Benign Lichenoid Keratosis
|
|
|
- Aubrie Flynn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Benign Lichenoid Keratosis ALAN F. FRIGY, M.D. AND PHILIP H. COOPER, M.D. The microscopic spectrum of benign lichenoid keratosis (BLK) was studied by examination of 30 examples. BLK consists of a segment of hyperplastic epidermis accompanied by a lymphoid infiltrate in the papillary dermis. Although termed "lichen planus-like," saw-tooth acanthosis predominated in only seven lesions, whereas irregular acanthosis was widespread in 23. The infiltrate had both a band-like (lichenoid) and perivascular arrangement, but a lichenoid appearance predominated in only half the specimens. Liquefaction of the basal layer was widespread, and hydropic change often involved the midepidermis. Mild cytologic atypicality was present in each case, but other features of actinic keratosis were lacking. Changes of senile lentigo were observed adjacent to 7 lesions. Partial involution was present in several cases. BLK often is confused clinically with a variety of other cutaneous tumors. Nevertheless, the diagnosis usually can be made on histologic grounds alone when the history indicates a solitary lesion. (Key words: Lichenoid keratosis; Lichen planus-like keratosis; Solitary lichen planus; Benign keratosis; Lichenoid inflammation; Senile lentigo; Involution) Am J Clin Pathol 985; 83: BENIGN LICHENOID KERATOSIS (BLK), first defined nearly two decades ago, 5 ' 8 is a relatively common cutaneous lesion, frequently excised for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. Despite several publications describing BLK, 2 " 8 all in the dermatologic literature, a recent report 2 indicates that the lesion usually is misdiagnosed, both clinically,and pathologically. Although there may be some basis for the clinical confusion, the pathologic features of BLK are sufficiently characteristic that the diagnosis can be suggested strongly on histologic grounds alone and usually can be made with confidence when the clinical impression indicates a solitary lesion. There are no descriptions of BLK in the pathology literature, however, and textbooks contain only brief sections of parenthetic comments about the lesion. Moreover, most descriptions in the dermatologic literature are of a summary nature, and only a few touch on most of the salient features. 2 ' 8 We studied a series of BLK in order to better document its microscopic spectrum, to clarify certain of its histologic features that remain unsettled, and to provide a description sufficiently thorough that pathologists could become skillful at researching a secure morphologic diagnosis. Received May 30, 984; accepted for publication June 26, 984. Address reprint requests to Dr. Cooper: Department of Pathology, Box 24, University of Virginia Medical Center, Charlottesville, Virginia Departments of Pathology and Dermatology, University of Virginia Medical Center, Charlottesville, Virginia Materials and Methods Included for study were 30 BLK evaluated by the Department of Pathology, University of Virginia Medical Center, between January 98 and June 983. Twentytwo of the lesions were received from dermatologists for processing and diagnosis in our laboratory. Slides of eight others were submitted for consultation by dermatologists or pathologists. We obtained a clinical description, history, and followup information for each case. In order to document the histologic range of BLK, we recorded the presence and extent of a variety of specific microscopic features during joint examination of the lesions. Clinical Data Results There were 29 patients (one patient had two lesions). They ranged in age from 28 to 8 years (mean, 52; median, 54). All were white, and 2 (72%) were women. Two-thirds of the lesions were located on the chest, upper extremities, or face (Table ). Their duration was from two weeks to two years, and 60% were present less than one year. The lesions were described as red or brown papules or plaques with shiny, waxy, or slightly scaly surfaces. They varied in size from 3 to 20 mm. The majority were apparently asymptomatic, but three were pruritic. The examining dermatologists entertained a variety of diagnoses (Table 2). BLK was considered in nine cases, but in only two instances was it the only diagnosis offered. Twenty-six of the lesions were treated with either shave or excisional biopsy. There were no recurrences during periods of follow-up that ranged from to 2 months (mean, 5.8; median, ). Microscopic Observations Shave and excisional biopsy specimens of BLK had a characteristic low-power appearance (Figs. -3). The lesions were composed of a segment of thickened epidermis and a coinciding mononuclear cell infiltrate in Downloaded from by guest on 25 September
2 440 FRIGY AND COOPER A.J.C.P. April 985 Table. Anatomic Location of Benign Lichenoid Keratosis Location Number of Cases Upper anterior chest 0 Arm 8 Leg 4 Shoulder 3 Temple 2 Back Hand Thigh Total 30 the superficial dermis. The epidermal surfaces were gently curved or slightly undulating or angular. There were often accentuated dells, however, where follicular infundibula (Fig. 3) or acrosyringeal units with little or no hyperplasia connected with hyperplastic epidermis. The margins of the lesions were rounded, sloped, or more gradually tapered as they joined adjacent normal epidermis. They were obvious in ellipse excisions and often discernable in shave biopsy specimens. Mild to moderate hyperkeratosis, usually diffuse, was present in all BLK, but a basket-weave pattern was retained partially in each. The keratin layer was often loosely adherent or partially detached. Two-thirds of the lesions displayed focal or segmental parakeratosis. Hypergranulosis was mild to moderate in all specimens. The degree of epidermal hyperplasia ranged from slight to marked, and there were several patterns, often present in combination. Irregular elongation and widening of rete ridges was the predominant pattern in 23 lesions (Fig. ). A saw-tooth appearance was present in 20 cases but predominated in only seven (Fig. 2). Areas of more uniform, plaque-like acanthosis, with effacement of the rete ridges, were observed in 4 specimens (Fig. 3). Three lesions had foci of epidermal thinning; in one, this was extensive. The dermis contained a lymphoid infiltrate, most marked in the papillary dermis but also present about blood vessels of the superficial reticular dermis. The infiltrate was arranged in two basic patterns: either as Table 2. Clinical Diagnoses Considered in Differential Diagnosis of Benign Lichenoid Keratosis bands that closely hugged the dermal-epidermal junction (Figs. 2 and 3) or as more discrete aggregates, separate from the epidermis and centered about vessels in the papillary dermis (Fig. ). The band-like arrangement predominated in half the specimens but was the sole pattern in only six lesions. Combinations of both patterns were observed in 2 cases. The band-like infiltrate often was associated with regions of saw-tooth acanthosis, whereas the perivascular pattern was most common beneath segments of irregular epidermal hyperplasia. Foci of mononuclear cell exocytosis extending to the midepidermis were observed in nearly every lesion. In addition to lymphoid cells, a few eosinophils were observed in six cases, and rare plasma cells or neutrophils were noted in four and three lesions, respectively. Five cases had small extravasations of red blood cells. Melanin incontinence, mild to focally marked, was present in 27 biopsies. A minority of specimens had fields or larger segments, either within the lesions or at its margin, where the infiltrate was scattered haphazardly and markedly diminished (Fig. 4). The papillary dermis in such areas was thickened and slightly sclerotic and often contained melanin. Liquefaction of the basal cell layer, segmental or diffuse, was present in each specimen (Fig. 5). The change was particularly marked in areas with a bandlike infiltrate where there were numerous apoptotic (colloid, Civatte) bodies, small dermal-epidermal clefts, and vacuolar change in the midepidermis. Liquefaction involved follicular infundibula and acrosyringia in some instances. It was minimal or absent in epidermis, overlying thickened, sclerotic papillary dermis (Fig. 4). Epidermal cells within the lesions often were mildly enlarged and often had increased eosinophilia in comparison with adjacent, unaffected epidermis (Figs. and 5). In addition, some degree of cytologic atypicality affected the basal and suprabasal cells in nearly every lesion (Fig. 6). There was some loss of normal polarity, and nuclei were enlarged, vesicular, and had prominent nucleoli. Solar elastosis was usually mild, and in only a few lesions was it of the degree typically associated with actinic keratosis. In 7 cases, the adjacent epidermis had changes consistent with senile lentigo (Fig. ). In two, small fields suggested a preexisting seborrheic keratosis (Fig. 7). Downloaded from by guest on 25 September 208 Diagnosis Basal cell carcinoma Bowen's disease Seborrheic keratosis Benign lichenoid keratosis Actinic keratosis Keratosis, not otherwise specified Nevus Wart Lichenoid dermatitis Epidermoid carcinoma Prurigo nodularis Number of Cases Discussion The diagnosis of BLK is often apparent upon lowpower microscopic inspection of excised lesions. 2 The two essential findings are a segment of thickened epidermis and a mononuclear cell infiltrate in the papillary dermis that, in combination, create a well-defined papule or plaque. Microscopic recognition of the borders of the lesion is diagnostically useful, in our experience, as this allows the pathologist to appreciate its circumscribed
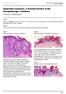
3 Vol. 83 No. 4 LICHENOID KERATOSIS 44 FIG. (upper). Low-power view of BLK. The epidermal hyperplasia is irregular, and the infiltrate is primarily perivascular. Paler staining epidermis within the lesion contrasts with darkly staining epidermis at the margin. Lentiginous epidermal change is present adjacent to the lesion at far left. Hematoxylin and eosin (X40). FIG. 2 (center). Low-power view of BLK. The saw-tooth pattern of epidermal hyperplasia is obscured partially by a dense hugging dermal inflammatory infiltrate. Note the loosely adherent keratotic scale and the contrast between the pale epidermis of the lesion and darker staining epidermis laterally (left). Hematoxylin and eosin (X65). Downloaded from by guest on 25 September 208 FIG. 3 (lower). Segments of uniform, plaque-like epidermal thickening were present in some BLK. There often were accentuated dells at adnexal orifices. The infiltrate in this lesion is distinctly band-like. Hematoxylin and eosin (X60). nature. The transition to normal skin is often abrupt and unmistakable, but in BLK with tapered edges the transition is more gradual. The surfaces of BLK are slightly curved or gently undulating or angular. In addition, we noted small but distinct dells at appendigeal orifices. When numerous, they created more complex surface configurations, but well-developed papillomatosis is uncharacteristic of BLK. 8 Mild to moderate hyperkeratosis is an invariable feature, but the basket-weave pattern almost always is retained to some dgree, and dense, compact hyperkeratosis is rare. Parakeratosis often is mentioned in descrip-
4 442 FRIGY AND COOPER A.J.C.P. -April 985 tions of BLK, but in two series 2,6 it was noted specifically in substantially less than half the cases. We observed scattered foci and occasional broader segments of parakeratosis in two-thirds of the lesions. Epidermal hyperplasia and a cellular infiltrate in the papillary dermis, the two most characteristic microscopic findings in BLK, have been described only in general terms. An early report, noting microscopic similarities between BLK and lichen planus, emphasized a sawtooth pattern of epidermal hyperplasia, 5 but others described the acanthosis as irregular 2,7 or uniform 3 or supplied no descriptive details. Irregular elongation and widening of rete ridges was the predominant pattern in 23 of the 30 specimens in this series. A saw-tooth configuration was predominant in only seven lesions, and ten lacked this finding. Approximately one-half the specimens had segments of uniform epidermal thickening. Combinations of these patterns were common, and the degree of epidermal hyperplasia varied considerably within individual specimens. Regarding the inflammatory infiltrate, some observers emphasized a band-like distribution, 2 " 5 but others, noted, in addition, that the infiltrate could be more discrete and perivascular. ' 7,8 We found that combinations of the two arrangements were common and that a distinctly lichenoid, band-like pattern was dominant in only onehalf the lesions. Moreover, the band-like pattern was associated typically with saw-tooth acanthosis, whereas the perivascular pattern, with relative sparing of the dermal-epidermal junction, was usually present in zones with irregular acanthosis. Liquefactive change is an essential feature of BLK, but some of its features have not been emphasized. The change is best developed in areas with a band-like infiltrate where it is by no means limited to basal cells. The midepidermis can show prominent vacuolar change, accompanied by striking mononuclear cell exocytosis. < FIG. 4 {upper). Portions of some BLK (left) contained only sparse mononuclear cell infiltrate and showed sclerosis of the papillary dermis. Such fields were interpreted as evidence of partial involution. Hematoxylin and eosin (X75). FIG. 5 (upper, center). Liquefaction of basal and suprabasal cells often was marked, with clustering of apoptotic (colloid, Civatte) bodies and prominent mononuclear cell exocytosis. Hematoxylin and eosin (X20). Downloaded from by guest on 25 September 208 FIG. 6 (lower, center). A mild degree of epidermal disorder and cytologic atypicality was present in each BLK. Hematoxylin and eosin (X250). FIG. 7 (lower). BLK were observed to merge with seborrheic keratosis in two instances. Note that the inflammatory component of the BLK is contiguous with similar changes affecting the seborrheic keratosis. Hematoxylin and eosin (X50).
5 Vol. 83 No. 4 LICHENOID KERATOSIS 443 In contrast, a substantial minority of specimens in this study had fields, occasionally large, that suggested partial involution of the lesion. The epidermis was hyperplastic but lacked liquefaction, and the papillary dermis was thickened, slightly sclerotic, and contained sparse, scattered inflammatory cells and variable amounts of melanin. Clinical observations indicate that BLK can involute,' but the histologic correlate of this has not been recorded. As dermatologists continue to confuse BLK with a variety of other lesions, 2 ' 4 pathologists need to recognize its clinical aspects. Published reports vary in detail, and the description and clinical photographs of Laur and associates 4 are recommended. Patients with BLK. are, with few exceptions, white. Most are in the fifth to seventh decade of life, and women outnumber men two to one. The lesions are nearly always solitary and have a predilection for the forearm and dorsum of the hand (30%), face (25%), and upper trunk (20%). The onset is often abrupt, and the clinical duration is frequently just a few weeks or months. Longer histories are not unusual, however. The lesions consist of round, polygonal, or irregular papules or plaques with distinct borders. Most are between 5 and 5 mm in diameter. The color can be pink, red, violaceous, tan, or brown. The surfaces are smooth, velvety, waxy, slightly scaly, or occasionally more ketatotic. Some patients complain of mild pruritis, stinging, or burning. As a variety of other more common cutaneous lesions manifest one or more of these clinical features, it is not surprising that BLK often are misinterpreted clinically. In a recent series, the proper clinical diagnosis was considered in only 3 of 43 instances. 2 BLK most commonly is confused with basal cell carcinoma, actinic keratosis, unspecified keratoses, Bowen's disease, and melanocytic nevi. 4 Inflammatory dermatoses rarely are considered. Pathologists, suspecting a BLK, usually can make the diagnosis with confidence when the specimen is accompanied by a clinical impression, albeit incorrect, indicating that the lesion is likely to be isolated or solitary. The nature of BLK is uncertain. Lumpkin and Helwig, 5 in an initial report, speculated that it might be a solitary variant of lichen planus. Shapiro and Ackerman, 8 in the same year, concluded that BLK was a distinct entity, an opinion shared by subsequent observers. BLK only infrequently resembles lesions of lichen planus, clinically, and the latter has not developed in patients with BLK. The possibility that BLK is actinically induced has been considered by some. Hirsch and Marmelzat 3 described five lesions with epidermal atypia and a lichenoid reaction that they termed lichenoid actinic keratosis. These lesions now are accepted as BLK. 4,7 Nevertheless, subsequent reports either failed to comment on dysplasia, 4 ' 8 noted its occasional presence, 2 or, in one instance, emphasized the finding. Cellular and nuclear enlargement, prominent nucleoli, and loss of cellular polarity were invariably present in our series. Features typical of actinic keratosis, however, such as disproportionate nuclear-cytoplasmic ratios, nuclear hyperchromatism, alternating areas of epidermal atrophy and hyperplasia, columns of parakeratosis, and suprabasal acantholysis were uniformly absent. Other factors that mitigate against an actinic etiology for BLK include their occasional appearance on non-sun-exposed portions of the body or in dark-skinned individuals, the absence of actinically related lesions in most patients, and the frequent presence of only mild solar elastosis in the underlying dermis. The cytologic atypicality in BLK probably represents an epidermal reaction to inflammatory injury, perhaps enhanced, to some degree, by the cytologic changes of regeneration. There were scattered mitotic figures in the majority of lesions. A dense mononuclear cell infiltrate, at times lichenoid, is a well-recognized histologic sign of host response or regression in a variety of benign and malignant cutaneous tumors. That BLK may represent a host reaction to a preexisting epidermal lesion is supported by our findings and those of others. Laur and associates 4 provided clinical evidence of preexisting senile lentigines at the sites of 29 of 59 cases, and Mehregan 6 claimed that there was histologic evidence of such lesions in all BLK he examined. We identified lentiginous changes adjacent to 57% of BLK, and two lesions contained recognizable foci of seborrheic keratosis. A host response to a preexisting lentigo or, rarely, a flat seborrheic keratosis would account for the abrupt onset of BLK, many of its clinical and microscopic features, and the fact that it can involute over a period of months. References. Berman A, Herszenson S, Winkelman RK: The involuting lichenoid plaque. Arch Dermatol 982; 8: Goette DK: Benign lichenoid keratosis. Arch Dermatol 980; 6: Hirsch P, Marmelzat WL: Lichenoid actinic keratosis. Dermatol Internat 967;6: Laur WE, Posey RE, Waller JD: Lichen planus-like keratosis, a clinicohistopathologic correlation. J Am Acad Dermatol 98; 4: Lumpkin LR, Helwig EB: Solitary lichen planus. Arch Dermatol 966; 93: Mehregan AH: Lentigo senilis and its evolutions. J Invest Dermatol 975; 65: Scott MA, Johnson WC: Lichenoid benign keratosis. J Cutan Pathol 976; 3: Shapiro L, Ackerman AB: Solitary lichen planus-like keratosis. Dermatologica 966; 32: Downloaded from by guest on 25 September 208
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more
 Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide
 Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Actinic keratosis (AK): Dr Sarma s simple guide Actinic keratosis is a very common lesion that you will see in your day-to-day practice. First, let me explain the name Actinic keratosis. It means keratosis
Pathology of the skin. 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University
 Pathology of the skin 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Histology of the skin Epidermis: Stratum corneum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale Dermis: papillary and reticular
Pathology of the skin 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Histology of the skin Epidermis: Stratum corneum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale Dermis: papillary and reticular
المركب النموذج--- سبيتز وحمة = Type Spitz's Nevus, Compound SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7
 SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
SPITZ NEVUS 1 / 7 Epidemiology An annual incidence rate of 1.4 cases of Spitz nevus per 100,000 individuals has been estimated in Australia, compared with 25.4 per 100,000 individuals for cutaneous melanoma
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Basal cell carcinoma 5/28/2011
 Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB. Friday, February 12, :30 am 11:00 am
 MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 12, 2012 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 12, 2012 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
Histopathology of Melanoma
 THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 48, 409-416 (1975) Histopathology of Melanoma G. J. WALKER SMITH Department ofpathology, Yale University School ofmedicine, 333 Cedar Street, New Haven, Connecticut
THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 48, 409-416 (1975) Histopathology of Melanoma G. J. WALKER SMITH Department ofpathology, Yale University School ofmedicine, 333 Cedar Street, New Haven, Connecticut
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB. Friday, February 13, :30 am 11:00 am
 MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 13, 2009 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 13, 2009 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), available at
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Two cases of blaschkitis with promi Author(s) Utani, Atsushi Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), Issue Date 2010-08 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25634
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Two cases of blaschkitis with promi Author(s) Utani, Atsushi Citation The Journal of Dermatology, 37(8), Issue Date 2010-08 URL Right http://hdl.handle.net/10069/25634
Lichenoid Tissue Reaction in Malignant Melanoma A Potential Diagnostic Pitfall
 natomic Pathology / LICHENOID TISSUE RECTION IN MLIGNNT MELNOM Lichenoid Tissue Reaction in Malignant Melanoma Potential Diagnostic Pitfall CPT Scott R. Dalton, MC, US, 1,3 Capt Matt. aptista, USF, MC,
natomic Pathology / LICHENOID TISSUE RECTION IN MLIGNNT MELNOM Lichenoid Tissue Reaction in Malignant Melanoma Potential Diagnostic Pitfall CPT Scott R. Dalton, MC, US, 1,3 Capt Matt. aptista, USF, MC,
ISPUB.COM. Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations. D Sarma, S Repertinger
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 2 Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations D Sarma, S Repertinger Citation D Sarma, S Repertinger.. The Internet
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 7 Number 2 Seborrheic Keratosis: A Pictorial Review of the Histopathologic Variations D Sarma, S Repertinger Citation D Sarma, S Repertinger.. The Internet
Chapter 6 Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Variants and Challenges
 Chapter 6 Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Variants and Challenges Michael B. Morgan EPIDEMIOLOGY: Second most common skin cancer, rare in the dark-skinned races. ETIOLOGY: Ultraviolet light, HPV infection. PATHOGENESIS:
Chapter 6 Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Variants and Challenges Michael B. Morgan EPIDEMIOLOGY: Second most common skin cancer, rare in the dark-skinned races. ETIOLOGY: Ultraviolet light, HPV infection. PATHOGENESIS:
Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc
 1 Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc Benign lesions Seborrheic Keratoses: Warty, stuck-on Genetics and birthdays Can start in late
1 Benign versus Cancerous Lesions How to tell the difference FMF 2014 Christie Freeman MD, CCFP, DipPDerm, MSc Benign lesions Seborrheic Keratoses: Warty, stuck-on Genetics and birthdays Can start in late
04/09/2018. Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions. Agenda. Squamous Dysplasia. Squamo-proliferative lesions. Architectural features
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
LENTIGO SIMPLEX. Epidemiology
 LENTIGO SIMPLEX Epidemiology The frequency of lentigo simplex in children and adults has not been determined. There does not appear to be a racial or gender predilection. Lentigo simplex is the most common
LENTIGO SIMPLEX Epidemiology The frequency of lentigo simplex in children and adults has not been determined. There does not appear to be a racial or gender predilection. Lentigo simplex is the most common
Dermatopathology: The tumor is composed of keratinocytes which show atypia, increase mitoses and abnormal mitoses.
 Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
A dinical and histopathologic entity associated with an increased risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer
 PUVA keratosis A dinical and histopathologic entity associated with an increased risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer M. C. G. van Praag, MD, a J. N. Bouwes Bavinck, MD, a W. Bergman, MD, PhD, a F. R. Rosendaal,
PUVA keratosis A dinical and histopathologic entity associated with an increased risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer M. C. G. van Praag, MD, a J. N. Bouwes Bavinck, MD, a W. Bergman, MD, PhD, a F. R. Rosendaal,
Desmoplastic Melanoma R/O BCC. Clinical Information. 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o BCC
 R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Abrupt Intralesional Color Change on Dermoscopy as a New Indicator of Early Superficial Spreading Melanoma in a Japanese Woman
 Published online: June 24, 2015 1662 6567/15/0072 0123$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Published online: June 24, 2015 1662 6567/15/0072 0123$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Associate Clinical Professor of Dermatology MUSC
 Re-excision of Moderately Dysplastic Nevi: Should we or shouldn t we? John C. Maize, Jr, M.D. Dermatologist and Dermatopathologist Trident Dermatology, Charleston SC Associate Clinical Professor of Dermatology
Re-excision of Moderately Dysplastic Nevi: Should we or shouldn t we? John C. Maize, Jr, M.D. Dermatologist and Dermatopathologist Trident Dermatology, Charleston SC Associate Clinical Professor of Dermatology
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation. Dermatopathology Specialists Needed. Changing Trends
 Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
Important Decisions in Dermatopathology: The Clinico- Pathologic Correlation Uma Sundram, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Dermatology Stanford University May 29, 2008 Dermatopathology Specialists
DERMATITIS CHRONICA HELICIS
 J. clin. Path. (1957), 10, 46. THE HISTOLOGICAL APPEARANCES OF CHONDRO- DERMATITIS CHRONICA HELICIS BY E. M. McCONNELL From the Department of Pathology, Liverpool Radium Institute, Liverpool (RECEIVED
J. clin. Path. (1957), 10, 46. THE HISTOLOGICAL APPEARANCES OF CHONDRO- DERMATITIS CHRONICA HELICIS BY E. M. McCONNELL From the Department of Pathology, Liverpool Radium Institute, Liverpool (RECEIVED
Appendix : Dermoscopy
 Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details APP Appendix : Dermoscopy Dermoscopy, also known as dermatoscopy, epiluminoscopy and epiluminescent microscopy, is an effective non-invasive
Go Back to the Top To Order, Visit the Purchasing Page for Details APP Appendix : Dermoscopy Dermoscopy, also known as dermatoscopy, epiluminoscopy and epiluminescent microscopy, is an effective non-invasive
Rameshwar Gutte and Uday Khopkar
 Extragenital unilateral lichen sclerosus et atrophicus in a child: a case report Rameshwar Gutte and Uday Khopkar Department of Dermatolgy, Seth GSMC and KEM Hospital, Parel, Mumbai-400012, India Egyptian
Extragenital unilateral lichen sclerosus et atrophicus in a child: a case report Rameshwar Gutte and Uday Khopkar Department of Dermatolgy, Seth GSMC and KEM Hospital, Parel, Mumbai-400012, India Egyptian
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies
 Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
6/17/2018. Breaking Bad (Part 1) Dermoscopy of Brown(ish) Things. Bad?
 Breaking Bad (Part 1) Dermoscopy of Brown(ish) Things Jennie T. Clarke, MD ssociate Professor of Dermatology University of Utah School of Medicine Bad? 1 Brown(ish) Things Bad Melanoma Pigmented basal
Breaking Bad (Part 1) Dermoscopy of Brown(ish) Things Jennie T. Clarke, MD ssociate Professor of Dermatology University of Utah School of Medicine Bad? 1 Brown(ish) Things Bad Melanoma Pigmented basal
Chronology of lichen planus-like keratosis features by dermoscopy: a summary of 17 cases
 DERMATOLOGY PRACTICAL & CONCEPTUAL www.derm101.com Chronology of lichen planus-like keratosis features by dermoscopy: a summary of 17 cases Soko Watanabe 1, Mizuki Sawada 1, Itaru Dekio 1, Sumiko Ishizaki
DERMATOLOGY PRACTICAL & CONCEPTUAL www.derm101.com Chronology of lichen planus-like keratosis features by dermoscopy: a summary of 17 cases Soko Watanabe 1, Mizuki Sawada 1, Itaru Dekio 1, Sumiko Ishizaki
NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES)
 NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES) Papillary Lesions Precancerous Lesions Keratinocyte Proliferations Carcinomas Melanotic Lesions Melanomas Normal Mucosa Keratin layer Spinous layer Basal
NEOPLASMS OF THE SURFACE EPITHELIUM (KERATINOCYTES) Papillary Lesions Precancerous Lesions Keratinocyte Proliferations Carcinomas Melanotic Lesions Melanomas Normal Mucosa Keratin layer Spinous layer Basal
Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2
 Interface diseases Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2 Histological findings Severe hydropic vacuolation of epidermal and follicular basal cells/ interface dermatitis Multifocally apoptotic keratinocytes
Interface diseases Case No. 5; Slide No. B13/8956/2 Histological findings Severe hydropic vacuolation of epidermal and follicular basal cells/ interface dermatitis Multifocally apoptotic keratinocytes
A Descriptive Study on Patients of Papulosquamous Lesion at Tertiary Care Institute
 MVP Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol 1(1), 30 35, January 2014 A Descriptive Study on Patients of Papulosquamous Lesion at Tertiary Care Institute S. D. Chavhan 1*, S. V. Mahajan 2 and A. J. Vankudre 3
MVP Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol 1(1), 30 35, January 2014 A Descriptive Study on Patients of Papulosquamous Lesion at Tertiary Care Institute S. D. Chavhan 1*, S. V. Mahajan 2 and A. J. Vankudre 3
ISPUB.COM. A Case of Actinic Lichen Planus. K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 8 Number K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park Citation K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park.. The Internet Journal of Dermatology. 2009 Volume 8 Number. Abstract The
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dermatology Volume 8 Number K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park Citation K Choi, H Kim, H Kim, Y Park.. The Internet Journal of Dermatology. 2009 Volume 8 Number. Abstract The
Keratinocyte tumors. Actinic Keratosis. Squamous cell carcinoma in situ. Squamous Cell Carcinoma. (aka Bowen s disease)
 Actinic Keratosis Keratinocyte tumors Prepared by Kurt Schaberg Precancerous, risk of malignancy ~8-20% per year (progresses to SCC); Due to chronic sun exposure Rough scaly plaque; typically due to sun
Actinic Keratosis Keratinocyte tumors Prepared by Kurt Schaberg Precancerous, risk of malignancy ~8-20% per year (progresses to SCC); Due to chronic sun exposure Rough scaly plaque; typically due to sun
Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA)
 Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) Ahmed Abdullah Alhumidi King saud university, Riyadh, kingdom of Saudi Arabia Abstract Background: This
Retrospective 10 years review of 100 patients with psoriasis in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA) Ahmed Abdullah Alhumidi King saud university, Riyadh, kingdom of Saudi Arabia Abstract Background: This
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Pathology of the skin. Dr Fónyad László, 1sz. Patológiai és Kísérleti Rákkutató Intézet, SE
 Pathology of the skin Dr Fónyad László, 1sz. Patológiai és Kísérleti Rákkutató Intézet, SE The skin Biggest organ Kb. 1.8 nm Kb. 10 kg Most frequent site for tumor development (BCC) Pathology of the skin
Pathology of the skin Dr Fónyad László, 1sz. Patológiai és Kísérleti Rákkutató Intézet, SE The skin Biggest organ Kb. 1.8 nm Kb. 10 kg Most frequent site for tumor development (BCC) Pathology of the skin
Skin lesions The Good and the Bad. Dr Virginia Hubbard Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry
 Skin lesions The Good and the Bad Dr Virginia Hubbard Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry Case 1 32 year old woman Australian Lesion on back New hair growing
Skin lesions The Good and the Bad Dr Virginia Hubbard Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry Case 1 32 year old woman Australian Lesion on back New hair growing
IT S FUNDAMENTAL MY DEAR WATSON! A SHERLOCKIAN APPROACH TO DERMATOLOGY
 IT S FUNDAMENTAL MY DEAR WATSON! A SHERLOCKIAN APPROACH TO DERMATOLOGY Skin, Bones, and other Private Parts Symposium Dermatology Lectures by Debra Shelby, PhD, DNP, FNP-BC, FADNP, FAANP Debra Shelby,
IT S FUNDAMENTAL MY DEAR WATSON! A SHERLOCKIAN APPROACH TO DERMATOLOGY Skin, Bones, and other Private Parts Symposium Dermatology Lectures by Debra Shelby, PhD, DNP, FNP-BC, FADNP, FAANP Debra Shelby,
Morphologic Features of Melanocytes, Pigmented Keratinocytes, and Melanophages by In Vivo Confocal Scanning Laser Microscopy
 Morphologic Features of Melanocytes, Pigmented Keratinocytes, and Melanophages by In Vivo Confocal Scanning Laser Microscopy Klaus J. Busam, M.D., Carlos Charles, M.D., Grace Lee, M.D., Allan C Halpern,
Morphologic Features of Melanocytes, Pigmented Keratinocytes, and Melanophages by In Vivo Confocal Scanning Laser Microscopy Klaus J. Busam, M.D., Carlos Charles, M.D., Grace Lee, M.D., Allan C Halpern,
Disclosure. Objectives. PAFP CME Conference Lou Mancano MD, FAAFP Reading Health System November 18, 2016
 PAFP CME Conference Lou Mancano MD, FAAFP Reading Health System November 18, 2016 1 Disclosure The speaker has no conflict of interest, financial agreement, or working affiliation with any group or organization.
PAFP CME Conference Lou Mancano MD, FAAFP Reading Health System November 18, 2016 1 Disclosure The speaker has no conflict of interest, financial agreement, or working affiliation with any group or organization.
Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
 Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
Journal of Helminthology, ~ol. XXXVIII, Nos. 1/2, 1964, pp. 171-174. Observations on the Pathology of Lesions Associated with Stephanofilaria dinniki Round, 1964 from the Black Rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis)
CASE REPORT Superficial Spreading Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Face: A Surgical Challenge
 CASE REPORT Superficial Spreading Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Face: A Surgical Challenge Yuri T. Jadotte, MD, a Navér A. Sarkissian, MD, PhD, b,c Helchem Kadire, MD, c and W. Clark Lambert, MD, PhD b,c
CASE REPORT Superficial Spreading Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Face: A Surgical Challenge Yuri T. Jadotte, MD, a Navér A. Sarkissian, MD, PhD, b,c Helchem Kadire, MD, c and W. Clark Lambert, MD, PhD b,c
Clinically Microscopically Pathogenesis: autoimmune not lifetime
 Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma
 Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma Laura B. Pincus, MD Co-Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Clinic Associate Professor Dermatology and Pathology University of California, San Francisco I HAVE NO RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS
Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma Laura B. Pincus, MD Co-Director, Cutaneous Lymphoma Clinic Associate Professor Dermatology and Pathology University of California, San Francisco I HAVE NO RELEVANT RELATIONSHIPS
Simulators of melanoma
 Simulators of melanoma Philip E. LeBoit, M.D. Depts. of Pathology and Dermatology University of California, San Francisco Simulators of melanoma Simulators of melanoma in situ Melanocytic Non-melanocytic
Simulators of melanoma Philip E. LeBoit, M.D. Depts. of Pathology and Dermatology University of California, San Francisco Simulators of melanoma Simulators of melanoma in situ Melanocytic Non-melanocytic
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 10 Page October 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i10.125 Histomorphological Study of Lichen Planus
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i10.125 Histomorphological Study of Lichen Planus
ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A SMALL PIGMENTED CUTANEOUS LESION*
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A SMALL PIGMENTED CUTANEOUS LESION* The description of the lesion in the title of this rcport is intentionally non-committal. Diagnosed clinically as a lentigo, it was removed as
ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF A SMALL PIGMENTED CUTANEOUS LESION* The description of the lesion in the title of this rcport is intentionally non-committal. Diagnosed clinically as a lentigo, it was removed as
Basics in Dermoscopy
 Basics in Dermoscopy Manal Bosseila Professor of Dermatology, Cairo University Member of European Academy Dermatology & Venereology EADV Member of International Dermoscopy Society IDS Member of Aesthetic
Basics in Dermoscopy Manal Bosseila Professor of Dermatology, Cairo University Member of European Academy Dermatology & Venereology EADV Member of International Dermoscopy Society IDS Member of Aesthetic
Polypoid Melanoma, A Virulent Variant of the Nodular Growth Pattern
 Polypoid Melanoma, A Virulent Variant of the Nodular Growth Pattern ELIZABETH A. MANCI, M.D., CHARLES M. BALCH, M.D..TARIQ M. MURAD, M.D., PH.D., AND SENG/JAW SOONG, PH.D. Manci, Elizabeth A., Balch, Charles
Polypoid Melanoma, A Virulent Variant of the Nodular Growth Pattern ELIZABETH A. MANCI, M.D., CHARLES M. BALCH, M.D..TARIQ M. MURAD, M.D., PH.D., AND SENG/JAW SOONG, PH.D. Manci, Elizabeth A., Balch, Charles
David B. Troxel, MD. Common Medicolegal Situations: Misdiagnosis of Melanoma
 Common Medicolegal Situations: Misdiagnosis of Melanoma David B. Troxel, MD Medical Director, The Doctors Company, Napa, California Clinical Professor Emeritus, University of California at Berkeley Past
Common Medicolegal Situations: Misdiagnosis of Melanoma David B. Troxel, MD Medical Director, The Doctors Company, Napa, California Clinical Professor Emeritus, University of California at Berkeley Past
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease. Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia
 Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
Gastrooesophageal reflux disease Jera Jeruc Institute of pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Ljubljana, Slovenia Reflux esophagitis (RE) GERD: a spectrum of clinical conditions and histologic alterations resulting
Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
LGM International, Inc.
 Liqui-PREP TM Cytology Atlas Preface The following pictures are examples with descriptions of cytology slides processed with the Liqui-PREP TM System.. The descriptions are reviewed by Pathologists. It
Liqui-PREP TM Cytology Atlas Preface The following pictures are examples with descriptions of cytology slides processed with the Liqui-PREP TM System.. The descriptions are reviewed by Pathologists. It
Malignant tumors of melanocytes: Part 1. Deba P Sarma, MD., Omaha
 Malignant tumors of melanocytes: Part 1 Deba P Sarma, MD., Omaha The melanocytic tumor is one of the most difficult and confusing areas in Dematopathology. It is true that most (95%) of such lesions are
Malignant tumors of melanocytes: Part 1 Deba P Sarma, MD., Omaha The melanocytic tumor is one of the most difficult and confusing areas in Dematopathology. It is true that most (95%) of such lesions are
الاكزيماتيد= Eczematid
 1 / 7 2 / 7 Pityriasis Debate confusing of hypopigmentation characterized increasing surrounded differ hypomelanotic "progressive exists alba misnomer extensive a to observed term the applied term derived
1 / 7 2 / 7 Pityriasis Debate confusing of hypopigmentation characterized increasing surrounded differ hypomelanotic "progressive exists alba misnomer extensive a to observed term the applied term derived
Eruptive Tumors of the Follicular Infundibulum: An Unexpected Diagnosis of Hypopigmented Macules
 Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) (2015) 5:207 211 DOI 10.1007/s13555-015-0079-0 CASE REPORT Eruptive Tumors of the Follicular Infundibulum: An Unexpected Diagnosis of Hypopigmented Macules Poonkiat Suchonwanit.
Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) (2015) 5:207 211 DOI 10.1007/s13555-015-0079-0 CASE REPORT Eruptive Tumors of the Follicular Infundibulum: An Unexpected Diagnosis of Hypopigmented Macules Poonkiat Suchonwanit.
Gross Appearance & Histology of Skin Cancer. Kyle Mannion M.D. January 21, 2005
 Gross Appearance & Histology of Skin Cancer Kyle Mannion M.D. January 21, 2005 Actinic Keratosis 5-20% will develop squamous/basal cell ca Almost solely from solar damage Usually develop during 4 th decade
Gross Appearance & Histology of Skin Cancer Kyle Mannion M.D. January 21, 2005 Actinic Keratosis 5-20% will develop squamous/basal cell ca Almost solely from solar damage Usually develop during 4 th decade
BASAL CELL CARCINOMA WITH ECCRINE DIFFERENTIATION: A RARE ENTITY Divvya B 1, Rehana Tippoo 2, P. Viswanathan 3, B. Krishnaswamy 4, A.
 BASAL CELL CARCINOMA WITH ECCRINE DIFFERENTIATION: A RARE ENTITY Divvya B 1, Rehana Tippoo 2, P. Viswanathan 3, B. Krishnaswamy 4, A. Anvar Ali 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Divvya B, Rehana Tippoo, P. Viswanathan,
BASAL CELL CARCINOMA WITH ECCRINE DIFFERENTIATION: A RARE ENTITY Divvya B 1, Rehana Tippoo 2, P. Viswanathan 3, B. Krishnaswamy 4, A. Anvar Ali 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Divvya B, Rehana Tippoo, P. Viswanathan,
أملس عضلي غرن = Leiomyosarcoma. Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5
 Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
CD30 + cells in benign inflammatory infiltrate of some dermatological diseases. Abstract. Latef M. El Balshy. Benha University-Benha, Egypt.
 CD30 + cells in benign inflammatory infiltrate of some dermatological diseases 1 Asmaa M. El Refaeie, 1 Osama H. Abdel Salam, 1 Sherine H.Abd EL-Rahman and 2 Abdel Latef M. El Balshy. 1 Dermatology & Andrology
CD30 + cells in benign inflammatory infiltrate of some dermatological diseases 1 Asmaa M. El Refaeie, 1 Osama H. Abdel Salam, 1 Sherine H.Abd EL-Rahman and 2 Abdel Latef M. El Balshy. 1 Dermatology & Andrology
F006 Imaging in Dermatology Melanocytic Neoplasia Clinical-Confocal-Pathological-Correlations
 F006 Imaging in Dermatology Melanocytic Neoplasia Clinical-Confocal-Pathological-Correlations Melissa Gill, MD SkinMedical Research and Diagnostics Dobbs Ferry, NY, USA Department of Pathology SUNY Downstate
F006 Imaging in Dermatology Melanocytic Neoplasia Clinical-Confocal-Pathological-Correlations Melissa Gill, MD SkinMedical Research and Diagnostics Dobbs Ferry, NY, USA Department of Pathology SUNY Downstate
Objectives. Atypical Glandular Cells. Atypical Endocervical Cells. Reactive Endocervical Cells
 2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
Pigmented Seborrheic Keratosis (Melanoacanthoma) of Nipple A case report with review of literature
 Case Report Pigmented Seborrheic Keratosis (Melanoacanthoma) of Nipple A case report with review of literature Aparna Narasimha, Harendra Kumar ML, Divyarani MN, Bhaskaran A* Department of Pathology and
Case Report Pigmented Seborrheic Keratosis (Melanoacanthoma) of Nipple A case report with review of literature Aparna Narasimha, Harendra Kumar ML, Divyarani MN, Bhaskaran A* Department of Pathology and
Oral Manifestations of Dermatologic Disease: A Focus on Lichenoid Lesions. Proceedings of the NASHNP Companion Meeting, March, 2011, San Antonio, TX
 1 Oral Manifestations of Dermatologic Disease: A Focus on Lichenoid Lesions Proceedings of the NASHNP Companion Meeting, March, 2011, San Antonio, TX Susan Müller, DMD, MS Professor Department of Pathology
1 Oral Manifestations of Dermatologic Disease: A Focus on Lichenoid Lesions Proceedings of the NASHNP Companion Meeting, March, 2011, San Antonio, TX Susan Müller, DMD, MS Professor Department of Pathology
EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I. A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin.
 EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin. RJ Brennan, M.D. and B. Rovatti M.D. The purpose of this study was to determine the progressive
EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin. RJ Brennan, M.D. and B. Rovatti M.D. The purpose of this study was to determine the progressive
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas
 CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
Identifying Benign and Malignant Skin Lesions. No Disclosures. Common Benign Lesions. Benign Lesions 2/25/2018. Stucco Keratoses.
 Dermatology in Primary Care Identifying Benign and Malignant Skin Lesions Christy Quire Baker, APRN, FNP-BC, DCNP Dermatology Certified Nurse Practitioner No Disclosures Common Benign Lesions Seborrheic
Dermatology in Primary Care Identifying Benign and Malignant Skin Lesions Christy Quire Baker, APRN, FNP-BC, DCNP Dermatology Certified Nurse Practitioner No Disclosures Common Benign Lesions Seborrheic
Identifying Skin Cancer. Mary S. Stone MD Professor of Dermatology and Pathology University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine March, 2018
 Identifying Skin Cancer Mary S. Stone MD Professor of Dermatology and Pathology University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine March, 2018 American Cancer Society web site Skin Cancer Melanoma Non-Melanoma
Identifying Skin Cancer Mary S. Stone MD Professor of Dermatology and Pathology University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine March, 2018 American Cancer Society web site Skin Cancer Melanoma Non-Melanoma
Clinical characteristics
 Skin Cancer Fernando Vega, MD Seattle Healing Arts Clinical characteristics Precancerous lesions Common skin cancers ACTINIC KERATOSIS Precancerous skin lesions Actinic keratoses Dysplastic melanocytic
Skin Cancer Fernando Vega, MD Seattle Healing Arts Clinical characteristics Precancerous lesions Common skin cancers ACTINIC KERATOSIS Precancerous skin lesions Actinic keratoses Dysplastic melanocytic
Glistening, Skin-Colored Nodule
 To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/436334 Medscape Dermatology Clinic Glistening, Skin-Colored Nodule
To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/436334 Medscape Dermatology Clinic Glistening, Skin-Colored Nodule
Self assessment case. Dr Saleem Taibjee Dorset County Hospital, Dorchester
 Self assessment case Dr Saleem Taibjee saleemtaibjee@gmail.com Dorset County Hospital, Dorchester Clinical details 34-year-old man: Shave excision Skin tag / papilloma left thigh The best diagnosis is:
Self assessment case Dr Saleem Taibjee saleemtaibjee@gmail.com Dorset County Hospital, Dorchester Clinical details 34-year-old man: Shave excision Skin tag / papilloma left thigh The best diagnosis is:
Multiple Primary Melanoma in a Thai Male: A Case Report
 Case Report Multiple Primary Melanoma in a Thai Male: A Case Report J Med Assoc Thai 2014; 97 (Suppl. 2): S234-S238 Full text. e-journal: http://www.jmatonline.com Kittisak Payapvipapong MD*, Pinyapat
Case Report Multiple Primary Melanoma in a Thai Male: A Case Report J Med Assoc Thai 2014; 97 (Suppl. 2): S234-S238 Full text. e-journal: http://www.jmatonline.com Kittisak Payapvipapong MD*, Pinyapat
ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY. Jonathan I. Epstein.
 1 ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY Jonathan I. Epstein Professor Pathology, Urology, Oncology The Reinhard Professor of Urological
1 ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY Jonathan I. Epstein Professor Pathology, Urology, Oncology The Reinhard Professor of Urological
Disseminated epidermolytic acanthoma probably related to trauma
 Disseminated epidermolytic acanthoma probably related to trauma I. Sánchez-Carpintero, A. España and M.A. Idoate* Departments of Dermatology and *Pathology, University Clinic of Navarra, School of Medicine,
Disseminated epidermolytic acanthoma probably related to trauma I. Sánchez-Carpintero, A. España and M.A. Idoate* Departments of Dermatology and *Pathology, University Clinic of Navarra, School of Medicine,
THYMIC CARCINOMAS AN UPDATE
 THYMIC CARCINOMAS AN UPDATE Mark R. Wick, M.D. University of Virginia Medical Center Charlottesville, VA CARCINOMA OF THE THYMUS General Clinical Features No apparent gender predilection Age range of 35-75
THYMIC CARCINOMAS AN UPDATE Mark R. Wick, M.D. University of Virginia Medical Center Charlottesville, VA CARCINOMA OF THE THYMUS General Clinical Features No apparent gender predilection Age range of 35-75
Inflammatory skin disease I Jade Wititsuwannakul, MD Chulalongkorn University, Thailand
 Inflammatory skin disease I Jade Wititsuwannakul, MD Chulalongkorn University, Thailand Superficial Perivascular Dermatitis Interface Dermatitis Vacuolar Dermatitis Lichenoid Dermatitis Barnhill Textbook
Inflammatory skin disease I Jade Wititsuwannakul, MD Chulalongkorn University, Thailand Superficial Perivascular Dermatitis Interface Dermatitis Vacuolar Dermatitis Lichenoid Dermatitis Barnhill Textbook
21/07/2017. Hobnail endothelial cells are not the same as epithelioid endothelial cells
 UPDATE IN CUTANEOUS VASCULAR S DERMATOPATHOLOGY SESSION BELFAST PATHOLOGY JUNE 21/2017 Dr E Calonje St John s Institute of Dermatology, London, United Kingdom THE FAMILY OF VASCULAR S WITH EPITHELIOID
UPDATE IN CUTANEOUS VASCULAR S DERMATOPATHOLOGY SESSION BELFAST PATHOLOGY JUNE 21/2017 Dr E Calonje St John s Institute of Dermatology, London, United Kingdom THE FAMILY OF VASCULAR S WITH EPITHELIOID
Cutaneous Adnexal Tumors
 Cutaneous Adnexal Tumors Lesions with Predominant Follicular Differentiation Special Emphasis on Basal Cell Carcinoma 2014-04-01 Prof. Dr. med. Katharina Glatz Pathologie Cutaneous Adnexal Tumors Hair
Cutaneous Adnexal Tumors Lesions with Predominant Follicular Differentiation Special Emphasis on Basal Cell Carcinoma 2014-04-01 Prof. Dr. med. Katharina Glatz Pathologie Cutaneous Adnexal Tumors Hair
Histopathological spectrum of non-infectious erythematous, papulo-squamous lesions
 Histopathological spectrum of non-infectious erythematous, papulo-squamous lesions B. Rajasekhar Reddy 1*, Nalini Krishna.M 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, Mediciti Institute of Medical
Histopathological spectrum of non-infectious erythematous, papulo-squamous lesions B. Rajasekhar Reddy 1*, Nalini Krishna.M 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Pathology, Mediciti Institute of Medical
Type IV collagen and laminin staining patterns in benign
 J Clin Pathol 1989;42:1173-1177 Type IV collagen and laminin staining patterns in benign and malignant cutaneous lesions RONA M MacKIE, D B CLELLAND, CHRISTINE J SKERROW From the Department ofdermatology,
J Clin Pathol 1989;42:1173-1177 Type IV collagen and laminin staining patterns in benign and malignant cutaneous lesions RONA M MacKIE, D B CLELLAND, CHRISTINE J SKERROW From the Department ofdermatology,
Pathology. Skin Tumor. Bayan N. Mohammad 15/10/2015. Mohammad al-orjani. Page 0 of 23
 #7 35 Pathology Skin Tumor Bayan N. Mohammad 15/10/2015 Mohammad al-orjani Page 0 of 23 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم GREETINGS This lecture is about skin tumors, all the slides are included and every slide will
#7 35 Pathology Skin Tumor Bayan N. Mohammad 15/10/2015 Mohammad al-orjani Page 0 of 23 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم GREETINGS This lecture is about skin tumors, all the slides are included and every slide will
haematoxylin and eosin, and occasionally with stains for reticulin. In most patients one section from one
 J Clin Pathol 1985;38:1273-1277 Basal cell carcinoma of the skin with areas of squamous cell carcinoma: a basosquamous cell carcinoma? J LOPES DE FARIA Department ofanatomical Pathology, Faculdade de Ciencias
J Clin Pathol 1985;38:1273-1277 Basal cell carcinoma of the skin with areas of squamous cell carcinoma: a basosquamous cell carcinoma? J LOPES DE FARIA Department ofanatomical Pathology, Faculdade de Ciencias
Assisting diagnosis of melanoma through the noninvasive biopsy of skin lesions
 Assisting diagnosis of melanoma through the noninvasive biopsy of skin lesions Symon D Oyly Cotton Ela Claridge School of Computer Science, The University of Birmingham Birmingham B15 2TT, UK Per Hall
Assisting diagnosis of melanoma through the noninvasive biopsy of skin lesions Symon D Oyly Cotton Ela Claridge School of Computer Science, The University of Birmingham Birmingham B15 2TT, UK Per Hall
MALIGNANT POROMA SYNONYM: POROCARCINOMA ECCRINE POROMA MALIGNANT Divvya B 1, M. Valluvan 2, Rehana Tippoo 3, P. Viswanathan 4, R.
 MALIGNANT POROMA SYNONYM: POROCARCINOMA ECCRINE POROMA MALIGNANT Divvya B 1, M. Valluvan 2, Rehana Tippoo 3, P. Viswanathan 4, R. Ramesh 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Divvya B, M. Valluvan, Rehana Tippoo,
MALIGNANT POROMA SYNONYM: POROCARCINOMA ECCRINE POROMA MALIGNANT Divvya B 1, M. Valluvan 2, Rehana Tippoo 3, P. Viswanathan 4, R. Ramesh 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Divvya B, M. Valluvan, Rehana Tippoo,
Actinic keratosis (AK) is the most common precancerous
 Confocal laser microscopic imaging of actinic keratoses in vivo: A preliminary report David Aghassi, MD, R. Rox Anderson, MD, and Salvador González, MD Boston, Massachusetts Background: Real-time near-infrared
Confocal laser microscopic imaging of actinic keratoses in vivo: A preliminary report David Aghassi, MD, R. Rox Anderson, MD, and Salvador González, MD Boston, Massachusetts Background: Real-time near-infrared
Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT
 Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT Two different neoplasia in the same biopsy material called
Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT Two different neoplasia in the same biopsy material called
Premalignant lesions may expose to a promoting. factor & may be induced to undergo malignant. Carcinoma in situ displays the cytologic features of
 بسم رلاهللا Def. Premalignant lesions may expose to a promoting factor & may be induced to undergo malignant transformation. Carcinoma in situ displays the cytologic features of malignancy without invasion
بسم رلاهللا Def. Premalignant lesions may expose to a promoting factor & may be induced to undergo malignant transformation. Carcinoma in situ displays the cytologic features of malignancy without invasion
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9
 Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Glenn D. Goldman, MD. University of Vermont Medical Center. University of Vermont College of Medicine
 Glenn D. Goldman, MD University of Vermont Medical Center University of Vermont College of Medicine Recognize and identify the main types of skin cancer and their precursors Identify and understand new
Glenn D. Goldman, MD University of Vermont Medical Center University of Vermont College of Medicine Recognize and identify the main types of skin cancer and their precursors Identify and understand new
Dermoscopy: Recognizing Top Five Common In- Office Diagnoses
 Dermoscopy: Recognizing Top Five Common In- Office Diagnoses Vu A. Ngo, DO Department of Family Medicine and Dermatology Choctaw Nation Health Services Authority Learning Objectives Introduction to dermoscopy
Dermoscopy: Recognizing Top Five Common In- Office Diagnoses Vu A. Ngo, DO Department of Family Medicine and Dermatology Choctaw Nation Health Services Authority Learning Objectives Introduction to dermoscopy
Regression 2/3/18. Histologically regression is characterized: melanosis fibrosis combination of both. Distribution: partial or focal!
 Regression Margaret Oliviero MSN, ARNP Harold S. Rabinovitz MD Histologically regression is characterized: melanosis fibrosis combination of both Distribution: partial or focal! Dermatoscopic terminology
Regression Margaret Oliviero MSN, ARNP Harold S. Rabinovitz MD Histologically regression is characterized: melanosis fibrosis combination of both Distribution: partial or focal! Dermatoscopic terminology
Pathology Slides. [Pathology]
![Pathology Slides. [Pathology] Pathology Slides. [Pathology]](/thumbs/94/120604575.jpg) Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Title: Dermographic, clinical and histopathological pro le of cutaneous lichen planus
 Original Research Paper Dermatology Title: Dermographic, clinical and histopathological pro le of cutaneous lichen planus Dr. Rikeeta S. Deshmukh Dr. Raju G. Chaudhary ABSTRACT KEYWORDS Introduction: Unique,
Original Research Paper Dermatology Title: Dermographic, clinical and histopathological pro le of cutaneous lichen planus Dr. Rikeeta S. Deshmukh Dr. Raju G. Chaudhary ABSTRACT KEYWORDS Introduction: Unique,
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Trichofolliculoma of the Guinea Pig 1,2
 Trichofolliculoma of the Guinea Pig 1,2 Raymond D. Ediger, Garrett S. Dill, Jr., and Robert M. Kovatch, Aerobiology and Evaluation Laboratories and Medical Sciences Laboratories, Fort Detrick, Frederick,
Trichofolliculoma of the Guinea Pig 1,2 Raymond D. Ediger, Garrett S. Dill, Jr., and Robert M. Kovatch, Aerobiology and Evaluation Laboratories and Medical Sciences Laboratories, Fort Detrick, Frederick,
Squamous papilloma Squamous acanthoma Keratoacanthoma Verruca vulgaris Condyloma acuminatum Focal epithelial hyperplasia Sino nasal papilloma
 Benign tumors Epithelial origin Squamous papilloma Squamous acanthoma Keratoacanthoma Verruca vulgaris Condyloma acuminatum Focal epithelial hyperplasia Sino nasal papilloma Squamous papilloma Exophytic
Benign tumors Epithelial origin Squamous papilloma Squamous acanthoma Keratoacanthoma Verruca vulgaris Condyloma acuminatum Focal epithelial hyperplasia Sino nasal papilloma Squamous papilloma Exophytic
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast. Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London
 Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
