Overview of Presentation. The State of Farming: But it has always been this way! Prevalence of depression in farmers. Mental Health in UK Farmers
|
|
|
- Virgil Briggs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pesticide Poisoning and Depressive Symptoms as Associated with Safety Behaviors and Injury in Colorado Farm Residents Cheryl L. Beseler, PhD University of Nebraska Medical Center Lorann Stallones, PhD, MPH Colorado State University August 4, 2009 Overview of Presentation Impact of depression in farmers The biological connection: pesticides and depression Cross-sectional, longitudinal and case-control studies show high pesticide exposure associated with depression Effects on safety and injuries Future directions The State of Farming: But it has always been this way! Prevalence of depression in farmers General population: Lifetime 21.3% women; 12.7% men; Current 6.7% women; 4.0 men Colorado (1993): CES-D 7.9% men and 11.1% women Iowa (2000): CES-D 12.2% men Tennessee ( ): CES-D 19% in farmers 17% in non-farmers; only 5.3% (5.7%) of those depressed (CES-D scale) sought treatment (Linn & Husaini, 1987) Mental Health in UK Farmers UK (1995): Hospital Anxiety and Scale (Booth & Lloyd, 1999) 3% men; 12% women Anxiety: 13% men; 38% women 6% of British farmers reported significant psychiatric morbidity, lower than general population, but: Significantly more likely to think that life was not worth living (OR 3.26; 95% CI ) (Thomas et al., 2003) Mental Health of Farmers in Norway Hordaland Health Survey collected depression and anxiety data on 17,295 farmers and non-farmers using HADS-A and HADS-D Using a cut-off for caseness of 8, male farmers were 2.3 times and females were 2.1 times more likely to be depressed than nonfarmers; this was higher for male animal producers (OR=3.1); no difference between full-time farmers and part-time farmers Sanne et al.,
2 Suicide in agriculturally-intensive region of Spain, Conclusions from these studies Higher rates of depression and anxiety are found in farmers compared to their nonfarming counterparts in many countries Farmers are at an increased risk of suicide Relationship between depression and suicide ideation may be different in farmers than in the general population Parron et al., 1996 Background of Organophosphates The role of organophosphates and carbamates in the mental health of farmers Organophosphate (OPs) compounds were first synthesized in All OPs are structurally and functionally related. Over 20,000 OP agents have been developed, especially during and after World War II. Since 1937 when the insecticidal properties of OPs were described, the most common use of OPs has been as pesticides. Physiological effects of OP exposure CNS manifestations of acute OP poisoning Acute OP poisoning is produced by the phosphorylation and inhibition of cholinesterases leading to accumulation of acetylcholine at synapses in central, peripheral, and autonomic systems. Routes of exposure include: dermal absorption, inhalation Giddiness; emotional lability Excessive dreaming Insomnia Nightmares Drowsiness Anxiety; restlessness Apathy; withdrawal Confusion; difficulty concentrating Headache Tremors Slurred speech Ataxia; generalized weakness Coma with absence of reflexes Convulsion of respiratory and circulatory centers 2
3 Long term effects of OP exposure Long term sequelae of acute OP poisoning include: anxiety, depression, sleep disruption, mood disturbances, inability to concentrate, and spatial disorientation. can be detected 10 years after acute poisoning Serine hydrolase inhibition and neurological effects associated with organophosphate pesticides Serine Acetylcholinesterase Neuropathy target esterase Fatty acid amide hydroxylase Tubulin protein Physiological vomiting abdominal pain numbness in extremities fatigue headaches excessive salivation diarrhea PON-1 status + OP Serine-P Inhibited serine hydrolase; Binding tubulin Psychological anxiety depression irritability restlessness? Covalent Modification Serine-O - Aged Neuropathy target esterase Axonal degeneration Delay-Onset Neuropathy Neuropsychological/ Neuropathies difficulty concentrating word finding problems memory impairments decreased alertness generalized weakness Catecholamines norepinephrine epinephrine Adrenergic predominance Mania Behavioral despair forced swim model Hypoactivity model BALANCE Cholinomimetics Learned helplessness Acetylcholine Affective disorders Chronic stress model Cholinergic predominance Genetic FSL Rats Epidemiological evidence for an association between OPs and depression and pesticide exposure have rarely been addressed in hypothesis-driven research Previous epidemiological studies have shown that an acute poisoning is associated with depression (Savage et al., 1988) Some studies have shown mood effects (irritability) from chronic pesticide exposures (Amr et al., 1997; Salvi et al., 2003) Objectives of the Colorado Eight County Study Evaluate the association between pesticides and depression among a population exposed to pesticides as a result of agricultural use Characterize the type of pesticides used and symptoms of poisoning most frequently associated with depression Study design: Study Population The Colorado Farm Family Health and Hazard Surveillance (CFFHHS) was a cross sectional survey conducted between CFFHHS was a multi-stage area sample that included eight counties in Northeastern Colorado. 479 farm representing 761 farm resident operators and their spouses were enrolled 3
4 Study design: Interview Study design: Variables measured In-person interviews on the farms were conducted and took 45 minutes-2 hours Extensive information obtained on farming operation (crops, safety practices, pesticides used), injuries, medical care, health status and health-related behaviors, negative life events Primary risk factor: Past pesticide poisoning Outcome: Depressive symptoms assessed using the 20 question Center for Epidemiological Studies- (CES-D) scale Symptoms experienced in the past week prior to the interview were based on a scale of less than 1 day, 1-2 days, 3-4 days, or 5-7 days Age Distribution of Colorado Farmers Results >60 27% <30 4% % 69 pesticide poisonings reported (9.1%) 24 sought medical attention 6% depressed by CES-D scale; 9.5% in women and 4.0% in men % % < >60 Conditional logistic regression of depression and risk factors for depression Risk Factor for Pesticide Poisoning Odds Ratio % Confidence Interval 2.56, Longitudinal analyses of pesticide poisoning and depression Female gender , Poor health , Income Loss , 4.32 Stallones and Beseler,
5 Objectives of Study Describe the pattern of association between pesticide poisoning and depressive symptoms (CES-D scale) over a three-year period in a cohort of farm residents. Identify specific depressive symptoms in the CES-D scale which are significantly associated with having reported a pesticide poisoning Methods: Study Population A stratified sample of farms was randomly selected to represent approximately 2.55% of all rural farm residents with an operator living on the farm The sample was proportional to the number of farms with resident operators in each of six crop reporting districts and identified using farm truck registration Eligibility requirements included an income of at least $1,000 in a normal year from sales of agricultural product; operator had to make at least 51% of his or her income from farming owned or leased land 485 farms representing 872 individuals enrolled in longitudinal study; 745 in yr 2; 653 in yr 3 Methods: Interview The survey was conducted by telephone and designed to take approximately 20 minutes Data were collected on types of crops, the number of acres farmed, number of workers and pesticides used Depressive symptoms measured using CES-D scale Respondents were asked about their health status, including the use of tobacco and alcohol, and whether they had ever become ill from any exposure to pesticides Methods: Analysis Weighted Least Squares (WLS) for repeated measures to examine the time-dependence of depression with and without having reported a pesticide-related illness in a univariate analysis Generalized Estimating Equations (GEE) for multivariate modeling of depression and pesticide-related illness with other explanatory variables in the model Characteristic Demographics of farm cohort Age < > 60 Involved in farm work Good to excellent health Pesticide Poisoning Depressed in Year 1 Depressed in Year 2 Depressed in Year 3 Males % (n) (n=467) 5.4 (25) 71.0 (331) 23.6 (110) 99.4 (464) 91.9 (429) 6.8 (32) 8.0 (37) 2.9 (11) 4.2 (13) Females % (n) (n=400) 8.3 (33) 76.7 (307) 15.0 (60) 77.8 (311) 94.5 (378) 5.0 (20) 10.6 (42) 7.3 (26) 6.7 (21) Missing depression data over three year period by reported pesticide illness % 0.0% 15.1% 11.5% 28.1% 28.8% Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 No pesticide illness Pesticide illness 5
6 Time-dependent WLS regression modeling the probability of depression and poisoning Generalized Estimating Equations modeling the probability of depression and pesticide poisoning Weighted Least Squares Model Time only Year 2 Year 3 Time & poisoning Year 2 Year 3 Poisoning Regression Coefficient Standard Deviation Chi-square P-value Regression Standard OR 95% CI or Symptom coefficient error by CES-D , 5.78 Bothered by things , 7.77 Felt depressed , 6.16 Talked less than usual , 5.89 adjusted for gender, age, health status, financial problems Results WLS results indicated that reporting a pesticide poisoning at the first year was significantly associated with depression over the three year period Adjusted GEE models showed pesticide poisoning was significantly associated with depression by the CES-D scale and with several symptoms including being bothered by things that do not usually bother them, feeling depressed and talking less than usual Comparisons to and Poisoning in the Agricultural Health Study Study Population CFFHHS 8 county survey Statewide 3 yr survey AHS spouses AHS farmer applicators OR % CI 2.56, , , , 5.60 Injuries as an occupational hazard Consequences of The Relationship of Injury to Pesticide Poisoning Approximately 1.8 million agricultural workers in the U.S. On average, 516 workers die on a farm every year (CDC: ) Every day 243 agricultural workers suffer lost-work time due to injuries and 5% are permanently impaired 6
7 Safety practices, depression and pesticides Organophosphates Acute poisoning Increased risk of suicide Long term sequelae Inability to concentrate Sleep disturbances Decreased use of proper safety practices I n j u r i e s Safety behaviors, depression and pesticides-study design Ten safety behaviors were assessed related to personal protective equipment, animal handling, farm equipment safety, and miscellaneous safety practices including chemical storage. Ten safety knowledge questions related to above activities Exact logistic regression of safety behavior and depression by pesticide poisoning, Colorado Characteristic Farm machinery Moving parts shielded Replace shields Read manuals Animal-related Restraining facilities Calm OR (95% CI) 1.50 (0.33, 6.83) 2.92 (0.88,9.64) 2.24 (0.69, 7.28) 2.68 (1.00, 7.20) 3.13 (1.23, 7.99) among poisoned OR (95% CI) 4.19 (1.06, 16.5) 2.04 (0.42, 9.96) 3.42 (0.97, 12.1) 2.99 (0.56, 15.8) 4.25 (1.05, 17.2) Next steps in modeling safety, pesticide poisoning and depression Using Structural Equation Modeling, identify the model that best explains the covariance structure between the risk factors for depression (financial problems, poor health, pesticide poisoning) and exercising a safety behavior Modeling the probability of never, rarely or sometimes vs. most of the time or always exercising the safety behavior SEM for keeping moving equipment parts shielded 8 County Sample Association of safety knowledge, safety behaviors and depression in three years of Colorado farm resident data N=652 individuals representing 124 of the most severe injuries over three years 57 injuries in year 1; 42 injuries in year 2 and 54 injuries in year 3 Of the 124 with at least one injury in three years, 77 missed at least one day of work and 73 sought medical attention Safety knowledge score was based on individual factor scores dichotomized at the median; sum scores and factor-weighted score also used Beseler and Stallones, J of Agromedicine
8 Logistic regression modeling the probability of injury over a 3- year period and low safety knowledge score and depression at baseline* Further observations from this study Risk Factor OR 95% CI Hours/week , 1.06 Financial problems , , 2.40 Safety Score , 1.43 *Safety Score , 15.0 Variable Used Summed safety knowledge score*depression Factor-weighted safety factor score * depression Not Depressed Depressed + High knowledge Depressed + Low knowledge Odds Ratio % CI 1.11, , 4.31 reference , 7.29 *Adjusted for age and gender Additional analyses using Poisson in GEE models Only depression was associated with total injury count (153 injuries) over the 3-year period Unadjusted model: OR 1.96; 95% CI 1.12, 3.43 Adjusted by age, gender, financial problems OR 2.53; 95% CI 1.09, 5.87 Conclude that the most serious injuries may be related to both depression and safety knowledge/perception and total injuries show only the effects of depression Relationship of Safety Knowledge to Safety Behaviors Not wearing a dust mask during dusty operations (OR 1.65; CI 1.14, 2.38) or wearing hearing protection when tending to noisy operations (OR 1.51; CI 1.01, 2.26) were the only safety behaviors significantly associated with safety knowledge in age- and gender-adjusted model logistic regression models Relationship of safety behaviors to injury Not keeping passageways clear of slippery substances was the only safety behavior that was significantly associated with the risk of injuries (OR 2.08; CI 1.08, 3.99) Not keeping chemicals out of the reach of children showed an elevated risk for injury (OR 3.03; CI 0.84, 10.9) Combining the two Colorado studies to look at all risk factors 1,600 farm residents included in the analysis Depressive symptoms were ordinal scale Safety behaviors were ordinal scale Structural Equation Modeling used to simultaneously assess stressors, pesticide poisoning, depressive symptoms, safety knowledge and safety behaviors 8
9 Factor loadings for Depressive Symptoms (Somatic/Negative Affect) Symptom Factor Symptom loading Felt bothered 0.62 Felt fearful Not eating 0.55 Slept restlessly Felt blue 0.85 Talked less Trouble concentrating 0.60 Couldn t get going Felt depressed 0.89 Crying Everything an effort 0.58 Felt sad Life had been a failure 0.70 Felt lonely Factor loading Safety Behavior Questions Safety Behavior Question: Exercise this behavior always, most of the time, occasionally, rarely, never, n/a Wearing respirator when handling dusty or moldy grain Being calm around animals in close quarters Replacing protective shields after working on equipment Wearing a dust mask during dusty operations Using restraining or handling facilities for treating animals Wearing hearing protection when tending to noisy operations Keeping chemicals out of the reach of children Keeping passageways clear of slippery substances Reading instruction manuals for farm machinery Keeping moving equipment parts shielded n Question Safety Knowledge Questions More falls are connected with the use of farm machinery than any other farm work operation Children are rarely injured in falls from farm equipment Agriculture has one of the lowest injury rates of the major U.S. industries Tractors are involved in many fatal farm injuries Inattention is a leading cause of injuries Farmer s lung disease results from overexertion Fatigue can lead to injuries Hearing loss is common among farm workers Animals are rarely responsible for injuries Amputation injuries are more common when working with farm equipment than when involved in other agricultural work % correct Factor loading Item Response Theory analysis of safety knowledge questions Safety questions in sample of farm residents Falls Kids Agriculture Tractor Inattention Lung Disease Fatigue Hearing Loss Animals Amputation 14 Somatic Retarded Activity Negative Affect Symptoms *p<0.001 Financial Pesticide Problems Age Fair/Poor Poisoning Health Factor Safety Knowledge Factor 0.15 * 0.15 * Keep passageways clear 0.10 P= safety questions Injury (n=154) Final Remarks and Future Directions Pesticide poisoning is associated with depression Pesticide poisoning may decrease concentration as does depression and the combination may reduce safety behaviors and low safety knowledge appear to reduce safety behaviors and increase the risk for injury Need interventions to detect depression in the context of farm safety programs SEM Results 9
10 Acknowledgements: Funding Funding for the original survey was provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health, U04/CCU806060, additional funding was provided by the CDC, National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, R49/CCR
Depressive Symptoms Among Colorado Farmers 1
 February 1995 Depressive Symptoms Among Colorado Farmers 1 L. Stallones, M. Leff, C. Garrett, L. Criswell, T. Gillan 2 ARTICLE ABSTRACT Previous studies have reported farmers to be at higher risk of suicide
February 1995 Depressive Symptoms Among Colorado Farmers 1 L. Stallones, M. Leff, C. Garrett, L. Criswell, T. Gillan 2 ARTICLE ABSTRACT Previous studies have reported farmers to be at higher risk of suicide
Biology Change Pressure Identity and Self-Image
 Victoria L Foster Biology Change Pressure Identity and Self-Image Sadness Sadness is something we all experience. Sadness is usually tied to one event or reason. Sadness is what happens when normal
Victoria L Foster Biology Change Pressure Identity and Self-Image Sadness Sadness is something we all experience. Sadness is usually tied to one event or reason. Sadness is what happens when normal
ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF PSYCHOLOGICAL CONSEQUENSES OF TRAUMA AND TERRORISM
 Patient Care Guidelines: ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF PSYCHOLOGICAL CONSEQUENSES OF TRAUMA AND TERRORISM NORMAL REACTIONS Children, like adults, are resilient, and with appropriate support will cope with
Patient Care Guidelines: ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF PSYCHOLOGICAL CONSEQUENSES OF TRAUMA AND TERRORISM NORMAL REACTIONS Children, like adults, are resilient, and with appropriate support will cope with
PSYCHIATRIC CO-MORBIDITY STEVE SUGDEN MD MPH
 PSYCHIATRIC CO-MORBIDITY STEVE SUGDEN MD MPH OVERVIEW: PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS Mood Disorders Anxiety Disorders Psychotic Disorders Personality Disorders PTSD Eating Disorders EXAMPLE What is the diagnosis?
PSYCHIATRIC CO-MORBIDITY STEVE SUGDEN MD MPH OVERVIEW: PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS Mood Disorders Anxiety Disorders Psychotic Disorders Personality Disorders PTSD Eating Disorders EXAMPLE What is the diagnosis?
Mrs. Vicky Major, 2 Professor Hans Kromhout, 2. Dr. Tim Meijster, 3 Professor Leslie London
 THE ROLE OF ORGANOPHOSPHATE EXPOSURE IN THE AETIOLOGY OF DEPRESSION & SUICIDALITY AMONGST FARM WORKERS ON GRAPE FARMS IN THE WESTERN CAPE PROVINCE, SOUTH AFRICA 1 Mrs. Vicky Major, 2 Professor Hans Kromhout,
THE ROLE OF ORGANOPHOSPHATE EXPOSURE IN THE AETIOLOGY OF DEPRESSION & SUICIDALITY AMONGST FARM WORKERS ON GRAPE FARMS IN THE WESTERN CAPE PROVINCE, SOUTH AFRICA 1 Mrs. Vicky Major, 2 Professor Hans Kromhout,
Certified safe farm injuries as they pertain to chronic disease
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Spring 2014 Certified safe farm injuries as they pertain to chronic disease Shannon M. Meppelink University of Iowa Copyright 2014 Shannon
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Spring 2014 Certified safe farm injuries as they pertain to chronic disease Shannon M. Meppelink University of Iowa Copyright 2014 Shannon
BACKGROUND HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE
 BACKGROUND HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Name: Sex M F Address: Home Number: Work Number: Cell Number: Email: SSN: Name and Address of Employer: Date of Birth: Age: Ethnicity: Referred By: Referral Question or
BACKGROUND HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Name: Sex M F Address: Home Number: Work Number: Cell Number: Email: SSN: Name and Address of Employer: Date of Birth: Age: Ethnicity: Referred By: Referral Question or
Symptoms Duration Impact on functioning
 Dr. Lori Triano- Antidormi Dr. Jane Storrie OPA Annual Conference February 21, 2015 Symptoms Duration Impact on functioning Numbness, shock, disbelief, denial Sadness Apathy, lack of interest, enthusiasm
Dr. Lori Triano- Antidormi Dr. Jane Storrie OPA Annual Conference February 21, 2015 Symptoms Duration Impact on functioning Numbness, shock, disbelief, denial Sadness Apathy, lack of interest, enthusiasm
Handout 3: Mood Disorders
 Handout 3: Mood Disorders Mood disorders are called affective (emotional) disorders. There are two categories of mood disorders: Depressive Disorders Bipolar Affective Disorders Depressive Disorders Minor
Handout 3: Mood Disorders Mood disorders are called affective (emotional) disorders. There are two categories of mood disorders: Depressive Disorders Bipolar Affective Disorders Depressive Disorders Minor
Presenter. Dr. Ronald Lucchino
 Adverse Drug Reactions in Adults with Down Syndrome Presenter Dr. Ronald Lucchino rvluc@comcast.net PURPOSE To increase staff awareness that older adults with DD may have higher levels of medication in
Adverse Drug Reactions in Adults with Down Syndrome Presenter Dr. Ronald Lucchino rvluc@comcast.net PURPOSE To increase staff awareness that older adults with DD may have higher levels of medication in
By Dr. Magdy M. Awny. (nerve agent)
 By Dr. Magdy M. Awny (nerve agent) Pesticides Is any chemical substance or mixture of substances intended for preventing, destroying, repelling, or mitigating any pest are a group of insecticides or Organophosphorous
By Dr. Magdy M. Awny (nerve agent) Pesticides Is any chemical substance or mixture of substances intended for preventing, destroying, repelling, or mitigating any pest are a group of insecticides or Organophosphorous
Aging and Mental Health Current Challenges in Long Term Care
 Aging and Mental Health Current Challenges in Long Term Care Stephanie Saur & Christina Pacheco Acute Care Behavioural Consultants Alzheimer Society Peel What is Mental Health? Mental health includes our
Aging and Mental Health Current Challenges in Long Term Care Stephanie Saur & Christina Pacheco Acute Care Behavioural Consultants Alzheimer Society Peel What is Mental Health? Mental health includes our
Mental Health Issues and Treatment
 Mental Health Issues and Treatment Mental health in older age Depression Causes of depression Effects of depression Suicide Newsom, Winter 2017, Psy 462/562 Psychology of Adult Development and Aging 1
Mental Health Issues and Treatment Mental health in older age Depression Causes of depression Effects of depression Suicide Newsom, Winter 2017, Psy 462/562 Psychology of Adult Development and Aging 1
Are All Older Adults Depressed? Common Mental Health Disorders in Older Adults
 Are All Older Adults Depressed? Common Mental Health Disorders in Older Adults Cherie Simpson, PhD, APRN, CNS-BC Myth vs Fact All old people get depressed. Depression in late life is more enduring and
Are All Older Adults Depressed? Common Mental Health Disorders in Older Adults Cherie Simpson, PhD, APRN, CNS-BC Myth vs Fact All old people get depressed. Depression in late life is more enduring and
Depression Fact Sheet
 Depression Fact Sheet Please feel free to alter and use this fact sheet to spread awareness of depression, its causes and symptoms, and what can be done. What is Depression? Depression is an illness that
Depression Fact Sheet Please feel free to alter and use this fact sheet to spread awareness of depression, its causes and symptoms, and what can be done. What is Depression? Depression is an illness that
PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE
 PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE Personal Information please include all requested information Date Name Date of Birth* Age Address* City State Zip* Home Phone Cell phone* E-mail address* SSN*: - - *required information
PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE Personal Information please include all requested information Date Name Date of Birth* Age Address* City State Zip* Home Phone Cell phone* E-mail address* SSN*: - - *required information
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centers: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 Study No.: 29060/717 Title: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, 3-Arm, Fixed-Dose Study of CR Intermittent Dosing (12.5 mg and 25 mg) for Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder Rationale: In most trials investigating
Study No.: 29060/717 Title: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, 3-Arm, Fixed-Dose Study of CR Intermittent Dosing (12.5 mg and 25 mg) for Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder Rationale: In most trials investigating
MODULE IX. The Emotional Impact of Disasters on Children and their Families
 MODULE IX The Emotional Impact of Disasters on Children and their Families Outline of presentation Psychological first aid in the aftermath of a disaster Common reactions to disaster Risk factors for difficulty
MODULE IX The Emotional Impact of Disasters on Children and their Families Outline of presentation Psychological first aid in the aftermath of a disaster Common reactions to disaster Risk factors for difficulty
Mental Health First Aid at a Glance
 Mental Health First Aid at a Glance Candice M. Haines, LCPC Program Supervisor Mental Health First Aid Instructor Pilsen Wellness Center chaines@pilsenmh.org Overview Address myths vs facts Warning signs
Mental Health First Aid at a Glance Candice M. Haines, LCPC Program Supervisor Mental Health First Aid Instructor Pilsen Wellness Center chaines@pilsenmh.org Overview Address myths vs facts Warning signs
OCFP 2012 Systematic Review of Pesticide Health Effects: Executive Summary
 OCFP 2012 Systematic Review of Pesticide Health Effects: Executive Summary The second Ontario College of Family Physicians (OCFP) Systematic Review of Pesticide Health Effects reviewed the relevant literature
OCFP 2012 Systematic Review of Pesticide Health Effects: Executive Summary The second Ontario College of Family Physicians (OCFP) Systematic Review of Pesticide Health Effects reviewed the relevant literature
FMS Psychology, PLLC Adult Intake Form. Phone Number (Day): Phone Number (Evening):
 FMS Psychology, PLLC Adult Intake Form General Information: Name: Date of Birth: / / Age: Gender: Address: Phone Number (Day): Phone Number (Evening): Primary Care Physician: Highest Level of Formal Education:
FMS Psychology, PLLC Adult Intake Form General Information: Name: Date of Birth: / / Age: Gender: Address: Phone Number (Day): Phone Number (Evening): Primary Care Physician: Highest Level of Formal Education:
Adolescent Mental Health. Vicky Ward, MA Sociology Manager of Prevention Services
 Adolescent Mental Health Vicky Ward, MA Sociology Manager of Prevention Services What is a Mental Disorder? Affects a person s thinking, emotional state and behavior Disrupts the person s ability to Work
Adolescent Mental Health Vicky Ward, MA Sociology Manager of Prevention Services What is a Mental Disorder? Affects a person s thinking, emotional state and behavior Disrupts the person s ability to Work
PATIENT SURVEY FOR ADMINISTRATIVE USE ONLY. TO BE COMPLETED BY STUDY COORDINATOR.
 PATIENT SURVEY FOR ADMINISTRATIVE USE ONLY. TO BE COMPLETED BY STUDY COORDINATOR. DATE OF VISIT: / / PATIENT ID: REGULAR PROVIDER: SITE OF VISIT: Cleveland Houston Manhattan Pittsburgh Thank you for agreeing
PATIENT SURVEY FOR ADMINISTRATIVE USE ONLY. TO BE COMPLETED BY STUDY COORDINATOR. DATE OF VISIT: / / PATIENT ID: REGULAR PROVIDER: SITE OF VISIT: Cleveland Houston Manhattan Pittsburgh Thank you for agreeing
PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE
 PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE Personal Information Date Name Date of Birth Age Height Weight Gender: Male / Female Address City State / Zip Home Phone Cell phone Work phone E-mail address Do you currently have
PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE Personal Information Date Name Date of Birth Age Height Weight Gender: Male / Female Address City State / Zip Home Phone Cell phone Work phone E-mail address Do you currently have
6800$5< /,)(7,0( ',$*126(6 &+(&./,67 'DWH RI &XUUHQW BBBB BBBB BBBBBB
 Criteria for Probable Diagnosis: 1. Meets criteria for core symptoms of the disorder. 2. Meets all but one, or a minimum of 75% of the remaining criteria required for the diagnosis 3. Evidence of functional
Criteria for Probable Diagnosis: 1. Meets criteria for core symptoms of the disorder. 2. Meets all but one, or a minimum of 75% of the remaining criteria required for the diagnosis 3. Evidence of functional
IMPORTANT: PLEASE READ
 PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION Pr BACLOFEN Baclofen Tablets 10 mg and 20 mg This leaflet is part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when BACLOFEN was approved for sale in Canada and is designed
PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION Pr BACLOFEN Baclofen Tablets 10 mg and 20 mg This leaflet is part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when BACLOFEN was approved for sale in Canada and is designed
PFIZER INC. THERAPEUTIC AREA AND FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS: See USPI.
 PFIZER INC. These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert. For publications based on this study, see associated bibliography.
PFIZER INC. These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert. For publications based on this study, see associated bibliography.
Can Animals Experience Emotions? Model Diagnostics Demographic variable Companion Animal. Deviance
 1 2 3 Table 1: Table showing significant demographic influences on responses to the question can animals experience the following emotions? Significance of odds ratios: * p
1 2 3 Table 1: Table showing significant demographic influences on responses to the question can animals experience the following emotions? Significance of odds ratios: * p
Module Objectives 10/28/2009. Chapter 6 Mood Disorders. Depressive Disorders. What are Unipolar Mood Disorders?
 Chapter 6 Mood Disorders Module Objectives Depressive Disorders What are Mood Disorders? What is Major Depressive Disorder? What is Post Partum Disorder? What are Unipolar Mood Disorders? What is Mania?
Chapter 6 Mood Disorders Module Objectives Depressive Disorders What are Mood Disorders? What is Major Depressive Disorder? What is Post Partum Disorder? What are Unipolar Mood Disorders? What is Mania?
Delirium. Delirium is characterized by an acute onset (hours or days) and fluctuating course of deterioration in mental functioning.
 Delirium Delirium is characterized by an acute onset (hours or days) and fluctuating course of deterioration in mental functioning. DELIRIUM IS A MEDICAL EMERGENCY! Delirium: Hallmark Features Inattention-
Delirium Delirium is characterized by an acute onset (hours or days) and fluctuating course of deterioration in mental functioning. DELIRIUM IS A MEDICAL EMERGENCY! Delirium: Hallmark Features Inattention-
BRL /RSD-101C0D/1/CPMS-704. Report Synopsis
 Report Synopsis Study Title: A Randomized, Multicenter, 10-Week, Double-Blind, Placebo- Controlled, Flexible-Dose Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Paroxetine in Children and Adolescents with
Report Synopsis Study Title: A Randomized, Multicenter, 10-Week, Double-Blind, Placebo- Controlled, Flexible-Dose Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Paroxetine in Children and Adolescents with
Pesticide Hazards in Outdoor Marijuana Grows
 Pesticide Hazards in Outdoor Marijuana Grows Robert Ford CIH,CSP Environmental Program Manager California Department of Pesticide Regulation 2014 Pesticide Exposures to Law Enforcement -Drug task force
Pesticide Hazards in Outdoor Marijuana Grows Robert Ford CIH,CSP Environmental Program Manager California Department of Pesticide Regulation 2014 Pesticide Exposures to Law Enforcement -Drug task force
Depression among B.Ed college students
 Depression among B.Ed college students Ramesh O. Prajapati* ABSTRACT Aim of the research is to find out the depression among B.ed College students, So, investigator selected two groups one is male and
Depression among B.Ed college students Ramesh O. Prajapati* ABSTRACT Aim of the research is to find out the depression among B.ed College students, So, investigator selected two groups one is male and
Post Combat Care. The Road Home
 Post Combat Care The Road Home 1 Demographics: OEF/OIF Veterans Using VA Health Care Approximately 2.04 million individuals have been deployed since 2002 1,094,502 OEF and OIF veterans who have left active
Post Combat Care The Road Home 1 Demographics: OEF/OIF Veterans Using VA Health Care Approximately 2.04 million individuals have been deployed since 2002 1,094,502 OEF and OIF veterans who have left active
OCCUPATIONAL CARBAMATE POISONING IN THAILAND
 OCCUPATIONAL CARBAMATE POISONING IN THAILAND Achara Tongpoo 1, Charuwan Sriapha 1, Sunun Wongvisawakorn 1, Panee Rittilert 1, Satariya Trakulsrichai 1,2 and Winai Wananukul 1 1 Ramathibodi Poison Center
OCCUPATIONAL CARBAMATE POISONING IN THAILAND Achara Tongpoo 1, Charuwan Sriapha 1, Sunun Wongvisawakorn 1, Panee Rittilert 1, Satariya Trakulsrichai 1,2 and Winai Wananukul 1 1 Ramathibodi Poison Center
AN OVERVIEW OF ANXIETY
 AN OVERVIEW OF ANXIETY Fear and anxiety are a normal part of life. Normal anxiety keeps us alert. Intervention is required when fear and anxiety becomes overwhelming intruding on a persons quality of life.
AN OVERVIEW OF ANXIETY Fear and anxiety are a normal part of life. Normal anxiety keeps us alert. Intervention is required when fear and anxiety becomes overwhelming intruding on a persons quality of life.
Many people are confused about what Social Security benefits might be available to them. Here are answers to frequently asked questions.
 Many people are confused about what Social Security benefits might be available to them. Here are answers to frequently asked questions. What is the difference between SSI and SSDI? SSDI or Social Security
Many people are confused about what Social Security benefits might be available to them. Here are answers to frequently asked questions. What is the difference between SSI and SSDI? SSDI or Social Security
MENTAL HEALTH AND MENTAL ILLNESS: OUR JOURNEY ACROSS THE CONTINUUM LLI PROGRAM OCTOBER 5, 2018 VIRGINIA F. RIGGS MS, MSN, RN
 MENTAL HEALTH AND MENTAL ILLNESS: OUR JOURNEY ACROSS THE CONTINUUM LLI PROGRAM OCTOBER 5, 2018 VIRGINIA F. RIGGS MS, MSN, RN OBJECTIVES: Focus on a continuum from mental health to mental illness Examine
MENTAL HEALTH AND MENTAL ILLNESS: OUR JOURNEY ACROSS THE CONTINUUM LLI PROGRAM OCTOBER 5, 2018 VIRGINIA F. RIGGS MS, MSN, RN OBJECTIVES: Focus on a continuum from mental health to mental illness Examine
Mental Health Issues in Nursing Homes. I m glad you asked.
 Mental Health Issues in Nursing Homes I m glad you asked. I m glad you asked Susan Wehry, M.D. Associate Professor of Psychiatry, College of Medicine, University of Vermont Consultant, State of Vermont
Mental Health Issues in Nursing Homes I m glad you asked. I m glad you asked Susan Wehry, M.D. Associate Professor of Psychiatry, College of Medicine, University of Vermont Consultant, State of Vermont
Recognizing and Applying Tools to Alleviate Stress. Josie M. Rudolphi, PhD National Farm Medicine Center Marshfield, WI
 Recognizing and Applying Tools to Alleviate Stress Josie M. Rudolphi, PhD National Farm Medicine Center Marshfield, WI Overview Stress in agriculture Stress and health Signs of stress and mental health
Recognizing and Applying Tools to Alleviate Stress Josie M. Rudolphi, PhD National Farm Medicine Center Marshfield, WI Overview Stress in agriculture Stress and health Signs of stress and mental health
SGRQ Questionnaire assessing respiratory disease-specific quality of life. Questionnaire assessing general quality of life
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL e-table 1: Outcomes studied in present analysis. Outcome Abbreviation Definition Nature of data, direction indicating adverse effect (continuous only) Clinical outcomes- subjective
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL e-table 1: Outcomes studied in present analysis. Outcome Abbreviation Definition Nature of data, direction indicating adverse effect (continuous only) Clinical outcomes- subjective
Suicide Prevention Carroll County Public Schools
 Suicide Prevention Carroll County Public Schools 2012-13 The Facts Statistics 3 rd leading cause of death for adolescents (15-24 yrs. old) 6 th leading cause of death for children (5-14 yrs. old) 11 th
Suicide Prevention Carroll County Public Schools 2012-13 The Facts Statistics 3 rd leading cause of death for adolescents (15-24 yrs. old) 6 th leading cause of death for children (5-14 yrs. old) 11 th
Dr. Catherine Mancini and Laura Mishko
 Dr. Catherine Mancini and Laura Mishko Interviewing Depression, with case study Screening When it needs treatment Anxiety, with case study Screening When it needs treatment Observation Asking questions
Dr. Catherine Mancini and Laura Mishko Interviewing Depression, with case study Screening When it needs treatment Anxiety, with case study Screening When it needs treatment Observation Asking questions
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition. Introduction. Introduction 9/10/ % of US suffers from Mood Disorders
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 17 Mood Disorders Introduction 12% of US suffers from Mood Disorders MD are a group of psychiatric DO characterized by physical, emotional
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 17 Mood Disorders Introduction 12% of US suffers from Mood Disorders MD are a group of psychiatric DO characterized by physical, emotional
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS FOR BENZODIAZEPINES AS ANXIOLYTICS OR HYPNOTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS FOR BENZODIAZEPINES AS ANXIOLYTICS OR HYPNOTICS Guideline Title Summary of Product Characteristics for Benzodiazepines as Anxiolytics or Hypnotics Legislative basis Directive
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS FOR BENZODIAZEPINES AS ANXIOLYTICS OR HYPNOTICS Guideline Title Summary of Product Characteristics for Benzodiazepines as Anxiolytics or Hypnotics Legislative basis Directive
See Through The Masquerade To Avoid Paying Twice
 See Through The Masquerade To Avoid Paying Twice Vladimir Bokarius, MD, PhD, QME CWCDAA Conference, October, 2018 Las Vegas, NV Agenda Mental Health Mental or Medical? Mental Health Disorders Due to General
See Through The Masquerade To Avoid Paying Twice Vladimir Bokarius, MD, PhD, QME CWCDAA Conference, October, 2018 Las Vegas, NV Agenda Mental Health Mental or Medical? Mental Health Disorders Due to General
The Third Annual Conference of the Caribbean Poison Information Network (CARPIN)
 CARIBBEAN POISON INFORMATION NETWORK THIRD ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE UHWI KINGSTON, JAMAICA MAY 31-JUNE 1,2008 The Use of Pesticides at the Farm Level The Third Annual Conference of the Caribbean Poison
CARIBBEAN POISON INFORMATION NETWORK THIRD ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE UHWI KINGSTON, JAMAICA MAY 31-JUNE 1,2008 The Use of Pesticides at the Farm Level The Third Annual Conference of the Caribbean Poison
Emotions as infectious diseases in a large social network: the SISa. model
 1 2 Emotions as infectious diseases in a large social network: the SISa model 3 4 Alison L. Hill, David G. Rand, Martin A. Nowak, Nicholas A. Christakis June 6, 2010 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Supplementary
1 2 Emotions as infectious diseases in a large social network: the SISa model 3 4 Alison L. Hill, David G. Rand, Martin A. Nowak, Nicholas A. Christakis June 6, 2010 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Supplementary
Dementia. Assessing Brain Damage. Mental Status Examination
 Dementia Assessing Brain Damage Mental status examination Information about current behavior and thought including orientation to reality, memory, and ability to follow instructions Neuropsychological
Dementia Assessing Brain Damage Mental status examination Information about current behavior and thought including orientation to reality, memory, and ability to follow instructions Neuropsychological
ADULT HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE
 ADULT HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Date: Full Name: Date of Birth: If applicable, please complete the following: Partner s Name: Partner s Age: Partner s Occupation: IF YOU HAVE CHILDREN PLEASE LIST THEIR NAMES
ADULT HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Date: Full Name: Date of Birth: If applicable, please complete the following: Partner s Name: Partner s Age: Partner s Occupation: IF YOU HAVE CHILDREN PLEASE LIST THEIR NAMES
ADULT History Form (To be filled out by the person seeking treatment)
 1 ADULT History Form (To be filled out by the person seeking treatment) Client s Name Date: SS# - - DOB: / / Age: Person completing this form: Client Other: (give name) Who referred you to Namsate Counseling?
1 ADULT History Form (To be filled out by the person seeking treatment) Client s Name Date: SS# - - DOB: / / Age: Person completing this form: Client Other: (give name) Who referred you to Namsate Counseling?
The New Mexico Refugee Symptom Checklist-121 (NMRSCL-121)
 The New Mexico Refugee Symptom Checklist-121 (NMRSCL-121) Michael Hollifield, MD 2007 New Mexico Refugee Symptom Checklist-121 Instructions: Using the scale beside each symptom, please indicate the degree
The New Mexico Refugee Symptom Checklist-121 (NMRSCL-121) Michael Hollifield, MD 2007 New Mexico Refugee Symptom Checklist-121 Instructions: Using the scale beside each symptom, please indicate the degree
MO DRI-2 Instructions We realize this is a difficult time for you. Nevertheless, we need more information so we can better understand your situation.
 MO DRI-2 Instructions We realize this is a difficult time for you. Nevertheless, we need more information so we can better understand your situation. All questions in this questionnaire should be answered.
MO DRI-2 Instructions We realize this is a difficult time for you. Nevertheless, we need more information so we can better understand your situation. All questions in this questionnaire should be answered.
"LEAD EXPOSURE IN GENERAL INDUSTRY"
 PRESENTER'S GUIDE "LEAD EXPOSURE IN GENERAL INDUSTRY" Training For THE OSHA LEAD STANDARD Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR
PRESENTER'S GUIDE "LEAD EXPOSURE IN GENERAL INDUSTRY" Training For THE OSHA LEAD STANDARD Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR
How does cannabis affect my work performance?
 How does cannabis affect my work performance? How does cannabis affect my work performance? Driving skills and ability to operate machinery Using cannabis negatively affects your balance, coordination,
How does cannabis affect my work performance? How does cannabis affect my work performance? Driving skills and ability to operate machinery Using cannabis negatively affects your balance, coordination,
DEPRESSION. There are a couple of kinds, or forms. The most common are major depression and dysthymic disorder.
 DEPRESSION OBJECTIVES: At the end of this class, you will be able to: 1.list and describe several kinds of depression, 2.discuss the signs of depression, and 3.relate the treatment of depression. INTRODUCTION
DEPRESSION OBJECTIVES: At the end of this class, you will be able to: 1.list and describe several kinds of depression, 2.discuss the signs of depression, and 3.relate the treatment of depression. INTRODUCTION
Previous Study Return to List Next Study
 A service of the U.S. National Institutes of Health Trial record 1 of 1 for: 42603ATT3013 Previous Study Return to List Next Study A Study to Evaluate Effectiveness and Safety of Prolonged Release OROS
A service of the U.S. National Institutes of Health Trial record 1 of 1 for: 42603ATT3013 Previous Study Return to List Next Study A Study to Evaluate Effectiveness and Safety of Prolonged Release OROS
Medications and the I/DD Population
 Medications and the I/DD Population A Supplemental Document to Session 4 in Webinar Series ADR Symptoms that Mimic Age Related/Associated Changes and Diseases Biological Changes Impaired senses Cardiovascular
Medications and the I/DD Population A Supplemental Document to Session 4 in Webinar Series ADR Symptoms that Mimic Age Related/Associated Changes and Diseases Biological Changes Impaired senses Cardiovascular
Major Depression Major Depression
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 17 Mood Disorders Major Depression Major Depression Characterized by a change in several aspects of a person s life and emotional state
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 17 Mood Disorders Major Depression Major Depression Characterized by a change in several aspects of a person s life and emotional state
Non-prescription Drugs. Wasted Youth
 Non-prescription Drugs Wasted Youth Marijuana (Cannabis) Short-Term Effects Using cannabis will probably make you feel more relaxed, free and open. If you smoke cannabis, you will probably feel the high
Non-prescription Drugs Wasted Youth Marijuana (Cannabis) Short-Term Effects Using cannabis will probably make you feel more relaxed, free and open. If you smoke cannabis, you will probably feel the high
Mental Health: Subjective evaluation of overall quality of life (QOL) Happiness, life satisfaction, morale, trait effect, etc. Quality of Life (QOL)
 Mental Health: Subjective evaluation of overall quality of life (QOL) Happiness, life satisfaction, morale, trait effect, etc. Quality of Life (QOL) Multidimensional concept Includes: Physical health Cognitive
Mental Health: Subjective evaluation of overall quality of life (QOL) Happiness, life satisfaction, morale, trait effect, etc. Quality of Life (QOL) Multidimensional concept Includes: Physical health Cognitive
Seek, Test, Treat and Retain for Vulnerable Populations: Data Harmonization Measure
 Seek, Test, Treat and Retain for Vulnerable Populations: Measure MENTAL HEALTH Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) Reference: Radloff, L.S. (1977). The CES-D Scale: a self-report
Seek, Test, Treat and Retain for Vulnerable Populations: Measure MENTAL HEALTH Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D) Reference: Radloff, L.S. (1977). The CES-D Scale: a self-report
8/22/2016. Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition. Theories: Anxiety Disorders. Theories: Anxiety Disorders (cont'd)
 Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 18 Anxiety Disorders Theories: Anxiety Disorders Biological changes in the brain Noradrenergic system is sensitive to norepinephrine;
Contemporary Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing Third Edition CHAPTER 18 Anxiety Disorders Theories: Anxiety Disorders Biological changes in the brain Noradrenergic system is sensitive to norepinephrine;
PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE
 PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE Personal Information Date Name Date of Birth Age Height Weight Address City State Zip Home Phone Cell phone Work phone E-mail address SSN: - - Medical History - you must enter information
PATIENT QUESTIONNAIRE Personal Information Date Name Date of Birth Age Height Weight Address City State Zip Home Phone Cell phone Work phone E-mail address SSN: - - Medical History - you must enter information
Case Study Mental Evaluation
 Case Study Mental Evaluation Facts Service: 3/65 11/69 8/06 Regional Office (RO) granted service connection (S/C) for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) at 30% from 3/06 7/07 Statement of Case (SOC)
Case Study Mental Evaluation Facts Service: 3/65 11/69 8/06 Regional Office (RO) granted service connection (S/C) for posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) at 30% from 3/06 7/07 Statement of Case (SOC)
Depression: More than just the blues
 Depression: More than just the blues August 2011 Knowing When to Get Help Is it depression? How do you know if you re depressed? That s a good question! Depression can be a byproduct of stress and anxiety.
Depression: More than just the blues August 2011 Knowing When to Get Help Is it depression? How do you know if you re depressed? That s a good question! Depression can be a byproduct of stress and anxiety.
A Guide to Mental Disorders
 A Guide to Mental Disorders Objectives 1. Identify at least 5 mental illnesses. 2. Describe the warning signs of various mental illnesses. 3. Share ways to promote mental health. Affective Disorders *These
A Guide to Mental Disorders Objectives 1. Identify at least 5 mental illnesses. 2. Describe the warning signs of various mental illnesses. 3. Share ways to promote mental health. Affective Disorders *These
MINOR TRANQUILIZERS CHAPTER TWO : MINOR TRANQUILIZERS
 MINOR TRANQUILIZERS 76. The term 'minor tranquilizers' was introduced into the scientific literature in the 1950s to distinguish the medicines prescribed to reduce anxiety and tension from the major tranquillizers,
MINOR TRANQUILIZERS 76. The term 'minor tranquilizers' was introduced into the scientific literature in the 1950s to distinguish the medicines prescribed to reduce anxiety and tension from the major tranquillizers,
MINDFUL WELLNESS CENTER, PLLC
 PATIENT HISTORY NAME DATE PLEASE TAKE YOUR TIME AND COMPLETE THE ENTIRE FORM. You may use the back if needed for more explanation. Identifying Information: Date of Birth: Age: Sex: Place of Birth: Religion:
PATIENT HISTORY NAME DATE PLEASE TAKE YOUR TIME AND COMPLETE THE ENTIRE FORM. You may use the back if needed for more explanation. Identifying Information: Date of Birth: Age: Sex: Place of Birth: Religion:
Psychological First Aid: Overview Helping Others in Times of Stress
 Welcome Psychological First Aid: Overview Helping Others in Times of Stress February 2012 Instructor Anita Laffey, LCSW Licensed Clinical Social Worker, retired Red Cross disaster volunteer since 2005
Welcome Psychological First Aid: Overview Helping Others in Times of Stress February 2012 Instructor Anita Laffey, LCSW Licensed Clinical Social Worker, retired Red Cross disaster volunteer since 2005
A Healthy Brain. An Injured Brain
 A Healthy Brain Before we can understand what happens when a brain is injured, we must realize what a healthy brain is made of and what it does. The brain is enclosed inside the skull. The skull acts as
A Healthy Brain Before we can understand what happens when a brain is injured, we must realize what a healthy brain is made of and what it does. The brain is enclosed inside the skull. The skull acts as
Expiry Date: yyyy-mm-dd Lot # XXXX-XXX This product is not to be sold or applied after the expiry date above.
 GROUP 1B INSECTICIDE UBG MALATHION GRAIN PROTECTOR DUST COMMERCIAL INSECTICIDE READ THE LABEL BEFORE USING FOR USE ON STORED GRAINS Protects against damage from Confused Flour Beetle, Granary Weevil, Saw-toothed
GROUP 1B INSECTICIDE UBG MALATHION GRAIN PROTECTOR DUST COMMERCIAL INSECTICIDE READ THE LABEL BEFORE USING FOR USE ON STORED GRAINS Protects against damage from Confused Flour Beetle, Granary Weevil, Saw-toothed
Excerpted From "Staying Sober" By: Terence T. Gorski
 Excerpted From "Staying Sober" By: Terence T. Gorski With additions by: Lee Jamison When most people think about alcoholism or drug addiction they think only of the alcohol/drug-based symptoms and forget
Excerpted From "Staying Sober" By: Terence T. Gorski With additions by: Lee Jamison When most people think about alcoholism or drug addiction they think only of the alcohol/drug-based symptoms and forget
New Service Provider Provider Type Provider Name Phone Ext
 Substance Abuse Adult Assessment AST022 Assessment Information Assessment Number Assessment Date Assessment Type Contact Type Assessment Site Referred by Client Issue Presenting Problem Expectations Service
Substance Abuse Adult Assessment AST022 Assessment Information Assessment Number Assessment Date Assessment Type Contact Type Assessment Site Referred by Client Issue Presenting Problem Expectations Service
COUNSELING ASSESSMENT REFERRAL AND BACKGROUND INFORMATION (Adult Form) cell telephones/fax #s/ addresses: (Spouse): (Emergency Contact):
 Joanna C. Ioannides, LCSW *Lowry Counseling, LLC *7581 E. Academy Blvd. Ste 209 * Denver, CO 80230*Ph. (720)319-7319 Fax (303)379-4607* counseldenver@aol.com* COUNSELING ASSESSMENT REFERRAL AND BACKGROUND
Joanna C. Ioannides, LCSW *Lowry Counseling, LLC *7581 E. Academy Blvd. Ste 209 * Denver, CO 80230*Ph. (720)319-7319 Fax (303)379-4607* counseldenver@aol.com* COUNSELING ASSESSMENT REFERRAL AND BACKGROUND
Supplementary Materials:
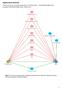 Supplementary Materials: Depression and risk of unintentional injury in rural communities a longitudinal analysis of the Australian Rural Mental Health Study (Inder at al.) Figure S1. Directed acyclic
Supplementary Materials: Depression and risk of unintentional injury in rural communities a longitudinal analysis of the Australian Rural Mental Health Study (Inder at al.) Figure S1. Directed acyclic
TIP 48 MANAGING DEPRESSIVE SYMPTOMS IN SUBSTANCE ABUSE CLIENTS DURING EARLY RECOVERY
 MANAGING DEPRESSIVE SYMPTOMS IN SUBSTANCE ABUSE CLIENTS DURING EARLY RECOVERY Presented by: William L. Mock, Ph.D., LISW,LICDC, SAP Professional Training Associates Inc North Ridgeville, Ohio 1 (216) 299-9506
MANAGING DEPRESSIVE SYMPTOMS IN SUBSTANCE ABUSE CLIENTS DURING EARLY RECOVERY Presented by: William L. Mock, Ph.D., LISW,LICDC, SAP Professional Training Associates Inc North Ridgeville, Ohio 1 (216) 299-9506
SLEEP QUESTIONNAIRE. Name: Sex: Age: Date: DOB: / / SSN: - - Address: Referring Physician: Family Physician: Height: Weight: Neck Size: Phone:
 SLEEP QUESTIONNAIRE Name: Sex: Age: Date: DOB: / / SSN: - - Address: Referring Physician: Family Physician: Height: Weight: Neck Size: Phone: Please fill in the blanks, and check appropriate areas on the
SLEEP QUESTIONNAIRE Name: Sex: Age: Date: DOB: / / SSN: - - Address: Referring Physician: Family Physician: Height: Weight: Neck Size: Phone: Please fill in the blanks, and check appropriate areas on the
WakeMed Health & Hospitals
 WakeMed Health & Hospitals The Power to Heal. A Passion for Care. WakeMed Health & Hospitals Raleigh, North Carolina Traumatic Brain Injury December 4th, 2012 Laurie Leach, Ph.D., FACPN Director of Neuropsychology
WakeMed Health & Hospitals The Power to Heal. A Passion for Care. WakeMed Health & Hospitals Raleigh, North Carolina Traumatic Brain Injury December 4th, 2012 Laurie Leach, Ph.D., FACPN Director of Neuropsychology
11/1/2013. Depression affects approximately 350 million people worldwide, and is the leading cause of disability globally (WHO, 2012)
 Depression affects approximately 350 million people worldwide, and is the leading cause of disability globally (WHO, 2012) College of Arts & Sciences Department of Sociology State University Of New York
Depression affects approximately 350 million people worldwide, and is the leading cause of disability globally (WHO, 2012) College of Arts & Sciences Department of Sociology State University Of New York
Mini Research Paper: Traumatic Brain Injury. Allison M McGee. Salt Lake Community College
 Running Head: Mini Research Paper: Traumatic Brain Injury Mini Research Paper: Traumatic Brain Injury Allison M McGee Salt Lake Community College Abstract A Traumatic Brain Injury (also known as a TBI)
Running Head: Mini Research Paper: Traumatic Brain Injury Mini Research Paper: Traumatic Brain Injury Allison M McGee Salt Lake Community College Abstract A Traumatic Brain Injury (also known as a TBI)
Affective or Mood Disorders. Dr. Alia Shatanawi March 12, 2018
 Affective or Mood Disorders Dr. Alia Shatanawi March 12, 2018 Affective or Mood Disorders Reactive Depression. Secondary: Medical Neurological Drugs Major (Endogenous) Depression = Unipolar: Depressed
Affective or Mood Disorders Dr. Alia Shatanawi March 12, 2018 Affective or Mood Disorders Reactive Depression. Secondary: Medical Neurological Drugs Major (Endogenous) Depression = Unipolar: Depressed
Ashok K. Modh, M.D., F.C.C.P. Naishadh K. Mandaliya, M.D., F.C.C.P. Jerges J. Cardona, M.D. Nirav B. Patel, M.D.
 Ashok K. Modh, M.D., F.C.C.P. Naishadh K. Mandaliya, M.D., F.C.C.P. Jerges J. Cardona, M.D. Nirav B. Patel, M.D. Dear, Your physician has requested that you be scheduled for a sleep study. Your appointment
Ashok K. Modh, M.D., F.C.C.P. Naishadh K. Mandaliya, M.D., F.C.C.P. Jerges J. Cardona, M.D. Nirav B. Patel, M.D. Dear, Your physician has requested that you be scheduled for a sleep study. Your appointment
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Rachel Glick, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Rachel Glick, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
SPRINGFIELD CLINIC S
 SPRINGFIELD CLINIC S HEAD INJURY MANAGEMENT GUIDE FOR PARENTS Given the complexities of concussion management, Springfield Clinic recognizes the importance of managing concussions on an individualized
SPRINGFIELD CLINIC S HEAD INJURY MANAGEMENT GUIDE FOR PARENTS Given the complexities of concussion management, Springfield Clinic recognizes the importance of managing concussions on an individualized
Neonatal Neurobehavioral Impacts of Iodine Insufficiency and Pesticide Exposures
 Neonatal Neurobehavioral Impacts of Iodine Insufficiency and Pesticide Exposures Susan Woskie, Pornpimol Kongtip, Noppanun Nankongnab, Wiroj Thanasanpaiboon, Napaporn Kiatdamrong, Nantha Charoonrungsirikul
Neonatal Neurobehavioral Impacts of Iodine Insufficiency and Pesticide Exposures Susan Woskie, Pornpimol Kongtip, Noppanun Nankongnab, Wiroj Thanasanpaiboon, Napaporn Kiatdamrong, Nantha Charoonrungsirikul
Dementia ALI ABBAS ASGHAR-ALI, MD STAFF PSYCHIATRIST MICHAEL E. DEBAKEY VA MEDICAL CENTER ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
 Dementia ALI ABBAS ASGHAR-ALI, MD STAFF PSYCHIATRIST MICHAEL E. DEBAKEY VA MEDICAL CENTER ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE Objectives At the conclusion of the session, participants will be
Dementia ALI ABBAS ASGHAR-ALI, MD STAFF PSYCHIATRIST MICHAEL E. DEBAKEY VA MEDICAL CENTER ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE Objectives At the conclusion of the session, participants will be
Research Article A Fatal Waterborne Outbreak of Pesticide Poisoning Caused by Damaged Pipelines, Sindhikela, Bolangir, Orissa, India, 2008
 Toxicology Volume 2009, Article ID 692496, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/692496 Research Article A Fatal Waterborne Outbreak of Pesticide Poisoning Caused by Damaged Pipelines, Sindhikela, Bolangir, Orissa,
Toxicology Volume 2009, Article ID 692496, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/692496 Research Article A Fatal Waterborne Outbreak of Pesticide Poisoning Caused by Damaged Pipelines, Sindhikela, Bolangir, Orissa,
Disaster Psychology. CERT Basic Training Unit 7
 Disaster Psychology Unit 7 Unit Objectives Describe disaster and post-disaster emotional environment for victims and rescuers Describe steps rescuers can take to relieve their own stress and that of other
Disaster Psychology Unit 7 Unit Objectives Describe disaster and post-disaster emotional environment for victims and rescuers Describe steps rescuers can take to relieve their own stress and that of other
Preventing Traumatic Brain Injury in Older Adults. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
 Preventing Traumatic Brain Injury in Older Adults U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Most of us worry about staying safe, healthy, and independent as
Preventing Traumatic Brain Injury in Older Adults U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Most of us worry about staying safe, healthy, and independent as
Pesticide Use and Safety Master Gardener Course Lydia Clayton February 26, 2013
 Pesticide Use and Safety 2013 Master Gardener Course Lydia Clayton February 26, 2013 TOXICITY VS HAZARD Are natural organic pesticides safer than synthetic pesticides?? TOXICITY VS HAZARD TOXICITY innate
Pesticide Use and Safety 2013 Master Gardener Course Lydia Clayton February 26, 2013 TOXICITY VS HAZARD Are natural organic pesticides safer than synthetic pesticides?? TOXICITY VS HAZARD TOXICITY innate
Material Safety Data Sheet
 Material Safety Data Sheet Version 3.0 Revision Date 10/21/2009 Print Date 06/23/2011 1. PRODUCT AND COMPANY IDENTIFICATION Product name : Lithium chloride/potassium chloride eutectic Product Number :
Material Safety Data Sheet Version 3.0 Revision Date 10/21/2009 Print Date 06/23/2011 1. PRODUCT AND COMPANY IDENTIFICATION Product name : Lithium chloride/potassium chloride eutectic Product Number :
Mental Health and Suicide Prevention: What Everyone Should Know
 Mental Health and Suicide Prevention: What Everyone Should Know OUTLINE Mental Health and Suicide How big is this issue? Mental Illness Depression Schizophrenia Suicide Who is at risk? Warning signs Suicide
Mental Health and Suicide Prevention: What Everyone Should Know OUTLINE Mental Health and Suicide How big is this issue? Mental Illness Depression Schizophrenia Suicide Who is at risk? Warning signs Suicide
Dr. Adeniyi Mofoluwake and Stacy Kramer
 Dr. Adeniyi Mofoluwake and Stacy Kramer Definition of Alzheimer s Disease Alzheimer's disease is a neurological disorder in which insidious onset of the death of brain cells causes memory loss and cognitive
Dr. Adeniyi Mofoluwake and Stacy Kramer Definition of Alzheimer s Disease Alzheimer's disease is a neurological disorder in which insidious onset of the death of brain cells causes memory loss and cognitive
12. I can be easily annoyed and angered while driving. 13. I am concerned about my drug use. 14. I have used my cell phone while driving.
 OK DRI-2 Instructions We realize this is a difficult time for you. Nevertheless, we need more information so we can better understand your situation. All questions in this questionnaire should be answered.
OK DRI-2 Instructions We realize this is a difficult time for you. Nevertheless, we need more information so we can better understand your situation. All questions in this questionnaire should be answered.
SMOKING HISTORY INSTRUCTIONS
 INSTRUCTIONS SMOKING HISTORY Please answer the following questions based on your experiences with smoking. Each question allows you to choose from several alternatives. Please select one of the alternatives
INSTRUCTIONS SMOKING HISTORY Please answer the following questions based on your experiences with smoking. Each question allows you to choose from several alternatives. Please select one of the alternatives
SURREY FIRE SERVICE CRITICAL INCIDENT STRESS MANAGEMENT TEAM
 CISM DEFUSING/ DEBRIEFING HANDOUTS Common Signs and Symptoms During a CIS Event You have experienced a traumatic event, or a critical incident. Even though the event may be over, you may now be experiencing,
CISM DEFUSING/ DEBRIEFING HANDOUTS Common Signs and Symptoms During a CIS Event You have experienced a traumatic event, or a critical incident. Even though the event may be over, you may now be experiencing,
De-stress from Deployment: Handling Stress after Deployment
 De-stress from Deployment: Handling Stress after Deployment Please download the De-Stress from Deployment: Handling Stress after Deployment Worksheet and Handouts before beginning this class. 1 There are
De-stress from Deployment: Handling Stress after Deployment Please download the De-Stress from Deployment: Handling Stress after Deployment Worksheet and Handouts before beginning this class. 1 There are
