Unusual Doesn t Mean Uncommon: Skin Diseases You Don t Want to Miss Darin Dell, DVM, DACVD. Wheat Ridge Animal Hospital, Wheat Ridge CO
|
|
|
- Noel Jones
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unusual Doesn t Mean Uncommon: Skin Diseases You Don t Want to Miss Darin Dell, DVM, DACVD. Wheat Ridge Animal Hospital, Wheat Ridge CO Calcinosis Cutis Calcinosis cutis describes the deposition of calcium salts into dermal tissue (usually calcium phosphate or calcium carbonate). Four types are recognized in humans: Iatrogenic, Idiopathic, Dystrophic, and Metastatic. There is overlap between categories and these labels are not particularly helpful in veterinary medicine. The most common cause of calcinosis cutis in veterinary species is hyperglucocorticoidism. Typically, this is either secondary to hyperadrenocorticism (endogenous or exogenous) or steroid administration. Lesions typically develop on the dorsal neck and then spread caudally down the topline. Localized calcinosis cutis can occur secondary to chronic application of topical steroids. This is often apparent on the caudal ventral abdomen secondary to steroid sprays. Less commonly, calcinosis cutis can develop secondary to percutaneous absorption of calcium. Such exposure to calcium can occur when a pet comes in contact with certain floor cleaners, fertilizers, and ice melt products. Calcinosis cutis can occur in any breed but it is more common in English Bulldogs. It is also more common in patients receiving Depo-Medrol injections. The clinical appearance of calcinosis cutis changes over the progression of the syndrome. Early lesions are chalky white to pink with indistinct margins. More advanced lesions are white, firm, and usually surrounded by intense inflammation. Pruritus is usually present and may be severe. Ulceration is common and secondary infection usually follows. Diagnosis is easily confirmed with biopsy as the changes are unique and often dramatic. Collect biopsy samples from areas not affected by self-trauma and ulceration. Biopsy reveals diffuse or multifocal calcification of dermal collagen. Epidermal thickening and dermal edema are typically present as well. Calcinosis cutis is one dermatologic condition that can be seen on radiographs. It should be noted that serum calcium levels are not elevated in this syndrome. Treatment involves eliminating exposure to environmental calcium and discontinuing steroid administration. If neither of these are a factor then cortisol testing is recommended, as hyperadrenocorticism is very likely. If the patient does have hyperadrenocorticism, then that condition needs to be managed in order to eliminate the calcinosis cutis. Patients without hyperadrenocorticism or exposure to external calcium or steroid containing products may have other severe systemic disease such as renal disease. Alternatively, some cases will develop secondary to repetitive micro-trauma (lesions typically on the pressure points of the limbs). No treatment directly removes the calcium (aside from surgical excision). DMSO gel can be used to dissolve the calcium deposits. However, DMSO should be applied twice daily and may require weeks to months of treatment. Most owners cannot tolerate the smell of DMSO in their house for that length of time. Without DMSO, the calcium deposits will dissolve in two to twelve months. Patients with a history of calcinosis cutis should not receive steroid therapy in the future. Hepatocutaneous Syndrome
2 Hepatocutaneous syndrome has also been called superficial necrolytic dermatitis (SND), metabolic epidermal necrosis (MEN), N\necrolytic migratory erythema (NME), and diabetic dermatopathy. I recommend against using the term diabetic dermatopathy because it is confusing and not descriptive. In addition, not every dog with hepatocutaneous syndrome has diabetes. The pathogenesis of hepatocutaneous syndrome involves death of keratinocytes in the upper layer of the epidermis due to presumed amino acid starvation. Most affected dogs have a distinctive chronic hepatopathy; but, serum chemistry evaluation may not reveal any abnormalities. Potential causes of the hepatopathy include phenobarbital, primidone, mycotoxin, and gastroenteritis. In humans, this syndrome is almost always associated with glucagonoma. However, Glucagonoma is rare in dogs and accounted for only 8% of cases in one study. Hepatocutaneous syndrome is generally a disease of older dogs. Only four cases have been reported in cats. Skin lesions are typically the first sign as opposed to more common systemic signs of liver disease. Crusts and erosions occur in areas of trauma/wear. Thus, the paw pads are usually severely affected. The elbows, hocks, and muzzle are frequently involved as well. Many affected patients are often reluctant to walk due to painful erosions and fissures on the paw pads. Diagnosis requires biopsy of skin lesions with intact crusts. Histopathologically the changes are often described as a French Flag. Abdominal ultrasound can also be very helpful. A classic honeycomb pattern to liver is present in most cases of hepatocutaneous syndrome. However, inexperienced ultrasonagraphers may misinterpret the liver changes. In addition, the degree of change found on ultrasound does not necessarily correlate to severity of skin disease. CBC, serum chemistry, and urinalysis are also recommended. Nonregenerative anemia is common due to chronic disease. As stated before, liver values may or may not be elevated. Hyperglycemia is common and may require insulin therapy. Glucagon levels are elevated in patients with glucagonoma. However, glucagonoma is rare in dogs and cats and glucagon measurement is not readily available. Management of hepatocutaneous syndrome is difficult because this disease is a marker of severe internal disease. Consider referring these patients. Affected animals may need both a dermatologist and an internist. For glucagonoma-related disease it is recommended to remove the glucagonoma surgically. Unfortunately, glucagonomas have usually metastasized to the liver and abdominal lymph nodes by the time dermatologic lesions manifest. Cats with glucagonoma may also develop metastasis to the lungs and intestines. Even if metastasis has not occurred, affected patients are typically geriatric and my not be good surgical candidates. Octreotide, a synthetic somatostatin analogue, may be helpful for glucagonoma related disease. Octreotide binds to somatostatin receptors 2 and 5 to inhibit the release of glucagon. Octreotide will not affect the actual tumor but can yield quick and dramatic improvement in skin lesions. Octreotide is given two to four times daily indefinitely until the neoplasm progresses to the point of euthanasia or natural death. Theoretically, Octreotride would also be helpful for hepatic neuroendocrine tumors causing elevated glucagon levels and thus hepatocutaneous syndrome. However, hepatic neuroendocrine tumors are extremely rare with only one case reported in the dog and one in the cat. A more common therapy is intravenous Aminosyn. Aminosyn can be useful regardless of the underlying cause (glucogonoma or hepatic disease). Aminosyn is the most effective therapy for hepatopathy related disease (which is the most common form). However, Aminosyn does not fix the underlying liver problem. Aminosyn provides nutrition to the starving keratinocytes. Aminosyn injections are typically given once to twice weekly initially and then spread out with injections given
3 every 4-8 weeks long term. Aminosyn can yield a clinical response for up to twenty-two months. Unfortunately, Aminosyn is expensive and the injections must be given over several hours which requires hospitalization. A typical Aminosyn dose is 500ml/dog or 25mg/kg over 6-8 hours. Supportive nutritional therapy is always recommended for hepatocutaneous syndrome. Nutritional therapy involves increased protein intake via supplementation with egg yolks and cottage cheese, increased fatty acid intake, and zinc supplementation (zinc methionine 2mg/kg/day). The typical life expectancy with supportive therapy alone is 2 to 5 months. Steroid therapy can provide temporary improvement of clinical signs. However, patients eventually become resistant to steroid effects, and steroid administration predisposes to diabetes mellitus (remember that many patients are hyperglycemic at presentation). Topical steroid sprays or ointments may be very useful for focal lesions and carry less risk of inducing diabetes. Monitoring for and addressing secondary infection becomes a constant battle in hepatocutaneous syndrome. Bacterial infection is common due to damage to the epidermal barrier. Malassezia dermatitis may develop as well. Bacterial culture and oral antibiotics may be necessary. Many of these patients do not eat well and it may be difficult for the owner to administer an oral antibiotic. Consequently, antiseptic sprays and wipes are particularly helpful. Cutaneous Lymphoma Cutaneous lymphoma is an uncommon malignant neoplasia of the dog and cat. Two types of cutaneous lymphoma are recognized: epitheliotrophic and non-epitheliotrophic. Epitheliotrophic lymphomas are classified T cell lymphomas and include mycosis fungoides, Sezary syndrome, and pategoid reticulosis. Non-epitheliotrophic lymphomas are typically large cell lymphomas and can be either B or T cell in origin. Older animals are usually affected but this disease can occur at any age. These neoplasms are important even though they are rare because they imitate many other diseases. Non-epitheliotrophic lymphoma typically manifests as single or multiple nodules. Exfoliative erythroderma may occur separately or in addition to nodular disease. Patients with exfoliative erythroderma can easily be misdiagnosed as allergy, scabies, or seborrhea. If the mucus membranes and/or muzzle are affected by non-epitheliotrophic lymphoma it can appear visually indistinct from lupus erythematosus, pemphigus vulgaris, and bullous pemphigoid. The most common epitheliotrophic lymphoma is mycosis fungoides. This condition displays multiple clinical manifestations. Erythroderma is typically present (same as non-epitheliotrophic). Once again, this erythroderma may appear visually indistinct from allergy, scabies, and seborrhea. Focal lesions progress from patches to plaques to tumors. The final stage involves wide-spread dissemination of tumors with lymph node involvement. Multiple types of lesions can be present at the same time and the speed of progression is not predictable or consistent. Additionally, initial lesions can be very subtle. For example, a client may notice the development of dry flaky seborrhea. During examination, you might find a couple small patches of alopecia without inflammation and a nodule which the owner cannot remember. Diagnosis is relatively straightforward via biopsy. The point of this lecture is merely to encourage you to biopsy older animals or animals with sudden onset of disease more quickly. Cytology is always recommended as well. Occasionally you will find an unusually large population of lymphocytes on cytology when what you expected was neutrophils and cocci.
4 Therapy depends on the location and the extent of the disease. Consultation with an oncologist should always be recommended. Survival time varies greatly based on aggressiveness of the neoplasia and when the disease is diagnosed. In my clinical experience, most patients survive 2-3 months after diagnosis but this can range from a few weeks up to 18 months. For clients un-interested in oncology referral or classical chemotherapy, I recommend steroids as monotherapy. Steroid monotherapy can provide 1-3 months of quality time by reducing the intensity of lesions and subsequent discomfort. Pemphigus foliaceus Pemphigus foliaceus is one of the most common auto-immune skin diseases seen in dogs and cats. This disease is characterized by pustules and honey colored crusts. This condition is typically idiopathic but it can develop secondary to drug exposure. Pemphigus foliaceus is often seen in patients previously diagnosed with allergic dermatitis; however, no link between the two has been proven. In pemphigus foliaceus the immune system is attacking a particular protein in the complex structure (called a desmosome) that links keratinocytes together. Destroying the bonds between keratinocytes is termed acantholysis and results in acantholytic cells. Acantholytic cells are typically plump and round because they are no longer connected to their neighbors. They stain darkly and have a clearly visible nucleus. Different forms of pemphigus exist and one of the primary differences between them is in what layer of the skin this acantholysis occurs. For pemphigus foliaceus the damage occurs in the two uppermost layers (the stratum corneum and the stratum granulosum). More serious forms of pemphigus affect deeper layers of the skin and cause significantly more damage. As acantholysis occurs, vesicles and sterile pustules are formed. These are fragile and easily damaged because they are located in the uppermost layers of the epidermis. Depending on the intensity of the immune response, pustules can develop and rupture in under an hour or over the course of days. For comparison, pyoderma pustules develop more slowly and are more resilient (more difficult to break). In addition, pyoderma pustules are typically centered around a hair follicle. Both pemphigus pustules and pyoderma pustules will contain neutrophils but intact pemphigus pustules will not contain bacteria. As already mentioned, the classic lesions of pemphigus foliaceus are pustules and crusts. These lesions can occur anywhere on the body but are commonly found on the face and trunk. Pustules can develop inside the aural opening resulting in serum leakage and crust debris falling into the ear canals. The result is typically a wicked otitis externa. In many cases the nasal planum is also abnormal. The planum typically becomes dry, thick, and crusted. Ulcerations of the nasal planum can occur secondary to crust being traumatically removed. However, pemphigus foliaceus does not cause ulceration of the oral cavity or mucus membranes. The paw pads may be affected as well. Discreet pustules may be seen on the pads but more often the pads are thickened, dry, and crusted. Some dogs will be reluctant to walk but that is uncommon with pemphigus (much more common with hepatocutaneous syndrome). Diagnosis is via biopsy. Intact pustules are preferred because they offer the clearest picture of the disease process. However, crusts are also very useful biopsy specimens. When collecting biopsies for potential pemphigus foliaceus it is critical not to scrub the skin. In most cases it is advised to avoid shaving the animal s fur as well. Even the slightest disturbance to the skin can damage the fragile pustules seen with this condition. In the event that no pustules are present, the proof of pemphigus might be in the crust on top of the skin rather than in the skin sample itself. Consequently, always include crust debris in the formalin jar and request the crust be processed, when you biopsy for pemphigus.
5 Treatment, which is really to say management, is almost always successful but required lifelong. Some cases of drug induced pemphigus foliaceus will remain in remission even when immune suppressive therapy is discontinued. However, it is often difficult to prove which cases are drug induced which makes predicting which patients will be able to stop therapy nearly impossible. Initial therapy requires steroid administration. Oral daily prednisolone/prednisone dosages of 2mg/kg to 6mg/kg are often required. Steroid therapy often yields dramatic improvement in two to four weeks when dosed adequately. Some patients will respond better to other steroids such as dexamethasone or triamcinolone. Recheck examinations every two to four weeks are critical to assess response to therapy and tailor drug therapy. Secondary bacterial infection is common in pemphigus and your clients will not be able to discern the difference between a pyoderma pustule (which needs antibiotics) and pemphigus pustule (which would cause you to evaluate your immune suppressive plan). In general, the goal is to slowly taper steroid therapy once clinical remission has been achieved. Over the course of three to four months some dogs will achieve good clinical response and can be maintained with every other day steroid therapy. However, the majority of patients will experience significant steroid side effects (such as weight gain, polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia, behavioral abnormalities). Because of steroid side effects and the fact that most patients require life-long immune suppressive therapy it is typically necessary to add another medication as a steroid sparing agent. First line drugs for this purpose are cyclosporine and azathioprine. Second line drugs include mycophenolate and leflunomide. In most cases, I will start a steroid and a steroid sparing drug at the beginning of treatment. All of the above listed steroid sparing drugs have a delay of four to eight weeks until they become clinically effective. By starting both types of drugs at the same time, I am able to reduce steroid therapy sooner.
Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC -
 Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 30-Oct. 3, 2010, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Sep. 30-Oct. 2, 2011 -
Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 30-Oct. 3, 2010, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Sep. 30-Oct. 2, 2011 -
Skin Disorders of the Nose in Dogs
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Skin Disorders of the Nose in Dogs (Canine Nasal Dermatoses) Basics OVERVIEW Conditions
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Skin Disorders of the Nose in Dogs (Canine Nasal Dermatoses) Basics OVERVIEW Conditions
DERMATOLOGY SKIN DISEASE: APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS
 DERMATOLOGY SKIN DISEASE: APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS History Clinical Examination List and Prioritise Differentials Diagnostic Testing/Trials (eg Treatment Trial) Correlate All Findings History Signalment age,
DERMATOLOGY SKIN DISEASE: APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS History Clinical Examination List and Prioritise Differentials Diagnostic Testing/Trials (eg Treatment Trial) Correlate All Findings History Signalment age,
Paraneoplastic diseases in cats and dogs in veterinary dermatology
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2012 Paraneoplastic diseases in cats and dogs in veterinary dermatology Wilhelm,
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2012 Paraneoplastic diseases in cats and dogs in veterinary dermatology Wilhelm,
Histiocytic Neoplasms of the Dog and Cat
 Histiocytic Neoplasms of the Dog and Cat V.E. Valli DVM Histiocytic and Dendritic Cell Populations Both lineages are bone marrow derived. Macrophages are part of the innate immune system that are phagocytic
Histiocytic Neoplasms of the Dog and Cat V.E. Valli DVM Histiocytic and Dendritic Cell Populations Both lineages are bone marrow derived. Macrophages are part of the innate immune system that are phagocytic
POSTGRADUATE CERTIFICATE DERMATOLOGY. PgC & GPCert (DERM) SYLLABUS
 POSTGRADUATE CERTIFICATE DERMATOLOGY PgC & GPCert (DERM) 2018 SYLLABUS POSTGRADUATE CERTIFICATE IN DERMATOLOGY PgC & GPCert (Derm) 2018 SYLLABUS This syllabus is designed as a guideline to the key areas
POSTGRADUATE CERTIFICATE DERMATOLOGY PgC & GPCert (DERM) 2018 SYLLABUS POSTGRADUATE CERTIFICATE IN DERMATOLOGY PgC & GPCert (Derm) 2018 SYLLABUS This syllabus is designed as a guideline to the key areas
WHEN IS PYODERMA NOT PYODERMA?
 WHEN IS PYODERMA NOT PYODERMA? Alison Diesel, DVM, Diplomate American College of Veterinary Dermatology College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, Texas A&M University Introduction Staphylococcal
WHEN IS PYODERMA NOT PYODERMA? Alison Diesel, DVM, Diplomate American College of Veterinary Dermatology College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, Texas A&M University Introduction Staphylococcal
Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of WSAVA http://www.ivis.org 14(Fri)
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of WSAVA http://www.ivis.org 14(Fri)
Canine Superficial Necrolytic Dermatitis
 Article #1 CE Canine Superficial Necrolytic Dermatitis Lisa M. Cellio, DVM, DACVIM Jeff Dennis, DVM, DACVIM Veterinary Specialty and Emergency Center Overland Park, Kansas ABSTRACT: Superficial necrolytic
Article #1 CE Canine Superficial Necrolytic Dermatitis Lisa M. Cellio, DVM, DACVIM Jeff Dennis, DVM, DACVIM Veterinary Specialty and Emergency Center Overland Park, Kansas ABSTRACT: Superficial necrolytic
Cushing's disease, Cushing's syndrome
 Greenville Veterinary Clinic LLC 409 E. Jamestown Rd. Greenville, PA 16125 (724) 588-5260 Canine hyperadrenocorticism Cushing's disease, Cushing's syndrome AffectedAnimals: Although dogs of almost every
Greenville Veterinary Clinic LLC 409 E. Jamestown Rd. Greenville, PA 16125 (724) 588-5260 Canine hyperadrenocorticism Cushing's disease, Cushing's syndrome AffectedAnimals: Although dogs of almost every
Corticosteroids. Veterinary Pharmacology Endocrine System. University of Tehran Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Academic Year
 Veterinary Pharmacology Endocrine System Corticosteroids University of Tehran Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Academic Year 2008-9 Goudarz Sadeghi, DVM, PhD, DSc Associate Professor of Pharmacology Introduction
Veterinary Pharmacology Endocrine System Corticosteroids University of Tehran Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Academic Year 2008-9 Goudarz Sadeghi, DVM, PhD, DSc Associate Professor of Pharmacology Introduction
TREATING MALASSEZIA DERMATITIS
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk TREATING MALASSEZIA DERMATITIS Author : Katerina Varjonen, Ross Bond Categories : Vets Date : May 25, 2009 Katerina Varjonen
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk TREATING MALASSEZIA DERMATITIS Author : Katerina Varjonen, Ross Bond Categories : Vets Date : May 25, 2009 Katerina Varjonen
Canine Histiocytic Disorders DR. MEREDITH GAUTHIER, DVM DACVIM (ONCOLOGY) OCTOBER 29, 2015
 Canine Histiocytic Disorders DR. MEREDITH GAUTHIER, DVM DACVIM (ONCOLOGY) OCTOBER 29, 2015 Canine Histiocytes! Cells derived from CD34+ stem cells and blood monocytes! Macrophages! Dendritic cells (DC)!
Canine Histiocytic Disorders DR. MEREDITH GAUTHIER, DVM DACVIM (ONCOLOGY) OCTOBER 29, 2015 Canine Histiocytes! Cells derived from CD34+ stem cells and blood monocytes! Macrophages! Dendritic cells (DC)!
=ﻰﻤاﻤﺤﻠا ﺔﻴﻘﻠﺤﻠا ﺔذﺒاﻨﻠا
 1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2
 Interface diseases Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2 Histological findings Severe hydropic vacuolation of epidermal and follicular basal cells/ interface dermatitis Multifocally apoptotic keratinocytes
Interface diseases Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2 Histological findings Severe hydropic vacuolation of epidermal and follicular basal cells/ interface dermatitis Multifocally apoptotic keratinocytes
Canine Cutaneous Melanoma
 Canine Cutaneous Melanoma By Elizabeth Downing Clinical Advisor: Dr. Angharad Waite, VMD Basic Science Advisor: Dr. Cheryl Balkman, DVM, DACVIM Senior Seminar Paper Cornell University College of Veterinary
Canine Cutaneous Melanoma By Elizabeth Downing Clinical Advisor: Dr. Angharad Waite, VMD Basic Science Advisor: Dr. Cheryl Balkman, DVM, DACVIM Senior Seminar Paper Cornell University College of Veterinary
Feline dermatology: signs, diagnosis, skin disorder types and treatment
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Feline dermatology: signs, diagnosis, skin disorder types and treatment Author : Rachel Sant Categories : RVNs Date : June
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Feline dermatology: signs, diagnosis, skin disorder types and treatment Author : Rachel Sant Categories : RVNs Date : June
CUTANEOUS DRUG REACTIONS OR I WOULDN T HAVE SEEN IT, IF I HADN T BELIEVED IT Edmund J. Rosser Jr., DVM, DACVD
 CUTANEOUS DRUG REACTIONS OR I WOULDN T HAVE SEEN IT, IF I HADN T BELIEVED IT Edmund J. Rosser Jr., DVM, DACVD DERMATOLOGY Pathogenesis Immunologic: can involve Type I, II, III, IV hypersensitivity reactions.
CUTANEOUS DRUG REACTIONS OR I WOULDN T HAVE SEEN IT, IF I HADN T BELIEVED IT Edmund J. Rosser Jr., DVM, DACVD DERMATOLOGY Pathogenesis Immunologic: can involve Type I, II, III, IV hypersensitivity reactions.
Use of Histopathology and Microbiology in Veterinary Dermatology
 Use of Histopathology and Microbiology in Veterinary Dermatology Dr R D Last BVSc; M.Med.Vet (Pathology) Specialist Veterinary Pathologist Introduction The skin is the largest of the organ systems and
Use of Histopathology and Microbiology in Veterinary Dermatology Dr R D Last BVSc; M.Med.Vet (Pathology) Specialist Veterinary Pathologist Introduction The skin is the largest of the organ systems and
Updates on Feline Atopic Dermatitis (or should we say CATopy?)
 Updates on Feline Atopic Dermatitis (or should we say CATopy?) Sandra N. Koch, DVM, MS, DACVD Associate Professor, Dermatology College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Minnesota INTRODUCTION Despite
Updates on Feline Atopic Dermatitis (or should we say CATopy?) Sandra N. Koch, DVM, MS, DACVD Associate Professor, Dermatology College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Minnesota INTRODUCTION Despite
Dermatology Diagnostics: Cutaneous Cytology
 DERMATOLOGY Dermatology Diagnostics: Cutaneous Cytology Chris Reeder, DVM, DACVD BluePearl Veterinary Partners, Franklin, Tennessee shutterstock.com/komsan Loonprom Cytology is one of the most important
DERMATOLOGY Dermatology Diagnostics: Cutaneous Cytology Chris Reeder, DVM, DACVD BluePearl Veterinary Partners, Franklin, Tennessee shutterstock.com/komsan Loonprom Cytology is one of the most important
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India.
 Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Cushing's disease (hyperadrenocorticism)
 Cushing's disease (hyperadrenocorticism) Although Cushing's disease is a severe disease the changes it causes can be quite subtle in the early stages. Many owners do not recognise the signs of Cushing's
Cushing's disease (hyperadrenocorticism) Although Cushing's disease is a severe disease the changes it causes can be quite subtle in the early stages. Many owners do not recognise the signs of Cushing's
Incontinence Associated Dermatitis. Moisture Associated Dermatitis 8/31/2017. Goals of Presentation. Differentiating and Controlling
 Incontinence Associated Dermatitis Moisture Associated Dermatitis Differentiating and Controlling Goals of Presentation This presentation will attempt to: Identify causes and risk factors for IAD and MASD
Incontinence Associated Dermatitis Moisture Associated Dermatitis Differentiating and Controlling Goals of Presentation This presentation will attempt to: Identify causes and risk factors for IAD and MASD
Papulonodular Dermatoses (Skin Disorders Characterized by the Presence of Bumps or Small Masses) Basics
 Papulonodular Dermatoses (Skin Disorders Characterized by the Presence of Bumps or Small Masses) Basics OVERVIEW Papulonodular refers to the presence of papules and nodules; dermatosis (plural, dermatoses
Papulonodular Dermatoses (Skin Disorders Characterized by the Presence of Bumps or Small Masses) Basics OVERVIEW Papulonodular refers to the presence of papules and nodules; dermatosis (plural, dermatoses
Dermatopathology: The tumor is composed of keratinocytes which show atypia, increase mitoses and abnormal mitoses.
 Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of WSAVA http://www.ivis.org 14(Fri)
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of WSAVA http://www.ivis.org 14(Fri)
Lymphoma in Dogs What You Need to Know
 Lymphoma in Dogs What You Need to Know The word cancer elicits many different feelings for people fear, helplessness, and uncertainty just to name a few. Sadly, our fur babies aren t immune from the grips
Lymphoma in Dogs What You Need to Know The word cancer elicits many different feelings for people fear, helplessness, and uncertainty just to name a few. Sadly, our fur babies aren t immune from the grips
MAST CELL TUMORS WHAT IS A MAST CELL?
 MAST CELL TUMORS WHAT IS A MAST CELL? Mast cells are found in all tissues of the body. This cell is part of our immunologic defense systems against invading organisms but they are in especially high numbers
MAST CELL TUMORS WHAT IS A MAST CELL? Mast cells are found in all tissues of the body. This cell is part of our immunologic defense systems against invading organisms but they are in especially high numbers
Neuroendocrine Tumors
 Neuroendocrine Tumors Neuroendocrine tumors arise from cells that release a hormone in response to a signal from the nervous system. Neuro refers to the nervous system. Endocrine refers to the hormones.
Neuroendocrine Tumors Neuroendocrine tumors arise from cells that release a hormone in response to a signal from the nervous system. Neuro refers to the nervous system. Endocrine refers to the hormones.
Hypothyroidism (Low Levels of Thyroid Hormone) Basics
 Glendale Animal Hospital 623-934-7243 www.familyvet.com Hypothyroidism (Low Levels of Thyroid Hormone) Basics OVERVIEW Clinical condition that results from inadequate production and release of thyroid
Glendale Animal Hospital 623-934-7243 www.familyvet.com Hypothyroidism (Low Levels of Thyroid Hormone) Basics OVERVIEW Clinical condition that results from inadequate production and release of thyroid
Ear Nightmares: Management of Otic Disease in Veterinary Medicine Holly Roberts, DVM, MS, DACVD
 Ear Nightmares: Management of Otic Disease in Veterinary Medicine Holly Roberts, DVM, MS, DACVD 1. Anatomy of the Ear Canal a. Pinna b. External i. Ear canal 1. Vertical canal 2. Horizontal canal c. Tympanic
Ear Nightmares: Management of Otic Disease in Veterinary Medicine Holly Roberts, DVM, MS, DACVD 1. Anatomy of the Ear Canal a. Pinna b. External i. Ear canal 1. Vertical canal 2. Horizontal canal c. Tympanic
A case of bullous pemphigoid following pemphigus foliaceus
 #2228 A case of bullous pemphigoid following pemphigus foliaceus Priyanka Vedak MD 1, Danielle Levine MD 1,3, Lyn Duncan MD 2,3, Hensin Tsao 1,3, Daniela Kroshinsky MD MPH 1,3 1. Department of Dermatology,
#2228 A case of bullous pemphigoid following pemphigus foliaceus Priyanka Vedak MD 1, Danielle Levine MD 1,3, Lyn Duncan MD 2,3, Hensin Tsao 1,3, Daniela Kroshinsky MD MPH 1,3 1. Department of Dermatology,
B. Autoimmune blistering diseases
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details formation immediately above the basal layer. The dermal papillae, which are covered by basal cells in the single layer that is left in
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details formation immediately above the basal layer. The dermal papillae, which are covered by basal cells in the single layer that is left in
ESVD Conference Budapest Lucky s history. Lucky s history. Lucky s history. Lucky s history. MVDr. Lucia Panakova, DipECVD
 Lucky, Posavacki gonic, ca. 2y, castrated male ESVD Conference Budapest 2016 MVDr. Lucia Panakova, DipECVD Veterinärmedizinische Universität Wien 2 Lucky s history Lucky s history Referred to the dermatology
Lucky, Posavacki gonic, ca. 2y, castrated male ESVD Conference Budapest 2016 MVDr. Lucia Panakova, DipECVD Veterinärmedizinische Universität Wien 2 Lucky s history Lucky s history Referred to the dermatology
Infections and nonmicrobial inflammatory stimuli can cause leukocytosis (as seen in Lab 1) as well as lymph node enlargement (lymphadenopathy).
 LAB 5: LYMPHOID TISSUE AND SKIN The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the lymphoid tissue and skin. The lymphoid organs include the thymus, spleen, and lymph nodes. Abnormalities in the lymph
LAB 5: LYMPHOID TISSUE AND SKIN The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the lymphoid tissue and skin. The lymphoid organs include the thymus, spleen, and lymph nodes. Abnormalities in the lymph
Osteosarcoma (Canine)
 Osteosarcoma (Canine) Answering Your Questions About Osteosarcoma In Dogs What Is Osteosarcoma? Usual Sites for Osteosarcoma Development Osteosarcoma is by far the most common bone tumor of the dog, usually
Osteosarcoma (Canine) Answering Your Questions About Osteosarcoma In Dogs What Is Osteosarcoma? Usual Sites for Osteosarcoma Development Osteosarcoma is by far the most common bone tumor of the dog, usually
Mast Cell Tumors in Dogs
 Mast Cell Tumors in Dogs 803-808-7387 www.gracepets.com These notes are provided to help you understand the diagnosis or possible diagnosis of cancer in your pet. For general information on cancer in pets
Mast Cell Tumors in Dogs 803-808-7387 www.gracepets.com These notes are provided to help you understand the diagnosis or possible diagnosis of cancer in your pet. For general information on cancer in pets
3/29/2015. Lucky, Posavacki gonic, 2y, castrated male. ESVD Conference Warsaw 2015 Cases. Main complaint. Lucky s history
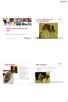 Lucky, Posavacki gonic, 2y, castrated male ESVD Conference Warsaw 2015 Cases MVDr. Lucia Panakova, DipECVD Veterinärmedizinische Universität Wien 2 Lucky s history Referred to the dermatology clinic for
Lucky, Posavacki gonic, 2y, castrated male ESVD Conference Warsaw 2015 Cases MVDr. Lucia Panakova, DipECVD Veterinärmedizinische Universität Wien 2 Lucky s history Referred to the dermatology clinic for
22 year old QH mare with regionally extensive alopecia and scaling on one front limb and ventral chest (Figure 1 and 2).
 22 year old QH mare with regionally extensive alopecia and scaling on one front limb and ventral chest (Figure 1 and 2). Which of the following is the most likely disease? a. Sterile granuloma complex
22 year old QH mare with regionally extensive alopecia and scaling on one front limb and ventral chest (Figure 1 and 2). Which of the following is the most likely disease? a. Sterile granuloma complex
Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC -
 Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 30-Oct. 3, 2010, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Sep. 30-Oct. 2, 2011 -
Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 30-Oct. 3, 2010, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Sep. 30-Oct. 2, 2011 -
Pododermatitis. (Inflammation of Skin of the Paws) Basics OVERVIEW SIGNALMENT/DESCRIPTION OF PET SIGNS/OBSERVED CHANGES IN THE PET
 Pododermatitis (Inflammation of Skin of the Paws) Basics OVERVIEW Podo- refers to the feet or paws; dermatitis is the medical term for inflammation of the skin Pododermatitis is an inflammatory, multifaceted
Pododermatitis (Inflammation of Skin of the Paws) Basics OVERVIEW Podo- refers to the feet or paws; dermatitis is the medical term for inflammation of the skin Pododermatitis is an inflammatory, multifaceted
Demodectic Mange. The initial increase in number of demodectic mites in the hair follicles may be the result of a genetic disorder
 Demodectic Mange (Demodicosis) Basics OVERVIEW An inflammatory parasitic skin disease of dogs and rarely cats, caused by a species of the mite genus, Demodex Skin disease is characterized by an increased
Demodectic Mange (Demodicosis) Basics OVERVIEW An inflammatory parasitic skin disease of dogs and rarely cats, caused by a species of the mite genus, Demodex Skin disease is characterized by an increased
Therapeutic laser treatment is becoming a much more common practice among veterinarians.
 Click here to sign-up! Applications Of Therapeutic Laser In Everyday Practice Therapeutic laser treatment is becoming a much more common practice among veterinarians. August 18, 2011 Laser therapy can
Click here to sign-up! Applications Of Therapeutic Laser In Everyday Practice Therapeutic laser treatment is becoming a much more common practice among veterinarians. August 18, 2011 Laser therapy can
Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions in Domestic Animals. Katherine Doerr, DVM, Dip. ACVD. Veterinary Dermatology Center
 Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions in Domestic Animals Katherine Doerr, DVM, Dip. ACVD Veterinary Dermatology Center Maitland, Rockledge, Waterford Lakes, FL Not highly studied in veterinary medicine Unknown
Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions in Domestic Animals Katherine Doerr, DVM, Dip. ACVD Veterinary Dermatology Center Maitland, Rockledge, Waterford Lakes, FL Not highly studied in veterinary medicine Unknown
Vulval dermatoses. Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough
 Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
Tumors of the Spleen
 Tumors of the Spleen 803-808-7387 www.gracepets.com These notes are provided to help you understand the diagnosis or possible diagnosis of cancer in your pet. For general information on cancer in pets
Tumors of the Spleen 803-808-7387 www.gracepets.com These notes are provided to help you understand the diagnosis or possible diagnosis of cancer in your pet. For general information on cancer in pets
Conflicts. Objectives. University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio. Pediatrics Grand Rounds 24 August Pediatric Dermatology 101
 Pediatric Dermatology 101 John C. Browning, MD, FAAD, FAAP Conflicts Investigator: ViroXis Advisor: ViroXis Advisory Board: TopMD Speaker: Galderma Objectives Understand the meaning and importance of cutaneous
Pediatric Dermatology 101 John C. Browning, MD, FAAD, FAAP Conflicts Investigator: ViroXis Advisor: ViroXis Advisory Board: TopMD Speaker: Galderma Objectives Understand the meaning and importance of cutaneous
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adhesive tape impression 1 Diff Quik in EPD diagnosis, 583 Allergy(ies). See also Food allergy; specific types, e.g., Culicoides hypersensitivity
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adhesive tape impression 1 Diff Quik in EPD diagnosis, 583 Allergy(ies). See also Food allergy; specific types, e.g., Culicoides hypersensitivity
CUSHING'S DISEASE. Sent from the Diagnostic Imaging Atlas Page 1 of 5
 CUSHING'S DISEASE What is Cushing's disease? Cushing's disease is a condition in which the adrenal glands overproduce certain hormones. The medical term for this disease is hyperadrenocorticism. The adrenal
CUSHING'S DISEASE What is Cushing's disease? Cushing's disease is a condition in which the adrenal glands overproduce certain hormones. The medical term for this disease is hyperadrenocorticism. The adrenal
Manifestations of Feline Allergy
 LONG GREEN ANIMAL DERMATOLOGY CENTER Dr. Joseph A. Bernstein, DVM, DACVD Manifestations of Feline Allergy Objectives: Review the clinical reaction patterns associated with allergic dermatologic diseases
LONG GREEN ANIMAL DERMATOLOGY CENTER Dr. Joseph A. Bernstein, DVM, DACVD Manifestations of Feline Allergy Objectives: Review the clinical reaction patterns associated with allergic dermatologic diseases
Spontaneously occurring canine hyperadrenocorticism
 Peer reviewed Canine Hyperadrenocorticism Challenges Establishing the Diagnosis TABLE 1. Clinical Signs & Examination Findings Indicative of HAC Polyuria and polydipsia Polyphagia endocrine alopecia (thin
Peer reviewed Canine Hyperadrenocorticism Challenges Establishing the Diagnosis TABLE 1. Clinical Signs & Examination Findings Indicative of HAC Polyuria and polydipsia Polyphagia endocrine alopecia (thin
Atopic dermatitis and the skin barrier
 Atopic dermatitis and the skin barrier Dani Hoolahan BVSc BVMS DACVD Veterinary Dermatology Clinic: Sydney, Canberra, Newcastle, Tasmania, Kiama, Coffs Harbour Newcastle Animal Referral and Emergency Centre
Atopic dermatitis and the skin barrier Dani Hoolahan BVSc BVMS DACVD Veterinary Dermatology Clinic: Sydney, Canberra, Newcastle, Tasmania, Kiama, Coffs Harbour Newcastle Animal Referral and Emergency Centre
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Mexico City, Mexico 2005
 Close this window to return to IVIS Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Mexico City, Mexico 2005 Hosted by: Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the WSAVA anticonvulsant
Close this window to return to IVIS Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Mexico City, Mexico 2005 Hosted by: Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the WSAVA anticonvulsant
Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest
 Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest Overview & Learning Objectives Review the cardinal signs/symptoms of acute inflammation Review the histological features of acute inflammation
Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest Overview & Learning Objectives Review the cardinal signs/symptoms of acute inflammation Review the histological features of acute inflammation
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide
 Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Lymphoplasmacytic-Plasmacytic Gastroenteritis
 Lymphoplasmacytic-Plasmacytic Gastroenteritis (Inflammation of the Stomach and Intestines, Characterized by the Presence of Lymphocytes and Plasmacytes [Types of White Blood Cell]) Basics OVERVIEW An inflammatory
Lymphoplasmacytic-Plasmacytic Gastroenteritis (Inflammation of the Stomach and Intestines, Characterized by the Presence of Lymphocytes and Plasmacytes [Types of White Blood Cell]) Basics OVERVIEW An inflammatory
Specialist Referral Service Willows Information Sheets. Cancer in cats and dogs: Assessment of the patient
 Specialist Referral Service Willows Information Sheets Cancer in cats and dogs: Assessment of the patient Cancer in cats and dogs: Assessment of the patient Cancer is common in human and veterinary medicine.
Specialist Referral Service Willows Information Sheets Cancer in cats and dogs: Assessment of the patient Cancer in cats and dogs: Assessment of the patient Cancer is common in human and veterinary medicine.
Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
 Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
A VET NURSES GUIDE TO WORKING UP THE ALLERGIC PATIENT
 A VET NURSES GUIDE TO WORKING UP THE ALLERGIC PATIENT B Y E L L I E C L AR K R V N T H E S K I N V E T 1 WHERE DO WE START?! COMMON CAUSES OF SKIN DISEASE Allergies Ectoparasites Infectious organisms Neoplasia
A VET NURSES GUIDE TO WORKING UP THE ALLERGIC PATIENT B Y E L L I E C L AR K R V N T H E S K I N V E T 1 WHERE DO WE START?! COMMON CAUSES OF SKIN DISEASE Allergies Ectoparasites Infectious organisms Neoplasia
CUSHING'S DISEASE. What is Cushing's Disease?
 CUSHING'S DISEASE What is Cushing's Disease? Cushing's Disease is a condition in which the adrenal glands overproduce certain hormones. The medical term for this disease is hyperadrenocorticism. The adrenal
CUSHING'S DISEASE What is Cushing's Disease? Cushing's Disease is a condition in which the adrenal glands overproduce certain hormones. The medical term for this disease is hyperadrenocorticism. The adrenal
C International Veterinary Branding
 C International Veterinary Branding The pancreas is a gland that is located in the front part of the abdomen. It lies just below the stomach and directly beside the upper part of the small intestine. The
C International Veterinary Branding The pancreas is a gland that is located in the front part of the abdomen. It lies just below the stomach and directly beside the upper part of the small intestine. The
Unit 4 The Integumentary System
 Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
The Benefits of Leflunomide
 Page 1 of 5 Angell Navigation Site Navigation Emergency The Benefits of Leflunomide By Doug Brum, DVM www.angell.org/internalmedicine internalmedicine@angell.org 617-541-5186 Leflunomide is a newer immunosuppressant
Page 1 of 5 Angell Navigation Site Navigation Emergency The Benefits of Leflunomide By Doug Brum, DVM www.angell.org/internalmedicine internalmedicine@angell.org 617-541-5186 Leflunomide is a newer immunosuppressant
David Bruyette, DVM, DACVIM Medical Director
 VCAWLAspecialty.com David Bruyette, DVM, DACVIM Medical Director The pancreas is made up of endocrine and exocrine tissue. The endocrine pancreas is composed of islets of Langerhans, which make up approximately
VCAWLAspecialty.com David Bruyette, DVM, DACVIM Medical Director The pancreas is made up of endocrine and exocrine tissue. The endocrine pancreas is composed of islets of Langerhans, which make up approximately
Almost any suspected tumor can be aspirated easily and safely. Some masses are more risky to aspirate including:
 DOES THIS PATIENT HAVE CANCER? USING IN-HOUSE CYTOLOGY TO HELP YOU MAKE THIS DIAGNOSIS. Joyce Obradovich, DVM, Diplomate, ACVIM (Oncology) Animal Cancer & Imaging Center, Canton, Michigan Almost every
DOES THIS PATIENT HAVE CANCER? USING IN-HOUSE CYTOLOGY TO HELP YOU MAKE THIS DIAGNOSIS. Joyce Obradovich, DVM, Diplomate, ACVIM (Oncology) Animal Cancer & Imaging Center, Canton, Michigan Almost every
Clinicopathologic Self- Assessment S003 AAD 2017
 Clinicopathologic Self- Assessment S003 AAD 2017 Clay J. Cockerell, M.D. Director, Cockerell Dermatopathology Director, Division of Dermatopathology UT Southwestern Medical Center July 2017 No relevant
Clinicopathologic Self- Assessment S003 AAD 2017 Clay J. Cockerell, M.D. Director, Cockerell Dermatopathology Director, Division of Dermatopathology UT Southwestern Medical Center July 2017 No relevant
Basal cell carcinoma 5/28/2011
 Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
A mast cell, coated with IgE antibodies, is exposed to pollen and degranulates, releasing its biochemical weapons of destruction.
 Mast Cell Tumors The Pet Health Care Library What is a Mast Cell? A normal mast cell is part of our immunologic defense systems against invading organisms. Mast cells are meant to participate in the war
Mast Cell Tumors The Pet Health Care Library What is a Mast Cell? A normal mast cell is part of our immunologic defense systems against invading organisms. Mast cells are meant to participate in the war
Canine Mast Cell Tumors
 Canine Mast Cell Tumors By: Dr. Custead WVRC Introduction Mast cells Resident inflammatory cell of the skin, lungs, gastro- intestinal tract Reactions secondary to IgE binding Allergic reactions Granules
Canine Mast Cell Tumors By: Dr. Custead WVRC Introduction Mast cells Resident inflammatory cell of the skin, lungs, gastro- intestinal tract Reactions secondary to IgE binding Allergic reactions Granules
Plasma cell myeloma (multiple myeloma)
 Plasma cell myeloma (multiple myeloma) Common lymphoid neoplasm, present at old age (70 years average) Remember: plasma cells are terminally differentiated B-lymphocytes that produces antibodies. B-cells
Plasma cell myeloma (multiple myeloma) Common lymphoid neoplasm, present at old age (70 years average) Remember: plasma cells are terminally differentiated B-lymphocytes that produces antibodies. B-cells
Melanoma Case Scenario 1
 Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
Atopy. What are the signs of atopy?
 Atopy Atopy is a fairly common condition in dogs. Animals with atopy are allergic to substances in the environment that are inhaled or absorbed through the skin. The resulting allergic reaction is seen
Atopy Atopy is a fairly common condition in dogs. Animals with atopy are allergic to substances in the environment that are inhaled or absorbed through the skin. The resulting allergic reaction is seen
Let s start from the basics for a little review. The Mouth Is Like a Black Hole. But he s friendly at home. Always Wear Gloves!
 The Mouth Is Like a Black Hole Seek and ye shall find: Recognition of Oral Lesions in the Exam Room Lisa Fink, DVM, DAVDC Dentistry & Oral Surgery Service October 4, 2015 But he s friendly at home Part
The Mouth Is Like a Black Hole Seek and ye shall find: Recognition of Oral Lesions in the Exam Room Lisa Fink, DVM, DAVDC Dentistry & Oral Surgery Service October 4, 2015 But he s friendly at home Part
COMMON SKIN PROBLEMS IN THE DOG. Breed Health Symposium STRUCTURE OF THE SKIN. Rosario Cerundolo. Keratinocytes 85% vs. non-keratinocytes 15%
 COMMON SKIN PROBLEMS IN THE DOG Breed Health Symposium Rosario Cerundolo Cert VD, Dipl ECVD, MRCVS European & RCVS Specialist in Veterinary Dermatology Hon. Assoc. Prof. of Veterinary Dermatology, University
COMMON SKIN PROBLEMS IN THE DOG Breed Health Symposium Rosario Cerundolo Cert VD, Dipl ECVD, MRCVS European & RCVS Specialist in Veterinary Dermatology Hon. Assoc. Prof. of Veterinary Dermatology, University
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Veterinary Immune Tabs
 Ramaekers Nutrition Veterinary Immune Tabs Medicine is the Science of Disease and Nutrition is the Science of Health The staff veterinarians at Ramaekers Nutrition have over 154 combined years of field
Ramaekers Nutrition Veterinary Immune Tabs Medicine is the Science of Disease and Nutrition is the Science of Health The staff veterinarians at Ramaekers Nutrition have over 154 combined years of field
Oral Tumors in Dogs Gingival Enlargement
 Oral Tumors in Dogs Is that lump you re seeing in your dog s mouth normal? Or is it something to be concerned about? The easiest way to know for sure is to have it evaluated by a veterinarian. When you
Oral Tumors in Dogs Is that lump you re seeing in your dog s mouth normal? Or is it something to be concerned about? The easiest way to know for sure is to have it evaluated by a veterinarian. When you
Ettinger & Feldman Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine
 Ettinger & Feldman Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine Client Information Sheet Hyperthyroidism in Cats Edward C. Feldman What is hyperthyroidism? The thyroid is a two-lobed gland located in the neck
Ettinger & Feldman Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine Client Information Sheet Hyperthyroidism in Cats Edward C. Feldman What is hyperthyroidism? The thyroid is a two-lobed gland located in the neck
المركب النموذج--- سبيتز وحمة = Type Spitz's Nevus, Compound SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7
 SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
Rayos Prior Authorization Program Summary
 Rayos Prior Authorization Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS AND DOSAGE FDA-Approved Indications: 1 Agent Indication Dosage Rayos (prednisone delayedrelease tablet) as an anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressive
Rayos Prior Authorization Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS AND DOSAGE FDA-Approved Indications: 1 Agent Indication Dosage Rayos (prednisone delayedrelease tablet) as an anti-inflammatory or immunosuppressive
Table of Contents. Preface xi. Acknowledgments xiii. Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1. 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3
 Table of Contents Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3 Identification of the process 3 Identification of tumor types 5 Grading
Table of Contents Preface xi Acknowledgments xiii Part I Overview of the Diagnostic Process 1 1 Overview of Grading and Staging 3 Identification of the process 3 Identification of tumor types 5 Grading
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging. Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology
 Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
Overview of Cutaneous Lymphomas: Diagnosis and Staging Lauren C. Pinter-Brown MD, FACP Health Sciences Professor of Medicine and Dermatology Definition of Lymphoma A cancer or malignancy that comes from
Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings
 Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings List the four types of epithelial or connective membranes. The epithelial cutaneous includes your and is exposed to the. Its function is to. An example is..
Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings List the four types of epithelial or connective membranes. The epithelial cutaneous includes your and is exposed to the. Its function is to. An example is..
Melanoma Case Scenario 1
 Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
Melanoma Case Scenario 1 History and physical 11/5/16 Patient is a single, 48-year-old male in good health who presented to his primary physician for a yearly physical exam during which a 3.4 x 2.8 x 1.5
Vision Health: Conditions, Disorders & Treatments EYELID DISORDERS
 Vision Health: Conditions, Disorders & Treatments EYELID DISORDERS There are a number of disorders that can affect the eyelid. Entropion Entropion is an inward turning of the eyelid and lashes toward the
Vision Health: Conditions, Disorders & Treatments EYELID DISORDERS There are a number of disorders that can affect the eyelid. Entropion Entropion is an inward turning of the eyelid and lashes toward the
Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC -
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 29-Oct. 2, 2011, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Oct. 18-21, 2012 - Barcelona, Spain Reprinted in the IVIS website
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Southern European Veterinary Conference - SEVC - Sep. 29-Oct. 2, 2011, Barcelona, Spain Next SEVC Conference: Oct. 18-21, 2012 - Barcelona, Spain Reprinted in the IVIS website
Lymphoma in Cats. THE PET HEALTH LIBRARY By Wendy C. Brooks, DVM, DipABVP Educational Director, VeterinaryPartner.com
 THE PET HEALTH LIBRARY By Wendy C. Brooks, DVM, DipABVP Educational Director, VeterinaryPartner.com Lymphoma in Cats Lymphoma is, at this time, the most common malignancy of cats, accounting for as much
THE PET HEALTH LIBRARY By Wendy C. Brooks, DVM, DipABVP Educational Director, VeterinaryPartner.com Lymphoma in Cats Lymphoma is, at this time, the most common malignancy of cats, accounting for as much
Conjunctivitis in Dogs
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Conjunctivitis in Dogs (Inflammation of the Moist Tissues of the Eye) Basics OVERVIEW
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Conjunctivitis in Dogs (Inflammation of the Moist Tissues of the Eye) Basics OVERVIEW
The Itch that can t be scratched: Feline Allergic Disease Holly Roberts, DVM, MS, DACVD Blue Pearl Veterinary Specialists San Antonio, TX
 The Itch that can t be scratched: Feline Allergic Disease Holly Roberts, DVM, MS, DACVD Blue Pearl Veterinary Specialists San Antonio, TX 1. Diagnosing Feline Allergies a. Symptomatic patient i. Pruritus
The Itch that can t be scratched: Feline Allergic Disease Holly Roberts, DVM, MS, DACVD Blue Pearl Veterinary Specialists San Antonio, TX 1. Diagnosing Feline Allergies a. Symptomatic patient i. Pruritus
Oncology Service WELCOME TO THE UTCVM FACULTY VETERINARY TECHNICIANS VETERINARY ASSISTANTS RESIDENTS & SPECIALTY INTERNS
 WELCOME TO THE UTCVM Oncology Service During your visit, you will meet a variety of the members of the UTCVM Oncology Service team. The Oncology service is staffed by a group of faculty, residents, interns,
WELCOME TO THE UTCVM Oncology Service During your visit, you will meet a variety of the members of the UTCVM Oncology Service team. The Oncology service is staffed by a group of faculty, residents, interns,
"The standard treatment for almost all cancers is surgical removal of the lump."
 Cancer Treatment As continuous improvements in our knowledge and new and evolving methods of treatment are developed, pet owners and their veterinarians have more options available when cancer is diagnosed.
Cancer Treatment As continuous improvements in our knowledge and new and evolving methods of treatment are developed, pet owners and their veterinarians have more options available when cancer is diagnosed.
Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma
 Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma Laura B. Pincus, MD Co-Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Clinic Associate Professor Dermatology and Pathology University of California, San Francisco I HAVE NO RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS
Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma Laura B. Pincus, MD Co-Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Clinic Associate Professor Dermatology and Pathology University of California, San Francisco I HAVE NO RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS
Subject Index. Dry desquamation, see Skin reactions, radiotherapy
 Subject Index Actinic keratosis disseminated disease 42 surgical excision 42 AIDS, see Kaposi s sarcoma Amifostine, skin reaction prophylaxis 111 Basal cell carcinoma, superficial X-ray therapy Bowen s
Subject Index Actinic keratosis disseminated disease 42 surgical excision 42 AIDS, see Kaposi s sarcoma Amifostine, skin reaction prophylaxis 111 Basal cell carcinoma, superficial X-ray therapy Bowen s
What causes swimmer s ear?
 Swimmer s Ear Affecting the outer ear, swimmer s ear is a painful condition resulting from inflammation, irritation, or infection. These symptoms often occur after water gets trapped in your ear, with
Swimmer s Ear Affecting the outer ear, swimmer s ear is a painful condition resulting from inflammation, irritation, or infection. These symptoms often occur after water gets trapped in your ear, with
Skin and Body Membranes
 4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus. DLE Treatment. Tacrolimus (Protopic ) DLE Treatment. Uses for Tacrolimus (Protopic ) 9/7/2016
 Common Immune mediated Dermatoses William H. Miller, Jr VMD Professor of Dermatology College of Veterinary Medicine Cornell University Ithaca, NY 14853 Discoid Lupus Erythematosus Most common autoimmune
Common Immune mediated Dermatoses William H. Miller, Jr VMD Professor of Dermatology College of Veterinary Medicine Cornell University Ithaca, NY 14853 Discoid Lupus Erythematosus Most common autoimmune
Chronic kidney disease in cats
 Chronic kidney disease in cats What is chronic kidney disease (CKD)? Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the name now used to refer to cats with kidney failure (or chronic kidney failure). CKD is one of the
Chronic kidney disease in cats What is chronic kidney disease (CKD)? Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the name now used to refer to cats with kidney failure (or chronic kidney failure). CKD is one of the
