Sensory Changes In The Upper Limb In Type 2 Diabetic Patients - A Case Control Study
|
|
|
- Lorin Stevenson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Sensory Changes In The Upper Limb In Type 2 Diabetic Patients - A Case Control Study Internal Medicine Smita Sarkar, Charu Eapen and Prabha Adhikari THE USE OF A TWO POINT DISCRIMINATION TEST IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF UPPER LIMB NEUROPATHY IN TYPE 2 DIABETES Context: Sensory changes are associated with diabetic neuropathy and the assessment of sensation is commonly done in the foot to prevent ulcers. Though sensory changes may be present in the upper limb also, its documentation is not done routinely. Aims: To find out the two point discrimination values and other sensory changes in the upper limb in type 2 diabetic patients. Settings and design: This was a cross sectional design using a case control study, which was done in a hospital with both inpatients and outpatients.methods and material: 75 subjects with type 2 diabetes were included in the case group; patients with a diagnosed case of neuropathy were excluded. These were compared with age and sex matched subjects in the control group with no diabetes. sensation, pressure threshold and two point discrimination were assessed on the hands in both the groups. The Duruoz s Hand was used to assess the general functional status with regards to the abilities of daily living in both the groups. Statistical analysis: The data was analysed by using the SPSS package, version 13, with p values <.05 being taken as significant. Results: In the diabetic group, approximately 11 % of the patients had the loss of protective sensation; the median value of the vibration sensation was volts as compared to 3-4 volts in the control group and the mean value of the two point discrimination was 4-5mm. The results were significantly different between the diabetic and the control groups. The median value of DHI was eight in the diabetic group. Conclusions: All the sensations which were checked were altered in the diabetic patients, thus indicating the possible underlying neuropathy changes. The two point discrimination test can be used to detect upper limb neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes, which can further be validated with nerve conduction velocity tests. A sensory evaluation should be done in the upper limb, especially with patients who had diabetes for more than five years, for the possible presence of neuropathy. Key Words: Two point discrimination, hand, type 2 diabetes Key Messages: In some instances, patients with diabetic neuropathy have few complaints, but their physical examinations reveals mild to moderate severe sensory loss. The sensibility testing is important in diabetic patients with sensory neuropathy, to prevent any complications that may arise because of the loss of sensation. Various modalities of touch sensation like pressure, vibration and two-point discrimination (TPD) are used to test sensation loss or sensibility. Sensory changes may be present in the upper limb, possibly due to the underlying neuropathy. The patients may be unaware of this and may be at a risk of causing harm to their hands through burns or injuries. All the sensations were found to be decreased in the diabetic group as compared to the non diabetic group. Though no symptoms were reported by these patients, the clinical evaluation of the sensations revealed the changes. Sensations should be checked on the hands of all the patients who have had diabetes for more than five years. Changes in the sensations also indicate the possible presence of neuropathy in the upper limb, which can further be confirmed by Nerve Conduction studies. 96 Introduction Diabetes mellitus is associated with reduced life expectancy, significant morbidity and a diminished quality of life [1], affecting more than 135 million people worldwide and the number is expected to reach approximately 300 million by [2] Type 2 diabetes accounts for 90-95% of the total diabetes cases [3] and is age related, peaking at years of age [4]. Because of its gradual progression, usually a mean of 4-7 years will pass by from the initial onset of type 2 diabetes until the time of its diagnosis [3]. Diabetic neuropathy is among the most common long term complications of diabetes, affecting up to 50%-60% of the patients who have poor glycaemic control [5]. It is one of the most important factors for foot ulceration in diabetes mellitus (DM) patients. [6] In some instances, patients with diabetic neuropathy have few complaints, but their physical examinations reveals mild to moderate severe sensory loss. [7] These symptoms are commonly seen in the feet before they are seen in the hands and arms (upper extremity). [8] In sensory nerve damage, as the sensory loss ascends and reaches approximately mid calf, it appears in the hands. This gradual evocation causes the typical stocking glove sensory loss which reflects preferential damage according to axon length,
2 the longest axons being affected first. [9] Sensibility testing is thus important in diabetic patients with sensory neuropathy to prevent any complications that may arise because of the loss of sensation. Various modalities of touch sensation like pressure, vibration and two-point discrimination (TPD) are used to test sensation loss or sensibility.[10] The main purpose of the examination of vibration is to assess the evidence of dysfunction in the peripheral sensory nerves in the extremities, mainly during neuropathy, as the vibration sense diminishes with a variety of neuropathies [11] and it may be the first sensation to be lost Its loss can be detected before the loss of the Two point Discrimination. [9] loss in the upper extremity suggests severe neuropathy. The more severe the vibratory loss, the more likely the finding is to be clinically significant. [9] Static Two Point Discrimination has been used as a tool to measure sensory loss and to determine digital nerve integrity in diabetes mellitus patients. [10],[6] Although the method is subjective, the patient must report whether or not the pressure is felt, it is more reliable than the previously available methods and it is a quantitative measure of the sensory loss. [6] The Semmes-Weinstein monofilament testing divided the huge population of diabetes mellitus patients into subjects who were at risk and it is one of the primary screening methods for measuring cutaneous sensibility. [10] The onset of the loss of sensation in the lower extremities is the commonest symptom which is associated with peripheral neuropathy [12] and all these methods have been shown to be of value in identifying the patients who are at a risk of diabetes related foot complications. [13] Sensory changes may be present in the upper limb, possibly due to the underlying neuropathy. The patients may be unaware of this and may be at a risk of causing harm to their hands through burns or injuries. The aim of this study was to assess and document the sensory changes in the upper limb of the diabetic patients and to compare them with those which were seen in normal individuals. MATERIALS AND METHODS This study was approved by the Time Bound Ethical Committee and the Scientific Committee. Informed consent was taken from all the subjects. Seventy five subjects with type 2 diabetes between the age group of >40 to 82 years and in whom the duration of diabetes was more than five years, were taken for the study by using a non random sampling method. The exclusion criteria were, patients with a diagnosed case of upper limb diabetic neuropathy, neuropathy other than diabetic neuropathy or radiculopathy, patients with autonomic neuropathy andthose with diagnosed neuro musculoskeletal disorders of the hand, symptomatic peripheral vascular disease, traumatic nerve injury of the upper limb, trauma to the hand, congenital anomalies of wrist and hand, skin infections and Hansen s disease. The control group consisted of 75 subjects who were matched according to their age and sex and those who were not diagnosed with diabetes. The Pressure Threshold was by using the Touch-Test TM 5 piece Hand Kit (NC12772). The subject s extremity was rested on a stable, padded surface. The testing was done in a quiet area to help the subject to fully pay attention to the testing procedure. The S Sarkar, et al, Sensory changes in Type 2 Diabetes subject s vision was occluded. The testing procedure proceeded from the small to large Semmes-Weinstein Monofilaments. It was on the palmar surface of the index finger, the little finger and the first dorsum web space. The filament was pressed at a 900 angle against the skin until it was bowed, was held in place for 1.5 seconds and was then removed. A stimulus was applied in the same location up to three times to detect a response. A single response indicated a positive response. For 4.56 and 6.65, the stimulus was applied only once. The vibration was measured by using Vibrotherm - Dx (serial No V ). The subject s hands were held in a relaxed, supported position on the table. The procedure was explained to the patients and they were told that they would experience the vibration sensation. testing was done on the pulps of the index finger and on the little fingers of both the hands. The readings were recorded in Volts. An Aesthesiometer device (Baseline Evaluation Instruments 7-Piece Hand Evaluation Set) which was marked in millimeters was used for checking the two point discrimination. The subject s hands were fully supported on the examining table, while the vision was occluded. The finger tips of the index finger and the little fingers of both the and hands were, as they are very important in the active and tactile scanning of an object. The testing was done with a five mm distance between the two points. One or two points were applied lightly to the finger tip in a random sequence in a longitudinal orientation to avoid a crossover from the overlapping digital nerves. The applications were stopped just at a point of blanching. Seven out of ten responses were accurate for scoring. The testing was stopped at 15 mm if the responses were inaccurate at that level. The Duruöz s Hand (DHI) is a functional disability scale, a selfreport questionnaire that is efficient in the accurate assessment of hand dysfunction in diabetic patients. [14] The DHI was used to assess the general functional status with regards to the abilities of daily living in both the groups. All statistical tests were carried out by using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences, version 13.0 for Windows software. The differences were considered as statistically significant at p values <0.05. The Mann Whitney test was used to find out the differences in the vibration and the two point discrimination between the diabetic and the non diabetic groups. The Students unpaired t test was used to find the difference between the pressure threshold values in both the diabetic and the non diabetic groups. The correlation between the three variables and with the duration of diabetes was done by using Pearson s Correlation Coefficient at a 95% confidence interval. RESULTS The mean duration of diabetes in the subjects was years. When the sensations were correlated to the duration of diabetes, all the sensations showed a partial positive co-relation with the duration of diabetes. Pressure threshold index (r=0.35, p=.002), vibration index (r=0.29, p=0.013), two point discrimination index (r=0.38, p=0.001) 1. Pressure Threshold Variations The variation in the monofilament which was by the subjects in the diabetic and non diabetic groups is shown in [Table/Fig 1]. 97
3 S Sarkar, et al, Sensory changes in Type 2 Diabetes 98 Monofilament Frequency Percent Diabetic Comparison When compared between the groups, the difference in the pressure threshold values was significant for all the three sites [Table/Fig 2]. finger finger Web space pressure threshold Pressure threshold Median T value [Table / Fig 2]: Amount of alcohol consumed in ml per day 2. Sensation and Two point discrimination The diabetic group had a significantly higher value (p<0.0001) as compared to the non diabetic group [Table/Fig 3] and [Table/Fig 4]. Median Mann Whitney tes Z value Diabetic Non Diabetic Diabetic Non Diabetic Diabetic Non Diabetic Diabetic Non Diabetic [Table/Fig 3]: Comparison between perception threshold values in diabetic and non diabetic group Total Non Diabetic Total [Table/Fig 1]: Pressure threshold variation in diabetic and non diabetic group 3. Correlation between the three sensations which were evaluated. A significant correlation was found between two point discrimination and vibration perception on the side index Median Diabetic Non Diabetic Mann Whitney test Z value Diabetic Non Diabetic Diabetic Non Diabetic Diabetic Non Diabetic [Table 4]: Comparison between two point discrimination values in diabetic and non diabetic group finger (r =.37, p=.001) and on the side little finger ( r =.48, p=.000), between pressure threshold and the vibration perception threshold on the side finger ( r =..47, p=.000) and on the side little finger (r =.49, p=.000). A high correlation was also found between the pressure threshold and two point discrimination on the side finger ( r =.36, p=.002) and on the side little finger ( r =.36, p=.002). The Dorouz s Hand median value was 8.00 in the diabetic group. DISCUSSION The evaluation of sensibility in the hand of the diabetic patients is of para- mount importance in order to provide the proper identification of the group with neuropathy. Sensory changes in the hand could help to detect the involvement of UL neuropathy in the diabetes group. In most of the previous studies, various modalities of sensations like temperature, vibration, point localization and 2 PD have been used to measure sensory loss in the diabetic foot [10,15,16] Neuropathy is more severe in the lower limbs than in the upper limbs, as the lower limb nerves are affected more often than the upper limb nerves [17]; for this reason, probably less studies have assessed UL neuropathy. In our study, we assessed the sensations and compared the values with age and sex matched non diabetic populations. Patients with the involvement of type 2 diabetes for > 5 years, between the ages of 40 years and 82 years, were taken. Previous studies have mentioned that neuropathy should be suspected in all patients for more than five years. [18],[19] In our study, all the sensations showed a high correlation with the duration of diabetes. Kasturi BA et al study showed that a significant relationship exists between the duration of the disease and the grade of neuropathy. Also, the study observed that the severity of the neuropathy increases as its duration increases. [17] Dutta et al s study also showed that the prevalence of peripheral neuropathy had a highly significant correlation with the duration of diabetes. [20] Monofilaments have been shown to be one of the gold-standard instrumentations [21] which can be used for measuring cutaneous sensibility [10], and to check large fibre neuropathy. [5] Our study found that in the non diabetic group, 45.3% subjects were able to perceive 2.83, which showed that normal sensation was present in this group. 54.7% participants were able to perceive a diminished light touch (3.61). These findings could be because of skin thickness
4 and a normal ageing manifestation. [21] This indicates that these participants had fairly used their hands and that they had good temperature appreciation and good protective sensation. [22] But in the diabetic group, 2.83 was not by anyone. Only 32.0% the diminished light touch, 57.3% a diminished protective sensation and 10.7% the loss of protective sensation. According to Callahan AD, the diminished protective sensation indicates the diminished use of the hand, difficulty in manipulating some objects and the tendency to drop objects, and the weakness of the hand. But appreciation of pain and temperature is present that helps to keep a subject away from the injury. The loss of protective sensation indicates little use of the hand, and a diminished or the absence of temperature appreciation, which may cause injury easily. [22] In our study, since 10.7% subjects fell in this category, these subjects needed to be given advice regarding protecting themselves from injury. When compared between the two groups, the diabetic group was found to have a significantly higher value as compared to the non diabetic group. The reason for the decreased sensation in the diabetic group could be due to the involvement of large myelinated A-beta fibres which were responsible for the pressure threshold. These nerve fibres get involved in neuropathy, thus indicating that neuropathy may be present in the diabetic group. [10] The ability to feel vibrations is reflected by the function in the large nerve fibres and in the delicate receptors which are located in the finger pulps. [23] The investigation of the Vibrotectile sense in the finger pulps is important to detect any large fibre neuropathy in the hands of diabetics, since such subjects may have neurological symptoms that sometimes may be over looked in clinical practice. perception sensitively reflects the disturbances in the function of the fast adapting mechanoreceptors and in the thick myelinated sensory nerve fibres. Both are commonly affected in diabetes [10]. We found that there was a highly significant difference between the vibration sensations in both the diabetic and the non diabetic patients. As the vibration is conducted by the large myelinated nerve fibres in the diabetic patients, the longest nerves are affected first, possibly due to a metabolic abnormality, leading to the failure of axonal transport and subsequent degeneration [24], causing more impaired sensations among the diabetic patients. [25] The two point discrimination (2PD) is the current recommended method for evaluating the loss of sensation or the degree of sensation loss in the diabetic patients. [6] Our study also found that the two point discrimination values were very highly significant between the diabetic and the non diabetic individuals. R. Periyasamy et al in their study, also found that the 2PD values of the DM subjects were always higher than that of the normal subjects. [10] Our study also found that there was a significant correlation between vibration, perception threshold and two point discrimination in the diabetic group. sensation is used to detect the changes in neuropathy. Since there was a significant correlation between vibration and two point discrimination, for assessment purposes in clinical settings, the two point discrimination test can be used to detect changes in the upper limb due to neuropathy, as it is a relatively easy test and as elaborate instrumentation is also not required. Whereas in the non diabetic group, there was no significant difference between the vibration perception threshold and the two point discrimination. This indicates that in the non diabetic group, all the tests should to be checked in the clinical settings. S Sarkar, et al, Sensory changes in Type 2 Diabetes Our study showed that the mean value of DHI was among the diabetic group. As the DHI score ranges between 0-90, the mean value of DHI in our study showed that patients with diabetes had less hand-related activity limitation. In the non diabetic group, activity limitations were not present. The results of the present study have shown a significant difference in the sensations which were found in the diabetic and the non diabetic groups. All the sensations were found to be decreased in the diabetic groups as compared to those in the non diabetic groups. Though no symptoms were reported by these patients, the clinical evaluation of the sensations revealed the changes. This may suggest the presence of underlying neuropathy, which can be further confirmed by nerve conduction studies. Electrophysiology has been used as the gold standard to detect and verify large fibre neuropathy in the upper extremity. [23] Peripheral neuropathy can be diagnosed if abnormal Nerve Conduction Velocity is present. [20] Nerve Conduction studies (NCSs) are strongly correlated with the underlying structural changes and are the least subjective and the most reliable single criterion standard. [26] Our patients who presented with decreased sensations could be subjected to Nerve Conduction (NC) tests to find any association between the clinical testing methods and the NC test which is considered to be the gold standard. Once neuropathy is established, significant recovery does not occur. Hence, the early detection of neuropathy helps in aggressive treatment. [17] This study also signifies that sensory changes are present in the hands of diabetics and that a considerable amount of patients fall into the category that needs advice regarding the care of their hands. Sensations should be checked in the hands of patients with diabetes for at least five years. Conflict of Interest : None Funding : Nil REFERENCES [1] Tesfaye S. Epidemiology and Etiology of Diabetic peripheral neuropathies. Adv Stud Med 2004; 4: [2] Ammari F.Long- term complications of Type I Diabetes Mellitus in the western area of Saudi Arabia. Diabetologia Croatica 200;33: [3] Khazai MH, Khazai B, Zargaran Z, Moosavi Z, Zand FK. Diabetic complications and risk factors in recently diagnosed type II diabetes: a case-control study. ARYA J 2006; 2: [4] Subramaniam I, Gold JL. Diabetes Mellitus in Elderly - An Overview. J Indian Acad Geriatr 2005; 2: [5] Dros J, Wewerinke A, Bindels PJ, Weert HC. Accuracy of Monofilament Testing to Diagnose Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review. Ann Fam Med 2009; 7: [6] Periyasamy R, Manivannan M, Narayanamurthy VB. Correlation between two-point discrimination with other measures of sensory loss in diabetes mellitus patients. Int J Diab Dev Ctries 2008; 28(3):71-8. [7] Aring AM, Jones DE, Falko JM. Evaluation and prevention of Diabetic neuropathy. Am Fam Physician 2005; 71: [8] Menz HB, George RS, Fitzpatrick, Lord SR, Bpod, Richard C. Walking stability and sensorimotor function in older people with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2004; 85: [9] Gerard Said. Diabetic Neuropathy a review. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2007;3: [10] Periyasamy R, Manivannan M, Narayanamurthy VB. Changes in two point discrimination and the law of mobility in Diabetes Mellitus patients. J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj 2008; 3:1-6. [11] Lewis SL. Field Guide to the Neurologic examination. In: Lewis SL, editor. Sensory Assessment.3rd ed. New York (NY): Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; p [12] Capes S, Pacaud D. Putting your patient s best foot forward. Canadian Diabetes 2007;20:1-12. [13] Gin H, Rigalleau V, Baillet L, Rabemanantsoa C. Comparison between monofilament, tuning fork and vibration perception tests for 99
5 S Sarkar, et al, Sensory changes in Type 2 Diabetes screening patients at risk of foot complication. Diabetes Metab 2002; 28: [14] Turan Y, Duroz MT, Aksakalli E, Gurgan A,Yasemin MD,Tuncay M. Validation of Duruöz Hand for diabetic hand dysfunction. J Investig Med 2009; 57: [15] Boulon AJ. Diabetic foot: from art to science.the 18th camillo golgi lecture. Diabetologia 2004; 47: [16] Kamei N, Yamane K, Nakanishi S, Yamashita Y, Tamura T, Ohshita k et al. Effectiveness of semmes weinstein monofilament examination for diabetic peripheral neuropathy screening. J Diabetes Complication 2005; 19: [17] Kasthuri AS, Sofat MS, Kumar CN. Somatic Neuropathy in Diabetes Mellitus. MJAFI 2000; 56:33-6. [18] anen J, Niskanen L, Lehtinen J, Mervaala E. Natural history of peripheral neuropathy in patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1995; 33: [19] Vrancken FJ, Franssen H, Wokke JH, Teunissen L, Notermans NC. Chronic Idiopathic Axonal Polyneuropathy and Successful Aging of the Peripheral Nervous System in Elderly People. Arch Neurol 2002; 59: [20] Dutta A, Naorem S, Singh TP, Wangjam K. Prevalence of peripheral neuropathy in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetics. Int J Diab Dev Ctries 2005;25: [21] Shy ME, Frohman EM, Arezzo JC, Cornblath DR, Giuliani MJ, Lincaid JC, et al. Quantitative sensory testing. Neurology 2003; 60; [22] Hunter JM, Mackin EJ, Callahan AD. Rehabilitation of the Hand: Surgery and therapy. In: Callahan AD, editor. Sensibility Assessment: prerequisites and techniques for nerve lesions in continuity and nerve lacerations. 4th ed. Philadelphia: USA: Mosby; p [23] Dahlin LB, Thrainsdottir S, Cederlund R, Thomsen NB, Rosen I, Eriksson KF et al. Complications Vibrotactile sense in median and ulnar nerve innervated fingers of men with Type 2 diabetes, normal or impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetic Med 2008; 25: [24] Martina I J, Koningsveld RV, Schmitz P I,Van der Meché F, Van Doorn P A. Measuring vibration threshold with a graduated tuning fork in normal aging and in patients with Polyneuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1998;65: [25] Attia J, Duke J, Mcevoy M, Sibbritt D, Guest M, Smith W. Vibrotactile threshold measurement for detecting peripheral neuropathy, Defining Variability and a normal range for clinical and research use. Diabetologia 2007;50: [26] Perkins AB, Ohaleye D, Zinman B, Bril V. Simple screening test for peripheral Neuropathy in the Diabetes Clinic. Diabetes care 2001; 24: AUTHORS: 1. Dr. Smita Sarkar : BPT, Post graduate Student, Department of Physiotherapy, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal University, Mangalore ,Karnataka, India 2. Dr. Charu Eapen: MPT, (PhD), Associate Professor, Department of Physiotherapy, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal University, Mangalore Karnataka, India 3. Dr. Prabha Adhikari: MD, Professor, Department of Medicine, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal University, Mangalore , Karnataka, India. NAME, ADDRESS, TELEPHONE, ID OF THE CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: Charu Eapen, MPT, PhD, Associate Professor, Department of Physiotherapy, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal University, Mangalore Karnataka, India., Telephone number Ext 5332, Fax number , address- charu_mak@hotmail.com DECLARATION ON COMPETING INTERESTS: No competing Interests. Date of Submission: 12/03/2010 Date of Peer Review Completion: 12/22/2010 Date of Acceptance: 01/03/2010 Date of Online first Publication: 01/06/2011 Date of Publication: 01/06/
Clinical and Electrodiagnostic Profile of Diabetic Neuropathy in a Tertiary Hospital in Punjab, India
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical and Electrodiagnostic Profile of Diabetic Neuropathy in a Tertiary Hospital in Punjab, India Vishali Kotwal, Amit Thakur* Abstract Peripheral neuropathy is commonly seen in diabetic
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical and Electrodiagnostic Profile of Diabetic Neuropathy in a Tertiary Hospital in Punjab, India Vishali Kotwal, Amit Thakur* Abstract Peripheral neuropathy is commonly seen in diabetic
DIAGNOSIS OF DIABETIC NEUROPATHY
 DIAGNOSIS OF DIABETIC NEUROPATHY Dept of PM&R, College of Medicine, Korea University Dong Hwee Kim Electrodiagnosis ANS Clinical Measures QST DIAGRAM OF CASUAL PATHWAYS TO FOOT ULCERATION Rathur & Boulton.
DIAGNOSIS OF DIABETIC NEUROPATHY Dept of PM&R, College of Medicine, Korea University Dong Hwee Kim Electrodiagnosis ANS Clinical Measures QST DIAGRAM OF CASUAL PATHWAYS TO FOOT ULCERATION Rathur & Boulton.
JAPMA JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN PODIATRIC MEDICAL ASSOCIATION
 JAPMA JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN PODIATRIC MEDICAL ASSOCIATION An Initial Evaluation of a Proof-of-Concept 128-Hz Electronic Tuning Fork in the Detection of Peripheral Neuropathy Todd O Brien, DPM* Joseph
JAPMA JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN PODIATRIC MEDICAL ASSOCIATION An Initial Evaluation of a Proof-of-Concept 128-Hz Electronic Tuning Fork in the Detection of Peripheral Neuropathy Todd O Brien, DPM* Joseph
A preliminary study of Locognosia in people affected by leprosy
 Indian J Lepr 2011, 83 : 209-213 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Original Article A preliminary study of Locognosia in people affected by leprosy 1 2 3 Mannam Ebenezer, Kelly
Indian J Lepr 2011, 83 : 209-213 Hind Kusht Nivaran Sangh, New Delhi http://www.ijl.org.in Original Article A preliminary study of Locognosia in people affected by leprosy 1 2 3 Mannam Ebenezer, Kelly
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. STUDY OF CLINICO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL PROFILE OF DIABETIC NEUROPATHY Sachin. G. J, Ravi Vaswani, Shilpa. B.
 STUDY OF CLINICO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL PROFILE OF DIABETIC NEUROPATHY Sachin. G. J, Ravi Vaswani, Shilpa. B. 1. Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Vijayanagara Institute of Medical Sciences. Bellary.
STUDY OF CLINICO ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL PROFILE OF DIABETIC NEUROPATHY Sachin. G. J, Ravi Vaswani, Shilpa. B. 1. Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Vijayanagara Institute of Medical Sciences. Bellary.
Motor and sensory nerve conduction studies
 3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Hands-on Course 2 Assessment of peripheral nerves function and structure in suspected peripheral neuropathies
3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Hands-on Course 2 Assessment of peripheral nerves function and structure in suspected peripheral neuropathies
Diabetic Neuropathy: Discordance between Symptoms and Electrophysiological Testing in Saudi Diabetics
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.24, No.1, March 2002 Diabetic Neuropathy: Discordance between Symptoms and Electrophysiological Testing in Saudi Diabetics Daad H Akbar, FRCP(UK), Arab Board, Saudi Board
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.24, No.1, March 2002 Diabetic Neuropathy: Discordance between Symptoms and Electrophysiological Testing in Saudi Diabetics Daad H Akbar, FRCP(UK), Arab Board, Saudi Board
2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY. MEASURE TYPE: Process
 Quality ID #126 (NQF 0417): Diabetes Mellitus: Diabetic Foot and Ankle Care, Peripheral Neuropathy Neurological Evaluation National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL
Quality ID #126 (NQF 0417): Diabetes Mellitus: Diabetic Foot and Ankle Care, Peripheral Neuropathy Neurological Evaluation National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL
Clinical assessment of diabetic foot in 5 minutes
 Clinical assessment of diabetic foot in 5 minutes Assoc. Prof. N. Tentolouris, MD 1 st Department of Propaedeutic Internal Medicine Medical School Laiko General Hospital Leading Innovative Vascular Education
Clinical assessment of diabetic foot in 5 minutes Assoc. Prof. N. Tentolouris, MD 1 st Department of Propaedeutic Internal Medicine Medical School Laiko General Hospital Leading Innovative Vascular Education
DIABETIC NEUROPATHY ASSESSED AT TWO TIME POINTS FIVE YEARS APART
 1 University Department of Neurology, Sarajevo Clinical Center, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina 2 Zenica Cantonal Hospital, Zenica, Bosnia and Herzegovina 3 Department of Hemodialysis, Sarajevo Clinical
1 University Department of Neurology, Sarajevo Clinical Center, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina 2 Zenica Cantonal Hospital, Zenica, Bosnia and Herzegovina 3 Department of Hemodialysis, Sarajevo Clinical
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 12 Page December 2016
 JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 12 Page 14551-14556 December 2016 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i12.42
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 12 Page 14551-14556 December 2016 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i12.42
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine. University of Oradea, Institute for Doctoral Studies, Oradea, Bihor County, Romania
 MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2018; 13(3): 229-234 https://doi.org/10.26574/maedica.2018.13.3.229 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine Original paper Diabetic Neuropathy Prevalence and Its
MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2018; 13(3): 229-234 https://doi.org/10.26574/maedica.2018.13.3.229 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine Original paper Diabetic Neuropathy Prevalence and Its
peripheral neuropathy peripheral neuropathy neuropathy peripheral neuropathy neuropathic foot heel Bilateral foot pain Bilateral heel pain bilateral
 Peripheral neuropathy (PN) is damage to or disease affecting nerves, which may impair sensation, movement, gland or organ function, or other aspects of health. The 2018 edition of ICD-10-CM G62.9. Auditory
Peripheral neuropathy (PN) is damage to or disease affecting nerves, which may impair sensation, movement, gland or organ function, or other aspects of health. The 2018 edition of ICD-10-CM G62.9. Auditory
Comparison of Sudomotor and Sensory Nerve Testing in Painful Sensory Neuropathies
 138 Original Article Comparison of Sudomotor and Sensory Nerve Testing in Painful Sensory Neuropathies James M. Killian, MD,* Shane Smyth, MD,* Rudy Guerra, PhD, Ishan Adhikari, MD,* and Yadollah Harati,
138 Original Article Comparison of Sudomotor and Sensory Nerve Testing in Painful Sensory Neuropathies James M. Killian, MD,* Shane Smyth, MD,* Rudy Guerra, PhD, Ishan Adhikari, MD,* and Yadollah Harati,
Restoration of Sensation, Reduced Pain, and Improved Balance in Subjects With Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
 Emerging Treatments and Technologies O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Restoration of Sensation, Reduced Pain, and Improved Balance in Subjects With Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy A double-blind, randomized,
Emerging Treatments and Technologies O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Restoration of Sensation, Reduced Pain, and Improved Balance in Subjects With Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy A double-blind, randomized,
Prevalence and determinants of peripheral neuropathy among diabetics in a rural cum costal area of Villupuram district, Tamil Nadu
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Sankari Mansa Devi H et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Oct;3(10):2567-2571 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20150791
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Sankari Mansa Devi H et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Oct;3(10):2567-2571 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20150791
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Touch PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 33 Why is the Braille system better? Vision and audition involve perception of objects from a distance Safe and dependent on the transfer of energy (light, air pressure)
Touch PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 33 Why is the Braille system better? Vision and audition involve perception of objects from a distance Safe and dependent on the transfer of energy (light, air pressure)
Touch PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 33. Touch perception
 Touch PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 33 Why is the Braille system better? Touch perception Vision and audition involve perception of objects from a distance Safe and dependent on the transfer of energy (light,
Touch PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 33 Why is the Braille system better? Touch perception Vision and audition involve perception of objects from a distance Safe and dependent on the transfer of energy (light,
ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Research Received on:15/05/12 Revised on:20/05/12 Accepted on:25/05/12
 SCREENING OF SUBCLINICAL SENSORY IMPAIRMENT IN HAND AMONG DIABETIC BLINDS ijcrr Vol 04 issue 1 Category: Research Received on:15/05/1 Revised on:/05/1 Accepted on:5/05/1 Janakiraman Balamurugan 1, Ravichandran
SCREENING OF SUBCLINICAL SENSORY IMPAIRMENT IN HAND AMONG DIABETIC BLINDS ijcrr Vol 04 issue 1 Category: Research Received on:15/05/1 Revised on:/05/1 Accepted on:5/05/1 Janakiraman Balamurugan 1, Ravichandran
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: Assessment and Treatment
 Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: Assessment and Treatment Denise Soltow Hershey PhD, FNP-BC Michigan Council of Nurse Practitioners Annual Conference March 17, 2018 Objectives 1) Describe the clinical features
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: Assessment and Treatment Denise Soltow Hershey PhD, FNP-BC Michigan Council of Nurse Practitioners Annual Conference March 17, 2018 Objectives 1) Describe the clinical features
Medical Policy An Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association
 Anodyne -Skin Contact Monochromatic Infrared Energy as a Page 1 of 7 Medical Policy An Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association Title: Anodyne - Skin Contact Monochromatic Infrared
Anodyne -Skin Contact Monochromatic Infrared Energy as a Page 1 of 7 Medical Policy An Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association Title: Anodyne - Skin Contact Monochromatic Infrared
International Journal of Medical and Exercise Science (Multidisciplinary, Peer Reviewed and Indexed Journal)
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE International Journal of Medical and Exercise Science (Multidisciplinary, Peer Reviewed and Indexed Journal) PHYSICAL THERAPY MANAGEMENT IN PATIENTS WITH CERVICOGENIC DIZZINESS-A CASE
ORIGINAL ARTICLE International Journal of Medical and Exercise Science (Multidisciplinary, Peer Reviewed and Indexed Journal) PHYSICAL THERAPY MANAGEMENT IN PATIENTS WITH CERVICOGENIC DIZZINESS-A CASE
Lateral view of human brain! Cortical processing of touch!
 Lateral view of human brain! Cortical processing of touch! How do we perceive objects held in the hand?! Touch receptors deconstruct objects to detect local features! Information is transmitted in parallel
Lateral view of human brain! Cortical processing of touch! How do we perceive objects held in the hand?! Touch receptors deconstruct objects to detect local features! Information is transmitted in parallel
Proper Performance and Interpretation of Electrodiagnostic Studies
 Proper Performance and Interpretation of Electrodiagnostic Studies Introduction The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) has developed the following position statement
Proper Performance and Interpretation of Electrodiagnostic Studies Introduction The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) has developed the following position statement
Evaluation of clinical tools and their diagnostic use in distal symmetric polyneuropathy
 Evaluation of clinical tools and their diagnostic use in distal symmetric polyneuropathy Pourhamidi, Kaveh; Dahlin, Lars; Englund, Elisabet; Rolandsson, Olov Published in: Primary Care Diabetes DOI: 10.1016/j.pcd.2013.04.004
Evaluation of clinical tools and their diagnostic use in distal symmetric polyneuropathy Pourhamidi, Kaveh; Dahlin, Lars; Englund, Elisabet; Rolandsson, Olov Published in: Primary Care Diabetes DOI: 10.1016/j.pcd.2013.04.004
Evaluation of nerve conduction abnormalities in type 2 diabetic patients
 Original article: Evaluation of nerve conduction abnormalities in type 2 diabetic patients 1Kannan K, 2 Sivaraj M 1Asst Professor, Dept of Physiology, kilpauk Medical College, Kilpauk, Chennai, Tamil Nadu,
Original article: Evaluation of nerve conduction abnormalities in type 2 diabetic patients 1Kannan K, 2 Sivaraj M 1Asst Professor, Dept of Physiology, kilpauk Medical College, Kilpauk, Chennai, Tamil Nadu,
1. Tactile sensibility. Use a wisp of cotton-wool or a fine camel-fir brush. If it is desired to test the sensibility or the skin to light touch over
 SENSORY EXAMINATION 1. Tactile sensibility. Use a wisp of cotton-wool or a fine camel-fir brush. If it is desired to test the sensibility or the skin to light touch over a hairy part, it is essential to
SENSORY EXAMINATION 1. Tactile sensibility. Use a wisp of cotton-wool or a fine camel-fir brush. If it is desired to test the sensibility or the skin to light touch over a hairy part, it is essential to
Kim Chong Hwa MD,PhD Sejong general hospital, Division of endocrine & metabolism
 Kim Chong Hwa MD,PhD Sejong general hospital, Division of endocrine & metabolism st1 Classification and definition of diabetic neuropathies Painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy Diabetic autonomic neuropathy
Kim Chong Hwa MD,PhD Sejong general hospital, Division of endocrine & metabolism st1 Classification and definition of diabetic neuropathies Painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy Diabetic autonomic neuropathy
Subject: Nerve Conduction Studies; F-Wave Studies; H- Reflex Studies
 01-95805-02 Original Effective Date: 11/15/01 Reviewed: 06/28/18 Revised: 07/15/18 Subject: Nerve Conduction Studies; F-Wave Studies; H- Reflex Studies THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION,
01-95805-02 Original Effective Date: 11/15/01 Reviewed: 06/28/18 Revised: 07/15/18 Subject: Nerve Conduction Studies; F-Wave Studies; H- Reflex Studies THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION,
Prevention Of Falls In Older People With Diabetes. Ng Jia Lin, Podiatrist Toylyn Lee, Snr Physiotherapist
 Prevention Of Falls In Older People With Diabetes Ng Jia Lin, Podiatrist Toylyn Lee, Snr Physiotherapist Content Assessments - Foot assessment - Physical mobility Management - Footwear/callus - Exercise
Prevention Of Falls In Older People With Diabetes Ng Jia Lin, Podiatrist Toylyn Lee, Snr Physiotherapist Content Assessments - Foot assessment - Physical mobility Management - Footwear/callus - Exercise
Sensory conduction of the sural nerve in polyneuropathy'
 Jourtial of Neurology, Neurosurgery, anid Psychiatry, 1974, 37, 647-652 Sensory conduction of the sural nerve in polyneuropathy' DAVID BURKE, NEVELL F. SKUSE, AND A. KEITH LETHLEAN From the Unit of Clinical
Jourtial of Neurology, Neurosurgery, anid Psychiatry, 1974, 37, 647-652 Sensory conduction of the sural nerve in polyneuropathy' DAVID BURKE, NEVELL F. SKUSE, AND A. KEITH LETHLEAN From the Unit of Clinical
NEUROPATHY IN PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE 1
 267 616.833-02:616.13-005 NEUROPATHY IN PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE 1 Its Bearing on Diabetic Neuropathy BY E. C. HUTCHINSON AND L. A. LIVERSKDGE (From the Department of Neurology, Manchester Royal Infirmary)
267 616.833-02:616.13-005 NEUROPATHY IN PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISEASE 1 Its Bearing on Diabetic Neuropathy BY E. C. HUTCHINSON AND L. A. LIVERSKDGE (From the Department of Neurology, Manchester Royal Infirmary)
LUP. Lund University Publications Institutional Repository of Lund University
 LUP Lund University Publications Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published Diabetic medicine : a journal of the British Diabetic Association. This
LUP Lund University Publications Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published Diabetic medicine : a journal of the British Diabetic Association. This
Clinical,Radiological and Monofilament study of HIV positive patients depending on the type of neurological symptoms manifestations.
 Original article: Clinical,Radiological and Monofilament study of HIV positive patients depending on the type of neurological symptoms manifestations. 1Dr Anu N. Gaikwad, 2 Dr Satish Nirhale, 3 Dr Midhun
Original article: Clinical,Radiological and Monofilament study of HIV positive patients depending on the type of neurological symptoms manifestations. 1Dr Anu N. Gaikwad, 2 Dr Satish Nirhale, 3 Dr Midhun
Peripheral Neuropathy
 Peripheral Neuropathy Neuropathy affects 30-50% of patient population with diabetes and this prevalence tends to increase proportionally with duration of diabetes and dependant on control. Often presents
Peripheral Neuropathy Neuropathy affects 30-50% of patient population with diabetes and this prevalence tends to increase proportionally with duration of diabetes and dependant on control. Often presents
Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Pain Management Lippinott 2002; 350:382 In most cases of neck and back pain the anatomic and physiologic
 HISTORY OF PF-NCS Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Pain Management Lippinott 2002; 350:382 In most cases of neck and back pain the anatomic and physiologic diagnosis remains unclear. EMG/NCV
HISTORY OF PF-NCS Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Pain Management Lippinott 2002; 350:382 In most cases of neck and back pain the anatomic and physiologic diagnosis remains unclear. EMG/NCV
Managing Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain
 Managing Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain Juzar Hooker Consulting Neurologist, Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi juzar.hooker@aku.edu Disclosure Eli lilly (have not driven, reviewed or controlled
Managing Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain Juzar Hooker Consulting Neurologist, Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi juzar.hooker@aku.edu Disclosure Eli lilly (have not driven, reviewed or controlled
Compound Action Potential, CAP
 Stimulus Strength UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY INTRODUCTION TO NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Spring, 2013 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition
Stimulus Strength UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY INTRODUCTION TO NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Spring, 2013 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition
Evaluation of the Hand. Learning Objectives. Sitting down with the Client. Observation 2/16/2012
 Introduction to Hand & UE Rehabilitation Hand Evaluation Basics J. Robin Janson, MS, OTR, CHT Indiana University Department of Occupational Therapy Learning Objectives After actively engaging with this
Introduction to Hand & UE Rehabilitation Hand Evaluation Basics J. Robin Janson, MS, OTR, CHT Indiana University Department of Occupational Therapy Learning Objectives After actively engaging with this
Validation of a Novel Point-of-Care Nerve Conduction Device for the Detection of. Diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy
 Emerging Trends and Technologies O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Validation of a Novel Point-of-Care Nerve Conduction Device for the Detection of Diabetic Sensorimotor Polyneuropathy BRUCE A. PERKINS, MD,
Emerging Trends and Technologies O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Validation of a Novel Point-of-Care Nerve Conduction Device for the Detection of Diabetic Sensorimotor Polyneuropathy BRUCE A. PERKINS, MD,
A STUDY OF ASSESSMENT IN PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY IN PATIENTS WITH NEWLY DETECTED THYROID DISORDERS IN A TERTIARY CARE TEACHING INSTITUTE
 A STUDY OF ASSESSMENT IN PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY IN PATIENTS WITH NEWLY DETECTED THYROID DISORDERS IN A TERTIARY CARE TEACHING INSTITUTE Rajan Ganesan 1, Marimuthu Arumugam 2, Arungandhi Pachaiappan 3, Thilakavathi
A STUDY OF ASSESSMENT IN PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY IN PATIENTS WITH NEWLY DETECTED THYROID DISORDERS IN A TERTIARY CARE TEACHING INSTITUTE Rajan Ganesan 1, Marimuthu Arumugam 2, Arungandhi Pachaiappan 3, Thilakavathi
Accuracy of Monofilament Testing to Diagnose Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review Dros, J.; Wewerinke, A.; Bindels, P.J.; van Weert, H.C.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Accuracy of Monofilament Testing to Diagnose Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review Dros, J.; Wewerinke, A.; Bindels, P.J.; van Weert, H.C. Published in: Annals
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Accuracy of Monofilament Testing to Diagnose Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review Dros, J.; Wewerinke, A.; Bindels, P.J.; van Weert, H.C. Published in: Annals
Epidermal Nerve Fiber and Schwann cell densities in the distal leg of Nine-banded Armadillos with Experimental Leprosy neuropathy
 Epidermal Nerve Fiber and Schwann cell densities in the distal leg of Nine-banded Armadillos with Experimental Leprosy neuropathy Gigi J Ebenezer 1 Richard Truman 2 David Scollard 2 Michael Polydefkis
Epidermal Nerve Fiber and Schwann cell densities in the distal leg of Nine-banded Armadillos with Experimental Leprosy neuropathy Gigi J Ebenezer 1 Richard Truman 2 David Scollard 2 Michael Polydefkis
Nerve Conduction Response by Using Low-Dose Oral Steroid in the Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 8 Ver. 6 (August. 2018), PP 62-69 www.iosrjournals.org Nerve Conduction Response by Using Low-Dose
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 8 Ver. 6 (August. 2018), PP 62-69 www.iosrjournals.org Nerve Conduction Response by Using Low-Dose
A comparison of the monofilament with other testing modalities for foot ulcer susceptibility
 Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 70 (2005) 8 12 www.elsevier.com/locate/diabres A comparison of the monofilament with other testing modalities for foot ulcer susceptibility B. Miranda-Palma a, J.M.
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 70 (2005) 8 12 www.elsevier.com/locate/diabres A comparison of the monofilament with other testing modalities for foot ulcer susceptibility B. Miranda-Palma a, J.M.
AGE RELATED CHANGES 2. Dr. Rehab gwada
 AGE RELATED CHANGES 2 Dr. Rehab gwada Objectives of lecture At the end of this lecture the student will be able to: Determine Age-related sensory, proprioceptive, vestibular Changes in addition to nervous
AGE RELATED CHANGES 2 Dr. Rehab gwada Objectives of lecture At the end of this lecture the student will be able to: Determine Age-related sensory, proprioceptive, vestibular Changes in addition to nervous
Power Line to your Line to your Circuit Line to the station neighborhood house breaker living room. Outlet lamp Lamp with socket, Light bulb
 IMC 606 Neuroscience and Behavior Module Dr. Margaret Paroski Analysis of Sensory Lesions You walk into your living room and turn on the lamp. But no light comes on. What would you do? You would probably
IMC 606 Neuroscience and Behavior Module Dr. Margaret Paroski Analysis of Sensory Lesions You walk into your living room and turn on the lamp. But no light comes on. What would you do? You would probably
Diabetic Neuropathy. Nicholas J. Silvestri, M.D.
 Diabetic Neuropathy Nicholas J. Silvestri, M.D. Types of Neuropathies Associated with Diabetes Mellitus p Chronic distal sensorimotor polyneuropathy p Focal compression neuropathies p Autonomic neuropathy
Diabetic Neuropathy Nicholas J. Silvestri, M.D. Types of Neuropathies Associated with Diabetes Mellitus p Chronic distal sensorimotor polyneuropathy p Focal compression neuropathies p Autonomic neuropathy
Bullosis diabeticorum in median nerve innervated fingers shortly after carpal tunnel release: case report.
 Bullosis diabeticorum in median nerve innervated fingers shortly after carpal tunnel release: case report. Brogren, Elisabeth; Dahlin, Lars Published in: Journal of Hand Surgery DOI: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2014.09.014
Bullosis diabeticorum in median nerve innervated fingers shortly after carpal tunnel release: case report. Brogren, Elisabeth; Dahlin, Lars Published in: Journal of Hand Surgery DOI: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2014.09.014
Introduction. Epidemiology Pathophysiology Classification Treatment
 Diabetic Foot Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology Classification Treatment Epidemiology DM largest cause of neuropathy in N.A. 1 million DM patients in Canada Half don t know Foot ulcerations is
Diabetic Foot Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology Classification Treatment Epidemiology DM largest cause of neuropathy in N.A. 1 million DM patients in Canada Half don t know Foot ulcerations is
Medical technologies guidance Published: 10 September 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/mtg38
 Neuropad for detecting preclinical diabetic peripheral neuropathy Medical technologies guidance Published: 10 September 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/mtg38 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice
Neuropad for detecting preclinical diabetic peripheral neuropathy Medical technologies guidance Published: 10 September 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/mtg38 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice
AWMA MODULE ACCREDITATION. Module Five: The High Risk Foot (Including the Diabetic Foot)
 AWMA MODULE ACCREDITATION Module Five: The High Risk Foot (Including the Diabetic Foot) Introduction - The Australian Wound Management Association Education & Professional Development Sub Committee-(AWMA
AWMA MODULE ACCREDITATION Module Five: The High Risk Foot (Including the Diabetic Foot) Introduction - The Australian Wound Management Association Education & Professional Development Sub Committee-(AWMA
Nervous system Reflexes and Senses
 Nervous system Reflexes and Senses Physiology Lab-4 Wrood Slaim, MSc Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology University of Al-Mustansyria 2017-2018 Nervous System The nervous system is the part of an
Nervous system Reflexes and Senses Physiology Lab-4 Wrood Slaim, MSc Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology University of Al-Mustansyria 2017-2018 Nervous System The nervous system is the part of an
Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be?
 Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be? Neurological disorders take away sensation without a choice! http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter04.html
Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be? Neurological disorders take away sensation without a choice! http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter04.html
How can DIABETES affect my FEET? Emma Howard Specialist Podiatrist and Team Leader, Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust
 How can DIABETES affect my FEET? By: Emma Howard Specialist Podiatrist and Team Leader, Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust HOW CAN DIABETES AFFECT MY FEET? What is neuropathy? This leaflet explains how
How can DIABETES affect my FEET? By: Emma Howard Specialist Podiatrist and Team Leader, Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust HOW CAN DIABETES AFFECT MY FEET? What is neuropathy? This leaflet explains how
Coding of Sensory Information
 Coding of Sensory Information 22 November, 2016 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Sensory Systems Mediate Four Attributes of
Coding of Sensory Information 22 November, 2016 Touqeer Ahmed PhD Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Sensory Systems Mediate Four Attributes of
LATE RESPONSES IN THE ELECTRODIAGNOSIS OF CERVICAL RADICULOPATHIES
 Neurology DOI: 10.15386/cjmed-382 LATE RESPONSES IN THE ELECTRODIAGNOSIS OF CERVICAL RADICULOPATHIES ANA MARIA GALAMB, IOAN DAN MINEA Department of Medical and Surgical Specialities, Faculty of Medicine,
Neurology DOI: 10.15386/cjmed-382 LATE RESPONSES IN THE ELECTRODIAGNOSIS OF CERVICAL RADICULOPATHIES ANA MARIA GALAMB, IOAN DAN MINEA Department of Medical and Surgical Specialities, Faculty of Medicine,
Making sense of Nerve conduction & EMG
 Making sense of Nerve conduction & EMG Drs R Arunachalam Consultant Clinical Neurophysiologist Wessex Neurological Centre Southampton University Hospital EMG/NCS EMG machine For the assessment of patients
Making sense of Nerve conduction & EMG Drs R Arunachalam Consultant Clinical Neurophysiologist Wessex Neurological Centre Southampton University Hospital EMG/NCS EMG machine For the assessment of patients
LOCALIZED. Screening Tool. This Screening Tool facilitates your daily practice, as it: Focuses on chronic pain patients Facilitates the diagnosing
 LOCALIZED Neuropathic pain Screening Tool This Screening Tool facilitates your daily practice, as it: Focuses on chronic pain patients Facilitates the diagnosing of Neuropathic Pain Allows for specifying
LOCALIZED Neuropathic pain Screening Tool This Screening Tool facilitates your daily practice, as it: Focuses on chronic pain patients Facilitates the diagnosing of Neuropathic Pain Allows for specifying
Evaluation of the finger wrinkling test: a pilot study
 Clin Auton Res (2010) 20:249 253 DOI 10.1007/s10286-010-0071-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Evaluation of the finger wrinkling test: a pilot study S. van Barneveld J. van der Palen M. J. A. M. van Putten Received:
Clin Auton Res (2010) 20:249 253 DOI 10.1007/s10286-010-0071-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Evaluation of the finger wrinkling test: a pilot study S. van Barneveld J. van der Palen M. J. A. M. van Putten Received:
10/19/2017. Shawn M Sanicola DPM, FACFAS Foot And Ankle Associates of WI. Consultant with J&J-Depuy-Synthesis
 Shawn M Sanicola DPM, FACFAS Foot And Ankle Associates of WI Consultant with J&J-Depuy-Synthesis Understand the systemic effects of diabetes on the lower extremity The significance of structural and biomechanical
Shawn M Sanicola DPM, FACFAS Foot And Ankle Associates of WI Consultant with J&J-Depuy-Synthesis Understand the systemic effects of diabetes on the lower extremity The significance of structural and biomechanical
Discuss the Process for PQRS Reporting. Explain How Often Therapists Should Report
 2016 Define PQRS Explain Who Should Participate Discuss the Process for PQRS Reporting Explain How Often Therapists Should Report Physician Quality Reporting System A quality reporting system for Medicare
2016 Define PQRS Explain Who Should Participate Discuss the Process for PQRS Reporting Explain How Often Therapists Should Report Physician Quality Reporting System A quality reporting system for Medicare
Numbness in right leg icd 10
 Search Search Numbness in right leg icd 10 A list of the most commonly used ICD -9 codes in Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation and Pain Management clinics. ICD - 10 codes will be slowly added over time.
Search Search Numbness in right leg icd 10 A list of the most commonly used ICD -9 codes in Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation and Pain Management clinics. ICD - 10 codes will be slowly added over time.
OBSERVATIONS ON THE REACTION TIME TO CUTANEOUS
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1955, 18, 120. OBSERVATIONS ON THE REACTION TIME TO CUTANEOUS THERMAL STIMULI BY P. P. LELE* and D. C. SINCLAIR From the Department of Anatomy, University of Oxford The
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1955, 18, 120. OBSERVATIONS ON THE REACTION TIME TO CUTANEOUS THERMAL STIMULI BY P. P. LELE* and D. C. SINCLAIR From the Department of Anatomy, University of Oxford The
Int J Physiother.Vol1 (2), 40-45, June (2014) ISSN:
 Int J Physiother.Vol1 (2), 40-45, June (2014) ISSN: 2348-8336 Sandesh Rayamajhi 1 Dipika Khanal 2 Mallikarjunaiah H S 3 ABSTRACT Background: Stroke has been considered to be the most common cause of neurological
Int J Physiother.Vol1 (2), 40-45, June (2014) ISSN: 2348-8336 Sandesh Rayamajhi 1 Dipika Khanal 2 Mallikarjunaiah H S 3 ABSTRACT Background: Stroke has been considered to be the most common cause of neurological
Somatosensory modalities!
 Somatosensory modalities! The somatosensory system codes five major sensory modalities:! 1. Discriminative touch! 2. Proprioception (body position and motion)! 3. Nociception (pain and itch)! 4. Temperature!
Somatosensory modalities! The somatosensory system codes five major sensory modalities:! 1. Discriminative touch! 2. Proprioception (body position and motion)! 3. Nociception (pain and itch)! 4. Temperature!
Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases
 Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases Peripheral neuropathies according to which part affected Axonal Demyelinating with axonal sparing Many times: mixed features
Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases Peripheral neuropathies according to which part affected Axonal Demyelinating with axonal sparing Many times: mixed features
Autonomic Variation of Blood Pressure in Middle Aged Diabetics: A Prospective Study
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/16 Autonomic Variation of Blood Pressure in Middle Aged Diabetics: A Prospective Study M Usharani 1, K Chandini 2 1 Professor and Head, Department of Physiology,
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/16 Autonomic Variation of Blood Pressure in Middle Aged Diabetics: A Prospective Study M Usharani 1, K Chandini 2 1 Professor and Head, Department of Physiology,
Helping Hands versus ERSP Vision: Comparing object recognition technologies for the visually impaired
 Helping Hands versus ERSP Vision: Comparing object recognition technologies for the visually impaired Marc A. Lawson, Ellen Yi-Luen Do, James R. Marston, David A. Ross College of Computing, Georgia Institute
Helping Hands versus ERSP Vision: Comparing object recognition technologies for the visually impaired Marc A. Lawson, Ellen Yi-Luen Do, James R. Marston, David A. Ross College of Computing, Georgia Institute
Three patients in a Chinese family with hereditary sensory neuropathy mimicking leprosy
 Lepr Rev (2008) 79, 441 446 CASE REPORT Three patients in a Chinese family with hereditary sensory neuropathy mimicking leprosy JIANPING SHEN*, GUOCHENG ZHANG*, RONGDE YANG**, TINGYING HU** & MIN ZHOU*
Lepr Rev (2008) 79, 441 446 CASE REPORT Three patients in a Chinese family with hereditary sensory neuropathy mimicking leprosy JIANPING SHEN*, GUOCHENG ZHANG*, RONGDE YANG**, TINGYING HU** & MIN ZHOU*
Original Research Article
 NERVE CONDUCTION STUDY IN CHILDREN WITH INSULIN DEPENDENT DIABETES MELLITUS Hannah John, Sahila M 2 Senior Resident, Department of Physiology, Government Medical College, Trivandrum, Kerala, India. 2Professor,
NERVE CONDUCTION STUDY IN CHILDREN WITH INSULIN DEPENDENT DIABETES MELLITUS Hannah John, Sahila M 2 Senior Resident, Department of Physiology, Government Medical College, Trivandrum, Kerala, India. 2Professor,
MUSCULOSKELETAL AND NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS
 MUSCULOSKELETAL AND NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS There are a wide variety of Neurologic and Musculoskeletal disorders which can impact driving safety. Impairment may be the result of altered muscular, skeletal,
MUSCULOSKELETAL AND NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS There are a wide variety of Neurologic and Musculoskeletal disorders which can impact driving safety. Impairment may be the result of altered muscular, skeletal,
Chapter 2 Biothesiometry
 Chapter 2 Biothesiometry John P. Mulhall and Lawrence C. Jenkins Background The biothesiometry device is used to measure the threshold of appreciation of vibration in patients. A decreased sensitivity
Chapter 2 Biothesiometry John P. Mulhall and Lawrence C. Jenkins Background The biothesiometry device is used to measure the threshold of appreciation of vibration in patients. A decreased sensitivity
NERVE CONDUCTION STUDY AMONG HEALTHY MALAYS. THE INFLUENCE OF AGE, HEIGHT AND BODY MASS INDEX ON MEDIAN, ULNAR, COMMON PERONEAL AND SURAL NERVES
 Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 13, No. 2, July 2006 (19-23) ORIGINAL ARTICLE NERVE CONDUCTION STUDY AMONG HEALTHY MALAYS. THE INFLUENCE OF AGE, HEIGHT AND BODY MASS INDEX ON MEDIAN, ULNAR,
Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 13, No. 2, July 2006 (19-23) ORIGINAL ARTICLE NERVE CONDUCTION STUDY AMONG HEALTHY MALAYS. THE INFLUENCE OF AGE, HEIGHT AND BODY MASS INDEX ON MEDIAN, ULNAR,
Neuronal Circuits and Neuronal Pools
 Neuronal Circuits and Neuronal Pools Anatomical Orientation Clinical Orientation Atlas Fig. 6-24 The Reality of the Clinical Environment Atlas Fig. 6-24A One Cardinal Plane to Learn AND Understand
Neuronal Circuits and Neuronal Pools Anatomical Orientation Clinical Orientation Atlas Fig. 6-24 The Reality of the Clinical Environment Atlas Fig. 6-24A One Cardinal Plane to Learn AND Understand
MEDIA BACKGROUNDER. Multiple Sclerosis: A serious and unpredictable neurological disease
 MEDIA BACKGROUNDER Multiple Sclerosis: A serious and unpredictable neurological disease Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a complex chronic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system (CNS) that still
MEDIA BACKGROUNDER Multiple Sclerosis: A serious and unpredictable neurological disease Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a complex chronic inflammatory disease of the central nervous system (CNS) that still
increasing pressure registered in kilograms was applied until the subject began to feel a sensation of pain. With an intelligent person the responses
 VARIATIONS IN THE SENSIBILITY TO PRESSURE PAIN CAUSED BY NERVE STIMULATION IN MAN. BY R. C. SHAWE. (From the Royal Infirmary, Manchester.) IN a previous paper (Brit. Journ. Surgery, Jan. 1922) I have given
VARIATIONS IN THE SENSIBILITY TO PRESSURE PAIN CAUSED BY NERVE STIMULATION IN MAN. BY R. C. SHAWE. (From the Royal Infirmary, Manchester.) IN a previous paper (Brit. Journ. Surgery, Jan. 1922) I have given
Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of
 Peripheral Nervous System Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of non-insulin dependent diabetes
Peripheral Nervous System Case 1 A 65 year old college professor came to the neurology clinic referred by her family physician because of frequent falling. She had a history of non-insulin dependent diabetes
ABSTRACT KEY WORDS KATHMANDU UNIVERSITY MEDICAL JOURNAL. Page 120. Background
 Prevalence of Sensory Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Correlation with Duration of Disease Karki DB, 1 Yadava SK, 1 Pant S, 2 Thusa N, 1 Dangol E, 1 Ghimire S 1 ABSTRACT Background 1 Department
Prevalence of Sensory Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Correlation with Duration of Disease Karki DB, 1 Yadava SK, 1 Pant S, 2 Thusa N, 1 Dangol E, 1 Ghimire S 1 ABSTRACT Background 1 Department
Diabetes is associated with increased risk
 DIABETIC PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY: ADVANCES IN UNDERSTANDING AND TREATMENT * Vera Bril, MD, PhD, FRCP ABSTRACT Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) affects approximately 50% of patients with diabetes and
DIABETIC PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY: ADVANCES IN UNDERSTANDING AND TREATMENT * Vera Bril, MD, PhD, FRCP ABSTRACT Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) affects approximately 50% of patients with diabetes and
A Comparison of Nerve Conduction Properties in Male and Female of 20 to 30 Years of Age Group
 A Comparison of Nerve Conduction Properties in Male and Female of 20 to 30 Years of Age Group Gakhar 1, M., Verma 2, S.K. and Lehri 3, A. 1 Research Scholar, Department of Sports Science, Punjabi University,
A Comparison of Nerve Conduction Properties in Male and Female of 20 to 30 Years of Age Group Gakhar 1, M., Verma 2, S.K. and Lehri 3, A. 1 Research Scholar, Department of Sports Science, Punjabi University,
Work, vibration, & the neurosensory system. Close effects Remote effects Stress and pressure
 Work, vibration, & the neurosensory system Close effects Remote effects Stress and pressure Temporary neurosensory effects Reduced sensibility due to: - Temporary threshold shift Reduced motor control
Work, vibration, & the neurosensory system Close effects Remote effects Stress and pressure Temporary neurosensory effects Reduced sensibility due to: - Temporary threshold shift Reduced motor control
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists
 Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
Carpal tunnel syndrome
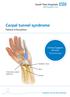 Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
ii. Reduction of tone in upper limb Lycra arm splints improve movement fluency in children with cerebral palsy.
 Guidelines for the Provision of Dynamic Compression for people diagnosed with Multiple Sclerosis The use of Lycra garments in patients with the diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis has been initiated with very
Guidelines for the Provision of Dynamic Compression for people diagnosed with Multiple Sclerosis The use of Lycra garments in patients with the diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis has been initiated with very
Pathways of proprioception
 The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
PDF of Trial CTRI Website URL -
 Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Sat, 03 Nov 2018 09:24:50 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 10/06/2013 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Sat, 03 Nov 2018 09:24:50 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 10/06/2013 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
FEP Medical Policy Manual
 FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: October 15, 2018 Related Policies: None Quantitative Sensory Testing Description Quantitative sensory (QST) systems are used for the noninvasive assessment and
FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: October 15, 2018 Related Policies: None Quantitative Sensory Testing Description Quantitative sensory (QST) systems are used for the noninvasive assessment and
Diabetes Foot Health and Prevention Program:
 Diabetes Foot Health and Prevention Program: A Podiatrist / RN Collaborative Practice Dr. Pamela Monk Visiting Podiatrist drpamelamonk@live.ca(204) 391-9719 Danna Ferry RN Ferry RN Services dlferry@live.ca
Diabetes Foot Health and Prevention Program: A Podiatrist / RN Collaborative Practice Dr. Pamela Monk Visiting Podiatrist drpamelamonk@live.ca(204) 391-9719 Danna Ferry RN Ferry RN Services dlferry@live.ca
Pain and Touch. Academic Press. Edited by Lawrence Kruger. Department of Neurobiology University of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, California
 Pain and Touch Edited by Lawrence Kruger Department of Neurobiology University of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, California San Diego New York Sydney Academic Press London Boston Tokyo Toronto Contributors
Pain and Touch Edited by Lawrence Kruger Department of Neurobiology University of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, California San Diego New York Sydney Academic Press London Boston Tokyo Toronto Contributors
Quick Response code. Original Article ABSTRACT. Access this Article online
 Original Article HEIGHT, WEIGHT, BMI, FBS, PPBS, CORRELATED WITH CONDUCTION VELOCITY IN TYPE II DIABETES MELLITUS PATIENTS Athikari ChandraSekhar * 1,Masimukku Venkata Muralidhar 2,Kaarna Munisekhar 3.
Original Article HEIGHT, WEIGHT, BMI, FBS, PPBS, CORRELATED WITH CONDUCTION VELOCITY IN TYPE II DIABETES MELLITUS PATIENTS Athikari ChandraSekhar * 1,Masimukku Venkata Muralidhar 2,Kaarna Munisekhar 3.
NORMATIVE DATA OF UPPER LIMB NERVE CONDUCTION IN CENTRAL INDIA
 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2011; 55 (3) : 241 245 NORMATIVE DATA OF UPPER LIMB NERVE CONDUCTION IN CENTRAL INDIA SACHIN M. PAWAR, AVINASH B. TAKSANDE AND RAMJI SINGH* Department of Physiology, Mahatma
Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2011; 55 (3) : 241 245 NORMATIVE DATA OF UPPER LIMB NERVE CONDUCTION IN CENTRAL INDIA SACHIN M. PAWAR, AVINASH B. TAKSANDE AND RAMJI SINGH* Department of Physiology, Mahatma
P1: OTA/XYZ P2: ABC c01 BLBK231-Ginsberg December 23, :43 Printer Name: Yet to Come. Part 1. The Neurological Approach COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
 Part 1 The Neurological Approach COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 2 Chapter 1 Neurological history-taking The diagnosis and management of diseases of the nervous system have been revolutionized in recent years by
Part 1 The Neurological Approach COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 2 Chapter 1 Neurological history-taking The diagnosis and management of diseases of the nervous system have been revolutionized in recent years by
Quantitative Sensory Testing. Description. Section: Medicine Effective Date: April 15, 2016
 2.01.39 Subject: Quantitative Sensory Testing Page: 1 of 11 Last Review Status/Date: March 2016 Quantitative Sensory Testing Description Quantitative sensory testing (QST) systems are used for the noninvasive
2.01.39 Subject: Quantitative Sensory Testing Page: 1 of 11 Last Review Status/Date: March 2016 Quantitative Sensory Testing Description Quantitative sensory testing (QST) systems are used for the noninvasive
The Internist s Approach to Neuropathy
 The Internist s Approach to Neuropathy VOLKAN GRANIT, MD, MSC ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY NEUROMUSCU LAR DIVISION UNIVERSITY OF MIAMI, MILLER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE RELEVANT DECLARATIONS Financial disclosures:
The Internist s Approach to Neuropathy VOLKAN GRANIT, MD, MSC ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY NEUROMUSCU LAR DIVISION UNIVERSITY OF MIAMI, MILLER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE RELEVANT DECLARATIONS Financial disclosures:
Manipulation according to Maigne
 1 Manipulation according to Maigne Roger Baecher, MD Roger BAECHER, MD March 2001 1st International Congress of Osteopathic Medicine Freiburg / Breisgau Germany, 15-18 September 1st International Congress
1 Manipulation according to Maigne Roger Baecher, MD Roger BAECHER, MD March 2001 1st International Congress of Osteopathic Medicine Freiburg / Breisgau Germany, 15-18 September 1st International Congress
Medical Policy. MP Quantitative Sensory Testing
 Medical Policy MP 2.01.39 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.39 Last Review: 06/22/2017 Effective Date: 06/22/2017 Section: Medicine End Date: 06/26/2018 Related Policies 2.04.58 Nerve Fiber Density Testing DISCLAIMER
Medical Policy MP 2.01.39 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.39 Last Review: 06/22/2017 Effective Date: 06/22/2017 Section: Medicine End Date: 06/26/2018 Related Policies 2.04.58 Nerve Fiber Density Testing DISCLAIMER
Dynamic Investigation Test-rig on haptics (DITA)
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Dynamic Investigation Test-rig on haptics (DITA) To cite this article: F Cannella et al 2013 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 459 012032 View the article online for
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Dynamic Investigation Test-rig on haptics (DITA) To cite this article: F Cannella et al 2013 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 459 012032 View the article online for
FEP Medical Policy Manual
 FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: January 15, 2018 Related Policies: 2.01.39 Quantitative Sensory Testing Automated Point-of-Care Nerve Conduction Tests Description Portable devices have been developed
FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: January 15, 2018 Related Policies: 2.01.39 Quantitative Sensory Testing Automated Point-of-Care Nerve Conduction Tests Description Portable devices have been developed
Adaptive shortening of long flexor in patients with claw hand: A short report
 Lepr Rev (2016) 87, 548 552 SHORT REPORT Adaptive shortening of long flexor in patients with claw hand: A short report PANKAJ GUPTA*, KENNETH KEVIN JOSHUA* & TASMIN JAHAN* *The Leprosy Mission Community
Lepr Rev (2016) 87, 548 552 SHORT REPORT Adaptive shortening of long flexor in patients with claw hand: A short report PANKAJ GUPTA*, KENNETH KEVIN JOSHUA* & TASMIN JAHAN* *The Leprosy Mission Community
