Chapter 5 The Integumentary System
|
|
|
- Marjorie Mills
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Functions of the Skin n regulation of body temperature n blood reservoir n protection n cutaneous sensations n excretion and absorption n synthesis of vitamin D Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 2 Components of the Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 3 1
2 Introduction n The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and glands, as well as blood vessels, muscles and nerves n Who do you go see when you have a skin problem? n Dermatology is the medical specialty for the diagnosis and treatment of disorders of the integumentary system. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 4 Structure of the Skin n The skin (cutaneous membrane) covers the body and is the largest organ of the body by surface area and weight n Its area is about 2 square meters (22 square feet) and weighs 4.5-5kg (10-11 lb), about 16% of body weight q How BIG!!! n It is mm thick, thinnest on the eyelids, thickest on the heels; the average thickness is 1 2 mm Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5 Structure of the Skin n It consists of two major layers: n outer, thinner layer called the epidermis, consists of epithelial tissue n inner, thicker layer called the dermis n Beneath the dermis is a subcutaneous (subq) layer (also called hypodermis) which attaches the skin to the underlying tissues and organs. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 6 2
3 Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 7 Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 8 Structure of the Skin n The epidermis has a number of important characteristics: n the epidermis is composed of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium n it contains four major types of cells: n Keratinocytes (90% of the cells) produce keratin which is a tough fibrous protein that provides protection Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 9 3
4 Types of Cells in the Epidermis Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 11 Cell types of the Epidermis n Keratinocytes--90% q produce keratin n Melanocytes % q produces melanin pigment q melanin transferred to other cells with long cell processes n Langerhan cells q from bone marrow q provide immunity n Merkel cells q in deepest layer 5-12 q form touch receptor with sensory neuron Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 13 4
5 Types of Skin n There are two major types of skin: n thin (hairy) skin covers all body regions except the palms, palmar surfaces of digits, and soles (4 layers) n thick (hairless) skin covers the palms, palmar surfaces of digits, and soles (5 layers) q stratum lucidum Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 14 Epidermis n Keratinization, the accumulation of more and more protective keratin, occurs as cells move from the deepest layer to the surface layer n Dandruff - an excess of keratinized cells shed from the scalp Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 15 Epidermis n Stratum basale (deepest layer) or stratum germinativum, where continuous cell division (stem cells) occurs which produces all the other layers n Stratum spinosum, 8-10 layers of keratinocytes n Stratum granulosum, which includes keratohyalin (hard protein envelope) and lamellar granules (release lipids), the most superficial layers die off Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 16 5
6 Epidermis n Stratum lucidum is present only in thick skin (the skin of the fingertips, palms, and soles) and is there to protect against usage n Stratum corneum: composed of many layers of flat, dead keratinocytes these are squamous cell shaped, they are continuously shed and replaced by cells from deeper strata; constant friction can stimulate formation of a callus. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 17 Come Let s Get Sun Burnt Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 18 Layers of the Epidermis Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 19 6
7 Skin Color Pigments (1) n Melanin produced in epidermis by melanocytes q same number of melanocytes in everyone, but differing amounts of pigment produced q results vary from yellow to tan to black color q melanocytes convert tyrosine to melanin n UV in sunlight increases melanin production n Clinical observations q freckles or liver spots = melanocytes in a patch q albinism = inherited lack of tyrosinase; no pigment q vitiligo = autoimmune loss of melanocytes in areas of the skin produces white patches 5-21 Skin Color Pigments (2) n n Carotene in dermis q yellow-orange pigment (precursor of vitamin A) q found in stratum corneum & dermis Hemoglobin q red, oxygen-carrying pigment in blood cells q if other pigments are not present, epidermis is translucent so pinkness will be evident 5-22 Skin Color as Diagnostic Clue n Jaundice q yellowish color to skin and whites of eyes q buildup of yellow bilirubin in blood from liver disease n Cyanotic q bluish color to nail beds and skin q hemoglobin depleted of oxygen looks purple-blue n Erythema q redness of skin due to enlargement of capillaries in dermis q during inflammation, infection, allergy or burns
8 Structural Basis of Skin Color n A benign localized overgrowth of melanocytes is a nevus or mole n Albinism is an inherited inability to produce melanin - vitiligo is a condition in which there is a partial or complete loss of melanocytes from patches of skin Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 24 Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 25 Structural Basis of Skin Color n Carotene - yellow-orange pigment (found in the stratum corneum, dermis, and subcutaneous layer) n Hemoglobin - red color (located in erythrocytes flowing through dermal capillaries) Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 26 8
9 Story Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 27 Synthesis of Vitamin D n Sunlight activates a precursor to vitamin D n Enzymes in the liver and kidneys transform that molecule into calcitriol (most active form of vitamin D) n Necessary vitamin for absorption of calcium from food in the gastrointestinal tract 5-28 Photodamage n Ultraviolet light (UVA and UVB) both damage the skin n Acute overexposure causes sunburn n DNA damage in epidermal cells can lead to skin cancer n UVA produces oxygen free radicals that damage collagen and elastic fibers and lead to wrinkling of the skin
10 Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 30 Dermis n The dermis has several important characteristics: n is composed of connective tissue containing collagen and elastic fibers n contains two layers n the outer papillary region consists of areolar connective tissue containing thin collagen and elastic fibers, dermal papillae (including capillary loops), corpuscles of touch and free nerve endings Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 31 Dermis n The deeper reticular region consists of dense irregular connective tissue containing collagen and elastic fibers adipose cells, hair follicles, nerves, sebaceous (oil) glands, and sudoriferous (sweat) glands n Striae or stretch marks can appear if the skin is stretched too much Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc
11 Dermis n Lines of cleavage - tension lines in the skin indicate the predominant direction of underlying collagen fibers (can be visible if you have stretch marks) n Epidermal ridges reflect contours of the underlying dermal papillae and form the basis for fingerprints (and footprints); their function is to increase firmness of grip by increasing friction. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 33 Subcutaneous Layer n Subcutaneous (subq) layer (also called hypodermis) is not part of the skin but, among its functions, it attaches the skin to the underlying tissues and organs; n this layer (and sometimes the dermis) contains lamellated (pacinian) corpuscles which detect external pressure applied to the skin. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 34 Blood vessels dilate and expand WBC & platelets released from blood vessels Scab forms 11
12 Granulation tissue forms to form a base Epithelial tissue begins regeneration on top of base Clean up begins Scar area has contracted Epithelium regeneration finishes Skin Grafts n New skin can not regenerate if stratum basale and its stem cells are destroyed n Skin graft is covering of wound with piece of healthy skin q autograft from self q isograft from twin q autologous skin n transplantation of patients skin grown in culture
13 Aging and the Integumentary System Effects: wrinkling decrease of skin s immune responsiveness dehydration and cracking of the skin decreased sweat production decreased numbers of functional melanocytes resulting in gray hair and atypical skin pigmentation loss of subcutaneous fat a general decrease in skin thickness an increased susceptibility to pathological conditions n Growth of hair and nails decreases; nails may also become more brittle with age. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 45 Age Related Structural Changes n Collagen fibers decrease in number & stiffen n Elastic fibers become less elastic n Fibroblasts decrease in number n Langerhans cells and macrophages decrease in number and become less-efficient phagocytes n Oil glands shrink and the skin becomes dry n Walls of blood vessels in dermis thicken so decreased nutrient availability leads to thinner skin as subcutaneous fat is lost 5-46 Skin Cancer n 1 million cases diagnosed per year n 3 common forms of skin cancer q basal cell carcinoma (rarely metastasize) q squamous cell carcinoma (may metastasize) q malignant melanomas (metastasize rapidly) n most common cancer in young women n arise from melanocytes ----life threatening n key to treatment is early detection watch for changes in symmetry, border, color and size n risks factors include-- skin color, sun exposure, family history, age and immunological status
14 Malignant melanoma 2% of all cancers Risks: 1. Skin type 2. Sun exposure 3. Family history 4. Age 5. Immunological status Normal mole Melanoma A= asymmetry B= border C= color D= diameter Basal cell carcinoma Easily treated with surgery. (most common skin cancer) Pearly translucent to fleshy color, tiny blood vessels on the surface. Squamous cell Seen as a red, carcinoma (somewhat crusted, or scaly patch common) or bump. Often a very rapid growing tumor. Malignant melanoma (rare, most deadly) The common appearance very asymmetrical and irregular borders 1. In which lay of skin are blood vessels located? 2. Where does epithelium regeneration begin? 3. What color is a persons skin if they are cyanotic? 4. List the layer of the epidermis in order from top to bottom. 5. What is the primary tissue of the hypodermis? 30 14
15 Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 51 Excretion and Absorption n Only a minor role is played by the skin n 400 ml of water evaporates from it daily n Small amounts salt, CO2, ammonia and urea are excreted n Lipid soluble substances can be absorbed through the skin q vitamins A, D, E and K, Oxygen and CO2 q acetone and dry-cleaning fluid, lead, mercury, arsenic, poisons in poison ivy and oak 5-53 Burns n Destruction of proteins of the skin q chemicals, electricity, heat n Problems that result q shock due to water, plasma and plasma protein loss q circulatory & kidney problems from loss of plasma q bacterial infection
16 Types of Burns n First-degree q only epidermis (sunburn) n Second-degree burn q destroys entire epidermis & part of dermis q fluid-filled blisters separate epidermis & dermis q epidermal derivatives are not damaged q heals without grafting in 3 to 4 weeks & may scar n Third-degree or full-thickness q destroy epidermis, dermis & epidermal derivatives q damaged area is numb due to loss of sensory nerves 5-55 Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 56 Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc
17 Accessory Structures of the Skin n include hair, skin glands, and nails n Hairs (pili) have a number of important functions: q protection q reduction of heat loss q sensing light touch Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 58 Accessory Structures of the Skin - Hair n Hair is composed of dead, keratinized epidermal cells n Hair consists of: n shaft which mostly projects above the surface of the skin n root which penetrates into the dermis n hair follicle n epithelial root sheath n dermal root sheath n Sebaceous (oil) glands are connected to hair follicles Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 59 Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc
18 Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 61 Skin Glands n Sebaceous glands secrete an oily substance called sebum which prevents dehydration of hair and skin, and inhibits growth of certain bacteria n Sudoriferous (sweat) glands-- 2 types: q Eccrine sweat glands q Apocrine sweat glands Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 62 Sudoriferous (Sweat) Glands n Numerous eccrine (or merocrine) sweat glands helps to cool the body by evaporating, and also eliminates small amounts of wastes n Apocrine sweat glands, located mainly in the skin of the axilla, groin, areolae, and bearded facial regions of adult males. q their excretory ducts open into hair follicles- this sweat is secreted during emotional stress and sexual excitement. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc
19 Ceruminous Glands n Modified sweat glands located in the ear canal n Along with nearby sebaceous glands, they are involved in producing a waxy secretion called cerumen (earwax) which provides a sticky barrier that prevents entry of foreign bodies into the ear canal. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 64 Nails n Nails are composed of hard, keratinized epidermal cells located over the dorsal surfaces of the ends of fingers and toes n Each nail consists of: q free edge q transparent nail body (plate) with a whitish lunula at its base q nail root embedded in a fold of skin Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 65 Nails Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc
20 Some Diseases and Conditions Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 67 Acne vulgaris- common disorder of the sebaceous glands. -Oil is deposited at the opening of the glands. -Oil hardens, clogging openings. -Prevents escape of oil. - White blood cells rush to the area Athlete s foot is a contagious fungal infection. It leads to cracking and scaling. Common in public bathrooms and showers. 20
21 Dermatitisinflammation of the skin caused by various reasons: soap, perfumes, stress, etc. Eczema- not contagious, inflammation of the skin. Dry, red, itchy, and scaly. Usually from allergic reactions to nickel (a common metal found in sterling silver) Psoriasis- chronic inflammatory skin disease with dry red patches covered by silvery-white scales. Affects elbows, knees, shins, scalp, lower back. Cause: unknown. 21
22 Ringwormhighly contagious fungal infection. Raised, itchy, circular patches. (has nothing to do with worms) Hives (urticaria) skin condition that shows intensely itching welts. Usually in response to an allergen. Herpes simplex (type 1)- viral infection around the mouth known as a fever blister or cold sore Genital Herpes simplex (type 2)- viral infection around the genitalia (different from type 1) 22
23 Warts- (Human Papilloma Virus- HPV) Common warts tend to cause no discomfort unless they are in areas of repeated friction or pressure. Warts often go away on their own within two years. Can be treated with chemicals, garlic or freezing methods. Chicken Pox Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 77 Shingles (herpes zoster)- viral infection of nerve endings. This is the same virus that causes chicken pox in children. After you get better from chickenpox, the virus "sleeps" (is dormant) in your nerve roots. Usually, it stays dormant forever. In others, the virus "wakes up" when disease, stress, or aging weakens the immune system 23
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Chapter 6: Skin & the. 6.1 Skin and its Tissues 6.2 Accessory Organs of the Skin 6.3 Regulation of Body Temperature 6.4 Healing of Wounds
 Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1-6.2 September 10, 2012 Chapter 6: Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1 Skin and its Tissues 6.2 Accessory Organs of the Skin 6.3 Regulation of Body Temperature 6.4 Healing
Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1-6.2 September 10, 2012 Chapter 6: Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1 Skin and its Tissues 6.2 Accessory Organs of the Skin 6.3 Regulation of Body Temperature 6.4 Healing
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
11/8/2012. Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Skin = Integument = Cutaneous Membrane. The Structure of Skin. Epidermis
 Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function.
 Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1
 Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY
 CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System 5.1-5.4 September 10, 2012 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System 5.1 Structure of the Skin 5.2 Accessory Structures of the Skin 5.3 Types of Skin 5.4 Functions of the Skin 5.5 Maintaining
The Integumentary System 5.1-5.4 September 10, 2012 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System 5.1 Structure of the Skin 5.2 Accessory Structures of the Skin 5.3 Types of Skin 5.4 Functions of the Skin 5.5 Maintaining
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
Chapter 4 Opener Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
Skin and Body Membranes
 4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System. Skin Cells. Layers of Skin. Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous layer beneath dermis not part of skin
 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
The Integumentary System: ANATOMY Includes: - Skin (integument) MEMBRANES. PHYSIOLOGY (functions) Protection. EPITHELIAL (cont.
 Did you know. Membranes & The Integumentary System The skin is the largest organ of the human body. It has a surface area of about 25 square-feet! You shed about 1.5 pounds of skin particles each year.
Did you know. Membranes & The Integumentary System The skin is the largest organ of the human body. It has a surface area of about 25 square-feet! You shed about 1.5 pounds of skin particles each year.
The Integumentary System: An Overview
 The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
Chapter 05. Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes.
 Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Integumentary System. Packet #12
 Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 4
 *We are revisiting Ch 3B on body tissues (Connective) prior to our study of Ch 4 Integumentary. Start on p.90 I. Connective Tissue A. Functions of Connective 1. Protection 2. Support 3. Binding Together
*We are revisiting Ch 3B on body tissues (Connective) prior to our study of Ch 4 Integumentary. Start on p.90 I. Connective Tissue A. Functions of Connective 1. Protection 2. Support 3. Binding Together
Introduction. Skin and Body Membranes. Cutaneous Membranes Skin 9/14/2017. Classification of Body Membranes. Classification of Body Membranes
 Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Eleventh Edition. Chapter 6
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
Ex. 7: Integumentary
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System The integumentary system is commonly known as the Skin Largest organ of human body 10% total body weight and would cover over 20 square feet Functions of Skin 1. Protection Barrier
Integumentary System The integumentary system is commonly known as the Skin Largest organ of human body 10% total body weight and would cover over 20 square feet Functions of Skin 1. Protection Barrier
B. Incorrect! The ectoderm does not produce the dermis. C. Incorrect! The dermis is derived from the mesoderm.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM This system consists of skin and its derivatives. The skin is one of the largest organs of the body in terms of surface area. The functions of the integumentary system include:
CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM This system consists of skin and its derivatives. The skin is one of the largest organs of the body in terms of surface area. The functions of the integumentary system include:
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Body Membranes & Skin
 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
The Integementary System. The Skin & Its Parts
 The Integementary System The Skin & Its Parts General Structure 2. Accessory structures: hair, nails, exocrine glands 1. Cutaneous membrane: various layers Major Functions 1. Protection 2. Temperature
The Integementary System The Skin & Its Parts General Structure 2. Accessory structures: hair, nails, exocrine glands 1. Cutaneous membrane: various layers Major Functions 1. Protection 2. Temperature
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. General Anatomy. Overview. Skin and its accessory structures
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Skin and its accessory structures structure function growth and repair development aging disorders 5-1 General Anatomy A large organ composed of all 4 tissue types 22
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Skin and its accessory structures structure function growth and repair development aging disorders 5-1 General Anatomy A large organ composed of all 4 tissue types 22
The Integumentary System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System. Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system
 Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
Integumentary System. 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1
 Integumentary System 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1 Functions of Skin Protection Temperature regulation Sensation Excretion Vitamin D production 2/20/02 S. Davenport 2 Protection A Barrier Three types of barriers:
Integumentary System 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1 Functions of Skin Protection Temperature regulation Sensation Excretion Vitamin D production 2/20/02 S. Davenport 2 Protection A Barrier Three types of barriers:
Integumentary System and Body Membranes
 Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Skin (Integument) Consists of two major regions 1. Epidermis superficial region 2. Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia) deepest region Subcutaneous layer deep to
The Integumentary System Skin (Integument) Consists of two major regions 1. Epidermis superficial region 2. Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia) deepest region Subcutaneous layer deep to
Ch 5: Integumentary System
 Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Skin and Body Membranes
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Slides 4.1 4.32 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Skin and Body Membranes Function
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Slides 4.1 4.32 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Skin and Body Membranes Function
2/5/2019. Organ System: Skin or Integumentary System. Hypodermis (or superficial fascia) Integumentary System - Learn and Understand
 Integumentary System - Learn and Understand Skin is an organ comprised of all four tissues Each layer of the skin contributes to one or more of its numerous functions Skin is both strong and flexible Keratinization
Integumentary System - Learn and Understand Skin is an organ comprised of all four tissues Each layer of the skin contributes to one or more of its numerous functions Skin is both strong and flexible Keratinization
Chapter 5. Integumentary System 5-1
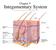 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System
 Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
B. Connective tissue membranes lubricate & cushion 1. made of areolar tissue 2. synovial line fibrous joint capsules & secrete fluid
 I. Body Membranes A. Epithelial membranes cover & line 1. epithelial sheet over underlying connective tissue 2. 3 types a. Cutaneous = skin b. Mucous = lines cavities open to exterior Skin and Body Membranes
I. Body Membranes A. Epithelial membranes cover & line 1. epithelial sheet over underlying connective tissue 2. 3 types a. Cutaneous = skin b. Mucous = lines cavities open to exterior Skin and Body Membranes
Unit 4 The Integumentary System
 Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
II. Skin and Its Tissues. I. Introduction. Unit Two. Integument URLs.
 6 Integument URLs http://www.nurseminerva.co.uk/integ.html http://www.aap.org/policy/s010116.html Chapter 6 Karen Webb Smith Unit Two I. Introduction A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more
6 Integument URLs http://www.nurseminerva.co.uk/integ.html http://www.aap.org/policy/s010116.html Chapter 6 Karen Webb Smith Unit Two I. Introduction A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition)
 Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
Integumentary System
 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
Lesson Plan: Integumentary System
 Integumentary System The skin is no more separate from the brain than the surface of a lake is separate from its depths. They are two different locations in a continuous medium. To touch the surface is
Integumentary System The skin is no more separate from the brain than the surface of a lake is separate from its depths. They are two different locations in a continuous medium. To touch the surface is
Ch 4. Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
7/10/18. Introduction. Integumentary System. Physiology. Anatomy. Structure of the Skin. Epidermis
 Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
Chapter 6: Integumentary System
 Chapter 6: Integumentary System 6.1 Introduction Why is skin considered to be an organ? What makes up the integumentary system? Integumentary System Skin (cutaneous membrane) Skin derivatives Sweat glands
Chapter 6: Integumentary System 6.1 Introduction Why is skin considered to be an organ? What makes up the integumentary system? Integumentary System Skin (cutaneous membrane) Skin derivatives Sweat glands
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system o Integumentary system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 6
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4 FUNCTIONS Waterproofs Protein called keratin Protection 1 st line of defense against pathogens, chemicals & abrasions Insulation Regulates heat loss by controlling blood
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4 FUNCTIONS Waterproofs Protein called keratin Protection 1 st line of defense against pathogens, chemicals & abrasions Insulation Regulates heat loss by controlling blood
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
Levels of Organization
 Levels of Organization Oklahoma Laws Violators can be fined, arrested or jailed for making ugly faces at a dog. Females are forbidden from doing their own hair without being licensed by the state. Dogs
Levels of Organization Oklahoma Laws Violators can be fined, arrested or jailed for making ugly faces at a dog. Females are forbidden from doing their own hair without being licensed by the state. Dogs
Chapter 5: Integumentary System
 Chapter 5: Integumentary System I. Overview of the Integumentary System A. List the five major functions of the integumentary system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Il. Skin A. Epidermis 1. The epidermis consists of 2.
Chapter 5: Integumentary System I. Overview of the Integumentary System A. List the five major functions of the integumentary system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Il. Skin A. Epidermis 1. The epidermis consists of 2.
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Chapter 4: Body Membranes and the Integumentary System. Introduction. Membranes
 Slide 1 Chapter 4: Body Membranes and the Integumentary System Slide 2 Introduction Skin often reveals our inner workings and general health In most manual therapies, the skin is primary interface with
Slide 1 Chapter 4: Body Membranes and the Integumentary System Slide 2 Introduction Skin often reveals our inner workings and general health In most manual therapies, the skin is primary interface with
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
The Integumentary System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 5 The Integumentary System Chapter 5 Learning Outcomes 5-1 5-2 5-3 5-4 5-5 Describe the main structural features
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 5 The Integumentary System Chapter 5 Learning Outcomes 5-1 5-2 5-3 5-4 5-5 Describe the main structural features
Student Objectives. 7. Describe the structure of nails.
 Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: The Skin 1. Name the tissue types composing the epidermis and dermis. List
Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: The Skin 1. Name the tissue types composing the epidermis and dermis. List
Figure 4.1. Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 115
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Short Answer Figure 4.1 Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Short Answer Figure 4.1 Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated
The Integumentary System. Health & Anatomy
 The Integumentary System Health & Anatomy Review of Membranes -Serous Membranes are composed of simple squamous epithelium resting on a thin layer of areolar connective tissue. *Name depends on the location
The Integumentary System Health & Anatomy Review of Membranes -Serous Membranes are composed of simple squamous epithelium resting on a thin layer of areolar connective tissue. *Name depends on the location
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Chapter 5. The Integumentary System. The largest organ in the body (~18 sq. feet)
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System The largest organ in the body (~18 sq. feet) Cool facts about the skin There are approximately 19,000,000 skin cells on every square inch of your body Millions of skin
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System The largest organ in the body (~18 sq. feet) Cool facts about the skin There are approximately 19,000,000 skin cells on every square inch of your body Millions of skin
Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
The Integumentary System
 C h a p t e r 5 The Integumentary System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Introduction to the Integumentary System The integument is the largest system
C h a p t e r 5 The Integumentary System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Introduction to the Integumentary System The integument is the largest system
Notes on Chapter 6 Integumentary System (Lecture notes-shortened)
 Notes on Chapter 6 Integumentary System (Lecture notes-shortened) I. Integumentary system- the skin and all of its accessory organs such hair, nails & gland II. Skin & its Tissues A. Skin is largest organ
Notes on Chapter 6 Integumentary System (Lecture notes-shortened) I. Integumentary system- the skin and all of its accessory organs such hair, nails & gland II. Skin & its Tissues A. Skin is largest organ
Contents: The skin and its derivatives: hair, nails and glands. Functions: 1. Regulaiton of body temperature -sweating
 The Integumentary System Of all the body s organs, none is more easily inspected or more exposed to infection, disease, and injury than the skin. Because of its visibility, skin reflects our emotions and
The Integumentary System Of all the body s organs, none is more easily inspected or more exposed to infection, disease, and injury than the skin. Because of its visibility, skin reflects our emotions and
Chapter 6: Integumentary System
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 12 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Integumentary System I. Introduction 1. The skin is composed of of tissues.
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 12 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Integumentary System I. Introduction 1. The skin is composed of of tissues.
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9
 Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
All the Rest. What is All the Rest? Integumentary System. First are the FUNCTI0NS. THERMOREGULATION function. PROTECTION function 10/12/16
 What is All the Rest? Integumentary System All the Rest Integumentary System Homeostatic Imbalances Skin Cancer Burns First are the FUNCTI0NS Chemical, Physical/Mechanical, Biological Thermoregulation
What is All the Rest? Integumentary System All the Rest Integumentary System Homeostatic Imbalances Skin Cancer Burns First are the FUNCTI0NS Chemical, Physical/Mechanical, Biological Thermoregulation
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 C H A P T E R 51 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY THE HUMAN INTEGUMENTARY BODY: AN SYSTEM ORIENTATION C H A P T E R 1 PART I THE HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION
C H A P T E R 51 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY THE HUMAN INTEGUMENTARY BODY: AN SYSTEM ORIENTATION C H A P T E R 1 PART I THE HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION
Skin. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
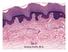 Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Chapter 4 The Integumentary System and Body Membranes. HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Chapter 4 The Integumentary System and Body Membranes HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial Membranes Cutaneous Membranes = The Skin Mucous Membranes Serous
Chapter 4 The Integumentary System and Body Membranes HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial Membranes Cutaneous Membranes = The Skin Mucous Membranes Serous
Overview of the Integumentary System. Lab #7. Layers of the epidermis are known as strata. Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the Epidermis
 Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
CHAPTER 7:3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7:3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM I. OBJECTIVES A. Label a diagram of a cross section of the skin B. Differentiate between the two types of skin glands C. Identify six functions of the skin D. Provide the
CHAPTER 7:3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM I. OBJECTIVES A. Label a diagram of a cross section of the skin B. Differentiate between the two types of skin glands C. Identify six functions of the skin D. Provide the
Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System I. Skin and Its Tissues A. Introduction
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System I. Skin and Its Tissues A. Introduction
Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings
 Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings List the four types of epithelial or connective membranes. The epithelial cutaneous includes your and is exposed to the. Its function is to. An example is..
Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings List the four types of epithelial or connective membranes. The epithelial cutaneous includes your and is exposed to the. Its function is to. An example is..
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6
 AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS
 Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide
 Name: SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES: 4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide Period: Body membranes, which cover body surfaces, line its cavities, and form protective sheets around organs, fall into two major
Name: SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES: 4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide Period: Body membranes, which cover body surfaces, line its cavities, and form protective sheets around organs, fall into two major
The Integumentary System. Vocabulary Important Info Headings
 The Integumentary System Vocabulary Important Info Headings 1 General Anatomy A large organ composed of all 4 tissue types 22 square feet 1-2 mm thick Weight 10 lbs. 2 Major layers of skin Epidermis is
The Integumentary System Vocabulary Important Info Headings 1 General Anatomy A large organ composed of all 4 tissue types 22 square feet 1-2 mm thick Weight 10 lbs. 2 Major layers of skin Epidermis is
The integumentary system includes
 Survivor The integumentary system includes What are 3 of the 5 basic functions of the integumentary system? The integumentary system protects against what types of tissue damage? List at least two types
Survivor The integumentary system includes What are 3 of the 5 basic functions of the integumentary system? The integumentary system protects against what types of tissue damage? List at least two types
3. Dense connective tissue is found in skin, & surrounding blood vessels, nerves, and organs.
 Ch.4&5 Group Quiz True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. There are 4 basic types of tissue in the human body. 2. Cartilage is also known as osseous tissue. 3. Dense connective tissue
Ch.4&5 Group Quiz True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. There are 4 basic types of tissue in the human body. 2. Cartilage is also known as osseous tissue. 3. Dense connective tissue
ABCD rule. apocrine glands. arrector pili. ceruminous glands. contact dermatitis
 ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Consists of: - skin hair nails sebaceous (oil) glands sudoriferous (sweat) glands Functions: 1. Thermoregulation - through sweating and adjusting blood flow in the dermis 2. Protection
Integumentary System Consists of: - skin hair nails sebaceous (oil) glands sudoriferous (sweat) glands Functions: 1. Thermoregulation - through sweating and adjusting blood flow in the dermis 2. Protection
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Integumentary System Skin (cutaneous membrane or integument) Skin derivatives
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Integumentary System Skin (cutaneous membrane or integument) Skin derivatives
2.2 Integumentary System. Chapter 5
 2.2 Integumentary System Chapter 5 Skin Disorder Mini-Project The Integumentary System Written Response #12 In your notebook, complete the following items: 1. Drawing of a cross section of skin that includes
2.2 Integumentary System Chapter 5 Skin Disorder Mini-Project The Integumentary System Written Response #12 In your notebook, complete the following items: 1. Drawing of a cross section of skin that includes
Integumentary System. Remember: Types of Membranes: Bio 250
 Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
Objectives. To explain the function of the integumentary system. To identify the components of the epidermis. To list the strata of the epidermis.
 Objectives To explain the function of the integumentary system. To identify the components of the epidermis. To list the strata of the epidermis. Definitions Epi upon, on top of Hypo under Derm skin Serous
Objectives To explain the function of the integumentary system. To identify the components of the epidermis. To list the strata of the epidermis. Definitions Epi upon, on top of Hypo under Derm skin Serous
28a A&P - Integumentary System
 28a A&P - Integumentary System 28a A&P - Integumentary System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
28a A&P - Integumentary System 28a A&P - Integumentary System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM (SKIN) Human Anatomy and Physiology S. McElwee CHS
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM (SKIN) Human Anatomy and Physiology S. McElwee CHS WHAT IS THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM? The integumentary system is 1 of 11 organ systems. It consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane),
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM (SKIN) Human Anatomy and Physiology S. McElwee CHS WHAT IS THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM? The integumentary system is 1 of 11 organ systems. It consists of the skin (cutaneous membrane),
Chapter 4. Skin and Body Membranes. Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Body Membranes Functions of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form
Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Body Membranes Functions of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form
The Integumentary System. Chapter 6
 The Integumentary System Chapter 6 What is the integumentary system? skin hair nails glands blood vessels sensory receptors What is your skin made of? 3 layers epidermis (outside) dermis (middle) subcutaneous
The Integumentary System Chapter 6 What is the integumentary system? skin hair nails glands blood vessels sensory receptors What is your skin made of? 3 layers epidermis (outside) dermis (middle) subcutaneous
Integumentary System. Study of the Skin
 Integumentary System Study of the Skin Skin is used to: Maintain homeostasis Provide a protective covering Slow down water loss from deeper tissues House sensory receptors Synthesize various biochemicals
Integumentary System Study of the Skin Skin is used to: Maintain homeostasis Provide a protective covering Slow down water loss from deeper tissues House sensory receptors Synthesize various biochemicals
Chapter 4. The Integumentary System. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 The Integumentary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary
Chapter 4 The Integumentary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary
