Serious Rashes You Won t Want to Miss! Miriam Weinstein MD FRCPC (Paediatrics) FRCPC (Dermatology)
|
|
|
- Dortha Heath
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Serious Rashes You Won t Want to Miss! Miriam Weinstein MD FRCPC (Paediatrics) FRCPC (Dermatology)
2 Good Resources for Clinical Derm Photos **This website currently under construction
3 Objectives Participants will be able to: Use morphologic and historical clues to identify and differentiate rashes Identify the major causes of bullous eruptions and use historical and morphologic clues to distinguish each from one another Discuss the varied morphologies of drug eruptions
4 Outline Approach to rashes Test your knowledge Morphologic groups of rashes Examples of differentiating rashes Summary
5 Approach to Rashes 1. Disease categories 2. Morphology
6 Disease Category Infectious Inflammatory Drug eruptions Toxin mediated Allergic Neoplastic Environmental
7 Morphologic Approach Describe what is seen Designate it to a morphologic category Differentiate the rashes in the DDx
8 Morphologic Approach Describe what is seen Designate it to a morphologic category Differentiate the rashes in the DDx Diagnose Deal with the problem (management!)
9 Morphologic Approach 1. Known (pattern recognition) 2. Unsure 3. Unkown
10 What to do if unsure or unknown? Need tools to sort out search literature ask a colleague dermatology referral trial of treatment if suspected diagnosis observe utilize visual literacy skills
11 What to do if unsure or unknown? Need tools to sort out search literature ask a colleague dermatology referral trial of treatment if suspected diagnosis observe utilize visual literacy skills
12 Visual Literacy Ability to read visual images and extract meaningful information from what is seen
13 Visual Literacy in Dermatology The ability to derive diagnostic interpretations form observed visual clues
14 Visual Literacy Not just looking.but observing! To observe incorporates: History Morphology Experience Knowledge
15 Clinical Skin Problem Known Unsure Unknown Develop DDx Manage Appropriately Visual Literacy Skills Try to refine Dx How? Visual Literacy Skills? Visual Literacy Skills
16 Morbilliform Eruptions Blanchable Erythematous Small flat macules Slightly raised papules May coalesce NO: scale, crust, vesicle, nodules
17 Morbilliform Eruptions Not to Miss Eruptions Travel related exanthems Kawasaki Disease GVHD Drug eruption Viral exanthem (measles) Mild Moderate Eruptions Common viral exanthems
18 Morbilliform Eruptions Travel related: Dengue Typhoid fever Early spotted fevers
19 Dengue Flaviviruses 4 serotypes: DEN1, DEN2, DEN3, DEN4 Immunity after infection is distinct to serotype Aedes aegypti mosquito transmits to humans Significant global increase
20 Dengue Fever Many parts of Mexico, Central and South America Many parts of Africa India
21 Dengue Fever Clinical Features (~ 3 12 days after bite) Fever Bone pain Pain with eye movements Joint/muscle aches Adenopathy Morbilliform eruption From extremities to central Spares face Palms and soles can be involved
22 Dengue fever Illness can last two weeks Symptomatic treatment Diagnosis: Isolating virus or viral DNA (PCR) Paired serology Prevention Mosquito avoidance strategies No vaccine
23 Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Specific syndrome Usually 2 5 days after start of illness Usually on second exposure of different serotype Most common < 10 years old Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia,hemoconcentration Features: High fever Pneumonia, myocarditis Systemic circulatory collapse Hemmorhage Bleeding, bruising, petichiae, mucosal bleeding Mortality up to 30%
24 Typhoid fever Salmonella Typhi In blood and stool Shed in stool if ill & chronically in carriers Fecal oral spread In most developing countries Especially Asia, Africa, Latin America
25 Typhoid fever High fever and rose spots In 10% Discrete pink macules on trunk and abdomen during 2 nd week of illness Vaccination available can wane over time, may need booster
26 Kawasaki Disease: Diagnostic Criteria Fever for 5 days or more Plus 4 of: Bilateral conjunctivitis (no purulent) Changes of the lips and oral cavity Dry, fissures, crack, swelling, strawberry tongue Swelling of the cervical lymph nodes >1.5 cm Polymorphous exanthem of body Red and swollen palms and soles
27 Measles Cough Coryza Conjunctivitis Koplik s spots On day 3 7 morbilliform eruption Starts at head and face and spreads down Turns brownish and fine desquamation Fever that lasts more than 3 days into rash: Consider measles related complications
28 Measles Still accounts for 250,000 childhood deaths per year Still common in developing countries INCOMPLETE vaccination rates in developed countries must keep this disease in mind Spread: respiratory droplets Incubation 7 14 days Infectious from: 2 days before symptoms Until at least 5 days after the rash
29 Measles Treat complications Vitamin A Reduces blindness Reduces death rates by 50% Complications Pneumonia, encephalitis, otitis media Vaccine within 72 hours of contact May prevent developing disease Immunoglobulin May prevent disease If given within 6 days of contact For high risk patients
30 Papulosquamous Eruptions Erythematous purple Raised papules and/or plaques Sharply marginated Have scale Many different types of scale
31 Papulosquamous Eruptions Not to Miss Eruptions Neonatal Lupus Mild Moderate Eruptions Psoriasis Tinea corporis Nummular eczema Pityriasis rosea
32 Neonatal Lupus Discrete, round oval scaly papules Raccoon pattern Appears up to 6 weeks, resolve ~6 months Maternal antibodies cross placenta Anti Ro +/ Anti La Mother often asymptomatic 2% of exposed fetuses
33 Neonatal Lupus Can have associated heart disease Typically heart block (1 st, 2 nd, 3 rd ) Cardiomyopathy +/ Hepatic or Hematologic disease
34 Neonatal Lupus Cutaneous NL self resolves, may leave scar Importance is in recognizing this sign May predict cardiac NL in baby Marker for risk of cardiac NL in future baby
35 Neonatal Lupus Once baby diagnosed Work up including heme/liver parameters Mother should have Examination for rheumatologic disease Antibodies checked Followed during subsequent pregnancies Risk of next baby having NL elevated Cutaneous Heart Block Hepatic involvement/hematologic Izmirly et al, Arthritis and Rheumatism, April 2010
36 Dermatitic Eruptions Erythematous Macular and/or papular Often poorly marginated +/ scale +/ crust
37 Dermatitic Eruptions Not to Miss Eruptions Zinc deficiency Scabies Mild Moderate Eruptions Atopic dermatitis Irritant contact dermatitis Seborrheic dermatitis
38 Zinc Deficiency Etiology: Acrodermatitis enteropathica AR Affects intestinal absorption and transport of zinc Impaired zinc excretion in breast milk Clinical: Diarrhea Skin eruption: perioral, acral, diaper area +/- alopecia Irritability Collect blood in special tubes Rapid improvement with zinc supplement
39 Scabies Polymorphous eruption: Dermatitis Papules and pustules Acute eruption Palms/soles, web space, axillae, areola, umbilicus
40 Treatment of Scabies 1. Treat scabies 2. Treat close contacts 3. Environmental measures 4. Treat pruritus 5. Treat 2 0 infection from scratching
41 Treatment of scabies: Patients and Close Contacts Permethrin 5% cream most effective Infants: treat whole body Children & Adults: treat from neck down Leave on overnight and wash in am Re treat 1 week later Low side effect profile
42 Treatment of Scabies Environmental: Linen & clothing from last 3 days: launder Routine cleaning and vacuuming of house Pruritus Antihistamines Topical cortisones Itch may last weeks after scabies gone Secondary infection Topical or oral antibiotics
43 Vesicluar Eruptions Fluid filled (blood/pus/serum or combination) Some present as papules first Can present as open erosions/ulcer (de roofed) Can present as small crusts May have mixed morphology with above Usually well demarcated Can range from flaccid to tense
44 Vesicular Bullous Eruptions Not to Miss Eruptions Varicella Eczema Herpeticum Coxsackie Virus Poison Ivy (acute ACD) Immunobullous eruption Staph Scalded Skin SJS TEN Bullous Erythema Multifore Mild Moderate Eruptions Bullous impetigo Herpes labialis
45 Varicella Papules, crusts and vesicles May be very mild in vaccinated child Children can get zoster Post disease or post vaccine NOT a sign of immunodeficiency Don t tend to get post herpetic neuralgia
46 Eczema Herpeticum Widespread herpes in atopic derm patient Can be recurrent Often superinfected with bacteria Punched out erosions and vesicles Patient may have systemic symptoms
47 Eczema Herpeticum Management High index of suspicion for diagnosis Confirm with viral culture/pcr from lesion If unwell, <1 year, poor fluid intake, severe: Admit and treat with IV acyclovir If well, good fluid intake, good follow up Oral acyclovir for 10 days Add antibiotics if necessary Saline compresses help wound healing
48 Enanthem: Enterovirus: Hand foot mouth Vesicles rupture leaving erosions on red base buccal mucosa, tongue, palate, uvula, tonsils Painful causing anorexia and dehydration Exanthem: Gray white vesiculopustules/papules +/ erythema Palms, soles, dorsal hands & feet, buttocks, perineum
49 Hand Foot Mouth Disease New Manifestations Can cause much more substantial eruption More extensive than classic HFM Different morphologies: Vesicular>papular> petechial 2 Vesicular patterns Can produce an eczema coxsackium in pts with eczema Can look like eczema herpeticum Widespread vesicular eruption beyond palms and soles Pediatrics June 2013; 132(1): e149 e157
50 Hand Foot Mouth Disease New Manifestations Newer eruptions may be caused by serotype A6 classic HFM most commonly caused by A16 (CVA16): N America classic HFM most commonly caused by EV 71: Asia Nail abnormalities more common with A6 Work up: PCR and/or culture NP swab, viral skin swab, stool Self limited Supportive management Pediatrics June 2013; 132(1): e149 e157
51 Allergic Contact Dermatitis Acute Vesicular
52 Allergic Contact Dermatitis Different patterns: Plant based Nickel Topical active ingredients
53 Allergic Contact Dermatitis Plant based Poison ivy is prototype (poison oak, sumac) Acute, intensely itchy Bullous eruptions Crusting Often linear Extremities, face, genitals common
54 Allergic Contact Dermatitis Management Identify and eliminate allergen May need patch testing to determine Topical steroids for localized dermatitis 1% hydrocortisone for face, groin, folds 0.05% betamethasone valerate for body 0.1% betamethasone valerate for thick areas Poison Ivy or other severe, acute ACD 3 week tapering course of oral steroids
55 Autoimmune Bullous Diseases Rare group of bullous disorders Antibodies to key proteins in skin Proteins destroyed through immune system Integrity of skin lost creating blisters Many disorders each targeting a different protein Problems: Pain, infection, can have severe mucosal involvement Can have significant morbidity
56 Autoimmune Bullous Diseases Treatment is usually with high dose steroids to start Usually add steroid sparing agents Examples: Pemphigus vulgaris Pemphigus foliaceus Bullous pemphigoid Linear IgA disease
57 Staphlococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome Bullous eruption from S. aureus toxins Large, flaccid bullae Rupture easily Often present only with collarette of scale Pain is common Fever and systemic symptoms uncommon Axilla, groin: peeling, erythema Face (crusts around mouth, eyes)
58 Staph Scalded Skin Treatment Swab possible sites for Staph Eyes, peri-rectal, nares, umbilicus, pustules Intravenous Cloxacillin Some will add Clindamycin (anti-toxin) Pain control Compresses to healing skin Switch to oral when well
59 SJS-TEN Spectrum with different degrees of severity SJS: <30% BSA involved with bullae TEN: >30% BSA involved with bullae Mucous membranes involved Almost always caused by drugs Steroids not usually used Treatment: IVIG or Cyclosporin
60 Bullous Erythema Multiforme Atypical targets With central vesicle Vesicles without targets Discrete lesions Erosions and crusts Mucous membranes involved Mycoplasma most common identified cause
61 Bullous Erythema Multiforme Management Admit for management Check for Mycoplasma Consider starting Abx for mycoplasma Ophtho and derm consult Oral care Systemic steroids often needed Wound care
62 History Bacterial Folliculitis Staph Aureus Acute eruption No pruritus Usually systemically well Physical Exam Perifollicular red papules and pustules Any hair bearing area
63 Hot Tub Folliculitis (Pseudomonos) History Acute eruption No pruritus Often painful History of exposure Usually systemically well Physical Exam Perifollicular red papules and pustules Usually lower limbs and buttocks
64 Hot tub folliculitis Pseudomonas folliculitis From hot tubs, pools, water slides etc. Risk factors: High water temperature Turbulence Aeration Heavy bather load Low chlorine levels
65 Hot tub folliculitis Treatment: Self resolves Can persist for several weeks Can be recurrent Topical steroids may WORSEN eruption Prevention: chlorine levels at 0.5mg/l and maintain ph between 7.2 and 7.8
66 Papular Eruptions Solid papules or plaques Flesh, pink, red, purple Vary in degree of infiltration Appear to sit on skin (vs. nodules in skin) Usually no scale or crust
67 Papular Eruptions Not to Miss Eruptions Erythema Multiforme Urticaria Urticaria Multiforme Arthropod bites Mild Moderate Eruptions Molluscum Verrucae
68 Distinguishing EM from Erythema Migrans Erythema Multiforme Erythema Migrans Most common cause Herpes simplex virus Lyme Disease Target lesions Multiple Solitary (usually) Expanding lesion(s) rare typical Mucosal involvement often none Recurrent Often Unlikely
69 Lyme Disease Borrelia burgdorferi (spirochete) Transmitted by Ixodes tick Transmission rare in 1 st 24h of attachment Transmission high after 48h of attachment Clinical stages: Primary: erythema migrans +/ systemic (~60%) Secondary: after above ends, 5 6 months Tertiary: ~7 months after infection (skin/internal) Untreated: Heart, rheum, neuro problems
70 Erythema Migrans 7 days after tick bite (2 28) at bite site Target lesions Often asymptomatic and unnoticed Gone by 1 month alone or 2 3 days (Tx d) Multi focal erythema migrans Can be seen in early disseminated Lyme disease
71 Erythema Migrans History Exposure (relevant travel)? Tick removed +/ mild systemic symptoms Expanding target lesion Physical exam Target lesion (usually solitary) Examine joint, cardiac, neuro and general
72 Lyme Disease Primarily a clinical diagnosis Serology Culturing Borrelia low yeild but unequivocal PCR (synovial or CSF fluid) Prevention Typical arthropod avoidance measures Treatment Doxycycline (only >9), amoxicillin, cefuroxime Oral antibiotics: days IV antibiotics: days (systemic disease) 200mg doxy within 72h of tick bite may reduce risk LD
73 Urticaria Wheals from transient dermal edema No scale and they leave no marks Often targetoid ; rarely true target lesions Each lesion last no more than 48 hours Crops can recur intermittently Chronic Urticaria: Crops last > 6 weeks Giant urticaria: serpiginous border with central clearing
74 Urticaria Many cases are idiopathic Viral illness is a common cause Food allergy is an uncommon cause IgE mediated drug eruption Other rare causes: Cholinergic urticaria Cold urticaria Exercise induced urticaria
75 Urticaria Management Acute: If think food: eliminate food & refer to allergy If viral: reassure, antihistamines, symptomatic If idiopathic: reassure, antihistamines Epipen if anaphylaxis symptoms Chronic: Above measures Consider workup in select patients Workup based on history and exam No standard workup
76 Arthropod Bites Hard to distinguish arthropod based on lesion Lesions often grouped 2 3 (can be many groups) Usually excoriated papule Can have urticarial wheal surrounding Common causes: mosquitoes, fleas, bedbugs
77 Arthropod Bites Management Prevention Avoid mosquito avoidance measures No standing water Avoid outside at dawn/dusk Insect repellent (follow CPS guidelines) Have pets checked and treated for fleas Treatment Antihistamines Topical corticosteroids Cool compresses
78 Petechial/Purpuric Eruptions Non blanchable Red purple Small large non palpable macules/patches Can get palpable purpura Usually suggests vasculitis
79 Petechial Eruptions Not to Miss Travel related: Spotted fevers Viral hemorrhagic fevers Non travel related: Henoch Schonlein Purpura ITP Vasculitis Meningococcemia Mild Moderate Eruptions Petechiae 2 0 to scratch, cough Bruising from minor injury PPGSS (Papular purpuric glove and socks syndrome) Progressive pigmentary purpura
80 Rickettsial Disease Intracellular parasites with endothelial cell as target Many different rickettsia in different parts of world Divided into: Spotted fevers Typhus group (variation of above) Transmitted via infected ticks and other arthropods Worldwide distribution Necrotic eschars in some tache noire Eschar at bite site with surrounding inflammation
81 Spotted fevers Different parts of the world Different rickettsia types Tick bite transmits rickettsia to blood and disseminates Risk of spotted fever depends on: Prevelenace of rickettsial infected ticks in given area Abundance of ticks Affinity of tick for human Tick needs attachement for at least 6 hours Asymptomatic so not usually recalaled
82 Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever Incubation 6 8 days Flu like syndrome High fever, non specific general symptoms Rash (90%): 2 4 days after fever Red macules at wrists/ankles Becomes papular then petechiae Spreads centrally Trunk, palms, soles Multi organ involvement Long term sequelae possible
83 Spotted fevers All similar to RMSF Varying degrees of eschar Rare (RMSF) 50% of lesions (eg., African tick bite fever) Diagnosis: Non specific lab changes Histology not that helpful Serology Can t differentiate between the rickettsiae Rise in titres during second week of illness Culture, PCR, immunohistochemistry: special labs
84 Spotted fevers Treatment Empiric therapy must be started before serology confirmed Doxycycline 200 q12 for 2 7 days Data suggests dental staining NOT an issue <8 Prophylactic Abx after tick bite NOT helpful Avoid tick infested areas in given country Volovitz et al 2007
85 Typhus group Mites or fleas are vectors Usually eschar at bite site generalized flu like symptoms maculopaoulr and petichial rash Epidemic typhus: Spread by body lice Parts of Africa, S. America Scrub typhus R. tsutsugamushi Endemic in South East Asia Dx: serology Tx: doxycycline or tetracycline
86 Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers Several distinct families of viruses arenaviruses, filoviruses, bunyaviruses, flaviviruses Severe multisystem disease Shock, bleeding, multiorgan failure Vascular damage Hemorrhage often major feature Reside in animal host or arthropod vector Some can spread human human Ebola, Marburg, Lassa South America and Africa Treatment: symptomatic Ribavirin has been tried
87 Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers Mucocutaneous findings Non specific Macular eruption Flushing Petechiae (axillary especially) Hemmorhage Accompanied by severe systemic signs
88 Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever Specific syndrome Usually 2 5 days after start of illness Usually on second exposure of different serotype Most common < 10 years old Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia,hemoconcentration Features: High fever Pneumonia, myocarditis Systemic circulatory collapse Hemorrhage Bleeding, bruising, petechiae, mucosal bleeding Mortality up to 30%
89 Erythema Multiforme Urticaria Erythema Migrans Arthropod bite Tinea Corporis True Target YES Rare YES Rare No Associations HSV +/ Viral illness Often None None None Pruritus Rare YES NO YES NO Exposure HSV +/ Viral Illness Tick bite; travel Outside, pets, travel Known contact; Tinea Capitis Distribution Acral Prominent Widespread Usually solitary Grouped (2 3) One many
90 Summary Use visual clues Use historical clues Distinguish red flags from red herrings
91 Summary Describe what is seen Designate it to a morphologic category Differentiate the rashes in the DDx Diagnose Deal with the problem (management!)
92 Maculopapular Papulosquamous Dermatitic Vesicular Papular Purpuric/Petechial
93 Vesicular Bullous Eruptions Not to Miss Eruptions Varicella Eczema Herpeticum Coxsackie Virus Poison Ivy (acute ACD) Immunobullous eruption Staph Scalded Skin SJS TEN Bullous Erythema Multifore Mild Moderate Eruptions Bullous impetigo Herpes labialis
Objectives. Terminology. Recognize common pediatric dermatologic conditions. Review treatment plans Identify skin manifestations of systemic disease
 Pediatric Visual Dermatological Diagnosis Fernando Vega, M.D. Objectives Recognize common pediatric dermatologic conditions Expand differential diagnosis Review treatment plans Identify skin manifestations
Pediatric Visual Dermatological Diagnosis Fernando Vega, M.D. Objectives Recognize common pediatric dermatologic conditions Expand differential diagnosis Review treatment plans Identify skin manifestations
Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children
 May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
May 2016 Rashes Not To Be Missed In Children Dr Chan Yuin Chew Dermatologist Dermatology Associates Gleneagles Medical Centre Scope of presentation Focus on rashes May lead to significant morbidity if
Learning Objectives. History 8/1/2016. An Approach to Pediatric Rashes
 An Approach to Pediatric Rashes Neethi Patel, D.O. Learning Objectives 1.To identify common features of rashes seen in the pediatric population as well as pathognomonic features of certain pathologies
An Approach to Pediatric Rashes Neethi Patel, D.O. Learning Objectives 1.To identify common features of rashes seen in the pediatric population as well as pathognomonic features of certain pathologies
Future of Pediatrics: Blisters, Hives and Other Tales from the Emergency Room June 14 th, 2016
 A. Yasmine Kirkorian MD Assistant Professor of Dermatology & Pediatrics Children s National Health System George Washington University School of Medicine & Health Sciences Future of Pediatrics: Blisters,
A. Yasmine Kirkorian MD Assistant Professor of Dermatology & Pediatrics Children s National Health System George Washington University School of Medicine & Health Sciences Future of Pediatrics: Blisters,
Bacterial Infections in Pediatric Dermatology. Patrick McMahon, MD Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
 Bacterial Infections in Pediatric Dermatology Patrick McMahon, MD Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Fill In The Blank When you see on the skin, you think of a bacterial skin infection SEND SWABS VIRAL
Bacterial Infections in Pediatric Dermatology Patrick McMahon, MD Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Fill In The Blank When you see on the skin, you think of a bacterial skin infection SEND SWABS VIRAL
Patricia A. Treadwell, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics
 EXANTHEMS Patricia A. Treadwell, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics Indiana University School of Medicine FACULTY DISCLOSURE I have the following financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial
EXANTHEMS Patricia A. Treadwell, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics Indiana University School of Medicine FACULTY DISCLOSURE I have the following financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial
Suzan Schneeweiss MD, MEd, FRCPC
 Suzan Schneeweiss MD, MEd, FRCPC I have nothing to disclose 1. Discuss common pitfalls in the diagnosis and management of common paediatric rashes in the ED 2. Identify dermatologic conditions requiring
Suzan Schneeweiss MD, MEd, FRCPC I have nothing to disclose 1. Discuss common pitfalls in the diagnosis and management of common paediatric rashes in the ED 2. Identify dermatologic conditions requiring
VARICELLA. Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division, Department of Child Health, Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 VARICELLA (Chicken pox) Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division, Department of Child Health, Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition : Varicella is a common contagious disease caused
VARICELLA (Chicken pox) Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division, Department of Child Health, Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition : Varicella is a common contagious disease caused
An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc
 An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc 1 Common Rashes Tinea Corporis: Annular- this is not the only criteria Advancing erythematous
An Approach to Common and not so Common Rashes in the Office FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc 1 Common Rashes Tinea Corporis: Annular- this is not the only criteria Advancing erythematous
EXANTHEMATOUS ILLNESS. IAP UG Teaching slides
 EXANTHEMATOUS ILLNESS 1 DEFINITIONS Exanthema eruption of the skin Exanthema eruption of mucosae Macule flat nonpalpable lesion Papule small palpable lesion Nodule large palpable lesion Vesicle small fluid
EXANTHEMATOUS ILLNESS 1 DEFINITIONS Exanthema eruption of the skin Exanthema eruption of mucosae Macule flat nonpalpable lesion Papule small palpable lesion Nodule large palpable lesion Vesicle small fluid
Bacteria: Scarlet fever, Staph infection (sepsis, 4S,toxic shock syndrome), Meningococcemia, typhoid Mycoplasma Rickettsial infection
 Exanthematous Fever objectives FEVER WITH RASH 1 Determine the feature of skin rashes 2 Enumerate the most common causes of skin rashes in children (measles, chicken pox, rubella,erythema infectiosum,
Exanthematous Fever objectives FEVER WITH RASH 1 Determine the feature of skin rashes 2 Enumerate the most common causes of skin rashes in children (measles, chicken pox, rubella,erythema infectiosum,
Infectious Disease. Chloe Duke
 Infectious Disease Chloe Duke Learning Objectives Essential - Causes, recognition and Treatment of: Meningitis Sepsis Purpura Important Cervical Adenopathy Tonsillitis and Pharyngitis Otitis Media Pneumonia
Infectious Disease Chloe Duke Learning Objectives Essential - Causes, recognition and Treatment of: Meningitis Sepsis Purpura Important Cervical Adenopathy Tonsillitis and Pharyngitis Otitis Media Pneumonia
Pediatric Rashes: To Play or Not to Play
 Objectives Pediatric Rashes: To Play or Not to Play Tami Jakubowski DNP, CPNP-PC, CSN Tracy Perron PhD, RN,CSN Pediatric Nursing Conference July 27,2018 Identify rashes commonly encountered among school-aged
Objectives Pediatric Rashes: To Play or Not to Play Tami Jakubowski DNP, CPNP-PC, CSN Tracy Perron PhD, RN,CSN Pediatric Nursing Conference July 27,2018 Identify rashes commonly encountered among school-aged
Discussion. Infection & ER combine meeting. Fever and rash. Fever and rash. Fever and skin rash Measles
 Discussion Infection & ER combine meeting Fever and skin rash Measles Reporter R2 李尚 Supervisor VS 陳威宇洪世文 Date 99/03/20 Fever and rash Age of the patient Season of the year Travel history, Geographic location
Discussion Infection & ER combine meeting Fever and skin rash Measles Reporter R2 李尚 Supervisor VS 陳威宇洪世文 Date 99/03/20 Fever and rash Age of the patient Season of the year Travel history, Geographic location
Pediatric Dermatology. Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital
 Pediatric Dermatology Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Conflict of interest! No financial conflict of interest! Individual products shown are examples only not a product endorsement Pediatric
Pediatric Dermatology Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Conflict of interest! No financial conflict of interest! Individual products shown are examples only not a product endorsement Pediatric
- Mycoplasma and Ureaplasma. - Rickettsia
 - Mycoplasma and Ureaplasma - Rickettsia Mycoplasma and Ureaplasma Family: Mycoplasmataceae Genus: Mycoplasma Species: M. pneumoniae Species: M. hominis Species: M. genitalium Genus: Ureaplasma Species:
- Mycoplasma and Ureaplasma - Rickettsia Mycoplasma and Ureaplasma Family: Mycoplasmataceae Genus: Mycoplasma Species: M. pneumoniae Species: M. hominis Species: M. genitalium Genus: Ureaplasma Species:
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level
 Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
Diagnosis and Management of Common and Infective Skin Diseases in Children at primary care level Dr Ng Su Yuen Paediatrician and Paediatric Dermatologist Hospital Pulau Pinang Outline Common inflammatory
Childhood Contagious Diseases)5(
 Childhood Contagious Diseases)5( Children have maturing immune systems and are often in close proximity to one another, such as in day-care centers, classrooms, and on school buss. This makes the transmission
Childhood Contagious Diseases)5( Children have maturing immune systems and are often in close proximity to one another, such as in day-care centers, classrooms, and on school buss. This makes the transmission
12/12/2018. Childhood Skin Infections. Objectives. Verruca vulgaris. Case #1. Case #2. Management 1. Evidence Updates
 Objectives Childhood Skin Infections Evidence Updates Brian Z. Rayala, MD Associate Professor Department of Family Medicine UNC School of Medicine At the end of lecture, learner will be able to:» Diagnose
Objectives Childhood Skin Infections Evidence Updates Brian Z. Rayala, MD Associate Professor Department of Family Medicine UNC School of Medicine At the end of lecture, learner will be able to:» Diagnose
Chapter 40. Alterations of the Integument in Children
 Chapter 40 Alterations of the Integument in Children Acne Vulgaris Most common skin disease Affects 85% of the population between ages 12 and 25 years Develops at sebaceous follicles located primarily
Chapter 40 Alterations of the Integument in Children Acne Vulgaris Most common skin disease Affects 85% of the population between ages 12 and 25 years Develops at sebaceous follicles located primarily
DERMATOLOGICAL EMERGENCIES. DR. Ian Hoyle MBBS DIP IMC RCS (Ed), DA (UK),FRACGP,FACRRM,DIP DERM(Wales) TASMANIAN SKIN AND BODY CENTRE
 DERMATOLOGICAL EMERGENCIES DR. Ian Hoyle MBBS DIP IMC RCS (Ed), DA (UK),FRACGP,FACRRM,DIP DERM(Wales) TASMANIAN SKIN AND BODY CENTRE Dermatological Emergencies INFECTIONS ERYTHRODERMA DRUG ERUPTIONS STEVENS-JOHNSON
DERMATOLOGICAL EMERGENCIES DR. Ian Hoyle MBBS DIP IMC RCS (Ed), DA (UK),FRACGP,FACRRM,DIP DERM(Wales) TASMANIAN SKIN AND BODY CENTRE Dermatological Emergencies INFECTIONS ERYTHRODERMA DRUG ERUPTIONS STEVENS-JOHNSON
Visual Diagnosis: A Review of Pediatric Rashes
 Visual Diagnosis: A Review of Pediatric Rashes Frank J. Sloan, MD FAAP Emergency Services Department Thank you to VisualDX for allowing the use of their images for educational purposes. 1 Modern Medicine
Visual Diagnosis: A Review of Pediatric Rashes Frank J. Sloan, MD FAAP Emergency Services Department Thank you to VisualDX for allowing the use of their images for educational purposes. 1 Modern Medicine
Rash Decisions Approach to the patient with a skin condition
 National Conference for Nurse Practitioners April 25, 2014 Rash Decisions Approach to the patient with a skin condition Margaret A. Bobonich, DNP, FNP C, DCNP, FAANP Assistant Professor, Case Western Reserve
National Conference for Nurse Practitioners April 25, 2014 Rash Decisions Approach to the patient with a skin condition Margaret A. Bobonich, DNP, FNP C, DCNP, FAANP Assistant Professor, Case Western Reserve
Fever and rash in children. Haider Arishi MD Consultant, pediatrics and infectious diseases Director, infection control program
 Fever and rash in children Haider Arishi MD Consultant, pediatrics and infectious diseases Director, infection control program objectives To understand importance of fever and rash. To discuss the clinical
Fever and rash in children Haider Arishi MD Consultant, pediatrics and infectious diseases Director, infection control program objectives To understand importance of fever and rash. To discuss the clinical
Test Your Skills: Dermatologic Conditions in Children HANDOUT. Objectives. Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Atopic Dermatitis con t 11/7/2013
 No Conflicts of Interest to Disclose Test Your Skills: Dermatologic Conditions in Children Vicky Weill, MSN, CPNP-PC HANDOUT This will be a fun, interactive session to test your skills To make it more
No Conflicts of Interest to Disclose Test Your Skills: Dermatologic Conditions in Children Vicky Weill, MSN, CPNP-PC HANDOUT This will be a fun, interactive session to test your skills To make it more
Visual Diagnosis. Q-PEM: Jan Dr. Rafah F. Sayyed PEC - Al Sadd, Doha
 Visual Diagnosis Q-PEM: Jan 2017 Dr. Rafah F. Sayyed PEC - Al Sadd, Doha DISCLOSURE I do not have any relevant financial relationship with commercial interest to disclose. Introduction Speed and Accuracy
Visual Diagnosis Q-PEM: Jan 2017 Dr. Rafah F. Sayyed PEC - Al Sadd, Doha DISCLOSURE I do not have any relevant financial relationship with commercial interest to disclose. Introduction Speed and Accuracy
Disclaimer. This is a broad survey and cannot cover all differential diagnoses or each condition in thorough detail
 Objectives Pediatric Infections: Differentiating Benign from Serious Eileen Klein, MD, MPH Rashes Infectious vs non-infectious Viral vs bacterial Respiratory and GI illnesses When do you treat When do
Objectives Pediatric Infections: Differentiating Benign from Serious Eileen Klein, MD, MPH Rashes Infectious vs non-infectious Viral vs bacterial Respiratory and GI illnesses When do you treat When do
Common Childhood Rashes. The Itchy and the Scratchy presented by Trina Blythe MD, FAAP
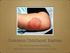 Common Childhood Rashes The Itchy and the Scratchy presented by Trina Blythe MD, FAAP Objectives Be able to identify some of the most common rashes of school age children Determine which rashes require
Common Childhood Rashes The Itchy and the Scratchy presented by Trina Blythe MD, FAAP Objectives Be able to identify some of the most common rashes of school age children Determine which rashes require
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT
 HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
Pediatric Dermatology
 Pediatric Dermatology --------- Emergencies & Urgencies Nicholas V. Nguyen, M.D. Director, Pediatric Dermatology Disclosures In the past 12 months, I have had the following financial relationships with
Pediatric Dermatology --------- Emergencies & Urgencies Nicholas V. Nguyen, M.D. Director, Pediatric Dermatology Disclosures In the past 12 months, I have had the following financial relationships with
Alphaherpesvirinae. Simplexvirus (HHV1&2/ HSV1&2) Varicellovirus (HHV3/VZV)
 Alphaherpesvirinae Simplexvirus (HHV1&2/ HSV1&2) Varicellovirus (HHV3/VZV) HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS First human herpesvirus discovered (1922) Two serotypes recognised HSV-1 & HSV-2 (1962) HSV polymorphism
Alphaherpesvirinae Simplexvirus (HHV1&2/ HSV1&2) Varicellovirus (HHV3/VZV) HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS First human herpesvirus discovered (1922) Two serotypes recognised HSV-1 & HSV-2 (1962) HSV polymorphism
Concentrate on Descriptors. An Approach to Skin Diseases in the ER
 Concentrate on Descriptors An Approach to Skin Diseases in the ER Toby Maurer, MD University of California, San Francisco Vasculitis-leaky blood vessels Targetoid lesions-round lesions with blue or red
Concentrate on Descriptors An Approach to Skin Diseases in the ER Toby Maurer, MD University of California, San Francisco Vasculitis-leaky blood vessels Targetoid lesions-round lesions with blue or red
Cutaneous Drug Reactions
 Cutaneous Drug Reactions Andrei Metelitsa, MD, FRCPC, FAAD Co-Director, Institute for Skin Advancement Clinical Associate Professor, Dermatology University of Calgary, Canada Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses
Cutaneous Drug Reactions Andrei Metelitsa, MD, FRCPC, FAAD Co-Director, Institute for Skin Advancement Clinical Associate Professor, Dermatology University of Calgary, Canada Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses
in Pediatric Medicine
 in Pediatric Medicine Martin Belson, MD Pediatric Emergency Medicine Associates, LLC Pediatric Sedation Services, LLC Children s Healthcare of Atlanta, Scottish Rite and Egleston Wellstar Hospital Systems
in Pediatric Medicine Martin Belson, MD Pediatric Emergency Medicine Associates, LLC Pediatric Sedation Services, LLC Children s Healthcare of Atlanta, Scottish Rite and Egleston Wellstar Hospital Systems
Kawasaki Disease. 1:45 2:30 p.m. James Nocton, MD Benjamin Goot, MD. Children s Specialty Group. All rights reserved.
 Kawasaki Disease 1:45 2:30 p.m. James Nocton, MD Benjamin Goot, MD Disclosures We have no relevant financial relationships to disclose. Objectives Describe the characteristic signs and symptoms of Kawasaki
Kawasaki Disease 1:45 2:30 p.m. James Nocton, MD Benjamin Goot, MD Disclosures We have no relevant financial relationships to disclose. Objectives Describe the characteristic signs and symptoms of Kawasaki
Dermergency! An Approach to Identification and Management of Life-Threatening Rashes
 Dermergency! An Approach to Identification and Management of Life-Threatening Rashes Gabby Anderson, PharmD PGY2 Emergency Medicine Pharmacy Resident anderson.gabrielle@mayo.edu Pharmacy Grand Rounds January
Dermergency! An Approach to Identification and Management of Life-Threatening Rashes Gabby Anderson, PharmD PGY2 Emergency Medicine Pharmacy Resident anderson.gabrielle@mayo.edu Pharmacy Grand Rounds January
Core Content In Urgent Care Medicine
 Pediatric Rash Emory Petrack, MD, FAAP, FACEP President, Petrack Consulting, Inc. Associate Clinical Professor of Pediatrics Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine Cleveland, Ohio Disclosure:
Pediatric Rash Emory Petrack, MD, FAAP, FACEP President, Petrack Consulting, Inc. Associate Clinical Professor of Pediatrics Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine Cleveland, Ohio Disclosure:
Dermatologic Emergencies Sept 2014
 Dermatologic Emergencies Sept 2014 SJS YES MUCOSAL INVOLVEMENT MCC drugs >> HSV TARGET LESIONS, +NIKOLSKY, painful Prodromal flu-like symptoms
Dermatologic Emergencies Sept 2014 SJS YES MUCOSAL INVOLVEMENT MCC drugs >> HSV TARGET LESIONS, +NIKOLSKY, painful Prodromal flu-like symptoms
OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH DISEASE SPECIFIC RECOMMENDATIONS
 Herpes simplex virus (HSV) Cold sores Genital herpes Herpetic whitlow OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH DISEASE SPECIFIC RECOMMENDATIONS contact with primary or recurrent lesions, infectious saliva or genital secretions
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) Cold sores Genital herpes Herpetic whitlow OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH DISEASE SPECIFIC RECOMMENDATIONS contact with primary or recurrent lesions, infectious saliva or genital secretions
0BCore Safety Profile. Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Cream 1% DK/H/PSUR/0009/005 Date of FAR:
 0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Pimecrolimus Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Cream 1% P-RMS: DK/H/PSUR/0009/005 Date of FAR: 06.06.2013 4.3 Contraindications Hypersensitivity to pimecrolimus,
0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Pimecrolimus Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Cream 1% P-RMS: DK/H/PSUR/0009/005 Date of FAR: 06.06.2013 4.3 Contraindications Hypersensitivity to pimecrolimus,
Rashes/Dermatology. Jackie Weaver-Agostoni, DO, MPH UPMC Shadyside. Director, Osteopathic Family Medicine Residency 1/28/17
 Rashes/Dermatology Jackie Weaver-Agostoni, DO, MPH UPMC Shadyside Director, Osteopathic Family Medicine Residency 1/28/17 Pre-Test #1 Pre-Test #2 Pre-Test #3 Pre-Test #4 Pre-Test #5 Pre-Test #6 Pre-Test
Rashes/Dermatology Jackie Weaver-Agostoni, DO, MPH UPMC Shadyside Director, Osteopathic Family Medicine Residency 1/28/17 Pre-Test #1 Pre-Test #2 Pre-Test #3 Pre-Test #4 Pre-Test #5 Pre-Test #6 Pre-Test
Burrowing Bugs in a 5 week-old that Mite be Difficult to Diagnosis
 Burrowing Bugs in a 5 week-old that Mite be Difficult to Diagnosis Farbod Bahadori-Esfahani,MD Pediatrics LSU Health Shreveport Louisiana Chapter AAP Red Stick Potpourri Disclosure I have nothing to disclose
Burrowing Bugs in a 5 week-old that Mite be Difficult to Diagnosis Farbod Bahadori-Esfahani,MD Pediatrics LSU Health Shreveport Louisiana Chapter AAP Red Stick Potpourri Disclosure I have nothing to disclose
Vulval dermatoses. Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough
 Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
Vulval dermatoses Dr Fiona Lewis, Consultant Dermatologist St John s Institute of Dermatology, London & Heatherwood & Wexham Park Hospital, Slough Pigmentation Vulvodynia Ulcers Genetic Pruritus VULVAL
Controlling Communicable Diseases in the School Setting LCDR C. SCOTT LOVE, MD, MPH, FAAP DEPARTMENT HEAD, PEDIATRICS
 Controlling Communicable Diseases in the School Setting LCDR C. SCOTT LOVE, MD, MPH, FAAP DEPARTMENT HEAD, PEDIATRICS Disclosure There is no conflict of interest pertaining to this presentation, materials,
Controlling Communicable Diseases in the School Setting LCDR C. SCOTT LOVE, MD, MPH, FAAP DEPARTMENT HEAD, PEDIATRICS Disclosure There is no conflict of interest pertaining to this presentation, materials,
Common Childhood Infections. BSME school nurses June Dr David Cremonesini
 Common Childhood Infections BSME school nurses June 3 2016 Dr David Cremonesini Chicken Pox Contagious from 1-2 days BEFORE rash starts until all blisters crusted over (usually 5-6 days after rash) Commonly
Common Childhood Infections BSME school nurses June 3 2016 Dr David Cremonesini Chicken Pox Contagious from 1-2 days BEFORE rash starts until all blisters crusted over (usually 5-6 days after rash) Commonly
Communicable Disease Guidelines
 Note: This information is to assist in making decisions regarding the control of communicable diseases. It is not intended for the purposes of making diagnoses. Refer to disease specific information sheets
Note: This information is to assist in making decisions regarding the control of communicable diseases. It is not intended for the purposes of making diagnoses. Refer to disease specific information sheets
PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE. Impetigo. This document should be read in conjunction with this DISCLAIMER
 Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Impetigo Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in conjunction
Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Impetigo Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in conjunction
Clinical profile of skin diseases in accident and emergency department attenders
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2007) 15, 4-9 Original Article Clinical profile of skin diseases in accident and emergency department attenders CY Chan, KL Kam, CA Graham, TH Rainer, NM Luk Skin problems
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2007) 15, 4-9 Original Article Clinical profile of skin diseases in accident and emergency department attenders CY Chan, KL Kam, CA Graham, TH Rainer, NM Luk Skin problems
Subspecialty Rotation: Dermatology
 Subspecialty Rotation: Dermatology Faculty: Wesley Galen, M.D. GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Dermatology). Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing illness and dysfunction related
Subspecialty Rotation: Dermatology Faculty: Wesley Galen, M.D. GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Dermatology). Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing illness and dysfunction related
BRAINZ POLICY AND PROCEDURE ON COMMUNICABLE DISEASES
 BRAINZ POLICY AND PROCEDURE ON COMMUNICABLE DISEASES PURPOSE: To prevent the spread of communicable diseases to client and staff of Brainz Home care Agency from staff with contagious illnesses. POLICY:
BRAINZ POLICY AND PROCEDURE ON COMMUNICABLE DISEASES PURPOSE: To prevent the spread of communicable diseases to client and staff of Brainz Home care Agency from staff with contagious illnesses. POLICY:
Infectious diseases Dr n. med. Agnieszka Topczewska-Cabanek
 Infectious diseases Dr n. med. Agnieszka Topczewska-Cabanek Viral: Exanthema subitum (Roseaola infantum) Herpetic stomatitis Measles Rubella Chickenpox Erythema infectious (5th Disease, Slapped cheec disease)
Infectious diseases Dr n. med. Agnieszka Topczewska-Cabanek Viral: Exanthema subitum (Roseaola infantum) Herpetic stomatitis Measles Rubella Chickenpox Erythema infectious (5th Disease, Slapped cheec disease)
Learning Circle: Jan 26, 2011 Childhood Eczema
 Learning Circle: Jan 26, 2011 Childhood Eczema Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Clinical Assistant Professor, UBC Department of Paediatrics Associate Member, UBC Department of Dermatology
Learning Circle: Jan 26, 2011 Childhood Eczema Wingfield Rehmus, MD MPH BC Children s Hospital Clinical Assistant Professor, UBC Department of Paediatrics Associate Member, UBC Department of Dermatology
Sickness and Illness Policy
 Sickness and Illness Policy Children should not be at nursery if they are unwell. If your child becomes unable to stay at nursery, a member of staff will contact the parent or carer, asking them to come
Sickness and Illness Policy Children should not be at nursery if they are unwell. If your child becomes unable to stay at nursery, a member of staff will contact the parent or carer, asking them to come
Midland infectious disease activity summary (MIDAS), Vol 2 (1) Feb 2011
 Midland infectious disease activity summary (MIDAS), Vol 2 (1) Feb 2011 Item Type Other Authors Health Service Executive (HSE) Dublin/Mid-Leinster (Midlands), Department of Public Health Publisher Health
Midland infectious disease activity summary (MIDAS), Vol 2 (1) Feb 2011 Item Type Other Authors Health Service Executive (HSE) Dublin/Mid-Leinster (Midlands), Department of Public Health Publisher Health
Emergency Dermatology Dr Melissa Barkham
 Emergency Dermatology Dr Melissa Barkham Spotlight Seminar 30 th September 2010 Why is this important? Urgent recognition and treatment of dermatologic emergencies can be life saving and prevent long term
Emergency Dermatology Dr Melissa Barkham Spotlight Seminar 30 th September 2010 Why is this important? Urgent recognition and treatment of dermatologic emergencies can be life saving and prevent long term
A summary of guidance related to viral rash in pregnancy
 A summary of guidance related to viral rash in pregnancy Wednesday 12 th July 2017 Dr Rukhsana Hussain Introduction Viral exanthema can cause rash in pregnant women and should be considered even in countries
A summary of guidance related to viral rash in pregnancy Wednesday 12 th July 2017 Dr Rukhsana Hussain Introduction Viral exanthema can cause rash in pregnant women and should be considered even in countries
STI s. (Sexually Transmitted Infections)
 STI s (Sexually Transmitted Infections) Build Awareness In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise. One of the primary defenses in the fight
STI s (Sexually Transmitted Infections) Build Awareness In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise. One of the primary defenses in the fight
THE PATIENT PRESENTS WITH
 THE PATIENT PRESENTS WITH 1. Fever or rash 3 2. Heart, lung or ENT problems 9 3. Gut or liver problems 19 4. Haematuria or proteinuria 27 5. Neurological problems 31 6. Musculoskeletal problems 37 7. Pallor,
THE PATIENT PRESENTS WITH 1. Fever or rash 3 2. Heart, lung or ENT problems 9 3. Gut or liver problems 19 4. Haematuria or proteinuria 27 5. Neurological problems 31 6. Musculoskeletal problems 37 7. Pallor,
=ﻰﻤاﻤﺤﻠا ﺔﻴﻘﻠﺤﻠا ﺔذﺒاﻨﻠا
 1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
1 / 15 Erythema Annulare Centrifugum and Other Figurate Erythemas The figurate erythemas include a variety of eruptions characterized by annular and polycyclic lesions. Classification of this group has
Diseases of Absence. Disclosures
 Diseases of Absence Meg Fisher, MD Medical Director, The Unterberg Children s Hospital Long Branch, NJ Disclosures I have no disclosures I do not intend to mention off label uses of drugs I have way too
Diseases of Absence Meg Fisher, MD Medical Director, The Unterberg Children s Hospital Long Branch, NJ Disclosures I have no disclosures I do not intend to mention off label uses of drugs I have way too
MEASLES (campak, rubeola, gabak, kerumut) Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division Department of Child Health, Medical Faculty, University of Sumate
 MEASLES (campak, rubeola, gabak, kerumut) Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division Department of Child Health, Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara 1 Maculapapular eruption : 1. Measles 2. Atypical
MEASLES (campak, rubeola, gabak, kerumut) Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division Department of Child Health, Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara 1 Maculapapular eruption : 1. Measles 2. Atypical
Eczema & Dermatitis Clinical features: Histopathological features: Classification:
 Eczema & Dermatitis Eczema is an inflammatory reactive pattern of skin to many and different stimuli characterized by itching, redness, scaling and clustered papulovesicles. Eczema and dermatitis are synonymous
Eczema & Dermatitis Eczema is an inflammatory reactive pattern of skin to many and different stimuli characterized by itching, redness, scaling and clustered papulovesicles. Eczema and dermatitis are synonymous
Isolation Precautions in Clinics
 Purpose Audience General principles Possible Exposures To define isolation precautions in a clinic setting. Clinics Isolation status should be determined primarily by the suspected disease and/or pathogen.
Purpose Audience General principles Possible Exposures To define isolation precautions in a clinic setting. Clinics Isolation status should be determined primarily by the suspected disease and/or pathogen.
Sickness and Illness Policy
 Sickness and Illness Policy Children should not be at nursery if they are unwell. If your child becomes unable to stay at nursery, a member of staff will contact the parent or carer, asking them to come
Sickness and Illness Policy Children should not be at nursery if they are unwell. If your child becomes unable to stay at nursery, a member of staff will contact the parent or carer, asking them to come
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
 Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) Overview Definition of STIs: What are they? Transmission: How are they spread? Types of infection: Bacterial (Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Syphilis) Viral (Hepatitis B,
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) Overview Definition of STIs: What are they? Transmission: How are they spread? Types of infection: Bacterial (Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Syphilis) Viral (Hepatitis B,
Skin Problems. Issues for a Child. Skin Problems. Paediatric Palliative Care For Home Based Carers. Common in children with HIV
 Skin Problems Paediatric Palliative Care For Home Based Carers Funded by British High Commission, Pretoria Small Grant Scheme Skin Problems Common in children with HIV Often conditions common in all children
Skin Problems Paediatric Palliative Care For Home Based Carers Funded by British High Commission, Pretoria Small Grant Scheme Skin Problems Common in children with HIV Often conditions common in all children
Objectives 8/6/2013. Erythema Toxicum Neonatorum
 Childhood Rashes E.J. Mayeaux, Jr., M.D. Professor of Family Medicine Professor of Obstetrics & Gynecology Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Shreveport, LA No disclosures to report. Objectives
Childhood Rashes E.J. Mayeaux, Jr., M.D. Professor of Family Medicine Professor of Obstetrics & Gynecology Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Shreveport, LA No disclosures to report. Objectives
Eczema. By:- Dr. Naif Al-Shahrani Salman bin Abdazziz University
 Eczema By:- Dr. Naif Al-Shahrani Salman bin Abdazziz University Dermatitis= Eczema =Spongiosis Eczema Atopic Seborrheic Contact Allergic Irritant Nummular Asteatotic Stasis Neurodermatitis/Lichen Simplex
Eczema By:- Dr. Naif Al-Shahrani Salman bin Abdazziz University Dermatitis= Eczema =Spongiosis Eczema Atopic Seborrheic Contact Allergic Irritant Nummular Asteatotic Stasis Neurodermatitis/Lichen Simplex
Prof Dr Najlaa Fawzi
 1 Prof Dr Najlaa Fawzi is an acute highly infectious disease, characterized by vesicular rash, mild fever and mild constitutional symptoms. is a local manifestation of reactivation of latent varicella
1 Prof Dr Najlaa Fawzi is an acute highly infectious disease, characterized by vesicular rash, mild fever and mild constitutional symptoms. is a local manifestation of reactivation of latent varicella
Disease Transmission( Spread) Symptoms Infectious Period/ Exclusion. Should see physician as antibiotic treatment may be required
 Management of Communicable Diseases Adopted April 26, 05 These guidelines, based on those developed by With the assistance of the Canadian Pediatric Society, these Guidelines have been developed to assist
Management of Communicable Diseases Adopted April 26, 05 These guidelines, based on those developed by With the assistance of the Canadian Pediatric Society, these Guidelines have been developed to assist
Notes to review (after ARS answer session) Case. Next best step? 2/12/2018. S004- Hunt Managing Tough Real Life Dermatology Cases
 S004- Hunt Managing Tough Real Life Dermatology s Raegan Hunt, MD, PhD Chief of Service, Pediatric Dermatology Assistant Professor, Pediatrics & Dermatology Texas Children s Hospital Baylor College of
S004- Hunt Managing Tough Real Life Dermatology s Raegan Hunt, MD, PhD Chief of Service, Pediatric Dermatology Assistant Professor, Pediatrics & Dermatology Texas Children s Hospital Baylor College of
Alberta Health Public Health Notifiable Disease Management Guidelines January 2013
 January 2013 Rickettsial Infections Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) January 2013 January 2013 December
January 2013 Rickettsial Infections Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) January 2013 January 2013 December
Communicable Disease Guidelines
 Communicable Disease Guidelines Note: This information is to assist in making decisions regarding the control of communicable diseases. It is NOT intended for the purposes of making diagnoses. Refer to
Communicable Disease Guidelines Note: This information is to assist in making decisions regarding the control of communicable diseases. It is NOT intended for the purposes of making diagnoses. Refer to
Issues in Dermatology. Rhonda Lesniak, PhD, ARNP, FNP-BC, NCSN
 Issues in Dermatology Rhonda Lesniak, PhD, ARNP, FNP-BC, NCSN Anatomy of the Skin Functions Protect Fluid balance Absorption Synthesis of Vitamin D Sensation/communication with external environment Thermoregulation
Issues in Dermatology Rhonda Lesniak, PhD, ARNP, FNP-BC, NCSN Anatomy of the Skin Functions Protect Fluid balance Absorption Synthesis of Vitamin D Sensation/communication with external environment Thermoregulation
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Integumentary System Skin, hair, and nails. Skin: Epidermis: outer layer. Dermis: also called corium, or true skin. Subcutaneous fascia: innermost layer. Integumentary Glands Sudoriferous:
Integumentary System Integumentary System Skin, hair, and nails. Skin: Epidermis: outer layer. Dermis: also called corium, or true skin. Subcutaneous fascia: innermost layer. Integumentary Glands Sudoriferous:
Emergency Dermatology. Emergency Dermatology
 Emergency Dermatology These are rapidly progressive skin conditions and some are potentially lifethreatening. Early recognition is important to implement prompt supportive care and therapy. Some are drug
Emergency Dermatology These are rapidly progressive skin conditions and some are potentially lifethreatening. Early recognition is important to implement prompt supportive care and therapy. Some are drug
Alberta Health Public Health Notifiable Disease Management Guidelines July 2012
 July 2012 Typhus - Louseborne Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) July 2012 July 2012 October 2005 Case Definition
July 2012 Typhus - Louseborne Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) July 2012 July 2012 October 2005 Case Definition
Infectious Rashes of Interest to Infection Control and Occupational Health Dr. Justin Graham A Webber Training Teleclass
 Spot That Spot! Infectious Rashes of Interest to Infection Control and Occupational Health Justin Graham, MD MS Webber Training Teleclass 2005 Hosted by Paul Webber paul@webbbertraining.com It s Friday
Spot That Spot! Infectious Rashes of Interest to Infection Control and Occupational Health Justin Graham, MD MS Webber Training Teleclass 2005 Hosted by Paul Webber paul@webbbertraining.com It s Friday
LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY ORAL CAVITY. Oral Cavity Subsites 4/10/2013 LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL MUCOUS MEMBRANES PALATE TONGUE ORAL LYMPHOID TISSUES
 LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY David I. Kutler, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology HNS Weill Cornell Medical Center ORAL CAVITY LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL
LESIONS OF THE ORAL CAVITY David I. Kutler, MD, FACS Associate Professor Division of Head and Neck Surgery Department of Otolaryngology HNS Weill Cornell Medical Center ORAL CAVITY LIPS TEETH GINGIVA ORAL
A. Erythema multiforme and related diseases
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Erythema, Erythroderma (Exfoliative Dermatitis) Erythema is caused by telangiectasia or hyperemia in the papillary and reticular
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Erythema, Erythroderma (Exfoliative Dermatitis) Erythema is caused by telangiectasia or hyperemia in the papillary and reticular
COMMON SKIN INFECTIONS. Sports Medicine
 COMMON SKIN INFECTIONS Sports Medicine IMPETIGO IS A SUPERFICIAL BACTERIAL INFECTION CAUSED BY: STREPTOCOCCI OR STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BOULOUS IMPETIGO IMPETIGO COMES IN TWO FORMS: BOULOUS OR NON- BOULOUS
COMMON SKIN INFECTIONS Sports Medicine IMPETIGO IS A SUPERFICIAL BACTERIAL INFECTION CAUSED BY: STREPTOCOCCI OR STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS BOULOUS IMPETIGO IMPETIGO COMES IN TWO FORMS: BOULOUS OR NON- BOULOUS
GOOD MORNING! AUGUST 5, 2014
 GOOD MORNING! AUGUST 5, 2014 PREP QUESTION During the health supervision visit of a term newborn boy, his mother relates that a cousins child died at age 4 months from sudden infant death syndrome. She
GOOD MORNING! AUGUST 5, 2014 PREP QUESTION During the health supervision visit of a term newborn boy, his mother relates that a cousins child died at age 4 months from sudden infant death syndrome. She
SPECIFIC DISEASE EXCLUSION GUIDELINES FOR CHILDCARE
 See individual fact sheets for exclusion and other information on the diseases listed below. Bed Bugs Acute Bronchitis (Chest Cold)/Bronchiolitis Campylobacteriosis Until fever is gone (without the use
See individual fact sheets for exclusion and other information on the diseases listed below. Bed Bugs Acute Bronchitis (Chest Cold)/Bronchiolitis Campylobacteriosis Until fever is gone (without the use
Five things not to miss in Dermatology. Dr Judy Wismer Associate Clinical Professor Michael G DeGroote School of Medicine
 Five things not to miss in Dermatology Dr Judy Wismer Associate Clinical Professor Michael G DeGroote School of Medicine Key Descriptives Fever, skin pain Purpura, necrosis Bullae, Mucosal, Skin sloughing
Five things not to miss in Dermatology Dr Judy Wismer Associate Clinical Professor Michael G DeGroote School of Medicine Key Descriptives Fever, skin pain Purpura, necrosis Bullae, Mucosal, Skin sloughing
REGISTRY OF SEVERE CUTANEOUS ADVERSE REACTIONS TO DRUGS AND COLLECTION OF BIOLOGICAL SAMPLES. R e g i S C A R PATIENT'S DATA. Age country of birth
 REGISTRY OF SEVERE CUTANEOUS ADVERSE REACTIONS TO DRUGS AND COLLECTION OF BIOLOGICAL SAMPLES R e g i S C A R PATIENT'S DATA Initials of the patient date of birth Age country of birth Gender male female
REGISTRY OF SEVERE CUTANEOUS ADVERSE REACTIONS TO DRUGS AND COLLECTION OF BIOLOGICAL SAMPLES R e g i S C A R PATIENT'S DATA Initials of the patient date of birth Age country of birth Gender male female
Chapter 29. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives (Cont d) 9/10/2012. Cutaneous Disorders
 Chapter 29 Cutaneous Disorders Learning Objectives Describe the three layers of skin, and their composition and functions Describe the morphology of primary skin lesions Describe the morphology of secondary
Chapter 29 Cutaneous Disorders Learning Objectives Describe the three layers of skin, and their composition and functions Describe the morphology of primary skin lesions Describe the morphology of secondary
DESCRIPTIONS FOR MED 3 ROTATIONS Dermatology A3S
 Regardless of your future field of practice, you will be exposed to a considerable amount of dermatology and this rotation provides you the chance to see a range of skin diseases. You will have the opportunity
Regardless of your future field of practice, you will be exposed to a considerable amount of dermatology and this rotation provides you the chance to see a range of skin diseases. You will have the opportunity
The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Functions: protection sensation maintain temperature vitamin synthesis
 Dermatology The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Functions: protection sensation maintain temperature vitamin synthesis The image to the left shows an image of skin cells and the proteins which
Dermatology The skin is the largest organ of the human body. Functions: protection sensation maintain temperature vitamin synthesis The image to the left shows an image of skin cells and the proteins which
Red Stick ID Visual Diagnosis Questions August 22, 2014
 Red Stick ID Visual Diagnosis Questions August 22, 2014 James H. Brien, DO Case #1 The setting is a Pediatric Clinic in San Antonio, Texas on a Saturday in 1989. However, it could have been yesterday in
Red Stick ID Visual Diagnosis Questions August 22, 2014 James H. Brien, DO Case #1 The setting is a Pediatric Clinic in San Antonio, Texas on a Saturday in 1989. However, it could have been yesterday in
My Algorithm. Questions to ask. Do you or your family have a history of?... Allergic rhinitis, Sensitive skin, Asthma Skin Cancer
 Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM Associate Professor, Temple University School of Podiatric Medicine My Algorithm Inflammatory Skin Disorder on Feet Family hx, clinical exam, look at hands! Defined plaques: Psoriasis
Tracey C. Vlahovic, DPM Associate Professor, Temple University School of Podiatric Medicine My Algorithm Inflammatory Skin Disorder on Feet Family hx, clinical exam, look at hands! Defined plaques: Psoriasis
DERMATOLOGY SKIN DISEASE: APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS
 DERMATOLOGY SKIN DISEASE: APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS History Clinical Examination List and Prioritise Differentials Diagnostic Testing/Trials (eg Treatment Trial) Correlate All Findings History Signalment age,
DERMATOLOGY SKIN DISEASE: APPROACH TO DIAGNOSIS History Clinical Examination List and Prioritise Differentials Diagnostic Testing/Trials (eg Treatment Trial) Correlate All Findings History Signalment age,
Section 10.5 Varicella
 Section 10.5 Varicella Chickenpox Introduction Transmission Signs and Symptoms Complications Diagnosis Treatment Infection Prevention and Control Precautions for Residents with Chickenpox Additional considerations
Section 10.5 Varicella Chickenpox Introduction Transmission Signs and Symptoms Complications Diagnosis Treatment Infection Prevention and Control Precautions for Residents with Chickenpox Additional considerations
A. Viral infections whose main symptom is blistering
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Viral Infections A virus is a particle of DNA or RNA enclosed by structural proteins. Viruses infect cells and proliferate to
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details Chapter Viral Infections A virus is a particle of DNA or RNA enclosed by structural proteins. Viruses infect cells and proliferate to
Speaker and paid consultant for Galderma, Novartis and Jansen. No other potential conflicts to disclose. Review of Relevant Physiology
 Speaker and paid consultant for Galderma, Novartis and Jansen No other potential conflicts to disclose Review of Relevant Physiology Discussion of Common Problems Treatment Options Counselling Knowing
Speaker and paid consultant for Galderma, Novartis and Jansen No other potential conflicts to disclose Review of Relevant Physiology Discussion of Common Problems Treatment Options Counselling Knowing
Khaled Ali Abu Ali. BSN. MPH. Ph.D. cand. -Nursing. Director of Epidemiology Department UCAS Lecturer
 Khaled Ali Abu Ali BSN. MPH. Ph.D. cand. Director of Epidemiology Department UCAS Lecturer -Nursing Khaled_abuali@yahoo.com Communicable Disease Surveillance during Gaza War, 214. Introduction Public Health
Khaled Ali Abu Ali BSN. MPH. Ph.D. cand. Director of Epidemiology Department UCAS Lecturer -Nursing Khaled_abuali@yahoo.com Communicable Disease Surveillance during Gaza War, 214. Introduction Public Health
Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India.
 Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Bullous pemphigoid mimicking granulomatous inflammation Abhilasha Williams, Emy Abi Thomas. Department of Dermatology, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India. Egyptian Dermatology
Conflicts. Objectives. University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio. Pediatrics Grand Rounds 24 August Pediatric Dermatology 101
 Pediatric Dermatology 101 John C. Browning, MD, FAAD, FAAP Conflicts Investigator: ViroXis Advisor: ViroXis Advisory Board: TopMD Speaker: Galderma Objectives Understand the meaning and importance of cutaneous
Pediatric Dermatology 101 John C. Browning, MD, FAAD, FAAP Conflicts Investigator: ViroXis Advisor: ViroXis Advisory Board: TopMD Speaker: Galderma Objectives Understand the meaning and importance of cutaneous
Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection
 Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection Defense Mechanisms Three lines of defense protect the body against foreign invasion: Physical or surface barriers Inflammation Immune response Inflammation Non-specific
Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection Defense Mechanisms Three lines of defense protect the body against foreign invasion: Physical or surface barriers Inflammation Immune response Inflammation Non-specific
INFECTIOUS EXANTHEMS OF CHILDHOOD. William C. Koch, M.D. Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases
 INFECTIOUS EXANTHEMS OF CHILDHOOD Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases I. General Considerations and Terms A. Exanthem - a generalized cutaneous eruption associated with a systemic disease B. Enanthem
INFECTIOUS EXANTHEMS OF CHILDHOOD Division of Pediatric Infectious Diseases I. General Considerations and Terms A. Exanthem - a generalized cutaneous eruption associated with a systemic disease B. Enanthem
Dermclinic
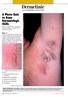 Dermclinic /Dermclinic A Photo Quiz to Hone Dermatologic Skills DAVID L. KAPLAN, MD Series Editor University of Missouri Kansas City, University of Kansas Case 1: Upon his return from a summer visit to
Dermclinic /Dermclinic A Photo Quiz to Hone Dermatologic Skills DAVID L. KAPLAN, MD Series Editor University of Missouri Kansas City, University of Kansas Case 1: Upon his return from a summer visit to
