Regulation of Systemic Energy Balance and Glucose Homeostasis by Protein-Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B
|
|
|
- Elfreda Greer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Regulation of Systemic Energy Balance and Glucose Homeostasis by Protein-Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Fawaz G. Haj Associate Professor
2 Diagnosed Obesity and Diabetes for Adults aged 20 years in United States
3 The Obesity Epidemic Has Reached America s Pets
4 System Regulation of Glucose Pancreas Insulin secretory defect Insulin + Adipocytes Glucose Liver Increased hepatic glucose production Impaired glucose utilization Muscle
5 Understand the Role of Cell Signaling, in Particular, Tyrosine Phosphorylation in the Pathogenesis of Metabolic Diseases
6 Phosphorylation is reversible P P YY Protein Y P PTPs PTKs YY Protein Y P P P
7 The Classical Protein-Tyrosine Phosphatase (PTP) Family Nontransmembrane PTP subtypes (NT) Receptor-like PTP Subtypes (R) HCSxGxGRxG Andersen et al
8 Protein-Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) Is ubiquitously expressed, including all insulin-responsive tissues Generate PTP1B knockout (KO) mice (protein no longer expressed) PTP1B KO mice are insulin-sensitive, and have increased insulin receptor (IR) phosphorylation (Elchebly et al, 1999 and Klaman et al, 2000) PTP1B KO mice are lean and resistant to diet-induced obesity (Elchebly et al, 1999 and Klaman et al, 2000) WT KO
9 PTP1B Inhibition for Treatment of Metabolic Diseases No obvious apparent side effects observed thus far, making PTP1B a good target for treating obesity and diabetes in humans Companies are competing to generate a readily bio-available, PTP1B-specific inhibitor Need to know the SITES and MECHANISMS of PTP1B action
10 Approach Genetically-engineered mice to achieve tissue-specific deletion of PTP1B Quantitative cellular imaging to dissect the mechanism of PTP1B action
11 Approach Genetically-engineered mice to achieve tissue-specific deletion of PTP1B Quantitative cellular imaging to dissect the mechanism of PTP1B action
12 Tissue-Specific Deletion of PTP1B Alb-Cre Liver PTP1B fl/fl Adp-Cre Adipose PDX1-Cre Pancreas MCK-Cre Muscle
13 Generation of Adipose-Specific PTP1B Knockout Mice using Adipoq-Cre PTP1B fl/fl X Adipoq-Cre FPTP1B KO PTP1B adipose-specific deletion
14 Efficient and Specific Deletion of PTP1B in Adipose Tissue PTP1B ERK1/2 Adipoq WT KO W1 CW1 W1 CW1 W2 CW2 W1 CW1 W2 CW2 W3 CW3 PTP1B expression * W CW ## 0 Adipoq WT KO WT KO W CW BAT Mac L M P Br W CW BAT Mac L M P Br PTP1B TCPTP SHP2 ERK1/2
15 Resistance to HFD-Induced Obesity in adipose PTP1B KO Mice Body weight (g) Males/HFD *# ** # # ** # # *# flx/flx ** +/+, Cre flx/flx, Cre (KO) Body weight (g) Females/HFD ** ** ** ** # # # # ** # # # # # # Age (weeks) Age (weeks) Body weight (g) Males/Chow Body weight (g) Females/Chow Age (weeks) Age (weeks)
16 Increased Energy Expenditure in Adipose PTP1B KO Mice 1200 Energy Expenditure (KJ/Min/Kg 0.75 ) ** ** * flx/flx flx/flx, Cre (KO) +/+, Cre (Adipoq) 0 Dark Fed Light Fed Dark Fast Total
17 Approach Genetically-engineered mice to achieve tissue-specific deletion of PTP1B Quantitative cellular imaging to dissect the mechanism of PTP1B action
18 Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching (FRAP) Pre-bleach Fluorescence intensity Bleach Recovery Time
19 Dynamics of Cellular PTP1B Mobility PTP1B WT (ER) PTP1B D/A (ER) PTP1B D/A (Cell-Cell)
20 Quantitative Determination of PTP1B Mobility Using FRAP WT ER, D eff = 0.20 mm 2 s -1 D/A ER, D eff = 0.07 mm 2 s -1 D/A cell-cell (D eff : Effective diffusion) Recovery consistent with: 1) Rapid turnover (<10 sec) 2) Replenishment from ER pool 3) No significant tight binding fraction
21 Summary Adipose-specific PTP1B deletion leads to decreased adiposity and resistance to high fat diet-induced obesity This is due to increased energy expenditure in adipose PTP1B deficient mice Cellular imaging identifies the endoplasmic reticulum and cell-cell contact as major cites of PTP1B action in the cell
22 Conclusion Tissue-specific deletion and cell biology approaches are necessary to decipher the sites and mechanisms of PTP1B action This is important for developing drugs that targets PTP1B at the correct site(s)
23 Future Studies Investigate the role of PTP1B in other tissues and it mechanism of action at these cites Investigate the role of other members of PTP superfamily as potential targets to treat obesity and diabetes Examine regulation of PTP activity by nutrients and diets
24 Acknowledgements Collaborators Peter Havel Lab (UCD) Lew Cantley Lab (Harvard) Philippe Bastiaens Lab (MPI) Thanks Ben Neel Evan Rosen FGH Lab Ahmed Bettaieb Jesse Bakke Siming Liu Yannan Xi Naoto Nagata Danny AbouBechara Kosuke Matsuo Izumi Matsuo Financial support from JDRF, ADA and NIH
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus
 Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Pathogenesis of Diabetes Mellitus Young-Bum Kim, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Definition of Diabetes Mellitus a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 how HFD how HFD Epi WT p p Hypothalamus p p Inguinal WT T Liver Lean mouse adipocytes p p p p p p Obese mouse adipocytes Kidney Muscle Spleen Heart p p p p p p p p Extracellular
Supplementary Figure 1 how HFD how HFD Epi WT p p Hypothalamus p p Inguinal WT T Liver Lean mouse adipocytes p p p p p p Obese mouse adipocytes Kidney Muscle Spleen Heart p p p p p p p p Extracellular
Regulation of the SNARE-interacting protein Munc18c tyrosine phosphorylation in adipocytes by protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B
 Bakke et al. Cell Communication and Signaling 2013, 11:57 RESEARCH Open Access Regulation of the SNARE-interacting protein Munc18c tyrosine phosphorylation in adipocytes by protein-tyrosine phosphatase
Bakke et al. Cell Communication and Signaling 2013, 11:57 RESEARCH Open Access Regulation of the SNARE-interacting protein Munc18c tyrosine phosphorylation in adipocytes by protein-tyrosine phosphatase
Supplemental Information. FGF19, FGF21, and an FGFR1/b-Klotho-Activating. Antibody Act on the Nervous System. to Regulate Body Weight and Glycemia
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 26 Supplemental Information FGF19, FGF21, and an FGFR1/b-Klotho-Activating Antibody Act on the Nervous System to Regulate Body Weight and Glycemia Tian Lan, Donald A. Morgan, Kamal
Cell Metabolism, Volume 26 Supplemental Information FGF19, FGF21, and an FGFR1/b-Klotho-Activating Antibody Act on the Nervous System to Regulate Body Weight and Glycemia Tian Lan, Donald A. Morgan, Kamal
Altered Mouse Adipose Tissue IGF-1 Expression Influences Glucose Control
 Altered Mouse Adipose Tissue IGF-1 Expression Influences Glucose Control Jan Trost Prof. Gudrun A. Brockmann Humboldt Universität zu Berlin Department of Crop and Animal Sciences Breeding Biology and Molecular
Altered Mouse Adipose Tissue IGF-1 Expression Influences Glucose Control Jan Trost Prof. Gudrun A. Brockmann Humboldt Universität zu Berlin Department of Crop and Animal Sciences Breeding Biology and Molecular
Tissue factor-par2 signaling promotes diet-induced obesity and adipose
 Supplementary figures for Tissue factor-par2 signaling promotes diet-induced obesity and adipose inflammation. Leylla Badeanlou 1, Christian Furlan-Freguia 2, Guang Yang 1, Wolfram Ruf 2,3, and Fahumiya
Supplementary figures for Tissue factor-par2 signaling promotes diet-induced obesity and adipose inflammation. Leylla Badeanlou 1, Christian Furlan-Freguia 2, Guang Yang 1, Wolfram Ruf 2,3, and Fahumiya
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
University of Groningen. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Sheedfar, Fareeba
 University of Groningen Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Sheedfar, Fareeba IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Sheedfar, Fareeba IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Akt regulates hepatic metabolism by suppressing a Foxo1 dependent global inhibition of adaptation to nutrient intake Mingjian Lu 1, Min Wan 1, Karla F. Leavens 1, Qingwei Chu
Supplementary Information Akt regulates hepatic metabolism by suppressing a Foxo1 dependent global inhibition of adaptation to nutrient intake Mingjian Lu 1, Min Wan 1, Karla F. Leavens 1, Qingwei Chu
Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants. Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± ± 9.
![Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants. Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± ± 9. Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants. Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± ± 9.](/thumbs/90/103696086.jpg) SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants Lean (n=15) Obese (n=12) Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± 9.5 44.8 ± 9.1 White, n
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Supplemental Table 1: Demographics and characteristics of study participants Lean (n=15) Obese (n=12) Male, n (%) 3 (20%) 6 (50%) Age, years [mean ± SD] 33.3 ± 9.5 44.8 ± 9.1 White, n
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/407/ra127/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss of FTO in adipose tissue decreases Angptl4 translation and alters triglyceride metabolism Chao-Yung Wang,* Shian-Sen
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/407/ra127/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss of FTO in adipose tissue decreases Angptl4 translation and alters triglyceride metabolism Chao-Yung Wang,* Shian-Sen
A microrna-34a/fgf21 Regulatory Axis and Browning of White Fat
 A microrna-34a/fgf21 Regulatory Axis and Browning of White Fat Jongsook Kim Kemper, Ph.D Department of Molecular and Integrative Physiology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA 213 International
A microrna-34a/fgf21 Regulatory Axis and Browning of White Fat Jongsook Kim Kemper, Ph.D Department of Molecular and Integrative Physiology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA 213 International
Analysis of AVP functions via V1a and V1b receptors with knockout mice. Akito Tanoue
 Analysis of AVP functions via V1a and V1b receptors with knockout mice Akito Tanoue Department of Pharmacology, National Research Institute for Child Health and Development Arginine-Vasopressin (AVP) is
Analysis of AVP functions via V1a and V1b receptors with knockout mice Akito Tanoue Department of Pharmacology, National Research Institute for Child Health and Development Arginine-Vasopressin (AVP) is
Hepatic Oxidative Stress Promotes Insulin-STAT-5 Signaling and Obesity by Inactivating Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase N2
 Article Hepatic Oxidative Stress Promotes Insulin-STAT-5 Signaling and Obesity by Inactivating Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase N2 Esteban N. Gurzov, 1 Melanie Tran, 1 Manuel A. Fernandez-Rojo, 1 Troy L. Merry,
Article Hepatic Oxidative Stress Promotes Insulin-STAT-5 Signaling and Obesity by Inactivating Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase N2 Esteban N. Gurzov, 1 Melanie Tran, 1 Manuel A. Fernandez-Rojo, 1 Troy L. Merry,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2211 a! mir-143! b! mir-103/107! let-7a! mir-144! mir-122a! mir-126-3p! mir-194! mir-27a! mir-30c! Figure S1 Northern blot analysis of mir-143 expression dependent on feeding conditions.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2211 a! mir-143! b! mir-103/107! let-7a! mir-144! mir-122a! mir-126-3p! mir-194! mir-27a! mir-30c! Figure S1 Northern blot analysis of mir-143 expression dependent on feeding conditions.
MOLECULAR MECHANISMS OF INSULIN RESISTANCE IN OBESITY
 January 2008 (Vol. 1, Issue 1, pages 5-9) MOLECULAR MECHANISMS OF INSULIN RESISTANCE IN OBESITY By André Marette, PhD Department of Anatomy and Physiology and Lipid Research Unit, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire
January 2008 (Vol. 1, Issue 1, pages 5-9) MOLECULAR MECHANISMS OF INSULIN RESISTANCE IN OBESITY By André Marette, PhD Department of Anatomy and Physiology and Lipid Research Unit, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire
WEIGHT GAIN DURING MENOPAUSE EMERGING RESEARCH
 MENOPAUSE WHEN DOES IT OCCUR? The cessation of the menstrual cycle for one year. WEIGHT GAIN DURING MENOPAUSE EMERGING RESEARCH Jan Schroeder, Ph.D. Chair of The Department of Kinesiology California State
MENOPAUSE WHEN DOES IT OCCUR? The cessation of the menstrual cycle for one year. WEIGHT GAIN DURING MENOPAUSE EMERGING RESEARCH Jan Schroeder, Ph.D. Chair of The Department of Kinesiology California State
Metabolic ER stress and inflammation in white adipose tissue (WAT) of mice with dietary obesity.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Metabolic ER stress and inflammation in white adipose tissue (WAT) of mice with dietary obesity. Male C57BL/6J mice were fed a normal chow (NC, 10% fat) or a high-fat diet (HFD,
Supplementary Figure 1 Metabolic ER stress and inflammation in white adipose tissue (WAT) of mice with dietary obesity. Male C57BL/6J mice were fed a normal chow (NC, 10% fat) or a high-fat diet (HFD,
A synergistic anti-obesity effect by a combination of capsinoids and cold temperature through the promotion of beige adipocyte biogenesis
 A synergistic anti-obesity effect by a combination of capsinoids and cold temperature through the promotion of beige adipocyte biogenesis Kana Ohyama, 1,2 Yoshihito Nogusa, 1 Kosaku Shinoda, 2 Katsuya
A synergistic anti-obesity effect by a combination of capsinoids and cold temperature through the promotion of beige adipocyte biogenesis Kana Ohyama, 1,2 Yoshihito Nogusa, 1 Kosaku Shinoda, 2 Katsuya
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11464 Supplemental Figure S1. The expression of Vegfb is increased in obese and diabetic mice as compared to lean mice. a-b, Body weight and postprandial blood
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11464 Supplemental Figure S1. The expression of Vegfb is increased in obese and diabetic mice as compared to lean mice. a-b, Body weight and postprandial blood
Expanded View Figures
 Expanded View Figures A B C D E F G H I J K L Figure EV1. The dysregulated lipid metabolic phenotype of mouse models of metabolic dysfunction is most pronounced in the fasted state. A L Male 12-weeks-old
Expanded View Figures A B C D E F G H I J K L Figure EV1. The dysregulated lipid metabolic phenotype of mouse models of metabolic dysfunction is most pronounced in the fasted state. A L Male 12-weeks-old
Inflammasome-mediated caspase-1 activity Gatekeeper of inflammation in the adipose tissue. Rinke Stienstra
 Inflammasome-mediated caspase-1 activity Gatekeeper of inflammation in the adipose tissue Rinke Stienstra Obesity promotes the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes County-level Estimates
Inflammasome-mediated caspase-1 activity Gatekeeper of inflammation in the adipose tissue Rinke Stienstra Obesity promotes the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes County-level Estimates
18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA. 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT. Acc1 AGCAGATCCGCAGCTTG ACCTCTGCTCGCTGAGTGC
 Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative PCR primer sequences Gene symbol Sequences (5 to 3 ) Forward Reverse 18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT Acc1
Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative PCR primer sequences Gene symbol Sequences (5 to 3 ) Forward Reverse 18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT Acc1
The Physiology of Weight Regulation: Implications for Effective Clinical Care
 Roundtable on Obesity Solutions The Physiology of Weight Regulation: Implications for Effective Clinical Care Lee M. Kaplan, MD, PhD Obesity, Metabolism & Nutrition Institute Massachusetts General Hospital
Roundtable on Obesity Solutions The Physiology of Weight Regulation: Implications for Effective Clinical Care Lee M. Kaplan, MD, PhD Obesity, Metabolism & Nutrition Institute Massachusetts General Hospital
Genetic ablation of Acp1 (Lmptp) in mice prevents heart failure
 Genetic ablation of Acp1 (Lmptp) in mice prevents heart failure Coralie Poizat, Ph.D. Director, Cardiovascular Research Program KFSHRC-Riyadh Saudi Heart Failure Working Group Jeddah, 5 December 2015 Cardiovascular
Genetic ablation of Acp1 (Lmptp) in mice prevents heart failure Coralie Poizat, Ph.D. Director, Cardiovascular Research Program KFSHRC-Riyadh Saudi Heart Failure Working Group Jeddah, 5 December 2015 Cardiovascular
Supplemental Information. Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects. against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin. Resistance in Male Mice
 Cell Reports, Volume 16 Supplemental Information Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Male Mice Shih-Yin Tsai, Ariana A. Rodriguez, Somasish G. Dastidar,
Cell Reports, Volume 16 Supplemental Information Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Male Mice Shih-Yin Tsai, Ariana A. Rodriguez, Somasish G. Dastidar,
Molecular pathways linking metabolic inflammation and thermogenesis G. Solinas Summary
 Published in "" which should be cited to refer to this work. Molecular pathways linking metabolic inflammation and thermogenesis G. Solinas http://doc.rero.ch Laboratory of Metabolic Stress Biology, Division
Published in "" which should be cited to refer to this work. Molecular pathways linking metabolic inflammation and thermogenesis G. Solinas http://doc.rero.ch Laboratory of Metabolic Stress Biology, Division
Effects of hepatic protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B and methionine restriction on hepatic and whole-body glucose and lipid metabolism in mice
 Accepted Manuscript Effects of hepatic protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B and methionine restriction on hepatic and whole-body glucose and lipid metabolism in mice E.K. Lees, E. Krol, K. Shearer, N. Mody,
Accepted Manuscript Effects of hepatic protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B and methionine restriction on hepatic and whole-body glucose and lipid metabolism in mice E.K. Lees, E. Krol, K. Shearer, N. Mody,
Hypothalamic inflammation: a double-edged sword to nutritional diseases
 Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. ISSN 0077-8923 ANNALS OF THE NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Issue: The Year in Diabetes and Obesity Hypothalamic inflammation: a double-edged sword to nutritional diseases Dongsheng
Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. ISSN 0077-8923 ANNALS OF THE NEW YORK ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Issue: The Year in Diabetes and Obesity Hypothalamic inflammation: a double-edged sword to nutritional diseases Dongsheng
1.5 ASK1KO fed. fasted 16 hrs w/o water. Fed. 4th. 4th WT ASK1KO N=29, 11(WT), ,5(ASK1KO) ASK1KO ASK1KO **** Time [h]
![1.5 ASK1KO fed. fasted 16 hrs w/o water. Fed. 4th. 4th WT ASK1KO N=29, 11(WT), ,5(ASK1KO) ASK1KO ASK1KO **** Time [h] 1.5 ASK1KO fed. fasted 16 hrs w/o water. Fed. 4th. 4th WT ASK1KO N=29, 11(WT), ,5(ASK1KO) ASK1KO ASK1KO **** Time [h]](/thumbs/87/97258189.jpg) 7: 13: 19: 1: 7: 151117 a 151117 4th 4th b c RQ.95 KO.9.85.8.75.7 light dark light dark.65 7: 19: 7: 19: 7: Means ± SEM, N=6 RQ 1..9.8.7.6.6 KO CL (-) CL (+) ibat weight ratio (/body weight) [%].5.4.3.2.1
7: 13: 19: 1: 7: 151117 a 151117 4th 4th b c RQ.95 KO.9.85.8.75.7 light dark light dark.65 7: 19: 7: 19: 7: Means ± SEM, N=6 RQ 1..9.8.7.6.6 KO CL (-) CL (+) ibat weight ratio (/body weight) [%].5.4.3.2.1
Supplemental Table 1. Plasma NEFA and liver triglyceride levels in ap2-hif1ako and ap2-hif2ako mice under control and high fat diets.
 Supplemental Table 1. Plasma NEFA and liver triglyceride levels in Hif1aKO and Hif2aKO mice under control and high fat diets. Hif1a (n=6) Hif1aK O (n=6) Hif2a Hif2aK O Hif1a (n=5) Hif1aKO (n=5) Hif2a Hif2aK
Supplemental Table 1. Plasma NEFA and liver triglyceride levels in Hif1aKO and Hif2aKO mice under control and high fat diets. Hif1a (n=6) Hif1aK O (n=6) Hif2a Hif2aK O Hif1a (n=5) Hif1aKO (n=5) Hif2a Hif2aK
Successful completion of Phase I clinical trial of AMPK activator O304
 Successful completion of Phase I clinical trial of AMPK activator O304 O304 is safe and very well tolerated in young healthy subjects, in middle aged obese subjects, and in type 2 diabetics in combination
Successful completion of Phase I clinical trial of AMPK activator O304 O304 is safe and very well tolerated in young healthy subjects, in middle aged obese subjects, and in type 2 diabetics in combination
MBB317. Dr D MANGNALL OBESITY. Lecture 2
 MBB317 Dr D MANGNALL OBESITY Lecture 2 When the structure of the insulin receptor was first discovered it was assumed that the active beta subunit tyrosine kinase would phosphorylate some intracellular
MBB317 Dr D MANGNALL OBESITY Lecture 2 When the structure of the insulin receptor was first discovered it was assumed that the active beta subunit tyrosine kinase would phosphorylate some intracellular
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures mir-150 regulates obesityassociated insulin resistance by controlling B cell functions Wei Ying, Alexander Tseng, Richard Cheng-An Chang, Haiqing Wang, Yu-lieh Lin, Srikanth Kanameni,
Supplementary Figures mir-150 regulates obesityassociated insulin resistance by controlling B cell functions Wei Ying, Alexander Tseng, Richard Cheng-An Chang, Haiqing Wang, Yu-lieh Lin, Srikanth Kanameni,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplemental Figure 1. Body weight and blood glucose parameters of chow-diet (CD)
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION LEGENDS Supplemental Figure. Body weight and blood glucose parameters of chow-diet (CD) fed and high-fat diet (HFD) fed mice. (A) Body weight was measured at the beginning of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION LEGENDS Supplemental Figure. Body weight and blood glucose parameters of chow-diet (CD) fed and high-fat diet (HFD) fed mice. (A) Body weight was measured at the beginning of
Roger J. Davis. Metabolic Stress Signaling by the JNK Pathway
 Roger J. Davis Metabolic Stress Signaling by the JNK Pathway Age-adjusted Percentage of U.S. Adults with Diagnosed Diabetes or Obesity Diabetes 1994 2000 2007 Obesity (BMI 30 kg/m 2 )
Roger J. Davis Metabolic Stress Signaling by the JNK Pathway Age-adjusted Percentage of U.S. Adults with Diagnosed Diabetes or Obesity Diabetes 1994 2000 2007 Obesity (BMI 30 kg/m 2 )
Review Article The Genetics of PTPN1 and Obesity: Insights from Mouse Models of Tissue-Specific PTP1B Deficiency
 Obesity Volume 2012, Article ID 926857, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2012/926857 Review Article The Genetics of PTPN1 and Obesity: Insights from Mouse Models of Tissue-Specific PTP1B Deficiency Ryan C. Tsou and
Obesity Volume 2012, Article ID 926857, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2012/926857 Review Article The Genetics of PTPN1 and Obesity: Insights from Mouse Models of Tissue-Specific PTP1B Deficiency Ryan C. Tsou and
Figure legends Supplemental Fig.1. Glucose-induced insulin secretion and insulin content of islets. Supplemental Fig. 2.
 Figure legends Supplemental Fig.. Glucose-induced insulin secretion and insulin content of islets. Insulin secretory responses to.,., and. mm glucose (A) (n = 7-), and the insulin content in the islets
Figure legends Supplemental Fig.. Glucose-induced insulin secretion and insulin content of islets. Insulin secretory responses to.,., and. mm glucose (A) (n = 7-), and the insulin content in the islets
Role of fatty acids in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus
 Emerging Science Role of fatty acids in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus George Wolf Insulin resistance is defined as the reduced responsiveness to normal circulating
Emerging Science Role of fatty acids in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus George Wolf Insulin resistance is defined as the reduced responsiveness to normal circulating
Interplay between FGF21 and insulin action in the liver regulates metabolism
 Research article Interplay between FGF21 and insulin action in the liver regulates metabolism Brice Emanuelli, 1 Sara G. Vienberg, 1 Graham Smyth, 1 Christine Cheng, 2 Kristin I. Stanford, 1 Manimozhiyan
Research article Interplay between FGF21 and insulin action in the liver regulates metabolism Brice Emanuelli, 1 Sara G. Vienberg, 1 Graham Smyth, 1 Christine Cheng, 2 Kristin I. Stanford, 1 Manimozhiyan
Adipocyte-specific deletion of Ip6k1 reduces diet-induced obesity by enhancing AMPKmediated
 Adipocyte-specific deletion of Ip6k1 reduces diet-induced obesity by enhancing AMPKmediated thermogenesis Qingzhang Zhu,, James C. Barrow, Anutosh Chakraborty J Clin Invest. 2016;126(11):4273-4288. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci85510.
Adipocyte-specific deletion of Ip6k1 reduces diet-induced obesity by enhancing AMPKmediated thermogenesis Qingzhang Zhu,, James C. Barrow, Anutosh Chakraborty J Clin Invest. 2016;126(11):4273-4288. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci85510.
Adipocyte-Specific Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Deletion Increases Lipogenesis, Adipocyte Cell Size and Is a Minor Regulator of Glucose Homeostasis
 Adipocyte-Specific Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Deletion Increases Lipogenesis, Adipocyte Cell Size and Is a Minor Regulator of Glucose Homeostasis Carl Owen 1, Alicja Czopek 1, Abdelali Agouni 1, Louise
Adipocyte-Specific Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Deletion Increases Lipogenesis, Adipocyte Cell Size and Is a Minor Regulator of Glucose Homeostasis Carl Owen 1, Alicja Czopek 1, Abdelali Agouni 1, Louise
CNS Control of Food Intake. Adena Zadourian & Andrea Shelton
 CNS Control of Food Intake Adena Zadourian & Andrea Shelton Controlling Food Intake Energy Homeostasis (Change in body adiposity + compensatory changes in food intake) Background Information/Review Insulin
CNS Control of Food Intake Adena Zadourian & Andrea Shelton Controlling Food Intake Energy Homeostasis (Change in body adiposity + compensatory changes in food intake) Background Information/Review Insulin
Supplementary Figure 1. DNA methylation of the adiponectin promoter R1, Pparg2, and Tnfa promoter in adipocytes is not affected by obesity.
 Supplementary Figure 1. DNA methylation of the adiponectin promoter R1, Pparg2, and Tnfa promoter in adipocytes is not affected by obesity. (a) Relative amounts of adiponectin, Ppar 2, C/ebp, and Tnf mrna
Supplementary Figure 1. DNA methylation of the adiponectin promoter R1, Pparg2, and Tnfa promoter in adipocytes is not affected by obesity. (a) Relative amounts of adiponectin, Ppar 2, C/ebp, and Tnf mrna
Bile acid receptor FXR: metabolic regulator in the gut. Sungsoon Fang
 Bile acid receptor FXR: metabolic regulator in the gut Sungsoon Fang Nuclear hormone receptor 1905: Ernest Starling coined hormone 1929: Estrogen structure 1958: Estrogen receptor by Elwood Jensen 1985:
Bile acid receptor FXR: metabolic regulator in the gut Sungsoon Fang Nuclear hormone receptor 1905: Ernest Starling coined hormone 1929: Estrogen structure 1958: Estrogen receptor by Elwood Jensen 1985:
SH2B1 Regulates Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Homeostasis by Multiple Mechanisms. David L. Morris
 SH2B1 Regulates Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Homeostasis by Multiple Mechanisms by David L. Morris A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
SH2B1 Regulates Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Homeostasis by Multiple Mechanisms by David L. Morris A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
Epigenetic regulation of macrophage polarization and inflammation by DNA methylation in obesity
 Downloaded from http:// on December 17, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.87748 Epigenetic regulation of macrophage polarization and inflammation by DNA methylation in obesity Xianfeng Wang, 1
Downloaded from http:// on December 17, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.87748 Epigenetic regulation of macrophage polarization and inflammation by DNA methylation in obesity Xianfeng Wang, 1
Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 11 Supplemental Information Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance Ling Yang, Ping Li, Suneng Fu, Ediz S. Calay, and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
Cell Metabolism, Volume 11 Supplemental Information Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance Ling Yang, Ping Li, Suneng Fu, Ediz S. Calay, and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
456 Diabetes Volume 63, February 2014
 456 Diabetes Volume 63, February 2014 Louise Grant, Kirsty D. Shearer, Alicja Czopek, Emma K. Lees, Carl Owen, Abdelali Agouni, James Workman, Cristina Martin-Granados, John V. Forrester, Heather M. Wilson,
456 Diabetes Volume 63, February 2014 Louise Grant, Kirsty D. Shearer, Alicja Czopek, Emma K. Lees, Carl Owen, Abdelali Agouni, James Workman, Cristina Martin-Granados, John V. Forrester, Heather M. Wilson,
Central insulin action regulates peripheral glucose and fat metabolism in mice
 Research article Central insulin action regulates peripheral glucose and fat metabolism in mice Linda Koch, 1 F. Thomas Wunderlich, 1 Jost Seibler, 2 A. Christine Könner, 1 Brigitte Hampel, 1 Sigrid Irlenbusch,
Research article Central insulin action regulates peripheral glucose and fat metabolism in mice Linda Koch, 1 F. Thomas Wunderlich, 1 Jost Seibler, 2 A. Christine Könner, 1 Brigitte Hampel, 1 Sigrid Irlenbusch,
Metabolic Syndrome. DOPE amines COGS 163
 Metabolic Syndrome DOPE amines COGS 163 Overview - M etabolic Syndrome - General definition and criteria - Importance of diagnosis - Glucose Homeostasis - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin Resistance
Metabolic Syndrome DOPE amines COGS 163 Overview - M etabolic Syndrome - General definition and criteria - Importance of diagnosis - Glucose Homeostasis - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - Insulin Resistance
Supplementary Table 2. Plasma lipid profiles in wild type and mutant female mice submitted to a HFD for 12 weeks wt ERα -/- AF-1 0 AF-2 0
 Supplementary Table 1. List of specific primers used for gene expression analysis. Genes Primer forward Primer reverse Hprt GCAGTACAGCCCCAAAATGG AACAAAGTCTGGCCTGTATCCA Srebp-1c GGAAGCTGTCGGGGTAGCGTC CATGTCTTCAAATGTGCAATCCAT
Supplementary Table 1. List of specific primers used for gene expression analysis. Genes Primer forward Primer reverse Hprt GCAGTACAGCCCCAAAATGG AACAAAGTCTGGCCTGTATCCA Srebp-1c GGAAGCTGTCGGGGTAGCGTC CATGTCTTCAAATGTGCAATCCAT
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3461 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 (associated to Figure 1). Cpeb4 gene-targeted mice develop liver steatosis. a, Immunoblot displaying CPEB4
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3461 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 (associated to Figure 1). Cpeb4 gene-targeted mice develop liver steatosis. a, Immunoblot displaying CPEB4
Autophagy in Insulin Resistance. Abstract. Introduction. Takeshi Yoshizaki. KEY WORDS: Autophagy, insulin resistance, aging, inflammation
 Received: Oct. 10, 2012 Accepted: Oct. 17, 2012 Published online: Oct. 31, 2012 Review Article Autophagy in Insulin Resistance Takeshi Yoshizaki Department of Medicine, Shiga University of Medical Science
Received: Oct. 10, 2012 Accepted: Oct. 17, 2012 Published online: Oct. 31, 2012 Review Article Autophagy in Insulin Resistance Takeshi Yoshizaki Department of Medicine, Shiga University of Medical Science
Regulation of Lipid Homeostasis: Lipid Droplets
 Regulation of Lipid Homeostasis: Lipid Droplets Bernd Helms Article Brand Recter Hendrik Mertens 1 The Basics I: FAs The Basics II: FA Activation 2 Basics III: TG-FA Interplay. Why? Adipocytes 3 Foam cells
Regulation of Lipid Homeostasis: Lipid Droplets Bernd Helms Article Brand Recter Hendrik Mertens 1 The Basics I: FAs The Basics II: FA Activation 2 Basics III: TG-FA Interplay. Why? Adipocytes 3 Foam cells
Supplemental Information Supplementary Table 1. Tph1+/+ Tph1 / Analyte Supplementary Table 2. Tissue Vehicle LP value
 Supplemental Information Supplementary Table. Urinary and adipose tissue catecholamines in Tph +/+ and Tph / mice fed a high fat diet for weeks. Tph +/+ Tph / Analyte ewat ibat ewat ibat Urine (ng/ml)
Supplemental Information Supplementary Table. Urinary and adipose tissue catecholamines in Tph +/+ and Tph / mice fed a high fat diet for weeks. Tph +/+ Tph / Analyte ewat ibat ewat ibat Urine (ng/ml)
In response to nutrients, insulin is secreted from
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Liver-Specific Deletion of Protein-Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) Improves Metabolic Syndrome and Attenuates Diet-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Mirela Delibegovic, 1,6 Derek Zimmer,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Liver-Specific Deletion of Protein-Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) Improves Metabolic Syndrome and Attenuates Diet-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Mirela Delibegovic, 1,6 Derek Zimmer,
THE ROLE OF INSULIN RECEPTOR SIGNALING IN THE BRAIN. COGS 163 By: Pranav Singh Alexandra Villar
 THE ROLE OF INSULIN RECEPTOR SIGNALING IN THE BRAIN COGS 163 By: Pranav Singh Alexandra Villar INTRODUCTION Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas by the islets of Langerhans that regulates the
THE ROLE OF INSULIN RECEPTOR SIGNALING IN THE BRAIN COGS 163 By: Pranav Singh Alexandra Villar INTRODUCTION Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas by the islets of Langerhans that regulates the
Leptin-Insulin Signaling in the Brain. BY TEAM CEPHALIC Aman Hamdard, Kevin Artiga, Megan Imreh, Ronald Baldonado, and Sharri Mo
 Leptin-Insulin Signaling in the Brain BY TEAM CEPHALIC Aman Hamdard, Kevin Artiga, Megan Imreh, Ronald Baldonado, and Sharri Mo Agenda Leptin in the Hypothalamus: Pathways and Roles Cross-talk between
Leptin-Insulin Signaling in the Brain BY TEAM CEPHALIC Aman Hamdard, Kevin Artiga, Megan Imreh, Ronald Baldonado, and Sharri Mo Agenda Leptin in the Hypothalamus: Pathways and Roles Cross-talk between
Final Review Sessions. 3/16 (FRI) 126 Wellman (4-6 6 pm) 3/19 (MON) 1309 Surge 3 (4-6 6 pm) Office Hours
 Final Review Sessions 3/16 (FRI) 126 Wellman (4-6 6 pm) 3/19 (MON) 1309 Surge 3 (4-6 6 pm) Office ours 3/14 (WED) 9:30 11:30 am (Rebecca) 3/16 (FRI) 9-11 am (Abel) Final ESSENTIALS Posted Lecture 20 ormonal
Final Review Sessions 3/16 (FRI) 126 Wellman (4-6 6 pm) 3/19 (MON) 1309 Surge 3 (4-6 6 pm) Office ours 3/14 (WED) 9:30 11:30 am (Rebecca) 3/16 (FRI) 9-11 am (Abel) Final ESSENTIALS Posted Lecture 20 ormonal
Regulation of adipose tissue remodeling by peripheral serotonin
 Regulation of adipose tissue remodeling by peripheral serotonin Sangkyu Park Catholic Kwandong University College of Medicine Department of Biochemistry Serotonin (5-HT) is a signaling molecule Hemostasis
Regulation of adipose tissue remodeling by peripheral serotonin Sangkyu Park Catholic Kwandong University College of Medicine Department of Biochemistry Serotonin (5-HT) is a signaling molecule Hemostasis
Effects of growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist and antagonist in nonobese type 2 diabetic MKR mice
 Effects of growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist and antagonist in nonobese type 2 diabetic MKR mice Rasha Mosa (MBCHC, M.D, PhD candidate) School of Biomedical Sciences University of Queensland
Effects of growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist and antagonist in nonobese type 2 diabetic MKR mice Rasha Mosa (MBCHC, M.D, PhD candidate) School of Biomedical Sciences University of Queensland
LS1a Fall 06 Problem Set #4
 LS1a Fall 06 Problem Set #4 Due Friday 10/27 at noon in your TF s drop box on the 2 nd floor of the Science Center all questions including the (*extra*) one should be turned in 1. To further investigate
LS1a Fall 06 Problem Set #4 Due Friday 10/27 at noon in your TF s drop box on the 2 nd floor of the Science Center all questions including the (*extra*) one should be turned in 1. To further investigate
Biochem 503 Fall Protein Tyr Phosphatases
 Biochem 503 Fall 2005 Protein Tyr Phosphatases David Brautigan assigned reading: Stoker (2005) J. Endocrin. 185:19-33 History 1981-1982 First description of P-Tyr specific phosphohydrolyase activity in
Biochem 503 Fall 2005 Protein Tyr Phosphatases David Brautigan assigned reading: Stoker (2005) J. Endocrin. 185:19-33 History 1981-1982 First description of P-Tyr specific phosphohydrolyase activity in
Mfn2 deletion in brown adipose tissue protects from insulin resistance and impairs thermogenesis
 Article Mfn2 deletion in brown adipose tissue protects from insulin resistance and impairs thermogenesis Kiana Mahdaviani 1,2, Ilan Y Benador 1,2, Shi Su 1, Raffi A Gharakhanian 1, Linsey Stiles 1,2, Kyle
Article Mfn2 deletion in brown adipose tissue protects from insulin resistance and impairs thermogenesis Kiana Mahdaviani 1,2, Ilan Y Benador 1,2, Shi Su 1, Raffi A Gharakhanian 1, Linsey Stiles 1,2, Kyle
Insulin-Leptin Interactions
 Insulin-Leptin Interactions Ahmed S., Al-Azzam N., Cao B. Karshaleva B., Sriram S., Vu K. If you understand a system, you can predict it. Agenda - Energy homeostasis Overview of leptin and insulin Signaling
Insulin-Leptin Interactions Ahmed S., Al-Azzam N., Cao B. Karshaleva B., Sriram S., Vu K. If you understand a system, you can predict it. Agenda - Energy homeostasis Overview of leptin and insulin Signaling
Hormonal regulation of. Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara
 Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
Primer sequences Target Sequence F Sequence R TNF-α (Tnfa) TCAGCCGATTTGCTATCTCAT A
 Supplementary Table 1. Q- and RT-PR primers used in this study. Primer sequences Target Sequence F Sequence R TNF-α (Tnfa) TGGTTTGTTTT GTTTGGGGTTG T hemokine (- motif) ligand 5 (cl5) GTGTTTGTTT TGGTGGTG
Supplementary Table 1. Q- and RT-PR primers used in this study. Primer sequences Target Sequence F Sequence R TNF-α (Tnfa) TGGTTTGTTTT GTTTGGGGTTG T hemokine (- motif) ligand 5 (cl5) GTGTTTGTTT TGGTGGTG
Tanycytes as gatekeepers of the Metabolic Brain
 Tanycytes as gatekeepers of the Metabolic Brain Vincent Prevot Inserm team Development and Plasticity of the Postnatal Brain Jean-Pierre Aubert Research Centre, U837, Lille France Metabolic signals and
Tanycytes as gatekeepers of the Metabolic Brain Vincent Prevot Inserm team Development and Plasticity of the Postnatal Brain Jean-Pierre Aubert Research Centre, U837, Lille France Metabolic signals and
Adipose tissue: Roles and function in diabetes and beyond. August 2015; SAGLB.DIA
 Adipose tissue: Roles and function in diabetes and beyond August 2015; SAGLB.DIA.15.07.0398 Acknowledgement The following slides intend to summarise the key points presented during the Banting Medal for
Adipose tissue: Roles and function in diabetes and beyond August 2015; SAGLB.DIA.15.07.0398 Acknowledgement The following slides intend to summarise the key points presented during the Banting Medal for
Hypothalamic Autophagy and Regulation of Energy Balance
 Hypothalamic Autophagy and Regulation of Energy Balance Rajat Singh, MD Albert Einstein College of Medicine New York NuGOweek 211 Sept 6-9, 211 Autophagy Evolutionarily conserved cellular recycling program
Hypothalamic Autophagy and Regulation of Energy Balance Rajat Singh, MD Albert Einstein College of Medicine New York NuGOweek 211 Sept 6-9, 211 Autophagy Evolutionarily conserved cellular recycling program
Lack of TRPV2 impairs thermogenesis in mouse brown adipose tissue
 Manuscript EMBO-2015-40819 Lack of TRPV2 impairs thermogenesis in mouse brown adipose tissue Wuping Sun, Kunitoshi Uchida, Yoshiro Suzuki, Yiming Zhou, Minji Kim, Yasunori Takayama, Nobuyuki Takahashi,
Manuscript EMBO-2015-40819 Lack of TRPV2 impairs thermogenesis in mouse brown adipose tissue Wuping Sun, Kunitoshi Uchida, Yoshiro Suzuki, Yiming Zhou, Minji Kim, Yasunori Takayama, Nobuyuki Takahashi,
Molecular and neural mechanisms of leptin action: Focus on Reproduction
 Molecular and neural mechanisms of leptin action: Focus on Reproduction Martin G. Myers, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. and collaborators Division of Metabolism, Endocrinology and Diabetes Department of Internal Medicine
Molecular and neural mechanisms of leptin action: Focus on Reproduction Martin G. Myers, Jr., M.D., Ph.D. and collaborators Division of Metabolism, Endocrinology and Diabetes Department of Internal Medicine
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Visualization of endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria interaction by in situ proximity ligation assay. A) Illustration of targeted proteins in mitochondria (M), endoplasmic reticulum
Supplementary Figure 1. Visualization of endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria interaction by in situ proximity ligation assay. A) Illustration of targeted proteins in mitochondria (M), endoplasmic reticulum
IL-6Rα IL-6RαT-KO KO. IL-6Rα f/f bp. f/f 628 bp deleted 368 bp. 500 bp
 STD H 2 O WT KO IL-6Rα f/f IL-6Rα IL-6RαT-KO KO 1000 bp 500 bp f/f 628 bp deleted 368 bp Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation of T-cell IL-6Rα deficiency. (a) Representative histograms and (b) quantification
STD H 2 O WT KO IL-6Rα f/f IL-6Rα IL-6RαT-KO KO 1000 bp 500 bp f/f 628 bp deleted 368 bp Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation of T-cell IL-6Rα deficiency. (a) Representative histograms and (b) quantification
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
The Effects of Low-Dose Endotoxin on Whole Body Glucose Metabolism. Joseph Robert Stevens
 The Effects of Low-Dose Endotoxin on Whole Body Glucose Metabolism Joseph Robert Stevens Dissertation submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment
The Effects of Low-Dose Endotoxin on Whole Body Glucose Metabolism Joseph Robert Stevens Dissertation submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment
ΦΛΕΓΜΟΝΗ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΒΗΤΗΣ
 ΦΛΕΓΜΟΝΗ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΒΗΤΗΣ ΘΩΜΑΣ ΠΑΠΑΔΟΠΟΥΛΟΣ, MD, PHD ΕΠΕΜΒΑΤΙΚΟΣ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ ΙΑΤΡΙΚΟ ΔΙΑΒΑΛΚΑΝΙΚΟ ΚΕΝΤΡΟ Inflammation as a cause of disease has entered the popular imagination. Diet ( macronutrients )
ΦΛΕΓΜΟΝΗ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΒΗΤΗΣ ΘΩΜΑΣ ΠΑΠΑΔΟΠΟΥΛΟΣ, MD, PHD ΕΠΕΜΒΑΤΙΚΟΣ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ ΙΑΤΡΙΚΟ ΔΙΑΒΑΛΚΑΝΙΚΟ ΚΕΝΤΡΟ Inflammation as a cause of disease has entered the popular imagination. Diet ( macronutrients )
Leptin and the Central Nervous System Control of Glucose Metabolism
 Physiol Rev 91: 389 411, 2011; doi:10.1152/physrev.00007.2010. Leptin and the Central Nervous System Control of Glucose Metabolism GREGORY J. MORTON AND MICHAEL W. SCHWARTZ Diabetes and Obesity Center
Physiol Rev 91: 389 411, 2011; doi:10.1152/physrev.00007.2010. Leptin and the Central Nervous System Control of Glucose Metabolism GREGORY J. MORTON AND MICHAEL W. SCHWARTZ Diabetes and Obesity Center
UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
control kda ATGL ATGLi HSL 82 GAPDH * ** *** WT/cTg WT/cTg ATGLi AKO/cTg AKO/cTg ATGLi WT/cTg WT/cTg ATGLi AKO/cTg AKO/cTg ATGLi iwat gwat ibat
 body weight (g) tissue weights (mg) ATGL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) HSL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) ### # # kda ATGL 55 HSL 82 GAPDH 37 2.5 2. 1.5 1..5 2. 1.5 1..5.. Supplementary
body weight (g) tissue weights (mg) ATGL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) HSL protein expression (relative to GAPDH) ### # # kda ATGL 55 HSL 82 GAPDH 37 2.5 2. 1.5 1..5 2. 1.5 1..5.. Supplementary
Professor Christopher Proud
 South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute Professor Christopher Proud Cell Signalling & Gene Regulation Professor Christopher G. Proud Nutrition and Metabolism Theme Leader South Australian
South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute Professor Christopher Proud Cell Signalling & Gene Regulation Professor Christopher G. Proud Nutrition and Metabolism Theme Leader South Australian
ENHANCEMENT OF BROWN ADIPOSE TISSUE DEVELOPMENT IN VIVO BY A NOVEL INSULIN SENSITIZER
 ENHANCEMENT F BRWN ADIPSE TISSUE DEVELPMENT IN VIV BY A NVEL INSULIN SENSITIZER William G. McDonald 1, Serena L. Cole 1, Brian N. Finck 2, Danielle D. Holewa 1, Angela S. Brightwell-Conrad 1, Charles Mackenzie
ENHANCEMENT F BRWN ADIPSE TISSUE DEVELPMENT IN VIV BY A NVEL INSULIN SENSITIZER William G. McDonald 1, Serena L. Cole 1, Brian N. Finck 2, Danielle D. Holewa 1, Angela S. Brightwell-Conrad 1, Charles Mackenzie
PTP1B: a new therapeutic target for Rett syndrome
 PTP1B: a new therapeutic target for Rett syndrome Lutz Tautz J Clin Invest. 2015;125(8):2931-2934. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci83192. Rett syndrome (RTT) is an X-linked neurodevelopmental disorder that
PTP1B: a new therapeutic target for Rett syndrome Lutz Tautz J Clin Invest. 2015;125(8):2931-2934. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci83192. Rett syndrome (RTT) is an X-linked neurodevelopmental disorder that
Obesity and insulin resistance
 Obesity and insulin resistance Barbara B. Kahn and Jeffrey S. Flier Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston,
Obesity and insulin resistance Barbara B. Kahn and Jeffrey S. Flier Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston,
Insulin resistance and pancreatic b cell failure
 Review series introduction Insulin resistance and pancreatic b cell failure Masato Kasuga Department of Clinical Molecular Medicine, Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine, Kobe, Japan. It is now
Review series introduction Insulin resistance and pancreatic b cell failure Masato Kasuga Department of Clinical Molecular Medicine, Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine, Kobe, Japan. It is now
Sphingolipid de novo synthesis: its relevance to metabolic diseases and cell polarity
 Sphingolipid de novo synthesis: its relevance to metabolic diseases and cell polarity Xian-Cheng Jiang (shian-chen chiang) SUNY Downstate Medical Center Cell plasma membrane Lipid rafts Sphingolipid =
Sphingolipid de novo synthesis: its relevance to metabolic diseases and cell polarity Xian-Cheng Jiang (shian-chen chiang) SUNY Downstate Medical Center Cell plasma membrane Lipid rafts Sphingolipid =
Islets of Langerhans consist mostly of insulin-producing β cells. They will appear to be densely labeled
 Are adult pancreatic beta cells formed by self-duplication or stem cell differentiation? Introduction Researchers have long been interested in how tissues produce and maintain the correct number of cells
Are adult pancreatic beta cells formed by self-duplication or stem cell differentiation? Introduction Researchers have long been interested in how tissues produce and maintain the correct number of cells
Increased Energy Expenditure, Decreased Adiposity, and Tissue-Specific Insulin Sensitivity in Protein-Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B-Deficient Mice
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Aug. 2000, p. 5479 5489 Vol. 20, No. 15 0270-7306/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Increased Energy Expenditure, Decreased
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, Aug. 2000, p. 5479 5489 Vol. 20, No. 15 0270-7306/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Increased Energy Expenditure, Decreased
a b c Physical appearance of mice Lean mass Adipocyte size d e f
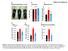 LFD HFD LFD HFD Area under curve (GTT) HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD Area under curve (ITT) HFD-VSL#3 Liver TG content (% l) HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD HFD + VSL#3 Lean mass (gm) Mean adipocyte
LFD HFD LFD HFD Area under curve (GTT) HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD Area under curve (ITT) HFD-VSL#3 Liver TG content (% l) HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD HFD-VSL#3 LFD HFD HFD + VSL#3 Lean mass (gm) Mean adipocyte
AGING, INSULIN RESISTANCE AND MITOCHONDRIAL FUNCTION. Kitt Falk Petersen, M.D. Yale University School of Medicine
 AGING, INSULIN RESISTANCE AND MITOCHONDRIAL FUNCTION Kitt Falk Petersen, M.D. Yale University School of Medicine % of Population Prevalence of Diabetes and Glucose Intolerance 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5
AGING, INSULIN RESISTANCE AND MITOCHONDRIAL FUNCTION Kitt Falk Petersen, M.D. Yale University School of Medicine % of Population Prevalence of Diabetes and Glucose Intolerance 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5
Title: Obesity in mice with adipocyte-specific deletion of clock component Bmal1
 Title: Obesity in mice with adipocyte-specific deletion of clock component Bmal1 Authors: Georgios K. Paschos, Salam Ibrahim, Wen-Liang Song, Takeshige Kunieda, Gregory Grant, Teresa M. Reyes, Christopher
Title: Obesity in mice with adipocyte-specific deletion of clock component Bmal1 Authors: Georgios K. Paschos, Salam Ibrahim, Wen-Liang Song, Takeshige Kunieda, Gregory Grant, Teresa M. Reyes, Christopher
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Overexpression of Fto leads to increased food intake and results in obesity Chris Church, Lee Moir, Fiona McMurray, Christophe Girard, Gareth T Banks, Lydia Teboul, Sara Wells,
Supplementary Information Overexpression of Fto leads to increased food intake and results in obesity Chris Church, Lee Moir, Fiona McMurray, Christophe Girard, Gareth T Banks, Lydia Teboul, Sara Wells,
Supplementary Figure 1
 VO (ml kg - min - ) VCO (ml kg - min - ) Respiratory exchange ratio Energy expenditure (cal kg - min - ) Locomotor activity (x count) Body temperature ( C) Relative mrna expression TA Sol EDL PT Heart
VO (ml kg - min - ) VCO (ml kg - min - ) Respiratory exchange ratio Energy expenditure (cal kg - min - ) Locomotor activity (x count) Body temperature ( C) Relative mrna expression TA Sol EDL PT Heart
ANSC/NUTR 601 GENERAL ANIMAL NUTRITION Stearoyl-CoA desaturase, VLDL metabolism, and obesity
 ANSC/NUTR 601 GENERAL ANIMAL NUTRITION Stearoyl-CoA desaturase, VLDL metabolism, and obesity I. Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase and obesity in rodents A. Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase (SCD) is the 9 desaturase.
ANSC/NUTR 601 GENERAL ANIMAL NUTRITION Stearoyl-CoA desaturase, VLDL metabolism, and obesity I. Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase and obesity in rodents A. Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase (SCD) is the 9 desaturase.
Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author)
 Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author) The authors provide an interesting data set concerning the effects of an ATGL inhibitor on energy balance and indices of insulin action in mice fed a high fat diet.
Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author) The authors provide an interesting data set concerning the effects of an ATGL inhibitor on energy balance and indices of insulin action in mice fed a high fat diet.
PKCδ regulates hepatic insulin sensitivity and hepatosteatosis in mice and humans
 Research article PKCδ regulates hepatic insulin sensitivity and hepatosteatosis in mice and humans Olivier Bezy, 1 Thien T. Tran, 1 Jussi Pihlajamäki, 2 Ryo Suzuki, 1 Brice Emanuelli, 1 Jonathan Winnay,
Research article PKCδ regulates hepatic insulin sensitivity and hepatosteatosis in mice and humans Olivier Bezy, 1 Thien T. Tran, 1 Jussi Pihlajamäki, 2 Ryo Suzuki, 1 Brice Emanuelli, 1 Jonathan Winnay,
REVIEW Tissue specificity on insulin action and resistance: past to recent mechanisms
 Acta Physiol 2011, 201, 297 312 REVIEW Tissue specificity on insulin action and resistance: past to recent mechanisms M. Benito Departamento de Bioquímica y Biología Molecular II, Facultad de Farmacia,
Acta Physiol 2011, 201, 297 312 REVIEW Tissue specificity on insulin action and resistance: past to recent mechanisms M. Benito Departamento de Bioquímica y Biología Molecular II, Facultad de Farmacia,
A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome. and Type-2 Diabetes
 A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome and Type-2 Diabetes Yan Zhang, Chunmei Cao, Rui-Ping Xiao Institute of Molecular Medicine (IMM) Peking University, Beijing, China Accelerated Aging in China
A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome and Type-2 Diabetes Yan Zhang, Chunmei Cao, Rui-Ping Xiao Institute of Molecular Medicine (IMM) Peking University, Beijing, China Accelerated Aging in China
