Chapter 4. Skin and Body Membranes. Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Pearson Education, Inc.
|
|
|
- Dinah Alice Hart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College
2 Body Membranes Functions of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classified according to tissue types
3 Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous membranes Mucous membranes Serous membranes Connective tissue membranes Synovial membranes
4 Cutaneous Membrane Cutaneous membrane = skin Dry membrane Outermost protective boundary Superficial epidermis is composed of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium Underlying dermis is mostly dense irregular connective tissue
5 Figure 4.1a Classes of epithelial membranes. Cutaneous membrane (skin) (a) Cutaneous membrane (the skin) covers the body surface.
6 Mucous Membranes Surface epithelium type depends on site Stratified squamous epithelium (mouth, esophagus) Simple columnar epithelium (rest of digestive tract) Underlying loose connective tissue (lamina propria) Lines all body cavities that open to the exterior body surface Moist membranes adapted for absorption or secretion
7 Figure 4.1b Classes of epithelial membranes. Mucosa of nasal cavity Mucosa of mouth Esophagus lining Mucosa of lung bronchi (b) Mucous membranes line body cavities open to the exterior.
8 Serous Membranes (Serosa) Surface is a layer of simple squamous epithelium Underlying layer is a thin layer of areolar connective tissue Lines open body cavities that are closed to the exterior of the body Serous membranes occur in pairs separated by serous fluid Visceral layer covers the outside of the organ Parietal layer lines a portion of the wall of ventral body cavity
9 Figure 4.1d Classes of epithelial membranes. Outer balloon wall (comparable to parietal serosa) Air (comparable to serous cavity) Inner balloon wall (comparable to visceral serosa) (d) A fist thrust into a flaccid balloon demonstrates the relationship between the parietal and visceral serous membrane layers.
10 Serous Membranes Specific serous membranes Peritoneum Abdominal cavity Pleura Around the lungs Pericardium Around the heart
11 Figure 4.1c Classes of epithelial membranes. Parietal peritoneum Visceral peritoneum Parietal pericardium Visceral pericardium Parietal pleura Visceral pleura (c) Serous membranes line body cavities closed to the exterior.
12 Connective Tissue Membrane Synovial membrane Connective tissue only Lines fibrous capsules surrounding joints Lines bursae Lines tendon sheaths Secretes a lubricating fluid
13 Figure 4.2 A typical synovial joint. Ligament Joint cavity (contains synovial fluid) Articular (hyaline) cartilage Fibrous layer Synovial membrane Articular capsule
14 Integumentary System Integumentary system includes: Skin (cutaneous membrane) Skin derivatives (accessory structures) Sweat glands Oil glands Hair Nails
15 Skin (Integument) Functions Protects deeper tissues from: Mechanical damage (bumps) Chemical damage (acids and bases) Bacterial damage Ultraviolet radiation (sunlight) Thermal damage (heat or cold) Desiccation (drying out) Keratin protects the skin from water loss
16 Skin Functions Aids in loss or retention of body heat as controlled by the nervous system Aids in excretion of urea and uric acid Synthesizes vitamin D Cutaneous sensory receptors detect touch, temperature, pressure, and pain
17 Table 4.1 Functions of the Integumentary System (1 of 2).
18 Table 4.1 Functions of the Integumentary System (2 of 2).
19 Skin Structure Epidermis outer layer Stratified squamous epithelium Cornified or keratinized (hardened by keratin) to prevent water loss Avascular Most cells are keratinocytes Dermis Dense irregular connective tissue
20 Figure 4.3 Skin structure. Hair shaft Epidermis Papillary layer Dermis Reticular layer Dermal papillae Pore Appendages of skin Eccrine sweat gland Arrector pili muscle Sebaceous (oil) gland Hair follicle Hair root Hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue) Nervous structures Sensory nerve fiber Lamellar corpuscle Hair follicle receptor (root hair plexus) Adipose tissue Cutaneous vascular plexus
21 Skin Structure Subcutaneous tissue/hypodermis is deep to dermis Not technically part of the skin Anchors skin to underlying organs Composed mostly of adipose tissue Serves as a shock absorber and insulates deeper tissues
22 Layers of the Epidermis The epidermis is composed of up to five layers avascular Most of the cells in the epidermis are keratinocytes Keratin, a fibrous protein, makes the epidermis tough The layers are covered, next, from deepest to most superficial
23 Layers of the Epidermis Stratum basale (stratum germinativum) Deepest layer of epidermis Lies next to dermis Wavy borderline with the dermis anchors the two together Cells undergoing mitosis Daughter cells are pushed upward to become the more superficial layers Stratum spinosum
24 Layers of the Epidermis Stratum granulosum Stratum lucidum Formed from dead cells of the deeper strata Occurs only in thick, hairless skin of the palms of hands and soles of feet Stratum corneum Outermost layer of epidermis Shingle-like dead cells are filled with keratin (protective protein prevents water loss from skin)
25 Layers of the Epidermis Summary of layers from deepest to most superficial Stratum basale Stratum spinosum Stratum granulosum Stratum lucidum (thick, hairless skin only) Stratum corneum
26 Figure 4.4 The main structural features of the epidermis. Keratinocytes Desmosomes Epidermal dendritic cell Stratum corneum. Cells are dead; represented only by flat membranous sacs filled with keratin. Glycolipids in extracellular space. Stratum granulosum. Cells are flattened, organelles are deteriorating; cytoplasm full of granules. Stratum spinosum. Cells contain thick bundles of intermediate filaments made of pre-keratin. Merkel cell Stratum basale. Cells are actively dividing stem cells; some newly formed cells become part of the more superficial layers. Melanocytes Melanin granules Sensory nerve ending Dermis
27 Melanin Pigment (melanin) produced by melanocytes Color is yellow to brown to black Melanocytes are mostly in the stratum basale Melanin accumulates in membrane-bound granules called melanosomes Amount of melanin produced depends upon genetics and exposure to sunlight
28 Epidermal Dendritic Cells & Merkel Cells Epidermal dendritic cells (Langerhans cells) Alert and activate immune cells to a threat (bacterial or viral invasion) Merkel cells Associated with sensory nerve endings Serve as touch receptors called Merkel discs
29 Dermis Two layers 1. Papillary layer (upper dermal region) Projections called dermal papillae Some contain capillary loops Others house pain receptors (free nerve endings) and touch receptors Fingerprints are identifying films of sweat
30 Dermis Two layers 2. Reticular layer (deepest skin layer) Blood vessels Sweat and oil glands Deep pressure receptors (Pacinian corpuscles)
31 Dermis Overall dermis structure Collagen and elastic fibers located throughout the dermis Collagen fibers give skin its toughness Elastic fibers give skin elasticity Blood vessels play a role in body temperature regulation Nerve supply sends messages to the central nervous system
32 Figure 4.5 Light micrograph of the two regions of the dermis (100 ). Epidermis Papillary layer Dermis Reticular layer
33 Skin Color Three pigments contribute to skin color: 1. Melanin Yellow, reddish brown, or black pigments 2. Carotene Orange-yellow pigment from some vegetables 3. Hemoglobin Red coloring from blood cells in dermal capillaries Oxygen content determines the extent of red coloring
34 Alterations in Skin Color Redness (erythema) due to embarrassment, inflammation, hypertension, fever, or allergy Pallor (blanching) due to emotional stress (such as fear), anemia, low blood pressure, impaired blood flow to an area Jaundice (yellowing) liver disorder Bruises (black and blue marks) hematomas
35 Appendages of the Skin Cutaneous glands are all exocrine glands Sebaceous glands Sweat glands Hair Hair follicles Nails
36 Figure 4.3 Skin structure. Hair shaft Epidermis Papillary layer Dermis Reticular layer Dermal papillae Pore Appendages of skin Eccrine sweat gland Arrector pili muscle Sebaceous (oil) gland Hair follicle Hair root Hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue) Nervous structures Sensory nerve fiber Pacinian corpuscle Hair follicle receptor (root hair plexus) Adipose tissue Cutaneous vascular plexus
37 Appendages of the Skin Sebaceous (oil) glands Produce sebum (oil) Lubricant for skin Prevents brittle hair Kills bacteria Most have ducts that empty into hair follicles; others open directly onto skin surface Glands are activated at puberty
38 Figure 4.7a Cutaneous glands. Sweat pore Sebaceous gland Eccrine gland Sebaceous gland duct Dermal connective tissue Hair in hair follicle Secretory cells (a) Photomicrograph of a sectioned sebaceous gland (100 )
39 Appendages of the Skin Sweat (sudoriferous) glands Produce sweat Widely distributed in skin
40 Appendages of the Skin Two types of sudoriferous glands 1. Eccrine glands Open via duct to pore on skin surface Produce sweat
41 Appendages of the Skin Two types of sudoriferous glands 2. Apocrine glands Ducts empty into hair follicles Begin to function at puberty Release sweat that also contains fatty acids and proteins (milky or yellowish color)
42 Appendages of the Skin Sweat: Composition Mostly water Salts and vitamin C Some metabolic waste Fatty acids and proteins (apocrine only) Function Helps dissipate excess heat Excretes waste products Acidic nature inhibits bacteria growth Odor is from associated bacteria
43 Figure 4.7b Cutaneous glands. Sebaceous gland Sweat pore Eccrine gland Dermal connective tissue Eccrine gland duct Secretory cells (b) Photomicrograph of a sectioned eccrine gland (205 )
44 Appendages of the Skin Hair Produced by hair follicle Root is enclosed in the follicle Shaft projects from the surface of the scalp or skin Consists of hard keratinized epithelial cells Melanocytes provide pigment for hair color Hair grows in the matrix of the hair bulb in stratum basale
45 Figure 4.8c Structure of a hair and hair follicle. Hair follicle Fibrous sheath Epithelial sheath Hair matrix (growth zone) in hair bulb Melanocyte Subcutaneous adipose tissue (c) Hair papilla containing blood vessels
46 Appendages of the Skin Hair anatomy Central medulla Cortex surrounds medulla Cuticle on outside of cortex Most heavily keratinized region of the hair
47 Figure 4.8b Structure of a hair and hair follicle. Cuticle Cortex Medulla (b) Hair
48 Appendages of the Skin Associated hair structures Hair follicle Dermal and epidermal sheath surround hair root Arrector pili muscle Smooth muscle Pulls hairs upright when person is cold or frightened Sebaceous gland Sudoriferous gland
49 Figure 4.8a Structure of a hair and hair follicle. Hair shaft Arrector pili Sebaceous gland Hair root Hair bulb in follicle (a)
50 Appendages of the Skin Notice how the scale-like cells of the cuticle overlap one another in this hair shaft image (660 )
51 Figure 4.9 Scanning electron micrograph showing a hair shaft emerging from a follicle at the skin surface.
52 Appendages of the Skin Nails Scale-like modifications of the epidermis Heavily keratinized Stratum basale extends beneath the nail bed Responsible for growth Lack of pigment makes them colorless
53 Appendages of the Skin Nail structures Free edge Body is the visible attached portion Nail folds are skin folds that overlap the edges of the nail Growth occurs from nail matrix Root of nail is embedded in skin Cuticle is the proximal nail fold that projects onto the nail body
54 Figure 4.10 Structure of a nail. Lunule Lateral nail fold (a) Free edge of nail Body of nail Cuticle Proximal nail fold Root of nail Nail matrix (b) Nail bed Bone of fingertip
55 Skin Homeostatic Imbalances Burns Tissue damage and cell death caused by heat, electricity, UV radiation, or chemicals Associated dangers Dehydration Electrolyte imbalance Circulatory shock Result in loss of body fluids and invasion of bacteria
56 Rule of Nines Way to determine the extent of burns Body is divided into 11 areas for quick estimation Each area represents about 9 percent of total body surface area The area surrounding the genitals (the perineum) represents 1 percent of body surface area
57 Figure 4.11a Burns. 4 1 / 2 % Totals Anterior and posterior head and neck, 9% 4 1 / 2 % 4 1 / 2 % Anterior trunk, 18% Anterior and posterior upper limbs, 18% Anterior and posterior trunk, 36% 9% 9% Perineum, 1% (a) Anterior and posterior lower limbs, 36% 100%
58 Severity of Burns First-degree burns (partial-thickness burn) Only epidermis is damaged Skin is red and swollen Second-degree burns (partial-thickness burn) Epidermis and upper dermis are damaged Skin is red with blisters Third-degree burns (full-thickness burn) Destroys entire skin layer; burned area is painless Requires skin grafts Burn is gray-white or black
59 Figure 4.11b Burns. Burns of increasing severity, from top to bottom: first-degree, second-degree, third-degree. (b)
60 Critical Burns Burns are considered critical if Over 25 percent of body has second-degree burns Over 10 percent of the body has third-degree burns There are third-degree burns of the face, hands, or feet
61 Skin Homeostatic Imbalances Infections Athlete s foot (tinea pedis) Caused by fungal infection Boils and carbuncles Caused by bacterial infection Cold sores Caused by virus
62 Skin Homeostatic Imbalances Infections and allergies Contact dermatitis Exposures cause allergic reaction Impetigo Caused by bacterial infection Psoriasis Cause is unknown Triggered by trauma, infection, stress
63 Figure 4.12 Cutaneous lesions. (a) Cold sores (b) Impetigo (c) Psoriasis
64 Skin Cancer Cancer abnormal cell mass Classified two ways 1. Benign Does not spread (encapsulated) 2. Malignant Metastasizes (moves) to other parts of the body Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer
65
66 Skin Cancer Types Basal cell carcinoma Least malignant Most common type Arises from stratum basale
67 Figure 4.13a Photographs of skin cancers. (a) Basal cell carcinoma
68 Skin Cancer Types Squamous cell carcinoma Metastasizes to lymph nodes if not removed Early removal allows a good chance of cure Believed to be sun-induced Arises from stratum spinosum
69 Figure 4.13b Photographs of skin cancers. (b) Squamous cell carcinoma
70 Skin Cancer Types Malignant melanoma Most deadly of skin cancers Cancer of melanocytes Metastasizes rapidly to lymph and blood vessels Detection uses ABCD rule
71 ABCD Rule A = Asymmetry Two sides of pigmented mole do not match B = Border irregularity Borders of mole are not smooth C = Color Different colors in pigmented area D = Diameter Spot is larger than 6 mm in diameter
72 Figure 4.13c Photographs of skin cancers. (c) Melanoma
73 Developmental Aspects of Skin In youth, skin is thick, resilient, and well hydrated With aging, skin loses elasticity and thins Skin cancer is a major threat to skin exposed to excessive sunlight Balding and/or graying occurs with aging; both are genetically determined; other factors that may contribute include drugs and emotional stress
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1
 Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Unit 4 - The Skin and Body Membranes 1 I. Unit 4: Skin and Body Membranes A. Body Membranes 1. Function of body membranes a) Cover body surfaces b) Line body cavities c) Form protective sheets around organs
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
Ch. 4: Skin and Body Membranes I. Body Membranes A. Function of body membranes 1. Cover body surfaces 2. Line body cavities 3. Form protective sheets around organs II. Classification of Body Membranes
Skin and Body Membranes
 4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
Integumentary System. Packet #12
 Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Integumentary System Packet #12 Introduction Skin/Integument Skin, considered an organ, is the major component of the integumentary system. The integumentary system is also composed of other accessory
Skin and Body Membranes
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Slides 4.1 4.32 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Skin and Body Membranes Function
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Slides 4.1 4.32 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Skin and Body Membranes Function
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities
Introduction. Skin and Body Membranes. Cutaneous Membranes Skin 9/14/2017. Classification of Body Membranes. Classification of Body Membranes
 Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 4
 *We are revisiting Ch 3B on body tissues (Connective) prior to our study of Ch 4 Integumentary. Start on p.90 I. Connective Tissue A. Functions of Connective 1. Protection 2. Support 3. Binding Together
*We are revisiting Ch 3B on body tissues (Connective) prior to our study of Ch 4 Integumentary. Start on p.90 I. Connective Tissue A. Functions of Connective 1. Protection 2. Support 3. Binding Together
Unit 4 The Integumentary System
 Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
Ch 4. Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
B. Connective tissue membranes lubricate & cushion 1. made of areolar tissue 2. synovial line fibrous joint capsules & secrete fluid
 I. Body Membranes A. Epithelial membranes cover & line 1. epithelial sheet over underlying connective tissue 2. 3 types a. Cutaneous = skin b. Mucous = lines cavities open to exterior Skin and Body Membranes
I. Body Membranes A. Epithelial membranes cover & line 1. epithelial sheet over underlying connective tissue 2. 3 types a. Cutaneous = skin b. Mucous = lines cavities open to exterior Skin and Body Membranes
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY
 CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
Figure 4.1. Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref: 115
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Short Answer Figure 4.1 Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Short Answer Figure 4.1 Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated
Integumentary System and Body Membranes
 Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
Integumentary System and Body Membranes The Skin and its appendages hair, nails, and skin glands Anatomy/Physiology NHS http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/corepages/integumentary/integum.htm I. System
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Body Membranes & Skin
 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
The Integumentary System: An Overview
 The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
ABCD rule. apocrine glands. arrector pili. ceruminous glands. contact dermatitis
 ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
Chapter 4 Opener Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4 FUNCTIONS Waterproofs Protein called keratin Protection 1 st line of defense against pathogens, chemicals & abrasions Insulation Regulates heat loss by controlling blood
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 4 FUNCTIONS Waterproofs Protein called keratin Protection 1 st line of defense against pathogens, chemicals & abrasions Insulation Regulates heat loss by controlling blood
The Integumentary System: ANATOMY Includes: - Skin (integument) MEMBRANES. PHYSIOLOGY (functions) Protection. EPITHELIAL (cont.
 Did you know. Membranes & The Integumentary System The skin is the largest organ of the human body. It has a surface area of about 25 square-feet! You shed about 1.5 pounds of skin particles each year.
Did you know. Membranes & The Integumentary System The skin is the largest organ of the human body. It has a surface area of about 25 square-feet! You shed about 1.5 pounds of skin particles each year.
11/8/2012. Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Skin = Integument = Cutaneous Membrane. The Structure of Skin. Epidermis
 Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide
 Name: SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES: 4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide Period: Body membranes, which cover body surfaces, line its cavities, and form protective sheets around organs, fall into two major
Name: SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES: 4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide Period: Body membranes, which cover body surfaces, line its cavities, and form protective sheets around organs, fall into two major
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Integumentary System Skin (cutaneous membrane or integument) Skin derivatives
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Skin and Body Membranes 4 Integumentary System Skin (cutaneous membrane or integument) Skin derivatives
Ex. 7: Integumentary
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Integumentary System. 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1
 Integumentary System 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1 Functions of Skin Protection Temperature regulation Sensation Excretion Vitamin D production 2/20/02 S. Davenport 2 Protection A Barrier Three types of barriers:
Integumentary System 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1 Functions of Skin Protection Temperature regulation Sensation Excretion Vitamin D production 2/20/02 S. Davenport 2 Protection A Barrier Three types of barriers:
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System. Skin Cells. Layers of Skin. Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous layer beneath dermis not part of skin
 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
2/5/2019. Organ System: Skin or Integumentary System. Hypodermis (or superficial fascia) Integumentary System - Learn and Understand
 Integumentary System - Learn and Understand Skin is an organ comprised of all four tissues Each layer of the skin contributes to one or more of its numerous functions Skin is both strong and flexible Keratinization
Integumentary System - Learn and Understand Skin is an organ comprised of all four tissues Each layer of the skin contributes to one or more of its numerous functions Skin is both strong and flexible Keratinization
Chapter 4 The Integumentary System and Body Membranes. HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Chapter 4 The Integumentary System and Body Membranes HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial Membranes Cutaneous Membranes = The Skin Mucous Membranes Serous
Chapter 4 The Integumentary System and Body Membranes HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial Membranes Cutaneous Membranes = The Skin Mucous Membranes Serous
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9
 Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM This system consists of skin and its derivatives. The skin is one of the largest organs of the body in terms of surface area. The functions of the integumentary system include:
CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM This system consists of skin and its derivatives. The skin is one of the largest organs of the body in terms of surface area. The functions of the integumentary system include:
Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function.
 Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Chapter 5 Describe the functions of the vertebrate integumentary system. Discuss the structure of the skin and how it relates to function. Explain the basis for different skin colors. Describe the structure
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System
 Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Chapter 6: Integumentary System
 Chapter 6: Integumentary System 6.1 Introduction Why is skin considered to be an organ? What makes up the integumentary system? Integumentary System Skin (cutaneous membrane) Skin derivatives Sweat glands
Chapter 6: Integumentary System 6.1 Introduction Why is skin considered to be an organ? What makes up the integumentary system? Integumentary System Skin (cutaneous membrane) Skin derivatives Sweat glands
Ch. 4 Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch. 4 Skin and Body Membranes http://www.udel.edu/biology/wags/histopage/colorpage/cin/cin.htm Title: Oct 20 7:35 AM (1 of 69) Essential Question: How is skin considered a body system? Title: Oct 20 7:41
Ch. 4 Skin and Body Membranes http://www.udel.edu/biology/wags/histopage/colorpage/cin/cin.htm Title: Oct 20 7:35 AM (1 of 69) Essential Question: How is skin considered a body system? Title: Oct 20 7:41
The Integementary System. The Skin & Its Parts
 The Integementary System The Skin & Its Parts General Structure 2. Accessory structures: hair, nails, exocrine glands 1. Cutaneous membrane: various layers Major Functions 1. Protection 2. Temperature
The Integementary System The Skin & Its Parts General Structure 2. Accessory structures: hair, nails, exocrine glands 1. Cutaneous membrane: various layers Major Functions 1. Protection 2. Temperature
Ch 5: Integumentary System
 Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Chapter 05. Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes.
 Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Objectives. To explain the function of the integumentary system. To identify the components of the epidermis. To list the strata of the epidermis.
 Objectives To explain the function of the integumentary system. To identify the components of the epidermis. To list the strata of the epidermis. Definitions Epi upon, on top of Hypo under Derm skin Serous
Objectives To explain the function of the integumentary system. To identify the components of the epidermis. To list the strata of the epidermis. Definitions Epi upon, on top of Hypo under Derm skin Serous
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5. Integumentary System 5-1
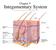 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Structures that are part of the integument Skin Hair Nails Glands Overview of Functions Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Immunity
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS
 Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Overview of the Integumentary System. Lab #7. Layers of the epidermis are known as strata. Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the Epidermis
 Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
Chapter 5: Integumentary System
 Chapter 5: Integumentary System I. Overview of the Integumentary System A. List the five major functions of the integumentary system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Il. Skin A. Epidermis 1. The epidermis consists of 2.
Chapter 5: Integumentary System I. Overview of the Integumentary System A. List the five major functions of the integumentary system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Il. Skin A. Epidermis 1. The epidermis consists of 2.
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
Student Objectives. 7. Describe the structure of nails.
 Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: The Skin 1. Name the tissue types composing the epidermis and dermis. List
Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: The Skin 1. Name the tissue types composing the epidermis and dermis. List
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Chapter 4: Body Membranes and the Integumentary System. Introduction. Membranes
 Slide 1 Chapter 4: Body Membranes and the Integumentary System Slide 2 Introduction Skin often reveals our inner workings and general health In most manual therapies, the skin is primary interface with
Slide 1 Chapter 4: Body Membranes and the Integumentary System Slide 2 Introduction Skin often reveals our inner workings and general health In most manual therapies, the skin is primary interface with
Skin. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
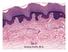 Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Figure ) The structure that is responsible for whorled ridges on the epidermal surfaces is indicated by letter. Answer: A Diff: 1 Page Ref: 117
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Short Answer Figure 4.1 Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Short Answer Figure 4.1 Using Figure 4.1, identify the following: 1) The region that contains adipose tissue is indicated
3. Dense connective tissue is found in skin, & surrounding blood vessels, nerves, and organs.
 Ch.4&5 Group Quiz True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. There are 4 basic types of tissue in the human body. 2. Cartilage is also known as osseous tissue. 3. Dense connective tissue
Ch.4&5 Group Quiz True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. There are 4 basic types of tissue in the human body. 2. Cartilage is also known as osseous tissue. 3. Dense connective tissue
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System The integumentary system is commonly known as the Skin Largest organ of human body 10% total body weight and would cover over 20 square feet Functions of Skin 1. Protection Barrier
Integumentary System The integumentary system is commonly known as the Skin Largest organ of human body 10% total body weight and would cover over 20 square feet Functions of Skin 1. Protection Barrier
INTEGUMENTARY 1-Epidermis, 2-Dermis, Structure of thick and thin skin I- Epidermis . Stratum basale
 INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
B. Incorrect! The ectoderm does not produce the dermis. C. Incorrect! The dermis is derived from the mesoderm.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
Integumentary System. Remember: Types of Membranes: Bio 250
 Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
7/10/18. Introduction. Integumentary System. Physiology. Anatomy. Structure of the Skin. Epidermis
 Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
Introduction Integumentary System Chapter 22 Skin is largest and heaviest organ of body (7% of body weight) Houses receptors for touch, heat, cold, movement, and vibration No other body system is more
The Integumentary System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 5 The Integumentary System Chapter 5 Learning Outcomes 5-1 5-2 5-3 5-4 5-5 Describe the main structural features
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 5 The Integumentary System Chapter 5 Learning Outcomes 5-1 5-2 5-3 5-4 5-5 Describe the main structural features
Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings
 Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings List the four types of epithelial or connective membranes. The epithelial cutaneous includes your and is exposed to the. Its function is to. An example is..
Integumentary System-Skin and Body Coverings List the four types of epithelial or connective membranes. The epithelial cutaneous includes your and is exposed to the. Its function is to. An example is..
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 6
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 6 1 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water
The Integumentary System
 C h a p t e r 5 The Integumentary System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Introduction to the Integumentary System The integument is the largest system
C h a p t e r 5 The Integumentary System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Introduction to the Integumentary System The integument is the largest system
Lesson Plan: Integumentary System
 Integumentary System The skin is no more separate from the brain than the surface of a lake is separate from its depths. They are two different locations in a continuous medium. To touch the surface is
Integumentary System The skin is no more separate from the brain than the surface of a lake is separate from its depths. They are two different locations in a continuous medium. To touch the surface is
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Skin (Integument) Consists of two major regions 1. Epidermis superficial region 2. Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia) deepest region Subcutaneous layer deep to
The Integumentary System Skin (Integument) Consists of two major regions 1. Epidermis superficial region 2. Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia) deepest region Subcutaneous layer deep to
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Eleventh Edition. Chapter 6
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
Anatomy & Physiology Joints and Girdles Exam 12/15/2015. Part I: Labeling. Provide the correct name for each marked bone, suture, landmark, etc. 14.
 Anatomy & Physiology Joints and Girdles Exam 12/15/2015 Part I: Labeling. Provide the correct name for each marked bone, suture, landmark, etc. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 11. 19. 20. 8. 7. 14. 15. 12. 17. 9. 13.
Anatomy & Physiology Joints and Girdles Exam 12/15/2015 Part I: Labeling. Provide the correct name for each marked bone, suture, landmark, etc. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 11. 19. 20. 8. 7. 14. 15. 12. 17. 9. 13.
The Integumentary System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
The Integumentary System The Skin Structure two primary layers called epidermis and dermis Epidermis Outermost and thinnest primary layer of skin Composed of several layers of stratified squamous epithelium
****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6
 AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
Name: Date: Class: Unit 1 Outline: Introduction, Cells, Tissues, and the Integumentary System
 Name: Date: Class: Unit 1 Outline: Introduction, Cells, Tissues, the Integumentary System Introduction to A&P The Human Body- An Orientation - study of the structure shape of the body its parts - study
Name: Date: Class: Unit 1 Outline: Introduction, Cells, Tissues, the Integumentary System Introduction to A&P The Human Body- An Orientation - study of the structure shape of the body its parts - study
Chapter 6: Skin & the. 6.1 Skin and its Tissues 6.2 Accessory Organs of the Skin 6.3 Regulation of Body Temperature 6.4 Healing of Wounds
 Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1-6.2 September 10, 2012 Chapter 6: Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1 Skin and its Tissues 6.2 Accessory Organs of the Skin 6.3 Regulation of Body Temperature 6.4 Healing
Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1-6.2 September 10, 2012 Chapter 6: Skin & the Integumentary System 6.1 Skin and its Tissues 6.2 Accessory Organs of the Skin 6.3 Regulation of Body Temperature 6.4 Healing
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System. Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system
 Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
Levels of Organization
 Levels of Organization Oklahoma Laws Violators can be fined, arrested or jailed for making ugly faces at a dog. Females are forbidden from doing their own hair without being licensed by the state. Dogs
Levels of Organization Oklahoma Laws Violators can be fined, arrested or jailed for making ugly faces at a dog. Females are forbidden from doing their own hair without being licensed by the state. Dogs
All the Rest. What is All the Rest? Integumentary System. First are the FUNCTI0NS. THERMOREGULATION function. PROTECTION function 10/12/16
 What is All the Rest? Integumentary System All the Rest Integumentary System Homeostatic Imbalances Skin Cancer Burns First are the FUNCTI0NS Chemical, Physical/Mechanical, Biological Thermoregulation
What is All the Rest? Integumentary System All the Rest Integumentary System Homeostatic Imbalances Skin Cancer Burns First are the FUNCTI0NS Chemical, Physical/Mechanical, Biological Thermoregulation
1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) i. Organ of the Integument. Connective Tissues. Epithelial Tissues
 Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
The Integumentary System. Health & Anatomy
 The Integumentary System Health & Anatomy Review of Membranes -Serous Membranes are composed of simple squamous epithelium resting on a thin layer of areolar connective tissue. *Name depends on the location
The Integumentary System Health & Anatomy Review of Membranes -Serous Membranes are composed of simple squamous epithelium resting on a thin layer of areolar connective tissue. *Name depends on the location
2.2 Integumentary System. Chapter 5
 2.2 Integumentary System Chapter 5 Skin Disorder Mini-Project The Integumentary System Written Response #12 In your notebook, complete the following items: 1. Drawing of a cross section of skin that includes
2.2 Integumentary System Chapter 5 Skin Disorder Mini-Project The Integumentary System Written Response #12 In your notebook, complete the following items: 1. Drawing of a cross section of skin that includes
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 C H A P T E R 51 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY THE HUMAN INTEGUMENTARY BODY: AN SYSTEM ORIENTATION C H A P T E R 1 PART I THE HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION
C H A P T E R 51 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY THE HUMAN INTEGUMENTARY BODY: AN SYSTEM ORIENTATION C H A P T E R 1 PART I THE HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM THE HUMAN BODY: AN ORIENTATION
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad. Lab 1
 Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
II. Skin and Its Tissues. I. Introduction. Unit Two. Integument URLs.
 6 Integument URLs http://www.nurseminerva.co.uk/integ.html http://www.aap.org/policy/s010116.html Chapter 6 Karen Webb Smith Unit Two I. Introduction A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more
6 Integument URLs http://www.nurseminerva.co.uk/integ.html http://www.aap.org/policy/s010116.html Chapter 6 Karen Webb Smith Unit Two I. Introduction A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more
Skin Histology. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skin Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Integumentary system The skin is considered the largest organ of the body Basic Skin Histology The skin is composed of two
Skin Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Integumentary system The skin is considered the largest organ of the body Basic Skin Histology The skin is composed of two
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System. Integumentary System. Page 1
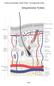 Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Integument. Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Melanoma. Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors
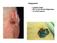 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Integument Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors Melanoma Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Derived from ectoderm Appendages hair follicles
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Integument Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors Melanoma Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Derived from ectoderm Appendages hair follicles
Integumentary System The Integumentary System
 Integumentary System The Integumentary System The integument, or skin, is the largest organ in the body. 16% of body weight. 1.5-2m 2 in area. The skin is one of the body s membranes, which are boundaries
Integumentary System The Integumentary System The integument, or skin, is the largest organ in the body. 16% of body weight. 1.5-2m 2 in area. The skin is one of the body s membranes, which are boundaries
Chapter 6: Integumentary System
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 12 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Integumentary System I. Introduction 1. The skin is composed of of tissues.
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 12 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Integumentary System I. Introduction 1. The skin is composed of of tissues.
28a A&P - Integumentary System
 28a A&P - Integumentary System 28a A&P - Integumentary System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
28a A&P - Integumentary System 28a A&P - Integumentary System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
Integumentary System
 Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
Chapter 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Skin: composed of dermis and epidermis Dermis. Gives structural strength. C.T. with many fibers, fibroblasts, macrophages. Some adipocytes and blood vessels. Contains
Figure 6.1 Transparency Master 37
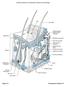 Pore Hair shaft Epidermis Dermal papillae (papillary layer of dermis) Meissner s corpuscle Dermis Free nerve ending Reticular layer of dermis Sebaceous (oil) gland Arrector pili muscle Sensory nerve fiber
Pore Hair shaft Epidermis Dermal papillae (papillary layer of dermis) Meissner s corpuscle Dermis Free nerve ending Reticular layer of dermis Sebaceous (oil) gland Arrector pili muscle Sensory nerve fiber
Integumentary System. Integumentary System
 1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System 5.1-5.4 September 10, 2012 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System 5.1 Structure of the Skin 5.2 Accessory Structures of the Skin 5.3 Types of Skin 5.4 Functions of the Skin 5.5 Maintaining
The Integumentary System 5.1-5.4 September 10, 2012 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System 5.1 Structure of the Skin 5.2 Accessory Structures of the Skin 5.3 Types of Skin 5.4 Functions of the Skin 5.5 Maintaining
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition)
 Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
Integumentary System (Skin) Unit 6.3 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.3 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major components (anatomy) of skin Differentiate between the two types of skin glands Explain
Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System I. Skin and Its Tissues A. Introduction
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System Chapter 6: Skin and the Integumentary System I. Skin and Its Tissues A. Introduction
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Define integumentary
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 The Human Integumentary and Fascial Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Define integumentary
