4/6/2018. Kimberly Jamison, MD, FACP, FAPWCA
|
|
|
- Posy Maxwell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Kimberly Jamison, MD, FACP, FAPWCA 1
2 From 1980 to 2011 the number of Americans with diagnosed diabetes more than tripled An estimated 12.7% of Americans with diabetes develop a foot ulcer 60% of all lower extremity amputations in the USA are among persons with diabetes It has been suggested that 85% of amputations can be avoided when an effective care plan is adopted DFU s are complex, chronic wounds, which have a major long-term impact on morbidity, mortality and quality of patients lives 2
3 Optimal diabetes control Effective local wound care Infection control Pressure relieving strategies Restoring pulsatile blood flow Multidisciplinary team approach 3
4 Neuropathic Ischemic Neuroischemic The loss of protective sensation experienced by patients with sensory neuropathy renders them vulnerable to physical, chemical and thermal trauma Motor neuropathy can cause foot deformities, which may result in abnormal pressure over bony prominences Autonomic neuropathy is typically associated with dry skin, which can result in fissures, cracking and callus. Peripheral Arterial Disease Narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to limbs Diabetics are 2x more likely to have PAD than those without diabetes Up to 50% of diabetics also have PAD Key risk factor for lower extremity amputation 4
5 Neuroischemic Combination of neuropathic and ischemic More difficult to treat TYPICAL FEATURES OF DFU S ACCORDING TO ETIOLOGY FEATURE NEUROPATHIC ISCHEMIC NEUROISCHEMIC Sensation Sensory loss Painful Degree of sensory loss Callus/necrosis Callus present and often thick Necrosis common Minimal callus Wound bed Pink and granulating, surrounded by callus Pale and sloughy with poor granulation Poor granulation Foot temperature and Warm with bounding pulses pulses Cool with absent pulses Cool with absent pulses Other Dry skin and fissuring Delayed healing High risk of infection Typical location Weight-bearing areas of the foot, such as metatarsal heads, the heel Tips of toes, nail edges and over the dorsum of and between the toes and Margins of the foot and the clawed toes lateral borders of the foot toes Prevalence 35% 15% 50% Key skill for non-specialist practitioner is knowing when and how to refer History Medications Comorbidities Diabetes status History of wound Previous wounds or amputations Symptoms suggestive of neuropathy of PAD 5
6 Neuropathic, ischemic or neuroischemic If ischemic, is there critical limb ischemia Musculoskeletal deformities Size/depth/location of wound Color/status of wound bed, exposed bone, necrosis or gangrene Infection, systemic signs of infection Odor, pain, exudate (color and consistency) Status of wound edge (callus, maceration, erythema, undermining) 10g Monofilament Most frequently used Apply filament to various sites along plantar aspect of the foot- a positive result is the inability to feel the monofilament when it is presses against the foot Tuning Fork Neuropathy is demonstrated by inability to sense vibration from a standard tuning fork 6
7 Testing for vascular status Palpation of peripheral pulses Refer to specialist for full vascular if PAD is suspected Doppler ultrasound, ABI, Doppler waveform Toe pressures Transcutaneous Oxygen Monitoring Common terms explained Critical limb ischemia - chronic manifestation of PAD where the arteries of the lower extremities are severely blocked. Results in ischemic pain in the feet or toes even at rest. Complications of poor circulation include skin ulcers or gangrene. If left untreated if will result in amputation of the affected limb. Acute limb ischemia - sudden lack of blood flow to a limb and is due to either an embolism or thrombosis. Without surgical intervention, complete acute ischemia can lead to extensive tissue necrosis within six hours Risk Factors A positive probe-to-bone test DFU present for more than 30 days A history of recurrent DFU A traumatic foot wound The presence of PAD in the affected limb A previous lower extremity amputation Loss of protective sensation The presence of renal insufficiency A history of walking barefoot Clinical Diagnosis and Cultures Cultures- preferably soft tissue (or bone if osteomyelitis is suspected) or aspirations of purulent secretions Superficial swabbing shown to be inaccurate Cultures should not be taken from clinically non-infected wounds as all ulcers will be contaminated; sampling cannot discriminate colonization from infection Refer patients urgently to a wound center, foot specialist or ER for urgent treatment if there is acute spreading infection, critical limb ischemia, wet gangrene or unexplained red, hot, swollen foot. These clinical signs and symptoms are potentially limb and lifethreatening 7
8 Where necrosis occurs on the distal part of the limb due to ischemia and in the absence of infection (dry gangrene), mummification of the toes and autoamputation may occur. In most of these situation surgery is not recommended. CHARCOT FOOT WITH PLANTAR ULCER CHARCOT FOOT WITH SEPSIS CHRONIC CHARCOT FOOT Assessing Bone Involvement Osteomyelitis may frequently be present in patients with moderate to severe diabetic foot infection Can be difficult to diagnose in early stages Chronic, large, deep and lie over a bony prominence are at high risk Visual bone is suggestive of osteomyelitis Inspect for Deformities High-arch foot Clawed or hammer toes Visible muscle wasting in the plantar arch Gait changes (such as foot slapping on ground) Hallux valgus, hallux rigidus and fat pad depletion Charcot foot 8
9 Classification systems grade ulcers according to the presence and extent of various physical characteristics, such as size, depth, appearance and location Classification systems should be used consistently across the healthcare team and be recorded appropriately in the patient s records. However, it is the assessment of the wound that informs management Treat underlying disease processes Ensure adequate blood supply Local wound care, including infection Pressure offloading Diabetes education Treating the underlying disease process Treating any severe ischemia is critical to wound healing Achieving optimal diabetic control. Tight glycemic control and managing risk factors such as high blood pressure, hyperlipidemia, smoking and nutritional deficiencies Addressing any physical cause of trauma, proper footwear, presence of any foreign bodies Adequate blood supply A patient with acute limb ischemia is a clinical emergency and may be at great risk if not managed in a timely and effective way Decreased perfusion or impaired circulation may be an indicator for revascularization in order to achieve and maintain healing and to avoid or delay a future amputation 9
10 Tissue Debridement Surgical/sharp debridement- The gold standard technique for tissue management in DFUs is regular, local, sharp debridement using a scalpel, scissors and/or forceps Removes necrotic/sloughy tissue and callus Reduces pressure Allows full inspection of the underlying tissues Helps drainage of secretions or pus Helps optimize the effectiveness of topical preparations Stimulates healing Tissue Debridement Sharp debridement should be carried out by experienced practitioners Practitioners must be able to distinguish tissue types and understand anatomy to avoid damage to blood vessels, nerves and tendons Sharp debridement is an invasive procedure and can be quite radical Vascular status must always be determined prior to sharp debridement Patients needing revascularization should not undergo extensive sharp debridement because of the risk of trauma to compromised tissues Not debriding a wound, not referring a patient to specialist staff for debridement, or choosing the wrong method of debridement, can cause rapid deterioration with potentially devastating consequences. Neuropathic ulcer pre- (top) and post- (bottom) debridement 10
11 Neuroischemic ulcer pre- (top) and post- (bottom) debridement Tissue Debridement Autolytic Debridement Natural process that uses a moist wound dressing to soften and remove devitalised tissue Hydrosurgical Debridement Forces water or saline into a nozzle to create a high-energy cutting beam. This enables precise visualization and removal of devitalized tissue in the wound bed Larval Debridement Larvae of the green bottle fly can achieve relatively rapid, atraumatic removal of moist, slimy slough, and can ingest pathogenic organisms present in the wound High morbidity and mortality associated with infection in DFU s means that early and aggressive treatment is necessary Oral antibiotic therapy Topical antimicrobials At initial presentation of infection it is important to assess its severity, take appropriate cultures and consider need for surgical procedures Optimal specimens for culture should be taken after initial cleansing and debridement of necrotic material Patients with severe infection require empiric broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy, pending culture results. Those with mild (and many with moderate) infection can be treated with a more focused and narrow-spectrum antibiotic Patients with diabetes have immunological disturbances; therefore even bacteria regarded as skin commensals can cause severe tissue damage and should be regarded as pathogens when isolated from correctly obtained tissue specimens Gram-negative bacteria, especially when isolated from an ulcer swab, are often colonizing organisms that do not require targeted therapy unless the person is at risk for infection with those organisms Blood cultures should be sent if fever and systemic toxicity are present Even with appropriate treatment, the wound should be inspected regularly for early signs of infection or spreading infection Clinical microbiologists/infectious diseases specialists have a crucial role; laboratory results should be used in combination with the clinical presentation and history to guide antibiotic selection Timely surgical intervention is crucial for deep abscesses, necrotic tissue and for some bone infections 11
12 Biofilms are complex polymicrobial communities that develop on the surface of chronic wounds and delay healing Microbes produce a matric that is thick, slimy and very difficult for topical antimicrobials to penetrate Treatment is aimed at disrupting the biofilm with repeated and debridement and vigorous wound cleansing and preventing reformation by using antimicrobial dressings Appropriate wound bed preparation remains the gold standard for biofilm removal Remember Dressings are not a substitute for sharp debridement, managing infection, offloading devices or diabetic control Balanced-not too moist or too dry Select dressings that best match appearance of the wound Factors to consider.. Location of the wound Extent (size/depth) of the wound Amount and type of exudate The predominant tissue type on the wound surface Condition of the periwound skin Compatibility with other therapies (e.g. contact casts) Wound bioburden and risk of infection Avoidance of pain and trauma at dressing changes Quality of life and patient wellbeing Does the dressing Stay intact and remain in place throughout wear time? Prevent leakage between dressing changes? Cause maceration/allergy or sensitivity? Reduce pain? Reduce odor? Retain fluid? Trap exudate components? Is the dressing.. Comfortable, conformable, flexible and of a bulk/weight that can be accommodated in an offloading device/footwear? Suitable for leaving in place for the required duration? Easy to remove (does not traumatize the surrounding skin or wound bed)? Easy to apply? Cost effective? Likely to cause iatrogenic lesions? 12
13 Dry necrotic wound: Select dressing to rehydrate and soften the eschar Sloughy wound bed with areas of necrosis: Select dressing to control moisture and promote debridement of devitalized tissue 13
14 Infected wound with evidence of swelling and Exudate: Start empiric antibiotic therapy and take cultures Consider selecting an antimicrobial dressing to reduce wound bio burden and manage exudate A newly epithelializing DFU: It is important to protect new tissue growth Regular inspection of wounds is vital If infected or highly exudative, a healthcare professional should change the dressing and inspect the wound daily As the status of the wound changes the dressing may need to change Educate patients to look for signs of deterioration, such as increased pain, swelling, odor, purulence or septic symptoms Mark/monitor extent of any cellulitis Avoid bandaging over toes as this may cause a tourniquet effect (instead, layer gauze over the toes and secure with a bandage from the metatarsal heads to a suitable point on foot) Use appropriate techniques (e.g. avoiding creases and being too bulky) and take care when dressing weight-bearing areas Avoid strong adhesive tapes on fragile skin Avoid tight bandaging at the fifth toe and the fifth metatarsal head (trim the bandage back) Ensure wound dead space is eliminated (e.g. use a dressing that conforms to the contours of the wound bed) Remember that footwear needs to accommodate any dressing. Wounds should be cleansed at each dressing change and after debridement with a wound cleansing solution or saline. Cleansing can help remove devitalized tissue, re-balance the bioburden and reduce exudate to help prepare the wound bed for healing. It may also help to remove biofilms. 14
15 Incorporate strategies to prevent trauma No unnecessary manipulation of wound When appropriate use low- or non-adherent dressings If a dressing becomes encrusted or difficult to remove, it is important to soak the dressing with saline to prevent trauma Disadvantages of TCC Important to offload at-risk areas to redistribute pressures evenly Inadequate offloading leads to tissue damage Gold standard is the total contact cast (TCC) Must be applied by fully trained and experienced practitioners May cause skin irritation and further ulcers if applied inappropriately Prevents daily inspection (signs of spreading infection may go unnoticed) May disturb sleep Makes bathing difficult Patient may not tolerate it (especially in warm climates) May prevent patient's ability to work Relatively high cost/low availability Contraindicated in patients with ischemia, infection or osteomyelitis Pressure relief should always be part of the treatment plan for an existing ulcer TCCs and non-removable walkers are the preferred interventions Forefoot offloading shoes or cast shoes may be used when above ankle devices are contraindicated Conventional or standard therapeutic footwear should not be used The hallmark of an appropriately offloaded wound is a noticeable lack of undermining at the wound s edge at follow up 15
16 Facts.. Lower-extremity amputation often results in disability and a loss of independence; amputation is often more costly than limb salvage Amputation should not be considered unless a detailed vascular assessment has been performed by vascular staff 50% of patients who undergo an amputation will develop a further DFU s of the other limb within 18 months Up to 50% of patients will develop critical limb ischemia in the other limb 50-60% mortality 5 years postamputation Amputation may be indicated in the following circumstances. Ischemic rest pain that cannot be managed by analgesia or revascularization A life-threatening foot infection that cannot be managed by other measures A non-healing ulcer that is accompanied by a higher burden of disease than would result from amputation. In some cases, for example, complications in a diabetic foot render it functionally useless and a well performed amputation is a better alternative for the patient 16
17 17
18 1. National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Diabetic foot problems: inpatient management of diabetic foot problems. Clinical guideline 119. London: NICE, Available at: uk/diabetic-foot-problems-cg119. Accessed March Abetz L, Sutton M, Brady L, et al. The diabetic foot ulcer scale: a quality of life instrument for use in clinical trials. Pract Diab Int 2002; 19: Brownrigg JR, Davey J, Holt et al. The association of ulceration of the foot with cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in patients with diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2012; 55(11): Diabetes UK. Putting feet first: national minimum skills framework. Joint initiative from the Diabetes UK, Foot in Diabetes UK, NHS Diabetes, the Association of British Clinical Diabetologists, the Primary Care Diabetes Society, the Society of Chiropodists and Podiatrists. London: Diabetes UK, Available at: Accessed March Kerr M. Foot care for people with diabetes: the economic case for change. NHS Diabetes, Newcastle-upon-Tyne, Available at: xjy7fs. Accessed March Singh N, Armstrong DA, Lipsky BA. Preventing foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. JAMA 2005; 293: Bakker K, Apelqvist J, Schaper NC on behalf of the International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot Editorial Board. Practical guidelines on the management and prevention of the diabetic foot Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2012; 28(Suppl 1): Diabetes UK. State of the nation 2012 England. London: Diabetes UK, Available at: Accessed March Ramsay SD, Newton K, Blough D, et al. Incidence, outcomes, and cost of foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 1999; 22: Assal JP, Mehnert H, Tritschler HS, et al. On your feet workshop on the diabetic foot. J Diabet Comp 2002; 16: Rathur HM, Boulton AJM. The diabetic foot. Clin Dermatol 2007; 25: Prompers L, Huijberts M, Schaper N, et al. Resource utilisation and costs associated with the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Prospective data from the EURODIALE Study. Diabetologia 2008; 51: Young MJ, McCardle JE, Randall LE, et al. Improved survival of diabetic foot ulcer patients : possible impact of aggressive cardiovascular risk management. Diabetes Care 2008; 31: Hinchcliffe RJ, Andros G, Apelqvist J, et al. A systematic review of the effectiveness of revascularisation of the ulcerated foot in patients with diabetes and peripheral arterial disease. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2012; 28(Suppl 1): Muller IS, Bartelink ML, Wim JC, et al. Foot ulceration and lower limb amputation in type 2 diabetic patients in Dutch Primary Health Care. Diabetes Care 2002; 25(3): Boulton AJ, Vileikyte L, Ragnarson-Tennvall G, et al. The global burden of diabetic foot disease. Lancet 2005; 366: Frykberg RG. Diabetic foot ulcers: pathogenesis and management. Am Fam Physician 2002; 66(9): Berthel M, Ehrler S. Aspects épidémiologiques de l'amputation de membre inférieur en france. Kinesitherapie Scientifique 2010; 7(512): Armstrong DG, Wrobel J, Robbins JM. Guest editorial: are diabetesrelated wounds and amputations worse than cancer? Int Wound J 2007; 4: Pecoraro RE, Reiber GE, Burgess EM. Pathways to diabetic limb amputation. Basis for prevention. Diabetes Care 1990; 13(5): Chadwick P, Jeffcoate W, McIntosh C. How can we improve the care of the diabetic foot? Wounds UK 2008; 4(4): TRIEPodD-UK. Podiatry competency framework for integrated diabetic foot care a user s guide. London: TRIEpodD-UK, Prompers L, Schaper N, Apelqvist J, et al. Prediction of outcome in individuals with diabetic foot ulcers: focus on the differences between individuals with and without peripheral arterial disease. The EURODIALE Study. Diabetologia 2008; 51(5):
The Diabetic Foot Screen and Management Foundation Series of Modules for Primary Care
 The Diabetic Foot Screen and Management Foundation Series of Modules for Primary Care Anita Murray - Senior Podiatrist Diabetes, SCH Learning Outcomes Knowledge of the Model of Care For The Diabetic Foot
The Diabetic Foot Screen and Management Foundation Series of Modules for Primary Care Anita Murray - Senior Podiatrist Diabetes, SCH Learning Outcomes Knowledge of the Model of Care For The Diabetic Foot
Definitions and criteria
 Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Care for Patients in All Settings
 Diabetic Foot Ulcers Care for Patients in All Settings Summary This quality standard focuses on care for people who have developed or are at risk of developing a diabetic foot ulcer. The scope of the standard
Diabetic Foot Ulcers Care for Patients in All Settings Summary This quality standard focuses on care for people who have developed or are at risk of developing a diabetic foot ulcer. The scope of the standard
Wound Jeopardy: Name That Wound Session 142 Saturday, September 10 th 2011
 Initial Wound Care Consult History Physical Examination Detailed examination of the wound Photographs Cultures Procedures TCOM ABI Debridement Management Decisions A Detailed History and Physical (wound)
Initial Wound Care Consult History Physical Examination Detailed examination of the wound Photographs Cultures Procedures TCOM ABI Debridement Management Decisions A Detailed History and Physical (wound)
AGONY FEET. The. of the. Prevention and management of diabetic foot ulcers
 The AGONY of the FEET Prevention and management of diabetic foot ulcers By Margaret Falconio-West, BSN, rn, APN/CNS, CWOCN, DAPWCA Nearly 25 percent of people with diabetes will develop a diabetic foot
The AGONY of the FEET Prevention and management of diabetic foot ulcers By Margaret Falconio-West, BSN, rn, APN/CNS, CWOCN, DAPWCA Nearly 25 percent of people with diabetes will develop a diabetic foot
Preventing Foot Ulcers in the Neuropathic Diabetic Foot. Glossary of Terms
 Preventing Foot Ulcers in the Neuropathic Diabetic Foot Warren Woods, Certified Orthotist, Health Sciences Centre, Rehabilitation Engineering Department What you need to know Glossary of Terms Neuropathic
Preventing Foot Ulcers in the Neuropathic Diabetic Foot Warren Woods, Certified Orthotist, Health Sciences Centre, Rehabilitation Engineering Department What you need to know Glossary of Terms Neuropathic
Wound Classification. Overview
 Overview Jeffrey A. Niezgoda, MD FACHM, MAPWCA, CHWS Review of Initial Wound Care Consultation Rational for Classification Wound Appearance Wound Etiology Management Algorithms Initial Wound Care Consult
Overview Jeffrey A. Niezgoda, MD FACHM, MAPWCA, CHWS Review of Initial Wound Care Consultation Rational for Classification Wound Appearance Wound Etiology Management Algorithms Initial Wound Care Consult
Your guide to wound debridement and assessment. Michelle Greenwood. Lorraine Grothier. Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust
 Your guide to wound debridement and assessment Michelle Greenwood Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust Lorraine Grothier Clinical Nurse Specialist, Tissue Viability, Central Essex
Your guide to wound debridement and assessment Michelle Greenwood Lead Nurse, Tissue Viability, Walsall Healthcare NHS Trust Lorraine Grothier Clinical Nurse Specialist, Tissue Viability, Central Essex
Service Development Tool for the Assessment of Provision of Services for Patients with Diabetes Related Foot Problems
 Division of Medicine & Community Services Service Development Tool for the Assessment of Provision of Services for Patients with Diabetes Related Foot Problems Graham Holt Advanced Practitioner / Podiatrist
Division of Medicine & Community Services Service Development Tool for the Assessment of Provision of Services for Patients with Diabetes Related Foot Problems Graham Holt Advanced Practitioner / Podiatrist
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment and Prevention
 Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment and Prevention Alexander Reyzelman DPM, FACFAS Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University Diabetic Foot Ulcers One of the most
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatment and Prevention Alexander Reyzelman DPM, FACFAS Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University Diabetic Foot Ulcers One of the most
VASCULAR WOUNDS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT
 VASCULAR WOUNDS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT Lucy Stopher, A/CNS Vascular Surgery ...it is best to think of a wound not as a disease, but rather as a manifestation of disease. Joe McCulloch In order
VASCULAR WOUNDS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT Lucy Stopher, A/CNS Vascular Surgery ...it is best to think of a wound not as a disease, but rather as a manifestation of disease. Joe McCulloch In order
Lower Extremity Wound Evaluation and Treatment
 Lower Extremity Wound Evaluation and Treatment Boni-Jo Silbernagel, DPM Describe effective lower extremity wound evaluation and treatment. Discuss changes in theories of treatment in wound care and implications
Lower Extremity Wound Evaluation and Treatment Boni-Jo Silbernagel, DPM Describe effective lower extremity wound evaluation and treatment. Discuss changes in theories of treatment in wound care and implications
Diabetic/Neuropathic Foot Ulcer Assessment Guide South West Regional Wound Care Program Last Updated April 7,
 Developed in collaboration with the Wound Care Champions, Wound Care Specialists, Enterostomal Nurses, and South West Regional Wound Care Program (SWRWCP) members from Long Term Care Homes, Hospitals,
Developed in collaboration with the Wound Care Champions, Wound Care Specialists, Enterostomal Nurses, and South West Regional Wound Care Program (SWRWCP) members from Long Term Care Homes, Hospitals,
Diabetes - Foot Care
 Diabetes - Foot Care Introduction People with diabetes are more likely than others to have problems with their feet. These problems can lead to dangerous infections of the foot. Recognizing and treating
Diabetes - Foot Care Introduction People with diabetes are more likely than others to have problems with their feet. These problems can lead to dangerous infections of the foot. Recognizing and treating
Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C. Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist
 Diabetic Foot Ulcers Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist Organization of Wound Care Nurses www.woundcarenurses.org Objectives Identify Diabetic/Neuropathic
Diabetic Foot Ulcers Alex Khan APRN ACNS-BC MSN CWCN CFCN WCN-C Advanced Practice Nurse / Adult Clinical Nurse Specialist Organization of Wound Care Nurses www.woundcarenurses.org Objectives Identify Diabetic/Neuropathic
Helen Gelly, MD, FUHM, FCCWS
 Helen Gelly, MD, FUHM, FCCWS Diabetes mellitus is a major risk factor that impairs wound healing, making foot wounds one of the major problems of diabetes. Over 60% of lower limb amputations in the US
Helen Gelly, MD, FUHM, FCCWS Diabetes mellitus is a major risk factor that impairs wound healing, making foot wounds one of the major problems of diabetes. Over 60% of lower limb amputations in the US
Introduction. Epidemiology Pathophysiology Classification Treatment
 Diabetic Foot Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology Classification Treatment Epidemiology DM largest cause of neuropathy in N.A. 1 million DM patients in Canada Half don t know Foot ulcerations is
Diabetic Foot Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology Classification Treatment Epidemiology DM largest cause of neuropathy in N.A. 1 million DM patients in Canada Half don t know Foot ulcerations is
Management Of The Diabetic foot
 Management Of The Diabetic foot Aims, Pathways, Treatments Nikki Coates 12/1/18 Diabetic foot pathology Neuropathy Foot deformity Vascular disease Sensory neuropathy Limited Joint Mobility Smoking Autonomic
Management Of The Diabetic foot Aims, Pathways, Treatments Nikki Coates 12/1/18 Diabetic foot pathology Neuropathy Foot deformity Vascular disease Sensory neuropathy Limited Joint Mobility Smoking Autonomic
Case Study 2 - Mr J. Medical history
 Case Study 2 - Mr J A 54 year-old male was referred to the podiatrist at Coast Provincial General Hospital Diabetic Clinic, for management of active foot disease. The patient s presenting complaint was
Case Study 2 - Mr J A 54 year-old male was referred to the podiatrist at Coast Provincial General Hospital Diabetic Clinic, for management of active foot disease. The patient s presenting complaint was
High Risk Podiatry in a Vascular Setting; A new paradigm in Diabetic Foot Disease? Ereena Torpey Senior Podiatrist - FMC
 High Risk Podiatry in a Vascular Setting; A new paradigm in Diabetic Foot Disease? Ereena Torpey Senior Podiatrist - FMC A new paradigm? Foot ulceration 101 Assessing Perfusion a new challenge Pressure
High Risk Podiatry in a Vascular Setting; A new paradigm in Diabetic Foot Disease? Ereena Torpey Senior Podiatrist - FMC A new paradigm? Foot ulceration 101 Assessing Perfusion a new challenge Pressure
Debridement: treatment, options and selection.
 This document is the Accepted Manuscript version of a Published Work that appeared in final form in Independent Nurse, copyright MA Healthcare, after peer review and technical editing by the publisher.
This document is the Accepted Manuscript version of a Published Work that appeared in final form in Independent Nurse, copyright MA Healthcare, after peer review and technical editing by the publisher.
How can DIABETES affect my FEET? Emma Howard Specialist Podiatrist and Team Leader, Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust
 How can DIABETES affect my FEET? By: Emma Howard Specialist Podiatrist and Team Leader, Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust HOW CAN DIABETES AFFECT MY FEET? What is neuropathy? This leaflet explains how
How can DIABETES affect my FEET? By: Emma Howard Specialist Podiatrist and Team Leader, Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust HOW CAN DIABETES AFFECT MY FEET? What is neuropathy? This leaflet explains how
Practical guidelines on the management and prevention of the diabetic foot 2011
 DIABETES/METABOLISM RESEARCH AND REVIEWS Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2012; 28(Suppl 1): 225 231. Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com).2253 IWGDF GUIDELINES Practical guidelines
DIABETES/METABOLISM RESEARCH AND REVIEWS Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2012; 28(Suppl 1): 225 231. Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com).2253 IWGDF GUIDELINES Practical guidelines
Diabetic/Neuropathic Foot Ulcer Assessment Guide South West Regional Wound Care Program Last Updated June 10,
 Developed in collaboration with the Wound Care Champions, Wound Care Specialists, Enterostomal Nurses, and South West Regional Wound Care Program (SWRWCP) members from Long Term Care Homes, Hospitals,
Developed in collaboration with the Wound Care Champions, Wound Care Specialists, Enterostomal Nurses, and South West Regional Wound Care Program (SWRWCP) members from Long Term Care Homes, Hospitals,
Wound Care Program for Nursing Assistants-
 Wound Care Program for Nursing Assistants- Wound Cleansing,Types & Presentation Elizabeth DeFeo, RN, WCC, OMS, CWOCN Wound, Ostomy, & Continence Specialist ldefeo@cornerstonevna.org Outline/Agenda At completion
Wound Care Program for Nursing Assistants- Wound Cleansing,Types & Presentation Elizabeth DeFeo, RN, WCC, OMS, CWOCN Wound, Ostomy, & Continence Specialist ldefeo@cornerstonevna.org Outline/Agenda At completion
Venous Leg Ulcers. Care for Patients in All Settings
 Venous Leg Ulcers Care for Patients in All Settings Summary This quality standard focuses on care for people who have developed or are at risk of developing a venous leg ulcer. The scope of the standard
Venous Leg Ulcers Care for Patients in All Settings Summary This quality standard focuses on care for people who have developed or are at risk of developing a venous leg ulcer. The scope of the standard
Acute and Chronic WOUND ASSESSMENT. Wound Assessment OBJECTIVES ITEMS TO CONSIDER
 WOUND ASSESSMENT Acute and Chronic OBJECTIVES Discuss classification systems and testing methods for pressure ulcers, venous, arterial and diabetic wounds List at least five items to be assessed and documented
WOUND ASSESSMENT Acute and Chronic OBJECTIVES Discuss classification systems and testing methods for pressure ulcers, venous, arterial and diabetic wounds List at least five items to be assessed and documented
Diabetic Foot Ulcer. A Complete Solution. Therapy Approach with Adapted Products
 Diabetic Foot Ulcer A Complete Solution Therapy Approach with Adapted Products A Complete Solution for Diabetic Foot Ulcers This booklet focuses on the recommended treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes
Diabetic Foot Ulcer A Complete Solution Therapy Approach with Adapted Products A Complete Solution for Diabetic Foot Ulcers This booklet focuses on the recommended treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Diabetes
Appropriate targeted foot care of
 Understanding the role of a monofilament fibre debridement pad in the management of diabetic foot ulcers Paul Chadwick, Andrew Findlow A diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) is a pivotal event for a person with diabetes,
Understanding the role of a monofilament fibre debridement pad in the management of diabetic foot ulcers Paul Chadwick, Andrew Findlow A diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) is a pivotal event for a person with diabetes,
Frank K. Galbraith D.P.M. Dr. Frank Galbraith
 Frank K. Galbraith D.P.M. Dr. Frank Galbraith Ingrown Toenails Paronychia (infected toenail) Onychomycosis (fungal nails) From improper trimming, leaving nail sharp corners Curved nails Thick (Hypertrophic)
Frank K. Galbraith D.P.M. Dr. Frank Galbraith Ingrown Toenails Paronychia (infected toenail) Onychomycosis (fungal nails) From improper trimming, leaving nail sharp corners Curved nails Thick (Hypertrophic)
AWMA MODULE ACCREDITATION. Module Five: The High Risk Foot (Including the Diabetic Foot)
 AWMA MODULE ACCREDITATION Module Five: The High Risk Foot (Including the Diabetic Foot) Introduction - The Australian Wound Management Association Education & Professional Development Sub Committee-(AWMA
AWMA MODULE ACCREDITATION Module Five: The High Risk Foot (Including the Diabetic Foot) Introduction - The Australian Wound Management Association Education & Professional Development Sub Committee-(AWMA
Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing Certification Board (WOCNCB) Certified Foot Care Nurse (CFCN) Detailed Content Outline
 Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing Certification Board (WOCNCB) Certified Foot Care Nurse (CFCN) Detailed Content Outline Description Domain I: Assessment and Care Planning 010000 40 Task 1: Obtain focused
Wound, Ostomy and Continence Nursing Certification Board (WOCNCB) Certified Foot Care Nurse (CFCN) Detailed Content Outline Description Domain I: Assessment and Care Planning 010000 40 Task 1: Obtain focused
of :07
 he diabetic foot ulcer - management and outcomes of 6 3-12-2012 11:07 The diabetic foot ulcer - management and outcomes Impaired perfusion Infection Extent and depth Condition of the ulcer Site Sensation
he diabetic foot ulcer - management and outcomes of 6 3-12-2012 11:07 The diabetic foot ulcer - management and outcomes Impaired perfusion Infection Extent and depth Condition of the ulcer Site Sensation
Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds
 Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds Criteria to Consider for an IDEAL DRESSING Exudate Management Be able to provide for moist wound healing by absorbing exudate or adding moisture Secure
Appropriate Dressing Selection For Treating Wounds Criteria to Consider for an IDEAL DRESSING Exudate Management Be able to provide for moist wound healing by absorbing exudate or adding moisture Secure
Project I - Background Worksheet. Team Members: Kira Brown, Paige Fallu. Clinical problem Diabetic Foot Ulcers
 Project I - Background Worksheet Team Members: Kira Brown, Paige Fallu Clinical problem Diabetic Foot Ulcers 1) Strategic Focus based on the Strategic focus powerpoint presentation and readings a. Team
Project I - Background Worksheet Team Members: Kira Brown, Paige Fallu Clinical problem Diabetic Foot Ulcers 1) Strategic Focus based on the Strategic focus powerpoint presentation and readings a. Team
CLI Therapy- LINCed Multi disciplinary discussions on CLI
 CLI Therapy- LINCed Multi disciplinary discussions on CLI Critical limb ischemia and managing the infected wound Michiel Schreve North West Clinics Alkmaar, The Netherlands Disclosure Speaker name: Michiel
CLI Therapy- LINCed Multi disciplinary discussions on CLI Critical limb ischemia and managing the infected wound Michiel Schreve North West Clinics Alkmaar, The Netherlands Disclosure Speaker name: Michiel
Foot Ulcer Workshop: Prevention and Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Aparna Pal, Consultant Endocrinologist, RBH Keith Hilston, Podiatrist, BHFT
 Foot Ulcer Workshop: Prevention and Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers Aparna Pal, Consultant Endocrinologist, RBH Keith Hilston, Podiatrist, BHFT High mortality and morbidity Complex condition, longterm
Foot Ulcer Workshop: Prevention and Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers Aparna Pal, Consultant Endocrinologist, RBH Keith Hilston, Podiatrist, BHFT High mortality and morbidity Complex condition, longterm
Front line management of the Diabetic Foot
 Front line management of the Diabetic Foot n o ti e b a i D + s te k o Sm = g in p Am a t u Sam Fratesi MD Smoking + diabetes = amputation Almost 2 million Canadians have diabetes In amputated diabetics
Front line management of the Diabetic Foot n o ti e b a i D + s te k o Sm = g in p Am a t u Sam Fratesi MD Smoking + diabetes = amputation Almost 2 million Canadians have diabetes In amputated diabetics
2008 American Medical Association and National Committee for Quality Assurance. All Rights Reserved. CPT Copyright 2007 American Medical Association
 Chronic Wound Care ASPS #1: Use of wound surface culture technique in patients with chronic skin ulcers (overuse measure) This measure may be used as an Accountability measure Clinical Performance Measure
Chronic Wound Care ASPS #1: Use of wound surface culture technique in patients with chronic skin ulcers (overuse measure) This measure may be used as an Accountability measure Clinical Performance Measure
Patient Product Information
 Patient Product Information REGEN-D 150 (India's First Recombinant Human Epidermal Growth Factor (rhegf) Gel for Diabetic Foot Ulcers) Generic name: [Recombinant Human Epidermal Growth Factor (rhegf)]
Patient Product Information REGEN-D 150 (India's First Recombinant Human Epidermal Growth Factor (rhegf) Gel for Diabetic Foot Ulcers) Generic name: [Recombinant Human Epidermal Growth Factor (rhegf)]
Essity Internal. Taking the fear out of wound infection: conquering everyday issues
 Taking the fear out of wound infection: conquering everyday issues Learning objectives 1. Identifying the cost which wound infection can have on both the patient and healthcare organisations 2. Understanding
Taking the fear out of wound infection: conquering everyday issues Learning objectives 1. Identifying the cost which wound infection can have on both the patient and healthcare organisations 2. Understanding
Total Contact Cast System
 Total Contact Cast System Instructions for Use Products Included in Cutimed Off-Loader Select kit Qty Cutimed Cavity Sterile 1 ea. Cutisorb Cotton Gauze 2" x 2" 4 ea. Delta-Lite Conformable Fiberglass
Total Contact Cast System Instructions for Use Products Included in Cutimed Off-Loader Select kit Qty Cutimed Cavity Sterile 1 ea. Cutisorb Cotton Gauze 2" x 2" 4 ea. Delta-Lite Conformable Fiberglass
Address: Left Leg. other: Nails: thick yellow brittle fungus abnormal thick yellow brittle fungus abnormal
 South West Regional Wound Care Toolkit: Interdisciplinary Lower Leg Assessment Form Instructions for use: Competent/ Proficient/ Expert level HCP to complete if lower leg ulcer present or risk of ulcer
South West Regional Wound Care Toolkit: Interdisciplinary Lower Leg Assessment Form Instructions for use: Competent/ Proficient/ Expert level HCP to complete if lower leg ulcer present or risk of ulcer
DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED
 10 DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED It must be recognised that no one dressing provides the optimum environment for the healing of all wounds (Mahoney, 2015) DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED Selecting the correct
10 DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED It must be recognised that no one dressing provides the optimum environment for the healing of all wounds (Mahoney, 2015) DRESSING SELECTION SIMPLIFIED Selecting the correct
Treat the whole patient, not just the hole in the patient! 3/21/2017 CAN YOU CONNECT THE DOTS?? PHILOSOPHY OBJECTIVES
 CAN YOU CONNECT THE DOTS?? Boone Hospital Wound Healing Center Kimberly Jamison, MD, FACP, FAPWCA, PCWC Kim Mitchell, RN, BSN OBJECTIVES Describe the basic concepts of chronic wound care to ensure an optimal
CAN YOU CONNECT THE DOTS?? Boone Hospital Wound Healing Center Kimberly Jamison, MD, FACP, FAPWCA, PCWC Kim Mitchell, RN, BSN OBJECTIVES Describe the basic concepts of chronic wound care to ensure an optimal
1 of :19
 1 of 8 3-12-2012 12:19 Diabetic foot ulcer classification system for research purposes Introduction Aims of the ulcer research classification system Definitions and categorisation for the ulcer research
1 of 8 3-12-2012 12:19 Diabetic foot ulcer classification system for research purposes Introduction Aims of the ulcer research classification system Definitions and categorisation for the ulcer research
DIABETES AND FOOTCARE
 DIABETES AND FOOTCARE Self-Care and Treatment for Healthy Feet Don t Take Your Feet for Granted Every day, you depend on your feet to keep you moving. But when you have diabetes, your feet need special
DIABETES AND FOOTCARE Self-Care and Treatment for Healthy Feet Don t Take Your Feet for Granted Every day, you depend on your feet to keep you moving. But when you have diabetes, your feet need special
WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL SIMPLIFIED
 WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL SIMPLIFIED 10 Some of the common signs of failure to heal with possible causes and some interventions WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL There must be adequate supplies of nutrients and oxygen
WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL SIMPLIFIED 10 Some of the common signs of failure to heal with possible causes and some interventions WHY WOUNDS FAIL TO HEAL There must be adequate supplies of nutrients and oxygen
Peripheral Neuropathy
 Peripheral Neuropathy Neuropathy affects 30-50% of patient population with diabetes and this prevalence tends to increase proportionally with duration of diabetes and dependant on control. Often presents
Peripheral Neuropathy Neuropathy affects 30-50% of patient population with diabetes and this prevalence tends to increase proportionally with duration of diabetes and dependant on control. Often presents
Diabetes Mellitus and the Associated Complications
 Understanding and the complications relating to the disease can assist the fitter to better serve patients. and the Associated Complications Released January, 2011 Total: 25.8 million people, or 8.3% of
Understanding and the complications relating to the disease can assist the fitter to better serve patients. and the Associated Complications Released January, 2011 Total: 25.8 million people, or 8.3% of
The Triangle of Wound Assessment
 The Triangle of Wound Assessment A simple and holistic framework for wound management CPWSC_TOWA_Brochure_210x210_2018.indd 1 10/01/2018 15.13 ? We asked healthcare professionals around the world about
The Triangle of Wound Assessment A simple and holistic framework for wound management CPWSC_TOWA_Brochure_210x210_2018.indd 1 10/01/2018 15.13 ? We asked healthcare professionals around the world about
Aetiology Macroangiopathy occurs mainly distally ie Popliteal artery There is arterial wall calcification Microangiopathy is less common
 DIABETIC FOOT Facts 5% of the population is diabetic 12% of diabetic admissions are with foot problems 1/3rd of diabetic foot ulcerations are neuropathic, 1/3rd are ischaemic and 1/3 are of a mixed in
DIABETIC FOOT Facts 5% of the population is diabetic 12% of diabetic admissions are with foot problems 1/3rd of diabetic foot ulcerations are neuropathic, 1/3rd are ischaemic and 1/3 are of a mixed in
Diabetic Foot Problems
 http://www.medicine-on-line.com Diabetic foot disease: 1/12 Diabetic Foot Problems Author: Affiliation: Rebecca Wong BN, MSc(Health Care) Prince of Wales Hospital, Hong Kong SAR Introduction Diabetes Mellitus
http://www.medicine-on-line.com Diabetic foot disease: 1/12 Diabetic Foot Problems Author: Affiliation: Rebecca Wong BN, MSc(Health Care) Prince of Wales Hospital, Hong Kong SAR Introduction Diabetes Mellitus
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Medical technology guidance SCOPE Debrisoft for the debridement of acute and chronic wounds 1 Technology 1.1 Description of the technology The Debrisoft
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Medical technology guidance SCOPE Debrisoft for the debridement of acute and chronic wounds 1 Technology 1.1 Description of the technology The Debrisoft
Assessment and Management of Wounds In Diabetes. Maria Mousley Northamptonshire NHS Foundation Trust
 Assessment and Management of Wounds In Diabetes Maria Mousley Northamptonshire NHS Foundation Trust Background At least 61000 people with diabetes in England have a foot ulcer at any given time There are
Assessment and Management of Wounds In Diabetes Maria Mousley Northamptonshire NHS Foundation Trust Background At least 61000 people with diabetes in England have a foot ulcer at any given time There are
Challenging wounds, improving outcomes. Treatment of complex diabetic foot wounds using topical oxygen therapy
 Challenging wounds, improving outcomes Treatment of complex diabetic foot wounds using topical oxygen therapy A FOREWORD The essential role of oxygen in wound healing is well documented, and recent developments
Challenging wounds, improving outcomes Treatment of complex diabetic foot wounds using topical oxygen therapy A FOREWORD The essential role of oxygen in wound healing is well documented, and recent developments
Rapid Foot Screening
 GP Symposium 2015 Workshop Rapid Foot Screening Ms Chelsea Law, Principal Podiatrist Mr Henry Lee, Podiatrist Ms Ng Jia Lin, Podiatrist Ms Polly Lim, Podiatrist Ms Wong Wan Mun, Podiatrist Mr Yeo Boon
GP Symposium 2015 Workshop Rapid Foot Screening Ms Chelsea Law, Principal Podiatrist Mr Henry Lee, Podiatrist Ms Ng Jia Lin, Podiatrist Ms Polly Lim, Podiatrist Ms Wong Wan Mun, Podiatrist Mr Yeo Boon
Wound Care per HHVNA Wound Product Formulary
 Venous Ulcers ABI of 0.9-1.2 = normal blood flow An ABI MUST be obtained prior to inititiation of compression therapy. Compression is the Gold Standard of care to promote wound of venous ulcers. Elevation
Venous Ulcers ABI of 0.9-1.2 = normal blood flow An ABI MUST be obtained prior to inititiation of compression therapy. Compression is the Gold Standard of care to promote wound of venous ulcers. Elevation
Wound debridement: guidelines and practice to remove barriers to healing
 Wound debridement: guidelines and practice to remove barriers to healing Learning objectives 1. The burden of wounds and the impact to the NHS 2. Understand what debridement is and why it is needed 3.
Wound debridement: guidelines and practice to remove barriers to healing Learning objectives 1. The burden of wounds and the impact to the NHS 2. Understand what debridement is and why it is needed 3.
Diabetic Foot Pathophysiology. Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations
 Diabetic Foot Pathophysiology Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations AGEs & RAGEs in Diabetes AGE levels increased & RAGEs highly expressed in diabetic
Diabetic Foot Pathophysiology Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations AGEs & RAGEs in Diabetes AGE levels increased & RAGEs highly expressed in diabetic
The Diabetic Foot. Michael Anthony, DPM. 422 million diabetic million % adult population 90% Type II
 The Diabetic Foot Michael Anthony, DPM Assistant Professor - Clinical Department of Orthopaedics The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Prevalence of Diabetes 422 million diabetic 2016 382 million
The Diabetic Foot Michael Anthony, DPM Assistant Professor - Clinical Department of Orthopaedics The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Prevalence of Diabetes 422 million diabetic 2016 382 million
The Diabetic Foot. Prevalence of Diabetes United States. Prevalence of Diabetes
 The Diabetic Foot Prevalence of Diabetes Michael Anthony, DPM Assistant Professor - Clinical Department of Orthopaedics The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center 422 million diabetic 2016 382 million
The Diabetic Foot Prevalence of Diabetes Michael Anthony, DPM Assistant Professor - Clinical Department of Orthopaedics The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center 422 million diabetic 2016 382 million
Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types. Summary
 Dressing selection Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types Summary Which wound dressing poster Ref: Which wound dressing? Practice Nursing, September
Dressing selection Agenda (45 minutes) Some questions for you. Which wound dressing? Dressing categories/types Summary Which wound dressing poster Ref: Which wound dressing? Practice Nursing, September
Wound Care Evaluation by Kris Dalseg MS PT CWS CLT
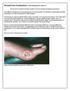 Wound Care Evaluation by Kris Dalseg MS PT CWS CLT This document is intended to describe a standard wound care evaluation for healthcare practitioners. In healthcare, all aspects of our treatment have
Wound Care Evaluation by Kris Dalseg MS PT CWS CLT This document is intended to describe a standard wound care evaluation for healthcare practitioners. In healthcare, all aspects of our treatment have
VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS
 VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS KANSAS ASSOCIATION OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE ANNUAL CME CONVENTION APRIL 13, 2018 THREE
VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS KANSAS ASSOCIATION OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE ANNUAL CME CONVENTION APRIL 13, 2018 THREE
ULCERS 1/12/ million diabetics in the US (2012) Reamputation Rate 26.7% at 1 year 48.3% at 3 years 60.7% at 5 years
 Jay Christensen D.P.M Advanced Foot and Ankle of Wisconsin 2-4% of the population at any given time will have ulcers 0.06-0.20% of the total population Average age of patients 70 years increased as more
Jay Christensen D.P.M Advanced Foot and Ankle of Wisconsin 2-4% of the population at any given time will have ulcers 0.06-0.20% of the total population Average age of patients 70 years increased as more
Diabetes is a serious disease that can develop from lack of insulin production in the body or due to
 Page 1 The Diabetic Foot Definition Diabetes is a serious disease that can develop from lack of insulin production in the body or due to the inability of the body's insulin to perform its normal everyday
Page 1 The Diabetic Foot Definition Diabetes is a serious disease that can develop from lack of insulin production in the body or due to the inability of the body's insulin to perform its normal everyday
CHAPTER.7 CARING THE DIABETIC FOOT
 CHAPTER.7 CARING THE DIABETIC FOOT Introduction Diabetes has become a global epidemic(144). The long term complications due to diabetes impose huge social and economic burden, mental and physical misery
CHAPTER.7 CARING THE DIABETIC FOOT Introduction Diabetes has become a global epidemic(144). The long term complications due to diabetes impose huge social and economic burden, mental and physical misery
Happy Feet: Feeling good about diabe.c foot screening! Family Medicine Forum 2014, Quebec City November 14, 2014
 Happy Feet: Feeling good about diabe.c foot screening! Family Medicine Forum 2014, Quebec City November 14, 2014 Dr. Michael Yan, MD, CCFP Clinical Lecturer, Department of Family Medicine, University of
Happy Feet: Feeling good about diabe.c foot screening! Family Medicine Forum 2014, Quebec City November 14, 2014 Dr. Michael Yan, MD, CCFP Clinical Lecturer, Department of Family Medicine, University of
Model of Care for the Diabetic Foot
 Model of Care for the Diabetic Foot National Clinical Programme for Diabetes Clinical Strategy and Programme Division 2018 Revision number Document drafted by National Clinical Programme for Diabetes Working
Model of Care for the Diabetic Foot National Clinical Programme for Diabetes Clinical Strategy and Programme Division 2018 Revision number Document drafted by National Clinical Programme for Diabetes Working
The Diabetic Foot Latest Statistics
 The Diabetic Foot Latest Statistics There are 2.6 million people with diagnosed diabetes in the UK. There are predicted to be 500,000 who have the condition but are unaware of it. There are 11,859 in TH
The Diabetic Foot Latest Statistics There are 2.6 million people with diagnosed diabetes in the UK. There are predicted to be 500,000 who have the condition but are unaware of it. There are 11,859 in TH
The word debridement derives from the
 Advertorial Is the scalpel the only way to debride? Duncan Stang Citation: Stang D (2013) Is the scalpel the only way to debride. The Diabetic Foot Journal 16: 74 8 Article points 1. A range of debridement
Advertorial Is the scalpel the only way to debride? Duncan Stang Citation: Stang D (2013) Is the scalpel the only way to debride. The Diabetic Foot Journal 16: 74 8 Article points 1. A range of debridement
Sores That Will Not Heal
 Sores That Will Not Heal Introduction Some sores have trouble healing on their own. Sores that will not heal are a common problem. Open sores that will not heal are also known as wounds or skin ulcers.
Sores That Will Not Heal Introduction Some sores have trouble healing on their own. Sores that will not heal are a common problem. Open sores that will not heal are also known as wounds or skin ulcers.
Pressure Ulcer Prevention Guidelines
 EUROPEAN PRESSURE ULCER ADVISORY PANEL Pressure Ulcer Prevention Guidelines INTRODUCTION Pressure damage is common in many healthcare settings across Europe, affecting all age groups, and is costly both
EUROPEAN PRESSURE ULCER ADVISORY PANEL Pressure Ulcer Prevention Guidelines INTRODUCTION Pressure damage is common in many healthcare settings across Europe, affecting all age groups, and is costly both
Determining Wound Diagnosis and Documentation Tips Job Aid
 Determining Wound Diagnosis and Job Aid 1 Coding Is this a traumatic injury from an accident? 800 Codes - Injury Section of the Coding Manual Code by specific site of injury. Only use for accidents or
Determining Wound Diagnosis and Job Aid 1 Coding Is this a traumatic injury from an accident? 800 Codes - Injury Section of the Coding Manual Code by specific site of injury. Only use for accidents or
Venous. Arterial. Neuropathic (e.g. diabetic foot ulcer) Describe Wound Types & Stages of. Pressure Ulcers. Identify Phases of Healing & Wound Care
 A dressing the situation at hand Describe Wound Types & Stages of Pressure Ulcers Identify Phases of Healing & Wound Care Goals Clarify Referral Protocol Lacerations- The goal is nearest to complete approximation
A dressing the situation at hand Describe Wound Types & Stages of Pressure Ulcers Identify Phases of Healing & Wound Care Goals Clarify Referral Protocol Lacerations- The goal is nearest to complete approximation
Advazorb. Hydrophilic foam dressing range
 Advazorb Hydrophilic foam dressing range Advazorb A comprehensive range of patient friendly, absorbent foam dressings Non-adhesive and atraumatic silicone adhesive options Designed to manage exudate whilst
Advazorb Hydrophilic foam dressing range Advazorb A comprehensive range of patient friendly, absorbent foam dressings Non-adhesive and atraumatic silicone adhesive options Designed to manage exudate whilst
Diabetes follow-up: What are the PHO Performance Programme goals and how are they best achieved? Supporting the PHO Performance Programme
 Diabetes follow-up: What are the PHO Performance Programme goals and how are they best achieved? Supporting the PHO Performance Programme 48 BPJ Issue 39 What are the goals? The PHO Performance Programme
Diabetes follow-up: What are the PHO Performance Programme goals and how are they best achieved? Supporting the PHO Performance Programme 48 BPJ Issue 39 What are the goals? The PHO Performance Programme
Surgical Off-loading. Reiber et al Goals of Diabetic Foot Surgery 4/28/2012. The most common causal pathway to a diabetic foot ulceration
 Reiber et al. 1999 Surgical Off-loading The most common causal pathway to a diabetic foot ulceration Alex Reyzelman DPM Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University
Reiber et al. 1999 Surgical Off-loading The most common causal pathway to a diabetic foot ulceration Alex Reyzelman DPM Associate Professor California School of Podiatric Medicine at Samuel Merritt University
DIABETIC ULCERS V PRESSURE ULCERS SO, WHAT DO YOU CALL IT?
 DIABETIC ULCERS V PRESSURE ULCERS SO, WHAT DO YOU CALL IT? Arthur Stone, DPM Mary Sieggreen, MSN,CNS,NP,CVN Faculty Disclosure Dr. Stone has listed an affiliation with: Advisory Board Member..FXI, Inc.
DIABETIC ULCERS V PRESSURE ULCERS SO, WHAT DO YOU CALL IT? Arthur Stone, DPM Mary Sieggreen, MSN,CNS,NP,CVN Faculty Disclosure Dr. Stone has listed an affiliation with: Advisory Board Member..FXI, Inc.
Diabetic Foot Ulcers. A guide to help minimise pain, trauma and stress
 Diabetic Foot Ulcers A guide to help minimise pain, trauma and stress From day one, Safetac was about less pain to patients. It s an easy story it does not stick to the wound, so it does not damage or
Diabetic Foot Ulcers A guide to help minimise pain, trauma and stress From day one, Safetac was about less pain to patients. It s an easy story it does not stick to the wound, so it does not damage or
DIABETIC FOOT RISK CLASSIFICATION IN A TERTIARY CARE TEACHING HOSPITAL OF PESHAWAR
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DIABETIC FOOT RISK CLASSIFICATION IN A TERTIARY CARE TEACHING HOSPITAL OF PESHAWAR Ghulam Shabbier, Said Amin, Ishaq Khattak, Sadeeq-ur-Rehman Department of Medicine Khyber Teaching Hospital
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DIABETIC FOOT RISK CLASSIFICATION IN A TERTIARY CARE TEACHING HOSPITAL OF PESHAWAR Ghulam Shabbier, Said Amin, Ishaq Khattak, Sadeeq-ur-Rehman Department of Medicine Khyber Teaching Hospital
People with diabetes often have trouble with their feet. Read this booklet to learn 7 steps to help keep your feet healthy.
 Form: D-5821 Treat Your Feet: Foot care for people with diabetes People with diabetes often have trouble with their feet. Read this booklet to learn 7 steps to help keep your feet healthy. Diabetes raises
Form: D-5821 Treat Your Feet: Foot care for people with diabetes People with diabetes often have trouble with their feet. Read this booklet to learn 7 steps to help keep your feet healthy. Diabetes raises
Podiatry in Practice. Alan M. Singer, DPM, FACFAS
 Podiatry in Practice Alan M. Singer, DPM, FACFAS Podiatry in Practice Alan Singer, D.P.M. UNIVERSITY PODIATRY GROUP Onychomycosis Anti-fungals Onychocryptosis (Ingrown Nails) Ingrown Nails Partial Nail
Podiatry in Practice Alan M. Singer, DPM, FACFAS Podiatry in Practice Alan Singer, D.P.M. UNIVERSITY PODIATRY GROUP Onychomycosis Anti-fungals Onychocryptosis (Ingrown Nails) Ingrown Nails Partial Nail
Clinical assessment of diabetic foot in 5 minutes
 Clinical assessment of diabetic foot in 5 minutes Assoc. Prof. N. Tentolouris, MD 1 st Department of Propaedeutic Internal Medicine Medical School Laiko General Hospital Leading Innovative Vascular Education
Clinical assessment of diabetic foot in 5 minutes Assoc. Prof. N. Tentolouris, MD 1 st Department of Propaedeutic Internal Medicine Medical School Laiko General Hospital Leading Innovative Vascular Education
Wound Management. E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP
 Wound Management E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP Assistant Professor, OHSU Wound Medical Director, VAPORHCS List the Four Principles of Wound Bed Preparation Determine safe debridement
Wound Management E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP E. Foy White-Chu, MD, CWSP Assistant Professor, OHSU Wound Medical Director, VAPORHCS List the Four Principles of Wound Bed Preparation Determine safe debridement
EVALUATION OF THE VASCULAR STATUS OF DIABETIC WOUNDS Travis Littman, MD NorthWest Surgical Specialists
 EVALUATION OF THE VASCULAR STATUS OF DIABETIC WOUNDS Travis Littman, MD NorthWest Surgical Specialists Nothing To Disclosure DISCLOSURES I have no outside conflicts of interest, financial incentives, or
EVALUATION OF THE VASCULAR STATUS OF DIABETIC WOUNDS Travis Littman, MD NorthWest Surgical Specialists Nothing To Disclosure DISCLOSURES I have no outside conflicts of interest, financial incentives, or
Recognizing Pressure Injury
 Recognizing Pressure Injury Karen Zulkowski, DNS, RN Hawaii Recorded on March 8, 2017 1 A Little About Myself Executive editor of the Journal of the World Council of Enterostomal Therapists (JWCET) and
Recognizing Pressure Injury Karen Zulkowski, DNS, RN Hawaii Recorded on March 8, 2017 1 A Little About Myself Executive editor of the Journal of the World Council of Enterostomal Therapists (JWCET) and
Clinical Guideline for: Diagnosis and Management of Charcot Foot
 Clinical Guideline for: Diagnosis and Management of Charcot Foot SUMMARY This guideline outlines the clinical features of Charcot foot (Charcot Neuroarthropathy). It also explains the process of diagnosis
Clinical Guideline for: Diagnosis and Management of Charcot Foot SUMMARY This guideline outlines the clinical features of Charcot foot (Charcot Neuroarthropathy). It also explains the process of diagnosis
Consider the possibility of pressure ulcer development
 Douglas Fronzaglia II, DO, MS LECOM Institute for Successful Aging LECOM Institute for Advanced Wound Care and Hyperbaric Medicine Consider the possibility of pressure ulcer development 1 Identify ulcer
Douglas Fronzaglia II, DO, MS LECOM Institute for Successful Aging LECOM Institute for Advanced Wound Care and Hyperbaric Medicine Consider the possibility of pressure ulcer development 1 Identify ulcer
Diabetes Foot Care Clinical Pathway Healthcare Provider s Guide
 Diabetes Foot Care Clinical Pathway Healthcare Provider s Guide Diabetes, Obesity & Nutrition Strategic Clinical Network Version 1.0 Acknowledgement This healthcare provider s guide has been adapted from
Diabetes Foot Care Clinical Pathway Healthcare Provider s Guide Diabetes, Obesity & Nutrition Strategic Clinical Network Version 1.0 Acknowledgement This healthcare provider s guide has been adapted from
Topical antimicrobials (antiseptics) Iodine, Silver, Honey
 Topical antimicrobials (antiseptics) Iodine, Silver, Honey Iodine Honey Silver Enzymatic debridement Proteolytic enzyme, also called Proteinase Proteinase breaks the long chainlike molecules of proteins
Topical antimicrobials (antiseptics) Iodine, Silver, Honey Iodine Honey Silver Enzymatic debridement Proteolytic enzyme, also called Proteinase Proteinase breaks the long chainlike molecules of proteins
TIME CONCEPT AND LOCAL WOUND MANAGEMENT
 TIME CONCEPT AND LOCAL WOUND MANAGEMENT B. BRAUN WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION: TIME is a global care framework used to implement appropriate care plans and promote wound healing Tissue Management Inflammation
TIME CONCEPT AND LOCAL WOUND MANAGEMENT B. BRAUN WOUND CARE INTRODUCTION: TIME is a global care framework used to implement appropriate care plans and promote wound healing Tissue Management Inflammation
LOOKING AFTER YOUR FEET
 LOOKING AFTER YOUR FEET Looking after your feet Diabetes can affect the nerves and blood supply to the feet. Over years, the nerve endings to the feet can be affected by high blood glucose levels, and
LOOKING AFTER YOUR FEET Looking after your feet Diabetes can affect the nerves and blood supply to the feet. Over years, the nerve endings to the feet can be affected by high blood glucose levels, and
Diabetic/Neuropathic Foot Ulcer Management Guide South West Regional Wound Care Program Last Updated April 8,
 Developed in collaboration with the Wound Care Champions, Wound Care Specialists, Enterostomal Nurses, and South West Regional Wound Care Program (SWRWCP) members from Long Term Care Homes, Hospitals,
Developed in collaboration with the Wound Care Champions, Wound Care Specialists, Enterostomal Nurses, and South West Regional Wound Care Program (SWRWCP) members from Long Term Care Homes, Hospitals,
Off Loading, TCC, Shoe 을지의대을지병원 족부정형외과 이경태
 Off Loading, TCC, Shoe 을지의대을지병원 족부정형외과 이경태 DMF Protocol VIPS approach V : Vascular I : infection P : Pressure off S : specific wound care Ulcer/Pressure off& Biomechanics PVD vs Peripheral neuropathy NP
Off Loading, TCC, Shoe 을지의대을지병원 족부정형외과 이경태 DMF Protocol VIPS approach V : Vascular I : infection P : Pressure off S : specific wound care Ulcer/Pressure off& Biomechanics PVD vs Peripheral neuropathy NP
Successful Wound Management Strategies : An Introduction. Alex Khan, APRN ACNS-BC. Organization of Wound Care Nurses
 Successful Wound Management Strategies : An Introduction Alex Khan, APRN ACNS-BC Organization of Wound Care Nurses www.woundcarenurses.org Goals & Objectives The role and importance of wound care management
Successful Wound Management Strategies : An Introduction Alex Khan, APRN ACNS-BC Organization of Wound Care Nurses www.woundcarenurses.org Goals & Objectives The role and importance of wound care management
