General Dermatology Objectives Learn to recognize some common dermatologic disorders d and some associated with systemic diseases Learn the causative
|
|
|
- Christine Berry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 General Dermatology Julia R. Nunley, MD, FAAD, FACP Professor Program Director Department of Dermatology
2 General Dermatology Objectives Learn to recognize some common dermatologic disorders d and some associated with systemic diseases Learn the causative organism or basic pathogenesis of these conditions Learn some diagnostic i clinical i l or laboratory clues to aid in diagnosis Learn to recognize common skin cancers Learn the risk factors, prognostic factors and clinical i l clues to melanoma
3 General Dermatology Papulosquamous disorders Infections Blistering disorders Acneiform eruptions Disorders of pigmentation Benign tumors Malignant tumors Urticaria / Vasculitis
4 Papulosquamous Disorders Primary skin disorders that effect the squamous epithelium Eczema Psoriasis Seborrheic dermatitis Pityriasis rosea
5 Question 1 This postoperative rash is most like a form of which of the following? A. Eczema B. Seborrheic dermatitis C. Psoriasis D. Tinea corporis E. Tinea versicolor
6 Question 2 Which of the papulosquamous pp disorders is associated with the development of a sero- negative rheumatoid arthritis-type type of arthritis? A. Ezcema B. Psoriasis C. Seborrheic dermatitis D. Pityriasis rosea
7 Eczema Inflammatory condition of the epidermis Acute Weeping, draining, frequently warm and red Chronic Dry, scaly, frequently hyperkeratotic Wide variety of causes Intrinsic Atopic dermatitis, dyshidrosis Extrinsic Allergic or irritant contact dermatitis
8 Acute Eczema
9 Acute Eczema Contact Dermatitis
10 Acute Eczema Poison Ivy
11 Acute Eczema - Spongiosis
12 Chronic Eczema
13 Chronic Eczema
14 Chronic Eczema
15 Acute Eczema Atopic Dermatitis
16 Chronic Eczema Nummular Eczema (Nickle Allergy)
17 Chronic Eczema
18 Psoriasis Vulgaris Heritable primary skin disorder Affects 1-2% of general population Multifactorial inheritance Characteristic clinical presentation Typical lesion Well demarcated plaques with silvery-white scale Typical distribution Knees, elbows, gluteal cleft, scalp Nail changes Associated with sero-negative arthritis
19 Psoriasis
20 Psoriasis
21 Psoriasis
22 Psoriasis
23 Psoriasis
24 Psoriasis
25 Psoriasis
26 Psoriasis
27 Psoriasis Koebnerization
28 Psoriasis Nail Changes
29 Psoriatic Arthritis
30 Seborrheic Dermatitis AKA: dandruff d Chronic cutaneous disorder involving sites of sebaceous gland activity Cradle cap as infant 15% of the population affected Thought to be due to a hypersensitivity y reaction to pityrosporum (Malassezia) More common in HIV and CNS disease
31 Seborrheic Dermatitis
32 Seborrheic Dermatitis
33 Sb Seborrheic hi Dermatitis ii
34 Cradle Cap
35 Pityriasis Rosea Common exanthem More common in spring and fall Unknown etiology Classic clinical presentation Herald patch Christmas tree pattern Secondary syphilis may mimic this disorder
36 Pityriasis Rosea
37 Pityriasis Rosea
38 Pityriasis Rosea
39 Question 3 A positive Tzanck test confirms the diagnosis of which of the following infections? A. Molluscum contagiosum B. Dermatophytosis C. Impetigo D. Erysipelas E. Herpes
40 Superficial Fungal Infections Dermatophytes 3 common genera Yeasts Microsporum, Trichophyton, Epidermophyton Pityrosporum (Malassezia) Candidiasis Diagnosis frequently made by KOH
41 Superficial Fungal Infections Dermatophytes - AKA: ring worm Thrive on non-viable keratinized structures: stratum corneum, hair, nails Tinea corporis -- body Tinea capitis -- head Trichophyton tonsurans Tinea pedis -- feet Tinea cruris -- groin Trichophyton rubrum Tinea unguium (onychomycosis) -- nails KOH of scale shows branching hyphae
42 Superficial Fungal Infections Yeasts Pityrosporum (Malassezia) Tinea versicolor -- most commonly on torso More common in humid environments KOH: short non-branching hyphae and spores Candidiasis: commonly due to candida albicans Affects warm, moist places Many predisposing factors Diabetes, antibiotics, immunosuppression KOH: pseudohyphae
43 Tinea Tinea Corporis Corporis
44 Tinea Corporis
45 Tinea Faciei
46 Tinea Manuum
47 Tinea Cruris
48 Tinea Pedis
49 Tinea unguium (onychomycosis)
50 Tinea Capitis
51 Tinea Versicolor
52 Candidiasis
53 Candidiasis
54 KOH
55 Common Warts Verruca Vulgaris
56 Viral Infections - Warts Human papilloma pp viruses Over 70 subtypes: specific subtypes prefer specific anatomic sites: Verruca vulgaris, plantar warts, verruca plana, condyloma acuminata... Some have malignancy potential Cervical carcinoma Molluscum contagiosum - Poxvirus Common in childhood Sexually transmitted disease in adults Can be extensive in HIV infection
57 Plantar Warts
58 Filiform Warts Flat Warts
59 Condyloma
60 HPV-Related Mucosal Changes
61 Molluscum Contagiosum
62 Molluscum Contagiosum
63 Viral Infections - Herpes Herpes simplex Primary infection vs recurrent outbreak HSV type Cold sores / fever er blisters HSV type 2 -- Genital herpes Herpetic whitlow Varicella zoster virus Primary - chickenpox Recurrent - shingles Diagnosis made with (+) Tzanck test
64 Primary HSV1 / Recurrent HSV1
65 Recurrent HSV 2
66 Chronic HSV Ulcer
67 Herpetic Whitlow
68 Primary Varicella Chickenpox
69 Recurrent Varicella - Shingles
70 Recurrent Varicella Herpes Zoster
71 Recurrent Varicella - Shingles
72 Recurrent Varicella - Shingles
73 Tzanck Preparation
74 Impetigo Bacterial Infections An acute and superficial skin infection Cellulitis Characteristic: honey-colored crust Suppurative inflammation involving i the subcutaneous tissue layer Erysipelas Group A beta-hemolytic strep infection of the superficial i dermal lymphatics
75 Impetigo
76 Cellulitis
77 Erysipelas
78 Scabies Infestations Female sarcoptes scabiei burrows into the stratum corneum and lays eggs Identified by wet prep Lice (Pediculosis) Can carry and transmit infectious disease Body louse - Pediculosis humanus var corporis Head louse - Pediculosis humanus var capitis Pubic or crab louse - Pthirus pubis Nits frequently found in hair and lashes
79 Scabitic Mite
80 Scabies
81 Scabies
82 Lice
83 Lice
84 Question 4 For which of the following primary blistering disorders is caused by autoantibodies to the desmosomal structural proteins? A. Epidermolysis bullosa B. Pemphigoid C. Pemphigus
85 Vesiculobullous Disorders Pemphigus Autoimmune disorder: desmosome Acantholysis with hi intraepidermal id lbli blister Bullous pemphigoid Autoimmune disorder: Hemidesmosome Subepithelial blister Epidermolysis bullosa Genetic defects in structural proteins of cutaneous basement membrane
86 Cartoon of Epidermis
87 Bullous Pemphigoid
88 Bullous Pemphigoid
89 Primary Subepidermal Blistering Disease
90 Bullous Pemphigoid
91 Pemphigus
92 Pemphigus
93 Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex
94 Question 5 Which of the following organisms is pivotal to the development of acne vulgaris? A. Beta-hemolytic group A streptococcus B. Staphylococcus aureus C. Pityrosporum (Malassezia) D. Propionibacterium E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
95 Folliculitis Common and superficial pyogenic infection of the hair follicles Staphylococcus aureus is the most common organism Others may also cause folliculitis li i Pityrosporum Candida species Pseudomonas sp. -- hot tub folliculitis Occurs anywhere there is hair
96 Folliculitis
97 Hot Tub Folliculitis / Pityrosporum
98 Acne Vulgaris Disorder of pilosebaceous units Pathobiology Obstruction of follicular orifice Abnormal keratinization Increase in sebum production Role of androgens Over growth of propionibacterium acnes Produces lipase which breaks down sebum to release proinflammatory free fatty acids
99 Pathogenesis of Acne Vulgaris
100 Acne Vulgaris Comedones
101 Acne Vulgaris
102 Acne Vulgaris
103 Acne Vulgaris
104 Acne Rosacea Common inflammatory condition i Northern European ancestry Significant ifi sun exposure Peculiar increase in vascular reactivity Flush and blush Fixed erythema Telangiectasia Inflammatory papules and facial edema Rhinophyma may occur in men
105 Acne Rosacea
106 Acne Rosacea
107 Disorders of Pigmentation All disorders deal with alterations in melanin production Tanning Vitiligo ili Albinism
108 Tanning A defensive response to UV light Skin types are partially defined by this Immediate tan -- UVA exposure Alteration in oxidized state of melanin Occurs immediately, fades quickly Delayed tan -- UVB exposure Increases production of melanin Occurs in a few days, fades in weeks
109 Tanning
110 Vitiligo Acquired, local l loss of melanocytes May be extensive and devastating Idiopathic Autoimmune disease Assoc. with FH, DM, thyroid disease, etc Results in DEPIGMENTATION Increase risk of skin cancer Variety of patterns
111 Vitiligo
112 Vitiligo
113 Vitiligo
114 Albinism i - Oculocutaneous Genetic abnormality Autosomal recessive disorder Affects skin, hair and eyes Variably hypopigmented Increased risk of skin cancer Reduction in visual acuity and nystagmus Several different genetic defects All result in defective melanin production or transfer
115 Albinism
116 Question 6 Which of the following cutaneous tumors is the most common cause of cutaneous malignancy? A. Basal cell carcinoma B. Dermatofibroma C. Seborrheic keratosis D. Squamous cell carcinoma E. Malignant melanoma
117 Cutaneous Tumors Benign Seborrheic keratosis Melanocytic nevi Hemangioma Cysts Dermatofibroma Malignant Basal cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Melanoma Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
118 Seborrheic Keratosis Common and benign Familial Occurs after age of 30 years Age spots etc More common on the face, trunk and upper extremities Localized and benign epidermal proliferation Stuck on appearance
119 Seborrheic Keratoses
120 Seborrheic Keratoses
121 Seborrheic e Keratoses
122 Melanocytic Nevi Most are acquired lesions Occur 5 years to 60 years Maybecongenital Benign melanocyte proliferation Sharply demarcated Flat or raised Flesh-colored to dark brown Risk of any one mole becoming malignant is miniscule
123 Melanocytic Nevus
124 Melanocytic Nevus
125 Melanocytic Nevi
126 Ml Melanocytic Nevi
127 Hemangioma All are a result of a vascular process Some are hypertrophic changes, some are proliferative disorders, some are caused by vasodilation, some are true arterio-venous abnormalities Some are congenital, some acquired Only a few have a health risk
128 Hemangiomas
129 Stork Bite Port Wine Stain
130 Hemangioma and Port Wine Stain
131 Cysts All have a cellular, epithelial lining Contents may be fluid or semi-solidsolid Depends on cell type lining Most common: Follicular cyst, infundibular type (epidermal inclusion cyst) Common on face, neck, torso, scrotum Stratified squamous epithelium Keratinous material content
132 Cysts
133 Cysts
134 Cysts Csts
135 Dermatofibroma Common, benign dermal tumor Composed of dermal fibroblasts Most common on extremities Cause unknown?? Trauma with abnormal scarring Clinical: Dermal tumor, tightly adherent to epidermis, with dimple sign
136 Dermatofibroma
137 Basal Cell Carcinoma Most common cutaneous malignancy > 400,000 cases this year Develops from the basal cell layer Most common on the head and neck Background of sun damage Pearly translucent papule with telangiectasia i Nickname: rodent ulcer
138 Basal Cell Carcinoma -Nodular
139 Basal Cell Carcinoma
140 Basal Cell Carcinoma
141 Basal Cell Carcinoma
142 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Second most common skin cancer Arises within the squamous epithelium Setting of sun damage and precancerous lesions: actinic keratosis Upper extremities, trunk, face and neck Associated with other exogenous insults Poorly demarcated scaly, indurated plaques Higher metastatic potential than BCC
143 Squamous Cell Carcinoma
144 Squamous Cell Carcinoma
145 Squamous Cell Carcinoma
146 Squamous Cell Carcinoma
147 Ml Melanoma Deadliest of the skin cancers Increasing at an alarming rate May arise in mole, but more often occurs de novo Risk factors Family history Skin type UV light exposure Number of moles, or giant congenital nevus
148 Melanoma Diagnostic clues: ABCD s A: Asymmetry B: Border C: Color D: Diameter E Evolution Completely excise suspicious lesions Most important prognostic indicator: Lesional thickness
149 Melanoma
150 Melanoma
151 Melanoma
152 Melanoma
153 Melanoma Acral Lentiginous Melanoma
154 Melanoma - Metastatic
155 Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma Most uncommon of skin malignancies AKA: Mycosis fungoides Malignancy of lymphocytes Predominately CD4 cells Presents as patches and poikiloderma Long term disease years Risk of systemic lymphoma Leukemic phase: Sezary syndrome
156 Mycosis Fungoides Patches Stage / Tumors
157 Mycosis Fungoides Sezary Syndrome
158 Urticaria Very common condition Transient wheals, hives Lesions last < 24 hours Generally very itchy Many causes or associations Acute urticaria, < 30 days Likely IgE mediated allergy Chronic urticaria, > 30 days Most likely l not allergic in mechanism m
159 Urticaria
160 Vasculitis Due to vascular inflammation i Different diseases affect different vessels and vessel sizes Arterioles, capillaries, venules etc. Clinical picture represents affected vessel Palpable purpura p -- small sized vessels Cutaneous nodules -- medium and large Ulcers -- may suggest larger sized vessel
161 Vasculitis
162 Vasculitis Palpable Purpura
163 Vasculitis
164 Question 1 This postoperative rash is most like a form of which of the following? A. Eczema B. Seborrheic dermatitis C. Psoriasis D. Tinea corporis E. Tinea versicolor
165 Question 2 Which of the papulosquamous pp disorders is associated with the development of a sero- negative rheumatoid arthritis-type type of arthritis? A. Ezcema B. Psoriasis C. Seborrheic dermatitis D. Pityriasis rosea
166 Question 3 A positive Tzanck test confirms the diagnosis of which of the following infections? A. Molluscum contagiosum B. Dermatophytosis C. Impetigo D. Erysipelas E. Herpes
167 Question 4 For which of the following primary blistering disorders is caused by autoantibodies to the desmosomal structural proteins? A. Epidermolysis bullosa B. Pemphigoid C. Pemphigus
168 Question 5 Which of the following organisms is pivotal to the development of acne vulgaris? A. Beta-hemolytic group A streptococcus B. Staphylococcus aureus C. Pityrosporum (Malassezia) D. Propionibacterium E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
169 Question 6 Which of the following cutaneous tumors is the most common cause of cutaneous malignancy? A. Basal cell carcinoma B. Dermatofibroma C. Seborrheic keratosis D. Squamous cell carcinoma E. Malignant melanoma
Chapter 8 Skin Disorders and Diseases
 Chapter 8 Skin Disorders and Diseases Attitude is more important than the past, than education, than money, than circumstances, than what people do or say. It is more important than appearance, giftedness,
Chapter 8 Skin Disorders and Diseases Attitude is more important than the past, than education, than money, than circumstances, than what people do or say. It is more important than appearance, giftedness,
29a Pathology - Integumentary System
 29a Pathology - Integumentary System 29a Pathology - Integumentary System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active
29a Pathology - Integumentary System 29a Pathology - Integumentary System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active
COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES. Sharon Seguin MD FAAD
 COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Sharon Seguin MD FAAD COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Rashes Infections And Infestations RASHES Dermatitis- Inflammation of the skin Eczema- Atopic Dermatitis Psoriasis Pityriasis
COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Sharon Seguin MD FAAD COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Rashes Infections And Infestations RASHES Dermatitis- Inflammation of the skin Eczema- Atopic Dermatitis Psoriasis Pityriasis
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Physiology of Touch Skin: our most sensitive organ Touch: first sense to develop in embryos Most important but most neglected sense How many sensory receptors do we have? (We have
Integumentary System Physiology of Touch Skin: our most sensitive organ Touch: first sense to develop in embryos Most important but most neglected sense How many sensory receptors do we have? (We have
Rash Decisions Approach to the patient with a skin condition
 National Conference for Nurse Practitioners April 25, 2014 Rash Decisions Approach to the patient with a skin condition Margaret A. Bobonich, DNP, FNP C, DCNP, FAANP Assistant Professor, Case Western Reserve
National Conference for Nurse Practitioners April 25, 2014 Rash Decisions Approach to the patient with a skin condition Margaret A. Bobonich, DNP, FNP C, DCNP, FAANP Assistant Professor, Case Western Reserve
DESCRIPTIONS FOR MED 3 ROTATIONS Dermatology A3S
 Regardless of your future field of practice, you will be exposed to a considerable amount of dermatology and this rotation provides you the chance to see a range of skin diseases. You will have the opportunity
Regardless of your future field of practice, you will be exposed to a considerable amount of dermatology and this rotation provides you the chance to see a range of skin diseases. You will have the opportunity
CONDITIONS OF THE SKIN
 CONDITIONS OF THE SKIN UCSF/SFGH Family & Community Medicine Residency Program Educational Objectives I. Knowledge The resident will be able to discuss the definition, diagnosis, and initial management
CONDITIONS OF THE SKIN UCSF/SFGH Family & Community Medicine Residency Program Educational Objectives I. Knowledge The resident will be able to discuss the definition, diagnosis, and initial management
Table of Contents: Part 1 Medical Dermatology. Chapter 1 Acneiform Disorders. Acne. Acne Vulgaris. Pomade Acne. Steroid Acne
 Table of Contents: Part 1 Medical Dermatology Chapter 1 Acneiform Disorders Acne Acne Vulgaris Pomade Acne Steroid Acne Infantile Acne Pediatric Perspectives Neonatal Acne (Acne Neonatorum) Pediatric Perspectives
Table of Contents: Part 1 Medical Dermatology Chapter 1 Acneiform Disorders Acne Acne Vulgaris Pomade Acne Steroid Acne Infantile Acne Pediatric Perspectives Neonatal Acne (Acne Neonatorum) Pediatric Perspectives
RASHES- Dermatitis nonspecific term for inflammation of the skin. 1. ECZEMA Atopic Dermatitis- specific form of eczema starting in childhood
 COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Sharon Seguin MD Dermatology- Confluence Health Wenatchee Rashes Infections and Infestations RASHES- Dermatitis nonspecific term for inflammation of the skin 1. ECZEMA Atopic
COMMON CHILDHOOD SKIN DISEASES Sharon Seguin MD Dermatology- Confluence Health Wenatchee Rashes Infections and Infestations RASHES- Dermatitis nonspecific term for inflammation of the skin 1. ECZEMA Atopic
The Integumentary System. Disorders, Conditions, and Diseases
 The Integumentary System Disorders, Conditions, and Diseases Definitions Disease- an abnormal condition of the body or the mind that causes dysfunction or discomfort. Disorder- a functional abnormality,
The Integumentary System Disorders, Conditions, and Diseases Definitions Disease- an abnormal condition of the body or the mind that causes dysfunction or discomfort. Disorder- a functional abnormality,
Undergraduate Dermatology Curriculum July 2016
 Undergraduate Dermatology Curriculum July 2016 British Association of Dermatologists Introduction This document is the 2016 revised dermatology undergraduate curriculum (UK) from the British Association
Undergraduate Dermatology Curriculum July 2016 British Association of Dermatologists Introduction This document is the 2016 revised dermatology undergraduate curriculum (UK) from the British Association
Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest
 Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest Overview & Learning Objectives Review the cardinal signs/symptoms of acute inflammation Review the histological features of acute inflammation
Pimples and Boils!! Dr Nathan Harvey Anatomical Pathology, PathWest Overview & Learning Objectives Review the cardinal signs/symptoms of acute inflammation Review the histological features of acute inflammation
CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM This system consists of skin and its derivatives. The skin is one of the largest organs of the body in terms of surface area. The functions of the integumentary system include:
CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM This system consists of skin and its derivatives. The skin is one of the largest organs of the body in terms of surface area. The functions of the integumentary system include:
1 Assessment Techniques General Survey Skin, Hair, and Nails. 2 Cultivating Your Senses
 1 Assessment Techniques General Survey Skin, Hair, and Nails 2 Cultivating Your Senses Inspection Always performed first Palpation Purpose Use different parts of the hands Light vs. deep palpation 3 Cultivating
1 Assessment Techniques General Survey Skin, Hair, and Nails 2 Cultivating Your Senses Inspection Always performed first Palpation Purpose Use different parts of the hands Light vs. deep palpation 3 Cultivating
Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc
 1 Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc Benign lesions Seborrheic Keratoses: Warty, stuck-on Genetics and birthdays Can start in late
1 Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc Benign lesions Seborrheic Keratoses: Warty, stuck-on Genetics and birthdays Can start in late
Index. Angiosarcoma diagnosis, 47 lymphedema-related vs. non-lymphedemarelated, 48
 A Acneiform rash biopsy, 134 cetuximab, EGFR, 132 133 diagnosis, 131 patient history, 131 134 treatment, 134 135 Acne vulgaris, 109 AGA. See Androgenetic alopecia Alopecia areata, 148 American Joint Committee
A Acneiform rash biopsy, 134 cetuximab, EGFR, 132 133 diagnosis, 131 patient history, 131 134 treatment, 134 135 Acne vulgaris, 109 AGA. See Androgenetic alopecia Alopecia areata, 148 American Joint Committee
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Body Membranes & Skin
 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
Contents. QAaptm-2. CAaptei-3. CAaptm-4. Cftapte%-5. Qfiaptvt-6. QhapteK-7. Qkaptefc-8 Clinical Immunology and Allergy 71
 Contents Ckaptm-1 Aaatomy, Physiology, Embryology, Bacteriology and Pathology ~ 1 Anatomy 1 Physiology 10 Embryology 14 Pathology 19 Bacteriology 22 Laboratory and other aids in dermatological pratice
Contents Ckaptm-1 Aaatomy, Physiology, Embryology, Bacteriology and Pathology ~ 1 Anatomy 1 Physiology 10 Embryology 14 Pathology 19 Bacteriology 22 Laboratory and other aids in dermatological pratice
Scrub In. What is a function of the skin: The innermost layer of the epidermis is constantly reproducing itself. This function enable the skin to:
 Scrub In What is a function of the skin: a. Convert glycogen to glucose b. Secretion of growth hormones c. Manufacture of vitamin C d. Protection from germ invasion The innermost layer of the epidermis
Scrub In What is a function of the skin: a. Convert glycogen to glucose b. Secretion of growth hormones c. Manufacture of vitamin C d. Protection from germ invasion The innermost layer of the epidermis
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level
 Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
Subspecialty Rotation: Dermatology
 Subspecialty Rotation: Dermatology Faculty: Wesley Galen, M.D. GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Dermatology). Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing illness and dysfunction related
Subspecialty Rotation: Dermatology Faculty: Wesley Galen, M.D. GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Dermatology). Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing illness and dysfunction related
Issues in Dermatology. Rhonda Lesniak, PhD, ARNP, FNP-BC, NCSN
 Issues in Dermatology Rhonda Lesniak, PhD, ARNP, FNP-BC, NCSN Anatomy of the Skin Functions Protect Fluid balance Absorption Synthesis of Vitamin D Sensation/communication with external environment Thermoregulation
Issues in Dermatology Rhonda Lesniak, PhD, ARNP, FNP-BC, NCSN Anatomy of the Skin Functions Protect Fluid balance Absorption Synthesis of Vitamin D Sensation/communication with external environment Thermoregulation
LUMPS AND BUMPS: AN ORGANIZED APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 LUMPS AND BUMPS: AN ORGANIZED APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT Tammy P. Than, M.S., O.D., F.A.A.O. The University of Alabama at Birmingham / School of Optometry 1716 University Blvd. Birmingham, AL
LUMPS AND BUMPS: AN ORGANIZED APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT Tammy P. Than, M.S., O.D., F.A.A.O. The University of Alabama at Birmingham / School of Optometry 1716 University Blvd. Birmingham, AL
Chapter 29. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives (Cont d) 9/10/2012. Cutaneous Disorders
 Chapter 29 Cutaneous Disorders Learning Objectives Describe the three layers of skin, and their composition and functions Describe the morphology of primary skin lesions Describe the morphology of secondary
Chapter 29 Cutaneous Disorders Learning Objectives Describe the three layers of skin, and their composition and functions Describe the morphology of primary skin lesions Describe the morphology of secondary
Dermatopathology: The tumor is composed of keratinocytes which show atypia, increase mitoses and abnormal mitoses.
 Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
What are the functions of the integumentary system? What are some disorders of the integumentary system?
 Essential Questions: What are the functions of the integumentary system? What are some disorders of the integumentary system? How are integumentary system disorders treated? How do you relate the integumentary
Essential Questions: What are the functions of the integumentary system? What are some disorders of the integumentary system? How are integumentary system disorders treated? How do you relate the integumentary
MERCY RETREAT Dermatology
 MERCY RETREAT 2016 Dermatology INFECTIONS IN DERMATOLOGY Why we do talk about infections today? These are some of the most commonly seen dermatologic diseases that present to primary care physician office
MERCY RETREAT 2016 Dermatology INFECTIONS IN DERMATOLOGY Why we do talk about infections today? These are some of the most commonly seen dermatologic diseases that present to primary care physician office
Conflicts. Objectives. University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio. Pediatrics Grand Rounds 24 August Pediatric Dermatology 101
 Pediatric Dermatology 101 John C. Browning, MD, FAAD, FAAP Conflicts Investigator: ViroXis Advisor: ViroXis Advisory Board: TopMD Speaker: Galderma Objectives Understand the meaning and importance of cutaneous
Pediatric Dermatology 101 John C. Browning, MD, FAAD, FAAP Conflicts Investigator: ViroXis Advisor: ViroXis Advisory Board: TopMD Speaker: Galderma Objectives Understand the meaning and importance of cutaneous
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition)
 Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
COMMON SKIN INFECTIONS. Sports Medicine
 COMMON SKIN INFECTIONS Sports Medicine IMPETIGO IS A SUPERFICIAL BACTERIAL INFECTION CAUSED BY: STREPTOCOCCI OR STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BOULOUS IMPETIGO IMPETIGO COMES IN TWO FORMS: BOULOUS OR NON- BOULOUS
COMMON SKIN INFECTIONS Sports Medicine IMPETIGO IS A SUPERFICIAL BACTERIAL INFECTION CAUSED BY: STREPTOCOCCI OR STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BOULOUS IMPETIGO IMPETIGO COMES IN TWO FORMS: BOULOUS OR NON- BOULOUS
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Integumentary System Skin, hair, and nails. Skin: Epidermis: outer layer. Dermis: also called corium, or true skin. Subcutaneous fascia: innermost layer. Integumentary Glands Sudoriferous:
Integumentary System Integumentary System Skin, hair, and nails. Skin: Epidermis: outer layer. Dermis: also called corium, or true skin. Subcutaneous fascia: innermost layer. Integumentary Glands Sudoriferous:
DERMATOLOGY ROTATION: COMPETENCY-BASED GOALS AND OBJECTIVES
 UNC DIVISION OF PLASTIC AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY DERMATOLOGY ROTATION: COMPETENCY-BASED GOALS AND OBJECTIVES MEDICAL KNOWLEDGE A. Anatomy/Physiology/Embryology Goal: The resident will have knowledge
UNC DIVISION OF PLASTIC AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY DERMATOLOGY ROTATION: COMPETENCY-BASED GOALS AND OBJECTIVES MEDICAL KNOWLEDGE A. Anatomy/Physiology/Embryology Goal: The resident will have knowledge
Some skin conditions
 Some skin conditions Some skin conditions Acute Inflammatory Dermatoses Chronic Inflammatory Dermatoses Blistering (Bullous) Diseases Panniculitis Disorders of Epidermal Appendages -Urticaria -Acute eczematous
Some skin conditions Some skin conditions Acute Inflammatory Dermatoses Chronic Inflammatory Dermatoses Blistering (Bullous) Diseases Panniculitis Disorders of Epidermal Appendages -Urticaria -Acute eczematous
An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc
 An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc 1 Common Rashes Tinea Corporis: Annular- this is not the only criteria Advancing erythematous
An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc 1 Common Rashes Tinea Corporis: Annular- this is not the only criteria Advancing erythematous
page: 582 alphabetical Index by Causes picture cause basic lesion search contents print last screen viewed back next
 page: 582 Index by Causes basic lesion cause picture alphabetical Index by Causes page: 583 Mechanical factors Acquired digital fibrokeratoma,393 Angioma,418 Atopic dermatitis in the adult: xerosis, lichenification
page: 582 Index by Causes basic lesion cause picture alphabetical Index by Causes page: 583 Mechanical factors Acquired digital fibrokeratoma,393 Angioma,418 Atopic dermatitis in the adult: xerosis, lichenification
Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E Chapter 21
 Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E Chapter 21 NURSING CARE OF THE CLIENT: INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM NVOC 22C Eliza Rivera-Mitu The Skin As the external covering of the body, the skin performs
Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach, 2E Chapter 21 NURSING CARE OF THE CLIENT: INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM NVOC 22C Eliza Rivera-Mitu The Skin As the external covering of the body, the skin performs
Dermatology for the Internist DREW M ANDERSON, MD VOLUNTEER CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, INDIANA UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
 Dermatology for the Internist DREW M ANDERSON, MD VOLUNTEER CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, INDIANA UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Why Should I Care? 53% of all skin related visits are to non
Dermatology for the Internist DREW M ANDERSON, MD VOLUNTEER CLINICAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, INDIANA UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Why Should I Care? 53% of all skin related visits are to non
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Thursday 21 st August Skin Problems
 Thursday 21 st August 2014 Skin Problems Skin Problems The Sun and the Skin Sun Damage Recognising the early signs of skin cancer The Big 3 inflammatory condi=ons Acne & Rosacea Eczema (Including Seborrhoeic
Thursday 21 st August 2014 Skin Problems Skin Problems The Sun and the Skin Sun Damage Recognising the early signs of skin cancer The Big 3 inflammatory condi=ons Acne & Rosacea Eczema (Including Seborrhoeic
Derm quiz. Go to this link: goo.gl/forms/kchrhmtzl3vfnlv52. bit.ly/2a8asoy. Scan the QR code with your phone
 Dermatology quiz Derm quiz Go to this link: goo.gl/forms/kchrhmtzl3vfnlv52 OR bit.ly/2a8asoy OR Scan the QR code with your phone Contents Childhood rashes Pigmented lesions Sun damage Pityriasis References
Dermatology quiz Derm quiz Go to this link: goo.gl/forms/kchrhmtzl3vfnlv52 OR bit.ly/2a8asoy OR Scan the QR code with your phone Contents Childhood rashes Pigmented lesions Sun damage Pityriasis References
Workbook Answers Chapter 6. Diseases and Conditions of the Integumentary System
 Workbook Answers Chapter 6 Diseases and Conditions of the Integumentary System Short Answer 1. Protects the body from trauma, infection, and toxic chemicals; synthesizes vitamin D; houses sensory receptors;
Workbook Answers Chapter 6 Diseases and Conditions of the Integumentary System Short Answer 1. Protects the body from trauma, infection, and toxic chemicals; synthesizes vitamin D; houses sensory receptors;
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System The integumentary system is commonly known as the Skin Largest organ of human body 10% total body weight and would cover over 20 square feet Functions of Skin 1. Protection Barrier
Integumentary System The integumentary system is commonly known as the Skin Largest organ of human body 10% total body weight and would cover over 20 square feet Functions of Skin 1. Protection Barrier
Pediatric Dermatology. Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital
 Pediatric Dermatology Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Conflict of interest! No financial conflict of interest! Individual products shown are examples only not a product endorsement Pediatric
Pediatric Dermatology Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Conflict of interest! No financial conflict of interest! Individual products shown are examples only not a product endorsement Pediatric
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children
 May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
Clinical characteristics
 Skin Cancer Fernando Vega, MD Seattle Healing Arts Clinical characteristics Precancerous lesions Common skin cancers ACTINIC KERATOSIS Precancerous skin lesions Actinic keratoses Dysplastic melanocytic
Skin Cancer Fernando Vega, MD Seattle Healing Arts Clinical characteristics Precancerous lesions Common skin cancers ACTINIC KERATOSIS Precancerous skin lesions Actinic keratoses Dysplastic melanocytic
Chapter 40. Alterations of the Integument in Children
 Chapter 40 Alterations of the Integument in Children Acne Vulgaris Most common skin disease Affects 85% of the population between ages 12 and 25 years Develops at sebaceous follicles located primarily
Chapter 40 Alterations of the Integument in Children Acne Vulgaris Most common skin disease Affects 85% of the population between ages 12 and 25 years Develops at sebaceous follicles located primarily
Skin and Body Membranes
 4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
Skin Malignancies. Presented by Dr. Douglas Paauw
 Skin Malignancies Presented by Dr. Douglas Paauw Disclosure: Dr. Paauw has no significant financial interest in any of the products or manufacturers mentioned. How Common Is Skin Cancer? *½ of all White
Skin Malignancies Presented by Dr. Douglas Paauw Disclosure: Dr. Paauw has no significant financial interest in any of the products or manufacturers mentioned. How Common Is Skin Cancer? *½ of all White
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Eleventh Edition. Chapter 6
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
Dermatologic Emergencies Sept 2014
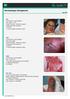 Dermatologic Emergencies Sept 2014 SJS YES MUCOSAL INVOLVEMENT MCC drugs >> HSV TARGET LESIONS, +NIKOLSKY, painful Prodromal flu-like symptoms
Dermatologic Emergencies Sept 2014 SJS YES MUCOSAL INVOLVEMENT MCC drugs >> HSV TARGET LESIONS, +NIKOLSKY, painful Prodromal flu-like symptoms
CHAPTER 7:3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7:3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM I. OBJECTIVES A. Label a diagram of a cross section of the skin B. Differentiate between the two types of skin glands C. Identify six functions of the skin D. Provide the
CHAPTER 7:3 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM I. OBJECTIVES A. Label a diagram of a cross section of the skin B. Differentiate between the two types of skin glands C. Identify six functions of the skin D. Provide the
WR SKIN. DERMATOLOGY
 WR SKIN. DERMATOLOGY 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect 15 Classification. Nomenclature 16 Tables. Statistics
WR SKIN. DERMATOLOGY 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect 15 Classification. Nomenclature 16 Tables. Statistics
Microbial Diseases of the Skin and Eyes
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 21 Microbial Diseases of the Skin and Eyes Microbial Diseases of the Skin and Eyes Structure
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 21 Microbial Diseases of the Skin and Eyes Microbial Diseases of the Skin and Eyes Structure
Dermatology Pearls. Leah Layman, ARNP Jefferson Healthcare Dermatology June 21, 2018
 Dermatology Pearls Leah Layman, ARNP Jefferson Healthcare Dermatology June 21, 2018 What s on the agenda? Common skin conditions and where to start with treatment Gentle skin care regimen PCP and Biologics
Dermatology Pearls Leah Layman, ARNP Jefferson Healthcare Dermatology June 21, 2018 What s on the agenda? Common skin conditions and where to start with treatment Gentle skin care regimen PCP and Biologics
9/9/17. Disclosures" Dermatology in Primary Care: Recognition and treatment of common disorders of the skin" A preview" Classic skin infections"
 Disclosures Dermatology in Primary Care: Recognition and treatment of common disorders of the skin I have no conflicts of interest to disclose. I may discuss off-label use of treatments for cutaneous disease.
Disclosures Dermatology in Primary Care: Recognition and treatment of common disorders of the skin I have no conflicts of interest to disclose. I may discuss off-label use of treatments for cutaneous disease.
المركب النموذج--- سبيتز وحمة = Type Spitz's Nevus, Compound SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7
 SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
DERMATOLOGY SKIN DISEASE: APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS
 DERMATOLOGY SKIN DISEASE: APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS History Clinical Examination List and Prioritise Differentials Diagnostic Testing/Trials (eg Treatment Trial) Correlate All Findings History Signalment age,
DERMATOLOGY SKIN DISEASE: APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS History Clinical Examination List and Prioritise Differentials Diagnostic Testing/Trials (eg Treatment Trial) Correlate All Findings History Signalment age,
COURSE DESCRIPTION AND STUDY REGULATIONS
 COURSE DESCRIPTION AND STUDY REGULATIONS Course: SKIN AND VENEREAL DISEASES Course type: COMPULSORY ELECTIVE ECTS credits: 6 Nominated teacher(s): prof. dr. Tomaž Lunder, izr. prof. dr. Mateja Dolenc-Voljč
COURSE DESCRIPTION AND STUDY REGULATIONS Course: SKIN AND VENEREAL DISEASES Course type: COMPULSORY ELECTIVE ECTS credits: 6 Nominated teacher(s): prof. dr. Tomaž Lunder, izr. prof. dr. Mateja Dolenc-Voljč
Common Superficial Fungal Infections
 How to recognise and treat Common Superficial Fungal Infections Dr Lilianne Scholtz (MBBCh) Types of superficial fungal infections Ringworm (Tinea) Candida (Thrush) Body Groin Feet Skin Nappy rash Vagina
How to recognise and treat Common Superficial Fungal Infections Dr Lilianne Scholtz (MBBCh) Types of superficial fungal infections Ringworm (Tinea) Candida (Thrush) Body Groin Feet Skin Nappy rash Vagina
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE. Integumentary System
 NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Integumentary System I. Integument A. The largest organ of the body covering all external surfaces and lining cavities that are exposed to the outside environment (e.g. mouth, nasal
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Integumentary System I. Integument A. The largest organ of the body covering all external surfaces and lining cavities that are exposed to the outside environment (e.g. mouth, nasal
Institute for Microbiology, Medical Faculty of Masaryk University and St. Anna Faculty Hospital in Brno Miroslav Votava, Vladana Woznicová
 Institute for Microbiology, Medical Faculty of Masaryk University and St. Anna Faculty Hospital in Brno Miroslav Votava, Vladana Woznicová Skin infections Infections with skin symptoms primary skin infections
Institute for Microbiology, Medical Faculty of Masaryk University and St. Anna Faculty Hospital in Brno Miroslav Votava, Vladana Woznicová Skin infections Infections with skin symptoms primary skin infections
Integumentary System. Anatomy of the Skin
 Integumentary System Chapter four Medical Terminology Hit # 141 Anatomy of the Skin Epidermis = outer layer of skin. Melanin = color or pigmentation of the skin. Dermis= inner layer of skin. Sweat glands
Integumentary System Chapter four Medical Terminology Hit # 141 Anatomy of the Skin Epidermis = outer layer of skin. Melanin = color or pigmentation of the skin. Dermis= inner layer of skin. Sweat glands
Introduction. Skin and Body Membranes. Cutaneous Membranes Skin 9/14/2017. Classification of Body Membranes. Classification of Body Membranes
 Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1
 Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Lagophthalmos. Lagophthalmos: signs. Lagophthalmos: clinical tips. Lagophthalmos: treatment plan. Madarosis
 Lagophthalmos Def: incomplete closure of the eyelid SX: FBS, irritation, red, burn, dry, chronic morning corneal irritation Lagophthalmos: signs 2-5 mm lid separation with slit lamp during blink can force
Lagophthalmos Def: incomplete closure of the eyelid SX: FBS, irritation, red, burn, dry, chronic morning corneal irritation Lagophthalmos: signs 2-5 mm lid separation with slit lamp during blink can force
My ear won t stop hurting!
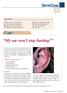 This month: 1. My ear won t stop hurting! 5. Cortisone Cream Didn t Help! 2. What are these red bumps? 6. Can my girlfriend get it? 3. Why won t this rash leave? 7. My wife noticed it! 4. What s the cause
This month: 1. My ear won t stop hurting! 5. Cortisone Cream Didn t Help! 2. What are these red bumps? 6. Can my girlfriend get it? 3. Why won t this rash leave? 7. My wife noticed it! 4. What s the cause
Course Regime. Course: SKIN AND VENEREAL DISEASES. Study Programme: Medicine. Year of the Course: 4 th study year.
 Komisija za študijske zadeve UL Medicinske fakultete Vrazov trg 2 SI-1000 Ljubljana E: ksz@mf.uni-lj.si T: +386 1 543 7700 Course Regime Course: SKIN AND VENEREAL DISEASES Study Programme: Medicine Year
Komisija za študijske zadeve UL Medicinske fakultete Vrazov trg 2 SI-1000 Ljubljana E: ksz@mf.uni-lj.si T: +386 1 543 7700 Course Regime Course: SKIN AND VENEREAL DISEASES Study Programme: Medicine Year
Learning Objectives. History 8/1/2016. An Approach to Pediatric Rashes
 An Approach to Pediatric Rashes Neethi Patel, D.O. Learning Objectives 1.To identify common features of rashes seen in the pediatric population as well as pathognomonic features of certain pathologies
An Approach to Pediatric Rashes Neethi Patel, D.O. Learning Objectives 1.To identify common features of rashes seen in the pediatric population as well as pathognomonic features of certain pathologies
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
Dr Janakan Natkunarajah (Dr Jana)
 Dr Janakan Natkunarajah (Dr Jana) Diagnosis Furuncle (Boil) Deep follicular abscess Anti-staph antibiotics Systemic & topical Carbuncle Deep abscess formed in a group of follicles Incise and Drain Recurrent
Dr Janakan Natkunarajah (Dr Jana) Diagnosis Furuncle (Boil) Deep follicular abscess Anti-staph antibiotics Systemic & topical Carbuncle Deep abscess formed in a group of follicles Incise and Drain Recurrent
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Introduction CHAPTER 1. Introduction
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction OVERVIEW The clinical features of skin lesions are related to the underlying pathological processes. Broadly skin conditions fall into three clinical groups: (a) those with a well-defined
CHAPTER 1 Introduction OVERVIEW The clinical features of skin lesions are related to the underlying pathological processes. Broadly skin conditions fall into three clinical groups: (a) those with a well-defined
4/24/2013. Staphylococcus epidermidis Gram-positive cocci, coagulase-negative Staphylococcus aureus Gram-positive cocci, coagulase-positive
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Chapter 21 Microbial Diseases of the Skin and Eyes The Structure of Human Skin Perspiration and sebum contain nutrients Salt inhibits microbes Lysozyme hydrolyzes peptidoglycan Fatty
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Chapter 21 Microbial Diseases of the Skin and Eyes The Structure of Human Skin Perspiration and sebum contain nutrients Salt inhibits microbes Lysozyme hydrolyzes peptidoglycan Fatty
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Chapter 4: Body Membranes and the Integumentary System. Introduction. Membranes
 Slide 1 Chapter 4: Body Membranes and the Integumentary System Slide 2 Introduction Skin often reveals our inner workings and general health In most manual therapies, the skin is primary interface with
Slide 1 Chapter 4: Body Membranes and the Integumentary System Slide 2 Introduction Skin often reveals our inner workings and general health In most manual therapies, the skin is primary interface with
Dermatology GP Referral Guidelines
 Austin Health Dermatology Department holds 5 Clinic sessions to discuss and plan the treatment of with Dermatology conditions. Department of Health clinical urgency categories for specialist clinics Urgent:
Austin Health Dermatology Department holds 5 Clinic sessions to discuss and plan the treatment of with Dermatology conditions. Department of Health clinical urgency categories for specialist clinics Urgent:
Your Skin. Section 14.2 Your Skin, Hair, and Nails
 Your Skin The skin covers and protects the body from injury, infection, and water loss. The skin also helps to regulate body temperature and gathers information from the environment. Protection The skin
Your Skin The skin covers and protects the body from injury, infection, and water loss. The skin also helps to regulate body temperature and gathers information from the environment. Protection The skin
Dermatology Syllabus for 5th Year Med Students
 Hawler Medical University College of Medicine Department of medicine 2011-2012 Dermatology Syllabus for 5th Year Med Students Course Information: Course Title : Dermatology Credit Hours : Time Theoretical:
Hawler Medical University College of Medicine Department of medicine 2011-2012 Dermatology Syllabus for 5th Year Med Students Course Information: Course Title : Dermatology Credit Hours : Time Theoretical:
DERMATOLOGY FOR THE NON-DERMATOLOGIST. Mackinac Island, Michigan The Grand Hotel. July 16 18, Participating Faculty
 DERMATOLOGY FOR THE NON-DERMATOLOGIST Mackinac Island, Michigan The Grand Hotel July 16 18, 2010 Participating Faculty Lori D. Prok, M.D. Assistant Professor Pediatric Dermatology and Dermatopathology
DERMATOLOGY FOR THE NON-DERMATOLOGIST Mackinac Island, Michigan The Grand Hotel July 16 18, 2010 Participating Faculty Lori D. Prok, M.D. Assistant Professor Pediatric Dermatology and Dermatopathology
Dermoscopy: Recognizing Top Five Common In- Office Diagnoses
 Dermoscopy: Recognizing Top Five Common In- Office Diagnoses Vu A. Ngo, DO Department of Family Medicine and Dermatology Choctaw Nation Health Services Authority Learning Objectives Introduction to dermoscopy
Dermoscopy: Recognizing Top Five Common In- Office Diagnoses Vu A. Ngo, DO Department of Family Medicine and Dermatology Choctaw Nation Health Services Authority Learning Objectives Introduction to dermoscopy
Pathology of the skin. 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University
 Pathology of the skin 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Histology of the skin Epidermis: Stratum corneum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale Dermis: papillary and reticular
Pathology of the skin 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Histology of the skin Epidermis: Stratum corneum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale Dermis: papillary and reticular
Lid Lesions: Relax or Refer
 Lid Lesions: Relax or Refer Blair Lonsberry, MS, OD, MEd., FAAO Professor of Optometry Pacific University College of Optometry blonsberry@pacificu.edu Agenda Benign vs. Malignant lesions Benign Eyelid
Lid Lesions: Relax or Refer Blair Lonsberry, MS, OD, MEd., FAAO Professor of Optometry Pacific University College of Optometry blonsberry@pacificu.edu Agenda Benign vs. Malignant lesions Benign Eyelid
Test your knowledge with multiple-choice cases. What are these speckled spots?
 Test your knowledge with multiple-choice cases Case 1 What are these speckled spots? A speckled, pigmented lesion is noticed on the upper arm of a 10-year-old girl. Her mother says the lesion has been
Test your knowledge with multiple-choice cases Case 1 What are these speckled spots? A speckled, pigmented lesion is noticed on the upper arm of a 10-year-old girl. Her mother says the lesion has been
Lumps and Bumps: An Organized Approach to Diagnosis and Management. Disclosure. Introduction. References. Structure of Skin.
 Lumps and Bumps: An Organized Approach to Diagnosis and Management Nothing to disclose Disclosure Tammy Pifer Than, MS, OD, FAAO Carl Vinson VAMC tammythan@bellsouth.net References Fitzpatrick's Color
Lumps and Bumps: An Organized Approach to Diagnosis and Management Nothing to disclose Disclosure Tammy Pifer Than, MS, OD, FAAO Carl Vinson VAMC tammythan@bellsouth.net References Fitzpatrick's Color
Types of Skin Infections
 Anatomy of Skin Types of Skin Infections Bacterial Impetigo Folliculitis Acne Fungal /Parasitic Tinea Pedis Tinea Cruris Tinea Versicolor Tinea Corporis Toenail fungus Allergic/Irritation conditions Dermatitis
Anatomy of Skin Types of Skin Infections Bacterial Impetigo Folliculitis Acne Fungal /Parasitic Tinea Pedis Tinea Cruris Tinea Versicolor Tinea Corporis Toenail fungus Allergic/Irritation conditions Dermatitis
B. Incorrect! Hypodermis is not part of the skin and lays under the dermis. D. Correct! The epidermis is the outermost region of the skin.
 Microbiology - Problem Drill 17: Microbial Infections of the Skin and Eye No. 1 of 10 1. What is the name of the most external region of the skin? (A) Dermis (B) Hypodermis (C) Hyperdermis (D) Epidermis
Microbiology - Problem Drill 17: Microbial Infections of the Skin and Eye No. 1 of 10 1. What is the name of the most external region of the skin? (A) Dermis (B) Hypodermis (C) Hyperdermis (D) Epidermis
Recommendations for the Control of Common Communicable Diseases in Educational Settings
 Recommendations for the Control of Common Communicable Diseases in Educational Settings Developed by the National Institute for Communicable Diseases (NICD) A Division of the National Health Laboratory
Recommendations for the Control of Common Communicable Diseases in Educational Settings Developed by the National Institute for Communicable Diseases (NICD) A Division of the National Health Laboratory
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Functions of the Skin n regulation of body temperature n blood reservoir n protection n cutaneous sensations n excretion and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Functions of the Skin n regulation of body temperature n blood reservoir n protection n cutaneous sensations n excretion and
Integumentary System. Packet #12
 Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Site and distribution: symmetrical, asymmetrical. Surface characteristics: smooth, scaly, warty
 B I O T E R R O R I S M PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE OF DERMATOLOGY Dr Matthew Ng Joo Ming INTRODUCTION Medical schools and textbooks teach us dermatology by subjects such as eczema and psoriasis. This is useful
B I O T E R R O R I S M PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE OF DERMATOLOGY Dr Matthew Ng Joo Ming INTRODUCTION Medical schools and textbooks teach us dermatology by subjects such as eczema and psoriasis. This is useful
Figure 4.1. Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 115
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Short Answer Figure 4.1 Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Short Answer Figure 4.1 Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated
Can You Take a Look at This? Objectives 4/18/12. Shane Scott, DO Internal Medicine & Pediatrics The
 Can You Take a Look at This? Shane Scott, DO Internal Medicine & Pediatrics The Objectives! Identify Common Presentations of Rashes in the Pediatric Patient! Decide if the rash is Communicable! Decide
Can You Take a Look at This? Shane Scott, DO Internal Medicine & Pediatrics The Objectives! Identify Common Presentations of Rashes in the Pediatric Patient! Decide if the rash is Communicable! Decide
Notes on Chapter 6 Integumentary System (Lecture notes-shortened)
 Notes on Chapter 6 Integumentary System (Lecture notes-shortened) I. Integumentary system- the skin and all of its accessory organs such hair, nails & gland II. Skin & its Tissues A. Skin is largest organ
Notes on Chapter 6 Integumentary System (Lecture notes-shortened) I. Integumentary system- the skin and all of its accessory organs such hair, nails & gland II. Skin & its Tissues A. Skin is largest organ
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB. Friday, February 12, :30 am 11:00 am
 MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 12, 2012 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 12, 2012 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
IT S FUNDAMENTAL MY DEAR WATSON! A SHERLOCKIAN APPROACH TO DERMATOLOGY
 IT S FUNDAMENTAL MY DEAR WATSON! A SHERLOCKIAN APPROACH TO DERMATOLOGY Skin, Bones, and other Private Parts Symposium Dermatology Lectures by Debra Shelby, PhD, DNP, FNP-BC, FADNP, FAANP Debra Shelby,
IT S FUNDAMENTAL MY DEAR WATSON! A SHERLOCKIAN APPROACH TO DERMATOLOGY Skin, Bones, and other Private Parts Symposium Dermatology Lectures by Debra Shelby, PhD, DNP, FNP-BC, FADNP, FAANP Debra Shelby,
The Integumentary System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
Treatments used Topical including cleansers and moisturizer Oral medications:
 Discipline: Dermatology Extended Topic: Acne & Rosacea : Onset: Location: Face Chest Back Menses if female: Regular Irregular PCOS Treatments used Topical including cleansers and moisturizer Oral medications:
Discipline: Dermatology Extended Topic: Acne & Rosacea : Onset: Location: Face Chest Back Menses if female: Regular Irregular PCOS Treatments used Topical including cleansers and moisturizer Oral medications:
MUCOCUTANEOUS MANIFESTATIONS OF HIV/AIDS IN ADOLESCENTS
 MUCOCUTANEOUS MANIFESTATIONS OF HIV/AIDS IN ADOLESCENTS Dr. Y.S.MARFATIA Prof. and Head, Dept. Skin & V.D. Medical college, Vadodara LET US CREATE BRILLIANCE TOGETHER MEDICAL COLLEGE, VADODARA Editor in
MUCOCUTANEOUS MANIFESTATIONS OF HIV/AIDS IN ADOLESCENTS Dr. Y.S.MARFATIA Prof. and Head, Dept. Skin & V.D. Medical college, Vadodara LET US CREATE BRILLIANCE TOGETHER MEDICAL COLLEGE, VADODARA Editor in
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more
 Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
