Aerobic bacteria isolated from diabetic septic wounds
|
|
|
- Winifred Beasley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Aerobic bacteria isolated from diabetic septic wounds Eithar Mohammed Mahgoub*, Mohammed Elfatih A. Omer Faculty of Pharmacy, Omdurman Islamic University Department of Pharmaceutical Microbiology, Omdurman Sudan Corresponding author Abstract Diabetic septic wounds are one of the most dangerous complications of diabetes mellitus that remain major cause of morbidity and mortality in diabetic patients. The present work included collection, purification, identifications of 187 clinical strains isolated from patients with diabetic septic wounds during August 2008 and March 2009.The samples were collected entirely from Jabir Abo Alezz diabetic center in Khartoum State. The clinical isolates were purified by streaking on suitable selective and differential culture media. They were identified on the basis of the results of microscopical examinations, Gram reactions, cultural characters and biochemical tests. The clinical strains identified as the following:- Staphylococcus aureus (46%), Enterococcus faecalis(8%), Coagulase- negative Staphylococci (5.9%). Streptococcus pyogenes (2.1%), Pseudomonas aeruginosa(13.4%), Proteus species (9.1%), E.coli (4.8%), Klebsiella Pneumoniae (3.7%), Providencia species (1.1%), Citrobacter freundii(1.6%) and Serratia species (4.3%). Key Words: diabetic; aerobic; bacteria; wound; infection {Citation: Eithar Mohammed Mahgoub, Mohammed Elfatih A. Omer. Aerobic bacteria isolated from diabetic septic wounds. American Journal of Research Communication, 2015, 3(10): 91-99}, ISSN: Mahgoub, et al., 2015: Vol 3(10) 91
2 1.1. Introduction Diabetes is a significant risk factor in coronary heart disease, stroke and it's the leading cause of blindness, end-stage renal disease, as well as a major contributor to lower extremity amputation, (Porth, 2002). Foot ulceration occurs as a result of trauma often trivial, in the presence of neuropathy and peripheral vascular diseases, (Boon et al, 1999). Once the protective layers of skin are breached, underlying tissues are exposed to bacterial colonization, (Lipsky et al, 2004). The progression from colonization of a wound to clinical depends on various factors such as the quantity, type and interaction of pathogens present combined with host factors such as immune response and tissues conditions if ischemic or not (Armstrong and Lipsky, 2004). These sequences of events can be rapid occurring over days or even hours, especially in an ischemic limb. (Lipsky et al 2004) Diabetic septic foot Diabetic foot infection is most simply defined as any infra-malleolar infection in patients with diabetes mellitus. These include paronychia, cellulitis, myositis, abscesses, necrotizing fasciitis, septic arthritis, tendonitis and osteomyelitis, (Lipsky et al, 2004) Causative agents of diabetic septic wounds Different types of bacteria have been associated with diabetic septic wounds. They range from single gram positive Cocci in acutely infected wound to multiple organisms (3-5 species in chronic infection). In addition, due to impaired host defense around necrotic soft tissues or bone may allow low virulence colonizer such as Coagulase-negative Staphylococci and Corynebacterium species "diphtheroids" to assume a pathological role,( Lipsky et al 2004). Moreover, Anaerobic species should be suspected if the wound has fetid smell, (Armstrong and Lipsky,2004). Fungi may be isolated from both infected and uninfected foot wound, but rarely require systemic antifungal therapy, (Lipsky, 2004). Hospitalization, surgical procedures and especially prolonged or broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy may predispose patients to colonization and or infection with antibiotic resistant organisms (MRSA or Vancomycin resistant Enterococci, (Lipsky et al, 2004). Mahgoub, et al., 2015: Vol 3(10) 92
3 2.1. Materials All the culture media are either from Conda Ltd. Spain or Himedia Ltd. India with expiry date until 1 / Epidemiology survey of diabetic septic wounds Between October 2008 and March 2009, 150 wound samples were collected from diabetic patients admitted to Jabir Abo Alezz diabetic center in Khartoum State-Sudan. The samples were collected from patients suffered from infected ulcer, wound osteomyelitis or previous amputation Specimens For elimination surface contaminants, the wounds, have been debrides of all necrotic material and mechanically cleansed, before collecting a culture specimen. (Armstrong and Lipsky, 2004). Adequate amounts of pus was taken on sterile cotton swab, which was inserted on a container of Amies transport medium. The swab stick was broke to allow the bottle top to close tightly. In moderate to severe wounds, the culture materials were either from curettage of debrided ulcer or tissues biopsy, (Apelquist et al, 2000) and (Wheat.et al,1986). The labeled specimen was taken to the microbiology laboratory in Faculty of pharmacy in Omdurman Islamic university as soon as possible, maximally within six hours since delay may cause the death of organisms Cultivation of isolates on different type of media For isolation and purification of bacteria isolates swabs from the transport media were inoculated on suitable sterile different culture media. The plates were incubated under aerobic condition at 37 C for 24 hours. The media used includes:- Nutrient agar, Blood agar, Cetrimide agar, MacConkey s agar, Mannitol salt agar and Eosin methylene blue agar. The purified bacterial isolates were preserved in the refrigerator at 4 C until they were used Identification of isolated bacteria strains Identification of isolates was done according to cultural characteristics, gram staining properties & results of different biochemical tests, (Cheesbrough,M.(2000). Mahgoub, et al., 2015: Vol 3(10) 93
4 3. Results &discussion 3.1 Site of diabetic septic wounds infection In this study as shown in figure No.1, the commonest primary site of infection was the foot (98.7%) followed by other sites of body (1.3%). This agrees with the findings of a study done by (Abdalrhman, 1999) foot 148 others No. of pateints 2 Figure 1: Sites of diabetic septic wounds infection. This may be explained by the fact that the lower limbs are more affected by peripheral neuropathy and vascular insufficiency that makes the lower limbs more prone to trauma and then infection Types of microbial infection of diabetic septic wounds From 150 diabetic patients with septic wounds 187 organisms were recovered indicating that there were two types of bacterial infections; monomicrobial infection which is the major (77.3%) and polymicrobial infections (22.7 %) figure No.2. Types of microbial infection Single microbial flora 34 Poly microbial flora Figure 2: Types of microbial infection of diabetic septic wounds. Mahgoub, et al., 2015: Vol 3(10) 94
5 The average numbers of isolates is 1,2 per case, similarly (Abdalrahman, 1999) found that the number of isolates per case was 1.39 and single infection was in 63% patients. It is also not far away from the study done in Malaysia, which documented that diabetic septic wounds were monomicrobial rather than polymicrobial, the number of isolates per case was 1.47, (Raja, 2007). A greater number of isolates per case was 1.6 & 3 was reported by (Abdulrazak et al, 2005) and (Goldstein et al, 1992). A culture with polymicrobial flora from diabetic foot ulcer does not reveal which microorganism is pathogenic. In fact bacteria are thought to be synergistic and form biofilm at the surface of chronic wound, thus allows anaerobes to survive on the wound surface and support the growth of bacteria not normally considered pathogenic, (Williams et al,2004). In contrasts to monomicrobial infections poly microbial infection is reported in serious infection that fail to response to previous antibiotic therapy (Armstrong and Lipsky, 2004) Type of bacterial isolates in diabetic septic wounds The type of bacteria involved in multiple infections was shown in figure No.3. 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% Staphylococcus aureus Enterococcus faecalis Pseudomonas aeruginosa Klebsiella pneumoniae Providencia species Serratia species bacterial isolates Coagulase negative Staphylococci Streptococcus pyogenes Escherichia coli Proteus species Citrobacter freundii Figure 3: Bacteria isolated from diabetic septic wounds. Mahgoub, et al., 2015: Vol 3(10) 95
6 The commonest isolated organisms in the present work were S. aureus (46%), These results agree with many studies done worldwide particularly in that S. aureus is the most frequent organism encountered as a causative agent of diabetic septic wounds. Similarly Abdalrhman, (1999) identified 139 clinical isolates from patients with diabetic septic wounds. They included S.aureus (52%), Streptococcus pyogenes (0.71%), Proteus mirabilis (25%), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (9%), Klebsiella pneumoniae (8%) and E.coli (4%). In addition, a more recent study in Sudan; found that the most common isolates from diabetic septic wounds were S. aureus that amount for 53.7% of all isolates. The strict aerobic Pseudomonas aeruginosa constituted 3.6% of all isolates, other isolated Gram-negative bacilli included, Proteus mirabilis 4.5% Proteus vulgaris 3.6%, Klebsiella pneumoniae 11.8% and E.coli 8.2%. Streptococcus pyogenes isolates were the least frequent, with prevalence rate of 1.8%, (Adam, 2007). In a study of 111 patients with diabetic septic foot infections, Gram-positive Cocci were collected from 40% of patients; among them S. aureus was the most frequently isolated bacteria (28% of wounds). Gram-negative aerobes were obtained from 47% of the cases, among them Pseudomonas aeruginosa accounted for 22% and Proteus mirabilis 18%. Gramnegative anaerobes were found in 7% of the patients. Likewise the present work Enterococcus was isolated, suggesting a relationship to prior antibiotics (especially cephalosporins) exposure,(el-tahawy,2000). Likewise Armstrong and Lipsky, (2004) noted that most commonly isolates from diabetic septic wounds were S. aureus, other frequently isolated aerobes included various Enterobacteriaceae, Streptococci especially group A and B, Enterococci, Proteus species, S.epidemidis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Corynebacterium. Anaerobic species were found less frequently but have been isolated in 13.5% to 36% in some studies. In consistent with the present work, Tentolouris et al, (1999) found that Gram-positive aerobic bacteria were the commonest isolated bacteria (56.7%) followed by Gram-negative aerobic bacteria (29.8%) and anaerobes (13.5%)., where S. aureus was the most frequently isolated microorganism; with some strains were Methicillin resistant S. aureus (MRSA). Other Gram-positive aerobes isolated include coagulase negative Staphylococci (4.8%), Streptococci species (10.6%), Enterococci species (5.8%),Corynebacterium (29.8%).Among Gram-negative, Enterobacteriaceae species were the most frequent pathogen (29.8%), where as Pseudomonas aeruginosa accounted for (3.8%). Similarly a study done in Kuwait, the most frequently isolated Gram-positive Cocci were S. Mahgoub, et al., 2015: Vol 3(10) 96
7 aureus (53%), Enterococcus species (17.2%) and group B Streptococci (12.5%).Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Proteus mirabilis were the predominant species among Gram-negative aerobes.in consistent with the present work Serratia marcescens was isolated from diabetic septic wounds with prevalence rate of 5.9 %. Moreover, Candida species were associated with (7%) of infections,(abdulrazak et al, 2005). Nonetheless, The present work disagrees with the study done in Malaysia, which arrived at that the most frequently isolated pathogens were Gram-negative bacteria (52%) including Proteus spp, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae and E.coli. Grampositive bacteria accounted only for (45%) of all bacteria isolates, (Raja, 2007). Also, the present work also disagrees with the study done in India which found that among aerobic pathogens Enterobacteriaceae accounts for (48%) while Staphylococcus species accounts only for (18.2%),Streptococci (16.8%) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (17%) of all isolates.(viswnathan et al,2002) Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) has emerged as serious and common problem with diabetic foot ulcers. Infections or colonization with MRSA may result in prolonged hospital stay and excessive economic cost. In the present work 79% of S. aureus isolates were MRSA, with 36.3% prevalence rate among pathogenic microorganisms associated with diabetic septic wounds, which is highly alarming. Similarly 38.2% and 30 of isolated S.aureus was MRSA, (Adam,S.O.(2007)& El-Tahawy,A.T,(2002). In a study done in U.K the prevalence of MRSA in diabetic foot clinics was 15% and associated with prolonged healing time for diabetic ulcer and with antibiotic use, (Tentolouris et al,1999). Investigators in a clinic in Manchester, England reported that the prevalence of MRSA infection among patients with diabetic foot infection was 30.2% and this indicated that the rate of infection with MRSA had doubled over the period of 3 years (Dang et al, 2002). Data suggested that the infection with antimicrobial resistant pathogens might play a role in lower extremity amputation and other complications of lower extremity ulcer. 4. Conclusion The primary site of infection was foot which was 98.7%. The major type of diabetic septic wounds infection was monomicrobial which approached 77.3%. Mahgoub, et al., 2015: Vol 3(10) 97
8 Different types of aerobic bacteria were isolated from diabetic septic wounds. Including Gram positive Cocci and gram negative rods. Staph.aureus was not only the prominent isolate, but also 79 % of it was Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) which play a role in lower extremity amputation and other complications of lower extremity ulcer. Acknowledgements We are heartily thankful to Professor Mohammed Elfatih Ahmed Omer, for his encouragement, guidance and support. My thanks are conveyed to the director and staff of JABiR Abo alezz diabetic center, from where all the samples were collected, for their great assistance during collecting samples Also I am very grateful to staff of Omdurman Islamic university for their co-operation. References: Abdalrahman,H.M,(1999). Antibacterial activity of some antibiotics against clinical isolates taken from diabetic septic wound. Thesis submitted for a degree of Master, University of Khartoum, faculty of Pharmacy. Abdulrazak,A;Bitar,Z.I ;Shamali, A.A; Mobashe L.A. (2005). Bacteriology study of diabetic foot infection.journal of Diabetes and its complication. 19 (3): Adam,S.O.(2007). The bacterial infection among diabetic foot ulcers in Jabir Abu-Eliz diabetic Center in Khartoum. A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of requirement of M.S.A. in Medical Microbiology. Sudan Academy for Science and Technology. Apelquist,J;Bakker,K;VanHouten,W.H;Nabuurs;Franssen,M.H;Schapter,N.C.(2000).On behalf of the international working group on the Diabetic, foot International Consensus and Practical guidelines on the management and prevention of the diabetic foot. Diabet. Metabol. Res.16(1): Armstrong, D.G and Lipsky, B.A.(2004).Diabetic foot infection: stepwise medical and surgical management. International wound Journal.1(2): Boon,N.A;Walker,B.R;Hunter,J.A.A(1999).Davidson s principle and practice.churchil livinstone 20 th editiond Mahgoub, et al., 2015: Vol 3(10) 98
9 Cheesbrough,M.(2000). Distinct Laboratory Practice in Tropical Countries. Part 2.University Press, Cambridge U.K.Egyptian edition Dang,C.N; Prasad,Y.D.M; Boultan,A.J.M.(2002).Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in diabetic foot clinic aworsening problem [abstract]lake Balalion Hungary.Eupopean Association for the study of Diabetes. El-Tahawy,A.T,(2002). Bacteriology of diabetic foot infection.saudi Med J.21: Goldstein,E.J;Citron,D.M;Goldman,R.J.(1992).National Hospital Survey of anaerobic Culture and Susceptibility testing Method:Results and recommendation for improvement.j.clin.microbiol.30: Lipsky,B.A.(2004).A report from the international Consensus on diagnosis and treating the infected diabetic foot. Diabetes and Metabolism Research and Review.20(1) Lipsky,B.A;Berendt,A.R;Deery,H.G;Embil,J.M;Joseph,W.S;Karchmer,A.W;Lefrock,J.L;Lew,D.P;Marder,J.T;Norden,C;Tan,J.s.(2004).Dignosis and treatment of diabetic foot infection. Clinical Infectious Diseases.39(1): Porth,C.M.(2002). Pathophysiology concepts of altered health state.lippincott Williams and Wikins.6 th edition. Raja,N.S.(2007). Microbiology of diabetic foot infection in teaching hospital in Malaysia: A retrospective study of 194 cases. J Microbiol Immunol infect.40: Tentolouris,N;Jude,E,B;Smirnof,I;Knowles,E;Boulton,J.M.(1999).Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus an increasing problem in diabetic foot clinic. Diabetic Medicine. 16,(9): Viswnathan,V;Jasmine,J.J;Snehalatha,C;Romachandrom,A.(2002).prevalence of pathogens in diabetic infection in South India Type 2 diabetic patients.j.association Physician India.50: Wheat,L.J;Allen,S.D;Henary,M;Kernek,C.B;Sidas,J.A;Kueber,T.(1986). Diabetic foot infection:bacteriologic analysis.arch intern. Med:246: Williams,D.T;Hilton,J.R;Harding,K.G.(2004). Diagnosing foot infection in Diabetes. Clinical Infectious Diseases.39.(1): Mahgoub, et al., 2015: Vol 3(10) 99
Bacteriological Profile of Post Traumatic Osteomyelitis in a Tertiary Care Centre
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 1 (2017) pp. 367-372 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.601.044
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 1 (2017) pp. 367-372 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.601.044
Correlation between the Treatment Result and Causative Bacteria in Amputation of Diabetic Foot
 Correlation between the Treatment Result and Causative Bacteria in Amputation of Diabetic Foot Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Dong-A university, Busan, Korea Myoung Jin Lee M.D.,
Correlation between the Treatment Result and Causative Bacteria in Amputation of Diabetic Foot Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Dong-A university, Busan, Korea Myoung Jin Lee M.D.,
Aerobic bacterial Profile of Diabetic Foot Ulcers and their Antibiotic Sensitivity Pattern
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.173
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.173
INVESTIGATING: WOUND INFECTION
 INVESTIGATING: WOUND INFECTION Diagnosing infection in surgical and other wounds involves nurses being able to observe the clinical signs in a wound rather than simply obtaining positive microbiology results
INVESTIGATING: WOUND INFECTION Diagnosing infection in surgical and other wounds involves nurses being able to observe the clinical signs in a wound rather than simply obtaining positive microbiology results
Prevalence of Bacteria Isolated from Type 2 Diabetic Foot Ulcers and the Antibiotic Susceptibility Pattern
 Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (213) 2(1): x-xx ISSN: 2319-776 Volume 2 Number 1 (213) pp. 329-337 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Prevalence of Bacteria Isolated from Type 2 Diabetic Foot
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (213) 2(1): x-xx ISSN: 2319-776 Volume 2 Number 1 (213) pp. 329-337 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Prevalence of Bacteria Isolated from Type 2 Diabetic Foot
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis. Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017
 320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Pathogens of the Urinary tract The urinary system is composed of organs that regulate the chemical composition and volume of
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Pathogens of the Urinary tract The urinary system is composed of organs that regulate the chemical composition and volume of
Bacteriological Profile in Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers with special reference to their antibiotic sensitivity pattern
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 3 (2015) pp. 706-712 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Bacteriological Profile in Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers with special reference to their antibiotic
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 3 (2015) pp. 706-712 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Bacteriological Profile in Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers with special reference to their antibiotic
Blood culture 壢新醫院 病理檢驗科 陳啟清技術主任
 Blood culture 壢新醫院 病理檢驗科 陳啟清技術主任 A Positive Blood Culture Clinically Important Organism Failure of host defenses to contain an infection at its primary focus Failure of the physician to effectively eradicate,
Blood culture 壢新醫院 病理檢驗科 陳啟清技術主任 A Positive Blood Culture Clinically Important Organism Failure of host defenses to contain an infection at its primary focus Failure of the physician to effectively eradicate,
Research Article. Saleem M., Joseph Pushpa Innocent D. ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION IJCRR
 IJCRR Research Article COMPARISON OF MICROBIAL FLORA BY DEEP TISSUE BIOPSY AND SUPERFICIAL SWAB CULTURE OF SPECIMEN COLLECTED FROM VARIOUS ANATOMICAL SITES IN EARLY WOUND INFECTIONS Saleem M., Joseph Pushpa
IJCRR Research Article COMPARISON OF MICROBIAL FLORA BY DEEP TISSUE BIOPSY AND SUPERFICIAL SWAB CULTURE OF SPECIMEN COLLECTED FROM VARIOUS ANATOMICAL SITES IN EARLY WOUND INFECTIONS Saleem M., Joseph Pushpa
Comparison of bacterial etiology of non-healing ulcers in diabetic and non- diabetic patients.
 Original article: Comparison of bacterial etiology of non-healing ulcers in diabetic and non- diabetic patients. Mrs Smita Watwe, Dr Sadhana Chate, Charan k Dardi, DrAruna Khare Dept. of Microbiology,
Original article: Comparison of bacterial etiology of non-healing ulcers in diabetic and non- diabetic patients. Mrs Smita Watwe, Dr Sadhana Chate, Charan k Dardi, DrAruna Khare Dept. of Microbiology,
Original article. Microorganisms Isolated From Foot Ulcers Infection Of Diabetic Iraqi Patients. Summary:
 Original article Microorganisms solated From Foot Ulcers nfection Of Diabetic raqi Patients. Ryath shaya AL-Hemedawi *MSc. Suhaila M. AL-Salloum ** PhD Saad S. AL-Azawi*** Ph.D Summary: J Fac Med Baghdad
Original article Microorganisms solated From Foot Ulcers nfection Of Diabetic raqi Patients. Ryath shaya AL-Hemedawi *MSc. Suhaila M. AL-Salloum ** PhD Saad S. AL-Azawi*** Ph.D Summary: J Fac Med Baghdad
Arglaes provides a seven-day, non-cytotoxic barrier against infection
 Arglaes provides a seven-day, non-cytotoxic barrier against infection Arglaes Controlled-Release Silver Technology Reduce bioburden with Arglaes Silver Barrier Dressings Antimicrobial Arglaes began the
Arglaes provides a seven-day, non-cytotoxic barrier against infection Arglaes Controlled-Release Silver Technology Reduce bioburden with Arglaes Silver Barrier Dressings Antimicrobial Arglaes began the
Prevalence of ESBL producing enterobacteriaceae in diabetic foot ulcers
 Original Research Article Prevalence of ESBL producing enterobacteriaceae in diabetic foot ulcers Anitha S 1*, Natarajan V 2 1 Post Graduate, 2 Professor and HOD Department of Microbiology, Rajah Muthiah
Original Research Article Prevalence of ESBL producing enterobacteriaceae in diabetic foot ulcers Anitha S 1*, Natarajan V 2 1 Post Graduate, 2 Professor and HOD Department of Microbiology, Rajah Muthiah
Study of etiological factors and sensitivity pattern in CSOM
 Indian Journal of Basic and Applied Medical Research; December 2015: Vol.-5, Issue- 1, P. 766-770 766-771 Original article: Study of etiological factors and sensitivity pattern in CSOM Paresh Chavan, G
Indian Journal of Basic and Applied Medical Research; December 2015: Vol.-5, Issue- 1, P. 766-770 766-771 Original article: Study of etiological factors and sensitivity pattern in CSOM Paresh Chavan, G
Evaluation of the feasibility of the VACUETTE Urine CCM tube for microbial testing of urine samples
 Evaluation of the feasibility of the VACUETTE Urine CCM tube for microbial testing of urine samples Background The VACUETTE Urine CCM tube is for the collection, transport and storage of urine samples
Evaluation of the feasibility of the VACUETTE Urine CCM tube for microbial testing of urine samples Background The VACUETTE Urine CCM tube is for the collection, transport and storage of urine samples
Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care. Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK
 Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK Antimicrobial agents Antibacterial agents Antifungal agents Antiviral agents Antiparasitic agents?others
Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK Antimicrobial agents Antibacterial agents Antifungal agents Antiviral agents Antiparasitic agents?others
Staphylococci. Gram stain: gram positive cocci arranged in clusters.
 Microbiology lab Respiratory system Third medical year Lab contents: Gram positive bacteria (Staphylococcus and Streptococcus spp), two types of filamentous fungi (Aspergillus and Penicillium spp), and
Microbiology lab Respiratory system Third medical year Lab contents: Gram positive bacteria (Staphylococcus and Streptococcus spp), two types of filamentous fungi (Aspergillus and Penicillium spp), and
BACTERIOLOGICAL PROFILE OF DIABETIC FOOT INFECTIONS
 ejpmr, 2018,5(6), 631-635 Khadse et al. SJIF Impact Factor 4.897 Research Article EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH ISSN 2394-3211 www.ejpmr.com EJPMR BACTERIOLOGICAL PROFILE OF DIABETIC
ejpmr, 2018,5(6), 631-635 Khadse et al. SJIF Impact Factor 4.897 Research Article EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH ISSN 2394-3211 www.ejpmr.com EJPMR BACTERIOLOGICAL PROFILE OF DIABETIC
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students. Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile.. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products,
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile.. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products,
BACTERIOLOGY PROGRAMME AND PLAN OF TEACHING 3 rd Semester (academic year )
 BACTERIOLOGY PROGRAMME AND PLAN OF TEACHING 3 rd Semester (academic year 2012-2013) 19. 10. 2012. Introduction in microbiology, bacterial taxonomy, general bacterial prop Bacterial structures, biosynthesis
BACTERIOLOGY PROGRAMME AND PLAN OF TEACHING 3 rd Semester (academic year 2012-2013) 19. 10. 2012. Introduction in microbiology, bacterial taxonomy, general bacterial prop Bacterial structures, biosynthesis
1430 West McCoy Lane Santa Maria, CA p:
 091217TR HardyCHROM BluEcoli 1 HardyCHROM Candida 2 HardyCHROM ECC 3 HardyCHROM ESBL 4 HardyCHROM Listeria 5 HardyCHROM MRSA 6 HardyCHROM O157 7 HardyCHROM Salmonella 8 HardyCHROM SS NoPRO 9 HardyCHROM
091217TR HardyCHROM BluEcoli 1 HardyCHROM Candida 2 HardyCHROM ECC 3 HardyCHROM ESBL 4 HardyCHROM Listeria 5 HardyCHROM MRSA 6 HardyCHROM O157 7 HardyCHROM Salmonella 8 HardyCHROM SS NoPRO 9 HardyCHROM
ISSN X (Print) Research Article
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2014; 2(2D):65-69 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2014; 2(2D):65-69 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Analysis on distribution, drug resistance and risk factors of multi drug resistant bacteria in diabetic foot infection.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (22): 10186-10190 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Analysis on distribution, drug resistance and risk factors of multi drug resistant bacteria in diabetic foot infection.
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (22): 10186-10190 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Analysis on distribution, drug resistance and risk factors of multi drug resistant bacteria in diabetic foot infection.
Work up of Respiratory & Wound Cultures:
 Work up of Respiratory & Wound Cultures: Culture work up 2 Systematic approaches 1 Work up of Respiratory & Wound Cultures Resident flora Colonizing organisms Pathogens 2 Work up of Respiratory & Wound
Work up of Respiratory & Wound Cultures: Culture work up 2 Systematic approaches 1 Work up of Respiratory & Wound Cultures Resident flora Colonizing organisms Pathogens 2 Work up of Respiratory & Wound
University of Alberta Hospital Antibiogram for 2007 and 2008 Division of Medical Microbiology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology
 University of Alberta Hospital Antibiogram for 2007 and 2008 Division of Medical Microbiology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology This material is supported in part by unrestricted educational
University of Alberta Hospital Antibiogram for 2007 and 2008 Division of Medical Microbiology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology This material is supported in part by unrestricted educational
Prosthetic Joint Infections Review of diagnosis including the role of molecular techniques. Dr Prema Singh
 Prosthetic Joint Infections Review of diagnosis including the role of molecular techniques Dr Prema Singh Consultant Microbiologist Watford General Hospital Structure of talk Introduction Case scenario
Prosthetic Joint Infections Review of diagnosis including the role of molecular techniques Dr Prema Singh Consultant Microbiologist Watford General Hospital Structure of talk Introduction Case scenario
Wounds and Infections: Wound Management From the ID Physician Standpoint. Alena Klochko, MD Orlando VA Medical Center Infectious Disease Department
 Wounds and Infections: Wound Management From the ID Physician Standpoint Alena Klochko, MD Orlando VA Medical Center Infectious Disease Department Objectives Distinguish between colonization, critical
Wounds and Infections: Wound Management From the ID Physician Standpoint Alena Klochko, MD Orlando VA Medical Center Infectious Disease Department Objectives Distinguish between colonization, critical
Microbiology products. Liofilchem Chromatic
 ET Microbiology products M IC R O PL A N www.liofilchem.net Liofilchem Chromatic c h ro m o g e n i c c u l t u re m e d i a LIOFILCHEM s.r.l. Via Scozia, Zona Industriale 64026 Roseto degli Abruzzi (Te)
ET Microbiology products M IC R O PL A N www.liofilchem.net Liofilchem Chromatic c h ro m o g e n i c c u l t u re m e d i a LIOFILCHEM s.r.l. Via Scozia, Zona Industriale 64026 Roseto degli Abruzzi (Te)
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 08 Page August 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i8.100 Original Research Article Clinico-Microbiological
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i8.100 Original Research Article Clinico-Microbiological
Foot infections are now among the most
 Article Progress in a pedestrian problem: A review of the revised Infectious Diseases Society of America diabetic foot infection guidelines Benjamin A Lipsky This article was first published in The Diabetic
Article Progress in a pedestrian problem: A review of the revised Infectious Diseases Society of America diabetic foot infection guidelines Benjamin A Lipsky This article was first published in The Diabetic
Received 30 March 2005; returned 16 June 2005; revised 8 September 2005; accepted 12 September 2005
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2005) 56, 1047 1052 doi:10.1093/jac/dki362 Advance Access publication 20 October 2005 Evaluation of PPI-0903M (T91825), a novel cephalosporin: bactericidal activity,
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2005) 56, 1047 1052 doi:10.1093/jac/dki362 Advance Access publication 20 October 2005 Evaluation of PPI-0903M (T91825), a novel cephalosporin: bactericidal activity,
Foot infections in persons with diabetes are
 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC FOOT INFECTION * James S. Tan, MD, MACP, FCCP ABSTRACT According to the American Diabetes Association, approximately 82 000 nontraumatic lower-limb amputations were
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF DIABETIC FOOT INFECTION * James S. Tan, MD, MACP, FCCP ABSTRACT According to the American Diabetes Association, approximately 82 000 nontraumatic lower-limb amputations were
Clinical observation study in 624 patients confirms good efficacy and tolerability
 Treatment of infected and infection-prone wounds with Atrauman Ag Clinical observation study in 624 patients confirms good efficacy and tolerability Wound management Summary More than 600 patients with
Treatment of infected and infection-prone wounds with Atrauman Ag Clinical observation study in 624 patients confirms good efficacy and tolerability Wound management Summary More than 600 patients with
Healthcare-associated infections acquired in intensive care units
 SURVEILLANCE REPORT Annual Epidemiological Report for 2015 Healthcare-associated infections acquired in intensive care units Key facts In 2015, 11 788 (8.3%) of patients staying in an intensive care unit
SURVEILLANCE REPORT Annual Epidemiological Report for 2015 Healthcare-associated infections acquired in intensive care units Key facts In 2015, 11 788 (8.3%) of patients staying in an intensive care unit
Bacteriemia and sepsis
 Bacteriemia and sepsis Case 1 An 80-year-old man is brought to the emergency room by his son, who noted that his father had become lethargic and has decreased urination over the past 4 days. The patient
Bacteriemia and sepsis Case 1 An 80-year-old man is brought to the emergency room by his son, who noted that his father had become lethargic and has decreased urination over the past 4 days. The patient
Mixed gram positive organisms uti
 Mixed gram positive organisms uti The Borg System is 100 % Mixed gram positive organisms uti Complicated UTIs are caused by a broader spectrum of bacteria, including Gram- positive in addition to Gramnegative
Mixed gram positive organisms uti The Borg System is 100 % Mixed gram positive organisms uti Complicated UTIs are caused by a broader spectrum of bacteria, including Gram- positive in addition to Gramnegative
Study on Bacterial Spectrum of Organism Causing Diabetic Foot Ulcers with its Antibiogram in Dr. B.R. Ambedkar Medical College, Bangalore, India
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 5 (2017) pp. 642-647 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.605.074
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 5 (2017) pp. 642-647 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.605.074
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN DIABETIC PATIENTS ATTENDING OUTPATIENT DEPARTMENTS AT KASTURBA MEDICAL COLLEGE TEACHING HOSPITAL, MANIPAL, INDIA
 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Gautam R. et al. Volume 2, Issue 3, 1141-1146. Research Article ISSN 2278 4357 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN DIABETIC PATIENTS ATTENDING OUTPATIENT DEPARTMENTS
WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Gautam R. et al. Volume 2, Issue 3, 1141-1146. Research Article ISSN 2278 4357 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN DIABETIC PATIENTS ATTENDING OUTPATIENT DEPARTMENTS
Pressure Injury Complications: Diagnostic Dilemmas
 Pressure Injury Complications: Diagnostic Dilemmas Aimée D. Garcia, MD, CWS, FACCWS Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Geriatrics Section Baylor College of Medicine Medical Director, Wound Clinic
Pressure Injury Complications: Diagnostic Dilemmas Aimée D. Garcia, MD, CWS, FACCWS Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Geriatrics Section Baylor College of Medicine Medical Director, Wound Clinic
Normal Human Flora. (Human Microbiome) Dr.Sarmad M.H. Zeiny Baghdad College of Medicine
 Normal Human Flora (Human Microbiome) Dr.Sarmad M.H. Zeiny Baghdad College of Medicine 2014-2015 Objectives Describe important human normal flora. Demonstrate the epidemiology of human normal flora. Determine
Normal Human Flora (Human Microbiome) Dr.Sarmad M.H. Zeiny Baghdad College of Medicine 2014-2015 Objectives Describe important human normal flora. Demonstrate the epidemiology of human normal flora. Determine
Correlation of Postoperative Wound Infection with Intraoperative Culture Results and Duration of Operation
 POSTOPERATIVE THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE WOUND INFECTION MEDICAL JOURNAL Correlation of Postoperative Wound Infection with Intraoperative Culture Results and Duration of Operation INTRODUCTION: Infection is
POSTOPERATIVE THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE WOUND INFECTION MEDICAL JOURNAL Correlation of Postoperative Wound Infection with Intraoperative Culture Results and Duration of Operation INTRODUCTION: Infection is
Clinical Case. ! 2am: Call from Surgeon, Ballarat Hospital. ! Suspicion of Necrotizing Fasciitis: ! Need of HBOT?
 Clinical Case! 2am: Call from Surgeon, Ballarat Hospital! Suspicion of Necrotizing Fasciitis:! 59y, Police Officer, diabetic, overweight! 4pm: pain in right arm! 8pm: pain worsening " ED! HD instability
Clinical Case! 2am: Call from Surgeon, Ballarat Hospital! Suspicion of Necrotizing Fasciitis:! 59y, Police Officer, diabetic, overweight! 4pm: pain in right arm! 8pm: pain worsening " ED! HD instability
Clinical observation study in 624 patients confirms good efficacy and tolerability
 Studie_Atrauman_Ag_GB.qxd 09.01.2006 13:32 Uhr Seite 6 Treatment of infected and infection-prone wounds with Atrauman Ag SD (0105) 087 078/3 Clinical observation study in 624 patients confirms good efficacy
Studie_Atrauman_Ag_GB.qxd 09.01.2006 13:32 Uhr Seite 6 Treatment of infected and infection-prone wounds with Atrauman Ag SD (0105) 087 078/3 Clinical observation study in 624 patients confirms good efficacy
Infectious Disease Testing. UriSelect 4 Medium. Direct Identification Visibly Reliable
 Infectious Disease Testing Urielect 4 Medium Direct Identification Visibly Reliable Urielect 4 Non selective chromogenic medium for the isolation, differentiation and enumeration of urinary tract infections
Infectious Disease Testing Urielect 4 Medium Direct Identification Visibly Reliable Urielect 4 Non selective chromogenic medium for the isolation, differentiation and enumeration of urinary tract infections
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Blood cultures in ED. Dr Sebastian Chang MBBS FACEM
 Blood cultures in ED Dr Sebastian Chang MBBS FACEM Why do we care about blood cultures? blood cultures are the most direct method for detecting bacteraemia in patients a positive blood culture: 1. can
Blood cultures in ED Dr Sebastian Chang MBBS FACEM Why do we care about blood cultures? blood cultures are the most direct method for detecting bacteraemia in patients a positive blood culture: 1. can
Cefotaxime Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version th September 2010
 Cefotaxime Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the European
Cefotaxime Rationale for the EUCAST clinical breakpoints, version 1.0 26 th September 2010 Foreword EUCAST The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) is organised by the European
A new selective blood agar medium for Streptococcus pyogenes and other haemolytic streptococci
 J. clin. Path. (1964), 17, 231 A new selective blood agar medium for Streptococcus pyogenes and other haemolytic streptococci E. J. L. LOWBURY, A. KIDSON, AND H. A. LILLY From the Medical Research Council
J. clin. Path. (1964), 17, 231 A new selective blood agar medium for Streptococcus pyogenes and other haemolytic streptococci E. J. L. LOWBURY, A. KIDSON, AND H. A. LILLY From the Medical Research Council
Bone and Joint Infections in Diabetics: Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot and Other Common Lower Extremity Infections
 Bone and Joint Infections in Diabetics: Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot and Other Common Lower Extremity Infections Objectives How do you to diagnose, classify and manage DFI? How do you diagnose
Bone and Joint Infections in Diabetics: Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot and Other Common Lower Extremity Infections Objectives How do you to diagnose, classify and manage DFI? How do you diagnose
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis. Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017
 320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Blood Culture What is a blood culture? A blood culture is a laboratory test in which blood is injected into bottles with culture
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Blood Culture What is a blood culture? A blood culture is a laboratory test in which blood is injected into bottles with culture
Surveillance of Surgical Site Infection in Surgical Hospital Wards in Bulgaria,
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.361
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.361
The Clinical Significance of Blood Cultures. Presented BY; Cindy Winfrey, MSN, RN, CIC, DON- LTC TM, VA- BC TM
 The Clinical Significance of Blood Cultures Presented BY; Cindy Winfrey, MSN, RN, CIC, DON- LTC TM, VA- BC TM OVERVIEW Blood cultures are considered an important laboratory tool used to diagnose serious
The Clinical Significance of Blood Cultures Presented BY; Cindy Winfrey, MSN, RN, CIC, DON- LTC TM, VA- BC TM OVERVIEW Blood cultures are considered an important laboratory tool used to diagnose serious
Lab 4. Blood Culture (Media) MIC AMAL-NORA-ALJAWHARA 1
 Lab 4. Blood Culture (Media) 2018 320 MIC AMAL-NORA-ALJAWHARA 1 Blood Culture 2018 320 MIC AMAL-NORA-ALJAWHARA 2 What is a blood culture? A blood culture is a laboratory test in which blood is injected
Lab 4. Blood Culture (Media) 2018 320 MIC AMAL-NORA-ALJAWHARA 1 Blood Culture 2018 320 MIC AMAL-NORA-ALJAWHARA 2 What is a blood culture? A blood culture is a laboratory test in which blood is injected
Bacterial Flora of Leg Ulcers in Patients Admitted to Department of Dermatology, Poznań University of Medical Sciences, during the Period
 2005;13(3):168-172 CLINICAL ARTICLE Bacterial Flora of Leg Ulcers in Patients Admitted to Department of Dermatology, Poznań University of Medical Sciences, during the 1998-2002 Period Maria Żmudzińska,
2005;13(3):168-172 CLINICAL ARTICLE Bacterial Flora of Leg Ulcers in Patients Admitted to Department of Dermatology, Poznań University of Medical Sciences, during the 1998-2002 Period Maria Żmudzińska,
St. Joseph's Journal of Humanities and Science ISSN:
 M. Parimala Celia et al. / St. Joseph s Journal of Humanities and Science (Volume 4 Issue 1 January 2017) 23-28 33 St. Joseph s Journal of Humanities and Science (Volume 4 Issue 2 August 2015) 33-38 St.
M. Parimala Celia et al. / St. Joseph s Journal of Humanities and Science (Volume 4 Issue 1 January 2017) 23-28 33 St. Joseph s Journal of Humanities and Science (Volume 4 Issue 2 August 2015) 33-38 St.
Labquality External Quality Assesment Programmes General Bacteriology 1 1/2010
 Labquality External Quality Assesment Programmes General Bacteriology 1 1/2010 Photos and text: Markku Koskela, M.D., Ph.D. Clinical microbiology specialist Oulu, Finland Sample 1/2010 Pus from an infected
Labquality External Quality Assesment Programmes General Bacteriology 1 1/2010 Photos and text: Markku Koskela, M.D., Ph.D. Clinical microbiology specialist Oulu, Finland Sample 1/2010 Pus from an infected
Complicated Skin and Soft Tissue Infection diagnosis and severity stratification
 Complicated Skin and Soft Tissue Infection diagnosis and severity stratification Muhammad Hussein Gasem Div Infectious Disease, TropMed, and Immunology Dr. Kariadi Hospital, Diponegoro University Semarang,
Complicated Skin and Soft Tissue Infection diagnosis and severity stratification Muhammad Hussein Gasem Div Infectious Disease, TropMed, and Immunology Dr. Kariadi Hospital, Diponegoro University Semarang,
Microbiology and Treatment of Diabetic Foot Infections
 Microbiology and Treatment of Diabetic Foot Infections 18 Adolf W. Karchmer Abstract Foot infections in diabetic patients are a major source of morbidity and an important proximate cause of amputations.
Microbiology and Treatment of Diabetic Foot Infections 18 Adolf W. Karchmer Abstract Foot infections in diabetic patients are a major source of morbidity and an important proximate cause of amputations.
Urine bench. John Ferguson Sept 2013
 Urine bench John Ferguson Sept 2013 Overview Specimen collection- separate presentation Urinalysis: protein, blood, white cells, nitrite Microscopy- crystals and casts- separate presentations quantitative
Urine bench John Ferguson Sept 2013 Overview Specimen collection- separate presentation Urinalysis: protein, blood, white cells, nitrite Microscopy- crystals and casts- separate presentations quantitative
Streptococci facultative anaerobe
 THE GENUS STREPTOCOCCUS The genus Streptococcus obtains Gram-positive cocci, nonmotile, nonsporeforming, arranged mostly in chains or in pairs. Most species are facultative anaerobes. Some of streptococci
THE GENUS STREPTOCOCCUS The genus Streptococcus obtains Gram-positive cocci, nonmotile, nonsporeforming, arranged mostly in chains or in pairs. Most species are facultative anaerobes. Some of streptococci
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL (A) Further inclusion criteria and categorisation of ICD-10 diagnostic codes Pneumonia: A310 Pulmonary mycobacterial infection A420 Pulmonary actinomycosis A481 Legionnaires' disease
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL (A) Further inclusion criteria and categorisation of ICD-10 diagnostic codes Pneumonia: A310 Pulmonary mycobacterial infection A420 Pulmonary actinomycosis A481 Legionnaires' disease
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 8, August ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 8, August-2016 105 Antimicrobial activity of Andrographis paniculata stem extracts. S.Gurupriya 1 and Dr.L.Cathrine 2 1 M.phil
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 8, August-2016 105 Antimicrobial activity of Andrographis paniculata stem extracts. S.Gurupriya 1 and Dr.L.Cathrine 2 1 M.phil
A Study on the Use of Cephalosporins in Patients with Diabetic Foot Infections
 Research Article A Study on the Use of Cephalosporins in Patients with Diabetic Foot Infections Prathap Balakrishna 1, Dharati Shah 2, Githa Kishore 2*, Sneha Keerthi 2 1 Kempegowda Institute of Medical
Research Article A Study on the Use of Cephalosporins in Patients with Diabetic Foot Infections Prathap Balakrishna 1, Dharati Shah 2, Githa Kishore 2*, Sneha Keerthi 2 1 Kempegowda Institute of Medical
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 Microbiological evaluation: how to report the results Alvaro Pascual MD, PhD Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology Unit. University Hospital Virgen Macarena University of Sevilla BSI management
Microbiological evaluation: how to report the results Alvaro Pascual MD, PhD Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology Unit. University Hospital Virgen Macarena University of Sevilla BSI management
Outcome in Patients of Diabetic Foot Infection with Multidrug Resistant Organisms
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Outcome in Patients of Diabetic Foot Infection with Multidrug Resistant Organisms 1 Sanjay Gupta, 2 Ashok Attri, 3 Sudhansoo Khanna, 4 Jagdish Chander, 5 Mayankjayant JFAS JFAS (AP) (AP)
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Outcome in Patients of Diabetic Foot Infection with Multidrug Resistant Organisms 1 Sanjay Gupta, 2 Ashok Attri, 3 Sudhansoo Khanna, 4 Jagdish Chander, 5 Mayankjayant JFAS JFAS (AP) (AP)
Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia
 Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia George Samonis MD, PhD Medical Oncologist Infectious Diseases Specialist Professor of Medicine The University of Crete, Heraklion,, Crete, Greece
Treatment of febrile neutropenia in patients with neoplasia George Samonis MD, PhD Medical Oncologist Infectious Diseases Specialist Professor of Medicine The University of Crete, Heraklion,, Crete, Greece
UTI IN ELDERLY. Zeinab Naderpour
 UTI IN ELDERLY Zeinab Naderpour Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most frequent bacterial infection in elderly populations. While urinary infection in the elderly person is usually asymptomatic, symptomatic
UTI IN ELDERLY Zeinab Naderpour Urinary tract infection (UTI) is the most frequent bacterial infection in elderly populations. While urinary infection in the elderly person is usually asymptomatic, symptomatic
Getting the Point of Injection Safety
 Getting the Point of Injection Safety Barbara Montana, MD, MPH, FACP Medical Director Communicable Disease Service Outbreak of Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis associated with an oral surgery practice
Getting the Point of Injection Safety Barbara Montana, MD, MPH, FACP Medical Director Communicable Disease Service Outbreak of Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis associated with an oral surgery practice
CHAPTER 8 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ETHANOLIC EXTRACT AND THE ISOLATED COMPOUNDS FROM THE STEM OF COSTUS IGNEUS
 CHAPTER 8 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ETHANOLIC EXTRACT AND THE ISOLATED COMPOUNDS FROM THE STEM OF COSTUS IGNEUS 8.1 INTRODUCTION Medicinal plants are the backbone of traditional medicine and
CHAPTER 8 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ETHANOLIC EXTRACT AND THE ISOLATED COMPOUNDS FROM THE STEM OF COSTUS IGNEUS 8.1 INTRODUCTION Medicinal plants are the backbone of traditional medicine and
Babak Valizadeh, DCLS
 Ocular Infections- Laboratory Diagnosis of Bacterial Infections of the Eye Babak Valizadeh, DCLS 1392. 02. 01 2012. 04. 21 Babak_Valizadeh@hotmail.com Discriminating Between Indigenous Microbiota and
Ocular Infections- Laboratory Diagnosis of Bacterial Infections of the Eye Babak Valizadeh, DCLS 1392. 02. 01 2012. 04. 21 Babak_Valizadeh@hotmail.com Discriminating Between Indigenous Microbiota and
Comparison of CPS ID 3 and CHROMagar Orientation chromogenic agars with standard biplate technique for culture of clinical urine samples
 J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2008;41:422-427 Comparison of CPS ID 3 and CHROMagar Orientation chromogenic agars with standard biplate technique for culture of clinical urine samples Jen-Chyi Chang 1,2,
J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2008;41:422-427 Comparison of CPS ID 3 and CHROMagar Orientation chromogenic agars with standard biplate technique for culture of clinical urine samples Jen-Chyi Chang 1,2,
Research Article Prevalence of Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Infections in Diabetic versus Nondiabetic Wounds
 Pathogens, Article ID 173053, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/173053 Research Article Prevalence of Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Infections in Diabetic versus Nondiabetic Wounds Urvish Trivedi,
Pathogens, Article ID 173053, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/173053 Research Article Prevalence of Multiple Antibiotic Resistant Infections in Diabetic versus Nondiabetic Wounds Urvish Trivedi,
Efficacy of fresh Aloe vera gel against multi- drug resistant bacteria in infected leg ulcers
 Efficacy of fresh Aloe vera gel against multi- drug resistant bacteria in infected leg ulcers Asima Banu, Sathyanarayana BC, Goura Chattannavar Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute RESEARCH
Efficacy of fresh Aloe vera gel against multi- drug resistant bacteria in infected leg ulcers Asima Banu, Sathyanarayana BC, Goura Chattannavar Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute RESEARCH
Affinity of Doripenem and Comparators to Penicillin-Binding Proteins in Escherichia coli and ACCEPTED
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on February 00 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:./aac.01-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on February 00 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:./aac.01-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
Clinical Comparison of Cefotaxime with Gentamicin plus Clindamycin in the Treatment of Peritonitis and Other Soft-Tissue Infections
 REVIEWS OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES. VOL. 4, SUPPLEMENT. SEPTEMBER-OCTOBER 982 982 by The University of Chicago. All rights reserved. 062-0886/82/0405-022$02.00 Clinical Comparison of with Gentamicin plus Clindamycin
REVIEWS OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES. VOL. 4, SUPPLEMENT. SEPTEMBER-OCTOBER 982 982 by The University of Chicago. All rights reserved. 062-0886/82/0405-022$02.00 Clinical Comparison of with Gentamicin plus Clindamycin
Gram-negative rods. Enterobacteriaceae. Biochemical Reactions. Manal AL khulaifi
 Gram-negative rods Enterobacteriaceae Biochemical Reactions Bacteria Gram positive Gram negative Cocci Bacilli Cocci Rods Characters of Enterobacteriaceae All Enterobacteriaciae Gram-negative rods Reduce
Gram-negative rods Enterobacteriaceae Biochemical Reactions Bacteria Gram positive Gram negative Cocci Bacilli Cocci Rods Characters of Enterobacteriaceae All Enterobacteriaciae Gram-negative rods Reduce
ZINEX. Composition Each tablet contains Cefuroxime (as axetil) 250 or 500 mg
 ZINEX Composition Each tablet contains Cefuroxime (as axetil) 250 or 500 mg Tablets Action Cefuroxime axetil owes its bactericidal activity to the parent compound cefuroxime. Cefuroxime is a well-characterized
ZINEX Composition Each tablet contains Cefuroxime (as axetil) 250 or 500 mg Tablets Action Cefuroxime axetil owes its bactericidal activity to the parent compound cefuroxime. Cefuroxime is a well-characterized
Antimicrobial prophylaxis in liver transplant A multicenter survey endorsed by the European Liver and Intestine Transplant Association
 Antimicrobial prophylaxis in liver transplant A multicenter survey endorsed by the European Liver and Intestine Transplant Association Els Vandecasteele, Jan De Waele, Dominique Vandijck, Stijn Blot, Dirk
Antimicrobial prophylaxis in liver transplant A multicenter survey endorsed by the European Liver and Intestine Transplant Association Els Vandecasteele, Jan De Waele, Dominique Vandijck, Stijn Blot, Dirk
Optimizing MALDI-TOF Use. Clinical Impact Laboratory Impact
 Optimizing MALDI-TOF Use Clinical Impact Laboratory Impact Christine C. Ginocchio, PhD, MT (ASCP) Clinical Professor of Medicine Hofstra North Shore-LIJ School of Medicine, NY VP, Global Microbiology Affairs,
Optimizing MALDI-TOF Use Clinical Impact Laboratory Impact Christine C. Ginocchio, PhD, MT (ASCP) Clinical Professor of Medicine Hofstra North Shore-LIJ School of Medicine, NY VP, Global Microbiology Affairs,
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 Hospital Universitario Virgen Macarena, Seville New drugs against MRSA and VRE L. Eduardo López Cortés Seville, 8th July Tedizolid Oxazolidinone Ceftaroline // Ceftobiprole 5 th gen cephalosporin Overview
Hospital Universitario Virgen Macarena, Seville New drugs against MRSA and VRE L. Eduardo López Cortés Seville, 8th July Tedizolid Oxazolidinone Ceftaroline // Ceftobiprole 5 th gen cephalosporin Overview
Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection
 Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection Defense Mechanisms Three lines of defense protect the body against foreign invasion: Physical or surface barriers Inflammation Immune response Inflammation Non-specific
Chapter 4 Inflammation and Infection Defense Mechanisms Three lines of defense protect the body against foreign invasion: Physical or surface barriers Inflammation Immune response Inflammation Non-specific
Reducing Blood Culture Contamination in Hospitalized Pediatric Patients
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 12 (2015) pp. 200-208 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Reducing Blood Culture Contamination in Hospitalized Pediatric Patients S. H. Khater Enas 1 * and Taha
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 12 (2015) pp. 200-208 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Reducing Blood Culture Contamination in Hospitalized Pediatric Patients S. H. Khater Enas 1 * and Taha
LESSON 2.6 WORKBOOK Diagnosing infections, and, what s up your nose?
 Staphylococcus aureus Morphology: The physical form or structure of a microbe.. LESSON 2.6 WORKBOOK Diagnosing infections, and, what s up your nose? Now we have discussed the different requirements that
Staphylococcus aureus Morphology: The physical form or structure of a microbe.. LESSON 2.6 WORKBOOK Diagnosing infections, and, what s up your nose? Now we have discussed the different requirements that
Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela
 Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela Microbiology Department Medical Faculty, University of Indonesia Urinary Tract Infection
Diagnostic approach and microorganism resistance pattern in UTI Yeva Rosana, Anis Karuniawati, Yulia Rosa, Budiman Bela Microbiology Department Medical Faculty, University of Indonesia Urinary Tract Infection
PATHWAY #4 DIABETIC FOOT DISORDERS VOLUME 45, NUMBER 5, SEPTEMBER/OCTOBER 2006 S 29
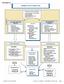 PATHWAY #4 DIABETIC FOOT DISORDERS VOLUME 45, NUMBER 5, SEPTEMBER/OCTOBER 2006 S 29 be present. Hospitalization is required to treat the infection as well as systemic sequelae. Patients with poor vascular
PATHWAY #4 DIABETIC FOOT DISORDERS VOLUME 45, NUMBER 5, SEPTEMBER/OCTOBER 2006 S 29 be present. Hospitalization is required to treat the infection as well as systemic sequelae. Patients with poor vascular
Research Article A Comparison of Tissue versus Swab Culturing of Infected Diabetic Foot Wounds
 International Endocrinology Volume 2016, Article ID 8198714, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8198714 Research Article A Comparison of Tissue versus Swab Culturing of Infected Diabetic Foot Wounds
International Endocrinology Volume 2016, Article ID 8198714, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8198714 Research Article A Comparison of Tissue versus Swab Culturing of Infected Diabetic Foot Wounds
Normal Flora PROF. HANAN HABIB DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY COLLEGE OF MEDICINE, KSU
 Normal Flora PROF. HANAN HABIB DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY COLLEGE OF MEDICINE, KSU Objectives 1. Define the terms: Normal Flora, Resident flora, Transient flora and carrier state 2. Know the origin of normal
Normal Flora PROF. HANAN HABIB DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY COLLEGE OF MEDICINE, KSU Objectives 1. Define the terms: Normal Flora, Resident flora, Transient flora and carrier state 2. Know the origin of normal
Bacterial Profile of Blood Stream Infections In Children Less Than Three Years Old
 J. Babylon Univ., 0(3) : 48485. March 2005. Bacterial Profile of Blood Stream Infections In Children Less Than Three Years Old Alaa H. AlCharrakh Ali M. AlMuhana 2 Zainab H. AlSaadi Dept. of Microbiology,
J. Babylon Univ., 0(3) : 48485. March 2005. Bacterial Profile of Blood Stream Infections In Children Less Than Three Years Old Alaa H. AlCharrakh Ali M. AlMuhana 2 Zainab H. AlSaadi Dept. of Microbiology,
Discrepancies in the recovery of bacteria from multiple sinuses in acute and chronic sinusitis
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2004), 53, 879 885 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.45655-0 Short Communication Correspondence Itzhak Brook ib6@georgetown.edu Received 1 March 2004 Accepted 18 May 2004 Discrepancies
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2004), 53, 879 885 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.45655-0 Short Communication Correspondence Itzhak Brook ib6@georgetown.edu Received 1 March 2004 Accepted 18 May 2004 Discrepancies
Prevalence of Extended Spectrum -Lactamases In E.coli and Klebsiella spp. in a Tertiary Care Hospital
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 10 (2014) pp. 474-478 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Prevalence of Extended Spectrum -Lactamases In E.coli and Klebsiella spp. in a Tertiary Care Hospital
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 10 (2014) pp. 474-478 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Prevalence of Extended Spectrum -Lactamases In E.coli and Klebsiella spp. in a Tertiary Care Hospital
In-House Standardization of Carba NP Test for Carbapenemase Detection in Gram Negative Bacteria
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.342
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.342
Next Generation in Acne treatment. A new approach in Acne Treatment. GramaDerm. Advanced Acne Vulgaris Management with Microcyn Technology
 Next Generation in Acne treatment A new approach in Acne Treatment GramaDerm Advanced Acne Vulgaris Management with Microcyn Technology Did you know? 85% of young people between the ages of 12 and 24 years
Next Generation in Acne treatment A new approach in Acne Treatment GramaDerm Advanced Acne Vulgaris Management with Microcyn Technology Did you know? 85% of young people between the ages of 12 and 24 years
Urinary Tract Infection at a University Hospital in Saudi Arabia: Incidence, Microbiology, and Antimicrobial Susceptibility
 Urinary Tract Infection at a University Hospital in Saudi Arabia: Incidence, Microbiology, and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Ahmed T. Eltahawy, MB, BCh, DipBact, PhD; Ragaa M. F. Khalaf, MB, BCh, DipBact,
Urinary Tract Infection at a University Hospital in Saudi Arabia: Incidence, Microbiology, and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Ahmed T. Eltahawy, MB, BCh, DipBact, PhD; Ragaa M. F. Khalaf, MB, BCh, DipBact,
Surveillance of Healthcare Associated Infections in Scottish Intensive Care Units
 Surveillance of Healthcare Associated Infections in Scottish Intensive Care Units Annual report of data from January 2010 to December 2010 Scottish Intensive Care Society Audit Group 1 Health Protection
Surveillance of Healthcare Associated Infections in Scottish Intensive Care Units Annual report of data from January 2010 to December 2010 Scottish Intensive Care Society Audit Group 1 Health Protection
Objectives 12/4/2013. Disclosure. Culture of Orthopaedic Infections. Microbiology Testing in the Diagnosis of Prosthetic Joint Infections
 Culture of Orthopaedic Infections Microbiology Testing in the Diagnosis of Prosthetic Joint Infections December 9, 2013 Raymond P. Podzorski, Ph.D., D(ABMM) Clinical Microbiologist ProHealth Care Laboratories
Culture of Orthopaedic Infections Microbiology Testing in the Diagnosis of Prosthetic Joint Infections December 9, 2013 Raymond P. Podzorski, Ph.D., D(ABMM) Clinical Microbiologist ProHealth Care Laboratories
Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate
 Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate Professor of Pharmacy & Associate Member of Medicine, UBC
Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate Professor of Pharmacy & Associate Member of Medicine, UBC
Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD
 Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Infective endocarditis (IE) is an inflammation of the endocardium.. inner of the heart muscle & the epithelial lining of heart valves.
Infective endocarditis (IE) By Assis. Prof. Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Infective endocarditis (IE) is an inflammation of the endocardium.. inner of the heart muscle & the epithelial lining of heart valves.
EWMA Educational Development Programme. Curriculum Development Project. Education Module. Wound Infection
 EWMA Educational Development Programme Curriculum Development Project Education Module Wound Infection Latest revision: February 2014 ABOUT THE EWMA EDUCATIONAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME The Programme is designed
EWMA Educational Development Programme Curriculum Development Project Education Module Wound Infection Latest revision: February 2014 ABOUT THE EWMA EDUCATIONAL DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME The Programme is designed
Kamaruddin MY.,Anwar S., Zainabe SA and Mohd Yassim MY Faculty of Medicine University of Malaya Kuala Lumpur MALAYSIA
 Kamaruddin MY.,Anwar S., Zainabe SA and Mohd Yassim MY Faculty of Medicine University of Malaya Kuala Lumpur MALAYSIA ANTIBACTERIAL SYSTEM IN HONEY THE ANTIBACTERIAL SYSTEM 1993 HIGH SUGAR CONCENTRATION
Kamaruddin MY.,Anwar S., Zainabe SA and Mohd Yassim MY Faculty of Medicine University of Malaya Kuala Lumpur MALAYSIA ANTIBACTERIAL SYSTEM IN HONEY THE ANTIBACTERIAL SYSTEM 1993 HIGH SUGAR CONCENTRATION
