MR Cholangiopancreatography Before and After Oral Blueberry Juice Administration
|
|
|
- Diane Heath
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 MR Cholangiopancreatography Before and After Oral Blueberry Juice Administration Papanikolaou, Nikolaos; Karantanas, Apostolos; Maris, Thomas; Gourtsoyiannis, Nickolas Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography. 24(2): , March/April Author Information From MR Clinical Science, Philips Medical Systems (N. Papanikolaou), Department of CT-MRI, Larissa General Hospital, Larissa (A. Karantanas), and Department of Radiology, University of Crete Heraklion, Crete (T. Maris and N. Gourtsoyiannis), Greece. This article was given as an oral presentation at RSNA '98. Address correspondence and reprint requests to Dr. A. Karantanas at Department of CT-MRI, Larissa General Hospital, 1 Tsakalof St., Larissa , Greece. apolsen@yahoo.com Abstract Abstract: Blueberry juice was used in 37 patients who underwent MR cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) examination. Quantitative and qualitative comparison between pre-and post-blueberry juice oral administration was made. Common bile duct and main pancreatic duct depiction improved statistically significantly (p < 0.05) after blueberry juice administration. Blueberry juice may be used routinely in MRCP studies as a natural, safe, and inexpensive negative contrast agent with high efficacy. Recently, several investigators have discussed the diagnostic performance of MR cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) as a noninvasive method applied with 2D and 3D turbo spin echo (2D and 3D TSE) and with single shot TSE and half-fourier TSE (SSTSE and HASTE) sequences (1 7). Respiratory artifacts were minimized by using respiratory triggering technique (RT) with 3D TSE or breath-hold (BH) technique with SSTSE and HASTE (8,9). However, overlap between the pancreatobiliary tree and high intensity structures like the stomach, duodenum, and proximal intestine (10) is a recognized limitation, especially in projectional techniques like SSTSE. This drawback could be overcome either by using multiple acquisitions of the same sequence planned in different angulations or by using negative contrast agents for the gastrointestinal tract to reduce high signal intensities arising from adjacent tissues (5). Various oral negative contrast agents for T2-weighted imaging in abdominal applications have been proposed (11 16). Hiraishi et al. (17) first used blueberry juice as an oral negative contrast agent in gastrointestinal MRI. They concluded that blueberry juice at appropriate concentrations could be an effective positive oral contrast agent on T1- weighted images and negative contrast agent on T2-weighted images. Experimental use of blueberry juice was also reported by Hirohashi et al. (10) to suppress high signal intensities in heavily T2- weighted images on phantoms. The purpose of our study was to evaluate the use of blueberry juice as a negative oral contrast agent for the gastrointestinal tract in MRCP studies.
3 MATERIALS AND METHODS Blueberry Juice Phantom Measurements The contents of iron (Fe 3+ ) and manganese (Mn 2+ ) ions were determined in tinned myrtilles in syrup. The contents of three cans were processed according to the method reported by Challa et al. (18). The results given are the means of the contents of the three cans. Iron was determined photometrically with the reagents of a kit by Elitech Diagnostics. Manganese was measured by atomic absorption on a spectrophotometer (Perkin-Elmer model 560). Subjects Thirty-seven patients with clinically suspected obstructive jaundice underwent 3D TSE RT and 2D SSTSE BH. The patient population consisted of 18 men and 19 women. The average age was 64.4 years (range years). All patients were informed about the nature and the purpose of the procedure, and informed consent was obtained from all subjects prior to examination. All subjects were studied before and after 430 ml of blueberry juice was administered orally. The juice was given as follows: 150 ml 30 min before scanning, 150 ml 15 min before scanning, and 130 ml just before scanning. Patients were asked to fast for >6 h before undergoing the MRCP examination. MRI All MR examinations were performed on a Gyroscan NT T10 superconductive MR system (Philips Medical Systems, Best, The Netherlands) using commercial available software (Rel 4.5) and maximum gradient strength of 15 mt/m (Figs. 1 3). The quadrature body coil was used as a transmitter in all cases and receiver in 28 of 37 cases. In nine cases of thin patients, a circular surface coil (17 cm diameter) was used on the anterior abdominal wall at the level of the biliary tree. A 3D multislab heavily T2-weighted TSE sequence with spectral fat suppression prepulse (SPIR) was utilized. Eight overlapping slabs were used. Each slab was mm thick with 41% overlap between adjacent slabs. Each slab was divided into 10 partitions with 2.5 mm thickness and 50% overlap between adjacent partitions. The total volume size was 10 cm, and the orientation of the slices in the coronal plane. Two-dimensional SSTSE was applied in the coronal plane, and the thickness of the projectional slice was mm. The phase-encoding direction for both sequences was left to right. The rest of the sequence parameters are shown in Table 1.
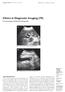
4 TABLE 1. Pulse sequence parameters3d TSE RT, 3D turbo spin echo with respiratory triggering technique; SSTSE, single shot turbo spin echo.ain this sequence, the first 18 echoes (dummy echoes) were excited but not measured to eliminate artifacts arising from tissues with short T2. FIG. 1. Patient with choledocholithiasis. A: Single shot turbo spin echo sequence before blueberry juice administration demonstrated the presence of a stone in the distal common bile duct (arrow). B: In the same sequence after blueberry juice administration, stone visualization was improved (arrow). Note the improvement for depiction of the main pancreatic duct (arrowheads) and especially at the junction area of the main pancreatic duct and the distal common bile duct after blueberry juice administration. High signal intensities of stomach [S] were eliminated, improving the distal and proximal delineation of the main pancreatic duct.
5 Figure 1. Continued FIG. 2. Patient with double pancreatic duct. Shown are single shot turbo spin echo (SSTSE) images before (A) and after (B) blueberry juice administration and 3D turbo spin echo maximum intensity projection (3D TSE MIP) images before (C) and after (D) blueberry juice administration. Signals from stomach [S] and duodenum [D] were suppressed, improving the depiction of pancreatic duct (arrows) in SSTSE (A and B) and both pancreatic duct (arrowheads) and the junction of the common bile duct and the main pancreatic duct (arrow) in 3D TSE MIP (C and D). *, renal cyst; GB, gallbladder.
6 Figure 2. Continued
7 Figure 2. Continued Figure 2. Continued
8 FIG. 3. Patient with a tumor in the head of the pancreas. Shown are 3D turbo spin echo maximum intensity projection image (A) before and (B) after blueberry juice administration. In B, stomach [S] and intestinal [I] signal intensities were suppressed, demonstrating the efficiency of blueberry juice in intestinal structures as well.
9 Figure 3. Continued Qualitative Analysis All source images acquired by the 3D TSE sequence were processed with a maximum intensity projection algorithm generating 15 projections at 12 intervals to produce cholangiograms. All images were reviewed independently by two reviewers who did not have any knowledge of the patient's clinical history or other imaging findings and were blinded to the presence of contrast agent. Images were displayed side by side, and the order in which the images were displayed was randomized. The reviewers were asked to record whether or not the segments of the pancreatobiliary tree were depicted by both sequences before and after the administration of blueberry juice. They graded the visualization of each segment using a 5 point scale system from 0 to 4 (0 = complete visualization sharp edges, 1 = sufficient visualization minor blurring, 2 = moderate visualization moderate blurring, 3 = poor visualization blurred borders, 4 = no visualization). The ducts that were studied included extrahepatic ducts: ampulla, common bile duct, common hepatic duct including the left-right hepatic ducts; intrahepatic ducts; and pancreatic duct: head, body, and tail. Additionally, vascular overlap and image ghost artifacts were evaluated by recording the degree of vascular signal and level of artifacts using a 4 point scale (0 = complete flow void no artifacts, 1 = mild vascular signal minor artifacts, 2 = moderate vascular signal moderate artifacts, 3 = marked vascular enhancement of the portal, splenic, and hepatic veins severe artifacts).
10 The scores of both reviewers were averaged. In cases of disagreement by 1 points, the final choice was made by consensus. Finally, the reviewers were asked to record the degree of dilatation of the extrahepatic bile duct using a 4 point scale (normal, mild, moderate, and severe). The same measurements were done with endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography examination, and the results were compared. Quantitative Analysis The quantitative comparison included calculation of signal-to-noise ratio of the common bile duct, main pancreatic duct, gallbladder, duodenum, and liver. Signal intensity was measured by using an elliptical region of interest on the system console, whereas noise represented the standard deviation of a measurement made by placing an elliptical region of interest 2 cm anteriorly from the abdominal wall (air). Contrast-to-noise ratios between common bile duct and duodenum, common bile duct and liver, and gallbladder and liver were calculated. Statistical Analysis Statistical data analysis was based on paired Student t test to determine statistically significant differences in signal-to-noise and contrast-to-noise ratios between pre-and post-blueberry juice sequences. Nonparametric Wilcoxon matched pairs signed ranks and Mann-Whitney tests were used to assess if blueberry juice administration provided statistically significant improvements in the image quality of 3D TSE RT and SSTSE MRCP studies by means of improving the conspicuity of various segments of the pancreaticobiliary tree. We considered p < 0.05 as a valid threshold for statistical significance. RESULTS Blueberry Juice Contents The mean ± SD concentrations of the ions found in the contents of the three cans were 3.3 ± 0.4 μg/g for iron and 20.6 ± 2.6 μg/g for manganese. The total manganese and iron doses for the patients were 8.17 and 1.32 mg, respectively. Qualitative Comparison Blueberry juice administration demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in the depiction of ampulla, common bile duct, common hepatic duct, and main pancreatic duct only for the SSTSE BH sequence (p < 0.05). The intrahepatic bile duct demonstrated a statistically nonsignificant difference between pre-and post-blueberry juice administration for both sequences. Depiction rates and subjective grading mean values of the pancreaticobiliary segments are shown in Table 2.
11 Blueberry juice administration demonstrated a statistically nonsignificant difference in vascular enhancement for both sequences, whereas in post-blueberry juice sequences, the ghost artifacts level was significantly reduced (p < 0.01). The signal intensity of duodenum was decreased statistically significantly (p < 0.01) in post-blueberry juice sequences, avoiding overlap with the common bile duct. Moreover, an increase in the signal intensity of the common bile duct was shown in 29 of 37 cases (78.37%) and in 9 of 16 cases (56.25%) of the main pancreatic duct for the SSTSE sequence after blueberry juice administration due to image scaling effects. TABLE 2. Depiction rates of biliary and pancreatic ductsnumbers in parentheses are means ± SD and refer to subjective grading. TSE, turbo spin echo; BJ, blueberry juice; SSTSE, single shot turbo spin echo; CBD, common bile duct; CHD, common hepatic duct; IHD, intrahepatic duct; MPD-H, -B, and -T, main pancreatic duct of head, body, and tail. Quantitative Comparison All quantitative comparison results between pre-and post-blueberry juice administration were not significantly different except mean contrast-to-noise ratio between the common bile duct and duodenum for 3D TSE RT and SSTSE BH sequences (Table 3; p < 0.01) and mean signal-to-noise ratio of the duodenum (Table 3; p << 0.01).
12 TABLE 3. Quantitative comparison results: SNR, CNR mean values ± standard deviationtse, turbo spin echo; BJ, blueberry juice; SSTSE, single shot turbo spin echo; CBD, common bile duct; MPD, main pancreatic duct; GB, gallbladder; DUOD, duodenum. DISCUSSION Oral magnetic particles have been used in MRCP with excellent results, although they have a high cost and are not widely available at present (19). Blueberry juice was proved a very efficient negative contrast agent for suppressing the signal of the stomach and duodenum. Moreover, its administration was well tolerated by the patients; no adverse effects were recorded, using 430 ml of blueberry juice. The manganese in blueberry juice exists as a divalent ion (20). The T2 relaxation enhancement effects of blueberry juice are due to manganese (17) and iron ions. Blueberry juice reduces the intraluminal signal of the gastrointestinal tract on T2-weighted images due to the paramagnetic properties of manganese and the superparamagnetic properties of iron ions found in it. Both ions result in T2 shortening, which is responsible for signal elimination. Hiraishi et al. (17) reported that the level of manganese in the blood of five healthy volunteers after ingestion of blueberry juice (total manganese dose 18 mg) did not change from preingestion values up to 6 h after ingestion. In another study (21), using a manganese chloride-based oral contrast agent, manganese blood levels for 18, 36, and 54 mg of total manganese dose demonstrated a slight increase 6 h after administration; these values returned to baseline levels within 24 h. In the present study, a total dose of 8.17 mg of manganese was administered to the patients, which is far lower than that of the previous studies. Daily requirements for iron of adults are 1 2 mg/day (22). The North American diet contains between 10 and 20 mg/day, of which 5 10% is absorbed. In the present study, a total dose of only 1.32 mg of iron was administered per patient. A lower manganese concentration was used in the present study as compared with that described by Hiraishi et al. (17) as optimal for signal suppression of the gastrointestinal tract. This may be explained by the fact that in the present study, a very long echo time was used. In Hiraishi et al. study, short echo times (70 ms) were utilized, whereas in the present study, echo time ranged from 1,000 to 1,300 ms, to achieve heavily T2-weighted contrast. Long echo times further enhance the T2- shortening effects by nulling the T1-shortening effects. This may be the reason why, in the present study, efficient gastrointestinal tract signal elimination was achieved with only a 1.9 mg/dl manganese concentration. The administration of a negative contrast agent further reduced the ghost artifacts due mainly to bowel motion, thus resulting in higher conspicuity of the pancreatobiliary tree. Qualitative and quantitative comparison between 3D TSE RT and SSTSE BH before and after blueberry juice administration showed that blueberry juice caused a statistically significant improvement in the image quality, mainly in SSTSE sequences. Ampulla and MPD visualization was improved in post-blueberry juice SSTSE BH. The signal-to-noise ratio of duodenum was statistically significantly reduced for both sequences after blueberry juice administration, whereas the contrast-to-noise ratio between the common bile duct and duodenum was significantly higher after blueberry juice administration for both sequences. The main drawback of the present study and of other studies using negative (in general) contrast
13 agents in the gastrointestinal tract is the inability to depict the exact entry point of the common bile duct and main pancreatic duct to the duodenum. However, in the particular clinical case in which the Oddi sphincter must be studied, we can alternatively administer 300 ml of water and repeat the MRCP examination. On the contrary, other investigators (23,24) reported the following as pitfalls of MRCP: (a) the presence of a duodenal diverticulum, which can distort the periampullary anatomy, giving the impression of a mass; and (b) the overlap between gastric fluid and the pancreatic duct, which can lead erroneously to a diagnosis of fluid within an ectatic, irregular pancreatic duct involved by chronic pancreatitis. Both pitfalls can be avoided by using blueberry juice. In summary, we suggest that oral administration of blueberry juice could be used for further improvement of image quality, especially for SSTSE projectional sequences. Moreover, it can reduce the motion artifacts in 3D TSE RT sequences. Blueberry juice proved to be a new, safe, and inexpensive negative oral contrast agent for the gastrointestinal tract in MRCP. Acknowledgment: Technical assistance by E. Lavdas, R.T., V. Ftikas, R.T., A. Lytrokapis, R.T., and A. H. Zibis, M.D., is greatly appreciated. REFERENCES 1. Reinhold C, Bret PM. MR cholangiopancreatography. Abdom Imag 1996; 21: Guibaud L, Bret MP, Reinhold C, Atri M, Barkun ANG. Diagnosis of choledocholithiasis: value of MR cholangiography. AJR 1994; 163: Ishizaki Y, Wakayama T, Okada Y, Kobayashi T. Magnetic resonance cholangiography for evaluation of obstructive jaundice. Am J Gastroenterol 1993; 88: Reuther G, Kiefer B, Tuchmann A, Pesendorfer FX. Imaging findings of pancreaticobiliary duct diseases with single-shot MR cholangiopancreatography. AJR 1997; 168: Laubenberger J, Buchert M, Scneider B, Blum U, Hennig J, Langer M. Breath-hold projection magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). Magn Res Med 1995; 33: Fulcher AS, Turner MA, Capps GW, Zfass AM, Baker KM. Half-Fourier RARE MR cholangiopancreatography: experience in 300 subjects. Radiology 1998; 207: Holzknecht N, Ganger J, Sackmann M, et al. Breath-hold MR cholangiography with snapshot techniques: prospective comparison with endoscopic retrograde cholangiography. Radiology 1998; 206: Barish MA, Yucel EK, Soto JA, Chuttani R, Ferrucci JT. MR cholangiopancreatography: efficacy of
14 three-dimensional turbo spin-echo technique. AJR 1995; 165: Ernst O, Calvo M, Sergent G, Mizrahi D, Carpentier F. Breath-hold MR cholangiopancreatography using a HASTE sequence: comparison of single-slice and multislice acquisition techniques. AJR 1997; 169: Hirohashi S, Hirohashi R, Uchida H, et al. MR cholangiopancreatography and MR urography: improved enhancement with a negative oral contrast agent. Radiology 1997; 203: Hirohashi S, Uchida H, Yoshikawa K, et al. Large scale clinical evaluation of bowel contrast agent containing ferric ammonium citrate in MRI. Magn Res Imag 1994; 12: Li KCP, Ang PCG, Tart RP, Storum BL, Rolfes R, Ho-Tai PCK. Paramagnetic oil emulsions as oral contrast agents. Magn Res Imag 1990; 8: Tart RP, Li KCP, Storm BL, Rolfes RJ, Ang PGP. Enteric MRI contrast agents: comparative study of five potential agents in humans. Magn Res Imag 1991; 9: Rinck PA, Smevik O, Nilsen G, et al. Oral magnetic particles in MR imaging of the abdomen and pelvis. Radiology 1991; 178: Brown JJ, Duncan JR, Heiken JP, et al. Perfluoroctylbromide as a gastrointestinal contrast agent for MR imaging: use with and without glucagon. Radiology 1991; 181: Mitchell DG, Vinitski S, Mohamed FB, Mammone JF, Haidet K, Rifkin MD. Comparison of Kaopectate with barium for negative and positive enteric contrast at MR imaging. Radiology 1991; 181: Hiraishi K, Narabayashi I, Fujita O, et al. Blueberry juice: preliminary evaluation as an oral contrast agent in gastrointestinal MR imaging. Radiology 1995; 194: Challa A, Papaefstathiou I, Lapatsanis D, Tsolas O. Primary idiopathic hypomagnesimia in two female siblings. Acta Paediatr 1995; 84: Matos C, Metens T, Deviere J, et al. Pancreatic duct: morphologic and functional evaluation with dynamic MR pancreatography after secretin stimulation. Radiology 1997; 203: Yamamoto Y, Hasegawa H. Components of oral contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging [Japanese]. Food Ingred J 1993; 158: Bernardino ME, Weinreb JC, Mitchell DG, William SC, Morris M. Safety and optimum concentration of a manganese chloride based oral MR contrast agent. J Magn Res Imag 1994; 4: Schreiber WE. Iron, porphyrin and bilirubin metabolism. In: Kaplan LA, Pesce AJ, eds. Clinical chemistry: theory, analysis and correlation. St. Louis: Mosby, 1989: David V, Reinhold C, Hochman M, et al. Pitfalls in the interpretation of MR
15 cholangiopancreatography. AJR 1998; 170: Fulcher AS, Turner MA. Pitfalls of MR cholangiopancreatography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1998; 22: Index Terms: Magnetic resonance imaging; Bile ducts; Cholangiography; Contrast medium 2000 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc.
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
MR CHOLANGIOPANCREATOGRAPHY: PROSPECTIVE COMPARISON OF 3-DIMENSIONAL TURBO SPIN ECHO AND SINGLE-SHOT TURBO SPIN ECHO WITH ERCP
 R.C. Chen, K.Y. Lin, J.M. Lii, et al MR CHOLANGIOPANCREATOGRAPHY: PROSPECTIVE COMPARISON OF 3-DIMENSIONAL TURBO SPIN ECHO AND SINGLE-SHOT TURBO SPIN ECHO WITH ERCP Ran-Chou Chen, 1,2 Kuang-Yang Lin, 3
R.C. Chen, K.Y. Lin, J.M. Lii, et al MR CHOLANGIOPANCREATOGRAPHY: PROSPECTIVE COMPARISON OF 3-DIMENSIONAL TURBO SPIN ECHO AND SINGLE-SHOT TURBO SPIN ECHO WITH ERCP Ran-Chou Chen, 1,2 Kuang-Yang Lin, 3
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast
 MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
Pineapple juice as a negative oral contrast agent in magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: a preliminary evaluation
 The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 991 999 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/36674326 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pineapple juice as a negative oral contrast agent in magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography:
The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 991 999 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/36674326 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pineapple juice as a negative oral contrast agent in magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography:
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is an imaging. technique that is able to non-invasively assess bile and pancreatic ducts,
 SECRETIN AUGMENTED MRCP Riccardo MANFREDI, MD, MBA, FESGAR Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is an imaging technique that is able to non-invasively assess bile and pancreatic ducts, in
SECRETIN AUGMENTED MRCP Riccardo MANFREDI, MD, MBA, FESGAR Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is an imaging technique that is able to non-invasively assess bile and pancreatic ducts, in
Usefulness of the Navigator-echo triggering Technique for Free-Breathing 3D MRCP
 Usefulness of the Navigator-echo triggering Technique for Free-Breathing 3D MRCP Poster No.: C-1257 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Matsunaga, G. Ogasawara, K. Fujii, T. Irie, T.
Usefulness of the Navigator-echo triggering Technique for Free-Breathing 3D MRCP Poster No.: C-1257 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Matsunaga, G. Ogasawara, K. Fujii, T. Irie, T.
Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 6.01.30 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 3:2005 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
MP 6.01.30 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 3:2005 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
Normal anatomy and anatomic variants of the biliary tree and pancreatic ductal system at MRCP - what the clinicians want to know
 Normal anatomy and anatomic variants of the biliary tree and pancreatic ductal system at MRCP - what the clinicians want to know Poster No.: C-1696 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Normal anatomy and anatomic variants of the biliary tree and pancreatic ductal system at MRCP - what the clinicians want to know Poster No.: C-1696 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree
 A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree Thomas Hocker, HMS IV BIDMC Core Radiology Case Presentation September 17, 2007 Review of Normal Pancreaticobiliary Tract Anatomy
A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree Thomas Hocker, HMS IV BIDMC Core Radiology Case Presentation September 17, 2007 Review of Normal Pancreaticobiliary Tract Anatomy
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (11):
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (11): 5167-5171 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Signal analysis of pineapple according to its anatomical region in magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: Which region
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (11): 5167-5171 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Signal analysis of pineapple according to its anatomical region in magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: Which region
Biliary tree dilation - and now what?
 Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Primary sclerosing cholangitis: Evaluation with MR cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
 The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (2011) 42, 351 356 Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrnm
The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (2011) 42, 351 356 Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrnm
Use of magnetic resonance cholangiography in the diagnosis of choledocholithiasis: prospective comparison with a reference imaging method
 118 Gut 1999;44:118 122 Department of Hepatogastroenterology, Bicêtre Hospital, 94 275 Le Kremlin Bicêtre, France S H Zidi F Prat J Fritsch A D Choury G Pelletier Department of Radiology, Bicêtre Hospital,
118 Gut 1999;44:118 122 Department of Hepatogastroenterology, Bicêtre Hospital, 94 275 Le Kremlin Bicêtre, France S H Zidi F Prat J Fritsch A D Choury G Pelletier Department of Radiology, Bicêtre Hospital,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Role of Oral Gadolinium as a Negative Contrast Medium in Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Role of Oral Gadolinium as a Negative Contrast Medium in Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: the ABC of MRCP
 Insights Imaging (2012) 3:11 21 DOI 10.1007/s13244-011-0129-9 PICTORIAL REVIEW Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: the ABC of MRCP Nyree Griffin & Geoff Charles-Edwards & Lee Alexander Grant Received:
Insights Imaging (2012) 3:11 21 DOI 10.1007/s13244-011-0129-9 PICTORIAL REVIEW Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: the ABC of MRCP Nyree Griffin & Geoff Charles-Edwards & Lee Alexander Grant Received:
INTRODUCTION. Jpn J Clin Oncol1999;29(6)
 Jpn J Clin Oncol1999;29(6)294-298 Clinical Significance of Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography for the Diagnosis of Cystic Tumor of the Pancreas Compared with Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography
Jpn J Clin Oncol1999;29(6)294-298 Clinical Significance of Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography for the Diagnosis of Cystic Tumor of the Pancreas Compared with Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography
MRI and MRCP in acute edematous interstitial pancreatitis
 MRI and MRCP in acute edematous interstitial pancreatitis Poster No.: C-0212 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid Organs) - Pancreas Authors: M. Di Girolamo, A. Grossi,
MRI and MRCP in acute edematous interstitial pancreatitis Poster No.: C-0212 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid Organs) - Pancreas Authors: M. Di Girolamo, A. Grossi,
UTILITY OF THREE DIMENSIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE CHOLANGIOPANCREATOGRAPHY IN EVALUATION OF BILIARY OBSTRUCTION IN ADULTS
 - 842 - UTILITY OF THREE DIMENSIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE CHOLANGIOPANCREATOGRAPHY IN EVALUATION OF BILIARY OBSTRUCTION IN ADULTS Moanes M. Enaba MD *Tarek H. ELKammash**MD,, Mansour M. Morsy ***MD * Department
- 842 - UTILITY OF THREE DIMENSIONAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE CHOLANGIOPANCREATOGRAPHY IN EVALUATION OF BILIARY OBSTRUCTION IN ADULTS Moanes M. Enaba MD *Tarek H. ELKammash**MD,, Mansour M. Morsy ***MD * Department
Reviews in Clinical Medicine
 Mashhad University of Medical Sciences (MUMS) Reviews in Clinical Medicine Clinical Research Development Center Ghaem Hospital Natural oral contrast agents for gastrointestinal magnetic resonance imaging
Mashhad University of Medical Sciences (MUMS) Reviews in Clinical Medicine Clinical Research Development Center Ghaem Hospital Natural oral contrast agents for gastrointestinal magnetic resonance imaging
MR cholangiopancreatography; Predicting imaging findings for differentiation of malignant bile ductal obstruction versus benign lesion
 Acta Med Kindai Univ Vol.43, No.1 1-8, 2018 1 MR cholangiopancreatography; Predicting imaging findings for differentiation of malignant bile ductal obstruction versus benign lesion Shojiro Hidaka 1,2,
Acta Med Kindai Univ Vol.43, No.1 1-8, 2018 1 MR cholangiopancreatography; Predicting imaging findings for differentiation of malignant bile ductal obstruction versus benign lesion Shojiro Hidaka 1,2,
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System
 Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
To describe normal anatomy and common variants in biliary tree anatomy including the prevalence of these.
 Up for debate: Should 3.0T magnetic resonance pancreatography (MRCP) become a routine part of preoperative planning for patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy? Poster No.: C-0196 Congress: ECR
Up for debate: Should 3.0T magnetic resonance pancreatography (MRCP) become a routine part of preoperative planning for patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy? Poster No.: C-0196 Congress: ECR
The role of Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography in the evaluation of biliary tree: A pictorial review
 The role of Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography in the evaluation of biliary tree: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-0522 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Alvarez-Hornia,
The role of Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography in the evaluation of biliary tree: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-0522 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Alvarez-Hornia,
ROLE OF RADIOLOGY IN INVESTIGATION OF JAUNDICE
 ROLE OF RADIOLOGY IN INVESTIGATION OF JAUNDICE Dr. Sohan kumar sah *, Dr. Liu Sibin, Dr. sumendra raj pandey, Dr. Prakashmaan shah, Dr. Gaurishankar pandit, Dr. Suraj kurmi and Dr. Sanjay kumar jaiswal
ROLE OF RADIOLOGY IN INVESTIGATION OF JAUNDICE Dr. Sohan kumar sah *, Dr. Liu Sibin, Dr. sumendra raj pandey, Dr. Prakashmaan shah, Dr. Gaurishankar pandit, Dr. Suraj kurmi and Dr. Sanjay kumar jaiswal
Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
 Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Single-Shot MR Cholangiopancreatography Neonates, Infants, and Young Children
 Toshiyuki Miyazaki Yasuyuki Yamashita1 ViTang Tadatoshi Tsuchigame1 Mutsumasa Takahashi1 Yoshihisa Sera2 Received November 21, 1996: accepted after revision July29, 1997. 1 Department of Radiology, Kumamoto
Toshiyuki Miyazaki Yasuyuki Yamashita1 ViTang Tadatoshi Tsuchigame1 Mutsumasa Takahashi1 Yoshihisa Sera2 Received November 21, 1996: accepted after revision July29, 1997. 1 Department of Radiology, Kumamoto
Abdominal ultrasound:
 Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class II
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
UNIVERSA MEDICINA. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: practical experience in 30 subjects
 UNIVERSA MEDICINA October-December, 2008 Vol.27 - No.4 Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: practical experience in 30 subjects A. Nurman* ABSTRACT * Department of Internal Medicine, Medical Faculty,
UNIVERSA MEDICINA October-December, 2008 Vol.27 - No.4 Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: practical experience in 30 subjects A. Nurman* ABSTRACT * Department of Internal Medicine, Medical Faculty,
THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 96, No. 10, by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN /01/$20.00
 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 96, No. 10, 2001 2001 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(01)02807-6 Can Endoscopic
THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 96, No. 10, 2001 2001 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(01)02807-6 Can Endoscopic
Nasogastric tube. Stomach. Pylorus. Duodenum 1. Duodenum 2. Duodenum 3. Duodenum 4
 Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Comparison of T2-weighted MRCP before and after injection of Gd-EOB-DTPA in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)
 Comparison of T2-weighted MRCP before and after injection of Gd-EOB-DTPA in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) Poster No.: C-0051 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Abdominal
Comparison of T2-weighted MRCP before and after injection of Gd-EOB-DTPA in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) Poster No.: C-0051 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Abdominal
Diagnosis of tumor extension in biliary carcinoma has. Differential Diagnosis and Treatment of Biliary Strictures
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:S79 S83 Differential Diagnosis and Treatment of Biliary Strictures KAZUO INUI, JUNJI YOSHINO, and HIRONAO MIYOSHI Department of Internal Medicine, Second
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:S79 S83 Differential Diagnosis and Treatment of Biliary Strictures KAZUO INUI, JUNJI YOSHINO, and HIRONAO MIYOSHI Department of Internal Medicine, Second
Caroli s disease: magnetic resonance imaging features
 Eur Radiol (2002) 12:2730 2736 DOI 10.1007/s00330-002-1471-6 HEPATOBILIARY PANCREAS France Guy François Cognet Marie Dranssart Jean-Pierre Cercueil Laurent Conciatori Denis Krausé Caroli s disease: magnetic
Eur Radiol (2002) 12:2730 2736 DOI 10.1007/s00330-002-1471-6 HEPATOBILIARY PANCREAS France Guy François Cognet Marie Dranssart Jean-Pierre Cercueil Laurent Conciatori Denis Krausé Caroli s disease: magnetic
Index words : Bile duct radiography, technology Bile ducts MR Bile ducts surgery Liver, transplantation
 Hilar Branching Anatomy of Living Adult Liver Donors: Comparison of T2-MR Cholangiography and Contrast Enhanced T1-MR Cholangiography in Terms of Diagnostic Utility 1 Joon Seok Lim, M.D. 1, Myeong-Jin
Hilar Branching Anatomy of Living Adult Liver Donors: Comparison of T2-MR Cholangiography and Contrast Enhanced T1-MR Cholangiography in Terms of Diagnostic Utility 1 Joon Seok Lim, M.D. 1, Myeong-Jin
Pancreatic Cancer. What is pancreatic cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic cancer is a tumor of the pancreas, an organ that is located behind the stomach in the abdomen. Pancreatic cancer does not always cause symptoms until
Scan for mobile link. Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic cancer is a tumor of the pancreas, an organ that is located behind the stomach in the abdomen. Pancreatic cancer does not always cause symptoms until
MRCP in Patient Care: A Prospective Survey of Gastroenterologists
 Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Akisik et al. MRCP Survey Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research M. Fatih Akisik 1 S. Gregory Jennings 1 Alex M. Aisen 1 Stuart Sherman 2 Gregory A. Cote
Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research Akisik et al. MRCP Survey Gastrointestinal Imaging Original Research M. Fatih Akisik 1 S. Gregory Jennings 1 Alex M. Aisen 1 Stuart Sherman 2 Gregory A. Cote
Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumors of the Pancreas: MR Cholangiopancreatography
 Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumors of the Pancreas: MR Cholangiopancreatography and MR Angiography Byung Se Choi, MD 1 Tae Kyoung Kim, MD 1 Ah Young Kim,
Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumors of the Pancreas: MR Cholangiopancreatography and MR Angiography Byung Se Choi, MD 1 Tae Kyoung Kim, MD 1 Ah Young Kim,
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) in a District General Hospital
 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) in a District General Hospital Poster No.: C-1790 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit J. A. Maguire 1, H. Kasem 2, M. Akhtar 2, M. Strauss
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) in a District General Hospital Poster No.: C-1790 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit J. A. Maguire 1, H. Kasem 2, M. Akhtar 2, M. Strauss
EVALUATION OF MRCP IN BILIARY OBSTRUCTION WITH ERCP, HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION
 EVALUATION OF MRCP IN BILIARY OBSTRUCTION WITH ERCP, HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE TAMIL NADU Dr. M.G.R MEDICAL UNIVERSITY, CHENNAI IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REGULATIONS
EVALUATION OF MRCP IN BILIARY OBSTRUCTION WITH ERCP, HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION DISSERTATION SUBMITTED TO THE TAMIL NADU Dr. M.G.R MEDICAL UNIVERSITY, CHENNAI IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REGULATIONS
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases. Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants
 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
SPHINCTER OF ODDI DYSFUNCTION (SOD)
 SPHINCTER OF ODDI DYSFUNCTION (SOD) Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction refers to structural or functional disorders involving the biliary sphincter that may result in impedance of bile and pancreatic juice
SPHINCTER OF ODDI DYSFUNCTION (SOD) Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction refers to structural or functional disorders involving the biliary sphincter that may result in impedance of bile and pancreatic juice
Clinics in Diagnostic Imaging (79)
 Singapore Med J 2002 Vol 43(11) : 591-596 M e d i c a l E d u c a t i o n Clinics in Diagnostic Imaging (79) P Lerttumnongtum, M Muttarak, K Wasanavijit 1a Fig. 1a Subcostal US scan taken at the porta
Singapore Med J 2002 Vol 43(11) : 591-596 M e d i c a l E d u c a t i o n Clinics in Diagnostic Imaging (79) P Lerttumnongtum, M Muttarak, K Wasanavijit 1a Fig. 1a Subcostal US scan taken at the porta
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer)
 Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Imaging of liver and pancreas
 Imaging of liver and pancreas.. Disease of the liver Focal liver disease Diffusion liver disease Focal liver disease Benign Cyst Abscess Hemangioma FNH Hepatic adenoma HCC Malignant Fibrolamellar carcinoma
Imaging of liver and pancreas.. Disease of the liver Focal liver disease Diffusion liver disease Focal liver disease Benign Cyst Abscess Hemangioma FNH Hepatic adenoma HCC Malignant Fibrolamellar carcinoma
Spectrum of congenital pancretico-biliary ductal anomalies Demonstration by MRCP positively impacts the management
 Spectrum of congenital pancretico-biliary ductal anomalies Demonstration by MRCP positively impacts the management protocol Poster No.: C-1539 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Patwari,
Spectrum of congenital pancretico-biliary ductal anomalies Demonstration by MRCP positively impacts the management protocol Poster No.: C-1539 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Patwari,
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract
 My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation
 Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
4/9/2018 OBJECTIVES PANCREAOTO BILIARY ULTRASOUND: BEYOND CHOLECYSTITIS
 PANCREAOTO BILIARY ULTRASOUND: BEYOND CHOLECYSTITIS Jean Yves Sewah Kaiser Permanente West Los Angeles 1 OBJECTIVES Discuss the role of ultrasound in the evaluation of the gallbladder, biliary tree and
PANCREAOTO BILIARY ULTRASOUND: BEYOND CHOLECYSTITIS Jean Yves Sewah Kaiser Permanente West Los Angeles 1 OBJECTIVES Discuss the role of ultrasound in the evaluation of the gallbladder, biliary tree and
Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst
 Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst Poster No.: C-1333 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit
Classification of choledochal cyst with MR cholangiopancreatography in children and infants: special reference to type Ic and type IVa cyst Poster No.: C-1333 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit
Medial Indentation of the Duodenal Sweep by Common Bile Duct Dilatation
 233 Medial Indentation of the Duodenal Sweep by Common Bile Duct Dilatation Richard Palmer Gold1 The dilated common bile duct has long been recognized as a cause for a smooth, tubular impression across
233 Medial Indentation of the Duodenal Sweep by Common Bile Duct Dilatation Richard Palmer Gold1 The dilated common bile duct has long been recognized as a cause for a smooth, tubular impression across
Surface Anatomy. Location Shape Weight Role of Five Surfaces Borders Fissures Lobes Peritoneal Lig
 The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
IMAGING OF ACUTE AND CHRONIC PANCREATITIS, INCLUDING EXOCRINE FUNCTION
 IMAGING OF ACUTE AND CHRONIC PANCREATITIS, INCLUDING EXOCRINE FUNCTION Andrew T. Trout, MD @AndrewTroutMD Disclosures Grant support National Pancreas Foundation In-kind support - ChiRhoClin modified from:
IMAGING OF ACUTE AND CHRONIC PANCREATITIS, INCLUDING EXOCRINE FUNCTION Andrew T. Trout, MD @AndrewTroutMD Disclosures Grant support National Pancreas Foundation In-kind support - ChiRhoClin modified from:
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction
 Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
Diagnostic accuracy of endoscopic ultrasonography in patients with inconclusive magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis of biliopancreatic abnormalities
 Indian J Gastroenterol (July August 2011) 30(4):156 160 DOI 10.1007/s12664-011-0120-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic accuracy of endoscopic ultrasonography in patients with inconclusive magnetic resonance
Indian J Gastroenterol (July August 2011) 30(4):156 160 DOI 10.1007/s12664-011-0120-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic accuracy of endoscopic ultrasonography in patients with inconclusive magnetic resonance
Biliary MRI w Eovist
 Biliary MRI w Eovist Is there any added value? Elmar M. Merkle, MD Director of MR Imaging Duke University Medical Center elmar.merkle@duke.edu Declaration of Conflict of Interest or Relationship Research
Biliary MRI w Eovist Is there any added value? Elmar M. Merkle, MD Director of MR Imaging Duke University Medical Center elmar.merkle@duke.edu Declaration of Conflict of Interest or Relationship Research
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Versus Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Findings in the Postorthotopic Liver Transplant Population Authors: *Ashok Shiani,
Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Versus Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Findings in the Postorthotopic Liver Transplant Population Authors: *Ashok Shiani,
IT 의료융합 1 차임상세미나 복부질환초음파 이재영
 IT 의료융합 1 차임상세미나 2013-4-3 복부질환초음파 이재영 나는오늘누구를위하여 종을울리나? 전통적의료 의사 공학설계자 의사 최첨단진단장비들 USG, CT, MRI 환자 환자 현대의료 사용자중심의사고 US in the Abdomen Detection DDx Look Behavior Response by external stimuli Guiding Tool
IT 의료융합 1 차임상세미나 2013-4-3 복부질환초음파 이재영 나는오늘누구를위하여 종을울리나? 전통적의료 의사 공학설계자 의사 최첨단진단장비들 USG, CT, MRI 환자 환자 현대의료 사용자중심의사고 US in the Abdomen Detection DDx Look Behavior Response by external stimuli Guiding Tool
Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain
 Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain 1 patient with recurrent episodes of pain (not daily), in the epigastrium/right upper quadrant, lasting >30 mins, building to a steady level, interrupting
Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain 1 patient with recurrent episodes of pain (not daily), in the epigastrium/right upper quadrant, lasting >30 mins, building to a steady level, interrupting
Variations of the Union between the Terminal Bile Duct and the Pancreatic Duct in Patients with Pancreaticobiliary Maljunction
 Yamanashi Med. J. 18(4), 67~ 75, 2003 Review Variations of the Union between the Terminal Bile Duct and the Pancreatic Duct in Patients with Pancreaticobiliary Maljunction Hideki FUJII 1) 1) Department
Yamanashi Med. J. 18(4), 67~ 75, 2003 Review Variations of the Union between the Terminal Bile Duct and the Pancreatic Duct in Patients with Pancreaticobiliary Maljunction Hideki FUJII 1) 1) Department
The Utility of MR Imaging Using the HASTE and True FISP Sequences in Diagnosing Bowel Obstruction 1
 The Utility of MR Imaging Using the HASTE and True FISP Sequences in Diagnosing Bowel Obstruction 1 Eun Joo Yun, M.D. 1, 2, Tae Kyoung Kim, M.D. 1, 3, Byung Ihn Choi, M.D. Purpose: To determine the value
The Utility of MR Imaging Using the HASTE and True FISP Sequences in Diagnosing Bowel Obstruction 1 Eun Joo Yun, M.D. 1, 2, Tae Kyoung Kim, M.D. 1, 3, Byung Ihn Choi, M.D. Purpose: To determine the value
State of the Art Imaging for Hepatic Malignancy: My Assignment
 State of the Art Imaging for Hepatic Malignancy: My Assignment CT vs MR vs MRCP Which one to choose for HCC vs Cholangiocarcinoma What special protocols to use for liver tumors Role of PET and Duplex US
State of the Art Imaging for Hepatic Malignancy: My Assignment CT vs MR vs MRCP Which one to choose for HCC vs Cholangiocarcinoma What special protocols to use for liver tumors Role of PET and Duplex US
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiography: Comparison With Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1996;110:589 597 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiography: Comparison With Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography JORGE A. SOTO,* MATTHEW A. BARISH,* E. KENT YUCEL,* DAVID SIEGENBERG,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1996;110:589 597 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiography: Comparison With Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography JORGE A. SOTO,* MATTHEW A. BARISH,* E. KENT YUCEL,* DAVID SIEGENBERG,
Case Scenario 1. Discharge Summary
 Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 69-year-old woman was on vacation and noted that she was becoming jaundiced. Two months prior to leaving on that trip, she had had a workup that included an abdominal
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 69-year-old woman was on vacation and noted that she was becoming jaundiced. Two months prior to leaving on that trip, she had had a workup that included an abdominal
Original Report. Duodenal Diverticula Mimicking Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas: CT and MR Imaging Findings in Seven. Patients
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.198.217 on 12/11/17 from IP address 46.3.198.217. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Michael Macari 1 Dawn Lazarus Gary Israel lec Megibow
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.198.217 on 12/11/17 from IP address 46.3.198.217. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Michael Macari 1 Dawn Lazarus Gary Israel lec Megibow
Accuracy of Multidetector Computed Tomographic Cholangiography In Evaluation of Causes of Biliary Tract Obstruction
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 7, December: 2613-2623, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Accuracy of Multidetector Computed Tomographic Cholangiography In Evaluation of Causes of Biliary
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 7, December: 2613-2623, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Accuracy of Multidetector Computed Tomographic Cholangiography In Evaluation of Causes of Biliary
Using Radial k-space Sampling and Steady-State Free Precession Imaging
 MRI of Coronary Vessel Walls Cardiac Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Marcus Katoh 1 Elmar Spuentrup 1 Arno Buecker 1 Tobias Schaeffter 2 Matthias Stuber 3 Rolf
MRI of Coronary Vessel Walls Cardiac Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Marcus Katoh 1 Elmar Spuentrup 1 Arno Buecker 1 Tobias Schaeffter 2 Matthias Stuber 3 Rolf
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols
 Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: March 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible flow
Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: March 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible flow
Predictors of abnormalities on magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: is there a role when the biliary tree is normal on previous imaging?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2019) 32, 1-6 Predictors of abnormalities on magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: is there a role when the biliary tree is normal on previous imaging?
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2019) 32, 1-6 Predictors of abnormalities on magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: is there a role when the biliary tree is normal on previous imaging?
Application of Magnetic Resonance Images in Gastrointestinal Malignancies
 Chin J Radiol 2003; 28: 269-275 269 Application of Magnetic Resonance Images in Gastrointestinal Malignancies SHENG-LAN YU 1 YUK-MING TSANG 1 PO-CHIN LIANG 1 HUNG-JUNG WANG 1 CHIEN-YAO HSU 1 TA-CHENG WEI
Chin J Radiol 2003; 28: 269-275 269 Application of Magnetic Resonance Images in Gastrointestinal Malignancies SHENG-LAN YU 1 YUK-MING TSANG 1 PO-CHIN LIANG 1 HUNG-JUNG WANG 1 CHIEN-YAO HSU 1 TA-CHENG WEI
MRI of the Hepatobiliary System
 BODY APPLICATIONS OF MRI 51 Chapter Four C H A P T E R F O U R MRI of the Hepatobiliary System After completing this chapter, the reader will be able to: Develop a protocol for liver MRI Identify benign
BODY APPLICATIONS OF MRI 51 Chapter Four C H A P T E R F O U R MRI of the Hepatobiliary System After completing this chapter, the reader will be able to: Develop a protocol for liver MRI Identify benign
Common and unusual CT and MRI manifestations of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a pictorial review
 Review Article Common and unusual CT and MRI manifestations of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a pictorial review Min-Jie Yang, Su Li, Yong-Guang Liu, Na Jiao, Jing-Shan Gong Department of Radiology, Shenzhen
Review Article Common and unusual CT and MRI manifestations of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a pictorial review Min-Jie Yang, Su Li, Yong-Guang Liu, Na Jiao, Jing-Shan Gong Department of Radiology, Shenzhen
MR of Pancreaticobiliary Diseases in Children
 SPR Body Imaging Course Sept 2015 MR of Pancreaticobiliary Diseases in Children Sudha A. Anupindi MD The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine
SPR Body Imaging Course Sept 2015 MR of Pancreaticobiliary Diseases in Children Sudha A. Anupindi MD The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine
Liver imaging takes a step forward with Ingenia
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community ISSUE 49 2013 / 2 Liver imaging takes a step forward with Ingenia Lyon South Hospital strives to move from several studies first CT, then MR or PET to using just
Publication for the Philips MRI Community ISSUE 49 2013 / 2 Liver imaging takes a step forward with Ingenia Lyon South Hospital strives to move from several studies first CT, then MR or PET to using just
ACCURACY OF MRCP COMPARED WITH ERCP IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF BILE DUCT STONES
 ejpmr, 2016,3(8), 27-32 SJIF Impact Factor 3.628 Research Article EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF European PHARMACEUTICAL Journal of Pharmaceutical and Medical Research AND MEDICAL RESEARCH ISSN 2394-3211 www.ejpmr.com
ejpmr, 2016,3(8), 27-32 SJIF Impact Factor 3.628 Research Article EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF European PHARMACEUTICAL Journal of Pharmaceutical and Medical Research AND MEDICAL RESEARCH ISSN 2394-3211 www.ejpmr.com
Pancreas Case Scenario #1
 Pancreas Case Scenario #1 An 85 year old white female presented to her primary care physician with increasing abdominal pain. On 8/19 she had a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis. This showed a 4.6 cm mass
Pancreas Case Scenario #1 An 85 year old white female presented to her primary care physician with increasing abdominal pain. On 8/19 she had a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis. This showed a 4.6 cm mass
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma
 Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
The efficacy of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography in assessing the etiology of acute idiopathic pancreatitis
 Yattoo et al. 32 Original article OPEN ACCESS The efficacy of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography in assessing the etiology of acute idiopathic pancreatitis Yattoo GN, Waiz Gowhar Amin, Feroze
Yattoo et al. 32 Original article OPEN ACCESS The efficacy of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography in assessing the etiology of acute idiopathic pancreatitis Yattoo GN, Waiz Gowhar Amin, Feroze
Biliary cancers: imaging diagnosis. Study of 30 cases
 Biliary cancers: imaging diagnosis. Study of 30 cases N Hammoune, S Semlali, M Eddarai, T. Amil, M Zentar, S. El Kandri,, M Benameur,, S Chaouir. Radiology Department. Mohamed V Military Hospital. Rabat-
Biliary cancers: imaging diagnosis. Study of 30 cases N Hammoune, S Semlali, M Eddarai, T. Amil, M Zentar, S. El Kandri,, M Benameur,, S Chaouir. Radiology Department. Mohamed V Military Hospital. Rabat-
BODY MRI PROTOCOLS 1.5T
 BODY MRI PROTOCOLS 1.5T Table of Contents Non Specific...3-5 Renals.....6-8 Adrenals.....9-11 Pancreas..12-14 Liver 15-17 Liver No Gad.18-21 Liver Eovist..22-24 Liver Iron Quant 25-29 MRCP.30-34 ENTEROGRAPHY.35-38
BODY MRI PROTOCOLS 1.5T Table of Contents Non Specific...3-5 Renals.....6-8 Adrenals.....9-11 Pancreas..12-14 Liver 15-17 Liver No Gad.18-21 Liver Eovist..22-24 Liver Iron Quant 25-29 MRCP.30-34 ENTEROGRAPHY.35-38
Lesions of the pancreaticoduodenal groove, a pictorial review
 Lesions of the pancreaticoduodenal groove, a pictorial review Poster No.: C-2131 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Ni Mhurchu, L. Lavelle, I. Murphy, S. Skehan ; IE, Dublin/ IE Keywords:
Lesions of the pancreaticoduodenal groove, a pictorial review Poster No.: C-2131 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Ni Mhurchu, L. Lavelle, I. Murphy, S. Skehan ; IE, Dublin/ IE Keywords:
Role of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography in diagnosing pancreatobiliary pathologies: a prospective study
 International Surgery Journal Nirhale DS et al. Int Surg J. 2018 Jun;5(6):2233-2237 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20182228
International Surgery Journal Nirhale DS et al. Int Surg J. 2018 Jun;5(6):2233-2237 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20182228
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O
 ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
Post-operative complications following hepatobiliary surgery: imaging findings and current radiological treatment options
 Post-operative complications following hepatobiliary surgery: imaging findings and current radiological treatment options Poster No.: C-1501 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Hadjivassiliou,
Post-operative complications following hepatobiliary surgery: imaging findings and current radiological treatment options Poster No.: C-1501 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Hadjivassiliou,
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen Surface Landmarks Xiphoid process T9/T10 Inferior costal margin L2/L3 Iliac Crest L4 level ASIS L5/S1 level Pubic symphysis level of greater trochanter
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM Topographic Anatomy of the Abdomen Surface Landmarks Xiphoid process T9/T10 Inferior costal margin L2/L3 Iliac Crest L4 level ASIS L5/S1 level Pubic symphysis level of greater trochanter
RADIOLOGY (SURGERY) BY MARYAM MALIK Rawalpindi Medical College
 RADIOLOGY (SURGERY) BY MARYAM MALIK Rawalpindi Medical College NORMAL BOWEL GAS PATTERN Any part of the bowel may be visible if it contains gas/air within the lumen. Gas/air is of low density and forms
RADIOLOGY (SURGERY) BY MARYAM MALIK Rawalpindi Medical College NORMAL BOWEL GAS PATTERN Any part of the bowel may be visible if it contains gas/air within the lumen. Gas/air is of low density and forms
Objectives. Hepatobiliary Ultrasound: Anatomy, Technique, Pathology. RUQ: Normal Anatomy. Emergency Ultrasound: Gallbladder Location
 Hepatobiliary Ultrasound: Anatomy, Technique, Pathology Laleh Gharahbaghian, MD FAAEM Associate Director, EM Ultrasound Co-Director, EM Ultrasound Fellowship Stanford University Medical Center Seric Cusick,
Hepatobiliary Ultrasound: Anatomy, Technique, Pathology Laleh Gharahbaghian, MD FAAEM Associate Director, EM Ultrasound Co-Director, EM Ultrasound Fellowship Stanford University Medical Center Seric Cusick,
What Are Gallstones? GALLSTONES. Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in. the gallbladder of some people.
 What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in the gallbladder of some people. The gallbladder sits under the liver and stores bile (a key digestive juice ). Gallstones
What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in the gallbladder of some people. The gallbladder sits under the liver and stores bile (a key digestive juice ). Gallstones
Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 821032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/821032 Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience Fransisca J. Siahaya,
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 821032, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/821032 Case Report Uncommon Mixed Type I and II Choledochal Cyst: An Indonesian Experience Fransisca J. Siahaya,
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer Ryota Shimofusa, MD,* Hajime Fujimoto, MD, Hajime Akamata, MD, Ken Motoori, MD,* Seiji Yamamoto, MD,* Takuya Ueda, MD,* and Hisao Ito, MD*
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer Ryota Shimofusa, MD,* Hajime Fujimoto, MD, Hajime Akamata, MD, Ken Motoori, MD,* Seiji Yamamoto, MD,* Takuya Ueda, MD,* and Hisao Ito, MD*
Role of MRCP in Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Causes of Biliary Obstruction
 Original Article Role of MRCP in Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Causes of Biliary Obstruction DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2015/14174.6771 Radiology Section Meena Suthar 1, Sunita Purohit 2, Vivek Bhargav
Original Article Role of MRCP in Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Causes of Biliary Obstruction DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2015/14174.6771 Radiology Section Meena Suthar 1, Sunita Purohit 2, Vivek Bhargav
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA
 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 65. Benign Hepatic Masses
 65. Benign Hepatic Masses Pulse sequences acquired for abdominal MRI typically consist of fast acquisition schemes such as single-shot turbo spin echo (i.e. HASTE) and gradient echo schemes such as FLASH
65. Benign Hepatic Masses Pulse sequences acquired for abdominal MRI typically consist of fast acquisition schemes such as single-shot turbo spin echo (i.e. HASTE) and gradient echo schemes such as FLASH
Morphine- and Glucagon-Augmented Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography To Evaluate Living Liver Donors
 LIVER TRANSPLANTATION 15:1021-1027, 2009 ORIGINAL ARTICLE - and Glucagon-Augmented Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography To Evaluate Living Liver Donors Yuan Heng Mo, 1,2 Po Chin Liang, 3 Ming Chih
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION 15:1021-1027, 2009 ORIGINAL ARTICLE - and Glucagon-Augmented Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography To Evaluate Living Liver Donors Yuan Heng Mo, 1,2 Po Chin Liang, 3 Ming Chih
Vascular complications in percutaneous biliary interventions: A series of 111 procedures
 Vascular complications in percutaneous biliary interventions: A series of 111 procedures Poster No.: C-0744 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. BHARADWAZ; AARHUS, Re/DK Keywords: Obstruction
Vascular complications in percutaneous biliary interventions: A series of 111 procedures Poster No.: C-0744 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. BHARADWAZ; AARHUS, Re/DK Keywords: Obstruction
ABDOMEN - GI. Duodenum
 TALA SALEH ABDOMEN - GI Duodenum - Notice the shape of the duodenum, it looks like capital G shape tube which extends from the pyloroduodenal junction to the duodenojejunal junction. - It is 10 inches
TALA SALEH ABDOMEN - GI Duodenum - Notice the shape of the duodenum, it looks like capital G shape tube which extends from the pyloroduodenal junction to the duodenojejunal junction. - It is 10 inches
MR imaging of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) using the hepatobiliary specific contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA
 MR imaging of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) using the hepatobiliary specific contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA Poster No.: C-0019 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid
MR imaging of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) using the hepatobiliary specific contrast agent Gd-EOB-DTPA Poster No.: C-0019 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Abdominal Viscera (Solid
