placement through virtual planning by producing a stereolithographic surgical template incorporating precision titanium drilling
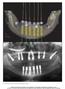
2 2 International Dentistry sleeves [4]. By retrofitting specialized implant components (implant replicas, and guided cylinders with pin) into the stereolithographic surgical template, an implant-level model, could be produced and a temporary prosthesis could be fabricated for immediate insertion at implant placement [12]. Furthermore, the use of technologies that merge computerized tomography (CT) X-ray imaging and 3-dimensional (3D) planning software allows the surgeon to digitally plan on the computer, the position, length, and diameter of every implant to be placed and, at the same time, helps to prevent damage to vital structures. Several studies seem to validate these concepts, but further prospective studies with medium to long term followup are needed [2 4]. The aim of this prospective case series study was to analyze the clinical and radiographic outcomes of 23 edentulous jaws treated with 3D software planning, guided surgery, and immediate loading and restored with CAD- CAM zirconia and titanium full arch frameworks. 2. Materials and Methods 2.1. Study Design. This was a prospective case series study in which clinical and radiological data analysis was carried out on consecutively treated patients to be prosthetically restored with fixed full arches prosthesis (patients were treated in private practice, while data were collected and analyzed at the University of Sassari). The investigation was conducted according to the principles embodied in the Helsinki Declaration of 1975 for biomedical research involving human subjects,asrevisedin2004,andwasapprovedbytheresearch Committee of the Department of Surgical, Microsurgical and Medical Science, University of Sassari. At the preliminary visit, all patients were duly informed of the nature of the study Selection Criteria. Patients of any race and gender were included in the study if they were at least 18 years old and in good general health, physically and psychologically able to undergo conventional implant surgery and restorative procedures (ASA-1, ASA-2). Inclusion criteria were edentulous patients or patients with hopeless teeth in need to be restored with full arches prosthesis. Exclusion criteria were presence of systemic diseases, (i.e., haematologic disease, uncontrolled diabetes, serious coagulopathies, and diseases of the immune system); irradiation totheheadorneckregionwithin12monthsbeforesurgery; severe bruxism or clenching habits; pregnancy; poor oral hygiene; poor motivation to return for scheduled follow-up visits.theincludedpatientsweretreatedinthesamedental office, by surgeons and prosthodontists with considerable clinical expertise in immediate loading procedures. According to the previously criteria mentioned, a total of 20 patients (23 ridges: 8 mandible, 15 maxilla) have been rehabilitated from April 2006 to January 2009 with an immediately loaded implant supported fixed full prosthesis. Following the 3D software treatment planning, four to six implants (Nobel Replace Tapered Groovy; Nobel Figure 1: Preoperative panoramic radiograph. Biocare AB, Goteborg, Sweden) were placed according to a guided implant protocol (NobelGuide Nobel Biocare) in the mandible or in the maxilla. A total of 120 fixtures were placed, 22 of which were placed in fresh postextraction sockets Clinical Procedure. For all cases, the following surgical and prosthetic protocol was followed. The patients were subjected to a clinical evaluation, and a medical history was taken. Informed consent was collected. Preliminary radiographic screening was performed using panoramic orthopantomographs (Figure 1). A careful clinical examination of the patients was performed assessing jaw sizes and relationships, bone volume, and occlusal relationships. Eligible patients received oral hygiene instructions, and impressions and baseline photographs of their dentition were taken. Registrations with a facial bow were also taken for aesthetic/functional evaluation. After the diagnostic phase, for each patient, the teeth to be removed and the implants to be inserted were determined. Two different approaches were used: (i) guided implant insertion in healed ridges (flapless or with flap when needed to preserve keratinized tissue). (ii) guided flapless implant insertion with some implants inserted in fresh extraction sockets and others in healed ridges. From each impression, a wax setup was developed and in case of implant insertion in healed a removable prosthesis ridges, (usedasradiographicguide)wascustomizedaccordingtothe aesthetic and functional evaluations. When guided flapless implant insertion in either healed or fresh extraction sites was planned, a teeth-supported provisional prosthesis was customized and only three or four hopeless teeth were left in the oral cavity of each patient to temporarily support the provisional prosthesis, while the other teeth were extracted. After 4 6 months, a radiological template was made according to the aesthetic and functional wax setup, and a silicone interocclusal record was made to be used as a radiographic index. In accordance with the NobelGuideTM data acquisition protocol (Nobel Biocare, Gothenburg, Sweden), two CT scans were performed: one with the patient wearing
3 International Dentistry 3 Figure 3: Guided flapless implant insertion in healed sites and fresh extraction sockets. Figure 2: Virtual implant planning. Occlusal view. the radiographic guide as well as the radiographic index, the other with the radiological template alone. CT scan data were transferred to the software program for 3D diagnostic analysis and virtual implant planning (Figure 2). Anatomical conditions had to allow the placement of at least four to six implants in the ideal position for prosthetic rehabilitation. When an implant was planned with the tooth in situ, it waseasytoseethevestibularandpalatalcorticalbones. After bone volume analysis, implants were planned on a palatal or lingual aspect and the implant platform virtually positioned at a level of 1.0 mm or less under the coronal part of the vestibular alveolar crest. The software planning data were sent to the manufacturer (Nobel Biocare, Gothenburg Sweden), where a surgical template with hollow metallic sleeves was produced to guide the implants according to the virtually planned position. Based on the surgical guide and the cast model obtained, metal-acrylic resin screw-retained provisional prostheses were prefabricated. The surgical procedure was performed under local anesthesia with articaine chlorhydrate plus 1 : 100,000 adrenaline (Pierrel S.p.A, Milan, Italy). All patients were given diazepam (Valium, 10 mg, Roche, USA) as a sedative agent before surgery. Antibiotics amoxicillin 875 mg and clavulanic acid 125 mg (GlaxoSmithKline S.p.A., Verona, Italy) were given 1 h before surgery and twice a day for 6 days thereafter. An antiinflammatory drug (ketoprofen 80 mg Dompé S.p.A, Milan, Italy) was administered twice a day for 4 days postoperatively. An antacid agent (omeprazole 20 mg, Pensa Pharma S.p.A, Milan, Italy) was administered on the day of surgery and once daily for 6 days postoperatively. Each patient rinsed with chlorhexidine gluconate (0.2%) for 1 min before the intervention (Curasept, Curaden healthcare srl, Saronno, Varese, Italy). In cases of implants planned in fresh extraction sockets, teeth used for temporary support of a provisional prosthesis were removed with an atraumatic technique 30 minutes beforesurgery.surgicaltemplateswerethenplacedintraorally in the correct position and in relation to the opposing arch (a silicone occlusal index was used) and then fixed with Figure 4: Immediate loading with screw-retained temporary prosthesis. three or more anchor pins. Considerable care was taken when placing the surgical template. After correct placement and stabilization of the surgical template, flapless implant surgery was performed in accordance with the drilling protocol for the type of implant used (Figure 3) (NobelReplace Tapered Groovy, Nobel Biocare, Gothenburg, Sweden) in 16 ridges (15 maxillas, 1 mandible), while in 7 mandibular cases, a small full-thickness flap was raised in order to preserve keratinized tissue. Implants were placed with a preset insertion torque of 35 to 45 Ncm. The implant length ranged from 8 to 13 mm and the implant diameter was 3.5, 4.3, or 5 mm. In the case where full-thickness flaps were raised, flaps were sutured after implant installation with interrupted sutures Vicryl 4.0 sutures (Vicryl, Ethicon J&J International, St-Stevens- Woluwe, Belgium). Sutures were removed after 7 days, when possible, without removing the immediate loaded prosthesis, or left in place until resorbed. When fixtures were installed in fresh extraction sockets, the space between the vestibular cortex and the implant surface was always filled with bovine bone grafts (Bio-OSS Geistlich, Wolhusen, Switzerland), and collagen or connective tissue was used to cover the graft and thicken soft tissues. 117 out of 120 implants were immediately loaded with the prefabricated screw-retained provisional prosthesis (Figures 4 and 5), while three remaining implants placed with an insertion torque less than 35 Ncm were delayed loaded. When needed, minor adjustments of provisional restorations were made to correct occlusion. In all postextraction sites, the profile of the prosthesis was relined with resin to provide better support for the soft tissues and to achieve a passive
4 4 International Dentistry Figure 5: Panoramic radiograph after immediate loading. fit of the temporary abutment. Ice packs were provided and a soft diet was recommended for 1 month. All patients were included in an implant maintenance program. Smokers were asked to refrain from smoking for at least 48 h postoperatively. Chlorhexidine gluconate mouthwash (0.2%) was prescribed for 1 min twice a day for 2 weeks after surgery. The patients were instructed on oral hygiene, and they returned every 3 months for a maintenance appointment. Scheduled visits after surgery were after 1 week, 2 weeks, 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months. After 6 months, the prostheses were removed and the implants were individually tested for stability. The definitive prosthetic restorations, either Procera implant bridge titaniumastheframeworkandresinasaestheticmaterial(18 ridges) or Procera implant bridge zirconia ceramic (5 ridges) were then inserted (Figures 6 and 7). After final prosthesis delivery, patients were checked every six months. The following outcome measures were used Success and Failure Criteria. The success criteria to be used in this investigation are a modification of the success criteria suggested by van Steenberghe et al. [4]. The success criteria of the investigation have been determined as follows. (i) A successful implant is an implant which (a) does not cause allergic, toxic, or gross infectious reactions either locally or systemically; (b) offers anchorage to a functional prosthesis; (c) does not show any signs of fracture or bending; (d)doesnotshowanymobilitywhenindividually tested by tapping or rocking with a hand instrument; (e) does not show any signs of radiolucency on an intraoral radiograph using a paralleling technique strictly perpendicular to the implantbone interface. (ii) A surviving implant is when the implant remains in the jaw and is stable, and when the subject s treatment is functionally successful even though all the individual success criteria are not fulfilled. (iii) A successful prosthesis is a prosthetic reconstructionthatisstableandingoodfunction. Figure 6: Final restoration with zirconia ceramic screw-retained prosthesis. Figure 7: Panoramic radiograph 30 months after loading. (iv) A failed implant is an implant that has been removed,fracturedbeyondrepair,orcannotbeclassified as a successful or surviving implant Complications. All types of complications, either mechanical or biological, were recorded Marginal Bone Levels and Marginal Bone Remodeling. Peri-implant marginal bone levels were evaluated on intraoral digital radiographs taken with the parallel technique at the time of implant placement, at 6, 12, and 30 months and after loading. If radiographs were inconclusive, they were repeated. A blinded radiologist, unaffiliated with the study center, interpreted all radiographs. The distances from the mesial and distal interproximal bone to the reference point (the horizontal interface between the implant and abutment) were measured with an image software measurement tool (NIH Scion Image Corporation 4.0.2, Frederick, MD, USA) calibrated against the space between two threads to the nearest 0.1 mm, and the mean of these two measurements was calculated for each implant. The measurements were recorded with reference to the implant axis. Mean values and standard deviation were recorded. The marginal bone remodeling was calculated as the difference between the reading at the examination and the baselinevalue.mesialanddistalboneheightmeasurements were averaged for each implant. Mean values and standard deviation were recorded Peri-Implant Mucosal Response. Probing pocket depth (PPD)inmmandbleedingonprobing(BOP)in%were measured by a blinded operator with a periodontal probe
5 International Dentistry 5 (UNC15)at6months,12months,and30monthsafter loading. Three vestibular and 3 lingual values were collected for every implant by the same dentist. Mean values and standard deviation were recorded. 3. Results Twenty consecutive patients, 8 males and 12 females, with a mean age of 56 (range, 39 78) were treated, and 23 ridges were restored. No patient dropped out of the study, and the followup was at least 30 months after implant insertion for all cases. No deviations from the protocol occurred. Data were collected in sheets (Excel, Microsoft, Redmond, WA USA) at baseline, 6 and 12, 30 months after implant loading. A total of 120 implants were placed, 117 of them with an insertion torque between Ncm, and were immediately loaded while three fixtures were delayed loaded Implant Survival. Threeoutof117immediatelyloaded implants and 1 out of 3 delayed loaded implants were lost in 3 patients, 6 months after implant insertion. No other implants failed in the remaining part of the study accounting for a CSR of 97.7% (calculated on 120 inserted implants) after 30 months. Lost implants were replaced Prosthesis Success. No Prosthesis failures were recorded: all final prosthetic reconstructions were stable and in good function after 30 months Complications. No major biological complications were recorded. Two patients had peri-implant mucosal inflammationwithbopafter6months.improvedoralhygienereduced the peri-implant inflammation. No major mechanical complications occurred. Fourprovisional acrylic bridges fractured 2 4 months after immediate loading and were repaired. Two zirconia ceramic implant bridges had ceramic chipping at 10 and 11 months after loading, which were easily repaired. Four resin titanium bridges experienced fracture of the acrylic resin after 10 and 12 months and were repaired by the dental technician Peri-Implant Marginal Bone Levels. The average marginal bone level at baseline was 0.16 ± 0.10 (calculatedon117 immediateloadedimplants).meanmarginalbonelevelafter 30 months was 1.25 ± 0.31 (calculated on 114 survived immediate loaded implants) (Table 1) Peri-Implant Marginal Bone Remodeling. The average marginal bone remodeling from baseline to last radiological control (30 months) was 1.08 ± 0.34 (calculated on 114 survived immediate loaded implants) (Table 2) Peri-Implant Mucosal Response. After 30 months, mean PPD value was 2.84 ± 0.55 mm, and mean BOP value was 4% ± 2.8%.(calculatedon114survivedimmediateloaded implants) (Tables 3 and 4). Table 1: Peri-implant mean marginal bone levels (n: number of implants). Mean marginal bone level Implant installation 12 months 30 months n = 117 n = 114 n = ± ± ± 0.31 Values represent mean ± SD. Table 2: Peri-implant mean marginal bone remodeling (n: number of implants). Mean marginal bone remodeling 12 months 30 months n = 114 n = ± ± 0.34 Values represent mean ± SD. Table 3: Mean PPD values in mm (n: number of implants). Mean PPD 6 months 12 months 30 months n = 114 n = 114 n = ± ± ± 0.56 Values represent mean ± SD. Table 4: Mean BoP values in % (n: number of implants). Mean BOP values 6 months 12 months 30 months n = 114 n = 114 n = ± 3% 6.4 ± 3.4% 4% ± 2.8% Values represent mean ± SD. 4. Discussion Correctdiagnosisandaccurateimplantplanningarekey factors for success in implant rehabilitation. The use of advanced 3D software planning, by using converted CT scans, reduces the risk of damaging nearby vital structures and allows more precise planning than conventional CT scans [13]. According to these concepts, computer-guided minimally invasive implant treatment protocols promise to revolutionize the way implant dentistry is practiced. Infact,theuseofguidedsurgeryreducestheriskof damaging anatomical structures while exploiting the residual bone volume and also allows a sensible reduction of surgery time while delivering immediate implant supported temporary bridges [3, 5, 10]. In this article, all cases used a full arch immediate loading technique with temporary bridge, avoiding a direct definitive bridge delivery. In fact, deviation of the virtual plan of few degrees can prevent a perfect passive fit of the bridge. To overcome this problem for immediate loading, we always use a screw-retained metal-acrylic temporary bridge and a passive fit, it is obtained directly in the oral cavity using resin
6 6 International Dentistry to connect the temporary cylinder to the metal framework and avoid using a guided abutment. Then after at least 6 months, the final CAD/CAM customized implant bridge is directly connected to the implant neck, and the passive fit of the framework (titanium or zirconia bridge) is clinically evaluatedbeforefinalprosthesisdelivery. Flapless implant placement delivers several advantages to the patient: minimal swelling, pain, and discomfort, elimination of a second surgical procedure, maintaining the softtissuearchitecture,andleavingtheperiosteumintacton buccal and lingual aspect of the ridge which, in turn, maintains a better blood supply and thus reduces the likelihood of bone resorption [14, 15]. On the other hand, flapless guided surgery presents increased risks compared to open surgical approaches due to the inability of the surgeon to verify the accuracy of the guide intraoperatively and to compare the clinical implant position with the virtual planned position. For this reason, guided flapless surgery requires greater surgical experience in implant placement and, in particular, guided surgery, and it does not represent the first option for young clinician not sufficiently trained in guided implant insertion. In spite of clinical skills in flapless implant insertion, an open flap approach is needed when either only few millimeters of keratinized tissue are present, or when an osteoplasty is required for prosthetic reasons. We think that this approach ismandatoryinmostofthemandiblerestorations. One of the main advantages of computer-guided technology in implant dentistry is the better control of the implant axis in relation to the prosthetic tooth position. This leads to a higher predictability of the treatment outcome with subsequent better patient information about the aesthetic final result. Despite some early skepticism about the usefulness of these techniques, it is well known that guided templates are more precise than conventional surgical guides produced by the laboratory when it comes to the soft tissue contours [2]. Different software planning and guided surgery systems exist with differences between them; NobelGuide protocols differentiate from others for the double CT-scanning approach, which allows for better visualization of soft tissue thickness and uses a calibration procedure which has the benefit of more precise implant installation with better visualization of the correct implant axis. This type of guided surgery has been tested in many clinical studies [2, 5, 16], including extremely challenging situations such as patients treated after oncologic resection or gun shot traumas [17]. Nevertheless, some limitations still exist in the application of this new technology. Minimum bone volumes and attached soft tissue are required to place the implant in ideal position in relation to the planned restoration. These limitations could be present in every kind of implant procedures [18]. In cases of flapless guided implant installation, a large amount of attached gingiva is needed, and major skills are required to evaluate if part of the implant surface is out of the bone and or if the planned implant position does not match perfectly the clinical situation. Other critical objections include increased costs, investment costs for the software, the training of the dentists, and the stereolithographically produced surgical templates. Investment of time for the planning process also means an increase in costs. However, three-dimensional analysis of computer tomograms and virtual implant placement, once the operator is familiar with the software, are fast and allow one easy and more precise prosthetic guided implant planning in challenging situation such as resorbed ridges or implant installation in fresh extraction sockets, often avoiding bone grafting procedures [19, 20]. Reduced patient morbidity is another important aspect that cannot be calculated directly in money but is beneficial for the patients. During the last few years, studies have increasingly investigated the clinical and radiological outcome of guided implant placement and they seem to confirm the high predictability of 3D planning software in regards to their ability to offer precision between what is planned and then executed surgically [21].Careful surgical and prosthetic planning is valuable in order to avoid implant misplacement [22]. Sanna et al. have reported in a 5-year prospective trial a cumulative survival rate of 95% with mean marginal bone changes of 2.6 mm in smokers and 1, 2 in non smokers patients [16]. Malo et al., in 2007, reported a CSR of 97.8% with a mean marginal bone loss of 1.9 after 12 months of followup [5]. Merli et al. in a clinical case series reported similar results [3]. Abboud et al. compared two different stereolithographic surgical guide systems, NobelGuide (Nobel Biocare) and SimPlant (Materialise), obtaining similar results in transferring the planned implant positions to the surgical field and allowing the placement of prefabricated provisional [23]. Platzer et al. obtained similar results in a pilot study [24]. Our team has recently retrospectively investigated Nobel- Guide protocol in full edentulous maxillae with a followup of 18 months with a CSR of 97.8% [2] andpublisheda pilot study on a modified protocol for implant installation in free-flaps [17]. High survival rate and marginal bone loss comparable with other procedures were reported and higher patient satisfaction in this challenging situation too. Within the limitations of this study, mainly the relatively low number of patients treated and short observation period, it can be concluded that according with the literature reviews [25], computer-guided surgery and immediate loading seem to represent a viable option for the immediate rehabilitations of completely edentulous jaws with fixed implant supported restorations. Conflict of Interests All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interests. Acknowledgment The authors would like to acknowledge Andrea Cialente for his technical support. References [1]L.Amorfini,S.Storelli,andE.Romeo, Rehabilitationofa dentate mandible requiring a full arch rehabilitation, immediate
7 International Dentistry 7 loading of a fixed complete denture on 8 implants placed with a bone-supported surgical computer-planned guide: a case report, JournalofOralImplantology, vol. 37, pp , [2] S. M. Meloni, G. de Riu, M. Pisano, G. Cattina, and A. Tullio, Implant treatment software planning and guided flapless surgery with immediate provisional prosthesis delivery in the fully edentulous maxilla. A retrospective analysis of 15 consecutively treated patients, European Oral Implantology,vol.3,no.3,pp ,2010. [3] M. Merli, F. Bernardelli, and M. Esposito, Computer-guided flapless placement of immediately loaded dental implants in the edentulous maxilla: a pilot prospective case series, European JournalofOralImplantology,vol.1,no.1,pp.61 69,2008. [4] D. van Steenberghe, R. Glauser, U. Blombäcketal., Acomputed tomographic scan-derived customized surgical template and fixed prosthesis for flapless surgery and immediate loading of implants in fully edentulous maxillae: a prospective multicenter study, Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research, vol. 7, supplement 1, pp. S111 S120, [5] P. Malo, M. D. Nobre, and A. Lopes, The use of computerguided flapless implant surgery and four implants placed in immediate function to support a fixed denture: preliminary results after a mean follow-up period of thirteen months, Prosthetic Dentistry, vol. 97, supplement 6, pp. S26 S34, [6] P.I. Brånemark, B. O. Hansson, R. Adell et al., Osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Experience from a 10-year period, Scandinavian Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. Supplementum,vol.16,pp.1 132,1977. [7] P. A. Schnitman, P. S. Wöhrle, J. E. Rubenstein, J. D. DaSilva, and N. Wang, Ten-year results for Branemark implants immediately loaded with fixed prostheses at implant placement, The International Oral and Maxillofacial Implants,vol.12, no. 4, pp , [8] M.S.Schwarz,S.L.Rothman,M.L.Rhodes,andN.Chafetz, Computed tomography, part I: preoperative assessment of the mandible for endosseous implant surgery, The International IournalofOralandMaxillofacialImplants,vol.2,no.3,pp , [9] K. Verstreken, J. van Cleynenbreugel, G. Marchal, I. Naert, P. Suetens, and D. van Steenberghe, Computer-assisted planning of oral implant surgery: a three-dimensional approach, The International Oral and Maxillofacial Implants, vol. 11, no. 6, pp , [10]S.M.Meloni,G.deRiu,M.Pisano,O.Massarelli,andA. Tullio, Computer assisted dental rehabilitation in free flaps reconstructed jaws: one year follow-up of a prospective clinical study, British Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, vol. 50, pp ,2012. [11] D. van Steenberghe, I. Naert, M. Andersson, I. Brajnovic, J. van Cleynenbreugel, and P. Suetens, A custom template and definitive prosthesis allowing immediate implant loading in the maxilla: a clinical report, The International Oral and Maxillofacial Implants,vol.17,no.5,pp ,2002. [12] E. O. de Almeida, E. P. Pellizzer, M. C. Goiatto et al., Computerguided surgery in implantology: review of basic concepts, JournalofCraniofacialSurgery,vol.21,no.6,pp ,2010. [13] J. J. Abrahams, The role of diagnostic imaging in dental implantology, Radiologic Clinics of North America, vol. 31, no. 1, pp , [14] N. Casap, E. Tarazi, A. Wexler, U. Sonnenfeld, and J. Lustmann, Intraoperative computerized navigation for flapless implant surgery and immediate loading in the edentulous mandible, TheInternationalJournalofOralandMaxillofacialImplants,vol. 20, no. 1, pp , [15] J. Hahn, Single-stage, immediate loading, and flapless surgery, JournaloforalImplantology, vol. 26, no. 3, pp , [16] A. M. Sanna, L. Molly, and D. van Steenberghe, Immediately loaded CAD-CAM manufactured fixed complete dentures using flapless implant placement procedures: a cohort study of consecutive patients, Prosthetic Dentistry,vol.97,no. 6, pp , [17] G. de Riu, S. M. Meloni, M. Pisano, O. Massarelli, and A. Tullio, Computed tomography-guided implant surgery for dental rehabilitation in mandible reconstructed with a fibular free flap: description of the technique, British Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery,vol.50,no.1,pp.30 35,2012. [18] S. M. Meloni, G. de Riu, M. Pisano, N. de Riu, and A. Tullio, Immediate versus delayed loading of single mandibular molars. One-year results from a randomised controlled trial, European Oral Implantology, vol.5,no.4,pp , [19] S. M. Meloni, G. de Riu, M. Pisano, and A. Tullio, Full arch restoration with computer-assisted implant surgery and immediate loading in edentulous ridges with dental fresh extraction sockets. One year results of 10 consecutively treated patients, Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery,2012. [20] T. Cantoni and P. Giovanni, Implant treatment planning in fresh extraction sockets: use of a novel radiographic guide and CAD/CAM technology, Quintessence International,vol.40,no. 9,pp ,2009. [21] D. P. Sarment, P. Sukovic, and N. Clinthorne, Accuracy of implant placement with a stereolithographic surgical guide, TheInternationalJournalofOralandMaxillofacialImplants,vol. 18, no. 4, pp , [22] O. Ozan, I. Turkyilmaz, A. E. Ersoy, E. A. McGlumphy, and S. F. Rosenstiel, Clinical accuracy of 3 different types of computed tomography-derived stereolithographic surgical guides in implant placement, JournalofOralandMaxillofacial Surgery,vol.67,no.2,pp ,2009. [23] M. Abboud, G. Wahl, J. L. Guirado, and G. Orentlicher, Application and success of two stereolithographic surgical guide systems for implant placement with immediate loading, TheInternationalJournalofOralandMaxillofacialImplants,vol. 27,no.3,pp ,2012. [24] S. Platzer, G. Bertha, A. Heschl, W. A. Wegscheider, and M. Lorenzoni, Three-dimensional accuracy of guided implant placement: indirect assessment of clinical outcomes, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery,vol.67,no.2,pp ,2009. [25]S.M.Meloni,G.deRiu,F.M.Lollietal., Computer-aided implant surgery: a critical review of treatment concepts, Journal oforalandmaxillofacialsurgery,medicine,andpathology,2013.
8 Advances in Preventive Medicine The Scientific World Journal Case Reports in Dentistry International Dentistry Scientifica Pain Research and Treatment International Biomaterials Environmental and Public Health Submit your manuscripts at Oral Implants Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine Advances in Oral Oncology Anesthesiology Research and Practice Orthopedics Drug Delivery Dental Surgery BioMed Research International International Oral Diseases Endocrinology Radiology Research and Practice
Guided Implant Surgery and Extraction Sockets. Silvio Mario Meloni Giacomo De Riu Milena Pisano Antonio Tullio
 J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. (July-Sept 2013) 12(3):321 325 DOI 10.1007/s12663-012-0429-8 ORIGINAL PAPER Full Arch Restoration with Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Loading in Edentulous Ridges
J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. (July-Sept 2013) 12(3):321 325 DOI 10.1007/s12663-012-0429-8 ORIGINAL PAPER Full Arch Restoration with Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Loading in Edentulous Ridges
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Available online at British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery xxx (2011) xxx xxx
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery xxx (2011) xxx xxx Computed tomography-guided implant surgery for dental rehabilitation in mandible reconstructed
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery xxx (2011) xxx xxx Computed tomography-guided implant surgery for dental rehabilitation in mandible reconstructed
Computer-guided minimally invasive
 CASE REPORT Guided Flapless Surgery With Immediate Loading for the High Narrow Ridge Without Grafting Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1,2 Sang J. Lee, DMD, MMSc 2 * Guillaume J. Campard, DMD, MMSc 3 Maria
CASE REPORT Guided Flapless Surgery With Immediate Loading for the High Narrow Ridge Without Grafting Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1,2 Sang J. Lee, DMD, MMSc 2 * Guillaume J. Campard, DMD, MMSc 3 Maria
CHAPTER. 1. Uncontrolled systemic disease 2. Retrognathic jaw relationship
 CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
Immediate versus delayed loading of single mandibular molars. One-year results from a randomised controlled trial
 RANDOMISED CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIAL 345 Silvio Mario Meloni, Giacomo De Riu, Milena Pisano, Nicola De Riu, Antonio Tullio Immediate versus delayed loading of single mandibular molars. One-year results
RANDOMISED CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIAL 345 Silvio Mario Meloni, Giacomo De Riu, Milena Pisano, Nicola De Riu, Antonio Tullio Immediate versus delayed loading of single mandibular molars. One-year results
Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space
 Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
Long-term success of osseointegrated implants
 Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 49 A Protocol for Immediate Placement of a Prefabricated Screw-Retained Provisional Prosthesis Using Computed Tomography and Guided Surgery
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 49 A Protocol for Immediate Placement of a Prefabricated Screw-Retained Provisional Prosthesis Using Computed Tomography and Guided Surgery
From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement
 Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1.
 Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Screw retained implant crown restoration with digital workflow using scan body and surgical guide
 Dr. Anthony Mak W Dental Screw retained implant crown restoration with digital workflow using scan body and surgical guide Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Implant Studio 3Shape scan bodies 3Shape
Dr. Anthony Mak W Dental Screw retained implant crown restoration with digital workflow using scan body and surgical guide Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Implant Studio 3Shape scan bodies 3Shape
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants. by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD
 Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Use of Intraoral Welding to Increase the Predictability of Immediately Loaded Computer-Guided Implants
 591 Use of Intraoral Welding to Increase the Predictability of Immediately Loaded Computer-Guided Implants 1 Specialist in Maxillofacial Surgery, Private Practice, Udine, Italy. 2 Private Practice, Udine,
591 Use of Intraoral Welding to Increase the Predictability of Immediately Loaded Computer-Guided Implants 1 Specialist in Maxillofacial Surgery, Private Practice, Udine, Italy. 2 Private Practice, Udine,
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
GuidedService. The ultimate guide for precise implantations
 GuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations ABGuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations At A.B. Dental we've brought implantology into the future with a 3D digitally planned
GuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations ABGuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations At A.B. Dental we've brought implantology into the future with a 3D digitally planned
The patient gave a history of hypertension and gastritis for which was taking Lacidipine 4mg, Omeprazole 20mg and Simvastatin 40mg.
 A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
The development of Teeth-in-an-Hour
 The development of Teeth-in-an-Hour Interview with Daniel van Steenberghe, DDS, MD, PhD, Drhc, HFRCS (Dubl) by Christina Darle Daniel van Steenberghe Professor van Steenberghe is the President of the School
The development of Teeth-in-an-Hour Interview with Daniel van Steenberghe, DDS, MD, PhD, Drhc, HFRCS (Dubl) by Christina Darle Daniel van Steenberghe Professor van Steenberghe is the President of the School
Solid Zirconia Full-Arch Implant Prosthesis (Protocol C All-CAD with Multi-Unit Abutments) BruxZir. FIRST Appointment. The BruxZir
 (Protocol C All-CAD with Multi-Unit Abutments) Step-by-Step Restorative Protocol C The BruxZir Full-Arch Implant Prosthesis offers a fixed, all-zirconia implant solution for edentulous patients desiring
(Protocol C All-CAD with Multi-Unit Abutments) Step-by-Step Restorative Protocol C The BruxZir Full-Arch Implant Prosthesis offers a fixed, all-zirconia implant solution for edentulous patients desiring
Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident
 Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior
 Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
4. What about age? There is no age limit. After puberty, anyone can get dental implants.
 Dental Implants 1. What are Osseointegrated implants? Osseointegrated implants are a new generation of dental implants in Rio de Janeiro, introduced in the 1960 s, they come in different shapes and sizes.
Dental Implants 1. What are Osseointegrated implants? Osseointegrated implants are a new generation of dental implants in Rio de Janeiro, introduced in the 1960 s, they come in different shapes and sizes.
Implant restoration in the aesthetic zone using guided surgery and immediate functional loading
 Prachatipat Hospital Prathumtani Province Dr. Nawakamon Suriyan Implant restoration in the aesthetic zone using guided surgery and immediate functional loading Digital Workflow: clinical patient information
Prachatipat Hospital Prathumtani Province Dr. Nawakamon Suriyan Implant restoration in the aesthetic zone using guided surgery and immediate functional loading Digital Workflow: clinical patient information
Implant Studio Patient Case
 Jung-plant dental office Dr. Jae-min, Lee D.D.S. Implant Studio Patient Case Full mouth rehabilitation Case information On first visit, the patient was wearing a removable partial denture on lower jaw
Jung-plant dental office Dr. Jae-min, Lee D.D.S. Implant Studio Patient Case Full mouth rehabilitation Case information On first visit, the patient was wearing a removable partial denture on lower jaw
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
IMMEDIATE LOADED IMPLANTS IN EDENTULOUS PATIENTS: CLINICAL AND TECHNICAL ASPECTS USING BIOTEC TRE AND KORUM SP IMPLANTS
 ARTICLES MB IMMEDIATE LOADED IMPLANTS IN EDENTULOUS PATIENTS: CLINICAL AND TECHNICAL ASPECTS USING BIOTEC TRE AND KORUM SP IMPLANTS F. Vedove, F. Soda Smile Service, Bassano del Grappa, Vicenza, Italy
ARTICLES MB IMMEDIATE LOADED IMPLANTS IN EDENTULOUS PATIENTS: CLINICAL AND TECHNICAL ASPECTS USING BIOTEC TRE AND KORUM SP IMPLANTS F. Vedove, F. Soda Smile Service, Bassano del Grappa, Vicenza, Italy
Computer-aided design/computer-assisted manufacturing
 Use of a Digitally Planned and Fabricated Mandibular Complete Denture for Easy Conversion to an Immediately Loaded Provisional Fixed Complete Denture. Part 1. Planning and Surgical Phase Jaime L. Lozada,
Use of a Digitally Planned and Fabricated Mandibular Complete Denture for Easy Conversion to an Immediately Loaded Provisional Fixed Complete Denture. Part 1. Planning and Surgical Phase Jaime L. Lozada,
SCD Case Study. Implant-supported overdentures
 SCD Case Study Implant-supported overdentures An implant-retained overdenture may be indicated in patients with changed anatomy, neuromuscular disorders, significant gag reflex or considerable ridge resorption
SCD Case Study Implant-supported overdentures An implant-retained overdenture may be indicated in patients with changed anatomy, neuromuscular disorders, significant gag reflex or considerable ridge resorption
Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment
 Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment Complete dentures have largely become the domain of the denturist due to the dissatisfaction general dentists feel with this treatment. Multiple visits,
Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment Complete dentures have largely become the domain of the denturist due to the dissatisfaction general dentists feel with this treatment. Multiple visits,
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions
 synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions INTRODUCTION synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations 1 The synocta Meso abutments, available
synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations PROSTHETICS Step-by-step instructions INTRODUCTION synocta Meso abutment for cement-retained restorations 1 The synocta Meso abutments, available
Full mouth rehabilitation with digital workflow
 Jung-plant dental office Dr. Jae-min, Lee D.D.S. Full mouth rehabilitation with digital workflow Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Dental System 3Shape Implant Studio Case information On first visit,
Jung-plant dental office Dr. Jae-min, Lee D.D.S. Full mouth rehabilitation with digital workflow Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Dental System 3Shape Implant Studio Case information On first visit,
Restorative Driven Implant Solutions Utilizing the Latest Technology
 Restorative Driven Implant Solutions Utilizing the Latest Technology Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD As a general dentist who has placed nearly 7,000 dental implants, I
Restorative Driven Implant Solutions Utilizing the Latest Technology Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD As a general dentist who has placed nearly 7,000 dental implants, I
Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System)
 Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System) Mucosa-supported complete prostheses with poor fit greatly reduce people's quality of life. This is why the importance of implant-supported
Locator retained mandibular complete prosthesis (isy Implant System) Mucosa-supported complete prostheses with poor fit greatly reduce people's quality of life. This is why the importance of implant-supported
EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/24/14 REVISED DATE: 04/23/15, 04/28/16, 06/22/17, 06/28/18 POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Dental
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
MALO CLINIC PROTOCOL IMMEDIATE-FUNCTION CONCEPT UPPER AND LOWER JAW REHABILITATION: A CLINICAL REPORT
 MALO CLINIC PROTOCOL IMMEDIATE-FUNCTION CONCEPT UPPER AND LOWER JAW REHABILITATION: A CLINICAL REPORT PURPOSE Rehabilitation case with an implant-supported rehabilitation with immediate function implants.
MALO CLINIC PROTOCOL IMMEDIATE-FUNCTION CONCEPT UPPER AND LOWER JAW REHABILITATION: A CLINICAL REPORT PURPOSE Rehabilitation case with an implant-supported rehabilitation with immediate function implants.
Clinical Perspectives
 Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
BUILDING A. Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation. 70 OCTOBER 2016 // dentaltown.com
 BUILDING A MANDI Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation by Dr. Fayette C. Williams Fayette C. Williams, DDS, MD, FACS, is clinical faculty at John Peter Smith Hospital in Fort Worth, Texas,
BUILDING A MANDI Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation by Dr. Fayette C. Williams Fayette C. Williams, DDS, MD, FACS, is clinical faculty at John Peter Smith Hospital in Fort Worth, Texas,
Guided surgery for single-implant placement: A critical review
 Guided surgery for single-implant placement: A critical review Abstract Objective Marco Tallarico, a Silvio Mario Meloni, b Luigi Canullo, a Erta Xhanari c & Giovanni Polizzi d a Private practice, Rome,
Guided surgery for single-implant placement: A critical review Abstract Objective Marco Tallarico, a Silvio Mario Meloni, b Luigi Canullo, a Erta Xhanari c & Giovanni Polizzi d a Private practice, Rome,
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
Guided immediate loading implant surgery planned with Implant Studio D.D.S. Jae-min, Lee
 Guided immediate loading implant surgery planned with Implant Studio D.D.S. Jae-min, Lee Jung-plant Dental office 1 PROLOGUE How can we deal with the immediate loading implant cases easier and more accurate
Guided immediate loading implant surgery planned with Implant Studio D.D.S. Jae-min, Lee Jung-plant Dental office 1 PROLOGUE How can we deal with the immediate loading implant cases easier and more accurate
A novel technique for fabrication of immediate provisional restorations
 Clinical A novel technique for fabrication of immediate provisional restorations Pär-Olov Östman 1 Prosthetic rehabilitation of the edentulous patient with implant-supported restorations is a commonly
Clinical A novel technique for fabrication of immediate provisional restorations Pär-Olov Östman 1 Prosthetic rehabilitation of the edentulous patient with implant-supported restorations is a commonly
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note
 Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Since the introduction of osseointegrated dental implants
 CLINICAL Papilla Formation in Response to Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Restoration Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1 * Chie Hayashi, DDS, PhD, MMSc 2 This retrospective analysis was undertaken
CLINICAL Papilla Formation in Response to Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Restoration Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1 * Chie Hayashi, DDS, PhD, MMSc 2 This retrospective analysis was undertaken
Basic information on the. Straumann Pro Arch TL. Straumann Pro Arch TL
 Basic information on the Straumann Pro Arch TL Straumann Pro Arch TL Contents 1. Introduction 2 1.1 Discover more treatment options with the 4 mm Short Implant 2 2. Technical information 3 3. Step-by-step
Basic information on the Straumann Pro Arch TL Straumann Pro Arch TL Contents 1. Introduction 2 1.1 Discover more treatment options with the 4 mm Short Implant 2 2. Technical information 3 3. Step-by-step
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This
 1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
Immediate post-extraction BIOMIMETIC CORAL IC implant placement in the anterior esthetic zone
 Immediate post-extraction BIOMIMETIC CORAL IC implant placement in the anterior esthetic zone AUTHORS Dr. Antonio Mallebrera Clinica Mallebrera Centro Dental (Petrer, Alicante) Sr. Juan José Sempere Matarredona
Immediate post-extraction BIOMIMETIC CORAL IC implant placement in the anterior esthetic zone AUTHORS Dr. Antonio Mallebrera Clinica Mallebrera Centro Dental (Petrer, Alicante) Sr. Juan José Sempere Matarredona
How successful and predictable are implants placed with flapless guided surgery in fully edentulous rehabilitations?
 C L I N I C A L How successful and predictable are implants placed with flapless guided surgery in fully edentulous rehabilitations? Johan Hartshorne 1 A critical appraisal of a systematic review: V. Moraschini,
C L I N I C A L How successful and predictable are implants placed with flapless guided surgery in fully edentulous rehabilitations? Johan Hartshorne 1 A critical appraisal of a systematic review: V. Moraschini,
Element-Z Screw-Retained Hybrid
 Element-Z Screw-Retained Hybrid Implant-Level Restoration Step-by-Step Restorative Protocol The Element-Z Screw-Retained Hybrid offers a fixed, all-ceramic implant solution for edentulous patients desiring
Element-Z Screw-Retained Hybrid Implant-Level Restoration Step-by-Step Restorative Protocol The Element-Z Screw-Retained Hybrid offers a fixed, all-ceramic implant solution for edentulous patients desiring
Specialty Dentistry. Dentistry has nine specialty fields recognized by the American Dental Association
 Specialty Dentistry Dentistry has nine specialty fields recognized by the American Dental Association Dental Public Health Endodontics Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology
Specialty Dentistry Dentistry has nine specialty fields recognized by the American Dental Association Dental Public Health Endodontics Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology
Immediate fixed teeth a treatment concept for edentulous patients
 52 Maxillary rehabilitation using the All-on-4 concept Immediate fixed teeth a treatment concept for edentulous patients DR DUSAN VASILJEVIC AND VLADAN VASILJEVIC, FRIEDEBURG, GERMANY The number of edentulous
52 Maxillary rehabilitation using the All-on-4 concept Immediate fixed teeth a treatment concept for edentulous patients DR DUSAN VASILJEVIC AND VLADAN VASILJEVIC, FRIEDEBURG, GERMANY The number of edentulous
A FAMILY FULL OF SMILES
 A FAMILY FULL OF SMILES Prologue The saga started years ago. As a poor southern boy, when Danny had a toothache, the normal protocol was to extract the offending tooth. Subsequently, as an adult, Dan chewed
A FAMILY FULL OF SMILES Prologue The saga started years ago. As a poor southern boy, when Danny had a toothache, the normal protocol was to extract the offending tooth. Subsequently, as an adult, Dan chewed
Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft
 The Atrophic crest Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft Dr. Paolo Borelli DDS, Italy Dr. Massimiliano Favetti DDS, Italy
The Atrophic crest Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft Dr. Paolo Borelli DDS, Italy Dr. Massimiliano Favetti DDS, Italy
Inclusive Tooth Replacement System
 Optimizing Anterior Esthetics with the Inclusive Tooth Replacement System by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant treatment has changed so much over the years. In the past it was acceptable to place
Optimizing Anterior Esthetics with the Inclusive Tooth Replacement System by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant treatment has changed so much over the years. In the past it was acceptable to place
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel
 PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Intraoperative Computerized Navigation for Flapless Implant Surgery and Immediate Loading in the Edentulous Mandible
 Intraoperative Computerized Navigation for Flapless Implant Surgery and Immediate Loading in the Edentulous Mandible Nardy Casap, DMD, MD 1 /Eyal Tarazi, DMD 2 /Alon Wexler, DMD 2 /Uri Sonnenfeld, DMD
Intraoperative Computerized Navigation for Flapless Implant Surgery and Immediate Loading in the Edentulous Mandible Nardy Casap, DMD, MD 1 /Eyal Tarazi, DMD 2 /Alon Wexler, DMD 2 /Uri Sonnenfeld, DMD
An Introduction to Dental Implants
 An Introduction to Dental Implants Aims: This article provides an introduction to dental implants, outlining the categories of dental implants, the phases involved in implant dentistry and assessing a
An Introduction to Dental Implants Aims: This article provides an introduction to dental implants, outlining the categories of dental implants, the phases involved in implant dentistry and assessing a
Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options
 Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options First Name Last Name Objectives Identify the need and opportunity to treat full arch patients with fixed detachable
Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options First Name Last Name Objectives Identify the need and opportunity to treat full arch patients with fixed detachable
loading of implant supported hybrid prostheses after multiple extractions: A case series
 Planning implant placement on 3D stereolithographic models applied with immediate loading of implant supported hybrid prostheses after multiple extractions: A case series Ian Aires* *Corresponding author:
Planning implant placement on 3D stereolithographic models applied with immediate loading of implant supported hybrid prostheses after multiple extractions: A case series Ian Aires* *Corresponding author:
DIGITAL DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING FOR PLACEMENT AND RESTORATION OF SINGLE IMPLANTS IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA By Timothy Kosinski, DDS
 DIGITAL DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING FOR PLACEMENT AND RESTORATION OF SINGLE IMPLANTS IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA By Timothy Kosinski, DDS Dental implants have undergone many positive advances in recent
DIGITAL DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING FOR PLACEMENT AND RESTORATION OF SINGLE IMPLANTS IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA By Timothy Kosinski, DDS Dental implants have undergone many positive advances in recent
DIOnavi. Brochure Ver.2. Product Introduction: DIOnavi. Clinical Case Report
 DIOnavi. Brochure Ver.2 Product Introduction: DIOnavi. Clinical Case Report Evolved for Precision and Stability Digital Navigation Implant 04 Product Introduction: DIOnavi. One-Step Protocol 10 Clinical
DIOnavi. Brochure Ver.2 Product Introduction: DIOnavi. Clinical Case Report Evolved for Precision and Stability Digital Navigation Implant 04 Product Introduction: DIOnavi. One-Step Protocol 10 Clinical
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
INTRODUCTION. General Information. Important Warning
 S u r g i c a l M a n u a l F o r M a g i x D e n t a l I m p l a n t INTRODUCTION General Information Read this manual carefully before starting treatment. This manual should be used as a reference guide
S u r g i c a l M a n u a l F o r M a g i x D e n t a l I m p l a n t INTRODUCTION General Information Read this manual carefully before starting treatment. This manual should be used as a reference guide
Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide
 Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide Drago, Carl DDS, MS ISBN-13: 9780813828831 Table of Contents Contributors. Foreword. Acknowledgments. Chapter 1. Introduction To Implant Dentistry. 1. Introduction.
Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide Drago, Carl DDS, MS ISBN-13: 9780813828831 Table of Contents Contributors. Foreword. Acknowledgments. Chapter 1. Introduction To Implant Dentistry. 1. Introduction.
PART 6. Implant Prosthodontics
 PART 6 Implant Prosthodontics 26/11/2015 LIMU Dr. Rafik M. Alkowafi 188 In many respects the prosthodontic treatment for a single tooth is straightforward if the planning and placement of the implant is
PART 6 Implant Prosthodontics 26/11/2015 LIMU Dr. Rafik M. Alkowafi 188 In many respects the prosthodontic treatment for a single tooth is straightforward if the planning and placement of the implant is
Guided implant placement using the trephine drill nonsleeve and immediate provisional crown or bridge in the esthetic zone
 Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences Vol. 8(5) pp. 054-059, August 2017 DOI: http:/dx.doi.org/10.14303/jmms.2017.050 Available online http://www.interesjournals.org/jmms Copyright 2017 International
Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences Vol. 8(5) pp. 054-059, August 2017 DOI: http:/dx.doi.org/10.14303/jmms.2017.050 Available online http://www.interesjournals.org/jmms Copyright 2017 International
Simultaneous implant reconstruction of the maxilla and mandible
 Simultaneous implant reconstruction of the maxilla and mandible By Dr Prashant Patel, Gusseppi Zuppardi and Oliver Tilch A 67-year-old female patient was referred to our practice complaining of her dislike
Simultaneous implant reconstruction of the maxilla and mandible By Dr Prashant Patel, Gusseppi Zuppardi and Oliver Tilch A 67-year-old female patient was referred to our practice complaining of her dislike
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
SCD Case Study. The ability of the integrated implant to bear a load must be greater than the anticipated load during function.
 SCD Case Study Dental implants offer an effective and predictable way to replace teeth. Function, aesthetics and phonetics are regained. The long-term success clinically and aesthetically depends upon
SCD Case Study Dental implants offer an effective and predictable way to replace teeth. Function, aesthetics and phonetics are regained. The long-term success clinically and aesthetically depends upon
NobelActive. The NobelActive technical story
 NobelActive The NobelActive technical story The NobelActive technical story NobelActive origins The life cycle of NobelActive began following years of research and development on a self-drilling and bone-condensing
NobelActive The NobelActive technical story The NobelActive technical story NobelActive origins The life cycle of NobelActive began following years of research and development on a self-drilling and bone-condensing
Case Report Total CAD/CAM Supported Method for Manufacturing Removable Complete Dentures
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 1259581, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1259581 Case Report Total CAD/CAM Supported Method for Manufacturing Removable Complete Dentures Arthur
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 1259581, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1259581 Case Report Total CAD/CAM Supported Method for Manufacturing Removable Complete Dentures Arthur
Digital Implant Dentistry Workflow
 Digital Implant Dentistry Workflow Ahmad Kutkut, DDS, MS, FICOI, DICOI Director of Predoctoral Implant Program Chair UKCD Implant Board ahmad.kutkut@uky.edu Disclaimer Neither I or any of my immediate
Digital Implant Dentistry Workflow Ahmad Kutkut, DDS, MS, FICOI, DICOI Director of Predoctoral Implant Program Chair UKCD Implant Board ahmad.kutkut@uky.edu Disclaimer Neither I or any of my immediate
International Journal of Applied Dental Sciences 2018; 4(1): Dr. Renu gupta, Dr. RP Luthra, Suhani Kukreja
 2018; 4(1): 213-218 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2018; 4(1): 213-218 2018 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 06-11-2017 Accepted: 07-12-2017 Dr. Renu gupta Professor and head, Department
2018; 4(1): 213-218 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2018; 4(1): 213-218 2018 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 06-11-2017 Accepted: 07-12-2017 Dr. Renu gupta Professor and head, Department
UTILISATION OF COMPUTER BASED
 UTILISATION OF COMPUTER BASED GUIDED SURGERY IN THE MANAGEMENT OF PARTIAL EDENTULISM PATRICK HENRY 1, JILL DEPIAZZI 1, GLEN LIDDELOW 1, BRENT ALLAN 2, DAVID DUNN 3 Introduction Recently, increased emphasis
UTILISATION OF COMPUTER BASED GUIDED SURGERY IN THE MANAGEMENT OF PARTIAL EDENTULISM PATRICK HENRY 1, JILL DEPIAZZI 1, GLEN LIDDELOW 1, BRENT ALLAN 2, DAVID DUNN 3 Introduction Recently, increased emphasis
Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior Region Along with Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting- A Case Report.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
NobelProcera Product Overview
 NobelProcera Product Overview TM EXPERIENCE THE NEW WORLD OF CAD/CAM DENTISTRY Most versatile product and material portfolio Latest production technology for Precision Milled Restorations PMR Cutting-edge
NobelProcera Product Overview TM EXPERIENCE THE NEW WORLD OF CAD/CAM DENTISTRY Most versatile product and material portfolio Latest production technology for Precision Milled Restorations PMR Cutting-edge
Immediate loading and implant surgery with digital workflow
 Mirero Dental Clinic Dr. Jaemin Lee Immediate loading and implant surgery with digital workflow Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Dental System 3Shape Implant Studio Case information Patient, 32-year
Mirero Dental Clinic Dr. Jaemin Lee Immediate loading and implant surgery with digital workflow Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Dental System 3Shape Implant Studio Case information Patient, 32-year
SIMPLANT Guided Surgery delivering restorative-driven implant treatment
 SIMPLANT Guided Surgery delivering restorative-driven implant treatment SIMPLANT the key to unlocking digital potential As part of the DENTSPLY Implants Digital Solutions portfolio, SIMPLANT digital implant
SIMPLANT Guided Surgery delivering restorative-driven implant treatment SIMPLANT the key to unlocking digital potential As part of the DENTSPLY Implants Digital Solutions portfolio, SIMPLANT digital implant
TRIPOD A new protocol for immediate loading
 I industry report _ TRIPOD procedure TRIPOD A new protocol for immediate loading Complete maxillary implant-supported prostheses Author_Dr Jean-Nicolas Hasson, Dr Jacques Hassid & Dominique Fricker, France
I industry report _ TRIPOD procedure TRIPOD A new protocol for immediate loading Complete maxillary implant-supported prostheses Author_Dr Jean-Nicolas Hasson, Dr Jacques Hassid & Dominique Fricker, France
Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois Phone: Fax:
 Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D. 2325 N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois 60614 Phone: 312-608-6881 Fax: 773-296-0601 Samanthawchou@gmail.com What is our role as the dentist? "We live in a culture in which people
Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D. 2325 N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois 60614 Phone: 312-608-6881 Fax: 773-296-0601 Samanthawchou@gmail.com What is our role as the dentist? "We live in a culture in which people
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
Use of Technology for Improved Implant Use in The OMS Practice AAOMS 93rd Annual Meeting, Philadelphia, PA
 Use of Technology for Improved Implant Use in The OMS Practice AAOMS 93rd Annual Meeting, Philadelphia, PA Image Navigation Surgery For Implant Placement - A Comparison To Guided Stent Use Robert W. Emery
Use of Technology for Improved Implant Use in The OMS Practice AAOMS 93rd Annual Meeting, Philadelphia, PA Image Navigation Surgery For Implant Placement - A Comparison To Guided Stent Use Robert W. Emery
 16 www.inclusivemagazine.com Maximizing Clinical Flexibility with the Open Platform Inclusive Tooth Replacement Solution by Tarun Agarwal, DDS, PA Go online for in-depth content The Inclusive Tooth Replacement
16 www.inclusivemagazine.com Maximizing Clinical Flexibility with the Open Platform Inclusive Tooth Replacement Solution by Tarun Agarwal, DDS, PA Go online for in-depth content The Inclusive Tooth Replacement
Case Report Prosthodontic Rehabilitation of the Patient with Severely Worn Dentition: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 961826, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/961826 Case Report Prosthodontic Rehabilitation of the Patient with Severely Worn Dentition: A Case Report Mahnaz Hatami,
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 961826, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/961826 Case Report Prosthodontic Rehabilitation of the Patient with Severely Worn Dentition: A Case Report Mahnaz Hatami,
م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION
 Lec.1 م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION االسنان طب Prosthodontics is the branch of dentistry pertaining to the restoration and maintenance of oral function, comfort, appearance,
Lec.1 م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION االسنان طب Prosthodontics is the branch of dentistry pertaining to the restoration and maintenance of oral function, comfort, appearance,
M. Daas, 1,2 A. Assaf, 3,4 K. Dada, 2,5 and J. Makzoumé Introduction
 International Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 824127, 10 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/824127 Clinical Study Computer-Guided Implant Surgery in Fresh Extraction Sockets and Immediate Loading of
International Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 824127, 10 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/824127 Clinical Study Computer-Guided Implant Surgery in Fresh Extraction Sockets and Immediate Loading of
Benefits of CBCT in Implant Planning
 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
Real World Implant Prosthetics: Fixed and Removable Samuel M. Strong, DDS
 Real World Implant Prosthetics: Fixed and Removable Samuel M. Strong, DDS Presurgical planning Health history-systemic conditions Case presentation Financial agreement Radiographs- PA s, FMX, Panoramic,
Real World Implant Prosthetics: Fixed and Removable Samuel M. Strong, DDS Presurgical planning Health history-systemic conditions Case presentation Financial agreement Radiographs- PA s, FMX, Panoramic,
COMPUTER-ASSISTED VIRTUAL TREATMENT
 COMPUTER-ASSISTED VIRTUAL TREATMENT PLANNING COMBINED WITH FLAPLESS SURGERY AND IMMEDIATE LOADING IN THE REHABILITATION OF PARTIAL EDENTULIES G. DE VICO, D. SPINELLI, M. BONINO, R. SCHIAVETTI, A. POZZI,
COMPUTER-ASSISTED VIRTUAL TREATMENT PLANNING COMBINED WITH FLAPLESS SURGERY AND IMMEDIATE LOADING IN THE REHABILITATION OF PARTIAL EDENTULIES G. DE VICO, D. SPINELLI, M. BONINO, R. SCHIAVETTI, A. POZZI,
4766 Research Dr. San Antonio, TX insightdentalsystems.com
 OVERVIEW OF THE INSIGHT DENTAL IMPLANT DELIVERY SYSTEM The IDS system comes in a unit dose implant system where its advantage provides sterile instrumentation in one single-use kit. It is organized to
OVERVIEW OF THE INSIGHT DENTAL IMPLANT DELIVERY SYSTEM The IDS system comes in a unit dose implant system where its advantage provides sterile instrumentation in one single-use kit. It is organized to
Peri-implant health and peri-implant bone stability after immediate implant placement
 2 First report of a two-year retrospective study with a newly developed bone-level implant system Peri-implant health and peri-implant bone stability after immediate implant placement DR-MEDIC STOM. HENRIETTE
2 First report of a two-year retrospective study with a newly developed bone-level implant system Peri-implant health and peri-implant bone stability after immediate implant placement DR-MEDIC STOM. HENRIETTE
In 1977, Lew1 developed a passive
 CLINICAL AN OVERVIEW OF THE LEW ATTACHMENT: CLINICAL REPORTS Jack Piermatti, DMD Sheldon Winkler, DDS KEY WORDS Lew attachment Atrophic mandible Subperiosteal implant Root form implant Although the Lew
CLINICAL AN OVERVIEW OF THE LEW ATTACHMENT: CLINICAL REPORTS Jack Piermatti, DMD Sheldon Winkler, DDS KEY WORDS Lew attachment Atrophic mandible Subperiosteal implant Root form implant Although the Lew
Osseointegrated implant-supported
 CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
