PSYCHOMETRIC PROPERTIES OF ROMANIAN VERSION OF WHO- 5 WELL-BEING INDEX IN DENTAL STUDENTS
|
|
|
- Miranda Baker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PSYCHOMETRIC PROPERTIES OF ROMANIAN VERSION OF WHO- 5 WELL-BEING INDEX IN DENTAL STUDENTS Cristina Teodora Preoteasa* 1, Elena Preoteasa 2 1 Carol Davila" U.M.Ph. - Bucharest, Romania, Faculty of Dental Medicine, Department of Oral Diagnosis, Ergonomics, Scientific Research Methodology 2 Carol Davila" U.M.Ph. - Bucharest, Romania, Faculty of Dental Medicine, Department of Prosthodontics *Corresponding author: Cristina Teodora Preoteasa, Assistant Professor, DMD, PhD Carol Davila" University of Medicine and Pharmacy - Bucharest, Romania cristina_5013@yahoo.com ABSTRACT Aim of the study: To evaluate psychometric properties of Romanian version of WHO-5 Well-Being Index, as a brief well-being scale and as a depression screening questionnaire, in dental students. Material and methods: This cross-sectional study was implemented on second and third dental students. Data was collected during winter semester evaluation period of academic year. Psychological well-being was assessed by WHO-Five Well-being Index (WHO-5) and Major Depression Inventory (MDI). Results: The target population included 317 second and third year dental students, overall response rate being 87%. The mean WHO-5 score was 12.67, and 59.3% of dental students were recommended to be tested for depression. The mean MDI score was 16.20, and 35.8% of students were likely to present depression. Female students and those of Romanian nationality registered lower levels of psychological well-being. The Cronbach s alpha coefficient for the Romanian version of WHO-5 total scale was The average inter-item correlation was coefficient 0.599, with individual correlations ranging from to Analysing convergent validity a significant association was identified between WHO-5 and MDI (r=-0.640; p<0.001; n=264), and also between WHO-5 and selfreported perception about life as a whole (r=-0.358; p=<0.001; n=262). The area under the curve (AUC) was 0.822; 95% CI: ; p< For the cut-off value of WHO-5 score of 12, respectively WHO-5 score 12 or choosing answers with the minimum scores, the sensitivity was 87%, respectively 89% in detecting depression. Conclusions: The Romanian version of WHO-5 was found to have good psychometric properties as well-being scale and as a screening instrument in detecting depression in dental students. It presented a satisfactory sensitivity with a cut-off of 12 in detecting depression in dental students. Key words: depression, screening, sensitivity, psychological, mental, academic, exam INTRODUCTION Psychological well-being is an important component of mental health, with probable impact on student s personal life and academic achievement. As being suspected a reduction of well-being in medical and dental students in time, as a response to the related inherent distress, recommendations were made to address this issue on an individual and institutional level. In order to do that, one basic factor may be to early identify students with a decrease level of psychological wellbeing. Considering the relatively large number of students in some dental schools, simple instruments of depression screening tools, as WHO-5 Well-Being Index, may be 21
2 appropriate to this particular situation. WHO- 5 has been translated in many languages and proved to be an adequate instrument for the screening of depression in various health conditions, and may be appropriate in this situation too [1]. This study aimed to evaluate psychometric properties of Romanian version of WHO-5 Well-Being Index, as a brief well-being scale and as a depression screening questionnaire, in dental students. MATERIAL AND METHODS The study was approved by the Ethics Committee for Scientific Research at the Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania (PO-35-F-03, No. 55). Subjects and study settings. This crosssectional study was implemented on second and third dental students from the Faculty of Dental Medicine, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania. One series of second year dental students and two series of third year dental students were included. Study inclusion was done on a voluntary basis, considering all students. Participants were informed upon the main characteristics of this study and a written informed consent was granted. Data was collected during winter semester evaluation period of academic year, namely between January 17, 2015 and February 2, Instruments. The main study variable was psychological well-being, assessed by WHO-Five Well-being Index (WHO-5) and Major Depression Inventory (MDI). WHO-Five Well-being Index (WHO-5) is an instrument developed by the World Health Organization. It consists of a 5-item questionnaire, positively worded, with a time frame of previous two weeks. Its interpretation is in accordance to the score obtained, that ranges from 0 to 25, where higher score means better well-being. WHO-5 is also a depression screening tool. Obtaining WHO-5 score 12, or choosing answers with the minimum scores ( at no time or some of the time ), suggests poor well-being and recommendations are made for testing for depression [2-5]. The Romanian language version of WHO-5 that was used was the one available on the website of Psychiatric Research Unit at the Mental Health Centre North Zealand, Hillerod, Denmark, a World Health Organization Collaborating Centre. Major Depression Inventory (MDI) is also an instrument developed by the World Health Organization, in this study being used as a self-rating depression scale. It consists of a 10-item questionnaire, two of them having two alternative questions, with a time frame of previous two weeks. Its interpretation is in accordance to the score obtained, that ranges from 0 to 50. MDI results were recorded as standardized scale score, and dichotomized according to the cut-off value of 20 into likely depressed or not, and on an ordinal level (mild depression: 20 to 24; moderate depression: 25 to 29; severe depression: 30) [6]. Statistical analysis. Internal consistency was evaluated by calculating the Cronbach s alpha and the average inter-item correlation coefficient. Spearman correlation coefficient was used to evaluate convergent validity between WHO-5 and self-reported perception about life as a whole [3; 4], and the association between WHO-5 and MDI. Perception about life as a whole was evaluated using a scale from 1 to 10 (1- very unsatisfied; 10- very satisfied). The analysis of receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC curve) and area under the curve (AUC) were computed, with the establishment of the cut-off point in accordance with the sensitivity and specificity of the thresholds. For the cut-off score established, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), 22
3 negative predictive value (NPV), positive likelihood ratio (LR+) and negative likelihood ratio (LR-) were computed, at 95% confidence interval. Statistical analysis was performed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) software, version 13. The p-values 0.05were considered to be statistically significant. RESULTS Participants. The target population included 317 dental students, from which 92 second year dental students and 225 third year dental students. From these 83 second year dental students agreed to participate in this study (response rate 90%), and 193 third year dental students agreed to participate in this study (response rate 86%), overall response rate being 87% (n=276). Also, some students didn t fully filled the questionnaire and therefore were excluded from the analysis. The majority of students that participated in this study were females 74% (n=203), aged 20 (n=78; 28%), 21 (n=121; 44%) or 22 (n=47; 17%) years old. Psychological well-being of dental students. The mean WHO-5 score was 12.67, ranging from 0 to 25. From the 275 of the students who filled the WHO-5 questionnaire, 163 (59.3%) were recommended to be tested for depression. The mean MDI score was 16.20, ranging from 0 to 46. From the 265 students who filled MDI questionnaire, 95 (35.8%) students were likely to present depression (scored 20), from which 48 (18.1%) mild depression, 22 (8.3%) moderate depression and 25 (9.4%) severe depression. From the 112 students that were not recommended to be tested for depression according to their WHO-5 results, 106 filled the MDI questionnaire. From these only 10 (9.4%) were likely to present depression. From the 163 students that were recommended to be tested for depression according to their WHO-5 results, 158 filled also MDI questionnaire. From these, 85 (53.8%) students were likely to present depression, namely mild depression in 43 (27.2%) of them, moderate depression in 19 (12.0%) of them and as severe depression in 23 (14.6%) of them. Female students registered during semester evaluation period statistically significant lower levels of psychological well-being compared to male students, and also Romanian students tend to register lower levels of well-being compared to students with another nationality (Table 1). Table 1. Dental students psychological well-being subgroup analysis Subgroup WHO-5 (mean) p MDI (mean) p Sex Male female Nationality Romanian other Hometown Bucharest other Year of study second third Psychometric properties of Romanian version of WHO-5. The Cronbach s alpha coefficient for the Romanian version of WHO-5 total scale was The average inter-item correlation coefficient was 0.599, with individual correlations ranging from 23
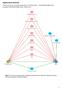
4 0.519 to If items were deleted would decrease the total scale alpha (Table 2). Table 2. Internal consistency analysis of Romanian version of WHO-5 WHO-5 item Mean Inter-item correlation matrix Item-total correlation Cronbach's alpha if item deleted I2 I3 I4 I5 I I I I I Table 3. The performance of Romanian version of WHO-5 Statistic Cut off of 12 (95% CI) Recommended to be tested for depression according to WHO-5 criteria (95% CI) Sensitivity 87.37% (CI: 78.97% to 93.30%) 89.47% (CI: 81.49% to 94.84%) Specificity % (CI: 54.36% to 69.47%) 56.80% (CI: 48.98% to 64.39%) PPV 56.46% (CI: 48.05% to 64.61%) 53.80% (CI: 45.70% to 61.75%) NPV % (CI: 82.77% to 94.59%) 90.57% (CI: 83.33% to 95.38%) LR (CI: 1.72 to 2.50) 2.07 (CI: 1.72 to 2.50) LR (CI: 0.12 to 0.35) 0.19 (CI: 0.10 to 0.34) Table 4. Relationship between Romanian version of WHO-5 and depression severity MDI score No Mean WHO-5 95%CI No depression to Mild depression to 9.65 Moderate depression to Severe depression o Analysing convergent validity a significant association was identified between WHO-5 and MDI (r=-0.640; p=<0.001; n=264), and also between WHO-5 and selfreported perception about life as a whole (r= ; p=<0.001; n=262). WHO-5 was evaluated as screening tool for depression using ROC curve, classification into likely depressed or not being done using MDI results (Figure 1). The area under the curve (AUC) was 0.822; 95% CI: , p< For WHO-5 thresholds of 11/12 sensitivity was 80% and specificity 70.4%. Figure 1. ROC curve for Romanian version of WHO-5, in association to likely to be depressed according to MDI criteria For the cut-off value of WHO-5 score of 24
5 12, but also for the criteria of WHO-5 for recommendation to be tested for depression (score 12, or choosing answers with the minimum scores), at a prevalence of likely to be depressed of 35.98%, the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), positive likelihood ratio (LR+), negative likelihood ratio (LR-) for WHO-5 in diagnosing depression are mentioned in table 3. Analysing the relation between mean WHO-5 scores and depression severity there can be observed that the main difference was found between likely to be depressed or not (Table 4). DISCUSSIONS In this study, considering its limitation, there was found that Romanian version of WHO-5 has good psychometric properties, and therefore can be used as a screening instrument for depression in dental students, and also as a well-being scale. Similar to other previous studies, WHO-5 showed significant correlation with depression scale, in this study MDI scale being used. For example, Awata et al. found that Japanese version of WHO-5 significantly correlates with Zung s Self-Rating Depression Scale and State-Trait Anxiety Inventory [7]. Additionally, in this study there was fund a moderate significant correlation between WHO-5 and self-reported perception about life as a whole, suggesting it can be used as a well-being scale. WHO-5, it is well accepted nowadays as a screening tool for depression in primary care, being found to have high sensitivity and negative predict value [8]. According to Hajos et al. WHO-5 has a sensitivity of 88% and specificity of 76% [9]. By Awata et al., the Japanese version of WHO-5 has a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 78% [7]. According to Saipanish et al., Thai version of WHO-5 has a sensitivity of 89% and specificity of 71% in detecting depression [1]. The previous mention studies were all conducted on samples with various medical conditions, all having in common the high specificity found, as mention before. Topp et al. in a systematic review published in 2015, reported after analysing of 18 selected studies, a sensitivity of 86% and a specificity of 81% of WHO-5 in detecting depression [10]. Similar to other previous researches, in this study Romanian version of WHO-5 was found to have good sensitivity, of almost 90% in our study, but a lower specificity, of about 60% in this study. Therefore, as recommended, WHO-5 should be used as first step screening tool followed by a second step screening tool to confirm depression [7]. In this study there was found a high prevalence of likely to be depressed for the dental students, namely of about 36%. This findings are somewhat different from the ones reported in general population in Europe, where depression is reported as being found at a prevalence usually below 20%, being also observed some important geographical differences [11; 12]. These findings may be related to the moment when data was collected, in the semester examination period, during a period with many final written examination, when the high academic demands may act as an acute and high intensity stressor. Examinations have been previously identified as main stressors related to the academic process in medical and dental students [13-15], that might relate to a decrease of the level of well-being. This study results also suggest there are gender differences regarding the psychological wellbeing of dental students during semester examination periods, female students having significantly reduced level of well-being compared to male dental students. This results are concordant with other studies in Romanians, which report females as having 25
6 higher prevalence of depression compared to males [16]. Considering the reduced level of well-being in dental students during semester examination period, that may interfere with the validity of student s evaluation and have negative long-term effects on a personal and professional level, it may be recommended to implement adequate strategies to help students cope with examination s distress [17]. Among the limitations of this study should be mentioned that participants belonged only to one dental school, and were only second and third year students, situation being possible to be different in final years, considering the potential cumulative effect of distress related to the academic activities. CONCLUSIONS The Romanian version of WHO-5 was found to have adequate psychometric properties as well-being scale and as a screening instrument for the detection of depression in dental students. It has a satisfactory sensitivity with a cut-off of 12 for detecting depression in dental students. Acknowledgements This research was supported by a postdoctoral fellowship from the project Programme of excellency in multidisciplinary doctoral and postdoctoral research of chronic diseases, contract no. POSDRU/159/1.5/S/133377, project co-financed from European Social Fund through Sectoral Operational Programme for Human Resources Development (SOP HRD) REFERENCES 1. Saipanish R, Lotrakul M, Sumrithe S.Reliability and validity of the Thai version of the WHO- Five Well-Being Index in primary care patients. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2009;63(2): Löwe B, Spitzer RL, Gräfe K, Kroenke K, Quenter A, Zipfel S, Buchholz C, Witte S, Herzog W. Comparative validity of three screening questionnaires for DSM-IV depressive disorders and physicians' diagnoses. J Affect Disord. 2004;78(2): Bech P. Clinical Psychometrics. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell Bech P. Subjective positive well-being. World Psychiatry. 2012;11(2): Singh R, Goyal M, Tiwari S, Ghildiyal A, Nattu SM, Das S. Effect of examination stress on mood, performance and cortisol levels in medical students. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012;56(1): Thorsen SV, Rugulies R, Hjarsbech PU, Bjorner JB. The predictive value of mental health for long-term sickness absence: the Major Depression Inventory (MDI) and the Mental Health Inventory (MHI-5) compared. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2013;13: Awata S, Bech P, Yoshida S, Hirai M, Suzuki S, Yamashita M, Ohara A, Hinokio Y, Matsuoka H, Oka Y. Reliability and validity of the Japanese version of the World Health Organization- Five Well-Being Index in the context of detecting depression in diabetic patients. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2007;61(1): Henkel V, Mergl R, Kohnen R, Maier W, Möller H-J, Hegerl U. Identifying depression in primary care: a comparison of different methods in a prospective cohort study. BMJ 2003; 326: Hajos TR, Pouwer F, Skovlund SE, Den Oudsten BL, Geelhoed-Duijvestijn PH, Tack CJ, Snoek FJ.Psychometric and screening properties of the WHO-5 well-being index in adult outpatients with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med. 2013;30(2):e Topp CW, Østergaard SD, Søndergaard S, Bech P. The WHO-5 Well-Being Index: a systematic 26
7 review of the literature.psychother Psychosom. 2015;84(3): Veerman JL, Dowrick C, Ayuso-Mateos JL, Dunn G, Barendregt JJ. Population prevalence of depression and mean Beck Depression Inventory score. Br J Psychiatry. 2009;195(6): doi: /bjp.bp Ayuso-Mateos JL, Vázquez-Barquero JL, Dowrick C, Lehtinen V, Dalgard OS, Casey P, Wilkinson C, Lasa L, Page H, Dunn G, Wilkinson G; ODIN Group. Depressive disorders in Europe: prevalence figures from the ODIN study. Br J Psychiatry. 2001;179: Elani HW, Bedos C, Allison PJ.Sources of stress in Canadian dental students: a prospective mixed methods study. J Dent Educ. 2013;77(11): Alzahem AM, van der Molen HT, Alaujan AH, Schmidt HG, Zamakhshary MH. Stress amongst dental students: a systematic review. Eur J Dent Educ. 2011;15(1):8-18. doi: /j x. 15. Preoteasa CT, Mircescu G, Buzea MC, Preoteasa E. Sources of stress and well-being in dental students. Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation. 2015;7(1): Florescu S, Popovici G, Ciutan M, Ladea M, Sorel E. Main features of prevalence and severity of major depressive episode in Romania. Management in health. 2010; 14(2): Preoteasa CT, Imre M, Preoteasa E. Dental students' psychological well-being during examination period and holiday. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 2015;119(2):
Screening for depressive symptoms: Validation of the CES-D scale in a multi-ethnic group of patients with diabetes in Singapore
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online March 25, 2008 Screening for depressive symptoms: Validation of the CES-D scale in a multi-ethnic group of patients with diabetes in Singapore Stahl
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online March 25, 2008 Screening for depressive symptoms: Validation of the CES-D scale in a multi-ethnic group of patients with diabetes in Singapore Stahl
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online February 25, 2010
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online February 25, 2010 Quality of Life and costs of IP vs. Health related quality of life, treatment satisfaction and costs associated with intraperitoneal
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online February 25, 2010 Quality of Life and costs of IP vs. Health related quality of life, treatment satisfaction and costs associated with intraperitoneal
European Psychiatry, 24 (5):
 Provided by the author(s) and University College Dublin Library in accordance with publisher policies. Please cite the published version when available. Title Impact of severity of personality disorder
Provided by the author(s) and University College Dublin Library in accordance with publisher policies. Please cite the published version when available. Title Impact of severity of personality disorder
Are dimensions of psycho-social well-being different among Latvian and Romanian University students?
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 33 (202) 855 859 PSIWORLD 20 Are dimensions of psycho-social different among and University students? Santa Vorone a,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 33 (202) 855 859 PSIWORLD 20 Are dimensions of psycho-social different among and University students? Santa Vorone a,
Using the WHO 5 Well-Being Index to Identify College Students at Risk for Mental Health Problems
 Using the WHO 5 Well-Being Index to Identify College Students at Risk for Mental Health Problems Andrew Downs, Laura A. Boucher, Duncan G. Campbell, Anita Polyakov Journal of College Student Development,
Using the WHO 5 Well-Being Index to Identify College Students at Risk for Mental Health Problems Andrew Downs, Laura A. Boucher, Duncan G. Campbell, Anita Polyakov Journal of College Student Development,
CHAPTER 2 CRITERION VALIDITY OF AN ATTENTION- DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) SCREENING LIST FOR SCREENING ADHD IN OLDER ADULTS AGED YEARS
 CHAPTER 2 CRITERION VALIDITY OF AN ATTENTION- DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) SCREENING LIST FOR SCREENING ADHD IN OLDER ADULTS AGED 60 94 YEARS AM. J. GERIATR. PSYCHIATRY. 2013;21(7):631 635 DOI:
CHAPTER 2 CRITERION VALIDITY OF AN ATTENTION- DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) SCREENING LIST FOR SCREENING ADHD IN OLDER ADULTS AGED 60 94 YEARS AM. J. GERIATR. PSYCHIATRY. 2013;21(7):631 635 DOI:
Utility and limitations of PHQ-9 in a clinic specializing in psychiatric care
 Inoue et al. BMC Psychiatry 2012, 12:73 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Utility and limitations of PHQ-9 in a clinic specializing in psychiatric care Takeshi Inoue *, Teruaki Tanaka, Shin Nakagawa, Yasuya
Inoue et al. BMC Psychiatry 2012, 12:73 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Utility and limitations of PHQ-9 in a clinic specializing in psychiatric care Takeshi Inoue *, Teruaki Tanaka, Shin Nakagawa, Yasuya
Hubley Depression Scale for Older Adults (HDS-OA): Reliability, Validity, and a Comparison to the Geriatric Depression Scale
 The University of British Columbia Hubley Depression Scale for Older Adults (HDS-OA): Reliability, Validity, and a Comparison to the Geriatric Depression Scale Sherrie L. Myers & Anita M. Hubley University
The University of British Columbia Hubley Depression Scale for Older Adults (HDS-OA): Reliability, Validity, and a Comparison to the Geriatric Depression Scale Sherrie L. Myers & Anita M. Hubley University
Use of Talbinah (Barley Broth) As a Pattern of Depression Management Among Saudi Female Medical Students. Dr. Nahlaa Khalifa
 Use of Talbinah (Barley Broth) As a Pattern of Depression Management Among Saudi Female Medical Students Dr. Nahlaa Khalifa King Abdulaziz University Faculty of Applied Medical Sciences Clinical Nutrition
Use of Talbinah (Barley Broth) As a Pattern of Depression Management Among Saudi Female Medical Students Dr. Nahlaa Khalifa King Abdulaziz University Faculty of Applied Medical Sciences Clinical Nutrition
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. A Brief Measure for Assessing Generalized Anxiety Disorder
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION A Brief Measure for Assessing Generalized Anxiety Disorder The GAD-7 Robert L. Spitzer, MD; Kurt Kroenke, MD; Janet B. W. Williams, DSW; Bernd Löwe, MD, PhD Background: Generalized
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION A Brief Measure for Assessing Generalized Anxiety Disorder The GAD-7 Robert L. Spitzer, MD; Kurt Kroenke, MD; Janet B. W. Williams, DSW; Bernd Löwe, MD, PhD Background: Generalized
Proceedings of the International Conference on RISK MANAGEMENT, ASSESSMENT and MITIGATION
 COGNITIVE-BEHAVIOURAL THERAPY EFFICACY IN MAJOR DEPRESSION WITH ASSOCIATED AXIS II RISK FACTOR FOR NEGATIVE PROGNOSIS DANIEL VASILE*, OCTAVIAN VASILIU** *UMF Carol Davila Bucharest, ** Universitary Military
COGNITIVE-BEHAVIOURAL THERAPY EFFICACY IN MAJOR DEPRESSION WITH ASSOCIATED AXIS II RISK FACTOR FOR NEGATIVE PROGNOSIS DANIEL VASILE*, OCTAVIAN VASILIU** *UMF Carol Davila Bucharest, ** Universitary Military
How accurately does the Brief Job Stress Questionnaire identify workers with or without potential psychological distress?
 J Occup Health 2017; 59: 356-360 Brief Report How accurately does the Brief Job Stress Questionnaire identify workers with or without potential psychological distress? Akizumi Tsutsumi 1, Akiomi Inoue
J Occup Health 2017; 59: 356-360 Brief Report How accurately does the Brief Job Stress Questionnaire identify workers with or without potential psychological distress? Akizumi Tsutsumi 1, Akiomi Inoue
Information about the Critically Appraised Topic (CAT) Series
 Information about the Critically Appraised Topic (CAT) Series The objective of the Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) program at George Mason University is to prepare graduates for the highest level of nursing
Information about the Critically Appraised Topic (CAT) Series The objective of the Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) program at George Mason University is to prepare graduates for the highest level of nursing
THE VALIDITY OF TWO MALAY VERSIONS OF THE GENERAL HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE (GHQ) IN DETECTING DISTRESSED MEDICAL STUDENTS. Muhamad Saiful Bahri Yusoff
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE THE VALIDITY OF TWO MALAY VERSIONS OF THE GENERAL HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE (GHQ) IN DETECTING DISTRESSED MEDICAL STUDENTS. Muhamad Saiful Bahri Yusoff Medical Education Department of School
ORIGINAL ARTICLE THE VALIDITY OF TWO MALAY VERSIONS OF THE GENERAL HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE (GHQ) IN DETECTING DISTRESSED MEDICAL STUDENTS. Muhamad Saiful Bahri Yusoff Medical Education Department of School
Table S1. Search terms applied to electronic databases. The African Journal Archive African Journals Online. depression OR distress
 Supplemental Digital Content to accompany: [authors]. Reliability and validity of depression assessment among persons with HIV in sub-saharan Africa: systematic review and metaanalysis. J Acquir Immune
Supplemental Digital Content to accompany: [authors]. Reliability and validity of depression assessment among persons with HIV in sub-saharan Africa: systematic review and metaanalysis. J Acquir Immune
Major depressive disorder in primary care: screening, diagnosis and treatment Baas, K.D.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Major depressive disorder in primary care: screening, diagnosis and treatment Baas, K.D. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Baas, K. D. (2013).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Major depressive disorder in primary care: screening, diagnosis and treatment Baas, K.D. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Baas, K. D. (2013).
An adult version of the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders (SCARED-A)
 Netherlands Journal of Psychology / SCARED adult version 81 An adult version of the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders (SCARED-A) Many questionnaires exist for measuring anxiety; however,
Netherlands Journal of Psychology / SCARED adult version 81 An adult version of the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders (SCARED-A) Many questionnaires exist for measuring anxiety; however,
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Instructions for Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) and GAD-7 Measures
 PHQ and GAD-7 Instructions P. 1/9 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Instructions for Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) and GAD-7 Measures TOPIC PAGES Background 1 Coding and Scoring 2, 4, 5 Versions 3 Use as Severity
PHQ and GAD-7 Instructions P. 1/9 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Instructions for Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) and GAD-7 Measures TOPIC PAGES Background 1 Coding and Scoring 2, 4, 5 Versions 3 Use as Severity
The Wellness Assessment: Global Distress and Indicators of Clinical Severity May 2010
 The Wellness Assessment: Global Distress and Indicators of Clinical Severity May 2010 Background Research has shown that the integration of outcomes measurement into clinical practice is associated with
The Wellness Assessment: Global Distress and Indicators of Clinical Severity May 2010 Background Research has shown that the integration of outcomes measurement into clinical practice is associated with
INTEGRATING REALISTIC RESEARCH INTO EVERY DAY PRACTICE
 INTEGRATING REALISTIC RESEARCH INTO EVERY DAY PRACTICE Professor Nigel Beail Consultant & Professional Lead for Psychological Services. South West Yorkshire Partnership NHS Foundation Trust & Clinical
INTEGRATING REALISTIC RESEARCH INTO EVERY DAY PRACTICE Professor Nigel Beail Consultant & Professional Lead for Psychological Services. South West Yorkshire Partnership NHS Foundation Trust & Clinical
How to measure mental health in the general population? Reiner Rugulies
 How to measure mental health in the general population? Reiner Rugulies National Research Centre for the Working Environment, Denmark Department of Public Health and Department of Psychology, University
How to measure mental health in the general population? Reiner Rugulies National Research Centre for the Working Environment, Denmark Department of Public Health and Department of Psychology, University
THE HAMILTON Depression Rating Scale
 Reliability and Validity of the Turkish Version of the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale A. Akdemir, M.H. Türkçapar, S.D. Örsel, N. Demirergi, I. Dag, and M.H. Özbay The aim of the study was to examine
Reliability and Validity of the Turkish Version of the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale A. Akdemir, M.H. Türkçapar, S.D. Örsel, N. Demirergi, I. Dag, and M.H. Özbay The aim of the study was to examine
Author's response to reviews
 Author's response to reviews Title: Effect of a multidisciplinary stress treatment programme on the return to work rate for persons with work-related stress. A non-randomized controlled study from a stress
Author's response to reviews Title: Effect of a multidisciplinary stress treatment programme on the return to work rate for persons with work-related stress. A non-randomized controlled study from a stress
Optimal cut-off score for diagnosing depression with the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9): a meta-analysis
 CMAJ Research Optimal cut-off score for diagnosing depression with the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9): a meta-analysis Laura Manea MSc, Simon Gilbody PhD, Dean McMillan PhD See related commentary
CMAJ Research Optimal cut-off score for diagnosing depression with the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9): a meta-analysis Laura Manea MSc, Simon Gilbody PhD, Dean McMillan PhD See related commentary
Appendix B: Screening and Assessment Instruments
 Appendix B: Screening and Assessment Instruments Appendix B-1: Quick Guide to the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) Purpose. The Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) is designed to facilitate the recognition
Appendix B: Screening and Assessment Instruments Appendix B-1: Quick Guide to the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) Purpose. The Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) is designed to facilitate the recognition
Suffering in silence: studies on screening for major depressive disorder in primary care Wittkampf, K.A.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Suffering in silence: studies on screening for major depressive disorder in primary care Wittkampf, K.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Suffering in silence: studies on screening for major depressive disorder in primary care Wittkampf, K.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA):
Occupational Burnout levels in Emergency Medicine a stage 2 nationwide study and analysis
 Journal of Medicine and Life Vol. 3, No.4, October December 2010, pp.449 453 Occupational Burnout levels in Emergency Medicine a stage 2 nationwide study and analysis Florian Popa *, Raed Arafat **, Victor
Journal of Medicine and Life Vol. 3, No.4, October December 2010, pp.449 453 Occupational Burnout levels in Emergency Medicine a stage 2 nationwide study and analysis Florian Popa *, Raed Arafat **, Victor
Service Use for Patients with Adjustment Disorder and Short Term Treatment: A Brief Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Mental Health Volume 4 Number 2 Service Use for Patients with Adjustment Disorder and Short Term Treatment: A Brief Report F Azocar, G Greenwood Citation F Azocar, G Greenwood.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Mental Health Volume 4 Number 2 Service Use for Patients with Adjustment Disorder and Short Term Treatment: A Brief Report F Azocar, G Greenwood Citation F Azocar, G Greenwood.
Validation of the PHQ-15 for Somatoform Disorder in the Occupational Health Care Setting
 J Occup Rehabil (2012) 22:51 58 DOI 10.1007/s10926-011-9320-6 Validation of the PHQ-15 for Somatoform Disorder in the Occupational Health Care Setting Lars de Vroege Rob Hoedeman Jasper Nuyen Klaas Sijtsma
J Occup Rehabil (2012) 22:51 58 DOI 10.1007/s10926-011-9320-6 Validation of the PHQ-15 for Somatoform Disorder in the Occupational Health Care Setting Lars de Vroege Rob Hoedeman Jasper Nuyen Klaas Sijtsma
Methodology METHODOLOGY
 METHODOLOGY This study was conducted at the department of Orthodontics, College of Dental Surgery, B.P. Koirala Institute of Health Sciences, Dharan, Nepal from January 2011 to November 2012. However the
METHODOLOGY This study was conducted at the department of Orthodontics, College of Dental Surgery, B.P. Koirala Institute of Health Sciences, Dharan, Nepal from January 2011 to November 2012. However the
Validation of the WHOQOL-BREF Quality of Life Questionnaire for Use with Medical Students
 B R I E F C O M M U N I C A T I O N Validation of the WHOQOL-BREF Quality of Life Questionnaire for Use with Medical Students CU Krägeloh 1, MA Henning 2, SJ Hawken 2, Y Zhao 1,2, D Shepherd 1, R Billington
B R I E F C O M M U N I C A T I O N Validation of the WHOQOL-BREF Quality of Life Questionnaire for Use with Medical Students CU Krägeloh 1, MA Henning 2, SJ Hawken 2, Y Zhao 1,2, D Shepherd 1, R Billington
When first published in 1992, the Research Diagnostic
 The Research Diagnostic Criteria for Temporomandibular Disorders. IV: Evaluation of Psychometric Properties of the Axis II Measures Richard Ohrbach, DDS, PhD Associate Professor Department of Oral Diagnostic
The Research Diagnostic Criteria for Temporomandibular Disorders. IV: Evaluation of Psychometric Properties of the Axis II Measures Richard Ohrbach, DDS, PhD Associate Professor Department of Oral Diagnostic
Evaluation of the Reliability of the Geriatric Oral Health Assessment Index (GOHAI) in Institutionalised Elderly in Romania: A Pilot Study
 Evaluation of the Reliability of the Geriatric Oral Health Assessment Index (GOHAI) in Institutionalised Elderly in Romania: A Pilot Study Alice Murariu 1, Carmen Hanganu 2, Livia Bobu 3 1 Ph.D., D.M.D.
Evaluation of the Reliability of the Geriatric Oral Health Assessment Index (GOHAI) in Institutionalised Elderly in Romania: A Pilot Study Alice Murariu 1, Carmen Hanganu 2, Livia Bobu 3 1 Ph.D., D.M.D.
CHAPTER 3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY. In this chapter, research design, data collection, sampling frame and analysis
 CHAPTER 3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 3.1 Introduction In this chapter, research design, data collection, sampling frame and analysis procedure will be discussed in order to meet the objectives of the study.
CHAPTER 3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 3.1 Introduction In this chapter, research design, data collection, sampling frame and analysis procedure will be discussed in order to meet the objectives of the study.
Relative Benefits of Narrowband and Broadband Tools for Behavioral Health Settings
 Relative Benefits of Narrowband and Broadband Tools for Behavioral Health Settings James V. Wojcik, Ph.D. Canvas Health Oakdale MN Variables: Correlations between PHQ 9 and Health Dynamics Inventory on
Relative Benefits of Narrowband and Broadband Tools for Behavioral Health Settings James V. Wojcik, Ph.D. Canvas Health Oakdale MN Variables: Correlations between PHQ 9 and Health Dynamics Inventory on
Screening for depression in primary care
 Ó The Author (2006). Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oxfordjournals.org doi:10.1093/fampra/cml052 Family Practice Advance
Ó The Author (2006). Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oxfordjournals.org doi:10.1093/fampra/cml052 Family Practice Advance
Supplementary Materials:
 Supplementary Materials: Depression and risk of unintentional injury in rural communities a longitudinal analysis of the Australian Rural Mental Health Study (Inder at al.) Figure S1. Directed acyclic
Supplementary Materials: Depression and risk of unintentional injury in rural communities a longitudinal analysis of the Australian Rural Mental Health Study (Inder at al.) Figure S1. Directed acyclic
CHARACTERISTICS OF NEURODEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS IN THE CLINICAL POPULATION OF A MENTAL HEALTH CENTER
 ANTON et al. ORIGINAL PAPERS CHARACTERISTICS OF NEURODEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS IN THE CLINICAL POPULATION OF A MENTAL HEALTH CENTER Miruna RĂDAN 1, Mihaela GĂIȘTEANU 1 1 Alessandrescu-Rusescu National Institute
ANTON et al. ORIGINAL PAPERS CHARACTERISTICS OF NEURODEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS IN THE CLINICAL POPULATION OF A MENTAL HEALTH CENTER Miruna RĂDAN 1, Mihaela GĂIȘTEANU 1 1 Alessandrescu-Rusescu National Institute
Sannie Vester Thorsen 1*, Reiner Rugulies 1, Pernille U Hjarsbech 1 and Jakob Bue Bjorner 1,2
 Thorsen et al. BMC Medical Research Methodology 2013, 13:115 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The predictive value of mental health for long-term sickness absence: the Major Depression Inventory (MDI) and
Thorsen et al. BMC Medical Research Methodology 2013, 13:115 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The predictive value of mental health for long-term sickness absence: the Major Depression Inventory (MDI) and
Does low well-being modify the effects of PRISMA (Dutch DESMOND), a structured self-management-education program for people with type 2 diabetes?
 primary care diabetes 10 (2016) 103 110 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Primary Care Diabetes journal homepage: http://www.elsevier.com/locate/pcd Original research Does low well-being modify
primary care diabetes 10 (2016) 103 110 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Primary Care Diabetes journal homepage: http://www.elsevier.com/locate/pcd Original research Does low well-being modify
Assessment in Integrated Care. J. Patrick Mooney, Ph.D.
 Assessment in Integrated Care J. Patrick Mooney, Ph.D. Purpose of assessment in integrated care: Assessment provides feedback to promote individual and group learning and change. Physicians Mental health
Assessment in Integrated Care J. Patrick Mooney, Ph.D. Purpose of assessment in integrated care: Assessment provides feedback to promote individual and group learning and change. Physicians Mental health
Validation of the Russian version of the Quality of Life-Rheumatoid Arthritis Scale (QOL-RA Scale)
 Advances in Medical Sciences Vol. 54(1) 2009 pp 27-31 DOI: 10.2478/v10039-009-0012-9 Medical University of Bialystok, Poland Validation of the Russian version of the Quality of Life-Rheumatoid Arthritis
Advances in Medical Sciences Vol. 54(1) 2009 pp 27-31 DOI: 10.2478/v10039-009-0012-9 Medical University of Bialystok, Poland Validation of the Russian version of the Quality of Life-Rheumatoid Arthritis
Reliability and validity of the International Spinal Cord Injury Basic Pain Data Set items as self-report measures
 (2010) 48, 230 238 & 2010 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/10 $32.00 www.nature.com/sc ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reliability and validity of the International Injury Basic Pain Data Set items
(2010) 48, 230 238 & 2010 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/10 $32.00 www.nature.com/sc ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reliability and validity of the International Injury Basic Pain Data Set items
The Hope, Agency and Opportunity PROM: A Recovery focused PROM for Mental Health Services
 The Hope, Agency and Opportunity PROM: A Recovery focused PROM for Mental Health Services Liz Vernon-Wilson, Outcomes Researcher Southern Health NHS Foundation Trust Overview Hope, Agency & Opportunity,
The Hope, Agency and Opportunity PROM: A Recovery focused PROM for Mental Health Services Liz Vernon-Wilson, Outcomes Researcher Southern Health NHS Foundation Trust Overview Hope, Agency & Opportunity,
Diabetic Medicine. Diabetes and mental health; the problem of co-morbidity
 Diabetes and mental health; the problem of co-morbidity Journal: Diabetic Medicine Manuscript ID: DME-0-00 Manuscript Type: Editorial Date Submitted by the Author: -Jun-0 Complete List of Authors: Lloyd,
Diabetes and mental health; the problem of co-morbidity Journal: Diabetic Medicine Manuscript ID: DME-0-00 Manuscript Type: Editorial Date Submitted by the Author: -Jun-0 Complete List of Authors: Lloyd,
Detecting mental disorders in general hospitals by the SCL-8 scale Fink, P.; Ornbol, E.; Hansen, M.S.; Sondergaard, L.; de Jonge, P.
 Tilburg University Detecting mental disorders in general hospitals by the SCL-8 scale Fink, P.; Ornbol, E.; Hansen, M.S.; Sondergaard, L.; de Jonge, P. Published in: Journal of psychosomatic research Publication
Tilburg University Detecting mental disorders in general hospitals by the SCL-8 scale Fink, P.; Ornbol, E.; Hansen, M.S.; Sondergaard, L.; de Jonge, P. Published in: Journal of psychosomatic research Publication
Casey, Patricia R.; Dunn, Graham; Kelly, Brendan D.; et al.
 Provided by the author(s) and University College Dublin Library in accordance with publisher policies. Please cite the published version when available. Title The prevalence of suicidal ideation in the
Provided by the author(s) and University College Dublin Library in accordance with publisher policies. Please cite the published version when available. Title The prevalence of suicidal ideation in the
SELF-REPORTED DENTURE SATISFACTION IN COMPLETELY EDENTULOUS PATIENTS
 SELF-REPORTED DENTURE SATISFACTION IN COMPLETELY EDENTULOUS PATIENTS N. Abdulla Mardan 1, Cristina Teodora Preoteasa 2, Marina Imre 3, Ana Maria Tancu 3, Elena Preoteasa 3* 1 Carol Davila" University of
SELF-REPORTED DENTURE SATISFACTION IN COMPLETELY EDENTULOUS PATIENTS N. Abdulla Mardan 1, Cristina Teodora Preoteasa 2, Marina Imre 3, Ana Maria Tancu 3, Elena Preoteasa 3* 1 Carol Davila" University of
CROSS-SECTIONAL STUDY AMONG MEDICAL STUDENTS IN LATVIA: DIFFERENCES OF MENTAL SYMPTOMS AND SOMATIC SYMPTOMS AMONG LATVIAN AND INTERNATIONAL STUDENTS
 Papers on Anthropology XXVII/1, 2018, pp. 47 54 Health Symptoms Among Medical Students In Latvia K.-K. Rueckert, G. Ancane CROSS-SECTIONAL STUDY AMONG MEDICAL STUDENTS IN LATVIA: DIFFERENCES OF MENTAL
Papers on Anthropology XXVII/1, 2018, pp. 47 54 Health Symptoms Among Medical Students In Latvia K.-K. Rueckert, G. Ancane CROSS-SECTIONAL STUDY AMONG MEDICAL STUDENTS IN LATVIA: DIFFERENCES OF MENTAL
Adjustment disorder (AjD) is defined
 Original Article The Adjustment Disorder New Module 20 as a Screening Instrument: Cluster Analysis and Cut-off Values L Lorenz, RC Bachem, A Maercker Abstract This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
Original Article The Adjustment Disorder New Module 20 as a Screening Instrument: Cluster Analysis and Cut-off Values L Lorenz, RC Bachem, A Maercker Abstract This work is licensed under a Creative Commons
STABILITY AND CHANGE IN THE CLINICAL COURSE OF SCHIZOAFFECTIVE DISORDER
 Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2013 vol. 117, no. 1 INTERNAL MEDICINE - PEDIATRICS ORIGINAL PAPERS STABILITY AND CHANGE IN THE CLINICAL COURSE OF SCHIZOAFFECTIVE DISORDER Anca Durla 1, M. Ienciu
Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2013 vol. 117, no. 1 INTERNAL MEDICINE - PEDIATRICS ORIGINAL PAPERS STABILITY AND CHANGE IN THE CLINICAL COURSE OF SCHIZOAFFECTIVE DISORDER Anca Durla 1, M. Ienciu
Psychometric Properties of Thought Fusion Instrument (TFI) in Students
 7-78 89 Iranian Journal of Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology, Vol. 6, No., Spring 00, 7-78 Short Scientific Article Psychometric Properties of Thought Fusion Instrument (TFI) in Students Kazem Khoramdel*,
7-78 89 Iranian Journal of Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology, Vol. 6, No., Spring 00, 7-78 Short Scientific Article Psychometric Properties of Thought Fusion Instrument (TFI) in Students Kazem Khoramdel*,
Validation of the Kessler s psychological distress scale among the Sinhalese population in Sri Lanka
 RESEARCH PAPERS Validation of the Kessler s psychological distress scale among the Sinhalese population in Sri Lanka Wijeratne LT 1, Williams SS 1, Rodrigo MDA 1, Peris MUPK 1, Kawamura N 2, Wickremasinghe
RESEARCH PAPERS Validation of the Kessler s psychological distress scale among the Sinhalese population in Sri Lanka Wijeratne LT 1, Williams SS 1, Rodrigo MDA 1, Peris MUPK 1, Kawamura N 2, Wickremasinghe
THE RELATION BETWEEN PERSONAL NEED FOR THOUGHTS STRUCTURE, HOPE AND WELL-BEING
 ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF PSYCHOLOGICAL STUDIES HYPERION UNIVERSITY www.hyperion.ro THE RELATION BETWEEN PERSONAL NEED FOR THOUGHTS STRUCTURE, HOPE AND WELL-BEING TEODOR, VASILE a a University of Bucharest,
ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF PSYCHOLOGICAL STUDIES HYPERION UNIVERSITY www.hyperion.ro THE RELATION BETWEEN PERSONAL NEED FOR THOUGHTS STRUCTURE, HOPE AND WELL-BEING TEODOR, VASILE a a University of Bucharest,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 74 Volume 2; Issue 1; Jan -Jun Abstract
 74 http://www.iccrjnr.com Volume 2; Issue 1; Jan -Jun 2017 Effectiveness of Autogenic Relaxation on Somatization Disorder and Biophysiologic Parameters among Chronic Disease Clients at Selected Villages,
74 http://www.iccrjnr.com Volume 2; Issue 1; Jan -Jun 2017 Effectiveness of Autogenic Relaxation on Somatization Disorder and Biophysiologic Parameters among Chronic Disease Clients at Selected Villages,
Validation of the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 for Major Depressive Disorder in the Occupational Health Setting
 J Occup Rehabil (2016) 26:237 244 DOI 10.1007/s10926-015-9607-0 Validation of the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 for Major Depressive Disorder in the Occupational Health Setting D. Volker 1,2 M. C. Zijlstra-Vlasveld
J Occup Rehabil (2016) 26:237 244 DOI 10.1007/s10926-015-9607-0 Validation of the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 for Major Depressive Disorder in the Occupational Health Setting D. Volker 1,2 M. C. Zijlstra-Vlasveld
Convergent Validity of a Single Question with Multiple Classification Options for Depression Screening in Medical Settings
 DOI 10.7603/s40790-014-0001-8 Convergent Validity of a Single Question with Multiple Classification Options for Depression Screening in Medical Settings H. Edward Fouty, Hanny C. Sanchez, Daniel S. Weitzner,
DOI 10.7603/s40790-014-0001-8 Convergent Validity of a Single Question with Multiple Classification Options for Depression Screening in Medical Settings H. Edward Fouty, Hanny C. Sanchez, Daniel S. Weitzner,
Psychometric evaluation of the self-test (PST) in the responsible gambling tool Playscan (GamTest)
 Psychometric evaluation of the self-test (PST) in the responsible gambling tool Playscan (GamTest) Background I Originally called GamTest. A questionnaire consisting of 15 items plus one general item.
Psychometric evaluation of the self-test (PST) in the responsible gambling tool Playscan (GamTest) Background I Originally called GamTest. A questionnaire consisting of 15 items plus one general item.
The prevalence of non communicable diseases
 Original Article Reliability and Validity of a Modified Phq-9 Item Inventory (Phq-12) as a Screening Instrument for Assessing Depression in Asian Indians (Cures - 65) S Poongothai, R Pradeepa, A Ganesan,
Original Article Reliability and Validity of a Modified Phq-9 Item Inventory (Phq-12) as a Screening Instrument for Assessing Depression in Asian Indians (Cures - 65) S Poongothai, R Pradeepa, A Ganesan,
Keywords: consultation, drug-related problems, pharmacists, Theory of Planned Behavior
 DEVELOPMENT OF A QUESTIONNAIRE BASED ON THE THEORY OF PLANNED BEHAVIOR TO IDENTIFY FACTORS AFFECTING PHARMACISTS INTENTION TO CONSULT PHYSICIANS ON DRUG-RELATED PROBLEMS Teeranan Charoenung 1, Piyarat
DEVELOPMENT OF A QUESTIONNAIRE BASED ON THE THEORY OF PLANNED BEHAVIOR TO IDENTIFY FACTORS AFFECTING PHARMACISTS INTENTION TO CONSULT PHYSICIANS ON DRUG-RELATED PROBLEMS Teeranan Charoenung 1, Piyarat
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA ADAPTATION, TRANSLATION AND VALIDATION OF THE DIABETES MELLITUS IN THE OFFSPRING QUESTIONNAIRE (DMOQ): THE MALAY VERSION
 UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA ADAPTATION, TRANSLATION AND VALIDATION OF THE DIABETES MELLITUS IN THE OFFSPRING QUESTIONNAIRE (DMOQ): THE MALAY VERSION SITI FATIMAH BINTI BADLISHAH SHAM MMED (FAM MED) MAY 2016
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MARA ADAPTATION, TRANSLATION AND VALIDATION OF THE DIABETES MELLITUS IN THE OFFSPRING QUESTIONNAIRE (DMOQ): THE MALAY VERSION SITI FATIMAH BINTI BADLISHAH SHAM MMED (FAM MED) MAY 2016
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTRODUCTION METHODOLOGY. Ehsan Ullah Syed 1, Sajida Abdul Hussein 1, Syed Iqbal Azam 2 and Abdul Ghani Khan 3
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Urdu Version of Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) and the Child Behaviour Check List (CBCL) Amongst Primary School Children in Karachi Ehsan Ullah Syed 1, Sajida
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Urdu Version of Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ) and the Child Behaviour Check List (CBCL) Amongst Primary School Children in Karachi Ehsan Ullah Syed 1, Sajida
Afzal Hakim*, Himani Tak, Savitri Nagar, Suman Bhansali
 International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Hakim A et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2017 Sep;4(9):3267-3272 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original Research
International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Hakim A et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2017 Sep;4(9):3267-3272 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original Research
Postpartum Depression and Marital Relationship
 Postpartum Depression and Marital Relationship Daniela Meçe 1 Aleksander Moisiu University, Durres, Albania E-mail: danielamece@gmail.com Doi:10.5901/ajis.2013.v2n4p319 Abstract Three hundred-ninety-eight
Postpartum Depression and Marital Relationship Daniela Meçe 1 Aleksander Moisiu University, Durres, Albania E-mail: danielamece@gmail.com Doi:10.5901/ajis.2013.v2n4p319 Abstract Three hundred-ninety-eight
Eighty percent of patients with chronic back pain (CBP)
 SPINE Volume 37, Number 8, pp 711 715 2012, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins HEALTH SERVICES RESEARCH Responsiveness and Minimal Clinically Important Change of the Pain Disability Index in Patients With Chronic
SPINE Volume 37, Number 8, pp 711 715 2012, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins HEALTH SERVICES RESEARCH Responsiveness and Minimal Clinically Important Change of the Pain Disability Index in Patients With Chronic
Unauthenticated Download Date 1/24/18 5:48 PM
 Material and Methods Participants Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes subjects, aged 18 or older and fluently speaking Romanian were included in the study. Patients with active anxiety, dementia, substance
Material and Methods Participants Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes subjects, aged 18 or older and fluently speaking Romanian were included in the study. Patients with active anxiety, dementia, substance
Depression and anxiety are reported to have a
 Validation of Mood Measures for People with Multiple Sclerosis Tessa M. Watson, DClinPsy; Emma Ford, BSc; Esme Worthington, PhD; Nadina B. Lincoln, PhD Background: Valid assessments are needed in order
Validation of Mood Measures for People with Multiple Sclerosis Tessa M. Watson, DClinPsy; Emma Ford, BSc; Esme Worthington, PhD; Nadina B. Lincoln, PhD Background: Valid assessments are needed in order
A Longitudinal Study of the Well-being of Students Using the Student Wellbeing Process Questionnaire (Student WPQ)
 Journal of Education, Society and Behavioural Science 24(4): 1-6, 2018; Article no.jesbs.40105 ISSN: 2456-981X (Past name: British Journal of Education, Society & Behavioural Science, Past ISSN: 2278-0998)
Journal of Education, Society and Behavioural Science 24(4): 1-6, 2018; Article no.jesbs.40105 ISSN: 2456-981X (Past name: British Journal of Education, Society & Behavioural Science, Past ISSN: 2278-0998)
CONCURRENT VALIDITY OF THE MALAY VERSION OF PERCEIVED STRESS SCALE (PSS-10)
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE CONCURRENT VALIDITY OF THE MALAY VERSION OF PERCEIVED STRESS SCALE (PSS-10) Sami AR Al-Dubai*, Ankur Barua*, Kurubaran Ganasegeran**, Saad A Jadoo***, Krishna G Rampal**** *Department
ORIGINAL ARTICLE CONCURRENT VALIDITY OF THE MALAY VERSION OF PERCEIVED STRESS SCALE (PSS-10) Sami AR Al-Dubai*, Ankur Barua*, Kurubaran Ganasegeran**, Saad A Jadoo***, Krishna G Rampal**** *Department
Mental Health, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. Psychiatry, Iran University of Medical Sciences (IUMS), Tehran, Iran.
 Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science 2019, Volume 7, Issue 1, Page No: 71-76 Copyright CC BY-NC 4.0 Available Online at: www.jrmds.in eissn
Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Science 2019, Volume 7, Issue 1, Page No: 71-76 Copyright CC BY-NC 4.0 Available Online at: www.jrmds.in eissn
Life Events and Postpartum Depression in Tirana, Albania
 Life Events and Postpartum Depression in Tirana, Albania Daniela Meçe 1 Aleksander Moisiu University, Durres, Albania E-mail: danielamece@gmail.com Doi: 10.5901/mjss.2013.v4n4p311 Abstract The aim of this
Life Events and Postpartum Depression in Tirana, Albania Daniela Meçe 1 Aleksander Moisiu University, Durres, Albania E-mail: danielamece@gmail.com Doi: 10.5901/mjss.2013.v4n4p311 Abstract The aim of this
Wan Mohd. Rushidi Wan Mahmud, Amir Awang*, Mahmood Nazar Mohamed*
 Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 10, No. 2, July 2003 (71-75) ORIGINAL ARTICLE REVALIDATION OF THE MALAY VERSION OF THE EDINBURGH POSTNATAL DEPRESSION SCALE (EPDS) AMONG MALAY POSTPARTUM WOMEN
Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 10, No. 2, July 2003 (71-75) ORIGINAL ARTICLE REVALIDATION OF THE MALAY VERSION OF THE EDINBURGH POSTNATAL DEPRESSION SCALE (EPDS) AMONG MALAY POSTPARTUM WOMEN
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD. method the major components include: Research Design, Research Site and
 CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD This chapter presents the research method and design. In this research method the major components include: Research Design, Research Site and Access, Population and Sample,
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD This chapter presents the research method and design. In this research method the major components include: Research Design, Research Site and Access, Population and Sample,
1/26/16 TREATMENT MONITORING. Treatment Monitoring. Psychologically Informed Physical Therapy Practice: Pragmatic Application for Low Back Pain
 1/26/16 Treatment Monitoring Jason Beneciuk, PT, PhD, MPH Research Assistant Professor University of Florida Brooks Rehabilitation PHHP Research Collaboration Psychologically Informed Physical Therapy
1/26/16 Treatment Monitoring Jason Beneciuk, PT, PhD, MPH Research Assistant Professor University of Florida Brooks Rehabilitation PHHP Research Collaboration Psychologically Informed Physical Therapy
CHAPTER 3. Research Methodology
 CHAPTER 3 Research Methodology The research studies the youth s attitude towards Thai cuisine in Dongguan City, China in 2013. Researcher has selected survey methodology by operating under procedures as
CHAPTER 3 Research Methodology The research studies the youth s attitude towards Thai cuisine in Dongguan City, China in 2013. Researcher has selected survey methodology by operating under procedures as
Sensitivity and specificity of depression screening tools among adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities (I/DD)
 Sensitivity and specificity of depression screening tools among adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities (I/DD) Sarah H Ailey PhD RNC Rush University College of Nursing College of Nursing
Sensitivity and specificity of depression screening tools among adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities (I/DD) Sarah H Ailey PhD RNC Rush University College of Nursing College of Nursing
The Somatic Symptom Disorder B Criteria Scale (SSD-12) in a Dutch Clinical Sample. A validation study.
 The Somatic Symptom Disorder B Criteria Scale (SSD-12) in a Dutch Clinical Sample. A validation study. C.A.D. Kamp 1,2, L. de Vroege 1,2, J. F. van Eck van der Sluijs 1,2, W.J. Kop 3, & C.M. van der Feltz-
The Somatic Symptom Disorder B Criteria Scale (SSD-12) in a Dutch Clinical Sample. A validation study. C.A.D. Kamp 1,2, L. de Vroege 1,2, J. F. van Eck van der Sluijs 1,2, W.J. Kop 3, & C.M. van der Feltz-
II3B GD2 Depression and Suicidality in Human Research
 Office of Human Research Protection University of Nevada, Reno II3B GD2 Depression and Suicidality in Human Research Overview Research studies that include measures for depression and suicidality should
Office of Human Research Protection University of Nevada, Reno II3B GD2 Depression and Suicidality in Human Research Overview Research studies that include measures for depression and suicidality should
AN INDIRECT EVALUATION OF THE NATIONAL PROGRAM OF DIABETES MELLITUS STUDY CASE OF ROMANIA
 Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2013 vol. 117, no. 2 PREVENTIVE MEDICINE - LABORATORY ORIGINAL PAPERS AN INDIRECT EVALUATION OF THE NATIONAL PROGRAM OF DIABETES MELLITUS STUDY CASE OF ROMANIA Maria
Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2013 vol. 117, no. 2 PREVENTIVE MEDICINE - LABORATORY ORIGINAL PAPERS AN INDIRECT EVALUATION OF THE NATIONAL PROGRAM OF DIABETES MELLITUS STUDY CASE OF ROMANIA Maria
The Bengali Adaptation of Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale
 IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 4, Issue 2 Ver. I (Mar.-Apr. 2015), PP 12-16 www.iosrjournals.org The Bengali Adaptation of Edinburgh
IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 4, Issue 2 Ver. I (Mar.-Apr. 2015), PP 12-16 www.iosrjournals.org The Bengali Adaptation of Edinburgh
SCREENING FOR ANXIETY IN BC: IS THE EPDS ENOUGH?
 SCREENING FOR ANXIETY IN BC: IS THE EPDS ENOUGH? NICHOLE FAIRBROTHER, PH.D. R.PSYCH. ASSISTANT PROFESSOR UBC DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHIATRY ISLAND MEDICAL PROGRAM TEAM & FUNDING TEAM FUNDING Nichole Fairbrother
SCREENING FOR ANXIETY IN BC: IS THE EPDS ENOUGH? NICHOLE FAIRBROTHER, PH.D. R.PSYCH. ASSISTANT PROFESSOR UBC DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHIATRY ISLAND MEDICAL PROGRAM TEAM & FUNDING TEAM FUNDING Nichole Fairbrother
Downloaded from ijem.sbmu.ac.ir at 9: on Saturday January 12th 2019 :(IR-PAID -5) . PAID-5.
 ( ) :(IR-PAID -5) ( ( : e-mail: FADAE@shmu.ac.ir : PAID-5.. PAID-5. ( ) :. (). / PAID-5 :. PAID. / PAID-20 PAID-5 PAID-5. PAID-5 :.. IR-PAID-5 : // : // : // :...... ,. vi CES-D BDI v PAID. vii viii. CES-D
( ) :(IR-PAID -5) ( ( : e-mail: FADAE@shmu.ac.ir : PAID-5.. PAID-5. ( ) :. (). / PAID-5 :. PAID. / PAID-20 PAID-5 PAID-5. PAID-5 :.. IR-PAID-5 : // : // : // :...... ,. vi CES-D BDI v PAID. vii viii. CES-D
1. Evaluate the methodological quality of a study with the COSMIN checklist
 Answers 1. Evaluate the methodological quality of a study with the COSMIN checklist We follow the four steps as presented in Table 9.2. Step 1: The following measurement properties are evaluated in the
Answers 1. Evaluate the methodological quality of a study with the COSMIN checklist We follow the four steps as presented in Table 9.2. Step 1: The following measurement properties are evaluated in the
Continuous intraperitoneal insulin infusion in the treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus van Dijk, P.R.
 University of Groningen Continuous intraperitoneal insulin infusion in the treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus van Dijk, P.R. IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
University of Groningen Continuous intraperitoneal insulin infusion in the treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus van Dijk, P.R. IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's
Factor Structure, Validity and Reliability of the Modified Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale for Body Dysmorphic Disorder in Students
 -0 Iranian Journal of Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology, Vol., No., Winter 00, - 0 - - Original Article Factor Structure, Validity and Reliability of the Modified Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale
-0 Iranian Journal of Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology, Vol., No., Winter 00, - 0 - - Original Article Factor Structure, Validity and Reliability of the Modified Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale
Development of a self-reported Chronic Respiratory Questionnaire (CRQ-SR)
 954 Department of Respiratory Medicine, University Hospitals of Leicester, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester LE3 9QP, UK J E A Williams S J Singh L Sewell M D L Morgan Department of Clinical Epidemiology and
954 Department of Respiratory Medicine, University Hospitals of Leicester, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester LE3 9QP, UK J E A Williams S J Singh L Sewell M D L Morgan Department of Clinical Epidemiology and
Behavioral Self-management in an Inpatient Headache Treatment Unit: Increasing Adherence and Relationship to Changes in Affective Distress
 Behavioral Self-management in an Inpatient Headache Treatment Unit: Increasing Adherence and Relationship to Changes in Affective Distress F. Hoodin, PhD; B.J. Brines, PhD; A.E. Lake III, PhD; J. Wilson,
Behavioral Self-management in an Inpatient Headache Treatment Unit: Increasing Adherence and Relationship to Changes in Affective Distress F. Hoodin, PhD; B.J. Brines, PhD; A.E. Lake III, PhD; J. Wilson,
Research Questions and Survey Development
 Research Questions and Survey Development R. Eric Heidel, PhD Associate Professor of Biostatistics Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Graduate School of Medicine Research Questions 1 Research
Research Questions and Survey Development R. Eric Heidel, PhD Associate Professor of Biostatistics Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Graduate School of Medicine Research Questions 1 Research
Follow-up data from the cross-national Diabetes Attitudes, Wishes, and Needs (DAWN) MIND study
 Clinical Care/Education/Nutrition/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Monitoring of Individual Needs in Diabetes (MIND)-2 Follow-up data from the cross-national Diabetes Attitudes, Wishes,
Clinical Care/Education/Nutrition/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Monitoring of Individual Needs in Diabetes (MIND)-2 Follow-up data from the cross-national Diabetes Attitudes, Wishes,
Calculating clinically significant change: Applications of the Clinical Global Impressions (CGI) Scale to evaluate client outcomes in private practice
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Health and Behavioural Sciences - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2010 Calculating clinically significant change: Applications
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Health and Behavioural Sciences - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2010 Calculating clinically significant change: Applications
Cognitive-Behavioral Assessment of Depression: Clinical Validation of the Automatic Thoughts Questionnaire
 Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1983, Vol. 51, No. 5, 721-725 Copyright 1983 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. Cognitive-Behavioral Assessment of Depression: Clinical Validation
Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1983, Vol. 51, No. 5, 721-725 Copyright 1983 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. Cognitive-Behavioral Assessment of Depression: Clinical Validation
Comparing and Contrasting Depression Screening Instruments for Use Among Adolescents in Primary Care
 Comparing and Contrasting Depression Screening Instruments for Use Among Adolescents in Primary Care Mary Clinton 1, SN-CCC Julie Kaszuba 2, MSN, RN 1 Research Scholar-LVPG Clinical Services, Student Nurse
Comparing and Contrasting Depression Screening Instruments for Use Among Adolescents in Primary Care Mary Clinton 1, SN-CCC Julie Kaszuba 2, MSN, RN 1 Research Scholar-LVPG Clinical Services, Student Nurse
Assessment of sexual function by DSFI among the Iranian married individuals
 Basic Research Journal of Medicine and Clinical Sciences ISSN 2315-6864 Vol. 4(2) pp. 68-74 February 2015 Available online http//www.basicresearchjournals.org Copyright 2015 Basic Research Journal Full
Basic Research Journal of Medicine and Clinical Sciences ISSN 2315-6864 Vol. 4(2) pp. 68-74 February 2015 Available online http//www.basicresearchjournals.org Copyright 2015 Basic Research Journal Full
Terluin et al. BMC Psychiatry 2014, 14:121
 Terluin et al. BMC Psychiatry 2014, 14:121 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access To what extent does the anxiety scale of the Four-Dimensional Symptom Questionnaire (4DSQ) detect specific types of anxiety disorder
Terluin et al. BMC Psychiatry 2014, 14:121 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access To what extent does the anxiety scale of the Four-Dimensional Symptom Questionnaire (4DSQ) detect specific types of anxiety disorder
PREVALENCE OF CONDUCT DISORDER IN PRIMARY SCHOOL CHILDREN OF RURAL AREA Nimisha Mishra 1, Ambrish Mishra 2, Rajeev Dwivedi 3
 PREVALENCE OF CONDUCT DISORDER IN PRIMARY SCHOOL CHILDREN OF RURAL AREA Nimisha Mishra 1, Ambrish Mishra 2, Rajeev Dwivedi 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Nimisha Mishra, Ambrish Mishra, Rajeev Dwivedi. Prevalence
PREVALENCE OF CONDUCT DISORDER IN PRIMARY SCHOOL CHILDREN OF RURAL AREA Nimisha Mishra 1, Ambrish Mishra 2, Rajeev Dwivedi 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Nimisha Mishra, Ambrish Mishra, Rajeev Dwivedi. Prevalence
Research Article Validation of the Turkish Version of the Problem Areas in Diabetes Scale
 Cardiovascular Psychiatry and Neurology Volume 2011, Article ID 315068, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2011/315068 Research Article Validation of the Turkish Version of the Problem Areas in Diabetes Scale Elisabeth
Cardiovascular Psychiatry and Neurology Volume 2011, Article ID 315068, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2011/315068 Research Article Validation of the Turkish Version of the Problem Areas in Diabetes Scale Elisabeth
A primary care Symptoms Clinic for patients with medically unexplained symptoms: pilot randomised trial
 Open Access To cite: Burton C, Weller D, Marsden W, et al. A primary care Symptoms Clinic for patients with medically unexplained symptoms: pilot randomised trial. BMJ Open 2012;2:e000513. doi:10.1136/
Open Access To cite: Burton C, Weller D, Marsden W, et al. A primary care Symptoms Clinic for patients with medically unexplained symptoms: pilot randomised trial. BMJ Open 2012;2:e000513. doi:10.1136/
Correlation between Personality Traits and Expression of Hostility in Adolescents
 The European Proceedings of Social & Behavioral Sciences eissn: 2357-1330 iccsbs 2015 August Correlation between Personality Traits and Expression of Hostility in Adolescents Ema Stroe a, & Simona Trifu
The European Proceedings of Social & Behavioral Sciences eissn: 2357-1330 iccsbs 2015 August Correlation between Personality Traits and Expression of Hostility in Adolescents Ema Stroe a, & Simona Trifu
Chapter 2 The validity of the Dutch K10 and EK10 screening scales for depressive and anxiety disorders
 Chapter 2 The validity of the Dutch K10 and EK10 screening scales for depressive and anxiety disorders Published: Donker, T., Comijs, H.C., Cuijpers, P., Terluin, B., Nolen, W.A., Zitman, F.G., Penninx,
Chapter 2 The validity of the Dutch K10 and EK10 screening scales for depressive and anxiety disorders Published: Donker, T., Comijs, H.C., Cuijpers, P., Terluin, B., Nolen, W.A., Zitman, F.G., Penninx,
