Jun SHIGEMI, Yoshio MINO and Toshihide TSUDA. Journal of Occupational Health
|
|
|
- Ralf Eaton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Occup Health 2000; 42: Journal of Occupational Health Stability of Factor Structure and Correlation with Perceived Job Stress in General Health Questionnaire: a Three-wave Survey over One Year in Japanese Workers Jun SHIGEMI, Yoshio MINO and Toshihide TSUDA Department of Hygiene and Preventive Medicine, Okayama University Medical School Abstract: Stability of Factor Structure and Correlation with Perceived Job Stress in General Health Questionnaire: a Three-wave Survey over One Year in Japanese Workers: Jun SHIGEMI, et al. Department of Hygiene and Preventive Medicine, Okayama University Medical School A crosssectional study was conducted to examine psychological symptoms and job stress in Japanese workers. To assess the stability of the relationship between the parameters for perceived job stress and mental health, two additional surveys were carried out six months and one year later. The surveys included demographic questions, the General Health Questionnaire (GHQ), and questions relating to perceived job stress to measure the worker s mental health and job stress. Factor analyses were conducted to clarify the factor structure of mental health. As for the GHQ, the 6 dominant factors were interpreted. These factors involved Anxiety and depression, Severe depression, Lack of interpersonal network or social support, Poor social activity, Insomnia, and Lack of a positive attitude. This structure was stable in the 2 follow up surveys. A multiple regression analysis was used to examine the relationship between extracted factors of the GHQ and job stress. The analysis showed that the factor Anxiety and depression had a significantly stable relationship with Too much responsibility at work and Cannot keep up with new technology. (J Occup Health 2000; 42: ) Key words: Perceived job stress, Mental health, GHQ, Factor analysis, Multiple regression analysis With advances in computer technology and office and factory automation, the type of labor that many workers engage in has changed significantly, often from Received Jan 11, 2000; Accepted Aug 5, 2000 Correspondence to: J. Shigemi, Department of Hygiene and Preventive Medicine, Okayama University Medical School, Shikata-cho, Okayama , Japan physically-oriented to mentally-oriented tasks. In Japan, the proportion of workers who had great anxiety or perceived their job as difficult increased from 51% in 1982 to 57% in ). The workplace today is therefore widely thought to be more emotionally and mentally stressful than the typical workplace hither to. Several studies have examined the relationship between job stress and mental health 2 9). The mental health state and job stress of workers may have various aspects. It is not enough to estimate the mental health state and job stress solely by the total score in a questionnaire but there have been few studies 10, 11) in Japan that investigated these factors which clarify the mental and emotional state of workers. Moreover, the stability of the factor structure has not been investigated. It was reported that the total score in psychometric tests including the GHQ (General Health Questionnaire) 12) was decreased after a retest of the questionnaire 13, 14). Therefore, the factor structure of the GHQ might have changed due to the retest effect of the questionnaire. Incidentally, in our previous study, specific perceived job stress as work overload was closely related to mental ill health in both a cross-sectional 2) and a cohort 8) study. In addition, an unsuitable job was a significantly related to mental health in a nested casecontrol 3) in a cohort and a longitudinal 4) study. Other studies 15, 16) confirmed an adverse effect of job overload on mental health. On the other hand, recovery from mental ill health 9) was observed in 48.7% after the first 6 months and in 66.1% after 1 yr. Moreover, perceived job stress such as Too much responsibility at work had a significant association with recovery. The working conditions of workers were therefore psychologically dynamic. In addition, Cohen et al. 17), in a book on measuring stress reported as follow. Because of the fallibility of memory, the duration of stressors measured in self-report questionnaires or in informants reports are not very reliable for sterssors or stressors that have been resolved prior to the data collection period. Therefore, when self-report questionnaires are used, an investigator
2 Jun SHIGEMI, et al.: The Factor Structure of Mental Health and Stability 285 should use multiple measurement periods with a short interval between measurements. Concerning about the questionnaire on perceived job stress, needless to say we are afraid that the GHQ as a self-report questionnaire might be biased as to answer on characteristics of the psychological condition, the tendency of thought and behavior, and memory in only a cross-sectional survey. As to the above content, no specific perceived job stress which has a stable relationship to extracted and interpreted mental ill health factors has been found. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the stability of the mental ill health factor structures from three crosssectional surveys at certain intervals, and to clarify the stable relationship between extracted mental health and job stress factors. Materials and Methods The study group consisted of 782 employees of a middle-sized electronics company in Okayama Prefecture, Japan. We conducted 3 cross-sectional surveys of the employees job stress and mental health at six-month intervals to examine the stability of the answers. Eligible workers were those who answered all of three cross-sectional surveys satisfactorily. The survey was self-administered and the questionnaire was composed of the 30-item Japanese version of the General Health Questionnaire (GHQ) 12) and a 14-item questionnaire about perceived job stress 18), which mainly measured psychological work overload with additional questions about the worker s demographics. The GHQ is a standard screening questionnaire for psychiatric morbidity and was used as the parameters of the worker s mental health in our study. The original English version of the GHQ was already validated by Goldberg and other researchers 19 21). The Japanese version of the 30-item GHQ was validated by Kitamura et al. 22) In this study, the GHQ was used as a mental health parameter and treated as a continuous variable. The response rates of the eligible workers were 69.1% (n=540). The demographic samples who were answered satisfactorily in the three surveys, are shown in Table 1. The demographic results were not significantly different for sex, age, marital status or departments among the three cross-sectional surveys. In this company, there were various workplace departments as shown in Table 1. The female employees mainly worked in the production department, but males worked in various departments. In our previous studies 2, 8, 9), the same data sources were used. The GHQ scores were assessed by the Lickert scoring method 12) instead of the GHQ method to avoid loss of information and a distorted correlation matrix due to a 0/1 value. The perceived job stress items were assessed by a three point Lickert type rating method 14) from the same method as in the GHQ. The mean total scores of the GHQ were compared in Table 1. Demographics of eligible workers who participated in our surveys Sex Male 250 Female 290 Total 540 Age 29yr yr yr yr 20 Total 540 Marital status Never married 222 Married 304 Separated or Divorced 14 Total 540 Departments Business 7 Production 271 Technology and Development 90 Investigation and Inspection 44 Personnel 8 Management 120 Total 540 Table 2. Total GHQ scores obtained by the Lickert type rating method Mean Standard deviation First survey Second survey Third survey three cross-sectional surveys. Total GHQ scores in the second and third surveys were improved by 0.6 points in the second survey and 0.9 points in the third survey, compared to that of the first survey, as shown in Table 2 but these differences were not significant in a t-test. These results did not represent a retest effect of the GHQ 13). We performed factor analyses to clarify the factor structure of the GHQ scores and checked the stability of their factor structure in three different questionnaires. To check the internal consistency and reliability of the GHQ and the questionnaire on perceived job stress, Cronbach s alpha coefficients for both of these questionnaires were calculated. Incidentally, in our study the distribution of the GHQ score for each item could be approximated to normal distribution. In addition, we thought that there might be a relationship between perceived job stress and GHQ factor scores. Therefore, the method of extraction was a maximum likelihood estimation with promax rotation (oblique rotation). The eigenvalues for the extracted factors were more than 1.0. The Kaiser-Meyer-
3 286 J Occup Health, Vol. 42, 2000 Olkin measure of sampling adequacy 23), which is a measure to compare the observed correlation coefficient with the partial correlation coeffcient, was used as a reliable measure. A highly reliable value was obtained by factor analysis. Since a worker s mental health has various aspects, a multiple regression analysis was performed to determine the interrelationship between the extracted factor score of the GHQ and the Lickert type rating response of the perceived job stress questions which were adjusted for sex, age and departments as potential confounders. The individual GHQ factor scores for the two groups were compared: a positive answer group regarding perceived job stress as always present or sometimes present and a negative answer group as absent. The significance was ascertained by t-tests of these two groups. In the multiple regression analysis, the continuous value of the GHQ factor score was used as the dependent variable and the significant items of perceived job stress in 2-tailed t-tests as the predictors or independent variables. These statistical analyses were carried out with the SPSS-Windows computer program. Results The Cronbach alpha coefficients from the perceived job stress questionnaires were in the first survey, in the second, and in the third and those of the GHQ were 0.905, 0.912, and 0.918, respectively, so that both the GHQ and the perceived job stress questionnaires were highly reliable. The Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin value for sampling adequacy in the GHQ were 0.90, 0.91, and 0.92 respectively. The values were sufficient to perform a factor analysis based on the questionnaires. In the GHQ, according to the maximum likelihood methods, eigenvalues of the first 6 or 7 factors were greater than unity but after promax rotation, the smallest 7th factors had less than a factor loading. These factors were therefore difficult to interpret. In this factor analyses, 6 factors could be interpreted. In the three surveys, they accounted for 54.7%, 56.3%, and 59.9% of the total variance, respectively. Table 3 indicates the promax rotated maximum factor loading of the GHQ items in the three surveys. The factors labeled in this study are as follows: Factor 1: Because this factor included some symptoms of anxiety and depression, we labeled this factor Anxiety and depression. Factor 2: Because this factor included such items as life entirely hopeless, life not worth living, and nervous too much, this factor was interpreted as Severe depression. Factor 3: This factor included the items able to feel warmth, and easy to get on with others, and was therefore labeled Lack of interpersonal network or social support, but in the second survey this factor was extracted as the 4th factor. Factor 4: There was high loading on items such as able to concentrate, mentally alert and worry, and doing things well. Therefore, this factor was interpreted as Poor social activity. Factor 5: This factor had high loading on items such as lost much sleep over worry, and been having restless, disturbed night. Therefore, this factor was interpreted as Insomnia. Factor 6: This factor had continuously high loading on such items as (not) feeling hopeful, and been feeling reasonably (un) happy. We interpreted this as Lack of positive attitude. Means and standard deviations of factor scores in all three surveys are shown in Table 4. Incidentally, some items in the Japanese version of the 30-item GHQ such as feeling unhappy and depressed, and losing confidence, which had maximum factor loading in the factor Anxiety and depression, showed high factor loading in the factor Severe depression as shown in Table 3. In only the first survey, the 7th factor was extracted with high factor loading in such as items: couldn t overcome your difficulties, thinking of yourself as a worthless person, and life is entirely hopeless as shown in Table 3, but this factor Depression was involved in the factors Anxiety and depression and Severe depression. Table 5 shows a person s correlations of factor scores for each extracted and interpreted factor in different crosssectional surveys. In the results, these factor scores for different periods were significantly associated with each other, and these results supported the stability of the factor structures in factor analyses. We also performed factor analyses on a 30-item GHQ by sex. The results were similar for both sexes. Next multiple regression analyses controlled by sex, age and workplace department were carried out to examine the relationship between the GHQ extracted factor score and the items on perceived job stress, as shown in Table 6. The first factor, which was interpreted as Anxiety and depression, had a positive relationship with the items too much responsibility, and cannot keep up with new technology in all the surveys. The second factor Severe depression had a consistently significant relationship with poor relationship with superiors, and cannot keep up with new technology. The third factor, Lack of interpersonal network or social support as a stress reaction, was significantly related to the item poor relationship with superiors in all the surveys. The fourth factor Poor social activity was significantly associated with the items too much trouble at work, and poor relationship with superiors in all surveys. The fifth factor Insomnia had a significant
4 Jun SHIGEMI, et al.: The Factor Structure of Mental Health and Stability 287 Table 3. Maximum likelihood method with promax rotation of the GHQ Items with factor loading First survey Second survey Third survey F1. Anxiety and depression 14. Felt constantly under strain? Felt you couldn t overcome your difficulties? Been taking things hard? Found everything getting on top of you? Been feeling unhappy and depressed? Been losing confidence in yourself? Been feeling nervous and strung-up all the time? Percentage accounting for total variance of factor % 29.3% 31.7% F2. Severe depression 22. Been feeling unhappy and depressed? Been losing confidence in yourself? Been thinking of yourself as a worthless person? Felt that life is entirely hopless? Felt that life isn t worth living? Found at times you couldn t do anything because your nerves were too bad? Percentage accounting for total variance of factor 2 8.8% 8.9% 9.8% F3. Lack of interpersonal network or social support 10. Been able to feel warmth and affection for those near to you? Been finding it easy to get on with other people? Felt that you are playing a useful part in things? Percentage accounting for total variance of factor 3 6.1% 4.5% 6.1% F4. Poor social activity 1. Been able to concentrate on whatever you re doing? Been feeling mentally alert and wide awake? Been feeling full of energy? Felt on the whole you were doing things well? Percentage accounting for total variance of factor 4 4.6% 5.8% 4.4% F5. Insomnia 2. Lost much sleep over worry? Been having restless, disturbed nights? Percentage accounting for total variance of factor 5 4.0% 3.9% 3.9% F6. Loss of positive attitude 26. Been feeling hopeful about your own future? Been feeling reasonably happy, all things considered? Percentage accounting for total variance of factor 6 3.8% 3.8% 4.0% F7. Depression 15. Felt you couldn t overcome your difficulties? Been thinking of yourself as a worthless person? Felt that life is entirely hopeless? 0.345
5 288 J Occup Health, Vol. 42, 2000 Table 4. Means and standard deviations of factor scores in three cross-sectional surveys First survey Second survey Third survey Factor M SD M SD M SD Anxiety and depression Severe depression Lack of interpersonal network and social support Poor social activity Insomnia Lack of a positive attitude M: Mean. SD: Standard deviation. Table 5. Correlations of factor scores for each extracted and interpreted factor Factor First to second survey First to third survey Second to third survey Anxiety and depression 0.564** 0.486** 0.544** Severe depression 0.590** 0.577** 0.565** Lack of interpersonal network and social support 0.432** 0.415** 0.476** Poor social activity 0.329** 0.394** 0.470** Insomnia 0.426** 0.390** 0.442** Lack of a positive attitude 0.488** 0.482** 0.518** **p<0.01. relationship with too much trouble at work in all the surveys, but the sixth factor Lack of a positive attitude showed no significant relationship with perceived job stress. Discussion Karasek 24 26) reported that job stress could be separated into two factors, job demand and job decision latitude or job control. He explained that a high job demand and a low decision latitude state was most stressful. Our perceived job stress questionnaire was based on psychological work overload. This could be related to Karasek s job demand. In our cross-sectional surveys, 6 factors as described before were stably extracted and interpreted. In contrust to our hypothesis, total GHQ scores rating the Lickert method were not significantly changed by the retest effect. We focused on the factor structure of the GHQ in a worker s sample and extracted the first factor, Anxiety and depression. Huppert et al. 27) reported that the same factor was extracted in their survey of 6317 community residents, including workers. Iwata et al. 10) found the same factor of Anxiety (General dysphoria) in the 30 item GHQ survey of 2108 Japanese adult employees. In their study, the Severe depression factor was extracted as a separate factor. The results of our study agreed with that observation. With regard to the Severe depression factor, Nadaoka et al. 28) reported that a Depression factor was extracted in the same version of GHQ in Japan and supported our results. The Lack of interpersonal network or social support factor was involved in the Social dysfunction factor in their study 10, 27), but the factors Feeling of incompetence, low self-esteem, and Difficulty in coping, dispirited described by Huppert et al. 27) could not be extracted in our study. As for the factor Poor social activity, this was not extracted and interpreted independently in other Japanese studies. Consequently, further study was required to confirm this factor in Japanese workers. The consistently extracted Insomnia factor was supported by Nadaoka s study 28). On the other hand, this factor was involved in the Anxiety factor in Iwata s study 10). The reason could be thought that Anxiety and Insomnia are closely related psychological symptom. However, the factor Loss of a positive attitude was extracted as in the study by Iwata et al. Iwata et al. 10) suggested that the Japanese tended to complain of Loss of a positive attitude, (not) hopeful and (not) happy, and that this tendency deteriorated the internal consistency of the scale. Therefore, the Japanese responses to two Loss of a positive attitude items might be an artifact on the GHQ-30 suggested by Iwata et al. 10) In our third survey, the proportion of 2 or 3 points in the Lickert
6 Jun SHIGEMI, et al.: The Factor Structure of Mental Health and Stability 289 Table 6. Multiple regression analyses in the factors of the General Health Questionnaire and items of perceived job stress First survey Second survey Third survey Standardized Standardized Standardized Beta (P) Beta (P) Beta (P) Factor 1 Anxiety and depression (dependent variable) 5. Too much trouble at work (0.000) (0.000) 6. Too much responsibility (0.004) (0.001) (0.000) 9. Feel pressed for time (0.000) 14. Cannot keep up with new technology (0.000) (0.000) (0.002) Adjusted R Square Factor 2 Severe depression (dependent variable) 1. Too much competition (0.024) 8. Poor relationship with superiors (0.007) (0.000) (0.000) 14. Cannot keep up with new technology (0.000) (0.000) Adjusted R Square Factor 3 Lack of interpersonal network or social support (dependent variable) 5. Too much trouble at work (0.000) (0.009) (0.000) 8. Poor relationship with superiors (0.003) (0.000) (0.000) 14. Cannot keep up with new technology (0.005) Adjusted R Square Factor 4 Poor social activity (dependent variable) 5. Too much trouble at work (0.000) (0.000) (0.000) 8. Poor relationship with superiors (0.014) (0.000) (0.005) Adjusted R Square Factor 5 Insomnia (dependent variable) 5. Too much trouble at work (0.016) (0.002) (0.001) Adjusted R Square method for these two items was 74.5% and 59.1%, respectively. It follows that the extraction of the factor Loss of a positive attitude in this study, might be explained by Iwata s suggestion, but in Nadaoka s study 28), the same factor which he interpreted as Unhappiness was extracted. In addition, in our study, this factor was stably extracted over three cross-sectional studies. Therefore, although this factor might be an artifact, it could be an independent factor indicating psychological distress in Japanese workers. Goldberg 29) asserted that there was a common language explaining psychological symptoms beyond the walls of cultures. Although there may be a variety of factors explaining psychological symptoms extracted among different races, cultures, and generations, as for anxiety and depression, our present results supported his hypothesis. The relationship between the extracted factor score of the GHQ and perceived job stress was examined by multiple regression analysis. The results suggest that the items too much responsibility, and cannot keep up with new technology have a consistent significant relationship to Anxiety and depression. These two items are representative of stress in the workplace, which account for the main psychological symptoms. To prevent the anxious and depressive state, reduction of these stressors might be helpful. According to our previous study 9) for recovery of mental ill health, the item Too much responsibility was an important item to recover. With regard to Severe depression, an item in
7 290 J Occup Health, Vol. 42, 2000 perceived job stress, Poor relationship with superiors had a significant stable association with this factor. This result confirmed that social support was important in preventing depression in workers. This item in perceived job stress could be closely related to Interpersonal conflict, one of the job stressors in the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) hypothesis 30, 31). It was related to Lack of interpersonal network or social support in all the surveys. It was reported that social support and a social network were important factors in preventing diseases which may lead to death 32). Moreover, Karasek 33) reported that a low decision latitude and low social support state were stressful, and this environment was related to psychological distress, especially depression. In addition, Landsbergis et al. 34) reported that social support accounted for significant additional variance perdicters for anger, anxiety and depression as in expanded Karasek s model 33). On the other hand, Bourbonnais et al. 35) reported that social support did not modify the association between job strain and psychological distress. It follows that multiple coefficients of determination were small in the factor in which this item including social support had a significant relationship. Consequently, further study is required to clarify the effect of social support on mental health. The factor Poor social activity was significantly related to the items: Too much trouble, and Poor relationship with superiors. Because these items of perceived job stress had high odds ratios in relation to mental health in our previous studies 2, 8) these results were consistent. The factor Insomnia had a stable relationship to the item Too much trouble at work. This item might be specifically cause sleep disturbance. The factor Lack of a positive attitude did not have a significant relationship with perceived job stress continuously. Generaly speaking Japanese workers have a tendency to not express their feelings according to Iwata 10). This might be one reason for our results. With regard to the results in Tables 5 and 6, we thought that although factors 2, 3 and 4 might be unstable in the dynamic working conditions, these factor structures were stable throughout our three cross-sectional surveys instead of the measuring bias in self-report questionnaires. These results suggest that the vulnerability of workers to job stressors was stable in dynamic working conditions rather than a fixed effect of job stressors chronically causing psychological distress in the specific workers. There are the limitations of this study. The extracted factor scores were used as dependent variables in the multiple regression analyses, but we could not guarantee that the variances of these extracted factor scores were dominant. Although we used the GHQ as a measure of mental health, it has not been validated in Japanese workers. Therefore, further studies are required to compensate for these limitations. References 1) Shimizu Y, Makino S, Takata T. Employee stress status during the past decade ( ) based on a nationwide survey conducted by the Ministry of Labour in Japan. Ind Health 1997; 35: ) Shigemi J, Mino Y, Tsuda T, Babazono A, Aoyama H. The relationship between job stress and Mental Health at work. Ind Health 1997; 35: ) Kawakami N, Araki S, Kawashima M. Effects of job stress on occurance of major depression in Japanese industry: A case control study nested in a cohort study. J Occup Med 1990; 32: ) Kawakami N, Haratani T, Araki S. Effects of perceived job stress on depressive symptoms in blue-collar workers of an electrical factory in Japan. Scand J Work Environ Health 1992; 18: ) Mino Y, Tsuda T, Babazono A, et al. Depressive states in workers using computers. Environ Res 1993; 63: ) Cooper CL, Rout U, Faragher B. Mental health, job satisfaction, and job stress among general practitioners. Br Med J 1989; 298: ) Sutherland VJ, Cooper CL. Job stress, satisfaction, and mental health among general practitioners before and after introduction of new contract. Br Med J 1992; 304: ) Mino Y, Shigemi J, Tsuda T, Yasuda N, Bebbington P. Perceived job stress and mental health in precision machine workers of Japan: a 2 year cohort study. Occup Environ Med 1999; 56: ) Mino Y, Shigemi J, Tsuda T, Yasuda N, Babazono A, Bebbington P. Recovery from mental ill health in an occupational setting: A cohort study in Japan. J Occup Health 2000; 42: ) Iwata N, Uno B, Suzuki T. Psychometric properties of the 30-item version General Health Questionnaire in Japanese. Jpn J Psychiatry Neurol 1994; 48: ) Kawakami N, Fujigaki Y. Reliability and validity of Japanese version of Job Content Questionnaire: replication and extension in computer company employees. Ind Health 1996; 34: ) Nakagawa Y, Daibou I. Japanese version of the General Health Questionnaire. Tokyo: Nihon Bunka Kagakusha, 1985 (in Japanese). 13) Henderson S, Byene DG, Duncan-Jones P. Neurosis and the Social Environment. Sydney: Academic press, ) Windle C. Test-retest effect on personality questionnaires. Educational and Psychological Measurement 1954; 14: ) Sugisawa A, Uehata T, Sekiya E, et al. Mental health and its related factors among middle-aged male workers: An eighteen-month follow-up study. Jpn J Ind Health 1994; 36: (in Japanese). 16) Tsukamoto K, Igata M, Hayashi T, Suzuki T. The relationship between work factors and psychiatric
8 Jun SHIGEMI, et al.: The Factor Structure of Mental Health and Stability 291 symptoms. J Occup Health 1995; 37: (in Japanese). 17) Cohen S, Kessler RC, Gordon LU. Measuring Stress. New York: Oxford University Press, ) Uehata T, Yamasaki Y, Sakano J, et al. An epidemiological survey on work stress and health in various kinds of occupations of Japan First report. Tokyo: Institute of Industrial Medicare, 1991 (in Japanese). 19) Goldberg DP, Blackwell B. Psychiatric illness in general practice. A detailed study using a new method of case identification. Br Med J 1970; 2: ) Tarnopolsky A, Hand DJ, Mclean EK, Robert H, Wiggins RD. Validity and uses of screening questionnaire (GHQ) in the community. Br J Psychiatry 1979; 134: ) Goldberg D. Identifying psychiatric illness among general medical patients. Br Med J 1985; 291: ) Kitamura T, Sugawara M, Aoki M, Shima S. Validity of Japanese version of the GHQ among antenatal clinic attendants. Psychol Med 1989; 19: ) SPSS for windows Professional statistics, release 7.5. Chicago: SPSS Inc., ) Karasek RA, Baker D, Marxer F, Ahlbom A, Theorell T. Job decision latitude, job demands, and cardiovascular disease: A prospective study of Swedish men. Am J Public Health 1981; 71: ) Karasek RA, Theorell T, Schwartz JE, Schnall PL, Pieper CF, Michela JL. Job characteristics in relation to the myocardial infarction in the US health examination survey (HES) and the health nutrition examination survey (HANES). Am J Public Health 1988; 78: ) Krasek RA. Job demand, job decision latitude and mental strain: implications for job redesign Administration Science Quarterly 1979; 24: ) Huppert FA, Walters DE, Day NE, Elliott BJ. The Factor Structure of the General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-30) A reliability Study on 6317 Community Residents. Br J Psychiatry 1989; 155: ) Nadaoka T, Kashiwakura M, Oiji A, Morioka Y, Totsuka S. Stress and psychiatric disorders in local goverment officials in Japan, in relation to their employment level. Acta Psychiatr Scand 1997; 96: ) Goldberg DP. The use of screening questionnaire by family Doctors. The 7th World Congress of Psychiatry, Vienna July, ) Hurrel JJ, Maclaney MA. Exposure to job stress-a new psychosomatic instrument. Scand J Work Environ Health 1988; 14 (supple 1): ) Salazal MK. Job stress. AAOHN Journal 1993; 41: ) Berkman LF, Syme SL. Social networks, host resistance, and mortality: A nine year follow up study of Alameda country residents. Am J Epidemiol 1979; 109: ) Karasek R, Theorell T. Healthy work. Stress productivity, and the reconstruction of working life. USA: Basic Books, ) Landsbergis PA, Schnall PL, Deitz D, Friedman R, Pickering T. The pattering of psychological attributes and distress by job strain and social support in a sample of working men. J Behavior Med 1992; 15: ) Bourbonnais R, Brisson C, Moisan J, Vezina M. Job strain and psychological distress in white-collar workers. Scand J Environ Health 1996; 22:
PSYCHOMETRIC INDICATORS OF GENERAL HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE IN LATVIA
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH PAPER LASE JOURNAL OF SPORT SCIENCE 2013/4/2 205 PSYCHOMETRIC INDICATORS OF GENERAL HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE IN LATVIA Iveta Zelča, Žermēna Vazne, Aleksandra Čuprika, Ingrīda Amantova, Zinta
ORIGINAL RESEARCH PAPER LASE JOURNAL OF SPORT SCIENCE 2013/4/2 205 PSYCHOMETRIC INDICATORS OF GENERAL HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE IN LATVIA Iveta Zelča, Žermēna Vazne, Aleksandra Čuprika, Ingrīda Amantova, Zinta
How accurately does the Brief Job Stress Questionnaire identify workers with or without potential psychological distress?
 J Occup Health 2017; 59: 356-360 Brief Report How accurately does the Brief Job Stress Questionnaire identify workers with or without potential psychological distress? Akizumi Tsutsumi 1, Akiomi Inoue
J Occup Health 2017; 59: 356-360 Brief Report How accurately does the Brief Job Stress Questionnaire identify workers with or without potential psychological distress? Akizumi Tsutsumi 1, Akiomi Inoue
RELIABILITY AND CONSTRUCT VALIDITY OF THE MALAY VERSION OF THE JOB CONTENT QUESTIONNAIRE (JCQ)
 RELIABILITY AND CONSTRUCT VALIDITY OF THE MALAY VERSION OF THE JOB CONTENT QUESTIONNAIRE (JCQ) BA Edimansyah, BN Rusli, L Naing and M Mazalisah Division of Occupational Medicine, Department of Community
RELIABILITY AND CONSTRUCT VALIDITY OF THE MALAY VERSION OF THE JOB CONTENT QUESTIONNAIRE (JCQ) BA Edimansyah, BN Rusli, L Naing and M Mazalisah Division of Occupational Medicine, Department of Community
Factor structure and psychometric properties of the General Health Questionnaire. (GHQ-12) among Ghanaian adolescents
 Factor structure and psychometric properties of the General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-12) among Ghanaian adolescents Franklin N Glozah 1* and David J Pevalin 1 1 School of Health and Human Sciences, University
Factor structure and psychometric properties of the General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-12) among Ghanaian adolescents Franklin N Glozah 1* and David J Pevalin 1 1 School of Health and Human Sciences, University
Mental Health Status of Female Workers in Private Apparel Manufacturing Industry in Bangalore City, Karnataka, India
 1893 Mental Health Status of Female Workers in Private Apparel Manufacturing Industry in Bangalore City, Karnataka, India Deepthi Shanbhag 1*, Bobby Joseph 2 1 Assistant Professor; Department of Community
1893 Mental Health Status of Female Workers in Private Apparel Manufacturing Industry in Bangalore City, Karnataka, India Deepthi Shanbhag 1*, Bobby Joseph 2 1 Assistant Professor; Department of Community
The Development of a Questionnaire to Assess the Attitude of Active Listening
 J Occup Health 2000; 42: 111 118 Journal of Occupational Health The Development of a Questionnaire to Assess the Attitude of Active Listening Norio MISHIMA 1, Shinya KUBOTA 2 and Shoji NAGATA 1 1 Department
J Occup Health 2000; 42: 111 118 Journal of Occupational Health The Development of a Questionnaire to Assess the Attitude of Active Listening Norio MISHIMA 1, Shinya KUBOTA 2 and Shoji NAGATA 1 1 Department
Factorial Validity and Reliability of 12 items General Health Questionnaire in a Bhutanese Population. Tshoki Zangmo *
 Factorial Validity and Reliability of 12 items General Health Questionnaire in a Bhutanese Population Tshoki Zangmo * Abstract The aim of this study is to test the factorial structure and the internal
Factorial Validity and Reliability of 12 items General Health Questionnaire in a Bhutanese Population Tshoki Zangmo * Abstract The aim of this study is to test the factorial structure and the internal
JOB STRESS, SOCIAL SUPPORT AT WORK, AND INSOMNIA IN JAPANESE SHIFT WORKERS
 J. Human Ergol., 30: 203-209, 2001 JOB STRESS, SOCIAL SUPPORT AT WORK, AND INSOMNIA IN JAPANESE SHIFT WORKERS Akinori NAKATA, Takashi HARATANI, Masaya TAKAHASHI, Norito KAWAKAMI, Heihachiro ARITO, Yosei
J. Human Ergol., 30: 203-209, 2001 JOB STRESS, SOCIAL SUPPORT AT WORK, AND INSOMNIA IN JAPANESE SHIFT WORKERS Akinori NAKATA, Takashi HARATANI, Masaya TAKAHASHI, Norito KAWAKAMI, Heihachiro ARITO, Yosei
General Health Questionnaire (GHQ12 & GHQ28): psychometric properties and factor structure of the scales in a Turkish primary care sample
 Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol (1997) 32:327-331 9 Springer-Verlag 1997 C. Kdlg-M. Rezaki. B. Rezaki" I. Kaplan" G. 0zgen A. Sa~duyu. M.O. 0ztiirk General Health Questionnaire (GHQ12 & GHQ28): psychometric
Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol (1997) 32:327-331 9 Springer-Verlag 1997 C. Kdlg-M. Rezaki. B. Rezaki" I. Kaplan" G. 0zgen A. Sa~duyu. M.O. 0ztiirk General Health Questionnaire (GHQ12 & GHQ28): psychometric
A Simultaneous Evaluation of Occupational Stress and Depression in Patients with Lifestyle-related Diseases
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Simultaneous Evaluation of Occupational Stress and Depression in Patients with Lifestylerelated Diseases Nobutaka Inoue, Kazunori Otsui, Takayuki Yoshioka, Atsushi Suzuki, Toru Ozawa,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Simultaneous Evaluation of Occupational Stress and Depression in Patients with Lifestylerelated Diseases Nobutaka Inoue, Kazunori Otsui, Takayuki Yoshioka, Atsushi Suzuki, Toru Ozawa,
Effects of Web-Based Supervisor Training on Job Stressors and Psychological Distress among Workers: A Workplace-Based Randomized Controlled Trial
 J Occup Health 2006; 48: 28 34 Journal of Occupational Health Effects of Web-Based Supervisor Training on Job Stressors and Psychological Distress among Workers: A Workplace-Based Randomized Controlled
J Occup Health 2006; 48: 28 34 Journal of Occupational Health Effects of Web-Based Supervisor Training on Job Stressors and Psychological Distress among Workers: A Workplace-Based Randomized Controlled
Health Behavioral Patterns Associated with Psychologic Distress Among Middle-Aged Korean Women
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Health Behavioral Patterns Associated with Psychologic Distress Among Middle-Aged Korean Women Hye-Sook Shin 1, PhD, RN, Jia Lee 2 *, PhD, RN, Kyung-Hee Lee 3, PhD, RN, Young-A Song 4,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Health Behavioral Patterns Associated with Psychologic Distress Among Middle-Aged Korean Women Hye-Sook Shin 1, PhD, RN, Jia Lee 2 *, PhD, RN, Kyung-Hee Lee 3, PhD, RN, Young-A Song 4,
Introduction into Psychiatric Disorders. Dr Jon Spear- Psychiatrist
 Introduction into Psychiatric Disorders Dr Jon Spear- Psychiatrist Content Stress Major depressive disorder Adjustment disorder Generalised anxiety disorder Post traumatic stress disorder Borderline personality
Introduction into Psychiatric Disorders Dr Jon Spear- Psychiatrist Content Stress Major depressive disorder Adjustment disorder Generalised anxiety disorder Post traumatic stress disorder Borderline personality
Physician you can heal yourself! Cognitive behavioural training reduces stress in GPs
 Family Practice Vol. 21, No. 5 Oxford University Press 04, all rights reserved. Doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmh511, available online at www.fampra.oupjournals.org Printed in Great Britain Physician you can heal
Family Practice Vol. 21, No. 5 Oxford University Press 04, all rights reserved. Doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmh511, available online at www.fampra.oupjournals.org Printed in Great Britain Physician you can heal
Measurement of Psychopathology in Populations. William W. Eaton, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Psychometric Evaluation of the Chinese (Mainland) Version of Job Content Questionnaire: A Study in University Hospitals
 Industrial Health 2004, 42, 260 267 Original Article Psychometric Evaluation of the Chinese (Mainland) Version of Job Content Questionnaire: A Study in University Hospitals Jian LI 1, 2, Wenjie YANG 3,
Industrial Health 2004, 42, 260 267 Original Article Psychometric Evaluation of the Chinese (Mainland) Version of Job Content Questionnaire: A Study in University Hospitals Jian LI 1, 2, Wenjie YANG 3,
Measurement issues in the assessment of psychosocial stressors at work
 Measurement issues in the assessment of psychosocial stressors at work Dr. Peter Schnall And Dr. Paul Landsbergis Session 3 2 nd Hour April 18 2012 Reliability* The degree of stability exhibited when a
Measurement issues in the assessment of psychosocial stressors at work Dr. Peter Schnall And Dr. Paul Landsbergis Session 3 2 nd Hour April 18 2012 Reliability* The degree of stability exhibited when a
ANSWERS TO EXERCISES AND REVIEW QUESTIONS
 ANSWERS TO EXERCISES AND REVIEW QUESTIONS PART THREE: PRELIMINARY ANALYSES Before attempting these questions read through Chapters 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10 of the SPSS Survival Manual. Descriptive statistics
ANSWERS TO EXERCISES AND REVIEW QUESTIONS PART THREE: PRELIMINARY ANALYSES Before attempting these questions read through Chapters 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10 of the SPSS Survival Manual. Descriptive statistics
W ork stress has repeatedly predicted increased health
 RESEARCH REPORT Work stress, smoking status, and smoking intensity: an observational study of 46 190 employees Anne Kouvonen, Mika Kivimäki, Marianna Virtanen, Jaana Pentti, Jussi Vahtera... See end of
RESEARCH REPORT Work stress, smoking status, and smoking intensity: an observational study of 46 190 employees Anne Kouvonen, Mika Kivimäki, Marianna Virtanen, Jaana Pentti, Jussi Vahtera... See end of
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) WCPCG 2014
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) 365 369 WCPCG 2014 The Full Mediator Role of Job Satisfaction in Relationship between Job
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) 365 369 WCPCG 2014 The Full Mediator Role of Job Satisfaction in Relationship between Job
Epidemiology ofjob Stress and Health in Japan: Review of Current Evidence and Future Direction
 Industrial Health 1999, 37,174-186 REVIEW ARTICLE Epidemiology ofjob Stress and Health in Japan: Review of Current Evidence and Future Direction Norito KAWAKAMII* and Takashi HARATANI2 ' Department of
Industrial Health 1999, 37,174-186 REVIEW ARTICLE Epidemiology ofjob Stress and Health in Japan: Review of Current Evidence and Future Direction Norito KAWAKAMII* and Takashi HARATANI2 ' Department of
Reliability and Exploratory Factor Analysis of Psychological Well-being in a Persian Sample
 From the SelectedWorks of Seyed Mohammad Kalantarkousheh June, 2012 Reliability and Exploratory Factor Analysis of Psychological Well-being in a Persian Sample دکتر سید محمد کالنتر کوشه Kalantarkousheh,
From the SelectedWorks of Seyed Mohammad Kalantarkousheh June, 2012 Reliability and Exploratory Factor Analysis of Psychological Well-being in a Persian Sample دکتر سید محمد کالنتر کوشه Kalantarkousheh,
Nobuko; Takemoto, Tai-Ichiro. Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 2002, 47
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) 30-Item General Health Questionnair University Freshmen Ozaki, Keiko; Nagata, Koji; Hayashi Nobuko; Takemoto, Tai-Ichiro Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia.
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) 30-Item General Health Questionnair University Freshmen Ozaki, Keiko; Nagata, Koji; Hayashi Nobuko; Takemoto, Tai-Ichiro Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia.
Supplementary Materials:
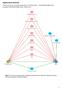 Supplementary Materials: Depression and risk of unintentional injury in rural communities a longitudinal analysis of the Australian Rural Mental Health Study (Inder at al.) Figure S1. Directed acyclic
Supplementary Materials: Depression and risk of unintentional injury in rural communities a longitudinal analysis of the Australian Rural Mental Health Study (Inder at al.) Figure S1. Directed acyclic
Pain Psychology: Disclosure Slide. Learning Objectives. Bio-psychosocial Model 8/12/2014. What we won t cover (today) What influences chronic pain?
 Disclosure Slide Pain Psychology: No commercial interests to disclose Screening for distress and maladaptive attitudes and beliefs Paul Taenzer PhD, CPsych Learning Objectives At the end of the session,
Disclosure Slide Pain Psychology: No commercial interests to disclose Screening for distress and maladaptive attitudes and beliefs Paul Taenzer PhD, CPsych Learning Objectives At the end of the session,
THEORETICAL ASSUMPTIONS AND PSYCHOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SENSE OF PERSONAL CONTROL AT WORK QUESTIONNAIRE
 International Journal of Occupational Medicine and Environmental Health, Vol. 5, No., 29 36, 2002 THEORETICAL ASSUMPTIONS AND PSYCHOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SENSE OF PERSONAL CONTROL AT WORK QUESTIONNAIRE
International Journal of Occupational Medicine and Environmental Health, Vol. 5, No., 29 36, 2002 THEORETICAL ASSUMPTIONS AND PSYCHOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SENSE OF PERSONAL CONTROL AT WORK QUESTIONNAIRE
Non-auditory: 9th International Congress on Noise as a Public Health Problem (ICBEN) 2008, Foxwoods, CT
 Relationship between subjective health and disturbances of daily life due to aircraft noise exposure Questionnaire study conducted around Narita International Airport Masamitsu Miyakawa 1*, Toshihito Matsui
Relationship between subjective health and disturbances of daily life due to aircraft noise exposure Questionnaire study conducted around Narita International Airport Masamitsu Miyakawa 1*, Toshihito Matsui
Journal of Management Info 4(1), (2014)
 Effects of Perceived Stressors and Psychiatric Morbidity on Academic Performance of University Students Aftab Alam Khan a,*, Abid Sultan b, Farzand Ali Jan b a,* Ayub Medical College, Abbotabad, Pakistan
Effects of Perceived Stressors and Psychiatric Morbidity on Academic Performance of University Students Aftab Alam Khan a,*, Abid Sultan b, Farzand Ali Jan b a,* Ayub Medical College, Abbotabad, Pakistan
Psychosocial Influences on Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
 Psychosocial Influences on Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Dr Rachel O Hara Section of Public Health School of Health and Related Research r.ohara@sheffield.ac.uk Learning objectives To examine the role of
Psychosocial Influences on Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Dr Rachel O Hara Section of Public Health School of Health and Related Research r.ohara@sheffield.ac.uk Learning objectives To examine the role of
Occupational Burnout and the Causes, Predisposing Factors, Consequences, and Prevention Strategies
 Parkland College A with Honors Projects Honors Program 2015 Occupational Burnout and the Causes, Predisposing Factors, Consequences, and Prevention Strategies Kelsey D. Howard Parkland College Recommended
Parkland College A with Honors Projects Honors Program 2015 Occupational Burnout and the Causes, Predisposing Factors, Consequences, and Prevention Strategies Kelsey D. Howard Parkland College Recommended
Mental Health in Workplaces in Taipei
 26 Taiwanese Journal of Psychiatry (Taipei) Vol. 25 No. 1 2011 Original Article Mental Health in Workplaces in Taipei Mei-Ju Chen, M.D. MPH 1,2, Tony Szu-Hsien Lee, Ph.D. 3, Huey-Mei Jeng, Ph.D. 3, Wen-Hsiang
26 Taiwanese Journal of Psychiatry (Taipei) Vol. 25 No. 1 2011 Original Article Mental Health in Workplaces in Taipei Mei-Ju Chen, M.D. MPH 1,2, Tony Szu-Hsien Lee, Ph.D. 3, Huey-Mei Jeng, Ph.D. 3, Wen-Hsiang
Mayo Hiroshima. Manami Amagai. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences MCSER Publishing, Rome-Italy. 1. Background
 Development of a Simple Version of the 7-item Version of an Instrument to Measure Self-Efficacy for Social Participation of People with Mental Illness Doi:.59/mjss.3.v4np5 Abstract Mayo Hiroshima Graduate
Development of a Simple Version of the 7-item Version of an Instrument to Measure Self-Efficacy for Social Participation of People with Mental Illness Doi:.59/mjss.3.v4np5 Abstract Mayo Hiroshima Graduate
Vijit Chaturvedi, Int.J.Buss.Mgt.Eco.Res., Vol 2(2),2011,
 A Study on Gender Differences with relation to Occupational Stress among Faculties in Management Colleges of Private and Government Institutes A Study with reference to Management Colleges in NCR Vijit
A Study on Gender Differences with relation to Occupational Stress among Faculties in Management Colleges of Private and Government Institutes A Study with reference to Management Colleges in NCR Vijit
The Impact of Weekend Working on Well-Being in the UK
 The Impact of Weekend Working on Well-Being in the UK Andrew Bryce, University of Sheffield Supervisors: Jennifer Roberts and Mark Bryan Labour Force and Annual Population Surveys User Conference 2016
The Impact of Weekend Working on Well-Being in the UK Andrew Bryce, University of Sheffield Supervisors: Jennifer Roberts and Mark Bryan Labour Force and Annual Population Surveys User Conference 2016
CROSS-SECTIONAL SURVEY ON RISK FACTORS FOR INSOMNIA IN JAPANESE FEMALE HOSPITAL NURSES WORKING RAPIDLY ROTATING SHIFT SYSTEMS
 J. Human Ergol., 30:149-154, 2001 CROSS-SECTIONAL SURVEY ON RISK FACTORS FOR INSOMNIA IN JAPANESE FEMALE HOSPITAL NURSES WORKING RAPIDLY ROTATING SHIFT SYSTEMS Takayuki KAGEYAMA, Noriko NISHIKIDO, Toshio
J. Human Ergol., 30:149-154, 2001 CROSS-SECTIONAL SURVEY ON RISK FACTORS FOR INSOMNIA IN JAPANESE FEMALE HOSPITAL NURSES WORKING RAPIDLY ROTATING SHIFT SYSTEMS Takayuki KAGEYAMA, Noriko NISHIKIDO, Toshio
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE AND STRESS MANAGEMENT
 THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE AND STRESS MANAGEMENT Ms S Ramesar Prof P Koortzen Dr R M Oosthuizen Department of Industrial and Organisational Psychology University of South Africa th
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE AND STRESS MANAGEMENT Ms S Ramesar Prof P Koortzen Dr R M Oosthuizen Department of Industrial and Organisational Psychology University of South Africa th
Multidimensional Perfectionism Scale. Interpretive Report. Paul L. Hewitt, Ph.D. & Gordon L. Flett, Ph.D.
 Multidimensional Perfectionism Scale Paul L. Hewitt, Ph.D. & Gordon L. Flett, Ph.D. Interpretive Report This Interpretive Report is intended for the sole use of the test administrator and is not to be
Multidimensional Perfectionism Scale Paul L. Hewitt, Ph.D. & Gordon L. Flett, Ph.D. Interpretive Report This Interpretive Report is intended for the sole use of the test administrator and is not to be
people experience in situations that they perceive as dangerous or threatening to their well-being.
 An Empirical study on Job Stress and its impact on health workers in Private Hospitals at Tiruchirappalli, South India Dr.C.Muthu Velayutham MBA., M.Phil, Ph.D Associate Professor Management Studies Anna
An Empirical study on Job Stress and its impact on health workers in Private Hospitals at Tiruchirappalli, South India Dr.C.Muthu Velayutham MBA., M.Phil, Ph.D Associate Professor Management Studies Anna
The scale of perceived occupational stress
 Occup. Med. Vol. 50, No. 5, pp. 294-298, 2000 Copyright 2000 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins for SOM Printed in Great Britain. All rights reserved 0962-7480/00 IN-DEPTH REVIEW The scale of perceived occupational
Occup. Med. Vol. 50, No. 5, pp. 294-298, 2000 Copyright 2000 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins for SOM Printed in Great Britain. All rights reserved 0962-7480/00 IN-DEPTH REVIEW The scale of perceived occupational
Extraversion. The Extraversion factor reliability is 0.90 and the trait scale reliabilities range from 0.70 to 0.81.
 MSP RESEARCH NOTE B5PQ Reliability and Validity This research note describes the reliability and validity of the B5PQ. Evidence for the reliability and validity of is presented against some of the key
MSP RESEARCH NOTE B5PQ Reliability and Validity This research note describes the reliability and validity of the B5PQ. Evidence for the reliability and validity of is presented against some of the key
Work characteristics and psychiatric disorder in civil servants in London
 4848ournal of Epidemiology and Community Health 1995;49:48-53 Academic Department of Psychiatry, University College London Medical School, Wolfson Building, Riding House Street, London W1N8AA S A Stansfeld
4848ournal of Epidemiology and Community Health 1995;49:48-53 Academic Department of Psychiatry, University College London Medical School, Wolfson Building, Riding House Street, London W1N8AA S A Stansfeld
ACSPRI Paper in progress. Confirmatory factor analysis of the Occupational Stress Inventory-Revised among Australian teachers
 ACSPRI Paper in progress. Confirmatory factor analysis of the Occupational Stress Inventory-Revised among Australian teachers Hicks, R.E., Fujiwara, D., & Bahr, M. Bond University Abstract Assessing teacher
ACSPRI Paper in progress. Confirmatory factor analysis of the Occupational Stress Inventory-Revised among Australian teachers Hicks, R.E., Fujiwara, D., & Bahr, M. Bond University Abstract Assessing teacher
BEHAVIORAL ASSESSMENT OF PAIN MEDICAL STABILITY QUICK SCREEN. Test Manual
 BEHAVIORAL ASSESSMENT OF PAIN MEDICAL STABILITY QUICK SCREEN Test Manual Michael J. Lewandowski, Ph.D. The Behavioral Assessment of Pain Medical Stability Quick Screen is intended for use by health care
BEHAVIORAL ASSESSMENT OF PAIN MEDICAL STABILITY QUICK SCREEN Test Manual Michael J. Lewandowski, Ph.D. The Behavioral Assessment of Pain Medical Stability Quick Screen is intended for use by health care
Study of the Relationship between Emotional Intelligence and Self Efficacy among School Going Adolescents
 Study of the Relationship between Emotional Intelligence and Self Efficacy among School Going Adolescents P.S FATHIMA SWAIN MAMTA SINHA V.K Department of Psychiatric Social Work, Central Institute of Psychiatry,
Study of the Relationship between Emotional Intelligence and Self Efficacy among School Going Adolescents P.S FATHIMA SWAIN MAMTA SINHA V.K Department of Psychiatric Social Work, Central Institute of Psychiatry,
Sense of coherence is associated with reduced psychological responses to job stressors among Japanese factory workers
 Urakawa et al. BMC Research Notes 2012, 5:247 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Sense of coherence is associated with reduced psychological responses to job stressors among Japanese factory workers Kayoko Urakawa
Urakawa et al. BMC Research Notes 2012, 5:247 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Sense of coherence is associated with reduced psychological responses to job stressors among Japanese factory workers Kayoko Urakawa
Understanding Psychological Distress, Job Satisfaction and Academic Performance in College Students
 Understanding Psychological Distress, Job Satisfaction and Academic Performance in College Students Amelia Do Abstract As the emphasis on higher education continues to be an increasing focus, the number
Understanding Psychological Distress, Job Satisfaction and Academic Performance in College Students Amelia Do Abstract As the emphasis on higher education continues to be an increasing focus, the number
Job satisfaction and stress. C&C Senior Medical Staff Survey revisited (Dr Neville Berry) September 2005
 Job satisfaction and stress C&C Senior Medical Staff Survey revisited (Dr Neville Berry) September 2005 Burnout (a definition) A syndrome of emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and reduced accomplishment
Job satisfaction and stress C&C Senior Medical Staff Survey revisited (Dr Neville Berry) September 2005 Burnout (a definition) A syndrome of emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and reduced accomplishment
Work characteristics predict psychiatric disorder: prospective results from the Whitehall II study
 302 International Centre for Health and Society, Department of Epidemiology and Public Health, and Department of Psychiatry and Behavioural Sciences, Royal Free and University College Medical School, University
302 International Centre for Health and Society, Department of Epidemiology and Public Health, and Department of Psychiatry and Behavioural Sciences, Royal Free and University College Medical School, University
What Causes Stress in Malaysian Students and it Effect on Academic Performance: A case Revisited
 Advanced Journal of Technical and Vocational Education 1 (1): 155-160, 2017 eissn: 2550-2174 RMP Publications, 2017 What Causes Stress in Malaysian Students and it Effect on Academic Performance: A case
Advanced Journal of Technical and Vocational Education 1 (1): 155-160, 2017 eissn: 2550-2174 RMP Publications, 2017 What Causes Stress in Malaysian Students and it Effect on Academic Performance: A case
A Longitudinal Study of the Well-being of Students Using the Student Wellbeing Process Questionnaire (Student WPQ)
 Journal of Education, Society and Behavioural Science 24(4): 1-6, 2018; Article no.jesbs.40105 ISSN: 2456-981X (Past name: British Journal of Education, Society & Behavioural Science, Past ISSN: 2278-0998)
Journal of Education, Society and Behavioural Science 24(4): 1-6, 2018; Article no.jesbs.40105 ISSN: 2456-981X (Past name: British Journal of Education, Society & Behavioural Science, Past ISSN: 2278-0998)
15 Minute Hour. Focus of Presentation. Epidemiology. Psychiatric Epidemiology. A Hands-on Workshop
 15 Minute Hour A Hands-on Workshop Faculty: Marian R. Stuart, Ph.D. Program: 51 st Annual Scientific Assembly Relationships with commercial interests: N/A Marian R. Stuart, Ph.D. Emeritus Professor of
15 Minute Hour A Hands-on Workshop Faculty: Marian R. Stuart, Ph.D. Program: 51 st Annual Scientific Assembly Relationships with commercial interests: N/A Marian R. Stuart, Ph.D. Emeritus Professor of
Mother-daughter Relationship and Sex Education from Mother to Daughter
 Kawasaki Journal of Medical Welfare Vol. 22, No. 2, 2017 77-87 Original Paper Mother-daughter Relationship and Sex Education from Mother to Daughter Hiroko SUIZU *1, Rie IKEDA (NAKAMURA) *2 and Kinuko
Kawasaki Journal of Medical Welfare Vol. 22, No. 2, 2017 77-87 Original Paper Mother-daughter Relationship and Sex Education from Mother to Daughter Hiroko SUIZU *1, Rie IKEDA (NAKAMURA) *2 and Kinuko
The Japanese Adaptation of the STAI Form Y in Japanese Working Adults -The Presence or Absence of Anxiety-
 Industrial Health 1998, 36, 8-13 The Japanese Adaptation of the STAI Form Y in Japanese Working Adults -The Presence or Absence of Anxiety- Noboru IWATA1*, Norio MISHIMAI, Takashi SHIMIZUI, Tetsuya MIZOUE',
Industrial Health 1998, 36, 8-13 The Japanese Adaptation of the STAI Form Y in Japanese Working Adults -The Presence or Absence of Anxiety- Noboru IWATA1*, Norio MISHIMAI, Takashi SHIMIZUI, Tetsuya MIZOUE',
The Association of Job Strain and Health Behaviours in Men and Women
 International Journal of Epidemiology International Epidemiological Association 1997 Vol. 26, No. 3 Printed in Great Britain The Association of Job Strain and Health Behaviours in Men and Women WENDY L
International Journal of Epidemiology International Epidemiological Association 1997 Vol. 26, No. 3 Printed in Great Britain The Association of Job Strain and Health Behaviours in Men and Women WENDY L
Asia Pacific Journal of Research ISSN (Print) : ISSN (Online) : STRESS MANAGEMENT
 STRESS MANAGEMENT Dr. B.SWARNALATHA Assistant professor (Senior Grade) Bharathiyar College of Engineering and Technology Karaikal ABSTRACT Stress has been defined in different ways over the years. It can
STRESS MANAGEMENT Dr. B.SWARNALATHA Assistant professor (Senior Grade) Bharathiyar College of Engineering and Technology Karaikal ABSTRACT Stress has been defined in different ways over the years. It can
MENTAL HEALTH HAS become one of the major
 Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 2011; 65: 434 441 doi:10.1111/j.1440-1819.2011.02236.x Regular Article Screening performance of K6/K10 and other screening instruments for mood and anxiety disorders
Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 2011; 65: 434 441 doi:10.1111/j.1440-1819.2011.02236.x Regular Article Screening performance of K6/K10 and other screening instruments for mood and anxiety disorders
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SOCIOMETRIC STATUS AND ANXIETY1. Nara Gakugei University
 Japanese Psychological Research19 64, Vol.6, No.2, 67-71 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SOCIOMETRIC STATUS AND ANXIETY1 TOSHIMI UEDA2 Nara Gakugei University An attempt was made to explore intensively the relationship
Japanese Psychological Research19 64, Vol.6, No.2, 67-71 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SOCIOMETRIC STATUS AND ANXIETY1 TOSHIMI UEDA2 Nara Gakugei University An attempt was made to explore intensively the relationship
The Study of Relationship between Neuroticism, Stressor and Stress Response
 International Journal of Economics and Finance; Vol. 7, No. 8; 2015 ISSN 1916-971X E-ISSN 1916-9728 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education The Study of Relationship between Neuroticism,
International Journal of Economics and Finance; Vol. 7, No. 8; 2015 ISSN 1916-971X E-ISSN 1916-9728 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education The Study of Relationship between Neuroticism,
Activating Event. irrational beliefs interfere with accurate perception and thus disrupt.
 Emotions Psychology 101 Emotion & Stress Emotions are: Like Like standard operating procedures Emotions involve physiological arousal expressive behaviors experience Thoughts and Emotions Activating Event
Emotions Psychology 101 Emotion & Stress Emotions are: Like Like standard operating procedures Emotions involve physiological arousal expressive behaviors experience Thoughts and Emotions Activating Event
Problem Solving
 www.working-minds.org.uk Problem Solving Problem Solving The psychological importance of effective problem solving is very underestimated and is often taken for granted. As human beings, we assume that
www.working-minds.org.uk Problem Solving Problem Solving The psychological importance of effective problem solving is very underestimated and is often taken for granted. As human beings, we assume that
Self-Compassion, Perceived Academic Stress, Depression and Anxiety Symptomology Among Australian University Students
 International Journal of Psychology and Cognitive Science 2018; 4(4): 130-143 http://www.aascit.org/journal/ijpcs ISSN: 2472-9450 (Print); ISSN: 2472-9469 (Online) Self-Compassion, Perceived Academic Stress,
International Journal of Psychology and Cognitive Science 2018; 4(4): 130-143 http://www.aascit.org/journal/ijpcs ISSN: 2472-9450 (Print); ISSN: 2472-9469 (Online) Self-Compassion, Perceived Academic Stress,
Validation of the ISTAS 21 / CoPsoQ in Chile
 Validation of the ISTAS 21 / CoPsoQ in Chile Ministry of Labour and Social Security Social Security Enforcement Agency Medical Department (SUSESO) 2 nd International Workshop COPSOQ Freiburg/D, sept. 9-10/
Validation of the ISTAS 21 / CoPsoQ in Chile Ministry of Labour and Social Security Social Security Enforcement Agency Medical Department (SUSESO) 2 nd International Workshop COPSOQ Freiburg/D, sept. 9-10/
Dr. Catherine Mancini and Laura Mishko
 Dr. Catherine Mancini and Laura Mishko Interviewing Depression, with case study Screening When it needs treatment Anxiety, with case study Screening When it needs treatment Observation Asking questions
Dr. Catherine Mancini and Laura Mishko Interviewing Depression, with case study Screening When it needs treatment Anxiety, with case study Screening When it needs treatment Observation Asking questions
DO GENDER DIFFERENCES HAVE INFLUENCE ON PSYCHOSOCIAL STRESS, QUALITY OF LIFE AND WORK DEMANDS? CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY
 Eur J Gen Med 2004; 1(4): 36-41 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DO GENDER DIFFERENCES HAVE INFLUENCE ON PSYCHOSOCIAL STRESS, QUALITY OF LIFE AND WORK DEMANDS? CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY Giedrius Vanagas 1,2, Susanna Bihari-Axelsson
Eur J Gen Med 2004; 1(4): 36-41 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DO GENDER DIFFERENCES HAVE INFLUENCE ON PSYCHOSOCIAL STRESS, QUALITY OF LIFE AND WORK DEMANDS? CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY Giedrius Vanagas 1,2, Susanna Bihari-Axelsson
ASSOCIATION BETWEEN JOB STRAIN (HIGH DEMAND-LOW CONTROL) AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE RISK FACTORS AMONG PETROCHEMICAL INDUSTRY WORKERS
 International Journal of Occupational Medicine and Environmental Health 2013;26(4):555 562 DOI 10.2478/s13382-013-0127-x ASSOCIATION BETWEEN JOB STRAIN (HIGH DEMAND-LOW CONTROL) AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE
International Journal of Occupational Medicine and Environmental Health 2013;26(4):555 562 DOI 10.2478/s13382-013-0127-x ASSOCIATION BETWEEN JOB STRAIN (HIGH DEMAND-LOW CONTROL) AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE
INSOMNIA SEVERITY INDEX
 Name: Date: INSOMNIA SEVERITY INDEX For each of the items below, please circle the number that most closely corresponds to how you feel. 1. Please rate the CURRENT (i.e. last 2 weeks) severity of your
Name: Date: INSOMNIA SEVERITY INDEX For each of the items below, please circle the number that most closely corresponds to how you feel. 1. Please rate the CURRENT (i.e. last 2 weeks) severity of your
Prevalence of Procrastination in the United States, United Kingdom, and Australia: Arousal and Avoidance Delays among Adults
 Prevalence of Procrastination in the United States, United Kingdom, and Australia: Arousal and Avoidance Delays among Adults Joseph R. Ferrari DePaul University Jean O'Callaghan & Ian Newbegin Roehampton
Prevalence of Procrastination in the United States, United Kingdom, and Australia: Arousal and Avoidance Delays among Adults Joseph R. Ferrari DePaul University Jean O'Callaghan & Ian Newbegin Roehampton
Journal of Occupational Health
 Advance Publication Journal of Occupational Health Accepted for Publication: May 8, 2015 J-STAGE Advance Published Date: Jun 17, 2015 Title Psychometric Properties of the Thai Version of the Work Ability
Advance Publication Journal of Occupational Health Accepted for Publication: May 8, 2015 J-STAGE Advance Published Date: Jun 17, 2015 Title Psychometric Properties of the Thai Version of the Work Ability
The psychosocial work environment:
 The psychosocial work environment: How much do we know to optimize sustainable employability? Els Clays Department of Public Health, Ghent University Brussels, 15/09/16 Presentation outline Background
The psychosocial work environment: How much do we know to optimize sustainable employability? Els Clays Department of Public Health, Ghent University Brussels, 15/09/16 Presentation outline Background
Workplace stress in South African mineworkers
 Workplace stress in South African mineworkers INRS Occupational Health Research Conference 2012: Health risks associated with mixed exposures Anita Edwards Centre for Mining Innovation Council for Scientific
Workplace stress in South African mineworkers INRS Occupational Health Research Conference 2012: Health risks associated with mixed exposures Anita Edwards Centre for Mining Innovation Council for Scientific
CONSTRUCT VALIDITY OF THE ADOLESCENT RESILIENCE SCALE I
 Psychological Reports, 2003,, 93,1217-1222. Psychological Reports 2003 CONSTRUCT VALIDITY OF THE ADOLESCENT RESILIENCE SCALE I ATSUSHIOSHIO Chubu University Universtfy SHINJI SHINJ! NAGAMINE Kanazawa University
Psychological Reports, 2003,, 93,1217-1222. Psychological Reports 2003 CONSTRUCT VALIDITY OF THE ADOLESCENT RESILIENCE SCALE I ATSUSHIOSHIO Chubu University Universtfy SHINJI SHINJ! NAGAMINE Kanazawa University
Strengthening policies through good information
 1 Strengthening policies through good information FPS PUBLIC HEALTH, SAFETY OF THE FOOD CHAIN AND ENVIRONMENT Belgium Pol Gerits, PH. D. Psychosocial Care Service Department Manager With the kind collaboration
1 Strengthening policies through good information FPS PUBLIC HEALTH, SAFETY OF THE FOOD CHAIN AND ENVIRONMENT Belgium Pol Gerits, PH. D. Psychosocial Care Service Department Manager With the kind collaboration
A Cross-Cultural Study of Psychological Well-being Among British and Malaysian Fire Fighters
 A Cross-Cultural Study of Psychological Well-being Among British and Malaysian Fire Fighters Mohd. Dahlan Hj. A. Malek, Ida Shafinaz Mohd Universiti Malaysia Sabah Abstract Psychological consideration
A Cross-Cultural Study of Psychological Well-being Among British and Malaysian Fire Fighters Mohd. Dahlan Hj. A. Malek, Ida Shafinaz Mohd Universiti Malaysia Sabah Abstract Psychological consideration
ADULT QUESTIONNAIRE. Date of Birth: Briefly describe the history and development of this issue from onset to present.
 ADULT QUESTIONNAIRE Name: Address: Preferred phone number to reach you: Is it okay to leave a message? Yes No (Please check one) Date of Birth: Reason(s) for seeking treatment at this time? Briefly describe
ADULT QUESTIONNAIRE Name: Address: Preferred phone number to reach you: Is it okay to leave a message? Yes No (Please check one) Date of Birth: Reason(s) for seeking treatment at this time? Briefly describe
Exposure to environmental stress, particularly
 214 Job Strain and Ambulatory Work Blood Pressure in Healthy Young Men and Women Kathleen C. light, J. Rick Turner, and Alan L. Hinderliter The effect of high job strain (defined as high psychological
214 Job Strain and Ambulatory Work Blood Pressure in Healthy Young Men and Women Kathleen C. light, J. Rick Turner, and Alan L. Hinderliter The effect of high job strain (defined as high psychological
Psychiatric Epidemiology
 Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol (1991) 26:252-258 Social Psychiatry an~ {3 Springer-Verlag 1991 Psychiatric Epidemiology Qualitative differences in psychiatric symptoms between high risk groups assessed
Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol (1991) 26:252-258 Social Psychiatry an~ {3 Springer-Verlag 1991 Psychiatric Epidemiology Qualitative differences in psychiatric symptoms between high risk groups assessed
Effect of job characteristics on satisfaction and performance: A test in Egyptian agricultural extension system
 Vol. 8(48), pp. 6126-6130, 12 December, 2013 DOI: 10.5897/AJAR09.698 ISSN 1991-637X 2013 Academic Journals http://www.academicjournals.org/ajar African Journal of Agricultural Research Full Length Research
Vol. 8(48), pp. 6126-6130, 12 December, 2013 DOI: 10.5897/AJAR09.698 ISSN 1991-637X 2013 Academic Journals http://www.academicjournals.org/ajar African Journal of Agricultural Research Full Length Research
Occupational Stress and Coping Strategies among Grade II Police Constables
 Occupational Stress and Coping Strategies among Grade II Police Constables M.Shanmuga Sundaram Assistant Professor, Department of Business Administration Kalasalingam University, Krishnan Kovil -626 126
Occupational Stress and Coping Strategies among Grade II Police Constables M.Shanmuga Sundaram Assistant Professor, Department of Business Administration Kalasalingam University, Krishnan Kovil -626 126
ADULT HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE
 ADULT HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Date: Full Name: Date of Birth: If applicable, please complete the following: Partner s Name: Partner s Age: Partner s Occupation: IF YOU HAVE CHILDREN PLEASE LIST THEIR NAMES
ADULT HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Date: Full Name: Date of Birth: If applicable, please complete the following: Partner s Name: Partner s Age: Partner s Occupation: IF YOU HAVE CHILDREN PLEASE LIST THEIR NAMES
Job strain, social support in the workplace, and haemoglobin A1c in Japanese men
 Occup Environ Med 2000;57:805 809 805 Public Health, Gifu University School of Medicine, Gifu 500 8705, N Kawakami H Shimizu Sanyo Electric Co, K Akachi National Institute of Industrial Health, Ministry
Occup Environ Med 2000;57:805 809 805 Public Health, Gifu University School of Medicine, Gifu 500 8705, N Kawakami H Shimizu Sanyo Electric Co, K Akachi National Institute of Industrial Health, Ministry
Development of a social survey questionnaire of reactions to vibration in residential buildings
 Development of a social survey questionnaire of reactions to vibration in residential buildings H. Howarth and M. J Griffin Institute of Sound and Vibration Research, University of Southampton, Human Factors
Development of a social survey questionnaire of reactions to vibration in residential buildings H. Howarth and M. J Griffin Institute of Sound and Vibration Research, University of Southampton, Human Factors
Evaluating the Greek Version of Religious Commitment Inventory-10 on a Sample of Pomak Households
 (Volume 12, Issue 2/2016), pp. 5-11 Evaluating the Greek Version of Religious Commitment Inventory-10 on a Sample of Pomak Households Nikolaos Satsios 1+ 1 University of Nicosia, Cyprus Abstract. The aim
(Volume 12, Issue 2/2016), pp. 5-11 Evaluating the Greek Version of Religious Commitment Inventory-10 on a Sample of Pomak Households Nikolaos Satsios 1+ 1 University of Nicosia, Cyprus Abstract. The aim
Psychiatric morbidity after screening for breast cancer
 Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 1986, 40, 71-75 Psychiatric morbidity after screening for breast cancer CHRISTINE DEAN,1 M MAUREEN ROBERTS,2 KATE FRENCH,2 AND SUSAN ROBINS ON 2 From the University
Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 1986, 40, 71-75 Psychiatric morbidity after screening for breast cancer CHRISTINE DEAN,1 M MAUREEN ROBERTS,2 KATE FRENCH,2 AND SUSAN ROBINS ON 2 From the University
Japanese version of the Quality of Relationship Inventory: Its reliability and validity among women with recurrent spontaneous abortion
 Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences (2002), 56, 527 532 Regular Article Japanese version of the Quality of Relationship Inventory: Its reliability and validity among women with recurrent spontaneous
Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences (2002), 56, 527 532 Regular Article Japanese version of the Quality of Relationship Inventory: Its reliability and validity among women with recurrent spontaneous
Wellness on the Run Webinar The stress factor: How to manage stress and depression in the workplace
 Wellness on the Run Webinar The stress factor: How to manage stress and depression in the workplace September 20 th, 2017 1 Welcome Today s presentation will begin shortly. In order to hear the audio for
Wellness on the Run Webinar The stress factor: How to manage stress and depression in the workplace September 20 th, 2017 1 Welcome Today s presentation will begin shortly. In order to hear the audio for
Downloaded from on January 04, Scand J Work Environ Health 1998;24(3):
 Downloaded from www.sjweh.fi on January 04, 2018 Original article Scand J Work Environ Health 1998;24(3):197-205 doi:10.5271/sjweh.299 Psychosocial factors at work and subsequent depressive symptoms in
Downloaded from www.sjweh.fi on January 04, 2018 Original article Scand J Work Environ Health 1998;24(3):197-205 doi:10.5271/sjweh.299 Psychosocial factors at work and subsequent depressive symptoms in
A Reliability Study of The Turkish Version of The Morningness-Eveningness Questionnaire
 Türk Psikiyatri Dergisi 2005; 16(1): Turkish Journal of Psychiatry A Reliability Study of The Turkish Version of The Morningness-Eveningness Questionnaire Zekine PÜNDÜK, Hakan GÜR, İlker ERCAN SUMMARY
Türk Psikiyatri Dergisi 2005; 16(1): Turkish Journal of Psychiatry A Reliability Study of The Turkish Version of The Morningness-Eveningness Questionnaire Zekine PÜNDÜK, Hakan GÜR, İlker ERCAN SUMMARY
Reliability of the Columbia Impairment Scale (C.I.S.) for adolescents: Survey among an Italian sample in Lazio Region
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Epidemiology Biostatistics and Public Health - 2016, Volume 13, Number 1 Reliability of the Columbia Impairment Scale (C.I.S.) for adolescents: Survey among an Italian sample in Lazio
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Epidemiology Biostatistics and Public Health - 2016, Volume 13, Number 1 Reliability of the Columbia Impairment Scale (C.I.S.) for adolescents: Survey among an Italian sample in Lazio
Advances in Environmental Biology
 AENSI Journals Advances in Environmental Biology ISSN-1995-0756 EISSN-1998-1066 Journal home page: http://www.aensiweb.com/aeb/ A survey of the relationship between EQ and resilience among married students
AENSI Journals Advances in Environmental Biology ISSN-1995-0756 EISSN-1998-1066 Journal home page: http://www.aensiweb.com/aeb/ A survey of the relationship between EQ and resilience among married students
The HSE indicator tool, psychological distress and work ability
 Occupational Medicine 2012;62:203 209 Advance Access publication on 6 March 2012 doi:10.1093/occmed/kqs021 The HSE indicator tool, psychological distress and work ability S. Guidi 1, S. Bagnara 2 and G.
Occupational Medicine 2012;62:203 209 Advance Access publication on 6 March 2012 doi:10.1093/occmed/kqs021 The HSE indicator tool, psychological distress and work ability S. Guidi 1, S. Bagnara 2 and G.
Work Personality Index Factorial Similarity Across 4 Countries
 Work Personality Index Factorial Similarity Across 4 Countries Donald Macnab Psychometrics Canada Copyright Psychometrics Canada 2011. All rights reserved. The Work Personality Index is a trademark of
Work Personality Index Factorial Similarity Across 4 Countries Donald Macnab Psychometrics Canada Copyright Psychometrics Canada 2011. All rights reserved. The Work Personality Index is a trademark of
T he importance of work for health goes beyond traditional
 27 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Organisational justice and health of employees: prospective cohort study M Kivimäki, M Elovainio, J Vahtera, J E Ferrie... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
27 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Organisational justice and health of employees: prospective cohort study M Kivimäki, M Elovainio, J Vahtera, J E Ferrie... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
Gang Zhou, Xiaochun Niu. Dalian University of Technology, Liao Ning, China
 Psychology Research, June 2015, Vol. 5, No. 6, 372-379 doi:10.17265/2159-5542/2015.06.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING An Investigation into the Prevalence of Voice Strain in Chinese University Teachers Gang Zhou,
Psychology Research, June 2015, Vol. 5, No. 6, 372-379 doi:10.17265/2159-5542/2015.06.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING An Investigation into the Prevalence of Voice Strain in Chinese University Teachers Gang Zhou,
Perceived Stress as Predictor of Psychological Well-being among Indian Youth
 The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 3, Issue 4, No. 68, DIP: 18.01.213/20160304 ISBN: 978-1-365-39398-3 http://www.ijip.in July-September, 2016
The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 3, Issue 4, No. 68, DIP: 18.01.213/20160304 ISBN: 978-1-365-39398-3 http://www.ijip.in July-September, 2016
F or over two decades, have investigated the
 EVIDENCE BASED PUBLIC HEALTH POLICY AND PRACTICE Work and health in a contemporary society: demands, control, and insecurity R M D Souza, L Strazdins, L L-Y Lim, D H Broom, B Rodgers... See end of article
EVIDENCE BASED PUBLIC HEALTH POLICY AND PRACTICE Work and health in a contemporary society: demands, control, and insecurity R M D Souza, L Strazdins, L L-Y Lim, D H Broom, B Rodgers... See end of article
Workplace Bullying could Play Important Roles in the Relationships between Job Strain and Symptoms of Depression and Sleep Disturbance
 J Occup Health 2010; 52: 367 374 Journal of Occupational Health Workplace Bullying could Play Important Roles in the Relationships between Job Strain and Symptoms of Depression and Sleep Disturbance Jiro
J Occup Health 2010; 52: 367 374 Journal of Occupational Health Workplace Bullying could Play Important Roles in the Relationships between Job Strain and Symptoms of Depression and Sleep Disturbance Jiro
From Confounders to Suspected Risk: The Role of Psychosocial Factors Michael Feuerstein, Ph.D., MPH
 From Confounders to Suspected Risk: The Role of Psychosocial Factors Michael Feuerstein, Ph.D., MPH Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences Bethesda, Maryland McGorry et al., 2002 2003 STAR
From Confounders to Suspected Risk: The Role of Psychosocial Factors Michael Feuerstein, Ph.D., MPH Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences Bethesda, Maryland McGorry et al., 2002 2003 STAR
Work and home stress: associations with anxiety and depression symptoms
 Occupational Medicine 2015;65:110 116 Advance Access publication 14 January 2015 doi:10.1093/occmed/kqu181 Work and home stress: associations with anxiety and depression symptoms L.-B. Fan 1,2, J. A. Blumenthal
Occupational Medicine 2015;65:110 116 Advance Access publication 14 January 2015 doi:10.1093/occmed/kqu181 Work and home stress: associations with anxiety and depression symptoms L.-B. Fan 1,2, J. A. Blumenthal
