Successfully providing
|
|
|
- Rosalind McCarthy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The role of cone-beam computed tomography in the planning and placement of implants Philip Worthington, MD, DDS, BSc, FDRCS; Jeffrey Rubenstein, DMD, MS; David C. Hatcher, DDS, MSc, MRCD(c) Successfully providing dental implants to patients who have lost teeth and frequently the surrounding bone relies on the careful gathering of clinical and radiological information, on interdisciplinary communication and on detailed planning. Early in the evolution of osseointegration surgery, clinicians placed implants in regions of maximum bone volume without fully taking into consideration where the crown eventually would be placed. Biomechanics, esthetics and maintenance can be compromised if the implant location does not align properly with the crown, ultimately resulting in substandard outcomes, including failure. In worst-case scenarios, implant placement can result in implants that are placed suboptimally and ultimately remain in the bone unrestored. Implant planning should be driven by prosthodontic concerns, using a crown-to-bone approach. The crown-to-bone concept takes into account the site-specific restorative requirements, followed by finding the ideal location for the supporting implant and finally investigating the bone to determine the feasibility of implant placement. IMAGING Imaging options began with twodimensional (2-D) imaging tech- ABSTRACT Background. Three-dimensional imaging, particularly cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT), has made significant contributions to the planning and placement of implants to replace missing teeth. The accuracy of CBCT data can be used to fabricate a surgical guide that transfers the implant planning information to the surgical site to facilitate implant placement. The authors describe a method for applying CBCT data to aid in the planning and placement of implants. Methods. The authors outline clinical goals for implant planning and placement and describe the anatomical and prosthetic requirements for successful implant placement. They also present imaging solutions, including CBCT scanning and software analysis, to the clinical goals. Conclusions. Virtual implant planning using CBCT data allows the clinicians to create and visualize the end result before initiating treatment. CBCT scans are accurate and cost effective and can be used to improve communication and coordination of a multidisciplinary team to achieve the desired clinical outcome. Virtual planning allows clinicians to investigate multiple treatment scenarios until the optimum treatment plan is attained. The optimized virtual plan may be converted through modeling to create a surgical guide for clinical implementation. Clinical Implications. The precise planning and delivery of implants to replace missing teeth can avert recognized and concealed treatment problems. This process aids the clinician and benefits the patient. Key Words. Cone-beam computed tomography; implant planning; surgical guide; virtual planning; simulations. JADA 2010;141(10 suppl):19s-24s. Dr. Worthington is a professor emeritus, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, University of Washington, Seattle. Dr. Rubenstein is a professor and the director, Maxillofacial Prosthetic Service, Department Restorative Dentistry/Division of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, University of Washington, Seattle. Dr. Hatcher is a clinical professor, College of Dental Medicine, University of Southern Nevada, Henderson, and an adjunct associate clinical professor, Arthur A. Dugoni School of Dentistry, University of the Pacific, San Francisco, and he maintains a private practice in oral and maxillofacial radiology. Address reprint requests to Dr. Hatcher at 99 Scripps Drive, Suite 101, Sacramento, Calif , David@ddicenters.com. JADA 141(10 suppl) October S
2 niques and now include three-dimensional (3-D) imaging techniques. Diagnostic information, treatment planning and treatment benefits levels have increased with the use of 3-D imaging techniques (Table 1 ). Using 3-D virtual planning techniques before treatment has resulted in optimal implant placement and improved clinical outcomes. The development of 3-D scanning such as cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) 1 instead of planar films has led to improved visualization and comprehension of the anatomy in the areas in which implants are being planned for placement. 1 Computed tomographic (CT) scans and CBCT scans reproduce the anatomy with a submillimetric accuracy. 2 Several methods have evolved to exploit 3-D data volumes (viewable CBCT data) to fulfill imaging goals. Specialized software allows for cross-referencing and display of multiple view angles from a specific implant site. The view angles commonly are axial, reconstructed panoramic and cross-sectional views of the jaws. The displayed reconstructed images can be measured directly on screen or on a true-sized printed copy to determine the anatomical dimensions. If clinicians are limited to a true-sized printed copy, it can be difficult for them to consider the prosthodontic management of the implant site. Clinicians can use implant radiographic guides to transfer the prosthodontic plan to the CBCT scan. A fabricated radiographic guide is positioned in the patient s mouth during the scan. Radiographic guides have evolved and can assist in a spectrum of restorative planning. The simple radiographic guide includes a radiopaque marker that indicates the desired placement position of an implant. A complex radiographic guide allows for visualization of the prosthetic tooth, occlusion with the opposing tooth, planned implant location, implant angle and thickness of the soft tissue between the bone and the tooth. CBCT visualization of the prosthodontic plan allows the clinician to evaluate the subjacent anatomy, test the feasibility of the proposed implant placement and make needed modifications to the plan to optimize the spatial and functional relationships between the planned prosthetic treatment and the anatomy. Historically, clinicians have facilitated the transfer of the crown-to-bone approach (transfer of virtual plan to surgical placement) by providing a surgical guide or template to the surgeon with the hope that the intended tooth position and implant placement would be in concert with the intended treatment goals. The radiographic guide now can be modified to become a surgical guide. A surgical guide can be designed and constructed on the basis of computer analysis of the available bone, the proximity of teeth to the proposed implant site and structures to be avoided in implant placement. This information can help clinicians comprehend better the optimal location of implant placement and ultimately lead to a better potential for a successful outcome. CBCT can accurately capture, display and provide visualization of 3-D maxillofacial anatomy. 2 For CBCT to be implemented optimally, clinicians first must consider exactly what information is essential. This step provides a clinical basis for the clinician to customize the radiographic evaluation and interpretation. CBCT can be used to assess alveolar bone height, bone width, bone quality, pathosis, interarch space, maxillomandibular relationships and temporomandibular joints. CBCT is valuable for the evaluation of the following anatomical features of the mandible, maxilla and facial bones. 3-9 Mandible. CBCT scans of the mandible can help clinicians determine the size of the lingual concavity in the symphyseal regions. Occasionally, the mandible may have an unexpected lingual concavity in the posterior region of the mandible. In the inferior alveolar canal (IAC), CBCT scans can show whether the canal is single or divided and how it is placed buccolingually. CBCT scans can help clinicians distinguish the IAC from large sinusoidal spaces in cases in which the walls of the IAC are not well defined. Studies have been published that outline the anatomical variations of the mental nerve region. 3-9 These variations can make implant placement problematic. CBCT scans can help clinicians answer the following questions: ddoes the mental nerve have an anterior loop? If so, what is its size? dis there an unusual branching pattern of the mental nerve as it leaves the IAC? How is it placed buccolingually? dis site preparation necessary? dwhat is the state of any previously placed bone graft material? ABBREVIATION KEY. CBCT: Cone-beam computed tomography. CT: Computed tomography. IAC: Inferior alveolar canal. 3-D: Three-dimensional. 2-D: Twodimensional. 20S JADA 141(10 suppl) October 2010
3 TABLE Value comparison of implant imaging modalities* commonly used to evaluate implant sites. IMAGING GOAL TWO-DIMENSIONAL IMAGING SOURCES THREE-DIMENSIONAL IMAGING SOURCES Cephalographic Periapical Panoramic Tomography Computed Tomography Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Bone Height Bone Width Long Axis or Ridge Anatomy Localized Bone Quality Pathosis Identified Jaw Boundaries Determination Virtual Planning Guide Fabrication Facilitated Communication Aid Benefit/Risk/Cost Ratio * The imaging modalities are ranked by their ability to satisfy implant planning imaging goals. Ranking scale: 0 = no value, 1 = low value, 2 = mild value, 3 = moderate value, 4 = high value. Adapted with permission of Journal of the California Dental Association from Hatcher and colleagues. 1 Maxilla. CBCT scans can help clinicians answer the following questions about the maxilla: dwhat is the size of the labial cortical concavity in the lateral incisor region? dif the maxillary sinus has an incomplete septum, is it substantial enough to accommodate an implant tip? Or is it merely a nuisance during membrane elevation? dhow substantial is the paranasal bony buttress in the maxillary canine region? Is site preparation needed? dwhat is the state of any previously placed bone graft material? dis there useful bone in the pterygoid region? Facial bones. Clinicians can use CBCT scans to determine how substantial the body of the zygoma is and what quantity of bone is available for craniofacial implants in the orbital rims and in the immediate paranasal region. They also can use CBCT scans to determine when unorthodox implant placement (for example, oblique implants in the posterior atrophic mandible) is a possibility. 10 Underlying all of these considerations is the desire to optimize implant placement to facilitate management by the restorative dentist and to satisfy the patient. But also and equally important is the desire to do no harm. We have seen many instances in which nerve injuries could have been avoided if the clinician had conducted a preliminary CBCT examination. Similarly, unintended lingual perforation of the mandible (with possible hematoma formation in the retrosymphyseal region, damage to the submandibular gland in the molar region or both) may be avoided if 3-D imaging is used. 1 MODELING SYSTEMS Several modeling systems, such as stereolithography and dot matrix model fabrication, can be used to fabricate surgical guides. Drilling sleeves facilitate the drilling precision during surgery. Although these modeling systems can be precise and accurate with regard to fabrication and guiding capabilities, there are inherent variables that can mitigate precise implant placement. These variables include dimensional change of the polymeric materials used in the fabrication of the guides, operator error in drilling despite significant constraints created by the guide designs, compression of soft tissues during guided placement, and accuracy and stabilization of the guide during placement. Implant placement involves a sequence of steps, and the inherent error in each step must be minimized. The results of evaluations of CBCT scans and comparison of them against a known standard 2,11 and standard 2-D JADA 141(10 suppl) October S
4 Figure 1. A virtual planning environment for implant replacement of teeth nos. 9, 10, 13 and 14. The patient and the stone casts were scanned using a cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) unit. Using anatomy imaging software, Anatomage (San Jose, Calif.) converted the scans into an interactive digital model (AnatoModel, Anatomage). The AnatoModel consists of several objects and CBCT volume, all of which are registered to the same global coordinate system (shown here with volume and exploded model). Each object (maxillary model, mandibular model, tooth objects and implant objects) has a local coordinate system that allows for object manipulation and monitoring by the global coordinate system. In this case, the virtual teeth were created by duplicating and mirroring the teeth from the opposite side. images 2 have shown CBCT scans to be spatially accurate and precise. Implant planning, surgical fabrication and implant placement have been tested to an accuracy of 0.9 millimeters at the ridge crest and 1.0 mm at the apex on an in vitro model. 12 The error range in implant placement is slightly higher in vivo, likely because of variations in surgical guide placement and stability and the clinician s inability to constrain the drill exactly along the drill guide path A recent software development has simplified the process of implant planning and placement by eliminating the requirement for fabrication of a radiographic guide (Figures 1-3). 18 This development allows the clinician to scan both the patient s maxillofacial region of interest and the stone dental casts with CBCT. The scans can be completed in less than a minute, and from that point until the implant is placed, all planning and guide fabrication can be completed by means of a virtual patient model. The virtual environment uses a multiobject viewer in which patient-specific objects (including the maxillary and mandibular dentition created from stone cast scans, library of teeth and implant objects, and the CT scan of the jaw) can be combined in the same 3-D matrix for planning (Figure 1). The dentition objects created from intraoral laser scanning of the dentition or scanning the stone casts reproduces the patient s tooth anatomy with a better fidelity than that of CBCT of the natural dentition because of a reduction in beam-hardening and scatter artifacts. The combination of CBCT with intraoral laser scanning or CBCT of stone casts provides optimal representation of surface and subsurface anatomy. This virtual environment allows clinicians to articulate the maxillary and mandibular dentition and to replace missing teeth in their ideal functional positions virtually. The quality and volume assessment of the subjacent bone and virtual planning of the implants position and axial orientation can be performed on the virtual model (Figure 2). The modeling environment allows for simultaneous iteration of all of variables (for example, tooth position, jaw articulation, bone quality, bone volume and implant placement) until the optimum treatment plan is achieved. Once the optimum implant plan has been determined, the virtual model can be submitted for fabrication of a surgical guide. CBCT scans and the associated software have led to an increase in implant placement. The next development in implant technology may be robotic or computer assistance for the surgical and restorative phases of implant therapy. This process is already in development, 19,20 albeit in its infancy. CONE-BEAM COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IMPLANT PLANNING PROTOCOL The following CBCT scanning protocol can help clinicians meet the imaging goals we defined previously in this article: dlimit the scanning field of view to the dental 22S JADA 141(10 suppl) October 2010
5 A B C Figure 2. The virtual placement of an implant (A) and interactive visualization of the volume and implant (B). The software computes and displays the attenuation value (bone density) of the bone adjacent to the virtual implant (B). Volume rendering of left posterior maxilla showing virtual 3-D placement of implants (C). The local coordinate system for tooth site no. 13 was activated. The bone density can be color mapped to approximate Hounsfield units (HUs). HUs express the relative attenuation value of various anatomical tissues or spaces by means of a scale that has been calibrated to give the radiodensity of distilled water an HU of zero. arch being evaluated and the crowns of the opposing arch; dorient the occlusal plane to be parallel to the horizon; dseparate the maxila B lary and mandibular teeth with a thin sheet of wax; dselect a relatively small volume element (voxel) size (0.20 mm or 0.25 mm) unless you are limited by the planc D ning software (a relatively small voxel size creates the best opportunity to visualize anatomical structures, such as the mandibular canal, particularly in patients with a low attenuation value [osteopenia]); E F duse patient immobifigure 3. Demonstration of the virtual replacement and articulation of missing teeth with the opposing lization techniques arch model (A, B and D). Note that the stone cast registration to the cone-beam computed tomography volume eliminates the beam-hardening and scatter artifacts that often occur with teeth and their metallic during scanning; (C). The model also shows gingival soft-tissue contours (C and F). During the virtual implant dscan stone models or restorations placement, the clinician can consider the location of the replacement crown and the subjacent anatomy impressions or scan (B). The three-dimensional positioning of the implants can be visualized without the model, and virtual teeth can be visualized (D). Teeth nos. 9, 10, 13 and 14 were duplicated from corresponding teeth on the teeth using an intraopposite side of the arch (E). oral laser. Creating an image portfolio a specific and communicate imaging goals and findings. The folprecise collection of image views and anatomical lowing are steps clinicians can take to create an renderings is an effective way to visualize and image portfolio. JADA 141(10 suppl) October S
6 ddisplay a reconstructed panoramic projection at a slab thickness that is sufficient to show alveolar process and teeth (approximately 15.0 mm thick). ddisplay a reconstructed panoramic projection at a slab thickness of 1.0 mm or less with nerves marked on mandible scans. ddisplay cross-sectional slices of each of the proposed implant sites (cross-sectional slices are generated automatically by the software to be perpendicular to the arch curve created on the axial section mapped for the panoramic reconstruction; these slices are displayed by selecting a 1.0-mm slice thickness and a spacing of 1.0 or 2.0 mm). dfabrication of a multiobject 3-D model of the planning sites. CLINICAL VALUE PROPOSITION A clinical value proposition is a subjective determination that considers the ratio of benefit to cost, risk and time efficiency. The variables that define a clinical value proposition include desired diagnostic information, the risks and costs to the patient, and time efficiency. The implant planning and placement exercise begins with developing clinical objectives, which sets into motion a sequence of steps designed to fulfill those objectives. The best implant placement plans are achieved when consideration is given to all of the key information. CBCT, unlike traditional 2-D imaging methods, provides anatomical accuracy. The use of virtual modeling provides the opportunity for clinicians to solicit and combine input from a multidisciplinary team to create a single optimal treatment plan. Using the virtual environment could be the most efficient and cost effective method for planning. Restricting the CBCT scanning field of view to only the areas of interest minimizes the radiation dose. Careful planning to avoid nerve injury, penetrations of jaw boundaries and implant proximity to adjacent teeth, as well as to facilitate implant alignment with the prosthetic elements, improves the potential for achieving successful outcomes. CONCLUSION CBCT provides the anatomical data that can generate a collaborative treatment plan and achieve optimal outcomes for the restorative dentist, radiologist, surgeon and patient. The evolution in CBCT hardware and software has been responsible, in part, for the increase in the precise planning and placement of implants while minimizing the associated risks. Disclosure. None of the authors reported any disclosures. 1. Hatcher DC, Dial C, Mayorga C. Cone beam CT for pre-surgical assessment of implant sites. J Calif Dent Assoc 2003;31(11): Stratemann SA, Huang JC, Maki K, Miller AJ, Hatcher DC. Comparison of cone beam computed tomography imaging with physical measures. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2008;37(2): Arzouman MJ., Otis L, Kipnis V, Levine D. Observations of the anterior loop of the inferior alveolar canal. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1993;8(3): Kieser J, Kuzmanovic D, Payne A, Dennison J, Herbison P. Patterns of emergence of the human mental nerve. Arch Oral Biol 2002;47(10): Kuzmanovic DV, Payne AG, Kieser JA, Dias GJ. Anterior loop of the mental nerve: a morphological and radiographic study. Clin Oral Implants Res 2003;14(4): Mardinger O, Chauschu G, Arensburg B, Taicher S, Kaffe I. Anterior loop of the mental canal: an anatomical-radiologic study. Implant Dent 2000;9(2): Rosenquist B. Is there an anterior loop of the inferior alveolar canal? Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 1996;16(1): Solar P, Ulm C, Frey G, Metjka M. A classification of the intraosseous paths of the mental nerve. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1994;9(3): Worthington P. Injury to the inferior alveolar nerve during implant placement: a formula for protection of the patient and clinician. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2004;19(5): Stella JP, Abolenen H. Restoration of the atrophied posterior mandible with transverse alveolar maxillary/mandibular implants: technical note and case report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2002;17(6): Peck JL, Sameshima GT, Miller A, Worth P, Hatcher DC. Mesiodistal root angulation using panoramic and cone beam CT. Angle Orthod 2007;77(2): Sarment DP, Sukovic P, Clinthorne N. Accuracy of implant placement with a sterolithographic surgical guide. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2003;18(4): Arisan V, Karabuda ZC, Ozdemir T. Accuracy of two stereolithographic guide systems for computer-aided implant placement: a computed tomography-based clinical comparative study. J Periodontol 2010;81(1): Katsoulis J, Pazera P, Mericske-Stern R. Prosthetically driven, computer-guided implant planning for the edentulous maxilla: a model study. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2009;11(3): Nickenig HJ, Eitner S. Reliability of implant placement after virtual planning of implant positions using cone beam CT data and surgical (guide) templates. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2007;35(4-5): Nickenig H-S, Wichmann M, Hamel J, Schlegel A, Eitner S. Evaluation of the difference in accuracy between implant placement by virtual planning data and surgical guide templates versus the conventional free-hand method: a combined in vivo-in vitro technique using cone-beam CT part II. J Craniomaxillofac Surg (in press). 17. Moreira CR, Sales MA, Lopes PM, Cavelcanti JP. Assessment of linear and angular measurements on three-dimensional cone-beam computed tomographic images. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2009;108(3): Curley A, Hatcher DC. Cone beam CT: anatomic assessment and legal issues the new standards of care. J Calif Dent Assoc 2009;37(9): Eggers G, Mühling J, Hofele C. Clinical use of navigation based on cone-beam computer tomography in maxillofacial surgery. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2009;47(5): Elian N, Jalbout ZN, Classi AJ, Wexler A, Sarment D, Tarnow DP. Precision of flapless implant placement using real-time surgical navigation: a case series. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2008;23(6): S JADA 141(10 suppl) October 2010
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants. by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD
 Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig
 Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Digital Implant Dentistry Workflow
 Digital Implant Dentistry Workflow Ahmad Kutkut, DDS, MS, FICOI, DICOI Director of Predoctoral Implant Program Chair UKCD Implant Board ahmad.kutkut@uky.edu Disclaimer Neither I or any of my immediate
Digital Implant Dentistry Workflow Ahmad Kutkut, DDS, MS, FICOI, DICOI Director of Predoctoral Implant Program Chair UKCD Implant Board ahmad.kutkut@uky.edu Disclaimer Neither I or any of my immediate
Digital Imaging from a new perspective
 TREATMENT CENTRES HANDPIECES HYGIENE SYSTEMS X-RAY SYSTEMS CEREC TREATMENT CENTRES HANDPIECES HYGIENE SYSTEMS X-RAY SYSTEMS CEREC SIRONA CREATING AND MAINTAINING VALUE. You are right to expect a great
TREATMENT CENTRES HANDPIECES HYGIENE SYSTEMS X-RAY SYSTEMS CEREC TREATMENT CENTRES HANDPIECES HYGIENE SYSTEMS X-RAY SYSTEMS CEREC SIRONA CREATING AND MAINTAINING VALUE. You are right to expect a great
Much has been written about the success of various
 Simplified Guide for Precise Implant Placement: A Technical Note Brent D. Kennedy, MD, DDS*/Thomas A. Collins, Jr, DDS**/ Patrick C. W. Kline, DMD, MD** Ideal implant placement is ultimately determined
Simplified Guide for Precise Implant Placement: A Technical Note Brent D. Kennedy, MD, DDS*/Thomas A. Collins, Jr, DDS**/ Patrick C. W. Kline, DMD, MD** Ideal implant placement is ultimately determined
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note
 Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment
 Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment Complete dentures have largely become the domain of the denturist due to the dissatisfaction general dentists feel with this treatment. Multiple visits,
Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment Complete dentures have largely become the domain of the denturist due to the dissatisfaction general dentists feel with this treatment. Multiple visits,
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Long-term success of osseointegrated implants
 Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
CPD Article ISSUE 59. Proud of our History, Looking Forward to the Future
 CPD Article ISSUE 59 Proud of our History, Looking Forward to the Future BIDST CPD This learning session has been judged as being equivalent to one hour of verifiable CPD. To claim your verifiable CPD
CPD Article ISSUE 59 Proud of our History, Looking Forward to the Future BIDST CPD This learning session has been judged as being equivalent to one hour of verifiable CPD. To claim your verifiable CPD
Implant restoration in the aesthetic zone using guided surgery and immediate functional loading
 Prachatipat Hospital Prathumtani Province Dr. Nawakamon Suriyan Implant restoration in the aesthetic zone using guided surgery and immediate functional loading Digital Workflow: clinical patient information
Prachatipat Hospital Prathumtani Province Dr. Nawakamon Suriyan Implant restoration in the aesthetic zone using guided surgery and immediate functional loading Digital Workflow: clinical patient information
THE USE OF KEYSTONE EASYGUIDE CT SCANNING SOFTWARE FOR DIAGNOSIS, DIRECTION AND DEPTH DETERMINATION
 CT DIAGNOSTICS IN 3D IMPLANT TREATMENT PLANNING THE USE OF KEYSTONE EASYGUIDE CT SCANNING SOFTWARE FOR DIAGNOSIS, DIRECTION AND DEPTH DETERMINATION Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Assistant Clinical Professor
CT DIAGNOSTICS IN 3D IMPLANT TREATMENT PLANNING THE USE OF KEYSTONE EASYGUIDE CT SCANNING SOFTWARE FOR DIAGNOSIS, DIRECTION AND DEPTH DETERMINATION Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Assistant Clinical Professor
Use of Technology for Improved Implant Use in The OMS Practice AAOMS 93rd Annual Meeting, Philadelphia, PA
 Use of Technology for Improved Implant Use in The OMS Practice AAOMS 93rd Annual Meeting, Philadelphia, PA Image Navigation Surgery For Implant Placement - A Comparison To Guided Stent Use Robert W. Emery
Use of Technology for Improved Implant Use in The OMS Practice AAOMS 93rd Annual Meeting, Philadelphia, PA Image Navigation Surgery For Implant Placement - A Comparison To Guided Stent Use Robert W. Emery
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
In-Office Cone Beam Computerized Tomography: Technology Review and Clinical Examples Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 8 Issue Date: June 2008, Posted On: 6/26/2008 In-Office Cone Beam Computerized Tomography: Technology Review and Clinical Examples Michael Tischler, DDS Electronic Medical Record Research EMR
Page 1 of 8 Issue Date: June 2008, Posted On: 6/26/2008 In-Office Cone Beam Computerized Tomography: Technology Review and Clinical Examples Michael Tischler, DDS Electronic Medical Record Research EMR
CT Scan Technology. An Evolving Tool for Avoiding Complications and Achieving Predictable Implant Placement and Restoration SCOTT D.
 CT Scan Technology An Evolving Tool for Avoiding Complications and Achieving Predictable Implant Placement and Restoration SCOTT D. GANZ, DMD / USA Abstract Implant dentistry, one of the most predictable
CT Scan Technology An Evolving Tool for Avoiding Complications and Achieving Predictable Implant Placement and Restoration SCOTT D. GANZ, DMD / USA Abstract Implant dentistry, one of the most predictable
Periapical Radiography
 Periapical Radiography BARBARA E. DIXON B.D.S., M.Sc., D.P.D.S. Main Indications Detection of Apical infection/inflammation Assessment of the periodontal status After trauma Assessment of Unerupted teeth
Periapical Radiography BARBARA E. DIXON B.D.S., M.Sc., D.P.D.S. Main Indications Detection of Apical infection/inflammation Assessment of the periodontal status After trauma Assessment of Unerupted teeth
Navigation in Implant Dentistry
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Short Communication Navigation in Implant Dentistry Varun Menon P* Craniomaxillofacial Surgery and Implantology Center, Thrissur, Kerala, India *Corresponding Author:
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Short Communication Navigation in Implant Dentistry Varun Menon P* Craniomaxillofacial Surgery and Implantology Center, Thrissur, Kerala, India *Corresponding Author:
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry
 Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Osseointegrated implant-supported
 CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting
 44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
The Diagnostic Wax Up and Planning Phase of Implant Therapy
 The beginning of implant therapy Beginning implant care with the end in mind. The Diagnostic Wax Up and Planning Phase of Implant Therapy Drs. Alan Rosenfeld and George Mandelaris Diplomates, American
The beginning of implant therapy Beginning implant care with the end in mind. The Diagnostic Wax Up and Planning Phase of Implant Therapy Drs. Alan Rosenfeld and George Mandelaris Diplomates, American
An Introduction to Dental Implants
 An Introduction to Dental Implants Aims: This article provides an introduction to dental implants, outlining the categories of dental implants, the phases involved in implant dentistry and assessing a
An Introduction to Dental Implants Aims: This article provides an introduction to dental implants, outlining the categories of dental implants, the phases involved in implant dentistry and assessing a
Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research. DOI: /sjodr. ISSN (Print) Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website:
 DOI:10.21276/sjodr Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-1300 (Print) ISSN 2518-1297 (Online)
DOI:10.21276/sjodr Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-1300 (Print) ISSN 2518-1297 (Online)
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF IMPLANT DENTISTRY
 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF IMPLANT DENTISTRY 211 East Chicago Ave., Suite 750, Chicago IL 60611-2616 312/335-1550 GUIDELINES FOR CASE REPORTS FOR FELLOW MEMBERSHIP* General Information Each Fellow candidate must
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF IMPLANT DENTISTRY 211 East Chicago Ave., Suite 750, Chicago IL 60611-2616 312/335-1550 GUIDELINES FOR CASE REPORTS FOR FELLOW MEMBERSHIP* General Information Each Fellow candidate must
Dental Implant Planning using Cone Beam CT imaging: a pictorial guide.
 Dental Implant Planning using Cone Beam CT imaging: a pictorial guide. Poster No.: C-1970 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. R. Rice, G. Price, S. Morley, T. Beale; London/UK Keywords:
Dental Implant Planning using Cone Beam CT imaging: a pictorial guide. Poster No.: C-1970 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. R. Rice, G. Price, S. Morley, T. Beale; London/UK Keywords:
DIGITAL DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING FOR PLACEMENT AND RESTORATION OF SINGLE IMPLANTS IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA By Timothy Kosinski, DDS
 DIGITAL DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING FOR PLACEMENT AND RESTORATION OF SINGLE IMPLANTS IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA By Timothy Kosinski, DDS Dental implants have undergone many positive advances in recent
DIGITAL DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING FOR PLACEMENT AND RESTORATION OF SINGLE IMPLANTS IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA By Timothy Kosinski, DDS Dental implants have undergone many positive advances in recent
ident CT Guide Protocol
 ident CT Guide Protocol The ident computer planning and iguide production starts with the CT Guide. This is a simple device which can be made by a dental technician, but it is essential that it is made
ident CT Guide Protocol The ident computer planning and iguide production starts with the CT Guide. This is a simple device which can be made by a dental technician, but it is essential that it is made
A retrospective radiographic evaluation of incisive canal and anterior loop of mental nerve using cone beam computed tomography
 Research Article A retrospective radiographic evaluation of incisive canal and anterior loop of mental nerve using cone beam computed tomography M. Sridhar 1, Dhanraj M 2, Thiyaneswaran N 3, Ashish R.
Research Article A retrospective radiographic evaluation of incisive canal and anterior loop of mental nerve using cone beam computed tomography M. Sridhar 1, Dhanraj M 2, Thiyaneswaran N 3, Ashish R.
Accuracy of guided osteotomy using dental implant treatment-planning software in combination with an optical scan of a dental cast
 POSEIDO. 2014;2(4) Accuracy of software- guided implant osteotomy 253 Research article Accuracy of guided osteotomy using dental implant treatment-planning software in combination with an optical scan
POSEIDO. 2014;2(4) Accuracy of software- guided implant osteotomy 253 Research article Accuracy of guided osteotomy using dental implant treatment-planning software in combination with an optical scan
Diagnostics and treatment planning. Dr. Attila Szűcs DDS
 Diagnostics and treatment planning. Dr. Attila Szűcs DDS Considering both surgical Aim and prosthetic aspects in the planning of implant prosthetics Arrangements for implant therapy Preliminary examinations
Diagnostics and treatment planning. Dr. Attila Szűcs DDS Considering both surgical Aim and prosthetic aspects in the planning of implant prosthetics Arrangements for implant therapy Preliminary examinations
CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature:
 CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature: CF Hoogendijk Maxillo- facial and Oral surgery: Trauma: 1. Facial trauma for the confirmation or exclusion of fractures
CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature: CF Hoogendijk Maxillo- facial and Oral surgery: Trauma: 1. Facial trauma for the confirmation or exclusion of fractures
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
A rare crestal branch of inferior alveolar nerve: case report 1 Mahdi Niknami 1 Reza Es haghi * 2 Hamed Mortazavi 3 Hadi Hamidi
 Journal Dental School 2012; 30(2):132-135 Case Report A rare crestal branch of inferior alveolar nerve: case report 1 Mahdi Niknami 1 Reza Es haghi * 2 Hamed Mortazavi 3 Hadi Hamidi 1 Assistant Professor,
Journal Dental School 2012; 30(2):132-135 Case Report A rare crestal branch of inferior alveolar nerve: case report 1 Mahdi Niknami 1 Reza Es haghi * 2 Hamed Mortazavi 3 Hadi Hamidi 1 Assistant Professor,
Guided immediate loading implant surgery planned with Implant Studio D.D.S. Jae-min, Lee
 Guided immediate loading implant surgery planned with Implant Studio D.D.S. Jae-min, Lee Jung-plant Dental office 1 PROLOGUE How can we deal with the immediate loading implant cases easier and more accurate
Guided immediate loading implant surgery planned with Implant Studio D.D.S. Jae-min, Lee Jung-plant Dental office 1 PROLOGUE How can we deal with the immediate loading implant cases easier and more accurate
Restorative Driven Implant Solutions Utilizing the Latest Technology
 Restorative Driven Implant Solutions Utilizing the Latest Technology Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD As a general dentist who has placed nearly 7,000 dental implants, I
Restorative Driven Implant Solutions Utilizing the Latest Technology Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD As a general dentist who has placed nearly 7,000 dental implants, I
Benefits of CBCT in Implant Planning
 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
Reliability of Orthopantomography and Cone-beam Computed Tomography in Presurgical Implant Planning: A Clinical Study
 JCDP Original Research Reliability of OPG and CBCT 10.5005/jp-journals-00000-0000 in Presurgical Implant Planning Reliability of Orthopantomography and Cone-beam Computed Tomography in Presurgical Implant
JCDP Original Research Reliability of OPG and CBCT 10.5005/jp-journals-00000-0000 in Presurgical Implant Planning Reliability of Orthopantomography and Cone-beam Computed Tomography in Presurgical Implant
anatomy in 71 cadavers.
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:744-750, 2009 Measurement of Anterior Loop Length for the Mandibular Canal and Diameter of the Mandibular Incisive Canal to Avoid Nerve Damage When Installing Endosseous Implants
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:744-750, 2009 Measurement of Anterior Loop Length for the Mandibular Canal and Diameter of the Mandibular Incisive Canal to Avoid Nerve Damage When Installing Endosseous Implants
OCCLUSION. Principles & Treatment. José dos Santos, Jr, DDS, PhD. São Paulo, Brazil
 OCCLUSION Principles & Treatment José dos Santos, Jr, DDS, PhD São Paulo, Brazil Former Professor Division of Occlusion Department of Restorative Dentistry University of Texas Health Science Center at
OCCLUSION Principles & Treatment José dos Santos, Jr, DDS, PhD São Paulo, Brazil Former Professor Division of Occlusion Department of Restorative Dentistry University of Texas Health Science Center at
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry
 Group 1 and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry Michael M. Bornstein, PD Dr Med Dent 1 /Bilal Al-Nawas, Prof Dr Med, Dr Med
Group 1 and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry Michael M. Bornstein, PD Dr Med Dent 1 /Bilal Al-Nawas, Prof Dr Med, Dr Med
Foundations of CBCT Imaging for Implant Planning and Surgical Guides
 Earn 3 CE credits This course was written for dentists, dental hygienists, and assistants. Foundations of CBCT Imaging for Implant Planning and Surgical Guides A Peer-Reviewed Publication Written by Douglas
Earn 3 CE credits This course was written for dentists, dental hygienists, and assistants. Foundations of CBCT Imaging for Implant Planning and Surgical Guides A Peer-Reviewed Publication Written by Douglas
Full mouth rehabilitation with digital workflow
 Jung-plant dental office Dr. Jae-min, Lee D.D.S. Full mouth rehabilitation with digital workflow Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Dental System 3Shape Implant Studio Case information On first visit,
Jung-plant dental office Dr. Jae-min, Lee D.D.S. Full mouth rehabilitation with digital workflow Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Dental System 3Shape Implant Studio Case information On first visit,
Implant Imaging JCD /jp-journals REVIEW ARTICLE ABSTRACT
 JCD 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1051 REVIEW ARTICLE Ajay R Bhoosreddy, Seema Bhoosreddy, Vinayak Umesh Shirsekar ABSTRACT Implants improve the quality of life for patients who are unable to keep their natural
JCD 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1051 REVIEW ARTICLE Ajay R Bhoosreddy, Seema Bhoosreddy, Vinayak Umesh Shirsekar ABSTRACT Implants improve the quality of life for patients who are unable to keep their natural
Dental Cone Beam CT. What is Dental Cone Beam CT?
 Scan for mobile link. Dental Cone Beam CT Dental cone beam computed tomography (CT) is a special type of x-ray equipment used when regular dental or facial x-rays are not sufficient. Your doctor may use
Scan for mobile link. Dental Cone Beam CT Dental cone beam computed tomography (CT) is a special type of x-ray equipment used when regular dental or facial x-rays are not sufficient. Your doctor may use
Xelis Dental - What New in
 Xelis Dental - What New in 1.0.6.1 Clinical Needs Why Xelis-Dental? Panorama Cephalography Intra-oral Digital Camera Traditional imaging systems - 2-Dimension view Incorrect anatomical information - Distortion
Xelis Dental - What New in 1.0.6.1 Clinical Needs Why Xelis-Dental? Panorama Cephalography Intra-oral Digital Camera Traditional imaging systems - 2-Dimension view Incorrect anatomical information - Distortion
Implant Studio Patient Case
 Jung-plant dental office Dr. Jae-min, Lee D.D.S. Implant Studio Patient Case Full mouth rehabilitation Case information On first visit, the patient was wearing a removable partial denture on lower jaw
Jung-plant dental office Dr. Jae-min, Lee D.D.S. Implant Studio Patient Case Full mouth rehabilitation Case information On first visit, the patient was wearing a removable partial denture on lower jaw
Cephalometric Analysis
 Cephalometric Analysis of Maxillary and Mandibular Growth and Dento-Alveolar Change Part III In two previous articles in the PCSO Bulletin s Faculty Files, we discussed the benefits and limitations of
Cephalometric Analysis of Maxillary and Mandibular Growth and Dento-Alveolar Change Part III In two previous articles in the PCSO Bulletin s Faculty Files, we discussed the benefits and limitations of
Assessment of Lingual Concavities in Submandibular Fossa Region in Patients requiring Dental Implants A Cone Beam Computed Tomography Study
 Assessment of Lingual Concavities in Submandibular Fossa via 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2427 Cone Beam Computed Tomography ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessment of Lingual Concavities in Submandibular Fossa Region
Assessment of Lingual Concavities in Submandibular Fossa via 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2427 Cone Beam Computed Tomography ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessment of Lingual Concavities in Submandibular Fossa Region
Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry
 Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Our ultimate goal is to provide you and your patients with the highest standards in implant case planning
Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Our ultimate goal is to provide you and your patients with the highest standards in implant case planning
Alveolar Bone Remodeling and Development after Immediate Orthodontic Root Movement
 Journal of Dental Health, Oral Disorders & Therapy Alveolar Bone Remodeling and Development after Immediate Orthodontic Root Abstract Introduction: Adult orthodontics is rapidly expanding primarily due
Journal of Dental Health, Oral Disorders & Therapy Alveolar Bone Remodeling and Development after Immediate Orthodontic Root Abstract Introduction: Adult orthodontics is rapidly expanding primarily due
For many years, patients with
 Dr. Robert Lowe is one of the great teachers in dentistry. Recently, he received the Gordon J. Christensen Award from the Chicago Dental Society in recognition of his excellence in teaching. Some of my
Dr. Robert Lowe is one of the great teachers in dentistry. Recently, he received the Gordon J. Christensen Award from the Chicago Dental Society in recognition of his excellence in teaching. Some of my
Orthodontic space opening during adolescence is
 ONLINE ONLY Postorthodontic root approximation after opening space for maxillary lateral incisor implants Taylor M. Olsen a and Vincent G. Kokich, Sr b Seattle, Wash Introduction: Orthodontic space opening
ONLINE ONLY Postorthodontic root approximation after opening space for maxillary lateral incisor implants Taylor M. Olsen a and Vincent G. Kokich, Sr b Seattle, Wash Introduction: Orthodontic space opening
GuidedService. The ultimate guide for precise implantations
 GuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations ABGuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations At A.B. Dental we've brought implantology into the future with a 3D digitally planned
GuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations ABGuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations At A.B. Dental we've brought implantology into the future with a 3D digitally planned
Fixed Partial Denture
 University of Minnesota School of Dentistry Fixed Partial Denture Self-guided Instructional Material for Dental Students Authors Ranier M. Adarve, DMD, MS, MHPE Lisa Fedor James, DDS, Cert. Pros. Fixed
University of Minnesota School of Dentistry Fixed Partial Denture Self-guided Instructional Material for Dental Students Authors Ranier M. Adarve, DMD, MS, MHPE Lisa Fedor James, DDS, Cert. Pros. Fixed
In 1977, Lew1 developed a passive
 CLINICAL AN OVERVIEW OF THE LEW ATTACHMENT: CLINICAL REPORTS Jack Piermatti, DMD Sheldon Winkler, DDS KEY WORDS Lew attachment Atrophic mandible Subperiosteal implant Root form implant Although the Lew
CLINICAL AN OVERVIEW OF THE LEW ATTACHMENT: CLINICAL REPORTS Jack Piermatti, DMD Sheldon Winkler, DDS KEY WORDS Lew attachment Atrophic mandible Subperiosteal implant Root form implant Although the Lew
EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/24/14 REVISED DATE: 04/23/15, 04/28/16, 06/22/17, 06/28/18 POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Dental
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
Implant Studio Patient Case
 Melbourne Bayside Dental Specialists Dr. Philip Tan Implant Studio Patient Case Benefits of guided surgery Case information Dr. Tan presents three different types of cases. Each case uses 3Shape Implant
Melbourne Bayside Dental Specialists Dr. Philip Tan Implant Studio Patient Case Benefits of guided surgery Case information Dr. Tan presents three different types of cases. Each case uses 3Shape Implant
Two- and Three-dimensional Orthodontic Imaging Using Limited Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Original Article Two- and Three-dimensional Orthodontic Imaging Using Limited Cone Beam Computed Tomography Akira Nakajima a ; Glenn T. Sameshima b ; Yoshinori Arai c ; Yoshito Homme d ; Noriyoshi Shimizu
Original Article Two- and Three-dimensional Orthodontic Imaging Using Limited Cone Beam Computed Tomography Akira Nakajima a ; Glenn T. Sameshima b ; Yoshinori Arai c ; Yoshito Homme d ; Noriyoshi Shimizu
Intramembranous autogenous bone graft is the gold
 CASE LETTER CBCT Morphologic Analysis of Edentulous Posterior Mandible for Mandibular Body Bone Graft Jae-Min Song, DDS, MSD, PhD 1 Jae-Yeol Lee, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Yong-Deok Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD 2,3 * INTRODUCTION
CASE LETTER CBCT Morphologic Analysis of Edentulous Posterior Mandible for Mandibular Body Bone Graft Jae-Min Song, DDS, MSD, PhD 1 Jae-Yeol Lee, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Yong-Deok Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD 2,3 * INTRODUCTION
CT Scanning Protocol For V2R Guided Surgery Solutions
 CT Scanning Protocol For V2R Guided Surgery Solutions 2 V2R CT Scanning Protocol \\ Contents Contents General requirements... 3 V2R Dual Scan Protocol... 5 V2R Single Scan Protocol... 8 Overview... 10
CT Scanning Protocol For V2R Guided Surgery Solutions 2 V2R CT Scanning Protocol \\ Contents Contents General requirements... 3 V2R Dual Scan Protocol... 5 V2R Single Scan Protocol... 8 Overview... 10
Maxillary Central Incisor Incisive Canal Relationship: A Cone Beam Computed Tomography Study
 Maxillary Central Incisor Incisive Canal Relationship: A Cone Beam Computed Tomography Study Joseph Y.K. Kan, DDS, MS Professor, Department of Restorative Dentistry, Loma Linda University School of Dentistry,
Maxillary Central Incisor Incisive Canal Relationship: A Cone Beam Computed Tomography Study Joseph Y.K. Kan, DDS, MS Professor, Department of Restorative Dentistry, Loma Linda University School of Dentistry,
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Clinical details: Details of scan: CONE BEAM CT REPORT: Name: H. B. Gender: Reason for referral: Referred by:
 Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Karl Maloney, DDS,* Jairo Bastidas, DMD, Katherine Freeman, DrPH, Todd R. Olson, PhD, and Richard A. Kraut, DDS. Materials and Methods
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 69:1923-1929, 2011 Cone Beam Computed Tomography and SimPlant Materialize Dental Software Versus Direct of the Width and Height of the Posterior Mandible: An Anatomic Study Karl
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 69:1923-1929, 2011 Cone Beam Computed Tomography and SimPlant Materialize Dental Software Versus Direct of the Width and Height of the Posterior Mandible: An Anatomic Study Karl
2015 Member Speaker Forum. Chair: L. Scott Brooksby, DDS, BS. Friday, October 23, :30 AM 3:45 PM. Coral Ballroom. 3.
 2015 Member Speaker Forum Chair: L. Scott Brooksby, DDS, BS Friday, October 23, 2015 11:30 AM 3:45 PM Coral Ballroom 3.25 CE Credits 11:30 a.m. 3:45 p.m. Member Speaker Forum 11:30 11:40 a.m. Introduction
2015 Member Speaker Forum Chair: L. Scott Brooksby, DDS, BS Friday, October 23, 2015 11:30 AM 3:45 PM Coral Ballroom 3.25 CE Credits 11:30 a.m. 3:45 p.m. Member Speaker Forum 11:30 11:40 a.m. Introduction
In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics.
 In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics. Chandrasenan.P 1, Vishnu.G 2, Akshay K Nair 3 1M Tech student, Department of Mechanical
In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics. Chandrasenan.P 1, Vishnu.G 2, Akshay K Nair 3 1M Tech student, Department of Mechanical
THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S.
 THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S. Skeletal anchorage, the concept of using the facial skeleton to control tooth
THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S. Skeletal anchorage, the concept of using the facial skeleton to control tooth
Oral Health and Dentistry
 Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama
 Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Principles of Removable Partial Denture Design Difference in Prosthesis Support and Influence on Design: For a tooth-supported prosthesis, the movement potential is less
Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Principles of Removable Partial Denture Design Difference in Prosthesis Support and Influence on Design: For a tooth-supported prosthesis, the movement potential is less
SCD Case Study. Implant-supported overdentures
 SCD Case Study Implant-supported overdentures An implant-retained overdenture may be indicated in patients with changed anatomy, neuromuscular disorders, significant gag reflex or considerable ridge resorption
SCD Case Study Implant-supported overdentures An implant-retained overdenture may be indicated in patients with changed anatomy, neuromuscular disorders, significant gag reflex or considerable ridge resorption
Inclusive Tooth Replacement System
 Optimizing Anterior Esthetics with the Inclusive Tooth Replacement System by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant treatment has changed so much over the years. In the past it was acceptable to place
Optimizing Anterior Esthetics with the Inclusive Tooth Replacement System by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant treatment has changed so much over the years. In the past it was acceptable to place
European Veterinary Dental College
 European Veterinary Dental College EVDC Training Support Document Preparation of Radiograph Sets (Cat and Dog) Document version : evdc-tsd-radiograph_positioning_(dog_and_cat)-20120121.docx page 1 of 13
European Veterinary Dental College EVDC Training Support Document Preparation of Radiograph Sets (Cat and Dog) Document version : evdc-tsd-radiograph_positioning_(dog_and_cat)-20120121.docx page 1 of 13
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Visibility of Maxillary and Mandibular Anatomical Landmarks in Digital Panoramic Radiographs: A Retrospective Study
 Visibility of Maxillary and Mandibular Anatomical Landmarks in Digital Panoramic Radiographs: A Retrospective Study Srisha Basappa, Smitha JD, Nishath Khanum*, Santosh Kanwar, Mahesh MS and Archana Patil
Visibility of Maxillary and Mandibular Anatomical Landmarks in Digital Panoramic Radiographs: A Retrospective Study Srisha Basappa, Smitha JD, Nishath Khanum*, Santosh Kanwar, Mahesh MS and Archana Patil
Guided implant placement using the trephine drill nonsleeve and immediate provisional crown or bridge in the esthetic zone
 Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences Vol. 8(5) pp. 054-059, August 2017 DOI: http:/dx.doi.org/10.14303/jmms.2017.050 Available online http://www.interesjournals.org/jmms Copyright 2017 International
Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences Vol. 8(5) pp. 054-059, August 2017 DOI: http:/dx.doi.org/10.14303/jmms.2017.050 Available online http://www.interesjournals.org/jmms Copyright 2017 International
م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION
 Lec.1 م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION االسنان طب Prosthodontics is the branch of dentistry pertaining to the restoration and maintenance of oral function, comfort, appearance,
Lec.1 م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION االسنان طب Prosthodontics is the branch of dentistry pertaining to the restoration and maintenance of oral function, comfort, appearance,
Benefits of guided surgery and the digital workflow
 Melbourne Bayside Dental Specialists Dr. Philip Tan Benefits of guided surgery and the digital workflow Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Dental System 3Shape Implant Studio Case information Dr.
Melbourne Bayside Dental Specialists Dr. Philip Tan Benefits of guided surgery and the digital workflow Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Dental System 3Shape Implant Studio Case information Dr.
Accuracy of Computer-Guided Implant Surgery by a CAD/CAM and Laser Scanning Technique
 Accuracy of Computer-Guided Implant Surgery by a CAD/CAM and Laser Scanning Technique Xue Zhu ZHAO 1, Wei Hua XU 2, Zhi Hui TANG 1, Min Jie WU 1, Jie ZHU 1, Si CHEN 1 Objectives: To explore the method
Accuracy of Computer-Guided Implant Surgery by a CAD/CAM and Laser Scanning Technique Xue Zhu ZHAO 1, Wei Hua XU 2, Zhi Hui TANG 1, Min Jie WU 1, Jie ZHU 1, Si CHEN 1 Objectives: To explore the method
It has been proposed that partially edentulous maxillectomy
 CLASSICAL ARTICLE Basic principles of obturator design for partially edentulous patients. Part II: Design principles Mohamed A. Aramany, DMD, MS* Eye and Ear Hospital of Pittsburgh and University of Pittsburgh,
CLASSICAL ARTICLE Basic principles of obturator design for partially edentulous patients. Part II: Design principles Mohamed A. Aramany, DMD, MS* Eye and Ear Hospital of Pittsburgh and University of Pittsburgh,
Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines
 Original Research Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines Seyed Hossein Hoseini Zarch 1, Farzin Heravi 2, Adineh Javadian Langaroodi 3,
Original Research Evaluation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Diagnosis and Treatment Plan of Impacted Maxillary Canines Seyed Hossein Hoseini Zarch 1, Farzin Heravi 2, Adineh Javadian Langaroodi 3,
Evaluation of maxillary protrusion malocclusion treatment effects with prosth-orthodontic method in old adults
 Evaluation of maxillary protrusion malocclusion treatment effects with prosth-orthodontic method in old adults Peicheng Xu, DDS, MSD, a and Honghu Liu, DDS, PhD b a Shanghai Xuhui Dental Hospital and b
Evaluation of maxillary protrusion malocclusion treatment effects with prosth-orthodontic method in old adults Peicheng Xu, DDS, MSD, a and Honghu Liu, DDS, PhD b a Shanghai Xuhui Dental Hospital and b
From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement
 Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
Featured Patient Case #1: Complete Mouth Reconstruction with Hybrid Restorations
 Philip L. Fava II, DMD, MDSc Robert A. Levine, DDS, FCPP, FISPPS 9880 Bustleton Ave, Suite 211 Philadelphia, PA 19115 PADentalImplants.com 215-677-8686 Featured Patient Case #1: Complete Mouth Reconstruction
Philip L. Fava II, DMD, MDSc Robert A. Levine, DDS, FCPP, FISPPS 9880 Bustleton Ave, Suite 211 Philadelphia, PA 19115 PADentalImplants.com 215-677-8686 Featured Patient Case #1: Complete Mouth Reconstruction
The influence of sensor size and orientation on image quality in intra-oral periapical radiography
 Clinical The influence of sensor size and orientation on image quality in intra-oral periapical radiography Tony Druttman 1 The periapical view is one of the standard intra-oral radiographs by which diagnostic
Clinical The influence of sensor size and orientation on image quality in intra-oral periapical radiography Tony Druttman 1 The periapical view is one of the standard intra-oral radiographs by which diagnostic
Extraoral Imaging. Chapter 42. Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1
 Extraoral Imaging Chapter 42 Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Learning Objectives Lesson 42.1: Panoramic Imaging 1. Pronounce, define, and spell the key terms. 2. Discuss panoramic
Extraoral Imaging Chapter 42 Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Learning Objectives Lesson 42.1: Panoramic Imaging 1. Pronounce, define, and spell the key terms. 2. Discuss panoramic
CBCT as an Emerging Gold Standard for Presurgical Planning in Implant Restorations
 10.5005/jp-journals-10011-1344 M Shiva Shankar et al CASE REPORT CBCT as an Emerging Gold Standard for Presurgical Planning in Implant Restorations M Shiva Shankar, Bhupinder Pal, Nitesh Rai, Digvijaya
10.5005/jp-journals-10011-1344 M Shiva Shankar et al CASE REPORT CBCT as an Emerging Gold Standard for Presurgical Planning in Implant Restorations M Shiva Shankar, Bhupinder Pal, Nitesh Rai, Digvijaya
The future of health is digital
 Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Interpretation Basics of Cone Beam Computed Tomography COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
 Interpretation Basics of Cone Beam Computed Tomography COPYIGHTED MATEIA 1 Introduction to Cone Beam Computed Tomography Shawneen M. Gonzalez Introduction This chapter will cover basics of cone beam computed
Interpretation Basics of Cone Beam Computed Tomography COPYIGHTED MATEIA 1 Introduction to Cone Beam Computed Tomography Shawneen M. Gonzalez Introduction This chapter will cover basics of cone beam computed
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Application of augmented reality for inferior alveolar nerve block anesthesia: A technical note
 Technical Note pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2017;17(2):129-134 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.2.129 Application of augmented reality for inferior alveolar nerve block
Technical Note pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2017;17(2):129-134 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.2.129 Application of augmented reality for inferior alveolar nerve block
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations
 Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
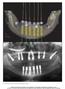 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 49 A Protocol for Immediate Placement of a Prefabricated Screw-Retained Provisional Prosthesis Using Computed Tomography and Guided Surgery
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 49 A Protocol for Immediate Placement of a Prefabricated Screw-Retained Provisional Prosthesis Using Computed Tomography and Guided Surgery
Screw retained implant crown restoration with digital workflow using scan body and surgical guide
 Dr. Anthony Mak W Dental Screw retained implant crown restoration with digital workflow using scan body and surgical guide Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Implant Studio 3Shape scan bodies 3Shape
Dr. Anthony Mak W Dental Screw retained implant crown restoration with digital workflow using scan body and surgical guide Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Implant Studio 3Shape scan bodies 3Shape
Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options
 Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options First Name Last Name Objectives Identify the need and opportunity to treat full arch patients with fixed detachable
Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options First Name Last Name Objectives Identify the need and opportunity to treat full arch patients with fixed detachable
Correction of a maxillary canine-first premolar transposition using mini-implant anchorage
 CASE REPORT Correction of a maxillary canine-first premolar transposition using mini-implant anchorage Mehmet Oguz Oztoprak, DDS, MSc, a Cigdem Demircan, DDS, b Tulin Arun, PhD, DDS, MSc c Transposition
CASE REPORT Correction of a maxillary canine-first premolar transposition using mini-implant anchorage Mehmet Oguz Oztoprak, DDS, MSc, a Cigdem Demircan, DDS, b Tulin Arun, PhD, DDS, MSc c Transposition
Assistant Professor, Head of Department Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, School of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran 2
 Original Article Assessment of Location and Anatomical Characteristics of Mental Foramen, Anterior Loop and Mandibular Incisive Canal Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Mehrdad Panjnoush 1, Zonnar Sadat
Original Article Assessment of Location and Anatomical Characteristics of Mental Foramen, Anterior Loop and Mandibular Incisive Canal Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography Mehrdad Panjnoush 1, Zonnar Sadat
