Note: During any ONE run the ph remains constant. It may be at any one of the above levels but it never change during a single run.
|
|
|
- Maryann Hawkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 BGYC34 (2007) PhysioEx Lab 10 AcidBase Balance Marking Scheme Part 1 Complete PhysioEx lab #10. Handin all of the pages associated with the lab. Note that there are 9 activities to be completed. You DO NOT need to hand in the histology review supplement. There are 10 questions in part 1 for which marks are assigned. Convert the mark out of 10 to a mark out of 5. Add the mark out of 5 to the mark out of 8 from part 2. The final mark is out of 13. Activity 1: Normal Breathing At 20 seconds, ph = 7.38 or 7.39 or 7.40 or 7.41 or 7.42 At 40 seconds, ph = 7.38 or 7.39 or 7.40 or 7.41 or 7.42 At 60 seconds, ph = 7.38 or 7.39 or 7.40 or 7.41 or 7.42 Note: During any ONE run the ph remains constant. It may be at any one of the above levels but it never change during a single run. Did the ph level of the blood change at all during normal breathing? If so, how? No, the ph level of the blood does not change (during any single run) during normal breathing. Was the ph level always within the normal range for the human body? Yes, the ph level remained within the normal range (7.38 to 7.42) during normal breathing. Did the PCO 2 level change during the course of normal breathing? If so, how? No, the PCO 2 level remained constant (40 mmhg) during normal breathing. Activity 2a: Hyperventilation Run 1 At 20 seconds, ph = approximately 7.45 At 40 seconds, ph = approximately 7.54 At 60 seconds, ph = approximately 7.67
2 2 Did the ph level of the blood change at all during this run? If so, how? Yes, the ph level of the blood increased over time. Was the ph level always within the normal range for the human body? No, the ph level was not in the normal range for the human body. It increased above normal values. If not when was the ph value outside of the normal range and what acidbase imbalance did this ph value indicate? The ph value began to rise above the normal range between 10 and 20 seconds. This is a respiratory alkalosis. (1 MARK) Did the PCO 2 level change during the course of this run? If so, how? Yes, the PCO 2 level progressively decreased over time (during the hyperventilation). If you observed an acidbase imbalance during this run, how would you expect the renal system to compensate for this condition? You would expect the renal system to compensate for the respiratory alkalosis by decreasing HCO 3 reabsorption and decreasing H + ion secretion. (1 MARK) How did the hyperventilation trace differ from the trace for normal breathing? Did the tidal volumes change? During hyperventilation, tidal volume was markedly increased and there was small increase in breathing frequency. What might cause a person to hyperventilate? Two of the major causes of hyperventilation are anxiety and fever. Some drugs (such as cocaine) will also induce hyperventilation. Activity 2b: Hyperventilation Run 2 What happened to the trace after the 20 second mark when you stopped the hyperventilation? Did the breathing return to normal immediately? Explain your observation. After the period of hyperventilation and the return to normal breathing there was approximately one normal breath before breathing stopped for a few (around ten)
3 3 seconds. This occurred because PCO 2 was low enough to shut off breathing due to the removal of the CO 2 stimulus from the central and peripheral chemoreceptors. (1 MARK) Activity 3: Rebreathing At 20 seconds, ph = approximately 7.35 At 40 seconds, ph = approximately 7.30 At 60 seconds, ph = approximately 7.25 Did the ph level of the blood change at all during this run? If so, how? Yes, blood ph decreased over time. Was the ph level always within the normal range for the human body? No, the ph level was not always within the normal range; it was lower. If not when was the ph value outside of the normal range and what acidbase imbalance did this ph value indicate? The ph value began to fall out of the normal range at about 2025 seconds. This was a respiratory acidosis. (1 MARK) Did the PCO 2 level change during the course of this run? If so, how? Yes, the PCO 2 level increased over the course of this run. If you observed an acidbase imbalance during this run, how would you expect the renal system to compensate for this condition? In order to compensate for a respiratory acidosis, the kidney would increase the rate of HCO 3 reabsorption and increase the rate of H + ion secretion. (1 MARK) How did the rebreathing trace differ from the trace for normal breathing? Did the tidal volumes change? The rebreathing trace showed greater levels of breathing compared to normal. Tidal volume was elevated as was breathing frequency (albeit the tidal volume change was more obvious than the frequency change). Give examples of respiratory problems that would result in ph and PCO 2 patterns similar to what you observed during rebreathing. Lung disease or airway obstruction could lead to the retention of CO 2 which would increase PCO 2 and decrease ph.
4 4 Activity 4: Renal Response to Normal AcidBase Balance At normal PCO 2 and ph levels, what level of H + was present in the urine? The [H + ]in the urine was normal. There is no quantitative answer to be given. What level of [HCO 3 ] was present in the urine? The [HCO 3 ] in the urine was normal. There is no quantitative answer to be given. Why does the blood ph change as the PCO 2 changes? This question seems out of place. As PCO 2 increases, blood ph decreases because CO 2 is being hydrated to a proton and bicarbonate ion. Activity 5: Renal Response to Respiratory Alkalosis What level of [H + ] was present in the urine at each of these PCO 2 /ph levels? At a PCO 2 level of 35 mmhg, urine [H + ] was normal. As PCO 2 was lowered to 30 and 20 mmhg, urine [H + ] was lowered (the kidney was retaining protons). What level of [HCO 3 ] was present in the urine at each of these PCO 2 /ph levels? At a PCO 2 level of 35 mmhg, urine [HCO 3 ] was normal. As PCO 2 was lowered to 30 and 20 mmhg, urine [HCO 3 ] was increased (the kidney is getting rid of bicarbonate). Recall that it may take hours or even days for the renal system to respond to disruptions in acidbase balance. Assuming that enough time has passed for the renal system to fully compensate for respiratory alkalosis, would you expect PCO 2 levels to increase or decrease? Would you expect blood ph levels to increase or decrease? The kidney can fully compensate for the ph changes (i.e., bring arterial ph back to normal) but PCO 2 (and HCO 3 ) levels will remain low until the respiratory disturbance (alkalosis) is removed. Blood PCO 2 levels would remain at the low level induced by the respiratory alkalosis. The renal compensation would not change this. (1 MARK)
5 5 Recall our discussion on renal compensation for respiratory disorders that occurred in lecture 20.See the slides on renal compensation for a respiratory alkalosis and the note that a new steady state PCO 2 level is achieved. Recall your activities in the first experiment on respiratory acidosis or alkalosis. Which type of breathing resulted in PCO 2 levels closest to the ones we experimented with in this activity normal breathing, hyperventilation or Rebreathing? The reduced PCO 2 levels resemble those observed during hyperventilation which, of course, would induce a respiratory alkalosis. Explain why this type of breathing resulted in alkalosis. Hyperventilation causes an increase in CO 2 excretion. Since CO 2 is hydrated to produce a proton and a bicarbonate ion, less CO 2 in the blood means less hydrogen ions and therefore an increase in blood ph. Activity 6: Renal Response to Respiratory Acidosis What level of [H + ] was present in the urine at each of these PCO 2 /ph levels? As PCO 2 was raised to lowered to 60, 75 and 90 mmhg, urine [H + ] was elevated (the kidney was secreting protons). What level of [HCO 3 ] was present in the urine at each of these PCO 2 /ph levels? As PCO 2 was raised to 60, 75 and 90 mmhg, urine [HCO 3 ] was lowered (the kidney was retaining bicarbonate). Recall that it may take hours or even days for the renal system to respond to disruptions in acidbase balance. Assuming that enough time has passed for the renal system to fully compensate for respiratory acidosis, would you expect PCO 2 levels to increase or decrease? Would you expect blood ph levels to increase or decrease? Ultimately the kidney can compensate for changes in blood ph and restore ph to normal. However, the kidney cannot restore PCO 2 and HCO 3 levels to normal. Both PCO 2 and HCO 3 levels remain elevated until the respiratory acidosis ceases. (1 MARK) Note, see the slides on renal compensation for a respiratory acidosis. The renal compensation occurs along a PCO 2 isobar so PCO 2 does not change during the renal compensation. A new steady state PCO 2 is achieved that is higher than normal. HCO 3 levels are also higher.
6 6 Recall your activities in the first experiment on respiratory acidosis or alkalosis. Which type of breathing resulted in PCO 2 levels closest to the ones we experimented with in this activity normal breathing, hyperventilation or Rebreathing? The elevated PCO 2 levels resemble those observed during rebreathing which would induce a respiratory acidosis. Explain why this type of breathing resulted in acidosis. Rebreathing or hypoventilation cause CO 2 retention therefore leading to a decrease in ph. Activity 7: Respiratory Response to Normal Metabolism What is the respiratory rate? 15 breaths per minute. Are the blood ph and PCO 2 values within the normal ranges? Yes. Activity 8: Respiratory Response to Increased Metabolism How did respiration change? As metabolic rate increased, breathing increased. How did blood ph change? As metabolic rate increased, blood ph decreased, despite the increase in breathing. How did PCO 2 change? As metabolic rate increased blood PCO 2 increased despite the increase in breathing. How did [H + ] change? As metabolic rate increased blood [H + ] increased despite the increase in breathing. How did [HCO 3 ] change? As metabolic rate increased blood [HCO 3 ] decreased. Explain why these changes took place as metabolic rate increased?
7 7 As metabolic rate increased, CO 2 levels increased because CO 2 is a metabolic waster product. This caused an increase in H + levels and hence a decrease in ph. Breathing increased (due to stimulation of chemoreceptors) in an attempt to restore blood CO 2 levels to normal but in this case the increase in breathing was not able to compensate for the elevated metabolism. (1 MARK) Which metabolic rates caused ph levels to decrease to a condition of metabolic acidosis? Metabolic rates of 60+ caused a metabolic acidosis. What were the ph values at each of these rates? 7.34, 7.26 and 7.25 were the ph levels at metabolic rates of 60, 70 and 80, respectively. By the time the respiratory system fully compensated for the acidosis, how would you expect the ph values to change? Once the respiratory system fully compensated for the acidosis you would expect ph to increase back to normal levels. (1 MARK) Activity 9: Respiratory Response to Decreased Metabolism How did respiration change? As metabolic rate decreased, breathing decreased. How did blood ph change? As metabolic rate decreased, ph increased. How did PCO 2 change? As metabolic rate decreased, PCO 2 decreased. How did [H + ] change? As metabolic rate decreased blood [H + ] decreased. How did [HCO 3 ] change? As metabolic rate increased, blood [HCO 3 ] increased. Explain why these changes took place as metabolic rate decreased?
8 8 As metabolism decreased, there was less CO 2 produced therefore less H + ions and a higher ph. Breathing decreased because the reduction in CO 2 and the increase in ph reduced the chemoreceptor stimulus for breathing. The changes in breathing in this case were not sufficient to restore these values to normal levels during the period of reduced metabolic rate. (1 MARK) Which metabolic rates caused ph levels to increase to a condition of metabolic acidosis? Metabolic rates of 20 and 30 raised ph above 7.45 which is the cutoff (see the introduction) for a metabolic alkalosis. What were the ph values at each of these rates? 7.45, 7.48, 7.52 were the values at metabolic rates of 40, 30 and 20, respectively. By the time the respiratory system fully compensated for the alkalosis, how would you expect the ph values to change? ph would return to normal levels once the respiratory system fully compensates for the alkalosis.
9 9 Part 2 (10 marks) Answer the following questions. Staple the answers to the back of the PhysioEx pages. 1) Drugs such as SIDS or DIDS block the activity of chloridebicarbonate exchangers. Illustrate, on a phbicarbonate (Davenport) diagram, the effects (on acidbase balance) of adding SIDS or DIDS to the proximal tubule epithelial cells in the kidneys. Explain your diagram. (2 marks). See the lecture 1920 notes for Davenport diagrams. If the activity of the chloridebicarbonate exchanger is blocked in the proximal tubule then there is going to be little or no bicarbonate reabsorption from the kidneys back into the blood. This would lead to a reduction in blood bicarbonate levels; hence a metabolic acidosis. A Davenport diagram such as the one below should be shown. The key point is that there should be some indication that the position has shifted from point 1 (normal blood values) to point 2 (along the pco 2 isobar; i.e., no change in pco 2 ) showing a reduction in ph and a reduction in bicarbonate levels). Give 1 mark for the diagram and 1 mark for the explanation. [HCO 3 ] mmhg mm pco 2 isobars ph HOWEVER, some students may offer an alternate explanation that is also worth full marks. Even if there is no bicarbonate reabsorption in the proximal tubule there still could be bicarbonate synthesis in the distal tubule and even the proximal tubule. Furthermore, there could also be bicarbonate reabsorption in the distal tubule. This doesn t normally occur since all bicarbonate is normally reabsorbed in the proximal tubule. In this case there would be no acidbase disturbance and the graph would simply show normal acidbase status at point 1. In this case give 1 mark for the diagram and 1 mark for the explanation.
10 10 2) Assume that the initial resting values for pco 2, [HCO 3 ] and ph are 40 mmhg, 25 mm and 7.4, respectively. If a metabolic acidosis occurs such that ph falls to 7.3, what would be the corresponding [HCO 3 ]? (2 marks) Use the HendersonHasselbach equation (below) and the following information to determine the answer. α = ; pk= 6.1 ph = pk + log ([HCO 3 ] / α pco 2 ) Given that it is a metabolic acidosis, ppco 2 does not change. Therefore, use the values of PCO 2 = 40 mmhg and ph = 7.3 in the calculation. ph = pk + log ([HCO 3 ] / α pco 2 ) ph = ph + log [HCO 3 ] log α pco = log [HCO 3 ] log (0.0301) (40) 1.2 = log [HCO 3 ] log = log [HCO 3 ] log [HCO 3 ] = Give 1 mark if the logical progression reaches this far. [HCO 3 ] = antilog [HCO 3 ] = 19.1 mm Give 1 mark if the correct answer is also given. NOTE: I expect that most of the students will show their work. However, I did not ask for this. If they just give the correct answer with no calculations they still get the full two marks. 3) Why do diarrhea and vomiting lead to metabolic acidosis and alkalosis, respectively? (2 marks) Diarrhea leads to a large loss of HCO 3 in the watery feces. (0.5 marks) This HCO 3 would normally have been reabsorbed into the blood across the intestine. Because bicarbonate is being lost in the diarrhea its level in the blood falls leading to a metabolic acidosis. (0.5 marks) Vomiting leads to a loss of H + ions in the vomit. (0.5 marks)
11 11 The H + ions that are secreted into the stomach can be reclaimed, into the blood, once the chyme (from the stomach) enters the intestine. Since they are no longer in the stomach contents they cannot be reabsorbed into the blood. Therefore blood H + levels fall leading to a metabolic alkalosis. (0.5 marks) 4) Rank the following in order from the least effective buffer to the most effective buffer. (2 marks) The following list goes from the most effective buffer (top of the list) to the least effective buffer (bottom of the list) Whole blood from a person with polycythaemia Whole blood from a normal person Whole blood from an anaemic person Blood plasma from a normal person = Blood plasma from an anaemic person Blood serum from a normal person Distilled water Give the full 2 marks if the list is correct. If two possibilities are switched around (just amongst the two of them) then remove 0.5 marks. If three possibilities are misplaced remove 1 mark. If more than 3 possibilities are misplaced then deduct all marks. The following is an explanation but the students didn t need to provide it in order to get marks. Blood is a better buffer than plasma because of the presence of haemoglobin in the red blood cells (this was covered in the lectures). The more red blood cells that are present in the blood, the more buffering capacity it will have. Polycythaemia is an increase in the number of red cells; anaemia is a decrease in the number of red blood cells. Plasma is blood without the red blood cells. There is no reason for the plasma to be different from a normal versus anaemic person. Serum is plasma with the clotting proteins removed. Since proteins act as buffers, serum is a worse buffer than plasma. Distilled water would have no buffering capacity.
There are many buffers in the kidney, but the main one is the phosphate buffer.
 9 Yanal Obada Zalat Renal Control of AcidBase Balance The kidneys play three major roles in the maintenance of normal acidbase balance: 1excretion of H+ (fixed _non volatile H+) 2Reabsorption of filtrated
9 Yanal Obada Zalat Renal Control of AcidBase Balance The kidneys play three major roles in the maintenance of normal acidbase balance: 1excretion of H+ (fixed _non volatile H+) 2Reabsorption of filtrated
Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + )
 Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration in body fluids Precise regulation of ph at
Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration in body fluids Precise regulation of ph at
Acid-Base Balance Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Acid-Base Balance Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration
Acid-Base Balance Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration
Acids, Bases, and Salts
 Acid / Base Balance Objectives Define an acid, a base, and the measure of ph. Discuss acid/base balance, the effects of acidosis or alkalosis on the body, and the mechanisms in place to maintain balance
Acid / Base Balance Objectives Define an acid, a base, and the measure of ph. Discuss acid/base balance, the effects of acidosis or alkalosis on the body, and the mechanisms in place to maintain balance
Acid-Base Imbalance. Shu-Yi (Emily) Wang, PhD, RN, CNS Denver School of Nursing
 Acid-Base Imbalance Shu-Yi (Emily) Wang, PhD, RN, CNS gpwsy@hotmail.com Denver School of Nursing ph Ranges Compatible With Life In blood, the ph represents the relationship between the respiratory and
Acid-Base Imbalance Shu-Yi (Emily) Wang, PhD, RN, CNS gpwsy@hotmail.com Denver School of Nursing ph Ranges Compatible With Life In blood, the ph represents the relationship between the respiratory and
Acid Base Balance. Professor Dr. Raid M. H. Al-Salih. Clinical Chemistry Professor Dr. Raid M. H. Al-Salih
 Acid Base Balance 1 HYDROGEN ION CONCENTRATION and CONCEPT OF ph Blood hydrogen ion concentration (abbreviated [H + ]) is maintained within tight limits in health, with the normal concentration being between
Acid Base Balance 1 HYDROGEN ION CONCENTRATION and CONCEPT OF ph Blood hydrogen ion concentration (abbreviated [H + ]) is maintained within tight limits in health, with the normal concentration being between
Acid/Base Balance. the concentrations of these two ions affect the acidity or alkalinity of body fluids
 Acid/Base Balance some of most critical ions in body fluids are H + (hydrogen) and OH - (hydroxyl) ions the concentrations of these two ions affect the acidity or alkalinity of body fluids acidity/alkalinity
Acid/Base Balance some of most critical ions in body fluids are H + (hydrogen) and OH - (hydroxyl) ions the concentrations of these two ions affect the acidity or alkalinity of body fluids acidity/alkalinity
UNIT VI: ACID BASE IMBALANCE
 UNIT VI: ACID BASE IMBALANCE 1 Objectives: Review the physiological mechanism responsible to regulate acid base balance in the body i.e.: Buffers (phosphate, hemoglobin, carbonate) Renal mechanism Respiratory
UNIT VI: ACID BASE IMBALANCE 1 Objectives: Review the physiological mechanism responsible to regulate acid base balance in the body i.e.: Buffers (phosphate, hemoglobin, carbonate) Renal mechanism Respiratory
D fini n tion: p = = -log [H+] ph=7 me m an s 10-7 Mol M H+ + (100 nmol m /l); ) p ; H=8 me m an s 10-8 Mol M H+ + (10 (10 n nmol m /l) Nor
![D fini n tion: p = = -log [H+] ph=7 me m an s 10-7 Mol M H+ + (100 nmol m /l); ) p ; H=8 me m an s 10-8 Mol M H+ + (10 (10 n nmol m /l) Nor D fini n tion: p = = -log [H+] ph=7 me m an s 10-7 Mol M H+ + (100 nmol m /l); ) p ; H=8 me m an s 10-8 Mol M H+ + (10 (10 n nmol m /l) Nor](/thumbs/75/72756397.jpg) Definition: ph regulation ph = -log [H + ] ph=7 means 10-7 Mol H + (100 nmol/l); ph=8 means 10 Normal plasma value: 7.35-7.45; 7.45; (H Acidosis: ph7.45 Intracellular ph = 7.1-7.3
Definition: ph regulation ph = -log [H + ] ph=7 means 10-7 Mol H + (100 nmol/l); ph=8 means 10 Normal plasma value: 7.35-7.45; 7.45; (H Acidosis: ph7.45 Intracellular ph = 7.1-7.3
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH ACID-BASE BALANCE-- CONTROLLING BLOOD PH
 !! www.clutchprep.com ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: INTRO. TO DISTURBING AND MAINTAINING BLOOD ph Physiological Sources of Acid (and Base): Acids are molecules/substances that H+ to a solution.
!! www.clutchprep.com ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CONCEPT: INTRO. TO DISTURBING AND MAINTAINING BLOOD ph Physiological Sources of Acid (and Base): Acids are molecules/substances that H+ to a solution.
adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) -42-
 Graphics are used with permission of : adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) -42-74. (1) Carbon dioxide arrives at the kidney tubule cell in the proximal
Graphics are used with permission of : adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) -42-74. (1) Carbon dioxide arrives at the kidney tubule cell in the proximal
Metabolic Alkalosis: Vomiting
 RENAL ANL) ACID-BASE PHYSIOLOGY 213 Case 37 Metabolic Alkalosis: Vomiting Maria Cuervo is a 20-year-old philosophy major at a state university. When the "24-hour" stomach flu went around campus during
RENAL ANL) ACID-BASE PHYSIOLOGY 213 Case 37 Metabolic Alkalosis: Vomiting Maria Cuervo is a 20-year-old philosophy major at a state university. When the "24-hour" stomach flu went around campus during
Acids and Bases their definitions and meanings
 Acids and Bases their definitions and meanings Molecules containing hydrogen atoms that can release hydrogen ions in solutions are referred to as acids. (HCl H + Cl ) (H 2 CO 3 H + HCO 3 ) A base is an
Acids and Bases their definitions and meanings Molecules containing hydrogen atoms that can release hydrogen ions in solutions are referred to as acids. (HCl H + Cl ) (H 2 CO 3 H + HCO 3 ) A base is an
Carbon Dioxide Transport. Carbon Dioxide. Carbon Dioxide Transport. Carbon Dioxide Transport - Plasma. Hydrolysis of Water
 Module H: Carbon Dioxide Transport Beachey Ch 9 & 10 Egan pp. 244-246, 281-284 Carbon Dioxide Transport At the end of today s session you will be able to : Describe the relationship free hydrogen ions
Module H: Carbon Dioxide Transport Beachey Ch 9 & 10 Egan pp. 244-246, 281-284 Carbon Dioxide Transport At the end of today s session you will be able to : Describe the relationship free hydrogen ions
Renal Physiology. April, J. Mohan, PhD. Lecturer, Physiology Unit, Faculty of Medical Sciences, U.W.I., St Augustine.
 Renal Physiology April, 2011 J. Mohan, PhD. Lecturer, Physiology Unit, Faculty of Medical Sciences, U.W.I., St Augustine. Office : Room 105, Physiology Unit. References: Koeppen B.E. & Stanton B.A. (2010).
Renal Physiology April, 2011 J. Mohan, PhD. Lecturer, Physiology Unit, Faculty of Medical Sciences, U.W.I., St Augustine. Office : Room 105, Physiology Unit. References: Koeppen B.E. & Stanton B.A. (2010).
1. 09/07/16 Ch 1: Intro to Human A & P 1
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 09/07/16 Ch 1: Intro to Human A & P 1 2. 09/19/16 Ch 18: Water, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance 5 i 1 09/19/16 Chapter 18: Water, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 09/07/16 Ch 1: Intro to Human A & P 1 2. 09/19/16 Ch 18: Water, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance 5 i 1 09/19/16 Chapter 18: Water, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base
Acid-Base Balance 11/18/2011. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulatory Site: Cortical Collecting Ducts.
 Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Acid-Base Imbalance-2 Lecture 9 (12/4/2015) Yanal A. Shafagoj MD. PhD
 AcidBase Imbalance2 Lecture 9 (12/4/2015) Yanal A. Shafagoj MD. PhD Introduction Disturbance in acidbase balance are common clinical problem that range in severity from mild to life threatening, the acute
AcidBase Imbalance2 Lecture 9 (12/4/2015) Yanal A. Shafagoj MD. PhD Introduction Disturbance in acidbase balance are common clinical problem that range in severity from mild to life threatening, the acute
Control of Ventilation [2]
![Control of Ventilation [2] Control of Ventilation [2]](/thumbs/83/87644191.jpg) Control of Ventilation [2] สรช ย ศร ส มะ พบ., Ph.D. ภาคว ชาสร รว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล มหาว ทยาล ยมห ดล Describe the effects of alterations in chemical stimuli, their mechanisms and response to
Control of Ventilation [2] สรช ย ศร ส มะ พบ., Ph.D. ภาคว ชาสร รว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล มหาว ทยาล ยมห ดล Describe the effects of alterations in chemical stimuli, their mechanisms and response to
ARTERIAL BLOOD GASES PART 1 BACK TO BASICS SSR OLIVIA ELSWORTH SEPT 2017
 ARTERIAL BLOOD GASES PART 1 BACK TO BASICS SSR OLIVIA ELSWORTH SEPT 2017 WHAT INFORMATION DOES AN ABG GIVE US? ph = measure of hydrogen ion concentration (acidity or alkalinity) PaCO2 = partial pressure
ARTERIAL BLOOD GASES PART 1 BACK TO BASICS SSR OLIVIA ELSWORTH SEPT 2017 WHAT INFORMATION DOES AN ABG GIVE US? ph = measure of hydrogen ion concentration (acidity or alkalinity) PaCO2 = partial pressure
CASE 27. What is the response of the kidney to metabolic acidosis? What is the response of the kidney to a respiratory alkalosis?
 CASE 27 A 21-year-old man with insulin-dependent diabetes presents to the emergency center with mental status changes, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and rapid respirations. On examination, the patient
CASE 27 A 21-year-old man with insulin-dependent diabetes presents to the emergency center with mental status changes, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and rapid respirations. On examination, the patient
Acid-Base Tutorial 2/10/2014. Overview. Physiology (2) Physiology (1)
 Overview Acid-Base Tutorial Nicola Barlow Physiology Buffering systems Control mechanisms Laboratory assessment of acid-base Disorders of H + ion homeostasis Respiratory acidosis Metabolic acidosis Respiratory
Overview Acid-Base Tutorial Nicola Barlow Physiology Buffering systems Control mechanisms Laboratory assessment of acid-base Disorders of H + ion homeostasis Respiratory acidosis Metabolic acidosis Respiratory
Acid and Base Balance
 Acid and Base Balance 1 2 The Body and ph Homeostasis of ph is tightly controlled Extracellular fluid = 7.4 Blood = 7.35 7.45 < 7.35: Acidosis (acidemia) > 7.45: Alkalosis (alkalemia) < 6.8 or > 8.0: death
Acid and Base Balance 1 2 The Body and ph Homeostasis of ph is tightly controlled Extracellular fluid = 7.4 Blood = 7.35 7.45 < 7.35: Acidosis (acidemia) > 7.45: Alkalosis (alkalemia) < 6.8 or > 8.0: death
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Learning Outcomes. Acid base terminology ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS INTERPRETATION
 Slide 1 ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS INTERPRETATION David O Neill MSc BSc RN NMP FHEA Associate Lecturer (Non Medical Prescribing) Cardiff University Advanced Nurse Practitioner Respiratory Medicine Slide 2 Learning
Slide 1 ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS INTERPRETATION David O Neill MSc BSc RN NMP FHEA Associate Lecturer (Non Medical Prescribing) Cardiff University Advanced Nurse Practitioner Respiratory Medicine Slide 2 Learning
Fluid and Electrolytes P A R T 4
 Fluid and Electrolytes P A R T 4 Mechanisms that control acid-base homeostasis Acids and bases continually enter and leave body Hydrogen ions also result from metabolic activity Acids Hydrogen ion donors
Fluid and Electrolytes P A R T 4 Mechanisms that control acid-base homeostasis Acids and bases continually enter and leave body Hydrogen ions also result from metabolic activity Acids Hydrogen ion donors
Acid Base Balance. Chapter 26 Balance. ph Imbalances. Acid Base Balance. CO 2 and ph. Carbonic Acid. Part 2. Acid/Base Balance
 Acid Base Balance Chapter 26 Balance Part 2. Acid/Base Balance Precisely balances production and loss of hydrogen ions (ph) The body generates acids during normal metabolism, tends to reduce ph Kidneys:
Acid Base Balance Chapter 26 Balance Part 2. Acid/Base Balance Precisely balances production and loss of hydrogen ions (ph) The body generates acids during normal metabolism, tends to reduce ph Kidneys:
Renal physiology V. Regulation of acid-base balance. Dr Alida Koorts BMS
 Renal physiology V Regulation of acidbase balance Dr Alida Koorts BMS 712 012 319 2921 akoorts@medic.up.ac.za Hydrogen ions (H + ): Concentration and origin Concentration in arterial blood, resting: [H
Renal physiology V Regulation of acidbase balance Dr Alida Koorts BMS 712 012 319 2921 akoorts@medic.up.ac.za Hydrogen ions (H + ): Concentration and origin Concentration in arterial blood, resting: [H
Disorders of Acid-Base
 Disorders of Acid-Base Balance Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Normal arterial blood ph is restricted to a very narrow range of 7.35 to 7.45. A person who has a blood ph below 7.35 is considered to be in acidosis
Disorders of Acid-Base Balance Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Normal arterial blood ph is restricted to a very narrow range of 7.35 to 7.45. A person who has a blood ph below 7.35 is considered to be in acidosis
ACID-BASE BALANCE URINE BLOOD AIR
 ACIDBASE BALANCE URINE BLOOD AIR H 2 PO 4 NH 4 HCO 3 KIDNEY H H HCO 3 CELLS Hb H LUNG H 2 CO 3 HHb CO 2 H 2 O ph = 7.4 [HCO 3 ] = 24 meq/l PCO 2 = 40 mm Hg CO 2 PRIMARY RENAL MECHANISMS INVOLVED IN ACIDBASE
ACIDBASE BALANCE URINE BLOOD AIR H 2 PO 4 NH 4 HCO 3 KIDNEY H H HCO 3 CELLS Hb H LUNG H 2 CO 3 HHb CO 2 H 2 O ph = 7.4 [HCO 3 ] = 24 meq/l PCO 2 = 40 mm Hg CO 2 PRIMARY RENAL MECHANISMS INVOLVED IN ACIDBASE
Chapter 15 Fluid and Acid-Base Balance
 Chapter 15 Fluid and Acid-Base Balance by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Fluid Balance Water constitutes ~60% of body weight. All cells and tissues are surrounded by an aqueous environment.
Chapter 15 Fluid and Acid-Base Balance by Dr. Jay M. Templin Brooks/Cole - Thomson Learning Fluid Balance Water constitutes ~60% of body weight. All cells and tissues are surrounded by an aqueous environment.
Introduction. Acids, Bases and ph; a review
 0 P a g e Introduction In this sheet, we discuss acidbase balance in our body and the role of kidneys in its establishment. Arrangement of topics is different from that of the lecture, to assure consistency
0 P a g e Introduction In this sheet, we discuss acidbase balance in our body and the role of kidneys in its establishment. Arrangement of topics is different from that of the lecture, to assure consistency
Arterial Blood Gases Interpretation Definition Values respiratory metabolic
 Arterial Blood Gases Interpretation Definition A blood gas test measures the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood. It is also useful in determining the ph level of the blood. The test is commonly
Arterial Blood Gases Interpretation Definition A blood gas test measures the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood. It is also useful in determining the ph level of the blood. The test is commonly
Acid - base equilibrium
 Acid base equilibrium ph concept ph = log [H + ] ph [H+] 1 100 mmol/l D = 90 mmol/l 2 10 mmol/l D = 9 mmol/l 3 1 mmol/l 2 ph = log [H + ] 3 ph ph = log [H + ] ph of capillary blood norm: 7,35 7,45 Sorensen
Acid base equilibrium ph concept ph = log [H + ] ph [H+] 1 100 mmol/l D = 90 mmol/l 2 10 mmol/l D = 9 mmol/l 3 1 mmol/l 2 ph = log [H + ] 3 ph ph = log [H + ] ph of capillary blood norm: 7,35 7,45 Sorensen
Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance
 Chapter 27 Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance 1 Body Fluids Intracellular fluid compartment All fluids inside cells of body About 40% of total body weight Extracellular fluid compartment All fluids
Chapter 27 Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance 1 Body Fluids Intracellular fluid compartment All fluids inside cells of body About 40% of total body weight Extracellular fluid compartment All fluids
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 27 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Fluid Compartments and Fluid In adults, body fluids make up between 55% and 65% of total body mass. Body
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 27 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Fluid Compartments and Fluid In adults, body fluids make up between 55% and 65% of total body mass. Body
Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Balance
 25 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Balance Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Note to the Instructor: For the third edition of Visual Anatomy & Physiology, we have updated our PowerPoints to fully
25 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Balance Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Note to the Instructor: For the third edition of Visual Anatomy & Physiology, we have updated our PowerPoints to fully
Neaam Al-Bahadili. Rana J. Rahhal. Mamoun Ahram
 5 Neaam Al-Bahadili Rana J. Rahhal Mamoun Ahram In this sheet we will continue taking about Titration curve and Buffers in human body. Let s begin Titration curve of phosphate buffer: 1. There are 3 buffering
5 Neaam Al-Bahadili Rana J. Rahhal Mamoun Ahram In this sheet we will continue taking about Titration curve and Buffers in human body. Let s begin Titration curve of phosphate buffer: 1. There are 3 buffering
The kidney. (Pseudo) Practical questions. The kidneys are all about keeping the body s homeostasis. for questions Ella
 The kidney (Pseudo) Practical questions for questions Ella (striemit@gmail.com) The kidneys are all about keeping the body s homeostasis Ingestion Product of metabolism H 2 O Ca ++ Cl - K + Na + H 2 O
The kidney (Pseudo) Practical questions for questions Ella (striemit@gmail.com) The kidneys are all about keeping the body s homeostasis Ingestion Product of metabolism H 2 O Ca ++ Cl - K + Na + H 2 O
MODULE 8: URINALYSIS AND ACID BASE BALANCE
 MODULE 8: URINALYSIS AND ACID BASE BALANCE This lab involves a tutorial that teaches you how to analyze a urine reagent strip. If you are taking the lab on campus, you will be given the opportunity to
MODULE 8: URINALYSIS AND ACID BASE BALANCE This lab involves a tutorial that teaches you how to analyze a urine reagent strip. If you are taking the lab on campus, you will be given the opportunity to
Acid-Base disturbances Physiological approach
 AcidBase disturbances Physiological approach Pieter Roel Tuinman, M.D., PhD, intensivist Department of Intensive Care, VU Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands p.tuinman@vumc.nl Content Introduction
AcidBase disturbances Physiological approach Pieter Roel Tuinman, M.D., PhD, intensivist Department of Intensive Care, VU Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands p.tuinman@vumc.nl Content Introduction
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Approach to Acid-Base Disturbance. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Approach to Acid-Base Disturbance. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in
Neaam Al-Bahadili. Rana J. Rahhal. Mamoun Ahram
 5 Neaam Al-Bahadili Rana J. Rahhal Mamoun Ahram In this sheet we will continue taking about Titration curve and Buffers in human body. Let s begin Titration curve of phosphate buffer: 1. There are 3 buffering
5 Neaam Al-Bahadili Rana J. Rahhal Mamoun Ahram In this sheet we will continue taking about Titration curve and Buffers in human body. Let s begin Titration curve of phosphate buffer: 1. There are 3 buffering
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance
 Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE
 Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE I. RELATED TOPICS Integumentary system Cerebrospinal fluid Aqueous humor Digestive juices Feces Capillary dynamics Lymph circulation Edema Osmosis
Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE I. RELATED TOPICS Integumentary system Cerebrospinal fluid Aqueous humor Digestive juices Feces Capillary dynamics Lymph circulation Edema Osmosis
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
 Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
There are number of parameters which are measured: ph Oxygen (O 2 ) Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Bicarbonate (HCO 3 -) AaDO 2 O 2 Content O 2 Saturation
 Arterial Blood Gases (ABG) A blood gas is exactly that...it measures the dissolved gases in your bloodstream. This provides one of the best measurements of what is known as the acid-base balance. The body
Arterial Blood Gases (ABG) A blood gas is exactly that...it measures the dissolved gases in your bloodstream. This provides one of the best measurements of what is known as the acid-base balance. The body
Disorders of Acid-Base Balance
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46413 1 Disorders of Acid-Base Balance OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m46413 1 Disorders of Acid-Base Balance OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
Acid-Base Balance * OpenStax
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46409 1 Acid-Base Balance * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be
OpenStax-CNX module: m46409 1 Acid-Base Balance * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM and ACID BASE
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM and ACID BASE Arif HM Marsaban Rudyanto Sedono Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Therapy Faculty of medicine University of Indonesia Dr Cipto Mangunkusumo General Hospital Jakarta
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM and ACID BASE Arif HM Marsaban Rudyanto Sedono Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Therapy Faculty of medicine University of Indonesia Dr Cipto Mangunkusumo General Hospital Jakarta
ACID BASE BALANCE & BODY FLUID. Ani Retno Prijanti Renal and Body Fluids Module Juni 2008
 ACID BASE BALANCE & BODY FLUID Ani Retno Prijanti Renal and Body Fluids Module Juni 2008 1 Continuous Mixing of Body Fluids 2 Water Balance and ECF Osmolality To remain properly hydrated, water intake
ACID BASE BALANCE & BODY FLUID Ani Retno Prijanti Renal and Body Fluids Module Juni 2008 1 Continuous Mixing of Body Fluids 2 Water Balance and ECF Osmolality To remain properly hydrated, water intake
Control of Breathing
 Physio # 11 Dr. Yanal Shafaqoj Done By: Lejan Al - Dof'at 13/12/13 Control of Breathing We talked previously about Oxygen extraction and CO 2 production, and how these are transfused through blood (in
Physio # 11 Dr. Yanal Shafaqoj Done By: Lejan Al - Dof'at 13/12/13 Control of Breathing We talked previously about Oxygen extraction and CO 2 production, and how these are transfused through blood (in
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Physiological Causes of Abnormal ABG s
 Physiological Causes of Abnormal ABG s Major Student Performance Objective 1 1. The student will be able to discuss causes for various types of blood gas results. 2. They will also be required to discuss
Physiological Causes of Abnormal ABG s Major Student Performance Objective 1 1. The student will be able to discuss causes for various types of blood gas results. 2. They will also be required to discuss
Dr. Suzana Voiculescu Discipline of Physiology and Fundamental Neurosciences Carol Davila Univ. of Medicine and Pharmacy
 Dr. Suzana Voiculescu Discipline of Physiology and Fundamental Neurosciences Carol Davila Univ. of Medicine and Pharmacy AB balance parameters Extracellular ph (plasmatic ph)= 7.35-7.45 < 7.35= acidosis
Dr. Suzana Voiculescu Discipline of Physiology and Fundamental Neurosciences Carol Davila Univ. of Medicine and Pharmacy AB balance parameters Extracellular ph (plasmatic ph)= 7.35-7.45 < 7.35= acidosis
Blood Gases, ph, Acid- Base Balance
 Blood Gases, ph, Acid- Base Balance Blood Gases Acid-Base Physiology Clinical Acid-Base Disturbances Blood Gases Respiratory Gas Exchange Chemical Control of Respiration Dyshemoglobins Oxygen Transport
Blood Gases, ph, Acid- Base Balance Blood Gases Acid-Base Physiology Clinical Acid-Base Disturbances Blood Gases Respiratory Gas Exchange Chemical Control of Respiration Dyshemoglobins Oxygen Transport
Acid Base Balance by: Susan Mberenga RN, BSN, MSN
 Acid Base Balance by: Susan Mberenga RN, BSN, MSN Acid Base Balance Refers to hydrogen ions as measured by ph Normal range: 7.35-7.45 Acidosis/acidemia: ph is less than 7.35 Alkalosis/alkalemia: ph is
Acid Base Balance by: Susan Mberenga RN, BSN, MSN Acid Base Balance Refers to hydrogen ions as measured by ph Normal range: 7.35-7.45 Acidosis/acidemia: ph is less than 7.35 Alkalosis/alkalemia: ph is
9/14/2017. Acid-Base Disturbances. Goal. Provide an approach to determine complex acid-base disorders
 Acid-Base Disturbances NCNP October 10, 2017 Eric Magaña, M.D. Presbyterian Medical Center Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Goal Provide an approach to determine complex acid-base disorders
Acid-Base Disturbances NCNP October 10, 2017 Eric Magaña, M.D. Presbyterian Medical Center Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Goal Provide an approach to determine complex acid-base disorders
UNIT 9 INVESTIGATION OF ACID-BASE DISTURBANCES
 UNIT 9 INVESTIGATION OF ACIDBASE DISTURBANCES LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this chapter, students must be able to: 1. Describe the main parametres that define the acidbase equilibrium 2. Identify
UNIT 9 INVESTIGATION OF ACIDBASE DISTURBANCES LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this chapter, students must be able to: 1. Describe the main parametres that define the acidbase equilibrium 2. Identify
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
PARAMEDIC RESOURCE MANUAL
 ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP PARAMEDIC RESOURCE MANUAL ACID-BASE BALANCE SECTION SIX Version 1.1 2010 Update PARAMEDIC RESOURCE MANUAL OBJECTIVES: ACID-BASE BALANCE The objectives indicate what you should
ONTARIO BASE HOSPITAL GROUP PARAMEDIC RESOURCE MANUAL ACID-BASE BALANCE SECTION SIX Version 1.1 2010 Update PARAMEDIC RESOURCE MANUAL OBJECTIVES: ACID-BASE BALANCE The objectives indicate what you should
The equilibrium between basis and acid can be calculated and termed as the equilibrium constant = Ka. (sometimes referred as the dissociation constant
 Acid base balance Dobroslav Hájek dhajek@med.muni.cz May 2004 The equilibrium between basis and acid can be calculated and termed as the equilibrium constant = Ka. (sometimes referred as the dissociation
Acid base balance Dobroslav Hájek dhajek@med.muni.cz May 2004 The equilibrium between basis and acid can be calculated and termed as the equilibrium constant = Ka. (sometimes referred as the dissociation
3/17/2017. Acid-Base Disturbances. Goal. Eric Magaña, M.D. Presbyterian Medical Center Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine
 Acid-Base Disturbances Eric Magaña, M.D. Presbyterian Medical Center Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Goal Provide an approach to determine complex acid-base disorders Discuss the approach
Acid-Base Disturbances Eric Magaña, M.D. Presbyterian Medical Center Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Goal Provide an approach to determine complex acid-base disorders Discuss the approach
Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys
 Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys Review Anatomy on your own SLOs List and describe the 4 major functions of the kidneys. List and explain the 4 processes of the urinary system. Diagram the filtration barriers
Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys Review Anatomy on your own SLOs List and describe the 4 major functions of the kidneys. List and explain the 4 processes of the urinary system. Diagram the filtration barriers
BUFFERING OF HYDROGEN LOAD
 BUFFERING OF HYDROGEN LOAD 1. Extracellular space minutes 2. Intracellular space minutes to hours 3. Respiratory compensation 6 to 12 hours 4. Renal compensation hours, up to 2-3 days RENAL HYDROGEN SECRETION
BUFFERING OF HYDROGEN LOAD 1. Extracellular space minutes 2. Intracellular space minutes to hours 3. Respiratory compensation 6 to 12 hours 4. Renal compensation hours, up to 2-3 days RENAL HYDROGEN SECRETION
Blood Gases For beginners
 Blood Gases For beginners Lynsey ward th February 2008 4 th Aims To have a basic understanding of Blood Gas analysis. Objectives To state what acid and alkaline in the value of PH When analysing a blood
Blood Gases For beginners Lynsey ward th February 2008 4 th Aims To have a basic understanding of Blood Gas analysis. Objectives To state what acid and alkaline in the value of PH When analysing a blood
The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion. What are the functions of the urinary system? Maintenance of water-salt and acidbase
 10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
Acid-Base Physiology. Dr. Tamás Bense Dr. Alexandra Turi
 Acid-Base Physiology Dr. Tamás Bense Dr. Alexandra Turi What is a blood gas assessment? We get it from an arterial sample (a.radialis, a. brachialis, a. femoralis) Invasive technique If the patient is
Acid-Base Physiology Dr. Tamás Bense Dr. Alexandra Turi What is a blood gas assessment? We get it from an arterial sample (a.radialis, a. brachialis, a. femoralis) Invasive technique If the patient is
Biochemistry of acid-base disorders. Alice Skoumalová
 Biochemistry of acid-base disorders Alice Skoumalová Main topics of the lecture: Measurement of acid-base dysbalance Classification of the acid-base disorders 4 basic acid-base disorders and their compensaiton
Biochemistry of acid-base disorders Alice Skoumalová Main topics of the lecture: Measurement of acid-base dysbalance Classification of the acid-base disorders 4 basic acid-base disorders and their compensaiton
Dr. Suzana Voiculescu
 Dr. Suzana Voiculescu AB balance parameters Extracellular ph (plasmatic ph)= 7.35-7.45 < 7.35= acidosis >7.45= alkalosis Kassirer-Bleich equation [H+] = 24 PCO2/ [HCO3-] predicts that the ratio of dissolved
Dr. Suzana Voiculescu AB balance parameters Extracellular ph (plasmatic ph)= 7.35-7.45 < 7.35= acidosis >7.45= alkalosis Kassirer-Bleich equation [H+] = 24 PCO2/ [HCO3-] predicts that the ratio of dissolved
Arterial Blood Gases. Dr Mark Young Mater Health Services
 Arterial Blood Gases Dr Mark Young Mater Health Services Why do them? Quick results Bedside test Range of important information Oxygenation Effectiveness of gas exchange Control of ventilation Acid base
Arterial Blood Gases Dr Mark Young Mater Health Services Why do them? Quick results Bedside test Range of important information Oxygenation Effectiveness of gas exchange Control of ventilation Acid base
The Excretory System. Biology 20
 The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
Acid-Base 1, 2, and 3 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Acid-Base 1, 2, and 3 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The relationship between hydrogen ion concentration and ph. 2. Production of acid
Acid-Base 1, 2, and 3 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The relationship between hydrogen ion concentration and ph. 2. Production of acid
[Chapter 25] The Liver and the Gut. John A Kellum
![[Chapter 25] The Liver and the Gut. John A Kellum [Chapter 25] The Liver and the Gut. John A Kellum](/thumbs/85/92127350.jpg) [Chapter 25] The Liver and the Gut John A Kellum 25.1 Introduction Throughout this book we have seen that the Stewart formulation can be used to help understand the mechanisms of acid-base equilibrium
[Chapter 25] The Liver and the Gut John A Kellum 25.1 Introduction Throughout this book we have seen that the Stewart formulation can be used to help understand the mechanisms of acid-base equilibrium
Renal System. Renal System. levels of organization. structure - function. homeostatic regulation
 Renal System The goal of these lectures is to discuss basic renal physiology. This lecture will present the regulation of H and Ca ions as well as discuss the hormonal and neural regulation of renal function.
Renal System The goal of these lectures is to discuss basic renal physiology. This lecture will present the regulation of H and Ca ions as well as discuss the hormonal and neural regulation of renal function.
3/19/2009. The task of the kidney in acid-base balance Excretion of the daily acid load. Buffering of an acid load. A o B - + H + B - A o +OH - C +
 The task of the kidney in acid-base balance Excretion of the daily acid load Buffering of an acid load Oxidation of amino acids, fats and carbohydrates often lead to acid production. On an average American
The task of the kidney in acid-base balance Excretion of the daily acid load Buffering of an acid load Oxidation of amino acids, fats and carbohydrates often lead to acid production. On an average American
Are you ready to have fun?
 Arterial Blood Gas INTERPRETATION By Nena Bonuel, MSN, RN, CCRN, CNS, ACNS-BC Nurse Specialist, Center for Professional Excellence Are you ready to have fun? 1. Yes! 2. I rather go shopping 3. I still
Arterial Blood Gas INTERPRETATION By Nena Bonuel, MSN, RN, CCRN, CNS, ACNS-BC Nurse Specialist, Center for Professional Excellence Are you ready to have fun? 1. Yes! 2. I rather go shopping 3. I still
RENAL TUBULAR ACIDOSIS An Overview
 RENAL TUBULAR ACIDOSIS An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY PBL MBBS IV VJ. Temple 1 What is Renal Tubular
RENAL TUBULAR ACIDOSIS An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY PBL MBBS IV VJ. Temple 1 What is Renal Tubular
Carbon Dioxide Transport and Acid-Base Balance
 CHAPTER 7 Carbon Dioxide Transport and Acid-Base Balance Carbon Dioxide Transport Dioxide Transport In plasma: Carbamino compound (bound to protein) Bicarbonate Dissolved CO 2 CO 2 Is Converted to HCO
CHAPTER 7 Carbon Dioxide Transport and Acid-Base Balance Carbon Dioxide Transport Dioxide Transport In plasma: Carbamino compound (bound to protein) Bicarbonate Dissolved CO 2 CO 2 Is Converted to HCO
Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gases. Prof. Dr. W. Vincken Head Respiratory Division Academisch Ziekenhuis Vrije Universiteit Brussel (AZ VUB)
 Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gases Prof. Dr. W. Vincken Head Respiratory Division Academisch Ziekenhuis Vrije Universiteit Brussel (AZ VUB) Before interpretation of ABG Make/Take note of Correct puncture
Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gases Prof. Dr. W. Vincken Head Respiratory Division Academisch Ziekenhuis Vrije Universiteit Brussel (AZ VUB) Before interpretation of ABG Make/Take note of Correct puncture
Arterial Blood Gas Interpretation: The Basics
 http://www.medicine-on-line.com ABG Basics: Page 1/10 Arterial Blood Gas Interpretation: The Basics Author: David C Chung MD, FRCPC Affiliation: The Chinese University of Hong Kong Sampling of arterial
http://www.medicine-on-line.com ABG Basics: Page 1/10 Arterial Blood Gas Interpretation: The Basics Author: David C Chung MD, FRCPC Affiliation: The Chinese University of Hong Kong Sampling of arterial
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Acid-Base Balance Workshop. Dr. Najla Al Kuwaiti Dr. Abdullah Al Ameri Dr. Amar Al Shibli
 Acid-Base Balance Workshop Dr. Najla Al Kuwaiti Dr. Abdullah Al Ameri Dr. Amar Al Shibli Objectives Normal Acid-Base Physiology Simple Acid-Base Disorders Compensations and Disorders The Anion Gap Mixed
Acid-Base Balance Workshop Dr. Najla Al Kuwaiti Dr. Abdullah Al Ameri Dr. Amar Al Shibli Objectives Normal Acid-Base Physiology Simple Acid-Base Disorders Compensations and Disorders The Anion Gap Mixed
Arterial Blood Gas Analysis
 Arterial Blood Gas Analysis L Lester www.3bv.org Bones, Brains & Blood Vessels Drawn from radial or femoral arteries. Invasive procedure Caution must be taken with patient on anticoagulants ph: 7.35-7.45
Arterial Blood Gas Analysis L Lester www.3bv.org Bones, Brains & Blood Vessels Drawn from radial or femoral arteries. Invasive procedure Caution must be taken with patient on anticoagulants ph: 7.35-7.45
1. What is the acid-base disturbance in this patient?
 /ABG QUIZ QUIZ 1. What is the acid-base disturbance in this patient? Presenting complaint: pneumonia 1 point Uncompensated metabolic alkalosis Partially compensated respiratory alkalosis Mixed alkalosis
/ABG QUIZ QUIZ 1. What is the acid-base disturbance in this patient? Presenting complaint: pneumonia 1 point Uncompensated metabolic alkalosis Partially compensated respiratory alkalosis Mixed alkalosis
The relationship between H+,PaCO₂ and HCO₃ are expressed in the equation of:
 [Acid-Base Balance] [Dr. Bashir Khasawneh] [5 th February 2012] Acid-Base Basic Concepts: The relationship between H+,PaCO₂ and HCO₃ are expressed in the equation of: Which is modified from Henderson-Hasselbach
[Acid-Base Balance] [Dr. Bashir Khasawneh] [5 th February 2012] Acid-Base Basic Concepts: The relationship between H+,PaCO₂ and HCO₃ are expressed in the equation of: Which is modified from Henderson-Hasselbach
Physio 12 -Summer 02 - Renal Physiology - Page 1
 Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Biology December 2009 Exam Four FORM W KEY
 Biology 251 3 December 2009 Exam Four FORM W KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your
Biology 251 3 December 2009 Exam Four FORM W KEY PRINT YOUR NAME AND ID NUMBER in the space that is provided on the answer sheet, and then blacken the letter boxes below the corresponding letters of your
Hyperaldosteronism: Conn's Syndrome
 RENAL AND ACID-BASE PHYSIOLOGY 177 Case 31 Hyperaldosteronism: Conn's Syndrome Seymour Simon is a 54-year-old college physics professor who maintains a healthy lifestyle. He exercises regularly, doesn't
RENAL AND ACID-BASE PHYSIOLOGY 177 Case 31 Hyperaldosteronism: Conn's Syndrome Seymour Simon is a 54-year-old college physics professor who maintains a healthy lifestyle. He exercises regularly, doesn't
Excretory System Workbook
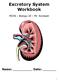 Excretory System Workbook MCHS Biology 20 Mr. Korotash Name: Date: 1 Study the diagram above. Name the structures and indicate their functions by completing the following table: Structure 1. Function 2.
Excretory System Workbook MCHS Biology 20 Mr. Korotash Name: Date: 1 Study the diagram above. Name the structures and indicate their functions by completing the following table: Structure 1. Function 2.
Urinary System. Dr. ZHANG Xiong. Dept. of Physiology. ZJU School of Medicine. QUESTION 6
 Urinary System Dr. ZHANG Xiong Dept. of Physiology ZJU School of Medicine http://10.71.121.158 Copyright@ Xiong Zhang QUESTION 6 How is the filtrate reabsorbed in tubular system? Copyright@ Xiong Zhang
Urinary System Dr. ZHANG Xiong Dept. of Physiology ZJU School of Medicine http://10.71.121.158 Copyright@ Xiong Zhang QUESTION 6 How is the filtrate reabsorbed in tubular system? Copyright@ Xiong Zhang
Dr. Suzana Voiculescu Discipline of Physiology and Fundamental Neurosciences Carol Davila Univ. of Medicine and Pharmacy
 Dr. Suzana Voiculescu Discipline of Physiology and Fundamental Neurosciences Carol Davila Univ. of Medicine and Pharmacy Definition All the processes inside the body which keep the H+ concentration within
Dr. Suzana Voiculescu Discipline of Physiology and Fundamental Neurosciences Carol Davila Univ. of Medicine and Pharmacy Definition All the processes inside the body which keep the H+ concentration within
Acid/Base Disorders 2015
 Objectives - 2 1. Identify acid/base disorders 2. Discuss etiologies for 1 0 acid/base disorders (will not include mixed disorders) 3. Interpret acid/base disorders by interpreting arterial blood gas &
Objectives - 2 1. Identify acid/base disorders 2. Discuss etiologies for 1 0 acid/base disorders (will not include mixed disorders) 3. Interpret acid/base disorders by interpreting arterial blood gas &
/ABG. It covers acid-base disturbance, respiratory failure, and a small summary for some other derangements. Causes of disturbance
 /ABG This page focuses on providing some possible causes for the various disturbances that may be seen on an ABG. Although not an exhaustive list, it attempts to outline the main headings for possible
/ABG This page focuses on providing some possible causes for the various disturbances that may be seen on an ABG. Although not an exhaustive list, it attempts to outline the main headings for possible
mmol.l -1 H+ Ca++ K+ Na+
 Disorders of acid-base equilibrium Pathobiochemistry and diagnostics of acid-base and mineral metabolism Physiologic ph Plasma and most extracellular fluids ph = 7.40 ± 0.02 Significance of constant ph
Disorders of acid-base equilibrium Pathobiochemistry and diagnostics of acid-base and mineral metabolism Physiologic ph Plasma and most extracellular fluids ph = 7.40 ± 0.02 Significance of constant ph
i-stat Alinity v Utilization Guide
 istat Alinity v Utilization Guide The istat Alinity v delivers blood gas, acidbase, electrolyte, chemistry, and hematology measurements in a completely portable, handheld package. Accuracy is ensured by
istat Alinity v Utilization Guide The istat Alinity v delivers blood gas, acidbase, electrolyte, chemistry, and hematology measurements in a completely portable, handheld package. Accuracy is ensured by
Interpretation of ABG. Chandra Shekhar Bala, FCPS( Medicine) Junior Consultant NINS and Hospital, Dhaka
 Interpretation of ABG Chandra Shekhar Bala, FCPS( Medicine) Junior Consultant NINS and Hospital, Dhaka ABG analysis of Ms Rubi Ms. Rubi, 20 year-old lady PH 7.29 presented with breathlessness. She had
Interpretation of ABG Chandra Shekhar Bala, FCPS( Medicine) Junior Consultant NINS and Hospital, Dhaka ABG analysis of Ms Rubi Ms. Rubi, 20 year-old lady PH 7.29 presented with breathlessness. She had
Disclaimer. Chapter 3 Disorder of Water, Electrolyte and Acid-base Professor A. S. Alhomida. Disorder of Water and Electrolyte
 Disclaimer King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry The texts, tables, figures and images contained in this course presentation (BCH 376) are not my own, they can be found on:
Disclaimer King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry The texts, tables, figures and images contained in this course presentation (BCH 376) are not my own, they can be found on:
Biology 12 June 2001 Provincial Examination
 Biology 12 June 2001 rovincial Examination ANWER KEY / CORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell rocesses and Applications 3. Human Biology ub-organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G, H I, J, K,
Biology 12 June 2001 rovincial Examination ANWER KEY / CORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell rocesses and Applications 3. Human Biology ub-organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G, H I, J, K,
3. Which statement is false about anatomical dead space?
 Respiratory MCQs 1. Which of these statements is correct? a. Regular bronchioles are the most distal part of the respiratory tract to contain glands. b. Larynx do contain significant amounts of smooth
Respiratory MCQs 1. Which of these statements is correct? a. Regular bronchioles are the most distal part of the respiratory tract to contain glands. b. Larynx do contain significant amounts of smooth
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology (Kristan) Lecture 18: Endocrine control of renal function. p. 1 Terms you should understand by the end of this section: diuresis, antidiuresis, osmoreceptors, atrial stretch
