Supplementary Figure 1
|
|
|
- Alice Wood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in the MnR and 4 tetrodes in the hippocampal CA1. c, An example of four well-isolated units and representative spike-waveforms recorded from one tetrode. Each dot represents one spike waveform. d, An example of the CA1 local field potential (LFP) recorded during active-awake and immobility/sleep states. All the data analyzed for MnR activity with respect to ripples during immobility were collected when mice were in the cardboard box filled with cotton fiber material (Nestlets TM ), i.e., bed, where they exclusively slept. Typically as soon as mice became immobile in their beds, a series of ripple activity and sleep-like LFPs were detected in the CA1. Outside of the bed, the mice walked around, drank water, ate food, and displayed little immobility, accompanied by no sleep. e, Power spectrogram of the CA1 LFP (as shown in d). Notice strong power levels in the theta band (6 10 Hz) during awake and in the delta band (1 4 Hz) during immobility/sleep. Theta/delta ratio was calculated and smoothed with a Gaussian filter in Matlab (top panel).
2 Supplementary Figure 2 Identification of MnR putative serotoninergic neurons and classification of non-serotoninergic type I and II neurons. a,b, Electrodes placements in the hippocampal CA1 (a) and the MnR (b) from the dual-site recording mice (n = 6). c, Representative spike-trains of two putative serotoninergic neurons. Note that neuron 1 displayed tonic activity only, while neuron 2 displayed both tonic and high-frequency firing (*). d, Inter-spike interval (ISI) histograms and representative spike waveforms of the neurons shown in c (5000 spikes overlapped; spike width, 1 ms). Arrows indicate the peaks of ISI that were used for neuron identification as shown in f. Seventy-nine percent (23/29) of the classified putative serotonin neurons displayed tonic activity only, while the other 21% displayed both tonic and high-frequency activity. e, Firing rate histograms of the two neurons shown in c,d upon i.p. injection of the serotonin 1A receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT (0.2 mg/kg; arrows indicate the injection time point, and the mice were freely moving before and after injection). Effects of 8-OH-DPAT were examined on 12 putative serotonergic neurons of freely-moving mice, since serotonergic neurons are known to be inhibited by the autoreceptor agonist. The most of them (11/12) were inhibited for at least 10 min: either completely (4/12) or partially (7/12), strengthening the validity of the ISI procedure in determining serotonergic neurons. f, Log-log plot of the mean firing frequency vs. latency of ISI peak for all the MnR neurons recorded during immobility. g, Mean firing-rate changes of individual type I and type II neurons prior to ripple events (left panel). A histogram showing a distribution pattern of the type I and type II neurons based on firing-rate changes prior to ripple (right panel). Firing-rate change was calculated 1 s prior to ripple compared against a 2-s baseline activity (between 2 and 4 s prior to ripple). A 20% or lower in frequency change was classified as type I; and the rest of the ripple-correlated neurons were classified as type II.
3 Supplementary Figure 3 Ripple correlated MnR neural activity during immobility and feeding. a, Firing rates of the 3 types of MnR neurons plotted in relation to the ripple peak during immobile state, most likely asleep (top panels) and during feeding rodent chow or rice (bottom panels). b, Firing rates of individual putative serotonin (5-HT; n = 12), type I (n = 17) and type II (n = 19) neurons during immobility (top panels) and feeding (bottom panels). Neurons were recorded in consecutive sessions and are arranged in the same order for the top and bottom panels. Colour bars represent z-scored firingfrequency.
4 Supplementary Figure 4 MnR type I neuron firing properties and its relation to ripple events. a, Histograms (bin = 10 ms) showing probability of inter-spike interval (ISI) of 3 representative type I neurons. ISIs varied extensively among type I neurons. Inserts: histograms with a 1-ms bin. b, Distribution of type I neurons based on their ISI ranges. c, Distribution of type I neurons based on their mean instant firing rates. d,e, Mean auto-correlations (solid line; s.e.m.: dashed line) of the MnR type I neurons (d) and ripple events (e). The inserts of panels d,e, show respective analyses in a finer time resolution.
5 Supplementary Figure 5 Coordinated activity between MnR 5-HT and type I neurons during immobility. a,b, Rate histograms (a) and cross-correlation histogram (b) of two simultaneously recorded MnR neurons. Representative tetroderecorded spike waveforms of the 2 neurons are shown in a (inserted panels, 1000 spikes overlapped; spike width, 1 ms). c, Z-scored cross-correlations for all the simultaneously recorded 5-HT and type I neuron pairs (n = 35 pairs). Type I neurons were used as the reference for cross-correlation analyses in b and c.
6 Supplementary Figure 6 Ripple cluster termination coincides with high-rate and synchronous firing of MnR type I neurons. a, Representative hippocampal CA1 LFP and the filtered ripple activity. Ripples tended to occur in clusters (# 1 5), which were defined as 3 or more consecutive ripple events occurring above 1 Hz. b, During immobility, 58.1 ± 1.7% (mean ± s.e.m.; n = 19) of ripple events occurred in clusters. c, e, Mean firing rates (solid line; s.e.m.: dashed line) of type I neurons in relation to the onset (blue lines) and offset (red lines) of ripple clusters during the high-, mid-, low-rate (c), and high-, mid- low-synchrony (e) states. For definition of the above six categories of firing states, see Online Methods. Inserts: mean firing rates and s.e.m. of type I neurons shown in a finer time resolution. d, f, Mean peak frequencies and s.e.m. of the type I neurons immediately after the onset and offset of ripple clusters. Peak frequency was defined as the maximum frequency within 100 ms (bin = 10 ms) after the onset or offset of ripple clusters. P values were derived with Wilcoxon signed rank tests (n = 32 for d and n = 26 for f; Type I neurons with mean frequency above 1 Hz were used for analyses). n.s., P > 0.05; * P < 0.05; ***P
7 Supplementary Figure 7 Characterization of hippocampal CA1 neurons upon MnR photostimulation. a, A plot of the mean firing frequency vs. the action potential (AP) width for all the recorded CA1 neurons. Blue and red dots represent individual inhibited and excited CA1 neurons, respectively, upon MnR photostimulation. b, Response latencies of the inhibited (top) and excited (bottom) CA1 neurons upon MnR photostimulation. Response latency was defined as the latency of the first bin from at least 3 consecutive bins (peri-event histogram bin = 2 ms) that exceed the z-score of 1.96.
8 Supplementary Figure 8 Optical fiber placements for the mice used in the fear conditioning experiment. The tips of optic fibers are shown by black rectangles, and just below, red colour-filled rectangles indicate zones (0.5 mm) most powerfully affected by photostimulation. ChR2-group mice (n = 11) and EYFP-group control mice (n = 10). One of the control mice was found at the level of bregma 3.88 mm, and its placement is not shown here.
9 Supplementary Figure 9 Addressing issues involving MnR photostimulation. a, Mean ripple-event frequencies (error bars: s.e.m.) upon MnR photostimulation delivered on two different interval schedules. We conducted additional experiments to verify that the MnR photostimulation on a fixed-interval schedule of 2 s (FI2; 2-pulse train per 2 s) suppresses ripples activity. Using a group of 5 mice, we compared two schedules of photostimulation: One was the same scheduled described in Fig. 4 a d, and the mice received photostimulation on a variable interval schedule of 10 s (VI10; ranged between 5 and 15 s). The other was essentially the same as the one used for disrupting ripple after fear conditioning; the mice received photostimulation on a FI2 for 3 4 hours. Compared to photostimulation on the VI10, FI2 photostimulation suppressed ripple activity with a shorter duration, followed by rebound activation (1 2 sec). These results confirm that MnR photostimulation on a FI2 readily suppress ripple activity with the caveat that this frequent suppression schedule triggers a compensatory process. b, Percentages of time spent on slow-wave sleep (SWS) and rapid-eye movement sleep (REM) with/without photostimulation. Sleep stages were determined by hippocampal LFPs, and the amounts of SWS and REM were compared between the session with the FI2 photostimulation and a session with no photostimulation. The photostimulation condition did not alter the amounts of SWS sleep, but slightly increased REM (unpaired t-tests; n = 5). c, Representative coronal sections of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) staining. GFAP expressions were compared between mice (n = 3) that did not receive photostimulation and mice (n = 3) that received MnR photostimulation (2 pulses with 3-ms pulse duration) on FI2 during immobility over the course of 4 hours (the same procedure as the fear conditioning mice as shown in Fig. 7a). Scale bars, 0.2 mm. d, Quantification of the GFAP fluorescence intensity. Fluorescence intensities were measured in areas below optical fiber placements as shown in the squares, and did not differ between the conditions with/without photostimulation (2 group x 3 section ANOVA: F 1, 4 = 0.70, P = 0.45; n = 3 per group).
10 Supplementary Figure 10 SWS/ REM cyclic sleeping pattern during MnR photostimulation session. a, Representative power spectrogram of the CA1 LFP recorded during a 20-min sleep session in a mouse that received no photostimulation. Notice strong power levels in the theta band (6 10 Hz) during REM sleep and in the delta band (1 4 Hz) during SWS. Theta / delta ratio was calculated and smoothed with a Gaussian filter in Matlab (top panel). b, Power spectrogram of the CA1 LFP recorded from the same mouse during MnR photostimulation session (2-pulse train per 2 s; pulse width, 3 ms; 16 mw).
Nov versus Fam. Fam 1 versus. Fam 2. Supplementary figure 1
 a Environment map similarity score (mean r ).5..3.2.1 Fam 1 versus Fam 2 Nov versus Fam b Environment cofiring similarity score (mean r ).7.6.5..3.2.1 Nov versus Fam Fam 1 versus Fam 2 First half versus
a Environment map similarity score (mean r ).5..3.2.1 Fam 1 versus Fam 2 Nov versus Fam b Environment cofiring similarity score (mean r ).7.6.5..3.2.1 Nov versus Fam Fam 1 versus Fam 2 First half versus
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) 108 (b-c) (d) (e) (f) (g)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Trial structure for go/no-go behavior
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task. Trial-averaged lick rate was averaged across all mice used for pyramidal cell imaging (n = 9). Different colors denote different
Supplementary Figure 1 Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task. Trial-averaged lick rate was averaged across all mice used for pyramidal cell imaging (n = 9). Different colors denote different
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06310 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION www.nature.com/nature 1 www.nature.com/nature 2 www.nature.com/nature 3 Supplementary Figure S1 Spontaneous duration of wake, SWS and REM sleep (expressed
doi: 10.1038/nature06310 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION www.nature.com/nature 1 www.nature.com/nature 2 www.nature.com/nature 3 Supplementary Figure S1 Spontaneous duration of wake, SWS and REM sleep (expressed
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields.
 Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
Supplementary Material for
 Supplementary Material for Selective neuronal lapses precede human cognitive lapses following sleep deprivation Supplementary Table 1. Data acquisition details Session Patient Brain regions monitored Time
Supplementary Material for Selective neuronal lapses precede human cognitive lapses following sleep deprivation Supplementary Table 1. Data acquisition details Session Patient Brain regions monitored Time
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol.
 Supplementary Figures 1-11 Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol. (a), Voltage-clamp recordings from CA1 pyramidal neurons
Supplementary Figures 1-11 Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol. (a), Voltage-clamp recordings from CA1 pyramidal neurons
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4084
 Supplementary Figure 1: Sample IEDs. (a) Sample hippocampal IEDs from different kindled rats (scale bar = 200 µv, 100 ms). (b) Sample temporal lobe IEDs from different subjects with epilepsy (scale bar
Supplementary Figure 1: Sample IEDs. (a) Sample hippocampal IEDs from different kindled rats (scale bar = 200 µv, 100 ms). (b) Sample temporal lobe IEDs from different subjects with epilepsy (scale bar
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Behavioral generalization
 Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral generalization. a. Behavioral generalization curves in four Individual sessions. Shown is the conditioned response (CR, mean ± SEM), as a function of absolute (main) or
Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral generalization. a. Behavioral generalization curves in four Individual sessions. Shown is the conditioned response (CR, mean ± SEM), as a function of absolute (main) or
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
Supplementary Figure 1
 8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
Supplemental Information. A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit. for Place Navigation
 Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Brain and Cognitive Sciences 9.96 Experimental Methods of Tetrode Array Neurophysiology IAP 2001
 Brain and Cognitive Sciences 9.96 Experimental Methods of Tetrode Array Neurophysiology IAP 2001 An Investigation into the Mechanisms of Memory through Hippocampal Microstimulation In rodents, the hippocampus
Brain and Cognitive Sciences 9.96 Experimental Methods of Tetrode Array Neurophysiology IAP 2001 An Investigation into the Mechanisms of Memory through Hippocampal Microstimulation In rodents, the hippocampus
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Bidirectional optogenetic modulation of the tonic activity of CEA PKCδ + neurons in vitro. a, Top, Cell-attached voltage recording illustrating the blue light-induced increase in
Supplementary Figure 1 Bidirectional optogenetic modulation of the tonic activity of CEA PKCδ + neurons in vitro. a, Top, Cell-attached voltage recording illustrating the blue light-induced increase in
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/3/e1600955/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Flexible and stretchable nanowire-coated fibers for optoelectronic probing of spinal cord circuits Chi Lu, Seongjun
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/3/e1600955/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Flexible and stretchable nanowire-coated fibers for optoelectronic probing of spinal cord circuits Chi Lu, Seongjun
Place-selective firing contributes to the reverse-order reactivation of CA1 pyramidal cells during sharp waves in open-field exploration
 European Journal of Neuroscience, Vol. 26, pp. 704 716, 2007 doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05684.x Place-selective firing contributes to the reverse-order reactivation of CA1 pyramidal cells during sharp
European Journal of Neuroscience, Vol. 26, pp. 704 716, 2007 doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05684.x Place-selective firing contributes to the reverse-order reactivation of CA1 pyramidal cells during sharp
Quick Guide - eabr with Eclipse
 What is eabr? Quick Guide - eabr with Eclipse An electrical Auditory Brainstem Response (eabr) is a measurement of the ABR using an electrical stimulus. Instead of a traditional acoustic stimulus the cochlear
What is eabr? Quick Guide - eabr with Eclipse An electrical Auditory Brainstem Response (eabr) is a measurement of the ABR using an electrical stimulus. Instead of a traditional acoustic stimulus the cochlear
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0150-0 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent homeostasis Michelle C.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0150-0 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent homeostasis Michelle C.
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more strongly when an image was negative than when the same
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of an amygdala neuron whose activity reflects value during the visual stimulus interval. This cell responded more strongly when an image was negative than when the same
Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC
 1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Hippocampal recordings. a. (top) Post-operative MRI (left, depicting a depth electrode implanted along the longitudinal hippocampal axis) and co-registered preoperative MRI (right)
Supplementary Figure 1 Hippocampal recordings. a. (top) Post-operative MRI (left, depicting a depth electrode implanted along the longitudinal hippocampal axis) and co-registered preoperative MRI (right)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12024 entary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine infusions in Shock-sensitive
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12024 entary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine infusions in Shock-sensitive
Supplemental Figure 1
 A C E Supplemental Figure 1 AP 1mm A+C 1mm Apo 1mm B D 1mm CGS F 1mm All 1mm Supplemental Figure 1. The locations of microinfusion cannulae. Each dot represents the cannula tip of a given rat in Figure.
A C E Supplemental Figure 1 AP 1mm A+C 1mm Apo 1mm B D 1mm CGS F 1mm All 1mm Supplemental Figure 1. The locations of microinfusion cannulae. Each dot represents the cannula tip of a given rat in Figure.
Supplemental Information. Dorsal Raphe Dual Serotonin-Glutamate Neurons. Drive Reward by Establishing Excitatory Synapses
 Cell Reports, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Dorsal Raphe Dual Serotonin-Glutamate Neurons Drive Reward by Establishing Excitatory Synapses on VTA Mesoaccumbens Dopamine Neurons Hui-Ling Wang, Shiliang
Cell Reports, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Dorsal Raphe Dual Serotonin-Glutamate Neurons Drive Reward by Establishing Excitatory Synapses on VTA Mesoaccumbens Dopamine Neurons Hui-Ling Wang, Shiliang
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Short latency of the fepsp evoked in CA3 by electrical stimulation of perforant path inputs (a) Single and superimposed representative perforant pathway-ca3
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Short latency of the fepsp evoked in CA3 by electrical stimulation of perforant path inputs (a) Single and superimposed representative perforant pathway-ca3
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory
 Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4642
 Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites and example waveform clustering, as well as electrophysiological recordings of auditory CS and shock processing following overtraining. (a) Recording sites in LC
Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites and example waveform clustering, as well as electrophysiological recordings of auditory CS and shock processing following overtraining. (a) Recording sites in LC
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice
 Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice (a) Sample behavioral trace as in Figure 1d, but with NpHR stimulation trials depicted as green blocks
Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice (a) Sample behavioral trace as in Figure 1d, but with NpHR stimulation trials depicted as green blocks
Dep. Control Time (min)
 aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
Sleep stages. Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM)
 Sleep stages Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM) EEG waves EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves
Sleep stages Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM) EEG waves EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
Informationsverarbeitung im zerebralen Cortex
 Informationsverarbeitung im zerebralen Cortex Thomas Klausberger Dept. Cognitive Neurobiology, Center for Brain Research, Med. Uni. Vienna The hippocampus is a key brain circuit for certain forms of memory
Informationsverarbeitung im zerebralen Cortex Thomas Klausberger Dept. Cognitive Neurobiology, Center for Brain Research, Med. Uni. Vienna The hippocampus is a key brain circuit for certain forms of memory
Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the
 Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the upper cortical layers at P3 4 in vivo. (a b) Cell-attached current-clamp recordings illustrate responses to puff-applied
Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the upper cortical layers at P3 4 in vivo. (a b) Cell-attached current-clamp recordings illustrate responses to puff-applied
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Rett Syndrome Mutation MeCP2 T158A Disrupts DNA Binding, Protein Stability and ERP Responses
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Rett Syndrome Mutation T158A Disrupts DNA Binding, Protein Stability and ERP Responses Darren Goffin, Megan Allen, Le Zhang, Maria Amorim, I-Ting Judy Wang, Arith-Ruth S. Reyes,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Rett Syndrome Mutation T158A Disrupts DNA Binding, Protein Stability and ERP Responses Darren Goffin, Megan Allen, Le Zhang, Maria Amorim, I-Ting Judy Wang, Arith-Ruth S. Reyes,
Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell
 2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane
 Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane potential recorded from POMC neurons following treatment with
Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane potential recorded from POMC neurons following treatment with
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Reward rate affects the decision to begin work. (a) Latency distributions are bimodal, and depend on reward rate. Very short latencies (early peak) preferentially occur when a greater
Supplementary Figure 1 Reward rate affects the decision to begin work. (a) Latency distributions are bimodal, and depend on reward rate. Very short latencies (early peak) preferentially occur when a greater
HHS Public Access Author manuscript Nat Neurosci. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 September 19.
 Selective optical drive of thalamic reticular nucleus generates thalamic bursts & cortical spindles Michael M. Halassa 1,2,4, Joshua H. Siegle 2,4, Jason T. Ritt 3, Jonathan T. Ting 2, Guoping Feng 2,
Selective optical drive of thalamic reticular nucleus generates thalamic bursts & cortical spindles Michael M. Halassa 1,2,4, Joshua H. Siegle 2,4, Jason T. Ritt 3, Jonathan T. Ting 2, Guoping Feng 2,
Supplementary Figure 1. Recording sites.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites. (a, b) Schematic of recording locations for mice used in the variable-reward task (a, n = 5) and the variable-expectation task (b, n = 5). RN, red nucleus. SNc,
Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites. (a, b) Schematic of recording locations for mice used in the variable-reward task (a, n = 5) and the variable-expectation task (b, n = 5). RN, red nucleus. SNc,
EEG Electrode Placement
 EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves per second, measured in Hertz (Hz) reflects the firing rate of neurons alpha, beta, theta, delta Amplitude:
EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves per second, measured in Hertz (Hz) reflects the firing rate of neurons alpha, beta, theta, delta Amplitude:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
SUPPLEMENTAL DIGITAL CONTENT
 SUPPLEMENTAL DIGITAL CONTENT FIGURE 1. Unilateral subthalamic nucleus (STN) deep brain stimulation (DBS) electrode and internal pulse generator. Copyright 2010 Oregon Health & Science University. Used
SUPPLEMENTAL DIGITAL CONTENT FIGURE 1. Unilateral subthalamic nucleus (STN) deep brain stimulation (DBS) electrode and internal pulse generator. Copyright 2010 Oregon Health & Science University. Used
Supplementary Figure S1: Histological analysis of kainate-treated animals
 Supplementary Figure S1: Histological analysis of kainate-treated animals Nissl stained coronal or horizontal sections were made from kainate injected (right) and saline injected (left) animals at different
Supplementary Figure S1: Histological analysis of kainate-treated animals Nissl stained coronal or horizontal sections were made from kainate injected (right) and saline injected (left) animals at different
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Differential Consolidation and Pattern Reverberations within Episodic Cell Assemblies in the Mouse Hippocampus
 Differential Consolidation and Pattern Reverberations within Episodic Cell Assemblies in the Mouse Hippocampus Remus Oşan 1., Guifen Chen 2., Ruiben Feng 2, Joe Z. Tsien 2 * 1 Department of Pharmacology
Differential Consolidation and Pattern Reverberations within Episodic Cell Assemblies in the Mouse Hippocampus Remus Oşan 1., Guifen Chen 2., Ruiben Feng 2, Joe Z. Tsien 2 * 1 Department of Pharmacology
Design Considerations and Clinical Applications of Closed-Loop Neural Disorder Control SoCs
 22nd Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (ASP-DAC 2017) Special Session 4S: Invited Talk Design Considerations and Clinical Applications of Closed-Loop Neural Disorder Control SoCs Chung-Yu
22nd Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (ASP-DAC 2017) Special Session 4S: Invited Talk Design Considerations and Clinical Applications of Closed-Loop Neural Disorder Control SoCs Chung-Yu
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral training.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
Selective optical drive of thalamic reticular nucleus generates thalamic bursts & cortical spindles
 Selective optical drive of thalamic reticular nucleus generates thalamic bursts & cortical spindles Michael M. Halassa, Joshua H. Siegle, Jason T. Ritt, Jonathan T. Ting, Guoping Feng and Christopher I.
Selective optical drive of thalamic reticular nucleus generates thalamic bursts & cortical spindles Michael M. Halassa, Joshua H. Siegle, Jason T. Ritt, Jonathan T. Ting, Guoping Feng and Christopher I.
Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements
 Y. Isomura et al. 1 Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements Yoshikazu Isomura, Rie Harukuni, Takashi Takekawa, Hidenori Aizawa & Tomoki Fukai
Y. Isomura et al. 1 Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements Yoshikazu Isomura, Rie Harukuni, Takashi Takekawa, Hidenori Aizawa & Tomoki Fukai
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes. (a) Left, circuit schematic with the imaged component (L2/3 excitatory neurons)
Supplementary Figure 1 Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes. (a) Left, circuit schematic with the imaged component (L2/3 excitatory neurons)
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4335
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA are concentrated in the caudal mesopontine region. (a) Schematic showing the sites of retrograde tracer injections in the VTA: cholera toxin
Supplementary Figure 1 Cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA are concentrated in the caudal mesopontine region. (a) Schematic showing the sites of retrograde tracer injections in the VTA: cholera toxin
Social transmission and buffering of synaptic changes after stress
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-017-0044-6 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social transmission and buffering of synaptic changes after stress Toni-Lee
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-017-0044-6 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social transmission and buffering of synaptic changes after stress Toni-Lee
Exclusion criteria and outlier detection
 1 Exclusion criteria and outlier detection 1 2 Supplementary Fig. 1 31 subjects complied with the inclusion criteria as tested during the familiarization session. The upper part of the figure (ovals) indicates
1 Exclusion criteria and outlier detection 1 2 Supplementary Fig. 1 31 subjects complied with the inclusion criteria as tested during the familiarization session. The upper part of the figure (ovals) indicates
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 SNARE Probes for FRET/2pFLIM Analysis Used in the Present Study. mturquoise (mtq) and Venus (Ven) are in blue and yellow, respectively. The soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 SNARE Probes for FRET/2pFLIM Analysis Used in the Present Study. mturquoise (mtq) and Venus (Ven) are in blue and yellow, respectively. The soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive
Neuron, Volume 63 Spatial attention decorrelates intrinsic activity fluctuations in Macaque area V4.
 Neuron, Volume 63 Spatial attention decorrelates intrinsic activity fluctuations in Macaque area V4. Jude F. Mitchell, Kristy A. Sundberg, and John H. Reynolds Systems Neurobiology Lab, The Salk Institute,
Neuron, Volume 63 Spatial attention decorrelates intrinsic activity fluctuations in Macaque area V4. Jude F. Mitchell, Kristy A. Sundberg, and John H. Reynolds Systems Neurobiology Lab, The Salk Institute,
Characterization of Sleep Spindles
 Characterization of Sleep Spindles Simon Freedman Illinois Institute of Technology and W.M. Keck Center for Neurophysics, UCLA (Dated: September 5, 2011) Local Field Potential (LFP) measurements from sleep
Characterization of Sleep Spindles Simon Freedman Illinois Institute of Technology and W.M. Keck Center for Neurophysics, UCLA (Dated: September 5, 2011) Local Field Potential (LFP) measurements from sleep
Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers
 Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers Paul Feyen 1,, Elisabetta Colombo 1,2,, Duco Endeman 1, Mattia Nova 1, Lucia Laudato 2, Nicola Martino 2,3, Maria Rosa Antognazza
Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers Paul Feyen 1,, Elisabetta Colombo 1,2,, Duco Endeman 1, Mattia Nova 1, Lucia Laudato 2, Nicola Martino 2,3, Maria Rosa Antognazza
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information D-Serine regulates cerebellar LTD and motor coordination through the 2 glutamate receptor Wataru Kakegawa, Yurika Miyoshi, Kenji Hamase, Shinji Matsuda, Keiko Matsuda, Kazuhisa
Supplementary Information D-Serine regulates cerebellar LTD and motor coordination through the 2 glutamate receptor Wataru Kakegawa, Yurika Miyoshi, Kenji Hamase, Shinji Matsuda, Keiko Matsuda, Kazuhisa
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
The individual animals, the basic design of the experiments and the electrophysiological
 SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL Material and Methods The individual animals, the basic design of the experiments and the electrophysiological techniques for extracellularly recording from dopamine neurons were
SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL Material and Methods The individual animals, the basic design of the experiments and the electrophysiological techniques for extracellularly recording from dopamine neurons were
Supplementary Figure 1. SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.
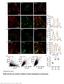 Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
Supplemental Information. Gamma and the Coordination of Spiking. Activity in Early Visual Cortex. Supplemental Information Inventory:
 Neuron, Volume 77 Supplemental Information Gamma and the Coordination of Spiking Activity in Early Visual Cortex Xiaoxuan Jia, Seiji Tanabe, and Adam Kohn Supplemental Information Inventory: Supplementary
Neuron, Volume 77 Supplemental Information Gamma and the Coordination of Spiking Activity in Early Visual Cortex Xiaoxuan Jia, Seiji Tanabe, and Adam Kohn Supplemental Information Inventory: Supplementary
Dopamine in Ube3a m-/p+ mice. Online Supplemental Material
 Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
Introduction to Electrophysiology
 Introduction to Electrophysiology Dr. Kwangyeol Baek Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School 2018-05-31s Contents Principles in Electrophysiology Techniques
Introduction to Electrophysiology Dr. Kwangyeol Baek Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School 2018-05-31s Contents Principles in Electrophysiology Techniques
Prefrontal-Hippocampal Interactions
 Prefrontal-Hippocampal Interactions Thesis by Casimir M. Wierzynski In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy California Institute of Technology Pasadena, California
Prefrontal-Hippocampal Interactions Thesis by Casimir M. Wierzynski In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy California Institute of Technology Pasadena, California
Supplementary Figure 1. Verification of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative
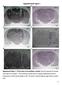
 Supplementary Figure 1. Verifiation of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative neutral red-stained oronal setion from a mouse with a guide annula targeting the IPN. The guide annula sar is irled
Supplementary Figure 1. Verifiation of drug infusions into the IPN. a. Representative neutral red-stained oronal setion from a mouse with a guide annula targeting the IPN. The guide annula sar is irled
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Encoding of conditioned fear in central amygdala inhibitory circuits Stephane Ciocchi 1,*, Cyril Herry 1,,*, François Grenier 1, Steffen B.E. Wolff 1, Johannes J. Letzkus 1, Ioannis Vlachos 3, Ingrid Ehrlich
Encoding of conditioned fear in central amygdala inhibitory circuits Stephane Ciocchi 1,*, Cyril Herry 1,,*, François Grenier 1, Steffen B.E. Wolff 1, Johannes J. Letzkus 1, Ioannis Vlachos 3, Ingrid Ehrlich
Hippocampal mechanisms of memory and cognition. Matthew Wilson Departments of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and Biology MIT
 Hippocampal mechanisms of memory and cognition Matthew Wilson Departments of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and Biology MIT 1 Courtesy of Elsevier, Inc., http://www.sciencedirect.com. Used with permission.
Hippocampal mechanisms of memory and cognition Matthew Wilson Departments of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and Biology MIT 1 Courtesy of Elsevier, Inc., http://www.sciencedirect.com. Used with permission.
Summary of behavioral performances for mice in imaging experiments.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Summary of behavioral performances for mice in imaging experiments. (a) Task performance for mice during M2 imaging experiments. Open triangles, individual experiments. Filled triangles,
Supplementary Figure 1 Summary of behavioral performances for mice in imaging experiments. (a) Task performance for mice during M2 imaging experiments. Open triangles, individual experiments. Filled triangles,
Distinct Roles of Parvalbumin- and Somatostatin- Expressing Interneurons in Working Memory
 Article Distinct Roles of Parvalbumin- and Somatostatin- Expressing Interneurons in Working Memory Highlights d Roles of parvalbumin and somatostatin neurons in working memory were investigated d d Somatostatin
Article Distinct Roles of Parvalbumin- and Somatostatin- Expressing Interneurons in Working Memory Highlights d Roles of parvalbumin and somatostatin neurons in working memory were investigated d d Somatostatin
Reward prediction based on stimulus categorization in. primate lateral prefrontal cortex
 Reward prediction based on stimulus categorization in primate lateral prefrontal cortex Xiaochuan Pan, Kosuke Sawa, Ichiro Tsuda, Minoro Tsukada, Masamichi Sakagami Supplementary Information This PDF file
Reward prediction based on stimulus categorization in primate lateral prefrontal cortex Xiaochuan Pan, Kosuke Sawa, Ichiro Tsuda, Minoro Tsukada, Masamichi Sakagami Supplementary Information This PDF file
Title. Author(s)Ono, Daisuke; Honma, Ken-Ichi; Honma, Sato. CitationScientific reports, 5: Issue Date Doc URL
 Title Circadian and ultradian rhythms of clock gene expres Author(s)Ono, Daisuke; Honma, Ken-Ichi; Honma, Sato CitationScientific reports, 5: 31 Issue Date 215-7-21 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/59574
Title Circadian and ultradian rhythms of clock gene expres Author(s)Ono, Daisuke; Honma, Ken-Ichi; Honma, Sato CitationScientific reports, 5: 31 Issue Date 215-7-21 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/59574
Supplementary Figure 1: Validation of labeling specificity of immature OSNs and presynaptic terminals. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
 Supplementary Figure 1: Validation of labeling specificity of immature OSNs and presynaptic terminals. (A) Confocal images of septal olfactory epithelium of an adult Gγ8-sypGFP-tdTom mouse showing colocalization
Supplementary Figure 1: Validation of labeling specificity of immature OSNs and presynaptic terminals. (A) Confocal images of septal olfactory epithelium of an adult Gγ8-sypGFP-tdTom mouse showing colocalization
Awake-behaving recordings in mice during fear conditioning. Eric H. Chang, Ph.D. Goldsmith Postdoctoral Fellow
 Awake-behaving recordings in mice during fear conditioning Eric H. Chang, Ph.D. Goldsmith Postdoctoral Fellow Weill Cornell Medical College Burke Cornell Medical Research Institute White Plains, NY Noldus
Awake-behaving recordings in mice during fear conditioning Eric H. Chang, Ph.D. Goldsmith Postdoctoral Fellow Weill Cornell Medical College Burke Cornell Medical Research Institute White Plains, NY Noldus
Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex
 Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Hippocampal Sharp Waves and Reactivation during Awake States Depend on Repeated Sequential Experience
 The Journal of Neuroscience, November 29, 2006 26(48):12415 12426 12415 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Hippocampal Sharp Waves and Reactivation during Awake States Depend on Repeated Sequential Experience
The Journal of Neuroscience, November 29, 2006 26(48):12415 12426 12415 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Hippocampal Sharp Waves and Reactivation during Awake States Depend on Repeated Sequential Experience
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Information Processing During Transient Responses in the Crayfish Visual System
 Information Processing During Transient Responses in the Crayfish Visual System Christopher J. Rozell, Don. H. Johnson and Raymon M. Glantz Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Department of
Information Processing During Transient Responses in the Crayfish Visual System Christopher J. Rozell, Don. H. Johnson and Raymon M. Glantz Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Department of
Facilitative Effects of the Ampakine CX516 on Short-Term Memory in Rats: Correlations with Hippocampal Neuronal Activity
 The Journal of Neuroscience, April 1, 1998, 18(7):2748 2763 Facilitative Effects of the Ampakine CX516 on Short-Term Memory in Rats: Correlations with Hippocampal Neuronal Activity Robert E. Hampson, 1
The Journal of Neuroscience, April 1, 1998, 18(7):2748 2763 Facilitative Effects of the Ampakine CX516 on Short-Term Memory in Rats: Correlations with Hippocampal Neuronal Activity Robert E. Hampson, 1
Restoring Communication and Mobility
 Restoring Communication and Mobility What are they? Artificial devices connected to the body that substitute, restore or supplement a sensory, cognitive, or motive function of the nervous system that has
Restoring Communication and Mobility What are they? Artificial devices connected to the body that substitute, restore or supplement a sensory, cognitive, or motive function of the nervous system that has
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus
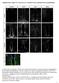 Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
Thalamic control of cortical states
 Supplementary Information Thalamic control of cortical states James F.A. Poulet, Laura M.J. Fernandez, Sylvain Crochet & Carl C.H. Petersen Supplementary Information consists of: 1. Methods 2. Supplementary
Supplementary Information Thalamic control of cortical states James F.A. Poulet, Laura M.J. Fernandez, Sylvain Crochet & Carl C.H. Petersen Supplementary Information consists of: 1. Methods 2. Supplementary
Supplementary information - Table (1), Figures (12), and Videos (5)
 Supplementary information - Table (1), Figures (12), and Videos (5) A soft, transparent, freely accessible cranial window for chronic imaging and electrophysiology Chaejeong Heo 1, Hyejin Park 1, 2, Yong-Tae
Supplementary information - Table (1), Figures (12), and Videos (5) A soft, transparent, freely accessible cranial window for chronic imaging and electrophysiology Chaejeong Heo 1, Hyejin Park 1, 2, Yong-Tae
Lecture 8. Arousal & Sleep. Cogs17 * UCSD
 Lecture 8 Arousal & Sleep Cogs17 * UCSD Arousal in the Brain Stimulated by sensory input Initiated, maintained endogenously Basal Forebrain Delivers ACh throughout cortex Arousal in the Brain Lateral Hypothalamus
Lecture 8 Arousal & Sleep Cogs17 * UCSD Arousal in the Brain Stimulated by sensory input Initiated, maintained endogenously Basal Forebrain Delivers ACh throughout cortex Arousal in the Brain Lateral Hypothalamus
Investigation of the hippocampal information processing in freely moving rats
 Investigation of the hippocampal information processing in freely moving rats Summary of the Ph.D. thesis Azahara Oliva University of Szeged, Department of Physiology Szeged 2016 Introduction A major goal
Investigation of the hippocampal information processing in freely moving rats Summary of the Ph.D. thesis Azahara Oliva University of Szeged, Department of Physiology Szeged 2016 Introduction A major goal
An Auditory-Model-Based Electrical Stimulation Strategy Incorporating Tonal Information for Cochlear Implant
 Annual Progress Report An Auditory-Model-Based Electrical Stimulation Strategy Incorporating Tonal Information for Cochlear Implant Joint Research Centre for Biomedical Engineering Mar.7, 26 Types of Hearing
Annual Progress Report An Auditory-Model-Based Electrical Stimulation Strategy Incorporating Tonal Information for Cochlear Implant Joint Research Centre for Biomedical Engineering Mar.7, 26 Types of Hearing
Hyatt Moore IV 1, 2 Steve Woodward 3, PhD Emmanuel Mignot 1, MD, PhD. Electrical Engineering Stanford University, CA 2
 HIGH RESOLUTION DETECTION OF POLYSOMNOGRAPHY BASED PHASIC EVENTS OF REM SLEEP IN POSTRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER IMPROVING TOOLS FOR PSG ANALYSIS OF REM SLEEP IN PTSD Hyatt Moore IV 1, 2 Steve Woodward 3,
HIGH RESOLUTION DETECTION OF POLYSOMNOGRAPHY BASED PHASIC EVENTS OF REM SLEEP IN POSTRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER IMPROVING TOOLS FOR PSG ANALYSIS OF REM SLEEP IN PTSD Hyatt Moore IV 1, 2 Steve Woodward 3,
SLEEP. -in 1953, first demonstration that brain was active during sleep. 4. Stages 3& 4: Delta Waves, large slow waves; deep sleep
 SLEEP DEF: altered state, between waking and unconsciousness, defined by specific patterns of brain activity. I. How much sleep do I need? 1. Long vs. Short Sleepers -across developmental stages -individual
SLEEP DEF: altered state, between waking and unconsciousness, defined by specific patterns of brain activity. I. How much sleep do I need? 1. Long vs. Short Sleepers -across developmental stages -individual
