Collaplug Effect on Extraction Sockets in Anticoagulated Patients. Abstract:
|
|
|
- Sophie Flynn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EFFECT OF COLLAPLUG ON THE HEALING OF EXTRACTION SOCKETS IN PATIENTS UNDER ORAL ANTICOAGULANT THERAPY (CLINICAL STUDY) Abdelaziz M 1 BDS, Shaaban R 2 PhD, Abdelhalim S 2 PhD, Sadaka M 3 PhD Abstract: Introduction: Dentists perform a variety of surgical procedures frequently requiring the need for a hemostatic agent, in cases where oral anticoagulants are used. Most cases of postoperative bleeding are easily treated with local measures such as packing with a haemostatic dressing, suturing and pressure. Objectives: We aimed to evaluate the efficacy of Collaplug in minimizing postoperative bleeding and pain following tooth extraction in patients under oral anticoagulant therapy. Materials and methods: A prospective study was conducted on a total of 40 adult patients under oral anticoagulant therapy, who needed tooth extraction. Patients were divided equally into two groups, each group consisting of 20 patients. Group A (Study group): the extraction of the tooth was followed by the application of Collaplug prior to suturing of the socket. Group B (Control group): the extraction of the tooth was followed by suturing only. Results: A total of 40 patients 21 female (52%) and 19 (48%) male, aged between 30 and 60 years were included in the present study. All patients underwent simple tooth extraction. In the study group: there was a clinical significance in cessation of bleeding 2 hours and 6 hours after extraction than the control group. All patients of study and control groups had their international normalized ratio (INR)<3 within the therapeutic range. Conclusion: The study concluded that Collaplug is an effective local hemostatic material following minor oral surgery in patients under oral anticoagulant therapy, also shows acceleration of soft tissue healing and reduce postoperative pain. Key Words: Extraction, collagen sponge, local hemostasis, warfarin, anticoagulants Resident in Maxillofacial and Plastic Surgery Department, Faculty of Dentistry, Alexandria University. 2. Professor in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Department, Faculty of Dentistry, Alexandria University. 3. Assistant professor in Cardiology Department, Faculty of Dentistry, Alexandria University. INTRODUCTION Despite advances in surgical technique, bleeding remains one of the major complications associated with surgery and may lead to poor clinical outcomes. The risk of bleeding is increased in patients taking anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents, those with underlying intrinsic bleeding disorders, or those with specific problems, including diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and renal insufficiency (1,2). Further, primary complications of surgery, such as infection, can lead to the development of disseminated intravascular coagulation and widespread diffuse bleeding (1). Many patients taking coumarin derivatives, such as warfarin, present to the oral and maxillofacial surgeon need to extract their teeth. The surgeon is faced with the choice of altering or stopping warfarin and risking thromboembolism or leaving the patient on the warfarin and risking uncontrolled bleeding (3). Warfarin, which acts by antagonizing the effect of vitamin K, is one of the most commonly used oral anticoagulants. The drug can be absorbed completely and reaches its peak in 1 hour after ingestion (4). Albumin is bound to circulating warfarin, and the half-life of warfarin is approximately 36 hours (5).The liver metabolizes warfarin into inactive compounds, which are then excreted, mainly into the urine. Warfarin has been used to decrease the thromboembolism in millions of patients worldwide (4,5). Its effect is measured by international normalized ratio (INR), which is a measure of patient s prothrombin time divided by the laboratory control value of prothrombin time (6). The level of INR suitable for the patient depends on the condition of the patient. The recommended INR level according to the American College of Chest Physicians is between 2.0 and 3.0 for most conditions; however, patients using prosthetic heart valves may require higher level of INR (7). Many reports stated that patients requiring a minor dental procedure and having an INR of up to 4.0 are able to continue warfarin without any dose adjustment (6,8,9).It has, however, been debated whether stopping warfarin can increase the risk of cerebrovascular accidents (CVA) (10). Most bleeding tendencies resulting from the use of anticoagulants (11), usually prescribed to treat a number of cardiac or vascular disorders, including atrial fibrillation, ischemic cardiac disease, cardiac valvular disease, prosthetic cardiac valves, post-myocardial infarction, deep venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, cerebrovascular accident, and many others (12-14). Assessing both risks and benefits is very important in patients receiving warfarin, and a very close communication and consultation with the patient s physician regarding the best management is critical (7). Various local measures to control bleeding in patients on warfarin treatment are available, including local hemostatic agents, suturing, and tranexamic acid (9,10). Local measures such as Bone wax which is a sterile mixture of beeswax, paraffin, and isopropyl palmitate (15). Mild inflammatory reactions have been reported in tissues adjacent to the site of Bone Wax implantation (15). 166
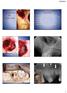
2 Gelfoam is one of the more commonly employed agents for the control of minor bleeding. It is a porous, pliable sponge made from dried and sterilized porcine skin gelatin. It is believed to be related to formation of a mechanical matrix that facilitates clot formation (16). Collagen-based agents were introduced in 1970 (17). The hemostatic collagen products in general are: soft, pliable, non-friable, coherent and sponge-like structures. They are fabricated from bovine collagen (15). Collaplug derived from bovine deep flexor tendons due to its rod-shape form, was found to be used in the extraction sites, 4-wall sockets and biopsy sites (18,19). It is an absorbable wound dressing, because of the coherent sponge structure, application of the dressings to the wound is easily controlled (18). In this study, we aimed to evaluate the efficacy of Collaplug in minimizing postoperative bleeding and pain following tooth extraction in patients under oral anticoagulant therapy. MATERIALS AND METHODS All patients included in this study were undergoing warfarin treatment and were referred to the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (OMF) for simple dental extraction, with age ranging from 30 to 60 years old, each patient was informed about the aim of the study and gave informed consent, medical and surgical history was taken from the patients, all patients were purely under oral anticoagulant treatment, their INR< 3 as shown in table (1). Exclusion criteria: any patient beyond the age range, patients with INR>3, patients with uncontrolled arterial blood pressure, and any patient who refused to sign the consent or otherwise refused to participate in the study. Table (1): INR (International normalized ratio). x 2 : Value for Chi square MC: Monte Carlo test The study was conducted on a total number of 40 adult patients treated with oral anticoagulant therapy, who were indicated for tooth extraction, in order to evaluate the efficacy of Collaplug in minimizing postoperative bleeding and pain following tooth extraction in patients under oral anticoagulant therapy, patients were divided equally into two groups, each consisting of 20 patients. Group (1) study group Physicians did not stop any of the anticoagulant therapies of the patients. In addition, their INR within the therapeutic range 3. Non surgical extraction was done then application of local hemostatic material Collaplug in the extracted socket and wound suturing. Group (2) Control group Physicians did not stop any of the anticoagulant therapies of the patients. In addition, their INR within the therapeutic range 3. Non surgical extraction was done, then suturing using atraumatic round needle. Materials: Collaplug is fabricated from bovine collagen (Collaplug produced by zimmer dental 1900 Aston Avenue Carlsbad, CA USA), it is highly porous, highly absorbent. - It controls bleeding and stabilizes blood clot. - It induces clot formation in half the time taken by the cotton gauze, allows hemostasis from 2 to 2.5 minutes, it is absorbed within 10 to 14 days. - It protects wound bed, provides matrix for tissue ingrowth. - Collaplug dressing holds up to 60 times its own weight in fluids. - Contains more than 90% open pores of its volume. - Absorbable collagen wound dressings soft, white, pliable, non friable sponges used in dental surgery. Because of the coherent sponge structure, application of the dressings to the wound was easily controlled. The dressings supplied in sterile individual bubble packs. Available in 1 cm x 2 cm wrapped dressings. Methods 1. Preoperative phase All the patients were subjected to complete history taking including name, age, gender, occupation, medical and dental history. All the patients were subjected to intraoral examination to determine the condition of the tooth before extraction as shown in (Fig.1) The following laboratory investigations were done 24 hours before dental extraction: - Complete blood count. - Coagulation profile. - International normalized ratio. (INR 3 within the therapeutic range as all patients are under oral anticoagulant therapy). - Aseptic surgical technique and infection control precautions were used during the whole procedures, including the use of sterilized instruments Fig. (1): Preoperative intraoral view of upper left central incisor. 167
3 2. Operative phase Group (1): Collaplug dental dressing was applied into the socket. Steps: Local Anesthesia without vasoconstrictor, Mepivacaine HCL3%, (Mepecaine 1.8ml carpule, produced by: Alexandria Co. for pharmaceuticals-egypt). Non surgical tooth extraction and immediate bleeding is recorded. (Fig.2). The socket was examined for any tooth or bone fragments. Insertion of Collaplug (Fig.3). Collaplug inserted in the socket and cessation of bleeding. (Fig.4). Visual inspection of the dressing before suturing of the socket,using atraumatic round needle. (Fig.5). Fig (4): After Collaplug inserted. Group (2): Same steps as group (1) without application of Collaplug Steps: Suturing using atraumatic round needle. A sterile cotton dressing was placed over the socket and the patient was asked to apply a gentle biting pressure. Fig (5): Suturing of the socket Fig (2): Immediate bleeding after extraction. 3. Postoperative phase Patients were given the usual postoperative instructions. Postoperative antibiotics 1gm Amoxycillin and Clavulinic acid (Augmentin manufactured by GalaxoSmithKline - United Kingdom).One tablet every 12 hours was given for cardiac patients with prosthetic valve replacement, analgesics Paracetamol 500 mg (Abimol manufactured by GalaxoSmithKline -United Kingdom) was prescribed if required. a. Immediate postoperative phase The patients were assessed :Immediately,2 hours, 6 hours, 24 hours, 48hours and 7 th day postoperatively. The results regarding postoperative bleeding were recorded. The post extraction instructions were explained thoroughly to the patients as: keep biting on the gauze pack, no mouth rinsing for the rest of the day and no hot food or hot drink for 24 hours. All the patients were asked to be in contact, in case of excessive bleeding occurred at the operative or postoperative days. Fig (3): During application of collaplug and cessation of bleeding b. Intermediate postoperative phase Evaluation of the postoperative findings including; bleeding 168
4 for the first 2 hours,6 hours,24 hours,48 hours and 7 th.day after extraction, pain was assessed for the first 24 hours. c. Delayed postoperative phase Sutures were removed at the seventh postoperative day. The postoperative evaluation was done clinically as follows: Postoperative bleeding Bleeding was assessed and recorded postoperatively from the extraction site by WHO bleeding scale (20). - Grade 0: Very low (almost no bleeding). - Grade 1: Low (slight oozing of blood from the socket which usually stopped by its self or after pressure was applied). - Grade 2: Normal. (Clinically significant) - Grade 3: High. (Bleeding occurred after clot significantly formed). - Grade 4: Very high (excessive bleeding that could not be controlled by local hemostatic agents or stitches). Postoperative pain Pain was assessed after 24 hours from extraction according to the numerical rating pain scale (21). RESULTS This study was conducted on 40 patients of both genders 21 females (52%) and 19 males (48%). Their ages ranged between years old, they were selected from the inpatients Department Faculty of Medicine, Alexandria University and from the out-patient Clinic of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Department, Faculty of Dentistry, Alexandria University. All patients were under oral anticoagulants therapy, patients were divided equally into two groups, each consisting of 20 patients as study and control group. All 40 patients were under oral anticoagulant therapy due to the following conditions: twenty six patients with valvular heart diseases (65%), ten patients with ischemic heart diseases (25%), two patients with cardiomyopathies (5%), and two patients with stroke (5%). After performing the extraction and placement of Collaplug, suturing for the study group and suturing only for the control group, hemostasis condition was assessed 2 hours, 6 hours, 24 hours, 48hours and 7 th day postoperatively, results of post operative bleeding after extraction were recorded in table (2). Table (2): Bleeding grades according to WHO scale Postoperative wound healing Healing was evaluated clinically at the seventh day postoperatively after sutures removal regarding the presence or absence of infection, inflammation or dry socket as shown in (Fig.6). Fig (6): Suture removal. Statistical analysis The data were collected and entered into the personal computer. Statistical analysis was done: Number and percentage of each group (study group and control group). Chi square test and monte carlo test used to compare between laboratory investigations of both groups. Wilcoxon signed ranks test for comparing between Immediate and each other period. Results of the immediate postoperative phase Study group: all 20 cases showed mild bleeding grade 2 (G2) according to WHO scale, after application of Collaplug 2 cases only showed bleeding grade 1 (G1)and the rest of cases showed grade 0 G (0) no bleeding. Control group: all 20 cases showed mild bleeding grade 2(G2) according to WHO scale. Results of the intermediate postoperative phase Six hours postoperatively after extraction; Study group: all patients showed no bleeding grade 0(G0) according to the WHO scale. Control group: 14 patients showed no bleeding grade 0 (G0), 4 patients showed bleeding grade 1(G1) and 2patients showed bleeding grade2 (G2). After 48 hours postoperatively; Study group: 17 cases showed no bleeding grade 0(G0) and 3 cases were grade 1(G1). Control group: 13 cases showed no bleeding grade0 (G0), 169
5 5 cases showed bleeding grade 1 (G1) and 2 cases showed bleeding grade 2(G2) cases according to the WHO scale. Results of delayed postoperative phase Study group: 18 cases showed no bleeding grade 0(G0) and 2 cases showed grade 1 (G1) in all the 20 cases. Control group: 16 cases showed no bleeding grade 0(G0) and 4 cases showed grade 1 (G1) according to WHO scale. Classification of teeth according to the site of extracted teeth is shown in table (3). Study group: There were bleeding grade1 G(1) in 3 cases, the 3 cases (100%) were maxillary teeth, after 48 hours. Control group: There were bleeding varying between grade 2(G2) and grade 1(G1) after first 48 hours in 7 cases (35%), 4 cases (57%) of them were maxillary teeth. Table (3): Classification of teeth according to site of extracted teeth. Pain Study group: Showed one case (5%) only needed paracetamol 500 mg, only one tablet in the day of the extraction. Control group: 8 cases showed pain (40%), prescribed for them paracetamol 500mg only one tablet in the day of the extraction, and there was no need for analgesics for rest of patients. DISCUSSION In this study we were facing difficult conditions not only due to the medical conditions of the patients but also for the consultation with their physicians, a patient undergoing anticoagulant treatment should be carefully evaluated prior to such a dental procedure. Simple tooth extraction involves gentle forceps manipulation of the tooth with minimal trauma to the tissue. A patient undergoing warfarin treatment should be carefully evaluated prior to such a dental procedure (7). In this study, we tried to compare between the study group which included the application of a local haemostatic material, that was effective to be locally applied in the extracted socket, sutures were taken over the material to keep it in place, without interruption of the anticoagulant treatment of those patients, and the control group underwent only suturing of the sockets, without interruption of their anticoagulant treatment, and without application of any local hemostatic materials, in order to evaluate the efficacy of Collaplug in minimizing postoperative bleeding and pain following tooth extraction in patients under oral anticoagulant therapy. In this study, there were nearly no postoperative complications from the use of the local haemostatic material (Collaplug ) but in contrast it enhanced wound healing, reduced bleeding and pain, so local hemostatic material helps in reducing the risk of bleeding and pain in these patients, this agrees with a study done in the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, University of Washington (3). The present study included forty patients of both genders 21 females (52%) and 19 males (48%). Their ages ranged between years, INR of both study and control groups <3,another study was done in the Oral and Maxillofacial Department, College of Dentistry, King Saud University, patients indicated for dental extractions, it was conducted on total of 35 patients (16 women and 19 men) aged between 38 and 57 years (mean =48.7) (7), both studies are nearly compatible with each other they showed that simple tooth extraction in patients on warfarin treatment can be performed safely without high risk of bleeding, providing that the INR is equal or less than 3.5 on the day of extraction. In this study we noticed that the laboratory investigations revealed no much increase in the bleeding time as expected due to the anticoagulant therapy to all the patients even those who were under combination of anticoagulants drugs this was accepted by many authors (22). So screening for preoperative bleeding time is not a reliable test for assessing the risk of clinically significant perioperative bleeding and should not be used for this purpose (23). There have been studies showing that no statistical correlation between the preoperative bleeding time and the amount of blood loss (24,25). The INR is used to monitor the level of anticoagulation (26), in this study it was found that it is safe to perform extraction for anticoagulated patients their INR 3with application of local hemostatic material, which nearly agrees with the literature which confirms that the rate of postoperative bleeding after tooth removal in patients on warfarin is low when the INR is 3.5 with the use of local hemostatic material (27). In addition, a number of articles confirm that even a higher INR than 3.5 is possible when a tooth removal is required, blinder et al. did not find a statistical significant correlation between preoperative INR value and incidence of postoperative bleeding (28). In this study most of cases which showed either intermediate or delayed postoperative bleeding after extraction of their teeth in both study and control groups 170
6 were posterior maxillary teeth. In this study the study group: there were signs of infection in only one case, socket closure showed improvement in the study group with no signs of inflammations or infection in most cases. Although as with most hemostatic agents, collagens are not to be used in infected or contaminated wounds. The agents may serve as a nidus for abscess formation and may potentiate bacterial growth. Such results are similar to what has been reported for other hemostatic agents (15,16,18). Like other local hemostatics agents may have side effects such as delayed wound healing as an example: at a hospital in Dammam, Saudi Arabia, it was noticed that many patients had developed dry socket after surgical removal of wisdom teeth and application of surgicel. (30) In periodontal surgery it was found to enhance healing (29).While in bone surgery it was reported to slightly retard healing (30,31). The major conclusions of this study were: Collaplug has been proven as an effective local haemostatic material following minor oral surgery in patients who are under oral anticoagulant therapy In the absence of history of a bleeding disorder, the bleeding time is not a useful predictor of the risk of hemorrhage associated with surgical procedures, normal bleeding time does not exclude the possibility of excessive hemorrhage associated with invasive procedures. The bleeding time cannot be used to reliably identify patients who may have recently ingested aspirin or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents, or those who have a platelet defect attributable to these drugs. The best preoperative screen to predict bleeding is to take a clinical history carefully that includes family history, previous dental, surgical, traumatic injury, and drug histories (32). The use of Collagen products as biocompatible material had been studied by many researchers with different points of views assured us about its safety especially when it is used to medically sensitive patients. CONCLUSIONS There is no need to stop the oral anticoagulants therapy,extraction is done safely within INR(International normalized ratio) < 3 with suturing of the socket but better to use a local hemostatic material as Collaplug prior to suturing, this will control postoperative bleeding specially in posterior maxillary teeth extracted sockets, also it enhances wound healing and reduces post operative pain, Collaplug has been proved as an effective local haemostatic material following minor oral surgery in patients under oral anticoagulant therapy which affects their coagulation mechanism and make them liable to prolonged post operative bleeding, also shows acceleration of soft tissue healing and postoperative pain reduction in patients who are under oral anticoagulant therapy and are liable to suffer from delayed wound healing and postoperative pain. CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. REFERENCES 1. Dagi TF. The management of postoperative bleeding. Surg Clin North Am 2005; 85: Spencer FA, Moscucci M, Granger CB, Gore JM, Goldberg RJ, Steg PG, et al. Does comorbidity account for the excess mortality in patients with major bleeding in acute myocardial infarction? Circulation 2007; 116: Beirne OR. Evidence to continue oral anticoagulant therapy for ambulatory oral surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2005; 63: Aframian, DJ, Lalla RV, Peterson DE. Management of dental patients taking common hemostasis-altering medications. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007;103 Suppl:S45 S Karsli ED, Erdogan O, Esen E, Acarturk E. Comparison of the effects of warfarin and heparin on bleeding caused by dental extraction: a clinical study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;69: Salam S, Yusuf H, Milosevic A. Bleeding after dental extractions in patients taking warfarin. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;45: Abdullah WA, Khalil H. Dental extraction in patients on warfarin treatment. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent 2014; 6: Nematullah A, Alabousi A, Blanas N, Douketis JD, Sutherland SE. Dental surgery for patients on anticoagulant therapy with warfarin: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Tex Dent J 2009; 126: Randall C. Surgical management of the primary care dental patient on warfarin. Dent Update 2005; 32: Gacina P, Carzavec D, Stancic V, Pejsa V. Dental Procedures in patients receiving oral anticoagulant therapy. Acta Clin Croat 2006; 45: Scully C, Cawson RA. Medical problems in dentistry. 4 th ed. Oxford, London, Boston: Wright, Butterworth- Heinemann, Little JW, Falace DA, Miller CS, Rhodus NL. Dental management of the medically compromised patient. 5 th ed. St Louis: CV Mosby Co, Blinder D, Manor Y, Martinowitz U, Taicher S, Hashomer T. Dental extractions in patients maintained on continued oral anticoagulant: comparison of local hemostatic modalities. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1999; 88: Schardt-Sacco D. Update on coagulopathies. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2000; 90: 171
7 Ogle OE. Perioperative hemorrhage. In: Dym H, Ogle OE (eds). Atlas of Minor Oral Surgery. Philadelphia, Pa: WB Saunders, McBee WL, Koerner KR. Review of hemostatic agents used in dentistry. Dent Today 2005; 24: Schonauer C, Tessitore E, Barbagallo G, Albanese V, Moraci A. The use of local agents: bone wax, gelatin, collagen, oxidized cellulose. Eur Spine J 2004; 13: Mahesh L, Kurtzman GM2, Shukla S. Regeneration in Periodontics: Collagen-A Review of Its Properties and Applications in Dentistry. Compend Contin Educ Dent 2015; 36: Sclar AG. Strategies for management of single-tooth extraction sites in aesthetic implant therapy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2005; 62: Miller AB, Hoogstraten B, Staquet M, Winkler A. Reporting results of cancer treatment. Cancer 1981; 47: Pain Rating Scale. British pain Society, Available at: _scales_eng.pdf 22. De Caterina R, Lanza M, Manca G, Strata GB, Maffei S, Salvatore L. Bleeding Time and Bleeding: An analysis of the relationship of the bleeding time test with parameters of surgical bleeding. Blood J 1994; 84: Gewirtz AS, Miller ML, Keys TF. The clinical usefulness of the preoperative bleeding time. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1996; 120: Lind SE. The Bleeding time does not predict surgical bleeding. Blood 1991; 77: Lehman CM. Discontinuation of BT without detectable adverse clinical impact. Clin Chem 2001; 47: Hirsh J, Dalen J, Anderson DR, Poller L, Bussey H, Ansell J, et al. Oral anticoagulants: Mechanism of action, clinical effectiveness and optimal therapeutic range. Chest 2001; 119: Svensson R, Hallmer F, Englesson CS, Svensson PJ, Becktor JP. Treatment with local hemostatic agents and primary closure after tooth extraction in warfarin treated patients. Swed Dent J 2013; 37: Blinder D, Manor Y, Martinowitz U, Taicher S. Dental extractions in patients maintained on oral anticoagulant therapy:. Comparison of INR value with occurrence of postoperative bleeding. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2001; 6: Suleiman AM. Influence of Surgicel gauze on the incidence of dry socket after wisdom tooth extraction. East Mediterr Health J 2006; 12: Mattsson T, Anneroth G, Köndell PA, Nordenram A. ACP and Surgicel in bone hemostasis. A comparative experimental and histologic study. Swed Dent J 1990; 14: Matthew IR, Browne RM, Frame JW, Millar BG. Subperiosteal behaviour of alginate and cellulose wound dressing materials. Biomaterials 1995; 16: Peterson P, Hayes TE, Arkin CF, Bovill EG, Fairweather RB, Rock WA Jr, et al. The Preoperative Bleeding Time Test Lacks Clinical Benefit; College of American Pathologists' and American Society of Clinical Pathologists' Position Article. Arch Surg 1998; 133:
Bleeding Management with Extractions
 Bleeding Management with Extractions WHAT YOU WILL LEARN IN THIS SEGMENT: What is INR? Do you stop Coumadin before extractions or not? If not, how many teeth can be removed per appointment? Which local
Bleeding Management with Extractions WHAT YOU WILL LEARN IN THIS SEGMENT: What is INR? Do you stop Coumadin before extractions or not? If not, how many teeth can be removed per appointment? Which local
Dental Management Considerations for Patients on Antithrombotic Therapy
 Dental Management Considerations for Patients on Antithrombotic Therapy Warfarin and Antiplatelet Joel J. Napeñas DDS FDSRCS(Ed) Program Director General Practice Residency Program Department of Oral Medicine
Dental Management Considerations for Patients on Antithrombotic Therapy Warfarin and Antiplatelet Joel J. Napeñas DDS FDSRCS(Ed) Program Director General Practice Residency Program Department of Oral Medicine
Anticoagulation in dental surgery: Is it rude to interrupt?
 COMMENTARY MICHAEL J. WAHL, DDS Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Hospital Dentistry, Christiana Care Health System, Wilmington, DE; Wahl Family Dentistry, Wilmington, DE Anticoagulation
COMMENTARY MICHAEL J. WAHL, DDS Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Hospital Dentistry, Christiana Care Health System, Wilmington, DE; Wahl Family Dentistry, Wilmington, DE Anticoagulation
differences between warfarin and
 differences between warfarin and new oral anticoagulants in dental clinical practice M. MIRANDA 1, L.S. MARTINEZ 1, R. FRANCO 1, V. FORTE 1, A. BARLATTANI Jr. 2, P. BOLLERO 1 1 Department of Systems Medicine,
differences between warfarin and new oral anticoagulants in dental clinical practice M. MIRANDA 1, L.S. MARTINEZ 1, R. FRANCO 1, V. FORTE 1, A. BARLATTANI Jr. 2, P. BOLLERO 1 1 Department of Systems Medicine,
An Absorbable and Soluble Haemostatic Gauze---BloodSTOP Yan Yin YY Labs, Medical, P.O.Box 597, Fremont, CA March. 2005
 An Absorbable and Soluble Haemostatic Gauze---BloodSTOP Yan Yin YY Labs, Medical, P.O.Box 597, Fremont, CA 94537 March. 2005 Abstract BloodSTOP TM [1] haemostatic gauze has been widely used in many countries
An Absorbable and Soluble Haemostatic Gauze---BloodSTOP Yan Yin YY Labs, Medical, P.O.Box 597, Fremont, CA 94537 March. 2005 Abstract BloodSTOP TM [1] haemostatic gauze has been widely used in many countries
Slide 1: Perioperative Management of Anticoagulation
 Perioperative Management of Anticoagulation by Steven L. Cohn, MD, FACP Director, Medical Consultation Service, Kings County Hospital Center, Clinical Professor of Medicine, SUNY Downstate, Brooklyn, NY
Perioperative Management of Anticoagulation by Steven L. Cohn, MD, FACP Director, Medical Consultation Service, Kings County Hospital Center, Clinical Professor of Medicine, SUNY Downstate, Brooklyn, NY
"DENTAL MANAGEMENT OF A PATIENT TAKING ANTICOAGULANTS"
 "DENTAL MANAGEMENT OF A PATIENT TAKING ANTICOAGULANTS" ------------------------------------------------------------------------ LT J.D. Molinaro, DC, USN 11 August 2000 Introduction Any patient receiving
"DENTAL MANAGEMENT OF A PATIENT TAKING ANTICOAGULANTS" ------------------------------------------------------------------------ LT J.D. Molinaro, DC, USN 11 August 2000 Introduction Any patient receiving
EFFICACY OF CHITOSAN AND ABSORBABLE GELATIN SPONGE ON HEMOSTASIS AND WOUND HEALING FOLLOWING TOOTH EXTRACTION "A COMPARATIVE STUDY"
 (07) EFFICACY OF CHITOSAN AND ABSORBABLE GELATIN SPONGE ON HEMOSTASIS AND WOUND HEALING FOLLOWING TOOTH EXTRACTION "A COMPARATIVE STUDY" Heba Yousif ElShiha*; Heba Abdel -Monem Tawfik**; Nashwa Khairat
(07) EFFICACY OF CHITOSAN AND ABSORBABLE GELATIN SPONGE ON HEMOSTASIS AND WOUND HEALING FOLLOWING TOOTH EXTRACTION "A COMPARATIVE STUDY" Heba Yousif ElShiha*; Heba Abdel -Monem Tawfik**; Nashwa Khairat
HeliMEND Advanced. Absorbable Collagen Membrane. Instructions for Use
 HeliMEND Advanced Absorbable Collagen Membrane Instructions for Use 2 Indications HeliMEND Advanced absorbable collagen membrane is an absorbable, implantable material that is indicated for guided tissue
HeliMEND Advanced Absorbable Collagen Membrane Instructions for Use 2 Indications HeliMEND Advanced absorbable collagen membrane is an absorbable, implantable material that is indicated for guided tissue
Extractions without eliminating anticoagulant treatment: A literature review
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Review doi:10.317/medoral.17065 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.317/medoral.17065 Extractions without eliminating anticoagulant treatment: A literature review
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Review doi:10.317/medoral.17065 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.317/medoral.17065 Extractions without eliminating anticoagulant treatment: A literature review
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF THE PRIMARY CARE DENTAL PATIENT ON WARFARIN
 SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF THE PRIMARY CARE DENTAL PATIENT ON WARFARIN Warfarin does not need to be stopped before primary care dental surgical procedures Contents Are patients at risk of thromboembolic events
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF THE PRIMARY CARE DENTAL PATIENT ON WARFARIN Warfarin does not need to be stopped before primary care dental surgical procedures Contents Are patients at risk of thromboembolic events
Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
CASE IN... Anticoagulation: When to Start,When to Stop. The management of patients who require an. Meet Tracey. Anticoagulation
 Anticoagulation: When to Start,When to Stop Ebtisam Bakhsh, MD; and James D. Douketis, MD, FRCPC Presented at McMaster University s Thrombosis and Hematology Update, October 2006. CASE IN... Anticoagulation
Anticoagulation: When to Start,When to Stop Ebtisam Bakhsh, MD; and James D. Douketis, MD, FRCPC Presented at McMaster University s Thrombosis and Hematology Update, October 2006. CASE IN... Anticoagulation
Delayed bleeding after implant surgery in patients taking novel oral anticoagulants: a case report
 Case Report pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2017;17(2):143-147 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.2.143 Delayed bleeding after implant surgery in patients taking novel oral anticoagulants:
Case Report pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2017;17(2):143-147 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.2.143 Delayed bleeding after implant surgery in patients taking novel oral anticoagulants:
Safety of Arthrocentesis and Joint Injection in Patients Receiving Anticoagulation at Therapeutic Levels
 CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Safety of Arthrocentesis and Joint Injection in Patients Receiving Anticoagulation at Therapeutic Levels Imdad Ahmed, MBBS, a,b Elie Gertner, MD a,b a Department of Internal Medicine,
CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Safety of Arthrocentesis and Joint Injection in Patients Receiving Anticoagulation at Therapeutic Levels Imdad Ahmed, MBBS, a,b Elie Gertner, MD a,b a Department of Internal Medicine,
Primary Care practice clinics within the Edmonton Southside Primary Care Network.
 INR Monitoring and Warfarin Dose Adjustment Last Review: November 2016 Intervention(s) and/or Procedure: Registered Nurses (RNs) adjust warfarin dosage according to individual patient International Normalized
INR Monitoring and Warfarin Dose Adjustment Last Review: November 2016 Intervention(s) and/or Procedure: Registered Nurses (RNs) adjust warfarin dosage according to individual patient International Normalized
Management of Anticoagulation during Device Implants; Coumadin to Novel Agents
 Management of Anticoagulation during Device Implants; Coumadin to Novel Agents DR D Birnie Invited Faculty Core Curriculum Heart Rhythm Society May 8 th 2014 Disclosures Boehringer Ingleheim Research Support
Management of Anticoagulation during Device Implants; Coumadin to Novel Agents DR D Birnie Invited Faculty Core Curriculum Heart Rhythm Society May 8 th 2014 Disclosures Boehringer Ingleheim Research Support
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF THE PRIMARY CARE DENTAL PATIENT ON ANTIPLATELET MEDICATION
 SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF THE PRIMARY CARE DENTAL PATIENT ON ANTIPLATELET MEDICATION Antiplatelet medications do not need to be stopped before primary care dental surgical procedures Contents Page How do
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF THE PRIMARY CARE DENTAL PATIENT ON ANTIPLATELET MEDICATION Antiplatelet medications do not need to be stopped before primary care dental surgical procedures Contents Page How do
Should warfarin be discontinued before a dental extraction? A decision-tree analysis
 Vol. 110 No. 6 December 2010 ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY Editor: James R. Hupp Should warfarin be discontinued before a dental extraction? A decision-tree analysis Ben Balevi, BEng, DDS, DipEBHC (Oxford),
Vol. 110 No. 6 December 2010 ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY Editor: James R. Hupp Should warfarin be discontinued before a dental extraction? A decision-tree analysis Ben Balevi, BEng, DDS, DipEBHC (Oxford),
NEW/NOVEL ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS (NOACS): COMPARISON AND FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 NEW/NOVEL ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS (NOACS): COMPARISON AND FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS OBJECTIVES: To provide a comparison of the new/novel oral anticoagulants (NOACs) currently available in Canada. To address
NEW/NOVEL ORAL ANTICOAGULANTS (NOACS): COMPARISON AND FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS OBJECTIVES: To provide a comparison of the new/novel oral anticoagulants (NOACs) currently available in Canada. To address
Dental practitioners who treat adults most
 ABSTRACT Lack of a scientific basis for routine discontinuation of oral anticoagulation therapy before dental treatment ARTHUR H. JESKE, D.M.D., Ph.D.; GEORGE D. SUCHKO, D.D.S. Dental practitioners who
ABSTRACT Lack of a scientific basis for routine discontinuation of oral anticoagulation therapy before dental treatment ARTHUR H. JESKE, D.M.D., Ph.D.; GEORGE D. SUCHKO, D.D.S. Dental practitioners who
WARFARIN: PERI OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT
 WARFARIN: PERI OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an approach to the perioperative management of warfarin treated patients who require an elective or urgent surgery/procedure. To provide an approach
WARFARIN: PERI OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an approach to the perioperative management of warfarin treated patients who require an elective or urgent surgery/procedure. To provide an approach
PRE-OP and POST-OP SURGICAL CONSIDERATIONS
 PRE-OP and POST-OP SURGICAL CONSIDERATIONS Darlene Sorrell, DMD, is not an oral surgeon. AIDC is an out-patient facility. 29 years of experience in IHS. Advanced General Practice Residency. No access
PRE-OP and POST-OP SURGICAL CONSIDERATIONS Darlene Sorrell, DMD, is not an oral surgeon. AIDC is an out-patient facility. 29 years of experience in IHS. Advanced General Practice Residency. No access
Guided Tissue and Bone Regeneration
 Guided Tissue and Bone Regeneration One toolbox for your needs! Tefguide 9000 742 401 12x24 mm pc 1 Osgide 9000 701 520 15 x 20 mm pc 1 Osbone 9000 800 255 250-1000 μm 0.25 cc 5 Product Specifications
Guided Tissue and Bone Regeneration One toolbox for your needs! Tefguide 9000 742 401 12x24 mm pc 1 Osgide 9000 701 520 15 x 20 mm pc 1 Osbone 9000 800 255 250-1000 μm 0.25 cc 5 Product Specifications
MANAGEMENT OF OVERANTICOAGULATION AND PREOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OF WARFARIN DOSE 1. GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF AN ELEVATED INR
 MANAGEMENT OF OVERANTICOAGULATION AND PREOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OF WARFARIN DOSE 1. GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF AN ELEVATED INR 1.1 Time to lower INR Prothrombinex-VF - 15 minutes Fresh Frozen Plasma
MANAGEMENT OF OVERANTICOAGULATION AND PREOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OF WARFARIN DOSE 1. GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF AN ELEVATED INR 1.1 Time to lower INR Prothrombinex-VF - 15 minutes Fresh Frozen Plasma
Asif Serajian DO FACC FSCAI
 Anticoagulation and Antiplatelet update: A case based approach Asif Serajian DO FACC FSCAI No disclosures relevant to this talk Objectives 1. Discuss the indication for antiplatelet therapy for cardiac
Anticoagulation and Antiplatelet update: A case based approach Asif Serajian DO FACC FSCAI No disclosures relevant to this talk Objectives 1. Discuss the indication for antiplatelet therapy for cardiac
Cerasorb M DENTAL. O:\Zulassung\Cerasorb Dental Kanada 2013\Texte\Cerasorb M Dental final IFU docx
 Cerasorb M DENTAL Resorbable, pure-phase beta-tricalcium phosphate matrix with interconnecting porosity for bone regeneration for use in dental and maxillofacial surgery DESCRIPTION: Cerasorb M DENTAL
Cerasorb M DENTAL Resorbable, pure-phase beta-tricalcium phosphate matrix with interconnecting porosity for bone regeneration for use in dental and maxillofacial surgery DESCRIPTION: Cerasorb M DENTAL
MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF UKRAINE Higher medical educational institution of Ukraine "Ukrainian medical stomatological academy"
 MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF UKRAINE Higher medical educational institution of Ukraine "Ukrainian medical stomatological academy" Approved On the meeting chair Of Pediatric Surgical Stomatology and Propaedeutics
MINISTRY OF HEALTH OF UKRAINE Higher medical educational institution of Ukraine "Ukrainian medical stomatological academy" Approved On the meeting chair Of Pediatric Surgical Stomatology and Propaedeutics
Complex Exodontia. Jone Kim, DDS, MS
 Complex Exodontia Jone Kim, DDS, MS Diplomate, American Board of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Lecturer, UCLA School of Dentistry, Dept. of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Principle of Complex Exodontia Principle
Complex Exodontia Jone Kim, DDS, MS Diplomate, American Board of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Lecturer, UCLA School of Dentistry, Dept. of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Principle of Complex Exodontia Principle
The effect of aspirin on bleeding after extraction of teeth
 The Saudi Dental Journal (2009) 21, 57 61 King Saud University The Saudi Dental Journal www.ksu.edu.sa www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effect of aspirin on bleeding after extraction of teeth
The Saudi Dental Journal (2009) 21, 57 61 King Saud University The Saudi Dental Journal www.ksu.edu.sa www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effect of aspirin on bleeding after extraction of teeth
Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation
 Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation Historical Background Guided tissue regeneration is a well established concept in the repair of oral bone defects. The exclusion of soft tissue epithelial
Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation Historical Background Guided tissue regeneration is a well established concept in the repair of oral bone defects. The exclusion of soft tissue epithelial
Cellistypt Oxidized Resorbable Cellulose Hemostats. Biosurgicals
 Oxidized Resorbable Cellulose Hemostats Biosurgicals Oxidized Resorbable Cellulose Hemostats Zriusscing 4.384 Peratldiup DVD-R is an oxidized resorbable cellulose hemostat, of 0 % vegetable origin made
Oxidized Resorbable Cellulose Hemostats Biosurgicals Oxidized Resorbable Cellulose Hemostats Zriusscing 4.384 Peratldiup DVD-R is an oxidized resorbable cellulose hemostat, of 0 % vegetable origin made
Title: Should oral anticoagulant therapy be continued during dental extraction? A meta-analysis
 Author s response to reviews Title: Should oral anticoagulant therapy be continued during dental extraction? A meta-analysis Authors: Shuo Yang (sophiasure@163.com) Quan Shi (shiquan3333@sina.cn) Jinglong
Author s response to reviews Title: Should oral anticoagulant therapy be continued during dental extraction? A meta-analysis Authors: Shuo Yang (sophiasure@163.com) Quan Shi (shiquan3333@sina.cn) Jinglong
Clinical Evaluation of atelocollagen sponge(tre-641) extraction wounds. Nobuyuki Mizuki et al, The Quintessence 15(6), (1996)
 Clinical Evaluation of atelocollagen sponge(tre-641) extraction wounds. Nobuyuki Mizuki et al, The Quintessence 15(6),1450-1468(1996) School of Medicine, Yokohama City University Department of Oral and
Clinical Evaluation of atelocollagen sponge(tre-641) extraction wounds. Nobuyuki Mizuki et al, The Quintessence 15(6),1450-1468(1996) School of Medicine, Yokohama City University Department of Oral and
WARFARIN: PERI-OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT
 WARFARIN: PERI-OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an approach to the perioperative management of warfarin-treated patients who require an elective or urgent surgery/procedure. To provide an approach
WARFARIN: PERI-OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an approach to the perioperative management of warfarin-treated patients who require an elective or urgent surgery/procedure. To provide an approach
Treatment of the Medically Compromised Patient
 Treatment of the Medically Compromised Patient Nashville Area Continuing Dental Education Series November 3, 2010 Harry J. Brown, MD Chief Medical Officer, Nashville Area Outline General Principles Specific
Treatment of the Medically Compromised Patient Nashville Area Continuing Dental Education Series November 3, 2010 Harry J. Brown, MD Chief Medical Officer, Nashville Area Outline General Principles Specific
Awareness And Knowledge Of Tooth Extraction Complications Management Among Riyadh Elm University Dental Interns
 Original Article Journal of Applied Dental and Medical Sciences NLM ID: 101671413 ISSN:2454-2288 Volume 4 Issue2 April-June 2018 Awareness And Knowledge Of Tooth Extraction Complications Management Among
Original Article Journal of Applied Dental and Medical Sciences NLM ID: 101671413 ISSN:2454-2288 Volume 4 Issue2 April-June 2018 Awareness And Knowledge Of Tooth Extraction Complications Management Among
1. What is the preferred method of anticoagulating a high-risk cardiac patient on chronic warfarin therapy. anticoagulation can be continued,
 Experts Answering Your Questions Anticoagulating a high-risk cardiac patient 1. What is the preferred method of anticoagulating a high-risk cardiac patient on chronic warfarin therapy for minor surgical
Experts Answering Your Questions Anticoagulating a high-risk cardiac patient 1. What is the preferred method of anticoagulating a high-risk cardiac patient on chronic warfarin therapy for minor surgical
Clinical Practice Committee Anticoagulation Bridging Document
 Original: 10/23/06 Last Updated: 10/30/07 Clinical Practice Committee Do patients on long term oral anticoagulant therapy who require short term interruption of warfarin for an elective invasive procedure
Original: 10/23/06 Last Updated: 10/30/07 Clinical Practice Committee Do patients on long term oral anticoagulant therapy who require short term interruption of warfarin for an elective invasive procedure
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction There are several disorders which carry an increased risk of thrombosis, clots that interfere with normal circulation, including: venous thromboembolism (VTE), comprising both deep
Chapter 1 Introduction There are several disorders which carry an increased risk of thrombosis, clots that interfere with normal circulation, including: venous thromboembolism (VTE), comprising both deep
Disclosures. Overview. Have you ever. The Perioperative Management of Anticoagulants. No financial conflicts of interest to disclose
 Disclosures No financial conflicts of interest to disclose The Perioperative Management of Anticoagulants Margaret C. Fang, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine UCSF Division of Hospital Medicine Medical
Disclosures No financial conflicts of interest to disclose The Perioperative Management of Anticoagulants Margaret C. Fang, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine UCSF Division of Hospital Medicine Medical
Systemic effect of tranexamic acid on Prothrombin and clotting times in rabbits after IV injection of heparin (Experimental study)
 ISSN: 1812 1217 Systemic effect of tranexamic acid on Prothrombin and clotting times in rabbits after IV injection of heparin (Experimental study) Raid M Basheer BDS, MSc (Assist Lect) Department of Oral
ISSN: 1812 1217 Systemic effect of tranexamic acid on Prothrombin and clotting times in rabbits after IV injection of heparin (Experimental study) Raid M Basheer BDS, MSc (Assist Lect) Department of Oral
CuraMedical. CuraMedical. Absorbable Haemostat Family. BCM proven performance in surgery
 CuraMedical CuraMedical CuraMedical B.V. Industrieweg 6B 1566 JP Assendelft The Netherlands Phone: +31 75 657 1885 Fax: +31 75 657 1184 Email: sales@curamedical.com www.curamedical.com BCM001.00 rev.2014-11
CuraMedical CuraMedical CuraMedical B.V. Industrieweg 6B 1566 JP Assendelft The Netherlands Phone: +31 75 657 1885 Fax: +31 75 657 1184 Email: sales@curamedical.com www.curamedical.com BCM001.00 rev.2014-11
Institution : College of dentistry Academic Department: Department of Maxillofacial Surgery & Diagnostic. Course:
 Institution : College of dentistry Academic Department: Department of Maxillofacial Surgery & Diagnostic Sciences Program BDS Course: Clinical Oral Surgery I (313 MDS) Course Coordinator : Maher Aboelgheit
Institution : College of dentistry Academic Department: Department of Maxillofacial Surgery & Diagnostic Sciences Program BDS Course: Clinical Oral Surgery I (313 MDS) Course Coordinator : Maher Aboelgheit
Preoperative Management of Patients Receiving Antithrombotics
 Preoperative Management of Patients Receiving Antithrombotics Bleeding complications remain an important concern for most surgical procedures. Attempts to minimize the risk of these complications by removing
Preoperative Management of Patients Receiving Antithrombotics Bleeding complications remain an important concern for most surgical procedures. Attempts to minimize the risk of these complications by removing
Detecting a sinus perforation.
 Extractions and the Sinus Dentistry s Black Hole. Detecting a sinus perforation. How to know when you have a small perforation? Need: Adequate light (headlight preferred) Small suction tip (2 mm diameter)
Extractions and the Sinus Dentistry s Black Hole. Detecting a sinus perforation. How to know when you have a small perforation? Need: Adequate light (headlight preferred) Small suction tip (2 mm diameter)
2017 Oregon Dental Conference Course Handout
 2017 Oregon Dental Conference Course Handout David Lasho, DDS, MSD Course 8171: Dental Management of Patients on Antithrombotic Medications Saturday, April 8 1 pm - 3 pm Dental Management of Patients on
2017 Oregon Dental Conference Course Handout David Lasho, DDS, MSD Course 8171: Dental Management of Patients on Antithrombotic Medications Saturday, April 8 1 pm - 3 pm Dental Management of Patients on
Prostate Biopsy Alerts
 Prostate Biopsy Alerts Saskatchewan Prostate Assessment Pathway Guidelines for the Primary Care Provider for Patient Preparation and the Management of Medications and Complications September 2016 Table
Prostate Biopsy Alerts Saskatchewan Prostate Assessment Pathway Guidelines for the Primary Care Provider for Patient Preparation and the Management of Medications and Complications September 2016 Table
FOUNDATION TM Collagen-Based Bone Filling Augmentation Material for Use in the Filling of Extraction Sockets. For in-house research
 FOUNDATION TM Collagen-Based Bone Filling Augmentation Material for Use in the Filling of Extraction Sockets Feb. 2006 Overview * FOUNDATION is made of atelo collagen to minimize antigenicity. * The atelo
FOUNDATION TM Collagen-Based Bone Filling Augmentation Material for Use in the Filling of Extraction Sockets Feb. 2006 Overview * FOUNDATION is made of atelo collagen to minimize antigenicity. * The atelo
Challenging Anticoagulation Case Studies. Earl J. Hope, M.D. Tower Health Cardiology
 Challenging Anticoagulation Case Studies Earl J. Hope, M.D. Tower Health Cardiology Financial Disclosures Nothing to disclose Objectives: 1. Understand indications for heparin bridging. 2. Recognize the
Challenging Anticoagulation Case Studies Earl J. Hope, M.D. Tower Health Cardiology Financial Disclosures Nothing to disclose Objectives: 1. Understand indications for heparin bridging. 2. Recognize the
Anticoagulation Task Force
 Anticoagulation Task Force Newest Recommendations Donald Zabriskie, BPharm, MBA, RPh Pharmacy Patient Care Services Cleveland Clinic- Fairview Hospital THE DRUGS THE PERFECT ANTICOAGULANT Oral administration
Anticoagulation Task Force Newest Recommendations Donald Zabriskie, BPharm, MBA, RPh Pharmacy Patient Care Services Cleveland Clinic- Fairview Hospital THE DRUGS THE PERFECT ANTICOAGULANT Oral administration
YOUR COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE TO. Wisdom Teeth. (03) omfs.com.au
 YOUR COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE TO Wisdom Teeth (03) 9347 3788 omfs.com.au Wisdom teeth 3 Symptoms caused by impacted wisdom teeth 4 Treatment options 5 The removal procedure 6 Important facts to consider with
YOUR COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE TO Wisdom Teeth (03) 9347 3788 omfs.com.au Wisdom teeth 3 Symptoms caused by impacted wisdom teeth 4 Treatment options 5 The removal procedure 6 Important facts to consider with
POSTOP CARE FOR WISDOM TEETH
 POSTOP CARE FOR WISDOM TEETH Bleeding Bleeding after surgery may continue for several hours. The best way to stop bleeding is to place a piece of folded, damp gauze over the extraction site and gently
POSTOP CARE FOR WISDOM TEETH Bleeding Bleeding after surgery may continue for several hours. The best way to stop bleeding is to place a piece of folded, damp gauze over the extraction site and gently
Day 1 10:50. Panel Discussions/Group Photo Coffee/Tea Break 11:15-11:30 (Networking) Different types of. Anesthesia. Day 2
 Day 1 Evening Sessions Morning Sessions Reception/Registration 08:3009:30 General Session Time 09:3009:55 Inaugural Address 10:0010:25 Keynote/Plenary Talk 1 Least of 3 Keynote/Plenary 10:25Talks 10:50
Day 1 Evening Sessions Morning Sessions Reception/Registration 08:3009:30 General Session Time 09:3009:55 Inaugural Address 10:0010:25 Keynote/Plenary Talk 1 Least of 3 Keynote/Plenary 10:25Talks 10:50
Implant surgery and oral
 Implant surgery and oral anticoagulant therapy: case report M. MIRANDA 1, P. BOLLERO 2, N. D OVIDIO 1, V. MARSANGO 1, A. BARLATTANI Jr 1 1 Department of Clinical Sciences and Translational Medicine, University
Implant surgery and oral anticoagulant therapy: case report M. MIRANDA 1, P. BOLLERO 2, N. D OVIDIO 1, V. MARSANGO 1, A. BARLATTANI Jr 1 1 Department of Clinical Sciences and Translational Medicine, University
References: Murtagh J. Murtagh s General Practice. 5 th edn. Sydney: McGraw Hill; 2010.
 This presentation is designed to be delivered to people who work in a health care setting; such as nurses, carers and other nursing home staff. If you are an accredited pharmacist, you can use this presentation
This presentation is designed to be delivered to people who work in a health care setting; such as nurses, carers and other nursing home staff. If you are an accredited pharmacist, you can use this presentation
A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
 Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Strong bone for beautiful teeth. Patient Information I Bone reconstruction with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide
 Strong bone for beautiful teeth Patient Information I Bone reconstruction with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide Contents Smiling is the most beautiful way to show your teeth 3 What are the causes
Strong bone for beautiful teeth Patient Information I Bone reconstruction with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide Contents Smiling is the most beautiful way to show your teeth 3 What are the causes
North East Essex Medicines Management Committee
 Colchester Hospital University NHS Foundation Trust North East Essex Clinical Commissioning Group North East Essex Medicines Management Committee ORAL ANTICOAGULANT (Vit K antagonist only) MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES
Colchester Hospital University NHS Foundation Trust North East Essex Clinical Commissioning Group North East Essex Medicines Management Committee ORAL ANTICOAGULANT (Vit K antagonist only) MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES
DMF Page 63. Description
 DMF Page 60 DMF Page 61 DMF Page 62 4 GB Description The SPONGOSTAN Absorbable Haemostatic Gelatin Powder is a sterile, water-insoluble, porcine gelatin absorbable powder intended for haemostatic use by
DMF Page 60 DMF Page 61 DMF Page 62 4 GB Description The SPONGOSTAN Absorbable Haemostatic Gelatin Powder is a sterile, water-insoluble, porcine gelatin absorbable powder intended for haemostatic use by
Stroke and ASA / FO REBUTTAL
 REBUTTAL Definition of an ischemic stroke Definition of a PFO Evidence for a causal role of PFO in stroke Evidence against a role of PFO in stroke Stroke recurrencies in stroke (PFO) patients Medical treatment
REBUTTAL Definition of an ischemic stroke Definition of a PFO Evidence for a causal role of PFO in stroke Evidence against a role of PFO in stroke Stroke recurrencies in stroke (PFO) patients Medical treatment
Anticoagulants and Head Injuries. Asaad Shujaa,MD,FRCPC,FAAEM Assistant Professor,weill Corneal Medicne Senior Consultant,HMC Qatar
 Anticoagulants and Head Injuries Asaad Shujaa,MD,FRCPC,FAAEM Assistant Professor,weill Corneal Medicne Senior Consultant,HMC Qatar Common Anticoagulants and Indications Coumadin (warfarin) indicated for
Anticoagulants and Head Injuries Asaad Shujaa,MD,FRCPC,FAAEM Assistant Professor,weill Corneal Medicne Senior Consultant,HMC Qatar Common Anticoagulants and Indications Coumadin (warfarin) indicated for
Continuous oral anticoagulant therapy has been used to decrease the risk of thromboembolism
 Dental Surgery in Anticoagulated Patients Michael J. Wahl, DDS REVIEW ARTICLE Continuous oral anticoagulant therapy has been used to decrease the risk of thromboembolism for more than half a century, prolonging
Dental Surgery in Anticoagulated Patients Michael J. Wahl, DDS REVIEW ARTICLE Continuous oral anticoagulant therapy has been used to decrease the risk of thromboembolism for more than half a century, prolonging
Unstable INR Has Implications for Healthcare Resource Use. Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
 Unstable INR Has Implications for Healthcare Resource Use Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Stable INR is essential for effective anticoagulation treatment Achieving a stable international normalized ratio
Unstable INR Has Implications for Healthcare Resource Use Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Stable INR is essential for effective anticoagulation treatment Achieving a stable international normalized ratio
Regaining Your Gum Tissue. Soft-Tissue Regeneration With Geistlich Mucograft
 Regaining Your Gum Tissue Soft-Tissue Regeneration With Geistlich Mucograft Why is Healthy Gum Tissue So Important? Gum tissue can recede due to grinding of the teeth, thin insufficient gum tissue, as
Regaining Your Gum Tissue Soft-Tissue Regeneration With Geistlich Mucograft Why is Healthy Gum Tissue So Important? Gum tissue can recede due to grinding of the teeth, thin insufficient gum tissue, as
Atrial Fibrillation. 2 nd Annual National Hospitalist Conference San Antonio, TX September 7, 2018
 2 nd Annual National Hospitalist Conference San Antonio, TX September 7, 2018, MSc, FACP, SFHM Division of Hospital Medicine Henry Ford Hospital Detroit, USA Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Wayne
2 nd Annual National Hospitalist Conference San Antonio, TX September 7, 2018, MSc, FACP, SFHM Division of Hospital Medicine Henry Ford Hospital Detroit, USA Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Wayne
2017 Bryan Health Primary Care Conference. Dale Hansen MD Bryan Heart 5/20/17
 2017 Bryan Health Primary Care Conference Dale Hansen MD Bryan Heart 5/20/17 I have no financial disclosures or conflicts of interest Bridging Anticoagulation Primum Non Nocere 67 y.o. male with mechanical
2017 Bryan Health Primary Care Conference Dale Hansen MD Bryan Heart 5/20/17 I have no financial disclosures or conflicts of interest Bridging Anticoagulation Primum Non Nocere 67 y.o. male with mechanical
FACTOR Xa AND PAR-1 BLOCKER : ATLAS-2, APPRAISE-2 & TRACER TRIALS
 New Horizons In Atherothrombosis Treatment 2012 순환기춘계학술대회 FACTOR Xa AND PAR-1 BLOCKER : ATLAS-2, APPRAISE-2 & TRACER TRIALS Division of Cardiology, Jeonbuk National University Medical School Jei Keon Chae,
New Horizons In Atherothrombosis Treatment 2012 순환기춘계학술대회 FACTOR Xa AND PAR-1 BLOCKER : ATLAS-2, APPRAISE-2 & TRACER TRIALS Division of Cardiology, Jeonbuk National University Medical School Jei Keon Chae,
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service
 M AY. 6. 2011 10:37 A M F D A - C D R H - O D E - P M O N O. 4147 P. 1 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue Document Control
M AY. 6. 2011 10:37 A M F D A - C D R H - O D E - P M O N O. 4147 P. 1 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue Document Control
Alveolar Osteitis. By: Michael Martins
 Alveolar Osteitis By: Michael Martins Teeth are routinely extracted in a general dental practice because they are deemed hopeless due to tooth decay or periodontal disease. Recently in the dental emergency
Alveolar Osteitis By: Michael Martins Teeth are routinely extracted in a general dental practice because they are deemed hopeless due to tooth decay or periodontal disease. Recently in the dental emergency
Indication for Intentional Replantation of Teeth
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. V (Dec. 2017), PP 36-42 www.iosrjournals.org Indication for Intentional Replantation
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. V (Dec. 2017), PP 36-42 www.iosrjournals.org Indication for Intentional Replantation
NOACS/DOACS*: COMPARISON AND FREQUENTLY-ASKED QUESTIONS
 NOACS/DOACS*: COMPARISON AND FREQUENTLY-ASKED QUESTIONS OBJECTIVES: To provide a comparison of the newer direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) currently available in Canada. To address frequently-asked questions
NOACS/DOACS*: COMPARISON AND FREQUENTLY-ASKED QUESTIONS OBJECTIVES: To provide a comparison of the newer direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) currently available in Canada. To address frequently-asked questions
Perioperative Management of Anticoagulation
 Perioperative Management of Anticoagulation Presented By: Nibal R. Chamoun, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Assistant Professor, Clinical Coordinator Lebanese American University, School of Pharmacy Presented at:
Perioperative Management of Anticoagulation Presented By: Nibal R. Chamoun, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Assistant Professor, Clinical Coordinator Lebanese American University, School of Pharmacy Presented at:
Potential Complications
 Potential Complications The risk of complications associated with wisdom teeth removal is less than 0.5 percent when performed by an experienced oral surgeons who uses contemporary techniques and surgical
Potential Complications The risk of complications associated with wisdom teeth removal is less than 0.5 percent when performed by an experienced oral surgeons who uses contemporary techniques and surgical
New Oral Anticoagulants in treatment of VTE, PE DR.AMR HANAFY (LECTURER OF CARDIOLOGY ) ASWAN UNIVERSITY
 New Oral Anticoagulants in treatment of VTE, PE DR.AMR HANAFY (LECTURER OF CARDIOLOGY ) ASWAN UNIVERSITY Fact VTE is deadly! It nibbles after it bites! The 30-day mortality rates for first-time DVT or
New Oral Anticoagulants in treatment of VTE, PE DR.AMR HANAFY (LECTURER OF CARDIOLOGY ) ASWAN UNIVERSITY Fact VTE is deadly! It nibbles after it bites! The 30-day mortality rates for first-time DVT or
POSTOP CARE FOR TOOTH EXTRACTION
 POSTOP CARE FOR TOOTH Bleeding EXTRACTION Bleeding after surgery may continue for several hours. The best way to stop bleeding is to place a piece of folded, damp gauze over the extraction site and gently
POSTOP CARE FOR TOOTH Bleeding EXTRACTION Bleeding after surgery may continue for several hours. The best way to stop bleeding is to place a piece of folded, damp gauze over the extraction site and gently
Landmark Phase III Study of Bayer s Xarelto (Rivaroxaban) Initiated for the Secondary Prevention of Myo
 Xarelto (Rivaroxaban) Landmark Phase III Study of Bayer s Xarelto (Rivaroxaban) Initiated for the Secondary Prevention of Myocardial Infarction and Death in Patients with Coronary or Peripheral Artery
Xarelto (Rivaroxaban) Landmark Phase III Study of Bayer s Xarelto (Rivaroxaban) Initiated for the Secondary Prevention of Myocardial Infarction and Death in Patients with Coronary or Peripheral Artery
Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) Oct-Dec;23(4) Original article
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org METHODS Sociological Methods A questionnaire containing ten questions was develhttps://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017234.1737 Journal of IMAB
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org METHODS Sociological Methods A questionnaire containing ten questions was develhttps://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017234.1737 Journal of IMAB
LANAP. Non-invasive laser gum therapy. LANAP Information Pack
 LANAP Non-invasive laser gum therapy LANAP Information Pack GumSurgeryConcord.com What is LANAP? LANAP vs Traditional Treatment Frequently Asked Questions Gum Tissue & Bone Regeneration Treatment Plan
LANAP Non-invasive laser gum therapy LANAP Information Pack GumSurgeryConcord.com What is LANAP? LANAP vs Traditional Treatment Frequently Asked Questions Gum Tissue & Bone Regeneration Treatment Plan
Regaining your gum tissue. Soft tissue regeneration with Geistlich Mucograft
 Regaining your gum tissue Soft tissue regeneration with Geistlich Mucograft Why is healthy gum tissue so important? Gum tissue can recede due to grinding of the teeth, thin insufficient gum tissue, as
Regaining your gum tissue Soft tissue regeneration with Geistlich Mucograft Why is healthy gum tissue so important? Gum tissue can recede due to grinding of the teeth, thin insufficient gum tissue, as
Guidance for management of bleeding in patients taking the new oral anticoagulant drugs: rivaroxaban, dabigatran or apixaban
 Guidance for management of bleeding in patients taking the new oral anticoagulant drugs: rivaroxaban, dabigatran or apixaban Purpose The aim of this guidance is to outline the management of patients presenting
Guidance for management of bleeding in patients taking the new oral anticoagulant drugs: rivaroxaban, dabigatran or apixaban Purpose The aim of this guidance is to outline the management of patients presenting
CABG in the Post-Aprotinin Era: Are We Doing Better? Ziv Beckerman, David Kadosh, Zvi Peled, Keren Bitton-Worms, Oved Cohen and Gil Bolotin
 CABG in the Post-Aprotinin Era: Are We Doing Better? Ziv Beckerman, David Kadosh, Zvi Peled, Keren Bitton-Worms, Oved Cohen and Gil Bolotin DISCLOSURES None Objective(s): Our department routinely used
CABG in the Post-Aprotinin Era: Are We Doing Better? Ziv Beckerman, David Kadosh, Zvi Peled, Keren Bitton-Worms, Oved Cohen and Gil Bolotin DISCLOSURES None Objective(s): Our department routinely used
Apixaban for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation. August 2010
 Apixaban for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation August 2010 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended to
Apixaban for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation August 2010 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended to
PEER REVIEW HISTORY ARTICLE DETAILS TITLE (PROVISIONAL)
 PEER REVIEW HISTORY BMJ Open publishes all reviews undertaken for accepted manuscripts. Reviewers are asked to complete a checklist review form (http://bmjopen.bmj.com/site/about/resources/checklist.pdf)
PEER REVIEW HISTORY BMJ Open publishes all reviews undertaken for accepted manuscripts. Reviewers are asked to complete a checklist review form (http://bmjopen.bmj.com/site/about/resources/checklist.pdf)
Patients on anticoagulant or antiplatelet therapy undergoing elective endoscopic procedures
 This is an official Northern Trust policy and should not be edited in any way Patients on anticoagulant or antiplatelet therapy undergoing elective endoscopic procedures Reference Number: NHSCT/11/454
This is an official Northern Trust policy and should not be edited in any way Patients on anticoagulant or antiplatelet therapy undergoing elective endoscopic procedures Reference Number: NHSCT/11/454
ADVANCES IN ANTICOAGULATION
 ADVANCES IN ANTICOAGULATION The Clinicians Perspective Claudine M. Lewis Cardiologist OUTLINE Indications for anticoagulants Review - Physiology of Hemostasis Types of anticoagulants New anticoagulants
ADVANCES IN ANTICOAGULATION The Clinicians Perspective Claudine M. Lewis Cardiologist OUTLINE Indications for anticoagulants Review - Physiology of Hemostasis Types of anticoagulants New anticoagulants
Review Article Sri Lanka Dental Journal 2016; 46(01) 05-13
 Review Article Sri Lanka Dental Journal 2016; 46(01) 05-13 The Importance of Knowing the Patient s Clotting Profile before Dental Treatment N.A. Alles, N.S. Soysa Introduction Patients having bleeding
Review Article Sri Lanka Dental Journal 2016; 46(01) 05-13 The Importance of Knowing the Patient s Clotting Profile before Dental Treatment N.A. Alles, N.S. Soysa Introduction Patients having bleeding
RICHARD J. SORBERA, D.D.S. SHIBLY D. MALOUF, D.D.S., INC. DIPLOMATES AMERICAN BOARD OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY
 RICHARD J. SORBERA, D.D.S. SHIBLY D. MALOUF, D.D.S., INC. DIPLOMATES AMERICAN BOARD OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY INFORMATION AND CONSENT FOR IMPLANT SURGERY PURPOSE OF THIS FORM: State law requires
RICHARD J. SORBERA, D.D.S. SHIBLY D. MALOUF, D.D.S., INC. DIPLOMATES AMERICAN BOARD OF ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY INFORMATION AND CONSENT FOR IMPLANT SURGERY PURPOSE OF THIS FORM: State law requires
Extractions and the Maxillary Sinus
 Extractions and the Maxillary Sinus Four levels of sinus membrane involvement: Level One: Sinus membrane showing within the socket after an extraction. Not perforated. Level Two: 1-2mm tear. Level three:
Extractions and the Maxillary Sinus Four levels of sinus membrane involvement: Level One: Sinus membrane showing within the socket after an extraction. Not perforated. Level Two: 1-2mm tear. Level three:
After Wisdom Teeth Removal Do You Eat With Gauze In
 After Wisdom Teeth Removal Do You Eat With Gauze In How To Stop Bleeding After A Tooth Extraction (Gauze) Watch Cheryl, senior surgical. After an hour, the gauze pad should be removed and discarded. When
After Wisdom Teeth Removal Do You Eat With Gauze In How To Stop Bleeding After A Tooth Extraction (Gauze) Watch Cheryl, senior surgical. After an hour, the gauze pad should be removed and discarded. When
We Want to Keep You Smiling. Bone Regeneration with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide
 We Want to Keep You Smiling Bone Regeneration with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide Strong Bone for a Healthier Smile Strong and healthy teeth provide a feeling of well-being, self-confidence and
We Want to Keep You Smiling Bone Regeneration with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide Strong Bone for a Healthier Smile Strong and healthy teeth provide a feeling of well-being, self-confidence and
PERSONALIZĒTA ANTIKOAGULANTU TERAPIJA KARDIOLOĢIJĀ INDIVIDUALIZED ANTICOAGULATION THERAPY IN CARDIOLOGY
 PERSONALIZĒTA ANTIKOAGULANTU TERAPIJA KARDIOLOĢIJĀ INDIVIDUALIZED ANTICOAGULATION THERAPY IN CARDIOLOGY Inga Urtāne 1, Jānis Ansabergs 2, Aina Silvija Štokmane 1, Dace Bandere 1 1 Rīgas Stradiľa universitāte,
PERSONALIZĒTA ANTIKOAGULANTU TERAPIJA KARDIOLOĢIJĀ INDIVIDUALIZED ANTICOAGULATION THERAPY IN CARDIOLOGY Inga Urtāne 1, Jānis Ansabergs 2, Aina Silvija Štokmane 1, Dace Bandere 1 1 Rīgas Stradiľa universitāte,
Heart Valve Replacement
 Heart Valve Replacement Introduction Sometimes people have serious problems with the valves in their hearts. A heart valve repair or replacement surgery restores or replaces a defective heart valve. If
Heart Valve Replacement Introduction Sometimes people have serious problems with the valves in their hearts. A heart valve repair or replacement surgery restores or replaces a defective heart valve. If
NOACS/DOACS*: PERI-OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT
 NOACS/DOACS*: PERI-OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide guidance for the peri-operative management of patients who are receiving a newer direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) and require an elective surgery/procedure.
NOACS/DOACS*: PERI-OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide guidance for the peri-operative management of patients who are receiving a newer direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) and require an elective surgery/procedure.
Anticoagulation Overview Jed Delmore, MD, FACS, FACOG Professor Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Kansas School of Medicine, Wichita
 Anticoagulation Overview 2018 Jed Delmore, MD, FACS, FACOG Professor Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Kansas School of Medicine, Wichita The ideal lecture is like a miniskirt. Short enough to get
Anticoagulation Overview 2018 Jed Delmore, MD, FACS, FACOG Professor Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Kansas School of Medicine, Wichita The ideal lecture is like a miniskirt. Short enough to get
Acute spontaneous subdural hematomas unusual complication after tooth extraction
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXX Number 3 2016 July-September Article Acute spontaneous subdural hematomas unusual complication after tooth extraction Willem Guillermo Calderon-Miranda 1, Nidia Escobar
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXX Number 3 2016 July-September Article Acute spontaneous subdural hematomas unusual complication after tooth extraction Willem Guillermo Calderon-Miranda 1, Nidia Escobar
Liver transplantation has become a standard treatment for end-stage liver disease and
 www.scielo.br/jaos Assessment and management of oral health in liver transplant candidates Paulo Sérgio da SILVA SANTOS 1, Karin Sá FERNANDES 2, Marina H. C. GALLOTTINI 3 1- PhD, Department of Stomatology,
www.scielo.br/jaos Assessment and management of oral health in liver transplant candidates Paulo Sérgio da SILVA SANTOS 1, Karin Sá FERNANDES 2, Marina H. C. GALLOTTINI 3 1- PhD, Department of Stomatology,
A guide to anticoagulation management and self-testing
 A guide to management and self-testing Understanding If you re reading this, you, or someone you care about, may be on oral therapy, usually treated with a vitamin K antagonist (VKA). VKAs, such as warfarin,
A guide to management and self-testing Understanding If you re reading this, you, or someone you care about, may be on oral therapy, usually treated with a vitamin K antagonist (VKA). VKAs, such as warfarin,
Perioperative Treatment of the Patient Taking Anticoagulation Medication
 Oral Maxillofacial Surg Clin N Am 18 (2006) 151 159 Perioperative Treatment of the Patient Taking Anticoagulation Medication Larry L. Cunningham, Jr, DDS, MDT, M. Todd Brandt, DDS, MD, Eron Aldridge, MD
Oral Maxillofacial Surg Clin N Am 18 (2006) 151 159 Perioperative Treatment of the Patient Taking Anticoagulation Medication Larry L. Cunningham, Jr, DDS, MDT, M. Todd Brandt, DDS, MD, Eron Aldridge, MD
