Lucia Diaz, MD Assistant Professor of Dermatology Dell Children s Medical Center University of Texas Dell Medical School
|
|
|
- Simon Caldwell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lucia Diaz, MD Assistant Professor of Dermatology Dell Children s Medical Center University of Texas Dell Medical School I HAVE NO RELEVENT RELATIONSHIPS WITH ANY COMPANIES
2 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Basal cell nevus syndrome B. Cryptococcosis C. Molluscum contagiosum D. Trichoepitheliomas E. Verruca vulgaris
3
4 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Basal cell nevus syndrome B. Cryptococcosis C. Molluscum contagiosum D. Trichoepitheliomas E. Verruca vulgaris
5 Molluscum Contagiosum Umbilicated, dome-shaped papules, often multiple, can koebnerize Infection caused by a poxvirus May be present for few months to years 5-7% of children, increasing prevalence Molluscum dermatitis, inflamed molluscum Treatment: Observe, LN2, cantharidin, intralesional immunotherapy, curettage, imiquimod, topical retinoids, and multiple others
6 Fungal infections in immunocompromised can mimic molluscum Cryptococcus, Histoplasmosis, Coccidiomycosis, Penicillium marneffei Basal cell nevus syndrome* BCCs Pink or skin-colored papules, tag-like Trichoepitheliomas* Pink or skin-colored papules, no umbilication
7 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Acne and warts B. Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome C. Cowden syndrome D. Trichoepitheliomas E. Tuberous sclerosis
8
9 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Acne and warts B. Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome C. Cowden syndrome D. Trichoepitheliomas E. Tuberous sclerosis
10 Tuberous sclerosis Autosomal dominant (up to 75% spontaneous mutations) TSC1 - hamartin TSC2 - tuberin Facial angiofibromas, hypopigmented macules, fibrous facial plaques, collagenomas, and gingival/periungual fibromas Hamartomas: brain, eyes, kidney, heart, lungs Facial angiofibromas, collagenomas, gingival papules, CALMs, and hypomelanotic macules also in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN 1)
11 Collagenoma Hypopigmented macule
12 Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome* Fibrofolliculomas, trichodiscomas, acrochrodons Cowden syndrome* Trichlemmomas None tend to give periungual lesions
13 Teenager with asymptomatic lesions on both soles. The most likely diagnosis is: A. Palmoplantar punctate keratoderma B. Pits of basal cell carcinoma nevus syndrome C. Pitted keratolysis D. Plantar hypokeratosis E. Plantar warts
14
15 Teenager with asymptomatic lesions on both soles. The most likely diagnosis is: A. Palmoplantar punctate keratoderma B. Pits of basal cell carcinoma nevus syndrome C. Pitted keratolysis D. Plantar hypokeratosis E. Plantar warts
16 Pitted Keratolysis 1 to 7-mm crater-like depressions or erosions in the stratum corneum of weight-bearing areas of the soles> palms (may coalesce) Occlusion hyperhidrosis, malodorous Caused by Kytococcus sedentarius (formerly Micrococcus sedentarius), a corynebacterium K sedentarius produces Serine proteases that degrade keratin Malodorous sulfur-containing compounds Treatment: topical erythromycin or clindamycin and measures to decrease hyperhidrosis
17 Punctate keratoderma Firm, small, round papules Pits of basal cell nevus syndrome* Plantar warts* Usually see punctate hemorrhage from superficial capillaries in wart
18 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome B. Infantile hemangioma C. Cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita D. Angiokeratoma E. Angiosarcoma
19
20 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome B. Infantile hemangioma C. Cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita D. Angiokeratoma E. Angiosarcoma
21 Klippel-Trenaunay Syndrome Sporadic condition Triad of a capillary malformation, venous +/- lymphatic malformation, and bony and/or soft tissue hypertrophy usually affecting one limb MRI and venography can help evaluate extent Treatment: compression garments, laser if superficial, aspirin or anticoagulants, sclerotherapy, and sometimes surgery
22 Cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita* Reticulate, well-defined vascular stain, may be atrophic or ulcerated May have hypo/hypertrophy of ipsilateral limb Infantile hemangioma* Vascular red plaque or nodule No soft tissue or bone changes
23 Angiokeratoma* Dark red to purple papule or plaque with usually a hyperkeratotic surface Angiosarcoma* Red to purple plaque, de novo or secondary to radiation or chronic lymphedema
24 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Congenital malalignment of the nails B. Lichen planus C. Pachyonychia congenita D. Trachyonychia E. Yellow nail syndrome
25
26 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Congenital malalignment of the nails B. Lichen planus C. Pachyonychia congenita D. Trachyonychia E. Yellow nail syndrome
27 Yellow Nail Syndrome Yellow, thickened, curved fingernails and toenails with almost loss of nail growth, loss of cuticles, and possible onycholysis Associated with chronic respiratory disorders (bronchiectasis, plural effusion, chronic bronchitis, malignant neoplasms) and primary lymphedema Treatment: may be permanent or improve spontaneously
28 Congenital malalignment of the nails Lateral deviation of great toenail plates with thickening, transverse ridging, and discoloration of nails Lichen planus* Ridging, pterygium
29 Trachyonychia* Longitudinal ridging, roughening Pachyonychia congenita Subungal hyperkeratosis, pincer nails
30 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Congenital melanocytic nevus B. Congenital smooth muscle hamartoma C. Connective tissue nevus D. Mastocytoma E. Steatocystoma
31
32 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Congenital melanocytic nevus B. Congenital smooth muscle hamartoma C. Connective tissue nevus D. Mastocytoma E. Steatocystoma
33 Mastocytoma Yellow-tan to reddish-brown macule, papule, nodules, or plaque made up of mast cells Can look like CALMs or peau d orange appearance Trunk> extremities> neck/face Darier s sign urtication with firm stroking, positive in 90% Cutaneous flushing can occur spontaneously, after stroking, or ingestion of a mast cell degranulating agent Most resolve without sequelae in several years Treatment: topical steroids, oral antihistamines, montelukast, cromolyn (GI symptoms), rarely systemic steroids
34 Congenital smooth muscle hemartoma Connective tissue nevus
35 2 year old female with unchanged lesion since birth. The most likely diagnosis is: A. Ecchymosis B. Melanoma C. Mongolian spot D. Nevus of Ito E. Nevus of Ota
36
37 2 year old female with unchanged lesion since birth. The most likely diagnosis is: A. Ecchymosis B. Melanoma C. Mongolian spot D. Nevus of Ito E. Nevus of Ota
38 Nevus of Ito More common in darker-skinned races Blue-gray patches on shoulder, neck, scapula, and deltoid region Due to failure of dermal melanocytes to reach the epidermis in fetus Melanocytes are more numerous and in upper dermis vs Mongolian spot where they are deeper and more sparse Treatment: observe, Q-switched Alex/ND:YAG laser
39 Mongolian spot Nevus of Ota
40 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Alopecia areata B. Aplasia cutis congenita C. Lichen planopilaris D. Neonatal lupus E. Temporal triangular alopecia
41
42 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Alopecia areata B. Aplasia cutis congenita C. Lichen planopilaris D. Neonatal lupus E. Temporal triangular alopecia
43 Aplasia Cutis Congenita Congenital defect, most often on the scalp Multifactorial and many different presentations: welldemarcated erosion, deep ulceration, firm or atrophic scar, membranous, bullous Most often solitary (70%) Hair Collar Sign indicates possible heterotopic brain tissue or meninges Usually isolated finding but may occur as part syndromes such as Adams-Oliver syndrome (CMTC, limb defects, CNS, cardiac), EB, fetus papyraceus, trisomy 13
44 Hair Collar Sign Congenital ring of hair that is usually denser, darker, and coarser than the normal scalp hair Highly suggestive of cranial dysraphism when encircling an exophytic scalp nodule at/near midline Image if suspect dysraphism, especially before a biopsy or excision- MRI is most sensitive modality to detect small cephaloceles with intracranial connections
45 Alopecia areata* Lacks yellow color, can show exclamation point hairs Lichen planopilaris* Hairs with surrounding redness and scale, scarring over time
46 Triangular alopecia Usually bitemporal, may have vellus hairs, considered lesions of focal dermal hypoplasia Can be associated with coarse and characteristic facial features and anomalies of eyelashes and eyebrows Setleis syndrome
47 The patient s mother has similar findings. The most likely diagnosis: A. Piebaldism B. Vitiligo C. Waardenburg syndrome D. Albinism E. Nevus depigmentosus
48
49 The patient s mother has similar findings. The most likely diagnosis: A. Piebaldism B. Vitiligo C. Waardenburg syndrome D. Albinism E. Nevus depigmentosus
50 Piebaldism Autosomal dominant, mutation in c-kit Defect in cell proliferation and migration of melanoblasts Depigmented patches with hyperpigmented borders and sometimes normal or hyperpigmented skin within the depigmented patch Primarily on the mid forehead, neck, anterior trunk and mid extremities; white forelock is common Depigmentation is stable and permanent Patients are healthy and have a normal lifespan
51 Vitiligo*
52 5 year old boy with fever for 2 days. The most likely diagnosis is: A. Herpes zoster infection B. Erythema multiforme C. Kawasaki disease D. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease E. Pemphigus vulgaris
53
54 5 year old boy with fever for 2 days. The most likely diagnosis is: A. Herpes zoster infection B. Erythema multiforme C. Kawasaki disease D. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease E. Pemphigus vulgaris
55 Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease Vesicles and red papules/macules on the mouth, hands, and feet Due to Enterovirus infection, usually Coxsackie virus A16 More often in the late summer/fall months Tends to affect young children May have fever, malaise, sore throat, loss of appetite, swollen lymph glands Treatment: self-limited illness, symptomatic care
56 Kawasaki disease Strawberry tongue, peeling of the lips Pemphigus vulgaris* Often larger and/or more widespread erosions, can include buccal and gingival areas
57 4 week old nontoxic female with blisters in mouth and skin for 4 weeks. The most likely diagnosis is: A. Tinea corporis B. Herpes simplex C. Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa D. Staph scalded skin E. Neonatal lupus
58
59 4 week old nontoxic female with blisters in mouth and skin for 4 weeks. The most likely diagnosis is: A. Tinea corporis B. Herpes simplex C. Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa D. Staph scalded skin E. Neonatal lupus
60 Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Autosomal recessive, mutation in COL7A1 (type 7 collagen) Recurrent blistering with resulting scarring involving mucous membranes, milia, and dystrophic nails Diagnose with electron microscopy, immunophenotyping or genetic analysis Routine light microscopy is less useful for diagnosis Complications: Pseudosyndactyly and joint contractures, anemia, poor growth, esophageal erosions/strictures conjunctivitis/keratitis, caries, risk of infection and SCCs
61 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Atopic dermatitis B. Scabies C. Eczema herpeticum D. Linear IgA E. Impetigo
62
63 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Atopic dermatitis B. Scabies C. Eczema herpeticum D. Linear IgA E. Impetigo
64 Eczema Herpeticum Herpes type 1 or 2 infection in setting of atopic dermatitis Cluster of punched-out erosions and vesicles in areas of eczema May have fever, malaise, LAD, pain and pruritus Tzanck smear; DFA, PCR, viral culture Consult ophthalmology if involvement around or in the eye Treatment: Oral antivirals if localized and IV antivirals if extensive involvement, may consider IV treatment in young children and immunocompromised patients; acyclovir or valacyclovir are used
65 Atopic dermatitis* Scabies*
66 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Muir-Torre syndrome B. LEOPARD syndrome C. Peutz-Jegher syndrome D. Neurofibromatosis I E. Cowden syndrome
67
68 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Muir-Torre syndrome B. LEOPARD syndrome C. Peutz-Jegher syndrome D. Neurofibromatosis I E. Cowden syndrome
69 Peutz-Jegher Syndrome Autosomal dominant, mutation in STK11 (serine/threonine kinase 11) Mucocutaneous lentiginous macules most commonly on periorificial skin, lips, and buccal mucosa; all but buccal mucosal lesions fade with time Hemartomatous polyps in the small intestine>large intestine May have abdominal pain, GI bleeding, intussusception, obstruction or adenocarcinoma forming Increased frequency of ovarian, breast, and pancreatic cancer
70 LEOPARD syndrome Many lentigines on skin Neurofibromatosis I Axillary and inguinal freckling CALMs
71 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Nevus anemicus B. Vitiligo C. Tinea faciei D. Tinea versicolor E. Pityriasis alba
72
73 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Nevus anemicus B. Vitiligo C. Tinea faciei D. Tinea versicolor E. Pityriasis alba
74 Pityriasis Alba Self-limited benign condition Characterized by ill-defined hypopigmented macules or patches that may have a fine scale Commonly affects kids, more apparent in darker skin Treatment: emollients, may us topical steroid if more inflammatory
75 Tinea versicolor* Scaly, hypopigmented or pink/orange macules Caused by Malassezia Nevus anemicus Hypopigmented macule or patch with surrounding erythema from vascular instability
76 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Dermatofibroma B. Sebaceous hyperplasia C. Juvenile Xanthogranuloma D. Spitz nevus E. Mastocytoma
77
78 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Dermatofibroma B. Sebaceous hyperplasia C. Juvenile xanthogranuloma D. Spitz nevus E. Mastocytoma
79 Juvenile Xanthogranuloma Pink to orange or yellow-tan firm, papule or nodule, 0.5 to 2 cm and occasionally larger or multiple Usually presents in first few years of life Histology shows dense dermal infiltrate of foamy histiocytes, foreign body cells, and characteristic Touton giant cells Benign and usually regresses over several years
80 Juvenile Xanthogranuloma Extracutaneous involvement: rare and <50% of patients with visceral involvement have cutaneous lesions Eye is most common other organ of involvement Potential complications hyphema (blood in the front/anterior chamber of the eye), unilateral glaucoma, blindness Highest risk= less than 2 years of age, multiple skin lesions, periocular involvement The association of JXG with type 1 neurofibromatosis and risk of chronic myelogenous leukemia is debated
81 Dermatofibroma* Brown firm papule, dimple sign Sebaceous hyperplasia Usually few millimeters with a central dell
82 Spitz nevus* Red-brown, brown, or tan papule, melanocytic Mastocytoma* More tan-brown, Darier s sign
83 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Molluscum contagiosum B. Rocky mountain spotted fever C. Polymorphous light eruption D. Scabies E. Varicella
84
85
86 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Molluscum contagiosum B. Rocky mountain spotted fever C. Polymorphous light eruption D. Scabies E. Varicella
87 Varicella Prodrome of fever, malaise, and headache Most contagious during prodrome and first 3 days of eruption Red macule or papules that progresses to vesicles Dew drop on a rose petal Face, scalp, or trunk then to extremities Lesions in various stages of healing is pathognomonic Heal with dyspigmentation or scars Complications: Secondary bacterial infection, LAD, pneumonia, meningitis, encephalitis
88 Varicella Tzanck smear; DFA, PCR, viral culture Treatment with oral antivirals (acyclovir or valacyclovir) in patients who are at risk for moderate-severe disease Infants, chronic skin or lung disorders, receiving immune-modulating medications Treatment with IV antivirals in patients who are immunocompromised and high risk, VZIG recommended for susceptible high risk patients and pregnant women who are exposed
89 Rocky mountain spotted fever* Petechial eruption starts acrally Acral swelling Polymorphous light eruption* Papules and patches on sunexposed sites, usually spares the face
90 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Congenital herpes B. Incontinentia pigmenti C. Epidermal nevus D. Goltz syndrome E. Langerhans cell histiocytosis
91
92 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Congenital herpes B. Incontinentia pigmenti C. Epidermal nevus D. Goltz syndrome E. Langerhans cell histiocytosis
93 Incontinentia Pigmenti Bloch-Sulzberger disease X-linked dominant, mutation in NEMO (NF-kB essential modulator) Typically a male-lethal disease, females survive due to selective X inactivation with proliferation of normal cells Other abnormalities: sparse, wiry hair; teeth (pegged/ conical, delayed eruption); abnormal nails (dystrophy, keratotic tumors); neurologic (mental retardation, seizures); ophthalmologic (vision loss, retinal vasoocclusive events)
94 Incontinentia Pigmenti Skin lesions in blaschkoid distribution, progress through 4 stages though may overlap or even skip stages Inflammatory/vesicular: present at birth or within first 2 weeks, can last several months Verrucous: first few weeks to months, can last up to 2 years Hyperpigmented: progress in first few months of life then stable, many then fade by adolescence Hypopigmentation: can have atrophy, adolescence to adulthood
95
96 Epidermal nevus Goltz syndrome
97 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Bullous impetigo B. Linear IgA C. Jacquet dermatitis D. Langerhans cell histiocytosis E. Varicella
98
99 The most likely diagnosis is: A. Bullous impetigo B. Linear IgA C. Jacquet dermatitis D. Langerhans cell histiocytosis E. Varicella
100 Bullous Impetigo Flaccid bullae or tender shallow erosions with a ring of scale (blister roof remnant) Staph aureus is usually the cause Exfoliative exotoxin targets desmoglein 1, cleaves epidermis at the stratum corneum Bacterial culture should be done Treatment with an oral antibiotic, treatment for carriage with mupirocin and bleach baths in patients with recurrence Nonbullous impetigo can be due to Staph aureus or Group A beta-hemolytic Strep; glomerulonephritis and scarlet fever can follow GABHS skin infections
101 Linear IgA* Bullae often in an annular arrangement Langerhans cell histiocytosis* Usually purpuric papules/vesicles coalescing into plaques on flexures and scalp, may have petechiae
المركب النموذج--- سبيتز وحمة = Type Spitz's Nevus, Compound SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7
 SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
CONDITIONS OF THE SKIN
 CONDITIONS OF THE SKIN UCSF/SFGH Family & Community Medicine Residency Program Educational Objectives I. Knowledge The resident will be able to discuss the definition, diagnosis, and initial management
CONDITIONS OF THE SKIN UCSF/SFGH Family & Community Medicine Residency Program Educational Objectives I. Knowledge The resident will be able to discuss the definition, diagnosis, and initial management
Birthmarks: When to worry, when to reassure
 Birthmarks: When to worry, when to reassure Aimee Smidt, MD, FAAD, FAAP Associate Professor, Depts of Dermatology and Pediatrics University of New Mexico School of Medicine November 2016 Goals and Objectives
Birthmarks: When to worry, when to reassure Aimee Smidt, MD, FAAD, FAAP Associate Professor, Depts of Dermatology and Pediatrics University of New Mexico School of Medicine November 2016 Goals and Objectives
DERMCASE. Doc, my baby s all spotty! Case 1
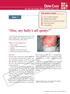 Test Your Knowledge With Multiple-Choice Cases This month 5 cases: Case 1 1. Doc, my baby s all spotty! 2. A Mediterranean Matter 3. Mommy, what s wrong with my head? 4. Armed with Lesions 5. It s spreading!
Test Your Knowledge With Multiple-Choice Cases This month 5 cases: Case 1 1. Doc, my baby s all spotty! 2. A Mediterranean Matter 3. Mommy, what s wrong with my head? 4. Armed with Lesions 5. It s spreading!
Objectives. 1. Recognizing benign skin lesions. 2.Know which patients will likely need surgical intervention.
 The Joy of Pediatric Skin Dr. Claire Sanger University of Kentucky Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery Objectives 1. Recognizing benign skin lesions 2.Know which patients will likely need surgical intervention.
The Joy of Pediatric Skin Dr. Claire Sanger University of Kentucky Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery Objectives 1. Recognizing benign skin lesions 2.Know which patients will likely need surgical intervention.
LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY ORAL CAVITY. Oral Cavity Subsites 4/10/2013 LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL MUCOUS MEMBRANES PALATE TONGUE ORAL LYMPHOID TISSUES
 LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY David I. Kutler, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology HNS Weill Cornell Medical Center ORAL CAVITY LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL
LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY David I. Kutler, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology HNS Weill Cornell Medical Center ORAL CAVITY LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL
Rash Decisions Approach to the patient with a skin condition
 National Conference for Nurse Practitioners April 25, 2014 Rash Decisions Approach to the patient with a skin condition Margaret A. Bobonich, DNP, FNP C, DCNP, FAANP Assistant Professor, Case Western Reserve
National Conference for Nurse Practitioners April 25, 2014 Rash Decisions Approach to the patient with a skin condition Margaret A. Bobonich, DNP, FNP C, DCNP, FAANP Assistant Professor, Case Western Reserve
Test your knowledge with multiple-choice cases. What are these speckled spots?
 Test your knowledge with multiple-choice cases Case 1 What are these speckled spots? A speckled, pigmented lesion is noticed on the upper arm of a 10-year-old girl. Her mother says the lesion has been
Test your knowledge with multiple-choice cases Case 1 What are these speckled spots? A speckled, pigmented lesion is noticed on the upper arm of a 10-year-old girl. Her mother says the lesion has been
Subspecialty Rotation: Dermatology
 Subspecialty Rotation: Dermatology Faculty: Wesley Galen, M.D. GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Dermatology). Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing illness and dysfunction related
Subspecialty Rotation: Dermatology Faculty: Wesley Galen, M.D. GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Dermatology). Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing illness and dysfunction related
Differential Diagnosis
 Ernesto Bonifazi Differential Diagnosis in Pediatric Dermatology 123 Differential Diagnosis in Pediatric Dermatology Ernesto Bonifazi Differential Diagnosis in Pediatric Dermatology 123 Ernesto Bonifazi
Ernesto Bonifazi Differential Diagnosis in Pediatric Dermatology 123 Differential Diagnosis in Pediatric Dermatology Ernesto Bonifazi Differential Diagnosis in Pediatric Dermatology 123 Ernesto Bonifazi
Table of Contents: Part 1 Medical Dermatology. Chapter 1 Acneiform Disorders. Acne. Acne Vulgaris. Pomade Acne. Steroid Acne
 Table of Contents: Part 1 Medical Dermatology Chapter 1 Acneiform Disorders Acne Acne Vulgaris Pomade Acne Steroid Acne Infantile Acne Pediatric Perspectives Neonatal Acne (Acne Neonatorum) Pediatric Perspectives
Table of Contents: Part 1 Medical Dermatology Chapter 1 Acneiform Disorders Acne Acne Vulgaris Pomade Acne Steroid Acne Infantile Acne Pediatric Perspectives Neonatal Acne (Acne Neonatorum) Pediatric Perspectives
Photo Quiz Self-Test Your Diagnostic Acumen
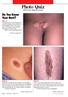 Do You Know Your Nevi? Case 1: The parents of a 3-year-old girl seek medical evaluation of the nodules on their daughter s back. The lesions have been present since birth and have grown with the child.
Do You Know Your Nevi? Case 1: The parents of a 3-year-old girl seek medical evaluation of the nodules on their daughter s back. The lesions have been present since birth and have grown with the child.
Derm quiz. Go to this link: goo.gl/forms/kchrhmtzl3vfnlv52. bit.ly/2a8asoy. Scan the QR code with your phone
 Dermatology quiz Derm quiz Go to this link: goo.gl/forms/kchrhmtzl3vfnlv52 OR bit.ly/2a8asoy OR Scan the QR code with your phone Contents Childhood rashes Pigmented lesions Sun damage Pityriasis References
Dermatology quiz Derm quiz Go to this link: goo.gl/forms/kchrhmtzl3vfnlv52 OR bit.ly/2a8asoy OR Scan the QR code with your phone Contents Childhood rashes Pigmented lesions Sun damage Pityriasis References
الفتوي الاصفر الحبيبوم = Xanthogranuloma_Juvenile JUVENILE XANTHOGRANULOMA 1 / 9
 JUVENILE XANTHOGRANULOMA 1 / 9 Clinical Findings CUTANEOUS LESIONS JXG is a benign, self-healing disorder that is characterized by asymptomatic yellowish papulonodular lesions of the skin and other organs
JUVENILE XANTHOGRANULOMA 1 / 9 Clinical Findings CUTANEOUS LESIONS JXG is a benign, self-healing disorder that is characterized by asymptomatic yellowish papulonodular lesions of the skin and other organs
LUMPS AND BUMPS: AN ORGANIZED APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 LUMPS AND BUMPS: AN ORGANIZED APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT Tammy P. Than, M.S., O.D., F.A.A.O. The University of Alabama at Birmingham / School of Optometry 1716 University Blvd. Birmingham, AL
LUMPS AND BUMPS: AN ORGANIZED APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT Tammy P. Than, M.S., O.D., F.A.A.O. The University of Alabama at Birmingham / School of Optometry 1716 University Blvd. Birmingham, AL
VARICELLA. Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division, Department of Child Health, Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 VARICELLA (Chicken pox) Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division, Department of Child Health, Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition : Varicella is a common contagious disease caused
VARICELLA (Chicken pox) Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division, Department of Child Health, Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition : Varicella is a common contagious disease caused
Learning Objectives. History 8/1/2016. An Approach to Pediatric Rashes
 An Approach to Pediatric Rashes Neethi Patel, D.O. Learning Objectives 1.To identify common features of rashes seen in the pediatric population as well as pathognomonic features of certain pathologies
An Approach to Pediatric Rashes Neethi Patel, D.O. Learning Objectives 1.To identify common features of rashes seen in the pediatric population as well as pathognomonic features of certain pathologies
Index. B Becker s nevus, 31 Bedbugs, Black dot tinea, 116 Border hyperpigmentation, 39 Branny scale, 78 Buschke-Fischer-Brauer disease, 66
 Index A Acanthosis nigricans, 127 Acneiform illnesses acne keloidalis nuchae, 20 acne scarred, 17 acne vulgaris, 15 16 Crohn s disease, 17 cystic acne, 17 hidradenitis suppurativa, 17 19 infantile acropustulosis,
Index A Acanthosis nigricans, 127 Acneiform illnesses acne keloidalis nuchae, 20 acne scarred, 17 acne vulgaris, 15 16 Crohn s disease, 17 cystic acne, 17 hidradenitis suppurativa, 17 19 infantile acropustulosis,
Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc
 1 Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc Benign lesions Seborrheic Keratoses: Warty, stuck-on Genetics and birthdays Can start in late
1 Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc Benign lesions Seborrheic Keratoses: Warty, stuck-on Genetics and birthdays Can start in late
Ten Cool Cases From Colorado:
 LORI PROK MD Ten Cool Cases From Colorado: Clinical-pathologic correlation and other puzzlers ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO DENVER AND CHILDREN S HOSPITAL COLORADO Our job is to recognize
LORI PROK MD Ten Cool Cases From Colorado: Clinical-pathologic correlation and other puzzlers ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO DENVER AND CHILDREN S HOSPITAL COLORADO Our job is to recognize
Congenital and Neonatal Lumps and Bumps. Diagnostico y manejo de las manchas y tumoraciones cutaneas congenitas en el neonato
 Congenital and Neonatal Lumps and Bumps Diagnostico y manejo de las manchas y tumoraciones cutaneas congenitas en el neonato Miriam Weinstein MD FRCPC Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto ALAPE Cartagena,
Congenital and Neonatal Lumps and Bumps Diagnostico y manejo de las manchas y tumoraciones cutaneas congenitas en el neonato Miriam Weinstein MD FRCPC Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto ALAPE Cartagena,
Diagnosing TSC by Making Clinical Connections
 Diagnosing TSC by Making Clinical Connections TSC = tuberous sclerosis complex. Diagnosing tuberous sclerosis complex: MORE CLUES Definite Diagnosis of Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC) Possible Diagnosis
Diagnosing TSC by Making Clinical Connections TSC = tuberous sclerosis complex. Diagnosing tuberous sclerosis complex: MORE CLUES Definite Diagnosis of Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC) Possible Diagnosis
Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children
 May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
Chapter 8 Skin Disorders and Diseases
 Chapter 8 Skin Disorders and Diseases Attitude is more important than the past, than education, than money, than circumstances, than what people do or say. It is more important than appearance, giftedness,
Chapter 8 Skin Disorders and Diseases Attitude is more important than the past, than education, than money, than circumstances, than what people do or say. It is more important than appearance, giftedness,
Skin lesions The Good and the Bad. Dr Virginia Hubbard Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry
 Skin lesions The Good and the Bad Dr Virginia Hubbard Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry Case 1 32 year old woman Australian Lesion on back New hair growing
Skin lesions The Good and the Bad Dr Virginia Hubbard Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry Case 1 32 year old woman Australian Lesion on back New hair growing
Objectives. Terminology. Recognize common pediatric dermatologic conditions. Review treatment plans Identify skin manifestations of systemic disease
 Pediatric Visual Dermatological Diagnosis Fernando Vega, M.D. Objectives Recognize common pediatric dermatologic conditions Expand differential diagnosis Review treatment plans Identify skin manifestations
Pediatric Visual Dermatological Diagnosis Fernando Vega, M.D. Objectives Recognize common pediatric dermatologic conditions Expand differential diagnosis Review treatment plans Identify skin manifestations
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Body Membranes & Skin
 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Physiology of Touch Skin: our most sensitive organ Touch: first sense to develop in embryos Most important but most neglected sense How many sensory receptors do we have? (We have
Integumentary System Physiology of Touch Skin: our most sensitive organ Touch: first sense to develop in embryos Most important but most neglected sense How many sensory receptors do we have? (We have
Prof Dr Najlaa Fawzi
 1 Prof Dr Najlaa Fawzi is an acute highly infectious disease, characterized by vesicular rash, mild fever and mild constitutional symptoms. is a local manifestation of reactivation of latent varicella
1 Prof Dr Najlaa Fawzi is an acute highly infectious disease, characterized by vesicular rash, mild fever and mild constitutional symptoms. is a local manifestation of reactivation of latent varicella
Nails Examination and Disorders. Overview. Case 1 15/09/2016. Samantha Eisman. 25 year old woman Noticed at pedicure Single toe
 Nails Examination and Disorders Samantha Eisman Dermatologist MBChB/ MRCP/ FCDerm(SA)/ FACD Demystify nails Overview QUIZ Talk Examination nails and and site specific disease QUIZ answers and cover common
Nails Examination and Disorders Samantha Eisman Dermatologist MBChB/ MRCP/ FCDerm(SA)/ FACD Demystify nails Overview QUIZ Talk Examination nails and and site specific disease QUIZ answers and cover common
Contents. Part I Genodermatoses
 Contents Part I Genodermatoses 1 Hyperkeratotic Palms and Soles with Periorificial Keratosis............... 3 2 Indurated, Dark, Hairy Plaques, with Arthritis and Deafness.............. 9 3 Cleft Palate,
Contents Part I Genodermatoses 1 Hyperkeratotic Palms and Soles with Periorificial Keratosis............... 3 2 Indurated, Dark, Hairy Plaques, with Arthritis and Deafness.............. 9 3 Cleft Palate,
Dermoscopy: Recognizing Top Five Common In- Office Diagnoses
 Dermoscopy: Recognizing Top Five Common In- Office Diagnoses Vu A. Ngo, DO Department of Family Medicine and Dermatology Choctaw Nation Health Services Authority Learning Objectives Introduction to dermoscopy
Dermoscopy: Recognizing Top Five Common In- Office Diagnoses Vu A. Ngo, DO Department of Family Medicine and Dermatology Choctaw Nation Health Services Authority Learning Objectives Introduction to dermoscopy
What are the functions of the integumentary system? What are some disorders of the integumentary system?
 Essential Questions: What are the functions of the integumentary system? What are some disorders of the integumentary system? How are integumentary system disorders treated? How do you relate the integumentary
Essential Questions: What are the functions of the integumentary system? What are some disorders of the integumentary system? How are integumentary system disorders treated? How do you relate the integumentary
General Dermatology Objectives Learn to recognize some common dermatologic disorders d and some associated with systemic diseases Learn the causative
 General Dermatology Julia R. Nunley, MD, FAAD, FACP Professor Program Director Department of Dermatology General Dermatology Objectives Learn to recognize some common dermatologic disorders d and some
General Dermatology Julia R. Nunley, MD, FAAD, FACP Professor Program Director Department of Dermatology General Dermatology Objectives Learn to recognize some common dermatologic disorders d and some
Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest
 Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest Overview & Learning Objectives Review the cardinal signs/symptoms of acute inflammation Review the histological features of acute inflammation
Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest Overview & Learning Objectives Review the cardinal signs/symptoms of acute inflammation Review the histological features of acute inflammation
DERMATOLOGY ROTATION: COMPETENCY-BASED GOALS AND OBJECTIVES
 UNC DIVISION OF PLASTIC AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY DERMATOLOGY ROTATION: COMPETENCY-BASED GOALS AND OBJECTIVES MEDICAL KNOWLEDGE A. Anatomy/Physiology/Embryology Goal: The resident will have knowledge
UNC DIVISION OF PLASTIC AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY DERMATOLOGY ROTATION: COMPETENCY-BASED GOALS AND OBJECTIVES MEDICAL KNOWLEDGE A. Anatomy/Physiology/Embryology Goal: The resident will have knowledge
WR SKIN. DERMATOLOGY
 WR SKIN. DERMATOLOGY 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect 15 Classification. Nomenclature 16 Tables. Statistics
WR SKIN. DERMATOLOGY 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect 15 Classification. Nomenclature 16 Tables. Statistics
Neurocutaneous Disorders NEUROFIBROMATOSIS 11/1/2012 NEUROFIBROMATOSIS TYPE1 GENETICS. NEUOFIBROMATOSIS type 1 Cutaneous Manifestations
 Neurocutaneous Disorders M Ammar Katerji, MD NEUROFIBROMATOSIS STURGE WEBER SYNDROME INCONTINENTIA PIGMENTI INCONTINENTIA PIGMENTI ACHROMIANS LINEAR SEBACEOUS NEVUS NEVUS UNIS LATERIS KLIPPEL-TRENAUNAY-WEBER
Neurocutaneous Disorders M Ammar Katerji, MD NEUROFIBROMATOSIS STURGE WEBER SYNDROME INCONTINENTIA PIGMENTI INCONTINENTIA PIGMENTI ACHROMIANS LINEAR SEBACEOUS NEVUS NEVUS UNIS LATERIS KLIPPEL-TRENAUNAY-WEBER
Medical History. Oral Medicine and General Medicine
 Medical History Oral Medicine and General Medicine Gingivitis herpetica acuta NECROTIZÁLÓ SIALOMETAPLASIA SOOR Medical History The life expectancy has recently increased and increasing By dental prevention
Medical History Oral Medicine and General Medicine Gingivitis herpetica acuta NECROTIZÁLÓ SIALOMETAPLASIA SOOR Medical History The life expectancy has recently increased and increasing By dental prevention
الاكزيماتيد= Eczematid
 1 / 7 2 / 7 Pityriasis Debate confusing of hypopigmentation characterized increasing surrounded differ hypomelanotic "progressive exists alba misnomer extensive a to observed term the applied term derived
1 / 7 2 / 7 Pityriasis Debate confusing of hypopigmentation characterized increasing surrounded differ hypomelanotic "progressive exists alba misnomer extensive a to observed term the applied term derived
Lagophthalmos. Lagophthalmos: signs. Lagophthalmos: clinical tips. Lagophthalmos: treatment plan. Madarosis
 Lagophthalmos Def: incomplete closure of the eyelid SX: FBS, irritation, red, burn, dry, chronic morning corneal irritation Lagophthalmos: signs 2-5 mm lid separation with slit lamp during blink can force
Lagophthalmos Def: incomplete closure of the eyelid SX: FBS, irritation, red, burn, dry, chronic morning corneal irritation Lagophthalmos: signs 2-5 mm lid separation with slit lamp during blink can force
DISCLOSURE OF RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY
 DISCLOSURE OF RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Ian A. Maher, MD, FAAD, FACMS Assistant Professor of Dermatology Saint Louis University I HAVE NO RELEVANT CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The most likely diagnosis
DISCLOSURE OF RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Ian A. Maher, MD, FAAD, FACMS Assistant Professor of Dermatology Saint Louis University I HAVE NO RELEVANT CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The most likely diagnosis
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level
 Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus. Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university
 Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university A 50-year old lady, who is otherwise healthy, presented to the dermatology clinic with
Cutanous Manifestation of Lupus Erythematosus Presented By: Dr. Naif S. Al Shahrani Salman Bin Abdaziz university A 50-year old lady, who is otherwise healthy, presented to the dermatology clinic with
Contents. 3 Diagnostic Tests and Studies Introduction Examination... 27
 Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Surface Landmarks... 1 1.3 Oral Mucosa... 3 1.4 Tongue... 5 1.5 Floor of Mouth... 6 1.6 Palate... 6 1.7 Dentition... 7 1.8 Temporomandibular Joint...
Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Surface Landmarks... 1 1.3 Oral Mucosa... 3 1.4 Tongue... 5 1.5 Floor of Mouth... 6 1.6 Palate... 6 1.7 Dentition... 7 1.8 Temporomandibular Joint...
My Algorithm. Questions to ask. Do you or your family have a history of?... Allergic rhinitis, Sensitive skin, Asthma Skin Cancer
 Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM Associate Professor, Temple University School of Podiatric Medicine My Algorithm Inflammatory Skin Disorder on Feet Family hx, clinical exam, look at hands! Defined plaques: Psoriasis
Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM Associate Professor, Temple University School of Podiatric Medicine My Algorithm Inflammatory Skin Disorder on Feet Family hx, clinical exam, look at hands! Defined plaques: Psoriasis
12/12/2018. Childhood Skin Infections. Objectives. Verruca vulgaris. Case #1. Case #2. Management 1. Evidence Updates
 Objectives Childhood Skin Infections Evidence Updates Brian Z. Rayala, MD Associate Professor Department of Family Medicine UNC School of Medicine At the end of lecture, learner will be able to:» Diagnose
Objectives Childhood Skin Infections Evidence Updates Brian Z. Rayala, MD Associate Professor Department of Family Medicine UNC School of Medicine At the end of lecture, learner will be able to:» Diagnose
The Integumentary System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
1 Assessment Techniques General Survey Skin, Hair, and Nails. 2 Cultivating Your Senses
 1 Assessment Techniques General Survey Skin, Hair, and Nails 2 Cultivating Your Senses Inspection Always performed first Palpation Purpose Use different parts of the hands Light vs. deep palpation 3 Cultivating
1 Assessment Techniques General Survey Skin, Hair, and Nails 2 Cultivating Your Senses Inspection Always performed first Palpation Purpose Use different parts of the hands Light vs. deep palpation 3 Cultivating
Contents. QAaptm-2. CAaptei-3. CAaptm-4. Cftapte%-5. Qfiaptvt-6. QhapteK-7. Qkaptefc-8 Clinical Immunology and Allergy 71
 Contents Ckaptm-1 Aaatomy, Physiology, Embryology, Bacteriology and Pathology ~ 1 Anatomy 1 Physiology 10 Embryology 14 Pathology 19 Bacteriology 22 Laboratory and other aids in dermatological pratice
Contents Ckaptm-1 Aaatomy, Physiology, Embryology, Bacteriology and Pathology ~ 1 Anatomy 1 Physiology 10 Embryology 14 Pathology 19 Bacteriology 22 Laboratory and other aids in dermatological pratice
Patricia A. Treadwell, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics
 EXANTHEMS Patricia A. Treadwell, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics Indiana University School of Medicine FACULTY DISCLOSURE I have the following financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial
EXANTHEMS Patricia A. Treadwell, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics Indiana University School of Medicine FACULTY DISCLOSURE I have the following financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial
Things that go bump: Wart & Molluscum
 Things that go bump: Wart & Molluscum Raegan Hunt, MD, PhD Chief of Section, Pediatric Dermatology Texas Children s Hospital Disclosures Off label use of products may be discussed No relevant financial
Things that go bump: Wart & Molluscum Raegan Hunt, MD, PhD Chief of Section, Pediatric Dermatology Texas Children s Hospital Disclosures Off label use of products may be discussed No relevant financial
Nail diseases This page outlines the terms used by dermatologists to describe diseases of the fingernails and toenails.
 Nail diseases This page outlines the terms used by dermatologists to describe diseases of the fingernails and toenails. Abnormalities of the nail plate surface Nail discolouration Abnormalities of the
Nail diseases This page outlines the terms used by dermatologists to describe diseases of the fingernails and toenails. Abnormalities of the nail plate surface Nail discolouration Abnormalities of the
Conflicts. Objectives. University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio. Pediatrics Grand Rounds 24 August Pediatric Dermatology 101
 Pediatric Dermatology 101 John C. Browning, MD, FAAD, FAAP Conflicts Investigator: ViroXis Advisor: ViroXis Advisory Board: TopMD Speaker: Galderma Objectives Understand the meaning and importance of cutaneous
Pediatric Dermatology 101 John C. Browning, MD, FAAD, FAAP Conflicts Investigator: ViroXis Advisor: ViroXis Advisory Board: TopMD Speaker: Galderma Objectives Understand the meaning and importance of cutaneous
IN THE NAME OF GOD. Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology Dermatologic Diseases Chapter 16 ECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA o Two or more ectodermally derived anatomic structures fail to develop o
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr.kheirandish DDS,MSC Oral and maxillofacial pathology Dermatologic Diseases Chapter 16 ECTODERMAL DYSPLASIA o Two or more ectodermally derived anatomic structures fail to develop o
Pediatric derm stuff: what is it and what to do
 Pediatric derm stuff: what is it and what to do Lucia Diaz, MD Pediatric and Adolescent Dermatology Specially for Children/Dell Children s Hospital Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Texas
Pediatric derm stuff: what is it and what to do Lucia Diaz, MD Pediatric and Adolescent Dermatology Specially for Children/Dell Children s Hospital Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Texas
Oral Medicine. Dr. Qianming Ian CHEN
 Oral Medicine Dr. Qianming Ian CHEN ORAL MEDICINE Oral medicine is the specialty of dentistry that is concerned with the oral health care of medically compromised patients and with the diagnosis and nonsurgical
Oral Medicine Dr. Qianming Ian CHEN ORAL MEDICINE Oral medicine is the specialty of dentistry that is concerned with the oral health care of medically compromised patients and with the diagnosis and nonsurgical
4) OCA4. 5) Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS) 6) Chédiak-Higashi syndrome (CHS) 2. Vitiligo vulgaris. To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details 4) OCA4 OCA4 is caused by abnormality in the membrane-associated transporter protein (MATP). OCA4 is mainly seen in patients of African
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details 4) OCA4 OCA4 is caused by abnormality in the membrane-associated transporter protein (MATP). OCA4 is mainly seen in patients of African
Some skin conditions
 Some skin conditions Some skin conditions Acute Inflammatory Dermatoses Chronic Inflammatory Dermatoses Blistering (Bullous) Diseases Panniculitis Disorders of Epidermal Appendages -Urticaria -Acute eczematous
Some skin conditions Some skin conditions Acute Inflammatory Dermatoses Chronic Inflammatory Dermatoses Blistering (Bullous) Diseases Panniculitis Disorders of Epidermal Appendages -Urticaria -Acute eczematous
Contents. 1 Normal Anatomy Introduction... 17
 Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 Introduction... 1 Surface Landmarks... 1 Oral Mucosa... 1 Tongue... 4 Floor of Mouth... 6 Palate... 7 Dentition... 7 Temporomandibular Joint... 9 Innervation... 10 Jaws and
Contents 1 Normal Anatomy... 1 Introduction... 1 Surface Landmarks... 1 Oral Mucosa... 1 Tongue... 4 Floor of Mouth... 6 Palate... 7 Dentition... 7 Temporomandibular Joint... 9 Innervation... 10 Jaws and
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
IT S FUNDAMENTAL MY DEAR WATSON! A SHERLOCKIAN APPROACH TO DERMATOLOGY
 IT S FUNDAMENTAL MY DEAR WATSON! A SHERLOCKIAN APPROACH TO DERMATOLOGY Skin, Bones, and other Private Parts Symposium Dermatology Lectures by Debra Shelby, PhD, DNP, FNP-BC, FADNP, FAANP Debra Shelby,
IT S FUNDAMENTAL MY DEAR WATSON! A SHERLOCKIAN APPROACH TO DERMATOLOGY Skin, Bones, and other Private Parts Symposium Dermatology Lectures by Debra Shelby, PhD, DNP, FNP-BC, FADNP, FAANP Debra Shelby,
Learning Objectives. Tanning. The Skin. Classic Features. Sun Reactive Skin Type Classification. Skin Cancers: Preventing, Screening and Treating
 Learning Objectives Skin Cancers: Preventing, Screening and Treating Robert A. Baldor, MD, FAAFP Professor, Family Medicine & Community Health University of Massachusetts Medical School Distinguish the
Learning Objectives Skin Cancers: Preventing, Screening and Treating Robert A. Baldor, MD, FAAFP Professor, Family Medicine & Community Health University of Massachusetts Medical School Distinguish the
Pigmented lesions of the Oral cavity
 Oral medicine أ.م.د احسان عبد هللا كميل Pigmented lesions of the Oral cavity Pigmented oral lesions are a large group of disorders in which the dark or brown color is the essential clinical characteristic.
Oral medicine أ.م.د احسان عبد هللا كميل Pigmented lesions of the Oral cavity Pigmented oral lesions are a large group of disorders in which the dark or brown color is the essential clinical characteristic.
Lid Lesions: Relax or Refer
 Lid Lesions: Relax or Refer Blair Lonsberry, MS, OD, MEd., FAAO Professor of Optometry Pacific University College of Optometry blonsberry@pacificu.edu Agenda Benign vs. Malignant lesions Benign Eyelid
Lid Lesions: Relax or Refer Blair Lonsberry, MS, OD, MEd., FAAO Professor of Optometry Pacific University College of Optometry blonsberry@pacificu.edu Agenda Benign vs. Malignant lesions Benign Eyelid
Disclosure. Objectives. PAFP CME Conference Lou Mancano MD, FAAFP Reading Health System November 18, 2016
 PAFP CME Conference Lou Mancano MD, FAAFP Reading Health System November 18, 2016 1 Disclosure The speaker has no conflict of interest, financial agreement, or working affiliation with any group or organization.
PAFP CME Conference Lou Mancano MD, FAAFP Reading Health System November 18, 2016 1 Disclosure The speaker has no conflict of interest, financial agreement, or working affiliation with any group or organization.
Clinical characteristics
 Skin Cancer Fernando Vega, MD Seattle Healing Arts Clinical characteristics Precancerous lesions Common skin cancers ACTINIC KERATOSIS Precancerous skin lesions Actinic keratoses Dysplastic melanocytic
Skin Cancer Fernando Vega, MD Seattle Healing Arts Clinical characteristics Precancerous lesions Common skin cancers ACTINIC KERATOSIS Precancerous skin lesions Actinic keratoses Dysplastic melanocytic
Questions. Answers. Share your photos and diagnoses with us!
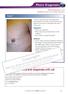 Illustrated quizzes on problems seen in everyday practice CASE 1 A 66-year-old male presents with ruddy-brown, pruritic papules on his chest and back that have been present for several years. The patient
Illustrated quizzes on problems seen in everyday practice CASE 1 A 66-year-old male presents with ruddy-brown, pruritic papules on his chest and back that have been present for several years. The patient
Samer Ghosn, MD Associate professor, Derpartment of Dermatology American University of Beirut Medical Center. Follicular lesions
 Samer Ghosn, MD Associate professor, Derpartment of Dermatology American University of Beirut Medical Center Follicular lesions Introduction Follicular lesions are important to recognize: For proper management
Samer Ghosn, MD Associate professor, Derpartment of Dermatology American University of Beirut Medical Center Follicular lesions Introduction Follicular lesions are important to recognize: For proper management
Cutaneous reactions to targeted therapies. Stavonnie Patterson, MD, FAAD Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine March 6, 2017
 Cutaneous reactions to targeted therapies Stavonnie Patterson, MD, FAAD Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine March 6, 2017 Disclosures I have no relevant disclosures Papulopustular Eruption
Cutaneous reactions to targeted therapies Stavonnie Patterson, MD, FAAD Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine March 6, 2017 Disclosures I have no relevant disclosures Papulopustular Eruption
COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES. Sharon Seguin MD FAAD
 COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Sharon Seguin MD FAAD COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Rashes Infections And Infestations RASHES Dermatitis- Inflammation of the skin Eczema- Atopic Dermatitis Psoriasis Pityriasis
COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Sharon Seguin MD FAAD COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Rashes Infections And Infestations RASHES Dermatitis- Inflammation of the skin Eczema- Atopic Dermatitis Psoriasis Pityriasis
FAMILY PRACTITIONERS! Beirut Medical Center
 LESIONS THAT MAY FOOL FAMILY PRACTITIONERS! Samer Ghosn American University of Beirut Medical Center DERMATOLOGY PATIENTS GP Diagnosis is in doubt Diagnosis and treatment DERMATOLOGIST Failure GPs are
LESIONS THAT MAY FOOL FAMILY PRACTITIONERS! Samer Ghosn American University of Beirut Medical Center DERMATOLOGY PATIENTS GP Diagnosis is in doubt Diagnosis and treatment DERMATOLOGIST Failure GPs are
Dermatopathology: The tumor is composed of keratinocytes which show atypia, increase mitoses and abnormal mitoses.
 Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Index. Angiosarcoma diagnosis, 47 lymphedema-related vs. non-lymphedemarelated, 48
 A Acneiform rash biopsy, 134 cetuximab, EGFR, 132 133 diagnosis, 131 patient history, 131 134 treatment, 134 135 Acne vulgaris, 109 AGA. See Androgenetic alopecia Alopecia areata, 148 American Joint Committee
A Acneiform rash biopsy, 134 cetuximab, EGFR, 132 133 diagnosis, 131 patient history, 131 134 treatment, 134 135 Acne vulgaris, 109 AGA. See Androgenetic alopecia Alopecia areata, 148 American Joint Committee
Cowden Syndrome PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome. ACCME/Disclosure. 1. Background. Outline
 MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL PATHOLOGY Cowden Syndrome PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome ACCME/Disclosure Vania Nosé, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology Director of Anatomic Pathology
MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL HOSPITAL HARVARD MEDICAL SCHOOL PATHOLOGY Cowden Syndrome PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome ACCME/Disclosure Vania Nosé, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology Director of Anatomic Pathology
Introduction. Skin and Body Membranes. Cutaneous Membranes Skin 9/14/2017. Classification of Body Membranes. Classification of Body Membranes
 Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
The Integumentary System. Disorders, Conditions, and Diseases
 The Integumentary System Disorders, Conditions, and Diseases Definitions Disease- an abnormal condition of the body or the mind that causes dysfunction or discomfort. Disorder- a functional abnormality,
The Integumentary System Disorders, Conditions, and Diseases Definitions Disease- an abnormal condition of the body or the mind that causes dysfunction or discomfort. Disorder- a functional abnormality,
COMMON VIRAL INFECTIONS. Dr D. Tenea Department of Dermatology University of Pretoria
 COMMON VIRAL INFECTIONS Dr D. Tenea Department of Dermatology University of Pretoria GENERAL Viral infections of the skin important in immunocompromised Pts. Infection: direct inoculation ( warts ) or
COMMON VIRAL INFECTIONS Dr D. Tenea Department of Dermatology University of Pretoria GENERAL Viral infections of the skin important in immunocompromised Pts. Infection: direct inoculation ( warts ) or
Communicable Disease Guidelines
 Note: This information is to assist in making decisions regarding the control of communicable diseases. It is not intended for the purposes of making diagnoses. Refer to disease specific information sheets
Note: This information is to assist in making decisions regarding the control of communicable diseases. It is not intended for the purposes of making diagnoses. Refer to disease specific information sheets
CHAPTER 7:3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7:3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM I. OBJECTIVES A. Label a diagram of a cross section of the skin B. Differentiate between the two types of skin glands C. Identify six functions of the skin D. Provide the
CHAPTER 7:3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM I. OBJECTIVES A. Label a diagram of a cross section of the skin B. Differentiate between the two types of skin glands C. Identify six functions of the skin D. Provide the
Bacterial Infections in Pediatric Dermatology. Patrick McMahon, MD Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
 Bacterial Infections in Pediatric Dermatology Patrick McMahon, MD Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Fill In The Blank When you see on the skin, you think of a bacterial skin infection SEND SWABS VIRAL
Bacterial Infections in Pediatric Dermatology Patrick McMahon, MD Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Fill In The Blank When you see on the skin, you think of a bacterial skin infection SEND SWABS VIRAL
Scrub In. What is a function of the skin: The innermost layer of the epidermis is constantly reproducing itself. This function enable the skin to:
 Scrub In What is a function of the skin: a. Convert glycogen to glucose b. Secretion of growth hormones c. Manufacture of vitamin C d. Protection from germ invasion The innermost layer of the epidermis
Scrub In What is a function of the skin: a. Convert glycogen to glucose b. Secretion of growth hormones c. Manufacture of vitamin C d. Protection from germ invasion The innermost layer of the epidermis
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1
 Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
DERMATOLOGICAL INFECTIONS
 DERMATOLOGICAL INFECTIONS BACTERIAL IMPETIGO/SSS FOLLICULITIS, FURUNCULOSIS FUNGAL TINEA VERSICOLOR DERMATOPHYTOSIS CANDIDA VIRAL HAND FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE MOLLUSCUM CONTAGIOSUM DIAGNOSIS????? 6 YEAR
DERMATOLOGICAL INFECTIONS BACTERIAL IMPETIGO/SSS FOLLICULITIS, FURUNCULOSIS FUNGAL TINEA VERSICOLOR DERMATOPHYTOSIS CANDIDA VIRAL HAND FOOT AND MOUTH DISEASE MOLLUSCUM CONTAGIOSUM DIAGNOSIS????? 6 YEAR
Chapter 40. Alterations of the Integument in Children
 Chapter 40 Alterations of the Integument in Children Acne Vulgaris Most common skin disease Affects 85% of the population between ages 12 and 25 years Develops at sebaceous follicles located primarily
Chapter 40 Alterations of the Integument in Children Acne Vulgaris Most common skin disease Affects 85% of the population between ages 12 and 25 years Develops at sebaceous follicles located primarily
An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc
 An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc 1 Common Rashes Tinea Corporis: Annular- this is not the only criteria Advancing erythematous
An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc 1 Common Rashes Tinea Corporis: Annular- this is not the only criteria Advancing erythematous
Dermatology for the PCP Deanna G. Brown, MD, FAAD Susong Dermatology Consulting Staff at CHI Memorial
 Dermatology for the PCP Deanna G. Brown, MD, FAAD Susong Dermatology Consulting Staff at CHI Memorial Cutaneous Oncology for the PCP Deanna G. Brown, MD, FAAD Susong Dermatology Consulting Staff at CHI
Dermatology for the PCP Deanna G. Brown, MD, FAAD Susong Dermatology Consulting Staff at CHI Memorial Cutaneous Oncology for the PCP Deanna G. Brown, MD, FAAD Susong Dermatology Consulting Staff at CHI
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Integumentary System Skin, hair, and nails. Skin: Epidermis: outer layer. Dermis: also called corium, or true skin. Subcutaneous fascia: innermost layer. Integumentary Glands Sudoriferous:
Integumentary System Integumentary System Skin, hair, and nails. Skin: Epidermis: outer layer. Dermis: also called corium, or true skin. Subcutaneous fascia: innermost layer. Integumentary Glands Sudoriferous:
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
Case1. 18 day old female. 5 day history of several red lesions over both cheeks. Full-term, vaginal birth with no complications
 QUIZ Case1 18 day old female 5 day history of several red lesions over both cheeks Full-term, vaginal birth with no complications Mother is a 25 year old with a history of migraines who took paracetamol
QUIZ Case1 18 day old female 5 day history of several red lesions over both cheeks Full-term, vaginal birth with no complications Mother is a 25 year old with a history of migraines who took paracetamol
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 4
 *We are revisiting Ch 3B on body tissues (Connective) prior to our study of Ch 4 Integumentary. Start on p.90 I. Connective Tissue A. Functions of Connective 1. Protection 2. Support 3. Binding Together
*We are revisiting Ch 3B on body tissues (Connective) prior to our study of Ch 4 Integumentary. Start on p.90 I. Connective Tissue A. Functions of Connective 1. Protection 2. Support 3. Binding Together
EXANTHEMATOUS ILLNESS. IAP UG Teaching slides
 EXANTHEMATOUS ILLNESS 1 DEFINITIONS Exanthema eruption of the skin Exanthema eruption of mucosae Macule flat nonpalpable lesion Papule small palpable lesion Nodule large palpable lesion Vesicle small fluid
EXANTHEMATOUS ILLNESS 1 DEFINITIONS Exanthema eruption of the skin Exanthema eruption of mucosae Macule flat nonpalpable lesion Papule small palpable lesion Nodule large palpable lesion Vesicle small fluid
Issues in Dermatology. Rhonda Lesniak, PhD, ARNP, FNP-BC, NCSN
 Issues in Dermatology Rhonda Lesniak, PhD, ARNP, FNP-BC, NCSN Anatomy of the Skin Functions Protect Fluid balance Absorption Synthesis of Vitamin D Sensation/communication with external environment Thermoregulation
Issues in Dermatology Rhonda Lesniak, PhD, ARNP, FNP-BC, NCSN Anatomy of the Skin Functions Protect Fluid balance Absorption Synthesis of Vitamin D Sensation/communication with external environment Thermoregulation
HERPES VIRUSES. Large DNA viruses, replication is intranuclear and produce typical intranuclear inclusions.
 Viral infections HERPES VIRUSES Large DNA viruses, replication is intranuclear and produce typical intranuclear inclusions. Typical feature: absence of viral elimination after infection, clinical latency
Viral infections HERPES VIRUSES Large DNA viruses, replication is intranuclear and produce typical intranuclear inclusions. Typical feature: absence of viral elimination after infection, clinical latency
NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES)
 NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES) Papillary Lesions Precancerous Lesions Keratinocyte Proliferations Carcinomas Melanotic Lesions Melanomas Normal Mucosa Keratin layer Spinous layer Basal
NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES) Papillary Lesions Precancerous Lesions Keratinocyte Proliferations Carcinomas Melanotic Lesions Melanomas Normal Mucosa Keratin layer Spinous layer Basal
Emergent and Urgent Dermatology, Eruptions, and Wound Care
 Emergent and Urgent Dermatology, Eruptions, and Wound Care G. Scott Drew, DO, FAAD, FAOCD Smith Clinic Department of Dermatology Tucson Osteopathic Medical Foundation April 27, 2018 Acute Cutaneous Lupus
Emergent and Urgent Dermatology, Eruptions, and Wound Care G. Scott Drew, DO, FAAD, FAOCD Smith Clinic Department of Dermatology Tucson Osteopathic Medical Foundation April 27, 2018 Acute Cutaneous Lupus
Lesions & Lifestyles
 Lesions & Lifestyles attended a 3 hour Continuing Education Seminar on Oral Pathology presented by Nancy Dewhirst, RDH,BS on (date) at (location):. Course material is directly related patient care. Notes:
Lesions & Lifestyles attended a 3 hour Continuing Education Seminar on Oral Pathology presented by Nancy Dewhirst, RDH,BS on (date) at (location):. Course material is directly related patient care. Notes:
