Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu
|
|
|
- Stanley Patterson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary Figure 1 Peak distribution of Na v 1.6 at the distal AIS. (a c) Double stainings for AnkG (red) and Na v 1.6 (green) in thick sections (100 μm). Note the peak distribution (arrows) of Na v 1.6 at the distal AIS. Arrow heads indicate the root of the axon hillock. Scale bar: 10 μm. Images were projections of confocal z-stacks. (d) Plot of the normalized fluorescence intensity as a function of distance from the soma (mean ± s.e.m., n = 7). 1
2 Supplementary Figure 2 Dependence of the activation curve slope on the amplitude of Na + current. (a) The slope of the activation curve for Na + currents in control (open, mean ± s.e.m., n = 8), with TTX (gray, n = 8) and in low-na + ACSF (black, n = 9). No statistical difference was found between the slope with TTX and that in low-na + ACSF (P = 0.92). **, P < (b) A plot of the slope as a function of peak Na + current revealed the dependence of activation slope on current amplitude. Data was obtained from the experiments shown in a (color coded). Solid line, single exponential fit. Supplementary Figure 3 Activation and inactivation curves for Na + channels implemented in the simulations. Green traces, Na v 1.2 (nasoma). Blue traces, Na v 1.6 (naaxon). Experimental data is shown for comparison (black symbols, data from somatic patches; red symbols, data from patches obtained from axon regions distal to the AIS, > 70 μm from the soma). 2
3 Supplementary Figure 4 Contribution of the proximal AIS Na v 1.2 channels in action potential backpropagation to the soma (simulations). (a) With the presence of Na v 1.2 channels at the proximal AIS, action potential backpropagation was dependent of the V m levels. (b) Removal of Na v 1.2 channels from the proximal AIS caused a decrease in the amplitude of the spikelets and a complete failure of the action potential backpropagation. Action potentials were evoked through current injection at the axon (see Supplementary Fig. 8). 3
4 Supplementary Figure 5 Differential contributions of perisomatic and distal AIS Na + channels to somatic action potentials. (a) Top, schematic graph showing whole-cell recording while puffing TTX locally at the soma. Bottom, action potentials evoked before (black) and after TTX application (red, early; blue, late). Arrow indicates the thresholds of action potentials. (b) Phase plots of the action potentials shown in a. Notice that the high-threshold component (somatodendritic potential) of the action potential was dramatically reduced after the TTX application, while the low-threshold component (AIS potential) was largely preserved. Inset: the rising phase was expanded for clarity. (c) Same as in a except that TTX puffing was made at the distal portion of the AIS. Note that the voltage threshold was increased and the rising phase was less steep after the TTX application. (d) Phase plots of the action potentials shown in c. The AIS potential was eliminated by TTX, while the somatodendritic potential was preserved. Inset: the rising phase was expanded for clarity. 4
5 Supplementary Figure 6 Light staining of AnkG in the axon bleb. (a1 a3) Double stainings for AnkG (red) and Na v 1.6 (green) in prefrontal cortical slices (thickness of 300 μm). Arrows indicate the root of the axon hillock. (b1 b3) Higher magnification of the area in the box shown in left panels. Note that the fluorescence intensity of Na v 1.6 in the bleb membrane is similar to that in the nearby axon trunk. The proximal AIS is not stained for Na v 1.6. Scale bar: 10 μm. 5
6 Supplementary Figure 7 Non-uniform distribution of Na v 1.6 channels at the AIS of layer 5 pyramidal neurons in somatosensory cortex. (a1 a3) Double stainings for AnkG (red) and Na v 1.6 (green). Note that the distal portion of the AIS was heavily stained for Na v 1.6. Arrow heads indicate the root of the axon hillock. (b1 b3) Another example shows that both thick and thin axons exhibit a proximal-distal gradient of immunoreactivity for Na v 1.6 at the AIS. Scale bar: 10 μm. 6
7 Supplementary Figure 8 Schematic diagram of the simulation on action potential backpropagation. Action potential was evoked by stimulating the axon with current injection. Action potential backpropagation failure occurred when the somatic V m was set equal to or lower (more negative) than the failure threshold. 7
Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon?
 Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale
 Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale (b) show stronger immunolabeling for CB 1 than those in
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale (b) show stronger immunolabeling for CB 1 than those in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
Short- and long-lasting consequences of in vivo nicotine treatment
 Short- and long-lasting consequences of in vivo nicotine treatment on hippocampal excitability Rachel E. Penton, Michael W. Quick, Robin A. J. Lester Supplementary Figure 1. Histogram showing the maximal
Short- and long-lasting consequences of in vivo nicotine treatment on hippocampal excitability Rachel E. Penton, Michael W. Quick, Robin A. J. Lester Supplementary Figure 1. Histogram showing the maximal
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC
 1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses
 Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the
 Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the upper cortical layers at P3 4 in vivo. (a b) Cell-attached current-clamp recordings illustrate responses to puff-applied
Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the upper cortical layers at P3 4 in vivo. (a b) Cell-attached current-clamp recordings illustrate responses to puff-applied
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 SNARE Probes for FRET/2pFLIM Analysis Used in the Present Study. mturquoise (mtq) and Venus (Ven) are in blue and yellow, respectively. The soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 SNARE Probes for FRET/2pFLIM Analysis Used in the Present Study. mturquoise (mtq) and Venus (Ven) are in blue and yellow, respectively. The soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a)
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes. (a) Left, circuit schematic with the imaged component (L2/3 excitatory neurons)
Supplementary Figure 1 Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes. (a) Left, circuit schematic with the imaged component (L2/3 excitatory neurons)
Axon Initial Segment Kv1 Channels Control Axonal Action Potential Waveform and Synaptic Efficacy
 Article Axon Initial Segment Kv1 Channels Control Axonal Action Potential Waveform and Synaptic Efficacy Maarten H.P. Kole, 1,2 Johannes J. Letzkus, 1,2 and Greg J. Stuart 1, * 1 Division of Neuroscience,
Article Axon Initial Segment Kv1 Channels Control Axonal Action Potential Waveform and Synaptic Efficacy Maarten H.P. Kole, 1,2 Johannes J. Letzkus, 1,2 and Greg J. Stuart 1, * 1 Division of Neuroscience,
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
Fig. S4. Current-voltage relations of iglurs. A-C: time courses of currents evoked by 100 ms pulses
 Fig. S1. Immunohistochemical detection of iglur2 protein in single islet cells. A: α cells identified using glucagon-specific antibody express the iglur2 subtype of AMPA receptor. 24 out of 26 identified
Fig. S1. Immunohistochemical detection of iglur2 protein in single islet cells. A: α cells identified using glucagon-specific antibody express the iglur2 subtype of AMPA receptor. 24 out of 26 identified
Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell
 2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Trial structure for go/no-go behavior
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Title: Plasticity of intrinsic excitability in mature granule cells of the dentate gyrus
 Title: Plasticity of intrinsic excitability in mature granule cells of the dentate gyrus Authors: Jeffrey Lopez-Rojas a1, Martin Heine b1 and Michael R. Kreutz ac1 a Research Group Neuroplasticity, b Research
Title: Plasticity of intrinsic excitability in mature granule cells of the dentate gyrus Authors: Jeffrey Lopez-Rojas a1, Martin Heine b1 and Michael R. Kreutz ac1 a Research Group Neuroplasticity, b Research
Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Information
 Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels inhibit EPSPs by interactions with M-type K + channels Meena S. George, L.F. Abbott, Steven A. Siegelbaum Supplementary Information Part 1: Supplementary Figures
Hyperpolarization-activated cation channels inhibit EPSPs by interactions with M-type K + channels Meena S. George, L.F. Abbott, Steven A. Siegelbaum Supplementary Information Part 1: Supplementary Figures
Supplementary Information. Errors in the measurement of voltage activated ion channels. in cell attached patch clamp recordings
 Supplementary Information Errors in the measurement of voltage activated ion channels in cell attached patch clamp recordings Stephen R. Williams 1,2 and Christian Wozny 2 1 Queensland Brain Institute,
Supplementary Information Errors in the measurement of voltage activated ion channels in cell attached patch clamp recordings Stephen R. Williams 1,2 and Christian Wozny 2 1 Queensland Brain Institute,
Supporting Information
 ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
ATP from synaptic terminals and astrocytes regulates NMDA receptors and synaptic plasticity through PSD- 95 multi- protein complex U.Lalo, O.Palygin, A.Verkhratsky, S.G.N. Grant and Y. Pankratov Supporting
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
Dep. Control Time (min)
 aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
aa Control Dep. RP 1s 1 mv 2s 1 mv b % potentiation of IPSP 2 15 1 5 Dep. * 1 2 3 4 Time (min) Supplementary Figure 1. Rebound potentiation of IPSPs in PCs. a, IPSPs recorded with a K + gluconate pipette
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
SOMATO-DENDRITIC INTERACTIONS UNDERLYING ACTION POTENTIAL GENERATION IN NEOCORTICAL PYRAMIDAL CELLS
 167 SOATO-ENRITIC INTERACTIONS UNERLYING ACTION POTENTIAL GENERATION IN NEOCORTICAL PYRAIAL CELLS IN VIVO Alain estexhe, 1 Eric J. Lang 2 and enis Pare 1 1 Laboratoire de Neurophysiologie, Universite Laval,
167 SOATO-ENRITIC INTERACTIONS UNERLYING ACTION POTENTIAL GENERATION IN NEOCORTICAL PYRAIAL CELLS IN VIVO Alain estexhe, 1 Eric J. Lang 2 and enis Pare 1 1 Laboratoire de Neurophysiologie, Universite Laval,
Supplementary Table I Blood pressure and heart rate measurements pre- and post-stroke
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09511 Supplementary Table I Blood pressure and heart rate measurements pre- and post-stroke Pre Post 7-days Systolic Diastolic BPM Systolic Diastolic BPM Systolic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09511 Supplementary Table I Blood pressure and heart rate measurements pre- and post-stroke Pre Post 7-days Systolic Diastolic BPM Systolic Diastolic BPM Systolic
Behavioral generalization
 Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral generalization. a. Behavioral generalization curves in four Individual sessions. Shown is the conditioned response (CR, mean ± SEM), as a function of absolute (main) or
Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral generalization. a. Behavioral generalization curves in four Individual sessions. Shown is the conditioned response (CR, mean ± SEM), as a function of absolute (main) or
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex
 Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity
 Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements
 Y. Isomura et al. 1 Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements Yoshikazu Isomura, Rie Harukuni, Takashi Takekawa, Hidenori Aizawa & Tomoki Fukai
Y. Isomura et al. 1 Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements Yoshikazu Isomura, Rie Harukuni, Takashi Takekawa, Hidenori Aizawa & Tomoki Fukai
Learning Rules for Spike Timing-Dependent Plasticity Depend on Dendritic Synapse Location
 10420 The Journal of Neuroscience, October 11, 2006 26(41):10420 10429 Cellular/Molecular Learning Rules for Spike Timing-Dependent Plasticity Depend on Dendritic Synapse Location Johannes J. Letzkus,
10420 The Journal of Neuroscience, October 11, 2006 26(41):10420 10429 Cellular/Molecular Learning Rules for Spike Timing-Dependent Plasticity Depend on Dendritic Synapse Location Johannes J. Letzkus,
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) 108 (b-c) (d) (e) (f) (g)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Nature Neuroscience doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of viral injections.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Action potential initiation and propagation in rat neocortical pyramidal neurons
 Keywords: Action potential, Cerebral cortex, Dendrite 6798 Journal of Physiology (1997), 505.3, pp. 617 632 617 Action potential initiation and propagation in rat neocortical pyramidal neurons Greg Stuart
Keywords: Action potential, Cerebral cortex, Dendrite 6798 Journal of Physiology (1997), 505.3, pp. 617 632 617 Action potential initiation and propagation in rat neocortical pyramidal neurons Greg Stuart
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral training.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
-51mV 30s 3mV. n=14 n=4 p=0.4. Depolarization (mv) 3
 Supplementary Figure 1 a optoβ 2 -AR b ChR2-51mV 30s 3mV -50mV 30s 3mV c 4 n=14 n=4 p=0.4 Depolarization (mv) 3 2 1 0 Both optogenetic actuators, optoβ 2 AR and ChR2, were effective in stimulating astrocytes
Supplementary Figure 1 a optoβ 2 -AR b ChR2-51mV 30s 3mV -50mV 30s 3mV c 4 n=14 n=4 p=0.4 Depolarization (mv) 3 2 1 0 Both optogenetic actuators, optoβ 2 AR and ChR2, were effective in stimulating astrocytes
Reward prediction based on stimulus categorization in. primate lateral prefrontal cortex
 Reward prediction based on stimulus categorization in primate lateral prefrontal cortex Xiaochuan Pan, Kosuke Sawa, Ichiro Tsuda, Minoro Tsukada, Masamichi Sakagami Supplementary Information This PDF file
Reward prediction based on stimulus categorization in primate lateral prefrontal cortex Xiaochuan Pan, Kosuke Sawa, Ichiro Tsuda, Minoro Tsukada, Masamichi Sakagami Supplementary Information This PDF file
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields.
 Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
mm Distance (mm)
 b a Magnet Illumination Coverslips MPs Objective 2575 µm 1875 µm 1575 µm 1075 µm 875 µm 545 µm 20µm 2 3 0.5 0.3mm 1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 Field Induction (Gauss) 1.5 0 5 10 15 20 Distance
b a Magnet Illumination Coverslips MPs Objective 2575 µm 1875 µm 1575 µm 1075 µm 875 µm 545 µm 20µm 2 3 0.5 0.3mm 1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 1000 100 10 1 0.1 Field Induction (Gauss) 1.5 0 5 10 15 20 Distance
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Supplementary Figure 1 Neuron class-specific arrangements of Khc::nod::lacZ label in dendrites. Staining with fluorescence antibodies to detect GFP (Green), β-galactosidase (magenta/white). (a, b) Class
Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components.
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL for Cardoso et al. 22 The Neuroimaging Signal is a Linear Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components. : Appendix: Homogeneous Linear ( Null ) and Modified Linear
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL for Cardoso et al. 22 The Neuroimaging Signal is a Linear Sum of Neurally Distinct Stimulus- and Task-Related Components. : Appendix: Homogeneous Linear ( Null ) and Modified Linear
Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4547
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of the Microfetti mouse model. (a) Gating strategy for 8-color flow analysis of peripheral Ly-6C + monocytes from Microfetti mice 5-7 days after TAM treatment. Living
Supplemental information Acid-sensing ion channel 1a contributes to hippocampal LTP inducibility through multiple mechanisms
 Supplemental information Acid-sensing ion channel 1a contributes to hippocampal LTP inducibility through multiple mechanisms Ming-Gang Liu, Hu-Song Li, Wei-Guang Li, Yan-Jiao Wu, Shi-Ning Deng, Chen Huang,
Supplemental information Acid-sensing ion channel 1a contributes to hippocampal LTP inducibility through multiple mechanisms Ming-Gang Liu, Hu-Song Li, Wei-Guang Li, Yan-Jiao Wu, Shi-Ning Deng, Chen Huang,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information D-Serine regulates cerebellar LTD and motor coordination through the 2 glutamate receptor Wataru Kakegawa, Yurika Miyoshi, Kenji Hamase, Shinji Matsuda, Keiko Matsuda, Kazuhisa
Supplementary Information D-Serine regulates cerebellar LTD and motor coordination through the 2 glutamate receptor Wataru Kakegawa, Yurika Miyoshi, Kenji Hamase, Shinji Matsuda, Keiko Matsuda, Kazuhisa
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Supplementary Figure 1 Drd1a-Cre driven ChR2 expression in the SCN. (a) Low-magnification image of a representative Drd1a-ChR2 coronal brain section (n = 2) showing endogenous tdtomato fluorescence (magenta).
Simulating inputs of parvalbumin inhibitory interneurons onto excitatory pyramidal cells in piriform cortex
 Simulating inputs of parvalbumin inhibitory interneurons onto excitatory pyramidal cells in piriform cortex Jeffrey E. Dahlen jdahlen@ucsd.edu and Kerin K. Higa khiga@ucsd.edu Department of Neuroscience
Simulating inputs of parvalbumin inhibitory interneurons onto excitatory pyramidal cells in piriform cortex Jeffrey E. Dahlen jdahlen@ucsd.edu and Kerin K. Higa khiga@ucsd.edu Department of Neuroscience
Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0150-0 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent homeostasis Michelle C.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0150-0 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Two distinct mechanisms for experiencedependent homeostasis Michelle C.
Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers
 Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers Paul Feyen 1,, Elisabetta Colombo 1,2,, Duco Endeman 1, Mattia Nova 1, Lucia Laudato 2, Nicola Martino 2,3, Maria Rosa Antognazza
Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers Paul Feyen 1,, Elisabetta Colombo 1,2,, Duco Endeman 1, Mattia Nova 1, Lucia Laudato 2, Nicola Martino 2,3, Maria Rosa Antognazza
A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes
 A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes 1 Eiji Shigetomi, 1 Sebastian Kracun, 2 Michael V. Sofroniew & 1,2 *Baljit S. Khakh Ψ 1 Departments of Physiology
A genetically targeted optical sensor to monitor calcium signals in astrocyte processes 1 Eiji Shigetomi, 1 Sebastian Kracun, 2 Michael V. Sofroniew & 1,2 *Baljit S. Khakh Ψ 1 Departments of Physiology
Calcium Store Depletion Induces Persistent Perisomatic Increases in the Functional Density of h Channels in Hippocampal Pyramidal Neurons
 Article Calcium Store Depletion Induces Persistent Perisomatic Increases in the Functional Density of h Channels in Hippocampal Pyramidal Neurons Rishikesh Narayanan, 1,2 Kevin J. Dougherty, 1 and Daniel
Article Calcium Store Depletion Induces Persistent Perisomatic Increases in the Functional Density of h Channels in Hippocampal Pyramidal Neurons Rishikesh Narayanan, 1,2 Kevin J. Dougherty, 1 and Daniel
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Global TeNT expression effectively impairs synaptic transmission. Injection of 100 pg tent mrna leads to a reduction of vesicle mediated synaptic transmission in the spinal cord
Supplementary Figure 1 Global TeNT expression effectively impairs synaptic transmission. Injection of 100 pg tent mrna leads to a reduction of vesicle mediated synaptic transmission in the spinal cord
Supplementary Figure 1. SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.
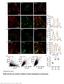 Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) .
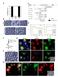 Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
Supplementary Figure 1. Properties of various IZUMO1 monoclonal antibodies and behavior of SPACA6. (a) The inhibitory effects of new antibodies (Mab17 and Mab18). They were investigated in in vitro fertilization
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of hair bundle morphology in Ush1c c.216g>a mice at P18 by SEM. (a-c) Heterozygous c.216ga mice displayed normal hair bundle morphology at P18. (d-i) Disorganized hair bundles
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Regulation of Neuronal Input Transformations by Tunable Dendritic Inhibition Matthew Lovett-Barron 1, Gergely F. Turi 1, Patrick Kaifosh 1, Peter H. Lee 2, Frédéric Bolze 3, Xiao-Hua
Supplementary Information Regulation of Neuronal Input Transformations by Tunable Dendritic Inhibition Matthew Lovett-Barron 1, Gergely F. Turi 1, Patrick Kaifosh 1, Peter H. Lee 2, Frédéric Bolze 3, Xiao-Hua
Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex
 Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Part 11: Mechanisms of Learning
 Neurophysiology and Information: Theory of Brain Function Christopher Fiorillo BiS 527, Spring 2012 042 350 4326, fiorillo@kaist.ac.kr Part 11: Mechanisms of Learning Reading: Bear, Connors, and Paradiso,
Neurophysiology and Information: Theory of Brain Function Christopher Fiorillo BiS 527, Spring 2012 042 350 4326, fiorillo@kaist.ac.kr Part 11: Mechanisms of Learning Reading: Bear, Connors, and Paradiso,
P/Q And N Channels Control Baseline and Spike-Triggered Calcium Levels in Neocortical Axons And Synaptic Boutons
 P/Q And N Channels Control Baseline and Spike-Triggered Calcium Levels in Neocortical Axons And Synaptic Boutons Yuguo Yu, Carlos Maureira, Xiuxin Liu and David McCormick Supplemental Figures 1-9 1 Figure
P/Q And N Channels Control Baseline and Spike-Triggered Calcium Levels in Neocortical Axons And Synaptic Boutons Yuguo Yu, Carlos Maureira, Xiuxin Liu and David McCormick Supplemental Figures 1-9 1 Figure
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task. Trial-averaged lick rate was averaged across all mice used for pyramidal cell imaging (n = 9). Different colors denote different
Supplementary Figure 1 Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task. Trial-averaged lick rate was averaged across all mice used for pyramidal cell imaging (n = 9). Different colors denote different
Supralinear increase of recurrent inhibition during sparse activity in the somatosensory cortex
 Supralinear increase of recurrent inhibition during sparse activity in the somatosensory cortex Christoph Kapfer 1,2, Lindsey L Glickfeld 1,3, Bassam V Atallah 1,3 & Massimo Scanziani 1 The balance between
Supralinear increase of recurrent inhibition during sparse activity in the somatosensory cortex Christoph Kapfer 1,2, Lindsey L Glickfeld 1,3, Bassam V Atallah 1,3 & Massimo Scanziani 1 The balance between
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice
 Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice (a) Sample behavioral trace as in Figure 1d, but with NpHR stimulation trials depicted as green blocks
Supplementary Figure 1 Confirmation that optogenetic inhibition of dopaminergic neurons affects choice (a) Sample behavioral trace as in Figure 1d, but with NpHR stimulation trials depicted as green blocks
J. Cell Sci. 129: doi: /jcs : Supplementary information
 Movie 1. AgLDL is contained in small sub-regions of the lysosomal synapse that are acidic. J774 cells were incubated with agldl dual labeled with a ph sensitive and a ph insensitive fluorophore for 1 hr.
Movie 1. AgLDL is contained in small sub-regions of the lysosomal synapse that are acidic. J774 cells were incubated with agldl dual labeled with a ph sensitive and a ph insensitive fluorophore for 1 hr.
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord
 What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
1.0. FSL NMDAR-fEPSP 0.8. amplitude (mv) Intensity (µa) 2.0 SD FSL Time (ms)
 a 2.5 1. AMPAR-fEPSP slope (mv/ms) 2. 1. NMDAR-fEPSP amplitude (mv).8.6.4.5.2. 2 4 6 8. 1 2 3 4 5 Intensity (µa) Intensity (µa) b 2. PPF Ratio (fepsp2/fepsp1) 1..5. 5 1 2 5 Time (ms) Supplementary Figure
a 2.5 1. AMPAR-fEPSP slope (mv/ms) 2. 1. NMDAR-fEPSP amplitude (mv).8.6.4.5.2. 2 4 6 8. 1 2 3 4 5 Intensity (µa) Intensity (µa) b 2. PPF Ratio (fepsp2/fepsp1) 1..5. 5 1 2 5 Time (ms) Supplementary Figure
Social deficits in Shank3-deficient mouse models of autism are rescued by histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0110-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social deficits in Shank3-deficient mouse models of autism are rescued by
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0110-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Social deficits in Shank3-deficient mouse models of autism are rescued by
Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell
 Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell Garcia-Alvarez et al. Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1.Expression and RNAi-mediated silencing of STIM1 in hippocampal neurons (DIV, days in vitro).
Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell Garcia-Alvarez et al. Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1.Expression and RNAi-mediated silencing of STIM1 in hippocampal neurons (DIV, days in vitro).
Matthew E. Larkum 1 and J. Julius Zhu 1,2,3
 The Journal of Neuroscience, August 15, 2002, 22(16):6991 7005 Signaling of Layer 1 and Whisker-Evoked Ca 2 and Na Action Potentials in Distal and Terminal Dendrites of Rat Neocortical Pyramidal Neurons
The Journal of Neuroscience, August 15, 2002, 22(16):6991 7005 Signaling of Layer 1 and Whisker-Evoked Ca 2 and Na Action Potentials in Distal and Terminal Dendrites of Rat Neocortical Pyramidal Neurons
Supplemental Information. A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit. for Place Navigation
 Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Authors: K. L. Arendt, M. Royo, M. Fernández-Monreal, S. Knafo, C. N. Petrok, J.
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Title: PIP 3 controls synaptic function by maintaining AMPA receptor clustering at the postsynaptic membrane Authors: K. L. Arendt, M. Royo, M. Fernández-Monreal, S. Knafo, C.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Title: PIP 3 controls synaptic function by maintaining AMPA receptor clustering at the postsynaptic membrane Authors: K. L. Arendt, M. Royo, M. Fernández-Monreal, S. Knafo, C.
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
Cellular/Molecular. The Journal of Neuroscience, February 21, (8):
 The Journal of Neuroscience, February 21, 2007 27(8):1853 1867 1853 Cellular/Molecular M-Channels (Kv7/KCNQ Channels) That Regulate Synaptic Integration, Excitability, and Spike Pattern of CA1 Pyramidal
The Journal of Neuroscience, February 21, 2007 27(8):1853 1867 1853 Cellular/Molecular M-Channels (Kv7/KCNQ Channels) That Regulate Synaptic Integration, Excitability, and Spike Pattern of CA1 Pyramidal
Supplementary Materials for VAMP4 directs synaptic vesicles to a pool that selectively maintains asynchronous neurotransmission
 Supplementary Materials for VAMP4 directs synaptic vesicles to a pool that selectively maintains asynchronous neurotransmission Jesica Raingo, Mikhail Khvotchev, Pei Liu, Frederic Darios, Ying C. Li, Denise
Supplementary Materials for VAMP4 directs synaptic vesicles to a pool that selectively maintains asynchronous neurotransmission Jesica Raingo, Mikhail Khvotchev, Pei Liu, Frederic Darios, Ying C. Li, Denise
Spatiotemporally Graded NMDA Spike/Plateau Potentials in Basal Dendrites of Neocortical Pyramidal Neurons
 J Neurophysiol 99: 2584 261, 28. First published March 12, 28; doi:1.1152/jn.11.28. Spatiotemporally Graded NMDA Spike/Plateau Potentials in Basal Dendrites of Neocortical Pyramidal Neurons Guy Major,
J Neurophysiol 99: 2584 261, 28. First published March 12, 28; doi:1.1152/jn.11.28. Spatiotemporally Graded NMDA Spike/Plateau Potentials in Basal Dendrites of Neocortical Pyramidal Neurons Guy Major,
Specimen. Humeral Head. Femoral Head. Objective. Femoral Condyle (medial) Supplementary Figure 1
 A B Specimen Humeral Head 2 1 µm 76 µm Femoral Head Objective Femoral Condyle (medial) Supplementary Figure 1 A Femoral Head Global Cell Density Superficial Cell Density Cell Number at 1 µm Nuclei /.1
A B Specimen Humeral Head 2 1 µm 76 µm Femoral Head Objective Femoral Condyle (medial) Supplementary Figure 1 A Femoral Head Global Cell Density Superficial Cell Density Cell Number at 1 µm Nuclei /.1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
Predictive Features of Persistent Activity Emergence in Regular Spiking and Intrinsic Bursting Model Neurons
 Emergence in Regular Spiking and Intrinsic Bursting Model Neurons Kyriaki Sidiropoulou, Panayiota Poirazi* Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology (IMBB), Foundation for Research and Technology-Hellas
Emergence in Regular Spiking and Intrinsic Bursting Model Neurons Kyriaki Sidiropoulou, Panayiota Poirazi* Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology (IMBB), Foundation for Research and Technology-Hellas
Supplementary Figure 1: Validation of labeling specificity of immature OSNs and presynaptic terminals. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
 Supplementary Figure 1: Validation of labeling specificity of immature OSNs and presynaptic terminals. (A) Confocal images of septal olfactory epithelium of an adult Gγ8-sypGFP-tdTom mouse showing colocalization
Supplementary Figure 1: Validation of labeling specificity of immature OSNs and presynaptic terminals. (A) Confocal images of septal olfactory epithelium of an adult Gγ8-sypGFP-tdTom mouse showing colocalization
Generation of directional selectivity by individual thin dendrites in neocortical pyramidal neurons.
 Generation of directional selectivity by individual thin dendrites in neocortical pyramidal neurons. NN Brief Communication. Guy Major atterned 2-photon glutamate uncaging and local iontophoresis were
Generation of directional selectivity by individual thin dendrites in neocortical pyramidal neurons. NN Brief Communication. Guy Major atterned 2-photon glutamate uncaging and local iontophoresis were
Supplementary Figure 1
 8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature6416 Supplementary Notes Spine Ca 2+ signals produced by glutamate uncaging We imaged uncaging-evoked [Ca 2+ ] transients in neurons loaded with a green Ca 2+ - sensitive indicator (G;
doi: 1.138/nature6416 Supplementary Notes Spine Ca 2+ signals produced by glutamate uncaging We imaged uncaging-evoked [Ca 2+ ] transients in neurons loaded with a green Ca 2+ - sensitive indicator (G;
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/10/e1500775/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Structural-functional connectivity deficits of neocortical circuits in the Fmr1 /y mouse model of autism Matthias
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/10/e1500775/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Structural-functional connectivity deficits of neocortical circuits in the Fmr1 /y mouse model of autism Matthias
Tanimoto et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb /DC1
 Supplemental material JCB Tanimoto et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510064 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Method for aster 3D tracking, extended characterization of
Supplemental material JCB Tanimoto et al., http ://www.jcb.org /cgi /content /full /jcb.201510064 /DC1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. Method for aster 3D tracking, extended characterization of
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Large-conductance calcium-dependent potassium channels prevent dendritic excitability in neocortical pyramidal neurons
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-857 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 29 Large-conductance calcium-dependent potassium channels prevent dendritic
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-857 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 29 Large-conductance calcium-dependent potassium channels prevent dendritic
The Subcellular Distribution of T-Type Ca 2+ Channels in Interneurons of the Lateral Geniculate Nucleus
 The Subcellular Distribution of T-Type Ca 2+ Channels in Interneurons of the Lateral Geniculate Nucleus Vaneeda Allken 1, Joy-Loi Chepkoech 1,2, Gaute T. Einevoll 1,3, Geir Halnes 1 * 1 Dept. of Mathematical
The Subcellular Distribution of T-Type Ca 2+ Channels in Interneurons of the Lateral Geniculate Nucleus Vaneeda Allken 1, Joy-Loi Chepkoech 1,2, Gaute T. Einevoll 1,3, Geir Halnes 1 * 1 Dept. of Mathematical
Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol.
 Supplementary Figures 1-11 Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol. (a), Voltage-clamp recordings from CA1 pyramidal neurons
Supplementary Figures 1-11 Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol. (a), Voltage-clamp recordings from CA1 pyramidal neurons
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.2860
 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1: Hypomorphic expression of IFT88 results in olfactory signaling proteins no longer localizing to the ciliary layer. (a) ACIII localizes to the cilia and
Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1: Hypomorphic expression of IFT88 results in olfactory signaling proteins no longer localizing to the ciliary layer. (a) ACIII localizes to the cilia and
Axon initial segment position changes CA1 pyramidal neuron excitability
 Axon initial segment position changes CA1 pyramidal neuron excitability Cristina Nigro and Jason Pipkin UCSD Neurosciences Graduate Program Abstract The axon initial segment (AIS) is the portion of the
Axon initial segment position changes CA1 pyramidal neuron excitability Cristina Nigro and Jason Pipkin UCSD Neurosciences Graduate Program Abstract The axon initial segment (AIS) is the portion of the
