CLINICAL PEARLS IN CONTRACEPTION
|
|
|
- Denis Paul
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CLINICAL PEARLS IN CONTRACEPTION Laura Borgelt, PharmD, FCCP, BCPS Associate Professor University of Colorado Denver PharmCon, Inc. is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education as a provider of continuing pharmacy education. Copyright PharmCon 2009
2 CLINICAL PEARLS IN CONTRACEPTION Speaker: Dr. Borgelt is an Associate Professor at the University of Colorado Denver in the Departments of Clinical Pharmacy and Family Medicine. She received her Bachelor of Science degree from the University of Iowa and her Doctor of Pharmacy degree from the University of Colorado. She completed a Primary Care Residency with the University of Colorado and Kaiser Permanente Rocky Mountain Division. Dr. Borgelt is a board certified pharmacotherapy specialist and a fellow of the American College of Clinical Pharmacy. Speaker Disclosure: Dr. Borgelt has no actual or potential conflicts of interest in relation to this program This program has been brought to you by PharmCon PharmCon, Inc. is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education as a provider of continuing pharmacy education. Legal Disclaimer: The material presented here does not necessarily reflect the views of Pharmaceutical Education Consultants (PharmCon) or the companies that support educational programming. A qualified healthcare professional should always be consulted before using any therapeutic product discussed. Participants should verify all information and data before treating patients or employing any therapies described in this educational activity.
3 CLINICAL PEARLS IN CONTRACEPTION Accreditation: Pharmacists: L01-P Technicians: L01-T Nurses: N L01 CE Credits: 1.0 Continuing Education Hour or 0.1 CEU for technicians Expiration Date: 12/15/2012 Target Audience: Pharmacists, Technicians, & Nurses Program Overview: Throughout history, little was known about women's reproductive systems. Even more, what people actually believed bordered on the bizarre. Even though it is now the 21st century, it's amazing what type of information is circling about regarding birth control and getting pregnant. Unfortunately, women (and men) still get a lot of misinformation from well-meaning friends, sisters, and others and when it comes to contraception, and this misinformation can cause big problems. The more health care providers know about contraceptives and the correct way to use them, the better guidance and/or counseling they can offer their patients. Objectives: Compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of combination oral contraceptives to other contraceptive methods Design a therapeutic plan to manage the most common side effects associated with combined contraceptives Describe how emergency contraception works and how to counsel patients regarding its proper use This program has been brought to you by PharmCon
4 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of combination oral contraceptives to other contraceptive methods. Design a therapeutic plan to manage the most common side effects associated with combined contraceptives. Describe how emergency contraception works and how to counsel patients regarding its proper use.
5 Outline Introduction Prescription contraceptives Clinical Pearls in Contraception *Contraindications *Initiation of method *Extended cycling *Drug interactions *Missed doses *Emergency Contraception *Generic vs. brand *Side effects Conclusions
6 Contraceptive Options Depo-Provera
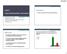
7 Contraceptive Use in the U.S. 9% 4% 5% 2% 4% 27% Tubal sterilization Pill Male condom Vasectomy Withdrawal Injectable 18% IUD Other 31% Alan Guttmacher Institute. Facts in Brief: Contraceptive Use
8 Perfect and Typical Use Percent of Women Experiencing Unintended Pregnancy in First Year of Use Method % with Typical Use % with Perfect Use No method 85% 85% Spermicide 29% 18% Withdrawal 18% 4% Periodic abstinence 25% --- Diaphragm 16% 6% Male condom 17% 2% Female condom 27% 5% Pill (COCs) 9% 0.3% Combined patch 8% 0.3% Depo-Provera 7% 0.3% Combined vaginal ring 8% 0.3% Copper T 380A IUD 1% 0.6% LNG 20 IUD 0.1% 0.1%
9 Optimizing Patient Choices Effectiveness Importance of not being pregnant Likelihood and ability to comply Frequency of intercourse Age Cost and ability to pay Side effects Risk/benefit, perceptions, misperceptions Other drugs used Health status and habits Noncontraceptive benefits
10 Prescription Contraceptives Combined contraceptives Oral Patch Vaginal ring Progestin-only contraceptives Oral Injectable Implant Intrauterine contraception Copper intrauterine device Levonorgestrel intrauterine system Barrier methods Cervical cap Diaphragm
11 Combined Contraceptives Estrogen Ethinyl estradiol Mestranol Progestin Norethindrone Norethindrone acetate Ethynodiol diacetate Norgestrel Levonorgestrel Desogestrel, etonogestrel Norgestimate, norelgestromin Drosperinone
12 Combined Contraceptives Mechanism of Action Suppress ovulation Reduce sperm transport in upper genital tract (fallopian tubes) Change endometrium making implantation less likely Thicken cervical mucus (preventing sperm penetration) 3
13 Clinical Pearl: Contraindications What women should not take combined contraceptives?
14 Contraindications for Combined Contraceptives World Health Organization (WHO) medical eligibility criteria Separated into four categories 1. A condition for which there is no restriction for the use of the contraceptive method. 2. A condition where the advantages of using the method generally outweigh the theoretical or proven risks. 3. A condition where the theoretical or proven risks usually outweigh the advantages of using the method. 4. A condition which represents an unacceptable health risk if the contraceptive method is used.
15 Contraindications for Combined Contraceptives (Category 4) Breastfeeding <6 wks postpartum Smoker 35 yrs, 15 cigs/d Multiple risk factors for CVD BP 160/100 Vascular disease Current, history of, or on treatment for DVT/PE Complicated diabetes Presence of liver tumors, severe cirrhosis, or active viral hepatitis Major surgery with prolonged mobilization Known thrombogenic mutations + antiphospholipid antibodies Current and history of ischemic heart disease Stroke (history of CVA) Complicated valvular heart disease Migraine headache with aura Current breast cancer
16 Clinical Pearl: Initiating Combined Oral Contraceptives (COCs) How and when should a woman start her birth control pill?
17 Oral: Starting Pills Choose backup method Take 1 pill daily at the same time Daily use: take 21 days, stop taking pills or take inactive pills for 7 days and then start new pack Extended use: take 21 days, begin new pack immediately (discard last 7 inactive days) Start according to appropriate schedule (next slide)
18 Oral: Administration When to start First day of menses (preferred) Immediately, if pregnancy excluded First Sunday after next menses begins Within 5 days after start of menstrual bleeding Back up contraception None needed Backup x 7days Backup x 7days (if more than 5 days since menstrual bleeding started) None needed *Backup contraception for the first cycle is useful with all contraceptives and is necessary for progestin-only oral contraceptives
19 Oral Contraceptives: Administration Switching from another hormonal method* Switching from a non-hormonal method Switching from IUD After emergency contraception pills (ECP) Start COC immediately if method has been used correctly. No backup needed. Start COC within 5 days of menstrual bleeding - no backup needed. Also can start any time if not pregnant backup x 7 days Start COC within 5 days of menstrual bleeding - no backup needed. Also can start any time if not pregnant backup x 7 days Day after ECP backup x 7 days. Sunday start and first day start also possible. *If hormonal method was injection, start COCs when repeat injection would have been given
20 Clinical Pearl: Extended Use Is it okay to have menstrual periods infrequently? Never?
21 Types of Oral Contraception Monophasic: same amount throughout Biphasic: same estrogen, but differing amounts of progestin that change half-way through active pills Triphasic: varying amounts of estrogen or progestin every week of active pills
22 Continuous or Extended Use Monophasic estrogen and progestin pills Extended-cycle birth control May have more spotting initially; no periods Seasonale, Seasonique 84 days of active pill, 7 days inactive or low dose estrogen pill Lybrel Pill taken every day Yaz, Loestrin-24 FE 24/4 day cycle
23 Clinical Pearl: Missed Doses and Emergency Contraception What do I tell a patient to do if she misses one or more doses? Should emergency contraception always be offered?
24 Oral: Missed Doses Missed one pill Take missed pill ASAP. Take next pill as usual. Back up x 7 days. May offer ECPs. Missed two pills Take one of forgotten pills every 12 hours until caught up, then continue pack. Backup x 7 days. May offer ECPs. Missed more than two pills Offer ECPs. If taken, restart OCPs next day and use backup x 7days. If ECPs not taken, skip missed pills and complete rest of pills in pack, but use barrier method until next menses. Pills may not provide protection, but will help control cycle. Hatcher RA, et al. A Pocket Guide to Managing Contraception
25 Emergency Contraception (EC) The use of hormonal medications within 72 to 120 hours after unprotected or underprotected coitus for the prevention of unintended pregnancy. Progestin-only (levonorgestrel) Plan B OneStep, Next Choice, Plan B Combined estrogen-progestin (Yuzpe - two doses of 100 mcg EE plus 0.5 mg levonorgestrel) Alesse 5 pink pills 100 mcg EE 0.50 mg LNG Nordette 4 light-orange pills 120 mcg EE 0.60 mg LNG Pediatrics 2005;116(4):
26 EC: Dosing Levonorgestrel (0.75 mg) regimen 2 doses: 1 tablet ASAP (within hours), 1 tablet 12 hours later 2 doses: 1 tablet ASAP (within hours), 1 tablet up to 24 hours later 1 dose: 2 tablets at the same time Yuzpe regimen 2 doses: #x tablets ASAP (within hours), #x tablets 12 hours later Lancet 2002;360: Contraception 2002;66: Hum Reprod 2004;20:
27 Hormonal EC: Mechanism of Action Preventing or postponing ovulation by suppressing, blunting, or delaying LH surge Interference with sperm transport by thickening cervical mucus and alkalinizing the uterine cavity to immobilize sperm Clin Obstet Gynecol 2007;50(4):
28 EC: Effectiveness Method Effectiveness # Expected Pregnancies No treatment N/A 80/1000 Copper IUD 99% (99-100%) 1/1000 Levonorgestrel 89% (59-94%) 10/1000 Yuzpe regimen 74% (47-89%) 20/1000 Contraceptive Technology. 19 th ed. New York: Ardent Media Inc, April 2008
29 EC: Effectiveness Clin Obstet Gynecol 2007;50(4): Lancet 1999;353:721
30 EC: Patient Counseling Make certain that the patient does not want pregnancy Explain that EC does not protect from STIs Explain how to take EC regimen Describe side effects: nausea and vomiting. headaches, breast tenderness, and dizziness Recommend an at home pregnancy test and medical follow up if the patient does not have a normal period within 3 weeks Recommend not having unprotected intercourse in the days or weeks following treatment If patient takes COCs, start again the following day
31 EC and Menstrual Cycle Changes The Menstrual Cycle Cycle length 1 day No diff 2 days Day of Month After EC taken, menses usually occurs within 1 week before or after the expected time. Contraception 2006;74:
32 EC: Patient Counseling As a pharmacist, if a woman comes in for EC, take the opportunity to counsel on the following: Proper contraception techniques and methods available Risk of sexually transmitted infections and regular examinations by a physician or health care provider
33 Clinical Pearl: Managing Common Side Effects Should a woman change her oral contraceptive if unexpected bleeding occurs? Nausea and/or vomiting?
34 Side Effects Discontinuation of contraceptives most often due to bleeding irregularities, nausea, weight gain and mood swings Side effects occur when hormone activity of contraceptive is greater or less than the hormone effect of a woman s own ovarian steroids Dickey, RP. Managing Contraceptive Pill Patients. Millenium ed
35 Estrogen Nausea Side Effects of Combined Contraceptives Estrogen and progestin Breast tenderness Progestin appetite and wt gain breast size Headaches Depression HTN HTN Fatigue libido Cyclic wt gain Acne, oily skin Bleeding Bloating
36 Management of Side Effects Determine if symptom indicates presence or potential for serious illness. If yes, discontinue immediately. Identify probable cause Make decision about probable clinical course of side effect if contraceptive continued Most side effects will diminish or disappear by 2 nd or 3 rd cycle encourage use for 3 months! Consider contraceptive switch
37 Management of Side Effects: Breakthrough Bleeding and Spotting If unexpected bleeding occurs, use additional contraception until bleeding completely ceases Rule out potential causes (i.e., PID) Encourage continuation if first few cycles When switch is indicated: Increase estrogen dose: If bleeding begins during first 14 days If absence of withdrawal menses If menses continues into active pill cycle
38 Management of Side Effects: Breakthrough Bleeding and Spotting When switch is indicated: Change progestin (more progestin activity or increase dose of same progestin): If bleeding begins after 14 days (of active med) Dysmenorrhea or heavy bleeding that occurs anytime in cycle May consider triphasic oral contraceptive (higher progestin doses at end of cycle) Progestin should have higher progestational (desogestrel) and/or androgenic activity (levonorgestrel) Increase both estrogen and progestin: If bleeding occurs midcycle
39 Management of Side Effects: Nausea and Vomiting Most severe during first cycles and usually disappear with time Related to estrogen dose Take with food or at bedtime If persists after third cycle, switch to contraceptive with lower estrogen dose
40 Management of Side Effects: Acne Non-pharmacologic measures Choose contraceptive with low androgenic activity Desogestrel Norgestimate Drosperinone Choose contraceptive with higher estrogen doses (30-35 mcg) FDA indications for acne: Ortho Tri-Cyclen, Estrostep, Yaz
41 Patient Case A 28 year-old female makes you aware that she is having unpredictable bleeding in between regular periods. She is taking Loestrin FE 1/20 (20 mcg EE, 1.0 mg norethindrone acetate). What information should you obtain before giving advice to this patient? The PCP inquires as to what COC would be good to use. What do you advise?
42 Patient Case A 25 year-old female calls your pharmacy complaining of nausea. Upon review of her patient profile, you find that she started Demulen 1/35 (35 mcg EE, 1.0 mg ethynodiol diacetate) taking two weeks ago. How would you handle this?
43 Clinical Pearl: Drug Interactions Does a backup method need to be used when antibiotics are taken while on combined oral contraceptives?
44 Combined Contraceptives: Drug Interactions Similar drug interactions reported for all forms of combined contraceptives The lower the dose of estrogen or progestin in a contraceptive, the greater the risk that another medication could decrease its effectiveness Back-up contraception should be used if a drug interaction is possible
45 Combined Contraceptives: Drug Interactions Hepatic enzyme inducers Agents most likely to cause breakdown of estrogen or progestin: phenobarbital, phenytoin, topirimate, carbamazepine, primidone Sodium valproate, ethosuximide, lamotrigine and vigabatrin do not effect contraceptive hormone levels Management Use another method Use different anticonvulsant Increase dose of contraceptive
46 Combined Contraceptives: Drug Interactions - Antibiotics Rifampin - significant risk of failure; counsel about the use of additional nonhormonal contraceptive methods during the course of rifampin therapy Other antibiotics - small risk of interactions; lack of pharmacokinetic and clinical evidence; not possible to identify women who may be at risk of OC failure. Counsel about the additional use of nonhormonal contraception or alternate methods for: Those not comfortable with small risk of interaction Those with previous failures or who develop breakthrough bleeding during use of antibiotics Obstet Gynecol 2001;98:53-60 Dent Clin North Am 2002;46(4): Journal of Gynecologic Surgery 2002;18(4):
47 Combined Contraceptives: Protease inhibitors Drug Interactions Can cause changes in mean AUC of estrogen Consider different contraceptive options St. John s Wort Induces cytochrome P450 and could decrease effectiveness of oral contraceptives Concurrent condom use is excellent safety measure
48 Patient Case A physician would like to start erythromycin in a 18-year old female who has been taking Nordette (30 mcg EE, 0.15 mg levonorgestrel) for six months. He asks you about potential drug interactions. How might an astute pharmacist handle this situation?
49 Clinical Pearl: Generic vs. Brand Are generic birth control pills really the same and as effective as brand name?
50 Generic Oral Contraceptives Not required to have clinical testing Must prove blood level equivalency to be considered equivalent (80-125% of parent compound s blood levels) Theoretically could have an impact for very low dose COCs (20 mcg ethinyl estradiol) No evidence that generics are less effective than brand name products
51 Combined Contraceptives: Advantages Effective Safe Easy to use Reversible Menstrual cycle Reduction of several cancers Decreased risk of benign breast tumors Prevention of ectopic pregnancy Improves androgenexcess conditions Suppression of endometriosis Sexual enjoyment Emergency contraception Transition therapy for perimenopause
52 Combined Contraceptives: Disadvantages No HIV/STI protection Patient adherence Expensive Side effects Circulatory complications Menstrual cycle changes Sexual/psychological effects Hepatocellular adenoma Gallbladder disease Drug interactions
53 Clinical Pearl: Contraceptive Alternatives If combined contraceptives are not ideal for an individual patient, what other options could be considered?
54 Contraceptive Alternatives Method Duration of effectiveness Hormone content Notes DMPA 3 months Progestin BMD warning Mirena IUS Copper IUD 5 years Progestin Approved for heavy bleeding 10 years None May increase bleeding Barrier Immediate None Adherence
55 Conclusions Important to consider perfect and typical use rates to determine contraceptive effectiveness. Combined hormonal contraceptives work primarily by suppressing ovulation. Side effects of combined contraceptives can be due to excess or deficiency of estrogen or progestin components, but 3 month trial often needed. Drug interactions with combined contraceptives may be significant enough to consider other forms of contraception. Missed doses of combined contraceptives should be managed appropriately and emergency contraception should be offered if needed. Monophasic combined contraceptives can be used in an extended manner to eliminate monthly menstrual cycles. Advantages and disadvantages of various contraceptives must be considered for individual use.
56 Questions? Phone:
Contraception: Common Problems Faced in Office Practice. Jane S. Sillman, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital
 Contraception: Common Problems Faced in Office Practice Jane S. Sillman, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Disclosures I have no conflicts of interest Contraception: Common Problems How to discuss contraception
Contraception: Common Problems Faced in Office Practice Jane S. Sillman, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Disclosures I have no conflicts of interest Contraception: Common Problems How to discuss contraception
What s New in Adolescent Contraception?
 What s New in Adolescent Contraception? Abby Furukawa, MD Legacy Medical Group Portland Obstetrics and Gynecology April 29, 2017 Objectives Provide an update on contraception options for the adolescent
What s New in Adolescent Contraception? Abby Furukawa, MD Legacy Medical Group Portland Obstetrics and Gynecology April 29, 2017 Objectives Provide an update on contraception options for the adolescent
Expanding Access to Birth Control: Will Women Get the Care They Need?
 Expanding Access to Birth Control: Will Women Get the Care They Need? Target Audience: Pharmacists ACPE#: 0202-0000-18-045-L01-P Activity Type: Application-based Target Audience: ACPE#: Activity Type:
Expanding Access to Birth Control: Will Women Get the Care They Need? Target Audience: Pharmacists ACPE#: 0202-0000-18-045-L01-P Activity Type: Application-based Target Audience: ACPE#: Activity Type:
Contraception. Objectives. Unintended Pregnancy. Unintended Pregnancy in the US. What s the Impact? 10/7/2014
 Contraception Tami Allen, RNC OB, MHA Robin Petersen, RN, MSN Perinatal Clinical Nurse Specialist Objectives Discuss the impact of unintended pregnancy in the United States Discuss the risks and benefits
Contraception Tami Allen, RNC OB, MHA Robin Petersen, RN, MSN Perinatal Clinical Nurse Specialist Objectives Discuss the impact of unintended pregnancy in the United States Discuss the risks and benefits
Clinical Challenges in Contraception. Disclosures. Objectives Pharmacists 4/3/2018
 Clinical Challenges in Contraception Kathleen Besinque, PharmD Sarah McBane, PharmD Disclosures Kathleen Besinque has nothing to disclose Sarah McBane has nothing to disclose Objectives Pharmacists Compare
Clinical Challenges in Contraception Kathleen Besinque, PharmD Sarah McBane, PharmD Disclosures Kathleen Besinque has nothing to disclose Sarah McBane has nothing to disclose Objectives Pharmacists Compare
LEARNING OBJECTIVES. Beyond the Pill: Long Acting Contraception. Distribution Of Contraception Use By Women In The Us. Unintended Pregnancy is Common
 4:15 5 pm Beyond the Pill: Long Acting Contraceptives and IUDs Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christine L. Curry, MD, PhD: No financial
4:15 5 pm Beyond the Pill: Long Acting Contraceptives and IUDs Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christine L. Curry, MD, PhD: No financial
Unintended Pregnancy is Common LEARNING OBJECTIVES. Distribution Of Contraception Use By Women In The Us. Unintended Pregnancy And Contraceptive Use
 3:45 4:30 pm Beyond the Pill: Long Acting Contraceptives and IUDs Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christine L. Curry, MD, PhD: No financial
3:45 4:30 pm Beyond the Pill: Long Acting Contraceptives and IUDs Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Christine L. Curry, MD, PhD: No financial
100% Highly effective No cost No side effects
 effective? Advantages Disadvantages How do I get Cost Abstinence For some it can mean no sexual contact. For others it is no sexual intercourse or vaginal penetration. A permanent surgical procedure available
effective? Advantages Disadvantages How do I get Cost Abstinence For some it can mean no sexual contact. For others it is no sexual intercourse or vaginal penetration. A permanent surgical procedure available
Contraception Choices: An Evidence Based Approach Case Study Approach. Susan Hellier PhD, DNP, FNP-BC, CNE
 Contraception Choices: An Evidence Based Approach Case Study Approach Susan Hellier PhD, DNP, FNP-BC, CNE Objectives Describe the U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use, 2016 (U.S. MEC)
Contraception Choices: An Evidence Based Approach Case Study Approach Susan Hellier PhD, DNP, FNP-BC, CNE Objectives Describe the U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use, 2016 (U.S. MEC)
WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES?
 CONTRACEPTION WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES? Methods used to prevent fertilization *Also referred to as birth control methods With contraceptives, it is important to look at what works for you and your body.
CONTRACEPTION WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES? Methods used to prevent fertilization *Also referred to as birth control methods With contraceptives, it is important to look at what works for you and your body.
Medical Eligibility for Contraception Use
 Medical Eligibility for Contraception Use DIVISION OF REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH CENTERS FOR DISEASE CONTROL AND PREVENTION 2016 US Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use (US MEC) Purpose To assist
Medical Eligibility for Contraception Use DIVISION OF REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH CENTERS FOR DISEASE CONTROL AND PREVENTION 2016 US Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use (US MEC) Purpose To assist
World Health Organization Medical Eligibility for Contraceptive Use. Connie Kraus, PharmD, BCACP Professor (CHS) Director Office of Global Health
 World Health Organization Medical Eligibility for Contraceptive Use Connie Kraus, PharmD, BCACP Professor (CHS) Director Office of Global Health Objectives After this session, learners should be able to:
World Health Organization Medical Eligibility for Contraceptive Use Connie Kraus, PharmD, BCACP Professor (CHS) Director Office of Global Health Objectives After this session, learners should be able to:
Instruction for the patient
 WS 4 Case 3 STI and IUD Your situation Instruction for the patient You are 32 years old, divorced and have one child; you have just started a new relationship You underwent surgical resection of the left
WS 4 Case 3 STI and IUD Your situation Instruction for the patient You are 32 years old, divorced and have one child; you have just started a new relationship You underwent surgical resection of the left
Who s The Daddy? What You Should Know About OTC Contraception
 Who s The Daddy? What You Should Know About OTC Contraception By: Vona Broughton, BS Public Health & Kevin McCarthy, RPH This program has been brought to you by PharmCon PharmCon is accredited by the accreditation
Who s The Daddy? What You Should Know About OTC Contraception By: Vona Broughton, BS Public Health & Kevin McCarthy, RPH This program has been brought to you by PharmCon PharmCon is accredited by the accreditation
Linda Gregg NP, Janet Isabell NP, Sue Montei NP Clinical Reviewers Reproductive Health Unit
 Linda Gregg NP, Janet Isabell NP, Sue Montei NP Clinical Reviewers Reproductive Health Unit What We Plan To Do Describe the U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use, 2016 (U.S. MEC) Explain
Linda Gregg NP, Janet Isabell NP, Sue Montei NP Clinical Reviewers Reproductive Health Unit What We Plan To Do Describe the U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use, 2016 (U.S. MEC) Explain
Contraception for Adolescents: What s New?
 Contraception for Adolescents: What s New? US Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use Kathryn M. Curtis, PhD Division of Reproductive Health, CDC Expanding Our Experience and Expertise: Implementing
Contraception for Adolescents: What s New? US Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use Kathryn M. Curtis, PhD Division of Reproductive Health, CDC Expanding Our Experience and Expertise: Implementing
Contraception Effective Methods of Birth Control
 Contraception Effective Methods of Birth Control Abstinence Means choosing NOT to have sex It is the ONLY method that is 100% effective It is your right to be in control of your body and say NO What are
Contraception Effective Methods of Birth Control Abstinence Means choosing NOT to have sex It is the ONLY method that is 100% effective It is your right to be in control of your body and say NO What are
Contraception. Yolanda Evans MD MPH Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Division of Adolescent Medicine
 Contraception Yolanda Evans MD MPH Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Division of Adolescent Medicine Disclosures No financial relationships to disclose I have no commercial, financial, research ties to
Contraception Yolanda Evans MD MPH Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Division of Adolescent Medicine Disclosures No financial relationships to disclose I have no commercial, financial, research ties to
BIRTH CONTROL METHOD COMPARISON CHART
 BIRTH CONTROL METHOD COMPARISON CHART Abstinence 100% Yes Male latex condom 86%-95% Can increase to 98% by using with a contraceptive jelly Yes Highly effective No side effects, as with other methods No
BIRTH CONTROL METHOD COMPARISON CHART Abstinence 100% Yes Male latex condom 86%-95% Can increase to 98% by using with a contraceptive jelly Yes Highly effective No side effects, as with other methods No
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling Patient Information Mirena (mur-ā-nah) (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system)
 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling Patient Information Mirena (mur-ā-nah) (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system) Mirena does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling Patient Information Mirena (mur-ā-nah) (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system) Mirena does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections
Contraceptives. Kim Dawson October 2010
 Contraceptives Kim Dawson October 2010 Objectives: You will learn about: The about the different methods of birth control. How to use each method of birth control. Emergency contraception What are they?
Contraceptives Kim Dawson October 2010 Objectives: You will learn about: The about the different methods of birth control. How to use each method of birth control. Emergency contraception What are they?
Disclosures. Objectives. Case: Anna. Case: Carla. Case: Beth. Contraception (for the Family Physician) 5/22/2015. Valary Gass, MD.
 Contraception (for the Family Physician) Disclosures None Valary Gass, MD For Family Medicine Update June 2015 Objectives Help a patient choose a contraceptive that fits her life Consider co-morbidities
Contraception (for the Family Physician) Disclosures None Valary Gass, MD For Family Medicine Update June 2015 Objectives Help a patient choose a contraceptive that fits her life Consider co-morbidities
Picking the Perfect Pill How to Effectively Choose an Oral Contraceptive
 Focus on CME at Queen s University Picking the Perfect Pill How to Effectively Choose an Oral Contraceptive By Susan Chamberlain, MD, FRCSC There are over 20 oral contraceptive (OC) preparations on the
Focus on CME at Queen s University Picking the Perfect Pill How to Effectively Choose an Oral Contraceptive By Susan Chamberlain, MD, FRCSC There are over 20 oral contraceptive (OC) preparations on the
Table I. Examples of Hormone and Tapering Regimens
 Table I. Examples of Hormone and Tapering Regimens Severe AUB Heavy bleeding (soaking through 2 maxi pads an hour, 2 hours in a row) History of heavy menses Hemodynamically un (tachycardia, hypotensive,
Table I. Examples of Hormone and Tapering Regimens Severe AUB Heavy bleeding (soaking through 2 maxi pads an hour, 2 hours in a row) History of heavy menses Hemodynamically un (tachycardia, hypotensive,
Patient Guide Levonorgestrel and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets USP (0.1 mg/0.02 mg) and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets USP (0.
 Patient Guide Levonorgestrel and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets USP (0.1 mg/0.02 mg) and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets USP (0.01 mg) Rx Only This product (like all oral contraceptives) is intended to prevent pregnancy.
Patient Guide Levonorgestrel and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets USP (0.1 mg/0.02 mg) and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets USP (0.01 mg) Rx Only This product (like all oral contraceptives) is intended to prevent pregnancy.
Oral Contraceptives. Mike Williams GPST2
 Oral Contraceptives Mike Williams GPST2 Curriculum Mechanism Efficacy Advantages/Disadvantages Starting Continuing Problems/complications Contraception: effectiveness rates, risks, benefits and appropriate
Oral Contraceptives Mike Williams GPST2 Curriculum Mechanism Efficacy Advantages/Disadvantages Starting Continuing Problems/complications Contraception: effectiveness rates, risks, benefits and appropriate
CURRENT HORMONAL CONTRACEPTION - LIMITATIONS
 CURRENT HORMONAL CONTRACEPTION - LIMITATIONS Oral Contraceptives - Features MERITS Up to 99.9% efficacy if used correctly and consistently Reversible method rapid return of fertility Offer non-contraceptive
CURRENT HORMONAL CONTRACEPTION - LIMITATIONS Oral Contraceptives - Features MERITS Up to 99.9% efficacy if used correctly and consistently Reversible method rapid return of fertility Offer non-contraceptive
The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that
 The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that may be used in the future Abstinence Choosing not to
The following lesson on contraception (birth control) is not intended to infer that you will be sexually active as a teen. This is information that may be used in the future Abstinence Choosing not to
Topic 24: Estrogens and Female Reproductive Drugs
 Topic 24: Estrogens and Female Reproductive Drugs I. Contraceptives A. Estrogen-Progestin Contraceptives Note all of these drugs contain one estrogen (listed first) and one progestin Drug to know: ethinyl
Topic 24: Estrogens and Female Reproductive Drugs I. Contraceptives A. Estrogen-Progestin Contraceptives Note all of these drugs contain one estrogen (listed first) and one progestin Drug to know: ethinyl
Peggy Piascik, PhD Associate Professor, Pharmacy Practice and Science
 Peggy Piascik, PhD Associate Professor, Pharmacy Practice and Science Department, UK College of Pharmacy Describe extended cycle oral contraceptive characteristics including dosing regimen, indications,
Peggy Piascik, PhD Associate Professor, Pharmacy Practice and Science Department, UK College of Pharmacy Describe extended cycle oral contraceptive characteristics including dosing regimen, indications,
Time Topic Speaker Abbreviation
 1. Programme Sunday, 4 th November 2018 Time Topic Speaker Abbreviation 08:00 Welcome, distribution materials 08:30 Overview of the Medical Eligibility Criteria (2015), and the Selected Practices Recommendations
1. Programme Sunday, 4 th November 2018 Time Topic Speaker Abbreviation 08:00 Welcome, distribution materials 08:30 Overview of the Medical Eligibility Criteria (2015), and the Selected Practices Recommendations
2/4/2011. What is your specialty? A. Family practice B. Internal medicine and subs C. OB/GYN D. Peds E. Surgery and subs
 Steve P. Buchanan D.O. FACOOG(Dist.) TOMA Mid Winter February 11, 2011 Dallas,TX Associate Professor OB/GYN UNTHSC/TCOM 1987- present Executive Vice President, American College of Osteopathic Obstetricians
Steve P. Buchanan D.O. FACOOG(Dist.) TOMA Mid Winter February 11, 2011 Dallas,TX Associate Professor OB/GYN UNTHSC/TCOM 1987- present Executive Vice President, American College of Osteopathic Obstetricians
Family Planning and Infertility
 Family Planning and Infertility Chapter 20 Objectives Discuss types of reversible contraception Natural methods Mechanical barrier methods Hormonal contraceptives Discuss types of permanent contraception
Family Planning and Infertility Chapter 20 Objectives Discuss types of reversible contraception Natural methods Mechanical barrier methods Hormonal contraceptives Discuss types of permanent contraception
CONTRACEPTION OLD FRIENDS, NEW TRENDS
 CONTRACEPTION OLD FRIENDS, NEW TRENDS AAP RECOMMENDATIONS 2014 1. Council about and ensure access to all contraceptive methods safe and appropriate describing most effective first. PEDIATRICS 134 (4)
CONTRACEPTION OLD FRIENDS, NEW TRENDS AAP RECOMMENDATIONS 2014 1. Council about and ensure access to all contraceptive methods safe and appropriate describing most effective first. PEDIATRICS 134 (4)
LARC: Disclosures. Long Acting Reversible Contraception. Objectives 10/23/2013. I have no relevant financial disclosures
 LARC: Long Acting Reversible Contraception Disclosures I have no relevant financial disclosures Jennifer Kerns, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, UCSF Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences San Francisco
LARC: Long Acting Reversible Contraception Disclosures I have no relevant financial disclosures Jennifer Kerns, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, UCSF Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences San Francisco
Notes to Teacher continued Contraceptive Considerations
 Abstinence a conscious decision to refrain from sexual intercourse 100% pregnancy will not occur if close contact between the penis and vagina does not take place. The risk of a number of STDs, including
Abstinence a conscious decision to refrain from sexual intercourse 100% pregnancy will not occur if close contact between the penis and vagina does not take place. The risk of a number of STDs, including
Disclosures. Learning Objectives 4/18/2017 ADOLESCENT CONTRACEPTION UPDATE APRIL 28, Nexplanon trainer for Merck
 ADOLESCENT CONTRACEPTION UPDATE APRIL 28, 2017 Brandy Mitchell, MN, RN, ANP BC, WHNP BC University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Obstetrics and Gynecology Iowa Association of Nurse Practitioners Spring
ADOLESCENT CONTRACEPTION UPDATE APRIL 28, 2017 Brandy Mitchell, MN, RN, ANP BC, WHNP BC University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Obstetrics and Gynecology Iowa Association of Nurse Practitioners Spring
Emergency Contraception THE FACTS
 Emergency Contraception Quick Facts What is it? Emergency contraception is birth control that you use after you have had unprotected sex--if you didn t use birth control or your regular birth control failed.
Emergency Contraception Quick Facts What is it? Emergency contraception is birth control that you use after you have had unprotected sex--if you didn t use birth control or your regular birth control failed.
Contraception and gynecological pathologies
 1 Contraception and gynecological pathologies 18 years old, 2 CMI normal First menstruation at 14 years old Irregular (every 2/3 months), painful + She does not need contraception She is worried about
1 Contraception and gynecological pathologies 18 years old, 2 CMI normal First menstruation at 14 years old Irregular (every 2/3 months), painful + She does not need contraception She is worried about
Information for Informed Consent for Insertion of a Mirena IUD
 Information for Informed Consent for Insertion of a Mirena IUD What is an IUD (intrauterine Device)? An intrauterine device (IUD) is a plastic device that is placed into your uterus to prevent pregnancy.
Information for Informed Consent for Insertion of a Mirena IUD What is an IUD (intrauterine Device)? An intrauterine device (IUD) is a plastic device that is placed into your uterus to prevent pregnancy.
Birth Control- an Overview. Keith Merritt, MD. Remember, all methods of birth control are safer and have fewer side effects than pregnancy
 Birth Control- an Overview Keith Merritt, MD Basics Remember, all methods of birth control are safer and have fewer side effects than pregnancy Even with perfect use, each method of birth control has a
Birth Control- an Overview Keith Merritt, MD Basics Remember, all methods of birth control are safer and have fewer side effects than pregnancy Even with perfect use, each method of birth control has a
Medications & Mothers Milk 2017
 See Monograph for Details Alesse, Aviane, Lessina, Levlite, Lutera, Sronyx Monophasic Ethinyl estradiol 20 mcg Levonorgestrel 0.1 mg Angeliq Monophasic Estradiol 1 mg Drospirenone 0.5 mg Approved in Europe
See Monograph for Details Alesse, Aviane, Lessina, Levlite, Lutera, Sronyx Monophasic Ethinyl estradiol 20 mcg Levonorgestrel 0.1 mg Angeliq Monophasic Estradiol 1 mg Drospirenone 0.5 mg Approved in Europe
BEST PRACTICES IN CONTRACEPTIVE COUNSELING
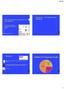 Condition Sub-condition Combined pill, patch, ring Anemias a) Thalassemia 1 1 1 1 1 2 b) Sickle cell disease 2 1 1 1 1 2 c) Iron-deficiency anemia 1 1 1 1 1 2 Benign ovarian (including cysts) 1 1 1 1 1
Condition Sub-condition Combined pill, patch, ring Anemias a) Thalassemia 1 1 1 1 1 2 b) Sickle cell disease 2 1 1 1 1 2 c) Iron-deficiency anemia 1 1 1 1 1 2 Benign ovarian (including cysts) 1 1 1 1 1
Birth Control Options Chart
 Hormonal Methods Birth control pills also known as mini-pills 91-99% A daily pill containing hormones that stops you from ovulating. There are combination estrogen or progestin-only (mini-pill) options.
Hormonal Methods Birth control pills also known as mini-pills 91-99% A daily pill containing hormones that stops you from ovulating. There are combination estrogen or progestin-only (mini-pill) options.
Prescriber and Pharmacy Guide for the Tracleer REMS Program
 Prescriber and Pharmacy Guide for the Tracleer REMS Program Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information, including BOXED WARNING for hepatotoxicity and teratogenicity. Introduction to Tracleer
Prescriber and Pharmacy Guide for the Tracleer REMS Program Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information, including BOXED WARNING for hepatotoxicity and teratogenicity. Introduction to Tracleer
U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use, 2010
 U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use, 2010 Division of Reproductive Health Centers for Disease Control and Prevention August 1, 2013 National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and
U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use, 2010 Division of Reproductive Health Centers for Disease Control and Prevention August 1, 2013 National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and
A Pharmacist s Update on the Efficacy, Safety and Role of Long-acting Reversible Contraception
 A Pharmacist s Update on the Efficacy, Safety and Role of Long-acting Reversible Contraception Shareen Y. El-Ibiary, PharmD, FCCP, BCPS Professor of Pharmacy Practice Department of Pharmacy Practice Midwestern
A Pharmacist s Update on the Efficacy, Safety and Role of Long-acting Reversible Contraception Shareen Y. El-Ibiary, PharmD, FCCP, BCPS Professor of Pharmacy Practice Department of Pharmacy Practice Midwestern
Wendy Shen, MD, PhD Refresher Course for the Family Physician April 5, 2018 Coralville, Iowa
 Wendy Shen, MD, PhD Refresher Course for the Family Physician April 5, 2018 Coralville, Iowa Objectives Distinguish the different types of IUDs Understand the mechanism of action and selection of candidates
Wendy Shen, MD, PhD Refresher Course for the Family Physician April 5, 2018 Coralville, Iowa Objectives Distinguish the different types of IUDs Understand the mechanism of action and selection of candidates
Global Contraception
 Video Companion Guide Global Contraception Learning Objectives: By the end of the session, learners will be able to: Describe of all contraceptive methods. Develop a basic understanding of patient-centered
Video Companion Guide Global Contraception Learning Objectives: By the end of the session, learners will be able to: Describe of all contraceptive methods. Develop a basic understanding of patient-centered
Learning objectives. Some fun facts. Presenter Disclosure Information. Discuss the newest contraceptive options available
 2:15 3pm Advances and Options in Female Contraception SPEAKER Pelin Batur, MD, FACP, NCMP, CCD Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Pelin Batur,
2:15 3pm Advances and Options in Female Contraception SPEAKER Pelin Batur, MD, FACP, NCMP, CCD Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Pelin Batur,
Contraception for Obese Women RENEE E. MESTAD, MD, MSCI ACOG DISTRICT II UPSTATE MEETING APRIL 29, 2016
 Contraception for Obese Women RENEE E. MESTAD, MD, MSCI ACOG DISTRICT II UPSTATE MEETING APRIL 29, 2016 Disclosure I am a Nexplanon trainer for Merck. Objectives Understand how obesity may affect pharmacokinetics
Contraception for Obese Women RENEE E. MESTAD, MD, MSCI ACOG DISTRICT II UPSTATE MEETING APRIL 29, 2016 Disclosure I am a Nexplanon trainer for Merck. Objectives Understand how obesity may affect pharmacokinetics
Learning objectives. Some fun facts. Presenter Disclosure Information. Become familiar with the newest contraceptive options available
 8:45 9:30 am Advances and Options in Female Contraception SPEAKER Pelin Batur, MD, FACP, NCMP, CCD Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Pelin
8:45 9:30 am Advances and Options in Female Contraception SPEAKER Pelin Batur, MD, FACP, NCMP, CCD Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Pelin
Prescriber Guide for the Letairis REMS Program
 LETAIRIS RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY (REMS) Prescriber Guide for the Letairis REMS Program Changes to the Letairis Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) Program (November 2018) Revised:
LETAIRIS RISK EVALUATION AND MITIGATION STRATEGY (REMS) Prescriber Guide for the Letairis REMS Program Changes to the Letairis Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) Program (November 2018) Revised:
Contraception Update: what s new in 2016? Felicity Young MA BSc (Hons) RMN RGN RM NDFSRH A08 Consultant Nurse for Sexual and Reproductive Healthcare
 Contraception Update: what s new in 2016? Felicity Young MA BSc (Hons) RMN RGN RM NDFSRH A08 Consultant Nurse for Sexual and Reproductive Healthcare Declaration of Competing Interests I have not received
Contraception Update: what s new in 2016? Felicity Young MA BSc (Hons) RMN RGN RM NDFSRH A08 Consultant Nurse for Sexual and Reproductive Healthcare Declaration of Competing Interests I have not received
Cue Cards for Counseling Adolescents on Contraception
 Cue Cards for Counseling Adolescents on Contraception About the Cue Cards This set of contraceptive counseling cue cards was developed to support a range of providers (such as facility-based providers,
Cue Cards for Counseling Adolescents on Contraception About the Cue Cards This set of contraceptive counseling cue cards was developed to support a range of providers (such as facility-based providers,
Long Acting Reversible Contraception: First Line Care for Adolescents. David A. Levine, MD, FAAP Melissa Kottke, MD, MPH, FACOG
 Long Acting Reversible Contraception: First Line Care for Adolescents David A. Levine, MD, FAAP Melissa Kottke, MD, MPH, FACOG Disclosures Melissa Kottke is a Nexplanon trainer for Merck Objectives Describe
Long Acting Reversible Contraception: First Line Care for Adolescents David A. Levine, MD, FAAP Melissa Kottke, MD, MPH, FACOG Disclosures Melissa Kottke is a Nexplanon trainer for Merck Objectives Describe
Prescriber and Pharmacy Guide for the Opsumit REMS Program
 Prescriber and Pharmacy Guide for the Opsumit REMS Program (Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy) including BOXED WARNING for teratogenicity. Risk of teratogenicity Introduction to Opsumit (macitentan)
Prescriber and Pharmacy Guide for the Opsumit REMS Program (Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy) including BOXED WARNING for teratogenicity. Risk of teratogenicity Introduction to Opsumit (macitentan)
1. Ng M et a l. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during : A systematic analysis
 1 2 3 1. Ng M et a l. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980 2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet
1 2 3 1. Ng M et a l. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980 2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet
Birth Control. Choosing the method that s right for you
 Birth Control Choosing the method that s right for you Contents Family planning services... 1 How to use this brochure... 2 Implant... 3 IUD/IUS... 5 Sterilization... 7 Depo-Provera : The shot...9 Pill/ring/patch...
Birth Control Choosing the method that s right for you Contents Family planning services... 1 How to use this brochure... 2 Implant... 3 IUD/IUS... 5 Sterilization... 7 Depo-Provera : The shot...9 Pill/ring/patch...
Chapter 7 Infertility, Contraception, and Abortion
 Chapter 7 Infertility, Contraception, and Abortion Infertility Incidence Affects about 10% to 15% of reproductive-age population Subfertility: prolonged time to conceive Sterility: inability to conceive
Chapter 7 Infertility, Contraception, and Abortion Infertility Incidence Affects about 10% to 15% of reproductive-age population Subfertility: prolonged time to conceive Sterility: inability to conceive
Unit 9 CONTRACEPTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES
 Unit 9 CONTRACEPTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Become aware of the magnitude of teen age sexual activity and pregnancy and some of the social and economic effects. 2. Learn about the various means of contraception,
Unit 9 CONTRACEPTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Become aware of the magnitude of teen age sexual activity and pregnancy and some of the social and economic effects. 2. Learn about the various means of contraception,
Welcome to Mirena. The Mirena Handbook: A Personal Guide to Your New Mirena. mirena.com. Mirena is the #1 prescribed IUD * in the U.S.
 Mirena is the #1 prescribed IUD * in the U.S. Welcome to Mirena The Mirena Handbook: A Personal Guide to Your New Mirena *Intrauterine Device Supported by 2015-2016 SHS data INDICATIONS FOR MIRENA Mirena
Mirena is the #1 prescribed IUD * in the U.S. Welcome to Mirena The Mirena Handbook: A Personal Guide to Your New Mirena *Intrauterine Device Supported by 2015-2016 SHS data INDICATIONS FOR MIRENA Mirena
One-day Essentials Contraception. Dr Paula Briggs, General Practitioner, Clinical Lead Community Sexual Health, Sefton and West Lancashire
 One-day Essentials Contraception { Dr Paula Briggs, General Practitioner, Clinical Lead Community Sexual Health, Sefton and West Lancashire 80% women access contraception from their GP Therefore it is
One-day Essentials Contraception { Dr Paula Briggs, General Practitioner, Clinical Lead Community Sexual Health, Sefton and West Lancashire 80% women access contraception from their GP Therefore it is
LONG-ACTING REVERSIBLE CONTRACEPTION. Summary Tables
 LONG-ACTING REVERSIBLE CONTRACEPTION Summary Tables Bridging the Divide: A Project of the Jacobs Institute of Women s Health June 2016 Table 1. Summary of LARC Methods Available Years Since Effective Copper
LONG-ACTING REVERSIBLE CONTRACEPTION Summary Tables Bridging the Divide: A Project of the Jacobs Institute of Women s Health June 2016 Table 1. Summary of LARC Methods Available Years Since Effective Copper
1.Abstinence no sex (Abstinence only education has been proven ineffective in preventing unwanted pregnancies)
 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Contraception 2. STDs 1. Ovary Transplants 2. Freezing Eggs 3. Choosing Gender 4. The Male Pill, parts 1&2 5. Male Birth Control: RISUG 6. Birth Control. 1.Abstinence
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Contraception 2. STDs 1. Ovary Transplants 2. Freezing Eggs 3. Choosing Gender 4. The Male Pill, parts 1&2 5. Male Birth Control: RISUG 6. Birth Control. 1.Abstinence
Package leaflet: Information for the user. Levonorgestrel 1.5 mg Tablet. levonorgestrel
 Package leaflet: Information for the user Levonorgestrel 1.5 mg Tablet levonorgestrel Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information
Package leaflet: Information for the user Levonorgestrel 1.5 mg Tablet levonorgestrel Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information
Sexual and Reproductive Health for Adolescents with Disabilities
 Wednesday, 10:00 11:30, D1 Objective: Sexual and Reproductive Health for Adolescents with Disabilities Colleen Dodich, MD Colleen.dodich@med.wmich.edu Identify effective methods for the practical application
Wednesday, 10:00 11:30, D1 Objective: Sexual and Reproductive Health for Adolescents with Disabilities Colleen Dodich, MD Colleen.dodich@med.wmich.edu Identify effective methods for the practical application
Contraception update. Gina M. Brown, M.D.
 Contraception update Gina M. Brown, M.D. IUDs cannot be used in HIV + women Women with thromboembolic disease can never use hormonal contraception Combined hormonal contraception increases blood pressure
Contraception update Gina M. Brown, M.D. IUDs cannot be used in HIV + women Women with thromboembolic disease can never use hormonal contraception Combined hormonal contraception increases blood pressure
Contraception update. Gina M. Brown, M.D.
 Contraception update Gina M. Brown, M.D. IUDs cannot be used in HIV + women Women with thromboembolic disease can never use hormonal contraception Combined hormonal contraception increases blood pressure
Contraception update Gina M. Brown, M.D. IUDs cannot be used in HIV + women Women with thromboembolic disease can never use hormonal contraception Combined hormonal contraception increases blood pressure
Complex Medical Problems? Complex Contraception. Objectives 4/17/2015. Sari Kives, MD,FRCSC ; Alene Toulany, MD, FRCPC
 Complex Medical Problems? Complex Contraception Sari Kives, MD,FRCSC ; Alene Toulany, MD, FRCPC Objectives Identify contraceptive options for an adolescent with Thrombophelia Diabetes SLE Migraines Epilepsy
Complex Medical Problems? Complex Contraception Sari Kives, MD,FRCSC ; Alene Toulany, MD, FRCPC Objectives Identify contraceptive options for an adolescent with Thrombophelia Diabetes SLE Migraines Epilepsy
PREVENTING PREGNANCY: TALKING ABOUT AND USING CONTRACEPTION
 PREVENTING PREGNANCY: TALKING ABOUT AND USING CONTRACEPTION Lesson 11 DIFFERING ABILITIES LEARNER OUTCOME Identify and describe basic types of contraceptives; i.e., abstinence, condom, foam, birth control
PREVENTING PREGNANCY: TALKING ABOUT AND USING CONTRACEPTION Lesson 11 DIFFERING ABILITIES LEARNER OUTCOME Identify and describe basic types of contraceptives; i.e., abstinence, condom, foam, birth control
Contraceptive Updates and Recommendations
 Contraceptive Updates and Recommendations Emily M. Godfrey, MD MPH Associate Professor, Departments of Family Medicine and Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Washington, Seattle WA Guest Researcher,
Contraceptive Updates and Recommendations Emily M. Godfrey, MD MPH Associate Professor, Departments of Family Medicine and Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Washington, Seattle WA Guest Researcher,
Contraceptive Updates and Recommendations
 Contraceptive Updates and Recommendations Emily M. Godfrey, MD MPH Associate Professor, Departments of Family Medicine and Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Washington, Seattle WA Guest Researcher,
Contraceptive Updates and Recommendations Emily M. Godfrey, MD MPH Associate Professor, Departments of Family Medicine and Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Washington, Seattle WA Guest Researcher,
Birth Control Methods
 Birth Control Methods This guide provides useful information to help you and your partner consider pregnancy prevention options. Options are available through the CHS Pharmacy, Women s Health Clinic, and
Birth Control Methods This guide provides useful information to help you and your partner consider pregnancy prevention options. Options are available through the CHS Pharmacy, Women s Health Clinic, and
Reproductive Health Care: Agenda. Reproductive Health Care: Reproductive Life Plans. Reproductive Life Plans: Provider Prospective
 Agenda An Integrated Approach Kimberly McClellan, MSN, WHNP-BC, CRNP Family Planning Council April 11, 2013 Primary Care Reproductive Health HIV Services Context for Integrative Services Contraceptive
Agenda An Integrated Approach Kimberly McClellan, MSN, WHNP-BC, CRNP Family Planning Council April 11, 2013 Primary Care Reproductive Health HIV Services Context for Integrative Services Contraceptive
Family Planning UNMET NEED. The Nurse Mildred Radio Talk Shows
 Family Planning UNMET NEED The Nurse Mildred Radio Talk Shows TOPIC 9: IUD/COIL Guests FP counsellor from MSU, RHU& UHMG Nurse Mildred Nurse Betty Objectives of the programme: To inform listeners about
Family Planning UNMET NEED The Nurse Mildred Radio Talk Shows TOPIC 9: IUD/COIL Guests FP counsellor from MSU, RHU& UHMG Nurse Mildred Nurse Betty Objectives of the programme: To inform listeners about
Birth Control in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease
 Birth Control in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease Arwa Saidi MB. BCh. MEd. FACC University of Florida Departments of Pediatrics and Internal Medicine Gainesville, FL There are an increasing number
Birth Control in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease Arwa Saidi MB. BCh. MEd. FACC University of Florida Departments of Pediatrics and Internal Medicine Gainesville, FL There are an increasing number
Adolescent Hot Topics: Contraception
 Adolescent Hot Topics: Contraception Dr. Stephanie Addison Holt Adolescent Medicine Objectives Discuss way to counsel the sexually active adolescent Explore the latest recommendations and updates regarding
Adolescent Hot Topics: Contraception Dr. Stephanie Addison Holt Adolescent Medicine Objectives Discuss way to counsel the sexually active adolescent Explore the latest recommendations and updates regarding
UKMEC SUMMARY TABLE HORMONAL AND INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTION
 SUMMARY TABLE SUMMARY TABLE HORMONAL AND INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTION Cu-IUD = Copper-bearing intrauterine device; LNG-IUS = Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system; IMP = Progestogen-only implant;
SUMMARY TABLE SUMMARY TABLE HORMONAL AND INTRAUTERINE CONTRACEPTION Cu-IUD = Copper-bearing intrauterine device; LNG-IUS = Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system; IMP = Progestogen-only implant;
Estrogens & Antiestrogens
 Estrogens & Antiestrogens Menstrual cycle... Changes and hormonal events Natural estrogens: Estadiol >> Estrone > Estriol Ineffective orally Synthesis: From cholesterol ; role of aromatase enzyme in converting
Estrogens & Antiestrogens Menstrual cycle... Changes and hormonal events Natural estrogens: Estadiol >> Estrone > Estriol Ineffective orally Synthesis: From cholesterol ; role of aromatase enzyme in converting
Can you imagine reversible birth control that s more than 99% effective and 100% hormone free, too?
 Can you imagine reversible birth control that s more than 99% effective and 100% hormone free, too? BIRTH CONTROL THAT FITS YOUR LIFE, NATURALLY. ParaGard is a registered trademark of Teva Women s Health,
Can you imagine reversible birth control that s more than 99% effective and 100% hormone free, too? BIRTH CONTROL THAT FITS YOUR LIFE, NATURALLY. ParaGard is a registered trademark of Teva Women s Health,
Contraceptive case studies. Dr Christine Roke National Medical Advisor Family Planning June 2015
 Contraceptive case studies Dr Christine Roke National Medical Advisor Family Planning June 2015 Case 1 Mary is a 47 year old who has come in for a routine cervical smear. She asks when her Multiload IUD
Contraceptive case studies Dr Christine Roke National Medical Advisor Family Planning June 2015 Case 1 Mary is a 47 year old who has come in for a routine cervical smear. She asks when her Multiload IUD
Hormonal Treatment of Acne and Hirsutism. Julie C Harper MD
 Hormonal Treatment of Acne and Hirsutism Julie C Harper MD none Conflict of Interest Androgen blockade Decrease androgen production by the gonads or adrenal gland Decrease circulating free testosterone
Hormonal Treatment of Acne and Hirsutism Julie C Harper MD none Conflict of Interest Androgen blockade Decrease androgen production by the gonads or adrenal gland Decrease circulating free testosterone
LARC. sample. ask brook about. Are any of them right for me? How effective is it? How long does it last? long acting reversible contraception
 72888_LARC:Layout 1 9/11/09 11:47 Page 1 Are any of them right for me? ask brook about LARC How effective is it? long acting reversible contraception How long does it last? 72888_LARC:Layout 1 9/11/09
72888_LARC:Layout 1 9/11/09 11:47 Page 1 Are any of them right for me? ask brook about LARC How effective is it? long acting reversible contraception How long does it last? 72888_LARC:Layout 1 9/11/09
Contraception for Women and Couples with HIV. Knowledge Test
 Contraception for Women and Couples with HIV Knowledge Test Instructions: For each question below, check/tick all responses that apply. 1. Which statements accurately describe the impact of HIV/AIDS in
Contraception for Women and Couples with HIV Knowledge Test Instructions: For each question below, check/tick all responses that apply. 1. Which statements accurately describe the impact of HIV/AIDS in
Guidance for Pharmacists on the Safe Supply of Non-Prescription Levonorgestrel 1500mcg for Emergency Hormonal Contraception
 Guidance for Pharmacists on the Safe Supply of Non-Prescription Levonorgestrel 1500mcg for Emergency Hormonal Contraception Pharmaceutical Society of Ireland Version 4 December 2016 Updates made following
Guidance for Pharmacists on the Safe Supply of Non-Prescription Levonorgestrel 1500mcg for Emergency Hormonal Contraception Pharmaceutical Society of Ireland Version 4 December 2016 Updates made following
Family Planning د. نجمه محمود كلية الطب جامعة بغداد فرع النسائية والتوليد
 Family Planning د. نجمه محمود كلية الطب جامعة بغداد فرع النسائية والتوليد Objectives:- To know the different types of contraception To know the failure rate & mechansim of action of each type To explain
Family Planning د. نجمه محمود كلية الطب جامعة بغداد فرع النسائية والتوليد Objectives:- To know the different types of contraception To know the failure rate & mechansim of action of each type To explain
CODING GUIDELINES FOR CONTRACEPTIVES. Effective June 1, 2017 Version 1.40
 CODING GUIDELINES FOR CONTRACEPTIVES Effective June 1, 2017 Version 1.40 TABLE OF CONTENTS ICD-10 CM Diagnosis Codes: Encounter for Contraception page 2 Coding for IUD Insertion and Removal Procedures
CODING GUIDELINES FOR CONTRACEPTIVES Effective June 1, 2017 Version 1.40 TABLE OF CONTENTS ICD-10 CM Diagnosis Codes: Encounter for Contraception page 2 Coding for IUD Insertion and Removal Procedures
International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Nano Sciences Journal homepage:
 Review Article ISSN: 2319 9563 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Nano Sciences Journal homepage: www.ijrpns.com A REVIEW ON INTRAUTERINE DEVICES Boddu Venkata Komali* 1, M. Kalyani
Review Article ISSN: 2319 9563 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Nano Sciences Journal homepage: www.ijrpns.com A REVIEW ON INTRAUTERINE DEVICES Boddu Venkata Komali* 1, M. Kalyani
Contraception in the medically complicated patient
 Contraception in the medically complicated patient Sarita Sonalkar, MD MPH Assistant Professor Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Pennsylvania Disclosures } Consultant for World Health
Contraception in the medically complicated patient Sarita Sonalkar, MD MPH Assistant Professor Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Pennsylvania Disclosures } Consultant for World Health
Discover the birth control you ve been looking for. Highly reliable. Virtually hassle-free. Totally hormone-free.
 Discover the birth control you ve been looking for Highly reliable. Virtually hassle-free. Totally hormone-free. Over 70 million women worldwide use a nonhormonal IUC like ParaGard. Millions of women with
Discover the birth control you ve been looking for Highly reliable. Virtually hassle-free. Totally hormone-free. Over 70 million women worldwide use a nonhormonal IUC like ParaGard. Millions of women with
Management of Emergency Contraception (EC)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Management of Emergency Contraception (EC) The risks and benefits of an IUD or oral EC should be discussed and documented (see appendix). Reasonable measures
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Management of Emergency Contraception (EC) The risks and benefits of an IUD or oral EC should be discussed and documented (see appendix). Reasonable measures
Breast Cancer Risk in Patients Using Hormonal Contraception
 Breast Cancer Risk in Patients Using Hormonal Contraception Bradley L. Smith, Pharm.D. Smith.bradley1@mayo.edu Pharmacy Ground Rounds Mayo Clinic Rochester April 3 rd, 2018 2017 MFMER slide-1 Presentation
Breast Cancer Risk in Patients Using Hormonal Contraception Bradley L. Smith, Pharm.D. Smith.bradley1@mayo.edu Pharmacy Ground Rounds Mayo Clinic Rochester April 3 rd, 2018 2017 MFMER slide-1 Presentation
Application for inclusion of levonorgestrel - releasing IUD for contraception in the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines
 Application for inclusion of levonorgestrel - releasing IUD for contraception in the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines 1. Summary statement of the proposal for inclusion LNG-IUS is an effective contraceptive;
Application for inclusion of levonorgestrel - releasing IUD for contraception in the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines 1. Summary statement of the proposal for inclusion LNG-IUS is an effective contraceptive;
New Zealand Datasheet
 New Zealand Datasheet 1 PRODUCT NAME POSTINOR-1 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Levonorgestrel 1.5 mg 3 PHARMACEUTICAL FORM Each round white tablet contains 1.5 mg of levonorgestrel. The tablet
New Zealand Datasheet 1 PRODUCT NAME POSTINOR-1 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Levonorgestrel 1.5 mg 3 PHARMACEUTICAL FORM Each round white tablet contains 1.5 mg of levonorgestrel. The tablet
the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD your guide to
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that s best for you IUD IUD the e IUD IU IUD the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that s put
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that s best for you IUD IUD the e IUD IU IUD the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that s put
Day of Learning: Current Best Practices for Contraceptive Provision
 Day of Learning: Current Best Practices for Contraceptive Provision Thank you to our Sponsors Carnegie Science Center Jewish Healthcare Foundation Allegheny Health Network s Center for Inclusion Health
Day of Learning: Current Best Practices for Contraceptive Provision Thank you to our Sponsors Carnegie Science Center Jewish Healthcare Foundation Allegheny Health Network s Center for Inclusion Health
The Balanced Counseling Strategy Plus: A Toolkit for Family Planning Service Providers Working in High STI/HIV Prevalence Settings.
 The Balanced Counseling Strategy Plus: A Toolkit for Family Planning Service Providers Working in High STI/HIV Prevalence Settings Counseling Cards Checklist to be reasonably sure a woman is not pregnant
The Balanced Counseling Strategy Plus: A Toolkit for Family Planning Service Providers Working in High STI/HIV Prevalence Settings Counseling Cards Checklist to be reasonably sure a woman is not pregnant
VCHIP LARC Needs Assessment Survey
 VCHIP LARC Needs Assessment Survey Demographics 1. How many have you been in practice (post-training)? Choose one of the following answers 0-5 6-10 11-15 16-20 21 or more 2. What are your professional
VCHIP LARC Needs Assessment Survey Demographics 1. How many have you been in practice (post-training)? Choose one of the following answers 0-5 6-10 11-15 16-20 21 or more 2. What are your professional
2
 1 2 3 1. Usinger KM et al. Intrauterine contraception continuation in adolescents and young women: a systematic review. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2016; 29: 659 67. 2. Kost K et al. Estimates of contraceptive
1 2 3 1. Usinger KM et al. Intrauterine contraception continuation in adolescents and young women: a systematic review. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2016; 29: 659 67. 2. Kost K et al. Estimates of contraceptive
