Compensatory renal hypertrophy in young rats: Increase in the number of nephrons
|
|
|
- Vanessa Robyn Shelton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Kidney International, Vol 1 (1972), p Compensatory renal hypertrophy in young rats: Increase in the number of nephrons JAN-PIRR BONVALT, MONIQU CHAMPION, FRIDA WANTOK, and Gu BRJAL Unite de recherches de pathologie cardio-vasculaire, I N R M Hôpital L Bernard, Limeil-Brevannes, France Compensatory renal hypertrophy in young rats: Increase in the number of nephrons The number of glomeruli per kidney (NG) was determined using Damadian's method in hypertrophic kidneys removed 2 to 36 days after a contralateral nephrectomy in young rats This study was carried out in relation to the age of the animals When unilateral nephrectomy was performed before the animals were 5 days old, the weight of the hypertrophic kidneys was approximately 3% greater than that of controls The NO was 47,36± D 3,18 (N= 12), a number significantly greater (P< 1) than that obtained in control kidneys from rats of the same age (32,15± D 4,55, N= 24) In rats 1 to 27 days of age, a similar 3% increase in weight occurred in the hypertrophic kidney, but the NO (34,12 D 3,38, N= 12) was no different than that of control kidneys from rats of the same age (NG= 35,36± D 3,15, N= 14) It is concluded that in rats younger than approximately two months, compensatory renal hypertrophy is due to an increase in the total number of nephrons, while in older rats it is due to enlargement of each preexistant nephron Hypertrophie rénale conpensatrice chez le jeune rat: Augmentation du nombre de néphrons A l'aide de Ia méthode de Damadian, nous avons déterminé chez le rat le nombre de glomerules (NG) contenus dans des reins hypertrophiés a Ia uite d'une néphrectomie contralatérale, effectuée 2 a 36 jours plus tot Dans cette étude, I'age des rats a été pris en consideration Quand Ia néphrectomie unilatérale est faite avant que les rats aient 5 jours, Ic poids des reins hypertrophies est supérieur de 3% a celui des témoins Le NO est de 47,36± sn 3,18 (N= 12), chiffre significativement plus élevéc P< 1) que celui constaté dans les reins témoins de rats de méme age Chez les rats âgés de 1 a 27 jours, on observe également une augmentation de 3% du poids des reins hypertrophiés, mais Ic NO (34,12± 5 3,38, N= 12), n'est pas different de celui des reins témoins de rats du même age (NG= 35,36± so 3,15 JV= 14) On peut ainsi conclure que, chez les rats âgés de moms de 2 mois environ, l'hypertrophie rénale compensatrice est due a une augmentation du nombre total de néphrons, alors que, lorsque les rats sont plus vieux, elle est due a une augmentation de taille des néphrons préexistants it is currently believed that there is no increase in the number of nephrons in the hypertrophic kidney following Received for publication October 28, 1971; accepted in revised form January 18, , by the International ociety of Nephrology contralateral nephrectomy [1] Therefore, the functional characteristics of these hypertrophic kidneys, particularly the increase in glomerular filtration rate, are considered compatible with functional modifications of preexistent nephrons [2] However, since the methods of enumeration of glomeruli are difficult, the results are often uncertain Prior to 1925 results concerning this question were conflicting [3] and since then very limited data have been obtained Moreover, functional studies in animals with compensatory renal hypertrophy have been performed without taking into account the age of animals at the day of the nephrectomy The results of the present study suggest that this factor can markedly affect the number of glomeruli in a hypertrophic kidney In 1965 Damadian, hawayri, and Bricker [4] described a very simple method of determining the number of gbmeruli contained in a kidney in the present study this technique was employed to determine the number of glomeruli that were present in normal and hypertrophic rat kidneys in relation to the age of the animals at the time of nephrectomy When a unilateral nephrectomy was performed in 3 to 5 day old rats the remaining kidney showed a significant increase in the number of glomeruli when compared to control kidneys from rats of the same age In contrast, when nephrectomy was performed in rats more than two months of age, no increase in the number of glomeruli was found, although a definite increase in kidney weight was observed Methods The number of glomeruli per kidney (NG) was determined using the method described by Damadian, hawayri and Bricker [4] The kidneys were excised, decapsulated and weighed They were then maccrated in a 5% HCI solution at 37 C for 15 minutes ach kidney was kept in 25 ml of distilled water at 4 C for one day before glomerular counts were performed Individual vials, each 391
2 392 Bonvalet et a! containing one kidney, were gently agitated by hand to obtain a homogeneous suspension of glomeruli and fragments of tubules and vessels One ml aliquots of the suspension were immediately placed in a circular plexiglas counting chamber 4 cm in diameter ii1 which a 2 mm grid pattern was etched The number of glomeruli present in the cell was counted with the aid of a microscope at a magnification of 4 x Two aliquots of each suspension were systematically counted When the results did not differ by more than 5 %, the mean value of the two counts was used for subsequent calculations; otherwise, a third aliquot was counted and the mean value of the three counts was used The total number of glomeruli contained in the kidney was determined from each mean value In the present study, 118 kidneys from 67 female Wistar rats were used The kidney remaining after unilateral nephrectomy is referred to as the "hypertrophic kidney" and all other kidneys are designated as the "control " In each case, the weight of the kidney and the age and weight of the rat on the day of nephrectomy were noted The glomerular counts were performed in such a way that the investigator did not know either the weight of the kidney or the type of kidney he was counting In the initial series of experiments the variation in the number of glomeruli in relation to the age of the animal was determined in normal kidneys ighty-five normal kidneys were examined Glomerular counts were carried out in both kidneys of 26 normal rats and in the excised kidney of 33 uninephrectomized rats Next, the number of glomeruli was determined in the remaining hypertrophic kidney following unilateral nephrectomy in 37 rats belonging to eight litters At least two animals in each litter underwent unilateral nephrectomy The remaining hypertrophic kidney was removed 21 to 36 days later Glomerular counts were carried out on both kidneys With the exception of two litters (litters six and eight), glomerular counts were also performed on both kidneys of litter mates taken on the date of the original unilateral nephrectomy and on the date of removal of the hypertrophic kidney (an additional eight hypertrophic kidneys from other rats were also included in this study) Results In normal animals it was found that the right kidney was slightly but significantly (P >5, paired t test) heavier than the left However, the number of glomeruli (NG) was not significantly different (P < 3) in the two kidneys (right, 3,622; left, 3,11) Consequently, the side from which the kidney was obtained was not taken into consideration in this study In Fig 1 the NG in control kidneys is plotted against the age of the rats It appears that the NG increases markedly with age until 1 days and that it then remains fairly constant Mean values were 25,27 D 2,5 (N= 6) for 15 to 2 day old rats and 32,15± D 4,55(N= 24) for x I :1! I Days Fig 1 Relation of the number of glomeruli in control kidneys to the age of the rat 5 x I- 5 sit o 5 3 : o I- I V 5% ii, s - I I I I I to 8 day old rats A significant positive correlation between the weight of the control kidney and the NG was found in our animals and it is illustrated in Fig 2(y = 1688x , N=81, r=694) The results of the glomerular counts on the "hypertrophic" kidneys are summarized in Table 1 and Figs 3 and 4 Data for "control" and "hypertrophic" kidneys are given separately for each litter in Table 1 It is apparent that the NG in hypertrophic kidneys was significantly greater than in control kidneys when unilateral nephrectomy was performed in 3 to 5 day old rats In contrast, when unilateral nephrectomy was performed in older rats Kidney weight, mg Fig 2 Relation of the number of glomeruli in control animals to kidney weight
3 Compensatory renal hypertrophy 393 (more than 55 days old), an increase in the NG in the remaining hypertrophic kidney was not apparent In litter number six where the unilateral nephrectomies were performed at 51 days, the results were conflicting, since one of the hypertrophic kidneys contained 28, glomeruli, while the second contained 41, glomeruli Table 1 Kidney weight and number of glomeruli in control and hypertrophic kidneys in 8 litters Litter No Rat No Hypertrophy Age: 31 Age: 63 Age: 63 1 R ,3 1 L ,3 1 2R 1 R I L 2 2 R 3 R 1 R I L 3 2 R 3 R 4L I R 1 L 2 R 2L 4 5 R 6 R 6 L 1 L 5 5 R 6 IL , ,7 Age: ,9 24z 24, , ,8 Age: , , , ,4 Age: , , , , , , Age: , , , ,2 Age: , , , 55 26,5 54 3, ,75 R ,25 R 7 46, Age: 63 Age: , , ,25 R ,5 R ,25 Age: 63 Age: , , , ,6 R72 49, R 65 41,6 Age: 72 Age: , , , ,75 Age: , ,3 R ,5 R , Age:78 R ,75 R 94 49,5 R 16 48, R , Age:81 R87 41, R , Litter x I- C C z No Rat No 7 3 R 4 R 8 Table 1 (continued) Hypertrophy Age: 57 Age: 78 Age: 78 I R , L ,75 2 R , , 1 L ,75 Age: , , , , , ,5 L ,25 Age: 27 R ,75 R , R ,2 R , R= right kidney; L= left kidney The age of the rats on the date of the removal of control and hypertrophic kidneys is given for each litter 5 o Days Fig 3 Relation of the number of glomeruli in control (closed circles) and hypertrophic (open circles) kidneys to the age of rats jbr animals 6 to 8 days of age Contralateral nephrectomy was performed before the animals were 5 days of age 8
4 394 Bonvalet et al Fig 3 illustrates the highly significant difference (P <1, paired t test) between the NO in control versus 5 hypertrophic kidneys of 6 to 8 day old rats in which the unilateral nephrectomies were performed before the age of 9 x 5 days (control, 32,15 D 4,55, N= 24; hypertrophic, 4 47,36± D 3,18, N= 12) In contrast, it can be seen in Fig 4 that there was no difference in the NO between control and hypertrophic kidneys of 1 to 27 day old rats in which unilateral nephrectomies were performed C- 3 after the age of 55 days (control, 35,36 D 3,15, N= 14; hypertrophy, 34,12± D 3,38, N= 12) The NG in control and hypertrophic kidneys of 6 to Z 1 day old rats (unilateral nephrectomy performed before 55 days) and in 11 to 27 day old rats (unilateral nephrectomy performed after 55 days) are plotted against the kidney weight in Figs and 6 It can be seen that with early nephrectomy the kidney weight as well as the NG was approximately 3 % higher in the hypertrophic than in the control kidneys (control, weight = 634 D143 g, NG = 32,15± D 4,55, N= 24; hypertrophy, weight = 935 D 25, NO = 46,4 D 5,83, N= 17) Thus, it appears that in this case the increase in the number of nephrons probably accounted for the major part of the o I I I Kidney weight, mg Fig 5 Relation of the number of glomeruli to kidney weight in control (closed circles) and hypertrophic (open circles) kidneys in animals 6 to 1 days of age Contralateral nephrectomy was performed before the animals were 55 days of age!q) I 9 4 x I I i 5 o C- C I Kidney weight, mg C- I- z2-4- L_J Fig 6 Relation of the number of glomeruli to kidney weight in I- control (closed circles) and hypertrophic (open triangles) kidneys in animals 11 to 27 days of age Contralateral nephrectomy C- was p performed after 55 days of age increased weight of hypertrophic kidneys In the 11 to Z 27 day old rats, although the weight of the hypertrophic 3 - kidneys was also 3% greater than that of the controls, there was no difference between the NG in control and - hypertrophic kidneys (control, weight = 859 D 13 g, NG= 35,36± D 3,15, N= 14; hypertrophic, weight ± D 123, NG= 34,12± D 3,38, N 12) Therefore, in the latter group of rats the increase in kidney - weight was probably due to hypertrophy of preexistent I I I I I I I I i neilirons Days Fig 4 Relation of the number of glomeruli in control (closed circles) and hypertrophic (open triangles) kidneys to the age of rats in animals 1 to 27 days of age Contralateral nephrectomy was performed after 55 days of age DICUIOn We believe that the Damadian method is a simple and convenient way to count kidney glomeruli After maceration of the kidney the glomeruli are easily recognizable in the tissue suspension (Fig 7) ach glomerular count requires
5 Compensatory renal hypertrophy a / t 1- '1 Fig 7 Photograph of kidney suspension, magnification x 4 no more than 3 minutes The variation between the number of glomeruli in two separate aliquots of the same kidney suspension was, in the present experiments, nearly always less than 5 %, attestingto the reproducibility of this method Furthermore, the reproducibility of the method was checked in a previous study (unpublished data of the authors) as follows Twelve suspensions of kidney tissue were prepared as already described and four samples of each suspension were counted The mean value and standard deviation of the glomerular counts were determined for each suspension The mean value of these standard deviations (expressed as percentage of the mean) for all suspensions was 54 % The effect of broken and altered glomeruli on total glomerular counts was also evaluated using the same suspensions When the volume of the altered glomerulus was estimated to be equal to or greater than 5 % of the total volume of an unaltered glomerulus, the fragment was counted as a "doubtful glomerulus" but included in the total count maller glomerular fragments were counted separately When expressed as a percentage of the total count, the larger broken glomeruli represented 19 % of the total count The smaller fragments not included in the final glomerular count were equal to 17 % of the total glomerular count Other methods used to enumerate glomeruli are based on histological techniques They require separation of the cortex from the medulla before glomerular counts can be performed on the cortical fragments [5], or before the total number of glomeruli can be counted on serial histological sections as described by Kittelson [61 and Arataki [7] Although the older method allowed Arataki to perform a very important study on post-natal kidney growth and compensatory renal hypertrophy, the excessive time required to perform glomerular counts on each kidney is a great disadvantage when studying large groups of animals This problem is further emphasized by the fact that to our knowledge, in the two studies that have been published since the original work of Arataki, glomerular counts were performed in a total of only six hypertrophic kidneys [3, 8] Our results in control kidneys indicate that the total number of glomeruli per kidney increases from approximately 2, to 25, at 2 days of age to 3, to 4, at 1 days of age Thereafter the total number of glomeruli appear to remain constant with age These results are similar to those of Kittelson [6] and Arataki [7] These workers demonstrated in 17 female rats that the NG was approximately 24, at 2 days of age and 29, at 1 days of age ince the kidney weight increases from 2 to 8 mg during the 2 to 1 day period it can be concluded that enlargement of pre-existing nephrons is the major factor accounting for postnatal weight gain in the kidney Recently Horster and Lewy [9] investigated the influence of maturation on GFR and renal plasma flow in rats between one and 18 days of age They observed an increase in PAH extraction during the first three weeks of life They concluded that the gradual increase in the extraction ratio for PAH may be related to an increase in the number of nephrons and proximal tubular mass Although this work was performed in rats younger than those used in our study, the results are in agreement with our findings in slightly older rats Our study also demonstrates that the NG increases in hypertrophic kidneys if the contralateral nephrectomy is performed before the rat is more than 5 to 55 days of age The 3 % increase in kidney weight could be accounted for by the increase in the total number of glomeruli, which in turn reflects an increase in total nephrons In contrast, when the unilateral nephrectomy was performed after the rats were more than 55 days of age, the 3 % increase in
6 396 Bonvalet et a! kidney weight was not accompanied by an increase in the NG, thus indicating that the increase in kidney weight probably resulted from the enlargement of pre-existing nephrons It is of particular interest to note that the hypertrophic kidneys were unable to increase the total number of nephrons when unilateral nephrectomy was perfomed at an age when neogenesis of nephrons has ceased in the normal developing rat kidney tudies of renal hypertrophy before 1926 have been extensively reviewed by Jackson and hiels [3] Only one study was reported in which the NG of hypertrophic kidneys was determined in young rats [1] It was concluded that an increase in the number of glomeruli did not occur Variable results were obtained in other studies of compensatory renal hypertrophy in dogs and rabbits; some investigators observed an increase in NG while others observed none In 1926 Arataki reported no difference between the NG in 14 hypertrophic kidneys when compared to those in control kidneys (11] imilar results were obtained in a single rat by Jackson and hiels [3] and in five rats by Moore [8] However, it should be noted in the latter study that the NG of control adult rats (2,) was markedly lower than that found by us as well as by Arataki [7,11] Hayslett, Kashgarian, and pstein [2] studied the functional changes in individual nephrons of hypertrophic kidneys following unilateral nephrectomy They observed an increase in both single nephron and whole kidney gomerular filtration rate, thus providing at least indirect evidence against the neogenesis of nephrons in hypertrophic kidneys However, the study was conducted in rats weighing from 2 to 45 g Although the age of the animals was not given, it is probable that most of them were more than 6 days old, in which case their results would support our findings in adult rats In the rat, neogenesis of nephrons has been described up to four weeks of age [12] Arataki noted that immature glomeruli were easily recognized in the rat kidney from birth up to 2 days He concluded that "the increase in the number of glomeruli between birth and 1 days is due to the new formation of glomeruli and the maturing of the glomeruli present at the earlier age, but not then fully formed and so not counted" [7] He also stated that there was probably a rapid formation of glomeruli up to the third week of life which was followed by a much longer period of slow formation and development In his study, only fully formed glomeruli were considered Although this point must be kept in mind when glomerular counts obtained by histological methods are compared with those obtained with Damadian's method, it is, in fact, quite possible that with the latter method only well developed glomeruli are able to resist maceration in HC1 Thus, the same glomerular population may actually be counted with the two methods Although it is quite evident that an increase in mature nephrons occurs in the hypertrophic kidney of very young rats (3 to 5 days of age) it is not at all clear whether the increase is due to neogenesis or to an increased maturation of pre-existing immature glomeruli However, the important point is that hypertrophy results in an increase in the total number of glomeruli per kidney when compared to kidneys of normal adult rats We believe it is unlikely that the observed increase in NG is due only to simple acceleration of the normal maturation of glomeruli It is of interest that the ability to increase the NG of the remaining kidney after unilateral nephrectomy was lost in rats older than two months even though there was a comparable increase in kidney weight In any case, whatever mechanism is responsible for the increase in NG during renal hypertrophy in young rats, it remains evident that the pattern of this hypertrophy is different between young and adult rats Whether, after unilateral nephrectomy, the remaining kidney responds differently to the same stimulus (or stimuli) in relation to the age of the rat, or different stimuli act in the two cases, is not known Reprint requests to Dr J P Bonvalet, INRM, Hópital L Bernard, 94 Limeil-Brevannes, France References 1 Nowinski, W W, and Goss, R J: Compensatory renal hypertrophy New York, Academic Press, Hayslett, J P, Kashgarian, M, and pstein, F H: Functional correlates of compensatory renal hypertrophy J Clin Invest 47: , Jackson, C M, and hiels, M: Compensatory hypertrophy of the kidney during various periods after unilateral nephrectomy in very young albino rats Anat Rec 36: , Damadian, R V, hawayri,, and Bricker, N : On the existence of non-urine forming nephrons in the diseased kidney of the dog J Lab Clin Med 65: 26 39, Nelson, B T: The number of glomeruli in the kidney of the adult rabbit Anat Rec 23: , Kittelson, J A: The postnatal growth of the kidney of the albino rat, with observations on an adult human kidney Anat Rec 13: , Arataki, M: On the postnatal growth of the kidney, with special reference to the number and size of the glomeruli (Albino rat) Am J Anat 36: , Moore, R A: Number of glomeruli in kidney of adult white rat unilaterally nephrectomized in early life J xp Med 5: , Horster, M, and Lewy, J : Filtration fraction and extraction of PAH during neonatal period in the rat Am J Physiol 219: , Debenedetti, : ull' ipertrofia funzionale del rene Arch PerLe c Med 35: , Arataki, M: xperimental researches on the compensatory enlargement of the surviving kidney after unilateral nephrectomy (Albino rat) Am J Anat 36: , Baxter, J, and Yoffey, J M: The postnatal development of renal tubules in the rat J Anat 82: , 1948
(From the Institute of Pathology, Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and the Department of Zoology, Yale University, New Haven) Method
 THE EFFECT OF UNILATERAL NEPHRECTOMY ON THE SENILE ATROPHY OF THE KIDNEY IN THE WHITE RAT BY ROBERT A. MOORE, M.D.,* A~ LOUIS M. HELLMAN (From the Institute of Pathology, Western Reserve University, Cleveland,
THE EFFECT OF UNILATERAL NEPHRECTOMY ON THE SENILE ATROPHY OF THE KIDNEY IN THE WHITE RAT BY ROBERT A. MOORE, M.D.,* A~ LOUIS M. HELLMAN (From the Institute of Pathology, Western Reserve University, Cleveland,
(From the Department of Pathology, School of Medicine, Western Reserve University, Cleveland)
 THE EFFECT OF UNILATERAL NEPHRECTOM ON THE TOTAL NUMBER OF OPEN GLOMERULI IN THE RABBIT BY ROBERT A. MOORE, M.D.,* AND GREGORY F. LUKIANOFF, M.D. (From the Department of Pathology, School of Medicine,
THE EFFECT OF UNILATERAL NEPHRECTOM ON THE TOTAL NUMBER OF OPEN GLOMERULI IN THE RABBIT BY ROBERT A. MOORE, M.D.,* AND GREGORY F. LUKIANOFF, M.D. (From the Department of Pathology, School of Medicine,
Compensatory adaptation of structure and function
 Kidney International, Vol. 6 (1974), p. 1O17 Compensatory adaptation of structure and function following progressive renal ablation JOEL M. KAUFMAN, HERBERT J. DIMEOLA, NORMAN J. SIEGEL, BERNARD LYTTON,
Kidney International, Vol. 6 (1974), p. 1O17 Compensatory adaptation of structure and function following progressive renal ablation JOEL M. KAUFMAN, HERBERT J. DIMEOLA, NORMAN J. SIEGEL, BERNARD LYTTON,
Compensatory Renal Hypertrophy in Dogs: Single Nephron Glomerular Filtration Rate
 THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 51 (1978), 307-313 Compensatory Renal Hypertrophy in Dogs: Single Nephron Glomerular Filtration Rate SERGE CARRIiRE Montreal, P.Q., Canada Kidney weight, length
THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 51 (1978), 307-313 Compensatory Renal Hypertrophy in Dogs: Single Nephron Glomerular Filtration Rate SERGE CARRIiRE Montreal, P.Q., Canada Kidney weight, length
superficial proximal tubular length, nephron number and kidney weight
 J. Physiol. (1977), 272, pp. 573589 573 With 8 teztft urea Printed in Great Britain DEVELOPMENTAL CHANGES IN NEPHRON NUMBER, PROXIMAL TUBULAR LENGTH AND SUPERFICIAL NEPHRON GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE OF
J. Physiol. (1977), 272, pp. 573589 573 With 8 teztft urea Printed in Great Britain DEVELOPMENTAL CHANGES IN NEPHRON NUMBER, PROXIMAL TUBULAR LENGTH AND SUPERFICIAL NEPHRON GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE OF
Actualités néphrologiques Jean Hamburger 23 Avril Marie Courbebaisse, Service de Physiologie Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris
 Single nephron GFR Actualités néphrologiques Jean Hamburger 23 Avril 2018 Marie Courbebaisse, Service de Physiologie Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris Introdution Glomerular filtration and SNGFR
Single nephron GFR Actualités néphrologiques Jean Hamburger 23 Avril 2018 Marie Courbebaisse, Service de Physiologie Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris Introdution Glomerular filtration and SNGFR
THE EFFECT OF UNILATERAL CASTRATION ON THE REMAINING TESTIS OF THE MOUSE
 402 THE EFFECT OF UNILATERAL CASTRATION ON THE REMAINING TESTIS OF THE MOUSE BY I. W. ROWLANDS. (From the Department of Zoology, University College of North Wales, Bangor.) (Received 14th April, 1934.)
402 THE EFFECT OF UNILATERAL CASTRATION ON THE REMAINING TESTIS OF THE MOUSE BY I. W. ROWLANDS. (From the Department of Zoology, University College of North Wales, Bangor.) (Received 14th April, 1934.)
Estimation of relative glomerular capillary surface area in normal and hypertrophic rat kidneys
 Kidney International, Vol. /4 (1978), pp. 437-443 Estimation of relative glomerular capillary surface area in normal and hypertrophic rat kidneys DAVID W. KNUTSON, FRANK CHIEU, CLEAVES M. BENNETT, and
Kidney International, Vol. /4 (1978), pp. 437-443 Estimation of relative glomerular capillary surface area in normal and hypertrophic rat kidneys DAVID W. KNUTSON, FRANK CHIEU, CLEAVES M. BENNETT, and
THE RESTORATION OF LOST ORGAN TISSUE* THE RATE AND DEGREE OF RESTORATION BY T. ADDIS, M.D., AND W. LEW
 Published Online: 1 March, 1940 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.71.3.325 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on November 20, 2018 THE RESTORATION OF LOST ORGAN TISSUE* THE RATE AND DEGREE OF RESTORATION
Published Online: 1 March, 1940 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.71.3.325 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on November 20, 2018 THE RESTORATION OF LOST ORGAN TISSUE* THE RATE AND DEGREE OF RESTORATION
QUANTITATIVE HISTOCHEMISTRY OF THE NEPHRON. V.
 QUANTITATIVE HISTOCHEMISTRY OF THE NEPHRON. V. ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE AND LACTIC DEHYDROGENASE ACTIVITIES IN LUPUS NEPHRITIS * By VICTOR E. POLLAK,t SJOERD L. BONTING, ROBERT C. MUEHRCKE AND ROBERT M. KARK
QUANTITATIVE HISTOCHEMISTRY OF THE NEPHRON. V. ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE AND LACTIC DEHYDROGENASE ACTIVITIES IN LUPUS NEPHRITIS * By VICTOR E. POLLAK,t SJOERD L. BONTING, ROBERT C. MUEHRCKE AND ROBERT M. KARK
formation of new nephrons, have been demonstrated
 CHANGES IN RENAL FUNCTION ACCOMPANYING THE HYPERTROPHY OF THE REMAINING KIDNEY AFTER UNILATERAL NEPHRECTOMY1 BY CATHERINE A. WELSH, IRWIN WELLEN, AND HOWARD C. TAYLOR, JR., WITH THIE TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE
CHANGES IN RENAL FUNCTION ACCOMPANYING THE HYPERTROPHY OF THE REMAINING KIDNEY AFTER UNILATERAL NEPHRECTOMY1 BY CATHERINE A. WELSH, IRWIN WELLEN, AND HOWARD C. TAYLOR, JR., WITH THIE TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE
ESTIMATION OF GLOMERULAR SIZE BY MICROMETRY IN MIDGESTATIONAL PERIOD
 Original Research Article ESTIMATION OF GLOMERULAR SIZE BY MICROMETRY IN MIDGESTATIONAL PERIOD Suvarna A. Gulanikar * 1, G.A. Shroff 2, A.R. kharkar 3, V.S.Mandhana 4. ABSTRACT Introduction: Changes in
Original Research Article ESTIMATION OF GLOMERULAR SIZE BY MICROMETRY IN MIDGESTATIONAL PERIOD Suvarna A. Gulanikar * 1, G.A. Shroff 2, A.R. kharkar 3, V.S.Mandhana 4. ABSTRACT Introduction: Changes in
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
~~I li~jllwl t... ~i d.. ud...!j.i..:.jj..u_,. ~I.:,.o \\- oo ~~1.:,-o L::...l_,
 Qatar Univ. Sci. J. (1993), 13(2): 264-270 PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE GUINEA PIG KIDNEY QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE MORPHOLOGY By ZEINAB M. A. EL GOHARY Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, University
Qatar Univ. Sci. J. (1993), 13(2): 264-270 PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE GUINEA PIG KIDNEY QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE MORPHOLOGY By ZEINAB M. A. EL GOHARY Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, University
Exaggerated carbohydrate-induced calciuria in the remaining kidney of transplant donors
 Kidney International, Vol. 3 (1973), p. 24 29 Exaggerated carbohydrate-induced calciuria in the remaining kidney of transplant donors GEOFFREY BONER, MARGARET NEWTON and RICHARD E. RIESELBACH Department
Kidney International, Vol. 3 (1973), p. 24 29 Exaggerated carbohydrate-induced calciuria in the remaining kidney of transplant donors GEOFFREY BONER, MARGARET NEWTON and RICHARD E. RIESELBACH Department
Effect of uninephrectomy on glomerulotubular functional-structural balance in the dog
 Kidney International, Vol. 5 (1974), p. 122 130 Effect of uninephrectomy on glomerulotubular functional-structural balance in the dog STANLEY E. BRADLEY, KUANG-CHUNG H. CHIEN, JAIME B. COELHO and RICHARD
Kidney International, Vol. 5 (1974), p. 122 130 Effect of uninephrectomy on glomerulotubular functional-structural balance in the dog STANLEY E. BRADLEY, KUANG-CHUNG H. CHIEN, JAIME B. COELHO and RICHARD
[ 331 ] THE LATE INTRAUTERINE AND POSTNATAL DEVELOP- MENT OF HUMAN RENAL GLOMERULI
![[ 331 ] THE LATE INTRAUTERINE AND POSTNATAL DEVELOP- MENT OF HUMAN RENAL GLOMERULI [ 331 ] THE LATE INTRAUTERINE AND POSTNATAL DEVELOP- MENT OF HUMAN RENAL GLOMERULI](/thumbs/85/92705171.jpg) [ 331 ] THE LATE INTRAUTERINE AND POSTNATAL DEVELOP- MENT OF HUMAN RENAL GLOMERULI BY MORAG S. MACDONALD* AND JOHN L. EMERY Department of Pathology, The Children's Hospital, Sheffield When examining a
[ 331 ] THE LATE INTRAUTERINE AND POSTNATAL DEVELOP- MENT OF HUMAN RENAL GLOMERULI BY MORAG S. MACDONALD* AND JOHN L. EMERY Department of Pathology, The Children's Hospital, Sheffield When examining a
The OS/+ mouse: a genetic animal model of reduced renal mass
 The OS/+ mouse: a genetic animal model of reduced renal mass RUDOLFS K. ZALUPS Division of Basic Medical Sciences, Mercer University School of Medicine, Macon, Georgia 31207 Zalups, Rudolfs K. The OS/+
The OS/+ mouse: a genetic animal model of reduced renal mass RUDOLFS K. ZALUPS Division of Basic Medical Sciences, Mercer University School of Medicine, Macon, Georgia 31207 Zalups, Rudolfs K. The OS/+
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Urinary System Filtration Reabsorption Secretion Concentration
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Urinary System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 25 For this lab you will use parts
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Urinary System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 25 For this lab you will use parts
possibility that the kidney which is known to have a 'growth' inhibitor factor (Dicker,
 J. Physiol. (1980), 301, pp. 1-5 1 Printed in Great Britain ORIGIN OF THE HUMORAL FACTOR RESPONSIBLE FOR COMPENSATORY RENAL HYPERTROPHY BY S. E. DICKER AND CHRISTINE A. MORRIS From the Department of Chemistry,
J. Physiol. (1980), 301, pp. 1-5 1 Printed in Great Britain ORIGIN OF THE HUMORAL FACTOR RESPONSIBLE FOR COMPENSATORY RENAL HYPERTROPHY BY S. E. DICKER AND CHRISTINE A. MORRIS From the Department of Chemistry,
Hereditary polycystic kidney disease (adult form): A microdissection study of two cases at an early stage of the disease
 Kidney International, Vol. 13 (1978), pp. 519 525 Hereditary polycystic kidney disease (adult form): A microdissection study of two cases at an early stage of the disease Luc BAERT Department of Urology,
Kidney International, Vol. 13 (1978), pp. 519 525 Hereditary polycystic kidney disease (adult form): A microdissection study of two cases at an early stage of the disease Luc BAERT Department of Urology,
The Urinary System. Medical Assisting Third Edition. Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
nephrons, this was not accompanied by concomitant disproportionate
 J. Phy8iol. (1976), 262, pp. 119-129 119 With 4 text-figures Printed in Great Britain FUNCTIONAL AND MORPHOLOGIC MATURATION OF SUPERFICIAL AND JUXTAMEDULLARY NEPHRONS IN THE RAT BY C. DE ROUFFIGNAC AND
J. Phy8iol. (1976), 262, pp. 119-129 119 With 4 text-figures Printed in Great Britain FUNCTIONAL AND MORPHOLOGIC MATURATION OF SUPERFICIAL AND JUXTAMEDULLARY NEPHRONS IN THE RAT BY C. DE ROUFFIGNAC AND
University Lollege London, 20, Gordon Street, London WC1H OAJ
 J. Physiol. (1977), 273, pp. 241-253 241 With 3 text-figurea Printed in Great Britain COMPENSATORY RENAL HYPERTROPHY IN HYPOPHYSECTOMIZED RATS BY S. E. DICKER*, A. L. GREENBAUM AND CHRISTINE A. MORRIS
J. Physiol. (1977), 273, pp. 241-253 241 With 3 text-figurea Printed in Great Britain COMPENSATORY RENAL HYPERTROPHY IN HYPOPHYSECTOMIZED RATS BY S. E. DICKER*, A. L. GREENBAUM AND CHRISTINE A. MORRIS
BIOACTIVE RENAL CELLS AUGMENT KIDNEY FUNCTION IN A RODENT MODEL OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
 BIOACTIVE RENAL CELLS AUGMENT KIDNEY FUNCTION IN A RODENT MODEL OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Rusty Kelley, PhD Regenerative Medicine & Biology Tengion Labs May 24, 2010 ISCT Annual Meeting, Philadelphia PA
BIOACTIVE RENAL CELLS AUGMENT KIDNEY FUNCTION IN A RODENT MODEL OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Rusty Kelley, PhD Regenerative Medicine & Biology Tengion Labs May 24, 2010 ISCT Annual Meeting, Philadelphia PA
Ultrafiltration coefficient of isolated glomeruli of rats aged 4 days to maturation
 Kidney International, Vol 28 (1985), pp 926 931 Ultrafiltration coefficient of isolated glomeruli of rats aged 4 days to maturation VIRGINIA J SAVIN, CHERYL BEASON-GRIFFIN, and WALTER P RICHARDSON Departments
Kidney International, Vol 28 (1985), pp 926 931 Ultrafiltration coefficient of isolated glomeruli of rats aged 4 days to maturation VIRGINIA J SAVIN, CHERYL BEASON-GRIFFIN, and WALTER P RICHARDSON Departments
Results and limitations of outpatient and overnight stay laminectomies for lumbar spinal stenosis
 RESEARCH RECHERCHE Results and limitations of outpatient and overnight stay laminectomies for lumbar spinal stenosis David Yen, MD Abdu Albargi, MD Accepted Mar. 3, 2017; Early-released Aug. 1, 2017; subject
RESEARCH RECHERCHE Results and limitations of outpatient and overnight stay laminectomies for lumbar spinal stenosis David Yen, MD Abdu Albargi, MD Accepted Mar. 3, 2017; Early-released Aug. 1, 2017; subject
A. Correct! Flushing acids from the system will assist in re-establishing the acid-base equilibrium in the blood.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
dynamic action of ingested amino acids effected
 THE.EFFECT OF GLYCINE ON THE PRODUCTION AND EXCRETION OF URIC ACID1 BY MEYER FRIEDMAN (Fromn the Harold Brunn Institute for Cardiovascular Research, San Francisco, California) Mt. Zion Hospital, (Received
THE.EFFECT OF GLYCINE ON THE PRODUCTION AND EXCRETION OF URIC ACID1 BY MEYER FRIEDMAN (Fromn the Harold Brunn Institute for Cardiovascular Research, San Francisco, California) Mt. Zion Hospital, (Received
PHGY210 Renal Physiology
 PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
PHGY210 Renal Physiology Tomoko Takano, MD, PhD *Associate Professor of Medicine and Physiology McGill University *Nephrologist, McGill University Health Centre Lecture plan Lecture 1: Anatomy, basics
Hydrostatic pressures in proximal tubules and peritubule capillaries in the dog
 Kidney International, Vol. 2 (1972), p. 11 16 Hydrostatic pressures in proximal tubules and peritubule capillaries in the dog FRANKLYN U. KNOX, L. R. WILLIS, JACK W. STRANDHOY and EDWARD U. SCHNEIDER Nephrology
Kidney International, Vol. 2 (1972), p. 11 16 Hydrostatic pressures in proximal tubules and peritubule capillaries in the dog FRANKLYN U. KNOX, L. R. WILLIS, JACK W. STRANDHOY and EDWARD U. SCHNEIDER Nephrology
Excretory System 1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
JINNAH SINDH MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
 MODULE TITLE INTRODUCTION TARGET STUDENTS DURATION MODULE OUTCOMES Spiral -1 Renal and Excretory-1 Module The Renal and Excretory-1 Module is designed to help the learners understand how the urinary system
MODULE TITLE INTRODUCTION TARGET STUDENTS DURATION MODULE OUTCOMES Spiral -1 Renal and Excretory-1 Module The Renal and Excretory-1 Module is designed to help the learners understand how the urinary system
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion. The Kidneys
 Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Renal growth in response to unilateral ureteral obstruction
 Kidney International, Vol. 23 (1983), pp. 594 598 Renal growth in response to unilateral ureteral obstruction STEVEN J. ZELMAN, TERRY V. ZENSER, and BERNARD B. DAVIS Veterans Administration Medical Center,
Kidney International, Vol. 23 (1983), pp. 594 598 Renal growth in response to unilateral ureteral obstruction STEVEN J. ZELMAN, TERRY V. ZENSER, and BERNARD B. DAVIS Veterans Administration Medical Center,
Structural and Functional Adaptation after Reduction of Nephron Population
 TIlE YALE JOUJRNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 52 (1979), 271-287 Structural and Functional Adaptation after Reduction of Nephron Population FREDRIC 0. FINKELSTEIN AND JOHN P. HAYSLETT Departments of Medicine
TIlE YALE JOUJRNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 52 (1979), 271-287 Structural and Functional Adaptation after Reduction of Nephron Population FREDRIC 0. FINKELSTEIN AND JOHN P. HAYSLETT Departments of Medicine
The Ebf1 knockout mouse and glomerular maturation
 Repository of the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin (Germany) http://edoc.mdc-berlin.de/14009/ The Ebf1 knockout mouse and glomerular maturation Schmidt-Ott, K.M. Published in final
Repository of the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin (Germany) http://edoc.mdc-berlin.de/14009/ The Ebf1 knockout mouse and glomerular maturation Schmidt-Ott, K.M. Published in final
Effect of renal vein constriction on the localization of immune complexes in the kidney
 Kidney International, Vol. 16 (1979), pp. 681-687 Effect of renal vein constriction on the localization of immune complexes in the kidney BOON S. 1, MARK A. WEIss, and TAHA HAMuI Division of Nephrology,
Kidney International, Vol. 16 (1979), pp. 681-687 Effect of renal vein constriction on the localization of immune complexes in the kidney BOON S. 1, MARK A. WEIss, and TAHA HAMuI Division of Nephrology,
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
Nephron functional heterogeneity in the postobstructive
 Kidney International, Vol. 7 (1975), p. 19 26 Nephron functional heterogeneity in the postobstructive kidney DOUGLAS R. WILSON with the technical assistance of U. HONRATH Department of Medicine, University
Kidney International, Vol. 7 (1975), p. 19 26 Nephron functional heterogeneity in the postobstructive kidney DOUGLAS R. WILSON with the technical assistance of U. HONRATH Department of Medicine, University
THE ACTION OF HANSON'S THYMUS EXTRACT ON THE MOUSE
 140 THE ACTION OF HANSON'S THYMUS EXTRACT ON THE MOUSE BY M. LAFON (From the Department of Genetics, University College, London) (Received July 26, 19) IN a recent paper Hanson (19) described important
140 THE ACTION OF HANSON'S THYMUS EXTRACT ON THE MOUSE BY M. LAFON (From the Department of Genetics, University College, London) (Received July 26, 19) IN a recent paper Hanson (19) described important
nevertheless, the arteriae rectee (subsequently called art. rect. verse) were completely injected. He gave figures "drawn as accurately as possible
 THE COURSE OF THE BLOOD OF THE RENAL ARTERY. BY J. N. LANGLEY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) THERE are many accounts of the blood flow through the kidney. A few only need here be mentioned.
THE COURSE OF THE BLOOD OF THE RENAL ARTERY. BY J. N. LANGLEY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) THERE are many accounts of the blood flow through the kidney. A few only need here be mentioned.
Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 1. In the diagram above, pressure filtration occurs in a. W b. X c. Y d. Z
 Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Excretion Chapter 29. The Mammalian Excretory System consists of. The Kidney. The Nephron: the basic unit of the kidney.
 Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
Renal-Related Questions
 Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
Enhanced Recovery from Postischemic Acute Renal Failure
 440 Enhanced Recovery from Postischemic Acute Renal Failure Micropuncture Studies in the Rat WILLIAM F. FINN SUMMARY Recovery from unilateral postischemic acute renal failure produced by 1 hour of complete
440 Enhanced Recovery from Postischemic Acute Renal Failure Micropuncture Studies in the Rat WILLIAM F. FINN SUMMARY Recovery from unilateral postischemic acute renal failure produced by 1 hour of complete
Surgical Pathology Report
 Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
Renal System Physiology
 M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
man of the effects of diabetes and of insulin on the maximum ability of the tubules to reabsorb glucose.
 EFFECT OF DIABETES AND INSULIN ON THE MAXIMUM CA- PACITY OF THE RENAL TUBULES TO REABSORB GLUCOSE t By SAUL J. FARBER, EUGENE Y. BERGER, AND DAVID P. EARLE (From the Department of Medicine, New York University
EFFECT OF DIABETES AND INSULIN ON THE MAXIMUM CA- PACITY OF THE RENAL TUBULES TO REABSORB GLUCOSE t By SAUL J. FARBER, EUGENE Y. BERGER, AND DAVID P. EARLE (From the Department of Medicine, New York University
The Urinary System 15PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
41B. Metabolism produces wastes that must be eliminated from the body. This. Renal System Physiology: Computer Simulation
 41B E X E R C I S E Renal System Physiology: Computer Simulation O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define the following terms: glomerulus, glomerular capsule, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, nephron, proximal convoluted
41B E X E R C I S E Renal System Physiology: Computer Simulation O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define the following terms: glomerulus, glomerular capsule, renal corpuscle, renal tubule, nephron, proximal convoluted
M6ller, McIntosh and Van Slyke (5) has been employed. The cases. changes in functional activity. Indications suggesting that such changes
 STUDIES OF UREA EXCRETION. VIII. THE EFFECTS ON THE UREA CLEARANCE OF CHANGES IN PROTEIN AND SALT CONTENTS OF THE DIET BY CUTHBERT L. COPE I (From the Hospital of the Rockefeller Institute for Medical
STUDIES OF UREA EXCRETION. VIII. THE EFFECTS ON THE UREA CLEARANCE OF CHANGES IN PROTEIN AND SALT CONTENTS OF THE DIET BY CUTHBERT L. COPE I (From the Hospital of the Rockefeller Institute for Medical
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (1)
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (1) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 Functional role of the kidney 1.Homeostasis of fluid compartments (isosmia, isovolemia, isoionia, isohydria,) 2. Elimination
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (1) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 Functional role of the kidney 1.Homeostasis of fluid compartments (isosmia, isovolemia, isoionia, isohydria,) 2. Elimination
The Urinary System PART A
 15 The Urinary System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Functions of the Urinary
15 The Urinary System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Functions of the Urinary
Lund, 1948), the effect of which was to produce glomerular lesions without. relationship between increased protein loads and the tubular reabsorption
 544 J. Phy8iol. (1961), 156, pp. 544-554 With 5 text-ftgure8 Printed in Great Britain TUBULAR REABSORPTION OF PROTEIN IN RATS WITH EXPERIMENTAL PROTEINURIA BY D. MENDEL* From the Department of Physiology,
544 J. Phy8iol. (1961), 156, pp. 544-554 With 5 text-ftgure8 Printed in Great Britain TUBULAR REABSORPTION OF PROTEIN IN RATS WITH EXPERIMENTAL PROTEINURIA BY D. MENDEL* From the Department of Physiology,
Cutler, Power & Wilder, 1938; Hall & Langley, 1940), in the dog (Winkler &
 8 J. Physiol. (I948) I07, 8-I3 6I2.46I.6 RENAL EXCRETION OF SODIUM AND POTASSIUM IN RATS BY S. E. DICKER (Beit Memorial Fellow) From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Bristol (Received 30 December
8 J. Physiol. (I948) I07, 8-I3 6I2.46I.6 RENAL EXCRETION OF SODIUM AND POTASSIUM IN RATS BY S. E. DICKER (Beit Memorial Fellow) From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Bristol (Received 30 December
Further Studies of a Lymphoutic Hemogram and Its Relation to Lymphocytopoiesis
 Further Studies of a Lymphoutic Hemogram and Its Relation to Lymphocytopoiesis III. The Mode of Reaction of the Blood Lymphocytes and of the Lymphatic Tissue to Ovalbumin in Young Adult Albino Rats By
Further Studies of a Lymphoutic Hemogram and Its Relation to Lymphocytopoiesis III. The Mode of Reaction of the Blood Lymphocytes and of the Lymphatic Tissue to Ovalbumin in Young Adult Albino Rats By
Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with
![Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with](/thumbs/91/106294335.jpg) 381 6I2.I34:6I2.893 THE CONSTRICTOR RESPONSE OF THE INFERIOR VENA CAVA TO STIMULATION OF THE SPLANCHNIC NERVE BY K. J. FRANKLIN AND A. D. McLACHLIN (From the University Department of Pharmacology, Oxford)
381 6I2.I34:6I2.893 THE CONSTRICTOR RESPONSE OF THE INFERIOR VENA CAVA TO STIMULATION OF THE SPLANCHNIC NERVE BY K. J. FRANKLIN AND A. D. McLACHLIN (From the University Department of Pharmacology, Oxford)
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion. What are the functions of the urinary system? Maintenance of water-salt and acidbase
 10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM
 AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY
 RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
RENAL HISTOPATHOLOGY Peter McCue, M.D. Department of Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College There are no conflicts of interest. 1 Goals and Objectives! Goals Provide introduction
Functions of the kidney:
 Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Sebastião Rodrigues Ferreira-Filho, Camila Caetano Cardoso, Luiz Augusto Vieira de Castro, Ricardo Mendes Oliveira, and Renata Rodrigues Sá
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Nephrology Volume 211, Article ID 626178, 4 pages doi:1.461/211/626178 Research Article Comparison of Measured Creatinine Clearance and Clearances Estimated
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Nephrology Volume 211, Article ID 626178, 4 pages doi:1.461/211/626178 Research Article Comparison of Measured Creatinine Clearance and Clearances Estimated
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1981
 Diabetologia (1981) 2:451-456 Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1981 Originals Increased Kidney Size, Glomerular Filtration Rate and Renal Plasma Flow in Short-Term Insulin-Dependent Diabetics J. Sandahl
Diabetologia (1981) 2:451-456 Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1981 Originals Increased Kidney Size, Glomerular Filtration Rate and Renal Plasma Flow in Short-Term Insulin-Dependent Diabetics J. Sandahl
FLUID RESUSCITATION OF ACUTE HEMORRHAGE IN UNINEPHRECTOMIZED RABBITS: EFFECTS ON THE EARLY FUNCTION OF THE REMNANT KIDNEY
 FLUID RESUSCITATION OF ACUTE HEMORRHAGE IN UNINEPHRECTOMIZED RABBITS: EFFECTS ON THE EARLY FUNCTION OF THE REMNANT KIDNEY ELIF A AKPEK 1, HALE TUFAN 2, PETEK KORKUSUZ 5, SELIM CANDAN 1, ESIN AŞAN 3, SERDAR
FLUID RESUSCITATION OF ACUTE HEMORRHAGE IN UNINEPHRECTOMIZED RABBITS: EFFECTS ON THE EARLY FUNCTION OF THE REMNANT KIDNEY ELIF A AKPEK 1, HALE TUFAN 2, PETEK KORKUSUZ 5, SELIM CANDAN 1, ESIN AŞAN 3, SERDAR
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp , Chapter 19: pp ,
 P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
a loose nylon ligature around the aorta in very young
 REVERSIBILITY OF RENAL ATROPHY CAUSED BY UNILATERAL REDUCTION OF RENAL BLOOD SUPPLY * BY T. OMAE AND G. M. C. MASSON (From the Research Division of the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, and the Frank E. Bunts
REVERSIBILITY OF RENAL ATROPHY CAUSED BY UNILATERAL REDUCTION OF RENAL BLOOD SUPPLY * BY T. OMAE AND G. M. C. MASSON (From the Research Division of the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, and the Frank E. Bunts
Construction of Nephron by Fusion of Adult Glomeruli to Ureteric Buds with Type V Collagen. Yusuke Murasawa, Pi-chao Wang
 Construction of Nephron by Fusion of Adult Glomeruli to Ureteric Buds with Type V Collagen Yusuke Murasawa, Pi-chao Wang Abstract Although tissue engineering of artificial organs such as skin or cartilage
Construction of Nephron by Fusion of Adult Glomeruli to Ureteric Buds with Type V Collagen Yusuke Murasawa, Pi-chao Wang Abstract Although tissue engineering of artificial organs such as skin or cartilage
Excretion: is the removal of waste products formed by metabolism, out of the body
 Excretion in Humans Excretion: is the removal of waste products formed by metabolism, out of the body Accumulation of wastes in the cells would affect the normal functioning of the cells By getting rid
Excretion in Humans Excretion: is the removal of waste products formed by metabolism, out of the body Accumulation of wastes in the cells would affect the normal functioning of the cells By getting rid
Osmoregulation and the Excretory System
 Honors Biology Study Guide Chapter 25.4 25.10 Name Osmoregulation and the Excretory System FUNCTIONS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM OSMOREGULATION Freshwater: Marine: Land Animals: Sources of Nitrogenous Wastes?
Honors Biology Study Guide Chapter 25.4 25.10 Name Osmoregulation and the Excretory System FUNCTIONS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM OSMOREGULATION Freshwater: Marine: Land Animals: Sources of Nitrogenous Wastes?
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
capillaries, and a consequent increased transudation, without necessarily altering to any marked extent the total circulation of blood
 612.463.4 THE CONTROL OF THE GLOMERULAR PRESSURE BY VASCULAR CHANGES WITHIN THE ISOLATED MAMMALIAN KIDNEY, DEMONSTRATED BY THE ACTIONS OF ADRENALINE. BY F. R. WINT0N (Beit Memorial Research Fellow). (Depaortment
612.463.4 THE CONTROL OF THE GLOMERULAR PRESSURE BY VASCULAR CHANGES WITHIN THE ISOLATED MAMMALIAN KIDNEY, DEMONSTRATED BY THE ACTIONS OF ADRENALINE. BY F. R. WINT0N (Beit Memorial Research Fellow). (Depaortment
HEALTHYSTART TRAINING MANUAL. Living well with Kidney Disease
 HEALTHYSTART TRAINING MANUAL Living well with Kidney Disease KIDNEY DISEASE CAN AFFECT ANYONE! 1 HEALTHYSTART PROGRAMME HEALTHYSTART is a lifestyle management programme to assist you to remain healthy
HEALTHYSTART TRAINING MANUAL Living well with Kidney Disease KIDNEY DISEASE CAN AFFECT ANYONE! 1 HEALTHYSTART PROGRAMME HEALTHYSTART is a lifestyle management programme to assist you to remain healthy
Chapter 23. Composition and Properties of Urine
 Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine (1 of 2) urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless
Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine (1 of 2) urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY ROLE OF THE URINARY SYSTEM THE URINARY SYSTEM. Components and function. V BS 122 Physiology II 151 Class of 2011
 19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
19. RENAL PHYSIOLOGY THE URINARY SYSTEM Components and function The urinary system is composed of two kidneys, the functionally filtering apparatus, which connect through two tubular structures called
The functions of the kidney:
 The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
Please remember that based on your personalized learning plan and your past experience you may not be required to complete all four modules.
 Course Overview Welcome to the Team PD pre-work participant guide. Team PD is a new education program offered by Baxter that utilizes individual learning maps so nurses receive a personalized approach
Course Overview Welcome to the Team PD pre-work participant guide. Team PD is a new education program offered by Baxter that utilizes individual learning maps so nurses receive a personalized approach
Trends in breast cancer incidence in Greater Bombay:
 Trends in breast cancer incidence in Greater Bombay: an epidemiological assessment B.B. Yeole,1 K. Jayant,2 & D.J. Jussawalla3 Reliable data from the Bombay CancerRegistryshowan increase in the age-adjusted
Trends in breast cancer incidence in Greater Bombay: an epidemiological assessment B.B. Yeole,1 K. Jayant,2 & D.J. Jussawalla3 Reliable data from the Bombay CancerRegistryshowan increase in the age-adjusted
ULAR LESIONS CAUSED BY CROTALUS VENOM.*
 AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE LATE GLOMER- ULAR LESIONS CAUSED BY CROTALUS VENOM.* BY RICHARD M. PEARCE, M.D. (From the John Herr Musser Department of Research Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania,
AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE LATE GLOMER- ULAR LESIONS CAUSED BY CROTALUS VENOM.* BY RICHARD M. PEARCE, M.D. (From the John Herr Musser Department of Research Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania,
Renal Clearance. Dr. Eman El Eter
 Renal Clearance Dr. Eman El Eter Concept of clearance Clearance is the volume of plasma that is completely cleared of a substance each minute. Example: Renal clearance of Substance X is defined as the
Renal Clearance Dr. Eman El Eter Concept of clearance Clearance is the volume of plasma that is completely cleared of a substance each minute. Example: Renal clearance of Substance X is defined as the
A. Incorrect! The urinary system is involved in the regulation of blood ph. B. Correct! The urinary system is involved in the synthesis of vitamin D.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
You should know the T max for any substance that you use and for PAH ; T max = mg / min
 Tubular function - What is clearance? o clearance referred to the theoretical volume of plasma from which a substance is cleared ( cleaned ) over a period of time and so its unit would be ((ml/min)) -
Tubular function - What is clearance? o clearance referred to the theoretical volume of plasma from which a substance is cleared ( cleaned ) over a period of time and so its unit would be ((ml/min)) -
temperature by Weil et al. (1975). The annual reproduction cycle in adult carp in Poland : ovarian
 The annual reproduction cycle in adult carp in Poland : ovarian state and serum gonadotropin level K. BIENIARZ P. EPLER B. BRETON Luong Noc THUY Institute of Applied Zoology, Academy of Agriculture, 30-059
The annual reproduction cycle in adult carp in Poland : ovarian state and serum gonadotropin level K. BIENIARZ P. EPLER B. BRETON Luong Noc THUY Institute of Applied Zoology, Academy of Agriculture, 30-059
The Functional Adaptation of the Diseased Kidney. I. Glomerular Filtration Rate *
 Journal of Clinical Investigation Vol. 43, No. 10, 1964 The Functional Adaptation of the Diseased Kidney. I. Glomerular Filtration Rate * NEAL S. BRICKERt SAULO KLAHR, AND RICHARD E. RIESELBACH t (From
Journal of Clinical Investigation Vol. 43, No. 10, 1964 The Functional Adaptation of the Diseased Kidney. I. Glomerular Filtration Rate * NEAL S. BRICKERt SAULO KLAHR, AND RICHARD E. RIESELBACH t (From
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Ultrastructural demonstration of a connection between afferent and efferent juxtamedullary glomerular arterioles
 Kidney International, Vol. 8 (1975), p. 239 244 Ultrastructural demonstration of a connection between afferent and efferent juxtamedullary glomerular arterioles ARNE LJuNGQvIsT Institute of Pathology,
Kidney International, Vol. 8 (1975), p. 239 244 Ultrastructural demonstration of a connection between afferent and efferent juxtamedullary glomerular arterioles ARNE LJuNGQvIsT Institute of Pathology,
A,kCetazolamide lowers intraocular pressure
 Ocular and systemic effects of acetazolamide in nephrectomized rabbits Zvi Friedman,* Theodore Krupin, and Bernard Becker The effects of acetazolamide on intraocular pressure (IOP) were studied on rabbits
Ocular and systemic effects of acetazolamide in nephrectomized rabbits Zvi Friedman,* Theodore Krupin, and Bernard Becker The effects of acetazolamide on intraocular pressure (IOP) were studied on rabbits
reported. METHODS Renin was prepared from fresh rabbit kidneys by the alcohol method of Pickering (Pickering &
 106 J. Physiol. (I954) I 24, I 06-I I 2 AN ANGIOGRAPHIC STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF RENIN UPON THE RENAL CIRCULATION By P. M. DANIEL, MARJORIE M. L. PRICHARD AND J. N. WARD-McQUAID* From the NufIeld Department
106 J. Physiol. (I954) I 24, I 06-I I 2 AN ANGIOGRAPHIC STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF RENIN UPON THE RENAL CIRCULATION By P. M. DANIEL, MARJORIE M. L. PRICHARD AND J. N. WARD-McQUAID* From the NufIeld Department
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY
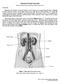 URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
The Urinary System. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 26 The Urinary System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
C h a p t e r 26 The Urinary System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
