Endocrine System. no clear distinction between nervous and endocrine systems. 2. most, if not all, organs produce hormones. =neuroendocrine system
|
|
|
- Silvia Foster
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Endocrine System no clear distinction between nervous and endocrine systems =neuroendocrine system they are intimately interrelated! complement each other! two ends of a single spectrum The Neuroendocrine System Nervous System Endocrine System localized effects: cell to cell widespread effects: throughout body targets: neurons, muscle cells or glands targets: all organs and tissues transmission by nerve impulses transmission as hormone through blood uses chemical signals only cell to cell uses only chemical signals immediate response (ms to seconds) gradual response (seconds to hours) short lived (ms to minutes) longer lived (minutes to days) Both both involved in coordination & control both produce biologically active chemicals some parts of brain are glands/some glands are nervous tissue some responses begin as nervous reflex and end as hormonal responses General Characteristics of Hormones 1. a chemical is considered a hormone if it is secreted and transported in the blood same chemical can also be a neurotransmitter, or lymphokine, etc the major hormones are secreted from ductless glands directly into blood Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, (exocrine vs endocrine glands) all major endocrine glands are richly supplied with blood capillaries 2. most, if not all, organs produce hormones officially the endocrine system consists of several major glands and many minor glands 3. Hormones are secreted in response to specific stimuli 3 mechanisms: neural, humoral, hormonal A. Humoral hormones secreted in direct response to changing blood levels of certain chemicals in blood affect endocrine gland directly B. Neural hormones secreted due to direct nervous stimulation C. Hormonal Anterior Pituitary = master gland secretes several hormones that control the secretion of other endocrine glands! Tropic Hormones 4. Many endocrine glands secrete more than one hormone hormones can be secreted independently of one another Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, hormone effects are highly specific to target organ! requires specific binding site (receptor proteins) even though every hormone comes in contact with every cell receptor can be on the surface of the target cell or inside the target cell target cells respond only to specific hormones 6. At the cellular level each hormone can affect a target cell in only a few ways: a. can change in cell membrane permeability eg. change in secretory activity of a cell b. can alter metabolic pathway(s) eg. enzymes activated or inactivated! make new products! cease making product! synergistic effects = presence of 1 enhances effects of other! antagonistic effects = 1 counteracts effects of other! permissive effects = one hormone primes target organ for another hormone; 8. Hormones don t accumulate in blood those that bind to target cells are destroyed! half-life ~ seconds 30 minutes excess are continually cleared by liver and kidney therefore for prolonged effect! hormones must be continuously secreted c. can change rate of cell division eg. speed up or slow down Maybe different effects in different target cells for same hormone 7. Most cells have receptors for more than one type of hormone hormones can interact with each other Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser,
2 Major Endocrine Glands Pituitary Gland (=Hypophysis) small but extremely important structure attached to a stalk (infindibulum) at base of hypothalamus housed in sella turcica of sphenoid bone consists of two separate glands Anterior Pituitary Gland master gland secretes tropic (or trophic) hormones: a. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)! stim development and secretions from thyroid gland b. Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)! normal growth and development of adrenal cortex c. Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, ! in women: stimulates follicles to begin growing to ovulation! in men: stimulates development of seminiferous tubules and sperm cells d. Leutinizing Hormone (LH)! in women: final maturation of follicle stimulates formation of corpus luteum [a temorary endocrine gland of pregnancy] promotes secretion of progesterone! in men: stimulates interstitial cells to secrete hormone = testosterone if pituitary gland is removed by radiation or surgery, need hormone treatment rest of life or some other glands will shut down in addition to tropic hormones, Ant Pit also secretes some other (nontropic) hormones: e. Growth Hormone (GH) promotes growth of bone and soft tissue Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, ! stim protein synthesis amt of GH secreted decreases with age HYPERSECRETION of GH during childhood! gigantism during adulthood! acromegaly enlargement esp of bones of hands, feet, jaws and cheeks HYPOSECRETION of GH during childhood! dwarfism f. Prolactin (PRL; = Lactogenic Hormone) affects female:! induces breast development during pregnancy! initiates milk secretion after childbirth prl release is stimulated by suckling no significant functions in males Posterior Pituitary Gland hormones released by direct nervous stimulation of posterior pituitary a. Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH, =vasopressin) (=against production of urea) ADH is released whenever receptors indicated dehydration b. Oxytocin ie. decreases urine output conserves water (=swift childbirth) stimulates contraction of uterine muscles during labor causes milk ejection into ducts as result of nursing infant [let down reflex] triggered by neural stimulus: suckling functions in societal memory : affects ability to recognize & trust others [deficiency may be correlated with autism] Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser,
3 Pineal Gland located behind the midbrain and 3 rd ventricle attached to roof of third ventricle not sure of all its functions in humans but seems to regulate cyclic activities Rene Descartes ( ) thought it was the seat of the human soul is light sensitive! monitors photoperiod a. Melatonin main hormone it secretes is melatonin light suppresses production dark stimulates production!secretion rises at night, fluctuates seasonally and with changing day length Thymus a temporary endocrine gland behind sternum, below thyroid large in fetus and child maximum size at puberty degenerates in adult (replaced with fat) functions as endocrine gland and as part of immune system secretes thymosin and related hormones! stimulates development of lymphatic organs! induces maturation and development of WBC s particularly T-lymphocytes in lower animals it helps regulate cyclic activities: hibernation estrous migration In humans:! may help regulate menstrual cycle! inhibits onset of puberty in males may be related to seasonal affective disorder and PMS Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, Thyroid Gland the largest endocrine gland in adults surrounds trachea just below larynx consists of 2 lobes!usually described as butterfly shaped Hormones: a. Thyroid Hormones (T3, T4) activated by TSH from Ant Pit contain Iodine atoms 98% of body s Iodine is in the thyroid gland inadequate iodine in diet! goiter thyroid hormones help to regulate metabolism in all cells:! increases metabolic rate & ATP production! increase oxygen consumption and bld O 2 levels! promotes maturation and development of the nervous system! increases protein synthesis!help maintain normal reproductive function many environmental stimuli can inhibit secretions of this gland: cold temp, physical stressors, noxious stimuli Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, HYPERSECRETION of Thyroid Hormones!Graves disease up to 30% increase in Metabolic Rate! appetite weight loss nervous irritability HYPOSECRETION of Thyroid Hormones During growing years! cretinism low metabolic rate retarded growth and sexual devel often mentally retarded b. Calcitonin As adult! Myxedema loss of mental and physical vigor weight gain thickened skin decreases blood Ca ++ / promote bone deposition by inhibiting osteoclasts stimulating osteoblasts its effects are significant only in children, negligable effect in adults HYPOSECRETION of Calcitonin can cause ricketts in children (but usually due to Ca ++ or Vit D deficiency) Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser,
4 Parathyroid Glands small round bodies attached to the posterior surfaces of the thyroid gland usually 4 or 5, but varies a. Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) helps maintain homeostasis of blood calcium antagonist to calcitonin raises blood Ca ++ levels:!promotes Ca ++ absorption by kidney tubules and intestine! stimulates osteoclasts to dissolve bone since bone contains both calcium and phosphorus this releases both into blood Calcium homeostasis is important in: neuromuscular function blood clotting synapses to activate certain enzymes affects cell membrane permeability surgical removal of thyroid gland requires PTH hormone replacement therapy if all parathyroids are removed at the time Pancreas both an exocrine and endocrine gland exocrine (98% of mass of pancreas): secretes digestive enzymes endocrine (<2% of mass of pancreas): contains clusters of endocrine cells = Islets of Langerhans (~1 Million clusters; each up to several 1000 cells) humoral regulation: monitors blood glucose conc & amino acid levels mainly secretes: insulin glucagon both are proteins a. Insulin regulate blood sugar levels levels rise immediately after a meal!moves glucose, amino acids and fatty acids out of blood, into cells (except liver cells)!lowers blood glucose concentrations Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, only brain, liver and red blood cells do not need insulin to take up glucose b. Glucagon secretion rises between meals acts mainly on liver glucose synthesis and release into blood!increases blood glucose concentration antagonist to insulin both hormones maintain constant blood glucose levels! to feed brain cells esp! to provide energy for all body cells secretion of hormones directly controlled by blood sugar levels: after meal! high blood sugar! insulin fasting! low blood sugar! glucagon Diabetes diabetes is a general name for a group of diseases two major varieties: diabetes insipidus diabetes mellitis (Types I & II) Diabetes insipidus a disease associated with Posterior Pituitary deficiency in ADH causes low reabsorption of water large volumes of dilute urine are produced: (up to 10 gallons/day vs normal 1 qt/day) leads to electrolyte imbalances etc Diabetes mellitis most common of all endocrine disorders!18.2 Million (2004) diabetics in US, 5-6 Million more may be borderline diabetics diabetes is 7 th leading cause of death & leading cause of blindness in US!40,000 die anually as result of disorder Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser,
5 diabetes is a group of disorders characaterized by high blood glucose concentrations caused by: inadequate insulin secretion by beta cells in Islets =Type I lack of response by target cells to insulin =Type II 10% = Juvenile Onset Diabetes (Type I) 90% = Maturity Onset Diabetes (Type II) Type I: Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitis usually develops during adolescence is an autoimmune disorder triggered by 2 factors: 1. genetic component! susceptibility 2. environmental component! still unknown, may be viral results in malfunction of Islet cells in pancreas!dramatic decrease in the number of beta cells!insulin is not produced in sufficient quantities results in all body cells (target cells): Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, decreased glucose utilization levels of glucose build up in blood since glucose can t be used alternate fuels are mobilized: increased fat mobilization fats in blood rise to up to 5x s normal as cells shift to fat catabolism! produce ketone bodies! lower blood ph = acidosis! acetone breath! increased risk of atherosclerosis without insulin to stimulate protein synthesis they are instead broken down and converted to glucose in cells! tissue wasting high levels of glucose in blood lead to large quantities of glucose spilling into urine! diagnostic test for disease (used to taste it, now have chemical indicators)! this draws large amts of water into urine Type 2, Non Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitis target tissues become less responsive to insulin = insulin resistance Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, causes are poorly understood: most are obese! but its not obesity per se seems to be a strong genetic component also associated with a sedentary lifestyle Immediate (Acute) Complications of both forms hyperglycemia, ketoacidosis, electrolyte imbalances (as cations such as Na + and K + accompany ketones into urine) effects: reduces life expectancy by ~1/3 rd 25 x s greater rate of blindness 17 x s greater rate of kidney disease 17 x s greater rate of gangrene 2 x s greater chance of heart attack Chronic Secondary Complications often involve gradual changes over years most common changes occur in vascular system 1. narrowing of large blood vessels in brain, heart and lower extermities! can result in stroke, heart attack or limb loss 2. lesions in microvasculature are common leads to development of scar tissue! especially affect kidneys and eyes 3. impaired nerve function esp autonomic fibers and peripheral sensory fibers leads to altered GI, bladder function and impotence and loss of sensation esp in lower limbs Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser,
6 Adrenal Glands on top of kidneys divided into cortex and medulla which function as two separate glands Adrenal Cortex cortex = outer layer of adrenal gland!comprises 80 90% of adrenal gland absolutely essential for life regulated mainly by ACTH from Ant. Pituitary secretes different hormones all hormones secreted by adrenal cortex are steroids all are made from cholesterol these hormones can be categorized as 3 different kinds: a. Mineralocorticoids (90% = aldosterone)! aldosterone increases salt and water reabsorption by kidneys and excreting K + 3. this also indirectly regulates water reabsorption [more salt reabsorbed! more water reabsorbed] HYPOSECRETION by Adrenal Cortex Addison s Disease due to inadequate mineralocorticoids & glucocorticoids b. Glucocorticoids (95% = cortisol (hydrocortisone)) affect every cell in body secretion follows circadian rhythm! highest ~8:00am; lowest ~12:00am 1. generally raise blood glucose levels: 2. inhibit inflammation and tissue destruction also immunosuppressive 3. additional effects on blood pressure immunity wound healing fetal devel of brain and lungs maintains constant blood Na + levels by reabsorbing Na + in kidney if needed Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, HYPOSECRETION of Mineralocorticoids Addison s Disease Kennedy had mild form low ACTH may also produce this symptoms: bronzing of skin kidney impairment water retention increased blood pressure weight loss apathy cannot cope with stress immunosuppression hypoglycemia lethargy and muscle weakness HYPOSECRETION of Mineralocorticoids Cushing s Syndrome weakens skin and muscles Adrenal Medulla unlike cortex, is not essential for life secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine (=catecholamines) also neurotransmitters of sympathetic NS!affect same structures as sympathetic NS: heart smooth muscle glands serves to prolong or increase effects initiated by sympathetic NS. c. Sex Hormones (=gonadocorticoids; eg. DHEA, estrogen, progesterone, testosterone) androgens: promote protein synthesis normally not masculinizing female hormones: HYPERSECRETION of gonadocorticoids women in early puberty: adrenogenital syndrome masculinizing effect Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser,
7 Ovaries & Testes endocrine and reproductive function Minor/Temporary Endocrine Glands secrete steroid hormones the same gonadotropins that are found in adrenal cortex Kidneys secrete most (85%) erythropoietin affect development and maturation of reproductive organs and reproductive behavior Steroid Abuse Liver! stimulates RBC production in bone marrow Taking large amounts of Androgens (steroids): has negative feedback effect on FSH & LH! almost shuts down! decreased sperm production! temporary or permanent sterility! increased cancer risk also when large amounts are take some is transformed into estrogen! breast enlargement Heart secretes ~ 15% of body s erythropoietin stimulates RBC formation atria contain some specialized muscle cells that secrete Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)! reduces blood volume, pressure, Na + conc Stomach & Duodenum mucosal lining secretes several hormones to help control digestion: Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, gastrin enterogastrone secretin cholecystokinin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser, regulates secretion of: gastric juices pancreatic enzymes bile Adipose Tissue releases leptin after uptake of glucose and lipids which is converted to fat leptin binds to CNS neurons in hypothalamus! produces sensation of satiety Placenta acts as temporary endocrine gland during pregnancy releases 3 hormones: a. chorionic gonadotropic hormone (CGH)! maintains hormonal activity of ovary pregnancy test b. estrogens & progesterone Human Anatomy & Physiology: Endocrine System; Ziser,
Endocrine System. Modified by M. Myers
 Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
The Endocrine System. Endocrine System. 1
 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1
 Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs
 9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
CHAPTER 12. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
Chapter 12 Endocrine System (export).notebook. February 27, Mar 17 2:59 PM. Mar 17 3:09 PM. Mar 17 3:05 PM. Mar 17 3:03 PM.
 Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Anatomy and Physiology. The Endocrine System
 Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Endocrine Notes Mrs. Laux AP Biology I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones
 I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
Endocrine System. Chapter 24. Copyright 2012, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
2/28/18. Endocrine System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Comparing Endocrine and Nervous System Functions
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System 7/6/2015. Outline. Function of the Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System
 Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Endocrine System Worksheet
 Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW
 THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW Functions: 1. Reproduction 2. Growth & development 3. Maintenance of electrolytes, water and nutrient balance of the blood 4. Regulation of cell metabolism and energy
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW Functions: 1. Reproduction 2. Growth & development 3. Maintenance of electrolytes, water and nutrient balance of the blood 4. Regulation of cell metabolism and energy
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 11. Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
Endocrine System. Chapter 9
 Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
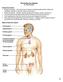 The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands 4/12/2016. Controlled by both nerves and hormones.
 Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes
 Operation of the Endocrine System Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes What is the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is comprised of the hormone producing glands and tissues of the body. Hypothalamus
Operation of the Endocrine System Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes What is the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is comprised of the hormone producing glands and tissues of the body. Hypothalamus
Endocrine Glands System. Agha Zohaib Khan
 Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Major endocrine glands and their hormones
 Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
The Endocrine System/Hormones
 The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11
 The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
The Endocrine System
 9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
Endocrine System. A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine. Endocrine: Exocrine:
 Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
CATEGORY Endocrine System Review. Provide labels for the following diagram CHAPTER 13 BLM
 CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
The Endocrine System. Lab Exercise 31. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
The Endocrine System
 C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
Endocrine System. A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body.
 Endocrine System A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body. HORMONES: chemical that circulates throughout the blood stream and influence the activity of distant
Endocrine System A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body. HORMONES: chemical that circulates throughout the blood stream and influence the activity of distant
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology
 Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Understand the functions and disorders of the endocrine system
 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
Endocrine Glands: Hormone-secreting organs are called endocrine glands
 University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
Robert Wadlow and his father
 Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System. Target Cells: Cells specialized to respond to hormones
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 26. Hormones and the Endocrine System. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Endocrine Glands Glands that secrete their products (HORMONES) into extracellular spaces around cells. The hormones then enter into the bloodstream by diffusing into the capillaries
The Endocrine System Endocrine Glands Glands that secrete their products (HORMONES) into extracellular spaces around cells. The hormones then enter into the bloodstream by diffusing into the capillaries
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL?
 Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
Human Biochemistry. Hormones
 Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Lab Activity 21. Endocrine System Glucometer. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Chapter 9. The Endocrine System. Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Introduction Hormone and Target Cells Steroids and Non-Steroids HW: Read / Take notes
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Introduction Hormone and Target Cells Steroids and Non-Steroids HW: Read / Take notes
ENDOCRINOLOGY. Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells.
 BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION
 CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System The nervous system allows the body to respond to various stimuli in a quick manner and this allows for homeostasis. The endocrine system, using hormones also allows the body to respond
The Endocrine System The nervous system allows the body to respond to various stimuli in a quick manner and this allows for homeostasis. The endocrine system, using hormones also allows the body to respond
Endocrine System. Part 2
 Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Endocrine system. Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to:
 Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
Biology 30. Morinville Community High School. Unit 2: Endocrine System. Name:
 Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Bell Work Day 1 Write the Standard in your notes. Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands. (page 197 in small books)
 Bell Work Day 1 Write the Standard in your notes. Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands. (page 197 in small books) 1 Standard Day 1 24) List the structures of the, explain the functions
Bell Work Day 1 Write the Standard in your notes. Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands. (page 197 in small books) 1 Standard Day 1 24) List the structures of the, explain the functions
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine System Functions
 Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
54a A&P: Endocrine System
 54a A&P: Endocrine System 54a A&P: Endocrine System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study skills:"
54a A&P: Endocrine System 54a A&P: Endocrine System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study skills:"
Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages )
 Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems 11 What is the function of the parathyroid glands? Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system?
Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems 11 What is the function of the parathyroid glands? Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system?
The Endocrine System Pearson Education, Inc.
 19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid
 Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species
 Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Chapter 16 - Endocrine system
 Chapter 16 - Endocrine system I. Overview Nervous control is fast but short-lived Hormonal control is slow and lasts a long time A. Organs: hypothalamus, pituitary (hypophysis), thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal,
Chapter 16 - Endocrine system I. Overview Nervous control is fast but short-lived Hormonal control is slow and lasts a long time A. Organs: hypothalamus, pituitary (hypophysis), thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal,
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System. Simple Hormone Pathways
 Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
Human Anatomy, First Edition. Endocrine System. Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System. McKinley & O'Loughlin
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages )
 Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system? How does the endocrine system maintain homeostasis?
Chapter 39 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Section 39 1 The Endocrine System (pages 997 1002) Key Concepts What is the function of the endocrine system? How does the endocrine system maintain homeostasis?
Chemical Regulation. Chapter 26. Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? THE NATURE OF CHEMICAL REGULATION
 Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
The Intricate Web Of Hormone Relationships Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo
 The Intricate Web Of Hormone Relationships Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one-onone relationship with a qualified health care
The Intricate Web Of Hormone Relationships Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one-onone relationship with a qualified health care
3. The function of that hormone. In other words, what change does that hormone facilitate.
 Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System
 I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
Summary The Endocrine System The Reproductive System Human Endocrine Glands. Endocrine and Reproductive Systems.
 Name Class Date Chapter 39 Summary Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 1 The Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands that release secretions
Name Class Date Chapter 39 Summary Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 1 The Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands that release secretions
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine Glands. Comparison of Nervous System and Endocrine System
 Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
2) Storehouse for the hormones produced by the hypothalamus of the brain. 2)
 AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
9.3 Stress Response and Blood Sugar
 9.3 Stress Response and Blood Sugar Regulate Stress Response Regulate Blood Sugar Stress Response Involves hormone pathways that regulate metabolism, heart, rate and breathing The Adrenal Glands a pair
9.3 Stress Response and Blood Sugar Regulate Stress Response Regulate Blood Sugar Stress Response Involves hormone pathways that regulate metabolism, heart, rate and breathing The Adrenal Glands a pair
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Biology 30 Unit II - The Endocrine System
 Biology 30 Unit II - The Endocrine System Nelson Biology chapter 14 Biology Directions chapter 18 The Endocrine System The endocrine system, like the nervous system is responsible for allowing communication
Biology 30 Unit II - The Endocrine System Nelson Biology chapter 14 Biology Directions chapter 18 The Endocrine System The endocrine system, like the nervous system is responsible for allowing communication
Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 16 - Endocrine System Lecture 16
 Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 16 - Endocrine System Lecture 16 1 Lecture Overview The Adrenal Glands The Pancreas Other Endocrine Tissues Stress and its effects
Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 16 - Endocrine System Lecture 16 1 Lecture Overview The Adrenal Glands The Pancreas Other Endocrine Tissues Stress and its effects
Endocrine System. The Endocrine Glands
 Endocrine System Working together with the nervous system, the endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis in the body. Where the nervous system uses electric signals, the endocrine system uses chemical
Endocrine System Working together with the nervous system, the endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis in the body. Where the nervous system uses electric signals, the endocrine system uses chemical
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
The Endocrine System PART A
 9 The Endocrine System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Endocrine System
9 The Endocrine System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Endocrine System
