Hyperfiltration Affects Accuracy of Creatinine egfr Measurement
|
|
|
- June Chambers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Article Hyperfiltration Affects Accuracy of Creatinine Measurement Shih-Han S. Huang,* Ajay P. Sharma, Abeer Yasin, Robert M. Lindsay,* William F. Clark,* and Guido Filler Summary Background and objectives Surrogate markers such as creatinine, cystatin C (CysC), and beta trace protein (BTP) have been used to estimate GFR (). The accuracy of may be altered with hyperfiltration and differences in filtration fraction (FF). It is hypothesized that the accuracy of creatinine for may be affected by hyperfiltration and different effective renal plasma flow (ERPF). Design, setting, participants, & measurements A total of 127 pediatric patients with various renal diseases underwent simultaneous measurements of GFR using 51 Cr-EDTA renal scan and ERPF ( 131 I-hippurate clearance) to calculate the FF (FF GFR/ERPF). The s were calculated using the commonly used Schwartz (creatinine), Filler (CysC), and Benlamri (BTP) formulas. Agreement of the s with the measured isotope GFRs was assessed by Bland Altman plots. Correlation analysis was performed using nonparametric tests to compare FF with GFR. Results The 127 children at a median age (with 25th percentile, 75th percentile) of 11.9 (8.5, 14.9) years had a mean 51 Cr EDTA-GFR of ml/min per 1.73 m 2 and a median 131 I-hippurate clearance (ERPF) of 588 (398,739) ml/min per 1.73 m 2. Mean FF was % with no correlation between the FF and the error ( GFR) for CysC and BTP, whereas there was a significant negative correlation between the error for Schwartz and FF. Conclusions There is a significant negative correlation between the error for the Schwartz and the FF. CysC and BTP are not affected by differences in FF. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6: , doi: /CJN Introduction Renal function measurement is often focused on the GFR and, to a lesser extent, on renal blood flow (1). The gold standard for measuring GFR is inulin clearance (2). However, nuclear medicine studies have replaced inulin clearance because of convenience and absence of urine collection. In Europe, 51 Cr-EDTA is the most widely used method for the determination of GFR (3), whereas in North America, the 99 Tc-diethylenetriamine pentaacetic acid renal scan enjoys the most widespread utilization (3 5). Although less demanding than inulin clearance studies, nuclear GFR studies are still cumbersome, invasive, and involve radiation. Endogenous markers for estimated GFR (), such as serum creatinine and more recently cystatin C (CysC), are hampered by diagnostic imprecision (6). Recently beta trace protein (BTP) has been introduced as a surrogate marker for GFR measurement (7). Creatinine (molecular weight 113 D, neutrally charged) is the metabolic product of creatine and phosphocreatine found in muscle; therefore, it reflects muscle mass (8,9). Given the large variability of muscle mass, there is substantial interpatient variability of serum creatinine concentration (10) because of its high water solubility (11). Serum CysC has been shown to be an excellent marker for GFR (6,12,13). It is a small-molecularweight protein (molecular weight 13 kd, positive charge with isoelectric point of 9.3) that was initially known as -trace protein and its amino acid sequence was determined in 1981 (14,15). This protein is produced at a very constant rate and is affected by only a few conditions, such as uncontrolled hyperthyroidism (16). BTP (molecular weight 23 to 29 kd, mildly negatively charged with isoelectric point of 5.8 to 6.7, also known as prostaglandin D synthase) has been traditionally used as a marker of cerebrospinal fluid leakage (17,18). It is expressed in all tissues except the ovaries (19). Preliminary studies have confirmed a good correlation between serum BTP levels and GFR measurement by inulin clearance and nuclear medicine techniques (5,20). Hyperfiltration is considered an abnormal increase in the GFR (21,22). However, this definition ignores the fact that hyperfiltration can take place in a single nephron even with globally decreased GFR. Other sources have defined hyperfiltration as the result of an increase in the glomerular capillary pressure (23,24). The filtration fraction (FF) is the ratio of GFR and effective renal plasma flow (ERPF) (24). A normal Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Nephrology, Children s Hospital, London Health Science Centre, Schulich School of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada; and *Department of Medicine, Division of Nephrology, Schulich School of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada Correspondence: Dr. Guido Filler, Children s Hospital, London Health Sciences Centre, University of Western Ontario, 800 Commissioner s Road East, Room E6-104, London ON, Canada, N6A 5W9. Phone: ; Fax: ; guido.filler@ lhsc.on.ca 274 Copyright 2011 by the American Society of Nephrology Vol 6 February, 2011
2 Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6: , February, 2011 Hyperfiltration and, Huang et al. 275 FF is % in healthy young adults between the ages of 20 and 30 years (25). Hyperfiltration should be considered if the FF is above the reference interval. We were interested in whether hyperfiltration affects the diagnostic accuracy of commonly used measurements using creatinine, CysC, and BTP in a pediatric population. The precision between the surrogate markers and the is reduced at higher GFR. One possible explanation for this phenomenon may be that some patients hyperfilter and others do not. Patients and Methods Patients The study received full approval of the local ethics boards and was in accordance with the ethical standards of the Helsinki declaration of 1975 (revised in 1983) (5). Written consent was obtained in each case from the parents and, in the case of a consenting minor, from the patients as well. One hundred twentyseven of the patients had a 51 Cr-EDTA renal scan with concomitant determination of the 131 I-hippurate clearance (ERPF), thus allowing for the calculation of the FF. Venous blood samples were obtained from 127 children with various renal pathologies, referred for determination of nuclear medicine GFR study. Patients were recruited consecutively and their ages ranged from 1.0 to 18.0 years with a mean of years. Thirty-five percent of patients were girls. Mean height was cm (range 62.3 to cm), mean weight was kg (range 6.5 to kg), and mean body surface area was m 2 (range 0.33 to 2.20 m 2 ). The main indications for GFR measurements were various forms of GN (44.7%), obstructive uropathy (19.9%), reflux nephropathy (13.6%), postrenal transplantation (5.4%), and others (16.4%, including posthemolytic uremic syndrome, steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome, cystinosis, orthostatic proteinuria, etc.). Materials and Methods The methods for the simultaneous measurement of GFR and ERPF using 51 Cr-EDTA renal scan with concomitant determination of the 131 I-hippurate clearance have been described elsewhere (25). GFR and ERPF were corrected to a standard body surface area of ml/min per 1.73 m 2. For consistency, by GFR and ERPF we mean the corrected values per 1.73 m 2 of body surface area throughout the manuscript. FF was calculated as the ratio between 51 Cr-EDTA GFR and 131 I-hippurate ERPF and was expressed in percent. Serum creatinine was measured with an enzymatic assay (Ortho Clinical Diagnostics). Because enzymatic assays measure approximately 20% lower than the Jaffé method that was used in the original formula by George Schwartz (26), we used 20% higher constants (38 for children 1 year of age, 48 for adolescent boys) to calculate the GFR estimate according to Schwartz. We validated these revised constants for the Schwartz formula in our patient cohort. For adolescent boys, the estimated constant was , not significantly different from 48 (P , one-sample t test). For the nonadolescent male patients, the constant was , again not significantly different from 38. We therefore used the constants of 38 and 48. The formula reads GFRestimate height (cm) constant serum creatinine ( mol/l) (1) The methods for the determination of CysC (Siemens Diagnostics GmbH) and BTP (Siemens Diagnostics) were described in the previous study (5). CysC was calculated using the Filler formula (27). For the BTP, we used a recently published and validated formula by Benlamri et al. (28). We calculated the error between the measured GFR and the for creatinine using Schwartz, CysC, and BTP using ( Parameter measured GFR)/measured GFR. Statistical Analyses All statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism Software for Science Version 4.0c (San Diego, CA). Standard regression and correlation analyses were applied. Normal distribution was assessed using the Shapiro Wilk test. Agreement between methods was tested using the Bland Altman plot method (29). The Bland Altman plot is a statistical method used to compare two measurement techniques. In this graphical method, the differences (or alternatively the ratios) between the two techniques are plotted against the averages of the two techniques. Horizontal lines are drawn at the mean difference, and at the mean difference 1.96 times the SD of the differences. If the differences within the mean 1.96 SD are not clinically important, the two methods may be used interchangeably. SD of the differences between the two assay methods is used to calculate the limits of agreement, computed as the mean bias 1.96 times its SD. The bias is computed as the value determined by one method minus the value determined by the other method. If one method is sometimes higher, and sometimes the other method is higher, the average of the differences will be close to zero. If it is not close to zero, this indicates that the two assay methods are producing different results. Correlation analysis was performed using appropriate parametric (in case of normal distribution) or nonparametric tests (Spearman rank). In the case of non-normal distribution, data are given as a median (25th percentile, 75th percentile). The percentiles in brackets are also known as the interquartile range (IQR). P 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results The 127 children had a median age of 11.9 (IQR 8.5, 14.9) years, weighed 39.9 (28.8, 54.3) kg, and had a height of (131.0, 163.8) cm. Mean body surface area was m 2. The mean measured 51 Cr-
3 276 Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology Table 1. Statistics of the most important measured and calculated parameters BTP BTP (mg/l) CysC CysC (mg/l) Schwartz Creatinine ( mol/l) FF (%) 123 I-Hippurate 51 Cr-EDTA Number th Percentile Median th Percentile Mean SD Shapiro Wilk normality test Wilk constant P P P P P EDTA GFR was ml/min per 1.73 m 2. The median 131 I-hippurate clearance (ERPF) was 588 (398, 739) ml/min per 1.73 m 2. The mean FF was %. Median serum creatinine was 56 (52, 74) mol/l, whereas median CysC was 0.98 (0.83, 1.21) mg/l and median BTP was 0.76 (0.62, 0.98) mg/l. The results of the most important parameters are summarized in Table 1. Bland Altman analysis revealed a bias of 10.8% 21.2%, with a 95% limit of agreement from 0.8% to 52.4% between the Schwartz formula and the measured GFR. For CysC, the bias was 9.6% 21.6% with a 95% limit of agreement from 52.0% to 32.7%, and for BTP the bias was with a 95% limit of agreement from 54.0% to 56.8% (Table 2). The median (IQR) relative error ( GFR/ GFR) for the Schwartz formula was 12 (IQR 4, 24)%, whereas the median error for CysC was 9 (IQR 21, 6)%, and for BTP was 5 (IQR 16, 25)% (Table 3). There was no correlation between the FF and the error for CysC and BTP, whereas there was a significant negative correlation between the error for the Schwartz and the FF (Figure 1). Furthermore, a significant negative correlation existed between FF and GFR, Schwartz GFR, CysC, and BTP. Clinically, this suggests that most patients with a lower GFR hyperfilter, whereas only some hyperfilter with normal GFR. Table 4 summarizes the correlation analysis (Spearman rank). There was no significant correlation between the error for the CysC and BTP and the FF. On the other hand, a significant negative correlation existed between FF and GFR, Schwartz GFR, CysC, and BTP. Discussion The main finding of the study was that creatininebased was influenced by the FF, whereas the accuracy of the from the Filler equation using serum CysC and the Belamri equation using serum Table 2. Bland Altman results summarized for agreement of various formulas with the measured isotope GFR Formula Schwartz Cystatin C BTP Bias SD % % Limit of agreement 0.80 to to to 56.8 Table 3. Error by level of ( GFR/GFR) for various formulas Formula Schwartz Cystatin C BTP Median error th percentile error th percentile error
4 Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6: , February, 2011 Hyperfiltration and, Huang et al. 277 Figure 1. The relationship between the percentage error of the Schwartz formula and the measured GFR plotted against the FF. There was a significant negative correlation (Spearman r , P ). For the nonlinear regression model, we used a one-phase exponential decay model with the constants SPAN 2295, K , PLATEAU 2295, and HalfLife Table 4. Spearman rank correlations between the error of the GFR estimate models (BTP, CysC, Schwartz) with FF Parameter Schwartz Percent Error CysC Percent Error BTP Percent Error Number of xy pairs Spearman r % Confidence interval to to to P value (two-tailed) P value summary Significant NS NS NS, not significant. BTP was unaffected. In fact, there was a significant negative correlation between error of calculated from the Schwartz formula and the measured GFR and the FF. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that demonstrates that the error between Schwartz formula and measured GFR is altered by hyperfiltration. By contrast, based on lowmolecular-weight proteins was not altered by hyperfiltration. This finding is novel and has significant implications. Previous studies have focused on the errors in from various surrogate markers and their respective formulas to the nuclear GFR studies (30 32). Better agreement was consistently found in the low GFR range, whereas the precision between measured GFR and surrogate marker worsened with normal and high GFR values (24,30). It was therefore logical to assess the effect of hyperfiltration on the diagnostic performance of surrogate markers. Previous studies did not include ERPF or FF. What does this mean? It appears that a small-molecular-weight soluble substance can be affected by hyperfiltration, which weakens its diagnostic performance as a GFR marker, whereas low-molecularweight proteins are unaffected. This would render serum creatinine a less accurate marker for in the presence of hyperfiltration. Because GFR may remain constant in the early stages of chronic kidney disease whereas the nephron endowment deteriorates secondary to a renal disease, patients with a normal GFR may or may not be hyperfiltrating. In advanced chronic kidney disease, all remaining nephrons hyperfilter (33). It is therefore conceivable that the degree of hyperfiltration may serve as the main explanation for the reduced precision of any surrogate GFR marker in the normal and high GFR range. Admittedly, the correlation was only 0.24, which was significant, but not very impressive. The study was not designed to discover a strong correlation between the error of a creatinine-based formula and the FF; rather, it was designed to test the hypothesis whether some of the variance of the scatter can be explained by the degree of hyperfiltration. The clinical significance of our findings lies in the fact that hyperfiltration can indeed explain some of the imprecision of creatininebased, and patients early in the course of diabetic nephropathy and IgA nephropathy may especially have significant hyperfiltration. In the low GFR range, the phenomenon becomes less important, but our data suggest that creatinine handling may be altered by the FF to a degree that it renders the marker less favorable when compared with the low-molecular-weight markers. Of course, the question arises as to why the small molecule creatinine is handled differently than the small-molecular-weight proteins CysC and BTP. All surrogate markers have different charges and isoelectric points. Because CysC and BTP are handled identically, electric charge is unlikely to explain the negative correlation between the error in for creatinine in the measurement of the FF. One possible explanation for this increase in error in creatininebased using the Schwartz formula is that creat-
5 278 Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology Figure 2. The relationship between the FF and efferent blood flow. When the FF decreases, there is an increase in efferent blood flow and creatinine availability. This will lead to an increase in tubular secretion. inine is also secreted by the renal tubule along with the excretion from glomerular filtration, whereas there is minimal or no tubular reabsorption of creatinine (34). CysC and BTP are exclusively eliminated through glomerular filtration. Therefore, with low FF, there is more blood flow in the efferent arteriole and subsequently more creatinine available in the peritubular capillaries for tubular secretion. This may lead to an increase of tubular secretion at lower FF, thereby creating an overestimation in the. It should be noted that the difference between the 25th and 75th percentile (i.e., IQR, a measure of precision) was inferior for BTP, suggesting that of the two low-molecular-weight proteins, CysC should be preferred. When the FF is increased, there is a decrease in efferent blood flow with a subsequent decrease of creatinine available for tubular secretion. Therefore, the from the creatinine-based formula correlates better with measured GFR at higher FF. The proposed differential handling of creatinine with lower and higher FF is demonstrated in Figure 2. Because tubular secretion does not modify CysC and BTP concentrations, the FF is unaffected by the error between the errors for CysC and the BTP-based formulas. Our study has limitations. The first limitation is related to the nuclear medicine methods chosen to determine GFR and ERPF. No separate gold standard such as inulin clearance and para-aminohippuric acid (PAH) clearance were used to evaluate the accuracy of the nuclear medicine methods. Nuclear medicine methods are known to be imperfect measures of GFR and ERPF. Inulin and PAH clearance studies are no longer performed in most tertiary centers. However, the methods were validated and performed as described in reference 25 as the standard of care. Although earlier studies comparing inulin clearance and 51 Cr-EDTA clearance mostly reported correlations upon introduction of the nuclear medicine methods, a recent study from Medeiros et al. used appropriate testing for agreement with Bland Altman analysis for an identical method to ours and revealed narrow limits of agreement and a difference (bias) of 2.8 and 2.7 ml/min, respectively. They concluded that 51 Cr- EDTA clearance was a reliable method to measure GFR compared with inulin clearance (35). We are unaware of any modern studies using Bland Altman analysis to study agreement between 131 I-hippurate clearance with PAH clearance; however, a study from 1980 demonstrated identical results with PAH clearance and slightly better performance of the 131 I-hippurate clearance that we used in our study when compared with PAH clearance (36). Furthermore, this study was conducted in a pediatric population and it is unclear whether these findings can be generalized to all ages. In children, is calculated using the Schwartz formula that is based on creatinine and patient height. Adult calculations based on serum creatinine, such as the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease study equation and the Cockcroft Gault equation, require additional information such as age, weight, gender, and ethnicity. In children, these formulas cannot be used (37). Before the findings of this study can be generalized, the increased errors that occur at lower FF will need to be confirmed in adult populations using adult equations that are based on serum creatinine. The errors using the Schwartz formula change with the state of FF. It is impractical to measure FF in every patient. FF can only be measured if GFR and ERPF are determined simultaneously. In Canada, 131 I or 121 I-PAH are not commercially available. Furthermore, for a simultaneous nuclear medicine method, two different isotopes with and radiation are required, which is impractical in North America because 51 Cr-EDTA is not commercially available (38). Although we have a general rule of thumb that the tubular secretion for creatinine is approximately 10% of the total excretion (34), this may not be applicable for different degrees of hyper-
6 Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6: , February, 2011 Hyperfiltration and, Huang et al. 279 filtration. The creatinine-based formulas may be unpredictable in terms of the errors. Other limitations include a relatively low sample size of 127 patients and a small proportion of patients with low GFR. Our study casts significant doubts on the accuracy of serum creatinine in patients with a variable degree of hyperfiltration. Early in the course of disease, hyperfiltration may or may not be operant. In the case of a GFR 150 ml/min per 1.73 m 2, hyperfiltration can be assumed, but in the case of normal GFR, hyperfiltration may or may not occur. Our study suggests that a surrogate marker for should be based on a low-molecular-weight protein rather than on serum creatinine. The question of the clinical applicability of these findings remains to be established. Short of performing a proper inulin and PAH clearance study, FF is not easily measurable. Clinically, we assume hyperfiltration whenever the GFR is high. Our study also suggests that all patients with a low GFR hyperfilter. The importance of this study lies less in the clinical applicability of the effect of hyperfiltration on creatinine excretion, but more points to an important factor that explains some of the scatter when using surrogate markers for the estimation of. The study also suggests that CysC is less affected by hyperfiltration than creatinine. In conclusion, this study showed that the creatinine-based Schwartz formula is influenced by FF. The errors of negatively correlate with FF. Only the s based on low-molecular-weight proteins (Filler equation using CysC and the Belarmi equation using BTP) are unaffected at different levels of FF. Further studies are required to test the result in adult populations with other creatinine-based formulas. Acknowledgments This work was supported by a grant from Dade Behring GmbH. Disclosures None. References 1. Cameron JS: Oxford textbook of clinical nephrology, 2nd ed., edited by Davidson AM, Cameron JS, Grunfeld JP, Kerr DN, Ritz E, Winearls CG: Oxford, United Kingdom, Oxford University Press, 1998, pp Gutman Y, Gottschalk CW, Lassiter WE: Micropunture study of inulin absorption in the rat kidney. Science 147: , Picciotto G, Cacace G, Cesana P, Mosso R, Ropolo R, De Filipi PG: Estimation of chromium-51 ethylenediamine tetra-acetic acid plasma clearance: A comparative assessment of simplified techniques. Eur J Nucl Med 19: 30 35, Chantler C, Barratt TM: Estimation of glomerular rate from plasma clearance of 51-chromium edetic acid. Arch Intern Med 47: , Filler G, Priem F, Lepage N, Singa P, Vollmer I, Clark H, Keely E, Matzinger M, Akbari A, Althaus H, Jung K: B-trace protein, cystatin C, B2-microglobulin, and creatinine compared for detecting impaired glomerular filtration rates in children. Clin Chem 48: , Dharnidharka VR, Kwon C, Stevens G: Serum cystatin C is superior to serum creatinine as a marker of kidney function: A meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 40: , Pöge U, Gerhardt TM, Stoffel-Wagner B, Palmedo H, Klehr HU, Sauerbruch T, Woitas PR: -trace protein is an alternative marker for glomerular filtration rate in renal transplantation patients. Clin Chem 51: , Heymsfield SB, Arteaga C, McManus C, Smith J, Moffitt S: Measurement of muscle mass in humans: Validity of the 24-hour urinary creatinine method. Am J Clin Nutr 37: , Okuda Y, Namba S, Nagata M, Hara H, Morita T: Plasma creatinine and cystatin C ratio is useful for discriminate diagnosis of postrenal renal failure [in Japanese]. Rinsho Byori 56: , Vinge E, Lindergard B, Nilsson-Ehle P, Grubb A: Relationship among serum cystatin C, serum creatinine, lean tissue mass and glomerular filtration rate in healthy adults. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 59: , Bjornsson TD: Use of serum creatinine concentrations to determine renal function [Review]. Clin Pharmacokinet 4: , Simonsen O, Grubb A, Thysell H: The blood serum concentration of cystatin C (gamma-trace) as a measure of the glomerular filtration rate. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 45: , Löfberg H, Grubb AO: Quantitation of -trace in human biological fluids: Indications for production in the central nervous system. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 39: , Grubb A, Löfberg H: Human -trace, a basic microprotein: Amino acid sequence and presence in the adenohypophysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 79: , Grubb AO: Cystatin C Properties and use as diagnostic marker. Adv Clin Chem 35: 63 99, Filler G, Bökenkamp A, Hofmann W, Le Bricon T, Martínez- Brú C, Grubb A: Cystatin C as a marker of GFR History, indications and future research. Clin Biochem 38: 1 8, Clausen J: Proteins in normal cerebrospinal fluid not found in serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 107: , Hoffmann A, Nimtz M, Conradt HS: Molecular characterization of -trace protein in human serum and urine: A potential diagnostic marker for renal diseases. Glycobiology 7: , Olsen JE, Sandberg M: Demonstration of synthesis of beta-trace protein in different tissues of squirrel monkey. Neurobiology 5: , Priem F, Althaus H, Birnbaum M, Sinha P, Conradt HS, Jung K: Beta-trace protein in serum: A new marker of glomerular filtration rate in the creatinine-blind range. Clin Chem 45: , Merriam-Webster Medical Dictionary: Hyperfiltration. Available at: hyperfiltration. Accessed December 10, Estorch M, Tembl A, Antonijoan R, Mari C, Flotats A, Camacho V, Sola R, Barbanoj M, Carrio I: Evaluation of renal graft haemodynamia by 51Cr-EDTA and o-[ 131 I]iodohippurate: Its use in the early diagnosis of glomerular hyperfiltration. Nucl Med Commun 24: , Kimura G, London G, Safar M, Kuramochi M, Omae T: Glomerular hypertension in renovascular hypertensive patients. Kidney Int 39: , Berg UB: Differences in decline in GFR with age between males and females. Reference data on clearances of inulin and PAH in potential kidney donors. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21: , Hüseman D, Gellermann J, Vollmer I, Ohde I, Devaux S, Ehrich JH, Filler G: Long-term prognosis of hemolytic uremic syndrome and effective renal plasma flow. Pediatr Nephrol 13: , Schwartz GJ, Haycock GB, Edelmann CM Jr, Spitzer A: A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in chil-
7 280 Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology dren derived from body length and plasma creatinine. Pediatrics 58: , Filler G, Lepage N: Should the Schwartz formula for estimation of GFR be replaced by cystatin C formula? Pediatr Nephrol 18: , Benlamri A, Nadarajah R, Yasin A, Lepage N, Sharma AP, Filler G: Development of a beta-trace protein based formula for estimation of glomerular filtration rate. Pediatr Nephrol 25: , Bland JM, Altman DG: Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1: , Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF III, Feldman HI, Kusek JW, Eggers P, Van Lente F, Greene T, Coresh J: A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med 150: , Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D: A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate form serum creatinine: A new prediction equation. Ann Intern Med 130: , Rule AD, Larson TS, Bergstralh EJ: Using serum creatinine to estimate glomerular filtration rate: Accuracy in good health and in chronic kidney disease. Ann Intern Med 141: , Schieppati A, Pisoni R, Remuzzi G: Pathophysiology and management of chronic kidney disease. In: Primer on Kidney Diseases, 4th ed., edited by Greenberg A, Philadelphia, Elsevier Saunders, 2005, pp Koeppen BM, Stanton BA: Renal Physiology, 4th ed., Philadelphia, Mosby, Inc., 2007, pp Medeiros FS, Sapienza MT, Prado ES, Agena F, Shimizu MH, Lemos FB, Buchpiguel CA, Ianhez LE, David-Neto E: Validation of plasma clearance of 51Cr-EDTA in adult renal transplant recipients: Comparison with inulin renal clearance. Transpl Int 22: , Stadalnik RC, Vogel JM, Jansholt AL, Krohn KA, Matolo NM, Lagunas-Solar MC, Zielinski FW: Renal clearance and extraction parameters of ortho-iodohippurate (I- 123) compared with OIH(I-131) and PAH. J Nucl Med 21: , Filler G, Foster J, Acker A, LePage N, Akbari A, Ehrich JH: The Cockcroft-Gault formula should not be used in children. Kidney Int 65: , Filler G, Sharma AP: How to monitor renal function in pediatric solid organ transplant recipients. Pediatr Transplant 12: , 2008 Received: March 24, 2010 Accepted: September 15, 2010 Published online ahead of print. Publication date available at
A New Approach for Evaluating Renal Function and Its Practical Application
 J Pharmacol Sci 105, 1 5 (2007) Journal of Pharmacological Sciences 2007 The Japanese Pharmacological Society Current Perspective A New Approach for Evaluating Renal Function and Its Practical Application
J Pharmacol Sci 105, 1 5 (2007) Journal of Pharmacological Sciences 2007 The Japanese Pharmacological Society Current Perspective A New Approach for Evaluating Renal Function and Its Practical Application
Evaluation of the Cockroft Gault, Jelliffe and Wright formulae in estimating renal function in elderly cancer patients
 Original article Annals of Oncology 15: 291 295, 2004 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdh079 Evaluation of the Cockroft Gault, Jelliffe and Wright formulae in estimating renal function in elderly cancer patients G.
Original article Annals of Oncology 15: 291 295, 2004 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdh079 Evaluation of the Cockroft Gault, Jelliffe and Wright formulae in estimating renal function in elderly cancer patients G.
Is the new Mayo Clinic Quadratic (MCQ) equation useful for the estimation of glomerular filtration rate in type 2 diabetic patients?
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online October 3, 2008 The MCQ equation in DM2 patients Is the new Mayo Clinic Quadratic (MCQ) equation useful for the estimation of glomerular filtration
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online October 3, 2008 The MCQ equation in DM2 patients Is the new Mayo Clinic Quadratic (MCQ) equation useful for the estimation of glomerular filtration
Glomerular Filtration Rate. Hui Li, PhD, FCACB, DABCC
 Glomerular Filtration Rate Hui Li, PhD, FCACB, DABCC Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR): Amount of blood that is filtered per unit time through glomeruli. It is a measure of the function of kidneys. The
Glomerular Filtration Rate Hui Li, PhD, FCACB, DABCC Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR): Amount of blood that is filtered per unit time through glomeruli. It is a measure of the function of kidneys. The
Can modifications of the MDRD formula improve the estimation of glomerular filtration rate in renal allograft recipients?
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (7) 22: 361 3615 doi:1.193/ndt/gfm282 Advance Access publication 22 September 7 Original Article Can modifications of the MDRD formula improve the estimation of glomerular filtration
Nephrol Dial Transplant (7) 22: 361 3615 doi:1.193/ndt/gfm282 Advance Access publication 22 September 7 Original Article Can modifications of the MDRD formula improve the estimation of glomerular filtration
Cystatin C-based calculation of glomerular filtration rate in kidney transplant recipients
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 26 International Society of Nephrology Cystatin C-based calculation of glomerular filtration rate in kidney transplant recipients UPöge 1, T Gerhardt 1, B Stoffel-Wagner
http://www.kidney-international.org & 26 International Society of Nephrology Cystatin C-based calculation of glomerular filtration rate in kidney transplant recipients UPöge 1, T Gerhardt 1, B Stoffel-Wagner
Assessment of glomerular filtration rate in healthy subjects and normoalbuminuric diabetic patients: validity of a new (MDRD) prediction equation
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2002) 17: 1909 1913 Original Article Assessment of glomerular filtration rate in healthy subjects and normoalbuminuric diabetic patients: validity of a new () prediction equation
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2002) 17: 1909 1913 Original Article Assessment of glomerular filtration rate in healthy subjects and normoalbuminuric diabetic patients: validity of a new () prediction equation
Am J Nephrol 2013;38: DOI: /
 American Journal of Nephrology Original Report: Patient-Oriented, Translational Research Received: June 14, 13 Accepted: August 11, 13 Published online: September 3, 13 Combined Serum Creatinine and Cystatin
American Journal of Nephrology Original Report: Patient-Oriented, Translational Research Received: June 14, 13 Accepted: August 11, 13 Published online: September 3, 13 Combined Serum Creatinine and Cystatin
Validation of El-Minia Equation for Estimation of Glomerular Filtration Rate in Different Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease
 Kidney Diseases Validation of El-Minia Equation for Estimation of Glomerular Filtration Rate in Different Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease Osama El Minshawy, 1 Eman El-Bassuoni 2 Original Paper 1 Department
Kidney Diseases Validation of El-Minia Equation for Estimation of Glomerular Filtration Rate in Different Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease Osama El Minshawy, 1 Eman El-Bassuoni 2 Original Paper 1 Department
Original Article. Saudi Journal of Kidney Diseases and Transplantation
 Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 2014;25(5):1004-1010 2014 Saudi Center for Organ Transplantation Saudi Journal of Kidney Diseases and Transplantation Original Article Comparison of the Performance of the Updated,
Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 2014;25(5):1004-1010 2014 Saudi Center for Organ Transplantation Saudi Journal of Kidney Diseases and Transplantation Original Article Comparison of the Performance of the Updated,
9. GFR - WHERE ARE WE NOW?
 How to Cite this article: GFR Where are We Now? - ejifcc 20/01 2009 http://www.ifcc.org 9. GFR - WHERE ARE WE NOW? Joris R. Delanghe 9.1 Abstract The availability of a worldwide standard for creatinine
How to Cite this article: GFR Where are We Now? - ejifcc 20/01 2009 http://www.ifcc.org 9. GFR - WHERE ARE WE NOW? Joris R. Delanghe 9.1 Abstract The availability of a worldwide standard for creatinine
Correlation of plasma concentrations of cystatin C and creatinine to inulin clearance in a pediatric population
 Clinical Chemistry 44:6 1334 1338 (1998) General Clinical Chemistry Correlation of plasma concentrations of cystatin C and creatinine to inulin clearance in a pediatric population Douglas Stickle, 1 Barbara
Clinical Chemistry 44:6 1334 1338 (1998) General Clinical Chemistry Correlation of plasma concentrations of cystatin C and creatinine to inulin clearance in a pediatric population Douglas Stickle, 1 Barbara
Estimating GFR using serum beta trace protein: accuracy and validation in kidney transplant and pediatric populations
 original article http://www.kidney-international.org & 9 International Society of Nephrology Estimating GFR using serum beta trace protein: accuracy and validation in kidney transplant and pediatric populations
original article http://www.kidney-international.org & 9 International Society of Nephrology Estimating GFR using serum beta trace protein: accuracy and validation in kidney transplant and pediatric populations
Validity of the use of Schwartz formula against creatinine clearance in the assessment of renal functions in children
 Validity of the use of Schwartz formula against creatinine clearance in the assessment of renal functions in children *H W Dilanthi 1, G A M Kularatnam 1, S Jayasena 1, E Jasinge 1, D B D L Samaranayake
Validity of the use of Schwartz formula against creatinine clearance in the assessment of renal functions in children *H W Dilanthi 1, G A M Kularatnam 1, S Jayasena 1, E Jasinge 1, D B D L Samaranayake
The estimation of kidney function with different formulas in overall population
 137 G E R I A T R I A 213; 7: 137-141 Akademia Medycyny ARTYKUŁ ORYGINALNY/ORIGINAL PAPER Otrzymano/Submitted: 28.8.213 Zaakceptowano/Accepted: 2.9.213 The estimation of kidney function with different
137 G E R I A T R I A 213; 7: 137-141 Akademia Medycyny ARTYKUŁ ORYGINALNY/ORIGINAL PAPER Otrzymano/Submitted: 28.8.213 Zaakceptowano/Accepted: 2.9.213 The estimation of kidney function with different
The inaccuracy of cystatin C and creatinine-based equations in predicting GFR in orthotopic liver transplant recipients
 NDT Advance Access published June 8, 2009 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2009) 1 5 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp255 Original Article The inaccuracy of cystatin C and creatinine-based equations in predicting GFR in orthotopic
NDT Advance Access published June 8, 2009 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2009) 1 5 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp255 Original Article The inaccuracy of cystatin C and creatinine-based equations in predicting GFR in orthotopic
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Estimating the glomerular filtration rate using serum cystatin C levels in patients with spinal cord injuries
 (2012) 50, 778 783 & 2012 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/12 www.nature.com/sc ORIGINAL ARTICLE Estimating the glomerular filtration rate using serum cystatin C levels in patients with
(2012) 50, 778 783 & 2012 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/12 www.nature.com/sc ORIGINAL ARTICLE Estimating the glomerular filtration rate using serum cystatin C levels in patients with
Comparison of Serum Cystatin C and Creatinine Levels to Evaluate Early Renal Function after Kidney Transplantation
 IJMS Vol 34, No 2, June 2009 Original Article Comparison of Serum Cystatin C and Creatinine Levels to Evaluate Early Renal Function after Kidney Transplantation Reza Hekmat, Hamid Eshraghi Abstract Background:
IJMS Vol 34, No 2, June 2009 Original Article Comparison of Serum Cystatin C and Creatinine Levels to Evaluate Early Renal Function after Kidney Transplantation Reza Hekmat, Hamid Eshraghi Abstract Background:
Serum and urinary markers of early impairment of GFR in chronic kidney disease patients: diagnostic accuracy of urinary -trace protein
 Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 299: F1407 F1423, 2010. First published September 15, 2010; doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00507.2009. Serum and urinary markers of early impairment of GFR in chronic kidney disease patients:
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 299: F1407 F1423, 2010. First published September 15, 2010; doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00507.2009. Serum and urinary markers of early impairment of GFR in chronic kidney disease patients:
Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 16 No. 02 April 17
 Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 16 No. 02 April 17 Original article: Comparison of Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration Equations with Other Accepted Equations for Estimation of
Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 16 No. 02 April 17 Original article: Comparison of Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration Equations with Other Accepted Equations for Estimation of
Filtration and Reabsorption Amount Filter/d
 Renal Physiology 2011 Lisa M. Harrison-Bernard, PhD Contact me at lharris@lsuhsc.edu Renal Physiology Lecture 3 Renal Clearance and Glomerular Filtration Filtration and Reabsorption Amount Filter/d Amount
Renal Physiology 2011 Lisa M. Harrison-Bernard, PhD Contact me at lharris@lsuhsc.edu Renal Physiology Lecture 3 Renal Clearance and Glomerular Filtration Filtration and Reabsorption Amount Filter/d Amount
Clinical Usefulness of Serum Cystatin C as a Marker of Renal Function
 Original Article Complications Diabetes Metab J 214;38:278-284 http://dx.doi.org/1.493/dmj.214.38.4.278 pissn 2233-79 eissn 2233-87 DIABETES & METABOLISM JOURNAL Clinical Usefulness of Serum Cystatin C
Original Article Complications Diabetes Metab J 214;38:278-284 http://dx.doi.org/1.493/dmj.214.38.4.278 pissn 2233-79 eissn 2233-87 DIABETES & METABOLISM JOURNAL Clinical Usefulness of Serum Cystatin C
Glomerular filtration rate estimated by cystatin C among different clinical presentations
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2006 International Society of Nephrology Glomerular filtration rate estimated by cystatin C among different clinical presentations AD Rule 1,2, EJ Bergstralh 3, JM
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2006 International Society of Nephrology Glomerular filtration rate estimated by cystatin C among different clinical presentations AD Rule 1,2, EJ Bergstralh 3, JM
Renal Clearance. Dr. Eman El Eter
 Renal Clearance Dr. Eman El Eter Concept of clearance Clearance is the volume of plasma that is completely cleared of a substance each minute. Example: Renal clearance of Substance X is defined as the
Renal Clearance Dr. Eman El Eter Concept of clearance Clearance is the volume of plasma that is completely cleared of a substance each minute. Example: Renal clearance of Substance X is defined as the
Renal Disease and PK/PD. Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology
 Renal Disease and PK/PD Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology Drugs and Kidneys Kidney is one of the major organ of drug elimination from the human body Renal disease and dialysis alters the pharmacokinetics
Renal Disease and PK/PD Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology Drugs and Kidneys Kidney is one of the major organ of drug elimination from the human body Renal disease and dialysis alters the pharmacokinetics
Estimation of Glomerular Filtration Rates After Orthotopic Liver Transplantation: Evaluation of Cystatin C Based Equations
 LIVER TRANSPLANTATION 12:1667-1672, 2006 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Estimation of Glomerular Filtration Rates After Orthotopic Liver Transplantation: Evaluation of Cystatin C Based Equations Thomas Gerhardt, 1 Uwe
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION 12:1667-1672, 2006 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Estimation of Glomerular Filtration Rates After Orthotopic Liver Transplantation: Evaluation of Cystatin C Based Equations Thomas Gerhardt, 1 Uwe
Characteristics of factor x so that its clearance = GFR. Such factors that meet these criteria. Renal Tests. Renal Tests
 Renal Tests Holly Kramer MD MPH Associate Professor of Public Health Sciences and Medicine Division of Nephrology and Hypertension Loyola University of Chicago Stritch School of Medicine Renal Tests 1.
Renal Tests Holly Kramer MD MPH Associate Professor of Public Health Sciences and Medicine Division of Nephrology and Hypertension Loyola University of Chicago Stritch School of Medicine Renal Tests 1.
Serum BTP concentrations are not affected by hepatic dysfunction
 Chakraborty et al. BMC Nephrology (2018) 19:87 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-018-0881-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Serum BTP concentrations are not affected by hepatic dysfunction Debarati Chakraborty
Chakraborty et al. BMC Nephrology (2018) 19:87 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-018-0881-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Serum BTP concentrations are not affected by hepatic dysfunction Debarati Chakraborty
Renal Physiology. April, J. Mohan, PhD. Lecturer, Physiology Unit, Faculty of Medical Sciences, U.W.I., St Augustine.
 Renal Physiology April, 2011 J. Mohan, PhD. Lecturer, Physiology Unit, Faculty of Medical Sciences, U.W.I., St Augustine. Office : Room 105, Physiology Unit. References: Koeppen B.E. & Stanton B.A. (2010).
Renal Physiology April, 2011 J. Mohan, PhD. Lecturer, Physiology Unit, Faculty of Medical Sciences, U.W.I., St Augustine. Office : Room 105, Physiology Unit. References: Koeppen B.E. & Stanton B.A. (2010).
Calculation of glomerular filtration rate based on Cystatin C in cirrhotic patients
 NDT Advance Access published December 2, 2005 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2005) 1 of 5 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfi305 Original Article Calculation of glomerular filtration rate based on Cystatin C in cirrhotic patients
NDT Advance Access published December 2, 2005 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2005) 1 of 5 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfi305 Original Article Calculation of glomerular filtration rate based on Cystatin C in cirrhotic patients
Estimating GFR: From Physiology to Public Health. Outline of Presentation. Applications of GFR Estimations
 stimating FR: From Physiology to Public Health Tufts: Andy Levey, Lesley (Stevens) Inker, Chris Schmid, Lucy Zhang, Hocine Tighiouart, Aghogho Okparavero, Cassandra Becker, Li Fan Hopkins: Josef Coresh,
stimating FR: From Physiology to Public Health Tufts: Andy Levey, Lesley (Stevens) Inker, Chris Schmid, Lucy Zhang, Hocine Tighiouart, Aghogho Okparavero, Cassandra Becker, Li Fan Hopkins: Josef Coresh,
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences IS CYSTATIN C ESTIMATION A BETTER MARKER IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE PATIENTS?
 International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE BIO CHEMISTRY IS CYSTATIN C ESTIMATION A BETTER MARKER IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE PATIENTS? Corresponding Author R.KUMARESAN Department
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE BIO CHEMISTRY IS CYSTATIN C ESTIMATION A BETTER MARKER IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE PATIENTS? Corresponding Author R.KUMARESAN Department
Antiviral Therapy 13:
 Antiviral Therapy 13:1091 1095 Short communication Cystatin C as a marker of renal function is affected by HIV replication leading to an underestimation of kidney function in HIV patients Stefan Mauss
Antiviral Therapy 13:1091 1095 Short communication Cystatin C as a marker of renal function is affected by HIV replication leading to an underestimation of kidney function in HIV patients Stefan Mauss
Εκηίμηζη ηης μεθρικής λειηοσργίας Ε. Μωραλίδης
 Εκηίμηζη ηης μεθρικής λειηοσργίας Ε. Μωραλίδης Ιατρική Σχολή ΑΠΘ Νοσοκομείο ΑΧΕΠA Θεσσαλομίκη Kidney in body homeostasis Excretory function Uremic toxins removal Vascular volume maintainance Fluid-electrolyte
Εκηίμηζη ηης μεθρικής λειηοσργίας Ε. Μωραλίδης Ιατρική Σχολή ΑΠΘ Νοσοκομείο ΑΧΕΠA Θεσσαλομίκη Kidney in body homeostasis Excretory function Uremic toxins removal Vascular volume maintainance Fluid-electrolyte
Lecture-2 Review of the previous lecture:
 Lecture-2 Review of the previous lecture: -Kidney s function is to clean the blood by the removing of the waste plus adding some valuable substances -kidney failure will lead to death for many reasons,
Lecture-2 Review of the previous lecture: -Kidney s function is to clean the blood by the removing of the waste plus adding some valuable substances -kidney failure will lead to death for many reasons,
Cystatin C-based Formula is Superior to MDRD, Cockcroft-Gault and Nankivell Formulae in Estimating the Glomerular Filtration Rate in Renal Allografts
 Cystatin C-based Formula is Superior to MDRD, Cockcroft-Gault and Nankivell Formulae in Estimating the Glomerular Filtration Rate in Renal Allografts Ammar Qutb, 1 Ghulam Syed, 2 Hani M. Tamim, 3 Mohammad
Cystatin C-based Formula is Superior to MDRD, Cockcroft-Gault and Nankivell Formulae in Estimating the Glomerular Filtration Rate in Renal Allografts Ammar Qutb, 1 Ghulam Syed, 2 Hani M. Tamim, 3 Mohammad
Calculation of glomerular filtration rate based on Cystatin C in cirrhotic patients
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2006) 21: 660 664 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfi305 Advance Access publication 2 December 2005 Original Article Calculation of glomerular filtration rate based on Cystatin C in cirrhotic
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2006) 21: 660 664 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfi305 Advance Access publication 2 December 2005 Original Article Calculation of glomerular filtration rate based on Cystatin C in cirrhotic
Citation: Sorkhi H, Raheleh Behzadi, Joghtaei N, et al. Glomerular filtration rate determination by
 Original Article Caspian J Intern Med 2018; 9(3):290-295 DOI: 10.22088/cjim.9.3.290 Glomerular filtration rate determination by creatinine and cystatin-c in patients with acute pyelonephritis Hadi Sorkhi
Original Article Caspian J Intern Med 2018; 9(3):290-295 DOI: 10.22088/cjim.9.3.290 Glomerular filtration rate determination by creatinine and cystatin-c in patients with acute pyelonephritis Hadi Sorkhi
Special Challenges and Co-Morbidities
 Special Challenges and Co-Morbidities Renal Disease/ Hypertension/ Diabetes in African-Americans M. Keith Rawlings, MD Medical Director Peabody Health Center AIDS Arms, Inc Dallas, TX Chair, Internal Medicine
Special Challenges and Co-Morbidities Renal Disease/ Hypertension/ Diabetes in African-Americans M. Keith Rawlings, MD Medical Director Peabody Health Center AIDS Arms, Inc Dallas, TX Chair, Internal Medicine
Prevalence of complications in children with chronic kidney disease according to KDOQI
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2006 International Society of Nephrology original article Prevalence of complications in children with chronic kidney disease according to DOQI H Wong 1, Mylrea 1,
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2006 International Society of Nephrology original article Prevalence of complications in children with chronic kidney disease according to DOQI H Wong 1, Mylrea 1,
Seung Hyeok Han, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine Yonsei University College of Medicine
 Seung Hyeok Han, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine Yonsei University College of Medicine Age and Kidney Weight renal weight and thickening of the vascular intima Platt et al. Gerentology 1999;45:243-253
Seung Hyeok Han, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine Yonsei University College of Medicine Age and Kidney Weight renal weight and thickening of the vascular intima Platt et al. Gerentology 1999;45:243-253
Screening for chronic kidney disease racial implications. Not everybody that pees has healthy kidneys!
 Screening for chronic kidney disease racial implications Not everybody that pees has healthy kidneys! Screening for chronic kidney disease racial implications 1) Definition of CKD 2) Why should we screen
Screening for chronic kidney disease racial implications Not everybody that pees has healthy kidneys! Screening for chronic kidney disease racial implications 1) Definition of CKD 2) Why should we screen
Environmental Variability
 1 Environmental Variability Body Size, Body Composition, Maturation and Organ Function Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology University of Auckland 2 Objectives Understand the major sources
1 Environmental Variability Body Size, Body Composition, Maturation and Organ Function Nick Holford Dept Pharmacology & Clinical Pharmacology University of Auckland 2 Objectives Understand the major sources
Measurement and Estimation of renal function. Professeur Pierre Delanaye Université de Liège CHU Sart Tilman BELGIQUE
 Measurement and Estimation of renal function Professeur Pierre Delanaye Université de Liège CHU Sart Tilman BELGIQUE 1 2 How to estimate GFR? How to measure GFR? How to estimate GFR? How to measure GFR?
Measurement and Estimation of renal function Professeur Pierre Delanaye Université de Liège CHU Sart Tilman BELGIQUE 1 2 How to estimate GFR? How to measure GFR? How to estimate GFR? How to measure GFR?
GFR Estimation in Adolescents and Young Adults
 GFR Estimation in Adolescents and Young Adults Luciano Selistre,* Vandréa De Souza,* Pierre Cochat,* Ivan Carlos Ferreira Antonello, Aoumeur Hadj-Aissa,* Bruno Ranchin, Olga Dolomanova,* Annie Varennes,
GFR Estimation in Adolescents and Young Adults Luciano Selistre,* Vandréa De Souza,* Pierre Cochat,* Ivan Carlos Ferreira Antonello, Aoumeur Hadj-Aissa,* Bruno Ranchin, Olga Dolomanova,* Annie Varennes,
New Combined Serum Creatinine and Cystatin C Quadratic Formula for GFR Assessment in Children
 Article New Combined Serum Creatinine and Cystatin C Quadratic Formula for GFR Assessment in Children Hassib Chehade,* Francois Cachat,* Anne-Sophie Jannot, Blaise-Julien Meyrat, Dolores Mosig,* Daniel
Article New Combined Serum Creatinine and Cystatin C Quadratic Formula for GFR Assessment in Children Hassib Chehade,* Francois Cachat,* Anne-Sophie Jannot, Blaise-Julien Meyrat, Dolores Mosig,* Daniel
Life Science Journal 2014;11(10)
 Performance of CKD-EPI versus MDRD among Diabetic Egyptians Khaled Abou-Seif, Yahya Makkeyah, Maha Behairy and Mohamed Mostafa Ali Internal Medicine & Nephrology Department, Ain Shams University Mahabehairy80@gmail.com
Performance of CKD-EPI versus MDRD among Diabetic Egyptians Khaled Abou-Seif, Yahya Makkeyah, Maha Behairy and Mohamed Mostafa Ali Internal Medicine & Nephrology Department, Ain Shams University Mahabehairy80@gmail.com
Performance of MDRD study and CKD-EPI equations for long-term follow-up of nondiabetic patients with chronic kidney disease
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2012) 27 (Supple 3): iii89 iii95 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr235 Advance Access publication 11 May 2011 Original Article Performance of MDRD study and CKD-EPI equations for long-term follow-up
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2012) 27 (Supple 3): iii89 iii95 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr235 Advance Access publication 11 May 2011 Original Article Performance of MDRD study and CKD-EPI equations for long-term follow-up
Steroid Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome. Sanjeev Gulati, Debashish Sengupta, Raj K. Sharma, Ajay Sharma, Ramesh K. Gupta*, Uttam Singh** and Amit Gupta
 Steroid Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome Sanjeev Gulati, Debashish Sengupta, Raj K. Sharma, Ajay Sharma, Ramesh K. Gupta*, Uttam Singh** and Amit Gupta From the Departments of Nephrology, Pathology* and Biostatistics**,
Steroid Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome Sanjeev Gulati, Debashish Sengupta, Raj K. Sharma, Ajay Sharma, Ramesh K. Gupta*, Uttam Singh** and Amit Gupta From the Departments of Nephrology, Pathology* and Biostatistics**,
Chapter 1: CKD in the General Population
 Chapter 1: CKD in the General Population Overall prevalence of CKD (Stages 1-5) in the U.S. adult general population was 14.8% in 2011-2014. CKD Stage 3 is the most prevalent (NHANES: Figure 1.2 and Table
Chapter 1: CKD in the General Population Overall prevalence of CKD (Stages 1-5) in the U.S. adult general population was 14.8% in 2011-2014. CKD Stage 3 is the most prevalent (NHANES: Figure 1.2 and Table
Comparison between a serum creatinineand a cystatin C-based glomerular filtration rate equation in patients receiving amphotericin B
 Karimzadeh and Khalili DARU Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (2016) 24:16 DOI 10.1186/s40199-016-0149-6 SHORT COMMUNICATION Comparison between a serum creatinineand a cystatin C-based glomerular filtration
Karimzadeh and Khalili DARU Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences (2016) 24:16 DOI 10.1186/s40199-016-0149-6 SHORT COMMUNICATION Comparison between a serum creatinineand a cystatin C-based glomerular filtration
BIOL 2402 Renal Function
 BIOL 2402 Renal Function Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College 1 Renal Clearance and GFR Refers to the volume of blood plasma from which a component is completely removed in one minute by all
BIOL 2402 Renal Function Dr. Chris Doumen Collin County Community College 1 Renal Clearance and GFR Refers to the volume of blood plasma from which a component is completely removed in one minute by all
Nowadays, many centers rely on estimating equations
 Renal Function Equations before and after Living Kidney Donation: A Within-Individual Comparison of Performance at Different Levels of Renal Function Hilde Tent,* Mieneke Rook,* Lesley A. Stevens, Willem
Renal Function Equations before and after Living Kidney Donation: A Within-Individual Comparison of Performance at Different Levels of Renal Function Hilde Tent,* Mieneke Rook,* Lesley A. Stevens, Willem
Evaluation of Renal Damage by Urinary Beta-Trace Protein in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
 Clin. Lab. 2011;57:XXX-XXX Copyright ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Renal Damage by Urinary Beta-Trace Protein in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease MARIJANA DAJAK 1, SVETLANA IGNJATOVIĆ 2, BILJANA STOJIMIROVIĆ
Clin. Lab. 2011;57:XXX-XXX Copyright ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Renal Damage by Urinary Beta-Trace Protein in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease MARIJANA DAJAK 1, SVETLANA IGNJATOVIĆ 2, BILJANA STOJIMIROVIĆ
Estimating Glomerular Filtration Rate from Serum Creatinine and Cystatin C
 T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e original article Estimating Glomerular Filtration Rate from Serum Creatinine and Cystatin C Lesley A. Inker, M.D., Christopher H. Schmid, Ph.D., Hocine
T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e original article Estimating Glomerular Filtration Rate from Serum Creatinine and Cystatin C Lesley A. Inker, M.D., Christopher H. Schmid, Ph.D., Hocine
Estimates of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) from serum
 Annals of Internal Medicine Review Estimating Equations for Glomerular Filtration Rate in the Era of Creatinine Standardization A Systematic Review Amy Earley, BS; Dana Miskulin, MD, MS; Edmund J. Lamb,
Annals of Internal Medicine Review Estimating Equations for Glomerular Filtration Rate in the Era of Creatinine Standardization A Systematic Review Amy Earley, BS; Dana Miskulin, MD, MS; Edmund J. Lamb,
AUTOMATIC REPORTING OF CREATININE-BASED ESTIMATED GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE IN CHILDREN: IS THIS FEASIBLE?
 AUTOMATIC REPORTING OF CREATININE-BASED ESTIMATED GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE IN CHILDREN: IS THIS FEASIBLE? *Andrew Lunn The Children s Renal and Urology Unit, tingham Children s Hospital, tingham University
AUTOMATIC REPORTING OF CREATININE-BASED ESTIMATED GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE IN CHILDREN: IS THIS FEASIBLE? *Andrew Lunn The Children s Renal and Urology Unit, tingham Children s Hospital, tingham University
Glomerular Filtration Rate Estimations and Measurements. Pierre Delanaye, MD, PhD University of Liège CHU Sart Tilman BELGIUM
 Glomerular Filtration Rate Estimations and Measurements Pierre Delanaye, MD, PhD University of Liège CHU Sart Tilman BELGIUM Summary Estimating GFR (creatinine, egfr, cystatin C) Measuring GFR Summary
Glomerular Filtration Rate Estimations and Measurements Pierre Delanaye, MD, PhD University of Liège CHU Sart Tilman BELGIUM Summary Estimating GFR (creatinine, egfr, cystatin C) Measuring GFR Summary
Assessing Renal Function: What you Didn t Know You Didn t Know
 Assessing Renal Function: What you Didn t Know You Didn t Know Presented By Tom Wadsworth PharmD, BCPS Associate Clinical Professor UAA/ISU Doctor of Pharmacy Program Idaho State University College of
Assessing Renal Function: What you Didn t Know You Didn t Know Presented By Tom Wadsworth PharmD, BCPS Associate Clinical Professor UAA/ISU Doctor of Pharmacy Program Idaho State University College of
GFR and Drug Dosage Adaptation: Are We still in the Mist?
 GFR and Drug Dosage Adaptation: Are We still in the Mist? Pierre Delanaye, MD, PhD Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation CHU Sart Tilman University of Liège BELGIUM I have no conflict of interest to declare
GFR and Drug Dosage Adaptation: Are We still in the Mist? Pierre Delanaye, MD, PhD Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation CHU Sart Tilman University of Liège BELGIUM I have no conflict of interest to declare
Case Studies: Renal and Urologic Impairments Workshop
 Case Studies: Renal and Urologic Impairments Workshop Justine Lee, MD, DBIM New York Life Insurance Co. Gina Guzman, MD, DBIM, FALU, ALMI Munich Re AAIM Triennial October, 2012 The Company You Keep 1 Case
Case Studies: Renal and Urologic Impairments Workshop Justine Lee, MD, DBIM New York Life Insurance Co. Gina Guzman, MD, DBIM, FALU, ALMI Munich Re AAIM Triennial October, 2012 The Company You Keep 1 Case
Impact of age on glomerular filtration estimates
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2009) 24: 97 103 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfn473 Advance Access publication 4 September 2008 Original Article Impact of age on glomerular filtration estimates Pierre Douville 1, Ariane
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2009) 24: 97 103 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfn473 Advance Access publication 4 September 2008 Original Article Impact of age on glomerular filtration estimates Pierre Douville 1, Ariane
RELATIVE MERITS OF DIFFERENT CLEARANCE TESTS USED TO MEASURE GFR
 RELATIVE MERITS OF DIFFERENT CLEARANCE TESTS USED TO MEASURE GFR Ankur *, Jahir Ul Haque.M. Desai ** *Assistant professor, **Professor and HOD, Department of Physiology, Mamata Medical College Khammam
RELATIVE MERITS OF DIFFERENT CLEARANCE TESTS USED TO MEASURE GFR Ankur *, Jahir Ul Haque.M. Desai ** *Assistant professor, **Professor and HOD, Department of Physiology, Mamata Medical College Khammam
Measurement and Estimation of renal function. Professeur Pierre Delanaye Université de Liège CHU Sart Tilman BELGIQUE
 Measurement and Estimation of renal function Professeur Pierre Delanaye Université de Liège CHU Sart Tilman BELGIQUE 1 2 How to estimate GFR? How to measure GFR? How to estimate GFR? How to measure GFR?
Measurement and Estimation of renal function Professeur Pierre Delanaye Université de Liège CHU Sart Tilman BELGIQUE 1 2 How to estimate GFR? How to measure GFR? How to estimate GFR? How to measure GFR?
Urinary System. consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
 Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Serum cystatin C is independently associated with renal impairment and high sensitivity C-reactive protein in systemic lupus erythematosus
 Serum cystatin C is independently associated with renal impairment and high sensitivity C-reactive protein in systemic lupus erythematosus C. Chew 1, P.W. Pemberton 2, A. Al-M. Husain 1,3, S. Haque 3,4,
Serum cystatin C is independently associated with renal impairment and high sensitivity C-reactive protein in systemic lupus erythematosus C. Chew 1, P.W. Pemberton 2, A. Al-M. Husain 1,3, S. Haque 3,4,
Serum cystatin C advantageous compared with serum creatinine in the detection of mild but not severe diabetic nephropathy.
 Serum cystatin C advantageous compared with serum creatinine in the detection of mild but not severe diabetic nephropathy. Christensson, Anders; Grubb, Anders; Nilsson, J-A; Norrgren, Kristina; Sterner,
Serum cystatin C advantageous compared with serum creatinine in the detection of mild but not severe diabetic nephropathy. Christensson, Anders; Grubb, Anders; Nilsson, J-A; Norrgren, Kristina; Sterner,
Creatinine (serum, plasma)
 Creatinine (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Creatinine 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 Description of analyte Creatinine is a heterocyclic nitrogenous compound (IUPAC
Creatinine (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Creatinine 1.2 Alternative names None 1.3 Description of analyte Creatinine is a heterocyclic nitrogenous compound (IUPAC
Correspondence should be addressed to Maisarah Jalalonmuhali;
 Hindawi International Journal of Nephrology Volume 2017, Article ID 2901581, 7 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2901581 Research Article Comparative Performance of Creatinine-Based Estimated Glomerular
Hindawi International Journal of Nephrology Volume 2017, Article ID 2901581, 7 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2901581 Research Article Comparative Performance of Creatinine-Based Estimated Glomerular
GFR prediction using the MDRD and Cockcroft and Gault equations in patients with end-stage renal disease
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2005) 20: 2394 2401 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfi076 Advance Access publication 23 August 2005 Original Article GFR prediction using the MDRD and Cockcroft and Gault equations in patients
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2005) 20: 2394 2401 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfi076 Advance Access publication 23 August 2005 Original Article GFR prediction using the MDRD and Cockcroft and Gault equations in patients
Department of Clinical Pathology, Faculty of Medicine Padjadjaran University-Dr. Hasan Sadikin General Hospital 2
 Original Article Comparison of Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Mean Value of HARUS 15-30-60, HADI, and ASIAN Fomula Accuracy in Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Sylvia Rachmayati, 1 Ida Parwati, 1 Abdul Hadi
Original Article Comparison of Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Mean Value of HARUS 15-30-60, HADI, and ASIAN Fomula Accuracy in Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Sylvia Rachmayati, 1 Ida Parwati, 1 Abdul Hadi
(KFTs) IACLD CME, Monday, February 20, Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari, DCLS, PhD
 Kidney Function Tests (KFTs) IACLD CME, Monday, February 20, 2012 Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari, DCLS, PhD Iranian Research Organization for Science & Technology (IROST) Tehran, Iran Composition and Properties
Kidney Function Tests (KFTs) IACLD CME, Monday, February 20, 2012 Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari, DCLS, PhD Iranian Research Organization for Science & Technology (IROST) Tehran, Iran Composition and Properties
Prediction of two-sample 99m Tc-diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid plasma clearance from single-sample method
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 19, No. 5, 399 405, 2005 Prediction of two-sample 99m Tc-diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid plasma clearance from single-sample method Li ZUO,* Ying-Chun
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 19, No. 5, 399 405, 2005 Prediction of two-sample 99m Tc-diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid plasma clearance from single-sample method Li ZUO,* Ying-Chun
Cystatin C: A New Approach to Improve Medication Dosing
 Cystatin C: A New Approach to Improve Medication Dosing Erin Frazee Barreto, PharmD, MSc, FCCM Assistant Professor of Pharmacy and Medicine Kern Scholar, Center for the Science of Health Care Delivery
Cystatin C: A New Approach to Improve Medication Dosing Erin Frazee Barreto, PharmD, MSc, FCCM Assistant Professor of Pharmacy and Medicine Kern Scholar, Center for the Science of Health Care Delivery
Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology
 Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College
Introduction to Clinical Diagnosis Nephrology I. David Weiner, M.D. C. Craig and Audrae Tisher Chair in Nephrology Professor of Medicine and Physiology and Functional Genomics University of Florida College
5/10/2014. Observation, control of blood pressure. Observation, control of blood pressure and risk factors.
 Overview The Kidneys Nicola Barlow Clinical Biochemistry Department City Hospital Renal physiology Renal pathophysiology Acute kidney injury Chronic kidney disease Assessing renal function GFR Proteinuria
Overview The Kidneys Nicola Barlow Clinical Biochemistry Department City Hospital Renal physiology Renal pathophysiology Acute kidney injury Chronic kidney disease Assessing renal function GFR Proteinuria
Page 1. Disclosures. Main Points of My Talk. Enlightened Views of Serum Creatinine, egfr, Measured GFR, and the Concept of Clearance
 1 Enlightened Views of Serum Creatinine, egfr, Measured GFR, and the Concept of Clearance John Toffaletti, PhD Director of Blood Gas and Clinical Pediatric Laboratories Professor of Pathology Duke University
1 Enlightened Views of Serum Creatinine, egfr, Measured GFR, and the Concept of Clearance John Toffaletti, PhD Director of Blood Gas and Clinical Pediatric Laboratories Professor of Pathology Duke University
Drug Dosing and Estimated Renal Function Any Step Forward from Effersoe?
 Clinical Practice: Mini-Review Received: September 1, 2016 Accepted after revision: December 13, 2016 Published online: February 18, 2017 Drug Dosing and Estimated Renal Function Any Step Forward from
Clinical Practice: Mini-Review Received: September 1, 2016 Accepted after revision: December 13, 2016 Published online: February 18, 2017 Drug Dosing and Estimated Renal Function Any Step Forward from
Salt Sensitivity in Blacks
 ONLINE SUPPLEMENT Salt Sensitivity in Blacks Evidence That the Initial Pressor Effect of NaCl Involves Inhibition of Vasodilatation by Asymmetrical Dimethylarginine Olga Schmidlin 1, Alex Forman 1, Anna
ONLINE SUPPLEMENT Salt Sensitivity in Blacks Evidence That the Initial Pressor Effect of NaCl Involves Inhibition of Vasodilatation by Asymmetrical Dimethylarginine Olga Schmidlin 1, Alex Forman 1, Anna
A Comparison Of Diagnostic Accuracy Of Cystatin C With Creatinine In The Sample Of Patient Of T2 DM With Diabetic Nephropathy
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. V (July. 2017), PP 53-57 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparison Of Diagnostic Accuracy Of
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. V (July. 2017), PP 53-57 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparison Of Diagnostic Accuracy Of
Acknowledgements. National Kidney Foundation of Connecticut Mark Perazella. Co-PI Slowing the progression of chronic kidney disease to ESRD
 A Practical Approach to Chronic Kidney Disease Management for the Primary Care Practioner: A web-site sponsored by the National Kidney Foundation of Connecticut Robert Reilly, M.D. Acknowledgements National
A Practical Approach to Chronic Kidney Disease Management for the Primary Care Practioner: A web-site sponsored by the National Kidney Foundation of Connecticut Robert Reilly, M.D. Acknowledgements National
Improved estimation of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) by comparison of egfr cystatin C. and egfr creatinine
 Scinavian Journal of Clinical & Laboratory Investigation 2012; 72: 73 77 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improved estimation of glomerular filtration rate (GFR by comparison of egfr cystatin C ANDERS GRUBB 1 ULF NYMAN
Scinavian Journal of Clinical & Laboratory Investigation 2012; 72: 73 77 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improved estimation of glomerular filtration rate (GFR by comparison of egfr cystatin C ANDERS GRUBB 1 ULF NYMAN
Renal-Related Questions
 Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Molarity number of moles of solute / Liter of solution. a) Terminology b) Body Fluid Compartments
 Integrative Sciences: Biological Systems A Fall 2011 Body Fluids Compartments, Renal Clearance and Renal Excretion of Drugs Monday, November 21, 2011 Lisa M. Harrison-Bernard, Ph.D. Department of Physiology;
Integrative Sciences: Biological Systems A Fall 2011 Body Fluids Compartments, Renal Clearance and Renal Excretion of Drugs Monday, November 21, 2011 Lisa M. Harrison-Bernard, Ph.D. Department of Physiology;
COMPLETE INHIBITION OF RENAL RESERVE IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BY A COMBINATION OF ACEI AND ARB
 COMPLETE INHIBITION OF RENAL RESERVE IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BY A COMBINATION OF ACEI AND ARB CG Musso ¹, J Reynaldi¹, N Imperiali ¹, L Algranati ¹, DG Oreopoulos ² Nephrology Department Hospital Italiano
COMPLETE INHIBITION OF RENAL RESERVE IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BY A COMBINATION OF ACEI AND ARB CG Musso ¹, J Reynaldi¹, N Imperiali ¹, L Algranati ¹, DG Oreopoulos ² Nephrology Department Hospital Italiano
Renal Function and Associated Laboratory Tests
 Renal Function and Associated Laboratory Tests Contents Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)... 2 Cockroft-Gault Calculation of Creatinine Clearance... 3 Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) to Serum Creatinine (SCr)
Renal Function and Associated Laboratory Tests Contents Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)... 2 Cockroft-Gault Calculation of Creatinine Clearance... 3 Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) to Serum Creatinine (SCr)
Comparison of Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Using Different Analytes in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Using Different Analytes in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients Bhoi Bharat K. 1*, Maheshwari Amitkumar V. 2, Sadariya Bhavesh R. 3, Shaikh
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Using Different Analytes in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients Bhoi Bharat K. 1*, Maheshwari Amitkumar V. 2, Sadariya Bhavesh R. 3, Shaikh
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol.69(1), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol.69(1), Page 1589-1594 Using Serum Beta Trace Protein to Estimate Residual Kidney Function in Hemodialysis Patients Hesham M. El-Sayed, Hussein
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol.69(1), Page 1589-1594 Using Serum Beta Trace Protein to Estimate Residual Kidney Function in Hemodialysis Patients Hesham M. El-Sayed, Hussein
Title: A novel differential diagnostic model based on multiple biological parameters for immunoglobulin A nephropathy
 Author's response to reviews Title: A novel differential diagnostic model based on multiple biological parameters for immunoglobulin A nephropathy Authors: Nan Zhen Dong (dongzn@301hospital.com.cn) Yong
Author's response to reviews Title: A novel differential diagnostic model based on multiple biological parameters for immunoglobulin A nephropathy Authors: Nan Zhen Dong (dongzn@301hospital.com.cn) Yong
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION
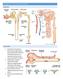 LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
Estimating 24-Hour Urine Sodium Level with Spot Urine Sodium and Creatinine
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/1.3346/jkms.214.29.s2.s97 J Korean Med Sci 214; 29: S97-12 Estimating 24-Hour Urine Sodium Level with Spot Urine Sodium and Creatinine Ho Seok Koo, 1 Yong Chul Kim, 2
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/1.3346/jkms.214.29.s2.s97 J Korean Med Sci 214; 29: S97-12 Estimating 24-Hour Urine Sodium Level with Spot Urine Sodium and Creatinine Ho Seok Koo, 1 Yong Chul Kim, 2
Creatinine- vs. cystatin C-based equations compared with 99m TcDTPA scintigraphy to assess glomerular filtration rate in chronic kidney disease
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JN EPHROL 25( DOI: 10.5301/jn.5000083 Creatinine- vs. cystatin C-based equations compared with Tc scintigraphy to assess glomerular filtration rate in chronic kidney disease Hernán Trimarchi
ORIGINAL ARTICLE JN EPHROL 25( DOI: 10.5301/jn.5000083 Creatinine- vs. cystatin C-based equations compared with Tc scintigraphy to assess glomerular filtration rate in chronic kidney disease Hernán Trimarchi
Objectives. Pre-dialysis CKD: The Problem. Pre-dialysis CKD: The Problem. Objectives
 The Role of the Primary Physician and the Nephrologist in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease () By Brian Young, M.D. Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
The Role of the Primary Physician and the Nephrologist in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease () By Brian Young, M.D. Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
Summary of Recommendation Statements Kidney International Supplements (2013) 3, 5 14; doi: /kisup
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2013 DIGO Summary of Recommendation Statements idney International Supplements (2013) 3, 5 14; doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.77 Chapter 1: Definition and classification of
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2013 DIGO Summary of Recommendation Statements idney International Supplements (2013) 3, 5 14; doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.77 Chapter 1: Definition and classification of
Foo Koon Mian Pharmacy Resident National University of Singapore Hematology / Oncology Pharmacy Residency Program. 4th APOPC November 2012
 Foo Koon Mian Pharmacy Resident National University of Singapore Hematology / Oncology Pharmacy Residency Program 4th APOPC 2012 1-3 November 2012 1 Outline Use of BSA in chemotherapy dosing Chemotherapy
Foo Koon Mian Pharmacy Resident National University of Singapore Hematology / Oncology Pharmacy Residency Program 4th APOPC 2012 1-3 November 2012 1 Outline Use of BSA in chemotherapy dosing Chemotherapy
MDRD vs. CKD-EPI in comparison to
 Jalalonmuhali et al. BMC Nephrology (2017) 18:363 DOI 10.1186/s12882-017-0776-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE MDRD vs. CKD-EPI in comparison to 51 Chromium EDTA: a cross sectional study of Malaysian CKD cohort Maisarah
Jalalonmuhali et al. BMC Nephrology (2017) 18:363 DOI 10.1186/s12882-017-0776-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE MDRD vs. CKD-EPI in comparison to 51 Chromium EDTA: a cross sectional study of Malaysian CKD cohort Maisarah
Outline. Outline CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW 7/23/2013. Question 1: Which of these patients has CKD?
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
Are prediction equations for glomerular filtration rate useful for the long-term monitoring of type 2 diabetic patients?
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (6) 21: 2152 2158 doi:1.193/ndt/gfl221 Advance Access publication 15 May 6 Original Article Are prediction equations for glomerular filtration rate useful for the long-term monitoring
Nephrol Dial Transplant (6) 21: 2152 2158 doi:1.193/ndt/gfl221 Advance Access publication 15 May 6 Original Article Are prediction equations for glomerular filtration rate useful for the long-term monitoring
Received 30 September 2004; accepted 26 April 2005 Available online 5 August 2005
 The European Journal of Heart Failure 8 (2006) 63 67 www.elsevier.com/locate/heafai The Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) equations provide valid estimations of glomerular filtration rates in
The European Journal of Heart Failure 8 (2006) 63 67 www.elsevier.com/locate/heafai The Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) equations provide valid estimations of glomerular filtration rates in
