Schistocytic anaemia, severe thrombocytopenia, and renal dysfunction: thrombotic microangiopathy due to severe acquired ADAMTS-13 deficiency Case 2
|
|
|
- Pierce Robertson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 103/ Schattauer GmbH Schistocytic anaemia, severe thrombocytopenia, and renal dysfunction: thrombotic microangiopathy due to severe acquired ADAMTS-13 deficiency Case 2 A. Winkler, J. A. Kremer Hovinga, V. Bianchi, J.-D. Studt, B. Lämmle Central Haematology Laboratory, Inselspital, University Hospital, Bern, Switzerland Keywords ADAMTS-13, microangiopathy, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease Summary We present the case of a woman (age: 64 years) with acute thrombotic microangiopathy due to severe acquired ADAMTS-13 (von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease) deficiency. She was successfully treated with plasma exchange therapy and glucocorticosteroids. She relapsed seven months later, and splenectomy led to lasting remission. Pathomechanisms of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, especially the role of ADAMTS-13, are discussed and therapeutic measures outlined. Awoman (age: 64 years) presented in July 1999 to a peripheral hospital with increasing fatigue and nausea. Upon admission she was somnolent and icteric. Neither fever nor petechiae were detectable. The patient s medical history was significant for a discoid lupus erythematosus diagnosed in 1984 with partial alopecia. She also reported phototoxicity. Schlüsselwörter Mikroangiopathie, thrombotisch-thrombozytopenische Purpura, von-willebrand-faktor-spaltende Protease, ADAMTS-13 Zusammenfassung Wir berichten über eine Frau (Alter: 64 Jahre) mit akuter thrombotischer Mikroangiopathie bei schwerem akquiriertem Mangel an von-willebrand-faktor-spaltender Protease (ADAMTS-13). Sie wurde erfolgreich mit Plasmapheresen und Glukokortikosteroiden behandelt. Sieben Monate später kam es zu einem Rezidiv, eine Splenektomie wurde vorgenommen und führte zu anhaltender Remission. Aktuelle Kenntnisse zur Pathophysiologie der thrombotisch-thrombozytopenischen Purpura werden diskutiert, insbesondere die Rolle von ADAMTS-13. Abschließend werden therapeutische Maßnahmen vorgestellt. Mikroangiopathisch-hämolytische Anämie, schwere Thrombozytopenie und Niereninsuffizienz: thrombotische Mikroangiopathie bei schwerem akquirierten ADAMTS-13-Mangel Hämostaseologie 2003: 23: Diagnosis Laboratory data revealed profound thrombocytopenia ( /l) and normochromic, normocytic anaemia (haemoglobin 78 g/l). The peripheral blood smear showed many schistocytes (Fig. 1). Serum creatinine was 264 µmol/l (reference range: µmol/l), urea was 39 mmol/l (reference range: mmol/l). There was no proteinuria. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 130 mm/h and C-reactive protein 15 mg/l (reference value <5 mg/l). Ultrasonography of the abdomen indicated no splenomegaly and computed tomography of the brain was normal. A diagnosis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura/hemolytic uremic syndrome (TTP/HUS) was suspected and the patient was referred to our hospital for further diagnostics and treatment. Additional investigations revealed negative direct Coombs test, elevated reticulocyte count ( /l; reference range: /l), free haemoglobin in plasma (0.09 g/l; reference value: <0.01 g/l), elevated total bilirubin concentration (45 µmol/l; reference range: 0-17 µmol/l), elevated lactate dehydrogenase (4605 U/l; reference range: <480 U/l), elevated hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase (1325 U/l; reference range: U/l). Haptoglobin was <0.06 g/l (reference range: g/l), haemosiderin was detected in the urine. Coagulation profile turned out as normal. Serologic examinations were negative for human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B and C virus infection. Immunologic tests were positive for antinuclear antibody (1 : 320), anti- RNP, and anti-ds DNA. Bone marrow aspiration showed hyperactive haematopoietic activity with increased megakaryopoiesis and erythropoiesis as well as focal lymphocyte clusters.
2 104/12 Fig. 1 Peripheral blood smear of the patient with acquired TTP: numerous fragmented erythrocytes (schistocytes) and severe thrombocytopenia count was /l and haemoglobin 93 g/l. Follow-up at our outpatient clinic 3 months later showed a normal platelet count, no signs of haemolysis, and an ADAMTS-13 activity of 100%. In February 2000, she suffered from a relapse of TTP: Haemoglobin was 73 g/l, platelet count amounted to /l, activity of lactate dehydrogenase was 2931 U/l. She had noted progressing general fatigue over the preceeding 3-4 weeks. The preexisting discoid skin lesion on the cheek had worsened. In January, prednisone had been tapered from 5 mg/d to 5 mg every other day. ANA were slightly elevated (1 : 80), anti-ds DNA antibodies were negative at that time. Plasma exchange therapy with replacement of FFP and glucocorticosteroids were reinitiated. ADAMTS-13 activity upon admission was 15%. After a first plasma exchange session it increased to 50%, after the second to 100%. No ADAMTS-13 inhibitor was detectable. Platelet count after four plasma exchange therapy sessions was /l. Two weeks later the patient underwent splenectomy. Vaccination against pneumococcal bacteria and Haemophilus influenzae type B was performed as soon as glucocorticosteroids were tapered to 5 mg/d (two weeks after splenectomy). On four follow-up visits (after 6, 12, 24, and 36 months), she was in a good general condition without any signs of haemolysis and platelet count within the reference range. ADAMTS-13 activity was 100% on each occasion. Therapy, follow-up Daily plasma exchange therapy of about 3 l using fresh frozen plasma (FFP) replacement was started immediately. Additional FFP was administered between plasma exchange sessions. The patient also received methylprednisolone (200 mg/d). Before each plasma exchange session the von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS-13) activity, as well as the protease inhibitor were determined. Initially, ADAMTS-13 activity was <3% and a weak inhibitor was detectable (Fig. 2). On day 4 ADAMTS-13 activity increased to about 30%, on day 10 to 100% with no detectable inhibitor. Platelet count and lactate dehydrogenase activity normalized on day 8. By that time, serum creatinine was within the reference range. After 18 days in the hospital the woman was discharged in good general condition with prednisone (dosage: 70 mg/d). Platelet Discussion Our patient suffered from acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura due to an antibody inhibiting the von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease, now denoted as ADAMTS(a disintegrin and metalloprotease with thrombospondin type 1 motifs)- 13. We here present a short overview of the thrombotic microangiopathies (TMAs), discuss the role of ADAMTS-13 in TTP, and outline therapeutic measures in patients with TMAs. TTP belongs to the thrombotic microangiopathies. It was described by Moschcowitz for the first time in 1924 (27). The concept consisting of the classical disease defining pentad: thrombocytopenia, microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia, neurological symptoms, renal dysfunction, fever evolved over the years. Fig. 2 ADAMTS-13 activity in acute acquired TTP: quantitative immunoblotting of purified vwf substrate degraded by barium chloride-activated ADAMTS-13 in plasma (1 : 20) Lane 1: initially (ADAMTS-13 activity <3% of the normal); lanes 2-11: during plasma exchange therapy (ADAMTS-13 activity 15% on day 2 and 100% on day 10); lanes 12-14: assay calibration by normal plasma dilutions 1 : 20, 1 : 80, 1 : 160 corresponding to ADAMTS-13 activity of 100, 25, and 12.5%, respectively. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome (HUS), first described by Gasser et al. (14), is a similar form of TMA. The diagnosis is often made in cases with predominating renal involvement, while TTP most often is diagnosed when neurological symptoms are present. HUS occurs mostly in young children after infection by E. coli O157 : H7 leading to haemorrhagic diarrhea (typical or D+ HUS), but is also diagnosed in the absence of enteropathogenic E. coli infection (atypical HUS).
3 105/14 Besides idiopathic TTP, E. coli O157 : H7-associated HUS and idiopathic HUS, thrombotic microangiopathies associated with a number of conditions are variably referred to as TTP, HUS, TTP-HUS, TTPlike disease or secondary TTP (Tab. 1). Tab. 1 Thrombotic microangiopathies Role of ADAMTS-13 in TTP Different mechanisms were reported to play a pathogenetic role in idiopathic TTP. Abnormal interaction of endothelial cells and circulating platelets is generally considered to be the crucial defect. High concentrations of thrombomodulin as well as plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 were found, indicating endothelial damage. Another observation was the presence of calpain or cathepsin-like cysteine protease activity in acute TTP, postulated to cause platelet agglutination. Specific platelet aggregating factors (e. g. 2 proteins with molecular mass of 37 and 59 kda, respectively) were described. Deficiencies as well as abnormalities of prostacyclin were also reported (for review see 9, 24, 30). New insights into the pathophysiology of TTP emerged in recent years. Moake et al. (23) observed unusually large von Willebrand factor multimers (ULvWF) in plasma samples of patients with chronic relapsing TTP. vwf is a glycoprotein synthesized and secreted into the plasma by endothelial cells and megakaryocytes. It mediates the initial platelet adhesion to the subendothelial wall of a damaged vessel. The vwf is composed of a variable number of subunits (molecular mass 250 kda) linked by disulfide bonds. The binding affinity for collagen and platelet receptors is enhanced in the large multimeric forms of vwf (Fig. 3). Proteolytic degradation of ULvWF at elevated shear stress is a physiologic event in healthy individuals (6, 37). A specific protease cleaving vwf at the peptide bond 842 Tyr 843 Met was isolated from normal human plasma (11, 38). Further studies showed that this vwfcleaving protease (vwf-cp) is absent in patients with constitutional TTP and blocked by an inhibitor in patients with acquired (non-familial) TTP. Furlan et al. (13) found a complete deficiency of vwf-cp in four a b c * reproduced with kind permission from Springer-Verlag GmbH & Co. KG, Heidelberg: Furlan M. Von Willebrand factor: molecular size and functional activity. Ann Hematol 1996; 72: 341-8, Fig. 1 patients (including two brothers) with relapsing TTP. No inhibitor was detected. The occurrence of relapsing TTP in two brothers suggested a hereditary nature of ADAMTS-13 deficiency. In 1998 an inhibitor of vwf-cp was detected in a patient with TTP who lacked any protease activity (12).The inhibitor was identified as IgG. It disappeared after the initial treatment, its reappearance was followed by a clinical relapse. In 2001 vwf-cp was purified, partially sequenced and identified as a new member of the ADAMTS family of metalloproteases (8, 16, 43). Independently, genome-wide linkage analysis in patients with hereditary TTP and their family members mapped the locus of the responsible gene to chromosome 9q34, showing that it encoded ADAMTS- 13 (21). Double heterozygous or homozygous ADAMTS-13 gene mutations were responsible for severe ADAMTS-13 deficiency in the affected patients. In the meantime several mutations throughout the ADAMTS-13 gene have been found in hereditary TTP (2, 20, 21, 31). Two large studies (10, 36) suggested that most patients diagnosed with TTP had a severe deficiency of ADAMTS-13 activity, most often due to IgG autoantibodies inhibiting enzymatic activity of the protease. Interestingly, patients clinically diagnosed with HUS exhibited most often normal ADAMTS-13 activity (10). This is rather surprising because TTP and HUS are often difficult to distinguish clinically (15). However, a prospective study of patients with TMA (41) confirmed that 47/66 patients (71%) clinically diagnosed with TTP had severe ADAMTS-13 deficiency whereas most patients with the diagnosis HUS had normal or subnormal ADAMTS-13 activity. Fig. 3 Structure of vwf in relation to its function* a) denaturing electrophoresis (1% SDS-agarose) of vwf in normal plasma: large multimers on top, electrophoretic migration towards the bottom of the gel; b) bottom band of dimeric vwf (~500 kda); c) arrow symbolizing the decrease in function (binding affinity to collagen and platelet glycoprotein Ib) from large to small sized vwf multimers
4 106/15 Schistocytic anaemia, thrombocytopenia, renal dysfunction mechanisms are involved in the pathogenesis of TTP (Fig. 4). During the 36 months of follow-up after splenectomy our patient did not experience a relapse. Fig. 4 Established and hypothetical mechanisms in the pathogenesis of acquired TTP A controversial discussion is taking place concerning the specificity of ADAMTS-13 deficiency for TTP. Mannucci et al. (22) reported decreased ADAMTS-13 activity in newborns, pregnant women, and patients with various disease conditions (liver cirrhosis, inflammatory diseases), concluding that ADAMTS-13 deficiency was not specific for TTP. Moore et al. (25) suggested that ADAMTS-13 deficiency was present also in several patients with thrombocytopenia caused by a variety of conditions other than TTP. However, in a large study on 68 patients with thrombocytopenia not caused by TTP or HUS, ADAMTS-13 activity was in none of these cases <10% even though it was mildly or moderately decreased in some patients (5). Therefore, we conclude that a severe deficiency of ADAMTS-13 activity (<3-5% of normal plasma) is a specific feature of TTP and must be distinguished from moderately (10-25%) and mildly decreased (25-50%) values. Another question addresses the sensitivity of ADAMTS-13 deficiency for the diagnosis of TTP. Furlan et al. (10) found 86% (26 of 30) of patients with TTP to be lacking ADAMTS-13 activity, and Tsai and Lian (36) reported a severe deficiency in 100% (37/37 patients). A prospective study by Veyradier et al. (41) found a severe protease deficiency in 71% (47/66) of the cases diagnosed as TTP. In a large inception cohort of 142 consecutive patients with TMA, Vesely et al. (40) found severely deficient ADAMTS-13 activity in only 33% (16/48) of the patients with idiopathic TTP. Thus, even though a severe deficiency of ADAMTS-13 activity is specific for a TMA that is generally diagnosed as TTP not all patients with TTP have severe ADAMTS- 13 deficiency. In our opinion, the absence of severe ADAMTS-13 deficiency should not rule out the diagnosis of TTP, which is based on clinical findings. It may be speculated that other mechanisms regulating the size of vwf multimers play a role in the pathogenesis of TTP. One interesting hypothesis concerns defective binding of ADAMTS-13 to the endothelium without interfering with the active site of the protease (24). This could, for instance, be due to anti-glycoprotein IV (CD36) antibodies, found in patients with TTP (34). Such autoantibodies might lead to impaired anchoring of ADAMTS-13 to the endothelium that is not detectable by current assays of ADAMTS-13 activity in plasma (Fig. 4). Finally, other still unknown pathogenetic mechanisms besides ULvWF multimers may lead to a clinical picture indistinguishable from TTP. Our patient initially presented with a severe ADAMTS-13 deficiency of <3% (Fig. 2). A weak inhibitor was detected. After 4 and 10 days of plasma exchange therapy the ADAMTS-13 activity had increased to about 30% and 100%, respectively. At the time of the clinical relapse, the protease activity interestingly was 15%, which is outside the range of severe deficiency (<3-5%) typically seen in many patients with classical TTP. No inhibitor was detectable during the second episode.the relapse, despite the absence of severe ADAMTS-13 deficiency, supports the hypothesis that additional Therapeutic strategies in TMAs If untreated, TTP generally follows a rapidly progressive fatal course in most patients. The mortality rate of >90% (1) was reduced to 8-25% by the introduction of therapeutic plasma exchange in clinical routine (15, 29). Plasma exchange should be started immediately when TTP is diagnosed or suspected. Plasma removal eliminates the acquired autoantibody and plasma infusion replaces the missing ADAMTS-13. It was shown by the Canadian Apheresis Study Group (28) that plasma exchange with fresh frozen plasma (FFP) was more effective than plasma infusion alone. However, this may reflect a dose phenomenon, as the patients treated with plasma exchange received threefold as much plasma as those with plasma infusion alone. It has been suggested that cryosupernatant plasma may be more efficient than FFP. However, equal outcomes were reported by the North American TTP Group (42). Mori et al. (26) showed a better response to plasma exchange therapy in those patients with severe ADAMTS-13 deficiency (10/12 patients with severe deficiency survived whereas 4/6 without severe deficiency died).this may suggest that plasma exchange with FFP replacement is not the optimal treatment in patients without severe autoantibody-mediated ADAMTS-13 deficiency. However, in the absence of knowledge of the pathomechanism in these patients, standard treatment with plasma exchange remains mandatory until improved therapeutic options based on the underlying pathogenesis become available. The strategy of performing plasma exchange in all patients with clinically diagnosed TTP is supported by data reported by Vesely et al. (40):Among the 48 patients with idiopathic TTP, treatment response, TTP-associated deaths and total mortality were not significantly different among the 16 patients with and the 32
5 107/16 without severe acquired ADAMTS-13 deficiency. Because many patients in all ADAMTS- 13 activity categories apparently respond to plasma exchange treatment, it does not seem justified at present to withhold plasma exchange in those without severe ADAMTS-13 deficiency. Plasma exchange is generally performed daily until platelet concentration and lactase dehydrogenase (LDH) activity are normalized. Usually, the neurological symptoms tend to improve first, followed by LDH and the platelets (35). After normalization of these parameters the frequency of plasma exchange is tapered. Typically, a response is seen during the first week and usually recovery is complete after 3 weeks, but large variations exist (40). For unknown reasons not all patients respond to plasma exchange therapy. In these cases, plasma exchange can be intensified to twice daily and/or additional FFP infusion between apheresis sessions may be applied. High doses of glucocorticosteroids are generally added to the treatment. This seems justified with regard to the frequent presence of autoantibodies inhibiting ADAMTS-13 activity. Vincristine is also often used in refractory TTP. Even though it acts as immunosuppressive agent, it is also known to have a direct effect on platelets by interfering with the polymerization of microtubules of the platelet membrane. Splenectomy was performed empirically in several patients with plasma refractory or relapsing TTP. As shown in the first patient described with autoantibody-mediated ADAMTS-13 deficiency and a relapsing course of TTP (12), splenectomy may lead to long-lasting remission by eliminating an important source of B-lymphocytes producing the inhibiting autoantibodies. Rituximab, the chimeric monoclonal anti-cd 20 antibody, currently is under investigation (17, 44). In the absence of life-threatening bleeding, platelet transfusions are contraindicated since they may lead to expanding microvascular thrombosis (19). Relapse of acquired TTP is common with an estimated recurrence rate of 36% after 10 years (32). Usually, patients relapse within the first year, but recurrences may occur as late as 10 years after the initial bout of TTP. Splenectomy might be beneficial in these cases as discussed above. The treatment of hereditary TTP differs from that of acquired TTP. Patients with severe constitutional ADAMTS-13 deficiency often manifest a first bout of TTP in early childhood but sometimes only in adulthood (9). They respond dramatically to FFP infusion alone (39). Regular infusions of FFP in order to substitute the deficient protease are an efficient prophylactic measure to avoid otherwise frequent relapses (3, 18). Children with diarrhea-associated HUS are generally not treated with plasma exchange and usually recover from acute episodes (33). Adults with HUS after E. coli O157 : H7 infection, however, have high mortality rates. One study suggested that plasma exchange therapy might be effective for them as well (7). Patients with ticlopidine-associated TMA had lower mortality rates when treated with plasma exchange therapy (4). Neoplasia-associated TMA and haematopoietic stem cell transplantation-associated TMA are sometimes treated by plasma exchange even though the outcome is usually fatal (40). References 1. Amorosi EL, Ultmann JE. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: report of 16 cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1966; 45: Antoine G, Zimmermann K, Plaimauer B et al. ADAMTS13 gene defects in two brothers with constitutional thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and normalization of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease activity by recombinant human ADAMTS13. Br J Haematol 2003; 120: Barbot J, Costa E, Guerra M et al. Ten years of prophylactic treatment with fresh-frozen plasma in a child with chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura as a result of a congenital deficiency of von Willebrand factorcleaving protease. Br J Haematol 2001; 113: Bennett CL, Weinberg PD, Rozenberg-Ben- Dror K et al. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura associated with ticlopidine. A review of 60 cases. Ann Intern Med 1998; 128: Bianchi V, Robles R,Alberio L et al.von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS13) in thrombocytopenic disorders: a severely deficient activity is specific for thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2002; 100: Dent JA, Galbusera M, Ruggeri ZM. Heterogeneity of plasma von Willebrand factor multimers resulting from proteolysis of the constituent subunit. J Clin Invest 1991; 88: Dundas S, Murphy J, Soutar RL et al. Effectiveness of therapeutic plasma exchange in the 1996 Lanarkshire Escherichia coli O157:H7 outbreak. Lancet 1999; 354: Fujikawa K, Suzuki H, McMullen B et al. Purification of human von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease and its identification as a new member of the metalloproteinase family. Blood 2001; 98: Furlan M, Lämmle B. Aetiology and pathogenesis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and haemolytic uraemic syndrome: the role of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2001; 14: Furlan M, Robles R, Galbusera M et al. Von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and the hemolytic-uremic syndrome. N Engl J Med 1998; 339: Furlan M, Robles R, Lämmle B. Partial purification and characterization of a protease from human plasma cleaving von Willebrand factor to fragments produced by in vivo proteolysis. Blood 1996; 87: Furlan M, Robles R, Solenthaler M et al. Acquired deficiency of von Willebrand factorcleaving protease in a patient with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 1998; 91: Furlan M, Robles R, Solenthaler M et al. Deficient activity of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 1997; 89: Gasser C, Gautier E, Steck A et al. Hämolytisch-urämische Syndrome: bilaterale Nierenrindennekrosen bei akuten erworbenen hämolytischen Anämien. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 1955; 85: George JN. How I treat patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood 2000; 96: Gerritsen HE, Robles R, Lämmle B et al. Partial amino acid sequence of purified von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease. Blood. 2001;98: Gutterman LA, Kloster B, Tsai HM. Rituximab therapy for refractory thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood Cells Mol Dis 2002; 28: Häberle J, Kehrel B, Ritter J et al. New strategies in diagnosis and treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: case report and review. Eur J Pediatr 1999; 158: Harkness DR, Byrnes JJ, Lian EC et al. Hazard of platelet transfusion in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. JAMA 1981; 246: Kokame K, Matsumoto M, Soejima K et al. Mutations and common polymorphisms in
6 108/18 ADAMTS13 gene responsible for von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: Levy GG, Nichols WC, Lian EC et al. Mutations in a member of the ADAMTS gene family cause thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nature 2001; 413: Mannucci PM, Canciani MT, Forza I et al. Changes in health and disease of the metalloprotease that cleaves von Willebrand factor. Blood 2001; 98: Moake JL, Rudy CK, Troll JH et al. Unusually large plasma factor VIII : von Willebrand factor multimers in chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med 1982; 307: Moake JL. Thrombotic microangiopathies. N Engl J Med 2002; 347: Moore JC, Hayward CP, Warkentin TE et al. Decreased von Willebrand factor protease activity associated with thrombocytopenic disorders. Blood 2001; 98: Mori Y, Wada H, Gabazza EC et al. Predicting response to plasma exchange in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura with measurement of vwf-cleaving protease activity. Transfusion 2002; 42: Moschcowitz E. Hyaline thrombosis of the terminal arterioles and capillaries: a hitherto undescribed disease. Proc N Y Pathol Soc 1924; 24: Rock GA, Shumak KH, Buskard NA et al. Comparison of plasma exchange with plasma infusion in the treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Canadian Apheresis Study Group. N Engl J Med 1991; 325: Rock GA. Management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol 2000; 109: Ruggenenti P, Remuzzi G.The pathophysiology and management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Eur J Haematol 1996; 56: Schneppenheim R, Budde U, Oyen F et al. Von Willebrand factor cleaving protease and ADAMTS13 mutations in childhood TTP. Blood 2003; 101: Shumak KH, Rock GA, Nair RC. Late relapses in patients successfully treated for thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Canadian Apheresis Group. Ann Intern Med 1995; 122: Siegler RL, Pavia AT, Hansen FL et al.atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome: a comparison with postdiarrheal disease. J Pediatr 1996; 128: Tandon NN, Rock G, Jamieson GA. Anti-CD36 antibodies in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol 1994; 88: Thompson CE, Damon LE, Ries CA et al. Thrombotic microangiopathies in the 1980s: clinical features, response to treatment, and the impact of the human immunodeficiency virus epidemic. Blood 1992; 80: Tsai HM, Lian EC. Antibodies to von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in acute thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med 1998; 339: Tsai HM, Sussman II, Nagel RL. Shear stress enhances the proteolysis of von Willebrand factor in normal plasma. Blood 1994; 83: Tsai HM. Physiologic cleavage of von Willebrand factor by a plasma protease is dependent on its conformation and requires calcium ion. Blood 1996; 87: Upshaw JD Jr. Congenital deficiency of a factor in normal plasma that reverses microangiopathic hemolysis and thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med 1978; 298: Vesely SK, George JN, Lämmle B et al. ADAMTS13 activity in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome: relation to presenting features and clinical outcomes in a prospective cohort of 142 patients. Blood 2003; 102: Veyradier A, Obert B, Houllier A et al. Specific von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in thrombotic microangiopathies: a study of 111 cases. Blood 2001; 98: Zeigler ZR, Shadduck RK, Gryn JF et al. Cryoprecipitate poor plasma does not improve early response in primary adult thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). J Clin Apheresis 2001; 16: Zheng X, Chung D, Takayama TK et al. Structure of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS13), a metalloprotease involved in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: Zheng X, Pallera AM, Goodnough LT et al. Remission of chronic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura after treatment with cyclophosphamide and rituximab. Ann Intern Med 2003; 138: Correspondence to: Bernhard Lämmle, MD Central Haematology Laboratory Inselspital, University Hospital 3010 Bern, Switzerland Tel. +41/31/ Fax +41/31/ bernhard.laemmle@insel.ch
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and the Role of ADAMTS-13
 Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and the Role of ADAMTS-13 Mark Cunningham,MD Director, Hematology Laboratory Department of Pathology University of Kansas Medical Center College of American Pathologists
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and the Role of ADAMTS-13 Mark Cunningham,MD Director, Hematology Laboratory Department of Pathology University of Kansas Medical Center College of American Pathologists
DR V PHILIP CLINICAL HAEMATOLOGY UNIT CHRIS HANI BARAGWANATH ACADEMIC HOSPITAL
 DR V PHILIP CLINICAL HAEMATOLOGY UNIT CHRIS HANI BARAGWANATH ACADEMIC HOSPITAL Rare but fatal disease if unrecognized and untreated Incidence about 1: 1 million in the USA Female preponderance of 2:1 Part
DR V PHILIP CLINICAL HAEMATOLOGY UNIT CHRIS HANI BARAGWANATH ACADEMIC HOSPITAL Rare but fatal disease if unrecognized and untreated Incidence about 1: 1 million in the USA Female preponderance of 2:1 Part
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura From Platelet Aggregates to Plasma
 Pathology Patterns Reviews Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura From Platelet Aggregates to Plasma Marisa B. Marques, MD, 1 Charles A. Mayfield, MD, PhD, 1 and Douglas P. Blackall, MD 2 Key Words: Thrombotic
Pathology Patterns Reviews Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura From Platelet Aggregates to Plasma Marisa B. Marques, MD, 1 Charles A. Mayfield, MD, PhD, 1 and Douglas P. Blackall, MD 2 Key Words: Thrombotic
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: a look at the future
 Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: a look at the future Andrea Artoni, MD Ph.D. Angelo Bianchi Bonomi Hemophilia and Thrombosis Center IRCCS Ca Granda Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico Milan, Italy andrea.artoni@policlinico.mi.it
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: a look at the future Andrea Artoni, MD Ph.D. Angelo Bianchi Bonomi Hemophilia and Thrombosis Center IRCCS Ca Granda Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico Milan, Italy andrea.artoni@policlinico.mi.it
TTP and ADAMTS13: When Is Testing Appropriate?
 TTP and ADAMTS13: When Is Testing Appropriate? Pier Mannuccio Mannucci and Flora Peyvandi A. Bianchi Bonomi Hemophilia and Thrombosis Center, Department of Medicine and Medical Specialities, University
TTP and ADAMTS13: When Is Testing Appropriate? Pier Mannuccio Mannucci and Flora Peyvandi A. Bianchi Bonomi Hemophilia and Thrombosis Center, Department of Medicine and Medical Specialities, University
The New England Journal of Medicine VON WILLEBRAND FACTOR CLEAVING PROTEASE IN THROMBOTIC THROMBOCYTOPENIC PURPURA AND THE HEMOLYTIC UREMIC SYNDROME
 VON WILLEBRAND FACTOR CLEAVING PROTEASE IN THROMBOTIC THROMBOCYTOPENIC PURPURA AND THE HEMOLYTIC UREMIC SYNDROME MIHA FURLAN, PH.D., RODOLFO ROBLES, MIRIAM GALBUSERA, SC.D., GIUSEPPE REMUZZI, M.D., PAUL
VON WILLEBRAND FACTOR CLEAVING PROTEASE IN THROMBOTIC THROMBOCYTOPENIC PURPURA AND THE HEMOLYTIC UREMIC SYNDROME MIHA FURLAN, PH.D., RODOLFO ROBLES, MIRIAM GALBUSERA, SC.D., GIUSEPPE REMUZZI, M.D., PAUL
THROMBOTIC MICROANGIOPATHY. Jun-Ki Park 7/19/11
 THROMBOTIC MICROANGIOPATHY Jun-Ki Park 7/19/11 TMAs are microvascular occlusive disorders characterized by systemic or intrarenal aggregation of platelets, thrombocytopenia, and mechanical injury to erythrocytes.
THROMBOTIC MICROANGIOPATHY Jun-Ki Park 7/19/11 TMAs are microvascular occlusive disorders characterized by systemic or intrarenal aggregation of platelets, thrombocytopenia, and mechanical injury to erythrocytes.
Beyond Plasma Exchange: Targeted Therapy for Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
 Beyond Plasma Exchange: Targeted Therapy for Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Kristen Knoph, PharmD, BCPS PGY2 Pharmacotherapy Resident Pharmacy Grand Rounds April 25, 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Objectives
Beyond Plasma Exchange: Targeted Therapy for Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Kristen Knoph, PharmD, BCPS PGY2 Pharmacotherapy Resident Pharmacy Grand Rounds April 25, 2017 2016 MFMER slide-1 Objectives
What is meant by Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TMA)?
 What is meant by Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TMA)? Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TMA) is a group of disorders characterized by injured endothelial cells, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA), with its
What is meant by Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TMA)? Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TMA) is a group of disorders characterized by injured endothelial cells, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA), with its
* Renal insufficiencies
 Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Behzad Poopak, DCLS PhD. Tehran medical Branch Islamic Azad university bpoopak@yahoo.com Case Summary Ms. X, a 35-year year-old woman Complained of weakness, low grade
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Behzad Poopak, DCLS PhD. Tehran medical Branch Islamic Azad university bpoopak@yahoo.com Case Summary Ms. X, a 35-year year-old woman Complained of weakness, low grade
New insights in thrombotic microangiopathies : TTP and ahus
 New insights in thrombotic microangiopathies : TTP and ahus Dr Catherine LAMBERT Hematology Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc Catherine.lambert@uclouvain.be New insights in thrombotic microangiopathies
New insights in thrombotic microangiopathies : TTP and ahus Dr Catherine LAMBERT Hematology Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc Catherine.lambert@uclouvain.be New insights in thrombotic microangiopathies
Approccio morfologico alle microangiopatie trombotiche
 Approccio morfologico alle microangiopatie trombotiche Gina Zini Polo Oncologia e Ematologia Policlinico A. Gemelli Università Cattolica S. Cuore - Roma 1 Thrombotic microangiopathies Occlusive microangiopathic
Approccio morfologico alle microangiopatie trombotiche Gina Zini Polo Oncologia e Ematologia Policlinico A. Gemelli Università Cattolica S. Cuore - Roma 1 Thrombotic microangiopathies Occlusive microangiopathic
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: 2008 Update
 MEDICAL GRAND ROUNDS CME CREDIT MARK A. CROWTHER, MD Director, Division of Hematology, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada JAMES N. GEORGE, MD Hematology-Oncology Section, Department of Medicine,
MEDICAL GRAND ROUNDS CME CREDIT MARK A. CROWTHER, MD Director, Division of Hematology, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada JAMES N. GEORGE, MD Hematology-Oncology Section, Department of Medicine,
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20119 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Lotta, Luca Andrea Title: Pathophysiology of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20119 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Lotta, Luca Andrea Title: Pathophysiology of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic
 The Treatment of TTP and the Prevention of Relapses GERALD APPEL, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons NY-Presbyterian Hospital New York, New York Thrombotic
The Treatment of TTP and the Prevention of Relapses GERALD APPEL, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons NY-Presbyterian Hospital New York, New York Thrombotic
Objectives. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) and ADAMTS13 Testing. Disclosure
 Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) and Testing Dong Chen MD PhD Special Coagulation Laboratory Mayo Clinic-Rochester 2018 Disclosure Chair, CAP Coagulation Resource Committee Mayo Medical Laboratory
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) and Testing Dong Chen MD PhD Special Coagulation Laboratory Mayo Clinic-Rochester 2018 Disclosure Chair, CAP Coagulation Resource Committee Mayo Medical Laboratory
Current understanding of the pathophysiology of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
 J Clin Pathol 2000;53:497 501 497 Haemostasis Research Unit, University College Hospital, 98 Chenies Mews, London WC1E 6HX, UK S L Allford S J Machin Correspondence to: Dr Allford email: mach263@msn.com
J Clin Pathol 2000;53:497 501 497 Haemostasis Research Unit, University College Hospital, 98 Chenies Mews, London WC1E 6HX, UK S L Allford S J Machin Correspondence to: Dr Allford email: mach263@msn.com
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and ADAMTS-13: New Insights into Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapy
 Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and ADAMTS-13: New Insights into Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapy Janis Wyrick-Glatzel, MS, MT(ASCP) (University of Nevada Las Vegas, Las Vegas, NV) DOI: 10.1309/77KRKLJW0EA75T2R
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and ADAMTS-13: New Insights into Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapy Janis Wyrick-Glatzel, MS, MT(ASCP) (University of Nevada Las Vegas, Las Vegas, NV) DOI: 10.1309/77KRKLJW0EA75T2R
1) unexplained microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (Coombs negative anemia),
 Ravi Sarode, MD Consensus Process The TTP-CC subcommittee developed 7 key questions Sent to the 7 speakers for electronic voting in Yes or No format Will be published in JCA soon Q.1 Untreated TTP carries
Ravi Sarode, MD Consensus Process The TTP-CC subcommittee developed 7 key questions Sent to the 7 speakers for electronic voting in Yes or No format Will be published in JCA soon Q.1 Untreated TTP carries
Platelets: Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
 Platelets: Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura James N. George, J. Evan Sadler, and Bernhard Lämmle Abnormalities of plasma von Willebrand factor (VWF) have been recognized to be associated with thrombotic
Platelets: Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura James N. George, J. Evan Sadler, and Bernhard Lämmle Abnormalities of plasma von Willebrand factor (VWF) have been recognized to be associated with thrombotic
Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: When the Environment and Mutations Affect Organ Systems. A Case Report with Review of Literature
 Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: When the Environment and Mutations Affect Organ Systems. A Case Report with Review of Literature Mouhanna Abu Ghanimeh 1, Omar Abughanimeh 1, Ayman Qasrawi 1, Abdulraheem
Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome: When the Environment and Mutations Affect Organ Systems. A Case Report with Review of Literature Mouhanna Abu Ghanimeh 1, Omar Abughanimeh 1, Ayman Qasrawi 1, Abdulraheem
TMA in HUS and TTP: new insights
 TMA in HUS and TTP: new insights Daan Dierickx University Hospitals Leuven, Department of Hematology, Belgium 20th Annual Meeting Belgian Society on Thrombosis and Haemostatis Antwerpen, 22 th November
TMA in HUS and TTP: new insights Daan Dierickx University Hospitals Leuven, Department of Hematology, Belgium 20th Annual Meeting Belgian Society on Thrombosis and Haemostatis Antwerpen, 22 th November
Let`s go for the diagnosis! Yazeed Toukan, MD Pediatric Pulmonary Institute, Ruth Rappaport Children`s Hospital July 2016
 Let`s go for the diagnosis! Yazeed Toukan, MD Pediatric Pulmonary Institute, Ruth Rappaport Children`s Hospital July 2016 Case report 20 months old girl Israeli Arab Muslim family, consanguineous marriage
Let`s go for the diagnosis! Yazeed Toukan, MD Pediatric Pulmonary Institute, Ruth Rappaport Children`s Hospital July 2016 Case report 20 months old girl Israeli Arab Muslim family, consanguineous marriage
Sara K. Vesely, James N. George, Bernhard Lämmle, Jan-Dirk Studt, Lorenzo Alberio, Mayez A. El-Harake, and Gary E. Raskob
 CLINICAL OBSERVATIONS, INTERVENTIONS, AND THERAPEUTIC TRIALS ADAMTS13 activity in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura hemolytic uremic syndrome: relation to presenting features and clinical outcomes in
CLINICAL OBSERVATIONS, INTERVENTIONS, AND THERAPEUTIC TRIALS ADAMTS13 activity in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura hemolytic uremic syndrome: relation to presenting features and clinical outcomes in
Hemolytic uremic syndrome: Investigations and management
 Hemolytic uremic syndrome: Investigations and management SAWAI Toshihiro M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pediatrics, Shiga University of Medical Science Otsu, JAPAN AGENDA TMA; Thrombotic micro angiopathy STEC-HUS;
Hemolytic uremic syndrome: Investigations and management SAWAI Toshihiro M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pediatrics, Shiga University of Medical Science Otsu, JAPAN AGENDA TMA; Thrombotic micro angiopathy STEC-HUS;
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura, Moschcowitz Syndrome
 Clinical Article Moschcowitz Syndrome Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura, Moschcowitz Syndrome Judit Müller, MD; Judit Czinyéri, MD; Ildikó Sasvári, MD; Miklós Garami, MD; Gábor Kovács, PhD Abstract The
Clinical Article Moschcowitz Syndrome Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura, Moschcowitz Syndrome Judit Müller, MD; Judit Czinyéri, MD; Ildikó Sasvári, MD; Miklós Garami, MD; Gábor Kovács, PhD Abstract The
Acquired Idiopathic ADAMTS13 Activity Deficient Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in a Population from Japan
 Acquired Idiopathic ADAMTS13 Activity Deficient Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in a Population from Japan Masanori Matsumoto 1, Charles L. Bennett 2, Ayami Isonishi 1, Zaina Qureshi 2, Yuji Hori 1,
Acquired Idiopathic ADAMTS13 Activity Deficient Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in a Population from Japan Masanori Matsumoto 1, Charles L. Bennett 2, Ayami Isonishi 1, Zaina Qureshi 2, Yuji Hori 1,
DRUG NAME: Eculizumab Brand(s): Soliris DOSAGE FORM/ STRENGTH: 10 mg/ml (300 mg per vial)
 Preamble: A confirmed diagnosis of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (ahus) is required for eculizumab funding. The information below is to provide clinicians with context for how a diagnosis of ahus
Preamble: A confirmed diagnosis of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (ahus) is required for eculizumab funding. The information below is to provide clinicians with context for how a diagnosis of ahus
Case Report ISSN:
 Case Report ISSN: 2581-6756 N-Acetylcysteine for Refractory Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: New Dosage Approaches Ignacio Español 1, Juan Diego Leal 1, José Ros 2, José Sanmartín 2, María
Case Report ISSN: 2581-6756 N-Acetylcysteine for Refractory Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: New Dosage Approaches Ignacio Español 1, Juan Diego Leal 1, José Ros 2, José Sanmartín 2, María
Clinical study of 9 patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
 Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine VOL.1,ISS.3,DEC 2017,1-5 ONLINE ISSN: 2523-2835 www.jocem.org PRINT ISSN: 2521-0084 DOI:10.29422/jocem.2017.03.001 Abstract: Clinical study of 9 patients with
Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine VOL.1,ISS.3,DEC 2017,1-5 ONLINE ISSN: 2523-2835 www.jocem.org PRINT ISSN: 2521-0084 DOI:10.29422/jocem.2017.03.001 Abstract: Clinical study of 9 patients with
A 60 year old woman with altered mental status and thrombotic microangiopathy. Josh Veatch
 A 60 year old woman with altered mental status and thrombotic microangiopathy Josh Veatch Previously healthy 60 year old woman 2 3 months of fatigue following a URI, transient episodes being out of it
A 60 year old woman with altered mental status and thrombotic microangiopathy Josh Veatch Previously healthy 60 year old woman 2 3 months of fatigue following a URI, transient episodes being out of it
Accepted Manuscript. No more thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura/hemolytic uremic syndrome please. Yeong-Hau H. Lien MD, PhD S (18)
 Accepted Manuscript No more thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura/hemolytic uremic syndrome please Yeong-Hau H. Lien MD, PhD PII: S0002-9343(18)30965-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2018.10.009 Reference:
Accepted Manuscript No more thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura/hemolytic uremic syndrome please Yeong-Hau H. Lien MD, PhD PII: S0002-9343(18)30965-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2018.10.009 Reference:
Aswanth P. Reddy, Ujjwal Gupta, and Jonathan S. Harrison. University of Connecticut, Farmington, Connecticut, USA
 CASE REPORT Rituximab in Relapsing acquired Thrombotic Thrombo cytopenic Purpura: Experience and Evidence 1 2 1* Aswanth P. Reddy, Ujjwal Gupta, and Jonathan S. Harrison 1 University of Connecticut, Farmington,
CASE REPORT Rituximab in Relapsing acquired Thrombotic Thrombo cytopenic Purpura: Experience and Evidence 1 2 1* Aswanth P. Reddy, Ujjwal Gupta, and Jonathan S. Harrison 1 University of Connecticut, Farmington,
Mayo Clin Proc, November 2001, Vol 76 TTP and HUS 1155 plasma samples from some patients with TTP have identified unusually large multimeric forms of
 1154 Concise Review for Clinicians Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome MICHELLE A. ELLIOTT, MD, AND WILLIAM L. NICHOLS, MD Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) and hemolytic
1154 Concise Review for Clinicians Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome MICHELLE A. ELLIOTT, MD, AND WILLIAM L. NICHOLS, MD Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) and hemolytic
Clinical Presentation and Follow-up of Eighteen Patients with Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Received in: March 2007 Accepted in: 14/1/2010
 Clinical Presentation and Follow-up of Eighteen Patients with Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Received in: March 2007 Accepted in: 14/1/2010 Dr. Ahmed Khudair Yaseen Elmeshhedany * Dr. Ahmed Abdulmajeed
Clinical Presentation and Follow-up of Eighteen Patients with Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Received in: March 2007 Accepted in: 14/1/2010 Dr. Ahmed Khudair Yaseen Elmeshhedany * Dr. Ahmed Abdulmajeed
Haemolytic uraemic syndrome the story of a whodunit
 Haemolytic uraemic syndrome the story of a whodunit Paul Warwicker Lancashire Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust RCP Kidney for the General Physician Conference Nov 17 Renal thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA)
Haemolytic uraemic syndrome the story of a whodunit Paul Warwicker Lancashire Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust RCP Kidney for the General Physician Conference Nov 17 Renal thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA)
Long-term follow-up of idiopathic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura treated with rituximab
 Long-term follow-up of idiopathic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura treated with rituximab Jens Marcus Chemnitz, Jens Uener, Michael Hallek, Christof Scheid To cite this version: Jens Marcus Chemnitz,
Long-term follow-up of idiopathic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura treated with rituximab Jens Marcus Chemnitz, Jens Uener, Michael Hallek, Christof Scheid To cite this version: Jens Marcus Chemnitz,
research paper Summary
 research paper Impact of severe ADAMTS13 deficiency on clinical presentation and outcomes in patients with thrombotic microangiopathies: the experience of the Harvard TMA Research Collaborative Pavan K.
research paper Impact of severe ADAMTS13 deficiency on clinical presentation and outcomes in patients with thrombotic microangiopathies: the experience of the Harvard TMA Research Collaborative Pavan K.
Association Between Thrombotic Microangiopathy and Reduced ADAMTS13 Activity in Malignant Hypertension
 Association Between Thrombotic Microangiopathy and Reduced ADAMTS13 Activity in Malignant Hypertension Bert-Jan H. van den Born, Niels V. van der Hoeven, Evelyn Groot, Peter J. Lenting, Joost C.M. Meijers,
Association Between Thrombotic Microangiopathy and Reduced ADAMTS13 Activity in Malignant Hypertension Bert-Jan H. van den Born, Niels V. van der Hoeven, Evelyn Groot, Peter J. Lenting, Joost C.M. Meijers,
Soliris (eculizumab) DRUG.00050
 Market DC Soliris (eculizumab) DRUG.00050 Override(s) Prior Authorization Approval Duration 1 year Medications Soliris (eculizumab) APPROVAL CRITERIA Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria I. Initiation of
Market DC Soliris (eculizumab) DRUG.00050 Override(s) Prior Authorization Approval Duration 1 year Medications Soliris (eculizumab) APPROVAL CRITERIA Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria I. Initiation of
HEME 10 Bleeding Disorders
 HEME 10 Bleeding Disorders When injury occurs, three mechanisms occur Blood vessels Primary hemostasis Secondary hemostasis Diseases of the blood vessels Platelet disorders Thrombocytopenia Functional
HEME 10 Bleeding Disorders When injury occurs, three mechanisms occur Blood vessels Primary hemostasis Secondary hemostasis Diseases of the blood vessels Platelet disorders Thrombocytopenia Functional
Rituximab Can Be Combined With Daily Plasma Exchange to Achieve Effective B-Cell Depletion and Clinical Improvement in Acute Autoimmune TTP
 Coagulation and Transfusion Medicine / REFRACTORY ACUTE AUTOIMMUNE TTP Rituximab Can Be Combined With Daily Plasma Exchange to Achieve Effective B-Cell Depletion and Clinical Improvement in Acute Autoimmune
Coagulation and Transfusion Medicine / REFRACTORY ACUTE AUTOIMMUNE TTP Rituximab Can Be Combined With Daily Plasma Exchange to Achieve Effective B-Cell Depletion and Clinical Improvement in Acute Autoimmune
Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders Kristine Krafts, M.D. Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders Bleeding disorders von Willebrand disease Hemophilia A and B DIC TTP/HUS ITP Thrombotic disorders Factor V Leiden
Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders Kristine Krafts, M.D. Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders Bleeding disorders von Willebrand disease Hemophilia A and B DIC TTP/HUS ITP Thrombotic disorders Factor V Leiden
Abnormalities of factor VIII related protein multimers in the haemolytic uraemic syndrome
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1984, 59, 1135-1140 Abnormalities of factor VIII related protein multimers in the haemolytic uraemic syndrome P E ROSE, S M ENAYAT, R SUNDERLAND, P E SHORT, C E WILLIAMS,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1984, 59, 1135-1140 Abnormalities of factor VIII related protein multimers in the haemolytic uraemic syndrome P E ROSE, S M ENAYAT, R SUNDERLAND, P E SHORT, C E WILLIAMS,
When a patient presents with TMA, identify the underlying cause for the appropriate diagnosis... IS IT TTP OR IS IT ahus?
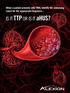 When a patient presents with TMA, identify the underlying cause for the appropriate diagnosis... IS IT TTP OR IS IT ahus? ADAMTS13 activity >5% RULES OUT a diagnosis of severe ADAMTS13 deficiency (TTP)
When a patient presents with TMA, identify the underlying cause for the appropriate diagnosis... IS IT TTP OR IS IT ahus? ADAMTS13 activity >5% RULES OUT a diagnosis of severe ADAMTS13 deficiency (TTP)
R. Coward has documented that he has received cooperative grants from Takeda and Novo Nordisk
 R. Coward has documented that he has received cooperative grants from Takeda and Novo Nordisk Advances in our understanding of the pathogenesis of glomerular thrombotic microangiopathy Lindsay Keir Richard
R. Coward has documented that he has received cooperative grants from Takeda and Novo Nordisk Advances in our understanding of the pathogenesis of glomerular thrombotic microangiopathy Lindsay Keir Richard
TTP, Sickle Cell Disease, and the role of von Willebrand factor
 TTP, Sickle Cell Disease, and the role of von Willebrand factor José A. López Puget Sound Blood Center University of Washington Seattle, WA Disclosures No conflicts to disclose. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic
TTP, Sickle Cell Disease, and the role of von Willebrand factor José A. López Puget Sound Blood Center University of Washington Seattle, WA Disclosures No conflicts to disclose. Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic
Thrombotic Microangiopathies, Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura, and ADAMTS-13
 47 Thrombotic Microangiopathies, Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura, and ADAMTS-13 Kent Chapman, B.Sc. (Biomed) 1 Michael Seldon, F.R.A.C.P., F.R.C.P.A., M.B.B.S., B.Sc. (Med) 2 Ross Richards, Ph.D.,
47 Thrombotic Microangiopathies, Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura, and ADAMTS-13 Kent Chapman, B.Sc. (Biomed) 1 Michael Seldon, F.R.A.C.P., F.R.C.P.A., M.B.B.S., B.Sc. (Med) 2 Ross Richards, Ph.D.,
LAMA SHATAT TTP, ITP, DIC
 TTP, ITP, DIC Reduction in platelet number (thrombocytopenia) constitutes an important cause of generalized bleeding. A count less than 100,000 platelets/μl is generally considered to constitute thrombocytopenia.
TTP, ITP, DIC Reduction in platelet number (thrombocytopenia) constitutes an important cause of generalized bleeding. A count less than 100,000 platelets/μl is generally considered to constitute thrombocytopenia.
Thrombotic Microangiopathy secondary to Malignant Hypertension presenting as acute Kidney injury-a Case Report
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 12 (2015) pp. 640-644 http://www.ijcmas.com Case Study Thrombotic Microangiopathy secondary to Malignant Hypertension presenting as acute Kidney injury-a Case Report Sandeep
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 12 (2015) pp. 640-644 http://www.ijcmas.com Case Study Thrombotic Microangiopathy secondary to Malignant Hypertension presenting as acute Kidney injury-a Case Report Sandeep
The utility of ADAMTS13 in differentiating TTP from other acute thrombotic microangiopathies: results from the UK TTP Registry
 research paper The utility of ADAMTS13 in differentiating TTP from other acute thrombotic microangiopathies: results from the UK TTP Registry Sevda Hassan, 1 John-Paul Westwood, 2 Debra Ellis, 2 Chris
research paper The utility of ADAMTS13 in differentiating TTP from other acute thrombotic microangiopathies: results from the UK TTP Registry Sevda Hassan, 1 John-Paul Westwood, 2 Debra Ellis, 2 Chris
Things to never miss in the office. Brett Houston MD FRCPC (PYG-5, hematology) Leonard Minuk MD FRCPC
 Things to never miss in the office Brett Houston MD FRCPC (PYG-5, hematology) Leonard Minuk MD FRCPC Presenter Disclosure Faculty / Speaker s name: Brett Houston / Leonard Minuk Relationships with commercial
Things to never miss in the office Brett Houston MD FRCPC (PYG-5, hematology) Leonard Minuk MD FRCPC Presenter Disclosure Faculty / Speaker s name: Brett Houston / Leonard Minuk Relationships with commercial
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
 The Intensive Care Society 2011 Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura J Thachil Thrombocytopenia is the most common coagulation problem in intensive care units with an incidence of up to 60% in some studies.
The Intensive Care Society 2011 Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura J Thachil Thrombocytopenia is the most common coagulation problem in intensive care units with an incidence of up to 60% in some studies.
Advances in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
 DISEASE OF THE MONTH Eberhard Ritz, Feature Editor J Am Soc Nephrol 14: 1072 1081, 2003 Advances in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura HAN-MOU TSAI Division
DISEASE OF THE MONTH Eberhard Ritz, Feature Editor J Am Soc Nephrol 14: 1072 1081, 2003 Advances in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura HAN-MOU TSAI Division
Acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: ADAMTS13 activity, anti-adamts13 autoantibodies and risk of recurrent disease
 tion of TPO mrna. Blood 1999;94:1480-2. 20. Ding J, Komatsu H, Wakita A, Kato-Uranishi M, Ito M, Satoh A, et al. Familial essential thrombocythemia associated with a dominant-positive activating mutation
tion of TPO mrna. Blood 1999;94:1480-2. 20. Ding J, Komatsu H, Wakita A, Kato-Uranishi M, Ito M, Satoh A, et al. Familial essential thrombocythemia associated with a dominant-positive activating mutation
ACTIFLUOR ADAMTS13 Activity *
 ACTIFLUOR ADAMTS13 Activity * A Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) assay for measuring ADAMTS13 activity in human plasma REF 812RUO 32 i 2 Cl8 C Sekisui Diagnostics, LLC 500 West Avenue, Stamford,
ACTIFLUOR ADAMTS13 Activity * A Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) assay for measuring ADAMTS13 activity in human plasma REF 812RUO 32 i 2 Cl8 C Sekisui Diagnostics, LLC 500 West Avenue, Stamford,
Dr. Rai Muhammad Asghar Associate Professor Head of Pediatric Department Rawalpindi Medical College
 Dr. Rai Muhammad Asghar Associate Professor Head of Pediatric Department Rawalpindi Medical College AN APPROACH TO BLEEDING DISORDERS NORMAL HEMOSTASIS After injury, 3 processes halt bleeding Vasoconstriction
Dr. Rai Muhammad Asghar Associate Professor Head of Pediatric Department Rawalpindi Medical College AN APPROACH TO BLEEDING DISORDERS NORMAL HEMOSTASIS After injury, 3 processes halt bleeding Vasoconstriction
Coagulation Disorders. Dr. Muhammad Shamim Assistant Professor, BMU
 Coagulation Disorders Dr. Muhammad Shamim Assistant Professor, BMU 1 Introduction Local Vs. General Hematoma & Joint bleed Coagulation Skin/Mucosal Petechiae & Purpura PLT wound / surgical bleeding Immediate
Coagulation Disorders Dr. Muhammad Shamim Assistant Professor, BMU 1 Introduction Local Vs. General Hematoma & Joint bleed Coagulation Skin/Mucosal Petechiae & Purpura PLT wound / surgical bleeding Immediate
The Oklahoma thrombotic thrombo - cytopenic purpura-haemolytic uraemic syndrome Registry
 Review 105 The Oklahoma thrombotic thrombo - cytopenic purpura-haemolytic uraemic syndrome Registry A model for clinical research, education and patient care J. N. George; S. K. Vesely; D. R. Terrell;
Review 105 The Oklahoma thrombotic thrombo - cytopenic purpura-haemolytic uraemic syndrome Registry A model for clinical research, education and patient care J. N. George; S. K. Vesely; D. R. Terrell;
ISTITUTO DI RICERCHE FARMACOLOGICHE MARIO NEGRI CLINICAL RESEARCH CENTER ALDO E FOR CELE RARE DACCO DISEASES ALDO E CELE DACCO
 ISTITUTO DI RICERCHE FARMACOLOGICHE MARIO NEGRI CENTRO MARIO DI NEGRI RICERCHE INSTITUTE CLINICHE FOR PHARMACOLOGICAL PER LE MALATTIE RESEARCH RARE CLINICAL RESEARCH CENTER ALDO E FOR CELE RARE DACCO DISEASES
ISTITUTO DI RICERCHE FARMACOLOGICHE MARIO NEGRI CENTRO MARIO DI NEGRI RICERCHE INSTITUTE CLINICHE FOR PHARMACOLOGICAL PER LE MALATTIE RESEARCH RARE CLINICAL RESEARCH CENTER ALDO E FOR CELE RARE DACCO DISEASES
Acute Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) in Childhood
 Acute Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) in Childhood Guideline developed by Robert Saylors, MD, in collaboration with the ANGELS team. Last reviewed by Robert Saylors, MD September 22, 2016. Key Points
Acute Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) in Childhood Guideline developed by Robert Saylors, MD, in collaboration with the ANGELS team. Last reviewed by Robert Saylors, MD September 22, 2016. Key Points
Case Report Ciprofloxacin-Induced Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: A Case of Successful Treatment and Review of the Literature
 Case Reports in Critical Care Volume 2015, Article ID 143832, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/143832 Case Report Ciprofloxacin-Induced Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: A Case of Successful Treatment
Case Reports in Critical Care Volume 2015, Article ID 143832, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/143832 Case Report Ciprofloxacin-Induced Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: A Case of Successful Treatment
Most Common Hemostasis Consults: Thrombocytopenia
 Most Common Hemostasis Consults: Thrombocytopenia Cindy Neunert, MS MSCS Assistant Professor, Pediatrics CUMC Columbia University TSHNA Meeting, April 15, 2016 Financial Disclosures No relevant financial
Most Common Hemostasis Consults: Thrombocytopenia Cindy Neunert, MS MSCS Assistant Professor, Pediatrics CUMC Columbia University TSHNA Meeting, April 15, 2016 Financial Disclosures No relevant financial
Splenectomy: Does it still play a role in the management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura?
 CASE SERIES Splenectomy: Does it still play a role in the management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura? Luc Dubois, MD Daryl K. Gray, MD From the Department of Surgery, University of Western Ontario,
CASE SERIES Splenectomy: Does it still play a role in the management of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura? Luc Dubois, MD Daryl K. Gray, MD From the Department of Surgery, University of Western Ontario,
von Willebrand factor (vwf), a multimeric glycoprotein
 ATVB In Focus Platelet Activation and the Formation of the Platelet Plug Series Editor: Lawrence Brass Deficiency of ADAMTS13 Causes Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Han-Mou Tsai Abstract In the circulation,
ATVB In Focus Platelet Activation and the Formation of the Platelet Plug Series Editor: Lawrence Brass Deficiency of ADAMTS13 Causes Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Han-Mou Tsai Abstract In the circulation,
1. INSTRUCTIONS 2. DEFINITION OF HUS
 CQ_IBK_aHUS_01 / version 25/11/09 European Paediatric Research Group for HUS and related disorders Case questionnaire for diarrhoea negative/vtec (STEC) negative cases acute phase 1. INSTRUCTIONS Please
CQ_IBK_aHUS_01 / version 25/11/09 European Paediatric Research Group for HUS and related disorders Case questionnaire for diarrhoea negative/vtec (STEC) negative cases acute phase 1. INSTRUCTIONS Please
Specialised Services Policy: CP98 Eculizumab for Atypical Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome (ahus)
 Specialised Services Policy: CP98 Eculizumab for Atypical Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome (ahus) Document Author: Assistant Director for Evidence, Evaluation and Effectiveness Executive Lead: Medical Director
Specialised Services Policy: CP98 Eculizumab for Atypical Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome (ahus) Document Author: Assistant Director for Evidence, Evaluation and Effectiveness Executive Lead: Medical Director
Behzad Poopak, DCLS PhD
 Behzad Poopak, DCLS PhD Test Report Name Age Critical Low HEMATOLOGY Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time, Plasma Critical High - 150 sec Units Fibrinogen 60 - mg/dl INR (International Normalizing
Behzad Poopak, DCLS PhD Test Report Name Age Critical Low HEMATOLOGY Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time, Plasma Critical High - 150 sec Units Fibrinogen 60 - mg/dl INR (International Normalizing
The Bleeding Patient. Sarah Stacey Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Hospital University of the Witwatersrand
 The Bleeding Patient Sarah Stacey Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Hospital University of the Witwatersrand The Bleeding Patient If you prick us, do we not bleed? Disorders of secondary homeostasis: dysfunction
The Bleeding Patient Sarah Stacey Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Hospital University of the Witwatersrand The Bleeding Patient If you prick us, do we not bleed? Disorders of secondary homeostasis: dysfunction
HUS and TTP Testing. Kenneth D. Friedman, M.D. Director, Hemostasis Reference Lab BloodCenter of Wisconsin, Milwaukee WI
 HUS and TTP Testing Kenneth D. Friedman, M.D. Director, Hemostasis Reference Lab BloodCenter of Wisconsin, Milwaukee WI Disclosures Relevant Financial Relationships Consultant: Ablynx, Bayer, CSL Behring,
HUS and TTP Testing Kenneth D. Friedman, M.D. Director, Hemostasis Reference Lab BloodCenter of Wisconsin, Milwaukee WI Disclosures Relevant Financial Relationships Consultant: Ablynx, Bayer, CSL Behring,
Thrombotic microangiopathy and indications for therapeutic plasma exchange
 SPIN DOCTORS:APHERESIS FOR HEMATOLOGISTS Thrombotic microangiopathy and indications for therapeutic plasma exchange Jill Adamski 1 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, Mayo Clinic Arizona,
SPIN DOCTORS:APHERESIS FOR HEMATOLOGISTS Thrombotic microangiopathy and indications for therapeutic plasma exchange Jill Adamski 1 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, Mayo Clinic Arizona,
monoclonal gammopathy of undetermin Citation Rheumatology international, 33(1),
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Renal thrombotic microangiopathies/ in a patient with primary Sjögren's monoclonal gammopathy of undetermin Koga, Tomohiro; Yamasaki, Satoshi; Atsushi;
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Renal thrombotic microangiopathies/ in a patient with primary Sjögren's monoclonal gammopathy of undetermin Koga, Tomohiro; Yamasaki, Satoshi; Atsushi;
Dr. E.SUDHA (Fellow in Pediatric Nephrology) DEPT OF PEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY & DIALYSIS Dr.MEHTA CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
 Dr. E.SUDHA (Fellow in Pediatric Nephrology) DEPT OF PEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY & DIALYSIS Dr.MEHTA CHILDRENS HOSPITAL CASE HISTORY 4 yrs old previously well boy Born to 2 nd degree consanguinity Fever x 5 days
Dr. E.SUDHA (Fellow in Pediatric Nephrology) DEPT OF PEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY & DIALYSIS Dr.MEHTA CHILDRENS HOSPITAL CASE HISTORY 4 yrs old previously well boy Born to 2 nd degree consanguinity Fever x 5 days
Non-immune acquired haemolytic anaemias. Dr.Maysem
 Non-immune acquired haemolytic anaemias Dr.Maysem Causes of Non-immune acquired haemolytic anaemias. Infections Infections can cause haemolysis in a variety of ways: -They may precipitate an acute haemolytic
Non-immune acquired haemolytic anaemias Dr.Maysem Causes of Non-immune acquired haemolytic anaemias. Infections Infections can cause haemolysis in a variety of ways: -They may precipitate an acute haemolytic
Rituximab as first-line treatment for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
 Clinical Note Rituximab as first-line treatment for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura Journal of International Medical Research 2017, Vol. 45(3) 1253 1260! The Author(s) 2017 Reprints and permissions:
Clinical Note Rituximab as first-line treatment for acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura Journal of International Medical Research 2017, Vol. 45(3) 1253 1260! The Author(s) 2017 Reprints and permissions:
Some renal vascular disorders
 Some renal vascular disorders Introduction Nearly all diseases of the kidney involve the renal blood vessels secondarily We will discuss: -Hypertension (arterionephrosclerosis in benign HTN & hyperplastic
Some renal vascular disorders Introduction Nearly all diseases of the kidney involve the renal blood vessels secondarily We will discuss: -Hypertension (arterionephrosclerosis in benign HTN & hyperplastic
THROMBOTIC THROMBOCYTOPENIC PURPURA; AT A TERTIARY CARE CENTRE IN LAHORE, PAKISTAN
 E:/Biomedica Vol.24 Jan. Jun. 2008/Bio-D (A) WC THROMBOTIC THROMBOCYTOPENIC PURPURA; AT A TERTIARY CARE CENTRE IN LAHORE, PAKISTAN MONA AZIZ AHMAD, RABIA AHMAD, NAZISH MAZARI S. WAQAR, H. SHAH, AIZAZ M.
E:/Biomedica Vol.24 Jan. Jun. 2008/Bio-D (A) WC THROMBOTIC THROMBOCYTOPENIC PURPURA; AT A TERTIARY CARE CENTRE IN LAHORE, PAKISTAN MONA AZIZ AHMAD, RABIA AHMAD, NAZISH MAZARI S. WAQAR, H. SHAH, AIZAZ M.
Understanding of the pathophysiology
 CMAJ Early release, published at www.cmaj.ca on October 17, 2016. Subject to revision. Review CME Thrombotic microangiopathies: a general approach to diagnosis and management Donald M. Arnold MD MSc, Christopher
CMAJ Early release, published at www.cmaj.ca on October 17, 2016. Subject to revision. Review CME Thrombotic microangiopathies: a general approach to diagnosis and management Donald M. Arnold MD MSc, Christopher
Renal failure and thrombocytopaenia? Don t forget TTP/HUS. Jonathan Wala Nephrologist
 Renal failure and thrombocytopaenia? Don t forget TTP/HUS Jonathan Wala Nephrologist Thrombotic microangiopathies Disorders characterized by: thrombocytopaenia microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia (MAHA)
Renal failure and thrombocytopaenia? Don t forget TTP/HUS Jonathan Wala Nephrologist Thrombotic microangiopathies Disorders characterized by: thrombocytopaenia microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia (MAHA)
Pathology note 8 BLEEDING DISORDER
 Pathology note 8 BLEEDING DISORDER Slide75 ( Types of clotting factors deficiency): Today we will talk about public public factor deficiency it could be acquired or inherited, acquired diseases are more
Pathology note 8 BLEEDING DISORDER Slide75 ( Types of clotting factors deficiency): Today we will talk about public public factor deficiency it could be acquired or inherited, acquired diseases are more
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20119 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Lotta, Luca Andrea Title: Pathophysiology of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20119 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Lotta, Luca Andrea Title: Pathophysiology of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Cyclosporine or steroids as an adjunct to plasma exchange in the treatment of immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
 REGULAR ARTICLE Cyclosporine or steroids as an adjunct to plasma exchange in the treatment of immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura Spero R. Cataland, 1 Peter J. Kourlas, 2 Shangbin Yang,
REGULAR ARTICLE Cyclosporine or steroids as an adjunct to plasma exchange in the treatment of immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura Spero R. Cataland, 1 Peter J. Kourlas, 2 Shangbin Yang,
Heme (Bleeding and Coagulopathies) in the ICU
 Heme (Bleeding and Coagulopathies) in the ICU General Topics To Discuss Transfusions DIC Thrombocytopenia Liver and renal disease related bleeding Lack of evidence in managing critical illness related
Heme (Bleeding and Coagulopathies) in the ICU General Topics To Discuss Transfusions DIC Thrombocytopenia Liver and renal disease related bleeding Lack of evidence in managing critical illness related
Long term outcome and sequelae in patients after acute thrombotic thrombo cytopenic purpura episodes *
 Original article Long term outcome and sequelae in patients after acute thrombotic thrombo cytopenic purpura episodes * T. Falter, # ; K. J. Alber # ; I. Scharrer Third Department of Medicine, Haematology,
Original article Long term outcome and sequelae in patients after acute thrombotic thrombo cytopenic purpura episodes * T. Falter, # ; K. J. Alber # ; I. Scharrer Third Department of Medicine, Haematology,
Paolo Gresele Dipartimento di Medicina, Sezione di Medicina Interna e Cardiovascolare, Università di Perugia
 Le sindromi trombotiche microangiopatiche: il ruolo del laboratorio Paolo Gresele Dipartimento di Medicina, Sezione di Medicina Interna e Cardiovascolare, Università di Perugia Microangiopatie trombotiche:
Le sindromi trombotiche microangiopatiche: il ruolo del laboratorio Paolo Gresele Dipartimento di Medicina, Sezione di Medicina Interna e Cardiovascolare, Università di Perugia Microangiopatie trombotiche:
Renal transplantation in adults with thrombotic thrombocv topenic purpura/ haemoly tic-uraemic syndrome
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (1996) 11: 1810-1814 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation Renal transplantation in adults with thrombotic thrombocv topenic purpura/ haemoly tic-uraemic syndrome
Nephrol Dial Transplant (1996) 11: 1810-1814 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation Renal transplantation in adults with thrombotic thrombocv topenic purpura/ haemoly tic-uraemic syndrome
Plasma Exchange for Renal Disease: Evidence and Use 2011
 Journal of Clinical Apheresis 27:112 116 (2012) Plasma Exchange for Renal Disease: Evidence and Use 2011 W.F. Clark* London Health Science Centre, Western University Canada, Lawson Health Research Institute
Journal of Clinical Apheresis 27:112 116 (2012) Plasma Exchange for Renal Disease: Evidence and Use 2011 W.F. Clark* London Health Science Centre, Western University Canada, Lawson Health Research Institute
Approach to bleeding disorders &treatment. by RAJESH.N General medicine post graduate
 Approach to bleeding disorders &treatment by RAJESH.N General medicine post graduate 2 Approach to a patient of bleeding diathesis 1. Clinical evaluation: History, Clinical features 2. Laboratory approach:
Approach to bleeding disorders &treatment by RAJESH.N General medicine post graduate 2 Approach to a patient of bleeding diathesis 1. Clinical evaluation: History, Clinical features 2. Laboratory approach:
Presentation Outline. Disease Background Previous research on platelet recovery rate Goal of our study Methods Results Limitations Conclusions
 Platelet Recovery Rate at Day 5 of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange for Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Can Aid in Identifying Risk of Disease Exacerbation Suzanne Zhou, Yara A. Park, Marian A.
Platelet Recovery Rate at Day 5 of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange for Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Can Aid in Identifying Risk of Disease Exacerbation Suzanne Zhou, Yara A. Park, Marian A.
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY PLATELET DISORDERS
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY PLATELET DISORDERS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY PLATELET DISORDERS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn
Diagnosis and Treatment of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura 1 2 Mary Muoneke and *Rasheed A Balogun Review Article ABSTRACT Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is a rare clinical emergency that
Diagnosis and Treatment of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura 1 2 Mary Muoneke and *Rasheed A Balogun Review Article ABSTRACT Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is a rare clinical emergency that
Blood transfusion. Dr. J. Potgieter Dept. of Haematology NHLS - TAD
 Blood transfusion Dr. J. Potgieter Dept. of Haematology NHLS - TAD General Blood is collected from volunteer donors >90% is separated into individual components and plasma Donors should be: healthy, have
Blood transfusion Dr. J. Potgieter Dept. of Haematology NHLS - TAD General Blood is collected from volunteer donors >90% is separated into individual components and plasma Donors should be: healthy, have
Thrombotic microangiopathy and associated renal disorders*
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2012) 27: 2673 2685 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs279 NDT Perspectives Thrombotic microangiopathy and associated renal disorders* Thomas Barbour 1, Sally Johnson 2, Solomon Cohney 3 and
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2012) 27: 2673 2685 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs279 NDT Perspectives Thrombotic microangiopathy and associated renal disorders* Thomas Barbour 1, Sally Johnson 2, Solomon Cohney 3 and
Results of the TITAN study for Caplacizumab
 Results of the TITAN study for Webcast presentation 17th June 2014 Nanobodies - Inspired by nature Forward looking statements Certain statements, beliefs and opinions in this presentation are forward-looking,
Results of the TITAN study for Webcast presentation 17th June 2014 Nanobodies - Inspired by nature Forward looking statements Certain statements, beliefs and opinions in this presentation are forward-looking,
Congenital bleeding disorders
 Congenital bleeding disorders Overview Factor VIII von Willebrand Factor Complex factor VIII von Willebrand factor (vwf) complex circulate as a complex + factor IX intrinsic pathway Platelets bind via
Congenital bleeding disorders Overview Factor VIII von Willebrand Factor Complex factor VIII von Willebrand factor (vwf) complex circulate as a complex + factor IX intrinsic pathway Platelets bind via
THE MULTIPLE FACETS OF THROMBOTIC MICROANGIOPATHIES
 THE MULTIPLE FACETS OF THROMBOTIC MICROANGIOPATHIES Summary of Presentations from the Alexion-Sponsored Symposium, held at the 19 th EHA Congress, Milan, Italy, on 12 th June 2014 Chairperson Pier Mannuccio
THE MULTIPLE FACETS OF THROMBOTIC MICROANGIOPATHIES Summary of Presentations from the Alexion-Sponsored Symposium, held at the 19 th EHA Congress, Milan, Italy, on 12 th June 2014 Chairperson Pier Mannuccio
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: Successful Treatment Unlocks Etiologic Secrets*
 Special Article Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: Successful Treatment Unlocks Etiologic Secrets* JUDY L. SCHMIDT, M.D., Division of Hematology and Internal Medicine The cause of platelet agglutination
Special Article Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: Successful Treatment Unlocks Etiologic Secrets* JUDY L. SCHMIDT, M.D., Division of Hematology and Internal Medicine The cause of platelet agglutination
Appendix to Notification Letter for rituximab and eltrombopag dated 20 February 2014
 Appendix to Notification Letter for rituximab and eltrombopag dated 20 February 2014 The notification letter which contains details of the decision to widen the restriction criteria for rituximab and eltrombopag
Appendix to Notification Letter for rituximab and eltrombopag dated 20 February 2014 The notification letter which contains details of the decision to widen the restriction criteria for rituximab and eltrombopag
Thrombocytopenia is not mandatory to diagnose haemolytic and uremic syndrome
 Sallée et al. BMC Nephrology 2013, 14:3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Thrombocytopenia is not mandatory to diagnose haemolytic and uremic syndrome Marion Sallée 1, Khalil Ismail 1, Fadi Fakhouri 2, Henri
Sallée et al. BMC Nephrology 2013, 14:3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Thrombocytopenia is not mandatory to diagnose haemolytic and uremic syndrome Marion Sallée 1, Khalil Ismail 1, Fadi Fakhouri 2, Henri
