The Endocrine System
|
|
|
- Amos Walton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Endocrine System
2 Endocrine Glands Glands that secrete their products (HORMONES) into extracellular spaces around cells. The hormones then enter into the bloodstream by diffusing into the capillaries located next to the glands.
3 Glands and Organs of the Endocrine System Hypothalamus Pituitary Thyroid Parathyroid Thymus Pancreas Adrenal Gonads Testes Ovaries Pineal Thalamus Kidneys Liver Stomach Lungs Heart Small Intestine Skin Placenta
4 Endocrine Glands
5 Hormone Function Regulates chemical and volume of the body s s internal environment Regulates metabolism and energy balance Regulates contraction of cardiac and smooth muscle Regulates certain activities of the immune system
6 Maintains homeostasis despite emergency environmental interruptions infection dehydration emotional stress - trauma - starvation - hemorrhage - temperature extremes Plays a role in normal growth and sequential development Contributes to the process of reproduction
7 Hormones Secretions of the endocrine glands Enter the bloodstream and have an effect on a target cell, tissue, or organ Over 50 different hormones Most only affect a few, specific types of cells
8 Endocrine Glands and The Hormones They Secrete
9 Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Often called the master gland because it secretes hormones that control other endocrine glands Structurally divided into two parts: Anterior Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) Posterior Pituitary Gland (Neurohypophysis)
10 Pituitary Gland
11 Pituitary Gland
12 Human Growth Hormone (hgh)) or Somatotropin The most abundant anterior pituitary hormone Stimulates growth of body cells Stimulates protein synthesis Inhibits protein breakdown Stimulates lipolysis (fat breakdown) Inhibits the use of glucose as a fuel for metabolism
13 Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Also called Thyrotropin Influences the body s s metabolic rate Stimulates the secretion of: T3 - Triiodothyronine T4 - Thyroxine
14 Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Controls the production and secretion of glucocorticoids by the cortex of the adrenal glands
15 Thyroid Gland Hormones The thyroid gland is located just below the larynx with its lobes lying on either side of the trachea The right and left lobes are connected to each other by the isthmus The only gland that can store its secretory product in large quantities normally about a 100 day supply
16 Thyroid Gland
17 Thyroid Gland
18 Thyroid Hormones Thyroxine (T4) Contains 4 iodine atoms Normally secreted in greater quantity Most is converted to T3 by the removal of an iodine atom
19 Actions of the Thyroid Hormones (T3 and T4) Regulates oxygen utilization and basal metabolic rate Regulates cellular metabolism Increases protein synthesis Increases lipolysis Increases glucose use in ATP production Works in conjunction with hgh to regulate growth and development catecholamines Enhances the actions of
20 Adrenal (Suprarenal) Glands and Hormones Glands located superior to each kidney Structurally divided into two regions Adrenal Cortex Outer region Makes up the majority of the gland Adrenal Medulla The inner portion of the gland
21 Adrenal Glands
22 Adrenal Cortex
23 Glucocorticoids regulates metabolism influences resistance to stress Cortisol (Hydrocortisone) makes up 95% of glucocorticoids primary role is that of gluconeogenesis synthesis of glucose and glycogen in the liver promotes normal metabolism provides resistance to stress acts as anti-inflammatory inflammatory compounds regulated by the secretion of ACTH
24 Adrenal Medulla Inner region of the adrenal glands Contains two sets of hormone producing cells Under the direct control of the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Hormone production and release can occur almost immediately
25 Adrenal Medulla
26 Hormones of the Adrenal Medulla Epinephrine and Norepinephrine (Adrenaline and Noradrenaline) Makes up over 80% of the secretions from the adrenal medulla Responsible for the Fight or Flight response Helps the body cope with stress
27 Actions of Epinephrine and Norepinephrine increases heart rate increases blood pressure increases heart contractility constricts blood vessels increases respiratory rate dilates respiratory passageways increases blood sugar levels stimulates cellular metabolism increases efficiency of muscular contractions
28 Pancreas A flattened oblong organ located just posterior and slightly inferior to the stomach Is both an endocrine and exocrine gland The endocrine tissue of the pancreas is called the Pancreatic Islets or Islets of Langerhans
29 Pancreas
30 Cell Types of the Islets of Langerhans Alpha Cells - secrete Glucagon raises blood sugar Beta Cells - secrete Insulin lowers blood sugar
31 Alpha Cells -Secretes Glucagon-
32 Glucagon Increases blood sugar when it falls below normal ranges Main target tissue is the liver Accelerates the conversion of glycogen into glucose (glycogenolysis( glycogenolysis) Promotes the formation of glucose from lactic acid (lactate) and certain amino acids (gluconeogenesis( gluconeogenesis) Suppresses appetite
33 Beta Cells -Secretes Insulin-
34 Insulin Decreases blood glucose levels if it gets too high Accelerates the transfer of glucose from the blood into the body s s cells Accelerates the conversion of glucose to glycogen (glycogenesis( glycogenesis) Accelerates the entry of amino acids into cells and the synthesis of proteins
35 Accelerates the conversion of glucose or other nutrients into fatty acids (lipogenesis) Inhibits glycogenolysis Inhibits gluconeogenesis Primarily influenced by blood glucose levels Also influenced by increased levels of certain amino acids and hormones hgh and ACTH stimulate Insulin release
36 Blood Glucose Regulation Insulin Decreases Blood Glucose Glucagon Increases Blood Glucose
37 Metabolic Diseases and Disorders of the Endocrine System
38 Dwarfism Caused by a hyposecretion of hgh during the growth years Slow bone growth Epiphyseal plates close before normal height is reached Other organs of the body may also fail to grow and develop Treatment requires administration of hgh during childhood
39 Dwarfism
40 Gigantism Caused by the hypersecretion of hgh during childhood Abnormal increase in bone length and size of other organs The person is very tall with normal body proportions
41 Gigantism De-Fen Yao 7 9 Robert Wadlow 8 3
42 Acromegaly Caused by the hypersecretion of hgh during adulthood May be caused by steroid and hgh use Bones of hands, feet, and skull thicken Eyelids, lips, and tongue enlarge Skin thickens and develops furrows
43 Acromegaly
44 Cretinism Caused by hyposecretion of thyroid hormones during fetal development Exhibits dwarfism because the skeleton fails to grow Individuals are usually severely mentally retarded Retarded sexual development Usually have a yellowish skin color
45 Cretinism
46 Myxedema Caused by hypothyroidism during the adult years Causes facial tissue to swell and look puffy About 5 times more common in females Other symptoms include: bradycardia - low body temperature lethargy - muscle weakness dry skin and hair - easily gains weight sensitivity to cold - hypersensitive to drugs
47 Myxedema
48 Graves Disease Caused by hyperthyroidism An autoimmune disorder increased metabolism - heat intolerance increased sweating - insomnia weight loss - nervousness tremors of hands May have a slightly enlarged thyroid gland (goiter) Causes the eyes to protrude (exophthalmos)
49 Graves Disease
50 Diabetes mellitus Metabolic malfunction that arises from a lack of insulin or the inability for cells to recognize it. Insulin stimulates the liver to form glycogen from glucose and inhibits conversion of non- carbohydrates into glucose. It also assists glucose in crossing some cell membranes (cardiac muscle, adipose tissue, and resting skeletal muscle).
51 Diabetes mellitus Blood sugar concentration rises and the excess is dumped by the kidneys. Glucose-starved starved cells use proteins for energy causing tissues to waste away. Drop in weight, hunger increases, slow healing, growth stops in children, exhaustion. Changes in fat metabolism cause fatty acids and ketones to accumulate in the blood, lowering the ph. Dehydration and acidosis can harm brain cells, cause disorientation, come, and eventually death
52 Diabetes mellitus Type I (insulin-dependent or juvenile) Usually before age 20. Immune system destroys the beta cells of the pancreas. Insulin injections several times per day. Type II (non-insulin insulin-dependent or maturity- onset) Insulin is produced, but the body cannot recognize it. Usually after age 40. Can be controlled with diet. Blood-glucose levels must be monitored daily Non-treatment causes coronary heart disease, peripheral nerve damage, and retinal damage..
53 Diabetes Mellitus A group of disorders that leads to an elevation of blood glucose (hyperglycemia) Symptoms include: polyuria polyphagia - polydipsia - glucosuria Two Types or Categories of Diabetes Type I Diabetes - Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM) Type II Diabetes - Non Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (NIDDM)
54 Type I Diabetes (IDDM) Pancreas does not produce insulin due to the destruction of beta cells in the Islets of Langerhans Requires regular injections of insulin to prevent death Most commonly develops in individuals younger than 20 years old (Juvenile Onset Diabetes Mellitus) Appears to be an autoimmune disorder
55 Type II Diabetes (NIDDM) Also called Maturity Onset Diabetes Much more common type of Diabetes (over 90% of Diabetes cases) Most often occurs in individuals over 40, but seeing more often now in children Most individuals are overweight or clinically obese Blood glucose levels can usually be controlled by medications, diet, exercise, and weight loss and control
56 Complications from Diabetes atherosclerosis heart disease peripheral vascular disease severe kidney damage Glaucoma and/or blindness gangrene ketoacidosis weight loss neuropathy
57 Treatments for Diabetes Regular insulin injections Artificial pancreas Transplantation of the pancreas transplantation of clusters of islet cells Injection of fetal islet cells
The Endocrine System Unit 7
 General Functions of the Endocrine System Coordinating and regulating body cells, tissues, organs, and systems to maintain homeostasis by secreting chemicals (hormones) The Endocrine System Unit 7 Effects
General Functions of the Endocrine System Coordinating and regulating body cells, tissues, organs, and systems to maintain homeostasis by secreting chemicals (hormones) The Endocrine System Unit 7 Effects
Endocrine Notes Mrs. Laux AP Biology I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones
 I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
Endocrine System. Modified by M. Myers
 Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
The Endocrine System
 C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
Chapter 12 Endocrine System (export).notebook. February 27, Mar 17 2:59 PM. Mar 17 3:09 PM. Mar 17 3:05 PM. Mar 17 3:03 PM.
 Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System. Chapter 9
 Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Understand the functions and disorders of the endocrine system
 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
CHAPTER 50 Endocrine Systems. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 CHAPTER 50 Endocrine Systems Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Endocrine system All the endocrine glands and other organs with hormonesecreting
CHAPTER 50 Endocrine Systems Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Endocrine system All the endocrine glands and other organs with hormonesecreting
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1
 Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
The Endocrine System. Endocrine System. 1
 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
The Endocrine System Part II
 The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System
 Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Endocrine System. A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine. Endocrine: Exocrine:
 Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
Chapter 21. Human Endocrine System
 Chapter 21 Human Endocrine System Endocrine System Consist of endocrine glands that secrete hormones which regulate a wide range of activities in humans Hormones- are secreted by glands and diffuse directly
Chapter 21 Human Endocrine System Endocrine System Consist of endocrine glands that secrete hormones which regulate a wide range of activities in humans Hormones- are secreted by glands and diffuse directly
The Endocrine SyStem. COMMUNICATION System
 The Endocrine SyStem COMMUNICATION System Endocrine FACTS The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products (hormones) directly into the bloodstream. The response of hormones is slower
The Endocrine SyStem COMMUNICATION System Endocrine FACTS The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products (hormones) directly into the bloodstream. The response of hormones is slower
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs
 9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
The Endocrine System 7/6/2015. Outline. Function of the Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
Anatomy and Physiology. The Endocrine System
 Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
C H A P T E R 1 3 : T H E E N D O C R I N E S Y S T E M
 C H A P T E R 1 3 : T H E E N D O C R I N E S Y S T E M U N I T 1: MAINTA I N I N G DYNAMIC EQ UILIBR IUM II NERVOUS SYSTEM VS. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The nervous system coordinates rapid and precise responses
C H A P T E R 1 3 : T H E E N D O C R I N E S Y S T E M U N I T 1: MAINTA I N I N G DYNAMIC EQ UILIBR IUM II NERVOUS SYSTEM VS. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The nervous system coordinates rapid and precise responses
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
Endocrine System. The Endocrine Glands
 Endocrine System Working together with the nervous system, the endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis in the body. Where the nervous system uses electric signals, the endocrine system uses chemical
Endocrine System Working together with the nervous system, the endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis in the body. Where the nervous system uses electric signals, the endocrine system uses chemical
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Endocrine System. Regulating Blood Sugar. Thursday, December 14, 17
 Endocrine System Regulating Blood Sugar Stress results in nervous and hormonal responses. The adrenal glands are located above each kidney. Involved in stress response. Stress Upsets Homeostasis Stress
Endocrine System Regulating Blood Sugar Stress results in nervous and hormonal responses. The adrenal glands are located above each kidney. Involved in stress response. Stress Upsets Homeostasis Stress
Hormonal regulation of. Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara
 Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands 4/12/2016. Controlled by both nerves and hormones.
 Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
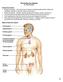 The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes
 Operation of the Endocrine System Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes What is the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is comprised of the hormone producing glands and tissues of the body. Hypothalamus
Operation of the Endocrine System Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes What is the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is comprised of the hormone producing glands and tissues of the body. Hypothalamus
Pancreas. Endocrine pancreas - Islets of Langerhans A or alpha cells glucagon B or beta cells insulin Delta cells somatostatin
 Endocrine System Pancreas Endocrine pancreas - Islets of Langerhans A or alpha cells glucagon B or beta cells insulin Delta cells somatostatin Glucagon & Metabolism Produced by beta cells of Islets Primary
Endocrine System Pancreas Endocrine pancreas - Islets of Langerhans A or alpha cells glucagon B or beta cells insulin Delta cells somatostatin Glucagon & Metabolism Produced by beta cells of Islets Primary
Endocrine System. Part 2
 Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System. Simple Hormone Pathways
 Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
9.3 Stress Response and Blood Sugar
 9.3 Stress Response and Blood Sugar Regulate Stress Response Regulate Blood Sugar Stress Response Involves hormone pathways that regulate metabolism, heart, rate and breathing The Adrenal Glands a pair
9.3 Stress Response and Blood Sugar Regulate Stress Response Regulate Blood Sugar Stress Response Involves hormone pathways that regulate metabolism, heart, rate and breathing The Adrenal Glands a pair
Collin College. BIOL Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 3. The Endocrine System. Adrenal Glands : medulla
 Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 3 The Endocrine System 1 Adrenal Glands : medulla Contains Chromaffin cells which are modified postganglionic sympathetic neurons They are activated
Collin College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 3 The Endocrine System 1 Adrenal Glands : medulla Contains Chromaffin cells which are modified postganglionic sympathetic neurons They are activated
Chapter 16: The Endocrine System
 Chapter 16: The Endocrine System Objectives Define the terms endocrine and exocrine. Describe the physiology of hormones including the different types and the mechanisms of their actions. Compare endocrine
Chapter 16: The Endocrine System Objectives Define the terms endocrine and exocrine. Describe the physiology of hormones including the different types and the mechanisms of their actions. Compare endocrine
Endocrine Glands System. Agha Zohaib Khan
 Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
CHAPTER 12. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL?
 Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
The Endocrine System. Lab Exercise 31. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Chapter 16 - Endocrine system
 Chapter 16 - Endocrine system I. Overview Nervous control is fast but short-lived Hormonal control is slow and lasts a long time A. Organs: hypothalamus, pituitary (hypophysis), thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal,
Chapter 16 - Endocrine system I. Overview Nervous control is fast but short-lived Hormonal control is slow and lasts a long time A. Organs: hypothalamus, pituitary (hypophysis), thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal,
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary
 Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands
 Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Lesson 1. Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms
 Lesson 1 Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms Nervous System Endocrine System 1. Uses neurons to transmit electrochemical messages (neurotransmitters) Regulation
Lesson 1 Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms Nervous System Endocrine System 1. Uses neurons to transmit electrochemical messages (neurotransmitters) Regulation
Ch. 39 Endocrine System
 Ch. 39 Endocrine System The Endocrine System The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products deliver messages throughout the body Hormones Hormones
Ch. 39 Endocrine System The Endocrine System The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products deliver messages throughout the body Hormones Hormones
The Endocrine System/Hormones
 The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
9.2 Hormonal Regulation of Growth
 9.2 Hormonal Regulation of Growth Hormonal Regulation of Growth Pituitary gland regulates growth and development Thyroid gland regulates metabolic rate (exception: some hormones for growth and development)
9.2 Hormonal Regulation of Growth Hormonal Regulation of Growth Pituitary gland regulates growth and development Thyroid gland regulates metabolic rate (exception: some hormones for growth and development)
The Endocrine System. Lipid-Soluble Hormones. Bio217 Sp14 Unit 5. Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow
 Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Unit V: Endocrine System Disorders Chapter 17 Chap. 17: Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Chap. 18: Alterations
Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Unit V: Endocrine System Disorders Chapter 17 Chap. 17: Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Chap. 18: Alterations
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 29 MAY 2013
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 29 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss the characteristics of hormones. Explain the differences between endocrine and exocrine glands. Look at the location and the functions
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 29 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss the characteristics of hormones. Explain the differences between endocrine and exocrine glands. Look at the location and the functions
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine System Functions
 Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Regula'ng Body Func'on
 Chapter 10 Regula'ng Body Func'on Working closely with your nervous system is the endocrine system, a chemical communication system that regulate many body functions. Exocrine vs Endocrine Exocrine Glands
Chapter 10 Regula'ng Body Func'on Working closely with your nervous system is the endocrine system, a chemical communication system that regulate many body functions. Exocrine vs Endocrine Exocrine Glands
The Endocrine System
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 3 The Endocrine System 1 Adrenal Glands : medulla Contains Chromaffin cells which are modified postganglionic sympathetic neurons They
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 3 The Endocrine System 1 Adrenal Glands : medulla Contains Chromaffin cells which are modified postganglionic sympathetic neurons They
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION
 CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine Glands. Comparison of Nervous System and Endocrine System
 Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Endocrine system. Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to:
 Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
Scrub In. TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of:
 Scrub In TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: a. Pancreas b. Testes c. Thymus gland d. Thyroid gland Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of: a. Calcium in the blood b. Endorphins
Scrub In TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: a. Pancreas b. Testes c. Thymus gland d. Thyroid gland Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of: a. Calcium in the blood b. Endorphins
Human Biochemistry. Hormones
 Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS
 BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - 1 of the 2 chemical control systems of the human body - function of the endocrine system: regulate body functions = maintain homeostasis ie. physical and mental
BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - 1 of the 2 chemical control systems of the human body - function of the endocrine system: regulate body functions = maintain homeostasis ie. physical and mental
Endocrine System. Collection of glands that secrete hormones.
 Endocrine System Collection of glands that secrete hormones. Gland- A single cell or a multicellular structure that secretes substances into the blood, a cavity, or onto a surface. Hormones Mediator molecules
Endocrine System Collection of glands that secrete hormones. Gland- A single cell or a multicellular structure that secretes substances into the blood, a cavity, or onto a surface. Hormones Mediator molecules
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Major endocrine glands and their hormones
 Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Hormonal Regula8on of Homeostasis
 Hormonal Regula8on of Homeostasis Chapter 13 (MH) 15 (N) MH: 436 N: 470 MH: 436 N: 470 Glands and hormones Endocrine glands secrete chemical messengers called hormones Hormones are delivered to target
Hormonal Regula8on of Homeostasis Chapter 13 (MH) 15 (N) MH: 436 N: 470 MH: 436 N: 470 Glands and hormones Endocrine glands secrete chemical messengers called hormones Hormones are delivered to target
ENDOCRINOLOGY. Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Chapter 13 worksheet
 Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Chapter 11. Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Hormones. Regulation. Endocrine System. What Do Endocrine Glands Release (Secrete)? Endocrine System
 Endocrine System Function: Endocrine System - For glands to release products into bloodstream to deliver messages throughout the body. Regulation Is the control & coordination of other life functions to
Endocrine System Function: Endocrine System - For glands to release products into bloodstream to deliver messages throughout the body. Regulation Is the control & coordination of other life functions to
ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions)
 ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions) 1. While the nervous system functions very slowly, the endocrine system works very quickly. a. True b. False 2. Hormones that act locally
ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions) 1. While the nervous system functions very slowly, the endocrine system works very quickly. a. True b. False 2. Hormones that act locally
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11
 The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine GLANDS: Question:1. Fill in the Blanks.
 Endocrine GLANDS: Question:1 Fill in the Blanks. 1. Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands which are poured in to the blood. 2. Adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to
Endocrine GLANDS: Question:1 Fill in the Blanks. 1. Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands which are poured in to the blood. 2. Adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Target cells only respond to specific signals Different target cells have different kinds of receptors in their membranes or cytoplasm
 1 2 3 4 5 6 BIO 1102 Lec. 9 (Guided): Chapter 13 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Controls many body functions through chemical signals Hormones Carried in blood stream Affect target cells Composed
1 2 3 4 5 6 BIO 1102 Lec. 9 (Guided): Chapter 13 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Controls many body functions through chemical signals Hormones Carried in blood stream Affect target cells Composed
Page 1. Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension
 Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following statements about hormones is incorrect? A) They are produced by endocrine glands. B) They are modified amino
Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following statements about hormones is incorrect? A) They are produced by endocrine glands. B) They are modified amino
Chapter 26. Hormones and the Endocrine System. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
Human Anatomy, First Edition. Endocrine System. Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System. McKinley & O'Loughlin
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System
 Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Exocrine glands Endocrine glands Hormone Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Thyroxine Pancreas KEYWORDS Insulin Islets of Langerhans Goitre Thymus Thymosin What are glands? Exocrine
The Endocrine System Exocrine glands Endocrine glands Hormone Pituitary gland Hypothalamus Thyroid Thyroxine Pancreas KEYWORDS Insulin Islets of Langerhans Goitre Thymus Thymosin What are glands? Exocrine
The Endocrine System 2
 The Endocrine System 2 Continuing on from the previous instalment, we will now look at the adrenal glands, the pancreas and the gonads as parts of the endocrine system. Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands
The Endocrine System 2 Continuing on from the previous instalment, we will now look at the adrenal glands, the pancreas and the gonads as parts of the endocrine system. Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013 Endocrine system includes 8 major glands. 1. Pituitary (master gland)
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013 Endocrine system includes 8 major glands. 1. Pituitary (master gland)
Glands of the Endocrine System
 Glands of the Endocrine System Key Questions What are the functions of the major endocrine glands? How are endocrine glands controlled? Vocabulary pituitary gland releasing hormone corticosteroid epinephrine
Glands of the Endocrine System Key Questions What are the functions of the major endocrine glands? How are endocrine glands controlled? Vocabulary pituitary gland releasing hormone corticosteroid epinephrine
Do Now: 1. Turn in your exit ticket that was due for homework 2. Pg 91: How did they use to test people for Diabetes?
 Do Now: 1. Turn in your exit ticket that was due for homework 2. Pg 91: How did they use to test people for Diabetes? Diabetes a disease in which the pancreas stops producing insulin, the hormone that
Do Now: 1. Turn in your exit ticket that was due for homework 2. Pg 91: How did they use to test people for Diabetes? Diabetes a disease in which the pancreas stops producing insulin, the hormone that
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System. Target Cells: Cells specialized to respond to hormones
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Robert Wadlow and his father
 Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
Chapter-13. Hormones and Signal Transduction. Page /8/2017 Dr. Amjid Iqbal PhD (University of Cambridge) 1
 Chapter-13 Hormones and Signal Transduction Page 396-401 Dr. Amjid Iqbal PhD (University of 1 Living things coordinate their activities through biochemical signaling system Intercellular signals are mediated
Chapter-13 Hormones and Signal Transduction Page 396-401 Dr. Amjid Iqbal PhD (University of 1 Living things coordinate their activities through biochemical signaling system Intercellular signals are mediated
Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species
 Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
