Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
|
|
|
- Maximilian Conley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Renal Quiz - June 22, The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) The extracellular volume of a 40 kg patient is about a) 3.2 liters b) 8 liters c) 16 liters d) 24 liters 3. Ingestion of 2 liters of hypertonic NaCl would do which of the following'? a) Increase intracellular volume b) Decrease intracellular osmolarity c) Increase extracellular volume d) Decrease extracellular osmolarity. 4. Which Starling pressure is physiologically controlled to regulate glomerular filtration rate. a) Plasma colloid osmotic pressure b) Glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure c) Proximal tubule hydrostatic pressure d) Tubular fluid colloid osmotic pressure 5. The osmolarity of tubular fluid at the end of the proximal tubule is a) the same as plasma b) less than plasma c) greater than plasma d) the same as urine
2 6. Your patient has a 24 hour urine output of 2 liters and the urine concentration of creatinine 100 mg%. What is the glomerular filtration rate if the plasma concentration of creatinine is 4 mg%? a) 40 liters/day b) 50 liters /day c) 100 liters/day d) 180 liters/day 7. Normally the proximal tubule reabsorbs a) about 2/3 of the filtered glucose b) about 2/3 of the filtered bicarbonate c) about 2/3 of the filtered sodium d) about 2/3 of the filtered amino acids 8. Aquaporins are located in the luminal membrane of all of the following nephron segments EXCEPT: a) The proximal tubule. b) The thin descending limb of the loop of Henle. c) The thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. d) The collecting tubule in the presence of ADH. 9. Which one of the following statements is INCORRECT'? a) Countercurrent multiplication occurs in the loop of Henle. b) Loop diuretics will inhibit the countercurrent multiplication process. c) Urea reabsorption occurs along the entire collecting tubule system. d) Increases in plasma osmolality as well as decreases in plasma volume can stimulate ADH secretion. 10. Which one of the following statements is INCORRECT? a) Atrial natriuretic peptide increases glomerular filtration rate. b) An increase in renal sympathetic nervous system activity will increase renin release. c) Aldosterone increases Na' reabsorption in the cortical collecting tubule. d) Conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II is the rate-limiting step in the renin-angiotensinaldosterone system.
3 Renal Quiz The rate limiting step in the generation of anglotensin II is the a) rate of renin secretion by the kidney b) amount of substrate made by the liver c) concentration of angiotensinases in the blood d) activity of converting enzymes in the lung 2. The starling pressure most responsible for the formation of edema in congestive heart failure is a) increased interstitial hydrostatic pressure b) decreased plasma colloid osmotic pressure c) increased capillary hydrostatic pressure d) decreased interstitial colloid osmotic pressure 3. A 50 kilogram patient probably has a total body water of a) 10 liters b) 20 liters c) 30 liters d) 50 liters 4. The most potent stimulus for the release of aldosterone by the adrenal gland is a) increased angiotensin II b) decreased plasma potassium concentration c) increased plasma sodium concentration d) decreased adrenocorticotropic hormone 5. Which of the following is NOT an action of angiotensin II? a) increased arteriolar constriction b) increased venous tone c) increased aldosterone secretion by the adrenal gland d) increased collecting duct permeability to water
4 Renal Antidiuretic Hormone release from the pituitary is stimulated by a) increased plasma osmolarity b) increased blood volume c) decreased angiotensin II d) decreased plasma sodium concentration 7. Pressure natriuresis refers to the observation that a) increased sodium in the blood increases blood pressure b) decreased blood pressure increases renin release by the kidney c) increased blood pressure increases sodium excretion d) increased angiotensin II increases blood pressure 8. The most important renal action of aldosterone is to a) increase collecting duct permeability to water b) increase glomerular filtration rate c) increase renal renin release d) increase renal tubular sodium reabsorption 9. The physiologic variable which is controlled to regulate glomerular filtration rate is a) plasma colloid pressure b) glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure c) bowman's space hydrostatic pressure d) tubular colloid osmotic pressure 10. The normal mechanism by which the kidney regulates sodium excretion is by a) altering the filtered amount of sodium b) altering proximal tubule reabsorption of sodium c) altering distal nephron reabsorption of sodium d) altering the collecting duct reabsorption of urea.
5 Renal Quiz - June 25, The rate limiting step in the formation of anglotensin II is a) the amount of angiotensinase in the blood b) the rate of renin substrate (angiotensinogen) release by the liver c) the amount of converting enzvme in the lungs d) the rate of renin release by the kidney 2. Ingestion of salt tablets without water will decrease which of the following volumes a) plasma volume b) interstitial volume c) extracellular volume d) intracellular volume 3. The variable most responsible for physiologically regulating glomerular filtration rate is a) pressure in Bowman's space b) plasma colloid osmotic pressure c) glomerular capillary pressure d) efferent arteriole resistance 4. The mechanism of edema formation in congestive heart failure is a) decreased blood pressure - b) decreased colloid osmotic pressure c) increased capillary pressure d) decreased intersitital pressure 5. Severely diminished renal function (as in the clinical case) results in loss of the ability to regulate a) water balance b) potassium balance c) calcium balance d) acid /base balance e) all of the above 6. The concentration of creatinine at the end of the proximal tubule is a) greater than plasma concentration of creatinine b) less than plasma concentration of creatinine c) the same as the plasma concentration of creatinine d) less than the urine concentration of creatinine
6 7. A patient with a high circulating ADH concentration would have a a) high urine output and a high urine concentration b) high urine output and a low urine concentration c) low urine output and a high urine concentration d) low urine output and a low urine concentration 8. Aldosterone act on the kidney to a) increase water reabsorption in the collecting duct b) increase the conversation of CO 2 + H 2 O to H + HC0 3 in the proximal tubule c) constrict the afferent arteriole d) increase the reabsorption of sodium in the collecting tubule 9. The greatest amount of the filtered sodium is reabsorbed in a) the proximal tubule b) the ascending loop of Henle c) the distal tubule d) the collecting tubule 10. Atrial natriuretic peptide is released by a) atrial myocytes b) the adrenal gland c) the juxtaglomerular apparatus d) the pituitary
7 Renal Quiz Reabsorption of water occurs in all of the following nephron segments except: a) The proximal tubule. b) The thin descending limb of the loop of Henle. c) The thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. d) The collecting tubule during antidiuresis. 2. Select the one INCORRECT statement: a) Countercurrent exchange occurs in the vasa recta. b) Loop diuretics will inhibit the countercurrent multiplication process. c) The cortical collecting tubule is highly permeable to urea. d) Both increased plasma osmolality and decreased plasma volume can stimulate ADH secretion. 3. Which one of the following statements is INCORRECT? a) The effect of antidiuretic hormone has a faster onset time than the effect of aldosterone. b) The stimulatory effect of aldosterone on both Na + reabsorption and K + secretion is due in part to increased Na+-K+-ATPase activity. c) Aldosterone can regulate the reabsorption of up to 50% of the filtered toad of Na +. d) ADH secretion is primarily regulated via hypothalamic osmoreceptors. 4. Select the one INCORRECT statement: a) Atrial natriuretic peptide decreases glomerular filtration rate. b) A decrease in afferent arteriolar pressure will increase renin release. c) Aldosterone increases Na+ reabsorption in the cortical collecting tubule. d) Angiotensin II can increase ADH release. 5. The proximal tubule reabsorbs all of the following EXCEPT a) water b) sodium c) creatinine d) glucose 6. The path of blood flow through the kidney is a) afferent arteriole -> glomerular capillary -> efferent arteriole -> peritubular capillary b) glomerular capillary -> efferent arteriole -> peritubular capillary -> afferent arteriole c) efferent arteriole -> peritubular capillary -> afferent arteriole -> glomerular capillary d) peritubular arteriole -> afferent capillary -> glomerular arteriole -> efferent capillary
8 7. The path of fluid flow through the kidney is a) loop of Henle -> distal. tubule -> collecting duct -> glomerular capillary -> proximal tubule b) proximal tubule -> loop of Henle -> distal tubule -> collecting duct -> glomerular capillary c) glomerular capillary -> proximal tubule -> loop of Henle -> distal tubule -> collecting duct d) collecting duct -> glomerular capillary -> proximal tubule -> loop of Henle -> distal tubule 8. You have a bottle of unknown volume. Ott wants you to determine the volume of the fluid in the bottle. If you put 6 grams of substance X in the bottle and measure the concentration of substance X, after you shake the bottle up, you find that it is 2 gm/l. What is the volume of fluid in the bottle? a) 2 liters b) 3 liters c) 6 liters d) 12 liters 9. According to the tubuloglomerular feedback theory of renal autoregulation, an increase in NaCl delivery to the macula densa should a) increase blood flow and increase glomerular filtration rate b) decrease blood flow and decrease glomerular filtration rate c) increase the ultrafiltration coefficient d) increase proximal reabsorption 10. Your patient has the following laboratory values Plasma creatinine concentration 1.0 mg% Urine creatinine concentration 60.0 mg% Urine flow rate 1.5 ml/min The calculated glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is a) 1 ml/min b) 15 ml/min c) 60 ml/min d) 90 ml/min
9 Renal Creatinine can be used to measure glomerular filtration rate because a) it is secreted by the kidney b) is reabsorbed by the kidney c) it is filtered and not reabsorbed d) it is metabolized by the muscles 2. Albumin does not cross the glomerular capillaries to any large extent because a) it is too big b) it has a negative charge c) the kidney reabsorbs filtered protein d) albumin is made in the liver 3. The kidney filters fluid along the entire length of the glomerular capillary because a) the hydrostatic pressure always exceeds the colloid osmotic pressure b) the colloid osmotic pressure always exceeds the hydrostatic pressure c) the blood flow is high d) Bowman's Space pressure is high 4. PAH can be used to measure renal plasma flow because a) it is actively secreted b) the clearance of PAH is equal to renal plasma flow c) PAH is bound to plasma proteins d) PAH is metabolized by the kidney 5. Use the following data to calculate glomerular filtration rate Plasma Creatinine = 2 mg%; Urine Flow = I ml/min; Urine Creatinine = 120 mg% a) 10 ml/min b) 20 ml/min c) 60 ml/min d) 120 ml/min
10 Renal Input signals to the juxtaglomerular segment of the kidney can come from a) the renal nerves b) blood pressure c) the macula densa d) all of the above 7. Reabsorption refers to a) movement of solute from the glomerulus to bowman's space b) novement of solute from tubule lumen to peritubular capillary c) movement of solute from peritubule capillary to tubule lumen d) loss of solute in the urine 8. Your patient has the following laboratory values Plasma creatinine concentration 1.0 mg% Urine creatinine concentration 60.0 mg% Urine flow rate 1.5 ml/min The calculated glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is a) 1 ml/min b) 15 ml/min c) 60 ml/min d) 90ml/min 9. You have a bottle of unknown volume. The mad Dr. Ott wants you to determine the volume of the fluid in the bottle. If you put 6 grams of substance X in the bottle and measure the concentration of substance X, after you shake the bottle up, you find that it is 2 gm/l. What is the volume of fluid in the bottle? a) 2 liters b) 3 liters c) 6 liters d) 12 liters 10. The osmolality of fluid at the end of the proximal tubule is a) the same as plasma b) greater than plasma c) less than plasma d) the same as urine
11 1. The path of blood flow through the kidney is PGY st Renal Quiz May 28, 1996 a) afferent arteriole -> glomerular capillary -> efferent arterlole -> peritubular capillary b) glomerular capillary -> efferent arteriole -> peritubular capillary -> afferent arteriole c) efferent arteriole -> peritubular capillary -> afferent arteriole -> glomerular capillary d) peritubular capillary -> afferent arteriole -> glomerular capillary -> efferent arteriole 2. The path of fluid flow through the kidney is a) loop of Henle -> distal tubule -> collecting duct -> glomerular capillary -> proximal tubule b) proximal tubule -> loop of Henle -> distal tubule -> collecting duct -> glomerular capillary c) glomerular capillary -> proximal tubule -> loop of Henle -> distal tubule -> collecting duct d) collecting duct -> glomerular capillary -> proximal tubule -> loop of Henle -> distal tubule 3. According to the tubuloglomerular feedback theory of renal autoregulation, an increase in solute delivery to the macula densa should a) increase blood flow and increase glomerular filtration rate b) decrease blood flow and decrease glomerular filtration rate c) increase the ultrafiltration coefficient d) increase proximal reabsorption 4. Infusion of 2 liters of a hypertonic solution such as 1500 mosm/l of saline should a) increase extracellular volume and increase intracellular volume b) increase extracellular volume and decrease intracellular volume c) decrease extracellular volume and decrease intracellular volume d) decrease extracellular volume and increase intracellular volume 5. In the proximal tubule Sodium is co-transported with a) glucose b) phosphate c) amino acids d) all of the above
12 PGY 818 2nd Renal Quiz May 31, The action of aldosterone on the renal tubule cell is to a) increase the permeability to sodium b) decrease hydrogen secretion c) increase the permeability to potassium d) both A and C 2. The rate limiting step in the formation of angiotensin II is a) the amount of angiotensinogen in the plasma b) the amount of converting enzyme in the lung c) the amount of antidiuretic hormone in the plasma d) the amount of renin secreted by the kidney 3. Which of the following is the most potent stimulator of aldosterone secretion by the Adrenal? a) increased plasma angiotensin II b) increased plasma potassium c) increased plasma sodium d) decreased adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) 4. A long term pathologic increase in aldosterone secretion by the adrenal can lead to a) increased plasma sodium concentration b) increased plasma potassium concentration c) increased blood pressure d) increased plasma hydrogen concentration 5. Two weeks after going from a low sodium intake to a high sodium intake a) plasma sodium concentration is increased b) plasma anglotensin II concentration is increased c) plasma volume is increased d) plasma osmolality is increased 6. On a constant sodium intake the continued use of a diuretic will increase sodium excretion a) True b) False
13 7. In addition to stimulating aldosterone secretion by the adrenal gland angiotensin II can also a) increase blood pressure by constricting systemic arterioles b) decrease proximal tubule reabsorption c) increase cardiac output by increasing venous tone d) both A and C 8. If the kidney was perfect (it isn't but sometimes it is kind of amazing) and glomerular tubular balance was perfect an increase in the filtered load would lead to a) increased transport and decreased excretion b) decreased transport and increased excretion c) increased transport and increased excretion d) decreased transport and decreased excretion 9. Effective circulating volume is the volume of blood a) in the veins b) in the arteries c) in the extracellular space d) necessary for adequate perfusion of the tissues 10. The kidney attempts to monitor effective circulating volume by a) listening to the sympathetic nervous system b) measuring pressure at the afferent arteriole c) looking at solute delivery at the macula densa d) all of the above
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin
![KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin](/thumbs/87/96174332.jpg) Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Physio 12 -Summer 02 - Renal Physiology - Page 1
 Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Physiology Unit 4
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure
 Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Urinary Physiology. Chapter 17 Outline. Kidney Function. Chapter 17
 Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System. Chapter 50
 Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Kidney and urine formation
 Kidney and urine formation Renal structure & function Urine formation Urinary y concentration and dilution Regulation of urine formation 1 Kidney and urine formation 1.Renal structure & function 1)General
Kidney and urine formation Renal structure & function Urine formation Urinary y concentration and dilution Regulation of urine formation 1 Kidney and urine formation 1.Renal structure & function 1)General
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Problem Set #8 Solutions p. 1 1. a. Proximal tubule. b. Proximal tubule. c. Glomerular endothelial fenestrae, filtration slits between podocytes of Bowman's capsule.
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX
 One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
Physiology Lecture 2. What controls GFR?
 Physiology Lecture 2 Too much blood is received by the glomerular capillaries, this blood contains plasma, once this plasma enters the glomerular capillaries it will be filtered to bowman s space. The
Physiology Lecture 2 Too much blood is received by the glomerular capillaries, this blood contains plasma, once this plasma enters the glomerular capillaries it will be filtered to bowman s space. The
Renal-Related Questions
 Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6
 BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
** TMP mean page 340 in 12 th edition. Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2:
 QUESTION Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2: Urine flow rate = 1 ml/min Urine inulin concentration = 100 mg/ml Plasma inulin concentration = 2 mg/ml
QUESTION Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2: Urine flow rate = 1 ml/min Urine inulin concentration = 100 mg/ml Plasma inulin concentration = 2 mg/ml
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume. Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM
 Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
Renal Regulation of Sodium and Volume Dr. Dave Johnson Associate Professor Dept. Physiology UNECOM Maintaining Volume Plasma water and sodium (Na + ) are regulated independently - you are already familiar
Chapter 25 The Urinary System
 Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
Urine Formation. Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages Urine Formation. Glomerular Filtration 4/24/2016
 Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Nephron Anatomy Nephron Anatomy
 Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Lecture 16: The Nephron
 Lecture 16: The Nephron Reading: OpenStax A&P Text Chapter 25 Primary functions of the kidneys 1. Regulating osmolarity (blood concentration!) A. Regulating blood pressure B. Maintaining ion balance C.
Lecture 16: The Nephron Reading: OpenStax A&P Text Chapter 25 Primary functions of the kidneys 1. Regulating osmolarity (blood concentration!) A. Regulating blood pressure B. Maintaining ion balance C.
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Urinary System. consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
 Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Counter-Current System Regulation of Renal Functions
 Counter-Current System Regulation of Renal Functions Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most
Counter-Current System Regulation of Renal Functions Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most
Osmoregulation and Renal Function
 1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.44 - OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
!! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
1.&Glomerular/Pressure&Filtration&
 Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
 Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY
 MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY REGULATION OF BODY FLUID VOLUME REGULATION OF OSMOTIC BALANCE REGULATION OF ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE ERYTHROPOIESIS
MAJOR FUNCTIONS OF THE KIDNEY REGULATION OF BODY FLUID VOLUME REGULATION OF OSMOTIC BALANCE REGULATION OF ELECTROLYTE COMPOSITION REGULATION OF ACID-BASE BALANCE REGULATION OF BLOOD PRESSURE ERYTHROPOIESIS
Kidney Structure. Renal Lobe = renal pyramid & overlying cortex. Renal Lobule = medullary ray & surrounding cortical labryinth.
 Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Functions of the kidney
 Physiology of Urinary tract Kidney, Ureter, Urinary bladder Urethra Kidney function Excretion Physiology of volume regulation Functions of the kidney Excretion of dangerous substances endogenous (metabolites):
Physiology of Urinary tract Kidney, Ureter, Urinary bladder Urethra Kidney function Excretion Physiology of volume regulation Functions of the kidney Excretion of dangerous substances endogenous (metabolites):
Renal Physiology Part II. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste:
 I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste: a) Carbon Dioxide: by-product of cellular respiration. b) Water: by-product of cellular respiration & dehydration synthesis reactions. c) Inorganic Salts: by-product
I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste: a) Carbon Dioxide: by-product of cellular respiration. b) Water: by-product of cellular respiration & dehydration synthesis reactions. c) Inorganic Salts: by-product
The kidneys are excretory and regulatory organs. By
 exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
exercise 9 Renal System Physiology Objectives 1. To define nephron, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, afferent arteriole, glomerular filtration, efferent arteriole, aldosterone, ADH, and reabsorption 2. To
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Excretion Chapter 29. The Mammalian Excretory System consists of. The Kidney. The Nephron: the basic unit of the kidney.
 Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
URINARY SYSTEM. Primary functions. Major organs & structures
 URINARY SYSTEM Primary functions Excretion of metabolic wastes Regulation of water and ion balances Regulation of blood pressure Vitamin D activation Regulation of rbc s (erythropoietin) Gluconeogenesis
URINARY SYSTEM Primary functions Excretion of metabolic wastes Regulation of water and ion balances Regulation of blood pressure Vitamin D activation Regulation of rbc s (erythropoietin) Gluconeogenesis
mid ihsan (Physiology ) GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B **
 (Physiology ) mid ihsan GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B ** Colloid pressure in the efferent arteriole is: A- More than that leaving
(Physiology ) mid ihsan GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B ** Colloid pressure in the efferent arteriole is: A- More than that leaving
Functional morphology of kidneys Clearance
 Functional morphology of kidneys Clearance Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most important
Functional morphology of kidneys Clearance Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most important
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal Physiology II Tubular functions
 Renal Physiology II Tubular functions LO. 42, 43 Dr. Kékesi Gabriella Basic points of renal physiology 1. Glomerular filtration (GF) a) Ultrafiltration 2. Tubular functions active and passive a) Reabsorption
Renal Physiology II Tubular functions LO. 42, 43 Dr. Kékesi Gabriella Basic points of renal physiology 1. Glomerular filtration (GF) a) Ultrafiltration 2. Tubular functions active and passive a) Reabsorption
Chapter 26 The Urinary System
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder & urethra Urine flows from each kidney, down its ureter to the bladder and to the outside via the urethra Filter the blood and return most
Excretory System-Training Handout
 Excretory System-Training Handout Karen L. Lancour National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science Excretion - Excretion is the removal of the metabolic wastes of an organism. Wastes that are removed include
Excretory System-Training Handout Karen L. Lancour National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science Excretion - Excretion is the removal of the metabolic wastes of an organism. Wastes that are removed include
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 19-1c. Efferent arteriole. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
 /6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
/6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 1. In the diagram above, pressure filtration occurs in a. W b. X c. Y d. Z
 Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
Renal physiology D.HAMMOUDI.MD
 Renal physiology D.HAMMOUDI.MD Functions Regulating blood ionic composition Regulating blood ph Regulating blood volume Regulating blood pressure Produce calcitrol and erythropoietin Regulating blood glucose
Renal physiology D.HAMMOUDI.MD Functions Regulating blood ionic composition Regulating blood ph Regulating blood volume Regulating blood pressure Produce calcitrol and erythropoietin Regulating blood glucose
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D.
 RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System)
 NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
Fal Fal P h y s i o l o g y 6 1 1, S a n F r a n c i s c o S t a t e U n i v e r s i t y
 Fall 12 OSMOTIC REGULATION OF THE RENAL SYSTEM: Effects of fasting and ingestion of water, coke, or Gatorade on urine flow rate and specific gravity Dorette Franks The purpose of the physiology experiment
Fall 12 OSMOTIC REGULATION OF THE RENAL SYSTEM: Effects of fasting and ingestion of water, coke, or Gatorade on urine flow rate and specific gravity Dorette Franks The purpose of the physiology experiment
osmoregulation mechanisms in gills, salt glands, and kidneys
 Ionic & Osmotic Homeostasis osmoregulation mechanisms in gills, salt glands, and kidneys extracellular intracellular 22 23 Salt Secretion: recycle Figure in Box 26.2 Hill et al. 2004 active Down electrochemical
Ionic & Osmotic Homeostasis osmoregulation mechanisms in gills, salt glands, and kidneys extracellular intracellular 22 23 Salt Secretion: recycle Figure in Box 26.2 Hill et al. 2004 active Down electrochemical
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp , Chapter 19: pp ,
 P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
Hill et al. 2004, Fig. 27.6
 Lecture 25, 15 November 2005 Osmoregulation (Chapters 25-28) Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 1. Osmoregulation 2. Kidney Function Text: Chapters
Lecture 25, 15 November 2005 Osmoregulation (Chapters 25-28) Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 1. Osmoregulation 2. Kidney Function Text: Chapters
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Chapter 17. Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes.
 Chapter 17 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 17 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Identify and describe. mechanism involved in Glucose reabsorption
 Define tubular reabsorption, tubular secretion, transcellular and paracellular transport. Identify and describe mechanism involved in Glucose reabsorption Describe tubular secretion with PAH transport
Define tubular reabsorption, tubular secretion, transcellular and paracellular transport. Identify and describe mechanism involved in Glucose reabsorption Describe tubular secretion with PAH transport
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION
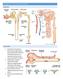 LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
BODY FLUID. Outline. Functions of body fluid Water distribution in the body Maintenance of body fluid. Regulation of fluid homeostasis
 BODY FLUID Nutritional Biochemistry Yue-Hwa Chen Dec 13, 2007 Chen 1 Outline Functions of body fluid Water distribution in the body Maintenance of body fluid Intake vs output Regulation of body fluid Fluid
BODY FLUID Nutritional Biochemistry Yue-Hwa Chen Dec 13, 2007 Chen 1 Outline Functions of body fluid Water distribution in the body Maintenance of body fluid Intake vs output Regulation of body fluid Fluid
Excretory System 1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance
 Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance Three Compartment Fluid Compartments Intracellular = Cytoplasmic (inside cells) Extracellular compartment is subdivided into Interstitial = Intercellular +
Regulation of fluid and electrolytes balance Three Compartment Fluid Compartments Intracellular = Cytoplasmic (inside cells) Extracellular compartment is subdivided into Interstitial = Intercellular +
Regulating the Internal Environment. AP Biology
 Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to external
Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to external
Physiology (4) 2/4/2018. Wael abu-anzeh
 Physiology (4) 2/4/2018 Wael abu-anzeh In the previous lectures we have discussed the filtration and the reabsorption processes but in this lecture we will talk about the factor that will regulate or control
Physiology (4) 2/4/2018 Wael abu-anzeh In the previous lectures we have discussed the filtration and the reabsorption processes but in this lecture we will talk about the factor that will regulate or control
Waste Products & Kidney Function
 Waste Products & Kidney Function urinary system principal means of metabolic waste removal urinary system is closely associated with reproductive system urogenital system share embryonic development share
Waste Products & Kidney Function urinary system principal means of metabolic waste removal urinary system is closely associated with reproductive system urogenital system share embryonic development share
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The terminology applied to single nephron function, including the meaning of TF/P
Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The terminology applied to single nephron function, including the meaning of TF/P
Fluid and electrolyte balance, imbalance
 Fluid and electrolyte balance, imbalance Body fluid The fluids are distributed throughout the body in various compartments. Body fluid is composed primarily of water Water is the solvent in which all solutes
Fluid and electrolyte balance, imbalance Body fluid The fluids are distributed throughout the body in various compartments. Body fluid is composed primarily of water Water is the solvent in which all solutes
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Basic Functions of the Kidneys
 Dr. Adelina Vlad Basic Functions of the Kidneys Eliminate plasma METABOLIC WASTE PRODUCTS and FOREIGN COMPOUNDS The kidney are the primary means for eliminating metabolic waste products (urea, creatinine,
Dr. Adelina Vlad Basic Functions of the Kidneys Eliminate plasma METABOLIC WASTE PRODUCTS and FOREIGN COMPOUNDS The kidney are the primary means for eliminating metabolic waste products (urea, creatinine,
The Urinary System. Jim Swan
 The Urinary System Jim Swan These slides are from class presentations, reformatted for static viewing. The content contained in these pages is also in the Class Notes pages in a narrative format. Best
The Urinary System Jim Swan These slides are from class presentations, reformatted for static viewing. The content contained in these pages is also in the Class Notes pages in a narrative format. Best
By: Dr. Foadoddini Department of Physiology & Pharmacology Birjand University of Medical Sciences. Body fluids and.
 By: Dr. Foadoddini Department of Physiology & Pharmacology Birjand University of Medical Sciences Body fluids and Renal physiology 25 Volume and Osmolality of Extracellular and Intracellular Fluids
By: Dr. Foadoddini Department of Physiology & Pharmacology Birjand University of Medical Sciences Body fluids and Renal physiology 25 Volume and Osmolality of Extracellular and Intracellular Fluids
1. remove: waste products: urea, creatinine, and uric acid foreign chemicals: drugs, water soluble vitamins, and food additives, etc.
 Making Water! OR is it really Just Water Just Ask the Nephron!! Author: Patricia L. Ostlund ostlundp@faytechcc.edu (910) 678-9892 Fayetteville Technical Community College Fayetteville, NC 28303 Its just
Making Water! OR is it really Just Water Just Ask the Nephron!! Author: Patricia L. Ostlund ostlundp@faytechcc.edu (910) 678-9892 Fayetteville Technical Community College Fayetteville, NC 28303 Its just
PHGY210 Renal Physiology
 PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
Physiology (6) 2/4/2018. Rahmeh Alsukkar
 Physiology (6) 2/4/2018 Rahmeh Alsukkar **unfortunately the sheet does not involve the slides. ** the doctor repeat a lot of things from the previous lecture so this sheet will begin from slide 139 to
Physiology (6) 2/4/2018 Rahmeh Alsukkar **unfortunately the sheet does not involve the slides. ** the doctor repeat a lot of things from the previous lecture so this sheet will begin from slide 139 to
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
November 30, 2016 & URINE FORMATION
 & URINE FORMATION REVIEW! Urinary/Renal System 200 litres of blood are filtered daily by the kidneys Usable material: reabsorbed back into blood Waste: drained into the bladder away from the heart to the
& URINE FORMATION REVIEW! Urinary/Renal System 200 litres of blood are filtered daily by the kidneys Usable material: reabsorbed back into blood Waste: drained into the bladder away from the heart to the
Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Why body sodium content determines ECF volume and the relationships
Regulation of Body Fluids: Na + and Water Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. Why body sodium content determines ECF volume and the relationships
Fluids and electrolytes
 Body Water Content Fluids and electrolytes Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; healthy females
Body Water Content Fluids and electrolytes Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; healthy females
RENAL. 6. Renal acid secretion is affected by all of the following except a. pco 2 b. K c. Carbonic anhydrase d. Aldosterone e. Ca
 RENAL 1. The reabsorption of Na in the proximal tubules a. Reabsorbs 80% of the filtered sodium load b. Causes increased hypertonicity c. Is powered by N/H ATPase d. Shares a common carrier with glucose
RENAL 1. The reabsorption of Na in the proximal tubules a. Reabsorbs 80% of the filtered sodium load b. Causes increased hypertonicity c. Is powered by N/H ATPase d. Shares a common carrier with glucose
Ch. 44 Regulating the Internal Environment
 Ch. 44 Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform
Ch. 44 Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform
Answers and Explanations
 Answers and Explanations 1. The answer is D [V B 4 b]. Distal K + secretion is decreased by factors that decrease the driving force for passive diffusion of K + across the luminal membrane. Because spironolactone
Answers and Explanations 1. The answer is D [V B 4 b]. Distal K + secretion is decreased by factors that decrease the driving force for passive diffusion of K + across the luminal membrane. Because spironolactone
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19](/thumbs/77/74887026.jpg) QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion,
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion,
Introduction to the kidney: regulation of sodium & glucose. Dr Nick Ashton Senior Lecturer in Renal Physiology Faculty of Biology, Medicine & Health
 Introduction to the kidney: regulation of sodium & glucose Dr Nick Ashton Senior Lecturer in Renal Physiology Faculty of Biology, Medicine & Health Objectives Overview of kidney structure & function Glomerular
Introduction to the kidney: regulation of sodium & glucose Dr Nick Ashton Senior Lecturer in Renal Physiology Faculty of Biology, Medicine & Health Objectives Overview of kidney structure & function Glomerular
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19](/thumbs/80/80449526.jpg) 1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion, excretion
1 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion, excretion
