Diabetes Renal Disease Management. Dr Paul Laboi Dr Vijay Jayagopal York Hospital
|
|
|
- Jodie Morrison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Diabetes Renal Disease Management Dr Paul Laboi Dr Vijay Jayagopal York Hospital 0
2 Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is a clinical syndrome characterised by the following: Persistent albuminuria (>300 mg/d or >200 μg/min) Progressive decline in the GFR Approximately 40% of people with diabetes will develop nephropathy. 1
3 Diabetic Nephropathy Is the leading cause of CKD in the UK Diabetes is responsible for 30-40% of all endstage renal disease (ESRD) Increases risk of CVD 3-5 fold and premature death 6 fold such that a significant number of patients do not survive long enough to receive RRT* * 2
4 Recommendations for screening of nephropathy in patients with Type 2 diabetes Screening for diabetic nephropathy 1 Check all patients at diagnosis and annually for proteinuria Measure serum creatinine and calculate GFR annually Repeat if an abnormal test is obtained Urine test Normal Testing and classification of proteinuria 2 (Stage of nephropathy) Microalbuminuria Overt nephropathy (macroalbuminuria) Urine dipstick Negative Positive 0 Urinary Albumin Level 24-hour 30 mg/day 300 mg/day 1000 mg/day ACR (male) 2.0 mg/mmol 20.0 mg/mmol 66.7 mg/mmol ACR (female) 2.8 mg/mmol 28.0 mg/mmol 93.3 mg/mmol ACR: albumin:creatinine ratio; GFR: glomerular filtration rate. 1. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Type 2 Diabetes. The management of type 2 diabetes. CG 87, May Available at: Last accessed January Canadian Diabetes Association Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Prevention and Management of Diabetes in Canada. September Available at: Last accessed January 2013.
5 The benefits of early tight control- UKPDS 10 year post-trial follow-up Randomisation Intensive vs Conventional Treatment 1997 (20 years) Trial End 10-year Post-Trial Follow Up (Non-Interventional) 2007 (30 years) 12%* 16%** (NS) 9%* 15%* 25%* 24%* Any diabetes related endpoint Microvascular disease Myocardial infarction 4
6 YH Audit 2004-Overall mortality 21% 5
7 Mortality At the end of the 12 month period A fifth of all patients were dead 30% of patients with CKD 3 were dead Highest mortality was in patients over 45 and those with low GFR s No deaths in patients under 35 6
8 Is this expected? Cumberland Infirmary, Carlisle: 10 year data review of Joint DM Renal clinic (QJM, 2006) 130 patients seen; 41 (32%) died Mean survival from first visit to death 47.8 months Glasgow Royal Infirmary: DM-Renal clinic, 170 consecutively referred patients over 10 years (QJM; 2002) FU data available for up to 3 years in of these were either dead or on dialysis 7
9 Key Staff: DSN Nephrologist Diabetologist Joint clinics York Model Additional Support: Dietician (diabetes/renal) Podiatry, pump team, renal psychologist, Dialysis nurses Not a recent development: Glasgow 1989 (initial data showed ESRD delayed by 2 years; QJM 1997) 8
10 Joint Clinic Audit Outcome Diabetes MDT clinic Total number of patients=97 Male=55(25-91). Mean age 66.6 yrs Female= 42( 35-87). Mean age yrs Change in egfr= -1.9% Change in A1c HbA1c 2012= ( ) HbA1c 2013= ( ) Mortality 10 patients/97 (9.7%) Total number of patients=27 Male=20 (54-91) Mean age 72.7 yrs Female =7(51-89) Mean age yrs Change in egfr= -11.5% Change in A1c HbA1c in 2012 = ( 41-94) HbA1c in 2013= ( ) Mortality 5 patients/27 (18.3%) 9
11 Issues covered in clinic.. Glycaemic control Blood pressure control Urine MA reduction Cardiovascular prevention Nephrotoxic meds Anaemia, K Metabolic bone Acid/base status Fluid status Low-protein, salt diet 10
12 Considerations VJ - Diabetes medication review PL Review of BP control, Albuminuria, Metabolic parameters 11
13 Metformin Sensitises body tissues to insulin and reduces glucose production by the liver Advantages Disadvantages Well established Contraindicated in patients at increased risk of lactic acidosis Low risk of hypoglycaemia Gastrointestinal (GI) side effects, including diarrhoea No weight gain Many contraindications (e.g. renal failure or dysfunction, Appetite not increased severe infection, cardiac or respiratory failure, recent Beneficial effects on microvascular and myocardial infarction) macrovascular risk with evidence of improved Requires dose titration due to GI side effects (available in long-term cardiovascular outcomes modified-release formulations to mitigate this side effect) Can be used in combination with many classes of anti-diabetes drugs Relatively low cost Renal considerations Review metformin if egfr <45 Stop metformin if egfr <30 12
14 Sulphonylureas Act as insulin secretagogues by directly stimulating the β cells of the pancreas to secrete insulin Renal considerations SU s should be used with caution in patients with later stages of CKD, with education on the risk of hypoglycaemia, weight gain and self blood glucose monitoring 13
15 Thiazolidinediones Act as insulin sensitisers Renal considerations No need to reduce dose of pioglitazone in renal impairment. Fluid retention, weight gain, anaemia, bone density No information is available from dialysed patients 14
16 DPP-4 inhibitors (gliptins) Enhance insulin secretion in response to a meal by inhibiting the breakdown of the incretin hormones GLP-1 and GIP by the DPP-4 enzyme Renal considerations Linagliptin can be used for mild, moderate and severe renal impairment; no dose adjustment required Sitagliptin, saxagliptin and vildagliptin all require dose adjustment in moderate to severe renal impairment 15
17 GLP-1 receptor agonists Work by enhancing glucose-dependent insulin secretion from β-cells in the pancreas, suppressing excessive glucagon levels and delaying gastric emptying Renal considerations Unsuitable for patients with end-stage renal disease or severe renal impairment. Used now in stage 3 CKD, especially when weight loss is a desired outcome. Doses not altered. 16
18 Insulin Replace reduced or deficient insulin levels in patients with T2D and work in the same way as endogenous insulin Renal Considerations Half-life of insulin is prolonged in renal impairment due to lower levels of degradation. Risk of hypoglycaemia greater. Dose adjustment may be needed as renal function declines. Fluid retention, weight gain. Adjustments for patients on HD and PD 17
19 Licensed indications in Type 2 diabetes and renal impairment in the UK Drug Mild Moderate Severe Metformin x x Acarbose x Sulphonylureas Dose adjustment Nateglinide Dose adjustment Dose adjustment Repaglinide Use with caution DPP-4 inhibitors Sitagliptin Dose reduction Saxagliptin Dose reduction Vildagliptin Dose reduction British National Formulary July 2013 Available at: Last accessed July Dose reduction Dose reduction Dose reduction Linagliptin Pioglitazone SGLT2 x x Liraglutide x GLP-1 analogue Insulin Exenatide Twice daily Once weekly Caution with dose escalation x x Lixisenatide Caution with dose escalation 18 x x
20 Primary composite endpoint* (%) Benefits of a multifactorial approach to type 2 diabetes management: Steno (n=160) Primary composite endpoint: conventional therapy (44%) and intensive therapy (24%) P= % risk reduction (Intensive vs conventional therapy) P=0.01 Conventional therapy 50% relative risk reduction in the primary composite endpoint Sustained benefit on cardiovascular events in the intensive management group over an additional 5.5 years 2 Conventional treatment: 20 Intensive therapy In accordance with national guidelines Intensive treatment: 0 Number at risk Conventional therapy Intensive therapy Time of follow-up (years) Stepwise implementation of behaviour modification and pharmacological therapy that targeted hyperglycaemia, hypertension, dyslipidaemia and microalbuminuria, with secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease with aspirin *Death from cardiovascular causes, non-fatal myocardial infarction, coronary artery bypass graft, percutaneous coronary intervention, non-fatal stroke, amputation or surgery for peripheral atherosclerotic artery disease 1. Adapted from: Gaede P, et al. N Engl J Med 2003;348: Gaede P, et al. N Engl J Med 2008;358:
21 Case study - 45 year old male taxi driver Newly diagnosed T2DM Raised fasting plasma glucose 7.8mmol/L BMI 29, conscious of his weight Lipids Tot Chol 6.0mmol/l LDL 2.5 mmol/l HDL 0.9 mmol/l Hypertensive BP= 152/92 mmhg No overt proteinuria dipstick negative 20
22 Case study - 45 year old male taxi driver Newly diagnosed T2DM Raised fasting plasma glucose 7.8mmol/L BMI 29, conscious of his weight Lipids Tot Chol 6.0mmol/l LDL 2.5 mmol/l HDL 0.9 mmol/l Hypertensive BP= 152/92 mmhg No overt proteinuria dipstick negative Q1. Dipstick is negative, would you consider this patient to have increased risk of declining renal function? 1. Yes 2. No 21
23 Case study - 45 year old male taxi driver Newly diagnosed T2DM Raised fasting plasma glucose 7.8mmol/L BMI 29, conscious of his weight Lipids Tot Chol 6.0mmol/l LDL 2.5 mmol/l HDL 0.9 mmol/l Hypertensive BP= 152/92 mmhg No overt proteinuria dipstick negative Q2. Which renal function test do you do? 1. egfr 2. Albuminuria 3. Both at same time 22
24 Case study - 45 year old male taxi driver Newly diagnosed T2DM Raised fasting plasma glucose 7.8mmol/L BMI 29, conscious of his weight Lipids Tot Chol 6.0mmol/l LDL 2.5 mmol/l HDL 0.9 mmol/l Hypertensive BP= 152/92 mmhg No overt proteinuria dipstick negative Q3. Which anti-diabetic drug would you initiate at this time? 1. Metformin 2. TZD 3. SU 4. DPP-4 inhibitor 5. SGLT2-I 6. GLP 7. Insulin 23
25 Case study - 45 year old male taxi driver Newly diagnosed T2DM Raised fasting plasma glucose 7.8mmol/l BMI 29, conscious of his weight Lipids Tot Chol 6.0mmol/l LDL 2.5 mmol/l HDL 0.9 mmol/l Hypertensive BP= 152/92 mmhg No overt proteinuria dipstick negative Q4. What other treatments should be initiated? 1. Antihypertensive medication 2. Statins 3. Both of the above 24
26 Diabetic CKD Your average Diabetic CKD 3/4 profile Age History of Diabetes for 7-10 yrs BMI BP Proteinuric Fluid overload Co-morbidities 2-3 BP meds 25
27 Diabetic kidney Pre-existing diabetes Persistent albuminuria/proteinuria Elevated Creatinine Diabetic retinopathy Normal or large kidneys on USS Non diabetes related kidney disease Other systemic disease Rapid increase in proteinuria, nephrotic syndrome Rapid rise in creatinine Refractory hypertension Active urinary sediment 26
28 CJASN October 07, 2013 vol. 8 no CJASN October 07, 2013 vol. 8 no CJASN October 07, 2013 vol. 8 no When is renal disease unlikely to be due to diabetes? Short duration of diabetes Accelerated worsening of proteinuria or creatinine Haematoproteinuria Biopsy findings FSGS 22% Hypertensive nephrosclerosis 18% ATN 17% IgA nephropathy 11% Membranous GN 8% Vasculitis 7% The Modern Spectrum of Renal Biopsy Findings in Patients with Diabetes, CJASN 2013, 8,
29 ACEI & ARB combination therapy Esp useful in proteinuric patients Treating 1000 patients with combination therapy for a year would prevent 3 ESRDs and reduce proteinuria in 90 patients. But would result in 38 AKI s and 65 hyperkalemias Cost of AKI is $ and cost of maintenance haemodialysis is $100,000/- Dual RAAS blockade for kidney failure: hope for the future. Vol 385 May 23, ,256 from 150 RCTs Cost of CKD2 $1700/-, CKD3 $3500/- and CKD4 12,700/- 28
30 SBP BP Either ACEi or ARB reduces progression by 16 to 30% Combination therapy in patients who have not responded to high dose single blockade? ONTARGET study did not show any benefit of 25,600 recruited patients, only 1200 had proteinuria Insufficient evidence but combination therapy is commonly prescribed in patients with refractory proteinuria >1gm Addition of Spironolactone Combination therapy ACEi + CCB / diuretic 29
31 Hyperkalemia When defined as >5.5, in patients with GFR < 60, average one episode per year. And more when treated with RAAS medications Drugs that increase potassium include ACEi, ARB, Aldosterone antagonists, potassium sparing diuretics and B blockers Management avoid Lo salt, use effective doses of thiazide and loop diuretics, manage acidosis, review drug combinations and reduce ACEi/ARB doses Patients on dialysis patients complain that arms and legs feel heavy & only way to remove potassium is by dialysis. 30
32 Acidosis Maintain venous bicarbonate >20-24 Starting dose of Sodium Bicarbonate is 500mgs three times a day Consider sodium loading and fluid overload Reduces potassium and ionised calcium Contraction alkalosis 31
33 Frusemide/Bumetanide Fluid balance Combinations loop plus Xipamide Loop plus spironolactone Drop in renal function, hyponatraemia, hypokalaemia, gout, cramps 32
34 Renal bone disease Secondary hyperparathyroidism low calcium, increasing phosphate and rising PTH Phosphate binders Calcium and non calcium based Calcium supplementation PTH suppression medically with alfa-calcidol and surgery 33
35 Symptom management Gout Prednisolone 10mgs for 5-7 days & Allopurinol 100mgs daily (cover with Pred at a lower dose) Restless legs & Cramps Gabapentin 100mgs daily or three times a week Neuropathic pain Gabapentin Chronic pain if small dose od Codeine or Tramadol does not work, consider Fentanyl patch starting at 6mcgs every 72 hrs Depression prevalence is 22%, 52% of patients with severe depression were prescribed antidepressants 34
36 Renal replacement therapy / dialysis Two options dependant on co-morbidities Palliative dialysis or aggressive dialysis as a means to transplantation(tb) Haemodialysis, chosen by 70-75% of patients, 12/150 dialyse at home Peritoneal dialysis and assisted form of PD glucose based solutions Transplantation Kidney pancreas tx or single organ tx 35
37 CKD and safety Antibiotic prescribing in CKD4 nitrofurantoin, aciclovir (shingles 400mgs stat followed by 200mgs BD) Severe hypoglycemia is 2.5 times more common in patients with proteinuria Non adherence linked with meds that have got to be taken more than twice a day and not related to number of medications Health supplements esp ginseng, fish oil. More so in the more educated and affluent population 36
38 The Elderly patient Creatinine is a function of muscle mass. Decreases in muscle mass might mask the association of reduced kidney function with decline in physical function. Fraility (slowness, weakness, energy, shrinking and physical activity) was twice as common in Cystatin diagnosed CKD3b, when serum creatinine was still normal 37
39 Which patients to refer to the joint clinic? Patients with egfr <30 or < 60 & progressively worsening renal function With persistent microalbuminuria, nephrotic syndrome, haemoproteinuria Those where egfr is falling despite control of proteinuria Those with anaemia or Ca<2.3 (and elevated PTH) or Phosphate>1.6 Raised K Uncontrolled hypertension/ fluid status 38
Guidelines to assist General Practitioners in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes. April 2010
 Guidelines to assist General Practitioners in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes April 2010 Foreword The guidelines were devised by the Diabetes Day Centre in Beaumont Hospital in consultation with a number
Guidelines to assist General Practitioners in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes April 2010 Foreword The guidelines were devised by the Diabetes Day Centre in Beaumont Hospital in consultation with a number
Dept of Diabetes Main Desk
 Dept of Diabetes Main Desk 01202 448060 Glucose management in Type 2 Diabetes in Adults The natural history of type 2 diabetes is for HbA1c to deteriorate with time. A stepwise approach to treatment is
Dept of Diabetes Main Desk 01202 448060 Glucose management in Type 2 Diabetes in Adults The natural history of type 2 diabetes is for HbA1c to deteriorate with time. A stepwise approach to treatment is
Dr A Pokrajac MD MSc MRCP Consultant
 Dr A Pokrajac MD MSc MRCP Consultant Onset at 5-15 years of T1DM Can be present at diagnosis of T2DM Detect in regular MA/Cr screening (2X first urine sample, no UTI, no other causes) Contributing Factors
Dr A Pokrajac MD MSc MRCP Consultant Onset at 5-15 years of T1DM Can be present at diagnosis of T2DM Detect in regular MA/Cr screening (2X first urine sample, no UTI, no other causes) Contributing Factors
Dr Tahseen A. Chowdhury Royal London Hospital. New Guidelines in Diabetes: NICE or Nasty?
 Dr Tahseen A. Chowdhury Royal London Hospital New Guidelines in Diabetes: NICE or Nasty? I have no conflicts of interest I do not undertake talks / advisory bodies / research for any pharma company Consultant
Dr Tahseen A. Chowdhury Royal London Hospital New Guidelines in Diabetes: NICE or Nasty? I have no conflicts of interest I do not undertake talks / advisory bodies / research for any pharma company Consultant
ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour
 ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour Dr Indranil Dasgupta Rationale No national practical
ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour Dr Indranil Dasgupta Rationale No national practical
Glucose Control drug treatments
 Glucose Control drug treatments It should be noted that glitazones are under suspicion of precipitating acute cardiac events and current recommendations contraindicate the use of glitazones in patients
Glucose Control drug treatments It should be noted that glitazones are under suspicion of precipitating acute cardiac events and current recommendations contraindicate the use of glitazones in patients
Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus
 Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 How to Screen for Diabetic Nephropathy... 4 What to Measure... 4 Frequency
Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 How to Screen for Diabetic Nephropathy... 4 What to Measure... 4 Frequency
Hot Topics in Diabetic Kidney Disease a primary care perspective
 Hot Topics in Diabetic Kidney Disease a primary care perspective DR SARAH DAVIES GP PARTNER WITH SPECIAL INTEREST IN DIABETES, CARDIFF DUK CLINICAL CHAMPION NB MEDICAL HOT TOPICS PRESENTER AND DIABETES
Hot Topics in Diabetic Kidney Disease a primary care perspective DR SARAH DAVIES GP PARTNER WITH SPECIAL INTEREST IN DIABETES, CARDIFF DUK CLINICAL CHAMPION NB MEDICAL HOT TOPICS PRESENTER AND DIABETES
YOU HAVE DIABETES. Angie O Connor Community Diabetes Nurse Specialist 25th September 2013
 YOU HAVE DIABETES Angie O Connor Community Diabetes Nurse Specialist 25th September 2013 Predicated 2015 figures are already met 1 in 20 have diabetes:1in8 over 60years old Definite Diagnosis is key Early
YOU HAVE DIABETES Angie O Connor Community Diabetes Nurse Specialist 25th September 2013 Predicated 2015 figures are already met 1 in 20 have diabetes:1in8 over 60years old Definite Diagnosis is key Early
Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
 Early Treatment is the Key Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stage Description GFR (ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) >90 1 Kidney damage with normal or GFR 2 Mild decrease in GFR 60-89 3 Moderate decrease in GFR
Early Treatment is the Key Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stage Description GFR (ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) >90 1 Kidney damage with normal or GFR 2 Mild decrease in GFR 60-89 3 Moderate decrease in GFR
Joslin Diabetes Center Joslin Diabetes Forum 2013: The Impact of Comorbidities on Glucose Control Scenario 2: Reduced Renal Function
 Scenario 2: Reduced Renal Function 62 y.o. white man with type 2 diabetes for 18 years Hypertension and hypercholesterolemia Known proliferative retinopathy Current medications: Metformin 1000 mg bid Glyburide
Scenario 2: Reduced Renal Function 62 y.o. white man with type 2 diabetes for 18 years Hypertension and hypercholesterolemia Known proliferative retinopathy Current medications: Metformin 1000 mg bid Glyburide
Type 2 Diabetes. Stopping Smoking. Consider referral to smoking cessation. Consider referring for weight management advice.
 Type 2 Diabetes Stopping Smoking Consider referral to smoking cessation BMI > 25 kg m² Set a weight loss target of a 5-10% reduction Consider referring for weight management advice Control BP to
Type 2 Diabetes Stopping Smoking Consider referral to smoking cessation BMI > 25 kg m² Set a weight loss target of a 5-10% reduction Consider referring for weight management advice Control BP to
Diabetic Kidney Disease in the Primary Care Clinic
 Diabetic Kidney Disease in the Primary Care Clinic Jess Wheeler, DO Nephrology 2015 Outline: 1. CKD/DKD is a growing problem 2. Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) 3. Diagnosis of Diabetic Kidney
Diabetic Kidney Disease in the Primary Care Clinic Jess Wheeler, DO Nephrology 2015 Outline: 1. CKD/DKD is a growing problem 2. Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) 3. Diagnosis of Diabetic Kidney
CKD FOR INTERNISTS. Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College
 CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
Diabetic Nephropathy. Objectives:
 There are, in truth, no specialties in medicine, since to know fully many of the most important diseases a man must be familiar with their manifestations in many organs. William Osler 1894. Objectives:
There are, in truth, no specialties in medicine, since to know fully many of the most important diseases a man must be familiar with their manifestations in many organs. William Osler 1894. Objectives:
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGNOSIS
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD Offer testing for CKD using egfr, serum creatinine and urinary ACR to people with any of the following risk factors: diabetes hypertension acute
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD Offer testing for CKD using egfr, serum creatinine and urinary ACR to people with any of the following risk factors: diabetes hypertension acute
Hypertension diagnosis (see detail document) Diabetic. Target less than 130/80mmHg
 Hypertension diagnosis (see detail document) Non-diabetic Diabetic Very elderly (older than 80 years) Target less than 140/90mmHg Target less than 130/80mmHg Consider SBP target less than 150mmHg Non-diabetic
Hypertension diagnosis (see detail document) Non-diabetic Diabetic Very elderly (older than 80 years) Target less than 140/90mmHg Target less than 130/80mmHg Consider SBP target less than 150mmHg Non-diabetic
Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease
 Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition of Metabolic Syndrome National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III Abdominal obesity, defined as a waist circumference
Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition of Metabolic Syndrome National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III Abdominal obesity, defined as a waist circumference
QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS
 KEY MESSAGES 1 SCREENING CRITERIA Screen: Patients with DM and/or hypertension at least yearly. Consider screening patients with: Age >65 years old Family history of stage 5 CKD or hereditary kidney disease
KEY MESSAGES 1 SCREENING CRITERIA Screen: Patients with DM and/or hypertension at least yearly. Consider screening patients with: Age >65 years old Family history of stage 5 CKD or hereditary kidney disease
Why is Earlier and More Aggressive Treatment of T2 Diabetes Better?
 Blood glucose (mmol/l) Why is Earlier and More Aggressive Treatment of T2 Diabetes Better? Disclosures Dr Kennedy has provided CME, been on advisory boards or received travel or conference support from:
Blood glucose (mmol/l) Why is Earlier and More Aggressive Treatment of T2 Diabetes Better? Disclosures Dr Kennedy has provided CME, been on advisory boards or received travel or conference support from:
Diabetes in Renal Patients. Contents. Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetes in Renal Patients Contents Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy What effect does CKD have on a patient s diabetic control? Diabetic Drugs in CKD and Dialysis Patients Hyper and Hypoglycaemia in
Diabetes in Renal Patients Contents Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy What effect does CKD have on a patient s diabetic control? Diabetic Drugs in CKD and Dialysis Patients Hyper and Hypoglycaemia in
ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
 ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Pr. Michel KOMAJDA Institute of Cardiology - IHU ICAN Pitie Salpetriere Hospital - University Pierre and Marie Curie, Paris (France) DEFINITION A
ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Pr. Michel KOMAJDA Institute of Cardiology - IHU ICAN Pitie Salpetriere Hospital - University Pierre and Marie Curie, Paris (France) DEFINITION A
Diabetic Nephropathy 2009
 Diabetic Nephropathy 2009 Michael T McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Michael.mcdermott@ucdenver.edu Diabetic Nephropathy Clinical Stages Hyperfunction
Diabetic Nephropathy 2009 Michael T McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Michael.mcdermott@ucdenver.edu Diabetic Nephropathy Clinical Stages Hyperfunction
Diabetes Mellitus: Implications of New Clinical Trials and New Medications
 Diabetes Mellitus: Implications of New Clinical Trials and New Medications Estimates of Diagnosed Diabetes in Adults, 2005 Alka M. Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine UCSF, Primary Care CME October
Diabetes Mellitus: Implications of New Clinical Trials and New Medications Estimates of Diagnosed Diabetes in Adults, 2005 Alka M. Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine UCSF, Primary Care CME October
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGNOSIS
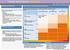 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS GFR categories, description and range WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD CLASSIFICATION OF CKD USING egfr AND ACR CATEGORIES Offer testing for CKD using egfr, creatinine and ACR
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS GFR categories, description and range WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD CLASSIFICATION OF CKD USING egfr AND ACR CATEGORIES Offer testing for CKD using egfr, creatinine and ACR
Oral Hypoglycemics and Risk of Adverse Cardiac Events: A Summary of the Controversy
 Oral Hypoglycemics and Risk of Adverse Cardiac Events: A Summary of the Controversy Jeffrey Boord, MD, MPH Advances in Cardiovascular Medicine Kingston, Jamaica December 7, 2012 VanderbiltHeart.com Outline
Oral Hypoglycemics and Risk of Adverse Cardiac Events: A Summary of the Controversy Jeffrey Boord, MD, MPH Advances in Cardiovascular Medicine Kingston, Jamaica December 7, 2012 VanderbiltHeart.com Outline
Management of early chronic kidney disease
 Management of early chronic kidney disease GREENLANE SUMMER GP SYMPOSIUM 2018 Jonathan Hsiao Renal and General Physician Introduction A growing public health problem in NZ and throughout the world. Unknown
Management of early chronic kidney disease GREENLANE SUMMER GP SYMPOSIUM 2018 Jonathan Hsiao Renal and General Physician Introduction A growing public health problem in NZ and throughout the world. Unknown
MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES
 MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES 3 Month trial of lifestyle changes. Refer to DESMOND structured education programme. Set glycaemic target HbA1c < 7.0% (53mmol/mol) or individualised If HbA1c > 53mmol/mol
MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES 3 Month trial of lifestyle changes. Refer to DESMOND structured education programme. Set glycaemic target HbA1c < 7.0% (53mmol/mol) or individualised If HbA1c > 53mmol/mol
Chronic Kidney Disease
 Chronic Kidney Disease Presence of kidney damage or decreased kidney function for three or more months, - necessary to distinguish CKD from acute kidney disease. Ascertained either by kidney biopsy or
Chronic Kidney Disease Presence of kidney damage or decreased kidney function for three or more months, - necessary to distinguish CKD from acute kidney disease. Ascertained either by kidney biopsy or
Management of Type 2 Diabetes
 Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
Diabetes and Hypertension
 Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Volume 2; Number 14 September 2008 NICE CLINICAL GUIDELINE 66: TYPE 2 DIABETES THE MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES (MAY 2008)
 Volume 2; Number 14 September 2008 NICE CLINICAL GUIDELINE 66: TYPE 2 DIABETES THE MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES (MAY 2008) The purpose of this special edition of the PACE Bulletin is to summarize the
Volume 2; Number 14 September 2008 NICE CLINICAL GUIDELINE 66: TYPE 2 DIABETES THE MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES (MAY 2008) The purpose of this special edition of the PACE Bulletin is to summarize the
1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease. albuminuria
 1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease albuminuria Cardio-renal continuum REGRESS Target organ damage Asymptomatic CKD New risk factors Atherosclerosis Target organ damage
1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease albuminuria Cardio-renal continuum REGRESS Target organ damage Asymptomatic CKD New risk factors Atherosclerosis Target organ damage
Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: Reducing Risk for CKD Progression
 Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: Reducing Risk for CKD Progression Arasu Gopinath, MD Clinical Nephrologist, Medical Director, Jordan Landing Dialysis Center Objectives: Identify the most important risks
Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: Reducing Risk for CKD Progression Arasu Gopinath, MD Clinical Nephrologist, Medical Director, Jordan Landing Dialysis Center Objectives: Identify the most important risks
Should Psychiatrists be diagnosing (and treating) metabolic syndrome
 Should Psychiatrists be diagnosing (and treating) metabolic syndrome David Hopkins Clinical Director, Diabetes King s College Hospital, London Diabetes prevalence (thousands) Diabetes in the UK: 1995-2010
Should Psychiatrists be diagnosing (and treating) metabolic syndrome David Hopkins Clinical Director, Diabetes King s College Hospital, London Diabetes prevalence (thousands) Diabetes in the UK: 1995-2010
The Flozins Quest for Clarity?
 The Flozins Quest for Clarity? Choosing Wisely with Academic Detailing 2018 ARE THEY THE REAL DEAL Disclosure statements The Academic Detailing Service is operated by Dalhousie Continuing Professional
The Flozins Quest for Clarity? Choosing Wisely with Academic Detailing 2018 ARE THEY THE REAL DEAL Disclosure statements The Academic Detailing Service is operated by Dalhousie Continuing Professional
egfr > 50 (n = 13,916)
 Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and egfr: Decision and Dilemma. Dr Bhavna K Pandya Consultant Nephrologist University Hospital Aintree
 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and egfr: Decision and Dilemma Dr Bhavna K Pandya Consultant Nephrologist University Hospital Aintree Topics CKD background egfr background Patient with egfr Referral Guidelines
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and egfr: Decision and Dilemma Dr Bhavna K Pandya Consultant Nephrologist University Hospital Aintree Topics CKD background egfr background Patient with egfr Referral Guidelines
Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy
 Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy Elisabeth R. Mathiesen Professor, Chief Physician, Dr sci Dep. Of Endocrinology Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen Denmark Hypertension Brain Eye Heart Kidney
Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy Elisabeth R. Mathiesen Professor, Chief Physician, Dr sci Dep. Of Endocrinology Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen Denmark Hypertension Brain Eye Heart Kidney
Diabetes and Kidney Disease. Kris Bentley Renal Nurse practitioner 2018
 Diabetes and Kidney Disease Kris Bentley Renal Nurse practitioner 2018 Aims Develop an understanding of Chronic Kidney Disease Understand how diabetes impacts on your kidneys Be able to recognise the risk
Diabetes and Kidney Disease Kris Bentley Renal Nurse practitioner 2018 Aims Develop an understanding of Chronic Kidney Disease Understand how diabetes impacts on your kidneys Be able to recognise the risk
Diabetes in the UK: Update on Diabetes Treatment and Care. Why is diabetes increasing? Obesity Increased waist circumference.
 Update on Diabetes Treatment and Care Tahseen A Chowdhury Consultant Diabetologist Royal London and Mile End Hospitals Diabetes prevalence (thousands) Diabetes in the UK: 1995-21 3 25 2 15 1 5 Type 1 Type
Update on Diabetes Treatment and Care Tahseen A Chowdhury Consultant Diabetologist Royal London and Mile End Hospitals Diabetes prevalence (thousands) Diabetes in the UK: 1995-21 3 25 2 15 1 5 Type 1 Type
Renal Protection Staying on Target
 Update Staying on Target James Barton, MD, FRCPC As presented at the University of Saskatchewan's Management of Diabetes & Its Complications (May 2004) Gwen s case Gwen, 49, asks you to take on her primary
Update Staying on Target James Barton, MD, FRCPC As presented at the University of Saskatchewan's Management of Diabetes & Its Complications (May 2004) Gwen s case Gwen, 49, asks you to take on her primary
Disclosures. Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management. Learning Objectives. Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
 Disclosures Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Tony Hampton, MD, MBA Medical Director Advocate Aurora Operating System Advocate Aurora Healthcare Downers Grove, IL No conflicts or disclosures
Disclosures Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Tony Hampton, MD, MBA Medical Director Advocate Aurora Operating System Advocate Aurora Healthcare Downers Grove, IL No conflicts or disclosures
Management of Type 2 Diabetes. Why Do We Bother to Achieve Good Control in DM2. Insulin Secretion. The Importance of BP and Glucose Control
 Insulin Secretion Management of Type 2 Diabetes DG van Zyl Why Do We Bother to Achieve Good Control in DM2 % reduction 0-5 -10-15 -20-25 -30-35 -40 The Importance of BP and Glucose Control Effects of tight
Insulin Secretion Management of Type 2 Diabetes DG van Zyl Why Do We Bother to Achieve Good Control in DM2 % reduction 0-5 -10-15 -20-25 -30-35 -40 The Importance of BP and Glucose Control Effects of tight
Adult Diabetes Clinician Guide NOVEMBER 2017
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Diabetes Clinician Guide Introduction NOVEMBER 2017 This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2017 KP National Diabetes Guideline.
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Diabetes Clinician Guide Introduction NOVEMBER 2017 This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2017 KP National Diabetes Guideline.
Newer Drugs in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 Newer Drugs in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Dr. C. Dinesh M. Naidu Professor of Pharmacology, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences, Narketpally. 1 Presentation Outline Introduction Pathogenesis
Newer Drugs in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Dr. C. Dinesh M. Naidu Professor of Pharmacology, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences, Narketpally. 1 Presentation Outline Introduction Pathogenesis
TREATMENTS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES. Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse
 TREATMENTS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse How can we improve outcomes in Type 2 diabetes? Earlier diagnosis Better patient education Stress central role of lifestyle management
TREATMENTS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse How can we improve outcomes in Type 2 diabetes? Earlier diagnosis Better patient education Stress central role of lifestyle management
Managing Patients with CKD in Primary Care: A Shared Care Pathway. 5 th April 2018
 Managing Patients with CKD in Primary Care: A Shared Care Pathway 5 th April 2018 Learning Objectives 1) What health risks does CKD represent? 2) Why change how we manage CKD in NWL? 1) How do we improve
Managing Patients with CKD in Primary Care: A Shared Care Pathway 5 th April 2018 Learning Objectives 1) What health risks does CKD represent? 2) Why change how we manage CKD in NWL? 1) How do we improve
GLP-1 agonists. Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK
 GLP-1 agonists Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK What do GLP-1 agonists do? Physiology of postprandial glucose regulation Meal ❶ ❷ Insulin Rising plasma
GLP-1 agonists Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK What do GLP-1 agonists do? Physiology of postprandial glucose regulation Meal ❶ ❷ Insulin Rising plasma
CANVAS Program Independent commentary
 CANVAS Program Independent commentary Cliff Bailey Aston University, Birmingham, UK 2017 Disclosures and disclaimers Clifford J Bailey CJB has attended advisory boards, undertaken ad hoc consultancy, received
CANVAS Program Independent commentary Cliff Bailey Aston University, Birmingham, UK 2017 Disclosures and disclaimers Clifford J Bailey CJB has attended advisory boards, undertaken ad hoc consultancy, received
01/09/2017. Outline. SGLT 2 inhibitor? Diabetes Patients: Complex and Heterogeneous. Association between diabetes and cardiovascular events
 MICROVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS Incidence of outcome g 1 Cardioprotective Effects of SGLT2s Relevant for Which T2 Diabetes Patient? SGLT 2 inhibitor? 58 year old, waist circumference 5 cm, PMH: IHD On statin,
MICROVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS Incidence of outcome g 1 Cardioprotective Effects of SGLT2s Relevant for Which T2 Diabetes Patient? SGLT 2 inhibitor? 58 year old, waist circumference 5 cm, PMH: IHD On statin,
Abbreviations DPP-IV dipeptidyl peptidase IV DREAM Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone
 Index Abbreviations DPP-IV dipeptidyl peptidase IV DREAM Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication GAD glutamic acid decarboxylase GLP-1 glucagon-like peptide 1 NPH neutral
Index Abbreviations DPP-IV dipeptidyl peptidase IV DREAM Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication GAD glutamic acid decarboxylase GLP-1 glucagon-like peptide 1 NPH neutral
Metformin should be considered in all patients with type 2 diabetes unless contra-indicated
 November 2001 N P S National Prescribing Service Limited PPR fifteen Prescribing Practice Review PPR Managing type 2 diabetes For General Practice Key messages Metformin should be considered in all patients
November 2001 N P S National Prescribing Service Limited PPR fifteen Prescribing Practice Review PPR Managing type 2 diabetes For General Practice Key messages Metformin should be considered in all patients
Diabetes Complications Guideline Based Screening, Management, and Referral
 Diabetes Complications Guideline Based Screening, Management, and Referral Eric L. Johnson, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Family and Community Medicine Assistant Medical Director Altru Diabetes
Diabetes Complications Guideline Based Screening, Management, and Referral Eric L. Johnson, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Family and Community Medicine Assistant Medical Director Altru Diabetes
Professor Rudy Bilous James Cook University Hospital
 Professor Rudy Bilous James Cook University Hospital Rate per 100 patient years Rate per 100 patient years 16 Risk of retinopathy progression 16 Risk of developing microalbuminuria 12 12 8 8 4 0 0 5 6
Professor Rudy Bilous James Cook University Hospital Rate per 100 patient years Rate per 100 patient years 16 Risk of retinopathy progression 16 Risk of developing microalbuminuria 12 12 8 8 4 0 0 5 6
Management of Hypertension. M Misra MD MRCP (UK) Division of Nephrology University of Missouri School of Medicine
 Management of Hypertension M Misra MD MRCP (UK) Division of Nephrology University of Missouri School of Medicine Disturbing Trends in Hypertension HTN awareness, treatment and control rates are decreasing
Management of Hypertension M Misra MD MRCP (UK) Division of Nephrology University of Missouri School of Medicine Disturbing Trends in Hypertension HTN awareness, treatment and control rates are decreasing
Diabetes Guidelines in View of Recent Clinical Trials Are They Still Applicable?
 Diabetes Guidelines in View of Recent Clinical Trials Are They Still Applicable? Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of
Diabetes Guidelines in View of Recent Clinical Trials Are They Still Applicable? Jay S. Skyler, MD, MACP Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism and Diabetes Research Institute University of
Diabetes Oral Agents Pharmacology. University of Hawai i Hilo Pre-Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D
 Diabetes Oral Agents Pharmacology University of Hawai i Hilo Pre-Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 Learning Objectives Understand the role of the utilization of free
Diabetes Oral Agents Pharmacology University of Hawai i Hilo Pre-Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 Learning Objectives Understand the role of the utilization of free
Office Management of Reduced GFR Practical advice for the management of CKD
 Office Management of Reduced GFR Practical advice for the management of CKD CKD Online Education CME for Primary Care April 27, 2016 Monica Beaulieu, MD FRCPC MHA CHAIR PROVINCIAL KIDNEY CARE COMMITTEE
Office Management of Reduced GFR Practical advice for the management of CKD CKD Online Education CME for Primary Care April 27, 2016 Monica Beaulieu, MD FRCPC MHA CHAIR PROVINCIAL KIDNEY CARE COMMITTEE
American Diabetes Association 2018 Guidelines Important Notable Points
 American Diabetes Association 2018 Guidelines Important Notable Points The Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018 by ADA include the most current evidencebased recommendations for diagnosing and treating
American Diabetes Association 2018 Guidelines Important Notable Points The Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018 by ADA include the most current evidencebased recommendations for diagnosing and treating
Tread Carefully Because you Tread on my Nephrons. Prescribing Hints in Renal Disease
 Tread Carefully Because you Tread on my Nephrons Prescribing Hints in Renal Disease David WP Lappin,, MB PhD FRCPI Clinical Lecturer in Medicine and Consultant Nephrologist and General Physician, Merlin
Tread Carefully Because you Tread on my Nephrons Prescribing Hints in Renal Disease David WP Lappin,, MB PhD FRCPI Clinical Lecturer in Medicine and Consultant Nephrologist and General Physician, Merlin
Medical therapy advances London/Manchester RCP February/June 2016
 Medical therapy advances London/Manchester RCP February/June 2016 Advances in medical therapies for diabetes mellitus Duality of interest: The speaker or institutions with which he is associated has received
Medical therapy advances London/Manchester RCP February/June 2016 Advances in medical therapies for diabetes mellitus Duality of interest: The speaker or institutions with which he is associated has received
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Proposed Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Dapagliflozin in combination therapy for the Final scope Remit/appraisal objective To appraise the clinical and
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Dapagliflozin in combination therapy for the Final scope Remit/appraisal objective To appraise the clinical and
NEW DIABETES CARE MEDICATIONS
 NEW DIABETES CARE MEDICATIONS James Bonucchi DO, ECNU, FACE Adult Medicine and Endocrinology Specialists Disclosures Speakers bureau Sanofi AZ BI Diabetes Diabetes cost ADA 2017 data Ever increasing disorder.
NEW DIABETES CARE MEDICATIONS James Bonucchi DO, ECNU, FACE Adult Medicine and Endocrinology Specialists Disclosures Speakers bureau Sanofi AZ BI Diabetes Diabetes cost ADA 2017 data Ever increasing disorder.
RENAAL, IRMA-2 and IDNT. Three featured trials linking a disease spectrum IDNT RENAAL. Death IRMA 2
 Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy and Proteinuria Background End stage renal disease is a major cause of death and disability among diabetics BP reduction is important to slow the progression of diabetic
Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy and Proteinuria Background End stage renal disease is a major cause of death and disability among diabetics BP reduction is important to slow the progression of diabetic
STEP 3: Add or Substitute with one of
 Prescribing of Hypoglycaemic Agents for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Sunderland Refer to DESMOND Structured Education classes to promote Increased Physical Activity, Weight Loss and Calories Reduction
Prescribing of Hypoglycaemic Agents for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Sunderland Refer to DESMOND Structured Education classes to promote Increased Physical Activity, Weight Loss and Calories Reduction
hypertension Head of prevention and control of CVD disease office Ministry of heath
 hypertension t. Samavat MD,Cadiologist,MPH Head of prevention and control of CVD disease office Ministry of heath RECOMMENDATIONS FOR HYPERTENSION DIAGNOSIS, ASSESSMENT, AND TREATMENT Definition of hypertension
hypertension t. Samavat MD,Cadiologist,MPH Head of prevention and control of CVD disease office Ministry of heath RECOMMENDATIONS FOR HYPERTENSION DIAGNOSIS, ASSESSMENT, AND TREATMENT Definition of hypertension
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australians with Renal Impairment. Specific effects of calcium channel blockers in diabetic nephropathy GUIDELINES
 Specific effects of calcium channel blockers in diabetic nephropathy Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES a. Non-dihydropyridine calcium channel
Specific effects of calcium channel blockers in diabetic nephropathy Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES a. Non-dihydropyridine calcium channel
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE. Single Technology Appraisal. Canagliflozin in combination therapy for treating type 2 diabetes
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Single Technology Appraisal Canagliflozin in combination therapy for Final scope Remit/appraisal objective To appraise the clinical and cost effectiveness
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Single Technology Appraisal Canagliflozin in combination therapy for Final scope Remit/appraisal objective To appraise the clinical and cost effectiveness
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) / Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) To STOP OR Not in Advanced Renal Disease
 Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) / Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) To STOP OR Not in Advanced Renal Disease Investigator Meeting 12 th September 2017 - Sheffield Prof Sunil Bhandari Consultant
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) / Angiotensin Receptor Blocker (ARB) To STOP OR Not in Advanced Renal Disease Investigator Meeting 12 th September 2017 - Sheffield Prof Sunil Bhandari Consultant
Alia Gilani Health Inequalities Pharmacist
 Alia Gilani Health Inequalities Pharmacist THE SOUTH ASIAN HEALTH FOUNDATION (U.K.) (Registered Charity No. 1073178) 1. Case Study 2. Factors influencing prescribing 3. Special Considerations 4. Prescribing
Alia Gilani Health Inequalities Pharmacist THE SOUTH ASIAN HEALTH FOUNDATION (U.K.) (Registered Charity No. 1073178) 1. Case Study 2. Factors influencing prescribing 3. Special Considerations 4. Prescribing
Chronic Kidney Disease Management for Primary Care Physicians. Dr. Allen Liu Consultant Nephrologist KTPH 21 November 2015
 Chronic Kidney Disease Management for Primary Care Physicians Dr. Allen Liu Consultant Nephrologist KTPH 21 November 2015 Singapore Renal Registry 2012 Incidence of Patients on Dialysis by Mode of Dialysis
Chronic Kidney Disease Management for Primary Care Physicians Dr. Allen Liu Consultant Nephrologist KTPH 21 November 2015 Singapore Renal Registry 2012 Incidence of Patients on Dialysis by Mode of Dialysis
Drugs used in Diabetes. Dr Andrew Smith
 Drugs used in Diabetes Dr Andrew Smith Plan Introduction Insulin Sensitising Drugs: Metformin Glitazones Insulin Secretagogues: Sulphonylureas Meglitinides Others: Acarbose Incretins Amylin Analogues Damaglifozin
Drugs used in Diabetes Dr Andrew Smith Plan Introduction Insulin Sensitising Drugs: Metformin Glitazones Insulin Secretagogues: Sulphonylureas Meglitinides Others: Acarbose Incretins Amylin Analogues Damaglifozin
Oral Treatments for Type 2 Diabetes. Prescribing Support Pharmacist
 Oral Treatments for Type 2 Diabetes Prescribing Support Pharmacist Learning Outcomes Familiar with classes of oral hypoglycaemic agents (OHAs) used in controlling blood glucose levels When to use each
Oral Treatments for Type 2 Diabetes Prescribing Support Pharmacist Learning Outcomes Familiar with classes of oral hypoglycaemic agents (OHAs) used in controlling blood glucose levels When to use each
in patients with diabetes, nephropathy and/or chronic kidney disease Summary of recommendations July 2017
 Association of British Clinical Diabetologists (ABCD) and Renal Association clinical guidelines: Hypertension management and reninangiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in patients with diabetes, nephropathy
Association of British Clinical Diabetologists (ABCD) and Renal Association clinical guidelines: Hypertension management and reninangiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in patients with diabetes, nephropathy
CKD & HT. Anne-Marie Angus
 CKD & HT Anne-Marie Angus Hypertension definitions Persisting BP >140/90 and HBPM >135/85 Stage 1 >140/90 (HBPM >135/85) Stage 2 >160/100 (HBPM >150/90) Severe >180/100 White coat HT Why treat? A major
CKD & HT Anne-Marie Angus Hypertension definitions Persisting BP >140/90 and HBPM >135/85 Stage 1 >140/90 (HBPM >135/85) Stage 2 >160/100 (HBPM >150/90) Severe >180/100 White coat HT Why treat? A major
Objectives. Kidney Complications With Diabetes. Case 10/21/2015
 Objectives Kidney Complications With Diabetes Brian Boerner, MD Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism University of Nebraska Medical Center Review screening for, and management of, albuminuria Review
Objectives Kidney Complications With Diabetes Brian Boerner, MD Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism University of Nebraska Medical Center Review screening for, and management of, albuminuria Review
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERENCE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERECE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease CKD VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERECE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease CKD VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management
The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities
 The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities Question #1 Which of the following is a risk factor for increased hypoglycemia in older patients that may suggest the need to relax hyperglycemia treatment
The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities Question #1 Which of the following is a risk factor for increased hypoglycemia in older patients that may suggest the need to relax hyperglycemia treatment
Practical Diabetes. Nic Crook. (and don t use so many charts) Kuirau Specialists 1239 Ranolf Street Rotorua. Rotorua Hospital Private Bag 3023 Rotorua
 Practical Diabetes (and don t use so many charts) Nic Crook Rotorua Hospital Private Bag 3023 Rotorua Kuirau Specialists 1239 Ranolf Street Rotorua Worldwide rates of diabetes mellitus: predictions 80
Practical Diabetes (and don t use so many charts) Nic Crook Rotorua Hospital Private Bag 3023 Rotorua Kuirau Specialists 1239 Ranolf Street Rotorua Worldwide rates of diabetes mellitus: predictions 80
Applying clinical guidelines treating and managing CKD
 Applying clinical guidelines treating and managing CKD Develop patient treatment plan according to level of severity. Source: Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012
Applying clinical guidelines treating and managing CKD Develop patient treatment plan according to level of severity. Source: Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012
Mr Rab Burtun. Dr David Kim. 8:30-10:30 WS #2: Diabetes Basic 11:00-13:00 WS #9: Diabetes Basic (Repeated)
 Dr David Kim Endocrinologist and General Physician Waitemata DHB and Apollo Specialist Clinic Albany Auckland Mr Rab Burtun Diabetes Nurse Specialist Waitemata DHB Waitakere Hospital Auckland 8:30-10:30
Dr David Kim Endocrinologist and General Physician Waitemata DHB and Apollo Specialist Clinic Albany Auckland Mr Rab Burtun Diabetes Nurse Specialist Waitemata DHB Waitakere Hospital Auckland 8:30-10:30
Aggressive blood pressure reduction and renin angiotensin system blockade in chronic kidney disease: time for re-evaluation?
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2013 International Society of Nephrology Aggressive blood pressure reduction and renin angiotensin system blockade in chronic kidney disease: time for re-evaluation?
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2013 International Society of Nephrology Aggressive blood pressure reduction and renin angiotensin system blockade in chronic kidney disease: time for re-evaluation?
VICTOSA and Renal impairment DR.R.S.SAJAD
 VICTOSA and Renal impairment DR.R.S.SAJAD February 2019 Main effect of GLP-1 is : Stimulating glucose dependent insulin release from the pancreatic islets. Slow gastric emptying Inhibit inappropriate
VICTOSA and Renal impairment DR.R.S.SAJAD February 2019 Main effect of GLP-1 is : Stimulating glucose dependent insulin release from the pancreatic islets. Slow gastric emptying Inhibit inappropriate
Cardiovascular Management of a Patient with Diabetes
 Cardiovascular Management of a Patient with Diabetes Dr Jeremy Krebs Clinical Leader Endocrinology and Diabetes Wellington Hospital Summary People with diabetes take a lot of medication Compliance and
Cardiovascular Management of a Patient with Diabetes Dr Jeremy Krebs Clinical Leader Endocrinology and Diabetes Wellington Hospital Summary People with diabetes take a lot of medication Compliance and
Kidney Disease. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) requiring dialysis. The F.P. s Role in the Management of Chronic. Stages
 Focus on CME at McMaster University The F.P. s Role in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease By David N. Churchill, MD, FRCPC, FACP Presented at McMaster University CME Half-Day in Nephrology for Family
Focus on CME at McMaster University The F.P. s Role in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease By David N. Churchill, MD, FRCPC, FACP Presented at McMaster University CME Half-Day in Nephrology for Family
CKD and risk management : NICE guideline
 CKD and risk management : NICE guideline 2008-2014 Shahed Ahmed Consultant Nephrologist shahed.ahmed@rlbuht.nhs.uk Key points : Changing parameters of CKD and NICE guidance CKD and age related change of
CKD and risk management : NICE guideline 2008-2014 Shahed Ahmed Consultant Nephrologist shahed.ahmed@rlbuht.nhs.uk Key points : Changing parameters of CKD and NICE guidance CKD and age related change of
The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009
 The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009 Teresa Northcutt, RN BSN Primaris Program Manager, Prevention - CKD MO-09-01-CKD This material was prepared by Primaris,
The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009 Teresa Northcutt, RN BSN Primaris Program Manager, Prevention - CKD MO-09-01-CKD This material was prepared by Primaris,
Diabetic Kidney Disease: Update. GKA Master Class. Istanbul 2011
 Diabetic Kidney Disease: Update GKA Master Class Istanbul 2011 DKD: Challenging dogmas Old Dogmas Type 1 and Type 2 DN have the same natural history Microalbuminuria is an early stage of DN Tight Glycemia
Diabetic Kidney Disease: Update GKA Master Class Istanbul 2011 DKD: Challenging dogmas Old Dogmas Type 1 and Type 2 DN have the same natural history Microalbuminuria is an early stage of DN Tight Glycemia
Vascular complications
 Vascular complications December 8, 2018 Faculty Disclosure Faculty: Kim Connelly, MBBS, PhD, FRACP Associate Professor of Medicine, University of Toronto Cardiologist, St. Michael s Hospital Relationships
Vascular complications December 8, 2018 Faculty Disclosure Faculty: Kim Connelly, MBBS, PhD, FRACP Associate Professor of Medicine, University of Toronto Cardiologist, St. Michael s Hospital Relationships
Oral and Injectable Non-insulin Antihyperglycemic Agents
 Appendix 5: Diabetes Education and Medical Management in Adults with Diabetes Oral and Injectable Non-insulin s This directive will be implemented by RPhs, RNs or RDs who have been deemed authorized implementers.
Appendix 5: Diabetes Education and Medical Management in Adults with Diabetes Oral and Injectable Non-insulin s This directive will be implemented by RPhs, RNs or RDs who have been deemed authorized implementers.
Interventions to reduce progression of CKD what is the evidence? John Feehally
 Interventions to reduce progression of CKD what is the evidence? John Feehally Interventions to reduce progression of CKD what is the evidence? CHALLENGES Understanding what we know. NOT.what we think
Interventions to reduce progression of CKD what is the evidence? John Feehally Interventions to reduce progression of CKD what is the evidence? CHALLENGES Understanding what we know. NOT.what we think
Diabetes Mellitus case studies. Jana Vinklerová
 Diabetes Mellitus case studies Jana Vinklerová Definition of diabetes (metabolic disorder) Chronically raised blood glucose (hyperglycaemia) Insulin/Glucagon Insulin is responsible for lowering glucose
Diabetes Mellitus case studies Jana Vinklerová Definition of diabetes (metabolic disorder) Chronically raised blood glucose (hyperglycaemia) Insulin/Glucagon Insulin is responsible for lowering glucose
Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim
 Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim Chosun University Hospital Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Committee of Scientific Affairs Insulin therapy is the mainstay
Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim Chosun University Hospital Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Committee of Scientific Affairs Insulin therapy is the mainstay
Chronic Kidney Disease. Paul Cockwell Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham
 Chronic Kidney Disease Paul Cockwell Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham Paradigms for chronic disease 1. Acute and chronic disease is closely linked 2. Stratify risk and tailor interventions around failure
Chronic Kidney Disease Paul Cockwell Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham Paradigms for chronic disease 1. Acute and chronic disease is closely linked 2. Stratify risk and tailor interventions around failure
Overview T2DM medications. Winnie Ho
 Overview T2DM medications Winnie Ho Diabetes in Australia 1.7 million Australians with diabetes, of these 85% have T2DM 2-fold excess risk CV death in patients with diabetes Risk factor for progression
Overview T2DM medications Winnie Ho Diabetes in Australia 1.7 million Australians with diabetes, of these 85% have T2DM 2-fold excess risk CV death in patients with diabetes Risk factor for progression
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and SGLT-2 Inhibitors. Debbie Hicks
 GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and SGLT-2 Inhibitors Debbie Hicks Prescribing and Adverse Event reporting information is available at this meeting from the AstraZeneca representative The views expressed by the
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and SGLT-2 Inhibitors Debbie Hicks Prescribing and Adverse Event reporting information is available at this meeting from the AstraZeneca representative The views expressed by the
Newer and Expensive treatment of diabetes. Endocrinology Visiting Associate Professor Institute of Medicine TUTH
 Newer and Expensive treatment of diabetes Jyoti Bhattarai MD Endocrinology Visiting Associate Professor Institute of Medicine TUTH Four out of every five people with diabetes now live in developing countries.
Newer and Expensive treatment of diabetes Jyoti Bhattarai MD Endocrinology Visiting Associate Professor Institute of Medicine TUTH Four out of every five people with diabetes now live in developing countries.
PLEASE CHECK FULL SPECIFIC PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS FOR MORE DETAILED AND CURRENT INFORMATION:
 Metformin Standard tablets Modified-release tablets Metformin 1g sachets Metformin liquid 500mg/5ml (avoid use as expensive) < 2.00 5.32 for 56 tabs 500mg 13.16 for 60 sachets > 120 Ketoacidosis General
Metformin Standard tablets Modified-release tablets Metformin 1g sachets Metformin liquid 500mg/5ml (avoid use as expensive) < 2.00 5.32 for 56 tabs 500mg 13.16 for 60 sachets > 120 Ketoacidosis General
Diabetic & Complications. Dr. A K Viswanath Consultant Diabetologist
 Diabetic & Complications Dr. A K Viswanath Consultant Diabetologist Outline Challenges in diabetes How do we fare? Diabetes complications Improving outcomes in diabetes Types of Diabetes Type-1 DM Genetic
Diabetic & Complications Dr. A K Viswanath Consultant Diabetologist Outline Challenges in diabetes How do we fare? Diabetes complications Improving outcomes in diabetes Types of Diabetes Type-1 DM Genetic
