Guidelines to assist General Practitioners in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes. April 2010
|
|
|
- Cassandra Green
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Guidelines to assist General Practitioners in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes April 2010
2 Foreword The guidelines were devised by the Diabetes Day Centre in Beaumont Hospital in consultation with a number of primary care practices in the North Dublin area. The guidelines have a number of objectives: To improve delivery and quality of care for patients with Type 2 diabetes attending both their primary care physician and the specialist diabetes team in Beaumont Hospital. To develop integration of care between primary care and the diabetes service in Beaumont Hospital for patients with Type 2 diabetes. As an educational resource for both primary care and Beaumont Hospital. It is hoped that these guidelines are the start of a process to improve communication and consultation between the hospital and primary care and that further initiatives will follow which will continue to develop integrated care for patients with Type 2 diabetes. Yours Sincerely Dr Diarmuid Smith Professor Chris Thompson Dr Amar Agha Helen Twamley Consultant Endocrinologist Consultant Endocrinologist Consultant Endocrinologist CNM 2 Diabetes Centre
3 Criteria for 2 Yearly Review Type 2 Diabetes HBA1c < 7.0% (< 53 mmol/mol) either on diet or oral hypoglycaemic agents No history of severe hypoglycaemia Normal 12-lead ECG No micro-vascular complications No renal failure (Creatinine >135umol/L) No retinopathy No history of foot ulcer / Charcot foot / peripheral neuritis or severe peripheral arterial disease (PAD)
4 Criteria for Annual Review Type 2 Diabetes HBA1c > 7.0% (>53 mmol/mol) either on diet or oral hypoglycaemic agents or GLP-1 injections History of severe hypoglycaemia Abnormal 12-lead ECG Documented micro-vascular complications Renal failure (Creatinine >135umol/L) Microalbuminuria Retinopathy History of foot ulcer / Charcot foot / peripheral neuritis or severe PAD Patients with Type 2 diabetes on insulin may need to be seen every 6 months in the clinic
5 Aim of the Guidelines Increase integration of care and improve communication between Beaumont Hospital diabetes service and primary care. Educational resource. Assist primary care in Management of type 2 diabetes between annual or 2-yearly hospital clinic visits
6 From July 2010, a new type of measurement is being introduced for measuring HbA1c. This will mean the HbA1c will be recorded in mmol/mol instead of %. A guide to the new values expressed as mmol/mol
7 Target HbA1c On Hypoglycaemic Agents 6.5% (48 mmol/mol) 7.0% (53 mmol/mol) with no severe hypoglycaemia On Insulin therapy < 7.0% (<53 mmol/mol) with no severe hypoglycaemia This is a guide only, as patients individual circumstances need to be taken into consideration, elderly, living alone, dementia, co-existing morbidities
8 Frequency of HbA1c testing Test HbA1c 3 months after change in dose or addition of new hypoglycaemic agent If patient is stable and HBA1c is in target then test every 6 months Do not test more than 3 monthly
9 Type 2 DM BMI ( kg/m²) Asymptomatic new T2 patient, no weight loss, no ketones Commence on Metformin 500mg bd Titrate Metformin to maximum dose (1g bd) if HbA1c > 7.0 % (> 53 mmol/mol) Add in Sulphonylurea once daily if HbA1c remains > 7.0 % (> 53 mmol/mol) (Titrate dose to maximum dose, to achieve target) For example: start Gliclazide MR 30mg once daily max dose is 120mg once daily If HbA1c remains > 7.0 % (>53 mmol/mol) Contact Diabetes Centre
10 Type 2 DM BMI ( kg/m²) Symptomatic, weight loss, ketones may be present Commence on Sulphonylurea once daily. Titrate dose of Sulphonylurea to maximum dose if blood glucose remains elevated Refer to Diabetes Day Centre HbA1c > 7.0% (> 53 mmol/mol) - Further weight loss or ketones present suggests need for insulin therapy - Refer to Diabetes Day Centre urgently. HbA1c > 7.0% (> 53 mmol/mol) - Weight stable, no ketones - Commence Metformin and titrate to maximum dose. Contact Diabetes Day Centre if HbA1c remains > 7.0 %(> 53 mmol/mol) on maximum oral agents - will need to commence insulin therapy
11 Overweight T2 DM BMI > kg/m² Commence on Metformin 500mg bd Increase Metformin to to maximum dose (1g bd) if HbA1c > 7.0% (>53 mmol/mol) If HbA1c remains > 7.0 % (> 53 mmol/mol) will need a second glucose lowering agent Option 1 Sulphonylurea Option 2 DPP- 4 Inhibitor The TZD Pioglitazone could also be used in this setting Liaise with Diabetes Centre or Community Diabetes Nurse for advice
12 Overweight T2DM BMI > kg/m² Treatment Option 1 in combination with Metformin Add Sulphonylurea Titrate dose of Sulphonylurea to maximum dose if HbA1c remains > 7.0% (> 53 mmol/mol) Assess patient for signs and symptoms of hypoglycaemia Failure to achieve target Hba1c with Metformin in combination with Sulphonylurea Contact Diabetes Centre
13 Overweight T2DM BMI > kg/m² Treatment Option 2 in combination with Metformin DPP-4 Inhibitor Janumet (1gm/50mg bd Metformin + Sitagliptin) or Eucreas (1gm/50mg bd Metformin + Vildagliptin) or Onglyza (Saxagliptin 5mg once daily) Failure to achieve target Hba1c with Metformin in combination with DPP 4 Inhibitor Add in Sulphonylurea Titrate dose of Sulphonylurea to maximum dose if HbA1c remains > 7.0 % (> 53 mmol/mol) Failure to achieve target Hba1c with Metformin + DPP-4 Inhibitor in combination with Sulphonylurea Contact Diabetes Centre
14 Obese T2DM BMI > 30 35kg/m² Commence on Metformin 500mg bd Increase Metformin to maximum dose (1g bd) if HbA1c > 7.0 % (> 53 mmol/mol) If HbA1c remains > 7.0 % (> 53 mmol/mol) will need a second glucose lowering agent Option 1 Sulphonylurea Option 2 DPP-4 Inhibitor Option 3 GLP-1 injection The TZD Pioglitazone could also be used in this setting
15 Obese T2DM BMI > 30-35kg/m² Treatment Option 1 in combination with Metformin Add Sulphonylurea Titrate dose of Sulphonylurea to maximum dose if HbA1c > 7.0 % (> 53mmol/mol) Assess patient for signs and symptoms of hypoglycaemia Failure to achieve target Hba1c with Metformin in combination with Sulphonylurea Contact Diabetes Centre or Community Diabetes Nurse for advice
16 Obese T2DM BMI > kg/m² Treatment Option 2 in combination with Metformin DPP-4 Inhibitor Janumet (1gm/50mg bd Metformin + Sitagliptin) or Eucreas (1gm/50mg bd Metformin + Vildagliptin) or Onglyza (Saxagliptin 5mg once daily) Failure to achieve target Hba1c with Metformin in combination with DPP-4 - Add in Sulphonylurea (continue DPP-4) or GLP 1 injection (stop DPP 4). Contact Diabetes Centre or Community Diabetes Nurse for advice
17 Obese T2DM BMI > kg/m² Treatment Option 3 in combination with Metformin GLP 1 Injection Exenatide BD Injection or Liraglutide OD Injection Failure to achieve target Hba1c with Metformin in combination with GLP-1 injection Add in Sulphonylurea Contact Diabetes Centre or Community Diabetes Nurse for advice
18 Obese T2DM BMI > 35kg/m² Commence on Metformin 500mg bd Increase Metformin to maximum dose (1g BD) if HbA1c > 7.0 % (> 53 mmol/mol) If HbA1c remains > 7.0 % (> 53 mmol/mol) will need a second glucose lowering agent Option 1 GLP-1 injection (preferred option) Option 2 DPP-4 Inhibitor Option 3 Sulphonylurea The TZD Pioglitazone could also be used in this setting
19 Obese T2DM BMI > 35 kg/m² Treatment Option 1 in combination with Metformin GLP 1 agonist (injection) Exenatide BD Injection or Liraglutide OD Injection Failure to achieve target Hba1c with Metformin in combination with GLP 1 agonist - Add in Sulphonylurea. Contact Diabetes Centre or Community Diabetes Nurse for advice
20 Obese T2DM BMI > 35 kg/m² Treatment Option 2 in combination with Metformin DPP-4 Inhibitor Janumet (1g / 50mg bd Metformin + Sitagliptin) or Eucreas (1g / 50mg bd Metformin + Vildagliptin) or Onglyza (Saxagliptin - 5mg once daily) Failure to achieve target Hba1c with Metformin in combination with DPP-4 - Add in Sulphonylurea (continue DPP-4) or GLP 1 injection (stop DPP 4). Contact Diabetes Centre or Community Diabetes Nurse for advice
21 Obese T2DM BMI > 35kg/m² Treatment Option 3 in combination with Metformin Add Sulphonylurea Titrate dose of Sulphonylurea to maximum dose if HbA1c > 7.0 % (> 53 mmol/mol) Assess patient for signs and symptoms of hypoglycaemia Failure to achieve target Hba1c with Metformin in combination with Sulphonylurea Contact Diabetes Centre or Community Diabetes Nurse for advice
22 Metformin Advantages Effective Promotes weight loss No hypoglycaemia Long term data Disadvantages Nausea, flatulence, diarrhoea titrate slowly Cannot be used in renal impairment (i.e. Creatinine 130 umol/l) risk of Lactic Acidosis Can cause B12 deficiency Maximum dose is typically 1gm twice daily Give dose with food breakfast and evening meal
23 Sulphonylurea Advantages Effective Long term data Disadvantages Hypoglycaemia Weight gain? Accelerate beta cell failure Caution in patients with hepatic cirrhosis and renal impairment increased risk of hypoglycaemia Medications in this class include: Gliclazide MR (preferred option) Glimepiride Patient must be educated on the risk and management of Hypoglycaemia
24 DPP 4 Inhibitors Advantages Weight neutral No increased risk of hypoglycaemia May preserve pancreatic beta cell function (speculation currently) Disadvantages Side effects nausea, abdominal bloating, diarrhoea No long-term safety data Medications in this class include: Sitagliptin 50mg bd (in combination with Metformin = Janumet) Vildagliptin 50mg bd (in combination with Metformin = Eucreas) Saxagliptin 5mg once daily
25 GLP 1 Agonist/Injection Advantages Weight loss No hypoglycaemia when used on its own Reduces post-prandial hyperglycaemia Delays gastric emptying May preserve pancreatic beta cell function (speculation currently) Disadvantages Nausea, bloating, diarrhoea Subcutaneous injection Pancreatitis (rare) No long-term safety data In combination with sulphonylurea, may need to reduce the dose of sulphonylurea to prevent hypoglycaemia Medications in this class include: Exenatide BD S/C injection Liraglutide OD S/C injection
26 PIOGLITAZONE (Thiazolidenedione or TZD) Advantages No hypoglycaemia Insulin sensitizer Some data suggests cardiovascular benefit Preserve beta cell function Disadvantages Weight gain Fluid overload NOT TO BE USED IN HEART FAILURE Increased risk of bone fracture avoid in patients with metabolic bone disease Drop in haemoglobin Starting dose is 15mg once daily, increased to 45mg a day Can be used in combination with Metformin or sulphonylurea or insulin or DPP-4
27
28
29 Hypertension in T2DM Target Blood Pressure is <130/80 mmhg Blood Pressure should be checked every 3 months Patients often require 3 to 4 antihypertensive agents to reach their target blood pressure
30 Hypertension in T2DM (1) Target Blood Pressure < 130/80 mmhg FIRST LINE AGENT ACE Inhibitor or ARB (first line agent) (If creatinine >130umol/l check U&E 2-4 weeks after starting therapy) Fail to achieve target Add in SECOND LINE AGENT ACE Inhibitor or ARB + Calcium channel blocker (Amlodipine/Lercandipine/Diltiazem) or + Diuretic: low dose Thiazide: 12.5 to 25mg Hydrochlorthiazide or Indapamide: 1.5mg once daily or Frusemide: 20 to 40mg once daily
31 Hypertension in T2DM (2) Target Blood Pressure < 130/80 mmhg Optimise combination of 1 st and 2 nd line agents to achieve target BP (*Thiazides/Indapamide should only be used in low dose) Fail to achieve target Add in THIRD LINE AGENT If on ACE I or ARB + calcium channel blocker then add in diuretic (as before) If on ACE I or ARB + diuretic then add in calcium channel blocker
32 Hypertension in T2DM (3) Add in beta-blocker or aldosterone anatagonist as 4 th or 5 th line agent Rules of thumb Beta blocker should be used as first line if patient has symptomatic angina If serum creatinine > 130umol/l use aldosterone antagonists with caution Careful monitoring of U&E required when on aldosterone antagonists If BP responds dramatically to aldosterone antagonists consider renal artery stenosis Add in alpha blockers as 6 th line agent (Can be prescribed earlier if contraindications to other therapies)
33 Lipids in T2DM Check fasting lipids 3 months after starting therapy or after change in dose Once on stable dose check fasting lipid profile every 6 months
34 Lipid-Lowering (1) no previous vascular event Targets: LDL cholesterol < 2.6mmol/L HDL > 1.0mmol/l in men, >1.1mmol/L in women Triglycerides <1.7mmol/L LDL cholesterol above target Start statin: Atorvastatin 10mg* od or Rosuvastatin 10mg* od or Simvastatin 10mg* od or Pravastatin 10mg od Give at bed-time Precaution: Renal failure Liver failure (LFT > 3 times the upper limit of normal-caution) Previous hx of myositis (avoid statins) Previous reaction to statin therapy Teratogenic *Caution with Warfarin
35 Lipid Lowering (2) no previous vascular event Repeat fasting lipid profile 3 months after starting therapy. Once stable check lipid profile 6 monthly If patient has a history of renal or liver dysfunction monitor CK and LFT LDL cholesterol remains above target Increase statin dose: Atorvastatin to max dose of 80mg od Rosuvastatin to max dose of 40mg od Simvastatin to max dose of 80mg od Pravastatin to max dose of 40mg od Fail to achieve LDL cholesterol despite max dose Try different statin agent (e.g. Atorvastatin more potent than Pravastatin) Reaction to Statin therapy Documented myositis: avoid statins Acute deterioration in liver function: avoid statin Non-specific symptoms: trial of another statin preparation
36 Lipid Lowering (3) (no previous vascular event) Baseline LDL cholesterol < 2.6 mmol/l on no treatment If more than one CV risk factor other than diabetes. Start low dose statin Aim for reduction of > 30% from baseline LDL cholesterol
37 Lipid-Lowering in patients who have had a previous vascular event. All patients should be on a statin no matter what their LDL cholesterol is Target LDL cholesterol < 1.8mmol/L Adjust therapy as per previous slide to achieve target LDL <1.8mmol/L
38 Anti-Platelet Agent Patients with a previous vascular event should be on an anti-platelet agent Aspirin 75mg daily or Clopidogrel 75 mg daily Patients with no history of a previous vascular event but have one or more of the following should be on an anti-platelet agent Microalbuminuria Smoker Asymptomatic carotid artery disease (stenosis >30%) Atrial fibrillation (consider Warfarin) Peripheral arterial disease Angina Abnormal 12-lead ECG Patients with no history of a previous vascular event do not necessarily need to be on an anti-platelet agent The usual contraindications to Aspirin and Clopidogrel therapy apply
39 Diabetes Centre Telephone: (01) / 5 Fax: (01) Opening Hours Monday to Friday: 8.00am to 4.00pm. Urgent referrals Please fax referral letter to Diabetes Centre
40 These protocols are also available on
41 Disclaimer This publication is intended as a guide for General Practitioners managing type 2 diabetes. Any other use will require the permission of the copyright owner of the material, Beaumont Hospital. Any commercial use of this material is strictly prohibited. All comments and requests should be directed to The Diabetes Day Centre, Beaumont Hospital. All rights reserved 2010 Beaumont Hospital
Glucose Control drug treatments
 Glucose Control drug treatments It should be noted that glitazones are under suspicion of precipitating acute cardiac events and current recommendations contraindicate the use of glitazones in patients
Glucose Control drug treatments It should be noted that glitazones are under suspicion of precipitating acute cardiac events and current recommendations contraindicate the use of glitazones in patients
YOU HAVE DIABETES. Angie O Connor Community Diabetes Nurse Specialist 25th September 2013
 YOU HAVE DIABETES Angie O Connor Community Diabetes Nurse Specialist 25th September 2013 Predicated 2015 figures are already met 1 in 20 have diabetes:1in8 over 60years old Definite Diagnosis is key Early
YOU HAVE DIABETES Angie O Connor Community Diabetes Nurse Specialist 25th September 2013 Predicated 2015 figures are already met 1 in 20 have diabetes:1in8 over 60years old Definite Diagnosis is key Early
TREATMENTS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES. Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse
 TREATMENTS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse How can we improve outcomes in Type 2 diabetes? Earlier diagnosis Better patient education Stress central role of lifestyle management
TREATMENTS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse How can we improve outcomes in Type 2 diabetes? Earlier diagnosis Better patient education Stress central role of lifestyle management
Dept of Diabetes Main Desk
 Dept of Diabetes Main Desk 01202 448060 Glucose management in Type 2 Diabetes in Adults The natural history of type 2 diabetes is for HbA1c to deteriorate with time. A stepwise approach to treatment is
Dept of Diabetes Main Desk 01202 448060 Glucose management in Type 2 Diabetes in Adults The natural history of type 2 diabetes is for HbA1c to deteriorate with time. A stepwise approach to treatment is
MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES
 MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES 3 Month trial of lifestyle changes. Refer to DESMOND structured education programme. Set glycaemic target HbA1c < 7.0% (53mmol/mol) or individualised If HbA1c > 53mmol/mol
MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES 3 Month trial of lifestyle changes. Refer to DESMOND structured education programme. Set glycaemic target HbA1c < 7.0% (53mmol/mol) or individualised If HbA1c > 53mmol/mol
Type 2 Diabetes. Stopping Smoking. Consider referral to smoking cessation. Consider referring for weight management advice.
 Type 2 Diabetes Stopping Smoking Consider referral to smoking cessation BMI > 25 kg m² Set a weight loss target of a 5-10% reduction Consider referring for weight management advice Control BP to
Type 2 Diabetes Stopping Smoking Consider referral to smoking cessation BMI > 25 kg m² Set a weight loss target of a 5-10% reduction Consider referring for weight management advice Control BP to
EXENATIDE (BYETTA ) PROTOCOL, 5mcg and 10mcg SC injection pre-filled pens
 EXENATIDE (BYETTA ) PROTOCOL, 5mcg and 10mcg SC injection pre-filled pens This document should be read in conjunction with the current Summary of Product Characteristics http://www.medicines.org.uk 1.
EXENATIDE (BYETTA ) PROTOCOL, 5mcg and 10mcg SC injection pre-filled pens This document should be read in conjunction with the current Summary of Product Characteristics http://www.medicines.org.uk 1.
Volume 2; Number 14 September 2008 NICE CLINICAL GUIDELINE 66: TYPE 2 DIABETES THE MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES (MAY 2008)
 Volume 2; Number 14 September 2008 NICE CLINICAL GUIDELINE 66: TYPE 2 DIABETES THE MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES (MAY 2008) The purpose of this special edition of the PACE Bulletin is to summarize the
Volume 2; Number 14 September 2008 NICE CLINICAL GUIDELINE 66: TYPE 2 DIABETES THE MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES (MAY 2008) The purpose of this special edition of the PACE Bulletin is to summarize the
American Diabetes Association 2018 Guidelines Important Notable Points
 American Diabetes Association 2018 Guidelines Important Notable Points The Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018 by ADA include the most current evidencebased recommendations for diagnosing and treating
American Diabetes Association 2018 Guidelines Important Notable Points The Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018 by ADA include the most current evidencebased recommendations for diagnosing and treating
Disclosures. Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management. Learning Objectives. Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
 Disclosures Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Tony Hampton, MD, MBA Medical Director Advocate Aurora Operating System Advocate Aurora Healthcare Downers Grove, IL No conflicts or disclosures
Disclosures Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Tony Hampton, MD, MBA Medical Director Advocate Aurora Operating System Advocate Aurora Healthcare Downers Grove, IL No conflicts or disclosures
Challenges in type 2 diabetes control: slipping control and weight gain
 control Earn 3 CPD Points online Case study Challenges in type 2 diabetes control: slipping control and weight gain Presenter Dr Sedeshan Govender Specialist Physician, Endocrinologist and Diabetologists
control Earn 3 CPD Points online Case study Challenges in type 2 diabetes control: slipping control and weight gain Presenter Dr Sedeshan Govender Specialist Physician, Endocrinologist and Diabetologists
Cardiovascular risk reduction in diabetes Lipids (NICE CG181)
 Cardiovascular risk reduction in diabetes Lipids (NICE CG181) Primary Prevention T1DM Offer Atorvastatin 20mg if >40 years old Diabetes duration >10 years Established nephropathy Other CVS risk factors
Cardiovascular risk reduction in diabetes Lipids (NICE CG181) Primary Prevention T1DM Offer Atorvastatin 20mg if >40 years old Diabetes duration >10 years Established nephropathy Other CVS risk factors
Management of Type 2 Diabetes. Why Do We Bother to Achieve Good Control in DM2. Insulin Secretion. The Importance of BP and Glucose Control
 Insulin Secretion Management of Type 2 Diabetes DG van Zyl Why Do We Bother to Achieve Good Control in DM2 % reduction 0-5 -10-15 -20-25 -30-35 -40 The Importance of BP and Glucose Control Effects of tight
Insulin Secretion Management of Type 2 Diabetes DG van Zyl Why Do We Bother to Achieve Good Control in DM2 % reduction 0-5 -10-15 -20-25 -30-35 -40 The Importance of BP and Glucose Control Effects of tight
How can we improve outcomes in Type 2 diabetes?
 How can we improve outcomes in Type 2 diabetes? Earlier diagnosis Better patient education Stress central role of lifestyle management Identify and treat all risk factors Use rational pharmacological therapy
How can we improve outcomes in Type 2 diabetes? Earlier diagnosis Better patient education Stress central role of lifestyle management Identify and treat all risk factors Use rational pharmacological therapy
Dr Tahseen A. Chowdhury Royal London Hospital. New Guidelines in Diabetes: NICE or Nasty?
 Dr Tahseen A. Chowdhury Royal London Hospital New Guidelines in Diabetes: NICE or Nasty? I have no conflicts of interest I do not undertake talks / advisory bodies / research for any pharma company Consultant
Dr Tahseen A. Chowdhury Royal London Hospital New Guidelines in Diabetes: NICE or Nasty? I have no conflicts of interest I do not undertake talks / advisory bodies / research for any pharma company Consultant
STEP 3: Add or Substitute with one of
 Prescribing of Hypoglycaemic Agents for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Sunderland Refer to DESMOND Structured Education classes to promote Increased Physical Activity, Weight Loss and Calories Reduction
Prescribing of Hypoglycaemic Agents for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Sunderland Refer to DESMOND Structured Education classes to promote Increased Physical Activity, Weight Loss and Calories Reduction
Pharmacological Glycaemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes
 Pharmacological Glycaemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Aim(s) and Objective(s) This guideline aims to offer advice on the pharmacological management for those who require measures beyond diet and exercise
Pharmacological Glycaemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Aim(s) and Objective(s) This guideline aims to offer advice on the pharmacological management for those who require measures beyond diet and exercise
Case study for CME Diabetes up-to-date management
 Case study for CME Diabetes up-to-date management Dr Ole Schmiedel, MRCP MD FRACP Physician and Endocrinologist Service Clinical Director Auckland Diabetes Centre GP referral to Auckland Diabetes Centre
Case study for CME Diabetes up-to-date management Dr Ole Schmiedel, MRCP MD FRACP Physician and Endocrinologist Service Clinical Director Auckland Diabetes Centre GP referral to Auckland Diabetes Centre
Mr Rab Burtun. Dr David Kim. 8:30-10:30 WS #2: Diabetes Basic 11:00-13:00 WS #9: Diabetes Basic (Repeated)
 Dr David Kim Endocrinologist and General Physician Waitemata DHB and Apollo Specialist Clinic Albany Auckland Mr Rab Burtun Diabetes Nurse Specialist Waitemata DHB Waitakere Hospital Auckland 8:30-10:30
Dr David Kim Endocrinologist and General Physician Waitemata DHB and Apollo Specialist Clinic Albany Auckland Mr Rab Burtun Diabetes Nurse Specialist Waitemata DHB Waitakere Hospital Auckland 8:30-10:30
EFFECTIVE SHARE CARE AGREEMENT. FOR THE off license use of GLP1 mimetics in combination with insulin IN DUDLEY
 Specialist details Patient identifier Name Tel: EFFECTIVE SHARE CARE AGREEMENT FOR THE off license use of GLP1 mimetics in combination with insulin IN DUDLEY The aim of Effective Shared Care Guidelines
Specialist details Patient identifier Name Tel: EFFECTIVE SHARE CARE AGREEMENT FOR THE off license use of GLP1 mimetics in combination with insulin IN DUDLEY The aim of Effective Shared Care Guidelines
Adult Diabetes Clinician Guide NOVEMBER 2017
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Diabetes Clinician Guide Introduction NOVEMBER 2017 This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2017 KP National Diabetes Guideline.
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Diabetes Clinician Guide Introduction NOVEMBER 2017 This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2017 KP National Diabetes Guideline.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and SGLT-2 Inhibitors. Debbie Hicks
 GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and SGLT-2 Inhibitors Debbie Hicks Prescribing and Adverse Event reporting information is available at this meeting from the AstraZeneca representative The views expressed by the
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and SGLT-2 Inhibitors Debbie Hicks Prescribing and Adverse Event reporting information is available at this meeting from the AstraZeneca representative The views expressed by the
Joslin Diabetes Center Joslin Diabetes Forum 2013: The Impact of Comorbidities on Glucose Control Scenario 2: Reduced Renal Function
 Scenario 2: Reduced Renal Function 62 y.o. white man with type 2 diabetes for 18 years Hypertension and hypercholesterolemia Known proliferative retinopathy Current medications: Metformin 1000 mg bid Glyburide
Scenario 2: Reduced Renal Function 62 y.o. white man with type 2 diabetes for 18 years Hypertension and hypercholesterolemia Known proliferative retinopathy Current medications: Metformin 1000 mg bid Glyburide
the person is intolerant of either metformin or a sulphonylurea, or treatment with metformin or a sulphonylurea is contraindicated, and
 Exenatide (Byetta) and Liraglutide (Victoza) prescribing guidance: Notes for initiation in primary care These incretin mimetics are given by subcutaneous injection once or twice daily. They have similar
Exenatide (Byetta) and Liraglutide (Victoza) prescribing guidance: Notes for initiation in primary care These incretin mimetics are given by subcutaneous injection once or twice daily. They have similar
IMPROVED DIAGNOSIS OF TYPE 2 DIABETES AND TAILORING MEDICATIONS
 IMPROVED DIAGNOSIS OF TYPE 2 DIABETES AND TAILORING MEDICATIONS Dr Bidhu Mohapatra, MBBS, MD, FRACP Consultant Physician Endocrinology and General Medicine Introduction 382 million people affected by diabetes
IMPROVED DIAGNOSIS OF TYPE 2 DIABETES AND TAILORING MEDICATIONS Dr Bidhu Mohapatra, MBBS, MD, FRACP Consultant Physician Endocrinology and General Medicine Introduction 382 million people affected by diabetes
Dr A Pokrajac MD MSc MRCP Consultant
 Dr A Pokrajac MD MSc MRCP Consultant Onset at 5-15 years of T1DM Can be present at diagnosis of T2DM Detect in regular MA/Cr screening (2X first urine sample, no UTI, no other causes) Contributing Factors
Dr A Pokrajac MD MSc MRCP Consultant Onset at 5-15 years of T1DM Can be present at diagnosis of T2DM Detect in regular MA/Cr screening (2X first urine sample, no UTI, no other causes) Contributing Factors
Drugs used in Diabetes. Dr Andrew Smith
 Drugs used in Diabetes Dr Andrew Smith Plan Introduction Insulin Sensitising Drugs: Metformin Glitazones Insulin Secretagogues: Sulphonylureas Meglitinides Others: Acarbose Incretins Amylin Analogues Damaglifozin
Drugs used in Diabetes Dr Andrew Smith Plan Introduction Insulin Sensitising Drugs: Metformin Glitazones Insulin Secretagogues: Sulphonylureas Meglitinides Others: Acarbose Incretins Amylin Analogues Damaglifozin
Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim
 Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim Chosun University Hospital Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Committee of Scientific Affairs Insulin therapy is the mainstay
Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim Chosun University Hospital Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Committee of Scientific Affairs Insulin therapy is the mainstay
Barns Medical Practice Service Specification: Diabetes
 Barns Medical Practice Service Specification: Diabetes DEVELOPED June 2017 REVIEW DATE June 2019 Introduction Diabetes mellitus is a life-long progressive condition that can be controlled but not cured.
Barns Medical Practice Service Specification: Diabetes DEVELOPED June 2017 REVIEW DATE June 2019 Introduction Diabetes mellitus is a life-long progressive condition that can be controlled but not cured.
Metformin should be considered in all patients with type 2 diabetes unless contra-indicated
 November 2001 N P S National Prescribing Service Limited PPR fifteen Prescribing Practice Review PPR Managing type 2 diabetes For General Practice Key messages Metformin should be considered in all patients
November 2001 N P S National Prescribing Service Limited PPR fifteen Prescribing Practice Review PPR Managing type 2 diabetes For General Practice Key messages Metformin should be considered in all patients
Arrange 3 Monthly Review Re-enforce LIFESTYLE advice and check DRUG COMPLIANCE at each visit Target HbA1c < 53mmol/mol
 Prescribing of Hypoglycaemic Agents for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Sunderland Refer to DESMOND Structured Education classes to promote Increased Physical Activity, Weight Loss and Calories Reduction
Prescribing of Hypoglycaemic Agents for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Sunderland Refer to DESMOND Structured Education classes to promote Increased Physical Activity, Weight Loss and Calories Reduction
Newer and Expensive treatment of diabetes. Endocrinology Visiting Associate Professor Institute of Medicine TUTH
 Newer and Expensive treatment of diabetes Jyoti Bhattarai MD Endocrinology Visiting Associate Professor Institute of Medicine TUTH Four out of every five people with diabetes now live in developing countries.
Newer and Expensive treatment of diabetes Jyoti Bhattarai MD Endocrinology Visiting Associate Professor Institute of Medicine TUTH Four out of every five people with diabetes now live in developing countries.
Practical Diabetes. Nic Crook. (and don t use so many charts) Kuirau Specialists 1239 Ranolf Street Rotorua. Rotorua Hospital Private Bag 3023 Rotorua
 Practical Diabetes (and don t use so many charts) Nic Crook Rotorua Hospital Private Bag 3023 Rotorua Kuirau Specialists 1239 Ranolf Street Rotorua Worldwide rates of diabetes mellitus: predictions 80
Practical Diabetes (and don t use so many charts) Nic Crook Rotorua Hospital Private Bag 3023 Rotorua Kuirau Specialists 1239 Ranolf Street Rotorua Worldwide rates of diabetes mellitus: predictions 80
Management of Type 2 Diabetes
 Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
New Treatments for Type 2 diabetes. Nandini Seevaratnam April 2016 Rushcliffe Patient Forum
 New Treatments for Type 2 diabetes Nandini Seevaratnam April 2016 Rushcliffe Patient Forum Overview Growing population of Type 2 diabetes Basic science on what goes wrong Current treatments Why there is
New Treatments for Type 2 diabetes Nandini Seevaratnam April 2016 Rushcliffe Patient Forum Overview Growing population of Type 2 diabetes Basic science on what goes wrong Current treatments Why there is
Case study: Lean adult with no complications, newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes
 Case study: Lean adult with no complications, newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes Authored by Clifford Bailey and James LaSalle on behalf of the Global Partnership for Effective Diabetes Management. The
Case study: Lean adult with no complications, newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes Authored by Clifford Bailey and James LaSalle on behalf of the Global Partnership for Effective Diabetes Management. The
Liraglutide (Victoza) in combination with basal insulin for type 2 diabetes
 Liraglutide (Victoza) in combination with basal insulin for type 2 diabetes May 2011 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It
Liraglutide (Victoza) in combination with basal insulin for type 2 diabetes May 2011 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It
GLP-1 agonists. Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK
 GLP-1 agonists Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK What do GLP-1 agonists do? Physiology of postprandial glucose regulation Meal ❶ ❷ Insulin Rising plasma
GLP-1 agonists Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK What do GLP-1 agonists do? Physiology of postprandial glucose regulation Meal ❶ ❷ Insulin Rising plasma
SIMPLICITY IN T2DM MANAGEMENT WITH DPP4 INHIBITORS: SPECIAL POPULATION
 SIMPLICITY IN T2DM MANAGEMENT WITH DPP4 INHIBITORS: SPECIAL POPULATION DR ROSE ZHAO-WEI TING ( 丁昭慧醫生 ) MBBS (HK), MRCP (UK), FHKCP, FHKAM (MEDICINE) Specialist in Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism
SIMPLICITY IN T2DM MANAGEMENT WITH DPP4 INHIBITORS: SPECIAL POPULATION DR ROSE ZHAO-WEI TING ( 丁昭慧醫生 ) MBBS (HK), MRCP (UK), FHKCP, FHKAM (MEDICINE) Specialist in Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism
Diabetes Complications Guideline Based Screening, Management, and Referral
 Diabetes Complications Guideline Based Screening, Management, and Referral Eric L. Johnson, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Family and Community Medicine Assistant Medical Director Altru Diabetes
Diabetes Complications Guideline Based Screening, Management, and Referral Eric L. Johnson, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Family and Community Medicine Assistant Medical Director Altru Diabetes
Should Psychiatrists be diagnosing (and treating) metabolic syndrome
 Should Psychiatrists be diagnosing (and treating) metabolic syndrome David Hopkins Clinical Director, Diabetes King s College Hospital, London Diabetes prevalence (thousands) Diabetes in the UK: 1995-2010
Should Psychiatrists be diagnosing (and treating) metabolic syndrome David Hopkins Clinical Director, Diabetes King s College Hospital, London Diabetes prevalence (thousands) Diabetes in the UK: 1995-2010
Dr Rick Cutfield Physician, Diabetologist and Endocrinologist Mercy Specialist Centre
 Dr Rick Cutfield Physician, Diabetologist and Endocrinologist Mercy Specialist Centre Diabetes Case Studies from the clinic Dr Rick Cutfield Physician and Endocrinologist Waitemata District Health Board
Dr Rick Cutfield Physician, Diabetologist and Endocrinologist Mercy Specialist Centre Diabetes Case Studies from the clinic Dr Rick Cutfield Physician and Endocrinologist Waitemata District Health Board
Alia Gilani Health Inequalities Pharmacist
 Alia Gilani Health Inequalities Pharmacist THE SOUTH ASIAN HEALTH FOUNDATION (U.K.) (Registered Charity No. 1073178) 1. Case Study 2. Factors influencing prescribing 3. Special Considerations 4. Prescribing
Alia Gilani Health Inequalities Pharmacist THE SOUTH ASIAN HEALTH FOUNDATION (U.K.) (Registered Charity No. 1073178) 1. Case Study 2. Factors influencing prescribing 3. Special Considerations 4. Prescribing
Oral Treatments for Type 2 Diabetes. Prescribing Support Pharmacist
 Oral Treatments for Type 2 Diabetes Prescribing Support Pharmacist Learning Outcomes Familiar with classes of oral hypoglycaemic agents (OHAs) used in controlling blood glucose levels When to use each
Oral Treatments for Type 2 Diabetes Prescribing Support Pharmacist Learning Outcomes Familiar with classes of oral hypoglycaemic agents (OHAs) used in controlling blood glucose levels When to use each
Heart Failure (HF) - Primary Care Flow Charts. Pre diagnosis Symptoms or signs suggestive of HF
 Heart Failure (HF) - Primary Care Flow Charts Pre diagnosis Symptoms or signs suggestive of HF 12 lead ECG Normal examination and 12 lead ECG HF highly unlikely Abnormal 12 lead ECG HF Possible Arrange
Heart Failure (HF) - Primary Care Flow Charts Pre diagnosis Symptoms or signs suggestive of HF 12 lead ECG Normal examination and 12 lead ECG HF highly unlikely Abnormal 12 lead ECG HF Possible Arrange
Heart Failure (HF) - Primary Care Flow Charts. Symptoms or signs suggestive of HF. Pre diagnosis. Refer to the Heart Failure Clinic at VHK for
 Heart Failure (HF) - Primary Care Flow Charts Pre diagnosis Symptoms or signs suggestive of HF 12 lead ECG Normal examination and 12 lead ECG HF highly unlikely Abnormal 12 lead ECG HF Possible Arrange
Heart Failure (HF) - Primary Care Flow Charts Pre diagnosis Symptoms or signs suggestive of HF 12 lead ECG Normal examination and 12 lead ECG HF highly unlikely Abnormal 12 lead ECG HF Possible Arrange
Diabetes and the Elderly: Medication Considerations When Determining Benefits and Risks
 Diabetes and the Elderly: Medication Considerations When Determining Benefits and Risks Gretchen M. Ray, PharmD, PhC, BCACP, CDE Associate Professor UNM College of Pharmacy September 7 th, 2018 DISCLOSURES
Diabetes and the Elderly: Medication Considerations When Determining Benefits and Risks Gretchen M. Ray, PharmD, PhC, BCACP, CDE Associate Professor UNM College of Pharmacy September 7 th, 2018 DISCLOSURES
Newer Drugs in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 Newer Drugs in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Dr. C. Dinesh M. Naidu Professor of Pharmacology, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences, Narketpally. 1 Presentation Outline Introduction Pathogenesis
Newer Drugs in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Dr. C. Dinesh M. Naidu Professor of Pharmacology, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences, Narketpally. 1 Presentation Outline Introduction Pathogenesis
Inpatient Diabetes 20/01/2015. What should I do? Hyperglycaemia why does it matter? Why are the BSLs unstable? BSL parameters
 Hyperglycaemia why does it matter? Inpatient Diabetes Angela Sheu Endocrine Registrar St George Hospital Hyperglycaemia at admission is a predictor of mortality May be part of stress response (eg post
Hyperglycaemia why does it matter? Inpatient Diabetes Angela Sheu Endocrine Registrar St George Hospital Hyperglycaemia at admission is a predictor of mortality May be part of stress response (eg post
A Practical Approach to the Use of Diabetes Medications
 A Practical Approach to the Use of Diabetes Medications Juan Pablo Frias, M.D., FACE President, National Research Institute, Los Angles, CA Clinical Faculty, University of California, San Diego, CA OUTLINE
A Practical Approach to the Use of Diabetes Medications Juan Pablo Frias, M.D., FACE President, National Research Institute, Los Angles, CA Clinical Faculty, University of California, San Diego, CA OUTLINE
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus hypoglycaemic agents
 Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus hypoglycaemic agents Name Metformin Drug Name (eg brand name) Metformin (Diaformin Diabex) Cost / PBS per 28d mth $10.24 (1.5g dly) 1000mg+500mg / $4.44+$5.80 Concerns? Lactic
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus hypoglycaemic agents Name Metformin Drug Name (eg brand name) Metformin (Diaformin Diabex) Cost / PBS per 28d mth $10.24 (1.5g dly) 1000mg+500mg / $4.44+$5.80 Concerns? Lactic
Type 2 Diabetes: Where Do We Start with Treatment? DIABETES EDUCATION. Diabetes Mellitus: Complications and Co-Morbid Conditions
 Diabetes Mellitus: Complications and Co-Morbid Conditions ADA Guidelines for Glycemic Control: 2016 Retinopathy Between 2005-2008, 28.5% of patients with diabetes 40 years and older diagnosed with diabetic
Diabetes Mellitus: Complications and Co-Morbid Conditions ADA Guidelines for Glycemic Control: 2016 Retinopathy Between 2005-2008, 28.5% of patients with diabetes 40 years and older diagnosed with diabetic
DIABETES DEBATE - IS NEW BETTER?
 DIABETES DEBATE - IS NEW BETTER? WHAT MEDICATION CLASS AFTER METFORMIN TO CONTROL BLOOD SUGAR Dr. Lydia Hatcher, MD, CCFP, FCFP, CHE, D-CAPM Associate Clinical Professor of Family Medicine, McMaster Chief
DIABETES DEBATE - IS NEW BETTER? WHAT MEDICATION CLASS AFTER METFORMIN TO CONTROL BLOOD SUGAR Dr. Lydia Hatcher, MD, CCFP, FCFP, CHE, D-CAPM Associate Clinical Professor of Family Medicine, McMaster Chief
Medicines Optimisation Team Standard Operating procedure for Alogliptin Audit:
 Medicines Optimisation Team Standard Operating procedure for Alogliptin Audit: To review type 2 diabetic patients prescribed dipedtidylpeptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors (linagliptin (Trajenta, saxagliptin
Medicines Optimisation Team Standard Operating procedure for Alogliptin Audit: To review type 2 diabetic patients prescribed dipedtidylpeptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors (linagliptin (Trajenta, saxagliptin
Primary Prevention Patients aged 85yrs and over
 Rotherham Guideline for the management of Non-Familial Hypercholesterolaemia Type 1 Diabetes Offer lifestyle advice Over 40yrs of age? Diabetic for more than 10 years? Established nephropathy? Other CVD
Rotherham Guideline for the management of Non-Familial Hypercholesterolaemia Type 1 Diabetes Offer lifestyle advice Over 40yrs of age? Diabetic for more than 10 years? Established nephropathy? Other CVD
ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
 ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Pr. Michel KOMAJDA Institute of Cardiology - IHU ICAN Pitie Salpetriere Hospital - University Pierre and Marie Curie, Paris (France) DEFINITION A
ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Pr. Michel KOMAJDA Institute of Cardiology - IHU ICAN Pitie Salpetriere Hospital - University Pierre and Marie Curie, Paris (France) DEFINITION A
Oral Treatments. SaminaAli Prescribing Support Pharmacist
 Oral Treatments for Type 2 Diabetes SaminaAli Prescribing Support Pharmacist Learning Outcomes National Guidance Familiar with classes of oral hypoglycaemic agents (OHAs) used in controlling blood glucose
Oral Treatments for Type 2 Diabetes SaminaAli Prescribing Support Pharmacist Learning Outcomes National Guidance Familiar with classes of oral hypoglycaemic agents (OHAs) used in controlling blood glucose
PLEASE CHECK FULL SPECIFIC PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS FOR MORE DETAILED AND CURRENT INFORMATION:
 Metformin Standard tablets Modified-release tablets Metformin 1g sachets Metformin liquid 500mg/5ml (avoid use as expensive) < 2.00 5.32 for 56 tabs 500mg 13.16 for 60 sachets > 120 Ketoacidosis General
Metformin Standard tablets Modified-release tablets Metformin 1g sachets Metformin liquid 500mg/5ml (avoid use as expensive) < 2.00 5.32 for 56 tabs 500mg 13.16 for 60 sachets > 120 Ketoacidosis General
667FM.5.1 MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES: BLOOD-GLUCOSE-LOWERING THERAPY
 667FM.5.1 MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES: BLOOD-GLUCOSE-LOWERING THERAPY Contents Introduction... 1 Patient Education for People with Type 2 Diabetes... 2 Dietary Advice for People with Type 2 Diabetes...
667FM.5.1 MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES: BLOOD-GLUCOSE-LOWERING THERAPY Contents Introduction... 1 Patient Education for People with Type 2 Diabetes... 2 Dietary Advice for People with Type 2 Diabetes...
Treatment Options for Diabetes: An Update
 Treatment Options for Diabetes: An Update A/Prof. Marg McGill Manager, Diabetes Centre Dr. Ted Wu Staff Specialist Endocrinologist Diabetes Centre Centre of Health Professional Education Education Provider
Treatment Options for Diabetes: An Update A/Prof. Marg McGill Manager, Diabetes Centre Dr. Ted Wu Staff Specialist Endocrinologist Diabetes Centre Centre of Health Professional Education Education Provider
DR HJ BODANSKY MD FRCP CONSULTANT PHYSICIAN LEEDS TEACHING HOSPITALS ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, UNIVERSITY OF LEEDS
 DR HJ BODANSKY MD FRCP CONSULTANT PHYSICIAN LEEDS TEACHING HOSPITALS ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, UNIVERSITY OF LEEDS DIABETETES UPDATE 2015 AIMS OF THE SEMINAR Diagnosis Investigation Management When to refer
DR HJ BODANSKY MD FRCP CONSULTANT PHYSICIAN LEEDS TEACHING HOSPITALS ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, UNIVERSITY OF LEEDS DIABETETES UPDATE 2015 AIMS OF THE SEMINAR Diagnosis Investigation Management When to refer
Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus
 Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 How to Screen for Diabetic Nephropathy... 4 What to Measure... 4 Frequency
Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 How to Screen for Diabetic Nephropathy... 4 What to Measure... 4 Frequency
The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities
 The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities Question #1 Which of the following is a risk factor for increased hypoglycemia in older patients that may suggest the need to relax hyperglycemia treatment
The Many Faces of T2DM in Long-term Care Facilities Question #1 Which of the following is a risk factor for increased hypoglycemia in older patients that may suggest the need to relax hyperglycemia treatment
Coronary Heart Disease and Stroke, Primary and Secondary Prevention Guidelines (Cholesterol)
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE Coronary Heart Disease and Stroke, Primary and Secondary Prevention Guidelines (Cholesterol) A guideline is intended to assist healthcare professionals in the choice of disease-specific
CLINICAL GUIDELINE Coronary Heart Disease and Stroke, Primary and Secondary Prevention Guidelines (Cholesterol) A guideline is intended to assist healthcare professionals in the choice of disease-specific
Complications of Diabetes mellitus. Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015
 Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
Diabetes Mellitus: Implications of New Clinical Trials and New Medications
 Diabetes Mellitus: Implications of New Clinical Trials and New Medications Estimates of Diagnosed Diabetes in Adults, 2005 Alka M. Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine UCSF, Primary Care CME October
Diabetes Mellitus: Implications of New Clinical Trials and New Medications Estimates of Diagnosed Diabetes in Adults, 2005 Alka M. Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine UCSF, Primary Care CME October
PERIOPERATIVE DIABETES GUIDELINE
 PERIOPERATIVE DIABETES GUIDELINE This Guideline does not replace the need for the application of clinical judgment in respect to each individual patient. Background Diabetes mellitus is estimated to affect
PERIOPERATIVE DIABETES GUIDELINE This Guideline does not replace the need for the application of clinical judgment in respect to each individual patient. Background Diabetes mellitus is estimated to affect
Chief of Endocrinology East Orange General Hospital
 Targeting the Incretins System: Can it Improve Our Ability to Treat Type 2 Diabetes? Darshi Sunderam, MD Darshi Sunderam, MD Chief of Endocrinology East Orange General Hospital Age-adjusted Percentage
Targeting the Incretins System: Can it Improve Our Ability to Treat Type 2 Diabetes? Darshi Sunderam, MD Darshi Sunderam, MD Chief of Endocrinology East Orange General Hospital Age-adjusted Percentage
Navigating the New Options for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes
 Navigating the New Options for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Clinical Associate Professor Mark Kennedy Department of General Practice, University of Melbourne Chair, Primary Care Diabetes Society of
Navigating the New Options for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Clinical Associate Professor Mark Kennedy Department of General Practice, University of Melbourne Chair, Primary Care Diabetes Society of
Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease
 Save Thais from Heart Diseases 2019 Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Orawan Anupraiwan, MD. Central Chest Institute of Thailand ASCVD Prevention Pyramid Risk categories Very high-risk High-risk Documented
Save Thais from Heart Diseases 2019 Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease Orawan Anupraiwan, MD. Central Chest Institute of Thailand ASCVD Prevention Pyramid Risk categories Very high-risk High-risk Documented
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE. Proposed Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Dapagliflozin in combination therapy for the Final scope Remit/appraisal objective To appraise the clinical and
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Dapagliflozin in combination therapy for the Final scope Remit/appraisal objective To appraise the clinical and
The older person with co morbidities. Eugene Hughes General Practitioner Isle of Wight
 The older person with co morbidities Eugene Hughes General Practitioner Isle of Wight Eugene Hughes Age 60 BMI 26.5 BP 125/70 Alcohol intake moderate (?) TC 5.6 Regular exercise Non smoker Stress free
The older person with co morbidities Eugene Hughes General Practitioner Isle of Wight Eugene Hughes Age 60 BMI 26.5 BP 125/70 Alcohol intake moderate (?) TC 5.6 Regular exercise Non smoker Stress free
Long-Term Complications of Diabetes Mellitus Macrovascular Complication
 Long-Term Complications of Diabetes Mellitus Macrovascular Complication Sung Hee Choi MD, PhD Professor, Seoul National University College of Medicine, SNUBH, Bundang Hospital Diabetes = CVD equivalent
Long-Term Complications of Diabetes Mellitus Macrovascular Complication Sung Hee Choi MD, PhD Professor, Seoul National University College of Medicine, SNUBH, Bundang Hospital Diabetes = CVD equivalent
Case study: Adult with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes of long duration and cardiovascular disease
 Case study: Adult with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes of long duration and cardiovascular disease Authored by Paul Zimmet and Richard Nesto on behalf of the Global Partnership for Effective Diabetes Management.
Case study: Adult with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes of long duration and cardiovascular disease Authored by Paul Zimmet and Richard Nesto on behalf of the Global Partnership for Effective Diabetes Management.
Early treatment for patients with Type 2 Diabetes
 Israel Society of Internal Medicine Kibutz Hagoshrim, June 22, 2012 Early treatment for patients with Type 2 Diabetes Eduard Montanya Hospital Universitari Bellvitge-IDIBELL CIBERDEM University of Barcelona
Israel Society of Internal Medicine Kibutz Hagoshrim, June 22, 2012 Early treatment for patients with Type 2 Diabetes Eduard Montanya Hospital Universitari Bellvitge-IDIBELL CIBERDEM University of Barcelona
Pre-diabetes. Pharmacological Approaches to Delay Progression to Diabetes
 Pre-diabetes Pharmacological Approaches to Delay Progression to Diabetes Overview Definition of Pre-diabetes Risk Factors for Pre-diabetes Clinical practice guidelines for diabetes Management, including
Pre-diabetes Pharmacological Approaches to Delay Progression to Diabetes Overview Definition of Pre-diabetes Risk Factors for Pre-diabetes Clinical practice guidelines for diabetes Management, including
Overview T2DM medications. Winnie Ho
 Overview T2DM medications Winnie Ho Diabetes in Australia 1.7 million Australians with diabetes, of these 85% have T2DM 2-fold excess risk CV death in patients with diabetes Risk factor for progression
Overview T2DM medications Winnie Ho Diabetes in Australia 1.7 million Australians with diabetes, of these 85% have T2DM 2-fold excess risk CV death in patients with diabetes Risk factor for progression
Cardiovascular Health Practice Guideline Outpatient Management of Coronary Artery Disease 2003
 Authorized By: Medical Management Guideline Committee Approval Date: 12/13/01 Revision Date: 12/11/03 Beta-Blockers Nitrates Calcium Channel Blockers MEDICATIONS Indicated in post-mi, unstable angina,
Authorized By: Medical Management Guideline Committee Approval Date: 12/13/01 Revision Date: 12/11/03 Beta-Blockers Nitrates Calcium Channel Blockers MEDICATIONS Indicated in post-mi, unstable angina,
Abbreviations DPP-IV dipeptidyl peptidase IV DREAM Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone
 Index Abbreviations DPP-IV dipeptidyl peptidase IV DREAM Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication GAD glutamic acid decarboxylase GLP-1 glucagon-like peptide 1 NPH neutral
Index Abbreviations DPP-IV dipeptidyl peptidase IV DREAM Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication GAD glutamic acid decarboxylase GLP-1 glucagon-like peptide 1 NPH neutral
SECONDARY PREVENTION OF CORONARY HEART DISEASE AND ISCHAEMIC STROKE/TIA
 PRIMARY PREVENTION OF CHD AND STROKE IN HIGH RISK PATIENTS Random non fasting test for total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol (TC:HDL ratio) and LFTs If cholesterol > 7.5 mmol/l or LDL C 5mmol/l exclude secondary
PRIMARY PREVENTION OF CHD AND STROKE IN HIGH RISK PATIENTS Random non fasting test for total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol (TC:HDL ratio) and LFTs If cholesterol > 7.5 mmol/l or LDL C 5mmol/l exclude secondary
Oral Hypoglycemics and Risk of Adverse Cardiac Events: A Summary of the Controversy
 Oral Hypoglycemics and Risk of Adverse Cardiac Events: A Summary of the Controversy Jeffrey Boord, MD, MPH Advances in Cardiovascular Medicine Kingston, Jamaica December 7, 2012 VanderbiltHeart.com Outline
Oral Hypoglycemics and Risk of Adverse Cardiac Events: A Summary of the Controversy Jeffrey Boord, MD, MPH Advances in Cardiovascular Medicine Kingston, Jamaica December 7, 2012 VanderbiltHeart.com Outline
New indicators to be added to the NICE menu for the QOF and amendments to existing indicators
 New indicators to be added to the for the QOF and amendments to existing indicators 1 st September 2015 Version 1.1 This document was originally published on 3 rd August 2015, it has since been updated.
New indicators to be added to the for the QOF and amendments to existing indicators 1 st September 2015 Version 1.1 This document was originally published on 3 rd August 2015, it has since been updated.
Type 2 diabetes in adults: controlling your blood glucose by taking a second medicine what are your options?
 Patient decision aid Type 2 diabetes in adults: controlling your blood glucose by taking a second medicine what are your options? nice.org.uk/guidance/ng28 Published: December 2015 About this decision
Patient decision aid Type 2 diabetes in adults: controlling your blood glucose by taking a second medicine what are your options? nice.org.uk/guidance/ng28 Published: December 2015 About this decision
HEALTH SERVICES POLICY & PROCEDURE MANUAL
 PAGE 1 of 5 PURPOSE To assure that DOP inmates with Diabetes are receiving high quality Primary Care for their condition. POLICY All DOP Primary Care Providers are to follow these guidelines when treating
PAGE 1 of 5 PURPOSE To assure that DOP inmates with Diabetes are receiving high quality Primary Care for their condition. POLICY All DOP Primary Care Providers are to follow these guidelines when treating
CONTRAINDICATIONS: Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients
 Galvus PRESENTATION: Each tablet contains 50 mg of Vildagliptin INDICATIONS: For the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults: i) As monotherapy in patients inadequately controlled by diet and exercise
Galvus PRESENTATION: Each tablet contains 50 mg of Vildagliptin INDICATIONS: For the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults: i) As monotherapy in patients inadequately controlled by diet and exercise
Management of Hypertension
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Diabetes in the UK: Update on Diabetes Treatment and Care. Why is diabetes increasing? Obesity Increased waist circumference.
 Update on Diabetes Treatment and Care Tahseen A Chowdhury Consultant Diabetologist Royal London and Mile End Hospitals Diabetes prevalence (thousands) Diabetes in the UK: 1995-21 3 25 2 15 1 5 Type 1 Type
Update on Diabetes Treatment and Care Tahseen A Chowdhury Consultant Diabetologist Royal London and Mile End Hospitals Diabetes prevalence (thousands) Diabetes in the UK: 1995-21 3 25 2 15 1 5 Type 1 Type
Hypertension diagnosis (see detail document) Diabetic. Target less than 130/80mmHg
 Hypertension diagnosis (see detail document) Non-diabetic Diabetic Very elderly (older than 80 years) Target less than 140/90mmHg Target less than 130/80mmHg Consider SBP target less than 150mmHg Non-diabetic
Hypertension diagnosis (see detail document) Non-diabetic Diabetic Very elderly (older than 80 years) Target less than 140/90mmHg Target less than 130/80mmHg Consider SBP target less than 150mmHg Non-diabetic
Diabetes Renal Disease Management. Dr Paul Laboi Dr Vijay Jayagopal York Hospital
 Diabetes Renal Disease Management Dr Paul Laboi Dr Vijay Jayagopal York Hospital 0 Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is a clinical syndrome characterised by the following: Persistent albuminuria
Diabetes Renal Disease Management Dr Paul Laboi Dr Vijay Jayagopal York Hospital 0 Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is a clinical syndrome characterised by the following: Persistent albuminuria
Frailty and Type 2 Diabetes Guidelines for clinicians
 H.G. WELLS PROJECT Frailty and Type 2 Diabetes Guidelines for clinicians Victoria Ruszala victoria.ruszala@nhs.net H.G. Wells Project team Dugal T, Partington E. Kernow CCG Diabetes and Frailty Guideline
H.G. WELLS PROJECT Frailty and Type 2 Diabetes Guidelines for clinicians Victoria Ruszala victoria.ruszala@nhs.net H.G. Wells Project team Dugal T, Partington E. Kernow CCG Diabetes and Frailty Guideline
Clinical Guidelines. Management of adult patients with diabetes undergoing endoscopic procedures
 Clinical Guidelines Management of adult patients with diabetes undergoing endoscopic s Document Detail Document type Clinical Guideline Management of adult Patients with diabetes Undergoing Document name
Clinical Guidelines Management of adult patients with diabetes undergoing endoscopic s Document Detail Document type Clinical Guideline Management of adult Patients with diabetes Undergoing Document name
ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour
 ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour Dr Indranil Dasgupta Rationale No national practical
ABCD and Renal Association Clinical Guidelines for Diabetic Nephropathy-CKD. Management of Dyslipidaemia and Hypertension in Adults Dr Peter Winocour Dr Indranil Dasgupta Rationale No national practical
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGNOSIS
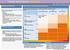 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS GFR categories, description and range WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD CLASSIFICATION OF CKD USING egfr AND ACR CATEGORIES Offer testing for CKD using egfr, creatinine and ACR
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS GFR categories, description and range WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD CLASSIFICATION OF CKD USING egfr AND ACR CATEGORIES Offer testing for CKD using egfr, creatinine and ACR
Optimal glucose control. DM Treatment. Glucose Control one out of many. Many guidelines: Confusing. Theorectically easy
 DM Treatment How to Achieve Optimal Glycaemic Control The Tung Wah Eastern Hospital Experience of DM Share Care Experience Optimal glucose control Theorectically easy More challenging in the real world
DM Treatment How to Achieve Optimal Glycaemic Control The Tung Wah Eastern Hospital Experience of DM Share Care Experience Optimal glucose control Theorectically easy More challenging in the real world
Chronic Benefit Application Form Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes
 Chronic Benefit Application Form Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes 19 West Street, Houghton, South Africa, 2198 Postnet Suite 411, Private Bag X1, Melrose Arch, 2076 Tel: +27 (11) 715 3000 Fax: +27 (11)
Chronic Benefit Application Form Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes 19 West Street, Houghton, South Africa, 2198 Postnet Suite 411, Private Bag X1, Melrose Arch, 2076 Tel: +27 (11) 715 3000 Fax: +27 (11)
NEW DIABETES CARE MEDICATIONS
 NEW DIABETES CARE MEDICATIONS James Bonucchi DO, ECNU, FACE Adult Medicine and Endocrinology Specialists Disclosures Speakers bureau Sanofi AZ BI Diabetes Diabetes cost ADA 2017 data Ever increasing disorder.
NEW DIABETES CARE MEDICATIONS James Bonucchi DO, ECNU, FACE Adult Medicine and Endocrinology Specialists Disclosures Speakers bureau Sanofi AZ BI Diabetes Diabetes cost ADA 2017 data Ever increasing disorder.
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005 1 Any adult in the health care system 2 Obtain blood pressure (BP) (Reliable,
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005 1 Any adult in the health care system 2 Obtain blood pressure (BP) (Reliable,
Application of the Diabetes Algorithm to a Patient
 Application of the Diabetes Algorithm to a Patient Apply knowledge gained from this activity to improve disease management and outcomes for patients with T2DM and obesity Note: The cases in this deck represent
Application of the Diabetes Algorithm to a Patient Apply knowledge gained from this activity to improve disease management and outcomes for patients with T2DM and obesity Note: The cases in this deck represent
Diabetes in the Elderly 1, 2, 3
 Diabetes in the Elderly 1, 2, 3 WF Mollentze Feb 2010 Diabetes in the elderly differs from diabetes in younger people Prevalence: o Diabetes increases with age affecting approximately 10% of people over
Diabetes in the Elderly 1, 2, 3 WF Mollentze Feb 2010 Diabetes in the elderly differs from diabetes in younger people Prevalence: o Diabetes increases with age affecting approximately 10% of people over
Diabetes and New Meds for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction. F. Dwight Chrisman, MD, FACC. Disclosures: BI Boehringer Ingelheim speaker
 Diabetes and New Meds for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction F. Dwight Chrisman, MD, FACC Disclosures: BI Boehringer Ingelheim speaker 1 Prevalence of DM DM state specific prevalence 2006 4%-6% 6-8% 8-10% 10-12%
Diabetes and New Meds for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction F. Dwight Chrisman, MD, FACC Disclosures: BI Boehringer Ingelheim speaker 1 Prevalence of DM DM state specific prevalence 2006 4%-6% 6-8% 8-10% 10-12%
