Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
- Andrea Stafford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: The Brain Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The most obvious difference between the human brain and the brain of a carp would be in the a. hypothalamus. b. thalamus. c. cerebellum. d. cerebral cortex. 2. The major link between the brain and the glandular system is the a. hypothalamus. b. pituitary. c. CNS. d. midbrain. 3. is closely related to grammar and pronunciation. a. Aphasia b. Broca's area c. Wernicke's area d. Agnosia 4. One of the main differences between the brains of people who score high on mental tests and those who score low indicate that higher scorers have a. higher levels of gray matter. b. lower levels of gray matter. c. lower PET scan recordings. d. higher PET scan recordings. 5. Damage to the cerebellum would most likely result in a. heart stoppage or respiratory failure. b. a loss of hearing ability. c. a loss of muscular coordination. d. a reduction in emotional response. 6. The endocrine system a. is the only communications network in the body. b. depends on electrical messages for communication.
2 c. secretes hormones into the blood stream for communication. d. secretes hormones into the exocrine ducts for communication. 7. An elderly acquaintance of yours has suffered from partial blindness since she had a stroke. Apparently the stroke damaged her a. occipital lobe. b. parietal lobe. c. temporal lobes. d. reticular formation. 8. The pons acts as a bridge between the medulla and other brain areas and influences a. activity. b. sleep and arousal. c. motor behavior. d. higher reasoning. 9. You are walking through a bad part of town, down a dark alley, and carrying a large amount of cash. Behind you, you hear a door open and close suddenly, and you immediately dive into the nearest trash container. The part of the forebrain mainly responsible for your reaction is the a. hippocampus. b. medulla. c. cerebrum. d. amygdala. 10. An EEG records a. the number of neurons in the brain. b. electrical impulses from the brain. c. chemical activity in the cranial nerves. d. direct electrical stimulation and activation of the brain. 11. As we move from lower to higher animals a larger proportion of the brain is devoted to a. unusually large occipital lobes. b. the corpus callosum. c. the cerebrum. d. the spinal cord. 12. Using an electrode, an experimenter produces flashes of colored light and simple visual experiences in a patient undergoing brain surgery. Most likely she has activated the a. parietal lobe. b. frontal lobe. c. occipital lobe. d. temporal lobe.
3 13. The cerebral cortex is composed of two sides or. a. pons b. positrons c. connector neurons d. hemispheres 14. The brainstem consists mainly of the a. cerebellum and the cerebral cortex. b. cerebrum and the medulla. c. medulla and the cerebellum. d. cerebral cortex and the medulla. 15. A person who had difficulty would be described as having aphasia. a. walking b. smelling c. eating d. communicating 16. In order to perform a split-brain operation, the must be severed. a. pons b. cerebellum c. corpus callosum d. cerebral cortex 17. The cerebral hemisphere is superior at perceptual skills and detecting and expressing emotion. a. right b. left c. cortical d. subcortical 18. By using electrical stimulation, reward (or "pleasure centers") and punishment (or "aversive" areas) can be shown to exist in the a. corpus callosum. b. limbic system. c. occipital lobe. d. thalamus. 19. Many addictive drugs stimulate the pleasure centers of the a. medulla. b. cerebellum. c. frontal cortex. d. limbic system. 20. Agnosia may sometimes be helped by
4 a. cues of touch. b. visual cues. c. waiting long enough to think through an answer. d. speech therapy. 21. There is a greater portion of motor cortex for the a. mouth. b. hands and fingers. c. feet and toes. d. legs. 22. The limbic system is responsible for a. the control of hunger, thirst, and sex. b. executive functions. c. heartbeat and breathing regulation. d. auditory processing. 23. An innovative scanning technique that uses magnetic technology to visualize brain activity is called a. PET. b. MRI. c. CAT. d. fmri. 24. The technique that uses a magnetic field to develop an image of the brain is called the a. clinical scan b. ablation technique c. MRI scan d. EEG 25. There is more somatosensory cortex for the a. mouth. b. shoulder. c. feet. d. legs. 26. The sense of smell depends on the lobe. a. frontal b. occipital c. parietal d. temporal 27. If the brain were similar to the postal system, the function of the thalamus would be similar to the role of a. postmaster.
5 b. mail sorter. c. mail carrier. d. Postmaster General. 28. The use of an electrode to destroy small areas of the brain beneath the surface is called a. ablation. b. deep lesioning. c. surface lesioning. d. electroencephalography. 29. Which of the following is most closely associated with language comprehension? a. aphasia b. Broca's area c. Wernicke's area d. agnosia 30. The cortex is all areas of the cerebral cortex that are not sensory or motor in function. a. association b. aphasia c. Broca's d. agnosia 31. Which of the following is most closely associated with language production? a. aphasia b. Broca's area c. Wernicke's area d. agnosia 32. The reflex control centers for vital life functions like heart rate and breathing are found in the a. forebrain. b. medulla. c. pleasure center. d. pituitary gland. 33. Experiments with animals have found pleasure centers to be located in the a. pituitary gland. b. left parietal lobe. c. hypothalamus. d. amygdala. 34. Which of the following involves electrical brain wave measurement? a. clinical studies b. ablation
6 c. MRI scan d. EEG 35. The area of the frontal lobe that directs the body's muscles is called the a. somatosensory area. b. associative area. c. motor cortex. d. cerebral cortex. 36. Bodily sensations such as touch, temperature, and pressure register in which brain area? a. the occipital lobes b. the parietal lobes c. the temporal lobes d. the frontal lobes 37. The surgical procedure of cutting the corpus callosum is done in cases of a. communication problems. b. severe epilepsy. c. injury or stroke. d. split personality. 38. Which of the following statements concerning the brain is true? a. Because the cerebrum is so indispensable to functioning, damage to it may endanger a person's life. b. Even if damage is limited to less crucial areas of the cortex, the person's behavior changes so radically that even casual observers know that some brain damage has occurred. c. Damage to the subcortex may endanger a person's life. d. The cerebral cortex is considered a part of the hindbrain. 39. Which of the following is a major function of the somatosensory area of the cerebral cortex? a. primary area for receiving visual information b. analysis of body sensations c. location of motor control of the body d. primary area for receiving auditory information 40. An elderly woman suffered a stroke, and there was injury to Broca's area of her brain. Her resulting speech impairment is called a. aphasia. b. agnosia. c. mind blindness. d. neglect. 41. Which of the following changes would you expect to occur in someone whose
7 frontal lobes were damaged in an accident? a. development of blank spots in the visual field b. reduced capacity to hear high frequency sounds c. reduced reasoning and planning abilities and changes in personality d. inability to demonstrate complex motor skills 42. Which of the following describes brains of persons who do well on mental tests? a. They seem to work the hardest. b. They seem to consume the least glucose. c. They have the largest corpus callosums. d. They are the easiest to study using EEGs. 43. Creating the magic of consciousness is carried out primarily by a. the hindbrain. b. the midbrain. c. the forebrain. d. the brainstem. 44. The two cerebral hemispheres are connected by a band of fibers called a. the corpus callosum. b. the cortex. c. connector neurons. d. association fibers. 45. Electrical stimulation of the brain a. begins with the implantation of thin metal electrodes deep within the brain. b. cannot be used to electrically activate specific brain areas. c. takes minutes to call forth aggressive behavior. d. cannot effect behaviors such as sleeping and euphoria. 46. Language is controlled by the of the brain. a. right hemisphere b. left hemisphere c. subcortical region d. occipital lobe 47. The gland is involved in the regulation of growth. a. pituitary b. pineal c. thyroid d. adrenal 48. The increased size and wrinkling of the cerebral cortex in higher animals is referred to as
8 a. cerebralization. b. hemispherization. c. corticalization. d. reticulation. 49. An accident victim is shown a picture of a car and says, "dar." This person is suffering from a. Broca's aphasia. b. mindblindness. c. damage to Wernicke's area. d. agnosia. 50. The visual area of the brain is located in the lobe. a. frontal b. parietal c. occipital d. temporal 51. Weeks after an automobile accident, a friend continues to have difficulty maintaining balance and movements. You should suspect that damage may have occurred to the a. corpus callosum. b. cerebellum. c. medulla. d. reticular formation. 52. An aphasia is a speech disturbance; an agnosia is a. the inability to identify objects. b. also related to the speech center. c. controlled by the thalamus. d. a thought disturbance. 53. The reticular formation (RF) is associated with a. hunger and thirst. b. attention and wakefulness. c. sex, rage, and emotion. d. pleasure and punishment. 54. The association areas of the cerebral cortex a. are largest in the brains of lower animals. b. are directly related to such functions as thinking, language, and memory and include Broca's and Wernicke's areas. c. process simple sensory information, like light, sound, and touch. d. are not essential to the performance of higher mental functions. 55. Which of the cerebral hemispheres is superior at drawing a picture?
9 a. left b. right c. subcortical d. mid 56. In most people, the right hemisphere of the brain is in charge of a. language. b. logic. c. art. d. mathematics. 57. If a "split-brain" subject were given a key (hidden from sight) to feel with his left hand, he a. could easily name what he had touched. b. would be unable to describe the object. c. would be able to point to the key with his right hand. d. would have to wait for the information transfer to take place before describing it. 58. As one moves up the evolutionary scale, development of the nervous system shows a. an increase in the brain tissue devoted to the cerebral cortex. b. corticalization of the peripheral nervous system. c. a decrease in the size of cortical association areas. d. a diminishing importance of the corpus callosum. 59. Which of the following is most involved in the production of emotion? a. the occipital lobe b. the limbic system c. the medulla d. the pituitary gland 60. In higher animals, visible portions of the brain are covered with a wrinkled layer of gray matter called the a. cerebral cortex. b. cerebellum. c. corpus callosum. d. forebrain. 61. Although the human brain weighs approximately 3 pounds, it is also important to take into consideration when comparing it to the brain of an elephant or whale. a. the cortex weight b. the body weight c. the caloric intake weight to brain weight ratio d. the brain weight to body weight ratio
10 62. The occipital lobe is to vision as the parietal lobe is to a. smell. b. touch. c. hearing. d. complex behaviors. 63. Surgical removal of parts of the brain to determine their function relies on a technique called a. positron emission. b. corticalization. c. ablation. d. ultrasound. 64. Broca's area is located on the a. right parietal lobe. b. left parietal lobe. c. right frontal lobe. d. left frontal lobe. 65. A patient who has suffered brain damage to the left hemisphere is likely to experience diminished capacity for a. naming objects. b. recognizing faces. c. composing melodies. d. identifying emotions. 66. The functions of the amygdala include a. delivery of electrical stimulation to the limbic system. b. stopping electrical stimulation to the limbic system. c. stimulating the "pleasure" centers of the limbic system. d. helping us react to dangerous stimuli through a quick fear response. 67. Does having a larger brain make a person smarter? a. Recent research found a positive correlation between intelligence and the size of several higher brain structures. b. The overall volume of gray matter is not correlated with IQ test scores. c. Brain size alone determines human intelligence. d. Environment has clearly been found to be the sole determinant of human intelligence. 68. The cerebral cortex is a. the two large hemispheres that cover the upper part of the brain. b. the highest and largest brain area in humans.
11 c. the bundle of fibers connecting the cerebral hemispheres. d. the outer layer of the cerebrum. 69. Brain centers for most vital functions are a. distributed randomly throughout the cerebral cortex. b. localized in the left cerebral hemisphere. c. localized in the right cerebral hemisphere. d. localized deep within the brain in the upper brainstem. 70. The hippocampus a. is part of the hypothalamus. b. is associated with forming lasting memories. c. has direct connections to the occipital lobe. d. is involved with sensing emotion. 71. Which statement concerning brain function is TRUE? a. The left side of the body is generally controlled by the left hemisphere. b. The left side of the body is generally controlled by the right hemisphere. c. The right hemisphere is the dominant hemisphere in males but not in females. d. A stroke to a person's left hemisphere will affect the left side of his or her body. 72. Sue has recovered from extensive injury to her left cerebral hemisphere and has continued her career with little sign of impairment. Her occupation is most likely a. graphic artist. b. accountant. c. English teacher. d. sports writer for a newspaper. 73. A new, improved brain imaging technique for measuring glucose metabolism of the brain is called a. MANSCAN. b. PET scan. c. MRI. d. CT scan. 74. The greater the sensitivity of a part of the body, a. the larger the area of somatosensory cortex associated with it. b. the smaller the area of somatosensory cortex associated with it. c. the smaller the area of motor cortex associated with it. d. the larger the area of the cerebellum associated with it. 75. The area in the brain acts as a final "switching station" for most
12 incoming sensory information. a. superior colliculus b. reticular formation (RF) c. autonomic nervous system d. thalamus 76. Which of the following is NOT controlled by the hypothalamus? a. sex b. eating and drinking c. temperature control d. posture 77. The somatosensory area is located in the a. temporal lobes. b. parietal lobes. c. occipital lobes. d. frontal lobes. 78. Destruction of the reticular activating system would result in a. coma. b. dizziness. c. blurred vision. d. aphasia. 79. The is the part of the brain that stores lasting memories. a. hindbrain b. temporal lobe c. occipital lobe d. hippocampus 80. measures the structure of the brain by utilizing a series of x-rays. a. EEG b. CT scan c. MRI scan d. PET 81. John has some paralysis and loss of sensation in his right side after a motorcycle accident. It is likely that there is brain damage in the a. cerebellum. b. left hemisphere. c. corpus callosum. d. right hemisphere. 82. Dave has just had some medical tests conducted. One of the tests recorded Dave's brain waves on a moving sheet of paper. Dave was probably given the a. EEG.
13 b. CT scan. c. MRI scan. d. PET scan. 83. The regulates the functioning of other glands. a. pituitary gland b. pineal gland c. thyroid gland d. adrenal gland 84. Hormones a. are the electrical messengers of the glands. b. are related to neurotransmitters. c. generally maintain a steady state in our bodily functions. d. are similar to neurotransmitters, but unlike neurotransmitters, hormones do not require receptor sites. 85. A brief electrical current is applied to the cortex causing movements and muscular twitches in various parts of the body. The area stimulated is the a. somesthetic area of the parietal lobe. b. association cortex of the occipital lobes. c. interpretative cortex of the temporal lobes. d. motor cortex of the frontal lobes. 86. The brain center for audition is in the lobe. a. temporal b. parietal c. occipital d. frontal 87. Jim does not understand algebra, but he's a good artist. Jim's brain is probably more fully developed. a. left b. right c. mid d. subcortical 88. In the brain, the function of the reticular formation is similar to the hotel service known as a. advance registration. b. maid service. c. wake-up call. d. room service.
14
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES
 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Ways we Study the Brain. Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI
 The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
Basic Brain Structure
 The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2
 Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
Brain Structures. Some scientists divide the brain up into three parts. Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain
 The Brain Phineas Gage Play The Frontal Lobes and Behavior: The Story of Phineas Gage (12:03) Module #25 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2 nd edition). http://www.learner.org/resources/series1 42.html
The Brain Phineas Gage Play The Frontal Lobes and Behavior: The Story of Phineas Gage (12:03) Module #25 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2 nd edition). http://www.learner.org/resources/series1 42.html
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
Chapter 6 Section 1. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
 Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology
 Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Chapter 6. Body and Behavior
 Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
IV. The Divisions of the Brain. Slide # 1
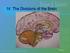 IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
Parts of the Brain. Hindbrain. Controls autonomic functions Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. Upper part of hindbrain
 Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures
 III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
Forebrain Brain Structures Limbic System. Brain Stem Midbrain Basil Ganglia. Cerebellum Reticular Formation Medulla oblongata
 Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER
 BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER ORCHESTRA Scientists now believe the brain functions much like an orchestra, where different instruments each play a different part. Scans show that the brain divides different aspects
BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER ORCHESTRA Scientists now believe the brain functions much like an orchestra, where different instruments each play a different part. Scans show that the brain divides different aspects
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Human Nervous System
 Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Test Bank. Multiple Choice
 Chapter 2: The Brain: An Overview of Structure and Function Test Bank Multiple Choice 1. Evolutionary structures within the are the most primitive. a. hindbrain b. thalamus c. forebrain d. midbrain Answer
Chapter 2: The Brain: An Overview of Structure and Function Test Bank Multiple Choice 1. Evolutionary structures within the are the most primitive. a. hindbrain b. thalamus c. forebrain d. midbrain Answer
The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized?
 Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Modules 4 & 6. The Biology of Mind
 Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
synapse neurotransmitters Extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands
 neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1
 PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
Chapter 2 Test. 1. Evolutionary structures within the are the most primitive. *a. hindbrain b. thalamus c. forebrain d. midbrain e.
 Cognitive Psychology In and Out of the Laboratory 5th Edition Galotti TEST BANK Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/cognitive-psychology-laboratory-5thedition-galotti-test-bank/
Cognitive Psychology In and Out of the Laboratory 5th Edition Galotti TEST BANK Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/cognitive-psychology-laboratory-5thedition-galotti-test-bank/
CNS Tour (Lecture 12)
 A. Introduction CNS Tour (Lecture 12) There are to a chemical pathways in the nervous system. These pathways also form different neurological structures B. Spinal Cord Receives sensory neurons from skin
A. Introduction CNS Tour (Lecture 12) There are to a chemical pathways in the nervous system. These pathways also form different neurological structures B. Spinal Cord Receives sensory neurons from skin
The Brain Studying & Structures. Unit 3
 The Brain Studying & Structures Unit 3 Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Learning Objectives Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and
The Brain Studying & Structures Unit 3 Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Learning Objectives Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts
 CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
Visualizing Psychology
 Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7)
 Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Chapter 3: Biology and Behavior
 Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
How do we study the brain? What are the parts of the hindbrain? What is the reticular formation? Parts of the forebrain? Parts of the limbic system?
 How do we study the brain? What are the parts of the hindbrain? What is the reticular formation? Parts of the forebrain? Parts of the limbic system? Lobes of the cerebral cortex? What is the sensory cortex?
How do we study the brain? What are the parts of the hindbrain? What is the reticular formation? Parts of the forebrain? Parts of the limbic system? Lobes of the cerebral cortex? What is the sensory cortex?
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior
 Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Curricular Requirement 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Name: Period: Due Key Terms for CR 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Key Term Definition Application Acetylcholine (Ach) Action potential Adrenal glands
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System
 Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN IS REGIONALLY SPECIALIZED
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN IS REGIONALLY SPECIALIZED Images of the human brain in popular culture almost always focus on the cerebrum, the part of the brain whose surface lies just
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN IS REGIONALLY SPECIALIZED Images of the human brain in popular culture almost always focus on the cerebrum, the part of the brain whose surface lies just
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain
 Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System
 49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System 49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of
49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System 49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of
General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain
 General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain These are general notes designed to assist students who are regularly attending class and reading assigned material: they are supplemental rather than exhaustive
General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain These are general notes designed to assist students who are regularly attending class and reading assigned material: they are supplemental rather than exhaustive
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES
 BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
Neural Communication. Neural Communication. Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior. Definitions
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior 1. Neural communication - Neurons - How Neurons Communicate - How Neurotransmitters Influence Us 2. The nervous system 3. The endocrine system 4.
Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior 1. Neural communication - Neurons - How Neurons Communicate - How Neurotransmitters Influence Us 2. The nervous system 3. The endocrine system 4.
Ch. 2: The Biological Perspective Take Home Test on Peripheral Nervous System and the Brain Human Behavior Mr. Minervini
 Ch. 2: The Biological Perspective Take Home Test on Peripheral Nervous System and the Brain Human Behavior Mr. Minervini Level 1 Only Name: Period: Please highlight the correct answer/response in yellow
Ch. 2: The Biological Perspective Take Home Test on Peripheral Nervous System and the Brain Human Behavior Mr. Minervini Level 1 Only Name: Period: Please highlight the correct answer/response in yellow
Vocabulary. Central Nervous System (CNS) Spinal Cord Reflexes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons Action Potential Threshold
 Unit 2: Biopsychology The Nervous System Vocabulary Central Nervous System (CNS) Spinal Cord Reflexes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons Action Potential Threshold Synapse Neurotransmitters Somatic
Unit 2: Biopsychology The Nervous System Vocabulary Central Nervous System (CNS) Spinal Cord Reflexes Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Neurons Action Potential Threshold Synapse Neurotransmitters Somatic
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
To understand AD, it is important to
 To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
8.3 The Central Nervous System. SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau
 8.3 The Central Nervous System SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau The Central Nervous System the structural and functional centre for the entire nervous system the site of neural integration and processing The Central
8.3 The Central Nervous System SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau The Central Nervous System the structural and functional centre for the entire nervous system the site of neural integration and processing The Central
Biology. Slide 1 of 37. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Biology 1 of 37 35-3 Divisions of the Nervous 2 of 37 The Nervous The human nervous system has two major divisions: central nervous system peripheral nervous system 3 of 37 The Central Nervous The Central
Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior. Neural Communication. Neural Communication. Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed)
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater arachnoid mater pia mater membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system
 membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
10/15/2010. Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: Biology and Behavior. The Nervous System
 Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
The Human Brain. I Think Therefore I am
 The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
Composed of gray matter and arranged in raised ridges (gyri), grooves (sulci), depressions (fissures).
 PSYC1020 Neuro and Pysc Notes Structure Description Major Functions Brainstem Stemlike portion of the brain, continuous with diencephalon above and spinal cord below. Composed of midbrain, pons, medulla
PSYC1020 Neuro and Pysc Notes Structure Description Major Functions Brainstem Stemlike portion of the brain, continuous with diencephalon above and spinal cord below. Composed of midbrain, pons, medulla
Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1
 Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1 Phineas Gage Phineas Gage was a railroad worker who had an iron bar go into his brain He survived but his personality was changed The Brain Lesion tissue destruction
Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1 Phineas Gage Phineas Gage was a railroad worker who had an iron bar go into his brain He survived but his personality was changed The Brain Lesion tissue destruction
Neurons. Biological Basis of Behavior. Three Types of Neurons. Three Types of Neurons. The Withdrawal Reflex. Transmission of message 10/2/2017
 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Bio 105
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Anatomy of the Human Brain
 Anatomy of the Human Brain Overview Lobes of the brain (Forebrain) Midbrain/Hindbrain Protection and Blood supply Structure and Function of a neuron Synaptic Transmission Neurotransmitters The brain Most
Anatomy of the Human Brain Overview Lobes of the brain (Forebrain) Midbrain/Hindbrain Protection and Blood supply Structure and Function of a neuron Synaptic Transmission Neurotransmitters The brain Most
3/15/17. Outline. Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Two Parts of the Nervous System
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Sincerely, Ms. Paoloni and Mrs. Whitney
 Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
AP Psychology Ch. 02 The Brain Study Guide
 Name: Period: 1. Which of the following was a major problem with phrenology? A) It was ahead of its time and no one believed it could be true. B) The brain is not neatly organized into structures that
Name: Period: 1. Which of the following was a major problem with phrenology? A) It was ahead of its time and no one believed it could be true. B) The brain is not neatly organized into structures that
3/20/13. :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System
 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System The nervous system is organized into several major branches, each
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System The nervous system is organized into several major branches, each
Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system:
 Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system: Some review & misc. parts [Fig. 28.11B, p. 573]: - white matter --> looks white due to the myelinated sheaths, which are quite fatty.
Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system: Some review & misc. parts [Fig. 28.11B, p. 573]: - white matter --> looks white due to the myelinated sheaths, which are quite fatty.
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy. Components of a Nervous System
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Somatic Nervous Systems. III. Autonomic Nervous System. Parasympathetic Nervous System. Sympathetic Nervous Systems
 7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
2) All of our thoughts, feelings, and behaviour can be traced to the activity of the a. neurons. b. ganglia. c. genes. d. nerve fibres.
 Chapter 2 Biology and Behaviour 1) The specialized cell that transmits signals throughout the nervous system is called the a. neuron. b. glial cell. c. myelin. d. neurotransmitter. Correct: The neuron
Chapter 2 Biology and Behaviour 1) The specialized cell that transmits signals throughout the nervous system is called the a. neuron. b. glial cell. c. myelin. d. neurotransmitter. Correct: The neuron
Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology
 Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology Activity Everyone stand up, raise your right hand, tell your neighbors your name 1 What part of the brain
Inside Your Patient s Brain Michelle Peterson, APRN, CNP Centracare Stroke and Vascular Neurology Activity Everyone stand up, raise your right hand, tell your neighbors your name 1 What part of the brain
Activity Overview. A Piece of Your Mind: Brain Anatomy Teacher Pages Activity 1A. The Brain: It s All In Your Mind
 A Piece of Your Mind: Brain Anatomy Teacher Pages Activity Objectives: Using diagrams of the brain, students will be able to: Observe the basic anatomy of the brain and its components Identify the parts
A Piece of Your Mind: Brain Anatomy Teacher Pages Activity Objectives: Using diagrams of the brain, students will be able to: Observe the basic anatomy of the brain and its components Identify the parts
Chapter 3. Biological Processes
 Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Biological Basis of Behavior. Chapter 2
 Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION
 UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION QUESTION BANK Complementary Courses in Counselling Psychology (2014 Admission onwards) II Semester Physiological Psychology 1. The central nervous system
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION QUESTION BANK Complementary Courses in Counselling Psychology (2014 Admission onwards) II Semester Physiological Psychology 1. The central nervous system
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
18. The visual cortex is located in the: A) occipital lobe. B) temporal lobe. C) frontal lobe. D) parietal lobe.
 Name: Date: 1. A biological psychologist would be more likely to study: A) how you learn to express emotions. B) how to help people overcome emotional disorders. C) life-span changes in the expression
Name: Date: 1. A biological psychologist would be more likely to study: A) how you learn to express emotions. B) how to help people overcome emotional disorders. C) life-span changes in the expression
Neuroscience. Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior 1/11/2010. The Brain and Behavior
 Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How is the Nervous System Organized? II. Methods of Studying the Brain III. How Does the Brain Function? IV. What Effects Do
Neuroscience The Brain and Behavior Neuroscience: The Brain and Behavior I. How is the Nervous System Organized? II. Methods of Studying the Brain III. How Does the Brain Function? IV. What Effects Do
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves. Origin of the Brain
 Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
The Nervous System. The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind.
 The Nervous System The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Central Nervous System Made up of brain and spinal cord
The Nervous System The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Central Nervous System Made up of brain and spinal cord
Chapter 9 Nervous System Test Review
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Test Review Multiple Choice Choose the best answer from the choices given 1. The central nervous system consists of: a) sensory nerves b) nerves that run throughout the body c)
Chapter 9 Nervous System Test Review Multiple Choice Choose the best answer from the choices given 1. The central nervous system consists of: a) sensory nerves b) nerves that run throughout the body c)
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System. Anatomy of the CNS
 CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet
 1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
AP Psychology Exam Review. The Brain. Brain Mnemonics by Michael Britt
 AP Psychology Exam Review The Brain Brain Mnemonics by Michael Britt www.thepsychfiles.com Figure 2.2, p. 67 Pons - regulates waking and relaxing. Put a d in pons and you have ponds. Ponds are relaxing
AP Psychology Exam Review The Brain Brain Mnemonics by Michael Britt www.thepsychfiles.com Figure 2.2, p. 67 Pons - regulates waking and relaxing. Put a d in pons and you have ponds. Ponds are relaxing
a) Central sulcus- shallow groove that runs across brain sagitally
 KEY BRAIN Brain Gross Anatomy Terms 1) Explain each of the following in terms of structure of the brain a) Central sulcus- shallow groove that runs across brain sagitally b) Lateral fissure- deep groove
KEY BRAIN Brain Gross Anatomy Terms 1) Explain each of the following in terms of structure of the brain a) Central sulcus- shallow groove that runs across brain sagitally b) Lateral fissure- deep groove
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Nervous Systems. Brain Development
 Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Page 1. Neurons Transmit Signal via Action Potentials: neuron At rest, neurons maintain an electrical difference across
 Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Body control systems. Nervous system. Organization of Nervous Systems. The Nervous System. Two types of cells. Organization of Nervous System
 Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
