50mM D-Glucose. Percentage PI. L-Glucose
|
|
|
- Morgan Quinn
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Monica Dus, Minrong Ai, Greg S.B Suh. Taste-independent nutrient selection is mediated by a brain-specific Na+/solute cotransporter in Drosophila. Control + Phlorizin mm D-Glucose 1 2mM 1 L-Glucose Gr5a;Gr64a Gr64a poxnδm22-b5; SuperA158 poxnδm22-b5 S1. Preventing the prandial rise in hemolymph glycemia impairs the taste-independent nutrient selection. The food choice behaviors of different mutants were measured in the two-choice assay with 2mM +phlorizin versus mm D-glucose+phlorizin after 18 hours of food deprivation (right). The experiments without the addition of phlorizin to glucose were used as controls (left). Gr5a;Gr64a and poxnδm22-b5 mutants failed to discriminate between L- glucose+phlorizin and D-glucose+phlorizin, whereas others chose the more concentrated (sweeter). n=4. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni test confirmed that the addition of phlorizin to sugars has significant effects on food choice behavior, P<.1. Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn.3372
2 mm D-glucose 1 poxnδm22-b5; SuperA 158 poxnδm22-b5 dslc5a11 1 poxnδm22-b5, dslc5a11 1 2mM 1 S2. Food choice defect in poxnm22-b5; dslc5a11 1 mutants. The food choice behaviors of poxnm22-b5; dslc5a11 1 double mutants and controls (poxnm22- B5;SuperA158, poxnm22-b5, and dslc5a11 1 ) were measured in the two-choice assay with 2mM L- glucose versus mm D-glucose after 18 hours of starvation. n=4-7. Asterisk, P<.1 (One-way ANOVA, Tukey test). Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn.3372
3 normalized mrna levels 1 dslc5a11 1 dslc5a11 2 S3. dslc5a11 mutants show a decrease in the dslc5a11 transcript levels. Measurement of the dslc5a11 mrna transcripts in the brains of WT (), dslc5a11 1 and dslc5a11 2 mutant alleles by qpcr. The dslc5a11 transcript levels in the mutants were normalized to those in controls and the relative abundance was calculated with respect to GAPDH. n=4. Asterisk, P<.1 (One-way ANOVA, Tukey test). Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn.3372
4 8 mm 1 D-galactose dslc5a11 1 ns 2mM 1 Filled- 5h Unfilled - 18h S4. Failure of dslc5a11 1 to select D-galactose upon starvation. The food choice behaviors of dslc5a11 1 mutant and control were measured in the two choice assay with 8mM D-galactose versus 2mM. n=4. Asterisks, P<.1 (One-way ANOVA, Tukey test). Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn.3372
5 Ratio (fed / starved) Starved Glucose Sorbitol Trehalose Galactose S5. The prandial rise in hemolymph glycemia upon feeding different sugars Measurements of the hemolymph sugar levels of flies that were starved for 18 hours and then fed with the indicated sugars were conducted 9 minutes after sugar feeding. n=5-11. Asterisk, P<.1 (One-way ANOVA, Tukey test with respect to starved flies). Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn.3372
6 a mg/ml (glucose+trehalose) dslc5a11 1 dslc5a11 1 /Def1 dslc5a11 1 /Def2 dslc5a11 1 revertant Sated Starved b 2. dslc5a dslc5a11 1 /Def1 dslc5a11 1 /Def2 dslc5a11 1 revertant glycogen/protein Sated Starved S6. dslc5a11 mutants have normal hemolymph glycemia and glycogen stores. (a) Measurements of the hemolymph glycemia and (b) the glycogen stores of sated and starved dslc5a11 mutants or controls were determined according to standard protocols (see Methods). The sated and starved flies were food-deprived for 5 and 18 hours. n=9-16. Twoway ANOVA with Bonferroni test indicates that there is no significant difference in hemolymph glycemia and glycogen levels between dslc5a11 mutant and control flies in sated or starved state. Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn.3372
7 a b a Intact b mm 1 D-glucose Control Antennae, palps ablation Antennae, palps ablation mm 1 D-Glucose PI % Percentage - a PI b 2mM -1 L-Glucose 2mM 1 Gr5a;Gr64a mm 1 D-Glucose cc d Control Antennae, palps ablation dslc111 Gr5a;Gr64a dslc5a111 d PI % Control Pprospero-GAL4 mm 1 D-Glucose - PI % 2mM -1 L-Glucose - Fore ec 2mM -1 L-Glucose Middle f d dslc111 Gr5a;Gr64a Hind UAS-dSLC5A11 RNAi Pprospero-GAL4: UAS-dSLC5A11 RNAi mm D-glucose1 Control Pprospero-GAL4 mm 1 D-Glucose 2mM 1 mm PI % D-glucose1-2mM -1 L-Glucose Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn mM 1 dslc5a111, UAS-dSLC5A11 dslc5a111, Pprospero-GAL4:UAS-dSLC5A11
8 S7. The expression of dslc5a11 outside the brain is not required for taste-independent nutrient selection. (a) Z-stack image of the antenna of a fly carrying P dslc5a11 -GAL4 and UAS-CD8GFP, visualized by native GFP fluorescence in green. Scale bar: 2m. (b) The food choice behaviors of, Gr5a;Gr64a and dslc5a11 1 flies with or without olfactory appendages (antennae and maxillary palps) were examined in the two-choice assay with 2mM versus mm D-glucose. n=4. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni test indicates that there is no significant difference between the indicated genotypes with and without olfactory appendages for food choice behavior. (c-d) The labellum (c) and tarsi (d) of a fly carrying P dslc5a11 -GAL4 and UAS-mCD8GFP visualized by TO-PRO (DNA labeling) in gray and native GFP fluorescence in green. These z-stack (c) and single representative (d) images were compared to those of Gr5a-GAL4;UAS-GFP (insets), which labels a subset of gustatory sensory neurons (arrowheads). Scale bar: (c) m and (d) 1m. (e) The image of a portion of the anterior midgut of a fly carrying P dslc5a11 -GAL4 and UAS-GFP, visualized by anti-prospero in magenta (white arrowheads), anti-gfp in green (yellow arrowheads) and TO-PRO (DNA) in blue. The co-labeling of prospero and GFP in a cell was illustrated in the inset. Thus, P dslc5a11 -GAL4 is expressed in a subset of Prospero+ enteroendocrine cells in the gut. Scale bar: 2m. (f) Top, the food choice behaviors of flies in which two independent UAS-dSLC5A11 RNAi lines (filled and unfilled) were expressed in enteroendocrine cells by P prospero -GAL4 were determined in the two-choice assay with 2mM versus mm D- glucose after 18 hours of starvation. Flies carrying UAS-dSLC5A11 RNAi lines without a driver were used as controls. n=4. ANOVA with Tukey test indicates that there is no significant difference between flies with knock-down of dslc5a11 and controls for food choice behavior. Bottom, the food choice behaviors of dslc5a11 1 mutants expressing UAS-dSLC5A11 in enteroendocrine cells by P prospero - GAL4 were determined in the two-choice assay after 18 hours of starvation. dslc5a11 1 mutants carrying UAS-dSLC5A11 alone were used as controls. n=5. One-way ANOVA with Tukey test showed there is no significant difference between control and dslc5a11 mutants with UAS-dSLC5A11 expression in the enteroendocrine cells. Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn.3372
9 a mm 1 D-glucose P dslc5a11 R4 R1/R4 R3/R4 R1 R3 Pros 2mM 1 RT b mm 1 D-glucose P dslc5a11 R4 R1/R4 R3/R4 R1 R3 Pros 2mM 1 29 C S8. Transgenic flies carrying GAL4 alone do not have defects in food choice behavior. The food choice behaviors of flies carrying GAL4 transgenes alone at RT (a) or 29 C (b) were measured in the two-choice assay after 18 hours of starvation. n=3-4. Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn.3372
10 Light Dark mm 1 D-glucose 2mM 1 Gr64a Gr5a;Gr64a S9. Vision is not required for taste-independent food selection in WT or sugar-blind flies. The food choice behaviors of sugar-blind Gr5a;Gr64a, Gr64a, and flies in the light (left) and in the dark (right) were measured in the two-choice assay with 2mM versus mm D-glucose after 18 hours of starvation. The sugar-blind flies had no defect in the selection of D-glucose in the absence of any visual cues. n=4. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni test indicates that there is no significant difference between flies tested in the dark and in the light for appropriate food selection. Nature Neuroscience: doi:1.138/nn.3372
Supplementary Figure 1. Flies form water-reward memory only in the thirsty state
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supplementary Figure 1. Flies form water-reward memory only in the thirsty state Thirsty but not sated wild-type flies form robust 3 min memory. For the thirsty group, the flies were water-deprived
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supplementary Figure 1. Flies form water-reward memory only in the thirsty state Thirsty but not sated wild-type flies form robust 3 min memory. For the thirsty group, the flies were water-deprived
Supplementary Figure 1. Procedures to independently control fly hunger and thirst states.
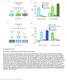 Supplementary Figure 1 Procedures to independently control fly hunger and thirst states. (a) Protocol to produce exclusively hungry or thirsty flies for 6 h water memory retrieval. (b) Consumption assays
Supplementary Figure 1 Procedures to independently control fly hunger and thirst states. (a) Protocol to produce exclusively hungry or thirsty flies for 6 h water memory retrieval. (b) Consumption assays
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary s Supplementary 1 All three types of foods suppress subsequent feeding in both sexes when the same food is used in the pre-feeding test feeding. (a) Adjusted pre-feeding
Supplementary Information Supplementary s Supplementary 1 All three types of foods suppress subsequent feeding in both sexes when the same food is used in the pre-feeding test feeding. (a) Adjusted pre-feeding
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fig. S1. Overexpression of Rpr causes progenitor cell death. (A) TUNEL assay of control intestines. No progenitor cell death could be observed, except that some ECs are undergoing
Supporting Information Fig. S1. Overexpression of Rpr causes progenitor cell death. (A) TUNEL assay of control intestines. No progenitor cell death could be observed, except that some ECs are undergoing
marker. DAPI labels nuclei. Flies were 20 days old. Scale bar is 5 µm. Ctrl is
 Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Nos is detected in glial cells in both control and GFAP R79H transgenic flies (arrows), but not in deletion mutant Nos Δ15 animals. Repo is a glial cell marker. DAPI labels
Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Nos is detected in glial cells in both control and GFAP R79H transgenic flies (arrows), but not in deletion mutant Nos Δ15 animals. Repo is a glial cell marker. DAPI labels
Supplementary Figures
 J. Cell Sci. 128: doi:10.1242/jcs.173807: Supplementary Material Supplementary Figures Fig. S1 Fig. S1. Description and/or validation of reagents used. All panels show Drosophila tissues oriented with
J. Cell Sci. 128: doi:10.1242/jcs.173807: Supplementary Material Supplementary Figures Fig. S1 Fig. S1. Description and/or validation of reagents used. All panels show Drosophila tissues oriented with
Supplementary Fig. 1 V-ATPase depletion induces unique and robust phenotype in Drosophila fat body cells.
 Supplementary Fig. 1 V-ATPase depletion induces unique and robust phenotype in Drosophila fat body cells. a. Schematic of the V-ATPase proton pump macro-complex structure. The V1 complex is composed of
Supplementary Fig. 1 V-ATPase depletion induces unique and robust phenotype in Drosophila fat body cells. a. Schematic of the V-ATPase proton pump macro-complex structure. The V1 complex is composed of
Drosophila DPM Neurons Form a Delayed and Branch-Specific Memory Trace after Olfactory Classical Conditioning
 Drosophila DPM Neurons Form a Delayed and Branch-Specific Memory Trace after Olfactory Classical Conditioning Dinghui Yu, 1 Alex C. Keene, 4 Anjana Srivatsan, 2 Scott Waddell, 4 and Ronald L. Davis 1,3,
Drosophila DPM Neurons Form a Delayed and Branch-Specific Memory Trace after Olfactory Classical Conditioning Dinghui Yu, 1 Alex C. Keene, 4 Anjana Srivatsan, 2 Scott Waddell, 4 and Ronald L. Davis 1,3,
100 mm Sucrose. +Berberine +Quinine
 8 mm Sucrose Probability (%) 7 6 5 4 3 Wild-type Gr32a / 2 +Caffeine +Berberine +Quinine +Denatonium Supplementary Figure 1: Detection of sucrose and bitter compounds is not affected in Gr32a / flies.
8 mm Sucrose Probability (%) 7 6 5 4 3 Wild-type Gr32a / 2 +Caffeine +Berberine +Quinine +Denatonium Supplementary Figure 1: Detection of sucrose and bitter compounds is not affected in Gr32a / flies.
A quantitative feeding assay in adult Drosophila reveals rapid modulation of food ingestion by its nutritional value
 Qi et al. Molecular Brain (215) 8:87 DOI 1.1186/s1341-15-179-x METHODOLOGY A quantitative feeding assay in adult Drosophila reveals rapid modulation of food ingestion by its nutritional value Wei Qi 1,2,
Qi et al. Molecular Brain (215) 8:87 DOI 1.1186/s1341-15-179-x METHODOLOGY A quantitative feeding assay in adult Drosophila reveals rapid modulation of food ingestion by its nutritional value Wei Qi 1,2,
Midgut-Derived Activin Regulates Glucagon-like Action in the Fat Body and Glycemic Control
 Article Midgut-Derived Activin Regulates Glucagon-like Action in the Fat Body and Glycemic Control Graphical Abstract Authors Wei Song, Daojun Cheng, Shangyu Hong,..., Michael B. O Connor, Pavlos Pissios,
Article Midgut-Derived Activin Regulates Glucagon-like Action in the Fat Body and Glycemic Control Graphical Abstract Authors Wei Song, Daojun Cheng, Shangyu Hong,..., Michael B. O Connor, Pavlos Pissios,
Concentration memory-dependent synaptic plasticity of a taste circuit regulates salt chemotaxis in Caenorhabditis elegans
 Supplementary Information for: Concentration memory-dependent synaptic plasticity of a taste circuit regulates salt chemotaxis in Caenorhabditis elegans Hirofumi Kunitomo, Hirofumi Sato, Ryo Iwata, Yohsuke
Supplementary Information for: Concentration memory-dependent synaptic plasticity of a taste circuit regulates salt chemotaxis in Caenorhabditis elegans Hirofumi Kunitomo, Hirofumi Sato, Ryo Iwata, Yohsuke
Regulation of sleep plasticity by a thermo-sensitive circuit in Drosophila
 Regulation of sleep plasticity by a thermo-sensitive circuit in Drosophila Angelique Lamaze 1, Arzu Öztürk-Çolak 2, Robin Fischer 3, Nicolai Peschel 3, Kyunghee Koh 2 and James E.C. Jepson 1* 1 UCL Institute
Regulation of sleep plasticity by a thermo-sensitive circuit in Drosophila Angelique Lamaze 1, Arzu Öztürk-Çolak 2, Robin Fischer 3, Nicolai Peschel 3, Kyunghee Koh 2 and James E.C. Jepson 1* 1 UCL Institute
Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation.
 ` Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation. (a) Overexpression of hlrrk2 in HeLa cells enhances total protein synthesis in [35S] methionine/cysteine incorporation assays.
` Supplementary Figure 1 hlrrk2 promotes CAP dependent protein translation. (a) Overexpression of hlrrk2 in HeLa cells enhances total protein synthesis in [35S] methionine/cysteine incorporation assays.
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of escargot (esg) and genetic approach for achieving IPC-specific knockdown. (a) esg MH766 -Gal4 UAS-cd8GFP (green) and esg-lacz B7-2-22 (red) show similar expression
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of escargot (esg) and genetic approach for achieving IPC-specific knockdown. (a) esg MH766 -Gal4 UAS-cd8GFP (green) and esg-lacz B7-2-22 (red) show similar expression
Supplemental Information. Proprioceptive Opsin Functions. in Drosophila Larval Locomotion
 Neuron, Volume 98 Supplemental Information Proprioceptive Opsin Functions in Drosophila Larval Locomotion Damiano Zanini, Diego Giraldo, Ben Warren, Radoslaw Katana, Marta Andrés, Suneel Reddy, Stephanie
Neuron, Volume 98 Supplemental Information Proprioceptive Opsin Functions in Drosophila Larval Locomotion Damiano Zanini, Diego Giraldo, Ben Warren, Radoslaw Katana, Marta Andrés, Suneel Reddy, Stephanie
A post-ingestive amino acid sensor promotes food consumption in Drosophila
 www.nature.com/cr www.cell-research.com ARTICLE OPEN A post-ingestive amino acid sensor promotes food consumption in Drosophila Zhe Yang 1,2, Rui Huang 3,4, Xin Fu 5,6,7, Gaohang Wang 1,2, Wei Qi 1,2,
www.nature.com/cr www.cell-research.com ARTICLE OPEN A post-ingestive amino acid sensor promotes food consumption in Drosophila Zhe Yang 1,2, Rui Huang 3,4, Xin Fu 5,6,7, Gaohang Wang 1,2, Wei Qi 1,2,
effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of ε j2b10 show no
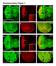 Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
A Drosophila model for alcohol reward. Supplemental Material
 Kaun et al. Supplemental Material 1 A Drosophila model for alcohol reward Supplemental Material Kaun, K.R. *, Azanchi, R. *, Maung, Z. *, Hirsh, J. and Heberlein, U. * * Department of Anatomy, University
Kaun et al. Supplemental Material 1 A Drosophila model for alcohol reward Supplemental Material Kaun, K.R. *, Azanchi, R. *, Maung, Z. *, Hirsh, J. and Heberlein, U. * * Department of Anatomy, University
PEER REVIEW FILE. Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 PEER REVIEW FILE Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): In this manuscript entitled "Neural circuits for long-term water-reward memory processing in thirsty Drosophila", the authors
PEER REVIEW FILE Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): In this manuscript entitled "Neural circuits for long-term water-reward memory processing in thirsty Drosophila", the authors
Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed
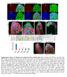 Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed in the testes. The testes were immunostained with GFP
Supplementary Figure 1 Madm is not required in GSCs and hub cells. (a,b) Act-Gal4-UAS-GFP (a), Act-Gal4-UAS- GFP.nls (b,c) is ubiquitously expressed in the testes. The testes were immunostained with GFP
Secondary Taste Neurons that Convey Sweet Taste and Starvation in the Drosophila Brain
 Article Secondary Taste Neurons that Convey Sweet Taste and Starvation in the Drosophila Brain Highlights d d d d Gustatory projection neurons (sgpns) are involved in sweet taste behaviors sgpn dendrites
Article Secondary Taste Neurons that Convey Sweet Taste and Starvation in the Drosophila Brain Highlights d d d d Gustatory projection neurons (sgpns) are involved in sweet taste behaviors sgpn dendrites
Sensory Integration Regulating Male Courtship Behavior in Drosophila
 Sensory Integration Regulating Male Courtship Behavior in Drosophila Dimitrije Krstic 1,2, Werner Boll 1, Markus Noll 1 * 1 Institute for Molecular Biology, University of Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland, 2
Sensory Integration Regulating Male Courtship Behavior in Drosophila Dimitrije Krstic 1,2, Werner Boll 1, Markus Noll 1 * 1 Institute for Molecular Biology, University of Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland, 2
Drosophila HNF4 Directs a Switch in Lipid Metabolism that Supports the Transition to Adulthood
 Article Drosophila HNF4 Directs a Switch in Lipid Metabolism that Supports the Transition to Adulthood Graphical Abstract Authors Gilles Storelli, Hyuck-Jin Nam, Judith Simcox, Claudio J. Villanueva, Carl
Article Drosophila HNF4 Directs a Switch in Lipid Metabolism that Supports the Transition to Adulthood Graphical Abstract Authors Gilles Storelli, Hyuck-Jin Nam, Judith Simcox, Claudio J. Villanueva, Carl
Joseph et al. Oviposition preference for and positional avoidance of acetic acid: A model for competing behavioral drives in Drosophila melanogaster
 Oviposition preference for and positional avoidance of acetic acid: A model for competing behavioral drives in Drosophila melanogaster Ryan Joseph 2, Anita Devineni 3, Ian King 1, and Ulrike Heberlein
Oviposition preference for and positional avoidance of acetic acid: A model for competing behavioral drives in Drosophila melanogaster Ryan Joseph 2, Anita Devineni 3, Ian King 1, and Ulrike Heberlein
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites.
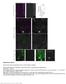 Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Diabetic pdx1-mutant zebrafish show conserved responses to nutrient overload and anti-glycemic treatment
 Supplementary Information Diabetic pdx1-mutant zebrafish show conserved responses to nutrient overload and anti-glycemic treatment Robin A. Kimmel, Stefan Dobler, Nicole Schmitner, Tanja Walsen, Julia
Supplementary Information Diabetic pdx1-mutant zebrafish show conserved responses to nutrient overload and anti-glycemic treatment Robin A. Kimmel, Stefan Dobler, Nicole Schmitner, Tanja Walsen, Julia
Two Gr Genes Underlie Sugar Reception in Drosophila
 Article Two Gr Genes Underlie Sugar Reception in Drosophila Anupama Dahanukar, 1 Ya-Ting Lei, 1 Jae Young Kwon, 1 and John R. Carlson 1, * 1 Department of Molecular, Cellular and Developmental Biology,
Article Two Gr Genes Underlie Sugar Reception in Drosophila Anupama Dahanukar, 1 Ya-Ting Lei, 1 Jae Young Kwon, 1 and John R. Carlson 1, * 1 Department of Molecular, Cellular and Developmental Biology,
GFP/Iba1/GFAP. Brain. Liver. Kidney. Lung. Hoechst/Iba1/TLR9!
 Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Head of College Scholars List Scheme. Summer Studentship Report Form
 Head of College Scholars List Scheme Summer Studentship 2019 Report Form This report should be completed by the student with his/her project supervisor. It should summarise the work undertaken during the
Head of College Scholars List Scheme Summer Studentship 2019 Report Form This report should be completed by the student with his/her project supervisor. It should summarise the work undertaken during the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Glucosylceramide synthase (GlcT-1) in the fat body controls energy metabolism in Drosophila
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Glucosylceramide synthase (GlcT-1) in the fat body controls energy metabolism in Drosophila Ayako Kohyama-Koganeya, 1,2 Takuji Nabetani, 1 Masayuki Miura, 2,3 Yoshio Hirabayashi
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Glucosylceramide synthase (GlcT-1) in the fat body controls energy metabolism in Drosophila Ayako Kohyama-Koganeya, 1,2 Takuji Nabetani, 1 Masayuki Miura, 2,3 Yoshio Hirabayashi
RNA-interference knockdown of Drosophila pigment dispersing factor in neuronal subsets: The anatomical basis of a neuropeptide s circadian functions
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2009 RNA-interference knockdown of Drosophila pigment dispersing factor in neuronal subsets: The anatomical basis
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2009 RNA-interference knockdown of Drosophila pigment dispersing factor in neuronal subsets: The anatomical basis
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
The Drosophila melanogaster life cycle
 The Drosophila melanogaster life cycle Eclosion The first phenotype described in Drosophila as an endogenous rhythm (1954): Number of eclosed flies Hamblen et al., Gene3cs 1998 rhythm with a periodicity
The Drosophila melanogaster life cycle Eclosion The first phenotype described in Drosophila as an endogenous rhythm (1954): Number of eclosed flies Hamblen et al., Gene3cs 1998 rhythm with a periodicity
Delayed Dopamine Signaling of Energy Level Builds Appetitive Long-Term Memory in Drosophila
 Report Delayed Dopamine Signaling of Energy Level Builds Appetitive Long-Term Memory in Drosophila Graphical Abstract Authors Pierre-Yves Musso, Paul Tchenio, Thomas Preat Correspondence paul.tchenio@espci.fr
Report Delayed Dopamine Signaling of Energy Level Builds Appetitive Long-Term Memory in Drosophila Graphical Abstract Authors Pierre-Yves Musso, Paul Tchenio, Thomas Preat Correspondence paul.tchenio@espci.fr
doi: /nature09554
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09554 Supplementary Figure 1: Optical Tracing with New Photoactivatable GFP Variants Reveals Enhanced Labeling of Neuronal Processes We qualitatively compare
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09554 Supplementary Figure 1: Optical Tracing with New Photoactivatable GFP Variants Reveals Enhanced Labeling of Neuronal Processes We qualitatively compare
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of Per2 deletion in neuronal cells in N Per2 -/- mice. (a) Western blot from liver extracts of mice held under ad
 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of Per2 deletion in neuronal cells in N Per2 -/- mice. (a) Western blot from liver extracts of mice held under ad libitum conditions detecting PER2 protein in brain and
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of Per2 deletion in neuronal cells in N Per2 -/- mice. (a) Western blot from liver extracts of mice held under ad libitum conditions detecting PER2 protein in brain and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature07173 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure Legends: Supplementary Figure 1: Model of SSC and CPC divisions a, Somatic stem cells (SSC) reside adjacent to the hub (red), self-renew
doi: 10.1038/nature07173 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure Legends: Supplementary Figure 1: Model of SSC and CPC divisions a, Somatic stem cells (SSC) reside adjacent to the hub (red), self-renew
Neural circuits for long-term water-reward memory processing in thirsty Drosophila
 Received 2 Jun 216 Accepted 3 Mar 217 Published 15 May 217 DOI: 1.138/ncomms1523 OPEN Neural circuits for long-term water-reward processing in thirsty Drosophila Wei-Huan Shyu 1, Tai-Hsiang Chiu 1, Meng-Hsuan
Received 2 Jun 216 Accepted 3 Mar 217 Published 15 May 217 DOI: 1.138/ncomms1523 OPEN Neural circuits for long-term water-reward processing in thirsty Drosophila Wei-Huan Shyu 1, Tai-Hsiang Chiu 1, Meng-Hsuan
A Neuronal Relay Mediates a Nutrient Responsive Gut/Fat Body Axis Regulating Energy Homeostasis in Adult Drosophila
 Article A Neuronal Relay Mediates a Nutrient Responsive Gut/Fat Body Axis Regulating Energy Homeostasis in Adult Drosophila Graphical Abstract Authors Alessandro Scopelliti, Christin Bauer, Yachuan Yu,...,
Article A Neuronal Relay Mediates a Nutrient Responsive Gut/Fat Body Axis Regulating Energy Homeostasis in Adult Drosophila Graphical Abstract Authors Alessandro Scopelliti, Christin Bauer, Yachuan Yu,...,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10643 Supplementary Table 1. Identification of hecw-1 coding polymorphisms at amino acid positions 322 and 325 in 162 strains of C. elegans. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 Supplementary Figure
doi:10.1038/nature10643 Supplementary Table 1. Identification of hecw-1 coding polymorphisms at amino acid positions 322 and 325 in 162 strains of C. elegans. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 Supplementary Figure
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3311 A B TSC2 -/- MEFs C Rapa Hours WCL 0 6 12 24 36 pakt.s473 AKT ps6k S6K CM IGF-1 Recipient WCL - + - + - + pigf-1r IGF-1R pakt ps6 AKT D 1 st SILAC 2 nd SILAC E GAPDH FGF21 ALKPGVIQILGVK
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3311 A B TSC2 -/- MEFs C Rapa Hours WCL 0 6 12 24 36 pakt.s473 AKT ps6k S6K CM IGF-1 Recipient WCL - + - + - + pigf-1r IGF-1R pakt ps6 AKT D 1 st SILAC 2 nd SILAC E GAPDH FGF21 ALKPGVIQILGVK
Supplemental Information. Memory-Relevant Mushroom Body. Output Synapses Are Cholinergic
 Neuron, Volume 89 Supplemental Information Memory-Relevant Mushroom Body Output Synapses Are Cholinergic Oliver Barnstedt, David Owald, Johannes Felsenberg, Ruth Brain, John-Paul Moszynski, Clifford B.
Neuron, Volume 89 Supplemental Information Memory-Relevant Mushroom Body Output Synapses Are Cholinergic Oliver Barnstedt, David Owald, Johannes Felsenberg, Ruth Brain, John-Paul Moszynski, Clifford B.
Soluble ADAM33 initiates airway remodeling to promote susceptibility for. Elizabeth R. Davies, Joanne F.C. Kelly, Peter H. Howarth, David I Wilson,
 Revised Suppl. Data: Soluble ADAM33 1 Soluble ADAM33 initiates airway remodeling to promote susceptibility for allergic asthma in early life Elizabeth R. Davies, Joanne F.C. Kelly, Peter H. Howarth, David
Revised Suppl. Data: Soluble ADAM33 1 Soluble ADAM33 initiates airway remodeling to promote susceptibility for allergic asthma in early life Elizabeth R. Davies, Joanne F.C. Kelly, Peter H. Howarth, David
Why am I working in a Drosophila lab? Dr. Stefan Pulver, Brandeis University
 Why am I working in a Drosophila lab? Dr. Stefan Pulver, Brandeis University !Short life span The advantages of Drosophila as a model organism in neurocience!genetic manipulations are relatively easy!forward
Why am I working in a Drosophila lab? Dr. Stefan Pulver, Brandeis University !Short life span The advantages of Drosophila as a model organism in neurocience!genetic manipulations are relatively easy!forward
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2988 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif7 L130P encodes a stable protein that does not localize to cilia tips. (a) Immunoblot with KIF7 antibody in cell lysates of wild-type, Kif7 L130P and Kif7
Table S1. Gal4 Driver Lines in This Study, Related to Figures 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, and S6
 Table S1. Gal4 Driver Lines in This Study, Related to s 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, and S6 Genotype Abbreviation Expression patterns Ubi-Gal4 Ubi Ubiquitous dome-gal4;elav-gal80 dome MZ Progenitor-specific
Table S1. Gal4 Driver Lines in This Study, Related to s 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, and S6 Genotype Abbreviation Expression patterns Ubi-Gal4 Ubi Ubiquitous dome-gal4;elav-gal80 dome MZ Progenitor-specific
Neural clocks and Neuropeptide F/Y regulate circadian gene expression in a peripheral metabolic tissue
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Neural clocks and Neuropeptide F/Y regulate circadian gene expression in a peripheral metabolic tissue Renske Erion 1, Anna N King 1, Gang Wu 2, John B Hogenesch 3, Amita Sehgal 1 * 1
RESEARCH ARTICLE Neural clocks and Neuropeptide F/Y regulate circadian gene expression in a peripheral metabolic tissue Renske Erion 1, Anna N King 1, Gang Wu 2, John B Hogenesch 3, Amita Sehgal 1 * 1
Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function
 ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENTS Santulli G. et al. A microrna-based strategy to suppress restenosis while preserving endothelial function Supplementary Figures Figure S1 Effect of Ad-p27-126TS on the expression
Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 )
 770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
islets scored 1 week month months
 Supplementary Table 1. Sampling parameters for the morphometrical analyses Time (post- DT) Control mice (age-matched) α-cells mice pancreatic surface (mm 2 ) scored DT-treated mice islets scored mice pancreatic
Supplementary Table 1. Sampling parameters for the morphometrical analyses Time (post- DT) Control mice (age-matched) α-cells mice pancreatic surface (mm 2 ) scored DT-treated mice islets scored mice pancreatic
A Pair of Dopamine Neurons Target the D1-Like Dopamine Receptor DopR in the Central Complex to Promote Ethanol-Stimulated Locomotion in Drosophila
 A Pair of Dopamine Neurons Target the D1-Like Dopamine Receptor DopR in the Central Complex to Promote Ethanol-Stimulated Locomotion in Drosophila Eric C. Kong 1, Katherine Woo 2, Haiyan Li 3, Tim Lebestky
A Pair of Dopamine Neurons Target the D1-Like Dopamine Receptor DopR in the Central Complex to Promote Ethanol-Stimulated Locomotion in Drosophila Eric C. Kong 1, Katherine Woo 2, Haiyan Li 3, Tim Lebestky
Ensheathing Glia Function as Phagocytes in the Adult Drosophila Brain
 4768 The Journal of Neuroscience, April 15, 2009 29(15):4768 4781 Cellular/Molecular Ensheathing Glia Function as Phagocytes in the Adult Drosophila Brain Johnna Doherty,* Mary A. Logan,* Özge E. Taşdemir,
4768 The Journal of Neuroscience, April 15, 2009 29(15):4768 4781 Cellular/Molecular Ensheathing Glia Function as Phagocytes in the Adult Drosophila Brain Johnna Doherty,* Mary A. Logan,* Özge E. Taşdemir,
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT ACTB AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT LCOR
 Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Ras V12 expression in the entire eye-antennal disc does not cause invasive tumours. a, Eye-antennal discs expressing Ras V12 in all cells (marked with GFP, green) overgrow moderately
Supplementary Figure 1. Ras V12 expression in the entire eye-antennal disc does not cause invasive tumours. a, Eye-antennal discs expressing Ras V12 in all cells (marked with GFP, green) overgrow moderately
Supplemental Information. Figures. Figure S1
 Supplemental Information Figures Figure S1 Identification of JAGGER T-DNA insertions. A. Positions of T-DNA and Ds insertions in JAGGER are indicated by inverted triangles, the grey box represents the
Supplemental Information Figures Figure S1 Identification of JAGGER T-DNA insertions. A. Positions of T-DNA and Ds insertions in JAGGER are indicated by inverted triangles, the grey box represents the
Ghrelin Facilitates GLUT2-, SGLT1- and SGLT2-mediated Intestinal. Glucose Transport in Goldfish (Carassius auratus)
 Ghrelin Facilitates GLUT2-, SGLT1- and SGLT2-mediated Intestinal Glucose Transport in Goldfish (Carassius auratus) Ayelén Melisa Blanco 1,2, Juan Ignacio Bertucci 2,3, Naresh Ramesh 2, María Jesús Delgado
Ghrelin Facilitates GLUT2-, SGLT1- and SGLT2-mediated Intestinal Glucose Transport in Goldfish (Carassius auratus) Ayelén Melisa Blanco 1,2, Juan Ignacio Bertucci 2,3, Naresh Ramesh 2, María Jesús Delgado
Functional studies of Drosophila zinc transporters reveal the mechanism for dietary zinc absorption and regulation
 Qin et al. BMC Biology 2013, 11:101 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Functional studies of Drosophila zinc transporters reveal the mechanism for dietary zinc absorption and regulation Qiuhong Qin, Xiaoxi Wang
Qin et al. BMC Biology 2013, 11:101 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Functional studies of Drosophila zinc transporters reveal the mechanism for dietary zinc absorption and regulation Qiuhong Qin, Xiaoxi Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
Drosophila Cytokine Unpaired 2 Regulates Physiological Homeostasis by Remotely Controlling Insulin Secretion
 Drosophila Cytokine Unpaired 2 Regulates Physiological Homeostasis by Remotely Controlling Insulin Secretion Akhila Rajan 1, * and Norbert Perrimon 1,2, * 1 Department of Genetics 2 Howard Hughes Medical
Drosophila Cytokine Unpaired 2 Regulates Physiological Homeostasis by Remotely Controlling Insulin Secretion Akhila Rajan 1, * and Norbert Perrimon 1,2, * 1 Department of Genetics 2 Howard Hughes Medical
SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences. Identification of neurons responsible for feeding behavior in the Drosophila brain
 SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences THEMATIC ISSUE: From brain function to therapy April 2014 Vol.57 No.4: 391 402 RESEARCH PAPER doi: 10.1007/s11427-014-4641-2 Identification of neurons responsible for feeding
SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences THEMATIC ISSUE: From brain function to therapy April 2014 Vol.57 No.4: 391 402 RESEARCH PAPER doi: 10.1007/s11427-014-4641-2 Identification of neurons responsible for feeding
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Figure S1. (A) Schematic diagram of dnrar transgene allele. (B) X-Gal staining of testis from
 Figure S1. (A) Schematic diagram of dnrar transgene allele. (B) X-Gal staining of testis from germ cell mutants (dnrar flox/flox, Stra8-Cre +, RARElacZ) (A ), controls (dnrar flox/flox, RARElacZ) (B ),
Figure S1. (A) Schematic diagram of dnrar transgene allele. (B) X-Gal staining of testis from germ cell mutants (dnrar flox/flox, Stra8-Cre +, RARElacZ) (A ), controls (dnrar flox/flox, RARElacZ) (B ),
Title: Epigenetic mechanisms underlying maternal diabetes-associated risk of congenital heart disease
 1 Supplemental Materials 2 3 Title: Epigenetic mechanisms underlying maternal diabetes-associated risk of congenital heart disease 4 5 6 Authors: Madhumita Basu, 1 Jun-Yi Zhu, 2 Stephanie LaHaye 1,3, Uddalak
1 Supplemental Materials 2 3 Title: Epigenetic mechanisms underlying maternal diabetes-associated risk of congenital heart disease 4 5 6 Authors: Madhumita Basu, 1 Jun-Yi Zhu, 2 Stephanie LaHaye 1,3, Uddalak
Isoform-Specific Control of Male Neuronal Differentiation and Behavior in Drosophila by the fruitless Gene
 Current Biology 16, 1063 1076, June 6, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2006.04.039 Isoform-Specific Control of Male Neuronal Differentiation and Behavior in Drosophila by
Current Biology 16, 1063 1076, June 6, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2006.04.039 Isoform-Specific Control of Male Neuronal Differentiation and Behavior in Drosophila by
Control of Metabolic Homeostasis by Stress Signaling Is Mediated by the Lipocalin NLaz
 Control of Metabolic Homeostasis by Stress Signaling Is Mediated by the Lipocalin NLaz Julie Hull-Thompson 1., Julien Muffat 2., Diego Sanchez 3, David W. Walker 2, Seymour Benzer 2, Maria D. Ganfornina
Control of Metabolic Homeostasis by Stress Signaling Is Mediated by the Lipocalin NLaz Julie Hull-Thompson 1., Julien Muffat 2., Diego Sanchez 3, David W. Walker 2, Seymour Benzer 2, Maria D. Ganfornina
Lmo Mutants Reveal a Novel Role for Circadian Pacemaker Neurons in Cocaine-Induced Behaviors
 Lmo Mutants Reveal a Novel Role for Circadian Pacemaker Neurons in Cocaine-Induced Behaviors Linus T.-Y. Tsai 1, Roland J. Bainton 2, Justin Blau 3, Ulrike Heberlein 4 * Open access, freely available online
Lmo Mutants Reveal a Novel Role for Circadian Pacemaker Neurons in Cocaine-Induced Behaviors Linus T.-Y. Tsai 1, Roland J. Bainton 2, Justin Blau 3, Ulrike Heberlein 4 * Open access, freely available online
Ahtiainen et al., http :// /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB Ahtiainen et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201512074 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Distinct distribution of different cell cycle phases in the
Supplemental material JCB Ahtiainen et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201512074 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Distinct distribution of different cell cycle phases in the
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Cold Spring Harbor, NY 11724
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0450 TITLE: The role of NF1 in memory retrieval PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yi Zhong, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Cold Spring Harbor, NY 11724
AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0450 TITLE: The role of NF1 in memory retrieval PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Yi Zhong, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Cold Spring Harbor, NY 11724
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2419 Figure S1 NiGFP localization in Dl mutant dividing SOPs. a-c) time-lapse analysis of NiGFP (green) in Dl mutant SOPs (H2B-RFP, red; clones were identified by the loss of nlsgfp) showing
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2419 Figure S1 NiGFP localization in Dl mutant dividing SOPs. a-c) time-lapse analysis of NiGFP (green) in Dl mutant SOPs (H2B-RFP, red; clones were identified by the loss of nlsgfp) showing
Capu and Spire Assemble a Cytoplasmic Actin Mesh
 Developmental Cell 13 Supplemental Data Capu and Spire Assemble a Cytoplasmic Actin Mesh that Maintains Microtubule Organization in the Drosophila Oocyte Katja Dahlgaard, Alexandre A.S.F. Raposo, Teresa
Developmental Cell 13 Supplemental Data Capu and Spire Assemble a Cytoplasmic Actin Mesh that Maintains Microtubule Organization in the Drosophila Oocyte Katja Dahlgaard, Alexandre A.S.F. Raposo, Teresa
Supplemental Information. Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate. Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation. through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway
 Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
8. Have the authors tested if the effects of expressing mir-92a are developmental or adult-specific?
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The manuscript from Chen and Rosbash identifies a specific microrna (mir -92a) that is rhythmically expressed in the master pacemaker clock neurons
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The manuscript from Chen and Rosbash identifies a specific microrna (mir -92a) that is rhythmically expressed in the master pacemaker clock neurons
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study
 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
The Drosophila Pox neuro gene: control of male courtship behavior and fertility as revealed by a complete dissection of all enhancers
 Development 129, 5667-5681 2002 The Company of Biologists Ltd doi:10.1242/dev.00157 5667 The Drosophila Pox neuro gene: control of male courtship behavior and fertility as revealed by a complete dissection
Development 129, 5667-5681 2002 The Company of Biologists Ltd doi:10.1242/dev.00157 5667 The Drosophila Pox neuro gene: control of male courtship behavior and fertility as revealed by a complete dissection
Octopamine Neuromodulatory Effects on a Social Behavior Decision- Making Network in Drosophila Males
 Octopamine Neuromodulatory Effects on a Social Behavior Decision- Making Network in Drosophila Males The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Octopamine Neuromodulatory Effects on a Social Behavior Decision- Making Network in Drosophila Males The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Old plants are more resistant to insect herbivores than young plants. (a) Image of young (1-day-old, 1D) and old (-day-old, D) plants of Arabidopsis
Supplementary Figures 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Old plants are more resistant to insect herbivores than young plants. (a) Image of young (1-day-old, 1D) and old (-day-old, D) plants of Arabidopsis
Identification of Sphingolipid Metabolites That Induce Obesity via Misregulation of Appetite, Caloric Intake and Fat Storage in Drosophila
 Identification of Sphingolipid Metabolites That Induce Obesity via Misregulation of Appetite, Caloric Intake and Fat Storage in Drosophila Stanley M. Walls, Jr 1, Steve J. Attle 1, Gregory B. Brulte 1,
Identification of Sphingolipid Metabolites That Induce Obesity via Misregulation of Appetite, Caloric Intake and Fat Storage in Drosophila Stanley M. Walls, Jr 1, Steve J. Attle 1, Gregory B. Brulte 1,
Supplemental Data. Deinlein et al. Plant Cell. (2012) /tpc
 µm Zn 2+ 15 µm Zn 2+ Growth (% of control) empty vector NS1 NS2 NS3 NS4 S. pombe zhfδ Supplemental Figure 1. Functional characterization of. halleri NS genes in Zn 2+ hypersensitive S. pombe Δzhf mutant
µm Zn 2+ 15 µm Zn 2+ Growth (% of control) empty vector NS1 NS2 NS3 NS4 S. pombe zhfδ Supplemental Figure 1. Functional characterization of. halleri NS genes in Zn 2+ hypersensitive S. pombe Δzhf mutant
Histone acetyltransferase CBP-related H3K23 acetylation contributes to courtship learning in Drosophila
 Li et al. BMC Developmental Biology (2018) 18:20 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12861-018-0179-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Histone acetyltransferase CBP-related H3K23 acetylation contributes to courtship
Li et al. BMC Developmental Biology (2018) 18:20 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12861-018-0179-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Histone acetyltransferase CBP-related H3K23 acetylation contributes to courtship
WKH$F02( (R539T( 957( 005( 24# 17# 32# 26# 30# 21# 21# 9# 14# 18# 9# 13# 21# 14# 14# 2# 42# 17#
 20 KH$C(( WT( WKH$F02( (R539T( WKH$F04( (Y493H( WKH$F03( C580Y( 18 027( 004( 010( 967( 005( 0.94 957( 0.96 887( 818$2( 0.98 829( 1.00 1.02 1.04 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 n 113 142 170 140 158 143 244 217 78
20 KH$C(( WT( WKH$F02( (R539T( WKH$F04( (Y493H( WKH$F03( C580Y( 18 027( 004( 010( 967( 005( 0.94 957( 0.96 887( 818$2( 0.98 829( 1.00 1.02 1.04 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 n 113 142 170 140 158 143 244 217 78
Report. Presynaptic Gain Control Drives Sweet and Bitter Taste Integration in Drosophila
 Current Biology 24, 1978 1984, September 8, 2014 ª2014 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved Presynaptic Gain Control Drives Sweet and Bitter Taste Integration in Drosophila http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2014.07.020
Current Biology 24, 1978 1984, September 8, 2014 ª2014 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved Presynaptic Gain Control Drives Sweet and Bitter Taste Integration in Drosophila http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2014.07.020
LABORATÓRIUMI GYAKORLAT SILLABUSZ SYLLABUS OF A PRACTICAL DEMOSTRATION. financed by the program
 TÁMOP-4.1.1.C-13/1/KONV-2014-0001 projekt Az élettudományi-klinikai felsőoktatás gyakorlatorientált és hallgatóbarát korszerűsítése a vidéki képzőhelyek nemzetközi versenyképességének erősítésére program
TÁMOP-4.1.1.C-13/1/KONV-2014-0001 projekt Az élettudományi-klinikai felsőoktatás gyakorlatorientált és hallgatóbarát korszerűsítése a vidéki képzőhelyek nemzetközi versenyképességének erősítésére program
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Central Brain Neurons Expressing doublesex Regulate Female Receptivity in Drosophila
 Article Central Brain Neurons Expressing doublesex Regulate Female Receptivity in Drosophila Chuan Zhou, 1 Yufeng Pan, 1 Carmen C. Robinett, 1 Geoffrey W. Meissner, 1 and Bruce S. Baker 1, 1 Janelia Farm
Article Central Brain Neurons Expressing doublesex Regulate Female Receptivity in Drosophila Chuan Zhou, 1 Yufeng Pan, 1 Carmen C. Robinett, 1 Geoffrey W. Meissner, 1 and Bruce S. Baker 1, 1 Janelia Farm
REGULATION OF FEEDING BEHAVIOR IN ADULT DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER VARIES WITH FEEDING REGIME AND NUTRITIONAL STATE
 J. exp. Biol. 97, 2 23 (99) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 99 2 REGULATION OF FEEDING BEHAVIOR IN ADULT DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER VARIES WITH FEEDING REGIME AND NUTRITIONAL STATE
J. exp. Biol. 97, 2 23 (99) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 99 2 REGULATION OF FEEDING BEHAVIOR IN ADULT DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER VARIES WITH FEEDING REGIME AND NUTRITIONAL STATE
Report. The Molecular Basis of Sugar Sensing in Drosophila Larvae
 Current Biology 23, 466 47, August 5, 23 ª23 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved http://dx.doi.org/.6/j.cub.23.6.28 The Molecular Basis of Sugar Seing in Drosophila Larvae Report Dushyant Mishra, Tetsuya
Current Biology 23, 466 47, August 5, 23 ª23 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved http://dx.doi.org/.6/j.cub.23.6.28 The Molecular Basis of Sugar Seing in Drosophila Larvae Report Dushyant Mishra, Tetsuya
Chapter 15: The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
 Name Period Chapter 15: The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Concept 15.1 Mendelian inheritance has its physical basis in the behavior of chromosomes 1. What is the chromosome theory of inheritance? 2.
Name Period Chapter 15: The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance Concept 15.1 Mendelian inheritance has its physical basis in the behavior of chromosomes 1. What is the chromosome theory of inheritance? 2.
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Targeting of the attenuated diphtheria toxin (adta) into the melanopsin locus. a,
 doi: 1.138/nature6829 a DTA HSV- TK PGK-Neo Targeting construct b kb.85.65 L WT adta/+ adta/ adta Melanopsin (Opn 4) Genomic Locus 1 kb.4 Supplementary Figure 1: Targeting of the attenuated diphtheria
doi: 1.138/nature6829 a DTA HSV- TK PGK-Neo Targeting construct b kb.85.65 L WT adta/+ adta/ adta Melanopsin (Opn 4) Genomic Locus 1 kb.4 Supplementary Figure 1: Targeting of the attenuated diphtheria
Supplemental Information. Ciliary Beating Compartmentalizes. Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow in the Brain. and Regulates Ventricular Development
 Current Biology, Volume Supplemental Information Ciliary Beating Compartmentalizes Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow in the Brain and Regulates Ventricular Development Emilie W. Olstad, Christa Ringers, Jan N.
Current Biology, Volume Supplemental Information Ciliary Beating Compartmentalizes Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow in the Brain and Regulates Ventricular Development Emilie W. Olstad, Christa Ringers, Jan N.
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4547
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures a miel1-2 (SALK_41369).1kb miel1-1 (SALK_978) b TUB MIEL1 Supplementary Figure 1. MIEL1 expression in miel1 mutant and S:MIEL1-MYC transgenic plants. (a) Mapping of the T-DNA insertion
Supplementary Figures a miel1-2 (SALK_41369).1kb miel1-1 (SALK_978) b TUB MIEL1 Supplementary Figure 1. MIEL1 expression in miel1 mutant and S:MIEL1-MYC transgenic plants. (a) Mapping of the T-DNA insertion
Role of Autophagy in Glycogen Breakdown and Its Relevance to Chloroquine Myopathy
 Role of Autophagy in Glycogen Breakdown and Its Relevance to Chloroquine Myopathy Jonathan Zirin 1 *, Joppe Nieuwenhuis 1, Norbert Perrimon 1,2 * 1 Department of Genetics, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
Role of Autophagy in Glycogen Breakdown and Its Relevance to Chloroquine Myopathy Jonathan Zirin 1 *, Joppe Nieuwenhuis 1, Norbert Perrimon 1,2 * 1 Department of Genetics, Harvard Medical School, Boston,
Expanded View Figures
 PEX13 functions in selective autophagy Ming Y Lee et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV1. PEX13 is required for Sindbis virophagy. A, B Quantification of mcherry-capsid puncta per cell (A) and GFP-LC3
PEX13 functions in selective autophagy Ming Y Lee et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV1. PEX13 is required for Sindbis virophagy. A, B Quantification of mcherry-capsid puncta per cell (A) and GFP-LC3
Meigo governs dendrite targeting specificity by modulating Ephrin level and N-glycosylation
 Meigo governs dendrite targeting specificity by modulating Ephrin level and N-glycosylation Sayaka U. Sekine, Shuka Haraguchi, Kinhong Chao, Tomoko Kato, Liqun Luo, Masayuki Miura, and Takahiro Chihara
Meigo governs dendrite targeting specificity by modulating Ephrin level and N-glycosylation Sayaka U. Sekine, Shuka Haraguchi, Kinhong Chao, Tomoko Kato, Liqun Luo, Masayuki Miura, and Takahiro Chihara
